Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples

What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on June 19, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on September 5, 2024.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, history, etc.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organization?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography , action research , phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasize different aims and perspectives.
| Approach | What does it involve? |
|---|---|
| Grounded theory | Researchers collect rich data on a topic of interest and develop theories . |
| Researchers immerse themselves in groups or organizations to understand their cultures. | |
| Action research | Researchers and participants collaboratively link theory to practice to drive social change. |
| Phenomenological research | Researchers investigate a phenomenon or event by describing and interpreting participants’ lived experiences. |
| Narrative research | Researchers examine how stories are told to understand how participants perceive and make sense of their experiences. |
Note that qualitative research is at risk for certain research biases including the Hawthorne effect , observer bias , recall bias , and social desirability bias . While not always totally avoidable, awareness of potential biases as you collect and analyze your data can prevent them from impacting your work too much.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves “instruments” in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analyzing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organize your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorize your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analyzing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasize different concepts.
| Approach | When to use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| To describe and categorize common words, phrases, and ideas in qualitative data. | A market researcher could perform content analysis to find out what kind of language is used in descriptions of therapeutic apps. | |
| To identify and interpret patterns and themes in qualitative data. | A psychologist could apply thematic analysis to travel blogs to explore how tourism shapes self-identity. | |
| To examine the content, structure, and design of texts. | A media researcher could use textual analysis to understand how news coverage of celebrities has changed in the past decade. | |
| To study communication and how language is used to achieve effects in specific contexts. | A political scientist could use discourse analysis to study how politicians generate trust in election campaigns. |
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analyzing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analyzing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalizability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalizable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labor-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organization to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organize your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2024, September 05). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, how to do thematic analysis | step-by-step guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
Qualitative Research : Definition
Qualitative research is the naturalistic study of social meanings and processes, using interviews, observations, and the analysis of texts and images. In contrast to quantitative researchers, whose statistical methods enable broad generalizations about populations (for example, comparisons of the percentages of U.S. demographic groups who vote in particular ways), qualitative researchers use in-depth studies of the social world to analyze how and why groups think and act in particular ways (for instance, case studies of the experiences that shape political views).
Events and Workshops
- Introduction to NVivo Have you just collected your data and wondered what to do next? Come join us for an introductory session on utilizing NVivo to support your analytical process. This session will only cover features of the software and how to import your records. Please feel free to attend any of the following sessions below: April 25th, 2024 12:30 pm - 1:45 pm Green Library - SVA Conference Room 125 May 9th, 2024 12:30 pm - 1:45 pm Green Library - SVA Conference Room 125
- Next: Choose an approach >>
- Choose an approach
- Find studies
- Learn methods
- Getting Started
- Get software
- Get data for secondary analysis
- Network with researchers

- Last Updated: Aug 9, 2024 2:09 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.stanford.edu/qualitative_research
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 30 January 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organisation?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography, action research, phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasise different aims and perspectives.
| Approach | What does it involve? |
|---|---|
| Grounded theory | Researchers collect rich data on a topic of interest and develop theories . |
| Researchers immerse themselves in groups or organisations to understand their cultures. | |
| Researchers and participants collaboratively link theory to practice to drive social change. | |
| Phenomenological research | Researchers investigate a phenomenon or event by describing and interpreting participants’ lived experiences. |
| Narrative research | Researchers examine how stories are told to understand how participants perceive and make sense of their experiences. |
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves ‘instruments’ in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analysing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organise your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorise your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analysing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasise different concepts.
| Approach | When to use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| To describe and categorise common words, phrases, and ideas in qualitative data. | A market researcher could perform content analysis to find out what kind of language is used in descriptions of therapeutic apps. | |
| To identify and interpret patterns and themes in qualitative data. | A psychologist could apply thematic analysis to travel blogs to explore how tourism shapes self-identity. | |
| To examine the content, structure, and design of texts. | A media researcher could use textual analysis to understand how news coverage of celebrities has changed in the past decade. | |
| To study communication and how language is used to achieve effects in specific contexts. | A political scientist could use discourse analysis to study how politicians generate trust in election campaigns. |
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analysing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analysing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalisability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalisable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labour-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organisation to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organise your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, January 30). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Qualitative Research: An Overview
- First Online: 24 April 2019
Cite this chapter

- Yanto Chandra 3 &
- Liang Shang 4
4306 Accesses
5 Citations
Qualitative research is one of the most commonly used types of research and methodology in the social sciences. Unfortunately, qualitative research is commonly misunderstood. In this chapter, we describe and explain the misconceptions surrounding qualitative research enterprise, why researchers need to care about when using qualitative research, the characteristics of qualitative research, and review the paradigms in qualitative research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Qualitative research is defined as the practice used to study things –– individuals and organizations and their reasons, opinions, and motivations, beliefs in their natural settings. It involves an observer (a researcher) who is located in the field , who transforms the world into a series of representations such as fieldnotes, interviews, conversations, photographs, recordings and memos (Denzin and Lincoln 2011 ). Many researchers employ qualitative research for exploratory purpose while others use it for ‘quasi’ theory testing approach. Qualitative research is a broad umbrella of research methodologies that encompasses grounded theory (Glaser and Strauss 2017 ; Strauss and Corbin 1990 ), case study (Flyvbjerg 2006 ; Yin 2003 ), phenomenology (Sanders 1982 ), discourse analysis (Fairclough 2003 ; Wodak and Meyer 2009 ), ethnography (Geertz 1973 ; Garfinkel 1967 ), and netnography (Kozinets 2002 ), among others. Qualitative research is often synonymous with ‘case study research’ because ‘case study’ primarily uses (but not always) qualitative data.
The quality standards or evaluation criteria of qualitative research comprises: (1) credibility (that a researcher can provide confidence in his/her findings), (2) transferability (that results are more plausible when transported to a highly similar contexts), (3) dependability (that errors have been minimized, proper documentation is provided), and (4) confirmability (that conclusions are internally consistent and supported by data) (see Lincoln and Guba 1985 ).
We classify research into a continuum of theory building — > theory elaboration — > theory testing . Theory building is also known as theory exploration. Theory elaboration refers to the use of qualitative data and a method to seek “confirmation” of the relationships among variables or processes or mechanisms of a social reality (Bartunek and Rynes 2015 ).
In the context of qualitative research, theory/ies usually refer(s) to conceptual model(s) or framework(s) that explain the relationships among a set of variables or processes that explain a social phenomenon. Theory or theories could also refer to general ideas or frameworks (e.g., institutional theory, emancipation theory, or identity theory) that are reviewed as background knowledge prior to the commencement of a qualitative research project.
For example, a qualitative research can ask the following question: “How can institutional change succeed in social contexts that are dominated by organized crime?” (Vaccaro and Palazzo 2015 ).
We have witnessed numerous cases in which committed positivist methodologists were asked to review qualitative papers, and they used a survey approach to assess the quality of an interpretivist work. This reviewers’ fallacy is dangerous and hampers the progress of a field of research. Editors must be cognizant of such fallacy and avoid it.
A social enterprises (SE) is an organization that combines social welfare and commercial logics (Doherty et al. 2014 ), or that uses business principles to address social problems (Mair and Marti 2006 ); thus, qualitative research that reports that ‘social impact’ is important for SEs is too descriptive and, arguably, tautological. It is not uncommon to see authors submitting purely descriptive papers to scholarly journals.
Some qualitative researchers have conducted qualitative work using primarily a checklist (ticking the boxes) to show the presence or absence of variables, as if it were a survey-based study. This is utterly inappropriate for a qualitative work. A qualitative work needs to show the richness and depth of qualitative findings. Nevertheless, it is acceptable to use such checklists as supplementary data if a study involves too many informants or variables of interest, or the data is too complex due to its longitudinal nature (e.g., a study that involves 15 cases observed and involving 59 interviews with 33 informants within a 7-year fieldwork used an excel sheet to tabulate the number of events that occurred as supplementary data to the main analysis; see Chandra 2017a , b ).
As mentioned earlier, there are different types of qualitative research. Thus, a qualitative researcher will customize the data collection process to fit the type of research being conducted. For example, for researchers using ethnography, the primary data will be in the form of photos and/or videos and interviews; for those using netnography, the primary data will be internet-based textual data. Interview data is perhaps the most common type of data used across all types of qualitative research designs and is often synonymous with qualitative research.
The purpose of qualitative research is to provide an explanation , not merely a description and certainly not a prediction (which is the realm of quantitative research). However, description is needed to illustrate qualitative data collected, and usually researchers describe their qualitative data by inserting a number of important “informant quotes” in the body of a qualitative research report.
We advise qualitative researchers to adhere to one approach to avoid any epistemological and ontological mismatch that may arise among different camps in qualitative research. For instance, mixing a positivist with a constructivist approach in qualitative research frequently leads to unnecessary criticism and even rejection from journal editors and reviewers; it shows a lack of methodological competence or awareness of one’s epistemological position.
Analytical generalization is not generalization to some defined population that has been sampled, but to a “theory” of the phenomenon being studied, a theory that may have much wider applicability than the particular case studied (Yin 2003 ).
There are different types of contributions. Typically, a researcher is expected to clearly articulate the theoretical contributions for a qualitative work submitted to a scholarly journal. Other types of contributions are practical (or managerial ), common for business/management journals, and policy , common for policy related journals.
There is ongoing debate on whether a template for qualitative research is desirable or necessary, with one camp of scholars (the pluralistic critical realists) that advocates a pluralistic approaches to qualitative research (“qualitative research should not follow a particular template or be prescriptive in its process”) and the other camps are advocating for some form of consensus via the use of particular approaches (e.g., the Eisenhardt or Gioia Approach, etc.). However, as shown in Table 1.1 , even the pluralistic critical realism in itself is a template and advocates an alternative form of consensus through the use of diverse and pluralistic approaches in doing qualitative research.
Alvesson, M., & Kärreman, D. (2007). Constructing mystery: Empirical matters in theory development. Academy of Management Review, 32 (4), 1265–1281.
Article Google Scholar
Bartunek, J. M., & Rynes, S. L. (2015). Qualitative research: It just keeps getting more interesting! In Handbook of qualitative organizational research (pp. 41–55). New York: Routledge.
Google Scholar
Brinkmann, S. (2018). Philosophies of qualitative research . New York: Oxford University Press.
Bucher, S., & Langley, A. (2016). The interplay of reflective and experimental spaces in interrupting and reorienting routine dynamics. Organization Science, 27 (3), 594–613.
Chandra, Y. (2017a). A time-based process model of international entrepreneurial opportunity evaluation. Journal of International Business Studies, 48 (4), 423–451.
Chandra, Y. (2017b). Social entrepreneurship as emancipatory work. Journal of Business Venturing, 32 (6), 657–673.
Corley, K. G., & Gioia, D. A. (2004). Identity ambiguity and change in the wake of a corporate spin-off. Administrative Science Quarterly, 49 (2), 173–208.
Cornelissen, J. P. (2017). Preserving theoretical divergence in management research: Why the explanatory potential of qualitative research should be harnessed rather than suppressed. Journal of Management Studies, 54 (3), 368–383.
Denis, J. L., Lamothe, L., & Langley, A. (2001). The dynamics of collective leadership and strategic change in pluralistic organizations. Academy of Management Journal, 44 (4), 809–837.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2011). Introduction. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The Sage handbook of qualitative research (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Doherty, B., Haugh, H., & Lyon, F. (2014). Social enterprises as hybrid organizations: A review and research agenda. International Journal of Management Reviews, 16 (4), 417–436.
Dubé, L., & Paré, G. (2003). Rigor in information systems positivist case research: Current practices, trends, and recommendations. MIS Quarterly, 27 (4), 597–636.
Easton, G. (2010). Critical realism in case study research. Industrial Marketing Management, 39 (1), 118–128.
Eisenhardt, K. M. (1989a). Building theories from case study research. Academy of Management Review, 14 (4), 532–550.
Eisenhardt, K. M. (1989b). Making fast strategic decisions in high-velocity environments. Academy of Management Journal, 32 (3), 543–576.
Fairclough, N. (2003). Analysing discourse: Textual analysis for social research . Abingdon: Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
Flyvbjerg, B. (2006). Five misunderstandings about case-study research. Qualitative Inquiry, 12 (2), 219–245.
Friese, S. (2011). Using ATLAS.ti for analyzing the financial crisis data [67 paragraphs]. Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung/Forum: Qualitative Social Research, 12 (1), Art. 39. http://nbn-resolving.de/urn:nbn:de:0114-fqs1101397
Garfinkel, H. (1967). Studies in ethnomethodology . Malden: Blackwell Publishers.
Geertz, C. (1973). Interpretation of cultures . New York: Basic Books.
Gehman, J., Glaser, V. L., Eisenhardt, K. M., Gioia, D., Langley, A., & Corley, K. G. (2017). Finding theory–method fit: A comparison of three qualitative approaches to theory building. Journal of Management Inquiry, 27 , 284–300. in press.
Gioia, D. A. (1992). Pinto fires and personal ethics: A script analysis of missed opportunities. Journal of Business Ethics, 11 (5–6), 379–389.
Gioia, D. A. (2007). Individual epistemology – Interpretive wisdom. In E. H. Kessler & J. R. Bailey (Eds.), The handbook of organizational and managerial wisdom (pp. 277–294). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Chapter Google Scholar
Gioia, D. (2019). If I had a magic wand: Reflections on developing a systematic approach to qualitative research. In B. Boyd, R. Crook, J. Le, & A. Smith (Eds.), Research methodology in strategy and management . https://books.emeraldinsight.com/page/detail/Standing-on-the-Shoulders-of-Giants/?k=9781787563360
Gioia, D. A., & Chittipeddi, K. (1991). Sensemaking and sensegiving in strategic change initiation. Strategic Management Journal, 12 (6), 433–448.
Gioia, D. A., Price, K. N., Hamilton, A. L., & Thomas, J. B. (2010). Forging an identity: An insider-outsider study of processes involved in the formation of organizational identity. Administrative Science Quarterly, 55 (1), 1–46.
Gioia, D. A., Corley, K. G., & Hamilton, A. L. (2013). Seeking qualitative rigor in inductive research: Notes on the Gioia methodology. Organizational Research Methods, 16 (1), 15–31.
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (2017). Discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research . New York: Routledge.
Graebner, M. E., & Eisenhardt, K. M. (2004). The seller’s side of the story: Acquisition as courtship and governance as syndicate in entrepreneurial firms. Administrative Science Quarterly, 49 (3), 366–403.
Grayson, K., & Shulman, D. (2000). Indexicality and the verification function of irreplaceable possessions: A semiotic analysis. Journal of Consumer Research, 27 (1), 17–30.
Hunt, S. D. (1991). Positivism and paradigm dominance in consumer research: Toward critical pluralism and rapprochement. Journal of Consumer Research, 18 (1), 32–44.
King, G., Keohane, R. O., & Verba, S. (1994). Designing social inquiry: Scientific inference in qualitative research . Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Kozinets, R. V. (2002). The field behind the screen: Using netnography for marketing research in online communities. Journal of Marketing Research, 39 (1), 61–72.
Langley, A. (1988). The roles of formal strategic planning. Long Range Planning, 21 (3), 40–50.
Langley, A., & Abdallah, C. (2011). Templates and turns in qualitative studies of strategy and management. In Building methodological bridges (pp. 201–235). Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing Limited.
Langley, A., Golden-Biddle, K., Reay, T., Denis, J. L., Hébert, Y., Lamothe, L., & Gervais, J. (2012). Identity struggles in merging organizations: Renegotiating the sameness–difference dialectic. The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science, 48 (2), 135–167.
Langley, A. N. N., Smallman, C., Tsoukas, H., & Van de Ven, A. H. (2013). Process studies of change in organization and management: Unveiling temporality, activity, and flow. Academy of Management Journal, 56 (1), 1–13.
Lin, A. C. (1998). Bridging positivist and interpretivist approaches to qualitative methods. Policy Studies Journal, 26 (1), 162–180.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1985). Naturalistic inquiry . Beverly Hills: Sage.
Mair, J., & Marti, I. (2006). Social entrepreneurship research: A source of explanation, prediction, and delight. Journal of World Business, 41 (1), 36–44.
Nag, R., Corley, K. G., & Gioia, D. A. (2007). The intersection of organizational identity, knowledge, and practice: Attempting strategic change via knowledge grafting. Academy of Management Journal, 50 (4), 821–847.
Ozcan, P., & Eisenhardt, K. M. (2009). Origin of alliance portfolios: Entrepreneurs, network strategies, and firm performance. Academy of Management Journal, 52 (2), 246–279.
Prasad, P. (2018). Crafting qualitative research: Beyond positivist traditions . New York: Taylor & Francis.
Pratt, M. G. (2009). From the editors: For the lack of a boilerplate: Tips on writing up (and reviewing) qualitative research. Academy of Management Journal, 52 (5), 856–862.
Ramoglou, S., & Tsang, E. W. (2016). A realist perspective of entrepreneurship: Opportunities as propensities. Academy of Management Review, 41 (3), 410–434.
Sanders, P. (1982). Phenomenology: A new way of viewing organizational research. Academy of Management Review, 7 (3), 353–360.
Sobh, R., & Perry, C. (2006). Research design and data analysis in realism research. European Journal of Marketing, 40 (11/12), 1194–1209.
Stake, R. E. (2010). Qualitative research: Studying how things work . New York: Guilford Press.
Strauss, A., & Corbin, J. M. (1990). Basics of qualitative research: Grounded theory procedures and techniques . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Vaccaro, A., & Palazzo, G. (2015). Values against violence: Institutional change in societies dominated by organized crime. Academy of Management Journal, 58 (4), 1075–1101.
Weick, K. E. (1989). Theory construction as disciplined imagination. Academy of Management Review, 14 (4), 516–531.
Welch, C. L., Welch, D. E., & Hewerdine, L. (2008). Gender and export behaviour: Evidence from women-owned enterprises. Journal of Business Ethics, 83 (1), 113–126.
Welch, C., Piekkari, R., Plakoyiannaki, E., & Paavilainen-Mäntymäki, E. (2011). Theorising from case studies: Towards a pluralist future for international business research. Journal of International Business Studies, 42 (5), 740–762.
Wodak, R., & Meyer, M. (Eds.). (2009). Methods for critical discourse analysis . London: Sage.
Yin, R. K. (1981). Life histories of innovations: How new practices become routinized. Public Administration Review, 41 , 21–28.
Yin, R. (2003). Case study research: Design and methods . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Young, R. A., & Collin, A. (2004). Introduction: Constructivism and social constructionism in the career field. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 64 (3), 373–388.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Yanto Chandra
City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Liang Shang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Chandra, Y., Shang, L. (2019). Qualitative Research: An Overview. In: Qualitative Research Using R: A Systematic Approach. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3170-1_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3170-1_1
Published : 24 April 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-13-3169-5
Online ISBN : 978-981-13-3170-1
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Social Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- UConn Library
- Scientific Research and Communication
- Qualitative Research: What is it?
Scientific Research and Communication — Qualitative Research: What is it?
- Essential Resources
- The Scientific Method
- Types of Scientific Papers
- Organization of a Scientific Paper
- Peer Review & Academic Journals
- Primary and Secondary Sources
- Scientific Information Literacy
- Critical Reading Methods
- Scientific Writing Guidebooks
- Science Literature Reviews
- Searching Strategies for Science Databases
- Engineering Career Exploration
- Quantitative Research: What Is It?
- AI Tools for Research
- Avoiding Plagiarism
What is qualitative research?
"Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. [1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data."
"Qualitative research at its core, ask open-ended questions whose answers are not easily put into numbers such as ‘how’ and ‘why’. [2] Due to the open-ended nature of the research questions at hand, qualitative research design is often not linear in the same way quantitative design is. [2] One of the strengths of qualitative research is its ability to explain processes and patterns of human behavior that can be difficult to quantify. [3] Phenomena such as experiences, attitudes, and behaviors can be difficult to accurately capture quantitatively, whereas a qualitative approach allows participants themselves to explain how, why, or what they were thinking, feeling, and experiencing at a certain time or during an event of interest."
- Qualitative Study - Steven Tenny; Grace D. Brannan; Janelle M. Brannan; Nancy C. Sharts-Hopko. This article details what qualitative research is, and some of the methodologies used.
Examples of Qualitative Research

- Quantitative vs Qualitative Chart Chart showing examples of quantitative vs. qualitative research.
EBooks on Qualitative Research Methodology
Physical Library Books
- << Previous: Engineering Career Exploration
- Next: Quantitative Research: What Is It? >>
- Last Updated: Sep 6, 2024 1:42 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/sciencecommunication
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Statistics By Jim
Making statistics intuitive
Qualitative Research: Goals, Methods & Benefits
By Jim Frost 5 Comments
Qualitative research aims to understand ideas, experiences, and opinions using non-numeric data, such as text, audio, and visual recordings. The focus is on language, behaviors, and social structures. Qualitative researchers want to present personal experiences and produce narrative stories that use natural language to provide meaningful answers to their research questions.
Qualitative research focuses on descriptions, opinions, and experiences rather than numbers. Standard data collection techniques include interviews, diaries, focus groups, documents, artifacts, and direct observations.
Qualitative research provides a sharp contrast to quantitative research, which uses numeric data and statistical analyses to understand a concrete reality. The vast majority of content on my website is about quantitative research and statistical analyses. However, there are areas where qualitative research is more effective at understanding dynamic social structures and subjective perceptions in a real-world that can be convoluted.
Psychologists created qualitative research because the traditional methods failed to understand the human experience. Consequently, they developed a naturalistic approach that focuses on human behavior, what gives people meaning, how they perceive things, and why they act in a particular manner. This process involves understanding the people in their natural settings and social interactions.
Psychology, sociology, anthropology, education, and history frequently use qualitative research. Marketing groups also use it to understand how real people use their products, what factors increase usage, and obstacles that reduce usage. Ultimately, they want to market their products better, which requires understanding consumer mindsets.
Examples of Qualitative Research Questions
Qualitative research can answer a wide range of questions. Below are six example research questions.
- What factors shape body image?
- How do single-parent homes affect children?
- What challenges do consumers face in adopting a company’s new product?
- How does social media affect anxiety?
- What effect does previous domestic violence have on current relationships?
- What are the unique problems that night shift workers face?
Learn how to create research questions for scientific studies .
Qualitative Research Methods

Ethnography
The researchers embed themselves in the daily lives of their subjects and their social groups. Their goal is to understand their habits, routines, beliefs, and challenges.
For an excellent guide to observing participants in the field, read Qualitative Research Methods: A Data Collector’s Field Guide [external PDF].
Narrative Research
An alternative qualitative approach is to interview several subjects in-depth, gather documents, and collect artifacts. The researchers then piece these multiple lines of evidence together to create a narrative that answers the research question.
Phenomenology
Qualitative researchers can study an event as it happens from different vantage points. For instance, they can conduct interviews, record videos, and directly observe the proceedings to understand the participants’ subjective experiences.
Grounded Theory
This form of qualitative research differs from most other methods. The researchers start with a qualitative dataset and then sort through these data, tagging concepts and ideas. As the study continues, they organize and group the conceptual tags. During this process, the researchers watch for hypotheses to emerge. This method seeks to let the scientists organically react to the dataset but yet ground the results in as much empirical data as possible.
Case Studies
A case study usually examines one subject in great detail. The subject can be a person, business, or other organization. The goal is to understand the subject as much as possible and use that information to understand the larger population to some extent. This qualitative research method can foster understanding of the motivations, influences, and factors that lead to success or failure. Learn more about What is a Case Study? Definition & Examples .
Qualitative Research Data Collection Methods

