
How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 5 min read

Using the Scientific Method to Solve Problems
How the scientific method and reasoning can help simplify processes and solve problems.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
The processes of problem-solving and decision-making can be complicated and drawn out. In this article we look at how the scientific method, along with deductive and inductive reasoning can help simplify these processes.

‘It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has information. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit our theories, instead of theories to suit facts.’ Sherlock Holmes
The Scientific Method
The scientific method is a process used to explore observations and answer questions. Originally used by scientists looking to prove new theories, its use has spread into many other areas, including that of problem-solving and decision-making.
The scientific method is designed to eliminate the influences of bias, prejudice and personal beliefs when testing a hypothesis or theory. It has developed alongside science itself, with origins going back to the 13th century. The scientific method is generally described as a series of steps.
- observations/theory
- explanation/conclusion
The first step is to develop a theory about the particular area of interest. A theory, in the context of logic or problem-solving, is a conjecture or speculation about something that is not necessarily fact, often based on a series of observations.
Once a theory has been devised, it can be questioned and refined into more specific hypotheses that can be tested. The hypotheses are potential explanations for the theory.
The testing, and subsequent analysis, of these hypotheses will eventually lead to a conclus ion which can prove or disprove the original theory.
Applying the Scientific Method to Problem-Solving
How can the scientific method be used to solve a problem, such as the color printer is not working?
1. Use observations to develop a theory.
In order to solve the problem, it must first be clear what the problem is. Observations made about the problem should be used to develop a theory. In this particular problem the theory might be that the color printer has run out of ink. This theory is developed as the result of observing the increasingly faded output from the printer.
2. Form a hypothesis.
Note down all the possible reasons for the problem. In this situation they might include:
- The printer is set up as the default printer for all 40 people in the department and so is used more frequently than necessary.
- There has been increased usage of the printer due to non-work related printing.
- In an attempt to reduce costs, poor quality ink cartridges with limited amounts of ink in them have been purchased.
- The printer is faulty.
All these possible reasons are hypotheses.
3. Test the hypothesis.
Once as many hypotheses (or reasons) as possible have been thought of, then each one can be tested to discern if it is the cause of the problem. An appropriate test needs to be devised for each hypothesis. For example, it is fairly quick to ask everyone to check the default settings of the printer on each PC, or to check if the cartridge supplier has changed.
4. Analyze the test results.
Once all the hypotheses have been tested, the results can be analyzed. The type and depth of analysis will be dependant on each individual problem, and the tests appropriate to it. In many cases the analysis will be a very quick thought process. In others, where considerable information has been collated, a more structured approach, such as the use of graphs, tables or spreadsheets, may be required.
5. Draw a conclusion.
Based on the results of the tests, a conclusion can then be drawn about exactly what is causing the problem. The appropriate remedial action can then be taken, such as asking everyone to amend their default print settings, or changing the cartridge supplier.
Inductive and Deductive Reasoning
The scientific method involves the use of two basic types of reasoning, inductive and deductive.
Inductive reasoning makes a conclusion based on a set of empirical results. Empirical results are the product of the collection of evidence from observations. For example:
‘Every time it rains the pavement gets wet, therefore rain must be water’.
There has been no scientific determination in the hypothesis that rain is water, it is purely based on observation. The formation of a hypothesis in this manner is sometimes referred to as an educated guess. An educated guess, whilst not based on hard facts, must still be plausible, and consistent with what we already know, in order to present a reasonable argument.
Deductive reasoning can be thought of most simply in terms of ‘If A and B, then C’. For example:
- if the window is above the desk, and
- the desk is above the floor, then
- the window must be above the floor
It works by building on a series of conclusions, which results in one final answer.
Social Sciences and the Scientific Method
The scientific method can be used to address any situation or problem where a theory can be developed. Although more often associated with natural sciences, it can also be used to develop theories in social sciences (such as psychology, sociology and linguistics), using both quantitative and qualitative methods.
Quantitative information is information that can be measured, and tends to focus on numbers and frequencies. Typically quantitative information might be gathered by experiments, questionnaires or psychometric tests. Qualitative information, on the other hand, is based on information describing meaning, such as human behavior, and the reasons behind it. Qualitative information is gathered by way of interviews and case studies, which are possibly not as statistically accurate as quantitative methods, but provide a more in-depth and rich description.
The resultant information can then be used to prove, or disprove, a hypothesis. Using a mix of quantitative and qualitative information is more likely to produce a rounded result based on the factual, quantitative information enriched and backed up by actual experience and qualitative information.
In terms of problem-solving or decision-making, for example, the qualitative information is that gained by looking at the ‘how’ and ‘why’ , whereas quantitative information would come from the ‘where’, ‘what’ and ‘when’.
It may seem easy to come up with a brilliant idea, or to suspect what the cause of a problem may be. However things can get more complicated when the idea needs to be evaluated, or when there may be more than one potential cause of a problem. In these situations, the use of the scientific method, and its associated reasoning, can help the user come to a decision, or reach a solution, secure in the knowledge that all options have been considered.
Join Mind Tools and get access to exclusive content.
This resource is only available to Mind Tools members.
Already a member? Please Login here

Get 20% off your first year of Mind Tools
Our on-demand e-learning resources let you learn at your own pace, fitting seamlessly into your busy workday. Join today and save with our limited time offer!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Team Management Skills

5 Phrases That Kill Collaboration
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
How do i manage a hybrid team.
Adjusting your management style to a hybrid world
The Life Career Rainbow
Finding a Work-Life Balance That Suits You
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
New year resolutions.
Planning for a Year of Achievement
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Pain Points

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 6 scientific method steps and how to use them.
General Education

When you’re faced with a scientific problem, solving it can seem like an impossible prospect. There are so many possible explanations for everything we see and experience—how can you possibly make sense of them all? Science has a simple answer: the scientific method.
The scientific method is a method of asking and answering questions about the world. These guiding principles give scientists a model to work through when trying to understand the world, but where did that model come from, and how does it work?
In this article, we’ll define the scientific method, discuss its long history, and cover each of the scientific method steps in detail.
What Is the Scientific Method?
At its most basic, the scientific method is a procedure for conducting scientific experiments. It’s a set model that scientists in a variety of fields can follow, going from initial observation to conclusion in a loose but concrete format.
The number of steps varies, but the process begins with an observation, progresses through an experiment, and concludes with analysis and sharing data. One of the most important pieces to the scientific method is skepticism —the goal is to find truth, not to confirm a particular thought. That requires reevaluation and repeated experimentation, as well as examining your thinking through rigorous study.
There are in fact multiple scientific methods, as the basic structure can be easily modified. The one we typically learn about in school is the basic method, based in logic and problem solving, typically used in “hard” science fields like biology, chemistry, and physics. It may vary in other fields, such as psychology, but the basic premise of making observations, testing, and continuing to improve a theory from the results remain the same.

The History of the Scientific Method
The scientific method as we know it today is based on thousands of years of scientific study. Its development goes all the way back to ancient Mesopotamia, Greece, and India.
The Ancient World
In ancient Greece, Aristotle devised an inductive-deductive process , which weighs broad generalizations from data against conclusions reached by narrowing down possibilities from a general statement. However, he favored deductive reasoning, as it identifies causes, which he saw as more important.
Aristotle wrote a great deal about logic and many of his ideas about reasoning echo those found in the modern scientific method, such as ignoring circular evidence and limiting the number of middle terms between the beginning of an experiment and the end. Though his model isn’t the one that we use today, the reliance on logic and thorough testing are still key parts of science today.
The Middle Ages
The next big step toward the development of the modern scientific method came in the Middle Ages, particularly in the Islamic world. Ibn al-Haytham, a physicist from what we now know as Iraq, developed a method of testing, observing, and deducing for his research on vision. al-Haytham was critical of Aristotle’s lack of inductive reasoning, which played an important role in his own research.
Other scientists, including Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī, Ibn Sina, and Robert Grosseteste also developed models of scientific reasoning to test their own theories. Though they frequently disagreed with one another and Aristotle, those disagreements and refinements of their methods led to the scientific method we have today.
Following those major developments, particularly Grosseteste’s work, Roger Bacon developed his own cycle of observation (seeing that something occurs), hypothesis (making a guess about why that thing occurs), experimentation (testing that the thing occurs), and verification (an outside person ensuring that the result of the experiment is consistent).
After joining the Franciscan Order, Bacon was granted a special commission to write about science; typically, Friars were not allowed to write books or pamphlets. With this commission, Bacon outlined important tenets of the scientific method, including causes of error, methods of knowledge, and the differences between speculative and experimental science. He also used his own principles to investigate the causes of a rainbow, demonstrating the method’s effectiveness.
Scientific Revolution
Throughout the Renaissance, more great thinkers became involved in devising a thorough, rigorous method of scientific study. Francis Bacon brought inductive reasoning further into the method, whereas Descartes argued that the laws of the universe meant that deductive reasoning was sufficient. Galileo’s research was also inductive reasoning-heavy, as he believed that researchers could not account for every possible variable; therefore, repetition was necessary to eliminate faulty hypotheses and experiments.
All of this led to the birth of the Scientific Revolution , which took place during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. In 1660, a group of philosophers and physicians joined together to work on scientific advancement. After approval from England’s crown , the group became known as the Royal Society, which helped create a thriving scientific community and an early academic journal to help introduce rigorous study and peer review.
Previous generations of scientists had touched on the importance of induction and deduction, but Sir Isaac Newton proposed that both were equally important. This contribution helped establish the importance of multiple kinds of reasoning, leading to more rigorous study.
As science began to splinter into separate areas of study, it became necessary to define different methods for different fields. Karl Popper was a leader in this area—he established that science could be subject to error, sometimes intentionally. This was particularly tricky for “soft” sciences like psychology and social sciences, which require different methods. Popper’s theories furthered the divide between sciences like psychology and “hard” sciences like chemistry or physics.
Paul Feyerabend argued that Popper’s methods were too restrictive for certain fields, and followed a less restrictive method hinged on “anything goes,” as great scientists had made discoveries without the Scientific Method. Feyerabend suggested that throughout history scientists had adapted their methods as necessary, and that sometimes it would be necessary to break the rules. This approach suited social and behavioral scientists particularly well, leading to a more diverse range of models for scientists in multiple fields to use.

