- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Occupational Therapy
- Healthy Aging
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board

What Is Breech?
When a fetus is delivered buttocks or feet first
- Types of Presentation
Risk Factors
Complications.
Breech concerns the position of the fetus before labor . Typically, the fetus comes out headfirst, but in a breech delivery, the buttocks or feet come out first. This type of delivery is risky for both the pregnant person and the fetus.
This article discusses the different types of breech presentations, risk factors that might make a breech presentation more likely, treatment options, and complications associated with a breech delivery.
Verywell / Jessica Olah
Types of Breech Presentation
During the last few weeks of pregnancy, a fetus usually rotates so that the head is positioned downward to come out of the vagina first. This is called the vertex position.
In a breech presentation, the fetus does not turn to lie in the correct position. Instead, the fetus’s buttocks or feet are positioned to come out of the vagina first.
At 28 weeks of gestation, approximately 20% of fetuses are in a breech position. However, the majority of these rotate to the proper vertex position. At full term, around 3%–4% of births are breech.
The different types of breech presentations include:
- Complete : The fetus’s knees are bent, and the buttocks are presenting first.
- Frank : The fetus’s legs are stretched upward toward the head, and the buttocks are presenting first.
- Footling : The fetus’s foot is showing first.
Signs of Breech
There are no specific symptoms associated with a breech presentation.
Diagnosing breech before the last few weeks of pregnancy is not helpful, since the fetus is likely to turn to the proper vertex position before 35 weeks gestation.
A healthcare provider may be able to tell which direction the fetus is facing by touching a pregnant person’s abdomen. However, an ultrasound examination is the best way to determine how the fetus is lying in the uterus.
Most breech presentations are not related to any specific risk factor. However, certain circumstances can increase the risk for breech presentation.
These can include:
- Previous pregnancies
- Multiple fetuses in the uterus
- An abnormally shaped uterus
- Uterine fibroids , which are noncancerous growths of the uterus that usually appear during the childbearing years
- Placenta previa, a condition in which the placenta covers the opening to the uterus
- Preterm labor or prematurity of the fetus
- Too much or too little amniotic fluid (the liquid that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy)
- Fetal congenital abnormalities
Most fetuses that are breech are born by cesarean delivery (cesarean section or C-section), a surgical procedure in which the baby is born through an incision in the pregnant person’s abdomen.
In rare instances, a healthcare provider may plan a vaginal birth of a breech fetus. However, there are more risks associated with this type of delivery than there are with cesarean delivery.
Before cesarean delivery, a healthcare provider might utilize the external cephalic version (ECV) procedure to turn the fetus so that the head is down and in the vertex position. This procedure involves pushing on the pregnant person’s belly to turn the fetus while viewing the maneuvers on an ultrasound. This can be an uncomfortable procedure, and it is usually done around 37 weeks gestation.
ECV reduces the risks associated with having a cesarean delivery. It is successful approximately 40%–60% of the time. The procedure cannot be done once a pregnant person is in active labor.
Complications related to ECV are low and include the placenta tearing away from the uterine lining, changes in the fetus’s heart rate, and preterm labor.
ECV is usually not recommended if the:
- Pregnant person is carrying more than one fetus
- Placenta is in the wrong place
- Healthcare provider has concerns about the health of the fetus
- Pregnant person has specific abnormalities of the reproductive system
Recommendations for Previous C-Sections
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) says that ECV can be considered if a person has had a previous cesarean delivery.
During a breech delivery, the umbilical cord might come out first and be pinched by the exiting fetus. This is called cord prolapse and puts the fetus at risk for decreased oxygen and blood flow. There’s also a risk that the fetus’s head or shoulders will get stuck inside the mother’s pelvis, leading to suffocation.
Complications associated with cesarean delivery include infection, bleeding, injury to other internal organs, and problems with future pregnancies.
A healthcare provider needs to weigh the risks and benefits of ECV, delivering a breech fetus vaginally, and cesarean delivery.
In a breech delivery, the fetus comes out buttocks or feet first rather than headfirst (vertex), the preferred and usual method. This type of delivery can be more dangerous than a vertex delivery and lead to complications. If your baby is in breech, your healthcare provider will likely recommend a C-section.
A Word From Verywell
Knowing that your baby is in the wrong position and that you may be facing a breech delivery can be extremely stressful. However, most fetuses turn to have their head down before a person goes into labor. It is not a cause for concern if your fetus is breech before 36 weeks. It is common for the fetus to move around in many different positions before that time.
At the end of your pregnancy, if your fetus is in a breech position, your healthcare provider can perform maneuvers to turn the fetus around. If these maneuvers are unsuccessful or not appropriate for your situation, cesarean delivery is most often recommended. Discussing all of these options in advance can help you feel prepared should you be faced with a breech delivery.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. If your baby is breech .
TeachMeObGyn. Breech presentation .
MedlinePlus. Breech birth .
Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R, West HM. External cephalic version for breech presentation at term . Cochrane Database Syst Rev . 2015 Apr 1;2015(4):CD000083. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000083.pub3
By Christine Zink, MD Dr. Christine Zink, MD, is a board-certified emergency medicine with expertise in the wilderness and global medicine. She completed her medical training at Weill Cornell Medical College and residency in emergency medicine at New York-Presbyterian Hospital. She utilizes 15-years of clinical experience in her medical writing.
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
- Labor & Delivery
What Causes Breech Presentation?
Learn more about the types, causes, and risks of breech presentation, along with how breech babies are typically delivered.
What Is Breech Presentation?
Types of breech presentation, what causes a breech baby, can you turn a breech baby, how are breech babies delivered.
FatCamera/Getty Images
Toward the end of pregnancy, your baby will start to get into position for delivery, with their head pointed down toward the vagina. This is otherwise known as vertex presentation. However, some babies turn inside the womb so that their feet or buttocks are poised to be delivered first, which is commonly referred to as breech presentation, or a breech baby.
As you near the end of your pregnancy journey, an OB-GYN or health care provider will check your baby's positioning. You might find yourself wondering: What causes breech presentation? Are there risks involved? And how are breech babies delivered? We turned to experts and research to answer some of the most common questions surrounding breech presentation, along with what causes this positioning in the first place.
During your pregnancy, your baby constantly moves around the uterus. Indeed, most babies do somersaults up until the 36th week of pregnancy , when they pick their final position in the womb, says Laura Riley , MD, an OB-GYN in New York City. Approximately 3-4% of babies end up “upside-down” in breech presentation, with their feet or buttocks near the cervix.
Breech presentation is typically diagnosed during a visit to an OB-GYN, midwife, or health care provider. Your physician can feel the position of your baby's head through your abdominal wall—or they can conduct a vaginal exam if your cervix is open. A suspected breech presentation should ultimately be confirmed via an ultrasound, after which you and your provider would have a discussion about delivery options, potential issues, and risks.
There are three types of breech babies: frank, footling, and complete. Learn about the differences between these breech presentations.
Frank Breech
With frank breech presentation, your baby’s bottom faces the cervix and their legs are straight up. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
Footling Breech
Like its name suggests, a footling breech is when one (single footling) or both (double footling) of the baby's feet are in the birth canal, where they’re positioned to be delivered first .
Complete Breech
In a complete breech presentation, baby’s bottom faces the cervix. Their legs are bent at the knees, and their feet are near their bottom. A complete breech is the least common type of breech presentation.
Other Types of Mal Presentations
The baby can also be in a transverse position, meaning that they're sideways in the uterus. Another type is called oblique presentation, which means they're pointing toward one of the pregnant person’s hips.
Typically, your baby's positioning is determined by the fetus itself and the shape of your uterus. Because you can't can’t control either of these factors, breech presentation typically isn’t considered preventable. And while the cause often isn't known, there are certain risk factors that may increase your risk of a breech baby, including the following:
- The fetus may have abnormalities involving the muscular or central nervous system
- The uterus may have abnormal growths or fibroids
- There might be insufficient amniotic fluid in the uterus (too much or too little)
- This isn’t your first pregnancy
- You have a history of premature delivery
- You have placenta previa (the placenta partially or fully covers the cervix)
- You’re pregnant with multiples
- You’ve had a previous breech baby
In some cases, your health care provider may attempt to help turn a baby in breech presentation through a procedure known as external cephalic version (ECV). This is when a health care professional applies gentle pressure on your lower abdomen to try and coax your baby into a head-down position. During the entire procedure, the fetus's health will be monitored, and an ECV is often performed near a delivery room, in the event of any potential issues or complications.
However, it's important to note that ECVs aren't for everyone. If you're carrying multiples, there's health concerns about you or the baby, or you've experienced certain complications with your placenta or based on placental location, a health care provider will not attempt an ECV.
The majority of breech babies are born through C-sections . These are usually scheduled between 38 and 39 weeks of pregnancy, before labor can begin naturally. However, with a health care provider experienced in delivering breech babies vaginally, a natural delivery might be a safe option for some people. In fact, a 2017 study showed similar complication and success rates with vaginal and C-section deliveries of breech babies.
That said, there are certain known risks and complications that can arise with an attempt to deliver a breech baby vaginally, many of which relate to problems with the umbilical cord. If you and your medical team decide on a vaginal delivery, your baby will be monitored closely for any potential signs of distress.
Ultimately, it's important to know that most breech babies are born healthy. Your provider will consider your specific medical condition and the position of your baby to determine which type of delivery will be the safest option for a healthy and successful birth.
ACOG. If Your Baby Is Breech .
American Pregnancy Association. Breech Presentation .
Gray CJ, Shanahan MM. Breech Presentation . [Updated 2022 Nov 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-.
Mount Sinai. Breech Babies .
Takeda J, Ishikawa G, Takeda S. Clinical Tips of Cesarean Section in Case of Breech, Transverse Presentation, and Incarcerated Uterus . Surg J (N Y). 2020 Mar 18;6(Suppl 2):S81-S91. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1702985. PMID: 32760790; PMCID: PMC7396468.
Shanahan MM, Gray CJ. External Cephalic Version . [Updated 2022 Nov 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-.
Fonseca A, Silva R, Rato I, Neves AR, Peixoto C, Ferraz Z, Ramalho I, Carocha A, Félix N, Valdoleiros S, Galvão A, Gonçalves D, Curado J, Palma MJ, Antunes IL, Clode N, Graça LM. Breech Presentation: Vaginal Versus Cesarean Delivery, Which Intervention Leads to the Best Outcomes? Acta Med Port. 2017 Jun 30;30(6):479-484. doi: 10.20344/amp.7920. Epub 2017 Jun 30. PMID: 28898615.
Related Articles
Enter search terms to find related medical topics, multimedia and more.
Advanced Search:
- Use “ “ for exact phrases.
- For example: “pediatric abdominal pain”
- Use – to remove results with certain keywords.
- For example: abdominal pain -pediatric
- Use OR to account for alternate keywords.
- For example: teenager OR adolescent
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
, MD, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
- 3D Models (0)
- Calculators (0)

Abnormal fetal lie or presentation may occur due to fetal size, fetal anomalies, uterine structural abnormalities, multiple gestation, or other factors. Diagnosis is by examination or ultrasonography. Management is with physical maneuvers to reposition the fetus, operative vaginal delivery Operative Vaginal Delivery Operative vaginal delivery involves application of forceps or a vacuum extractor to the fetal head to assist during the second stage of labor and facilitate delivery. Indications for forceps... read more , or cesarean delivery Cesarean Delivery Cesarean delivery is surgical delivery by incision into the uterus. The rate of cesarean delivery was 32% in the United States in 2021 (see March of Dimes: Delivery Method). The rate has fluctuated... read more .
Terms that describe the fetus in relation to the uterus, cervix, and maternal pelvis are
Fetal presentation: Fetal part that overlies the maternal pelvic inlet; vertex (cephalic), face, brow, breech, shoulder, funic (umbilical cord), or compound (more than one part, eg, shoulder and hand)
Fetal position: Relation of the presenting part to an anatomic axis; for transverse presentation, occiput anterior, occiput posterior, occiput transverse
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse
Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position.
Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with
Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
Fetal congenital anomalies
Uterine structural abnormalities (eg, fibroids, synechiae)
Multiple gestation
Several common types of abnormal lie or presentation are discussed here.

Transverse lie
Fetal position is transverse, with the fetal long axis oblique or perpendicular rather than parallel to the maternal long axis. Transverse lie is often accompanied by shoulder presentation, which requires cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation
There are several types of breech presentation.
Frank breech: The fetal hips are flexed, and the knees extended (pike position).
Complete breech: The fetus seems to be sitting with hips and knees flexed.
Single or double footling presentation: One or both legs are completely extended and present before the buttocks.
Types of breech presentations
Breech presentation makes delivery difficult ,primarily because the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge. Having a poor dilating wedge can lead to incomplete cervical dilation, because the presenting part is narrower than the head that follows. The head, which is the part with the largest diameter, can then be trapped during delivery.
Additionally, the trapped fetal head can compress the umbilical cord if the fetal umbilicus is visible at the introitus, particularly in primiparas whose pelvic tissues have not been dilated by previous deliveries. Umbilical cord compression may cause fetal hypoxemia.

Predisposing factors for breech presentation include
Preterm labor Preterm Labor Labor (regular uterine contractions resulting in cervical change) that begins before 37 weeks gestation is considered preterm. Risk factors include prelabor rupture of membranes, uterine abnormalities... read more
Multiple gestation Multifetal Pregnancy Multifetal pregnancy is presence of > 1 fetus in the uterus. Multifetal (multiple) pregnancy occurs in up to 1 of 30 deliveries. Risk factors for multiple pregnancy include Ovarian stimulation... read more
Uterine abnormalities
Fetal anomalies
If delivery is vaginal, breech presentation may increase risk of
Umbilical cord prolapse
Perinatal death
It is best to detect abnormal fetal lie or presentation before delivery. During routine prenatal care, clinicians assess fetal lie and presentation with physical examination in the late third trimester. Ultrasonography can also be done. If breech presentation is detected, external cephalic version can sometimes move the fetus to vertex presentation before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks. This technique involves gently pressing on the maternal abdomen to reposition the fetus. A dose of a short-acting tocolytic ( terbutaline 0.25 mg subcutaneously) may help. The success rate is about 50 to 75%. For persistent abnormal lie or presentation, cesarean delivery is usually done at 39 weeks or when the woman presents in labor.