Below are the standard data collection methods for qualitative research. Studies can combine multiple methods.
- Secondary research : Use existing documents, photographs, audio, and video.
- Interviews : One-on-one guided conversations.
- Direct observations : Researchers observe the subjects in the field and take notes.
- Questionnaires : Qualitative research frequently uses surveys with open-ended questions.
- Focus groups : A guided small group conversation where the discussion provides the data.
Analyzing Qualitative Data
After collecting their data, qualitative researchers have multiple ways to analyze the content. A common approach is to add codes that represent meaningful ideas to communications, documents, videos, etc. The researchers evaluate frequencies and patterns of these conceptual codes. They can also find the most common words, thematic patterns, communications structure, and the method by which communications obtain specific goals. Analysts refer to these approaches with names such as content analysis, thematic analysis, textual analysis, etc.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has many advantages because it seeks to record the subjects’ lived experiences and understand them in ways that quantitative data cannot. Going beyond just the numbers, they can gain insights into opinions, emotions, and perceptions. These studies frequently occur in natural environments and real-world social contexts rather than labs and other artificial environments that might affect the participants, particularly when talking about personal matters.
Unlike quantitative research, qualitative methods are flexible. Researchers can change their methodology and theories as they gather information. The open-ended nature of qualitative research allows the researchers to uncover new ideas they hadn’t anticipated and adjust accordingly.
However, qualitative research has some disadvantages.
Its primary disadvantage is that it is more subjective than quantitative research. It’s harder to separate the researchers’ opinions and predilections from the more personal nature of qualitative data. Determining what concepts to code and when to apply those codes can be highly subjective. Flexibly adapting the research on the fly can be great, but it also increases the prominence of the researcher’s personal determination of relevance.
Furthermore, consider how ordinary people can observe the same reality in all its real-world messiness and draw different conclusions. Similarly, qualitative researchers can evaluate the same real-world data and produce dissimilar findings.
Qualitative research typically uses small samples that are less likely to be representative , which limits generalizability . Finally, as with other types of observational studies , the real-world settings in qualitative research can be an advantage, but they potentially introduce a host of confounding variables that can bias the results.
Share this:

Reader Interactions
August 1, 2023 at 10:42 am
If qualitative data is counted in categorical, ordinal, or binary forms does it become quantitative data?
January 2, 2023 at 11:27 am
Who are the actual people at the foundations of qualitative research as we know it? We know they are generally psychologists, like creswell who seems to have updated a but for the modern era, but who stands out the most in research throughout the age of qualitative research?
November 22, 2022 at 11:04 am
Have you publish on qualitative methods and surveys?
November 22, 2022 at 4:19 pm
I haven’t as of yet. Probably down the road, particularly for surveys.
April 23, 2022 at 2:16 pm
Can regression results from another study be used for my data collection, as a form of secondary data? I believe that the regression results are important to my study, but I don’t know if “results” from another study, specifically taken from their appendix table can be pasted into my “data collection section” of my research paper. I wish to employ a grounded theory research methodology that is mixed methods in approach, because I can apply regression analysis to the regression results, but I question the possibility of doing this for my data collection section.
Comments and Questions Cancel reply
An Overview of Qualitative Research Methods
Direct Observation, Interviews, Participation, Immersion, Focus Groups
- Research, Samples, and Statistics
- Key Concepts
- Major Sociologists
- News & Issues
- Recommended Reading
- Archaeology
Qualitative research is a type of social science research that collects and works with non-numerical data and that seeks to interpret meaning from these data that help understand social life through the study of targeted populations or places.
People often frame it in opposition to quantitative research , which uses numerical data to identify large-scale trends and employs statistical operations to determine causal and correlative relationships between variables.
Within sociology, qualitative research is typically focused on the micro-level of social interaction that composes everyday life, whereas quantitative research typically focuses on macro-level trends and phenomena.
Key Takeaways
Methods of qualitative research include:
- observation and immersion
- open-ended surveys
- focus groups
- content analysis of visual and textual materials
- oral history
Qualitative research has a long history in sociology and has been used within it for as long as the field has existed.
This type of research has long appealed to social scientists because it allows the researchers to investigate the meanings people attribute to their behavior, actions, and interactions with others.
While quantitative research is useful for identifying relationships between variables, like, for example, the connection between poverty and racial hate, it is qualitative research that can illuminate why this connection exists by going directly to the source—the people themselves.
Qualitative research is designed to reveal the meaning that informs the action or outcomes that are typically measured by quantitative research. So qualitative researchers investigate meanings, interpretations, symbols, and the processes and relations of social life.
What this type of research produces is descriptive data that the researcher must then interpret using rigorous and systematic methods of transcribing, coding, and analysis of trends and themes.
Because its focus is everyday life and people's experiences, qualitative research lends itself well to creating new theories using the inductive method , which can then be tested with further research.
Qualitative researchers use their own eyes, ears, and intelligence to collect in-depth perceptions and descriptions of targeted populations, places, and events.
Their findings are collected through a variety of methods, and often a researcher will use at least two or several of the following while conducting a qualitative study:
- Direct observation : With direct observation, a researcher studies people as they go about their daily lives without participating or interfering. This type of research is often unknown to those under study, and as such, must be conducted in public settings where people do not have a reasonable expectation of privacy. For example, a researcher might observe the ways in which strangers interact in public as they gather to watch a street performer.
- Open-ended surveys : While many surveys are designed to generate quantitative data, many are also designed with open-ended questions that allow for the generation and analysis of qualitative data. For example, a survey might be used to investigate not just which political candidates voters chose, but why they chose them, in their own words.
- Focus group : In a focus group, a researcher engages a small group of participants in a conversation designed to generate data relevant to the research question. Focus groups can contain anywhere from 5 to 15 participants. Social scientists often use them in studies that examine an event or trend that occurs within a specific community. They are common in market research, too.
- In-depth interviews : Researchers conduct in-depth interviews by speaking with participants in a one-on-one setting. Sometimes a researcher approaches the interview with a predetermined list of questions or topics for discussion but allows the conversation to evolve based on how the participant responds. Other times, the researcher has identified certain topics of interest but does not have a formal guide for the conversation, but allows the participant to guide it.
- Oral history : The oral history method is used to create a historical account of an event, group, or community, and typically involves a series of in-depth interviews conducted with one or multiple participants over an extended period.
- Participant observation : This method is similar to observation, however with this one, the researcher also participates in the action or events to not only observe others but to gain the first-hand experience in the setting.
- Ethnographic observation : Ethnographic observation is the most intensive and in-depth observational method. Originating in anthropology, with this method, a researcher fully immerses themselves into the research setting and lives among the participants as one of them for anywhere from months to years. By doing this, the researcher attempts to experience day-to-day existence from the viewpoints of those studied to develop in-depth and long-term accounts of the community, events, or trends under observation.
- Content analysis : This method is used by sociologists to analyze social life by interpreting words and images from documents, film, art, music, and other cultural products and media. The researchers look at how the words and images are used, and the context in which they are used to draw inferences about the underlying culture. Content analysis of digital material, especially that generated by social media users, has become a popular technique within the social sciences.
While much of the data generated by qualitative research is coded and analyzed using just the researcher's eyes and brain, the use of computer software to do these processes is increasingly popular within the social sciences.
Such software analysis works well when the data is too large for humans to handle, though the lack of a human interpreter is a common criticism of the use of computer software.
Pros and Cons
Qualitative research has both benefits and drawbacks.
On the plus side, it creates an in-depth understanding of the attitudes, behaviors, interactions, events, and social processes that comprise everyday life. In doing so, it helps social scientists understand how everyday life is influenced by society-wide things like social structure , social order , and all kinds of social forces.
This set of methods also has the benefit of being flexible and easily adaptable to changes in the research environment and can be conducted with minimal cost in many cases.
Among the downsides of qualitative research is that its scope is fairly limited so its findings are not always widely able to be generalized.
Researchers also have to use caution with these methods to ensure that they do not influence the data in ways that significantly change it and that they do not bring undue personal bias to their interpretation of the findings.
Fortunately, qualitative researchers receive rigorous training designed to eliminate or reduce these types of research bias.
- How to Conduct a Sociology Research Interview
- What Is Participant Observation Research?
- Immersion Definition: Cultural, Language, and Virtual
- Definition and Overview of Grounded Theory
- The Differences Between Indexes and Scales
- Pros and Cons of Secondary Data Analysis
- Social Surveys: Questionnaires, Interviews, and Telephone Polls
- The Different Types of Sampling Designs in Sociology
- Principal Components and Factor Analysis
- Sociology Explains Why Some People Cheat on Their Spouses
- Deductive Versus Inductive Reasoning
- How to Construct an Index for Research
- Data Sources For Sociological Research
- A Review of Software Tools for Quantitative Data Analysis
- Constructing a Deductive Theory
- Scales Used in Social Science Research
Our systems are now restored following recent technical disruption, and we’re working hard to catch up on publishing. We apologise for the inconvenience caused. Find out more: https://www.cambridge.org/universitypress/about-us/news-and-blogs/cambridge-university-press-publishing-update-following-technical-disruption
We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to provide you with a better experience on our websites. Close this message to accept cookies or find out how to manage your cookie settings .
Login Alert

- > Journals
- > BJPsych Bulletin
- > The Psychiatrist
- > Volume 37 Issue 6
- > Qualitative research: its value and applicability

Article contents
What questions are best answered using qualitative research, countering some misconceptions, in conclusion, qualitative research: its value and applicability.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 January 2018
Qualitative research has a rich tradition in the study of human social behaviour and cultures. Its general aim is to develop concepts which help us to understand social phenomena in, wherever possible, natural rather than experimental settings, to gain an understanding of the experiences, perceptions and/or behaviours of individuals, and the meanings attached to them. The effective application of qualitative methods to other disciplines, including clinical, health service and education research, has a rapidly expanding and robust evidence base. Qualitative approaches have particular potential in psychiatry research, singularly and in combination with quantitative methods. This article outlines the nature and potential application of qualitative research as well as attempting to counter a number of misconceptions.
Qualitative research has a rich tradition in the social sciences. Since the late 19th century, researchers interested in studying the social behaviour and cultures of humankind have perceived limitations in trying to explain the phenomena they encounter in purely quantifiable, measurable terms. Anthropology, in its social and cultural forms, was one of the foremost disciplines in developing what would later be termed a qualitative approach, founded as it was on ethnographic studies which sought an understanding of the culture of people from other societies, often hitherto unknown and far removed in geography. Reference Bernard 1 Early researchers would spend extended periods of time living in societies, observing, noting and photographing the minutia of daily life, with the most committed often learning the language of peoples they observed, in the hope of gaining greater acceptance by them and a more detailed understanding of the cultural norms at play. All academic disciplines concerned with human and social behaviour, including anthropology, sociology and psychology, now make extensive use of qualitative research methods whose systematic application was first developed by these colonial-era social scientists.
Their methods, involving observation, participation and discussion of the individuals and groups being studied, as well as reading related textual and visual media and artefacts, form the bedrock of all qualitative social scientific inquiry. The general aim of qualitative research is thus to develop concepts which help us to understand social phenomena in, wherever possible, natural rather than experimental settings, to gain an understanding of the experiences, perceptions and/or behaviours of those studied, and the meanings attached to them. Reference Bryman 2 Researchers interested in finding out why people behave the way they do; how people are affected by events, how attitudes and opinions are formed; how and why cultures and practices have developed in the way they have, might well consider qualitative methods to answer their questions.
It is fair to say that clinical and health-related research is still dominated by quantitative methods, of which the randomised controlled trial, focused on hypothesis-testing through experiment controlled by randomisation, is perhaps the quintessential method. Qualitative approaches may seem obscure to the uninitiated when directly compared with the experimental, quantitative methods used in clinical research. There is increasing recognition among researchers in these fields, however, that qualitative methods such as observation, in-depth interviews, focus groups, consensus methods, case studies and the interpretation of texts can be more effective than quantitative approaches in exploring complex phenomena and as such are valuable additions to the methodological armoury available to them. Reference Denzin and Lincoln 3
In considering what kind of research questions are best answered using a qualitative approach, it is important to remember that, first and foremost, unlike quantitative research, inquiry conducted in the qualitative tradition seeks to answer the question ‘What?’ as opposed to ‘How often?’. Qualitative methods are designed to reveal what is going on by describing and interpreting phenomena; they do not attempt to measure how often an event or association occurs. Research conducted using qualitative methods is normally done with an intent to preserve the inherent complexities of human behaviour as opposed to assuming a reductive view of the subject in order to count and measure the occurrence of phenomena. Qualitative research normally takes an inductive approach, moving from observation to hypothesis rather than hypothesis-testing or deduction, although the latter is perfectly possible.
When conducting research in this tradition, the researcher should, if possible, avoid separating the stages of study design, data collection and analysis, but instead weave backwards and forwards between the raw data and the process of conceptualisation, thereby making sense of the data throughout the period of data collection. Although there are inevitable tensions among methodologists concerned with qualitative practice, there is broad consensus that a priori categories and concepts reflecting a researcher's own preconceptions should not be imposed on the process of data collection and analysis. The emphasis should be on capturing and interpreting research participants' true perceptions and/or behaviours.
Using combined approaches
The polarity between qualitative and quantitative research has been largely assuaged, to the benefit of all disciplines which now recognise the value, and compatibility, of both approaches. Indeed, there can be particular value in using quantitative methods in combination with qualitative methods. Reference Barbour 4 In the exploratory stages of a research project, qualitative methodology can be used to clarify or refine the research question, to aid conceptualisation and to generate a hypothesis. It can also help to identify the correct variables to be measured, as researchers have been known to measure before they fully understand the underlying issues pertaining to a study and, as a consequence, may not always target the most appropriate factors. Qualitative work can be valuable in the interpretation, qualification or illumination of quantitative research findings. This is particularly helpful when focusing on anomalous results, as they test the main hypothesis formulated. Qualitative methods can also be used in combination with quantitative methods to triangulate findings and support the validation process, for example, where three or more methods are used and the results compared for similarity (e.g. a survey, interviews and a period of observation in situ ).
‘There is little value in qualitative research findings because we cannot generalise from them’
Generalisability refers to the extent that the account can be applied to other people, times and settings other than those actually studied. A common criticism of qualitative research is that the results of a study are rarely, if ever, generalisable to a larger population because the sample groups are small and the participants are not chosen randomly. Such criticism fails to recognise the distinctiveness of qualitative research where sampling is concerned. In quantitative research, the intent is to secure a large random sample that is representative of the general population, with the purpose of eliminating individual variations, focusing on generalisations and thereby allowing for statistical inference of results that are applicable across an entire population. In qualitative research, generalisability is based on the assumption that it is valuable to begin to understand similar situations or people, rather than being representative of the target population. Qualitative research is rarely based on the use of random samples, so the kinds of reference to wider populations made on the basis of surveys cannot be used in qualitative analysis.
Qualitative researchers utilise purposive sampling, whereby research participants are selected deliberately to test a particular theoretical premise. The purpose of sampling here is not to identify a random subgroup of the general population from which statistically significant results can be extrapolated, but rather to identify, in a systematic way, individuals that possess relevant characteristics for the question being considered. Reference Strauss and Corbin 5 The researchers must instead ensure that any reference to people and settings beyond those in the study are justified, which is normally achieved by defining, in detail, the type of settings and people to whom the explanation or theory applies based on the identification of similar settings and people in the study. The intent is to permit a detailed examination of the phenomenon, resulting in a text-rich interpretation that can deepen our understanding and produce a plausible explanation of the phenomenon under study. The results are not intended to be statistically generalisable, although any theory they generate might well be.
‘Qualitative research cannot really claim reliability or validity’
In quantitative research, reliability is the extent to which different observers, or the same observers on different occasions, make the same observations or collect the same data about the same object of study. The changing nature of social phenomena scrutinised by qualitative researchers inevitably makes the possibility of the same kind of reliability problematic in their work. A number of alternative concepts to reliability have been developed by qualitative methodologists, however, known collectively as forms of trustworthiness. Reference Guba 6
One way to demonstrate trustworthiness is to present detailed evidence in the form of quotations from interviews and field notes, along with thick textual descriptions of episodes, events and settings. To be trustworthy, qualitative analysis should also be auditable, making it possible to retrace the steps leading to a certain interpretation or theory to check that no alternatives were left unexamined and that no researcher biases had any avoidable influence on the results. Usually, this involves the recording of information about who did what with the data and in what order so that the origin of interpretations can be retraced.
In general, within the research traditions of the natural sciences, findings are validated by their repeated replication, and if a second investigator cannot replicate the findings when they repeat the experiment then the original results are questioned. If no one else can replicate the original results then they are rejected as fatally flawed and therefore invalid. Natural scientists have developed a broad spectrum of procedures and study designs to ensure that experiments are dependable and that replication is possible. In the social sciences, particularly when using qualitative research methods, replication is rarely possible given that, when observed or questioned again, respondents will almost never say or do precisely the same things. Whether results have been successfully replicated is always a matter of interpretation. There are, however, procedures that, if followed, can significantly reduce the possibility of producing analyses that are partial or biased. Reference Altheide, Johnson, Denzin and Lincoln 7
Triangulation is one way of doing this. It essentially means combining multiple views, approaches or methods in an investigation to obtain a more accurate interpretation of the phenomena, thereby creating an analysis of greater depth and richness. As the process of analysing qualitative data normally involves some form of coding, whereby data are broken down into units of analysis, constant comparison can also be used. Constant comparison involves checking the consistency and accuracy of interpretations and especially the application of codes by constantly comparing one interpretation or code with others both of a similar sort and in other cases and settings. This in effect is a form of interrater reliability, involving multiple researchers or teams in the coding process so that it is possible to compare how they have coded the same passages and where there are areas of agreement and disagreement so that consensus can be reached about a code's definition, improving consistency and rigour. It is also good practice in qualitative analysis to look constantly for outliers – results that are out of line with your main findings or any which directly contradict what your explanations might predict, re-examining the data to try to find a way of explaining the atypical finding to produce a modified and more complex theory and explanation.
Qualitative research has been established for many decades in the social sciences and encompasses a valuable set of methodological tools for data collection, analysis and interpretation. Their effective application to other disciplines, including clinical, health service and education research, has a rapidly expanding and robust evidence base. The use of qualitative approaches to research in psychiatry has particular potential, singularly and in combination with quantitative methods. Reference Crabb and Chur-Hansen 8 When devising research questions in the specialty, careful thought should always be given to the most appropriate methodology, and consideration given to the great depth and richness of empirical evidence which a robust qualitative approach is able to provide.
Declaration of interest