The Scientific Method Steps
Though different fields may have variations on the model, the basic scientific method is as follows:
#1: Make Observations
Notice something, such as the air temperature during the winter, what happens when ice cream melts, or how your plants behave when you forget to water them.
#2: Ask a Question
Turn your observation into a question. Why is the temperature lower during the winter? Why does my ice cream melt? Why does my toast always fall butter-side down?
This step can also include doing some research. You may be able to find answers to these questions already, but you can still test them!
#3: Make a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is an educated guess of the answer to your question. Why does your toast always fall butter-side down? Maybe it’s because the butter makes that side of the bread heavier.
A good hypothesis leads to a prediction that you can test, phrased as an if/then statement. In this case, we can pick something like, “If toast is buttered, then it will hit the ground butter-first.”
#4: Experiment
Your experiment is designed to test whether your predication about what will happen is true. A good experiment will test one variable at a time —for example, we’re trying to test whether butter weighs down one side of toast, making it more likely to hit the ground first.
The unbuttered toast is our control variable. If we determine the chance that a slice of unbuttered toast, marked with a dot, will hit the ground on a particular side, we can compare those results to our buttered toast to see if there’s a correlation between the presence of butter and which way the toast falls.
If we decided not to toast the bread, that would be introducing a new question—whether or not toasting the bread has any impact on how it falls. Since that’s not part of our test, we’ll stick with determining whether the presence of butter has any impact on which side hits the ground first.
#5: Analyze Data
After our experiment, we discover that both buttered toast and unbuttered toast have a 50/50 chance of hitting the ground on the buttered or marked side when dropped from a consistent height, straight down. It looks like our hypothesis was incorrect—it’s not the butter that makes the toast hit the ground in a particular way, so it must be something else.
Since we didn’t get the desired result, it’s back to the drawing board. Our hypothesis wasn’t correct, so we’ll need to start fresh. Now that you think about it, your toast seems to hit the ground butter-first when it slides off your plate, not when you drop it from a consistent height. That can be the basis for your new experiment.
#6: Communicate Your Results
Good science needs verification. Your experiment should be replicable by other people, so you can put together a report about how you ran your experiment to see if other peoples’ findings are consistent with yours.
This may be useful for class or a science fair. Professional scientists may publish their findings in scientific journals, where other scientists can read and attempt their own versions of the same experiments. Being part of a scientific community helps your experiments be stronger because other people can see if there are flaws in your approach—such as if you tested with different kinds of bread, or sometimes used peanut butter instead of butter—that can lead you closer to a good answer.

A Scientific Method Example: Falling Toast
We’ve run through a quick recap of the scientific method steps, but let’s look a little deeper by trying again to figure out why toast so often falls butter side down.
#1: Make Observations
At the end of our last experiment, where we learned that butter doesn’t actually make toast more likely to hit the ground on that side, we remembered that the times when our toast hits the ground butter side first are usually when it’s falling off a plate.
The easiest question we can ask is, “Why is that?”
We can actually search this online and find a pretty detailed answer as to why this is true. But we’re budding scientists—we want to see it in action and verify it for ourselves! After all, good science should be replicable, and we have all the tools we need to test out what’s really going on.
Why do we think that buttered toast hits the ground butter-first? We know it’s not because it’s heavier, so we can strike that out. Maybe it’s because of the shape of our plate?
That’s something we can test. We’ll phrase our hypothesis as, “If my toast slides off my plate, then it will fall butter-side down.”
Just seeing that toast falls off a plate butter-side down isn’t enough for us. We want to know why, so we’re going to take things a step further—we’ll set up a slow-motion camera to capture what happens as the toast slides off the plate.
We’ll run the test ten times, each time tilting the same plate until the toast slides off. We’ll make note of each time the butter side lands first and see what’s happening on the video so we can see what’s going on.
When we review the footage, we’ll likely notice that the bread starts to flip when it slides off the edge, changing how it falls in a way that didn’t happen when we dropped it ourselves.
That answers our question, but it’s not the complete picture —how do other plates affect how often toast hits the ground butter-first? What if the toast is already butter-side down when it falls? These are things we can test in further experiments with new hypotheses!
Now that we have results, we can share them with others who can verify our results. As mentioned above, being part of the scientific community can lead to better results. If your results were wildly different from the established thinking about buttered toast, that might be cause for reevaluation. If they’re the same, they might lead others to make new discoveries about buttered toast. At the very least, you have a cool experiment you can share with your friends!
Key Scientific Method Tips
Though science can be complex, the benefit of the scientific method is that it gives you an easy-to-follow means of thinking about why and how things happen. To use it effectively, keep these things in mind!
Don’t Worry About Proving Your Hypothesis
One of the important things to remember about the scientific method is that it’s not necessarily meant to prove your hypothesis right. It’s great if you do manage to guess the reason for something right the first time, but the ultimate goal of an experiment is to find the true reason for your observation to occur, not to prove your hypothesis right.
Good science sometimes means that you’re wrong. That’s not a bad thing—a well-designed experiment with an unanticipated result can be just as revealing, if not more, than an experiment that confirms your hypothesis.
Be Prepared to Try Again
If the data from your experiment doesn’t match your hypothesis, that’s not a bad thing. You’ve eliminated one possible explanation, which brings you one step closer to discovering the truth.
The scientific method isn’t something you’re meant to do exactly once to prove a point. It’s meant to be repeated and adapted to bring you closer to a solution. Even if you can demonstrate truth in your hypothesis, a good scientist will run an experiment again to be sure that the results are replicable. You can even tweak a successful hypothesis to test another factor, such as if we redid our buttered toast experiment to find out whether different kinds of plates affect whether or not the toast falls butter-first. The more we test our hypothesis, the stronger it becomes!
What’s Next?
Want to learn more about the scientific method? These important high school science classes will no doubt cover it in a variety of different contexts.
Test your ability to follow the scientific method using these at-home science experiments for kids !
Need some proof that science is fun? Try making slime
Need more help with this topic? Check out Tutorbase!
Our vetted tutor database includes a range of experienced educators who can help you polish an essay for English or explain how derivatives work for Calculus. You can use dozens of filters and search criteria to find the perfect person for your needs.

Melissa Brinks graduated from the University of Washington in 2014 with a Bachelor's in English with a creative writing emphasis. She has spent several years tutoring K-12 students in many subjects, including in SAT prep, to help them prepare for their college education.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

- Science Projects
- Project Guides
- STEM Activities
- Lesson Plans
- Video Lessons

Steps of the Scientific Method
What is the scientific method.
Do all scientists follow the scientific method exactly ? No. Some areas of science can be more easily tested than others. For example, scientists studying how stars change as they age or how dinosaurs digested their food cannot fast-forward a star's life by a million years or run medical exams on feeding dinosaurs to test their hypotheses. When direct experimentation is not possible, scientists modify the scientific method. But even when modified, the goal (and many of the steps) remains the same: to discover cause and effect relationships by asking questions, carefully gathering and examining the evidence, and seeing if all the available information can be combined into a logical answer. New information or thinking might also cause a scientist to back up and repeat steps at any point during the process. Understanding the steps of the scientific method will help you focus your scientific question and work through your observations and data to answer the question as well as possible.
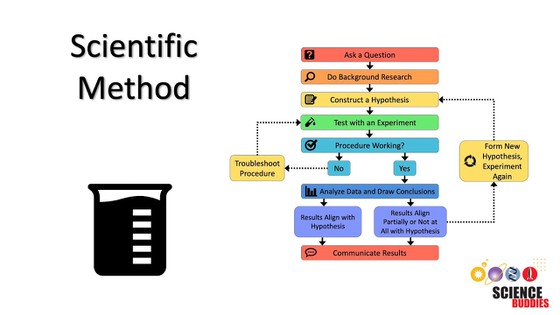
Diagram of the scientific method. The Scientific Method starts with aquestion, and background research is conducted to try to answer that question. If you want to find evidence for an answer or an answer itself then you construct a hypothesis and test that hypothesis in an experiment. If the experiment works and the data is analyzed you can either prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis is disproved, then you can go back with the new information gained and create a new hypothesis to start the scientific process over again.
1. Ask a Question
The scientific method starts when you ask a question about something that you observe: How, What, When, Who, Which, Why, or Where?
For a science fair project some teachers require that the question be something you can measure, preferably with a number.
- Your Question
- Laboratory Notebook
2. Do Background Research
Rather than starting from scratch in putting together a plan for answering your question, you want to be a savvy scientist using library and Internet research to help you find the best way to do things and ensure that you don't repeat mistakes from the past.
- Background Research Plan
- Finding Information
- How to Write a Bibliography in APA and MLA styles With Examples
- Research Paper
3. Construct a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is an educated guess about how things work. It is an attempt to answer your question with an explanation that can be tested. A good hypothesis allows you to then make a prediction: "If _____ [I do this] _____, then _____ [this] _____ will happen."
State both your hypothesis and the resulting prediction you will be testing. Predictions must be easy to measure.
- Variables for Beginners
- Writing a Hypothesis for Your Science Fair Project
4. Test Your Hypothesis by Doing an Experiment
Your experiment tests whether your prediction is accurate and thus your hypothesis is supported or not. It is important for your experiment to be a fair test. You conduct a fair test by making sure that you change only one factor at a time while keeping all other conditions the same.
You should also repeat your experiments several times to make sure that the first results weren't just an accident.
- Experimental Procedure
- Materials List
- Conducting an Experiment
5. Analyze Your Data and Draw a Conclusion
Once your experiment is complete, you collect your measurements and analyze them to see if they support your hypothesis or not.
Scientists often find that their predictions were not accurate and their hypothesis was not supported, and in such cases they will communicate the results of their experiment and then go back and construct a new hypothesis and prediction based on the information they learned during their experiment. This starts much of the process of the scientific method over again. Even if they find that their hypothesis was supported, they may want to test it again in a new way.
- Data Analysis & Graphs
- Conclusions
6. Communicate Your Results
To complete your science fair project you will communicate your results to others in a final report and/or a display board. Professional scientists do almost exactly the same thing by publishing their final report in a scientific journal or by presenting their results on a poster or during a talk at a scientific meeting. In a science fair, judges are interested in your findings regardless of whether or not they support your original hypothesis.
- Final Report
- Display Board
- Science Fair Judging
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the six steps of the scientific method, what is a scientific method example.
- Ask a Question: Why does Greenland look so large on a map?
- Background Research: Learn that Greenland is a quarter the size of the United States in land mass. Also learn that Mercator projection maps are made by transferring the images from a sphere to a sheet of paper wrapped around the sphere in a cylinder.
- Hypothesis: If I make a Mercator projection map, then the items in the middle of the map will look their true size and the items at the poles will look larger than they really are.
- Experiment: Use a sphere with 1-inch by 1-inch squares at each pole and the equator to make a Mercator projection map. Measure the squares on the Mercator projection map.
- Analyze Data and Make Conclusions: The middle-of-the-map squares average 1 inch per side while the squares at the poles average 3 inches per side. In conclusion, the projection process used to make Mercator projection maps creates distortion at the poles, but not at the equator. This is why Greenland, which is close to the North Pole, looks larger than it is.
- Communicate: Make a video, write a report, or give a presentation to educate others about the experiment.
Who invented the scientific method?
Do scientists actually use the scientific method.
- The Scientific Method: Steps and Examples
Try our lesson plans:
- Teaching the Scientific Method with Paper Rockets (Elementary School)
- Paper Rockets to Learn the Scientific Method (Middle School)
- Scientific Method: How Do Scientists Make Discoveries? (Video Lesson)
Assign a student quiz with Google Classroom:
- Scientific Method Quiz (Beginner)
- Scientific Method Quiz (Intermediate)
Explore Our Science Videos
Six Steps of the Scientific Method
Learn What Makes Each Stage Important
ThoughtCo. / Hugo Lin
- Scientific Method
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
The scientific method is a systematic way of learning about the world around us and answering questions. The key difference between the scientific method and other ways of acquiring knowledge are forming a hypothesis and then testing it with an experiment.
The Six Steps
The number of steps can vary from one description to another (which mainly happens when data and analysis are separated into separate steps), however, this is a fairly standard list of the six scientific method steps that you are expected to know for any science class:
- Purpose/Question Ask a question.
- Research Conduct background research. Write down your sources so you can cite your references. In the modern era, a lot of your research may be conducted online. Scroll to the bottom of articles to check the references. Even if you can't access the full text of a published article, you can usually view the abstract to see the summary of other experiments. Interview experts on a topic. The more you know about a subject, the easier it will be to conduct your investigation.
- Hypothesis Propose a hypothesis . This is a sort of educated guess about what you expect. It is a statement used to predict the outcome of an experiment. Usually, a hypothesis is written in terms of cause and effect. Alternatively, it may describe the relationship between two phenomena. One type of hypothesis is the null hypothesis or the no-difference hypothesis. This is an easy type of hypothesis to test because it assumes changing a variable will have no effect on the outcome. In reality, you probably expect a change but rejecting a hypothesis may be more useful than accepting one.
- Experiment Design and perform an experiment to test your hypothesis. An experiment has an independent and dependent variable. You change or control the independent variable and record the effect it has on the dependent variable . It's important to change only one variable for an experiment rather than try to combine the effects of variables in an experiment. For example, if you want to test the effects of light intensity and fertilizer concentration on the growth rate of a plant, you're really looking at two separate experiments.
- Data/Analysis Record observations and analyze the meaning of the data. Often, you'll prepare a table or graph of the data. Don't throw out data points you think are bad or that don't support your predictions. Some of the most incredible discoveries in science were made because the data looked wrong! Once you have the data, you may need to perform a mathematical analysis to support or refute your hypothesis.
- Conclusion Conclude whether to accept or reject your hypothesis. There is no right or wrong outcome to an experiment, so either result is fine. Accepting a hypothesis does not necessarily mean it's correct! Sometimes repeating an experiment may give a different result. In other cases, a hypothesis may predict an outcome, yet you might draw an incorrect conclusion. Communicate your results. The results may be compiled into a lab report or formally submitted as a paper. Whether you accept or reject the hypothesis, you likely learned something about the subject and may wish to revise the original hypothesis or form a new one for a future experiment.
When Are There Seven Steps?
Sometimes the scientific method is taught with seven steps instead of six. In this model, the first step of the scientific method is to make observations. Really, even if you don't make observations formally, you think about prior experiences with a subject in order to ask a question or solve a problem.
Formal observations are a type of brainstorming that can help you find an idea and form a hypothesis. Observe your subject and record everything about it. Include colors, timing, sounds, temperatures, changes, behavior, and anything that strikes you as interesting or significant.
When you design an experiment, you are controlling and measuring variables. There are three types of variables:
- Controlled Variables: You can have as many controlled variables as you like. These are parts of the experiment that you try to keep constant throughout an experiment so that they won't interfere with your test. Writing down controlled variables is a good idea because it helps make your experiment reproducible , which is important in science! If you have trouble duplicating results from one experiment to another, there may be a controlled variable that you missed.
- Independent Variable: This is the variable you control.
- Dependent Variable: This is the variable you measure. It is called the dependent variable because it depends on the independent variable.
- Scientific Method Flow Chart
- What Is an Experiment? Definition and Design
- How To Design a Science Fair Experiment
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- Scientific Variable
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- What Are Independent and Dependent Variables?
- Null Hypothesis Examples
- Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
- Scientific Method Lesson Plan
- Dependent Variable Definition and Examples
- What Is a Testable Hypothesis?
- How to Write a Lab Report