Face or brow presentation
In face presentation, the head is hyperextended, and position is designated by the position of the chin (mentum). When the chin is posterior, the head is less likely to rotate and less likely to deliver vaginally, necessitating cesarean delivery.
Brow presentation usually converts spontaneously to vertex or face presentation.
Occiput posterior position
The most common abnormal position is occiput posterior.
The fetal neck is usually somewhat deflexed; thus, a larger diameter of the head must pass through the pelvis.
Progress may arrest in the second phase of labor. Operative vaginal delivery Operative Vaginal Delivery Operative vaginal delivery involves application of forceps or a vacuum extractor to the fetal head to assist during the second stage of labor and facilitate delivery. Indications for forceps... read more or cesarean delivery Cesarean Delivery Cesarean delivery is surgical delivery by incision into the uterus. The rate of cesarean delivery was 32% in the United States in 2021 (see March of Dimes: Delivery Method). The rate has fluctuated... read more is often required.
Position and Presentation of the Fetus
If a fetus is in the occiput posterior position, operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
In breech presentation, the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge, which can cause the head to be trapped during delivery, often compressing the umbilical cord.
For breech presentation, usually do cesarean delivery at 39 weeks or during labor, but external cephalic version is sometimes successful before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.
Drugs Mentioned In This Article

Was This Page Helpful?

Test your knowledge
Brought to you by Merck & Co, Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA (known as MSD outside the US and Canada) — dedicated to using leading-edge science to save and improve lives around the world. Learn more about the Merck Manuals and our commitment to Global Medical Knowledge.
- Permissions
- Cookie Settings
- Terms of use
- Veterinary Manual
- IN THIS TOPIC
Breech Position: What It Means if Your Baby Is Breech
Medical review policy, latest update:.
Medically reviewed for accuracy.
What does it mean if a baby is breech?
What are the different types of breech positions, what causes a baby to be breech, recommended reading, how can you tell if your baby is in a breech position, what does it mean to turn a breech baby, how can you turn a breech baby, how does labor usually start with a breech baby.
If your cervix dilates too slowly, if your baby doesn’t move down the birth canal steadily or if other problems arise, you’ll likely have a C-section. Talk your options over with your practitioner now to be prepared. Remember that though you may feel disappointed things didn’t turn out exactly as you envisioned, these feelings will melt away once your bundle of joy safely enters the world.
Updates history
Jump to your week of pregnancy, trending on what to expect, signs of labor, pregnancy calculator, ⚠️ you can't see this cool content because you have ad block enabled., top 1,000 baby girl names in the u.s., top 1,000 baby boy names in the u.s., braxton hicks contractions and false labor.

- Pregnancy Classes

Breech Births
In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby’s buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3–4% of full-term births.
What are the different types of breech birth presentations?
- Complete breech: Here, the buttocks are pointing downward with the legs folded at the knees and feet near the buttocks.
- Frank breech: In this position, the baby’s buttocks are aimed at the birth canal with its legs sticking straight up in front of his or her body and the feet near the head.
- Footling breech: In this position, one or both of the baby’s feet point downward and will deliver before the rest of the body.
What causes a breech presentation?
The causes of breech presentations are not fully understood. However, the data show that breech birth is more common when:
- You have been pregnant before
- In pregnancies of multiples
- When there is a history of premature delivery
- When the uterus has too much or too little amniotic fluid
- When there is an abnormally shaped uterus or a uterus with abnormal growths, such as fibroids
- The placenta covers all or part of the opening of the uterus placenta previa
How is a breech presentation diagnosed?
A few weeks prior to the due date, the health care provider will place her hands on the mother’s lower abdomen to locate the baby’s head, back, and buttocks. If it appears that the baby might be in a breech position, they can use ultrasound or pelvic exam to confirm the position. Special x-rays can also be used to determine the baby’s position and the size of the pelvis to determine if a vaginal delivery of a breech baby can be safely attempted.
Can a breech presentation mean something is wrong?
Even though most breech babies are born healthy, there is a slightly elevated risk for certain problems. Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies and the defect might be the reason that the baby failed to move into the right position prior to delivery.
Can a breech presentation be changed?
It is preferable to try to turn a breech baby between the 32nd and 37th weeks of pregnancy . The methods of turning a baby will vary and the success rate for each method can also vary. It is best to discuss the options with the health care provider to see which method she recommends.
Medical Techniques
External Cephalic Version (EVC) is a non-surgical technique to move the baby in the uterus. In this procedure, a medication is given to help relax the uterus. There might also be the use of an ultrasound to determine the position of the baby, the location of the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus.
Gentle pushing on the lower abdomen can turn the baby into the head-down position. Throughout the external version the baby’s heartbeat will be closely monitored so that if a problem develops, the health care provider will immediately stop the procedure. ECV usually is done near a delivery room so if a problem occurs, a cesarean delivery can be performed quickly. The external version has a high success rate and can be considered if you have had a previous cesarean delivery.
ECV will not be tried if:
- You are carrying more than one fetus
- There are concerns about the health of the fetus
- You have certain abnormalities of the reproductive system
- The placenta is in the wrong place
- The placenta has come away from the wall of the uterus ( placental abruption )
Complications of EVC include:
- Prelabor rupture of membranes
- Changes in the fetus’s heart rate
- Placental abruption
- Preterm labor
Vaginal delivery versus cesarean for breech birth?
Most health care providers do not believe in attempting a vaginal delivery for a breech position. However, some will delay making a final decision until the woman is in labor. The following conditions are considered necessary in order to attempt a vaginal birth:
- The baby is full-term and in the frank breech presentation
- The baby does not show signs of distress while its heart rate is closely monitored.
- The process of labor is smooth and steady with the cervix widening as the baby descends.
- The health care provider estimates that the baby is not too big or the mother’s pelvis too narrow for the baby to pass safely through the birth canal.
- Anesthesia is available and a cesarean delivery possible on short notice
What are the risks and complications of a vaginal delivery?
In a breech birth, the baby’s head is the last part of its body to emerge making it more difficult to ease it through the birth canal. Sometimes forceps are used to guide the baby’s head out of the birth canal. Another potential problem is cord prolapse . In this situation the umbilical cord is squeezed as the baby moves toward the birth canal, thus slowing the baby’s supply of oxygen and blood. In a vaginal breech delivery, electronic fetal monitoring will be used to monitor the baby’s heartbeat throughout the course of labor. Cesarean delivery may be an option if signs develop that the baby may be in distress.
When is a cesarean delivery used with a breech presentation?
Most health care providers recommend a cesarean delivery for all babies in a breech position, especially babies that are premature. Since premature babies are small and more fragile, and because the head of a premature baby is relatively larger in proportion to its body, the baby is unlikely to stretch the cervix as much as a full-term baby. This means that there might be less room for the head to emerge.
Want to Know More?
- Creating Your Birth Plan
- Labor & Birth Terms to Know
- Cesarean Birth After Care
Compiled using information from the following sources:
- ACOG: If Your Baby is Breech
- William’s Obstetrics Twenty-Second Ed. Cunningham, F. Gary, et al, Ch. 24.
- Danforth’s Obstetrics and Gynecology Ninth Ed. Scott, James R., et al, Ch. 21.
BLOG CATEGORIES
- Can I get pregnant if… ? 3
- Child Adoption 19
- Fertility 54
- Pregnancy Loss 11
- Breastfeeding 29
- Changes In Your Body 5
- Cord Blood 4
- Genetic Disorders & Birth Defects 17
- Health & Nutrition 2
- Is it Safe While Pregnant 54
- Labor and Birth 65
- Multiple Births 10
- Planning and Preparing 24
- Pregnancy Complications 68
- Pregnancy Concerns 62
- Pregnancy Health and Wellness 149
- Pregnancy Products & Tests 8
- Pregnancy Supplements & Medications 14
- The First Year 41
- Week by Week Newsletter 40
- Your Developing Baby 16
- Options for Unplanned Pregnancy 18
- Paternity Tests 2
- Pregnancy Symptoms 5
- Prenatal Testing 16
- The Bumpy Truth Blog 7
- Uncategorized 4
- Abstinence 3
- Birth Control Pills, Patches & Devices 21
- Women's Health 34
- Thank You for Your Donation
- Unplanned Pregnancy
- Getting Pregnant
- Healthy Pregnancy
- Privacy Policy
Share this post:
Similar post.

Episiotomy: Advantages & Complications

Retained Placenta

What is Dilation in Pregnancy?
Track your baby’s development, subscribe to our week-by-week pregnancy newsletter.
- The Bumpy Truth Blog
- Fertility Products Resource Guide
Pregnancy Tools
- Ovulation Calendar
- Baby Names Directory
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Quiz
Pregnancy Journeys
- Partner With Us
- Corporate Sponsors
TYPES OF BREECH PRESENTATION
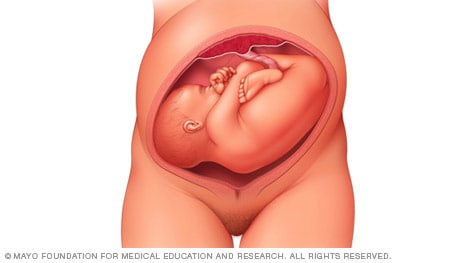
● Frank breech – Both hips are flexed and both knees are extended so that the feet are adjacent to the head ( figure 1 ); accounts for 50 to 70 percent of breech fetuses at term.
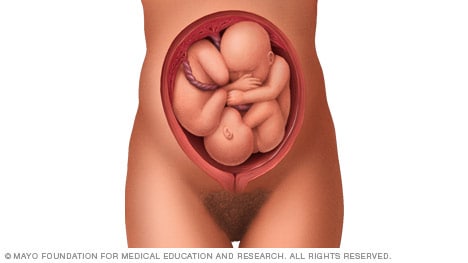
● Complete breech – Both hips and both knees are flexed ( figure 2 ); accounts for 5 to 10 percent of breech fetuses at term.
- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
What Does It Mean to Have a Frank Breech Baby?
Frank breech is the most common type of breech baby
Jamie Grill / Getty Images
Types of Breech Babies
- How to Tell If Baby Is Breech
Complications
A word from verywell.
If your baby is in a frank breech position, that means that their bottom is down toward the cervix rather than the head. The part of the baby that is near the birth canal is called the presenting part. It’s the part of the baby’s body that is born first and is usually the head (vertex presentation).
In a small number of deliveries, a baby’s bottom or feet are in a position to be born first. This is called a breech presentation, and frank breech (bottom first, with feet up near the head) is the most common type.
Breech presentations are more common in premature births than in full-term births. As a pregnancy continues, it’s more likely the baby will turn, and the head will be down when it's time for delivery. So, as a pregnancy gets closer to term, the chances of a breech birth go down.
- Before the 28th week of pregnancy , about 20% to 25% of babies are breech.
- By the 34th week of pregnancy , most babies will turn, and approximately 5% to 7% will be breech.
- By full term, only 3% to 4% of babies (3 or 4 out of every 100 births) are breech.
Most often, a baby will shift to the head-down position in the last weeks or days of pregnancy. However, sometimes, they are in a breech (bottom or leg down) position when labor begins. There are several types of breech babies.
Frank Breech
A frank breech is the most common breech presentation, especially when a baby is born at full term. Of the 3% to 4% of term breech births, babies are in the frank breech position 50% to 70% of the time. A frank breech is when the baby’s bottom is down, but their legs are straight up with their feet near their head. The presenting part is the buttocks. There are also other breech presentations.
Complete Breech
In this position, the bottom is down, but the baby's knees are also bent, so the feet are also down near the buttocks. The presenting part is not only the bottom but both feet as well. At delivery, about 10% of breech babies are in a complete breech position.
Incomplete or Footling Breech
A footling breech is when the baby’s legs are extended and facing straight down. Instead of the bottom, the presenting part is one foot (a single footling) or both feet (a double footling). Approximately 25% of breech deliveries are incomplete.
How to Tell If Your Baby Is Breech
As your pregnancy progresses, your doctor will examine you and keep track of your baby’s position. You might even be able to figure out where your baby is in your womb on your own. Here are some of the techniques you and your doctor can use to tell which way your baby is facing.
- Kicks : You can feel where your baby is kicking you and judge their general position. If you feel kicks in your lower pelvis, then the baby hasn’t turned head down yet. But if the kicks are up toward your ribs and the top of your uterus, then the baby’s head is most likely facing down.
- Palpation : At your prenatal visits , your doctor or midwife will check your baby's position by palpating or feeling your belly to find the baby’s head, back, and bottom.
- Heartbeat : Listening to the baby’s heartbeat is another way to tell where your baby is in your womb. By finding the heartbeat's location, the doctor or midwife can get a better idea of the baby’s position.
- Ultrasound : An ultrasound provides the best information. It shows you and your healthcare team a picture of the baby and their exact position in your uterus. If your baby is breech, the ultrasound can determine the type of breech position your baby is in, such as frank breech or complete breech.
- Pelvic exam : During labor, your healthcare provider can perform a pelvic examination. They will be able to feel whether the baby’s head or their bottom and feet are in the birth canal.
Causes of Breech Presentations
The size of the baby, how much amniotic fluid is in the uterus, and the amount of space inside the womb are all factors that can contribute to a baby’s ability to move around. A premature baby is smaller and has more room inside the uterus to move around, for example. Twins or other multiples have less room in the uterus to move around and get into the head-down position for delivery.
Uterine issues, such as fibroids or a heart-shaped uterus , can get in the way of the baby’s ability to turn. Similarly, if the umbilical cord is very short, the baby may not be able to move and turn.
Too much amniotic fluid gives the baby the ability to move around freely in the womb. As they grow, they may still be able to flip and turn. Too little amniotic fluid may prevent a baby from moving into the head-down position as they get closer to full-term.
When the placenta is low and covers all or part of the cervix, it’s called placenta previa . Since the placenta takes up the room at the bottom of the uterus, it makes it difficult for the baby to turn.
Some congenital abnormalities can affect the baby’s ability to move into the head-down position. These conditions are usually not a surprise at delivery since they are typically seen on ultrasound examinations during pregnancy.
The most common reason for a breech presentation is prematurity.
Treatment for Breech Presentations
From yoga and chiropractic adjustments to music and exercises, there are plenty of things you can do to try to get your baby to move head down for delivery . Your doctor might help is by performing a procedure called external cephalic version (ECV).
If there are no complications in your pregnancy and the baby has not yet turned on their own by the 36th or 37th week, your doctor may attempt to turn the baby using this procedure. This works approximately 60% of the time. If it is successful, your chances of having a cesarean are much lower.
Most babies who are born breech are healthy. But when a baby is in the frank breech position, or any breech position, there is more of a chance that labor and delivery can be difficult. Some of the complications of a vaginal breech birth are:
Umbilical Cord Prolapse
During a vaginal breech delivery, there is a chance that the umbilical cord will come down through the cervix before the baby is born. As the baby comes through the birth canal, their body and head can press on the cord and cut off the supply of blood and oxygen that the cord is carrying.
This can affect the baby’s heart rate and the flow of oxygen and blood to the baby’s brain. The danger of a prolapsed cord is greater with a footling breech and a complete breech. The risk is less when the baby is in the frank breech position.
Head Entrapment
The baby’s head can get stuck during the delivery if the baby’s body is born before the cervix fully dilates . This situation is dangerous since the head can press against the umbilical cord and cause asphyxia or a lack of oxygen. Head entrapment is more common in premature deliveries because the baby’s head is typically bigger than the body.
Physical Injuries to the Baby
The risk of injury to the baby is higher when the baby is breech compared to when the baby is not breech. Preemies are more likely to injure their head and skull. Bruising, broken bones, and dislocated joints can also occur depending on the baby's position during birth.
Additionally, after a baby is born, breech newborns have a higher incidence of neonatal hip instability, also called developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). This complication occurs in between 12% to 24% of breech babies.
Physical Injuries to the Parent
The vaginal delivery of a breech baby can include an episiotomy and the use of forceps, which can cause injury to the genital area. Breech presentation is one of the common reasons for a cesarean section. A cesarean is a surgery with anesthesia. Besides the surgical incision, a parent may experience pain, infection, bleeding, or other complications.
Delivery of a Frank Breech Baby
Many babies will turn to the head-down position before labor begins. However, if your child is still breech when it’s time to deliver, you and your doctor will have to decide between having a C-section or trying a vaginal birth. Typically, a surgical delivery is deemed the safer choice. However, when there are no other complications, a baby in the frank breech position may be delivered vaginally if:
- Emergency resources are available.
- The baby is at least 36 weeks gestation.
- The baby is not too big or too small.
- The baby’s head is in the right position (flexed).
- The healthcare team has experience with breech deliveries.
- The size of your pelvis is large enough.
- There is continuous monitoring of the baby.
- You have delivered vaginally before.
If any complications arise during the delivery, you may still need an emergency C-section. Whenever possible, the standard choice is to deliver any breech baby who is premature or in distress via cesarean section . Since vaginal deliveries, even when all the above criteria are met, come with a higher risk of a difficult birth and birth injuries , most doctors prefer to deliver all breech presentations by C-section.
While most babies are in the head-down position by the 37th week of pregnancy, some remain bottom-down. In these cases, they are typically in the frank breech position, with their bottom down and both legs up. When this occurs, the baby still may turn before labor begins. If not, most often, the baby will be delivered via C-section. However, in certain circumstances, frank breech babies can be born vaginally.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. If your baby is breech .
Toijonen AE, Heinonen ST, Gissler MVM, Macharey G. A comparison of risk factors for breech presentation in preterm and term labor: A nationwide, population-based case-control study . Arch Gynecol Obstet . 2020;301(2):393-403. doi:10.1007/s00404-019-05385-5
Fonseca A, Silva R, Rato I, et al. Breech presentation: Vaginal versus cesarean delivery, which intervention leads to the best outcomes? . Acta Med Port. 2017;30(6):479-484. doi:10.20344/amp.7920
Gallot D. [Breech presentation: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice - Information and management] . Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2020;48(1):132-135. doi:10.1016/j.gofs.2019.10.019
Brusalis CM, Price CT, Sankar WN. Incidence of acetabular dysplasia in breech infants following initially normal ultrasound: the effect of variable diagnostic criteria . J Child Orthop . 2017;11(4):272-276. doi:10.1302/1863-2548.11.160261
By Donna Murray, RN, BSN Donna Murray, RN, BSN has a Bachelor of Science in Nursing from Rutgers University and is a current member of Sigma Theta Tau, the Honor Society of Nursing.
- Getting Pregnant
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
- Birth Clubs
- See all in Community
- Ovulation Calculator
- How To Get Pregnant
- How To Get Pregnant Fast
- Ovulation Discharge
- Implantation Bleeding
- Ovulation Symptoms
- Pregnancy Symptoms
- Am I Pregnant?
- Pregnancy Tests
- See all in Getting Pregnant
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Pregnant Sex
- Weight Gain Tracker
- Signs of Labor
- Morning Sickness
- COVID Vaccine and Pregnancy
- Fetal Weight Chart
- Fetal Development
- Pregnancy Discharge
- Find Out Baby Gender
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- See all in Pregnancy
- Baby Name Generator
- Top Baby Names 2023
- Top Baby Names 2024
- How to Pick a Baby Name
- Most Popular Baby Names
- Baby Names by Letter
- Gender Neutral Names
- Unique Boy Names
- Unique Girl Names
- Top baby names by year
- See all in Baby Names
- Baby Development
- Baby Feeding Guide
- Newborn Sleep
- When Babies Roll Over
- First-Year Baby Costs Calculator
- Postpartum Health
- Baby Poop Chart
- See all in Baby
- Average Weight & Height
- Autism Signs
- Child Growth Chart
- Night Terrors
- Moving from Crib to Bed
- Toddler Feeding Guide
- Potty Training
- Bathing and Grooming
- See all in Toddler
- Height Predictor
- Potty Training: Boys
- Potty training: Girls
- How Much Sleep? (Ages 3+)
- Ready for Preschool?
- Thumb-Sucking
- Gross Motor Skills
- Napping (Ages 2 to 3)
- See all in Child
- Photos: Rashes & Skin Conditions
- Symptom Checker
- Vaccine Scheduler
- Reducing a Fever
- Acetaminophen Dosage Chart
- Constipation in Babies
- Ear Infection Symptoms
- Head Lice 101
- See all in Health
- Second Pregnancy
- Daycare Costs
- Family Finance
- Stay-At-Home Parents
- Breastfeeding Positions
- See all in Family
- Baby Sleep Training
- Preparing For Baby
- My Custom Checklist
- My Registries
- Take the Quiz
- Best Baby Products
- Best Breast Pump
- Best Convertible Car Seat
- Best Infant Car Seat
- Best Baby Bottle
- Best Baby Monitor
- Best Stroller
- Best Diapers
- Best Baby Carrier
- Best Diaper Bag
- Best Highchair
- See all in Baby Products
- Why Pregnant Belly Feels Tight
- Early Signs of Twins
- Teas During Pregnancy
- Baby Head Circumference Chart
- How Many Months Pregnant Am I
- What is a Rainbow Baby
- Braxton Hicks Contractions
- HCG Levels By Week
- When to Take a Pregnancy Test
- Am I Pregnant
- Why is Poop Green
- Can Pregnant Women Eat Shrimp
- Insemination
- UTI During Pregnancy
- Vitamin D Drops
- Best Baby Forumla
- Postpartum Depression
- Low Progesterone During Pregnancy
- Baby Shower
- Baby Shower Games
Breech, posterior, transverse lie: What position is my baby in?

