Free PDF Business Plan Templates and Samples
By Joe Weller | September 9, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
We’ve gathered the most useful collection of business plan PDF templates and samples, including options for organizations of any size and type.
On this page, you’ll find free PDF templates for a simple business plan , small business plan , startup business plan , and more.

Simple Business Plan PDF Templates
These simple business plan PDF templates are ready to use and customizable to fit the needs of any organization.
Simple Business Plan Template PDF

This template contains a traditional business plan layout to help you map out each aspect, from a company overview to sales projections and a marketing strategy. This template includes a table of contents, as well as space for financing details that startups looking for funding may need to provide.
Download Simple Business Plan Template - PDF
Lean Business Plan Template PDF

This scannable business plan template allows you to easily identify the most important elements of your plan. Use this template to outline key details pertaining to your business and industry, product or service offerings, target customer segments (and channels to reach them), and to identify sources of revenue. There is also space to include key performance metrics and a timeline of activities.
Download Lean Business Plan Template - PDF
Simple 30-60-90 Day Business Plan Template PDF

This template is designed to help you develop and implement a 90-day business plan by breaking it down into manageable chunks of time. Use the space provided to detail your main goals and deliverables for each timeframe, and then add the steps necessary to achieve your objectives. Assign task ownership and enter deadlines to ensure your plan stays on track every step of the way.
Download Simple 30-60-90 Day Business Plan Template
PDF | Smartsheet
One-Page Business Plan PDF Templates
The following single page business plan templates are designed to help you download your key ideas on paper, and can be used to create a pitch document to gain buy-in from partners, investors, and stakeholders.
One-Page Business Plan Template PDF
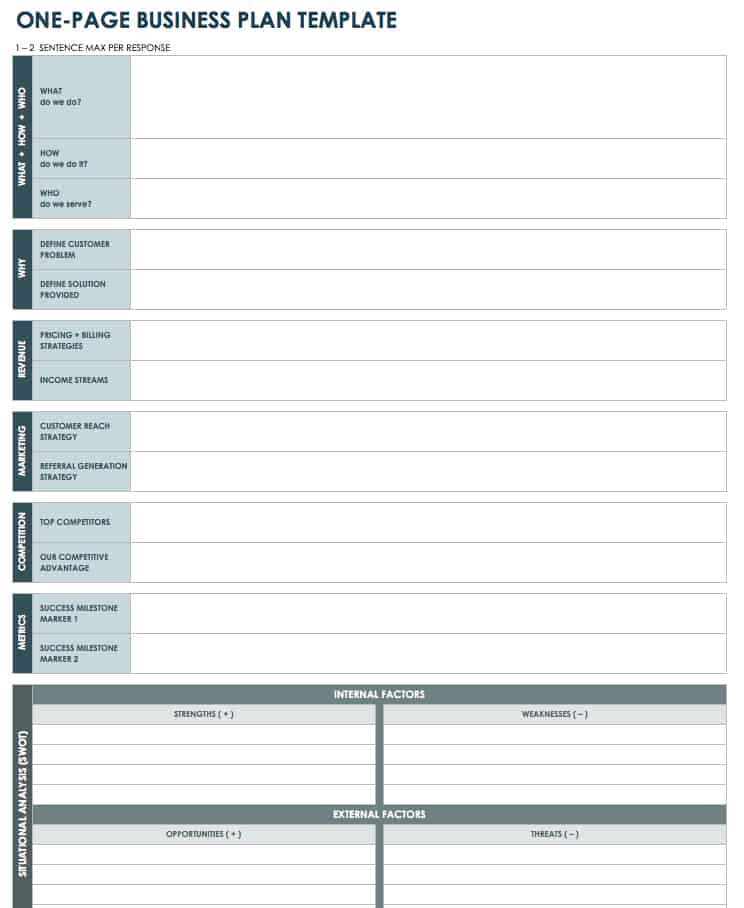
Use this one-page template to summarize each aspect of your business concept in a clear and concise manner. Define the who, what, why, and how of your idea, and use the space at the bottom to create a SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) for your business.
Download One-Page Business Plan Template
If you’re looking for a specific type of analysis, check out our collection of SWOT templates .
One-Page Lean Business Plan PDF

This one-page business plan template employs the Lean management concept, and encourages you to focus on the key assumptions of your business idea. A Lean plan is not stagnant, so update it as goals and objectives change — the visual timeline at the bottom is ideal for detailing milestones.
Download One-Page Lean Business Plan Template - PDF
One-Page 30-60-90 Day Business Plan Template
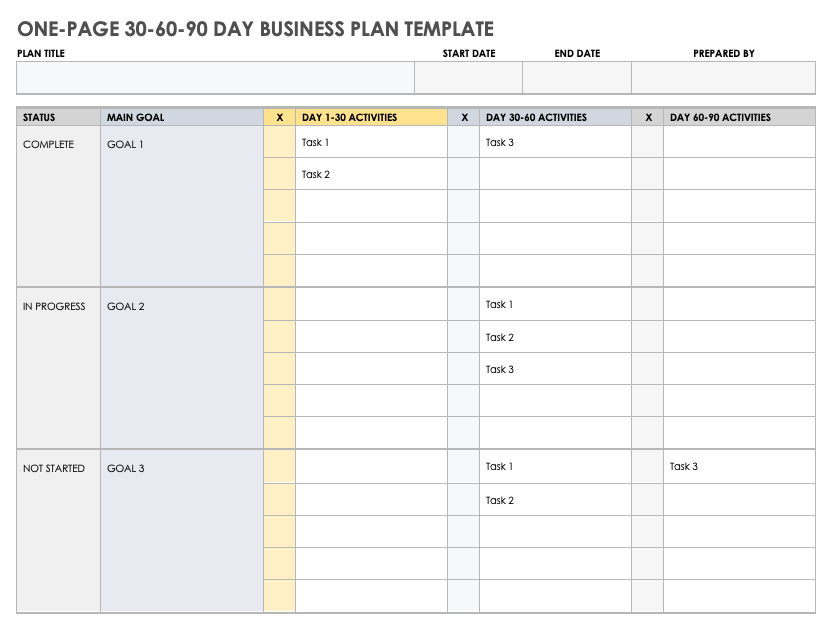
Use this business plan template to identify main goals and outline the necessary activities to achieve those goals in 30, 60, and 90-day increments. Easily customize this template to fit your needs while you track the status of each task and goal to keep your business plan on target.
Download One-Page 30-60-90 Day Business Plan Template
For additional single page plans, including an example of a one-page business plan , visit " One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide ."
Small Business Plan PDF Templates
These business plan templates are useful for small businesses that want to map out a way to meet organizational objectives, including how to structure, operate, and expand their business.
Simple Small Business Plan Template PDF
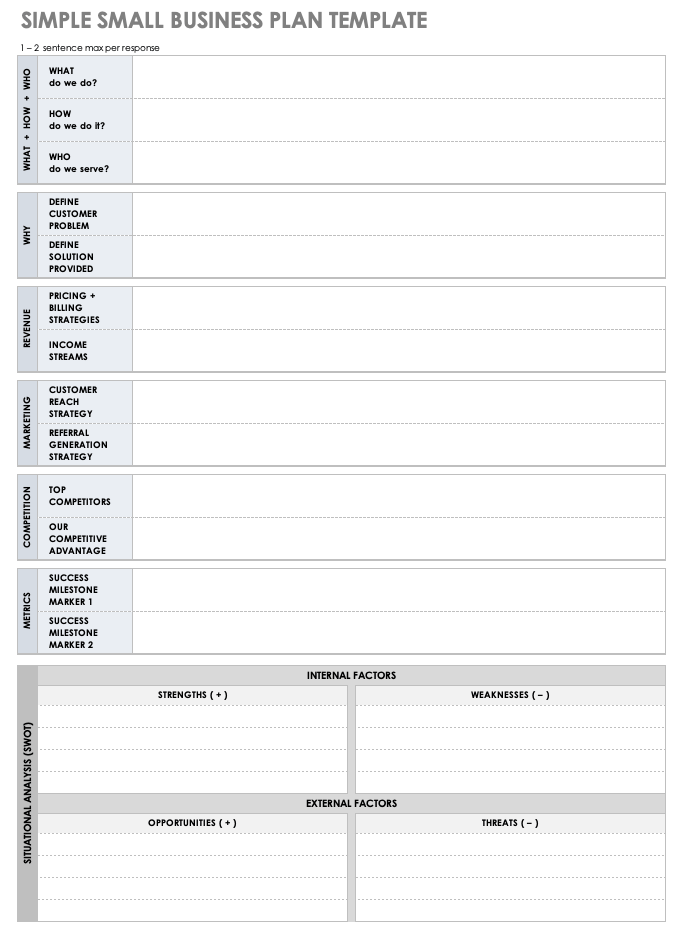
A small business can use this template to outline each critical component of a business plan. There is space to provide details about product or service offerings, target audience, customer reach strategy, competitive advantage, and more. Plus, there is space at the bottom of the document to include a SWOT analysis. Once complete, you can use the template as a basis to build out a more elaborate plan.
Download Simple Small Business Plan Template
Fill-In-the-Blank Small Business Plan Template PDF
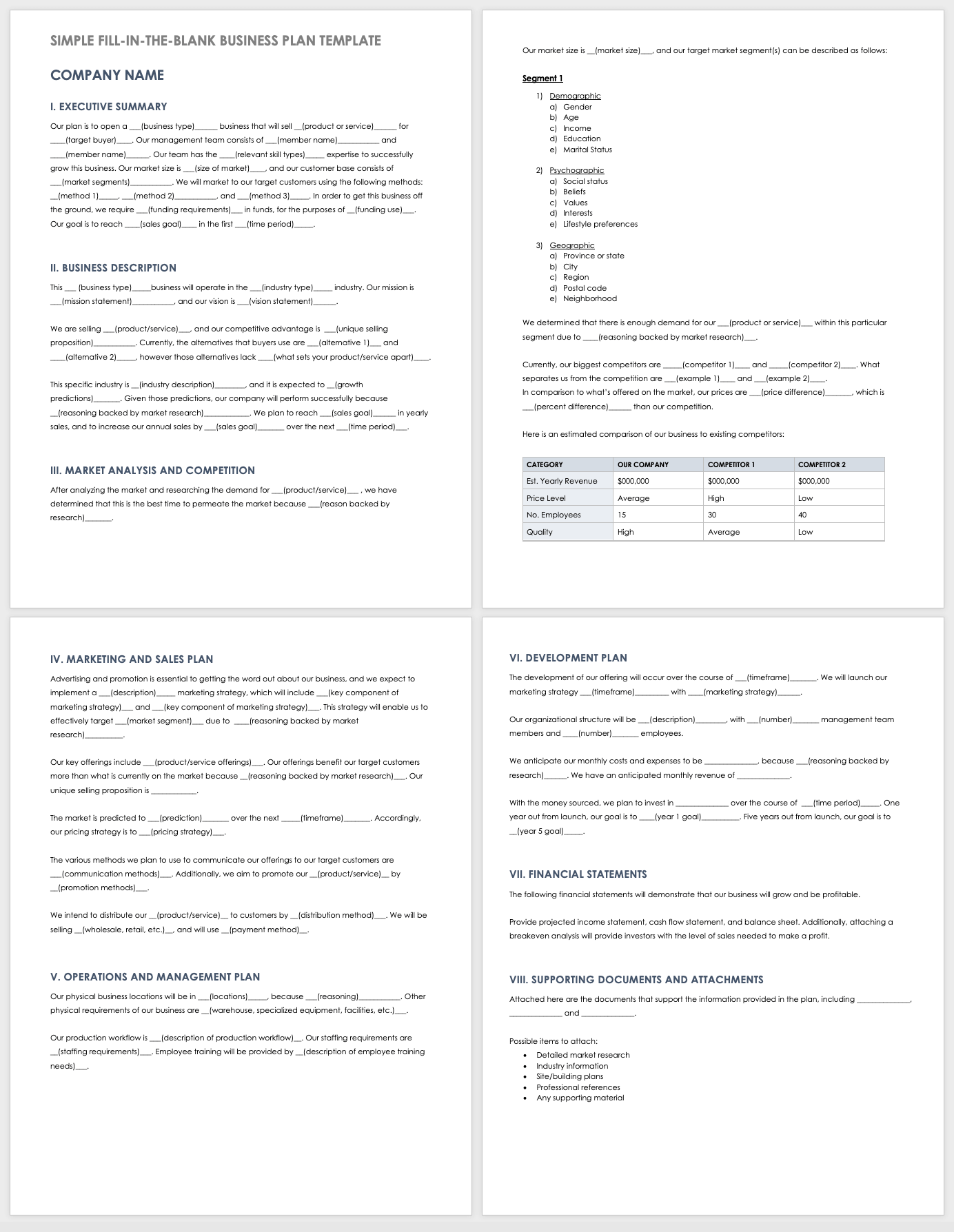
This fill-in-the-blank template walks you through each section of a business plan. Build upon the fill-in-the-blank content provided in each section to add information about your company, business idea, market analysis, implementation plan, timeline of milestones, and much more.
Download Fill-In-the-Blank Small Business Plan Template - PDF
One-Page Small Business Plan Template PDF