- News/Events
- Arts and Sciences
- Design and the Arts
- Engineering
- Global Futures
- Health Solutions
- Nursing and Health Innovation
- Public Service and Community Solutions
- University College
- Thunderbird School of Global Management
- Polytechnic
- Downtown Phoenix
- Online and Extended
- Lake Havasu
- Research Park
- Washington D.C.
- Biology Bits
- Bird Finder
- Coloring Pages
- Experiments and Activities
- Games and Simulations
- Quizzes in Other Languages
- Virtual Reality (VR)
- World of Biology
- Meet Our Biologists
- Listen and Watch
- PLOSable Biology
- All About Autism
- Xs and Ys: How Our Sex Is Decided
- When Blood Types Shouldn’t Mix: Rh and Pregnancy
- What Is the Menstrual Cycle?
- Understanding Intersex
- The Mysterious Case of the Missing Periods
- Summarizing Sex Traits
- Shedding Light on Endometriosis
- Periods: What Should You Expect?
- Menstruation Matters
- Investigating In Vitro Fertilization
- Introducing the IUD
- How Fast Do Embryos Grow?
- Helpful Sex Hormones
- Getting to Know the Germ Layers
- Gender versus Biological Sex: What’s the Difference?
- Gender Identities and Expression
- Focusing on Female Infertility
- Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Pregnancy
- Ectopic Pregnancy: An Unexpected Path
- Creating Chimeras
- Confronting Human Chimerism
- Cells, Frozen in Time
- EvMed Edits
- Stories in Other Languages
- Virtual Reality
- Zoom Gallery
- Ugly Bug Galleries
- Ask a Question
- Top Questions
- Question Guidelines
- Permissions
- Information Collected
- Author and Artist Notes
- Share Ask A Biologist
- Articles & News
- Our Volunteers
- Teacher Toolbox

show/hide words to know
Biased: when someone presents only one viewpoint. Biased articles do not give all the facts and often mislead the reader.
Conclusion: what a person decides based on information they get through research including experiments.
Method: following a certain set of steps to make something, or find an answer to a question. Like baking a pie or fixing the tire on a bicycle.
Research: looking for answers to questions using tools like the scientific method.
What is the Scientific Method?
If you have ever seen something going on and wondered why or how it happened, you have started down the road to discovery. If you continue your journey, you are likely to guess at some of your own answers for your question. Even further along the road you might think of ways to find out if your answers are correct. At this point, whether you know it or not, you are following a path that scientists call the scientific method. If you do some experiments to see if your answer is correct and write down what you learn in a report, you have pretty much completed everything a scientist might do in a laboratory or out in the field when doing research. In fact, the scientific method works well for many things that don’t usually seem so scientific.
The Flashlight Mystery...
Like a crime detective, you can use the elements of the scientific method to find the answer to everyday problems. For example you pick up a flashlight and turn it on, but the light does not work. You have observed that the light does not work. You ask the question, Why doesn't it work? With what you already know about flashlights, you might guess (hypothesize) that the batteries are dead. You say to yourself, if I buy new batteries and replace the old ones in the flashlight, the light should work. To test this prediction you replace the old batteries with new ones from the store. You click the switch on. Does the flashlight work? No?
What else could be the answer? You go back and hypothesize that it might be a broken light bulb. Your new prediction is if you replace the broken light bulb the flashlight will work. It’s time to go back to the store and buy a new light bulb. Now you test this new hypothesis and prediction by replacing the bulb in the flashlight. You flip the switch again. The flashlight lights up. Success!
If this were a scientific project, you would also have written down the results of your tests and a conclusion of your experiments. The results of only the light bulb hypothesis stood up to the test, and we had to reject the battery hypothesis. You would also communicate what you learned to others with a published report, article, or scientific paper.

More to the Mystery...
Not all questions can be answered with only two experiments. It can often take a lot more work and tests to find an answer. Even when you find an answer it may not always be the only answer to the question. This is one reason that different scientists will work on the same question and do their own experiments.
In our flashlight example, you might never get the light to turn on. This probably means you haven’t made enough different guesses (hypotheses) to test the problem. Were the new batteries in the right way? Was the switch rusty, or maybe a wire is broken. Think of all the possible guesses you could test.
No matter what the question, you can use the scientific method to guide you towards an answer. Even those questions that do not seem to be scientific can be solved using this process. Like with the flashlight, you might need to repeat several of the elements of the scientific method to find an answer. No matter how complex the diagram, the scientific method will include the following pieces in order to be complete.
The elements of the scientific method can be used by anyone to help answer questions. Even though these elements can be used in an ordered manner, they do not have to follow the same order. It is better to think of the scientific method as fluid process that can take different paths depending on the situation. Just be sure to incorporate all of the elements when seeking unbiased answers. You may also need to go back a few steps (or a few times) to test several different hypotheses before you come to a conclusion. Click on the image to see other versions of the scientific method.
- Observation – seeing, hearing, touching…
- Asking a question – why or how?
- Hypothesis – a fancy name for an educated guess about what causes something to happen.
- Prediction – what you think will happen if…
- Testing – this is where you get to experiment and be creative.
- Conclusion – decide how your test results relate to your predictions.
- Communicate – share your results so others can learn from your work.
Other Parts of the Scientific Method…
Now that you have an idea of how the scientific method works there are a few other things to learn so that you will be able test out your new skills and test your hypotheses.
- Control - A group that is similar to other groups but is left alone so that it can be compared to see what happened to the other groups that are tested.
- Data - the numbers and measurements you get from the test in a scientific experiment.
- Independent variable - a variable that you change as part of your experiment. It is important to only change one independent variable for each experiment.
- Dependent variable - a variable that changes when the independent variable is changed.
- Controlled Variable - these are variables that you never change in your experiment.
Practicing Observations and Wondering How and Why...
It is really hard not to notice things around us and wonder about them. This is how the scientific method begins, by observing and wondering why and how. Why do leaves on trees in many parts of the world turn from green to red, orange, or yellow and fall to the ground when winter comes? How does a spider move around their web without getting stuck like its victims? Both of these questions start with observing something and asking questions. The next time you see something and ask yourself, “I wonder why that does that, or how can it do that?” try out your new detective skills, and see what answer you can find.
Try Out Your Detective Skills
Now that you have the basics of the scientific method, why not test your skills? The Science Detectives Training Room will test your problem solving ability. Step inside and see if you can escape the room. While you are there, look around and see what other interesting things might be waiting. We think you find this game a great way to learn the scientific method. In fact, we bet you will discover that you already use the scientific method and didn't even know it.
After you've learned the basics of being a detective, practice those skills in The Case of the Mystery Images . While you are there, pay attention to what's around you as you figure out just what is happening in the mystery photos that surround you.
Ready for your next challenge? Try Science Detectives: Case of the Mystery Images for even more mysteries to solve. Take your scientific abilities one step further by making observations and formulating hypothesis about the mysterious images you find within.
Acknowledgements:
We thank John Alcock for his feedback and suggestions on this article.
Science Detectives - Mystery Room Escape was produced in partnership with the Arizona Science Education Collaborative (ASEC) and funded by ASU Women & Philanthropy.
Flashlight image via Wikimedia Commons - The Oxygen Team
Read more about: Using the Scientific Method to Solve Mysteries
View citation, bibliographic details:.
- Article: Using the Scientific Method to Solve Mysteries
- Author(s): CJ Kazilek and David Pearson
- Publisher: Arizona State University School of Life Sciences Ask A Biologist
- Site name: ASU - Ask A Biologist
- Date published: October 8, 2009
- Date accessed: March 23, 2024
- Link: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/explore/scientific-method
CJ Kazilek and David Pearson. (2009, October 08). Using the Scientific Method to Solve Mysteries . ASU - Ask A Biologist. Retrieved March 23, 2024 from https://askabiologist.asu.edu/explore/scientific-method
Chicago Manual of Style
CJ Kazilek and David Pearson. "Using the Scientific Method to Solve Mysteries ". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 08 October, 2009. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/explore/scientific-method
MLA 2017 Style
CJ Kazilek and David Pearson. "Using the Scientific Method to Solve Mysteries ". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 08 Oct 2009. ASU - Ask A Biologist, Web. 23 Mar 2024. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/explore/scientific-method
Do you think you can escape our Science Detectives Training Room ?
Using the Scientific Method to Solve Mysteries
Be part of ask a biologist.
By volunteering, or simply sending us feedback on the site. Scientists, teachers, writers, illustrators, and translators are all important to the program. If you are interested in helping with the website we have a Volunteers page to get the process started.
Share to Google Classroom
What is the Scientific Method: How does it work and why is it important?
The scientific method is a systematic process involving steps like defining questions, forming hypotheses, conducting experiments, and analyzing data. It minimizes biases and enables replicable research, leading to groundbreaking discoveries like Einstein's theory of relativity, penicillin, and the structure of DNA. This ongoing approach promotes reason, evidence, and the pursuit of truth in science.
Updated on November 18, 2023