Fetal presentation, or how your baby is situated in your womb at birth, is determined by the body part that's positioned to come out first, and it can affect the way you deliver. At the time of delivery, 97 percent of babies are head-down (cephalic presentation). But there are several other possibilities, including feet or bottom first (breech) as well as sideways (transverse lie) and diagonal (oblique lie).
Fetal presentation and position
During the last trimester of your pregnancy, your provider will check your baby's presentation by feeling your belly to locate the head, bottom, and back. If it's unclear, your provider may do an ultrasound or an internal exam to feel what part of the baby is in your pelvis.
Fetal position refers to whether the baby is facing your spine (anterior position) or facing your belly (posterior position). Fetal position can change often: Your baby may be face up at the beginning of labor and face down at delivery.
Here are the many possibilities for fetal presentation and position in the womb.
Medical illustrations by Jonathan Dimes
Head down, facing down (anterior position)
A baby who is head down and facing your spine is in the anterior position. This is the most common fetal presentation and the easiest position for a vaginal delivery.
This position is also known as "occiput anterior" because the back of your baby's skull (occipital bone) is in the front (anterior) of your pelvis.
Head down, facing up (posterior position)
In the posterior position , your baby is head down and facing your belly. You may also hear it called "sunny-side up" because babies who stay in this position are born facing up. But many babies who are facing up during labor rotate to the easier face down (anterior) position before birth.
Posterior position is formally known as "occiput posterior" because the back of your baby's skull (occipital bone) is in the back (posterior) of your pelvis.
Frank breech
In the frank breech presentation, both the baby's legs are extended so that the feet are up near the face. This is the most common type of breech presentation. Breech babies are difficult to deliver vaginally, so most arrive by c-section .
Some providers will attempt to turn your baby manually to the head down position by applying pressure to your belly. This is called an external cephalic version , and it has a 58 percent success rate for turning breech babies. For more information, see our article on breech birth .
Complete breech
A complete breech is when your baby is bottom down with hips and knees bent in a tuck or cross-legged position. If your baby is in a complete breech, you may feel kicking in your lower abdomen.
Incomplete breech
In an incomplete breech, one of the baby's knees is bent so that the foot is tucked next to the bottom with the other leg extended, positioning that foot closer to the face.
Single footling breech
In the single footling breech presentation, one of the baby's feet is pointed toward your cervix.
Double footling breech
In the double footling breech presentation, both of the baby's feet are pointed toward your cervix.
Transverse lie
In a transverse lie, the baby is lying horizontally in your uterus and may be facing up toward your head or down toward your feet. Babies settle this way less than 1 percent of the time, but it happens more commonly if you're carrying multiples or deliver before your due date.
If your baby stays in a transverse lie until the end of your pregnancy, it can be dangerous for delivery. Your provider will likely schedule a c-section or attempt an external cephalic version , which is highly successful for turning babies in this position.
Oblique lie
In rare cases, your baby may lie diagonally in your uterus, with his rump facing the side of your body at an angle.
Like the transverse lie, this position is more common earlier in pregnancy, and it's likely your provider will intervene if your baby is still in the oblique lie at the end of your third trimester.
Was this article helpful?
What to know if your baby is breech

What's a sunny-side up baby?

What happens to your baby right after birth

Perineal massage

BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies .
Ahmad A et al. 2014. Association of fetal position at onset of labor and mode of delivery: A prospective cohort study. Ultrasound in obstetrics & gynecology 43(2):176-182. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23929533 Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Gray CJ and Shanahan MM. 2019. Breech presentation. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448063/ Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Hankins GD. 1990. Transverse lie. American Journal of Perinatology 7(1):66-70. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2131781 Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Medline Plus. 2020. Your baby in the birth canal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002060.htm Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]

Where to go next

Appointments at Mayo Clinic
- Pregnancy week by week
- Fetal presentation before birth
The way a baby is positioned in the uterus just before birth can have a big effect on labor and delivery. This positioning is called fetal presentation.
Babies twist, stretch and tumble quite a bit during pregnancy. Before labor starts, however, they usually come to rest in a way that allows them to be delivered through the birth canal headfirst. This position is called cephalic presentation. But there are other ways a baby may settle just before labor begins.
Following are some of the possible ways a baby may be positioned at the end of pregnancy.
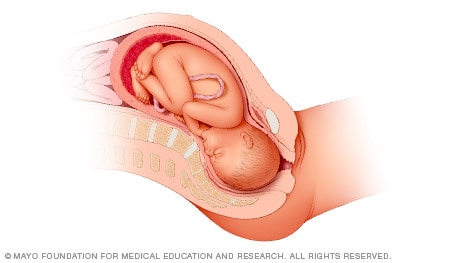
Head down, face down
When a baby is head down, face down, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput anterior position. This the most common position for a baby to be born in. With the face down and turned slightly to the side, the smallest part of the baby's head leads the way through the birth canal. It is the easiest way for a baby to be born.
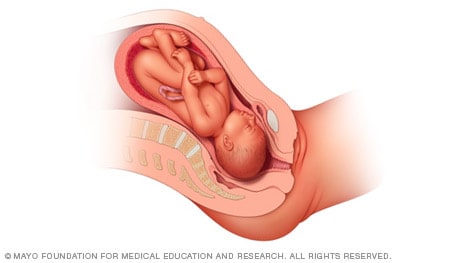
Head down, face up
When a baby is head down, face up, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput posterior position. In this position, it might be harder for a baby's head to go under the pubic bone during delivery. That can make labor take longer.
Most babies who begin labor in this position eventually turn to be face down. If that doesn't happen, and the second stage of labor is taking a long time, a member of the health care team may reach through the vagina to help the baby turn. This is called manual rotation.
In some cases, a baby can be born in the head-down, face-up position. Use of forceps or a vacuum device to help with delivery is more common when a baby is in this position than in the head-down, face-down position. In some cases, a C-section delivery may be needed.
Frank breech
When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a frank breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Most babies in a frank breech position are born by planned C-section.

Complete and incomplete breech
A complete breech presentation, as shown below, is when the baby has both knees bent and both legs pulled close to the body. In an incomplete breech, one or both of the legs are not pulled close to the body, and one or both of the feet or knees are below the baby's buttocks. If a baby is in either of these positions, you might feel kicking in the lower part of your belly.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a complete or incomplete breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies in a complete or incomplete breech position are born by planned C-section.