This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref .
- Google Scholar
View all Google Scholar citations for this article.
Save article to Kindle
To save this article to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about saving to your Kindle .
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service.
- Volume 37, Issue 6
- Steven J. Agius (a1)
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1192/pb.bp.113.042770
Save article to Dropbox
To save this article to your Dropbox account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Dropbox account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox .
Save article to Google Drive
To save this article to your Google Drive account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Google Drive account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive .
Reply to: Submit a response
- No HTML tags allowed - Web page URLs will display as text only - Lines and paragraphs break automatically - Attachments, images or tables are not permitted
Your details
Your email address will be used in order to notify you when your comment has been reviewed by the moderator and in case the author(s) of the article or the moderator need to contact you directly.
You have entered the maximum number of contributors
Conflicting interests.
Please list any fees and grants from, employment by, consultancy for, shared ownership in or any close relationship with, at any time over the preceding 36 months, any organisation whose interests may be affected by the publication of the response. Please also list any non-financial associations or interests (personal, professional, political, institutional, religious or other) that a reasonable reader would want to know about in relation to the submitted work. This pertains to all the authors of the piece, their spouses or partners.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
29 Conceptualization in qualitative research
Chapter outline
- 15.1 Alternative paradigms: Interpretivism, critical paradigm, and pragmatism
15.2 Multiparadigmatic research: An example
15.3 idiographic causal relationships, 15.4 qualitative research questions.
Now let’s change things up! In the previous chapters, we explored steps to create and carry out a quantitative research study. Quantitative studies are great when we want to summarize or test relationships between ideas using numbers and the power of statistics. However, qualitative research offers us a different and equally important tool. Sometimes the aim of research projects is to explore meaning and lived experience. Instead of trying to arrive at generalizable conclusions for all people, some research projects establish a deep, authentic description of a specific time, place, and group of people.
Qualitative research relies on the power of human expression through words, pictures, movies, performance and other artifacts that represent these things. All of these tell stories about the human experience and we want to learn from them and have them be represented in our research. Generally speaking, qualitative research is about the gathering up of these stories, breaking them into pieces so we can examine the ideas that make them up, and putting them back together in a way that allows us to tell a common or shared story that responds to our research question. To do that, we need to discuss the assumptions underlying social science.
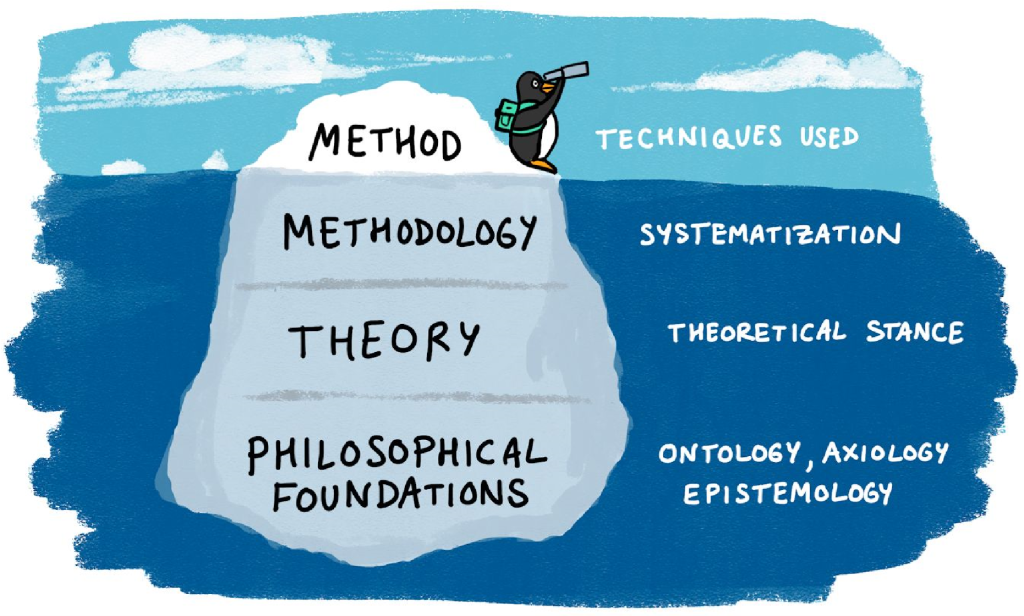
17.1 Alternative paradigms: Interpretivism, critical, and pragmatism
Learning objectives.
Students will be able to…
- Distinguish between the assumptions of positivism, interpretivism, critical, and pragmatist research paradigms.
- Use paradigm to describe how scientific thought changes over time.
In Chapter 10, we reviewed the assumptions that underly post-positivism (abbreviated hereafter as positivism for brevity). Quantitative methods are most often the choice for positivist research questions because they conform to these assumptions. Qualitative methods can conform to these assumptions; however, they are limited in their generalizability.
Kivunja & Kuyini (2017) [1] describe the essential features of positivism as:
- A belief that theory is universal and law-like generalizations can be made across contexts
- The assumption that context is not important
- The belief that truth or knowledge is ‘out there to be discovered’ by research
- The belief that cause and effect are distinguishable and analytically separable
- The belief that results of inquiry can be quantified
- The belief that theory can be used to predict and to control outcomes
- The belief that research should follow the scientific method of investigation
- Rests on formulation and testing of hypotheses
- Employs empirical or analytical approaches
- Pursues an objective search for facts
- Believes in ability to observe knowledge
- The researcher’s ultimate aim is to establish a comprehensive universal theory, to account for human and social behavior
- Application of the scientific method
Because positivism is the dominant social science research paradigm, it can be easy to ignore or be confused by research that does not use these assumptions. We covered in Chapter 10 the table reprinted below when discussing the assumptions underlying positivistic social science.
As you consider your research project, keep these philosophical assumptions in mind. They are useful shortcuts to understanding the deeper ideas and assumptions behind the construction of knowledge. The purpose of exploring these philosophical assumptions isn’t to find out which is true and which is false. Instead, the goal is to identify the assumptions that fit with how you think about your research question. Choosing a paradigm helps you make those assumptions explicit.
| Ontology: assumptions about what is real | |
| Epistemology: assumptions about how we come to know what is real |
|
| Assumptions about the researcher |
|
| Assumptions about human action |
|
| Assumptions about the social world | |
| Assumptions about the purpose of research |
|
Before we explore alternative paradigms, it’s important for us to review what paradigms are.
How do scientific ideas change over time?
Much like your ideas develop over time as you learn more, so does the body of scientific knowledge. Kuhn’s (1962) [2] The Structure of Scientific Revolutions is one of the most influential works on the philosophy of science, and is credited with introducing the idea of competing paradigms (or “disciplinary matrices”) in research. Kuhn investigated the way that scientific practices evolve over time, arguing that we don’t have a simple progression from “less knowledge” to “more knowledge” because the way that we approach inquiry is changing over time. This can happen gradually, but the process results in moments of change where our understanding of a phenomenon changes more radically (such as in the transition from Newtonian to Einsteinian physics; or from Lamarckian to Darwinian theories of evolution). For a social work practice example, Fleuridas & Krafcik (2019) [3] trace the development of the “four forces” of psychotherapy , from psychodynamics to behaviorism to humanism as well as the competition among emerging perspectives to establish itself as the fourth force to guide psychotherapeutic practice. But how did the problems in one paradigm inspire new paradigms? Kuhn presents us with a way of understanding the history of scientific development across all topics and disciplines.
As you can see in this video from Matthew J. Brown (CC-BY), there are four stages in the cycle of science in Kuhn’s approach. Firstly, a pre-paradigmatic state where competing approaches share no consensus. Secondly, the “normal” state where there is wide acceptance of a particular set of methods and assumptions. Thirdly, a state of crisis where anomalies that cannot be solved within the existing paradigm emerge and competing theories to address them follow. Fourthly, a revolutionary phase where some new paradigmatic approach becomes dominant and supplants the old. Shnieder (2009) [4] suggests that the Kuhnian phases are characterized by different kinds of scientific activity.
Newer approaches often build upon rather than replace older ones, but they also overlap and can exist within a state of competition. Scientists working within a particular paradigm often share methods, assumptions and values. In addition to supporting specific methods, research paradigms also influence things like the ambition and nature of research, the researcher-participant relationship and how the role of the researcher is understood.
Paradigm vs. theory
The terms ‘ paradigm ‘ and ‘ theory ‘ are often used interchangeably in social science. There is not a consensus among social scientists as to whether these are identical or distinct concepts. With that said, in this text, we will make a clear distinction between the two ideas because thinking about each concept separately is more useful for our purposes.
We define paradigm a set of common philosophical (ontological, epistemological, and axiological) assumptions that inform research. The four paradigms we describe in this section refer to patterns in how groups of researchers resolve philosophical questions. Some assumptions naturally make sense together, and paradigms grow out of researchers with shared assumptions about what is important and how to study it. Paradigms are like “analytic lenses” and a provide framework on top of which we can build theoretical and empirical knowledge (Kuhn, 1962). [5] Consider this video of an interview with world-famous physicist Richard Feynman in which he explains why “when you explain a ‘why,’ you have to be in some framework that you allow something to be true. Otherwise, you are perpetually asking why.” In order to answer basic physics question like “what is happening when two magnets attract?” or a social work research question like “what is the impact of this therapeutic intervention on depression,” you must understand the assumptions you are making about social science and the social world. Paradigmatic assumptions about objective and subjective truth support methodological choices like whether to conduct interviews or send out surveys, for example.
While paradigms are broad philosophical assumptions, theory is more specific, and refers to a set of concepts and relationships scientists use to explain the social world. Theories are more concrete, while paradigms are more abstract. Look back to Figure 7.1 at the beginning of this chapter. Theory helps you identify the concepts and relationships that align with your paradigmatic understanding of the problem. Moreover, theory informs how you will measure the concepts in your research question and the design of your project.
For both theories and paradigms, Kuhn’s observation of scientific paradigms, crises, and revolutions is instructive for understanding the history of science. Researchers inherit institutions, norms, and ideas that are marked by the battlegrounds of theoretical and paradigmatic debates that stretch back hundreds of years. We have necessarily simplified this history into four paradigms: positivism, interpretivism, critical, and pragmatism. Our framework and explanation are inspired by the framework of Guba and Lincoln (1990) [6] and Burrell and Morgan (1979). [7] while also incorporating pragmatism as a way of resolving paradigmatic questions. Most of social work research and theory can be classified as belonging to one of these four paradigms, though this classification system represents only one of many useful approaches to analyzing social science research paradigms.
Building on our discussion in section 7.1 on objective vs. subjective epistemologies and ontologies, we will start with the difference between positivism and interpretivism. Afterward, we will link our discussion of axiology in section 7.2 with the critical paradigm. Finally, we will situate pragmatism as a way to resolve paradigmatic questions strategically. The difference between positivism and interpretivism is a good place to start, since the critical paradigm and pragmatism build on their philosophical insights.
It’s important to think of paradigms less as distinct categories and more as a spectrum along which projects might fall. For example, some projects may be somewhat positivist, somewhat interpretivist, and a little critical. No project fits perfectly into one paradigm. Additionally, there is no paradigm that is more correct than the other. Each paradigm uses assumptions that are logically consistent, and when combined, are a useful approach to understanding the social world using science. The purpose of this section is to acquaint you with what research projects in each paradigm look like and how they are grounded in philosophical assumptions about social science.
You should read this section to situate yourself in terms of what paradigm feels most “at home” to both you as a person and to your project. You may find, as I have, that your research projects are more conventional and less radical than what feels most like home to you, personally. In a research project, however, students should start with their working question rather than their heart. Use the paradigm that fits with your question the best, rather than which paradigm you think fits you the best.

Interpretivism: Researcher as “empathizer”
Positivism is focused on generalizable truth. Interpretivism , by contrast, develops from the idea that we want to understand the truths of individuals, how they interpret and experience the world, their thought processes, and the social structures that emerge from sharing those interpretations through language and behavior. The process of interpretation (or social construction) is guided by the empathy of the researcher to understand the meaning behind what other people say.
Historically, interpretivism grew out of a specific critique of positivism: that knowledge in the human and social sciences cannot conform to the model of natural science because there are features of human experience that cannot objectively be “known”. The tools we use to understand objects that have no self-awareness may not be well-attuned to subjective experiences like emotions, understandings, values, feelings, socio-cultural factors, historical influences, and other meaningful aspects of social life. Instead of finding a single generalizable “truth,” the interpretivist researcher aims to generate understanding and often adopts a relativist position.
While positivists seek “the truth,” the social constructionist framework argues that “truth” varies. Truth differs based on who you ask, and people change what they believe is true based on social interactions. These subjective truths also exist within social and historical contexts, and our understanding of truth varies across communities and time periods. This is because we, according to this paradigm, create reality ourselves through our social interactions and our interpretations of those interactions. Key to the interpretivist perspective is the idea that social context and interaction frame our realities.
Researchers operating within this framework take keen interest in how people come to socially agree, or disagree, about what is real and true. Consider how people, depending on their social and geographical context, ascribe different meanings to certain hand gestures. When a person raises their middle finger, those of us in Western cultures will probably think that this person isn’t very happy (not to mention the person at whom the middle finger is being directed!). In other societies around the world, a thumbs-up gesture, rather than a middle finger, signifies discontent (Wong, 2007). [8] The fact that these hand gestures have different meanings across cultures aptly demonstrates that those meanings are socially and collectively constructed. What, then, is the “truth” of the middle finger or thumbs up? As we’ve seen in this section, the truth depends on the intention of the person making the gesture, the interpretation of the person receiving it, and the social context in which the action occurred.
Qualitative methods are preferred as ways to investigate these phenomena. Data collected might be unstructured (or “messy”) and correspondingly a range of techniques for approaching data collection have been developed. Interpretivism acknowledges that it is impossible to remove cultural and individual influence from research, often instead making a virtue of the positionality of the researcher and the socio-cultural context of a study.
One common objection positivists levy against interpretivists is that interpretivism tends to emphasize the subjective over the objective. If the starting point for an investigation is that we can’t fully and objectively know the world, how can we do research into this without everything being a matter of opinion? For the positivist, this risk for confirmation bias as well as invalid and unreliable measures makes interpretivist research unscientific. Clearly, we disagree with this assessment, and you should, too. Positivism and interpretivism have different ontologies and epistemologies with contrasting notions of rigor and validity (for more information on assumptions about measurement, see Chapter 11 for quantitative validity and reliability and Chapter 20 for qualitative rigor). Nevertheless, both paradigms apply the values and concepts of the scientific method through systematic investigation of the social world, even if their assumptions lead them to do so in different ways. Interpretivist research often embraces a relativist epistemology, bringing together different perspectives in search of a trustworthy and authentic understanding or narrative.
Kivunja & Kuyini (2017) [9] describe the essential features of interpretivism as:
- The belief that truths are multiple and socially constructed
- The acceptance that there is inevitable interaction between the researcher and his or her research participants
- The acceptance that context is vital for knowledge and knowing
- The belief that knowledge can be value laden and the researcher’s values need to be made explicit
- The need to understand specific cases and contexts rather deriving universal laws that apply to everyone, everywhere.
- The belief that causes and effects are mutually interdependent, and that causality may be circular or contradictory
- The belief that contextual factors need to be taken into consideration in any systematic pursuit of understanding
One important clarification: it’s important to think of the interpretivist perspective as not just about individual interpretations but the social life of interpretations. While individuals may construct their own realities, groups—from a small one such as a married couple to large ones such as nations—often agree on notions of what is true and what “is” and what “is not.” In other words, the meanings that we construct have power beyond the individuals who create them. Therefore, the ways that people and communities act based on such meanings is of as much interest to interpretivists as how they were created in the first place. Theories like social constructionism, phenomenology, and symbolic interactionism are often used in concert with interpretivism.
Is interpretivism right for your project?
An interpretivist orientation to research is appropriate when your working question asks about subjective truths. The cause-and-effect relationships that interpretivist studies produce are specific to the time and place in which the study happened, rather than a generalizable objective truth. More pragmatically, if you picture yourself having a conversation with participants like an interview or focus group, then interpretivism is likely going to be a major influence for your study.
Positivists critique the interpretivist paradigm as non-scientific. They view the interpretivist focus on subjectivity and values as sources of bias. Positivists and interpretivists differ on the degree to which social phenomena are like natural phenomena. Positivists believe that the assumptions of the social sciences and natural sciences are the same, while interpretivists strongly believe that social sciences differ from the natural sciences because their subjects are social creatures.
Similarly, the critical paradigm finds fault with the interpretivist focus on the status quo rather than social change. Although interpretivists often proceed from a feminist or other standpoint theory, the focus is less on liberation than on understanding the present from multiple perspectives. Other critical theorists may object to the consensus orientation of interpretivist research. By searching for commonalities between people’s stories, they may erase the uniqueness of each individual’s story. For example, while interpretivists may arrive at a consensus definition of what the experience of “coming out” is like for people who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, or queer, it cannot represent the diversity of each person’s unique “coming out” experience and what it meant to them. For example, see Rosario and colleagues’ (2009) [10] critique the literature on lesbians “coming out” because previous studies did not addressing how appearing, behaving, or identifying as a butch or femme impacted the experience of “coming out” for lesbians.
- From your literature search, identify an empirical article that uses qualitative methods to answer a research question similar to your working question or about your research topic.
- Review the assumptions of the interpretivist research paradigm.
- Discuss in a few sentences how the author’s conclusions are based on some of these paradigmatic assumptions. How might a researcher operating from a different paradigm (like positivism or the critical paradigm) critique the conclusions of this study?

Critical paradigm: Researcher as “activist”
As we’ve discussed a bit in the preceding sections, the critical paradigm focuses on power, inequality, and social change. Although some rather diverse perspectives are included here, the critical paradigm, in general, includes ideas developed by early social theorists, such as Max Horkheimer (Calhoun et al., 2007), [11] and later works developed by feminist scholars, such as Nancy Fraser (1989). [12] Unlike the positivist paradigm, the critical paradigm assumes that social science can never be truly objective or value-free. Furthermore, this paradigm operates from the perspective that scientific investigation should be conducted with the express goal of social change. Researchers in the critical paradigm foreground axiology, positionality and values . In contrast with the detached, “objective” observations associated with the positivist researcher, critical approaches make explicit the intention for research to act as a transformative or emancipatory force within and beyond the study.
Researchers in the critical paradigm might start with the knowledge that systems are biased against certain groups, such as women or ethnic minorities, building upon previous theory and empirical data. Moreover, their research projects are designed not only to collect data, but to impact the participants as well as the systems being studied. The critical paradigm applies its study of power and inequality to change those power imbalances as part of the research process itself. If this sounds familiar to you, you may remember hearing similar ideas when discussing social conflict theory in your human behavior in the social environment (HBSE) class. [13] Because of this focus on social change, the critical paradigm is a natural home for social work research. However, we fall far short of adopting this approach widely in our profession’s research efforts.
Is the critical paradigm right for your project?
Every social work research project impacts social justice in some way. What distinguishes critical research is how it integrates an analysis of power into the research process itself. Critical research is appropriate for projects that are activist in orientation. For example, critical research projects should have working questions that explicitly seek to raise the consciousness of an oppressed group or collaborate equitably with community members and clients to addresses issues of concern. Because of their transformative potential, critical research projects can be incredibly rewarding to complete. However, partnerships take a long time to develop and social change can evolve slowly on an issue, making critical research projects a more challenging fit for student research projects which must be completed under a tight deadline with few resources.
Positivists critique the critical paradigm on multiple fronts. First and foremost, the focus on oppression and values as part of the research process is seen as likely to bias the research process, most problematically, towards confirmation bias. If you start out with the assumption that oppression exists and must be dealt with, then you are likely to find that regardless of whether it is truly there or not. Similarly, positivists may fault critical researchers for focusing on how the world should be, rather than how it truly is . In this, they may focus too much on theoretical and abstract inquiry and less on traditional experimentation and empirical inquiry. Finally, the goal of social transformation is seen as inherently unscientific, as science is not a political practice.
Interpretivists often find common cause with critical researchers. Feminist studies, for example, may explore the perspectives of women while centering gender-based oppression as part of the research process. In interpretivist research, the focus is less on radical change as part of the research process and more on small, incremental changes based on the results and conclusions drawn from the research project. Additionally, some critical researchers’ focus on individuality of experience is in stark contrast to the consensus-orientation of interpretivists. Interpretivists seek to understand people’s true selves. Some critical theorists argue that people have multiple selves or no self at all.
- From your literature search, identify an article relevant to your working question or broad research topic that uses a critical perspective. You should look for articles where the authors are clear that they are applying a critical approach to research like feminism, anti-racism, Marxism and critical theory, decolonization, anti-oppressive practice, or other social justice-focused theoretical perspectives. To target your search further, include keywords in your queries to research methods commonly used in the critical paradigm like participatory action research and community-based participatory research. If you have trouble identifying an article for this exercise, consult your professor for some help. These articles may be more challenging to find, but reviewing one is necessary to get a feel for what research in this paradigm is like.
- Review the assumptions of the critical research paradigm.
- Discuss in a few sentences how the author’s conclusions are based on some of these paradigmatic assumptions. How might a researcher operating from different assumptions (like values-neutrality or researcher as neutral and unbiased) critique the conclusions of this study?

Pragmatism: Researcher as “strategist”
“Essentially, all models are wrong but some are useful.” (Box, 1976) [14]
Pragmatism is a research paradigm that suspends questions of philosophical ‘truth’ and focuses more on how different philosophies, theories, and methods can be used strategically to provide a multidimensional view of a topic. Researchers employing pragmatism will mix elements of positivist, interpretivist, and critical research depending on the purpose of a particular project and the practical constraints faced by the researcher and their research context. We favor this approach for student projects because it avoids getting bogged down in choosing the “right” paradigm and instead focuses on the assumptions that help you answer your question, given the limitations of your research context. Student research projects are completed quickly and moving in the direction of pragmatism can be a route to successfully completing a project. Your project is a representation of what you think is feasible, ethical, and important enough for you to study.
The crucial consideration for the pragmatist is whether the outcomes of research have any real-world application, rather than whether they are “true.” The methods, theories, and philosophies chosen by pragmatic researchers are guided by their working question. There are no distinctively pragmatic research methods since this approach is about making judicious use whichever methods fit best with the problem under investigation. Pragmatic approaches may be less likely to prioritize ontological, epistemological or axiological consistency when combining different research methods. Instead, the emphasis is on solving a pressing problem and adapting to the limitations and opportunities in the researchers’ context.
Adopt a multi-paradigmatic perspective
Believe it or not, there is a long literature of acrimonious conflict between scientists from positivist, interpretivist, and critical camps (see Heineman-Pieper et al., 2002 [15] for a longer discussion). Pragmatism is an old idea, but it is appealing precisely because it attempts to resolve the problem of multiple incompatible philosophical assumptions in social science. To a pragmatist, there is no “correct” paradigm. All paradigms rely on assumptions about the social world that are the subject of philosophical debate. Each paradigm is an incomplete understanding of the world, and it requires a scientific community using all of them to gain a comprehensive view of the social world. This multi-paradigmatic perspective is a unique gift of social work research, as our emphasis on empathy and social change makes us more critical of positivism, the dominant paradigm in social science.
We offered the metaphors of expert, empathizer, activist, and strategist for each paradigm. It’s important not to take these labels too seriously. For example, some may view that scientists should be experts or that activists are biased and unscientific. Nevertheless, we hope that these metaphors give you a sense of what it feels like to conduct research within each paradigm.
One of the unique aspects of paradigmatic thinking is that often where you think you are most at home may actually be the opposite of where your research project is. For example, in my graduate and doctoral education, I thought I was a critical researcher. In fact, I thought I was a radical researcher focused on social change and transformation. Yet, often times when I sit down to conceptualize and start a research project, I find myself squarely in the positivist paradigm, thinking through neat cause-and-effect relationships that can be mathematically measured. There is nothing wrong with that! Your task for your research project is to find the paradigm that best matches your research question. Think through what you really want to study and how you think about the topic, then use assumptions of that paradigm to guide your inquiry.
Another important lesson is that no research project fits perfectly in one paradigm or another. Instead, there is a spectrum along which studies are, to varying degrees, interpretivist, positivist, and critical. For example, all social work research is a bit activist in that our research projects are designed to inform action for change on behalf of clients and systems. However, some projects will focus on the conclusions and implications of projects informing social change (i.e., positivist and interpretivist projects) while others will partner with community members and design research projects collaboratively in a way that leads to social change (i.e. critical projects). In section 7.5, we will describe a pragmatic approach to research design guided by your paradigmatic and theoretical framework.
Key Takeaways
- Social work research falls, to some degree, in each of the four paradigms: positivism, interpretivism, critical, and pragmatist.
- Adopting a pragmatic, multi-paradigmatic approach to research makes sense for student researchers, as it directs students to use the philosophical assumptions and methodological approaches that best match their research question and research context.
- Research in all paradigms is necessary to come to a comprehensive understanding of a topic, and social workers must be able to understand and apply knowledge from each research paradigm.
- Describe which paradigm best fits your perspective on the world and which best fits with your project.
- Identify any similarities and differences in your personal assumptions and the assumption your research project relies upon. For example, are you a more critical and radical thinker but have chosen a more “expert” role for yourself in your research project?
Learners will be able to…
- Apply the assumptions of each paradigm to your project
- Summarize what aspects of your project stem from positivist, interpretivist, or critical assumptions
In the previous sections, we reviewed the major paradigms and theories in social work research. In this section, we will provide an example of how to apply theory and paradigm in research. This process is depicted in Figure 7.2 below with some quick summary questions for each stage. Some questions in the figure below have example answers like designs (i.e., experimental, survey) and data analysis approaches (i.e., discourse analysis). These examples are arbitrary. There are a lot of options that are not listed. So, don’t feel like you have to memorize them or use them in your study.
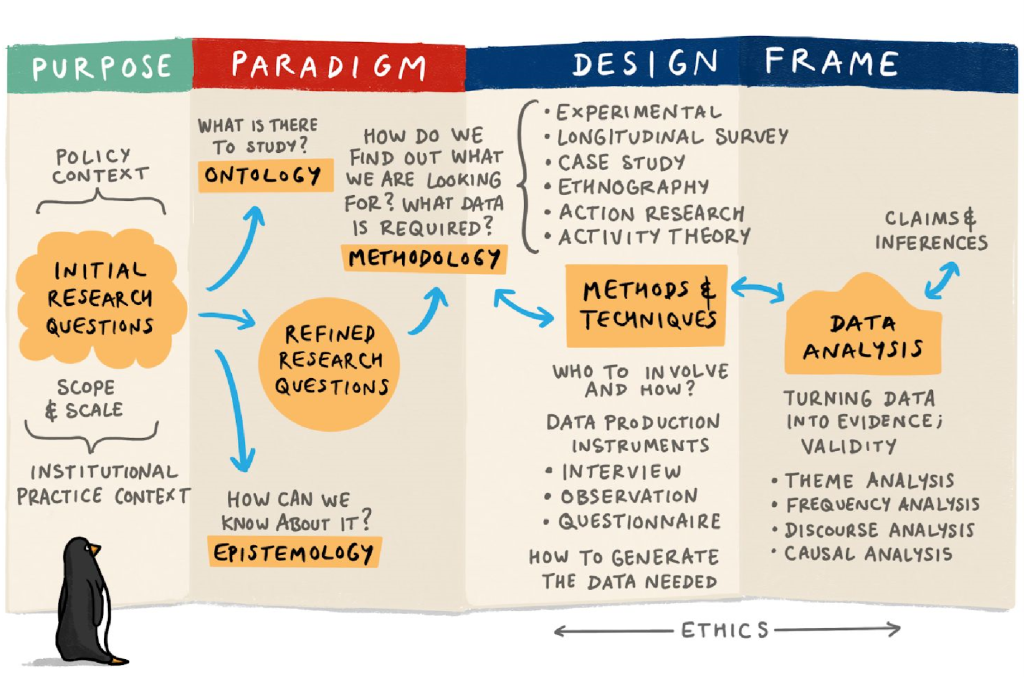
This diagram (taken from an archived Open University (UK) course entitled E89 - Educational Inquiry ) shows one way to visualize the research design process. While research is far from linear, in general, this is how research projects progress sequentially. Researchers begin with a working question, and through engaging with the literature, develop and refine those questions into research questions (a process we will finalize in Chapter 9 ). But in order to get to the part where you gather your sample, measure your participants, and analyze your data, you need to start with paradigm. Based on your work in section 7.3, you should have a sense of which paradigm or paradigms are best suited to answering your question. The approach taken will often reflect the nature of the research question; the kind of data it is possible to collect; and work previously done in the area under consideration. When evaluating paradigm and theory, it is important to look at what other authors have done previously and the framework used by studies that are similar to the one you are thinking of conducting.
Once you situate your project in a research paradigm, it becomes possible to start making concrete choices about methods. Depending on the project, this will involve choices about things like:
- What is my final research question?
- What are the key variables and concepts under investigation, and how will I measure them?
- How do I find a representative sample of people who experience the topic I’m studying?
- What design is most appropriate for my research question?
- How will I collect and analyze data?
- How do I determine whether my results describe real patterns in the world or are the result of bias or error?
The data collection phase can begin once these decisions are made. It can be very tempting to start collecting data as soon as possible in the research process as this gives a sense of progress. However, it is usually worth getting things exactly right before collecting data as an error found in your approach further down the line can be harder to correct or recalibrate around.
Designing a study using paradigm and theory: An example
Paradigm and theory have the potential to turn some people off since there is a lot of abstract terminology and thinking about real-world social work practice contexts. In this section, I’ll use an example from my own research, and I hope it will illustrate a few things. First, it will show that paradigms are really just philosophical statements about things you already understand and think about normally. It will also show that no project neatly sits in one paradigm and that a social work researcher should use whichever paradigm or combination of paradigms suit their question the best. Finally, I hope it is one example of how to be a pragmatist and strategically use the strengths of different theories and paradigms to answering a research question. We will pick up the discussion of mixed methods in the next chapter.
Thinking as an expert: Positivism
In my undergraduate research methods class, I used an open textbook much like this one and wanted to study whether it improved student learning. You can read a copy of the article we wrote on based on our study . We’ll learn more about the specifics of experiments and evaluation research in Chapter 13 , but you know enough to understand what evaluating an intervention might look like. My first thought was to conduct an experiment, which placed me firmly within the positivist or “expert” paradigm.
Experiments focus on isolating the relationship between cause and effect. For my study, this meant studying an open textbook (the cause, or intervention) and final grades (the effect, or outcome). Notice that my position as “expert” lets me assume many things in this process. First, it assumes that I can distill the many dimensions of student learning into one number—the final grade. Second, as the “expert,” I’ve determined what the intervention is: indeed, I created the book I was studying, and applied a theory from experts in the field that explains how and why it should impact student learning.
Theory is part of applying all paradigms, but I’ll discuss its impact within positivism first. Theories grounded in positivism help explain why one thing causes another. More specifically, these theories isolate a causal relationship between two (or more) concepts while holding constant the effects of other variables that might confound the relationship between the key variables. That is why experimental design is so common in positivist research. The researcher isolates the environment from anything that might impact or bias the cause and effect relationship they want to investigate.
But in order for one thing to lead to change in something else, there must be some logical, rational reason why it would do so. In open education, there are a few hypotheses (though no full-fledged theories) on why students might perform better using open textbooks. The most common is the access hypothesis , which states that students who cannot afford expensive textbooks or wouldn’t buy them anyway can access open textbooks because they are free, which will improve their grades. It’s important to note that I held this theory prior to starting the experiment, as in positivist research you spell out your hypotheses in advance and design an experiment to support or refute that hypothesis.
Notice that the hypothesis here applies not only to the people in my experiment, but to any student in higher education. Positivism seeks generalizable truth, or what is true for everyone. The results of my study should provide evidence that anyone who uses an open textbook would achieve similar outcomes. Of course, there were a number of limitations as it was difficult to tightly control the study. I could not randomly assign students or prevent them from sharing resources with one another, for example. So, while this study had many positivist elements, it was far from a perfect positivist study because I was forced to adapt to the pragmatic limitations of my research context (e.g., I cannot randomly assign students to classes) that made it difficult to establish an objective, generalizable truth.
Thinking like an empathizer: Interpretivism
One of the things that did not sit right with me about the study was the reliance on final grades to signify everything that was going on with students. I added another quantitative measure that measured research knowledge, but this was still too simplistic. I wanted to understand how students used the book and what they thought about it. I could create survey questions that ask about these things, but to get at the subjective truths here, I thought it best to use focus groups in which students would talk to one another with a researcher moderating the discussion and guiding it using predetermined questions. You will learn more about focus groups in Chapter 18 .
Researchers spoke with small groups of students during the last class of the semester. They prompted people to talk about aspects of the textbook they liked and didn’t like, compare it to textbooks from other classes, describe how they used it, and so forth. It was this focus on understanding and subjective experience that brought us into the interpretivist paradigm. Alongside other researchers, I created the focus group questions but encouraged researchers who moderated the focus groups to allow the conversation to flow organically.
We originally started out with the assumption, for which there is support in the literature, that students would be angry with the high-cost textbook that we used prior to the free one, and this cost shock might play a role in students’ negative attitudes about research. But unlike the hypotheses in positivism, these are merely a place to start and are open to revision throughout the research process. This is because the researchers are not the experts, the participants are! Just like your clients are the experts on their lives, so were the students in my study. Our job as researchers was to create a group in which they would reveal their informed thoughts about the issue, coming to consensus around a few key themes.