Beginning in elementary school, we are exposed to the scientific method and taught how to put it into practice. As a tool for learning, it prepares children to think logically and use reasoning when seeking answers to questions.
Rather than jumping to conclusions, the scientific method gives us a recipe for exploring the world through observation and trial and error. We use it regularly, sometimes knowingly in academics or research, and sometimes subconsciously in our daily lives.
In this article we will refresh our memories on the particulars of the scientific method, discussing where it comes from, which elements comprise it, and how it is put into practice. Then, we will consider the importance of the scientific method, who uses it and under what circumstances.
What is the scientific method?
The scientific method is a dynamic process that involves objectively investigating questions through observation and experimentation . Applicable to all scientific disciplines, this systematic approach to answering questions is more accurately described as a flexible set of principles than as a fixed series of steps.
The following representations of the scientific method illustrate how it can be both condensed into broad categories and also expanded to reveal more and more details of the process. These graphics capture the adaptability that makes this concept universally valuable as it is relevant and accessible not only across age groups and educational levels but also within various contexts.

Steps in the scientific method
While the scientific method is versatile in form and function, it encompasses a collection of principles that create a logical progression to the process of problem solving:
- Define a question : Constructing a clear and precise problem statement that identifies the main question or goal of the investigation is the first step. The wording must lend itself to experimentation by posing a question that is both testable and measurable.
- Gather information and resources : Researching the topic in question to find out what is already known and what types of related questions others are asking is the next step in this process. This background information is vital to gaining a full understanding of the subject and in determining the best design for experiments.
- Form a hypothesis : Composing a concise statement that identifies specific variables and potential results, which can then be tested, is a crucial step that must be completed before any experimentation. An imperfection in the composition of a hypothesis can result in weaknesses to the entire design of an experiment.
- Perform the experiments : Testing the hypothesis by performing replicable experiments and collecting resultant data is another fundamental step of the scientific method. By controlling some elements of an experiment while purposely manipulating others, cause and effect relationships are established.
- Analyze the data : Interpreting the experimental process and results by recognizing trends in the data is a necessary step for comprehending its meaning and supporting the conclusions. Drawing inferences through this systematic process lends substantive evidence for either supporting or rejecting the hypothesis.
- Report the results : Sharing the outcomes of an experiment, through an essay, presentation, graphic, or journal article, is often regarded as a final step in this process. Detailing the project's design, methods, and results not only promotes transparency and replicability but also adds to the body of knowledge for future research.
- Retest the hypothesis : Repeating experiments to see if a hypothesis holds up in all cases is a step that is manifested through varying scenarios. Sometimes a researcher immediately checks their own work or replicates it at a future time, or another researcher will repeat the experiments to further test the hypothesis.

Where did the scientific method come from?
Oftentimes, ancient peoples attempted to answer questions about the unknown by:
- Making simple observations
- Discussing the possibilities with others deemed worthy of a debate
- Drawing conclusions based on dominant opinions and preexisting beliefs
For example, take Greek and Roman mythology. Myths were used to explain everything from the seasons and stars to the sun and death itself.
However, as societies began to grow through advancements in agriculture and language, ancient civilizations like Egypt and Babylonia shifted to a more rational analysis for understanding the natural world. They increasingly employed empirical methods of observation and experimentation that would one day evolve into the scientific method .
In the 4th century, Aristotle, considered the Father of Science by many, suggested these elements , which closely resemble the contemporary scientific method, as part of his approach for conducting science:
- Study what others have written about the subject.
- Look for the general consensus about the subject.
- Perform a systematic study of everything even partially related to the topic.