Use this one-page template to create a scannable business plan that highlights the most essential parts of your organization’s strategy. Provide your business overview and management team details at the top, and then outline the target market, market size, competitive offerings, key objectives and success metrics, financial plan, and more.
Download One-Page Business Plan for Small Business - PDF
Startup Business Plan PDF Templates
Startups can use these business plan templates to check the feasibility of their idea, and articulate their vision to potential investors.
Startup Business Plan Template
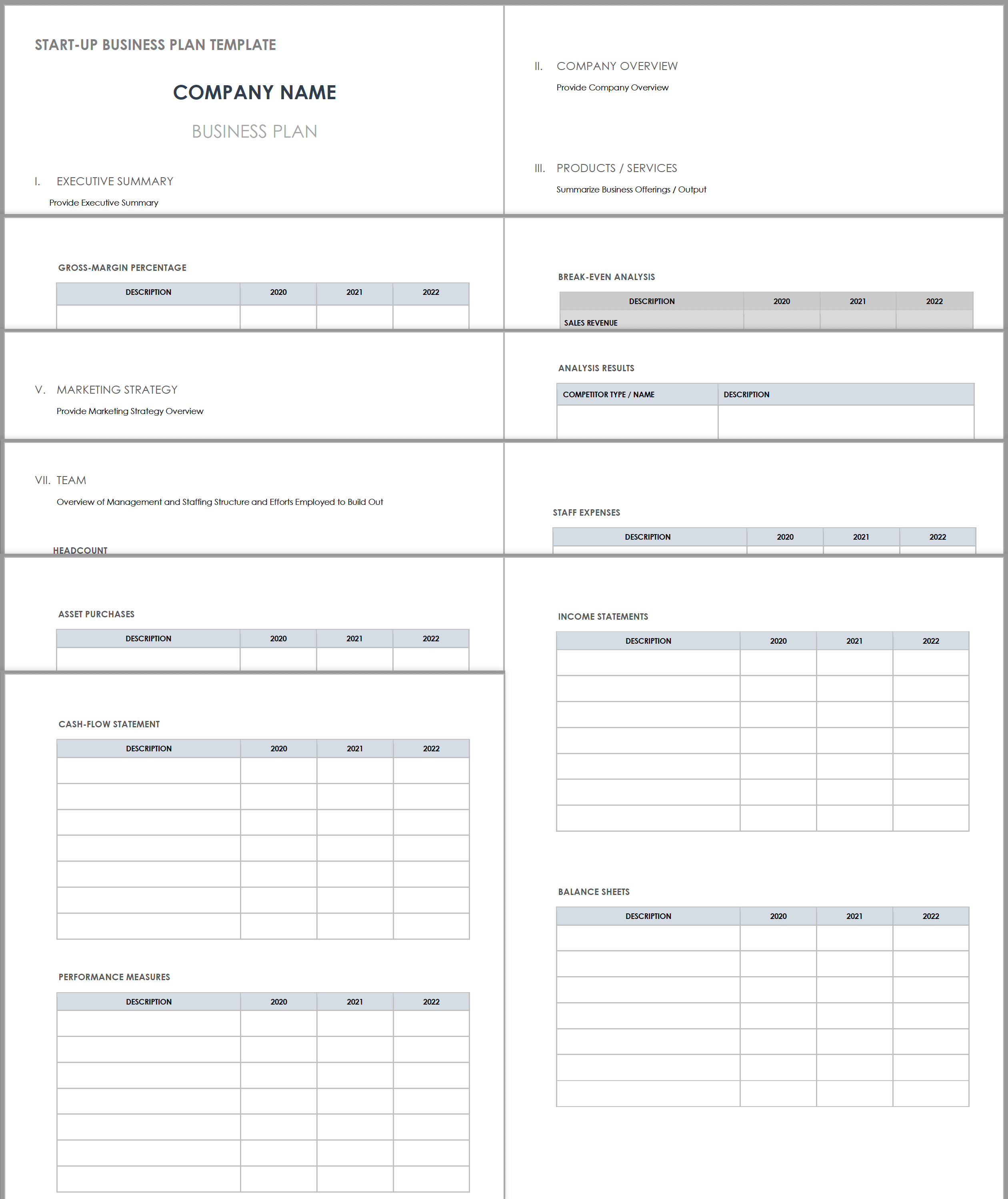
Use this business plan template to organize and prepare each essential component of your startup plan. Outline key details relevant to your concept and organization, including your mission and vision statement, product or services offered, pricing structure, marketing strategy, financial plan, and more.
Download Startup Business Plan Template
Sample 30-60-90 Day Business Plan for Startup
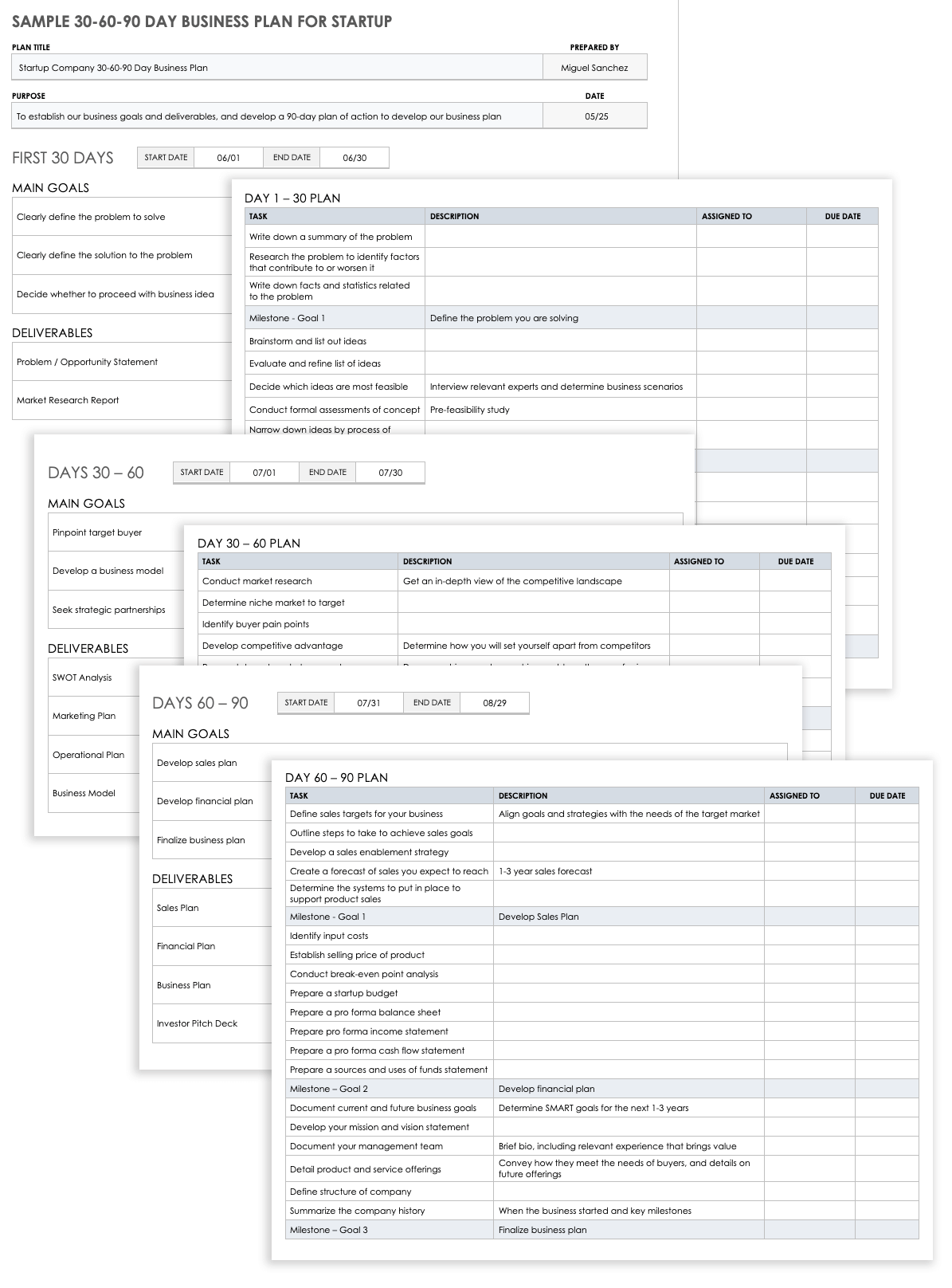
Startups can use this sample 30-60-90 day plan to establish main goals and deliverables spanning a 90-day period. Customize the sample goals, deliverables, and activities provided on this template according to the needs of your business. Then, assign task owners and set due dates to help ensure your 90-day plan stays on track.
Download Sample 30-60-90 Day Business Plan for Startup Template
For additional resources to create your plan, visit “ Free Startup Business Plan Templates and Examples .”
Nonprofit Business Plan PDF Templates
Use these business plan PDF templates to outline your organization’s mission, your plan to make a positive impact in your community, and the steps you will take to achieve your nonprofit’s goals.
Nonprofit Business Plan Template PDF
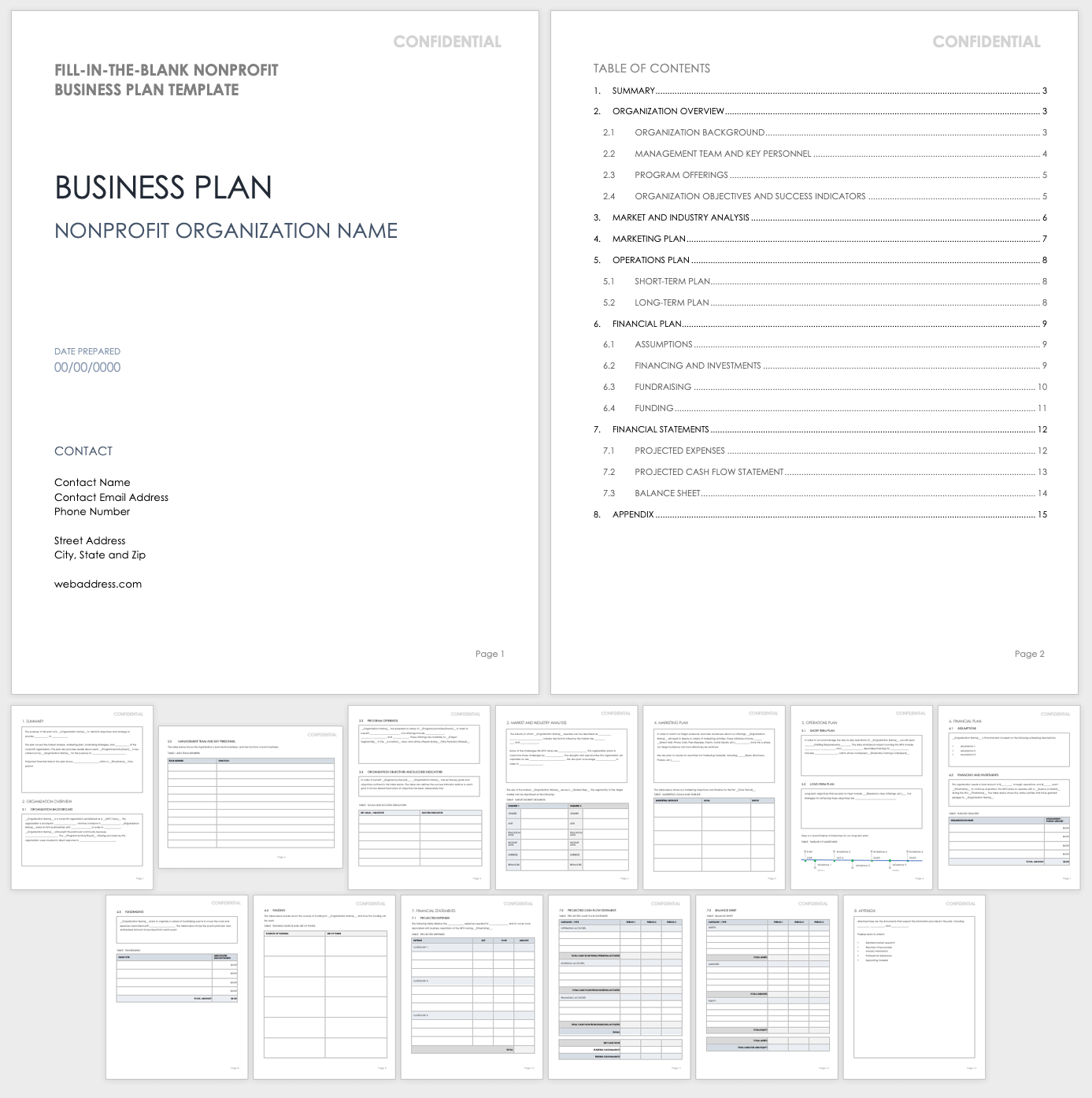
Use this customizable PDF template to develop a plan that details your organization’s purpose, objectives, and strategy. This template features a table of contents, with room to include your nonprofit’s mission and vision, key team and board members, program offerings, a market and industry analysis, promotional plan, financial plan, and more. This template also contains a visual timeline to display historic and future milestones.
Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template - PDF
One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Organization PDF