When we initially analyzed the focus groups, we uncovered themes that seemed to fit the data. But the overall picture was murky. How were themes related to each other? And how could we distill these themes and relationships into something meaningful? We went back to the data again. We could do this because there isn’t one truth, as in positivism, but multiple truths and multiple ways of interpreting the data. When we looked again, we focused on some of the effects of having a textbook customized to the course. It was that customization process that helped make the language more approachable, engaging, and relevant to social work practice.
Ultimately, our data revealed differences in how students perceived a free textbook versus a free textbook that is customized to the class. When we went to interpret this finding, the remix hypothesis of open textbook was helpful in understanding that relationship. It states that the more faculty incorporate editing and creating into the course, the better student learning will be. Our study helped flesh out that theory by discussing the customization process and how students made sense of a customized resource.
In this way, theoretical analysis operates differently in interpretivist research. While positivist research tests existing theories, interpretivist research creates theories based on the stories of research participants. However, it is difficult to say if this theory was totally emergent in the dataset or if my prior knowledge of the remix hypothesis influenced my thinking about the data. Interpretivist researchers are encouraged to put a box around their prior experiences and beliefs, acknowledging them, but trying to approach the data with fresh eyes. Interpretivists know that this is never perfectly possible, though, as we are always influenced by our previous experiences when interpreting data and conducting scientific research projects.
Thinking like an activist: Critical
Although adding focus groups helped ease my concern about reducing student learning down to just final grades by providing a more rich set of conversations to analyze. However, my role as researcher and “expert” was still an important part of the analysis. As someone who has been out of school for a while, and indeed has taught this course for years, I have lost touch with what it is like to be a student taking research methods for the first time. How could I accurately interpret or understand what students were saying? Perhaps I would overlook things that reflected poorly on my teaching or my book. I brought other faculty researchers on board to help me analyze the data, but this still didn’t feel like enough.
By luck, an undergraduate student approached me about wanting to work together on a research project. I asked her if she would like to collaborate on evaluating the textbook with me. Over the next year, she assisted me with conceptualizing the project, creating research questions, as well as conducting and analyzing the focus groups. Not only would she provide an “insider” perspective on coding the data, steeped in her lived experience as a student, but she would serve as a check on my power through the process.
Including people from the group you are measuring as part of your research team is a common component of critical research. Ultimately, critical theorists would find my study to be inadequate in many ways. I still developed the research question, created the intervention, and wrote up the results for publication, which privileges my voice and role as “expert.” Instead, critical theorists would emphasize the role of students (community members) in identifying research questions, choosing the best intervention to used, and so forth. But collaborating with students as part of a research team did address some of the power imbalances in the research process.
Critical research projects also aim to have an impact on the people and systems involved in research. No students or researchers had profound personal realizations as a result of my study, nor did it lessen the impact of oppressive structures in society. I can claim some small victory that my department switched to using my textbook after the study was complete (changing a system), though this was likely the result of factors other than the study (my advocacy for open textbooks).
Social work research is almost always designed to create change for people or systems. To that end, every social work project is at least somewhat critical. However, the additional steps of conducting research with people rather than on people reveal a depth to the critical paradigm. By bringing students on board the research team, study had student perspectives represented in conceptualization, data collection, and analysis. That said, there was much to critique about this study from a critical perspective. I retained a lot of the power in the research process, and students did not have the ability to determine the research question or purpose of the project. For example, students might likely have said that textbook costs and the quality of their research methods textbook were less important than student debt, racism, or other potential issues experienced by students in my class. Instead of a ground-up research process based in community engagement, my research included some important participation by students on project created and led by faculty.
Conceptualization is an iterative process
I hope this conversation was useful in applying paradigms to a research project. While my example discusses education research, the same would apply for social work research about social welfare programs, clinical interventions, or other topics. Paradigm and theory are covered at the beginning of the conceptualization of your project because these assumptions will structure the rest of your project. Each of the research steps that occur after this chapter (e.g., forming a question, choosing a design) rely upon philosophical and theoretical assumptions. As you continue conceptualizing your project over the next few weeks, you may find yourself shifting between paradigms. That is normal, as conceptualization is not a linear process. As you move through the next steps of conceptualizing and designing a project, you’ll find philosophies and theories that best match how you want to study your topic.
Viewing theoretical and empirical arguments through this lens is one of the true gifts of the social work approach to research. The multi-paradigmatic perspective is a hallmark of social work research and one that helps us contribute something unique on research teams and in practice.
- Multi-paradigmatic research is a distinguishing hallmark of social work research. Understanding the limitations and strengths of each paradigm will help you justify your research approach and strategically choose elements from one or more paradigms to answer your question.
- Paradigmatic assumptions help you understand the “blind spots” in your research project and how to adjust and address these areas. Keep in mind, it is not necessary to address all of your blind spots, as all projects have limitations.
- Sketch out which paradigm applies best to your project. Second, building on your answer to the exercise in section 7.3, identify how the theory you chose and the paradigm in which you find yourself are consistent or are in conflict with one another. For example, if you are using systems theory in a positivist framework, you might talk about how they both rely on a deterministic approach to human behavior with a focus on the status-quo and social order.
- Define and provide an example of an idiographic causal explanation
- Differentiate between idiographic and nomothetic causal relationships
- Link idiographic and nomothetic causal relationships with the process of theory building and theory testing
- Describe how idiographic and nomothetic causal explanations can be complementary
As we transition away from positivism, it is important to highlight the assumptions it makes about the scientific process–the hypothetico-deductive method, sometimes referred to as the research circle.
The hypothetico-deductive method
The primary way that researchers in the positivist paradigm use theories is sometimes called the hypothetico-deductive method (although this term is much more likely to be used by philosophers of science than by scientists themselves). Researchers choose an existing theory. Then, they make a prediction about some new phenomenon that should be observed if the theory is correct. Again, this prediction is called a hypothesis. The researchers then conduct an empirical study to test the hypothesis. Finally, they reevaluate the theory in light of the new results and revise it if necessary.
This process is usually conceptualized as a cycle because the researchers can then derive a new hypothesis from the revised theory, conduct a new empirical study to test the hypothesis, and so on. As Figure 8.8 shows, this approach meshes nicely with the process of conducting a research project—creating a more detailed model of “theoretically motivated” or “theory-driven” research. Together, they form a model of theoretically motivated research.
Keep in mind the hypothetico-deductive method is only one way of using social theory to inform social science research. It starts with describing one or more existing theories, deriving a hypothesis from one of those theories, testing your hypothesis in a new study, and finally reevaluating the theory based on the results data analyses. This format works well when there is an existing theory that addresses the research question—especially if the resulting hypothesis is surprising or conflicts with a hypothesis derived from a different theory.
But what if your research question is more interpretive? What if it is less about theory-testing and more about theory-building? This is what our next chapter covers: the process of inductively deriving theory from people’s stories and experiences. This process looks different than that depicted in Figure 8.8. It still starts with your research question and answering that question by conducting a research study. But instead of testing a hypothesis you created based on a theory, you will create a theory of your own that explain the data you collected. This format works well for qualitative research questions and for research questions that existing theories do not address.
Inductive reasoning is most commonly found in studies using qualitative methods, such as focus groups and interviews. Because inductive reasoning involves the creation of a new theory, researchers need very nuanced data on how the key concepts in their working question operate in the real world. Qualitative data is often drawn from lengthy interactions and observations with the individuals and phenomena under examination. For this reason, inductive reasoning is most often associated with qualitative methods, though it is used in both quantitative and qualitative research.

Whose truth does science establish?
Social work is concerned with the “isms” of oppression (ableism, ageism, cissexism, classism, heterosexism, racism, sexism, etc.), and so our approach to science must reconcile its history as both a tool of oppression and its exclusion of oppressed groups. Science grew out of the Enlightenment, a philosophical movement which applied reason and empirical analysis to understanding the world. While the Enlightenment brought forth tremendous achievements, the critiques of Marxian, feminist, and other critical theorists complicated the Enlightenment understanding of science. For this section, I will focus on feminist critiques of science, building upon an entry in the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Crasnow, 2020). [16]
In its original formulation, science was an individualistic endeavor. As we learned in Chapter 1 , a basic statement of the scientific method is that a researcher studies existing theories on a topic, formulates a hypothesis about what might be true, and either confirms or disconfirms their hypothesis through experiment and rigorous observation. Over time, our theories become more accurate in their predictions and more comprehensive in their conclusions. Scientists put aside their preconceptions, look at the data, and build their theories based on objective rationality.
Yet, this cannot be perfectly true. Scientists are human, after all. As a profession historically dominated by white men, scientists have dismissed women and other minorities as being psychologically unfit for the scientific profession. While attitudes have improved, science, technology, engineering, mathematics (STEM) and related fields remain dominated by white men (Grogan, 2019). [17] Biases can persist in social work theory and research when social scientists do not have similar experiences to the populations they study.
Gender bias can influence the research questions scientists choose to answer. Feminist critiques of medical science drew attention to women’s health issues, spurring research and changing standards of care. The focus on domestic violence in the empirical literature can also be seen as a result of feminist critique. Thus, critical theory helps us critique what is on the agenda for science. If science is to answer important questions, it must speak to the concerns of all people. Through the democratization in access to scientific knowledge and the means to produce it, science becomes a sister process of social development and social justice.
The goal of a diverse and participatory scientific community lies in contrast to much of what we understand to be “proper” scientific knowledge. Many of the older, classic social science theories were developed based on research which observed males or from university students in the United States or other Western nations. How these observations were made, what questions were asked, and how the data were interpreted were shaped by the same oppressive forces that existed in broader society, a process that continues into the present. In psychology, the concept of hysteria or hysterical women was believed to be caused by a wandering womb (Tasca et al., 2012). [18] Even today, there are gender biases in diagnoses of histrionic personality disorder and racial biases in psychotic disorders (Klonsky et al., 2002) [19] because the theories underlying them were created in a sexist and racist culture. In these ways, science can reinforce the truth of the white Western male perspective.
Finally, it is important to note that social science research is often conducted on populations rather than with populations. Historically, this has often meant Western men traveling to other countries and seeking to understand other cultures through a Western lens. Lacking cultural humility and failing to engage stakeholders, ethnocentric research of this sort has led to the view of non-Western cultures as inferior. Moreover, the use of these populations as research subjects rather than co-equal participants in the research process privileges the researcher’s knowledge over that from other groups or cultures. Researchers working with indigenous cultures, in particular, had a destructive habit of conducting research for a short time and then leaving, without regard for the impact their study had on the population. These critiques of Western science aim to decolonize social science and dismantle the racist ideas the oppress indigenous and non-Western peoples through research (Smith, 2013). [20]
The central concept in feminist, anti-racist, and decolonization critiques (among other critical frames) is epistemic injustice. Epistemic injustice happens when someone is treated unfairly in their capacity to know something or describe their experience of the world. As described by Fricker (2011), [21] the injustice emerges from the dismissal of knowledge from oppressed groups, discrimination against oppressed groups in scientific communities, and the resulting gap between what scientists can make sense of from their experience and the experiences of people with less power who have lived experience of the topic. We recommend this video from Edinburgh Law School which applies epistemic injustice to studying public health emergencies, disabilities, and refugee services .
Positivism relies on nomothetic causality, or the idea that “one event, behavior, or belief will result in the occurrence of another, subsequent event, behavior, or belief.” Then, we described one kind of causality: a simple cause-and-effect relationship supported by existing theory and research on the topic, also known as a nomothetic causal relationship. But what if there is not a lot of literature on your topic? What if your question is more exploratory than explanatory? Then, you need a different kind of causal explanation, one that accounts for the complexity of human interactions.
How can we build causal relationships if we are just describing or exploring a topic? Recall the definitions of exploratory research , descriptive research , and explanatory research from Chapter 2. Wouldn’t we need to do explanatory research to build any kind of causal explanation? Explanatory research attempts to establish nomothetic causal relationships: an independent variable is demonstrated to cause change in a dependent variable. Exploratory and descriptive qualitative research contains some causal relationships, but they are actually descriptions of the causal relationships established by the study participants.
What do idiographic causal explanations look like?
An idiographic causal relationship tries to identify the many, interrelated causes that account for the phenomenon the researcher is investigating. So, if idiographic causal explanations do not look like Figure 8.5, 8.6, or 8.7 what do they look like? Instead of saying “x causes y,” your participants will describe their experiences with “x,” which they will tell you was caused and influenced by a variety of other factors, as interpreted through their unique perspective, time, and environment. As we stated before, idiographic causal explanations are messy. Your job as a social science researcher is to accurately describe the patterns in what your participants tell you.
Let’s think about this using an example. If I asked you why you decided to become a social worker, what might you say? For me, I would say that I wanted to be a mental health clinician since I was in high school. I was interested in how people thought, and I was privileged enough to have psychology courses at my local high school. I thought I wanted to be a psychologist, but at my second internship in my undergraduate program, my supervisors advised me to become a social worker because the license provided greater authority for independent practice and flexibility for career change. Once I found out social workers were like psychologists who also raised trouble about social justice, I was hooked.
That’s not a simple explanation at all! But it’s definitely a causal explanation. It is my individual, subjective truth of a complex process. If we were to ask multiple social workers the same question, we might find out that many social workers begin their careers based on factors like personal experience with a disability or social injustice, positive experiences with social workers, or a desire to help others. No one factor is the “most important factor,” like with nomothetic causal relationships. Instead, a complex web of factors, contingent on context, emerge when you interpret what people tell you about their lives.
Understanding “why?”
In creating an idiographic explanation, you are still asking “why?” But the answer is going to be more complex. Those complexities are described in Table 8.1 as well as this short video comparing nomothetic and idiographic relationships .
| Nomothetic causal relationships | Idiographic causal relationships | |
|---|---|---|
| Paradigm | Positivist | Interpretivist |
| Purpose of research | Prediction & generalization | Understanding & particularity |
| Reasoning | Deductive | Inductive |
| Purpose of research | Explanatory | Exploratory or descriptive |
| Research methods | Quantitative | Qualitative |
| Causality | Simple: cause and effect | Complex: context-dependent, sometimes circular or contradictory |
| Role of theory | Theory testing | Theory building |
Remember our question from the last section, “Are you trying to generalize or nah?” If you answered nah (or no, like a normal person), you are trying to establish an idiographic causal explanation. The purpose of that explanation isn’t to predict the future or generalize to larger populations, but to describe the here-and-now as it is experienced by individuals within small groups and communities. Idiographic explanations are focused less on what is generally experienced by all people but more on the particularities of what specific individuals in a unique time and place experience.
Researchers seeking idiographic causal relationships are not trying to generalize or predict, so they have no need to reduce phenomena to mathematics. In fact, only examining things that can be counted can rob a causal relationship of its meaning and context. Instead, the goal of idiographic causal relationships is understanding, rather than prediction. Idiographic causal relationships are formed by interpreting people’s stories and experiences. Usually, these are expressed through words. Not all qualitative studies use word data, as some can use interpretations of visual or performance art. However, the vast majority of qualitative studies do use word data, like the transcripts from interviews and focus groups or documents like journal entries or meeting notes. Your participants are the experts on their lives—much like in social work practice—and as in practice, people’s experiences are embedded in their cultural, historical, and environmental context.
Idiographic causal explanations are powerful because they can describe the complicated and interconnected nature of human life. Nomothetic causal explanations, by comparison, are simplistic. Think about if someone asked you why you wanted to be a social worker. Your story might include a couple of vignettes from your education and early employment. It might include personal experience with the social welfare system or family traditions. Maybe you decided on a whim to enroll in a social work course during your graduate program. The impact of each of these events on your career is unique to you.
Idiographic causal explanations are concerned with individual stories, their idiosyncrasies, and the patterns that emerge when you collect and analyze multiple people’s stories. This is the inductive reasoning we discussed at the beginning of this chapter. Often, idiographic causal explanations begin by collecting a lot of qualitative data, whether though interviews, focus groups, or looking at available documents or cultural artifacts. Next, the researcher looks for patterns in the data and arrives at a tentative theory for how the key ideas in people’s stories are causally related.
Unlike nomothetic causal relationships, there are no formal criteria (e.g., covariation) for establishing causality in idiographic causal relationships. In fact, some criteria like temporality and nonspuriousness may be violated. For example, if an adolescent client says, “It’s hard for me to tell whether my depression began before my drinking, but both got worse when I was expelled from my first high school,” they are recognizing that it may not so simple that one thing causes another. Sometimes, there is a reciprocal relationship where one variable (depression) impacts another (alcohol abuse), which then feeds back into the first variable (depression) and into other variables as well (school). Other criteria, such as covariation and plausibility, still make sense, as the relationships you highlight as part of your idiographic causal explanation should still be plausible and its elements should vary together.
Theory building and theory testing
As we learned in the previous section, nomothetic causal explanations are created by researchers applying deductive reasoning to their topic and creating hypotheses using social science theories. Much of what we think of as social science is based on this hypothetico-deductive method, but this leaves out the other half of the equation. Where do theories come from? Are they all just revisions of one another? How do any new ideas enter social science?
Through inductive reasoning and idiographic causal explanations!
Let’s consider a social work example. If you plan to study domestic and sexual violence, you will likely encounter the Power and Control Wheel, also known as the Duluth Model (Figure 8.9). The wheel is a model designed to depict the process of domestic violence. The wheel was developed based on qualitative focus groups conducted by sexual and domestic violence advocates in Duluth, MN. This video explains more about the Duluth Model of domestic abuse.
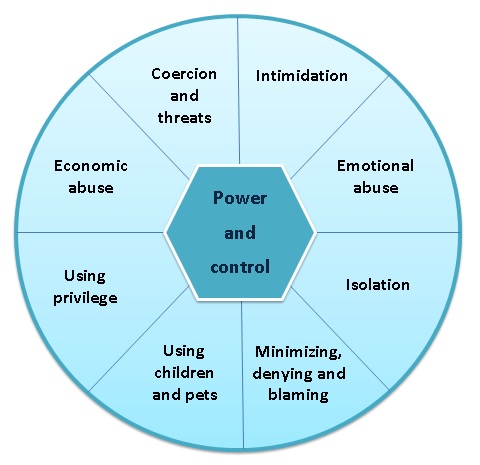
The Power and Control Wheel is an example of what an idiographic causal relationship looks like. By contrast, look back at the previous section’s Figure 8.5, 8.6, and 8.7 on nomothetic causal relationships between independent and dependent variables. See how much more complex idiographic causal explanations are?! They are complex, but not difficult to understand. At the center of domestic abuse is power and control, and while not every abuser would say that is what they were doing, that is the understanding of the survivors who informed this theoretical model. Their power and control is maintained through a variety of abusive tactics from social isolation to use of privilege to avoid consequences.
What about the role of hypotheses in idiographic causal explanations? In nomothetic causal explanations, researchers create hypotheses using existing theory and then test them for accuracy. Hypotheses in idiographic causality are much more tentative, and are probably best considered as “hunches” about what they think might be true. Importantly, they might indicate the researcher’s prior knowledge and biases before the project begins, but the goal of idiographic research is to let your participants guide you rather than existing social work knowledge. Continuing with our Duluth Model example, advocates likely had some tentative hypotheses about what was important in a relationship with domestic violence. After all, they worked with this population for years prior to the creation of the model. However, it was the stories of the participants in these focus groups that led the Power and Control Wheel explanation for domestic abuse.
As qualitative inquiry unfolds, hypotheses and hunches are likely to emerge and shift as researchers learn from what their participants share. Because the participants are the experts in idiographic causal relationships, a researcher should be open to emerging topics and shift their research questions and hypotheses accordingly. This is in contrast to hypotheses in quantitative research, which remain constant throughout the study and are shown to be true or false.
Over time, as more qualitative studies are done and patterns emerge across different studies and locations, more sophisticated theories emerge that explain phenomena across multiple contexts. Once a theory is developed from qualitative studies, a quantitative researcher can seek to test that theory. For example, a quantitative researcher may hypothesize that men who hold traditional gender roles are more likely to engage in domestic violence. That would make sense based on the Power and Control Wheel model, as the category of “using male privilege” speaks to this relationship. In this way, qualitatively-derived theory can inspire a hypothesis for a quantitative research project, as we will explore in the next section.
Complementary approaches
If idiographic and nomothetic still seem like obscure philosophy terms, let’s consider another example. Imagine you are working for a community-based non-profit agency serving people with disabilities. You are putting together a report to lobby the state government for additional funding for community support programs. As part of that lobbying, you are likely to rely on both nomothetic and idiographic causal relationships.
If you looked at nomothetic causal relationships, you might learn how previous studies have shown that, in general, community-based programs like yours are linked with better health and employment outcomes for people with disabilities. Nomothetic causal explanations seek to establish that community-based programs are better for everyone with disabilities, including people in your community.
If you looked at idiographic causal explanations, you would use stories and experiences of people in community-based programs. These individual stories are full of detail about the lived experience of being in a community-based program. You might use one story from a client in your lobbying campaign, so policymakers can understand the lived experience of what it’s like to be a person with a disability in this program. For example, a client who said “I feel at home when I’m at this agency because they treat me like a family member,” or “this is the agency that helped me get my first paycheck,” can communicate richer, more complex causal relationships.
Neither kind of causal explanation is better than the other. A decision to seek idiographic causal explanations means that you will attempt to explain or describe your phenomenon exhaustively, attending to cultural context and subjective interpretations. A decision to seek nomothetic causal explanations, on the other hand, means that you will try to explain what is true for everyone and predict what will be true in the future. In short, idiographic explanations have greater depth, and nomothetic explanations have greater breadth.
Most importantly, social workers understand the value of both approaches to understanding the social world. A social worker helping a client with substance abuse issues seeks idiographic explanations when they ask about that client’s life story, investigate their unique physical environment, or probe how their family relationships. At the same time, a social worker also uses nomothetic explanations to guide their interventions. Nomothetic explanations may help guide them to minimize risk factors and maximize protective factors or use an evidence-based therapy, relying on knowledge about what in general helps people with substance abuse issues.
So, which approach speaks to you? Are you interested in learning about (a) a few people’s experiences in a great deal of depth, or (b) a lot of people’s experiences more superficially, while also hoping your findings can be generalized to a greater number of people? The answer to this question will drive your research question and project. These approaches provide different types of information and both types are valuable.
- Idiographic causal explanations focus on subjectivity, context, and meaning.
- Idiographic causal explanations are best suited to exploratory research questions and qualitative methods.
- Idiographic causal explanations are used to create new theories in social science.
- Explore the literature on the theory you identified in section 8.1.
- Read about the origins of your theory. Who developed it and from what data?
- See if you can find a figure like Figure 8.9 in an article or book chapter that depicts the key concepts in your theory and how those concepts are related to one another causally. Write out a short statement on the causal relationships contained in the figure.
- List the key terms associated with qualitative research questions
- Distinguish between qualitative and quantitative research questions
Qualitative research questions differ from quantitative research questions. Because qualitative research questions seek to explore or describe phenomena, not provide a neat nomothetic explanation, they are often more general and openly worded. They may include only one concept, though many include more than one. Instead of asking how one variable causes changes in another, we are instead trying to understand the experiences , understandings , and meanings that people have about the concepts in our research question. These keywords often make an appearance in qualitative research questions.
Let’s work through an example from our last section. In Table 9.1, a student asked, “What is the relationship between sexual orientation or gender identity and homelessness for late adolescents in foster care?” In this question, it is pretty clear that the student believes that adolescents in foster care who identify as LGBTQ+ may be at greater risk for homelessness. This is a nomothetic causal relationship—LGBTQ+ status causes changes in homelessness.
However, what if the student were less interested in predicting homelessness based on LGBTQ+ status and more interested in understanding the stories of foster care youth who identify as LGBTQ+ and may be at risk for homelessness? In that case, the researcher would be building an idiographic causal explanation . The youths whom the researcher interviews may share stories of how their foster families, caseworkers, and others treated them. They may share stories about how they thought of their own sexuality or gender identity and how it changed over time. They may have different ideas about what it means to transition out of foster care.