By continuing to emphasize systematic observation and controlled experiments, scholars such as Al-Kindi and Ibn al-Haytham helped expand this concept throughout the Islamic Golden Age .
In his 1620 treatise, Novum Organum , Sir Francis Bacon codified the scientific method, arguing not only that hypotheses must be tested through experiments but also that the results must be replicated to establish a truth. Coming at the height of the Scientific Revolution, this text made the scientific method accessible to European thinkers like Galileo and Isaac Newton who then put the method into practice.
As science modernized in the 19th century, the scientific method became more formalized, leading to significant breakthroughs in fields such as evolution and germ theory. Today, it continues to evolve, underpinning scientific progress in diverse areas like quantum mechanics, genetics, and artificial intelligence.
Why is the scientific method important?
The history of the scientific method illustrates how the concept developed out of a need to find objective answers to scientific questions by overcoming biases based on fear, religion, power, and cultural norms. This still holds true today.
By implementing this standardized approach to conducting experiments, the impacts of researchers’ personal opinions and preconceived notions are minimized. The organized manner of the scientific method prevents these and other mistakes while promoting the replicability and transparency necessary for solid scientific research.
The importance of the scientific method is best observed through its successes, for example:
- “ Albert Einstein stands out among modern physicists as the scientist who not only formulated a theory of revolutionary significance but also had the genius to reflect in a conscious and technical way on the scientific method he was using.” Devising a hypothesis based on the prevailing understanding of Newtonian physics eventually led Einstein to devise the theory of general relativity .
- Howard Florey “Perhaps the most useful lesson which has come out of the work on penicillin has been the demonstration that success in this field depends on the development and coordinated use of technical methods.” After discovering a mold that prevented the growth of Staphylococcus bacteria, Dr. Alexander Flemimg designed experiments to identify and reproduce it in the lab, thus leading to the development of penicillin .
- James D. Watson “Every time you understand something, religion becomes less likely. Only with the discovery of the double helix and the ensuing genetic revolution have we had grounds for thinking that the powers held traditionally to be the exclusive property of the gods might one day be ours. . . .” By using wire models to conceive a structure for DNA, Watson and Crick crafted a hypothesis for testing combinations of amino acids, X-ray diffraction images, and the current research in atomic physics, resulting in the discovery of DNA’s double helix structure .
Final thoughts
As the cases exemplify, the scientific method is never truly completed, but rather started and restarted. It gave these researchers a structured process that was easily replicated, modified, and built upon.
While the scientific method may “end” in one context, it never literally ends. When a hypothesis, design, methods, and experiments are revisited, the scientific method simply picks up where it left off. Each time a researcher builds upon previous knowledge, the scientific method is restored with the pieces of past efforts.
By guiding researchers towards objective results based on transparency and reproducibility, the scientific method acts as a defense against bias, superstition, and preconceived notions. As we embrace the scientific method's enduring principles, we ensure that our quest for knowledge remains firmly rooted in reason, evidence, and the pursuit of truth.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
Forgot password? New user? Sign up
Existing user? Log in
Scientific Method
Already have an account? Log in here.
The scientific method is the process by which scientists of all fields attempt to explain the phenomena in the world. It is how science is conducted--through experimentation. Generally, the scientific method refers to a set of steps whereby a scientist can form a conjecture (the hypothesis) for why something functions the way it does and then test their hypothesis. It is an empirical process; it uses real world data to prove the hypothesis. There is no exact set of \(x\) number of steps to conduct scientific experiments, or even some exact \(y\) number of experiments, but the general process involves making an observation, forming an hypothesis, forming a prediction from that hypothesis, and then experimental testing. The scientific method isn't limited to the physical or biological sciences, but also the social sciences, mathematics, computing and other fields where experimentation can be used to prove beliefs.
We could observe that whenever a fire is smothered, it goes out. For instance a small fire that is covered with a blanket is extinguished. We could hypothesize that the reason for this is that fire requires some gas in our air to form and remain a flame. We could then use a vacuum chamber to test this theory. We would predict that outside of a vacuum, a fire could be lit but inside of a vacuum, with no air, that the fire would not ignite. If we were to test this theory, perhaps in multiple vacuums with multiple forms of tinder/fuel (wood, paper, petrol, etc.) and multiple means of ignition, we would notice that the fire never ignites. If we wished, we could further refine our hypothesis, suggesting that fire can only ignite if there is sufficient oxygen in the air. This we'd also test in the vacuum chamber, by pulling out all the air, then adding in different gases. We would notice that the fire would only ignite in the presence of oxygen or an oxidizing agent . It is possible that other, incorrect hypothesis could have been initially formed--such as smothering decreases the surface area the fire has, and could try making different sized fires--and been proven incorrect. Also, it is important to note that this single set of experiments is not enough to turn this hypothesis into a theorem. More experimentation and discovery would be necessary.
The scientific method also refers to the fact that science is ongoing . In some cases scientists continue to collect data to prove and disprove old theories. Or in other cases, scientists have hypothesis for why the universe behaves the way it does but are unable to gather sufficient data to prove their hypothesis. For instance, until recent discoveries at LIGO scientists could not confirm what happened when two black holes collided, although they believed (and it was confirmed in February 2016) that colliding black holes produced gravitational waves .
Steps of the Scientific Method
Falsifiability and why "theory" doesn't mean "untrue", avoiding bias, history and philosophy of science.
The scientific method is often presented as a set of steps, but not always with the same number or type of steps. However, philosophers of science generally agree that any presentation of the scientific method should have the following four steps:
- Observe - Sometimes referred to as characterizing, defining, or measuring, experimenters first witness some aspect of the universe, for instance, an apple falling. These observations then form a question, such as "Why do objects fall to the earth?"
- Hypothesize - Scientists then come up with a theory as to why this happens, for instance, the mass of the earth attracts the apple from the air to the ground.
- Predict - Using the hypothesis, a scientist calculates what measurable data points they believe will result in a given experiment, for instance an apple at a height of \(9.8\) meters should fall to the ground in \(\sqrt{2}\) seconds, or should be at a velocity of \(9.8\sqrt{2}\) m/s the moment before it hits the ground.
- Experiment - A test is run to determine if the prediction was correct.
With the notion that repeating these steps is also important. If a prediction is proven to be incorrect then alternative predictions and tests are conducted. Maybe even a new hypothesis could be formulated. Even if the hypothesis and prediction are correct, additional predictions and tests need to be run to best support any theory.
While this process can be explained or categorized differently than this, all formulations of the scientific method have empirical observations, a testable hypothesis, and testing data to prove or disprove that hypothesis. Crucial to this, is that an experimenter searches for experiments that produce the most unlikely results and experiments that are least likely to be coincidental . Hypotheses that produce highly unlikely predictions, in situations where little else could explain the result, are more likely to be true. Bayes' theorem can be used to show which predictions are more or less unlikely given some evidence, i.e. which proven predictions are "stronger" than others. For instance, the theory of evolution has been supported by the consistency of DNA across species whose phenomenology are significantly different. Despite the diversity of plant and animal species on Earth, the majority of our DNA is the same, and only 20 amino acids are the building blocks for every known living organism. It would be highly unlikely that vastly different forms of life have the same building blocks after millions, if not billions, of years of external manipulation, if not for some common origin.
The word "theory" can lead to confusion about how true some scientific principle is. Under the scientific method scientists use the word "theory" even for key principles (like gravity) that have been rigorously proven by modern science. This is because the scientific community believes it is important that hypothesis be falsifiable . Falsifiability refers to the fact that theories have been tested in experiments where they could have failed but did not. So when scientists refer to a principle as a theory, for instance Einstein's theory of relativity , they're actually referring to a hypothesis that has undergone the scientific method, i.e. that has been tested and proven true.
For instance, scientists sometimes refer to evolution as the "theory of evolution," which has contributed to the erroneous belief that the modern scientific theory of evolution is false. Really what the "theory of evolution" refers to is the ample research, testing, and empirical evidence that all consistently prove evolution to be true.
That isn't to say that theories can't be later disproven. Part of the advantage to the scientific method is that no theory is ever considered an unbreakable rule. Some theories seem correct given experiments that are run at the time they're created, but are proven wrong as new methods of experimentation are conducted. For instance, Einstein himself believed that the universe was static, not growing or contracting. That was later proven to be false and replaced with a theory that the universe was expanding (the Friedmann-LeMaitre model of an expanding universe , which Einstein himself accepted), but that its rate of expansion was slowing down. This was, in turn, also proven incorrect. The rate of the universe's expansion is speeding up. [1] Generally though, theories are modified over time, they are shown to be true under certain conditions, or partly true, and the strength of a theory may also be related to how long it has held up, without modification, to scrutiny.
Peer review: In modern science, experimenters present both their findings and their methodology for review by their peers, other talented scientists and experimenters. This is done before a work is published, but also publication itself is considered a way of inviting peer review. By sharing and disseminating work widely, the greatest number of others can review the work and offer criticism as needed.
Reproducibility: Related to peer review, is the notion that the results from experiments should be possible to reproduce. If one scientist conducts some experiment, others should be able to conduct the same experiment on their own and achieve the same results. Reproducible experiments strengthen theories.
Double-Blind Testing: Primarily used in medical , psychological , and behavioral economic testing, double-blind testing refers to having a test and control group, and running the experiment such that the person conducting the experiment does not know which is which. For instance, in testing the efficacy of a new drug, a pharmaceutical company may have a medical practitioner administer the new drug to one third of the test population, an existing known drug to another third, and a placebo, meaning something that isn't a drug but seems like it, to the remaining third of the test population, but without the nurse knowing which drug is which. The practitioner would then, still blind, track the progress of the entire testing population, gathering data about each test subject.
Double-blind studies are done to avoid biases that manipulate data, like controlling for the placebo effect where just giving a patient a drug that they perceive will be a cure can be causally linked to a decrease in symptoms. This positive causal effect occurs even with the drug that shouldn't affect the patient in anyway, when it is a sugar pill, or water, so long as the patient believes they are receiving a cure. Also double-blind studies help prevent observation bias, where the administrator of the drug may expect the population who received the new drug to outperform others, and so many inadvertently rate their progress better than other test groups.
A pharmaceutical company has a new drug they want to test to determine its efficacy. They have a hypothesis that this drug is super effective at curing a disease. Which of the following experiments/results best reflects the principles of the scientific method? Which is most scientific?
A) They gave 100 patients with the disease the drug and 100 patients a placebo from a population of 100,000 with the disease, they strictly controlled these patient's diet, limited other medication, and 77 of the subjects reported that their happiness improved significantly.
B) They found a remote island with an indigenous population that's genetically different from other populations and where 200 patients have the disease. They gave 100 patients on the island the drug and 100 a placebo. They strictly controlled these patient's diet, limited other medication, and found that 84 of the test patients had higher red and white blood cell count than the control group, and lower incidents of mortality from the disease than non-island populations.
C) They gave 100 patients with the disease the drug and 100 patients a placebo from a population of 100,000 with the disease, they strictly controlled these patient's diet, limited other medication, and found that only 5 of the test patients had higher red and white blood cell count than the control group, with no other changes in health.
D) They gave 100 patients with the disease the drug and 100 patients a placebo from a population of 100,000 with the disease, allowed both patients to consume and medicate in whatever way those patients desired, and found that 68 of the test patients had higher red and white blood cell count than the control group, with faster speed-to-recovery.
The theory of the scientific method has evolved over time, with modern historians pointing to Aristotle as an originator, and many looking to Thomas Kuhn's seminal work "The Structure of Scientific Revolutions" as a key influence on current conceptions of the method.
Aristotle classified reasoning into three types:
- Abductive - Also known as guessing, abductive reasoning supposes that the most likely inference is correct. While this isn't rigorous, a well-informed individual is likely to make good guesses, and many significant theories of science have developed first from a guess.
- Deductive - Deductive reasoning uses premises to reach conclusions. One of the most famous examples being "All men are mortal. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates is mortal."
- Inductive - Inductive reasoning is the one preferred by scientists, and can be considered an early version of the scientific method. Namely, inductive reasoning uses empirical observations to make inferences, and accounts for probability in those inferences. A theory reached by induction is said to be more or less likely to be true, stronger or weaker.
The philosophy of science refers to the logic and thinking behind the scientific method. It questions what makes something scientifically valid. For instance, the scientific method assumes that reality is objective, and that explanations exist for all phenomena humans can observe.
Thomas Kuhn's book is foundational to the philosophy of science and the way sociologists and historians look at science through the ages. In it, he popularized the term "paradigm shift" and promoted a historical understanding of scientific discovery not as a linear accumulation of understanding, but as a set of scientific revolutions that "shift" humanity's understanding. Further, paradigm shifts open up whole fields (for instance quantum mechanics , behavioral economics or genetics ) with new approaches to understand the universe. Also what scientists consider true is not purely objective, but based on the consensus of the scientific community.
- Nobelprize.org, . The Nobel Prize in Physics 2011 Saul Perlmutter, Brian P. Schmidt, Adam G. Riess . Retrieved October 24th 2016, from http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/2011/
Problem Loading...
Note Loading...
Set Loading...
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Mechanics (Essentials) - Class 11th
Course: mechanics (essentials) - class 11th > unit 2.
- Introduction to physics
- What is physics?
The scientific method
- Models and Approximations in Physics
Introduction
- Make an observation.
- Ask a question.
- Form a hypothesis , or testable explanation.
- Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
- Test the prediction.
- Iterate: use the results to make new hypotheses or predictions.
Scientific method example: Failure to toast
1. make an observation..
- Observation: the toaster won't toast.
2. Ask a question.
- Question: Why won't my toaster toast?
3. Propose a hypothesis.
- Hypothesis: Maybe the outlet is broken.
4. Make predictions.
- Prediction: If I plug the toaster into a different outlet, then it will toast the bread.
5. Test the predictions.
- Test of prediction: Plug the toaster into a different outlet and try again.
- If the toaster does toast, then the hypothesis is supported—likely correct.
- If the toaster doesn't toast, then the hypothesis is not supported—likely wrong.
Logical possibility
Practical possibility, building a body of evidence, 6. iterate..
- Iteration time!
- If the hypothesis was supported, we might do additional tests to confirm it, or revise it to be more specific. For instance, we might investigate why the outlet is broken.
- If the hypothesis was not supported, we would come up with a new hypothesis. For instance, the next hypothesis might be that there's a broken wire in the toaster.
Want to join the conversation?
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- About This Blog
- Official PLOS Blog
- EveryONE Blog
- Speaking of Medicine
- PLOS Biologue
- Absolutely Maybe
- DNA Science
- PLOS ECR Community
- All Models Are Wrong
- About PLOS Blogs
A Guide to Using the Scientific Method in Everyday Life