When a baby is sideways — lying horizontal across the uterus, rather than vertical — it's called a transverse lie. In this position, the baby's back might be:
- Down, with the back facing the birth canal.
- Sideways, with one shoulder pointing toward the birth canal.
- Up, with the hands and feet facing the birth canal.
Although many babies are sideways early in pregnancy, few stay this way when labor begins.
If your baby is in a transverse lie during week 37 of your pregnancy, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of your health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a transverse lie, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies who are in a transverse lie are born by C-section.
If you're pregnant with twins and only the twin that's lower in the uterus is head down, as shown below, your health care provider may first deliver that baby vaginally.
Then, in some cases, your health care team may suggest delivering the second twin in the breech position. Or they may try to move the second twin into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
Your health care team may suggest delivery by C-section for the second twin if:
- An attempt to deliver the baby in the breech position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to have the baby delivered vaginally in the breech position.
- An attempt to move the baby into a head-down position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to move the baby to a head-down position.
In some cases, your health care team may advise that you have both twins delivered by C-section. That might happen if the lower twin is not head down, the second twin has low or high birth weight as compared to the first twin, or if preterm labor starts.
- Landon MB, et al., eds. Normal labor and delivery. In: Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Holcroft Argani C, et al. Occiput posterior position. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Frequently asked questions: If your baby is breech. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/if-your-baby-is-breech. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Hofmeyr GJ. Overview of breech presentation. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Strauss RA, et al. Transverse fetal lie. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Chasen ST, et al. Twin pregnancy: Labor and delivery. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Cohen R, et al. Is vaginal delivery of a breech second twin safe? A comparison between delivery of vertex and non-vertex second twins. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. 2021; doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.2005569.
- Marnach ML (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. May 31, 2023.
Products and Services
- A Book: Obstetricks
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy
- 3rd trimester pregnancy
- Fetal development: The 3rd trimester
- Overdue pregnancy
- Pregnancy due date calculator
- Prenatal care: 3rd trimester
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.
Breech Presentation: What It Is and How It Can Affect Your Baby's Delivery

As you get close to your due date, your baby might sense she’s approaching her grand entrance and move into a head-down position in your uterus, ready to be born. However, in some cases, she might choose another position instead, such as bottom or feet down. When this happens, it’s called a breech presentation. Read on to learn how your healthcare provider checks the position of your baby, what delivery options you may have if your baby is breech, and what can cause a breech presentation.
What Is Breech?
During your pregnancy, your baby has likely taken every opportunity to let you know she means business by kicking up a storm and doing countless somersaults. It's natural for your baby to move and shift positions within the uterus. Then, usually between 32 and 36 weeks of pregnancy, your baby will likely get into a head-down position in preparation for being born.
There is a small chance — just 3 to 4 percent — that your baby may not move into this head-down position by the time your pregnancy is full term. This is called a breech presentation. The chance of a breech presentation is higher if your pregnancy is not yet full term or if you go into preterm labor .
Types of Birth Positions
There are many different types of positions, including a number of breech presentations, that your baby may take on before birth:
Frank breech presentation. Your baby's bottom is positioned downward. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
Complete breech presentation. Your baby's feet are positioned downward with her hips and knees flexed, almost cross-legged.
Incomplete breech presentation. Your baby's feet are positioned downward with only one hip or one knee flexed.
Shoulder presentation or transverse lie. This is a form of breech in which your baby is positioned horizontally in the uterus. Few babies remain this way at the time of delivery.
Footling breech. One or both of your baby's feet are pointed downward.
Cephalic or vertex presentation (occiput). Your baby is in the normal position for delivery. Her head is down and she’s facing toward your back.
Cephalic or vertex presentation (occiput posterior). In some cases, your baby may be in a downward position but with her face toward your front. If this happens in early labor, your baby may naturally turn to face your back on her own, or, later in labor, your provider may decide to manually assist the baby in getting into this position. If this doesn't work, your baby can still be delivered vaginally, but delivery may be prolonged and more painful.
The causes of your baby being in breech position aren't always clear, but it can be more common if any of the following apply to you:
You've been pregnant before
You are pregnant with twins (read on to learn more about twin breech)
The uterus has more or less amniotic fluid than usual
The uterus has an abnormal shape or has abnormal growths, such as fibroids.
You have a condition called placenta previa , which is when the placenta covers the cervix.
Your healthcare provider likely already knows whether any of these factors affect your situation, but you might want to mention it just to be sure.
Diagnosis of a Breech Presentation
At one of your prenatal visits in the lead up to your due date, your provider will check that everything is progressing as planned , and will examine your abdomen to try to find out whether your baby is in the correct head-down position. If your provider thinks there may be a breech presentation, she or he may recommend an ultrasound exam to confirm it.
Can a Breech Baby Be Turned?
If your baby is breech, your provider may consider turning your baby so that a vaginal delivery can proceed, if that’s in the cards for you anyway. Alternatively, your provider may recommend that a cesarean delivery is the safer option.
Keep in mind, your baby's position might change at some point before delivery day, so your provider may recommend waiting and seeing.
If you are 37 weeks pregnant or more, your provider may recommend turning your baby through a process called external cephalic version or ECV.
ECV involves your provider placing hands on your abdomen and applying firm pressure in order to turn the baby. This procedure will most likely be done near a delivery room. Your provider may offer an epidural block to help with any pain this procedure causes.
An ECV is about 50 percent effective and there is a small risk of complications. You and your baby will be monitored closely before, during, and after the procedure to ensure that both of you are doing well.
If the ECV procedure is successful, your baby can be delivered vaginally , if there’s no other impediment.
Delivery Options for a Breech Baby
If your baby is in a breech position, the risks associated with a vaginal delivery are much higher than with a cesarean section. Risks include the umbilical cord cutting off his blood supply or his head or shoulders becoming stuck. That’s why, in some cases, your provider may recommend a cesarean delivery .
It could be that your provider’s level of experience in delivering breech babies might also inform the discussion you have with your provider about what’s right for your situation. Ultimately, your provider will recommend the best course of action for you and your baby based on your personal situation.
Twins and Breech Presentation
It's possible for twins to be delivered vaginally if the first baby — the lower-positioned twin — is correctly positioned with the head facing down. Of course, that's if the twin pregnancy is otherwise progressing well and there are no complications. If the second twin is in a breech position, the provider may do an ECV procedure to get this baby in the correct head-down position for a vaginal delivery, too.
If the first twin baby (the one lower down) is in a breech position, the provider may recommend a cesarean section. Triplets or more will most likely require a cesarean section.
Although you might feel like the added stress of a breech baby is the last thing you need as you approach your due date, remember that your healthcare provider has seen this situation before and will know what to do to ensure your baby is delivered safely. Next thing you know, you'll be bringing your brand-new baby home , stocking up on diapers, waking up for late-night feedings, and reveling in your baby's growth .
See all sources
- Cleveland clinic: Cesarean Birth (C-Section)
- Cleveland Clinic: Fetal Positions for Birth
- Mayo Clinic: Fetal presentation before birth
- Mayo Clinic: Prenatal care: 3rd trimester visits
- Mayo Clinic: Third Trimester
- Book: Your Pregnancy and Childbirth: Month to Month, Sixth Edition Paperback – January 1, 2016 by American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (Author)
Review this article:
Read more about pregnancy.
- Pregnancy Announcement
- Pregnancy Calendar
- Pregnancy Symptoms
- Baby Shower & Registry
- Prenatal Health and Wellness
- Preparing For Your New Baby
- Giving Birth
- Due Date Calculator
Join a World of Support
through Pregnancy and Parenthood.

TRACK WITH TOOLS

LEARN WITH EXPERTS

GET REWARDED

Where You Already Belong
What happens if your baby is breech?
Babies often twist and turn during pregnancy, but most will have moved into the head-down (also known as head-first) position by the time labour begins. However, that does not always happen, and a baby may be:
- bottom first or feet first (breech position)
- lying sideways (transverse position)
Bottom first or feet first (breech baby)
If your baby is lying bottom or feet first, they are in the breech position. If they're still breech at around 36 weeks' gestation, the obstetrician and midwife will discuss your options for a safe delivery.
Turning a breech baby
If your baby is in a breech position at 36 weeks, you'll usually be offered an external cephalic version (ECV). This is when a healthcare professional, such as an obstetrician, tries to turn the baby into a head-down position by applying pressure on your abdomen. It's a safe procedure, although it can be a bit uncomfortable.
Giving birth to a breech baby
If an ECV does not work, you'll need to discuss your options for a vaginal birth or caesarean section with your midwife and obstetrician.
If you plan a caesarean and then go into labour before the operation, your obstetrician will assess whether it's safe to proceed with the caesarean delivery. If the baby is close to being born, it may be safer for you to have a vaginal breech birth.
The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) website has more information on what to expect if your baby is still breech at the end of pregnancy .
The RCOG advises against a vaginal breech delivery if:
- your baby's feet are below its bottom – known as a "footling breech"
- your baby is larger or smaller than average – your healthcare team will discuss this with you
- your baby is in a certain position – for example, their neck is very tilted back, which can make delivery of the head more difficult
- you have a low-lying placenta (placenta praevia)
- you have pre-eclampsia
Lying sideways (transverse baby)
If your baby is lying sideways across the womb, they are in the transverse position. Although many babies lie sideways early on in pregnancy, most turn themselves into the head-down position by the final trimester.
Giving birth to a transverse baby
Depending on how many weeks pregnant you are when your baby is in a transverse position, you may be admitted to hospital. This is because of the very small risk of the umbilical cord coming out of your womb before your baby is born (cord prolapse). If this happens, it's a medical emergency and the baby must be delivered very quickly.
Sometimes, it's possible to manually turn the baby to a head-down position, and you may be offered this.
But, if your baby is still in the transverse position when you approach your due date or by the time labour begins, you'll most likely be advised to have a caesarean section.
Video: My baby is breech. What help will I get?
In this video, a midwife describes what a breech position is and what can be done if your baby is breech.
Page last reviewed: 1 November 2023 Next review due: 1 November 2026
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.

- Management of breech presentation
Evidence review M
NICE Guideline, No. 201
National Guideline Alliance (UK) .
- Copyright and Permissions
Review question
What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy?
Introduction
Breech presentation of the fetus in late pregnancy may result in prolonged or obstructed labour with resulting risks to both woman and fetus. Interventions to correct breech presentation (to cephalic) before labour and birth are important for the woman’s and the baby’s health. The aim of this review is to determine the most effective way of managing a breech presentation in late pregnancy.
Summary of the protocol
Please see Table 1 for a summary of the Population, Intervention, Comparison and Outcome (PICO) characteristics of this review.
Summary of the protocol (PICO table).
For further details see the review protocol in appendix A .
Methods and process
This evidence review was developed using the methods and process described in Developing NICE guidelines: the manual 2014 . Methods specific to this review question are described in the review protocol in appendix A .
Declarations of interest were recorded according to NICE’s conflicts of interest policy .
Clinical evidence
Included studies.
Thirty-six randomised controlled trials (RCTs) were identified for this review.
The included studies are summarised in Table 2 .
Three studies reported on external cephalic version (ECV) versus no intervention ( Dafallah 2004 , Hofmeyr 1983 , Rita 2011 ). One study reported on a 4-arm trial comparing acupuncture, sweeping of fetal membranes, acupuncture plus sweeping, and no intervention ( Andersen 2013 ). Two studies reported on postural management versus no intervention ( Chenia 1987 , Smith 1999 ).
Seven studies reported on ECV plus anaesthesia ( Chalifoux 2017 , Dugoff 1999 , Khaw 2015 , Mancuso 2000 , Schorr 1997 , Sullivan 2009 , Weiniger 2010 ). Of these studies, 1 study compared ECV plus anaesthesia to ECV plus other dosages of the same anaesthetic ( Chalifoux 2017 ); 4 studies compared ECV plus anaesthesia to ECV only ( Dugoff 1999 , Mancuso 2000 , Schorr 1997 , Weiniger 2010 ); and 2 studies compared ECV plus anaesthesia to ECV plus a different anaesthetic ( Khaw 2015 , Sullivan 2009 ).
Ten studies reported ECV plus a β2 receptor agonist ( Brocks 1984 , Fernandez 1997 , Hindawi 2005 , Impey 2005 , Mahomed 1991 , Marquette 1996 , Nor Azlin 2005 , Robertson 1987 , Van Dorsten 1981 , Vani 2009 ). Of these studies, 5 studies compared ECV plus a β2 receptor agonist to ECV plus placebo ( Fernandez 1997 , Impey 2005 , Marquette 1996 , Nor Azlin 2005 , Vani 2009 ); 1 study compared ECV plus a β2 receptor agonist to ECV alone ( Robertson 1987 ); and 4 studies compared ECV plus a β2 receptor agonist to no intervention ( Brocks 1984 , Hindawi 2005 , Mahomed 1991 , Van Dorsten 1981 ).
One study reported on ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker versus ECV plus placebo ( Kok 2008 ). Two studies reported on ECV plus β2 receptor agonist versus ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker ( Collaris 2009 , Mohamed Ismail 2008 ). Four studies reported on ECV plus a µ-receptor agonist ( Burgos 2016 , Liu 2016 , Munoz 2014 , Wang 2017 ), of which 3 compared against ECV plus placebo ( Liu 2016 , Munoz 2014 , Wang 2017 ) and 1 compared to ECV plus nitrous oxide ( Burgos 2016 ).
Four studies reported on ECV plus nitroglycerin ( Bujold 2003a , Bujold 2003b , El-Sayed 2004 , Hilton 2009 ), of which 2 compared it to ECV plus β2 receptor agonist ( Bujold 2003b , El-Sayed 2004 ) and compared it to ECV plus placebo ( Bujold 2003a , Hilton 2009 ). One study compared ECV plus amnioinfusion versus ECV alone ( Diguisto 2018 ) and 1 study compared ECV plus talcum powder to ECV plus gel ( Vallikkannu 2014 ).
One study was conducted in Australia ( Smith 1999 ); 4 studies in Canada ( Bujold 2003a , Bujold 2003b , Hilton 2009 , Marquette 1996 ); 2 studies in China ( Liu 2016 , Wang 2017 ); 2 studies in Denmark ( Andersen 2013 , Brocks 1984 ); 1 study in France ( Diguisto 2018 ); 1 study in Hong Kong ( Khaw 2015 ); 1 study in India ( Rita 2011 ); 1 study in Israel ( Weiniger 2010 ); 1 study in Jordan ( Hindawi 2005 ); 5 studies in Malaysia ( Collaris 2009 , Mohamed Ismail 2008 , Nor Azlin 2005 , Vallikkannu 2014 , Vani 2009 ); 1 study in South Africa ( Hofmeyr 1983 ); 2 studies in Spain ( Burgos 2016 , Munoz 2014 ); 1 study in Sudan ( Dafallah 2004 ); 1 study in The Netherlands ( Kok 2008 ); 2 studies in the UK ( Impey 2005 , Chenia 1987 ); 9 studies in US ( Chalifoux 2017 , Dugoff 1999 , El-Sayed 2004 , Fernandez 1997 , Mancuso 2000 , Robertson 1987 , Schorr 1997 , Sullivan 2009 , Van Dorsten 1981 ); and 1 study in Zimbabwe ( Mahomed 1991 ).
The majority of studies were 2-arm trials, but there was one 3-arm trial ( Khaw 2015 ) and two 4-arm trials ( Andersen 2013 , Chalifoux 2017 ). All studies were conducted in a hospital or an outpatient ward connected to a hospital.
See the literature search strategy in appendix B and study selection flow chart in appendix C .