Because qualitative questions usually center on idiographic causal relationships, they look different than quantitative questions. Table 9.3 below takes the final research questions from Table 9.1 and adapts them for qualitative research. The guidelines for research questions previously described in this chapter still apply, but there are some new elements to qualitative research questions that are not present in quantitative questions.
- Qualitative research questions often ask about lived experience, personal experience, understanding, meaning, and stories.
- Qualitative research questions may be more general and less specific.
- Qualitative research questions may also contain only one variable, rather than asking about relationships between multiple variables.
| How does witnessing domestic violence impact a child’s romantic relationships in adulthood? | How do people who witness domestic violence understand its effects on their current relationships? |
| What is the relationship between sexual orientation or gender identity and homelessness for late adolescents in foster care? | What is the experience of identifying as LGBTQ+ in the foster care system? |
| How does income inequality affect ambivalence in high-density urban areas? | What does racial ambivalence mean to residents of an urban neighborhood with high income inequality? |
| How does race impact rates of mental health diagnosis for children in foster care? | How do African-Americans experience seeking help for mental health concerns? |
Qualitative research questions have one final feature that distinguishes them from quantitative research questions: they can change over the course of a study. Qualitative research is a reflexive process, one in which the researcher adapts their approach based on what participants say and do. The researcher must constantly evaluate whether their question is important and relevant to the participants. As the researcher gains information from participants, it is normal for the focus of the inquiry to shift.
For example, a qualitative researcher may want to study how a new truancy rule impacts youth at risk of expulsion. However, after interviewing some of the youth in their community, a researcher might find that the rule is actually irrelevant to their behavior and thoughts. Instead, their participants will direct the discussion to their frustration with the school administrators or the lack of job opportunities in the area. This is a natural part of qualitative research, and it is normal for research questions and hypothesis to evolve based on information gleaned from participants.
However, this reflexivity and openness unacceptable in quantitative research for good reasons. Researchers using quantitative methods are testing a hypothesis, and if they could revise that hypothesis to match what they found, they could never be wrong! Indeed, an important component of open science and reproducability is the preregistration of a researcher’s hypotheses and data analysis plan in a central repository that can be verified and replicated by reviewers and other researchers. This interactive graphic from 538 shows how an unscrupulous research could come up with a hypothesis and theoretical explanation after collecting data by hunting for a combination of factors that results in a statistically significant relationship. This is an excellent example of how the positivist assumptions behind quantitative research and intepretivist assumptions behind qualitative research result in different approaches to social science.
- Qualitative research questions often contain words or phrases like “lived experience,” “personal experience,” “understanding,” “meaning,” and “stories.”
- Qualitative research questions can change and evolve over the course of the study.
- Using the guidance in this chapter, write a qualitative research question. You may want to use some of the keywords mentioned above.
- Kivuna, C. & Kuyini, A. B. (2017). Understanding and applying research paradigms in educational contexts. International Journal of Higher Education, 6 (5), 26-41. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1154775 ↵
- Kuhn, T. (1962). The structure of scientific revolutions . Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ↵
- Fleuridas, C., & Krafcik, D. (2019). Beyond four forces: The evolution of psychotherapy. Sage Open , 9 (1), 2158244018824492. ↵
- Shneider, A. M. (2009). Four stages of a scientific discipline; four types of scientist. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 34 (5), 217-233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2009.02.00 ↵
- Burrell, G. & Morgan, G. (1979). Sociological paradigms and organizational analysis . Routledge. Guba, E. (ed.) (1990). The paradigm dialog . SAGE. ↵
- Routledge. Guba, E. (ed.) (1990). The paradigm dialog . SAGE. ↵
- Burrell, G. & Morgan, G. (1979). Sociological paradigms and organizational analysis . Here is a summary of Burrell & Morgan from Babson College , and our classification collapses radical humanism and radical structuralism into the critical paradigm, following Guba and Lincoln's three-paradigm framework. We feel this approach is more parsimonious and easier for students to understand on an introductory level. ↵
- For more about how the meanings of hand gestures vary by region, you might read the following blog entry: Wong, W. (2007). The top 10 hand gestures you’d better get right . Retrieved from: http://www.languagetrainers.co.uk/blog/2007/09/24/top-10-hand-gestures ↵
- Rosario, M., Schrimshaw, E. W., Hunter, J., & Levy-Warren, A. (2009). The coming-out process of young lesbian and bisexual women: Are there butch/femme differences in sexual identity development?. Archives of sexual behavior , 38 (1), 34-49. ↵
- Calhoun, C., Gerteis, J., Moody, J., Pfaff, S., & Virk, I. (Eds.). (2007). Classical sociological theory (2nd ed.). Malden, MA: Blackwell. ↵
- Fraser, N. (1989). Unruly practices: Power, discourse, and gender in contemporary social theory . Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota Press. ↵
- Here are links to two HBSE open textbooks, if you are unfamiliar with social work theories and would like more background. https://uark.pressbooks.pub/hbse1/ and https://uark.pressbooks.pub/humanbehaviorandthesocialenvironment2/ ↵
- Box, G. E. P.. (1976). Science and statistics. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 71 (356), 791. ↵
- Heineman-Pieper, J., Tyson, K., & Pieper, M. H. (2002). Doing good science without sacrificing good values: Why the heuristic paradigm is the best choice for social work. Families in Society , 83 (1), 15-28. ↵
- Crasnow, S. (2020). Feminist perspectives on science. In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Winter 2020 Edition). Retrieved from: https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/feminist-science/ ↵
- Grogan, K.E. (2019) How the entire scientific community can confront gender bias in the workplace. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 3 , 3–6. doi:10.1038/s41559-018-0747-4 ↵
- Tasca, C., Rapetti, M., Carta, M. G., & Fadda, B. (2012). Women and hysteria in the history of mental health. Clinical practice and epidemiology in mental health: Clinical practice & epidemiology in mental health , 8 , 110-119. ↵
- Klonsky, E. D., Jane, J. S., Turkheimer, E., & Oltmanns, T. F. (2002). Gender role and personality disorders. Journal of personality disorders , 16 (5), 464-476. ↵
- Smith, L. T. (2013). Decolonizing methodologies: Research and indigenous peoples . Zed Books Ltd. ↵
- Fricker, M. (2011). Epistemic injustice: Power and the ethics of knowing . Oxford University Press. ↵
The highest level of measurement. Denoted by mutually exclusive categories, a hierarchy (order), values can be added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided, and the presence of an absolute zero.
a paradigm based on the idea that social context and interaction frame our realities
a paradigm in social science research focused on power, inequality, and social change
a research paradigm that suspends questions of philosophical ‘truth’ and focuses more on how different philosophies, theories, and methods can be used strategically to resolve a problem or question within the researcher's unique context
A cyclical process of theory development, starting with an observed phenomenon, then developing or using a theory to make a specific prediction of what should happen if that theory is correct, testing that prediction, refining the theory in light of the findings, and using that refined theory to develop new hypotheses, and so on.
when someone is treated unfairly in their capacity to know something or describe their experience of the world
conducted during the early stages of a project, usually when a researcher wants to test the feasibility of conducting a more extensive study or if the topic has not been studied in the past
research that describes or defines a particular phenomenon
explains why particular phenomena work in the way that they do; answers “why” questions
attempts to explain or describe your phenomenon exhaustively, based on the subjective understandings of your participants
"Assuming that the null hypothesis is true and the study is repeated an infinite number times by drawing random samples from the same populations(s), less than 5% of these results will be more extreme than the current result" (Cassidy et al., 2019, p. 233).
Scientific Inquiry in Social Work (2nd Edition) Copyright © 2020 by Matthew DeCarlo, Cory Cummings, and Kate Agnelli is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Qualitative Research Definition
Qualitative research methods and examples, advantages and disadvantages of qualitative approaches, qualitative vs. quantitative research, showing qualitative research skills on resumes, what is qualitative research methods and examples.
- Share on Twitter Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn Share on LinkedIn

Forage puts students first. Our blog articles are written independently by our editorial team. They have not been paid for or sponsored by our partners. See our full editorial guidelines .
Table of Contents
Qualitative research seeks to understand people’s experiences and perspectives by studying social organizations and human behavior. Data in qualitative studies focuses on people’s beliefs and emotional responses. Qualitative data is especially helpful when a company wants to know how customers feel about a product or service, such as in user experience (UX) design or marketing .
Researchers use qualitative approaches to “determine answers to research questions on human behavior and the cultural values that drive our thinking and behavior,” says Margaret J. King, director at The Center for Cultural Studies & Analysis in Philadelphia.
Data in qualitative research typically can’t be assessed mathematically — the data is not sets of numbers or quantifiable information. Rather, it’s collections of images, words, notes on behaviors, descriptions of emotions, and historical context. Data is collected through observations, interviews, surveys, focus groups, and secondary research.
However, a qualitative study needs a “clear research question at its base,” notes King, and the research needs to be “observed, categorized, compared, and evaluated (along a scale or by a typology chart) by reference to a baseline in order to determine an outcome with value as new and reliable information.”

Quantium Data Analytics
Explore the power of data and its ability to power breakthrough possibilities for individuals, organisations and societies with this free job simulation from Quantium.
Avg. Time: 4 to 5 hours
Skills you’ll build: Data validation, data visualisation, data wrangling, programming, data analysis, commercial thinking, statistical testing, presentation skills
Who Uses Qualitative Research?
Researchers in social sciences and humanities often use qualitative research methods, especially in specific areas of study like anthropology, history, education, and sociology.
Qualitative methods are also applicable in business, technology , and marketing spaces. For example, product managers use qualitative research to understand how target audiences respond to their products. They may use focus groups to gain insights from potential customers on product prototypes and improvements or surveys from existing customers to understand what changes users want to see.
Other careers that may involve qualitative research include:
- Marketing analyst
- UX and UI analyst
- Market researcher
- Statistician
- Business analyst
- Data analyst
- Research assistant
- Claims investigator


Electronic Arts Product Management
Learn how product managers leverage qualitative and other types of research to build and improve products in this free job simulation from EA.
Avg. Time: 1 to 2 hours
Skills you’ll build: Critical thinking, problem solving, performance metrics, written communication, project planning
Good research begins with a question, and this question informs the approach used by qualitative researchers.
Grounded Theory
Grounded theory is an inductive approach to theory development. In many forms of research, you begin with a hypothesis and then test it to see if you’re correct. In grounded theory, though, you go in without any assumptions and rely on the data you collect to form theories. You start with an open question about a phenomenon you are studying and collect and analyze data until you can form a fully-fledged theory from the information.
Example: A company wants to improve its brand and marketing strategies. The company performs a grounded theory approach to solving this problem by conducting interviews and surveys with past, current, and prospective customers. The information gathered from these methods helps the company understand what type of branding and marketing their customer-base likes and dislikes, allowing the team to inductively craft a new brand and marketing strategy from the data.
Action Research
Action research is one part study and one part problem-solving . Through action research, analysts investigate a problem or weakness and develop practical solutions. The process of action research is cyclical —- researchers assess solutions for efficiency and effectiveness, and create further solutions to correct any issues found.
Example: A manager notices her employees struggle to cooperate on group projects. She carefully reviews how team members interact with each other and asks them all to respond to a survey about communication. Through the survey and study, she finds that guidelines for group projects are unclear. After changing the guidelines, she reviews her team again to see if there are any changes to their behavior.
>>MORE: Explore how action research helps consultants serve clients with Accenture’s Client Research and Problem Identification job simulation .
Phenomenological Research
Phenomenological research investigates a phenomenon in depth, looking at people’s experiences and understanding of the situation. This sort of study is primarily descriptive and seeks to broaden understanding around a specific incident and the people involved. Researchers in phenomenological studies must be careful to set aside any biases or assumptions because the information used should be entirely from the subjects themselves.
Example : A researcher wants to better understand the lived experience of college students with jobs. The purpose of this research is to gain insights into the pressures of college students who balance studying and working at the same time. The researcher conducts a series of interviews with several college students, learning about their past and current situations. Through the first few interviews, the researcher builds a relationship with the students. Later discussions are more targeted, with questions prompting the students to discuss their emotions surrounding both work and school and the difficulties and benefits arising from their situation. The researcher then analyzes these interviews, and identifies shared themes to contextualize the experiences of the students.

GE Aerospace Human Resources
Learn the research and conflict resolution skills necessary for a career in human resources in this free job simulation from GE.
Avg. Time: 3 to 4 hours
Skills you’ll build: Feedback giving, communication skills, empowering with insights, basics of lean, process mapping, continuous improvement tools, dataset handling in Excel
Ethnography
Ethnography is an immersive study of a particular culture or community. Through ethnographic research, analysts aim to learn about a group’s conventions, social dynamics, and cultural norms. Some researchers use active observation methods, finding ways to integrate themselves into the culture as much as possible. Others use passive observation, watching closely from the outside but not fully immersing themselves.
Example: A company hires an external researcher to learn what their company’s culture is actually like. The researcher studies the social dynamics of the employees and may even look at how these employees interact with clients and with each other outside of the office. The goal is to deliver a comprehensive report of the company’s culture and the social dynamics of its employees.
Case Studies
A case study is a type of in-depth analysis of a situation. Case studies can focus on an organization, belief system, event, person, or action. The goal of a case study is to understand the phenomenon and put it in a real-world context. Case studies are also commonly used in marketing and sales to highlight the benefits of a company’s products or services.
Example: A business performs a case study of its competitors’ strategies. This case study aims to show why the company should adopt a specific business strategy. The study looks at each competitor’s business structure, marketing campaigns, product offerings, and historical growth trends. Then, using this data on other businesses, the researcher can theorize how that strategy would benefit their company.
>>MORE: Learn how companies use case study interviews to assess candidates’ research and problem-solving skills.
Qualitative research methods are great for generating new ideas. The exploratory nature of qualitative research means uncovering unexpected information, which often leads to new theories and further research topics. Additionally, qualitative findings feel meaningful. These studies focus on people, emotions, and societies and may feel closer to their communities than quantitative research that relies on more mathematical and logical data.
However, qualitative research can be unreliable at times. It’s difficult to replicate qualitative studies since people’s opinions and emotions can change quickly. For example, a focus group has a lot of variables that can affect the outcome, and that same group, asked the same questions a year later, may have entirely different responses. The data collection can also be difficult and time-consuming with qualitative research. Ultimately, interviewing people, reviewing surveys, and understanding and explaining human emotions can be incredibly complex.
Find your career fit
See what career path is right for you with our free career quiz!
While qualitative research deals with data that isn’t easily manipulated by mathematics, quantitative research almost exclusively involves numbers and numerical data. Quantitative studies aim to find concrete details, like units of time, percentages, or statistics.
Besides the types of data used, a core difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the idea of control and replication.
“Qualitative is less subject to control (as in lab studies) and, therefore, less statistically measurable than quantitative approaches,” says King.
One person’s interview about a specific topic can have completely different responses than every other person’s interview since there are so many variables in qualitative research. On the other hand, quantitative studies can often be replicated. For instance, when testing the effects of a new medication, quantifiable data, like blood test results, can be repeated. Qualitative data, though, like how people feel about the medication, may differ from person to person and from moment to moment.

JPMorgan Quantitative Research
Discover how bankers use quantitative methods to analyze businesses and industry trends with this free job simulation.
Avg. Time: 6 to 7 hours
Skills you’ll build: Programming, data analysis, Python, critical thinking, statistics, dynamic programming
You can show your experience with qualitative research on your resume in your skills or work experience sections and your cover letter .
- In your skills section , you can list types of qualitative research you are skilled at, like conducting interviews, performing grounded theory research, or crafting case studies.
- In your work or internship experience descriptions , you can highlight specific examples, like talking about a time you used action research to solve a complex issue at your last job.
- In your cover letter , you can discuss in-depth qualitative research projects you’ve completed. For instance, say you spent a summer conducting ethnographic research or a whole semester running focus groups to get feedback on a product. You can talk about these experiences in your cover letter and note how these skills make you a great fit for the job.
Grow your skills and explore your career options with Forage’s free job simulations .
Image credit: Canva

Related Posts
6 negotiation skills to level up your work life, how to build conflict resolution skills: case studies and examples, what is github uses and getting started, upskill with forage.