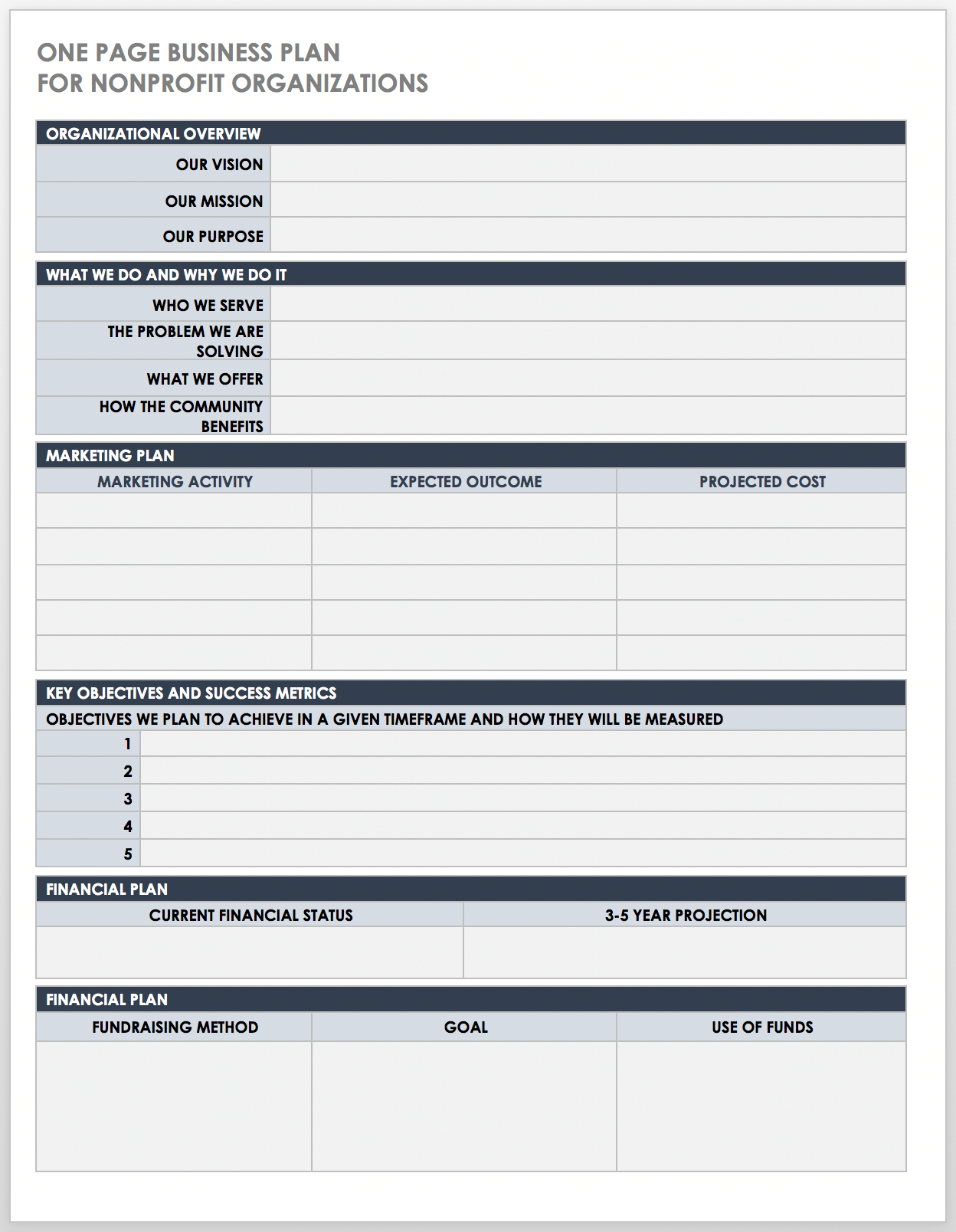
This one-page plan serves as a good starting point for established and startup nonprofit organizations to jot down their fundamental goals and objectives. This template contains all the essential aspects of a business plan in a concise and scannable format, including the organizational overview, purpose, promotional plan, key objectives and success metrics, fundraising goals, and more.
Download One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Organization Template - PDF
Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan PDF Templates
Use these fill-in-the-blank templates as a foundation for creating a comprehensive roadmap that aligns your business strategy with your marketing, sales, and financial goals.
Simple Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan PDF
The fill-in-the-blank template contains all the vital parts of a business plan, with sample content that you can customize to fit your needs. There is room to include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, marketing plan, operations plan, financial statements, and more.
Download Simple Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Template - PDF
Lean Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan PDF
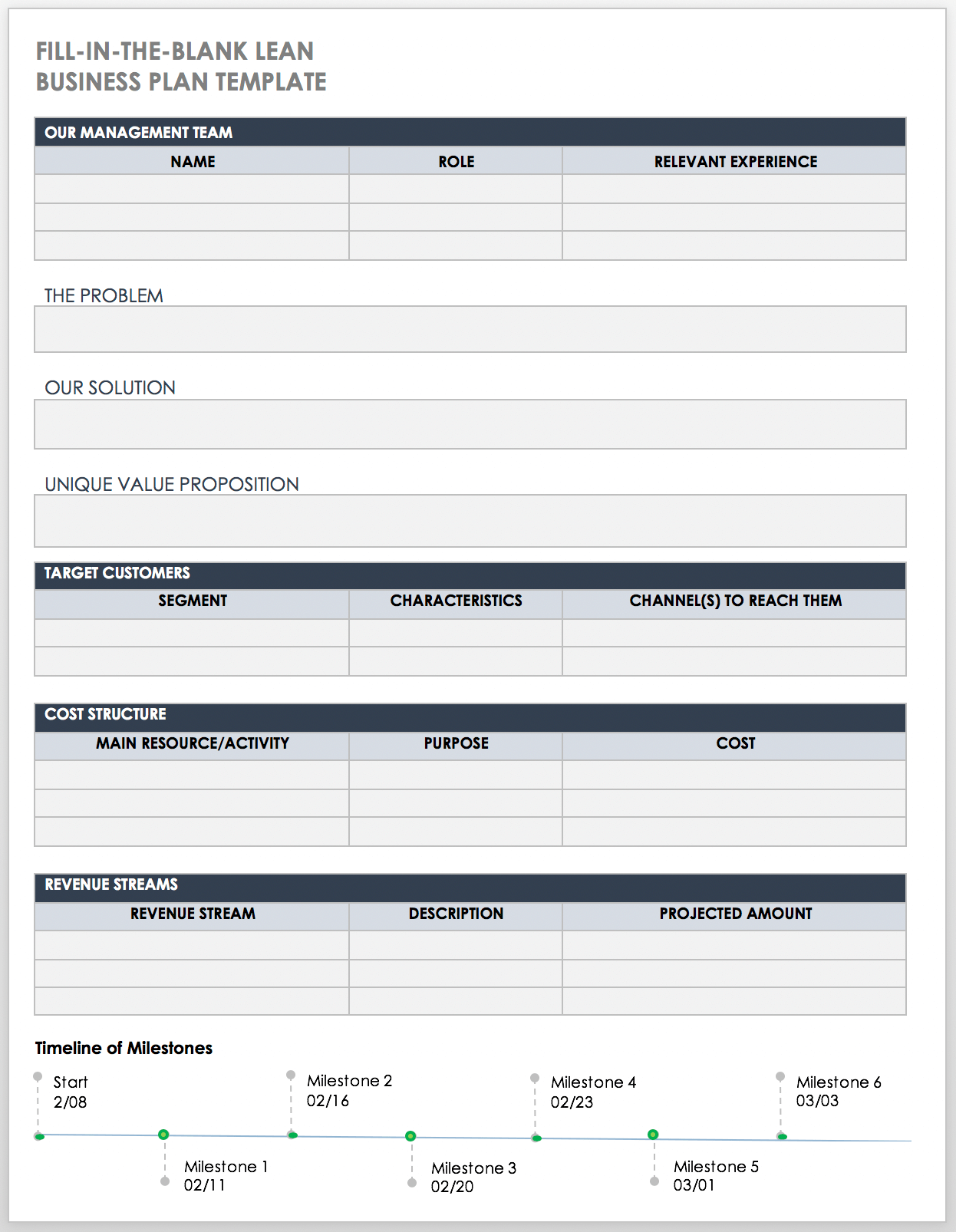
This business plan is designed with a Lean approach that encourages you to clarify and communicate your business idea in a clear and concise manner. This single page fill-in-the-blank template includes space to provide details about your management team, the problem you're solving, the solution, target customers, cost structure, and revenue streams. Use the timeline at the bottom to produce a visual illustration of key milestones.
Download Fill-In-the-Blank Lean Business Plan Template - PDF
For additional resources, take a look at " Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates ."
Sample Business Plan PDF Templates
These sample business plan PDF templates can help you to develop an organized, thorough, and professional business plan.
Business Plan Sample
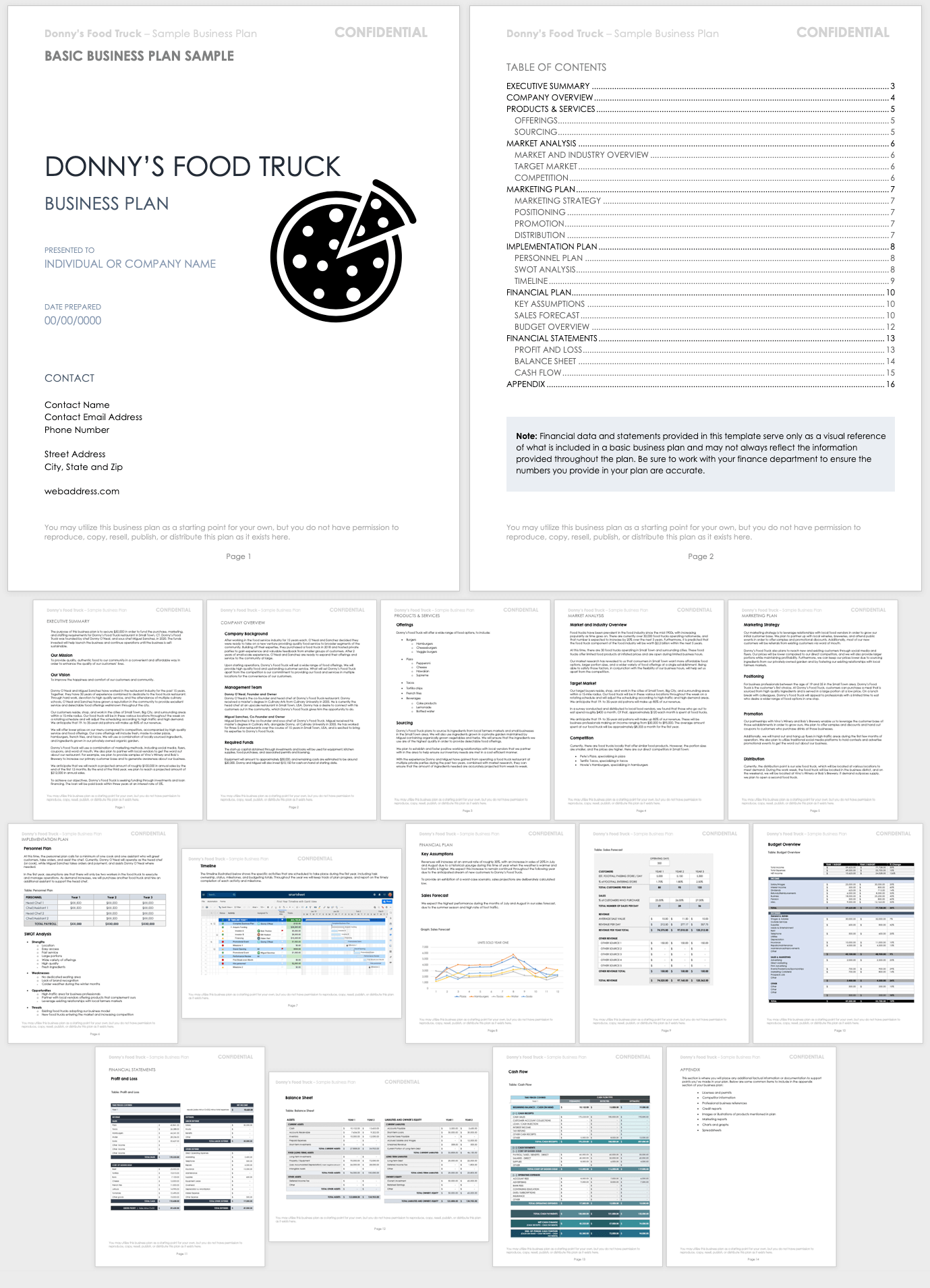
This business plan example demonstrates a plan for a fictional food truck company. The sample includes all of the elements in a traditional business plan, which makes it a useful starting point for developing a plan specific to your business needs.
Download Basic Business Plan Sample - PDF
Sample Business Plan Outline Template