Excluded studies
Studies not included in this review with reasons for their exclusions are provided in appendix K .
Summary of clinical studies included in the evidence review
Summaries of the studies that were included in this review are presented in Table 2 .
Summary of included studies.
See the full evidence tables in appendix D and the forest plots in appendix E .
Quality assessment of clinical outcomes included in the evidence review
See the evidence profiles in appendix F .
Economic evidence
A systematic review of the economic literature was conducted but no economic studies were identified which were applicable to this review question.
A single economic search was undertaken for all topics included in the scope of this guideline. See supplementary material 2 for details.
Economic studies not included in this review are listed, and reasons for their exclusion are provided in appendix K .
Summary of studies included in the economic evidence review
No economic studies were identified which were applicable to this review question.
Economic model
No economic modelling was undertaken for this review because the committee agreed that other topics were higher priorities for economic evaluation.
Evidence statements
Clinical evidence statements, comparison 1. complementary therapy versus control (no intervention), critical outcomes, cephalic presentation in labour.
No evidence was identified to inform this outcome.
Method of birth
Caesarean section.
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=204) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and control (no intervention) on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.74 (95% CI 0.38 to 1.43).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=200) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture plus membrane sweeping and control (no intervention) on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.29 (95% CI 0.73 to 2.29).
Admission to SCBU/NICU
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=204) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and control (no intervention) on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.19 (95% CI 0.02 to 1.62).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=200) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture plus membrane sweeping and control (no intervention) on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.40 (0.08 to 2.01).
Fetal death after 36 +0 weeks gestation
Infant death up to 4 weeks chronological age, important outcomes, apgar score <7 at 5 minutes.
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=204) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and control (no intervention) on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.32 (95% CI 0.01 to 7.78).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=200) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture plus membrane sweeping and control (no intervention) on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.33 (0.01 to 8.09).
Birth before 39 +0 weeks of gestation
Comparison 2. complementary therapy versus other treatment.
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=207) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and membrane sweeping on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.64 (95% CI 0.34 to 1.22).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=204) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and acupuncture plus membrane sweeping on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.57 (95% CI 0.30 to 1.07).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=203) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture plus membrane sweeping and membrane sweeping on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.13 (95% CI 0.66 to 1.94).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=207) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and membrane sweeping on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.33 (95% CI 0.03 to 3.12).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=204) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and acupuncture plus membrane sweeping on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.48 (95% CI 0.04 to 5.22).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=203) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture plus membrane sweeping and membrane sweeping on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.69 (95% CI 0.12 to 4.02).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=207) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and membrane sweeping on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.02 to 0.02).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=204) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and acupuncture plus membrane sweeping on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.02 to 0.02).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=203) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture plus membrane sweeping and membrane sweeping on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.02 to 0.02).
Comparison 3. ECV versus no ECV
- Moderate quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=680) showed that there is clinically important difference favouring ECV over no ECV on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.83 (95% CI 1.53 to 2.18).
Cephalic vaginal birth
- Very low quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=740) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV over no ECV on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.67 (95% CI 1.20 to 2.31).
Breech vaginal birth
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=680) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV and no ECV on breech vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.29 (95% CI 0.03 to 2.84).
- Very low quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=740) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV and no ECV on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.52 (95% CI 0.23 to 1.20).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=60) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV and no ECV on admission to SCBU//NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.50 (95% CI 0.14 to 1.82).
- Very low evidence from 3 RCTs (N=740) showed that there is no statistically significant difference between ECV and no ECV on fetal death after 36 +0 weeks gestation in pregnant women with breech presentation: Peto OR 0.29 (95% CI 0.05 to 1.73) p=0.18.
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV and no ECV on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: Peto OR 0.28 (95% CI 0.04 to 1.70).
Comparison 4. ECV + Amnioinfusion versus ECV only
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=109) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus amnioinfusion and ECV alone on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.74 (95% CI 0.74 to 4.12).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=109) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus amnioinfusion and ECV alone on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.95 (95% CI 0.75 to 1.19).
Comparison 5. ECV + Anaesthesia versus ECV only
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=210) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus anaesthesia and ECV alone on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.16 (95% CI 0.56 to 2.41).
- Very low quality evidence from 5 RCTs (N=435) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus anaesthesia and ECV alone on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.16 (95% CI 0.77 to 1.74).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=108) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus anaesthesia and ECV alone on breech vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.33 (95% CI 0.04 to 3.10).
- Very low quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=263) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus anaesthesia and ECV alone on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.76 (95% CI 0.42 to 1.38).
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=69) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus anaesthesia over ECV alone on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: MD −1.80 (95% CI −2.53 to −1.07).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=126) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus anaesthesia and ECV alone on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.03 to 0.03).
Comparison 6. ECV + Anaesthesia versus ECV + Anaesthesia
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.13 (95% CI 0.73 to 1.74).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=119) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 7.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.81 (95% CI 0.53 to 1.23).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 10mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.96 (95% CI 0.61 to 1.50).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=95) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 0.05mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.69 (95% CI 0.37 to 1.28).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=119) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 7.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.81 (95% CI 0.53 to 1.23).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 10mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.96 (95% CI 0.61 to 1.50).
- Very low evidence from 1 RCT (N=119) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 7.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 10mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.19 (95% CI 0.79 to 1.79).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.92 (95% CI 0.68 to 1.24).
- Very low evidence from 1 RCT (N=119) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 7.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.08 (95% CI 0.78 to 1.50).
- Very low evidence from 1 RCT (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 10mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.94 (95% CI 0.70 to 1.28).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=119) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 7.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.17 (95% CI 0.86 to 1.61).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 10mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.03 (95% CI 0.77 to 1.37).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=119) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 7.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 10mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.88 (95% CI 0.64 to 1.20).
Comparison 7. ECV + β2 agonist versus Control (no intervention)
- Moderate quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=256) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus β2 agonist over control (no intervention) on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 4.83 (95% CI 3.27 to 7.11).
- Very low quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=265) showed that there no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and control (no intervention) on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 2.03 (95% CI 0.22 to 19.01).
- Very low quality evidence from 4 RCTs (N=513) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus β2 agonist over control (no intervention) on breech vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.38 (95% CI 0.20 to 0.69).
- Low quality evidence from 4 RCTs (N=513) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus β2 agonist over control (no intervention) on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.53 (95% CI 0.41 to 0.67).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=48) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and control (no intervention) on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.08 to 0.08).
- Very low quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=208) showed that there is no statistically significant difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and control (no intervention) on fetal death after 36 +0 weeks gestation in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD −0.01 (95% CI −0.03 to 0.01) p=0.66.
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=208) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and control (no intervention) on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: Peto OR 0.80 (95% CI 0.31 to 2.10).
Comparison 8. ECV + β2 agonist versus ECV only
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=172) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV only on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.32 (95% CI 0.67 to 2.62).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=58) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV only on breech vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.75 (95% CI 0.22 to 2.50).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=172) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV only on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.79 (95% CI 0.27 to 2.28).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=114) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV only on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.00 (95% CI 0.21 to 4.75).
Comparison 9. ECV + β2 agonist versus ECV + Placebo
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=146) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus placebo on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.54 (95% CI 0.24 to 9.76).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=125) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus placebo on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.27 (95% CI 0.41 to 3.89).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=227) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus placebo on breech vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.00 (95% CI 0.33 to 2.97).
- Low quality evidence from 4 RCTs (N=532) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus placebo on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.81 (95% CI 0.72 to 0.92)
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=146) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus placebo on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.78 (95% CI 0.17 to 3.63).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=124) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus placebo on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.03 to 0.03).
Comparison 10. ECV + Ca 2+ channel blocker versus ECV + Placebo
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=310) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus placebo on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.13 (95% CI 0.87 to 1.48).
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=310) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus placebo on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.90 (95% CI 0.73 to 1.12).
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=310) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus placebo on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.11 (95% CI 0.88 to 1.40).
- High quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=310) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus placebo on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: MD −0.20 (95% CI −0.70 to 0.30).
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=310) showed that there is no statistically significant difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus placebo on fetal death after 36 +0 weeks gestation in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.01 to 0.01) p=1.00.
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=310) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus placebo on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: Peto OR 0.52 (95% 0.05 to 5.02).
Comparison 11. ECV + Ca2+ channel blocker versus ECV + β2 agonist
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=90) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus β2 agonist over ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.62 (95% CI 0.39 to 0.98).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=126) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus β2 agonist on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.26 (95% CI 0.55 to 2.89).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=132) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus β2 agonist over ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.42 (95% CI 1.06 to 1.91).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=176) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus β2 agonist on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: Peto OR 0.53 (95% CI 0.05 to 5.22).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=176) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus β2 agonist on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.03 to 0.03).
Comparison 12. ECV + µ-receptor agonist versus ECV only
- High quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=80) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV alone on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.00 (95% CI 0.80 to 1.24).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=80) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV alone on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.00 (95% CI 0.42 to 2.40).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=126) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV alone on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.03 to 0.03).
Comparison 13. ECV + µ-receptor agonist versus ECV + Placebo
Cephalic vaginal birth after successful ecv.
- High quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=98) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus placebo on cephalic vaginal birth after successful ECV in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.00 (95% CI 0.86 to 1.17).
Caesarean section after successful ECV
- Low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=98) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus placebo on caesarean section after successful ECV in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.97 (95% CI 0.33 to 2.84).
Breech vaginal birth after unsuccessful ECV
- High quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=186) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus µ-receptor agonist over ECV plus placebo on breech vaginal birth after unsuccessful ECV in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.10 (95% CI 0.02 to 0.53).
Caesarean section after unsuccessful ECV
- Moderate quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=186) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus placebo on caesarean section after unsuccessful ECV in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.19 (95% CI 1.09 to 1.31).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=137) showed that there is no statistically significant difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus placebo on fetal death after 36 +0 weeks gestation in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.03 to 0.03) p=1.00.
Comparison 14. ECV + µ-receptor agonist versus ECV + Anaesthesia
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=92) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus anaesthesia on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.04 (95% CI 0.84 to 1.29).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=212) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus anaesthesia on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.90 (95% CI 0.61 to 1.34).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=129) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus anaesthesia on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 2.30 (95% CI 0.21 to 24.74).
- Low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=255) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus anaesthesia on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.02 to 0.02).
Comparison 15. ECV + Nitric oxide donor versus ECV + Placebo
- Very low quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=224) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus nitric oxide donor and ECV plus placebo on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.13 (95% CI 0.59 to 2.16).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=99) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus nitric oxide donor and ECV plus placebo on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.78 (95% CI 0.49 to 1.22).
- Low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=125) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus nitric oxide donor and ECV plus placebo on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.83 (95% CI 0.68 to 1.01).
Comparison 16. ECV + Nitric oxide donor versus ECV + β2 agonist
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=74) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus nitric oxide donor on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.56 (95% CI 0.29 to 1.09).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=97) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus nitric oxide donor and ECV plus β2 agonist on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.98 (95% CI 0.47 to 2.05).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=59) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus nitric oxide donor and ECV plus β2 agonist on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.07 (95% CI 0.73 to 1.57).
Comparison 17. ECV + Talcum powder versus ECV + Gel
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=95) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus talcum powder and ECV plus gel on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.02 (95% CI 0.68 to 1.53).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=95) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus talcum powder and ECV plus gel on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.08 (95% CI 0.67 to 1.74).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=95) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus talcum powder and ECV plus gel on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.94 (95% CI 0.67 to 1.33).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=95) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus talcum powder and ECV plus gel on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.96 (95% CI 0.38 to 10.19).
Comparison 18. Postural management versus No postural management
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=76) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management and no postural management on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.26 (95% CI 0.70 to 2.30).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=76) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management and no postural management on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.11 (95% CI 0.59 to 2.07).
Breech vaginal delivery
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=76) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management and no postural management on breech vaginal delivery in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.15 (95% CI 0.67 to 1.99).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=76) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management and no postural management on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.69 (95% CI 0.31 to 1.52).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=76) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management and no postural management on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.24 (95% CI 0.03 to 2.03).
Comparison 19. Postural management + ECV versus ECV only
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=100) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management plus ECV and ECV only on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.05 (95% CI 0.80 to 1.38).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=100) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management plus ECV and ECV only on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: Peto OR 0.13 (95% CI 0.00 to 6.55).
Economic evidence statements
No economic evidence was identified which was applicable to this review question.
The committee’s discussion of the evidence
Interpreting the evidence, the outcomes that matter most.
Provision of antenatal care is important for the health and wellbeing of both mother and baby with the aim of avoiding adverse pregnancy outcomes and enhancing maternal satisfaction and wellbeing. Breech presentation in labour may be associated with adverse outcomes for the fetus, which has contributed to an increased likelihood of caesarean birth. The committee therefore agreed that cephalic presentation in labour and method of birth were critical outcomes for the woman, and admission to SCBU/NICU, fetal death after 36 +0 weeks gestation, and infant death up to 4 weeks chronological age were critical outcomes for the baby. Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes and birth before 39 +0 weeks of gestation were important outcomes for the baby.
The quality of the evidence
The quality of the evidence for interventions for managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (that is breech presentation) in late pregnancy ranged from very low to high, with most of the evidence being of a very low or low quality.
This was predominately due to serious overall risk of bias in some outcomes; imprecision around the effect estimate in some outcomes; indirect population in some outcomes; and the presence of serious heterogeneity in some outcomes, which was unresolved by subgroup analysis. The majority of included studies had a small sample size, which contributed to imprecision around the effect estimate.
No evidence was identified to inform the outcomes of infant death up to 4 weeks chronological age and birth before 39 +0 weeks of gestation.
There was no publication bias identified in the evidence. However, the committee noted the influence pharmacological developers may have in these trials as funders, and took this into account in their decision making.
Benefits and harms
The committee discussed that in the case of breech presentation, a discussion with the woman about the different options and their potential benefits, harms and implications is needed to ensure an informed decision. The committee discussed that some women may prefer a breech vaginal birth or choose an elective caesarean birth, and that her preferences should be supported, in line with shared decision making.
The committee discussed that external cephalic version is standard practice for managing breech presentation in uncomplicated singleton pregnancies at or after 36+0 weeks. The committee discussed that there could be variation in the success rates of ECV based on the experience of the healthcare professional providing the ECV. There was some evidence supporting the use of ECV for managing a breech presentation in late pregnancy. The evidence showed ECV had a clinically important benefit in terms of cephalic presentations in labour and cephalic vaginal deliveries, when compared to no intervention. The committee noted that the evidence suggested that ECV was not harmful to the baby, although the effect estimate was imprecise relating to the relative rarity of the fetal death as an outcome.
Cephalic (head-down) vaginal birth is preferred by many women and the evidence suggests that external cephalic version is an effective way to achieve this. The evidence suggested ECV increased the chance for a cephalic vaginal birth and the committee agreed that it was important to explain this to the woman during her consultation.
The committee discussed the optimum timing for ECV. Timing of ECV must take into account the likelihood of the baby turning naturally before a woman commences labour and the possibility of the baby turning back to a breech presentation after ECV if it is done too early. The committee noted that in their experience, current practice was to perform ECV at 37 gestational weeks. The majority of the evidence demonstrating a benefit of ECV in this review involved ECV performed around 37 gestational weeks, although the review did not look for studies directly comparing different timings of ECV and their relative success rates.
The evidence in this review excluded women with previous complicated pregnancies, such as those with previous caesarean section or uterine surgery. The committee discussed that a previous caesarean section indicates a complicated pregnancy and that this population of women are not the focus of this guideline, which concentrates on women with uncomplicated pregnancies.
The committee’s recommendations align with other NICE guidance and cross references to the NICE guideline on caesarean birth and the section on breech presenting in labour in the NICE guideline on intrapartum care for women with existing medical conditions or obstetric complications and their babies were made.
ECV combined with pharmacological agents
There were some small studies comparing a variety of pharmacological agents (including β2 agonists, Ca 2+ channel blockers, µ-receptor agonists and nitric oxide donors) given alongside ECV. Overall the evidence typically showed no clinically important benefit of adding any pharmacological agent to ECV except in comparisons with a control arm with no ECV where it was not possible to isolate the effect of the ECV versus the pharmacological agent. The evidence tended toward benefit most for β2 agonists and µ-receptor agonists however there was no consistent or high quality evidence of benefit even for these agents. The committee agreed that although these pharmacological agents are used in practice, there was insufficient evidence to make a recommendation supporting or refuting their use or on which pharmacological agent should be used.
The committee discussed that the evidence suggesting µ-receptor agonist, remifentanil, had a clinically important benefit in terms reducing breech vaginal births after unsuccessful ECV was biologically implausible. The committee noted that this pharmacological agent has strong sedative effects, depending on the dosage, and therefore studies comparing it to a placebo had possible design flaws as it would be obvious to all parties whether placebo or active drug had been received. The committee discussed that the risks associated with using remifentanil such as respiratory depression, likely outweigh any potential added benefit it may have on managing breech presentation.
There was some evidence comparing different anaesthetics together with ECV. Although there was little consistent evidence of benefit overall, one small study of low quality showed a combination of 2% lidocaine and epinephrine via epidural catheter (anaesthesia) with ECV showed a clinically important benefit in terms of cephalic presentations in labour and the method of birth. The committee discussed the evidence and agreed the use of anaesthesia via epidural catheter during ECV was uncommon practice in the UK and could be expensive, overall they agreed the strength of the evidence available was insufficient to support a change in practice.
Postural management
There was limited evidence on postural management as an intervention for managing breech presentation in late pregnancy, which showed no difference in effectiveness. Postural management was defined as ‘knee-chest position for 15 minutes, 3 times a day’. The committee agreed that in their experience women valued trying interventions at home first which might make postural management an attractive option for some women, however, there was no evidence that postural management was beneficial. The committee also noted that in their experience postural management can cause notable discomfort so it is not an intervention without disadvantages.
Cost effectiveness and resource use
A systematic review of the economic literature was conducted but no relevant studies were identified which were applicable to this review question.
The committee’s recommendations to offer external cephalic version reinforces current practice. The committee noted that, compared to no intervention, external cephalic version results in clinically important benefits and that there would also be overall downstream cost savings from lower adverse events. It was therefore the committee’s view that offering external cephalic version is cost effective and would not entail any resource impact.
Andersen 2013
Brocks 1984
Bujold 2003
Burgos 2016
Chalifoux 2017
Chenia 1987
Collaris 2009
Dafallah 2004
Diguisto 2018
Dugoff 1999
El-Sayed 2004
Fernandez 1997
Hindawi 2005
Hilton 2009
Hofmeyr 1983
Mahomed 1991
Mancuso 2000
Marquette 1996
Mohamed Ismail 2008
NorAzlin 2005
Robertson 1987
Schorr 1997
Sullivan 2009
VanDorsten 1981
Vallikkannu 2014
Weiniger 2010
Appendix A. Review protocols
Review protocol for review question: What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy? (PDF, 260K)
Appendix B. Literature search strategies
Literature search strategies for review question: What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy? (PDF, 281K)
Appendix C. Clinical evidence study selection
Clinical study selection for: What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy? (PDF, 113K)
Appendix D. Clinical evidence tables
Clinical evidence tables for review question: What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy? (PDF, 1.2M)
Appendix E. Forest plots
Forest plots for review question: What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy? (PDF, 678K)
Appendix F. GRADE tables
GRADE tables for review question: What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy? (PDF, 1.0M)
Appendix G. Economic evidence study selection
Economic evidence study selection for review question: what is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy, appendix h. economic evidence tables, economic evidence tables for review question: what is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy, appendix i. economic evidence profiles, economic evidence profiles for review question: what is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy, appendix j. economic analysis, economic evidence analysis for review question: what is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy.
No economic analysis was conducted for this review question.
Appendix K. Excluded studies
Excluded clinical and economic studies for review question: what is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy, clinical studies, table 24 excluded studies.
View in own window
Economic studies
No economic evidence was identified for this review.
Appendix L. Research recommendations
Research recommendations for review question: what is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy.
No research recommendations were made for this review question.
Evidence reviews underpinning recommendation 1.2.38
These evidence reviews were developed by the National Guideline Alliance, which is a part of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
Disclaimer : The recommendations in this guideline represent the view of NICE, arrived at after careful consideration of the evidence available. When exercising their judgement, professionals are expected to take this guideline fully into account, alongside the individual needs, preferences and values of their patients or service users. The recommendations in this guideline are not mandatory and the guideline does not override the responsibility of healthcare professionals to make decisions appropriate to the circumstances of the individual patient, in consultation with the patient and/or their carer or guardian.
Local commissioners and/or providers have a responsibility to enable the guideline to be applied when individual health professionals and their patients or service users wish to use it. They should do so in the context of local and national priorities for funding and developing services, and in light of their duties to have due regard to the need to eliminate unlawful discrimination, to advance equality of opportunity and to reduce health inequalities. Nothing in this guideline should be interpreted in a way that would be inconsistent with compliance with those duties.
NICE guidelines cover health and care in England. Decisions on how they apply in other UK countries are made by ministers in the Welsh Government , Scottish Government , and Northern Ireland Executive . All NICE guidance is subject to regular review and may be updated or withdrawn.
- Cite this Page National Guideline Alliance (UK). Management of breech presentation: Antenatal care: Evidence review M. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE); 2021 Aug. (NICE Guideline, No. 201.)
- PDF version of this title (2.2M)
In this Page
Other titles in this collection.
- NICE Evidence Reviews Collection
Related NICE guidance and evidence
- NICE Guideline 201: Antenatal care
Supplemental NICE documents
- Supplement 1: Methods (PDF)
- Supplement 2: Health economics (PDF)
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Review Identification of breech presentation: Antenatal care: Evidence review L [ 2021] Review Identification of breech presentation: Antenatal care: Evidence review L National Guideline Alliance (UK). 2021 Aug
- Vaginal delivery of breech presentation. [J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2009] Vaginal delivery of breech presentation. Kotaska A, Menticoglou S, Gagnon R, MATERNAL FETAL MEDICINE COMMITTEE. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2009 Jun; 31(6):557-566.
- Review Cephalic version by moxibustion for breech presentation. [Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005] Review Cephalic version by moxibustion for breech presentation. Coyle ME, Smith CA, Peat B. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18; (2):CD003928. Epub 2005 Apr 18.
- [Fetal expulsion: Which interventions for perineal prevention? CNGOF Perineal Prevention and Protection in Obstetrics Guidelines]. [Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2...] [Fetal expulsion: Which interventions for perineal prevention? CNGOF Perineal Prevention and Protection in Obstetrics Guidelines]. Riethmuller D, Ramanah R, Mottet N. Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2018 Dec; 46(12):937-947. Epub 2018 Oct 28.
- Foetal weight, presentaion and the progress of labour. II. Breech and occipito-posterior presentation related to the baby's weight and the length of the first stage of labour. [J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1961] Foetal weight, presentaion and the progress of labour. II. Breech and occipito-posterior presentation related to the baby's weight and the length of the first stage of labour. BAINBRIDGE MN, NIXON WC, SMYTH CN. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1961 Oct; 68:748-54.
Recent Activity
- Management of breech presentation Management of breech presentation
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