The scientific method —the process used by scientists to understand the natural world—has the merit of investigating natural phenomena in a rigorous manner. Working from hypotheses, scientists draw conclusions based on empirical data. These data are validated on large-scale numbers and take into consideration the intrinsic variability of the real world. For people unfamiliar with its intrinsic jargon and formalities, science may seem esoteric. And this is a huge problem: science invites criticism because it is not easily understood. So why is it important, then, that every person understand how science is done?
Because the scientific method is, first of all, a matter of logical reasoning and only afterwards, a procedure to be applied in a laboratory.
Individuals without training in logical reasoning are more easily victims of distorted perspectives about themselves and the world. An example is represented by the so-called “ cognitive biases ”—systematic mistakes that individuals make when they try to think rationally, and which lead to erroneous or inaccurate conclusions. People can easily overestimate the relevance of their own behaviors and choices. They can lack the ability to self-estimate the quality of their performances and thoughts . Unconsciously, they could even end up selecting only the arguments that support their hypothesis or beliefs . This is why the scientific framework should be conceived not only as a mechanism for understanding the natural world, but also as a framework for engaging in logical reasoning and discussion.
A brief history of the scientific method
The scientific method has its roots in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. Philosophers Francis Bacon and René Descartes are often credited with formalizing the scientific method because they contrasted the idea that research should be guided by metaphysical pre-conceived concepts of the nature of reality—a position that, at the time, was highly supported by their colleagues . In essence, Bacon thought that inductive reasoning based on empirical observation was critical to the formulation of hypotheses and the generation of new understanding : general or universal principles describing how nature works are derived only from observations of recurring phenomena and data recorded from them. The inductive method was used, for example, by the scientist Rudolf Virchow to formulate the third principle of the notorious cell theory , according to which every cell derives from a pre-existing one. The rationale behind this conclusion is that because all observations of cell behavior show that cells are only derived from other cells, this assertion must be always true.
Inductive reasoning, however, is not immune to mistakes and limitations. Referring back to cell theory, there may be rare occasions in which a cell does not arise from a pre-existing one, even though we haven’t observed it yet—our observations on cell behavior, although numerous, can still benefit from additional observations to either refute or support the conclusion that all cells arise from pre-existing ones. And this is where limited observations can lead to erroneous conclusions reasoned inductively. In another example, if one never has seen a swan that is not white, they might conclude that all swans are white, even when we know that black swans do exist, however rare they may be.
The universally accepted scientific method, as it is used in science laboratories today, is grounded in hypothetico-deductive reasoning . Research progresses via iterative empirical testing of formulated, testable hypotheses (formulated through inductive reasoning). A testable hypothesis is one that can be rejected (falsified) by empirical observations, a concept known as the principle of falsification . Initially, ideas and conjectures are formulated. Experiments are then performed to test them. If the body of evidence fails to reject the hypothesis, the hypothesis stands. It stands however until and unless another (even singular) empirical observation falsifies it. However, just as with inductive reasoning, hypothetico-deductive reasoning is not immune to pitfalls—assumptions built into hypotheses can be shown to be false, thereby nullifying previously unrejected hypotheses. The bottom line is that science does not work to prove anything about the natural world. Instead, it builds hypotheses that explain the natural world and then attempts to find the hole in the reasoning (i.e., it works to disprove things about the natural world).
How do scientists test hypotheses?
Controlled experiments
The word “experiment” can be misleading because it implies a lack of control over the process. Therefore, it is important to understand that science uses controlled experiments in order to test hypotheses and contribute new knowledge. So what exactly is a controlled experiment, then?
Let us take a practical example. Our starting hypothesis is the following: we have a novel drug that we think inhibits the division of cells, meaning that it prevents one cell from dividing into two cells (recall the description of cell theory above). To test this hypothesis, we could treat some cells with the drug on a plate that contains nutrients and fuel required for their survival and division (a standard cell biology assay). If the drug works as expected, the cells should stop dividing. This type of drug might be useful, for example, in treating cancers because slowing or stopping the division of cells would result in the slowing or stopping of tumor growth.
Although this experiment is relatively easy to do, the mere process of doing science means that several experimental variables (like temperature of the cells or drug, dosage, and so on) could play a major role in the experiment. This could result in a failed experiment when the drug actually does work, or it could give the appearance that the drug is working when it is not. Given that these variables cannot be eliminated, scientists always run control experiments in parallel to the real ones, so that the effects of these other variables can be determined. Control experiments are designed so that all variables, with the exception of the one under investigation, are kept constant. In simple terms, the conditions must be identical between the control and the actual experiment.
Coming back to our example, when a drug is administered it is not pure. Often, it is dissolved in a solvent like water or oil. Therefore, the perfect control to the actual experiment would be to administer pure solvent (without the added drug) at the same time and with the same tools, where all other experimental variables (like temperature, as mentioned above) are the same between the two (Figure 1). Any difference in effect on cell division in the actual experiment here can be attributed to an effect of the drug because the effects of the solvent were controlled.
In order to provide evidence of the quality of a single, specific experiment, it needs to be performed multiple times in the same experimental conditions. We call these multiple experiments “replicates” of the experiment (Figure 2). The more replicates of the same experiment, the more confident the scientist can be about the conclusions of that experiment under the given conditions. However, multiple replicates under the same experimental conditions are of no help when scientists aim at acquiring more empirical evidence to support their hypothesis. Instead, they need independent experiments (Figure 3), in their own lab and in other labs across the world, to validate their results.

Often times, especially when a given experiment has been repeated and its outcome is not fully clear, it is better to find alternative experimental assays to test the hypothesis.
Applying the scientific approach to everyday life
So, what can we take from the scientific approach to apply to our everyday lives?
A few weeks ago, I had an agitated conversation with a bunch of friends concerning the following question: What is the definition of intelligence?
Defining “intelligence” is not easy. At the beginning of the conversation, everybody had a different, “personal” conception of intelligence in mind, which – tacitly – implied that the conversation could have taken several different directions. We realized rather soon that someone thought that an intelligent person is whoever is able to adapt faster to new situations; someone else thought that an intelligent person is whoever is able to deal with other people and empathize with them. Personally, I thought that an intelligent person is whoever displays high cognitive skills, especially in abstract reasoning.
The scientific method has the merit of providing a reference system, with precise protocols and rules to follow. Remember: experiments must be reproducible, which means that an independent scientists in a different laboratory, when provided with the same equipment and protocols, should get comparable results. Fruitful conversations as well need precise language, a kind of reference vocabulary everybody should agree upon, in order to discuss about the same “content”. This is something we often forget, something that was somehow missing at the opening of the aforementioned conversation: even among friends, we should always agree on premises, and define them in a rigorous manner, so that they are the same for everybody. When speaking about “intelligence”, we must all make sure we understand meaning and context of the vocabulary adopted in the debate (Figure 4, point 1). This is the first step of “controlling” a conversation.
There is another downside that a discussion well-grounded in a scientific framework would avoid. The mistake is not structuring the debate so that all its elements, except for the one under investigation, are kept constant (Figure 4, point 2). This is particularly true when people aim at making comparisons between groups to support their claim. For example, they may try to define what intelligence is by comparing the achievements in life of different individuals: “Stephen Hawking is a brilliant example of intelligence because of his great contribution to the physics of black holes”. This statement does not help to define what intelligence is, simply because it compares Stephen Hawking, a famous and exceptional physicist, to any other person, who statistically speaking, knows nothing about physics. Hawking first went to the University of Oxford, then he moved to the University of Cambridge. He was in contact with the most influential physicists on Earth. Other people were not. All of this, of course, does not disprove Hawking’s intelligence; but from a logical and methodological point of view, given the multitude of variables included in this comparison, it cannot prove it. Thus, the sentence “Stephen Hawking is a brilliant example of intelligence because of his great contribution to the physics of black holes” is not a valid argument to describe what intelligence is. If we really intend to approximate a definition of intelligence, Steven Hawking should be compared to other physicists, even better if they were Hawking’s classmates at the time of college, and colleagues afterwards during years of academic research.
In simple terms, as scientists do in the lab, while debating we should try to compare groups of elements that display identical, or highly similar, features. As previously mentioned, all variables – except for the one under investigation – must be kept constant.
This insightful piece presents a detailed analysis of how and why science can help to develop critical thinking.
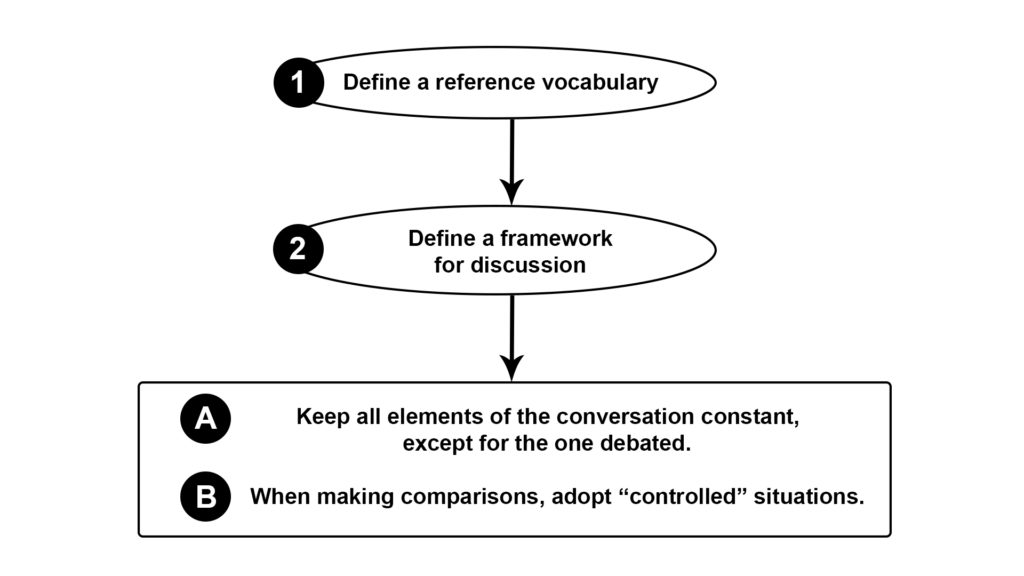
In a nutshell
Here is how to approach a daily conversation in a rigorous, scientific manner:
- First discuss about the reference vocabulary, then discuss about the content of the discussion. Think about a researcher who is writing down an experimental protocol that will be used by thousands of other scientists in varying continents. If the protocol is rigorously written, all scientists using it should get comparable experimental outcomes. In science this means reproducible knowledge, in daily life this means fruitful conversations in which individuals are on the same page.
- Adopt “controlled” arguments to support your claims. When making comparisons between groups, visualize two blank scenarios. As you start to add details to both of them, you have two options. If your aim is to hide a specific detail, the better is to design the two scenarios in a completely different manner—it is to increase the variables. But if your intention is to help the observer to isolate a specific detail, the better is to design identical scenarios, with the exception of the intended detail—it is therefore to keep most of the variables constant. This is precisely how scientists ideate adequate experiments to isolate new pieces of knowledge, and how individuals should orchestrate their thoughts in order to test them and facilitate their comprehension to others.
Not only the scientific method should offer individuals an elitist way to investigate reality, but also an accessible tool to properly reason and discuss about it.
Edited by Jason Organ, PhD, Indiana University School of Medicine.