Top companies are hiring now!
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed, qualitative study, affiliations.
- 1 University of Nebraska Medical Center
- 2 GDB Research and Statistical Consulting
- 3 GDB Research and Statistical Consulting/McLaren Macomb Hospital
- PMID: 29262162
- Bookshelf ID: NBK470395
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervening or introducing treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypothenar to further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions, and behavior. It answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much. It could be structured as a standalone study, purely relying on qualitative data, or part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data. This review introduces the readers to some basic concepts, definitions, terminology, and applications of qualitative research.
Qualitative research, at its core, asks open-ended questions whose answers are not easily put into numbers, such as "how" and "why." Due to the open-ended nature of the research questions, qualitative research design is often not linear like quantitative design. One of the strengths of qualitative research is its ability to explain processes and patterns of human behavior that can be difficult to quantify. Phenomena such as experiences, attitudes, and behaviors can be complex to capture accurately and quantitatively. In contrast, a qualitative approach allows participants themselves to explain how, why, or what they were thinking, feeling, and experiencing at a particular time or during an event of interest. Quantifying qualitative data certainly is possible, but at its core, qualitative data is looking for themes and patterns that can be difficult to quantify, and it is essential to ensure that the context and narrative of qualitative work are not lost by trying to quantify something that is not meant to be quantified.
However, while qualitative research is sometimes placed in opposition to quantitative research, where they are necessarily opposites and therefore "compete" against each other and the philosophical paradigms associated with each other, qualitative and quantitative work are neither necessarily opposites, nor are they incompatible. While qualitative and quantitative approaches are different, they are not necessarily opposites and certainly not mutually exclusive. For instance, qualitative research can help expand and deepen understanding of data or results obtained from quantitative analysis. For example, say a quantitative analysis has determined a correlation between length of stay and level of patient satisfaction, but why does this correlation exist? This dual-focus scenario shows one way in which qualitative and quantitative research could be integrated.
Copyright © 2024, StatPearls Publishing LLC.
PubMed Disclaimer
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: Steven Tenny declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Janelle Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Grace Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
- Introduction
- Issues of Concern
- Clinical Significance
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
- Review Questions
Similar articles
- Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, Moraleda C, Rogers L, Daniels K, Green P. Crider K, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
- Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012). Foffi G, Pastore A, Piazza F, Temussi PA. Foffi G, et al. Phys Biol. 2013 Aug;10(4):040301. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/10/4/040301. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Phys Biol. 2013. PMID: 23912807
- The future of Cochrane Neonatal. Soll RF, Ovelman C, McGuire W. Soll RF, et al. Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
- Invited review: Qualitative research in dairy science-A narrative review. Ritter C, Koralesky KE, Saraceni J, Roche S, Vaarst M, Kelton D. Ritter C, et al. J Dairy Sci. 2023 Sep;106(9):5880-5895. doi: 10.3168/jds.2022-23125. Epub 2023 Jul 18. J Dairy Sci. 2023. PMID: 37474366 Review.
- Participation in environmental enhancement and conservation activities for health and well-being in adults: a review of quantitative and qualitative evidence. Husk K, Lovell R, Cooper C, Stahl-Timmins W, Garside R. Husk K, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 21;2016(5):CD010351. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010351.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27207731 Free PMC article. Review.
- Moser A, Korstjens I. Series: Practical guidance to qualitative research. Part 1: Introduction. Eur J Gen Pract. 2017 Dec;23(1):271-273. - PMC - PubMed
- Cleland JA. The qualitative orientation in medical education research. Korean J Med Educ. 2017 Jun;29(2):61-71. - PMC - PubMed
- Foley G, Timonen V. Using Grounded Theory Method to Capture and Analyze Health Care Experiences. Health Serv Res. 2015 Aug;50(4):1195-210. - PMC - PubMed
- Devers KJ. How will we know "good" qualitative research when we see it? Beginning the dialogue in health services research. Health Serv Res. 1999 Dec;34(5 Pt 2):1153-88. - PMC - PubMed
- Huston P, Rowan M. Qualitative studies. Their role in medical research. Can Fam Physician. 1998 Nov;44:2453-8. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
Related information
- Cited in Books
LinkOut - more resources
Full text sources.
- NCBI Bookshelf

- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
A guide to conducting agile qualitative research for rapid insights with Digsite
Qualitative research is traditionally considered time-consuming and resource-intensive, and the turnaround to insights is slower than quantitative research. Digsite , a purpose-built asynchronous agile qualitative research platform, changes how you conduct qualitative research and get insights faster.
Digsite helps you deliver results in days rather than weeks!
Asynchronous agile qualitative research with Digsite
Digsite is a fast, flexible, and asynchronous qualitative research tool that enables teams to engage with carefully selected consumers to build better products, services, and communications. Whether you need self-service or full-service support, Digsite adapts to your research needs, delivering valuable insights in days, not weeks. This platform empowers you and your research teams to quickly gather consumer feedback, helping you innovate efficiently in a rapidly changing market.
We recently conducted a webinar to showcase how you can effectively change how you conduct qualitative research. Watch this video below:
You can also view the presentation deck from the webinar here:
Salient features of Digsite
Some salient features and advantages of using QuestionPro Digsite are:
- DIY or DIT models for flexible research support
- Quick-turnaround qualitative studies to save time and costs
- Agile tasks focused on gathering insights, not just data
- Fun and engaging tasks to uncover emotions driving decisions
- Suitable for innovation, marketing, and shopper insights research
- Supports detailed feedback on concepts via idea markup
- Features unmoderated video tasks and real-time voting
- Leverages AI and NLP for emotional insights and intelligent dashboards with easy report downloads within minutes.
- Topline with insights and recommendations delivered within a week from study kick-off.
Answers to some critical questions about Digsite that will help you get started
Below is a list of pressing questions in the webinar and other questions to help you get started with Digsite.
Q) What is the timeline from creating studies to delivering insights with Digsite?
- Monday – Kickoff meeting
- Tuesday – Design screener and activity guide
- Wednesday – Approve guide and program screener
- Thursday – Recruit
- Friday – Run study
- Monday – SmartDashboard available via editable PPT with key quotes delivered
- Following Monday – Topline with insights and recommendations delivered
Q) Can you recruit participants, or is there a panel of people to choose from for the studies?
- Digsite allows you to import participants and manually add members to a study. QuestionPro has an Audience platform that lets you access hard-to-reach panelists and participants for studies.
Q) What are the operational limitations of conducting qualitative research with Digsite?
- The Digsite platform is completely online and asynchronous. Hence, there are no operational limitations or geographical or demographic limiting factors for conducting studies.
Q) Can a study be tweaked once it is set up?
- Any study can be tweaked once it is set up. Once results start to come in, you can easily adjust the concepts needed based on these learnings and create new concepts.
Q) How do you probe responses like why, how, etc. like in traditional qualitative research studies?
- The community’s moderator can examine the responses in real-time to determine whether they meet the study objectives. If they don’t, or to obtain further information, tweaks can be made to the studies to elicit further participant responses. QuestionPro also has a specialized research services team that can extend your internal research team and help you derive actionable insights.
Q) Do you have an AI solution describing insights from qualitative responses? Or, e.g., teasing out takeaways from uploaded pics?
- AI Smart Summary provides the top 5 themes in conversation tasks to jumpstart the analysis process. Our AI engine also includes an automated natural language processing (NLP) engine that is deep-rooted in understanding and analyzing sentiments from video, text, and other rich media.
Q) How do qual-based learnings get integrated into the learnings dashboard?
- Each module under Digsite supports AI-driven research and learnings to nugget and analyze qualitative and quantitative information that flows into the SmartDashboards, which you can view online and download.
Q) Does AI help categorize and theme the content?
- Over the past 4-5 years, we’ve developed this engine by analyzing millions of open-ended responses to generate valuable insights. It categorizes data effectively, but if the output doesn’t meet your expectations, the dashboard allows you to refine and adjust to get the best insights for your needs. These adjustments also improve future studies and dashboards as the bot continues learning, making the process smoother and more efficient.
Q) The conventional approach to content analysis is an intellectual process. If AI partially or wholly supports this part, how shall we claim the originality of the interpretation?
- As with AI, you can train the bot to generate AI-driven insights, dashboards, and data in a way that works for you. You can set up your guardrails to create insights that matter to you.
Q) In what format can you export the study report?
- Currently (Sep 2024), you can download data from the SmartDashboards into ppt format. Other formats will be supported in due course.
Q) Is it possible to download a PowerPoint report from the platform that includes the company font, colors, etc.?
- Currently, the Digsite platform allows you to download a fully customizable PowerPoint export, which you can tweak to fit your brand identity .
Start using Digsite in your projects right away!
You can get started with Digsite and leverage it for your qualitative research today! For a detailed guide on how to set up your studies immediately, you can follow the steps below:
You can also contact your QuestionPro account representative to get started. Don’t have a QuestionPro account? No worries! Request a demo of the Digsite platform and get started right away!
MORE LIKE THIS

Participant Engagement: Strategies + Improving Interaction
Sep 12, 2024

Employee Recognition Programs: A Complete Guide
Sep 11, 2024

Cultural Insights: What it is, Importance + How to Collect?
Sep 10, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Can J Hosp Pharm
- v.68(3); May-Jun 2015