- Breech Presentation
Breech presentation means that your baby is in a buttocks-first or feet-first position. Babies are usually in a head-first position. A breech position can make it hard for the baby’s head to fit through the birth canal during delivery. This can cause lack of oxygen or nerve damage in your baby.
Checking for breech presentation
Your healthcare provider can tell that your baby is in a breech presentation by gently pressing on your belly. If after about 35 weeks your baby still isn’t head-first, you may have a test called an ultrasound. This test uses sound waves to form an image of your baby on a screen.
Types of breech presentations
As you get close to your due date, your baby may be in one of these breech positions:
Frank breech. The baby's buttocks are closest to the birth canal. The hips are flexed, and the legs are straight up in front of the body. The feet are near the baby's head.
Complete breech. The baby's knees are bent, and the feet and buttocks are closest to the birth canal.
Incomplete breech. One or both of the baby's feet are closest to the birth canal.
Delivering your baby
Even if the baby’s position can’t be changed, a breech baby can sometimes be born vaginally. But this is rare. Your healthcare provider will talk with you about the risks. More often, a surgical delivery (cesarean section or C-section) is done. You will have medicine to block pain (anesthesia). But you may stay awake and alert.
Once you deliver
Whether you give birth vaginally or by C-section, you and your baby will most likely be fine. Just because your baby is in a breech position doesn’t mean that they will have health problems.
Can you have a vaginal delivery?
In some cases, your healthcare provider may try to turn the baby head-down by putting pressure on your belly. This method is called an external cephalic version. If this works, you might be able to have a vaginal delivery. Your provider will talk about this with you.
Related Items
Patient education.
- After a Vaginal Birth
- If Your Baby Is Breech: External Cephalic Version (ECV)
- Labor and Childbirth- Right after Birth
- Labor and Childbirth: Active Labor
- View All 15
- How to Prepare for Childbirth
- How To Get Pregnant
- Infertility
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Second Pregnancy
- Giving Birth
- Post Pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
- Development
- Browse Names
- Play & Activities
- Coloring Pages
- Food & Nutrition
- Health & Fitness
- Style & Beauty Care
- Collaborations
- New Parents
- Single Parenting
- Relationships
- Baby Eye Color Calculator
- Online Pregnancy Test
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- Implantation Calculator
- hCG Calculator
- Period Calculator
- ovulation calculator
- pregnancy due date calculator
- Child Height Predictor
- Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator
- Breast Milk Calculator
- Child Growth Percentile Calculator
- Baby Cost Calculator
- BMI Calculator For Kids & Teens
- Contraction Calculator
- Immunization Scheduler and Chart
- C-Section Checklist
- Online Twin Pregnancy Quiz
- Numerology calculator
- Child Blood Type Calculator
- Nakshatra Calculator
- Diaper Bag Checklist
- Baby Name Combiner
Home • Baby • Health
7 Common Breech Baby Birth Defects And Their Complications
Follow the course of action your doctor recommends for a safe delivery in this situation.
Dr. Supriya Mahajan is a pediatrician and pediatric hepatologist with 16 years of experience. She completed her MBBS from Shyam Shah Medical College and diploma from the National Board of Education, New Delhi. She went on to gain specializa... more
Dr. Bisny T. Joseph is a Georgian Board-certified physician. She has completed her professional graduate degree as a medical doctor from Tbilisi State Medical University, Georgia. She has around 5 yea... more
Rohit Garoo is a writer-turned-editor with over 9 years of experience in content writing, editing, and content marketing. He did his bachelors in Science at St. Xavier's College, Hyderabad, and master... more
Vidya did her post-graduation in Biotechnology from Osmania University, Hyderabad. Her interest in scientific research and writing made her pursue a career in writing, in which she now has over five y... more
MomJunction believes in providing reliable, research-backed information to you. As per our strong editorial policy requirements, we base our health articles on references (citations) taken from authority sites, international journals, and research studies. However, if you find any incongruencies, feel free to write to us .
Image: Shutterstock
The breech presentation occurs during delivery when the baby’s buttocks, feet, or both emerge first from the birth canal. The birth position may increase the risk of birth defects or congenital malformations. Breech babies’ birth defects may vary from physical issues to genetic disorders.
Babies born breech do not move their heads down towards the birth canal as the due date approaches to be born with vertex presentation. About 3-4% of full-term infants are born with breech presentation (1) .
Despite the presence of a breech presentation, not all babies born with it may develop birth defects.
Types Of Breech Babies
There are three types of breech positions (2) .
- Frank breech: This is the most common breech position where buttocks are delivered first. Legs are positioned up in front of the body and feet near the head.
- Complete breech: The buttocks are presented near the birth canal. The knees are bent, and the feet are placed near the buttocks.
- Incomplete breech: Baby’s buttocks and a foot are presented in the birth canal. The other leg stays up towards the body like seen in the frank breech. If one foot and buttocks emerge first, it is called footling breech. If both feet appear first since both legs are extended, it is called double footling breech.
Besides these positions, a baby can be in a horizontal position across the uterus. In this position, the shoulder of the baby is positioned such that it will enter the birth canal first. It is called the transverse lie position ( 3 ).
What Causes A Baby To Be Breech?
Some common factors that might be responsible for a baby being in a breech position include ( 3 ) ( 4 ):
- The mother has been pregnant before.
- The amount of amniotic fluid present is either too much or too little.
- The mother is expecting twins or triplets.
- The uterus has abnormal growths, such as fibroids.
- The uterus has an irregular shape.
- The placenta covers most or a part of the uterus’s opening, a condition known as placenta previa.
- The fetus is preterm.
- The fetus has some type of congenital disability that prevents it from turning in the head-down position.
What Rate Of Breech Babies Have Birth Defects?
There may be a slight increase in the number of birth defects among breech babies. A study noted that 11.7% of infants born breech had at least one congenital anomaly . In comparison, only 5.1% of babies born with vertex presentation had any congenital anomaly (5) . This occurred regardless of the term of pregnancy.
The study established that breech presentation at birth may indicate congenital anomalies. Congenital defects could prevent the baby from moving to a cephalic position (head down) before delivery. Although the breech position may indicate a possible congenital anomaly, it may not be noted in all breech babies.
A study showed that the incidence of severe birth injury on breech presentation might differ with the gestational age. The graph below shows that most severe birth injuries due to breech vaginal delivery occurred at 32 weeks gestation. The incidence reduces with a stable occurrence between 37 and 39 weeks. The number of injuries spikes in the 41st week but does not reach a peak like it did at 32 weeks.
Incidence of severe birth injuries in breech delivery at different gestational weeks
What birth defects are associated with breech babies.
Studies have shown that the following birth defects are commonly seen in babies born breech (6) .
- Congenital hip deformity or hip dysplasia: Breech babies may have congenital hip problems, such as hip dysplasia , since their movements in the womb can be limited . It can be especially common in frank breech where knees are extended. Early detection and treatment of hip dysplasia are crucial for preventing developmental delays in walking and other motor skills.
- Nervous system and musculoskeletal system malformations: Breech babies may have a higher risk of neurological or musculoskeletal disorders due to reduced or lack of movements in the womb. These malformations can be the reason for the reduced ability to turn into the cephalic presentation (vertex) before delivery.
- Structural deformities of fetal ears, face, eyes, and neck: These conditions may affect the fetal rotation to a cephalic presentation near the due date.
- Cleft lip or cleft palate, respiratory and circulatory system problems: These conditions may increase breech presentation due to polyhydramnios (too much amniotic fluid).
- Genital and urinary malformations: These defects may contribute to breech position due to polyhydramnios (too much amniotic fluid) or oligohydramnios (too little amniotic fluid).
- Chromosomal anomalies: Intrauterine growth restrictions associated with chromosomal anomalies may cause breech presentation.
- Down syndrome: Babies with Down syndrome could be born breech due to their inability to turn to vertex position before birth.
Studies have shown that various malformations are associated with breech birth except for digestive system problems . Malformations may primarily cause the baby to fail to rotate to the cephalic presentation before birth.
Complications Of Breech Presentation
Umbilical cord prolapse and head entrapment are significant problems of breech delivery (7) . If the umbilical cord is compressed during breech birth, it could restrict the blood and oxygen flow to the fetus, leading to delivery complications, including premature birth and low birth weight.
Breech birth can be associated with fetal distress in many cases . Delay in delivery and meconium-stained amniotic fluid can be a reason for it. There is also an increased risk of hip dislocation during a breech delivery, which may require neonatal intensive care.
How To Prevent Problems Of Breech Births?
There is no way to prevent birth defects in breech babies. However, problems associated with breech birth could be prevented by changing the position of the fetus before the delivery. The following procedures or techniques may help to avoid breech birth.
1. External cephalic version
It is a procedure that turns the fetus from breech or side-lying (transverse) position to head-down or vertex position before the labor. This is usually done at 37 weeks of gestation before the labor begins but rarely done during the labor before the amniotic sac ruptures (3) .
Doctors may give tocolytic injections before the procedure to prevent uterine contractions and relax the uterus. After visualizing the baby’s position, placental location, and amniotic fluid volume, the doctor may gently push the abdomen to change the position. The fetus is closely monitored with fetal ultrasound and electronic fetal heart monitoring. If the first attempt fails, the second attempt may be made under epidural anesthesia.
Although complications are rare in the external cephalic version, there is always a possibility. Therefore, the procedure is always done in a hospital where women can have emergency C-sections. It is possible to have a vaginal birth after a successful external cephalic version. If there is no complication after an unsuccessful version, a scheduled cesarean section is done.
ECV may not be tried if there is more than one fetus, known fetal anomalies, abnormalities of the reproductive system, wrong placement of the placenta, or placental abruption (8) .
2. Chiropractic care
The Webster technique is a chiropractic method to move the fetus from breech position to normal position. This technique focuses on relaxing the uterus and ligaments, reducing stress on the pelvis. This technique is based on the theory that a more relaxed uterus lets the breech baby turn naturally.
Although it is attempted in chiropractic care, a few existing scientific studies backing the techniques are weak in conclusion (9) .
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are breech babies less intelligent?
Some people believe that a baby’s presentation at birth is related to their intelligence. However, research shows that there’s no relationship between a baby’s position at birth and their intelligence later in life (10) .
2. Do breech babies have learning disabilities?
According to a study, the average frequency of hyperkinesia (state of excessive restlessness and hyperactivity) and learning disability in children born with breech presentation was 14%. On the other hand, it was found to be two percent in children born in vertex position (11) . It can be deduced that babies born in the breech position might have learning disabilities. However, it doesn’t happen in all the babies born in this position.
3. Does breech position mean the baby will have Down syndrome?
No clinical studies or research studies were found that could demonstrate that babies born in the breech position will have Down syndrome.
4. Do breech babies have leg problems?
No studies or clinical reports suggest that all babies born in the breech position will have leg problems. Some breech babies after birth may keep their legs in the air for the first few days. However, the legs usually return to their normal position gradually (12) .
Congenital disabilities are sometimes caused by fetal malpresentation, such as breech birth. However, it is impossible to generalize that all babies born in breech positions will have congenital disabilities or that babies born with vertex presentation will be healthy. In fact, various maternal and fetal factors, such as the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus or intrauterine growth restrictions, can cause breech presentations. Therefore, doctors may recommend early hospitalization for interventions or cesarean section delivery if there is a risk of breech presentation or any possible risks for vaginal breech delivery.
Infographic: What Kinds Of Injuries Can Happen During Breech Birth?
Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Get the high-quality PDF version of this infographic.
Key Pointers
- The breech position has three types – Frank, incomplete, and complete.
- The breech position may indicate a risk of congenital anomaly, but not all breech babies have them.
- Hip dysplasia, cleft lip or palate, and down syndrome are a few congenital anomalies associated with the breech position.
- Changing the fetal position before the delivery could avert issues linked with a breech birth.
In this informative video, you can learn about breech babies, risks, natural vs cesarean birth, and more! Get the facts explained by an experienced midwife.
1. Management of Breech Presentation; Royal College of Obstetricians & Gynecologists 2. Breech Presentation; U.S. National Library of Medicine 3. If Your Baby Is Breech; The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists 4. Breech Baby; Cleveland Clinic 5. Breech presentation at delivery: a marker for congenital anomaly?; National Library of Medicine 6. Congenital anomalies in breech presentation: A nationwide record linkage study; Wiley Online Library 7. Breech position; Birth Injury Help Center 8. If Your Baby Is Breech; The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists 9. Breech repositioning unresponsive to Webster technique: coexistence of oligohydramnios; U.S. National Library of Medicine 10. Martha G Eide et al.; Breech delivery and intelligence: a population-based study of 8,738 breech infants ; NCBI (2005) 11. Stefan Fianu &Ingemar Joelsson; Minimal brain dysfunction in children born in breech presentation ; Taylor & Francis (1978) 12. Breech ; Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals NHS Trust 13. Breech Births ; American Pregnancy Association 14. Caesarean sections ; Australian Institute of Health and Welfare
- Fact-checker
Dr. Supriya Mahajan DNB, PDCC
Dr bisny t. joseph medical doctor, rohit garoo bsc, mba, vidya tadapatri msc (biotechnology), latest articles, metallic taste in mouth during pregnancy: its causes & tips.
Hormonal fluctuations may be a reason, but the condition does not occur in all women.
How To Burp A Newborn Baby: Right Time, Positions And Tips
Burping an infant could help relieve their irritability and discomfort after a feed.
What Causes Newborn Sneezing And Is It Normal?
It is a harmless protective reflex in babies, but see a doctor if it occurs frequently.
50 Surprising Pregnancy Facts & Myths Every Woman Should Know
These facts will enhance your awareness about pregnancy and help you enjoy the journey more.
3 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Baby Development & Tips To Follow
The signs of early pregnancy can help take timely medical steps and care.
Lexapro During Pregnancy: Safety, Risks And Side Effects
Miscarriage and the existence of congenital heart defects are possible associated risks.
When Do Sucking Reflexes In Babies Develop & How To Test Them?
Baby sucking their fingers or thumbs is not a developmental disorder but a reflex.
Is It Normal For A Baby To Be Born With Natal Teeth?
The presence of natal teeth at birth can be hereditary or due to a medical condition.
Do All Babies Have Blue Eyes When They Are Born?
Genetics and underlying conditions are often the possible causative factors.
What Is Asymmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex And Its Causes
Retainment of ATNR in babies past seven months needs to be evaluated to prevent adverse outcomes.
Ectopic Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, And Risks
As the egg is implanted in an improper place, prompt medical attention is required.
10 Types Of Primitive Reflex In Babies & Why It is Important
Each type of primitive reflex facilitates age-appropriate survival skills in babies.
Home » The Breech Presentation – What Does It Mean For Birth?
The Breech Presentation – What Does It Mean For Birth?