Use this sample outline as a starting point for your business plan. Shorten or expand the outline depending on your organization’s needs, and use it to develop a table of contents for your finalized plan.
Download Sample Business Plan Outline Template - PDF
Sample Business Financial Plan Template
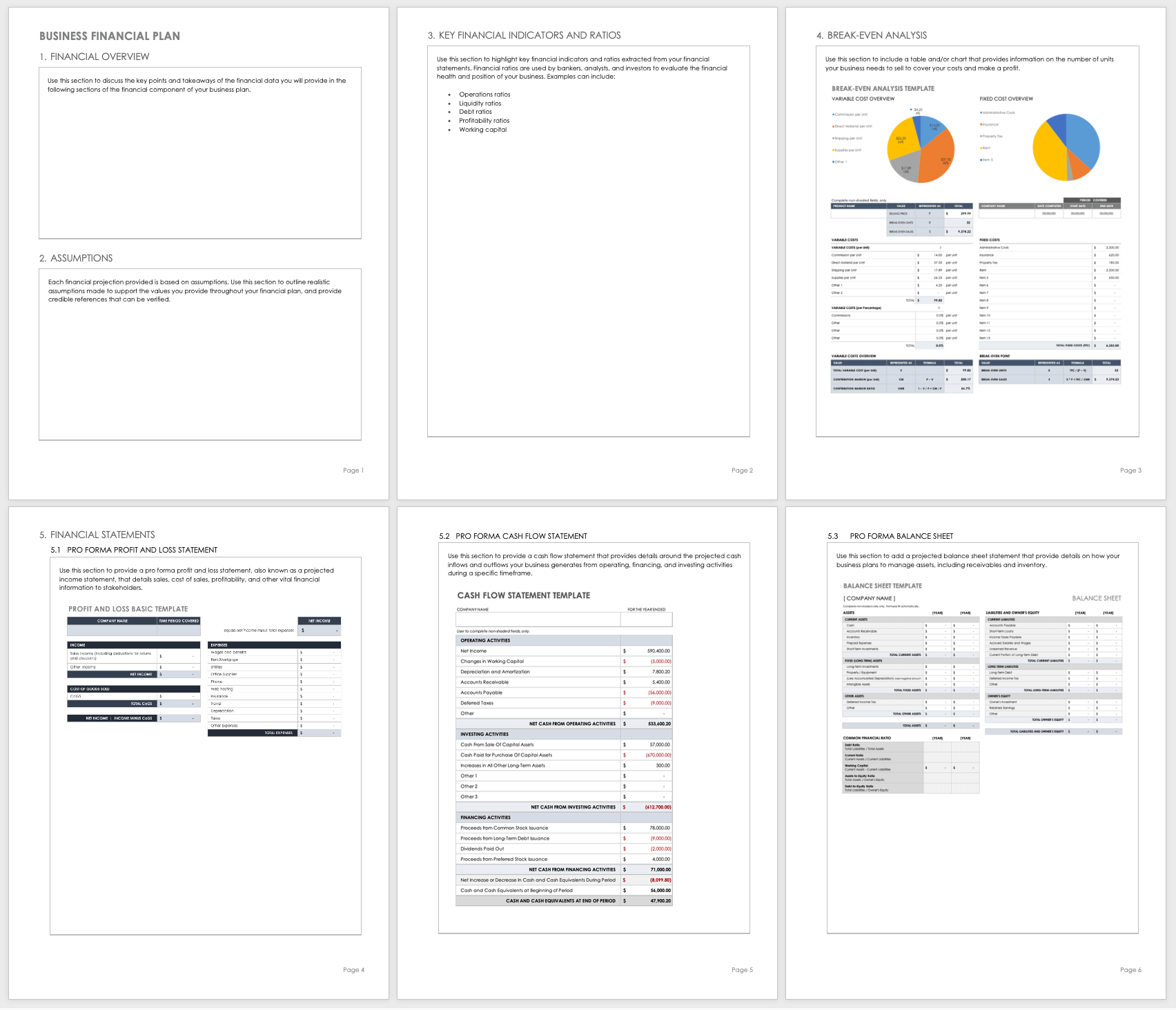
Use this sample template to develop the financial portion of your business plan. The template provides space to include a financial overview, key assumptions, financial indicators, and business ratios. Complete the break-even analysis and add your financial statements to help prove the viability of your organization’s business plan.
Download Business Financial Plan Template
PDF | Smartsheet
For more free, downloadable templates for all aspects of your business, check out “ Free Business Templates for Organizations of All Sizes .”
Improve Business Planning with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Brought to you by:

How to Write a Winning Business Plan
By: Stanley R. Rich, David E. Gumpert
A well-conceived business plan is essential to the success of an enterprise. Whether you are starting up a venture, seeking additional capital for an existing product line, or proposing a new…
- Length: 7 page(s)
- Publication Date: May 1, 1985
- Discipline: Organizational Behavior
- Product #: 85314-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Educator Copy
$4.50 per student
degree granting course
$7.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
A well-conceived business plan is essential to the success of an enterprise. Whether you are starting up a venture, seeking additional capital for an existing product line, or proposing a new activity for a corporate division, you will have to write a plan detailing your project's resource requirements, marketing decisions, financial projections, production demands, and personnel needs. The plan must reflect the viewpoint of three constituencies: the customer, the investor, and the producer. Too many business plans focus excessively on the producer.
Learning Objectives
To ensure that one's business plan includes proof that a large market exists for the proposed offering and that it addresses investors' concerns, such as when they can cash out.
May 1, 1985
Discipline:
Organizational Behavior
Harvard Business Review
85314-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Updating a Classic: Writing a Great Business Plan
- A business plan can't be a tightly crafted prediction of the future but rather a depiction of how events might unfold and a road map for change.
- The people making the forecasts are more important than the numbers themselves.
- What matters is having all the required ingredients (or a road map for getting them), not the exact form of communication.
- The best money comes from customers, not external investors.
Sean Silverthorne: " How to Write a Great Business Plan " has been one of the most downloaded articles on Harvard Business Publishing since you wrote it in 1997. Why do you think you hit a nerve?
Bill Sahlman: Writing a business plan is a seminal moment in the life of a new venture. Doing so entails committing to paper a vision of the factors that will affect the success or failure of the enterprise. People take the exercise very seriously and get emotionally invested in what they produce.
In that context, the article was written to give insights into how to think about the role of a business plan and its relation to new venture formation. I tried to explain that a business plan can't be a tightly crafted prediction of the future but rather a depiction of how events might unfold and a road map for change. I emphasized the notion that successful entrepreneurs constantly seek the right mixture of people, opportunity, context, and deal. They anticipate what can go wrong, what can go right, and they try to balance risk and reward.
Over the years, I have received many e-mails from folks trying to craft a business plan. They want feedback. Actually, they really want me to say that they are on the right track. I explain that I would need to get to know them and their opportunity much better than what is possible in an e-mail and that the written document is not as important as the people writing it. It's not science—it's art and craft.
Q: In the decade since the original article came out, business conditions have changed. If you were writing this piece today, would you change it much?
A: I don't think the world has changed materially. Successful ventures still have competent people pursuing sensible opportunities, using resources that help, in a favorable context. Yes, the context is very challenging today. But challenges create opportunities.
If gaining access to capital is hard, sometimes that means there will be fewer competitors. This period is almost the antithesis of the Internet bubble when everyone could raise money and start a company regardless of how lamebrained the idea. Also, we have difficult factor markets like energy, but that simply means that there are great opportunities for people with ideas for alternative energy.
Were I rewriting the article today, I might emphasize the importance of controlling your destiny by being conservative about access to capital. Many great ventures in the Internet era (pre-1999) ended up failing because they assumed they would have continued access to cheap capital. Many of those businesses failed, though the underlying idea was sensible. Similarly, we have seen a period when capital markets got ugly, which has a negative effect on all ventures, sensible and nonsensical.
I would also reinforce the idea that entrepreneurship is critical around the world. We are confronted with many crises from health care to the environment to global poverty. Solutions are likely to come from talented private sector and social entrepreneurs.
Q: You wrote in the original article that most business plans "waste too much ink on numbers and devote too little to the information that really matters to intelligent investors." Still true today? What really matters to investors?
A: When there is great uncertainty in the market, investors become quite risk averse. They will only back proven entrepreneurs with truly compelling ideas. People make the numbers, not conversely. So, I still think the people making the forecasts are more important than the numbers themselves.
Q: More and more entrepreneurial ventures are "born global": They seek to address a global market and attract funding from global investors. Should a business plan be tailored in some way for a global audience?
A: We live in a world of democratized access to ideas, human capital, and money. There are fabulous global ventures being started in every corner of the globe. These ventures can raise money locally or globally. They can disperse talent in many countries.
Take a company like Skype. When I visited Skype several years ago, it had 125 employees from 23 countries. The development team was in Estonia, and its headquarters in Europe. Skype had raised seed capital in Europe and in the United States. That's the new model.
Q: On the technology front, software applications such as Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint have added many charting, graphing, and visualizing capabilities. Some business plans are even written as Web pages. Should entrepreneurs avail themselves of these tools for business plans, or do they clutter the message too much?
A: On the first floor of the Rock Center at HBS there is a copy of the original business plan that Arthur Rock wrote for Intel some 40 years ago. It's only a few pages long, but it describes an outstanding team pursuing a new technology. I have seen compelling business plans in the form of a few PowerPoint slides, a couple of scribbled pages, and a brief video. What matters is having all the required ingredients (or a road map for getting them), not the exact form of communication.
Q: If you were to update your "Glossary of Business Plan Terms" and what they really mean ("We seek a value-added investor" really means "We are looking for a passive, dumb-as-rocks investor"), what current terms would you include?
A: The glossary holds today. I think entrepreneurs, investors, and employees need to be suitably skeptical about what they read in business plans. I have read perhaps 5,000 plans and have only seen three companies really meet their plan. That sounds like a pattern to me. If anyone makes a bet based on the company doing exactly as written, he or she will be sadly disappointed.
At the same time, every player has to be somewhat optimistic about the possibility of overcoming inevitable setbacks. I think of ventures as roller coasters, not rocket ships.
Q: Any general advice to entrepreneurs seeking funding in the uncertain capital markets of today?
A: The best money comes from customers, not external investors. I think entrepreneurs need ideas that are so compelling they can get early money from customers. I also believe that great teams with great ideas can continue to access capital on quite attractive terms from outstanding investors. If the short term looks unsettled, that often means that focusing on the long term has a big potential payoff.
- 26 Mar 2024
- Research & Ideas
How Humans Outshine AI in Adapting to Change
- 24 Jan 2024
Why Boeing’s Problems with the 737 MAX Began More Than 25 Years Ago
- 25 Jan 2022
More Proof That Money Can Buy Happiness (or a Life with Less Stress)
- Cold Call Podcast
How Do Great Leaders Overcome Adversity?
- 04 Mar 2024
- What Do You Think?
Do People Want to Work Anymore?
- Entrepreneurship
- Business Model
- Risk and Uncertainty
- Business Strategy
- Business Plan
- Forecasting and Prediction
Sign up for our weekly newsletter