Simone is a molecular biologist on the verge of obtaining a doctoral title at the University of Ulm, Germany. He is Vice-Director at Culturico (https://culturico.com/), where his writings span from Literature to Sociology, from Philosophy to Science. His writings recently appeared in Psychology Today, openDemocracy, Splice Today, Merion West, Uncommon Ground and The Society Pages. Follow Simone on Twitter: @simredaelli
- Pingback: Case Studies in Ethical Thinking: Day 1 | Education & Erudition
This has to be the best article I have ever read on Scientific Thinking. I am presently writing a treatise on how Scientific thinking can be adopted to entreat all situations.And how, a 4 year old child can be taught to adopt Scientific thinking, so that, the child can look at situations that bothers her and she could try to think about that situation by formulating the right questions. She may not have the tools to find right answers? But, forming questions by using right technique ? May just make her find a way to put her mind to rest even at that level. That is why, 4 year olds are often “eerily: (!)intelligent, I have iften been intimidated and plain embarrassed to see an intelligent and well spoken 4 year old deal with celibrity ! Of course, there are a lot of variables that have to be kept in mind in order to train children in such controlled thinking environment, as the screenplay of little Sheldon shows. Thanking the author with all my heart – #ershadspeak #wearescience #weareallscientists Ershad Khandker
Simone, thank you for this article. I have the idea that I want to apply what I learned in Biology to everyday life. You addressed this issue, and have given some basic steps in using the scientific method.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name and email for the next time I comment.
By Ana Santos-Carvalho and Carolina Lebre, edited by Andrew S. Cale Excessive use of technical jargon can be a significant barrier to…
By Ryan McRae and Briana Pobiner, edited by Andrew S. Cale In 2023, the field of human evolution benefited from a plethora…
By Elizabeth Fusco, edited by Michael Liesen Infection and pandemics have never been more relevant globally, and zombies have long been used…
Lucidly exploring and applying philosophy
- Fun Quizzes
- Logic Course
- Ethics Course
- Philosophy Course
Chapter 6: Scientific Problem Solving
If you prefer a video, click this button:
Scientific Problem Solving Video
Science is a method to discover empirical truths and patterns. Roughly speaking, the scientific method consists of
1) Observing
2) Forming a hypothesis
3) Testing the hypothesis and
4) Interpreting the data to confirm or disconfirm the hypothesis.
The beauty of science is that any scientific claim can be tested if you have the proper knowledge and equipment.
You can also use the scientific method to solve everyday problems: 1) Observe and clearly define the problem, 2) Form a hypothesis, 3) Test it, and 4) Confirm the hypothesis... or disconfirm it and start over.
So, the next time you are cursing in traffic or emotionally reacting to a problem, take a few deep breaths and then use this rational and scientific approach. Slow down, observe, hypothesize, and test.
Explain how you would solve these problems using the four steps of the scientific process.
Example: The fire alarm is not working.
1) Observe/Define the problem: it does not beep when I push the button.
2) Hypothesis: it is caused by a dead battery.
3) Test: try a new battery.
4) Confirm/Disconfirm: the alarm now works. If it does not work, start over by testing another hypothesis like “it has a loose wire.”
- My car will not start.
- My child is having problems reading.
- I owe $20,000, but only make $10 an hour.
- My boss is mean. I want him/her to stop using rude language towards me.
- My significant other is lazy. I want him/her to help out more.
6-8. Identify three problems where you can apply the scientific method.
*Answers will vary.
Application and Value
Science is more of a process than a body of knowledge. In our daily lives, we often emotionally react and jump to quick solutions when faced with problems, but following the four steps of the scientific process can help us slow down and discover more intelligent solutions.
In your study of philosophy, you will explore deeper questions about science. For example, are there any forms of knowledge that are nonscientific? Can science tell us what we ought to do? Can logical and mathematical truths be proven in a scientific way? Does introspection give knowledge even though I cannot scientifically observe your introspective thoughts? Is science truly objective? These are challenging questions that should help you discover the scope of science without diminishing its awesome power.
But the first step in answering these questions is knowing what science is, and this chapter clarifies its essence. Again, Science is not so much a body of knowledge as it is a method of observing, hypothesizing, and testing. This method is what all the sciences have in common.
Perhaps too science should involve falsifiability, which is a concept explored in the next chapter.
Return to Logic Home Next (Chapter 7, Falsifiability)

Click on my affiliate link above (Logic Book Image) to explore the most popular introduction to logic. If you purchase it, I recommend buying a less expensive older edition.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1.1: The Scientific Method
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 33373

- Melissa Ha, Maria Morrow, & Kammy Algiers
- Yuba College, College of the Redwoods, & Ventura College via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
Learning Objectives
- Identify the shared characteristics of the natural sciences.
- Summarize the steps of the scientific method.
- Compare inductive reasoning with deductive reasoning.
- Describe the goals of basic science and applied science.
The Process of Science
Science includes such diverse fields as astronomy, biology, computer sciences, geology, logic, physics, chemistry, and mathematics (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). However, those fields of science related to the physical world and its phenomena and processes are considered natural sciences . Natural sciences could be categorized as astronomy, biology, chemistry, earth science, and physics. One can divide natural sciences further into life sciences, which study living things and include biology, and physical sciences, which study nonliving matter and include astronomy, geology, physics, and chemistry. Some disciplines such as biophysics and biochemistry build on both life and physical sciences and are interdisciplinary. Natural sciences are sometimes referred to as “hard science” because they rely on the use of quantitative data; social sciences that study society and human behavior are more likely to use qualitative assessments to drive investigations and findings.
Not surprisingly, the natural science of biology has many branches or subdisciplines. Cell biologists study cell structure and function, while biologists who study anatomy investigate the structure of an entire organism. Those biologists studying physiology, however, focus on the internal functioning of an organism. Some areas of biology focus on only particular types of living things. For example, botanists explore plants, while zoologists specialize in animals.
Scientific Reasoning
One thing is common to all forms of science: an ultimate goal “to know.” Curiosity and inquiry are the driving forces for the development of science. Scientists seek to understand the world and the way it operates. To do this, they use two methods of logical thinking: inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning is a form of logical thinking that uses related observations to arrive at a general conclusion. This type of reasoning is common in descriptive science. A life scientist such as a biologist makes observations and records them. These data can be qualitative (descriptive) or quantitative (numeric), and the raw data can be supplemented with drawings, pictures, photos, or videos. From many observations, the scientist can infer conclusions (inductions) based on evidence. Inductive reasoning involves formulating generalizations inferred from careful observation and the analysis of a large amount of data.
Deductive reasoning , or deduction, is the type of logic used in hypothesis-based science. In deductive reason, the pattern of thinking moves in the opposite direction as compared to inductive reasoning; that is, specific results are predicted from a general premise. Deductive reasoning is a form of logical thinking that uses a general principle or law to forecast specific results. From those general principles, a scientist can extrapolate and predict the specific results that would be valid as long as the general principles are valid. Studies in climate change can illustrate this type of reasoning. For example, scientists may predict that if the climate becomes warmer in a particular region, then the distribution of plants and animals should change. These predictions have been made and tested, and many such changes have been found, such as the modification of arable areas for agriculture, with change based on temperature averages.
Inductive and deductive reasoning are often used in tandem to advance scientific knowledge (Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)) . Both types of logical thinking are related to the two main pathways of scientific study: descriptive science and hypothesis-based science. Descriptive (or discovery) science , which is usually inductive, aims to observe, explore, and discover, while hypothesis-based science , which is usually deductive, begins with a specific question or problem and a potential answer or solution that one can test. The boundary between these two forms of study is often blurred, and most scientific endeavors combine both approaches.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Here is an example of how the two types of reasoning might be used in similar situations.
In inductive reasoning, where a conclusion is drawn from a number of observations, one might observe that members of a species are not all the same, individuals compete for resources, and species are generally adapted to their environment. This observation could then lead to the conclusion that individuals most adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and pass their traits to the next generation.
In deductive reasoning, which uses a general premise to predict a specific result, one might start with that conclusion as a general premise, then predict the results. For example, from that premise, one might predict that if the average temperature in an ecosystem increases due to climate change, individuals better adapted to warmer temperatures will outcompete those that are not. A scientist could then design a study to test this prediction.
The Scientific Method
Biologists study the living world by posing questions about it and seeking science-based responses. The scientific method is a method of research with defined steps that include experiments and careful observation. The scientific method was used even in ancient times, but it was first documented by England’s Sir Francis Bacon (1561–1626; Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)), who set up inductive methods for scientific inquiry. The scientific method is not exclusively used by biologists but can be applied to almost all fields of study as a logical, rational problem-solving method.
It is important to note that even though there are specific steps to the scientific method, the process of science is often more fluid, with scientists going back and forth between steps until they reach their conclusions.