Qualitative Research: Data Collection, Analysis, and Management
Introduction.
In an earlier paper, 1 we presented an introduction to using qualitative research methods in pharmacy practice. In this article, we review some principles of the collection, analysis, and management of qualitative data to help pharmacists interested in doing research in their practice to continue their learning in this area. Qualitative research can help researchers to access the thoughts and feelings of research participants, which can enable development of an understanding of the meaning that people ascribe to their experiences. Whereas quantitative research methods can be used to determine how many people undertake particular behaviours, qualitative methods can help researchers to understand how and why such behaviours take place. Within the context of pharmacy practice research, qualitative approaches have been used to examine a diverse array of topics, including the perceptions of key stakeholders regarding prescribing by pharmacists and the postgraduation employment experiences of young pharmacists (see “Further Reading” section at the end of this article).
In the previous paper, 1 we outlined 3 commonly used methodologies: ethnography 2 , grounded theory 3 , and phenomenology. 4 Briefly, ethnography involves researchers using direct observation to study participants in their “real life” environment, sometimes over extended periods. Grounded theory and its later modified versions (e.g., Strauss and Corbin 5 ) use face-to-face interviews and interactions such as focus groups to explore a particular research phenomenon and may help in clarifying a less-well-understood problem, situation, or context. Phenomenology shares some features with grounded theory (such as an exploration of participants’ behaviour) and uses similar techniques to collect data, but it focuses on understanding how human beings experience their world. It gives researchers the opportunity to put themselves in another person’s shoes and to understand the subjective experiences of participants. 6 Some researchers use qualitative methodologies but adopt a different standpoint, and an example of this appears in the work of Thurston and others, 7 discussed later in this paper.
Qualitative work requires reflection on the part of researchers, both before and during the research process, as a way of providing context and understanding for readers. When being reflexive, researchers should not try to simply ignore or avoid their own biases (as this would likely be impossible); instead, reflexivity requires researchers to reflect upon and clearly articulate their position and subjectivities (world view, perspectives, biases), so that readers can better understand the filters through which questions were asked, data were gathered and analyzed, and findings were reported. From this perspective, bias and subjectivity are not inherently negative but they are unavoidable; as a result, it is best that they be articulated up-front in a manner that is clear and coherent for readers.
THE PARTICIPANT’S VIEWPOINT
What qualitative study seeks to convey is why people have thoughts and feelings that might affect the way they behave. Such study may occur in any number of contexts, but here, we focus on pharmacy practice and the way people behave with regard to medicines use (e.g., to understand patients’ reasons for nonadherence with medication therapy or to explore physicians’ resistance to pharmacists’ clinical suggestions). As we suggested in our earlier article, 1 an important point about qualitative research is that there is no attempt to generalize the findings to a wider population. Qualitative research is used to gain insights into people’s feelings and thoughts, which may provide the basis for a future stand-alone qualitative study or may help researchers to map out survey instruments for use in a quantitative study. It is also possible to use different types of research in the same study, an approach known as “mixed methods” research, and further reading on this topic may be found at the end of this paper.
The role of the researcher in qualitative research is to attempt to access the thoughts and feelings of study participants. This is not an easy task, as it involves asking people to talk about things that may be very personal to them. Sometimes the experiences being explored are fresh in the participant’s mind, whereas on other occasions reliving past experiences may be difficult. However the data are being collected, a primary responsibility of the researcher is to safeguard participants and their data. Mechanisms for such safeguarding must be clearly articulated to participants and must be approved by a relevant research ethics review board before the research begins. Researchers and practitioners new to qualitative research should seek advice from an experienced qualitative researcher before embarking on their project.
DATA COLLECTION
Whatever philosophical standpoint the researcher is taking and whatever the data collection method (e.g., focus group, one-to-one interviews), the process will involve the generation of large amounts of data. In addition to the variety of study methodologies available, there are also different ways of making a record of what is said and done during an interview or focus group, such as taking handwritten notes or video-recording. If the researcher is audio- or video-recording data collection, then the recordings must be transcribed verbatim before data analysis can begin. As a rough guide, it can take an experienced researcher/transcriber 8 hours to transcribe one 45-minute audio-recorded interview, a process than will generate 20–30 pages of written dialogue.
Many researchers will also maintain a folder of “field notes” to complement audio-taped interviews. Field notes allow the researcher to maintain and comment upon impressions, environmental contexts, behaviours, and nonverbal cues that may not be adequately captured through the audio-recording; they are typically handwritten in a small notebook at the same time the interview takes place. Field notes can provide important context to the interpretation of audio-taped data and can help remind the researcher of situational factors that may be important during data analysis. Such notes need not be formal, but they should be maintained and secured in a similar manner to audio tapes and transcripts, as they contain sensitive information and are relevant to the research. For more information about collecting qualitative data, please see the “Further Reading” section at the end of this paper.
DATA ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT
If, as suggested earlier, doing qualitative research is about putting oneself in another person’s shoes and seeing the world from that person’s perspective, the most important part of data analysis and management is to be true to the participants. It is their voices that the researcher is trying to hear, so that they can be interpreted and reported on for others to read and learn from. To illustrate this point, consider the anonymized transcript excerpt presented in Appendix 1 , which is taken from a research interview conducted by one of the authors (J.S.). We refer to this excerpt throughout the remainder of this paper to illustrate how data can be managed, analyzed, and presented.
Interpretation of Data
Interpretation of the data will depend on the theoretical standpoint taken by researchers. For example, the title of the research report by Thurston and others, 7 “Discordant indigenous and provider frames explain challenges in improving access to arthritis care: a qualitative study using constructivist grounded theory,” indicates at least 2 theoretical standpoints. The first is the culture of the indigenous population of Canada and the place of this population in society, and the second is the social constructivist theory used in the constructivist grounded theory method. With regard to the first standpoint, it can be surmised that, to have decided to conduct the research, the researchers must have felt that there was anecdotal evidence of differences in access to arthritis care for patients from indigenous and non-indigenous backgrounds. With regard to the second standpoint, it can be surmised that the researchers used social constructivist theory because it assumes that behaviour is socially constructed; in other words, people do things because of the expectations of those in their personal world or in the wider society in which they live. (Please see the “Further Reading” section for resources providing more information about social constructivist theory and reflexivity.) Thus, these 2 standpoints (and there may have been others relevant to the research of Thurston and others 7 ) will have affected the way in which these researchers interpreted the experiences of the indigenous population participants and those providing their care. Another standpoint is feminist standpoint theory which, among other things, focuses on marginalized groups in society. Such theories are helpful to researchers, as they enable us to think about things from a different perspective. Being aware of the standpoints you are taking in your own research is one of the foundations of qualitative work. Without such awareness, it is easy to slip into interpreting other people’s narratives from your own viewpoint, rather than that of the participants.
To analyze the example in Appendix 1 , we will adopt a phenomenological approach because we want to understand how the participant experienced the illness and we want to try to see the experience from that person’s perspective. It is important for the researcher to reflect upon and articulate his or her starting point for such analysis; for example, in the example, the coder could reflect upon her own experience as a female of a majority ethnocultural group who has lived within middle class and upper middle class settings. This personal history therefore forms the filter through which the data will be examined. This filter does not diminish the quality or significance of the analysis, since every researcher has his or her own filters; however, by explicitly stating and acknowledging what these filters are, the researcher makes it easer for readers to contextualize the work.
Transcribing and Checking
For the purposes of this paper it is assumed that interviews or focus groups have been audio-recorded. As mentioned above, transcribing is an arduous process, even for the most experienced transcribers, but it must be done to convert the spoken word to the written word to facilitate analysis. For anyone new to conducting qualitative research, it is beneficial to transcribe at least one interview and one focus group. It is only by doing this that researchers realize how difficult the task is, and this realization affects their expectations when asking others to transcribe. If the research project has sufficient funding, then a professional transcriber can be hired to do the work. If this is the case, then it is a good idea to sit down with the transcriber, if possible, and talk through the research and what the participants were talking about. This background knowledge for the transcriber is especially important in research in which people are using jargon or medical terms (as in pharmacy practice). Involving your transcriber in this way makes the work both easier and more rewarding, as he or she will feel part of the team. Transcription editing software is also available, but it is expensive. For example, ELAN (more formally known as EUDICO Linguistic Annotator, developed at the Technical University of Berlin) 8 is a tool that can help keep data organized by linking media and data files (particularly valuable if, for example, video-taping of interviews is complemented by transcriptions). It can also be helpful in searching complex data sets. Products such as ELAN do not actually automatically transcribe interviews or complete analyses, and they do require some time and effort to learn; nonetheless, for some research applications, it may be a valuable to consider such software tools.
All audio recordings should be transcribed verbatim, regardless of how intelligible the transcript may be when it is read back. Lines of text should be numbered. Once the transcription is complete, the researcher should read it while listening to the recording and do the following: correct any spelling or other errors; anonymize the transcript so that the participant cannot be identified from anything that is said (e.g., names, places, significant events); insert notations for pauses, laughter, looks of discomfort; insert any punctuation, such as commas and full stops (periods) (see Appendix 1 for examples of inserted punctuation), and include any other contextual information that might have affected the participant (e.g., temperature or comfort of the room).
Dealing with the transcription of a focus group is slightly more difficult, as multiple voices are involved. One way of transcribing such data is to “tag” each voice (e.g., Voice A, Voice B). In addition, the focus group will usually have 2 facilitators, whose respective roles will help in making sense of the data. While one facilitator guides participants through the topic, the other can make notes about context and group dynamics. More information about group dynamics and focus groups can be found in resources listed in the “Further Reading” section.
Reading between the Lines
During the process outlined above, the researcher can begin to get a feel for the participant’s experience of the phenomenon in question and can start to think about things that could be pursued in subsequent interviews or focus groups (if appropriate). In this way, one participant’s narrative informs the next, and the researcher can continue to interview until nothing new is being heard or, as it says in the text books, “saturation is reached”. While continuing with the processes of coding and theming (described in the next 2 sections), it is important to consider not just what the person is saying but also what they are not saying. For example, is a lengthy pause an indication that the participant is finding the subject difficult, or is the person simply deciding what to say? The aim of the whole process from data collection to presentation is to tell the participants’ stories using exemplars from their own narratives, thus grounding the research findings in the participants’ lived experiences.
Smith 9 suggested a qualitative research method known as interpretative phenomenological analysis, which has 2 basic tenets: first, that it is rooted in phenomenology, attempting to understand the meaning that individuals ascribe to their lived experiences, and second, that the researcher must attempt to interpret this meaning in the context of the research. That the researcher has some knowledge and expertise in the subject of the research means that he or she can have considerable scope in interpreting the participant’s experiences. Larkin and others 10 discussed the importance of not just providing a description of what participants say. Rather, interpretative phenomenological analysis is about getting underneath what a person is saying to try to truly understand the world from his or her perspective.
Once all of the research interviews have been transcribed and checked, it is time to begin coding. Field notes compiled during an interview can be a useful complementary source of information to facilitate this process, as the gap in time between an interview, transcribing, and coding can result in memory bias regarding nonverbal or environmental context issues that may affect interpretation of data.
Coding refers to the identification of topics, issues, similarities, and differences that are revealed through the participants’ narratives and interpreted by the researcher. This process enables the researcher to begin to understand the world from each participant’s perspective. Coding can be done by hand on a hard copy of the transcript, by making notes in the margin or by highlighting and naming sections of text. More commonly, researchers use qualitative research software (e.g., NVivo, QSR International Pty Ltd; www.qsrinternational.com/products_nvivo.aspx ) to help manage their transcriptions. It is advised that researchers undertake a formal course in the use of such software or seek supervision from a researcher experienced in these tools.
Returning to Appendix 1 and reading from lines 8–11, a code for this section might be “diagnosis of mental health condition”, but this would just be a description of what the participant is talking about at that point. If we read a little more deeply, we can ask ourselves how the participant might have come to feel that the doctor assumed he or she was aware of the diagnosis or indeed that they had only just been told the diagnosis. There are a number of pauses in the narrative that might suggest the participant is finding it difficult to recall that experience. Later in the text, the participant says “nobody asked me any questions about my life” (line 19). This could be coded simply as “health care professionals’ consultation skills”, but that would not reflect how the participant must have felt never to be asked anything about his or her personal life, about the participant as a human being. At the end of this excerpt, the participant just trails off, recalling that no-one showed any interest, which makes for very moving reading. For practitioners in pharmacy, it might also be pertinent to explore the participant’s experience of akathisia and why this was left untreated for 20 years.
One of the questions that arises about qualitative research relates to the reliability of the interpretation and representation of the participants’ narratives. There are no statistical tests that can be used to check reliability and validity as there are in quantitative research. However, work by Lincoln and Guba 11 suggests that there are other ways to “establish confidence in the ‘truth’ of the findings” (p. 218). They call this confidence “trustworthiness” and suggest that there are 4 criteria of trustworthiness: credibility (confidence in the “truth” of the findings), transferability (showing that the findings have applicability in other contexts), dependability (showing that the findings are consistent and could be repeated), and confirmability (the extent to which the findings of a study are shaped by the respondents and not researcher bias, motivation, or interest).
One way of establishing the “credibility” of the coding is to ask another researcher to code the same transcript and then to discuss any similarities and differences in the 2 resulting sets of codes. This simple act can result in revisions to the codes and can help to clarify and confirm the research findings.
Theming refers to the drawing together of codes from one or more transcripts to present the findings of qualitative research in a coherent and meaningful way. For example, there may be examples across participants’ narratives of the way in which they were treated in hospital, such as “not being listened to” or “lack of interest in personal experiences” (see Appendix 1 ). These may be drawn together as a theme running through the narratives that could be named “the patient’s experience of hospital care”. The importance of going through this process is that at its conclusion, it will be possible to present the data from the interviews using quotations from the individual transcripts to illustrate the source of the researchers’ interpretations. Thus, when the findings are organized for presentation, each theme can become the heading of a section in the report or presentation. Underneath each theme will be the codes, examples from the transcripts, and the researcher’s own interpretation of what the themes mean. Implications for real life (e.g., the treatment of people with chronic mental health problems) should also be given.
DATA SYNTHESIS
In this final section of this paper, we describe some ways of drawing together or “synthesizing” research findings to represent, as faithfully as possible, the meaning that participants ascribe to their life experiences. This synthesis is the aim of the final stage of qualitative research. For most readers, the synthesis of data presented by the researcher is of crucial significance—this is usually where “the story” of the participants can be distilled, summarized, and told in a manner that is both respectful to those participants and meaningful to readers. There are a number of ways in which researchers can synthesize and present their findings, but any conclusions drawn by the researchers must be supported by direct quotations from the participants. In this way, it is made clear to the reader that the themes under discussion have emerged from the participants’ interviews and not the mind of the researcher. The work of Latif and others 12 gives an example of how qualitative research findings might be presented.
Planning and Writing the Report
As has been suggested above, if researchers code and theme their material appropriately, they will naturally find the headings for sections of their report. Qualitative researchers tend to report “findings” rather than “results”, as the latter term typically implies that the data have come from a quantitative source. The final presentation of the research will usually be in the form of a report or a paper and so should follow accepted academic guidelines. In particular, the article should begin with an introduction, including a literature review and rationale for the research. There should be a section on the chosen methodology and a brief discussion about why qualitative methodology was most appropriate for the study question and why one particular methodology (e.g., interpretative phenomenological analysis rather than grounded theory) was selected to guide the research. The method itself should then be described, including ethics approval, choice of participants, mode of recruitment, and method of data collection (e.g., semistructured interviews or focus groups), followed by the research findings, which will be the main body of the report or paper. The findings should be written as if a story is being told; as such, it is not necessary to have a lengthy discussion section at the end. This is because much of the discussion will take place around the participants’ quotes, such that all that is needed to close the report or paper is a summary, limitations of the research, and the implications that the research has for practice. As stated earlier, it is not the intention of qualitative research to allow the findings to be generalized, and therefore this is not, in itself, a limitation.
Planning out the way that findings are to be presented is helpful. It is useful to insert the headings of the sections (the themes) and then make a note of the codes that exemplify the thoughts and feelings of your participants. It is generally advisable to put in the quotations that you want to use for each theme, using each quotation only once. After all this is done, the telling of the story can begin as you give your voice to the experiences of the participants, writing around their quotations. Do not be afraid to draw assumptions from the participants’ narratives, as this is necessary to give an in-depth account of the phenomena in question. Discuss these assumptions, drawing on your participants’ words to support you as you move from one code to another and from one theme to the next. Finally, as appropriate, it is possible to include examples from literature or policy documents that add support for your findings. As an exercise, you may wish to code and theme the sample excerpt in Appendix 1 and tell the participant’s story in your own way. Further reading about “doing” qualitative research can be found at the end of this paper.
CONCLUSIONS
Qualitative research can help researchers to access the thoughts and feelings of research participants, which can enable development of an understanding of the meaning that people ascribe to their experiences. It can be used in pharmacy practice research to explore how patients feel about their health and their treatment. Qualitative research has been used by pharmacists to explore a variety of questions and problems (see the “Further Reading” section for examples). An understanding of these issues can help pharmacists and other health care professionals to tailor health care to match the individual needs of patients and to develop a concordant relationship. Doing qualitative research is not easy and may require a complete rethink of how research is conducted, particularly for researchers who are more familiar with quantitative approaches. There are many ways of conducting qualitative research, and this paper has covered some of the practical issues regarding data collection, analysis, and management. Further reading around the subject will be essential to truly understand this method of accessing peoples’ thoughts and feelings to enable researchers to tell participants’ stories.
Appendix 1. Excerpt from a sample transcript
The participant (age late 50s) had suffered from a chronic mental health illness for 30 years. The participant had become a “revolving door patient,” someone who is frequently in and out of hospital. As the participant talked about past experiences, the researcher asked:
- What was treatment like 30 years ago?
- Umm—well it was pretty much they could do what they wanted with you because I was put into the er, the er kind of system er, I was just on
- endless section threes.
- Really…
- But what I didn’t realize until later was that if you haven’t actually posed a threat to someone or yourself they can’t really do that but I didn’t know
- that. So wh-when I first went into hospital they put me on the forensic ward ’cause they said, “We don’t think you’ll stay here we think you’ll just
- run-run away.” So they put me then onto the acute admissions ward and – er – I can remember one of the first things I recall when I got onto that
- ward was sitting down with a er a Dr XXX. He had a book this thick [gestures] and on each page it was like three questions and he went through
- all these questions and I answered all these questions. So we’re there for I don’t maybe two hours doing all that and he asked me he said “well
- when did somebody tell you then that you have schizophrenia” I said “well nobody’s told me that” so he seemed very surprised but nobody had
- actually [pause] whe-when I first went up there under police escort erm the senior kind of consultants people I’d been to where I was staying and
- ermm so er [pause] I . . . the, I can remember the very first night that I was there and given this injection in this muscle here [gestures] and just
- having dreadful side effects the next day I woke up [pause]
- . . . and I suffered that akathesia I swear to you, every minute of every day for about 20 years.
- Oh how awful.
- And that side of it just makes life impossible so the care on the wards [pause] umm I don’t know it’s kind of, it’s kind of hard to put into words
- [pause]. Because I’m not saying they were sort of like not friendly or interested but then nobody ever seemed to want to talk about your life [pause]
- nobody asked me any questions about my life. The only questions that came into was they asked me if I’d be a volunteer for these student exams
- and things and I said “yeah” so all the questions were like “oh what jobs have you done,” er about your relationships and things and er but
- nobody actually sat down and had a talk and showed some interest in you as a person you were just there basically [pause] um labelled and you
- know there was there was [pause] but umm [pause] yeah . . .
This article is the 10th in the CJHP Research Primer Series, an initiative of the CJHP Editorial Board and the CSHP Research Committee. The planned 2-year series is intended to appeal to relatively inexperienced researchers, with the goal of building research capacity among practising pharmacists. The articles, presenting simple but rigorous guidance to encourage and support novice researchers, are being solicited from authors with appropriate expertise.
Previous articles in this series:
Bond CM. The research jigsaw: how to get started. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(1):28–30.
Tully MP. Research: articulating questions, generating hypotheses, and choosing study designs. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(1):31–4.
Loewen P. Ethical issues in pharmacy practice research: an introductory guide. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2014;67(2):133–7.
Tsuyuki RT. Designing pharmacy practice research trials. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(3):226–9.
Bresee LC. An introduction to developing surveys for pharmacy practice research. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(4):286–91.
Gamble JM. An introduction to the fundamentals of cohort and case–control studies. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(5):366–72.
Austin Z, Sutton J. Qualitative research: getting started. C an J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(6):436–40.
Houle S. An introduction to the fundamentals of randomized controlled trials in pharmacy research. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014; 68(1):28–32.
Charrois TL. Systematic reviews: What do you need to know to get started? Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;68(2):144–8.
Competing interests: None declared.
Further Reading
Examples of qualitative research in pharmacy practice.
- Farrell B, Pottie K, Woodend K, Yao V, Dolovich L, Kennie N, et al. Shifts in expectations: evaluating physicians’ perceptions as pharmacists integrated into family practice. J Interprof Care. 2010; 24 (1):80–9. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gregory P, Austin Z. Postgraduation employment experiences of new pharmacists in Ontario in 2012–2013. Can Pharm J. 2014; 147 (5):290–9. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marks PZ, Jennnings B, Farrell B, Kennie-Kaulbach N, Jorgenson D, Pearson-Sharpe J, et al. “I gained a skill and a change in attitude”: a case study describing how an online continuing professional education course for pharmacists supported achievement of its transfer to practice outcomes. Can J Univ Contin Educ. 2014; 40 (2):1–18. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nair KM, Dolovich L, Brazil K, Raina P. It’s all about relationships: a qualitative study of health researchers’ perspectives on interdisciplinary research. BMC Health Serv Res. 2008; 8 :110. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pojskic N, MacKeigan L, Boon H, Austin Z. Initial perceptions of key stakeholders in Ontario regarding independent prescriptive authority for pharmacists. Res Soc Adm Pharm. 2014; 10 (2):341–54. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Qualitative Research in General
- Breakwell GM, Hammond S, Fife-Schaw C. Research methods in psychology. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Given LM. 100 questions (and answers) about qualitative research. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles B, Huberman AM. Qualitative data analysis. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Patton M. Qualitative research and evaluation methods. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Willig C. Introducing qualitative research in psychology. Buckingham (UK): Open University Press; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
Group Dynamics in Focus Groups
- Farnsworth J, Boon B. Analysing group dynamics within the focus group. Qual Res. 2010; 10 (5):605–24. [ Google Scholar ]
Social Constructivism
- Social constructivism. Berkeley (CA): University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley Graduate Division, Graduate Student Instruction Teaching & Resource Center; [cited 2015 June 4]. Available from: http://gsi.berkeley.edu/gsi-guide-contents/learning-theory-research/social-constructivism/ [ Google Scholar ]
Mixed Methods
- Creswell J. Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
Collecting Qualitative Data
- Arksey H, Knight P. Interviewing for social scientists: an introductory resource with examples. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 1999. [ Google Scholar ]
- Guest G, Namey EE, Mitchel ML. Collecting qualitative data: a field manual for applied research. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
Constructivist Grounded Theory
- Charmaz K. Grounded theory: objectivist and constructivist methods. In: Denzin N, Lincoln Y, editors. Handbook of qualitative research. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2000. pp. 509–35. [ Google Scholar ]
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- BMJ NPH Collections
- BMJ Journals
You are here
- Online First
- Exploring gaps, opportunities, barriers and enablers in malnutrition policy through key informant interviews: a qualitative inquiry from the CANDReaM initiative
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8620-9360 Katherine L Ford 1 ,
- Roseann Nasser 2 ,
- Carlota Basualdo-Hammond 3 ,
- Celia Laur 4 ,
- Maira Quintanilha 5 ,
- Heather Keller 1 and
- Leah Gramlich 6
- 1 Department of Kinesiology & Health Sciences , University of Waterloo , Waterloo , Ontario , Canada
- 2 Clinical Nutrition Services , Saskatchewan Health Authority , Regina , Saskatchewan , Canada
- 3 Clinical Nutrition Services , Alberta Health Services , Edmonton , Alberta , Canada
- 4 Institute for Health System Solutions and Virtual Care , Women's College Hospital , Toronto , Ontario , Canada
- 5 Department of Agricultural, Food & Nutritional Science , University of Alberta , Edmonton , Alberta , Canada
- 6 Department of Medicine , University of Alberta , Edmonton , Alberta , Canada
- Correspondence to Dr Leah Gramlich; lg3{at}ualberta.ca
Objectives Disease-related malnutrition (DRM) presents in up to half of adults and one-third of children admitted to Canadian hospitals and significantly impacts health outcomes. Strategies to screen, diagnose and treat DRM exist but policy to facilitate implementation and sustainability are lacking. The purpose of this study was to explore gaps, opportunities, barriers and enablers for DRM policy in Canada.
Methods A qualitative study was conducted with multi-national key informants in DRM and/or health policy. Purposive sampling identified participants for a semi-structured interview. The health policy triangle framework informs policy outcomes by considering actors, content, context and processes, and was used to guide this work. Inductive thematic analysis was completed, followed by deductive analysis based on the framework.
Results DRM policy actors were seen as champions in healthcare, senior leaders in healthcare administration and individuals with lived experience. Policy content focused on screening, diagnosis and treatment of DRM. Key areas related to policy context included system specifics related to setting, cost and capacity, and social determinants of health. DRM policy processes were viewed as cross-sectoral and multi-level governance, mandating and other reinforcement strategies, windows of opportunity, and evaluation and research.
Conclusions DRM care has advanced substantially, yet policy-level changes are sparse, and gaps exist. DRM policy is facilitated by similar content around the globe and needs to be tailored to address setting-specific needs. Actors, content, context and processes inform policy and can be a dominant lever to accelerate nutrition care best practices.
- Malnutrition
- Nutrition assessment
Data availability statement
No data are available. Data are transcripts of key informant interviews and contain personally identifying information thus cannot be shared publicly.
This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited, appropriate credit is given, any changes made indicated, and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ .
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjnph-2024-000891
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ON THIS TOPIC
The impact of policy on disease related malnutrition is relatively unexplored.
WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS
Policy considerations include consistent content related to processes in support of DRM in specific settings and is supported by champions in health care, senior leaders and individuals with lived experience.
HOW THIS STUDY MIGHT AFFECT RESEARCH, PRACTICE OR POLICY
Policy can be a lever to accelerate nutrition care best practices
Introduction
Disease-related malnutrition (DRM) occurs when a patient’s energy and nutrient intake is inadequate for their physiological requirements and is often exacerbated by a systemic inflammatory response. It is associated with poor outcomes (eg, functional decline, complications, hospital readmissions and mortality) and incurs increased healthcare costs. 1–3 DRM presents in up to half of Canadian adults and one-third of children admitted to hospital for ≥2 days. 4 In the community, DRM affects 3%–8.5% 5 of the population and has a disproportionate effect on older adults and those in seniors’ care. 6 7 Strategies to address DRM exist, yet policy approaches or frameworks to support implementation are lacking in Canadian health systems.
In the past two decades, several initiatives have progressed DRM identification and treatment. A worldwide initiative (nutritionDay) has advocated for a 1-day audit every year for the past 20 years to assess malnutrition in patients across settings. 8 In 2014, the Optimal Nutrition Care for All campaign (ONCA) was launched by the European Nutrition for Health Alliance to develop and implement patient-driven improved nutrition care practices in Europe. 9 In 2016, the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) built a global consensus on criteria to diagnose DRM in adults in clinical settings. 10 11 Also in 2016, the United Nations General Assembly proclaimed the Decade of Action on Nutrition (2016–2025). 12 In Canada, the Health Standards Organization published the Malnutrition Prevention, Detection and Treatment CAN/HSO 5066:2021(E) standard to improve patient nutrition care. 13 To further advance evidence-based practices and advocate for DRM policies, the Canadian Nutrition Society and the Canadian Malnutrition Task Force registered a commitment to the United Nations Decade of Action on Nutrition 14 for policy approaches to address DRM called CANDReaM (Creating Alliances Nationally for policy to address Disease Related Malnutrition). These initiatives were led by DRM champions (dedicated individuals who drive implementation efforts 15 ) and have created awareness of nutrition as an integral component of patient care, yet DRM remains under-recognised and under-treated.
There is a lack of health policy related to undernutrition and DRM in Canada and globally. Several definitions for health policy exist and include plans, decisions, law, regulation, procedures, organisational and behaviour change to promote improvements in health. The WHO defines health policy as decisions, plans and actions that are undertaken to achieve specific healthcare goals within a society. 16 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines policy as law, regulation, procedure, administrative action, incentive, or voluntary practice of governments and other institutions, where health policy more specifically influences systems development, organisational change and individual behaviour to promote improvements in health. 17
The health policy triangle (HPT) framework was designed for the examination of health policies and considers four areas related to policy development and implementation: actors, content, context and processes. 18 19 The HPT framework was developed to emphasise the importance of moving beyond the content of a policy, to consider the actors across levels who are needed to influence policy, the processes required for developing and implementing change, and the broader context of policy. 19 These four components of the HPT framework are inter-related, impact one another, and are more likely to inform policy outcomes and the effectiveness of health policy change. 19 Health policy is needed to facilitate prevention, detection and treatment of DRM in Canada and improve health outcomes for at-risk patients at health system levels. Thus, the purpose of this study was to conduct key informant (KI) interviews to explore gaps, opportunities, barriers and enablers to the development and implementation of DRM health policy in Canada.
This qualitative study consisted of KI interviews with multi-national DRM and/or health policy experts. The study was part of the larger CANDReaM commitment that also includes a scoping review and environmental scan of existing DRM policies. 14 Reporting was guided by the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research. 20
Purposive sampling 21 was used to recruit KIs from different roles or disciplines (eg, academia, health systems, governments, not-for-profit organisations, industry and patient groups) and from different geographic locations across Canada and internationally. Members of the Canadian Malnutrition Task Force and coauthors suggested KIs to approach from different communities of practice, including international groups. Additional KIs were recruited using snowball sampling 21 whereby participants suggested other KIs to approach for the study.
Interviews were held over videoconference between March and June 2023. Two members of the research team (LG and KLF) with knowledge and experience in DRM were present. One researcher (LG) conducted the interview while the other (KLF) took notes. A semi-structured interview guide ( online supplemental file 1 ) was created (by LG and KLF with input from all authors) around elements of the HPT framework to help identify actors, content, context and processes for DRM policy. 19 Questions sought to better understand KIs’ professional role in DRM, experiences with DRM in clinical practice, health administration and policy making, DRM policy adoption and implementation, and key DRM policy measures.
Supplemental material
Data analysis.