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: Chapter 1 – Developing a Business Plan
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 21274

- Lee A. Swanson
- University of Saskatchewan
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to
- Describe the purposes for business planning
- Describe common business planning principles
- Explain common business plan development guidelines and tools
- List and explain the elements of the business plan development process
- Explain the purposes of each element of the business plan development process
- Explain how applying the business plan development process can aid in developing a business plan that will meet entrepreneurs’ goals
This chapter describes the purposes, principles, and the general concepts and tools for business planning, and the process for developing a business plan.
Purposes for Developing Business Plans
Business plans are developed for both internal and external purposes. Internally, entrepreneurs develop business plans to help put the pieces of their business together. Externally, the most common purpose is to raise capital.
Internal Purposes
As the road map for a business’s development, the business plan
- Defines the vision for the company
- Establishes the company’s strategy
- Describes how the strategy will be implemented
- Provides a framework for analysis of key issues
- Provides a plan for the development of the business
- Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical success factors
- Helps the entrepreneur to be realistic and test theories
External Purposes
The business plan provides the most complete source of information for valuation of the business. Thus, it is often the main method of describing a company to external audiences such as potential sources for financing and key personnel being recruited. It should assist outside parties to understand the current status of the company, its opportunities, and its needs for resources such as capital and personnel.
Business Plan Development Principles
Hindle and Mainprize (2006) suggested that business plan writers must strive to effectively communicate their expectations about the nature of an uncertain future and to project credibility. The liabilities of newness make communicating the expected future of new ventures much more difficult than for existing businesses. Consequently, business plan writers should adhere to five specific communication principles .
First, business plans must be written to meet the expectations of targeted readers in terms of what they need to know to support the proposed business. They should also lay out the milestones that investors or other targeted readers need to know. Finally, writers must clearly outline the opportunity , the context within the proposed venture will operate (internal and external environment), and the business model (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006).
There are also five business plan credibility principles that writers should consider. Business plan writers should build and establish their credibility by highlighting important and relevant information about the venture team . Writers need to elaborate on the plans they outline in their document so that targeted readers have the information they need to assess the plan’s credibility. To build and establish credibility, they must integrate scenarios to show that the entrepreneur has made realistic assumptions and has effectively anticipated what the future holds for their proposed venture. Writers need to provide comprehensive and realistic financial links between all relevant components of the plan. Finally, they must outline the deal , or the value that targeted readers should expect to derive from their involvement with the venture (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006).
General Guidelines for Developing Business Plans
Many businesses must have a business plan to achieve their goals. Using a standard format helps the reader understand that the you have thought everything through, and that the returns justify the risk. The following are some basic guidelines for business plan development.
As You Write Your Business Plan
1. If appropriate, include nice, catchy, professional graphics on your title page to make it appealing to targeted readers, but don’t go overboard.
2. Bind your document so readers can go through it easily without it falling apart. You might use a three-ring binder, coil binding, or a similar method. Make sure the binding method you use does not obscure the information next to where it is bound.
3. Make certain all of your pages are ordered and numbered correctly.
4. The usual business plan convention is to number all major sections and subsections within your plan using the format as follows:
1. First main heading
1.1 First subheading under the first main heading
1.1.1. First sub-subheading under the first subheading
2. Second main heading
2.1 First subheading under the second main heading
Use the styles and references features in Word to automatically number and format your section titles and to generate your table of contents. Be sure that the last thing you do before printing your document is update your automatic numbering and automatically generated tables. If you fail to do this, your numbering may be incorrect.
5. Prior to submitting your plan, be 100% certain each of the following requirements are met:
- Everything must be completely integrated. The written part must say exactly the same thing as the financial part.
- All financial statements must be completely linked and valid. Make sure all of your balance sheets balance.
- Everything must be correct. There should be NO spelling, grammar, sentence structure, referencing, or calculation errors.
- Your document must be well organized and formatted. The layout you choose should make the document easy to read and comprehend. All of your diagrams, charts, statements, and other additions should be easy to find and be located in the parts of the plan best suited to them.
- In some cases it can strengthen your business plan to show some information in both text and table or figure formats. You should avoid unnecessary repetition , however, as it is usually unnecessary—and even damaging—to state the same thing more than once.
- You should include all the information necessary for readers to understand everything in your document.
- The terms you use in your plan should be clear and consistent. For example, the following statement in a business plan would leave a reader completely confused: “There is a shortage of 100,000 units with competitors currently producing 25,000. We can help fill this huge gap in demand with our capacity to produce 5,000 units.”
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Business plans
- Entrepreneurship
- Entrepreneurial business strategy
- Entrepreneurial exit strategy
- Entrepreneurial finance
- Entrepreneurial financing