written on 2 August 2023
Table of contents
What Is A Breech Presentation?
Different birth positions in breech presentation, pure breech presentation, complete breech-foot position, imperfect breech-foot position, perfect foot position with both legs extended downward, imperfect foot position, perfect knee position, imperfect knee position, what are the causes and risks of breech presentation.
- Premature birth , because the baby has not yet turned at the premature time of birth.
- Very large baby that has no room to turn in the uterus.
- Little amniotic fluid.
- Very much amniotic fluid.
- General inactivity of the baby, so he or she does not move much.
- Frequent movements of the baby.
- Very narrow uterus and abnormalities of the uterus.
- Narrow pelvis or pelvic anomaly.
- Unfavorable position of the placenta.
- Too short umbilical cord.
When Is It Time For The Baby To Turn?
What are the risks of breech presentation, allow birth baby from vagina by external turning, how to induce your baby to turn around by yourself, indian bridge, acupuncture and foot reflexology, moxibustion, requirements for the birth baby from the vagina in breech presentation, birth by cesarean section in breech presentation, breech presentation: conclusion, the best products for you and your baby..
With a baby monitor, you can use your time flexibly, sleep peacefully at night and still know at all times that your baby is doing well.
A good breastfeeding pillow has several advantages, because it helps you not only to breastfeed, but also to fall asleep and is also suitable as a nest.
A diaper bag offers you a lot of storage space, so that you have everything you need for your baby on the go - from the changing pad to the bottle.
A pucksack gives your baby the feeling of security, like in the womb, and thus supports a peaceful and restful sleep.
Bicycle trailers can be used in combination with a baby seat shortly after birth. They are not only safer than child seats but also more comfortable.
A playpen can be very practical in everyday life! Which model is suitable for your needs, you can read in my guide.
The first bed accompanies your child for years. Fortunately, there are beds that grow with your child. I have made for you on the search for the best baby beds.
A stroller is a worthwhile purchase. But there are the most diverse models on the market. Find out which is the right one.
Radiant heaters provide your child with the necessary warmth when changing diapers or after bathing.
Side beds are very practical and offer both mother and baby a lot of advantages, because for babies, especially in the first months of life, it is reassuring to be able to sleep next to their parents.
Ähnliche Beiträge

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Babies under 1 year
- Baby supplies
- Baby clothes
- Toddlers 1 to 3 years
- Books for toddlers
- Educational toys for toddlers
- Games for toddlers
- Children 4 to 7 years
- Children books 4 to 7 years
- Children's clothing
- Children's shoes
- Educational toys for children
- School Supplies
- Games for children
- Clothing for mothers
- Clothing for fathers
- Clothing for children
- Clothing for toddlers
- Clothing for babies
- Baby & children's beds
- Decoration & Lighting children's room
- Children's furniture
- Garden toys
- Movement & Coordination games
- Building & Construction toys
- Musical instruments
- Wooden toys
- Bath & Water toys
- Eductional toys
- Puppet &/ Role play
- Toys for girls
- Toy cars & Race tracks
- Rompers, T-shirts & Mugs
- Winter sports
- Leisure, sports und games
- Travel guides
- Strollers & Buggies
- Children's Vehicles
- Children's Bikes
- Balance bikes & Scooters
- Electric vehicles
- Child seats
- Birth gifts
- Gifts for children
- Gifts for women
- Gifts for men
- Radio plays
- Children's books
- Children's dictionaries
- Guide for parents
- Kitchen & Household
- Room air conditioners
- Fridges & Freezers
- Cleaning equipment
- Laundry care
- Sport & Fitness equipment
- Kitchen appliances
- Hardware stores
- Garden tools
- Sextoys for women
- Sextoys for men
- Sextoys for couples
Journalismus ist nicht umsonst.
Ihnen hat unser Beitrag gefallen? Dann unterstützen Sie unsere Redaktion und spenden Sie einen Betrag Ihrer Wahl, um die Website zu erhalten. Wir danken Ihnen!
AT&T resets account passcodes after millions of customer records leak online
Us telco giant takes action after 2019 data spill.

Phone giant AT&T has reset millions of customer account passcodes after a huge cache of data containing AT&T customer records was dumped online earlier this month, TechCrunch has exclusively learned.
The U.S. telco giant initiated the passcode mass-reset after TechCrunch informed AT&T on Monday that the leaked data contained encrypted passcodes that could be used to access AT&T customer accounts.
A security researcher who analyzed the leaked data told TechCrunch that the encrypted account passcodes are easy to decipher. TechCrunch alerted AT&T to the security researcher’s findings.
In a statement provided Saturday, AT&T said: “AT&T has launched a robust investigation supported by internal and external cybersecurity experts. Based on our preliminary analysis, the data set appears to be from 2019 or earlier, impacting approximately 7.6 million current AT&T account holders and approximately 65.4 million former account holders.”
“AT&T does not have evidence of unauthorized access to its systems resulting in exfiltration of the data set,” the statement also said.
TechCrunch held the publication of this story until AT&T could begin resetting customer account passcodes. AT&T also has a post on what customers can do to keep their accounts secure .
AT&T customer account passcodes are typically four-digit numbers that are used as an additional layer of security when accessing a customer’s account, such as calling AT&T customer service, in retail stores, and online.
This is the first time that AT&T has acknowledged that the leaked data belongs to its customers, some three years after a hacker claimed the theft of 73 million AT&T customer records. AT&T had denied a breach of its systems , but the source of the leak remains inconclusive.
AT&T said Saturday that “it is not yet known whether the data in those fields originated from AT&T or one of its vendors.”
In 2021, the hacker claiming the AT&T breach posted only a small sample of records, making it difficult to check if the data was authentic. Earlier in March, a data seller published the full 73 million alleged AT&T records online on a known cybercrime forum, allowing for a more detailed analysis of the leaked records. AT&T customers have since confirmed that their leaked account data is accurate .
The leaked data includes AT&T customer names, home addresses, phone numbers, dates of birth and Social Security numbers.
Security researcher Sam “Chick3nman” Croley told TechCrunch that each record in the leaked data also contains the AT&T customer’s account passcode in an encrypted format. Croley double-checked his findings by looking up records in the leaked data against AT&T account passcodes known only to him.
Croley said it was not necessary to crack the encryption cipher to unscramble the passcode data.
Croley took all of the encrypted passcodes from the 73 million dataset and removed every duplicate. The result amounted to about 10,000 unique encrypted values, which correlates to each four-digit passcode permutation ranging from 0000 to 9999, with a few outliers for the small number of AT&T customers with account passcodes longer than four digits.
According to Croley, the insufficient randomness of the encrypted data means it’s possible to guess the customer’s four-digit account passcode based on surrounding information in the leaked dataset.
It’s not uncommon for people to set passcodes — particularly if limited to four digits — that mean something to them. That might be the last four digits of a Social Security number or the person’s phone number, the year of someone’s birth, or even the four digits of a house number. All of this surrounding data is found in almost every record in the leaked dataset.
By correlating encrypted account passcodes to surrounding account data — such as customer dates of birth, house numbers, and partial Social Security numbers and phone numbers — Croley was able to reverse-engineer which encrypted values matched which plaintext passcode.
AT&T said it will contact all of the 7.6 million existing customers whose passcodes it reset, as well as current and former customers whose personal information was compromised.
AT&T won’t say how its customers’ data spilled online
Watch CBS News
AT&T informs users of data breach and resets millions of passcodes
March 30, 2024 / 2:51 PM EDT / CBS/AP
AT&T said it has begun notifying millions of customers about the theft of personal data recently discovered online.
The telecommunications giant said Saturday that a dataset found on the "dark web" contains information such as Social Security numbers for about 7.6 million current AT&T account holders and 65.4 million former account holders.
The company said it has already reset the passcodes of current users and will be communicating with account holders whose sensitive personal information was compromised.
It is not known if the data "originated from AT&T or one of its vendors," the company said in a statement. The compromised data is from 2019 or earlier and does not appear to include financial information or call history, it said. In addition to passcodes and Social Security numbers, it may include email and mailing addresses, phone numbers and birth dates.
It is not the first crisis this year for the Dallas-based company.
New York prosecutors said they are opening an investigation into a wireless network outage in February that left thousands of AT&T customers across the U.S. without cellphone service for roughly 12 hours.
The outage, which also affected some Consumer Cellular, T-Mobile, UScellular and Verizon subscribers, led to widespread frustration by phone users and briefly disrupted 911 service in some communities.
AT&T apologized for the network disruption and offered a $5 credit to customers .
More from CBS News