Interviews were audio recorded and transcribed verbatim. Qualitative data were managed and analysed with the support of NVivo software (QSR International, V.12). Analysis happened concurrent to the interviews to enhance rigour and support ongoing refinement of the questions and themes through researcher responsiveness. 22 Thematic analysis was applied to the transcripts and an inductive, followed by deductive, approach was used. 22 Reflexive thematic analysis is a flexible, six-phase method for analysing qualitative data that begins with data familiarisation and ends with detailed reporting of patterns (ie, themes). 23 24 Two members of the research team (LG and KLF) led the analysis with support from an experienced qualitative researcher (MQ). The researchers acknowledge that their expertise (LG: MD with >30 years of nutrition support and leadership experience; KLF: PhD, registered dietitian (RD); MQ: PhD, RD) and prior knowledge of some interviewees (LG) was relevant for the interviews and analysis process. All coauthors have a vested interest in advancing DRM policy development and implementation and most coauthors (KLF, RN, CB-H, CL, HK, LG) serve on the Canadian Malnutrition Task Force Advisory Committee.
Themes were iteratively developed, reviewed, discussed (by LG, KLF and MQ) and verified by all members of the research team. Findings initially appeared vast, thus an inductive approach was used to analyse the first seven transcripts to ensure that the broad nature of the data was captured. 22 As potential themes were identified, it became clear that these inductive themes aligned well with the HPT framework. 18 19 Given that the HPT framework had informed the study rationale and development of the interview guide, the researchers adopted the HPT framework to guide the remaining interviews and conducted deductive data analysis. 19 25 Using a deductive approach for the remaining interviews allowed the research team to proceed with data analysis and frame the findings purposefully using the HPT framework. 18 19 Thus, descriptive subthemes related to policy development and implementation were grouped by the categories of actors, content, context and process to align with this framework. 18 19
22 interviews were conducted and included 25 KIs from seven countries across four regions (North America n=14; Middle East n=2; Europe n=7; Global n=1; did not disclose n=1). 19 discussions were conducted as one-on-one interviews and three were carried out as dyadic interviews because of the opportunity to interview two KIs from the same setting simultaneously. Four KIs were global or multi-country representatives, eleven provided a national voice, eight represented a Canadian province and two provided insights from the institutional level. KIs self-identified as academics or healthcare professionals (n=17), government representatives or policy makers (n=9), from a not-for-profit organisation (n=5) or other (n=1); seven KIs identified dual roles across sectors. Themes, subthemes and exemplar quotes are described in detail, summarised in table 1 , and key findings based on the HPT framework are highlighted in figure 1 .
- View inline
Health policy triangle framework for disease-related malnutrition policies: themes and subthemes
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
An overview of findings from key informant interviews.
Actors in DRM policy
The HPT framework views actors as organisations, groups or individuals who effect policy. 18 This theme captured influential actors in the realm of DRM policy. These actors were actively working in specific settings and countries, or were described as key contributors to DRM policy development and implementation processes. Three subthemes further categorised actors: champions in healthcare, senior leaders in healthcare administration and individuals with lived experience.
Champions in healthcare
Actors that were referred to as ‘champions’ for DRM included healthcare professionals (eg, doctors, dietitians, nurses), and researchers or academics involved in DRM. Embedded healthcare providers were seen as champions of practice change, regardless of their role within the healthcare team. KI-03 (academic and healthcare professional) explained: ‘We [physicians] work together [with dietitians] and we prescribe oral nutritional supplements (ONS) and parental nutrition and ongoing therapy for at home. But normally it’s the dietitian that knows most, and we [physicians] just prescribe it. Some physicians do not know a lot about malnutrition’. Actors’ health backgrounds had evident connections to DRM, yet it was their role as DRM champions that made them essential for DRM policy development and implementation.
KIs commonly described champions in healthcare as individuals who were experts in DRM and trying to initiate DRM policy discussions and implementation efforts. Influential actors often had dual roles (eg, clinician and researcher) and championed practice change beyond what would typically be expected from either position. Roles and titles of champions in healthcare varied across countries and jurisdictions. In some instances, champions leveraged relationships with political actors to raise awareness and support DRM policy action. One KI explained: ‘It takes one or two effective leaders that know how to reach politicians, how to convince them … But if you’re not able to bring it to the leaders, to the politicians, it’s not going to work’ (KI-09, academic and healthcare professional)
One key strategy to advance DRM care, that was identified by KIs, was to engage champions (ie, actors) with the capacity to bring attention and action to DRM policy. In some organisations, this advocacy work was being done through position papers, conferences, meetings and other activities.
You have to keep people engaged. It’s really also a network activity. You need to keep investing in it [DRM policy and advocacy] and make it top priority because these are key opinion leaders with extremely busy schedules. So, you need to be on top of their schedule and you do that by innovating, by adding value through these concepts and inviting them to the conference . (KI-04, policy maker and not-for-profit organisation)
KIs recognised that champions in healthcare hold diverse positions (eg, embedded care provider, researcher, practice leader) and bring essential knowledge and experience that is needed to inform, develop and implement DRM policy.
Senior leaders in healthcare administration
Senior leaders in healthcare administration were identified as essential for organisational level policies targeting DRM. However, these leaders were different from DRM champions as they were often unaware of DRM and its relevance in healthcare (further described in the DRM policy content section). KIs with health policy experience suggested strategies for integrating senior healthcare administration leaders into DRM policy discussions: ‘We’re talking about huge savings if you can keep them [patients] living independently. I’d like to see it as part of the conversation in these provincial, federal […] health authorities because it benefits everybody, it absolutely is cost effective’ (KI-20; academic). Despite their lack of knowledge of the disease, it was evident that senior leaders are needed to progress the development and implementation of DRM policy at the administrative level.
Individuals with lived experience
Individuals with lived experience were identified as actors of utmost relevance for DRM policy. Patients were often discussed as crucial, yet missing, in DRM advocacy efforts. Some KIs noted that certain health conditions, such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease, had greater participation of patient groups in shaping care, whereas patients with other conditions (eg, liver and kidney disease) had less regard for the importance of nutrition. Raising awareness of DRM among patients while understanding their stance and engagement as actors were factors discussed. KI-09 (academic and healthcare professional) noted:
But it’s almost unknown to me that there is a renal patient who is aware that his or her nutritional status is important, or a liver patient. This kind of awareness is not there. So even working with the international patient organizations have honestly not been easy because we are missing the champions.
KIs firmly believed that patient groups need to have a voice in DRM policy discussions because food, as a component of DRM treatment, ought to be understood as a matter of ‘the dignity of the person’ (KI-03, academic and healthcare professional) as well as a human right. Moreover, patient groups would bring diverse voices to DRM policy discussions and provide a lived experience perspective for those who would be most affected by DRM policy.
DRM policy content
The HPT framework broadly considers content as the objectives of a policy. 18 This theme included KIs’ views on policy content objectives and areas of focus. KIs provided content examples from clinical practice and general insights pertinent to DRM policy. Three subthemes were identified as vital components of DRM policy content: screening, diagnosis and treatment.
Screening for DRM
KIs involved in DRM research or clinical practice discussed the importance of malnutrition screening as an essential component of care in hospital, especially among older adults. KIs commonly expressed that they were unaware of any consensus (in their respective countries) on how to screen for DRM, yet questions about unintentional weight loss, body mass index and loss of appetite were provided as examples of more widespread DRM indicators used in practice. KIs, primarily from Europe, who were knowledge experts in DRM discussed the GLIM framework 10 11 (includes criteria for screening) and its adoption by organisations in some countries.
Diagnosing DRM
DRM policy content needs to address how to formally identify and record a DRM diagnosis. KIs discussed the absence of a formal diagnosis of malnutrition (eg, using an existing International Classifications of Diseases (ICD) code) and how this impacted funding allocation, health professionals’ awareness of DRM and financial supports available to patients in the community. KIs deemed evidence for the diagnosis of malnutrition as key content in DRM policy. Such content could facilitate DRM advocacy and policy implementation in different contexts.
Treating DRM
KIs provided varying levels of detail on DRM treatment based on their experience and area of practice. Treatment-related content was perceived as overlapping with contextual factors and dependent on the setting (eg, hospital, care homes, community) and its priorities. Treatment in care homes is focused on quality of life, whereas the priority in hospital is on recovery, and on prevention in the community.
Regardless of setting and priority, dietitians were viewed as DRM experts, but not all were permitted to provide a medical diagnosis and/or prescribe medical foods (eg, ONS). Often, DRM diagnoses and treatment prescriptions are recognised by health systems with ICD-10 coding by a physician, despite many lacking expertise with DRM. In the community, lack of policy on funding and reimbursement for medical foods (eg, ONS, enteral nutrition) may prevent patients with DRM from accessing prescribed treatments. Access to, and ability to prescribe, medical foods were viewed by KIs as important factors for DRM policy content.
DRM policy context
In the HPT framework, context refers to the systemic factors that influence policy such as social, economic, political, cultural and environmental conditions. 18 Questions about policy context focused these factors across three settings: hospitals, care homes and community, as highlighted by the subthemes.
System specifics matter
The context (eg, hospital, care homes or community) is a critical consideration for any DRM policy. Setting-specific factors to consider included where health information is stored (eg, electronic medical record), the healthcare organisation’s capacity for research, the geographical space (eg, country size), the population being served, the workflow and how priorities are established in each context. KI-03 (academic and healthcare professional) explained: ‘In my hospital, the quality of nutrition care is quite high and, because of our research, it’s [quality of nutritional care] quite different from hospital to hospital or from the staff that is working there’.
System-related specific contexts mentioned by KIs were diverse (eg, role and experience of dietitian across care settings, access to home nutrition support, reimbursement process and structure of governing health authority). An enabler for DRM policy implementation in one setting may not be feasible, or be a barrier, in another context. For example, KI-10 (academic and healthcare professional) said: ‘we have one country, one policy. That’s really an enabler’ whereas KI-02 (academic and healthcare professional) described:
We have another problem in [country name]; healthcare is not governed on a national level. There are [number] regions, and they are enormous. All [number] regions have their own way of doing things. There are guidelines and they could follow them, but they can interpret the guidelines in their own way.
It was clear that each setting is unique and complex. Consequently, DRM policy context needs to be well understood to foresee implementation enablers and plan for overcoming potential barriers unique to each setting. Some KIs expressed caution when defining DRM policy context across more than one setting:
I think this is probably in some ways common sense, but the broader it gets, the harder it is to have clear minimum guidelines or standards for everyone. What this looks like in continuing care, you know, it’s probably quite different than what it looks like in community. So that can be tricky. (KI-16, policy maker)
Cost and capacity
KIs unanimously referred to cost savings that arise from proper DRM diagnosis and treatment. KIs discussed the importance of using healthcare data to calculate and demonstrate DRM cost across settings. This contextual factor commonly intersected with the process subtheme on evaluation and research. KIs described the continued need to examine DRM cost to the healthcare system as a contextual enabler to DRM policy. KIs agreed that addressing DRM represented a healthcare cost savings opportunity and that healthcare investment could foster capacity building related to DRM policy. This investment was discussed in relation to increasing the number of healthcare professionals—dietitians, doctors and nurses—who are trained to screen, diagnose and treat DRM in hospitals, care homes and communities. The role of dietitians was commonly emphasised as critical to the success of DRM policy as explained by KI-21 (academic and healthcare professional): ‘I think that we [dietitians] may be one of the only professionals that are not doctors of medicine that could diagnose disease and it is DRM’.
Social determinants of health
KIs commonly mentioned the social determinants of health as other contextual factors to consider. KI-22 (policy maker and healthcare professional) explained:
I do think it’s important to recognize those interrelations between the social determinants of health and malnutrition. Obviously, you’re never going to have a perfect policy … no policy is going to be perfect for everybody. But I do think in developing policies in general, understanding the determinants of health and having that health equity lens is really important.
Within the social determinants of health, food insecurity and the related concepts of access to food and affordability were prominent in the data. Food insecurity was described as lack of financial resources to buy foods needed for recovery from DRM postdischarge from acute care. In the context of community-based settings, food security and affordability were more encompassing concepts that included individuals’ ability to afford sufficient healthy foods for DRM prevention and treatment, as well as medical foods such as ONS prescribed for DRM. KIs discussed the intersection of food insecurity and DRM and believed that even though these two issues could be addressed separately (especially in hospital settings where the focus is on DRM), they would converge in the community. For example, a nutrition professional and policy maker (KI-18) said: ‘It has always seemed really disconcerting […] to do a lot of work screening for malnutrition, identifying and intervening in hospital and then discharging to the very communities where people became malnourished in the first place’ . Food insecurity was a contextual factor raised by various KI and acknowledged by all when probed. Consensus on how to address food insecurity in DRM policy was not achieved, yet KIs believed that food insecurity and DRM should be weaved together with other social determinants of health.
DRM policy processes
In the HPT framework, processes refer to initiation, development or formulation, negotiation, communication, implementation and evaluation of policies. 18 In this theme, the complexity of DRM policy processes was captured through four subthemes: cross-sectoral and multi-level governance, mandating and other reinforcement strategies, windows of opportunity, and research and evaluation.
Cross-sectoral and multi-level governance
KIs were emphatic that DRM policy should involve multiple disciplines, departments (eg, clinical, nutrition, food services), sectors (eg, social services, primary care) and actors. ‘We also need it to be … that promotion of interdisciplinary, right? It can’t just be an issue for nutrition and food services. It has to be everyone’ (KI-17, healthcare professional and policy maker). KIs believed that stronger engagement across sectors would increase the likelihood for the DRM policy to gain momentum. The importance of mobilising various levels of governance to develop, implement and evaluate DRM policy, was emphasised. Across countries and jurisdictions, there were examples of health policies that were more ‘successful’ when the issue being addressed (eg, fall prevention) was deemed relevant by multiple levels of governance, and the individuals representing them, within governments or organisations.
It would require a neutral platform to bring all of these organizations together and we have done that ourselves … Usually, it’s a third sector organization that provides that neutral platform. And essentially all of this needs to result in maybe two sets of policy actions which might be aimed for. One at the level of clinical policy guidance and the other one at the level of parliamentary policy action. (KI-11, academic and healthcare professional)
Mandating and other reinforcement strategies
KIs expressed support for DRM policy that mandates screening, diagnosis and treatment across settings, especially hospitals and care homes. They described that implementation challenges would persist regardless of policy mandates, secondary to the above mentioned contextual factors. This was exemplified by KIs from countries where national standards for DRM exist, or previously existed but had been removed. KI-10 (academic and healthcare professional) explained:
I think that these quality indicators that we have had for more than 12 years, they have made a difference because it [screening] was mandatory. It was implemented everywhere, 100% implementation. They let it go as of 2019 so I’m really anxious to see what will happen now, whether the hospitals will continue to register [outcome of screening] because it was built into the electronic patient files or whether they will lose attention and forget about it.
Many KIs expressed that implementation strategies such as establishing required organisational practices, moving to an accreditation process, measuring key performance indicators and having a reimbursement model for patients with DRM were required in addition to mandates to foster DRM policy development and implementation. KIs perceived these strategies as effective and more easily achievable than a mandated DRM policy across countries and jurisdictions.
Windows of opportunity
This subtheme captured the timing of DRM policy development and implementation processes. KIs suggested that policy negotiation would be facilitated when other HPT framework factors (ie, context, actors and content) aligned with opportunities to implement DRM policy. For example, KIs suggested that change in hospital meal service, release of new or updated national guidelines, or involvement of individuals with lived experience were windows of opportunity for DRM policy development and implementation.
Evaluation and research
Evaluation of DRM policies was discussed as vital for demonstrating the impact of DRM treatment, particularly for healthcare cost. This subtheme, overlapped with context (cost and capacity), as evaluation of the healthcare costs associated with DRM were thought to be a key driver to policy development and implementation. KIs discussed the importance of having measures in place to demonstrate impact and continuing to raise awareness of DRM among actors (eg, healthcare professionals, policy makers, patient advocates, etc).
Research was seen as key for knowledge generation and dissemination relevant to DRM policy initiatives that can extend to other countries, settings and organisations. KIs discussed research as it related to DRM screening, diagnosis and treatment. Many emphasised the vital role research played in raising awareness of DRM among key policy actors and healthcare professionals. KIs believed that DRM research was an important piece for DRM policy content and context development because it would enable different organisations and settings to prioritise DRM actions. KI-17 (healthcare professional and policy maker) explained:
In my role, we really are thankful for all of the work done by [name of research group] because that has enabled us to have the proof that we need to implement into action various strategies related to malnutrition. We didn’t have to gather all the evidence. The evidence is there.
As such, evaluation was tied to knowledge translation where results from DRM interventions and policies needed to be communicated broadly and effectively to actors across many sectors.
Findings from KI interviews suggest that DRM is not well recognised or addressed through health policy in Canada or globally. Key gaps and barriers to DRM policy development and implementation included multi-level governments, jurisdictional priorities and the need for continued advocacy. Social determinants of health, including food insecurity, also emerged as important considerations. These findings align with other work that suggested factors internal and external to the health system have inhibited incorporation of DRM into health policy. 26 Building on advances in the field over the past two decades, there is opportunity to leverage the capacity and momentum of DRM initiatives to generate policy that will positively impact health and decrease associated health systems costs. 1 This qualitative analysis of KI interviews contributes to the literature describing DRM policies and the value of incorporating implementation initiatives into policy.
KIs acknowledged coalitions, organisational champions and individuals with lived experiences as key actors for DRM policy development and implementation. Organisational leadership (eg, healthcare administrators), interdisciplinary champions (eg, healthcare providers, policy makers, researchers) and nutrition experts (ie, dietitians) are drivers of change and can embody implementation efforts through support, promotion and leadership. 15 These actors can be leaders and advocate for change within their local settings to propel DRM policy development and implementation. The conceptual model of champion impact by Shea suggests that commitment, experience and self-efficacy influence champion performance and ultimately impact. 27 These champion characteristics align with those mentioned by KIs and suggest that champions are fundamental leaders of change who can support DRM policy and advocacy.
Globally, coalitions of actors have been advocating for improved DRM management. NutritionDay aims to improve DRM awareness and nutrition care of patients. 8 This effort is a worldwide scientific programme that operates on a continuous improvement circle and encourages care institutions (hospitals, intensive care units and nursing homes) to register for the initiative, collect data during a 1-day cross-sectional audit and contribute to the growing body of global DRM literature. 8 These large-scale efforts to advance DRM would not be possible without key actors including champions, organisational leaders and individuals with lived experience. The results of the current study indicate that further involvement from organisational leaders and individuals with lived experience are needed. DRM policy development and implementation should occur based on setting-specific needs and contexts but can be informed by cross-country coalitions (eg, ONCA 9 ) that provide overarching goals and objectives.
Despite global and national advancements in DRM, gaps exist between current policy and evidence-informed practice. The economic impact of DRM was viewed as a key context consideration for future policy and a lever to gain attention from senior healthcare administrators. In Canada, it is estimated that DRM costs the healthcare system an additional $2 billion per year (pre-COVID-19). 1 Patients with DRM remained in hospital 3 days longer, on average, than patients without DRM and incurred approximately $2900 more in hospital costs compared with well nourished patients. 1 A complete economic impact analysis is needed to fully appreciate the gravity of this situation post-COVID-19. Appreciation for the problems and implications of DRM is lacking for many organisational leaders who can implement organisational and system-level change. Absence of widespread DRM diagnosis using ICD-codes relates to policy content and actors, as formal diagnoses would draw attention and awareness to DRM among a broader scope of actors (eg, interdisciplinary care team, hospital leadership, etc). Related to HPT context, specifically cost and capacity, the economic impact of poor screening tool sensitivity is one example of the importance of DRM diagnosis by ICD-codes, especially in settings where DRM is prevalent. 28 Strategies to combat DRM exist but are not widely implemented given the lack of policy mandate.
Another key group of actors with ability to influence DRM policy are individuals with lived experience. Patients with DRM have lived experience and play a critical role in shaping strategies, advocacy efforts and DRM policy that will impact patient-oriented outcomes, yet their voice is lacking in these initiatives. Similarly, a study that defined DRM as a health policy issue found that the patient plays a key role in policy development. 26 A phenomenological study suggested two key approaches to addressing clinical nutrition policy (eg, DRM) including the need for an interdisciplinary approach and a human rights-based approach. 26 Nutrition care as a human right has been recognised by an international declaration 29 and underpins our findings whereby access to food as treatment for DRM and implications of social determinants of health came through broadly across themes.
Our findings suggested that DRM policy development processes should centre around cross-sectoral and multi-level governance; mandating and other reinforcement strategies for policy; capitalising on windows of opportunity; and using research and evaluation. Current government health policy is focused on prevention of conditions related to overnutrition and chronic diseases whereas healthcare policy addressing disease states, such as DRM, was often viewed as a local facility or organisation responsibility by KIs, rather than the purview or mandate of government.
The need for research to inform policy development and implementation overlapped with all areas of the HPT framework. It was clear that DRM policy processes evolve relative to the HPT actors, content and contexts within the target setting. It is essential for actors invested in DRM policy to understand their setting, context, purpose and evaluative needs to foster targeted and sustainable policy. KIs identified need for policy processes, contexts and content, but provided few tangible examples of policy implementation or evaluation. Key initiatives to standardise the nutrition care process related to DRM (eg, GLIM) in countries that include screening, assessment and diagnosis of DRM 10 11 provide examples for others to build on in their efforts to advance DRM policy development and implementation. KIs discussed GLIM as one step towards DRM care consensus, but the need for tangible policy related to nutrition screening, diagnosis and treatment cannot be understated.
Strengths and limitations
The multi-national first-hand perspectives from experts in policy and/or DRM across settings was a strength of this work. We recognise that this is a large and complex topic, and our broad approach of focusing internationally and across multiple care settings introduced further complexity. The decision to take this broad approach was based on the lack of DRM policy within Canada, and the need to learn from the experiences of other countries and settings. The HPT framework provided structure to the interview questions and analysis. A broad range of perspectives were provided which further strengthens our results and their potential utility. Snowball sampling allowed for inclusion of KIs beyond the researcher’s networks. Finally, use of the HPT framework to inform our approach aligns with health policy analysis and is generalisable across jurisdictional settings (from local-level to global-level policy). 18
Purposive sampling is a strength and limitation. KIs were selected based on their ability to provide diverse perspectives from a range of expertise and levels of influence on DRM and health policy implementation, including senior leaders in prominent international organisations. Thus, KIs were selected from countries actively working in DRM policy development and/or implementation.
Potential impact
In line with the CANDReaM commitment to the United Nations Decade of Action on Nutrition, 14 our findings inform DRM policy development and implementation and are a key step towards advancing DRM policy efforts in Canada and globally. The opportunity identified is the need for DRM policy that involves interdisciplinary care team members, individuals with lived experience and policy makers. The creation of an alliance with involvement from these groups will facilitate DRM policy development. Guidance documents such as the Integrated Nutrition Pathway for Acute Care 30 and the CAN/HSO 5066:2021(E) Malnutrition Prevention, Detection and Treatment standard 13 are closely related to DRM policy content and exemplify important key steps towards DRM policy development and implementation in Canada. DRM policy context is system-specific and cost analysis is a facilitator for policy advocacy at the health system level. Direction on setting-specific standardised treatment remains a gap to be further explored. A further understanding of the linkage between food security and DRM may provide one avenue for considering the more systemic issues impacting prevention and treatment of DRM. Finally, DRM policy processes are complex and occur at the jurisdictional level (eg, health system, hospital or facility, other). Strategies to support policy implementation 13 30 exist but are not widespread. Research and evaluation throughout the policy development and implementation processes in the clinical setting has begun 31 and should be spread to community to better understand setting-specific processes.
Gaps and barriers to DRM policy development and implementation exist. There are opportunities and enablers to inform a DRM policy framework. Findings from this study can be used to guide implementation strategies across countries and jurisdictions that incorporate policy as a lever to accelerate practice change. Ultimately, DRM policy will vary and will likely be seen at country-, province-, zone- or site-levels around the world. The landing spot of DRM policy will be informed by actors, content, context and process specifics for each jurisdiction.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication.
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
This study involves human participants and this study was approved by the University of Alberta Research Ethics Board (Pro00127805). All participants provided verbal informed consent.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Andrea Grantham, Executive Director of the Canadian Nutrition Society and Rupinder Dhaliwal, Programme Manager of the Canadian Malnutrition Task Force for their leadership, commitment and project management support related to the Creating Alliances Nationally to address Disease Related Malnutrition (CANDReaM) initiative. We also wish to acknowledge the NNEdPro Global Institute for Food, Nutrition and Health for support in kinds including article processing charges for publication.
- Curtis LJ ,
- Bernier P ,
- Jeejeebhoy K , et al
- Allard JP ,
- Jeejeebhoy KN , et al
- Jeejeebhoy KN ,
- Gramlich L , et al
- Wendland BE ,
- Greenwood CE ,
- Weinberg I , et al
- Bracher M ,
- Tkacz D , et al
- Schindler K ,
- Pichard C ,
- Sulz I , et al
- Barazonni R ,
- Garel P , et al
- Cederholm T ,
- Jensen GL ,
- Correia MITD , et al
- ↵ CAN/HSO 5066:2021 - malnutrition prevention, detection, and treatment .
- Powell BJ ,
- Chinman MJ , et al
- Organization WH
- Prevention CfDCa
- O’Brien GL ,
- Sinnott S-J ,
- Walshe V , et al
- Sainsbury P ,
- O’ Flynn B , et al
- Cárdenas D ,
- Pérez Cano AM ,
- Díaz G , et al
- Capra S , et al
- Cardenas D ,
- Correia MITD ,
- Hardy G , et al
- Keller HH ,
- McCullough J ,
- Davidson B , et al
- Koechl JM ,
- Laur C , et al
Presented at A preliminary version of this paper will be presented in poster format at the 46th ESPEN Congress on Clinical Nutrition & Metabolism, Milan, Italy, 7–10 September 2024 and will be published in abstract form in a supplement of Clin Nutr ESPEN.
Contributors LG conceptualised the study; LG, KLF, MQ conducted the analysis; all authors reviewed the findings in detail; KLF drafted the manuscript; all authors reviewed and edited the manuscript and have read and agreed to the final version. LG is the guarantor.
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests KLF reports honoraria from Abbott Nutrition; RN and CB-H have no conflicts to declare; MQ owns Quali Q Inc. and provided support for data analysis related to this work; HK and CL report honoraria from Nestle Health Sciences; LG reports honoraria from Baxter, Fresenius Kabi, Takeda; consultancy with Baxter, Fresenius Kabi, Takeda and Abbott Nutrition; research funds from Baxter, Fresenius Kabi and Takeda.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Read the full text or download the PDF:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis. Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, history, etc.
Qualitative research enables us to make sense of reality, to describe and explain the social world and to develop explanatory models and theories. It is the primary means by which the theoretical foundations of social sciences may be constructed or re-examined.
The purpose of qualitative research is to explore and understand the subjective experiences, behaviors, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research aims to provide in-depth, descriptive information that can help ...
Abstract. This guide explains the focus, rigor, and relevance of qualitative research, highlighting its role in dissecting complex social phenomena and providing in-depth, human-centered insights. The guide also examines the rationale for employing qualitative methods, underscoring their critical importance. An exploration of the methodology ...
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervening or introducing treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypothenar to further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences ...
Qualitative research is the naturalistic study of social meanings and processes, using interviews, observations, and the analysis of texts and images. In contrast to quantitative researchers, whose statistical methods enable broad generalizations about populations (for example, comparisons of the percentages of U.S. demographic groups who vote in particular ways), qualitative researchers use ...
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them.
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
Qualitative research is a type of research that aims to gather and analyse non-numerical (descriptive) data in order to gain an understanding of individuals' social reality, including understanding their attitudes, beliefs, and motivation. This type of research typically involves in-depth interviews, focus groups, or observations in order to collect data that is rich in detail and context.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis. Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history. Qualitative research question examples
The purpose of qualitative research is to provide an explanation, not merely a description and certainly not a prediction (which is the realm of quantitative research). However, description is needed to illustrate qualitative data collected, and usually researchers describe their qualitative data by inserting a number of important "informant ...
Qualitative research is defined as an exploratory method that aims to understand complex phenomena, often within their natural settings, by examining subjective experiences, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical measurements and statistical analysis, qualitative research employs a range of ...
Abstract. This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions ...
Qualitative research design is continually evolving. It is not only more established in disciplines beyond the traditional social sciences in which it is a standard choice, but also just as impacted by the changes in what data, technologies, and approaches researchers are using. This Handbook takes readers through the foundational theories ...
Psychologists created qualitative research because the traditional methods failed to understand the human experience. Consequently, they developed a naturalistic approach that focuses on human behavior, what gives people meaning, how they perceive things, and why they act in a particular manner. This process involves understanding the people in their natural settings and social interactions.
Qualitative research is a type of social science research that collects and works with non-numerical data and that seeks to interpret meaning from these data that help understand social life through the study of targeted populations or places. People often frame it in opposition to quantitative research, which uses numerical data to identify ...
Qualitative research has a rich tradition in the study of human social behaviour and cultures. Its general aim is to develop concepts which help us to understand social phenomena in, wherever possible, natural rather than experimental settings, to gain an understanding of the experiences, perceptions and/or behaviours of individuals, and the meanings attached to them.
Qualitative research design is defined as a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding complex phenomena and the meanings attributed to them by individuals or groups. It is commonly used in social sciences, psychology, anthropology, and other fields where subjective experiences and interpretations are of interest.
Assumptions about the purpose of research: Study the status quo vs. create radical change. Values-neutral vs. values-informed. ... Qualitative research questions have one final feature that distinguishes them from quantitative research questions: they can change over the course of a study. Qualitative research is a reflexive process, one in ...
Qualitative research seeks to understand people's experiences and perspectives by studying social organizations and human behavior. Data in qualitative studies focuses on people's beliefs and emotional responses. Qualitative data is especially helpful when a company wants to know how customers feel about a product or service, such as in ...
Qualitative research methodology is not a single method, but instead offers a variety of different choices to researchers, according to specific parameters of topic, research question, participants, and settings. The method is the way you carry out your research within the paradigm of quantitative or qualitative research.
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the type of data they collect and analyze. Quantitative data is information about quantities, and therefore numbers, and qualitative data is descriptive, and regards phenomenon which can be observed but not measured, such as language. Quantitative research collects numerical ...
Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions, and behavior. It answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much. It could be structured as a standalone study, purely relying on qualitative data, or part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data. This review introduces the readers ...
The purpose here is to illuminate how five key features of naturalistic case study can be used in health research. Case studies are of use in various disciplines. ... & Stake, R. E. (2014). Science of the particular: An advocacy of naturalistic case study in health research. Qualitative Health Research, 24(8), 1150-1161. https:// https://doi ...
Digsite, a purpose-built asynchronous agile qualitative research platform, changes how you conduct qualitative research and get insights faster. Digsite helps you deliver results in days rather than weeks! Asynchronous agile qualitative research with Digsite. Digsite is a fast, flexible, and asynchronous qualitative research tool that enables ...
Qualitative research is used to gain insights into people's feelings and thoughts, which may provide the basis for a future stand-alone qualitative study or may help researchers to map out survey instruments for use in a quantitative study. It is also possible to use different types of research in the same study, an approach known as "mixed ...
Strategies to screen, diagnose and treat DRM exist but policy to facilitate implementation and sustainability are lacking. The purpose of this study was to explore gaps, opportunities, barriers and enablers for DRM policy in Canada. Methods A qualitative study was conducted with multi-national key informants in DRM and/or health policy.