When Your Business Needs a Second Growth Engine
- James Allen
- From the May–June 2022 Issue

Planning for Success
- Prashant Pundrik
- March 07, 2011
Fix Their Problem, Win the Deal
- Bill Taylor
- June 22, 2015
Introduction to Business Plan Development
- Harvard Business Publishing
- Steven S. Rogers
- March 12, 2014

How to Start Networking in a New City
- Meredith Fineman
- September 23, 2016
How We Built a Strong Company in a Weak Industry
- Roger Brown
- From the February 2001 Issue
Build a Flexible Business Plan
- Anthony K. Tjan
- February 28, 2012
Great Businesses Don't Start With a Plan
- May 16, 2012

When It's Time to Pivot, What's Your Story?
- Rory McDonald
- Robert Bremner
- From the September–October 2020 Issue

The CEO of Cabot Creamery on Beating Sustainability Benchmarks
- From the May–June 2020 Issue
Secure Your Plan with the Right Team
- Heide Abelli

How to Write a Great Business Plan
- William A. Sahlman
- From the July–August 1997 Issue
To Succeed in the Long Term, Focus on the Middle Term
- Geoffrey A. Moore
- From the July–August 2007 Issue

How to Write a Winning Business Plan (HBR OnPoint Enhanced Edition)
- Stanley R. Rich
- David E. Gumpert
- January 01, 2001
Preparing for the Perfect Product Launch
- James P. Hackett
- From the April 2007 Issue

The Explainer: How to Write a Great Business Plan
- April 17, 2017
Value Captor's Process: Getting the Most Out of Your New Business Ventures
- Rita Gunther McGrath
- Thomas Keil
- From the May 2007 Issue

Don't Waste Your Time on Networking Events
- Derek Coburn
- September 26, 2016
Crossing the River
- Lynda M. Applegate

Why the Best CEOs Are Already Thinking About Their Exits
- Stanislav Shekshnia
- October 31, 2019

Royal DSM: From Continuous Transformation to Organic Growth
- William W. George
- Carin-Isabel Knoop
- Amram Migdal
- January 30, 2017
Eli Lilly: The Evista Project
- Steven C. Wheelwright
- Matthew C. Verlinden
- March 09, 1999
Growing Pains at Santropol Roulant, Part A: A New Beginning
- Charlotte Cloutier
- Fannie Couture
- September 01, 2017
The Curious Case of Dell (B)
- Marshall Sonenshine
- March 07, 2014
Profits, Politics, and Pipelines: Europe, Russia, and the Challenge of Nord Stream 2 (A)
- Rawi Abdelal
- Galit Goldstein
- Cressida Arkwright
- Khilola Zakhidova
- March 13, 2019
Amalsad Cooperative: Process Innovation in Commodity Trading
- S.R. Asokan
- Harekrishna Misra
- June 18, 2019
Eve Hall: The African American Investment Fund in Milwaukee
- Alterrell Mills
- February 02, 2017
Zipcar: Refining the Business Model
- Myra M. Hart
- Michael J. Roberts
- Julia D. Stevens
- January 13, 2003
Business Plan Development: Overview
- Gregory B Fairchild
- Jacqueline Temkin
- Buzz Becker
- September 11, 2022
J. Perez Foods (A)
- John A. Davis
- Kacie Lachapelle
- November 01, 2000
- Andrew Janower
- August 16, 1996
Friend Bank: The Time for Hope (Abridged)
- Clayton Rose
- July 11, 2012
Digital Equipment Corp.: The Endpoint Model (A)
- David A. Garvin
- Janet Simpson
- January 21, 1988
IDEC and the Saga of Self-Sustainability
- Monica Bose
- Joao Teixeira Pires
- Paulo Da Rocha Ferreira Borba
- Paulo Da Rocha Borba
- Rosa Maria Fischer
- June 05, 2006
Excel(lence) with Interest
- Russell Walker
- April 13, 2018
Quincy Apparel (A)
- Thomas R. Eisenmann
- Lisa Mazzanti
- February 11, 2015
Henry Tam and the MGI Team
- Jeffrey T. Polzer
- Ingrid Vargas
- Hillary Anger Elfenbein
- October 20, 2003
Villeroy & Boch: Tradition, Innovation and 270 Years of a Franco-German Alliance
- Denise H. Kenyon-Rouvinez
- Philip Whiteley
- January 21, 2020
uMunch: Mobile Food-Delivery App Feasibility Analysis
- Jessica Welch
- July 26, 2019
Growing Pains at Santropol Roulant, Part B: Sustaining and Disseminating the "Magic"

Actively Managing and Redirecting Projects: Executing Specific Growth Opportunities Using Discovery-Driven Planning
- Ian C. MacMillan
- March 16, 2009

Madhyamam Newspaper: Which Way Forward? - Teaching Note
- M.K. Nandakumar
- Debi Prasanna Pati
- Chandra Sekhar Satpathy
- Biswarup Saha
- Kriti Saxena
- Arun Narayanan
- November 04, 2014
Marketplace Simulations: Venture Strategy - Bikes (Play against the computer), Teaching Note
- Ernest R. Cadotte
- Marketplace Simulations
- December 09, 2021
Hong Kong Broadband Network: Interview with William Yeung, CEO
- Shlomo Ben-Hur
- December 02, 2016
Popular Topics
Partner center.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