New shelter could house a third of Stockton's homeless population

Modesto home converted to pot grow house catches fire

Sacramento mom accused of letting her toddler drown in tub arrested in Stockton

$30K in stolen Nike apparel linked to one suspect, Sacramento County detectives say
What is Good Friday? What the holy day means for Christians around the world

Christians around the world observe Good Friday two days before Easter, but what is it, and why do they commemorate the holy day?
The holiday is part of Holy Week, which leads up to Easter Sunday. Palm Sunday kicks off the series of Christian holy days that commemorate the Crucifixion and celebrate Jesus Christ's resurrection.
"Good Friday has been, for centuries now, the heart of the Christian message because it is through the death of Jesus Christ that Christians believe that we have been forgiven of our sins," Daniel Alvarez, an associate teaching professor of religious studies at Florida International University, told USA TODAY.
What is Holy Saturday? What the day before Easter means for Christians around the world
When is Good Friday?
Good Friday is always the Friday before Easter. It's the second-to-last day of Holy Week.
In 2024, Good Friday will fall on March 29.
What is Good Friday?
Good Friday is the day Christ was sacrificed on the cross. According to Britannica , it is a day for "sorrow, penance, and fasting."
"Good Friday is part of something else," Gabriel Radle, an assistant professor of theology at the University of Notre Dame, previously told USA TODAY. "It's its own thing, but it's also part of something bigger."
Are Good Friday and Passover related?
Alvarez says that Good Friday is directly related to the Jewish holiday, Passover.
Passover , or Pesach, is a major Jewish holiday that celebrates the Israelites’ exodus from Egypt.
"The whole Christian idea of atoning for sin, that Jesus is our atonement, is strictly derived from the Jewish Passover tradition," said Alvarez.
How is that possible?
According to the professor, Passover celebrates the day the "Angel of Death" passed over the homes of Israelites who were enslaved by the Egyptians. He said that the Bible states when the exodus happened, families were told to paint their doors with lamb's blood so that God would spare the lives of their firstborn sons.
Alvarez says this is why Christians call Jesus the "lamb of God." He adds that the symbolism of the "blood of the lamb" ties the two stories together and is why Christians believe God sacrificed his firstborn son. Because, through his blood, humanity is protected from the "wrath of a righteous God that cannot tolerate sin."
He adds that the stories of the exodus and the Crucifixion not only further tie the stories together but also emphasize just how powerful the sacrifice of the firstborn and the shedding of blood are in religion.
"Jesus is the firstborn, so the whole idea of the death of the firstborn is crucial," said Alvarez.
He adds that the sacrifice of the firstborn, specifically a firstborn son, comes from an ancient and "primitive" idea that the sacrifice unleashes "tremendous power that is able to fend off any kind of force, including the wrath of God."
Why Is Good Friday so somber?
Alavarez says people might think this holiday is more depressing or sad than others because of how Catholics commemorate the Crucifixion.
"I think [it's] to a level that some people might think is morbid," said Alvarez.
He said Catholics not only meditate on Jesus' death, but primarily focus on the suffering he faced in the events that led up to his Crucifixion. That's what makes it such a mournful day for people.
But, the professor says that Jesus' suffering in crucial to Christianity as a whole.
"The suffering of Christ is central to the four Gospels," said Alvarez. "Everything else is incidental."
According to the professor, statues that use blood to emphasize the way Jesus and Catholic saints suffered is very common in Spanish and Hispanic Countries, but not as prevalent in American churches.
Do you fast on Good Friday?
Father Dustin Dought, the executive director of the Secretariat of Divine Worship of the United States Conference of Catholic Bishops, previously told USA TODAY that Good Friday and Ash Wednesday are the two days in the year that Roman Catholics are obliged to fast.
"This practice is a way of emptying ourselves so that we can be filled with God," said Dought.
What do you eat on Good Friday?
Many Catholics do not eat meat on any Friday during Lent. Anything with flesh is off-limits. Dought says this practice is to honor the way Jesus sacrificed his flesh on Good Friday.
Meat that is off limits includes:
Instead, many Catholics will eat fish. According to the Marine Stewardship Council , this is allowed because fish is considered to be a different type of flesh.
Contributing: Jordan Mendoza ; USA TODAY
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
AT&T Resets Millions of Passcodes After Customer Records Are Leaked
Nearly eight million customers and 65.4 million former account holders were affected by the data breach, the company said.

By Aimee Ortiz
The telecommunications giant AT&T announced on Saturday that it had reset the passcodes of 7.6 million customers after it determined that compromised customer data was “released on the dark web.”
“Our internal teams are working with external cybersecurity experts to analyze the situation,” AT&T said . “To the best of our knowledge, the compromised data appears to be from 2019 or earlier and does not contain personal financial information or call history.”
The company said that “information varied by customer and account,” but that it may have included a person’s full name, email address, mailing address, phone number, Social Security number, date of birth, AT&T account number and passcode.
In addition to those 7.6 million customers, 65.4 million former account holders were also affected.
The company said it would be “reaching out to individuals with compromised sensitive personal information separately and offering complimentary identity theft and credit monitoring services.”
AT&T said it reset the passcodes for those affected and directed customers to a site with details about how to reset them. It also said that it was starting a “robust investigation supported by internal and external cybersecurity experts.”
A company representative did not address specific questions about how the breach happened or why it went unnoticed for so long.
TechCrunch, which first reported on the passcode reset , said it informed AT&T on Monday that “the leaked data contained encrypted passcodes that could be used to access AT&T customer accounts.”
TechCrunch said it delayed publishing its article until the company “could begin resetting customer account passcodes.”
In its report, TechCrunch said that “this is the first time that AT&T has acknowledged that the leaked data belongs to its customers, some three years after a hacker claimed the theft of 73 million AT&T customer records.”
AT&T had previously denied a breach of its systems but how the leak happened was unclear, TechCrunch reported.
AT&T said that it did not know whether the leaked data “originated from AT&T or one of its vendors” and that it “does not have evidence of unauthorized access to its systems resulting in theft of the data set.”
The episode comes after AT&T customers experienced a widespread outage last month that temporarily cut off connections for users across the United States for several hours. The Feb. 22 outage affected customer in cities including Atlanta, Los Angeles and New York.
At its peak, there were around 70,000 reports of disrupted service for the wireless carrier, according to Downdetector.com , which tracks user reports of telecommunication and internet disruptions.
A few days later, AT&T offered customers affected by the outage a $5 credit in an effort to “make it right.”
Aimee Ortiz covers breaking news and other topics. More about Aimee Ortiz
Explore Our Business Coverage
Dive deeper into the people, issues and trends shaping the world of business..
Phoenix Housing Crunch: A swelling population coupled with development restrictions have contributed to a dire shortage of affordable housing in the biggest city in Arizona , one of the six states likely to determine the U.S. presidential election.
A Billionaire Online Warrior: Bill Ackman, an obstinate hedge-funder who loves a public crusade, has used X to push himself into a new realm of celebrity .
Cancel Smartphones: The N.Y.U. professor Jonathan Haidt became a favorite in Silicon Valley for his work on what he called the “coddling” of young people. Now, he has an idea for fixing Gen Z .
Landline Pride: Traditional phones may seem like relics in the iPhone era, but a recent AT&T cellular service outage had some landline lovers extolling their virtues.
C.E.O. Dreams: Fresh business school graduates are raising “search funds” from willing investors to buy companies they can lead.
Nelson Peltz Wants Respect: The longtime corporate agitator feels misunderstood . Maybe his fight with Disney could change that.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A breech baby, or breech birth, is when your baby's feet or buttocks are positioned to come out of your vagina first. Your baby's head is up closest to your chest and its bottom is closest to your vagina. Most babies will naturally move so their head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. Breech is common in early ...
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. The complete breech has the ...
At full term, around 3%-4% of births are breech. The different types of breech presentations include: Complete: The fetus's knees are bent, and the buttocks are presenting first. Frank: The fetus's legs are stretched upward toward the head, and the buttocks are presenting first. Footling: The fetus's foot is showing first.
A complete breech is the least common type of breech presentation. Other Types of Mal Presentations The baby can also be in a transverse position, meaning that they're sideways in the uterus.
Breech presentation makes delivery difficult ,primarily because the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge. Having a poor dilating wedge can lead to incomplete cervical dilation, because the presenting part is narrower than the head that follows. The head, which is the part with the largest diameter, can then be trapped during delivery.
What does it mean if a baby is breech? A breech position is when baby's buttocks, feet or both are poised to come out of the vagina first during birth. ... Very rarely, a problem with the baby's muscular or central nervous system can cause a breech presentation. Having an abnormally short umbilical cord may also limit your baby's movement.
What does it mean when a baby is breech? Breech is a term used to describe your baby's position in the womb. Breech position means your baby is bottom-down instead of head-down. ... New and old predictive factors for breech presentation: our experience in 14433 singleton pregnancies and a literature review. Journal of Maternal Fetal Neonatal ...
Breech Births. In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby's buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3-4% of full-term births.
In a breech presentation, the body comes out first, leaving the baby's head to be delivered last. The baby's body may not stretch the cervix enough to allow room for the baby's head to come out easily. There is a risk that the baby's head or shoulders may become wedged against the bones of the mother's pelvis.
Breech presentation, which occurs in approximately 3 percent of fetuses at term, describes the fetus whose presenting part is the buttocks and/or feet. Although most breech fetuses have normal anatomy, this presentation is associated with an increased risk for congenital malformations and mild deformations, torticollis, and developmental ...
Frank Breech. A frank breech is the most common breech presentation, especially when a baby is born at full term. Of the 3% to 4% of term breech births, babies are in the frank breech position 50% to 70% of the time. A frank breech is when the baby's bottom is down, but their legs are straight up with their feet near their head.
Breech birth is a divisive clinical issue, however vaginal breech births continue to occur despite a globally high caesarean section rate for breech presenting fetuses. Inconsistencies are known to exist between clinical practice guidelines relating to the management of breech presentation.
In the frank breech presentation, both the baby's legs are extended so that the feet are up near the face. This is the most common type of breech presentation. Breech babies are difficult to deliver vaginally, so most arrive by c-section.
Frank breech baby: bottom first with feet up near the head. Complete breech baby: bottom first with the legs crossed. Footling breech baby: either one or both feet are below their bottom in this position. Oblique breech baby: the head is down but is pointed toward one of your hips.
Breech presentation is a type of malpresentation and occurs when the fetal head lies over the uterine fundus and fetal buttocks or feet present over the maternal pelvis (instead of cephalic/head presentation). The incidence in the United Kingdom of breech presentation is 3-4% of all fetuses. 1.
Frank breech. When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head.
Incomplete breech presentation. Your baby's feet are positioned downward with only one hip or one knee flexed. Shoulder presentation or transverse lie. This is a form of breech in which your baby is positioned horizontally in the uterus. Few babies remain this way at the time of delivery. Footling breech. One or both of your baby's feet are ...
Turning a breech baby. If your baby is in a breech position at 36 weeks, you'll usually be offered an external cephalic version (ECV). This is when a healthcare professional, such as an obstetrician, tries to turn the baby into a head-down position by applying pressure on your abdomen. It's a safe procedure, although it can be a bit uncomfortable.
Introduction. Breech presentation of the fetus in late pregnancy may result in prolonged or obstructed labour with resulting risks to both woman and fetus. Interventions to correct breech presentation (to cephalic) before labour and birth are important for the woman's and the baby's health. The aim of this review is to determine the most ...
Breech Presentation. Breech presentation means that your baby is in a buttocks-first or feet-first position. Babies are usually in a head-first position. A breech position can make it hard for the baby's head to fit through the birth canal during delivery. This can cause lack of oxygen or nerve damage in your baby.
Image: Shutterstock. Umbilical cord prolapse and head entrapment are significant problems of breech delivery (7). If the umbilical cord is compressed during breech birth, it could restrict the blood and oxygen flow to the fetus, leading to delivery complications, including premature birth and low birth weight.
In a breech presentation, also called breech presentation, the baby does not turn during pregnancy. This means that at the end of pregnancy, he or she is lying in the womb with the breach facing down, rather than head down. A breech presentation occurs in about three to four percent of pregnancies.
This amendment does not change the Legislature's constitutional authority to require notification to a parent or guardian before a minor has an abortion. ... in the case of breech presentation ...
A security researcher told TechCrunch that leaked AT&T customer data contained encrypted account passcodes that can be easily unscrambled.
A look at what caused the massive AT&T outage nationwide 02:34. AT&T said it has begun notifying millions of customers about the theft of personal data recently discovered online.
AT&T has launched an investigation into the source of a data leak that includes personal information of 73 million current and former customers. In a news release Saturday morning, the ...
Alvarez says this is why Christians call Jesus the "lamb of God." He adds that the symbolism of the "blood of the lamb" ties the two stories together and is why Christians believe God sacrificed ...
The telecommunications giant AT&T announced on Saturday that it had reset the passcodes of 7.6 million customers after it determined that compromised customer data was "released on the dark web."