The Management of a Business Strategic Plan: A Systematic Literature Review

Journal of Economics, Finance And Management Studies
The viability of a company depends heavily on its ability to gain an edge not only in its competitors but also in the ever-changing business environment. In today's global economy, it is imperative that corporate leaders always make better decisions than their competitors and maintain a healthy economic position. This can only be achieved with insight, knowledge, skills, experience and leadership. All of this is built on the passage of time and effort. It also reveals and raises questions about the impact management and strategic thinkers have had on the profitability of successful businesses. Therefore, all this can be enshrined in the business strategic plan to create a clear road map for an institution for a specific period of time. After the development of the strategic business plan the next crucial stage is to manage it all the way up to the end of the specified period.
Related Papers
International Journal of Academic Research in Economics and Management Sciences
Canadian Public Administration-administration Publique Du Canada
Glenn Bloodworth
Benjamin Musumali
Many organizations do strategic planning in order to prepare for the future. The real value of strategic planning is not primarily in the final plan, but more in the intellectual journey that the participants take in exploring the future. This often sensitizes them to future possibilities that they had not been aware of. It also helps them prepare to shape that future. Over the past 10 years, the author has facilitated strategic planning efforts in two large (4,000 to 20,000 people) organizations, three small (25 to 100 people) organizations, and started teaching strategic planning. This paper will draw on the experiences from all of these strategic planning efforts, while focusing on the approach that one non-profit R&D organization used to take this intellectual journey. The research methodology is based on a strategic planning approach that calls for development of a core purpose, values, Big Hairy Audacious Goal (BHAG), and envisioned future. For a particular organization, a key element of the envisioned future was to “make critical contributions to critical challenges”. Immediately this raised the question of how one measures this element. The author and a co-worker developed an approach that involved interviewing knowledgeable people inside and outside of the organization. They were asked to rate the organization’s technical work on a grid and explain the basis for their grading. The narrative that accompanied the grading was very rich in feedback to the organization. The difference between the internal and external evaluations in a few cases served to focus the leadership group on several key strategic questions
I.E.R. Flambeau
Firdissa Jebessa
Business Horizons
Charles Schewe
The Journal of Social Sciences Research
ahmad areiqat
This study aims to shed light on the role of strategic planning by utilizing the resource-based view (RBV) model to achieve an organization’s success. Through reviewing related literature it becomes necessary for organizations to prepare their financial or non-financial resources as success instigators. This applies mainly to tangible assets that can produce high-quality products and human resources and can attract potential customers to achieve competitive advantage. Hence, the ultimate finding articulates that using strategic planning through a resource-based view is the key to success. For future study there is a need to include more resources in a resource-based view like a relationship with key stakeholders that is also considered an essential asset.
Asian Journal of Education and Social Studies
ANALYN REGIDOR
Problems in the educational system must be addressed immediately given their adverse effects on school operations. In dealing with these matters, strategic planning plays a vital role in creating a specific plan of action to overcome organizational issues. Thus, this systematic review explored the various literature on strategic planning in education through the PRISMA framework. Studies included in this review are focused on the challenges, processes, and impact of strategic planning in educational institutions written in the English language and conducted between 2020 and 2022 from Google Scholar. Out of 131 records identified from database searching, fifteen articles from eight countries revealed three themes for the challenges of strategic planning, namely: lack of knowledge and skills in strategic planning, improper conduct of strategic planning, and low level of stakeholder involvement in strategic planning. The analysis also showed three themes for the process of strategic pl...
Saudi Journal of Business and Management Studies
victor Biodun
Antonio Patti
The expected shortage of global phosphate has enforced the search for alternative resources for P fertilizers. Therefore, the present study focuses on the turnover of phosphorus (P) of hydrochars and pyrochars derived from sewage sludge (SS) in soils during plant growth. We designed a pot experiment in which Lolium perenne L. was allowed to grow on a Calcic Cambisol amended with SS-derived chars. Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) yielded the SS-hydrochars (200 °C, 260 °C; 30 min, 3 h), whereas the SS-pyrochars were obtained after dry pyrolysis (600 °C, 1 h). Increasing severity of HTC lowered the recovery of total P (PT) from the feedstock to 76%. The Olsen-P diminished from 4% PT in the untreated sludge to 1% PT in the hydrochars, whereas the pyrochars exhibited an Olsen-P between 3 and 6%. At the end of the pot experiment, the soils amended with pyrochars and with hydrochars produced at 200 °C contained more Olsen-P than the unamended soils, proving that P-rich chars can indeed ser...
Howard Thomas
RELATED PAPERS
Anuário Pesquisa e Extensão Unoesc São Miguel do Oeste
Helinton Schuster
Francisco José Mora Lizán
Capital natural de México vol I: Conocimiento actual de la biodiversidad
Andres Lira
Asian Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Sumedi P Nugraha
Danni Nur Cahyani
Jurnal Aplikasi Bisnis
Maman Sulaeman
Susianti Asry
Hydrological Sciences Journal
ABDOUL MALIK IBRAHIM
Brno studies in English
Tatiana Utkina
Jurnal Teknologi Agro-Industri
Anto susanto
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
Peter Ngene
Marketing & Tourism Review
Patrick Flores Soares
13th International Congress of the Brazilian Geophysical Society & EXPOGEF, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 26–29 August 2013
Physical review. E, Statistical, nonlinear, and soft matter physics
Info Singkat
KS Pusat Analisis Keparlemenan DPR RI
مهندسی فناوری اطلاعات مکانی
Tayebe Managhebi
Roman Ozimec
Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine
Jacqueline Filshie
Pazynych Wasyl
Applied Physics Letters
G. Sawatzky
The Lancet. Neurology
VIVEK DESHMUKH
elizabeth velazquez
See More Documents Like This
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A well-crafted plan will continue to serve you throughout the life of your business. Expect to update your document regularly to ensure the information is current and aligns with the overall goals and growth of your organization. Instructions: Use this workbook to solidify and document the core components of your business plan.
in section 388 of the CO, while the minimum contents for a business review are set out in Schedule 5 to the CO. The full text of Schedule 5 has been reproduced below for easy reference. Schedule 5 disclosure requirements for the business review Sch 5.1 . A directors' report for a financial year must contain a business review that consists of ...
by. Stanley R. Rich. and. David E. Gumpert. From the Magazine (May 1985) A comprehensive, carefully thought-out business plan is essential to the success of entrepreneurs and corporate managers ...
The Harvard Business Review Classics series now offers readers the opportunity to make these seminal pieces a part of your permanent management library. Each highly readable volume contains a groundbreaking idea that continues to shape best practices and inspire countless managers around the world-and will have a direct impact on you today and ...
Lean Business Plan Template PDF. This scannable business plan template allows you to easily identify the most important elements of your plan. Use this template to outline key details pertaining to your business and industry, product or service offerings, target customer segments (and channels to reach them), and to identify sources of revenue.
William Sahlman suggests that a great business plan is one that focuses on a series of questions. These questions relate to the four factors critical to the success of every new venture: the people, the opportunity, the context, and the possibilities for both risk and reward. A great business plan is not easy to compose, Sahlman acknowledges ...
William Sahlman suggests that a great business plan is one that focuses on a series of questions. These questions relate to the four factors critical to the success of every new venture: the ...
Abstract. In creating and building a business, the entrepreneur assumes all the responsibilities for development and management, as well as the risks and rewards. Many businesses do not survive because business owners fail to develop an effective plan. The business plan focuses on major areas of concern and their contribution to the success of ...
Start with a cogent and concise one sentence statement of the business idea. A sentence that is so clear and appealing that the reader can immediately visualise or 'see' the business. You can then go on to describe: The market at which you are aiming. The specific benefits offered by your product or service.
A well-conceived business plan is essential to the success of an enterprise. Whether you are starting up a venture, seeking additional capital for an existing product line, or proposing a new activity for a corporate division, you will have to write a plan detailing your project's resource requirements, marketing decisions, financial projections, production demands, and personnel needs. The ...
The business plan should clearly and concisely define the mission, val-ues, strategy, measurable objectives, and key results the owner expects. It is important to set aside enough time to formulate the plan. Experts recommend starting the planning pro-cess at least 6 months before initiating a new business.
Prepare the following projections place them in the Business Plan Appendix: • Income Statement by years for 5 years; by months for years 1-2 and by quarters for years 3-5. • Balance Sheet years for 5 years. • Cash Flow by years for 5 years; by months for years 1-2 and by quarters for years 3-5.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Bill Sahlman: Writing a business plan is a seminal moment in the life of a new venture. Doing so entails committing to paper a vision of the factors that will affect the success or failure of the enterprise. People take the exercise very seriously and get emotionally invested in what they produce. In that context, the article was written to ...
Partners assume the same risk that the business has trouble getting started or even fails. On the same note, partners stand to benefit as much as you will from your business' success. For all of these reasons, someone you are inviting to be a partner will want to review your plan carefully. 5) Your Salespeople.
As the road map for a business's development, the business plan. Defines the vision for the company. Establishes the company's strategy. Describes how the strategy will be implemented. Provides a framework for analysis of key issues. Provides a plan for the development of the business. Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical ...
Contact: [email protected]. ABSTRACT. Purpose: The aim of this chapter is to present an overview of how entrepreneurs'. management activity can be assisted by utilising business plans ...
BUSINESS PLAN GUIDE A structured guide with worksheets to assist you in the development of your business plan, financial projections, and operating budget. ... lender or investor to quickly review your document and determine if all the criteria for making a decision are contained in the package.
This is an MIT Sloan Management Review article. Nearly every aspiring entrepreneur or innovator has a business plan, and virtually all of these individuals believe that their business plan -- what we call Plan A -- will work. They can probably even imagine how they'll look on the cover of Fortune or Inc. And they are usually wrong. But what separates the ultimate successes from the rest is ...
When Your Business Needs a Second Growth Engine. Strategy & Execution Magazine Article. James Allen. Chris Zook. Traditionally, the most reliable way for a firm to find its next wave of growth was ...
a business plan are; how they read it; and what things different members of the audience will be looking for. The task of writing a business plan is a lot easier if you have a template that can be tailored to the specific needs of your business. Chapter 2 provides one. Also explained is how to design and present a business plan to maximise the ...
JEFMS, Volume 5 Issue 06 June 2022 www.ijefm.co.in Page 1776 The Management of a Business Strategic Plan: A Systematic Literature Review The strategic business plan is an important document for every organisation aiming at remaining focused and profitable in its area of operation and it further acts as a guide for the period specified therein.