Observation and Question
Scientists are good observers. In the field of biology, naturalists will often will make an observation that leads to a question. A naturalist is a person who studies nature. Naturalists often describe structures, processes, and behavior, either with their eyes or with the use of a tool such as a microscope. A naturalist may not conduct experiments, but they may ask many good questions that can lead to experimentation. Scientists are also very curious. They will research for known answers to their questions or run experiments to learn the answer to their questions.
Let’s think about a simple problem that starts with an observation and apply the scientific method to solve the problem. One Monday morning, a student arrives at class and quickly discovers that the classroom is too warm. That is an observation that also describes a problem: the classroom is too warm. The student then asks a question: “Why is the classroom so warm?”
Proposing a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is an educated guess or a suggested explanation for an event, which can be tested. Sometimes, more than one hypothesis may be proposed. Once a hypothesis has been selected, the student can make a prediction. A prediction is similar to a hypothesis but it typically has the format “If . . . then . . . .”.
For example, one hypothesis might be, “The classroom is warm because no one turned on the air conditioning.” However, there could be other responses to the question, and therefore one may propose other hypotheses. A second hypothesis might be, “The classroom is warm because there is a power failure, and so the air conditioning doesn’t work.” In this case, you would have to test both hypotheses to see if either one could be supported with data.
A hypothesis may become a verified theory . This can happen if it has been repeatedly tested and confirmed, is general, and has inspired many other hypotheses, facts, and experimentations. Not all hypotheses will become theories.
Testing a Hypothesis
A valid hypothesis must be testable. It should also be falsifiable , meaning that it can be disproven by experimental results. Importantly, science does not claim to “prove” anything because scientific understandings are always subject to modification with further information. This step—openness to disproving ideas—is what distinguishes sciences from non-sciences. The presence of the supernatural, for instance, is neither testable nor falsifiable. To test a hypothesis, a researcher will conduct one or more experiments designed to eliminate one or more of the hypotheses. Each experiment will have one or more variables and one or more controls. A variable is any part of the experiment that can vary or change during the experiment. The control group contains every feature of the experimental group except that it was not manipulated. Therefore, if the results of the experimental group differ from the control group, the difference must be due to the hypothesized manipulation, rather than some outside factor. Look for the variables and controls in the examples that follow. To test the first hypothesis, the student would find out if the air conditioning is on. If the air conditioning is turned on but does not work, there should be another reason, and this hypothesis should be rejected. To test the second hypothesis, the student could check if the lights in the classroom are functional. If so, there is no power failure, and this hypothesis should be rejected. Each hypothesis should be tested by carrying out appropriate experiments. Be aware that rejecting one hypothesis does not determine whether or not the other hypotheses can be accepted; it simply eliminates one hypothesis that is not valid (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)). Using the scientific method, the hypotheses that are inconsistent with experimental data are rejected.
While this “warm classroom” example is based on observational results, other hypotheses and experiments might have clearer controls. For instance, a student might attend class on Monday and realize she had difficulty concentrating on the lecture. One observation to explain this occurrence might be, “When I eat breakfast before class, I am better able to pay attention.” The student could then design an experiment with a control to test this hypothesis.
Visual Connection
The scientific method may seem too rigid and structured. It is important to keep in mind that, although scientists often follow this sequence, there is flexibility. Sometimes an experiment leads to conclusions that favor a change in approach; often, an experiment brings entirely new scientific questions to the puzzle. Many times, science does not operate in a linear fashion; instead, scientists continually draw inferences and make generalizations, finding patterns as their research proceeds. Scientific reasoning is more complex than the scientific method alone suggests. Notice, too, that the scientific method can be applied to solving problems that aren’t necessarily scientific in nature (Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)).
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
In the example below, the scientific method is used to solve an everyday problem. Match the scientific method steps (numbered items) with the process of solving the everyday problem (lettered items). Based on the results of the experiment, is the hypothesis correct? If it is incorrect, propose some alternative hypotheses.
Steps of the Scientific Method
- Observation
- Hypothesis (answer)
Process of Solving an Everyday Problem
- There is something wrong with the electrical outlet.
- If something is wrong with the outlet, my coffee maker also won’t work when plugged into it.
- My toaster doesn’t toast my bread.
- I plug my coffee maker into the outlet.
- My coffee maker works.
- Why doesn’t my toaster work?
Two Types of Science: Basic Science and Applied Science
The scientific community has been debating for the last few decades about the value of different types of science. Is it valuable to pursue science for the sake of simply gaining knowledge, or does scientific knowledge only have worth if we can apply it to solving a specific problem or to bettering our lives? This question focuses on the differences between two types of science: basic science and applied science.
Basic science or “pure” science seeks to expand knowledge regardless of the short-term application of that knowledge. It is not focused on developing a product or a service of immediate public or commercial value. The immediate goal of basic science is knowledge for knowledge’s sake, though this does not mean that, in the end, it may not result in a practical application.
In contrast, applied science or “technology,” aims to use science to solve real-world problems, making it possible, for example, to improve a crop yield or find a cure for a particular disease. In applied science, the problem is usually defined for the researcher.
Some individuals may perceive applied science as “useful” and basic science as “useless.” A question these people might pose to a scientist advocating knowledge acquisition would be, “What for?” A careful look at the history of science, however, reveals that basic knowledge has resulted in many remarkable applications of great value. Many scientists think that a basic understanding of science is necessary before an application is developed; therefore, applied science relies on the results generated through basic science. Other scientists think that it is time to move on from basic science and instead to find solutions to actual problems. Both approaches are valid. It is true that there are problems that demand immediate attention; however, few solutions would be found without the help of the wide knowledge foundation generated through basic science.
One example of how basic and applied science can work together to solve practical problems occurred after the discovery of DNA structure led to an understanding of the molecular mechanisms governing DNA replication. Strands of DNA, unique in every human, are found in our cells, where they provide the instructions necessary for life. During DNA replication, DNA makes new copies of itself, shortly before a cell divides. Understanding the mechanisms of DNA replication enabled scientists to develop laboratory techniques that are now used to identify genetic diseases, pinpoint individuals who were at a crime scene, and determine paternity. Without basic science, it is unlikely that applied science would exist.
Another example of the link between basic and applied research is the Human Genome Project, a study in which each human chromosome was analyzed and mapped to determine the precise sequence of DNA subunits and the exact location of each gene. (The gene is the basic unit of heredity; an individual’s complete collection of genes is their genome.) Other less complex organisms have also been studied as part of this project in order to gain a better understanding of human chromosomes. The Human Genome Project (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)) relied on basic research carried out with simple organisms and, later, with the human genome. An important end goal eventually became using the data for applied research, seeking cures and early diagnoses for genetically related diseases.

While research efforts in both basic science and applied science are usually carefully planned, it is important to note that some discoveries are made by serendipity , that is, by means of a fortunate accident or a lucky surprise. Penicillin was discovered when biologist Alexander Fleming accidentally left a petri dish of Staphylococcus bacteria open. An unwanted mold grew on the dish, killing the bacteria. The mold turned out to be Penicillium , and a new antibiotic was discovered. Even in the highly organized world of science, luck—when combined with an observant, curious mind—can lead to unexpected breakthroughs.
Reporting Scientific Work
Whether scientific research is basic science or applied science, scientists must share their findings in order for other researchers to expand and build upon their discoveries. Collaboration with other scientists—when planning, conducting, and analyzing results—are all important for scientific research. For this reason, important aspects of a scientist’s work are communicating with peers and disseminating results to peers. Scientists can share results by presenting them at a scientific meeting or conference (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)), but this approach can reach only the select few who are present. Instead, most scientists present their results in peer-reviewed manuscripts that are published in scientific journals. Peer-reviewed manuscripts are scientific papers that are reviewed by a scientist’s colleagues, or peers. These colleagues are qualified individuals, often experts in the same research area, who judge whether or not the scientist’s work is suitable for publication. The process of peer review helps to ensure that the research described in a scientific paper or grant proposal is original, significant, logical, and thorough. Grant proposals, which are requests for research funding, are also subject to peer review. Scientists publish their work so other scientists can reproduce their experiments under similar or different conditions to expand on the findings. The experimental results must be consistent with the findings of other scientists.

A scientific paper is very different from creative writing. Although creativity is required to design experiments, there are fixed guidelines when it comes to presenting scientific results. First, scientific writing must be brief, concise, and accurate. A scientific paper needs to be succinct but detailed enough to allow peers to reproduce the experiments.
The scientific paper consists of several specific sections—introduction, materials and methods, results, and discussion. This structure is sometimes called the “IMRaD” format, an acronym for Introduction, Method, Results, and Discussion. There are usually acknowledgment and reference sections as well as an abstract (a concise summary) at the beginning of the paper. There might be additional sections depending on the type of paper and the journal where it will be published; for example, some review papers require an outline.
The introduction starts with brief, but broad, background information about what is known in the field. A good introduction also gives the rationale of the work; it justifies the work carried out and also briefly mentions the end of the paper, where the hypothesis or research question driving the research will be presented. The introduction refers to the published scientific work of others and therefore requires citations following the style of the journal. Using the work or ideas of others without proper citation is considered plagiarism .
The materials and methods section includes a complete and accurate description of the substances used, and the method and techniques used by the researchers to gather data. The description should be thorough enough to allow another researcher to repeat the experiment and obtain similar results, but it does not have to be verbose. This section will also include information on how measurements were made and what types of calculations and statistical analyses were used to examine raw data. Although the materials and methods section gives an accurate description of the experiments, it does not discuss them.
Some journals require a results section followed by a discussion section, but it is more common to combine both. If the journal does not allow the combination of both sections, the results section simply narrates the findings without any further interpretation. The results are presented by means of tables or graphs, but no duplicate information should be presented. In the discussion section, the researcher will interpret the results, describe how variables may be related, and attempt to explain the observations. It is indispensable to conduct an extensive literature search to put the results in the context of previously published scientific research. Therefore, proper citations are included in this section as well.
Finally, the conclusion section summarizes the importance of the experimental findings. While the scientific paper almost certainly answered one or more scientific questions that were stated, any good research should lead to more questions. Therefore, a well-done scientific paper leaves doors open for the researcher and others to continue and expand on the findings.
Review articles do not follow the IMRaD format because they do not present original scientific findings (they are not primary literature); instead, they summarize and comment on findings that were published as primary literature and typically include extensive reference sections.
Attributions
Curated and authored by Kammy Algiers using 1.2 (The Process of Science) from Biology 2e by OpenStax (licensed CC-BY ).

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.4: The Scientific Method - How Chemists Think
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 182607
Learning Objectives
- Identify the components of the scientific method.
Scientists search for answers to questions and solutions to problems by using a procedure called the scientific method. This procedure consists of making observations, formulating hypotheses, and designing experiments; which leads to additional observations, hypotheses, and experiments in repeated cycles (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)).
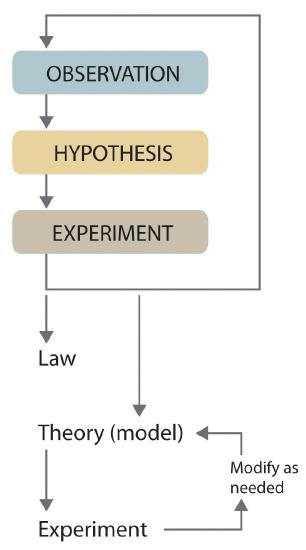
Step 1: Make observations
Observations can be qualitative or quantitative. Qualitative observations describe properties or occurrences in ways that do not rely on numbers. Examples of qualitative observations include the following: "the outside air temperature is cooler during the winter season," "table salt is a crystalline solid," "sulfur crystals are yellow," and "dissolving a penny in dilute nitric acid forms a blue solution and a brown gas." Quantitative observations are measurements, which by definition consist of both a number and a unit. Examples of quantitative observations include the following: "the melting point of crystalline sulfur is 115.21° Celsius," and "35.9 grams of table salt—the chemical name of which is sodium chloride—dissolve in 100 grams of water at 20° Celsius." For the question of the dinosaurs’ extinction, the initial observation was quantitative: iridium concentrations in sediments dating to 66 million years ago were 20–160 times higher than normal.
Step 2: Formulate a hypothesis
After deciding to learn more about an observation or a set of observations, scientists generally begin an investigation by forming a hypothesis, a tentative explanation for the observation(s). The hypothesis may not be correct, but it puts the scientist’s understanding of the system being studied into a form that can be tested. For example, the observation that we experience alternating periods of light and darkness corresponding to observed movements of the sun, moon, clouds, and shadows is consistent with either one of two hypotheses:
- Earth rotates on its axis every 24 hours, alternately exposing one side to the sun.
- The sun revolves around Earth every 24 hours.
Suitable experiments can be designed to choose between these two alternatives. For the disappearance of the dinosaurs, the hypothesis was that the impact of a large extraterrestrial object caused their extinction. Unfortunately (or perhaps fortunately), this hypothesis does not lend itself to direct testing by any obvious experiment, but scientists can collect additional data that either support or refute it.
Step 3: Design and perform experiments
After a hypothesis has been formed, scientists conduct experiments to test its validity. Experiments are systematic observations or measurements, preferably made under controlled conditions—that is—under conditions in which a single variable changes.
Step 4: Accept or modify the hypothesis
A properly designed and executed experiment enables a scientist to determine whether or not the original hypothesis is valid. If the hypothesis is valid, the scientist can proceed to step 5. In other cases, experiments often demonstrate that the hypothesis is incorrect or that it must be modified and requires further experimentation.
Step 5: Development into a law and/or theory
More experimental data are then collected and analyzed, at which point a scientist may begin to think that the results are sufficiently reproducible (i.e., dependable) to merit being summarized in a law, a verbal or mathematical description of a phenomenon that allows for general predictions. A law simply states what happens; it does not address the question of why.
One example of a law, the law of definite proportions , which was discovered by the French scientist Joseph Proust (1754–1826), states that a chemical substance always contains the same proportions of elements by mass. Thus, sodium chloride (table salt) always contains the same proportion by mass of sodium to chlorine, in this case 39.34% sodium and 60.66% chlorine by mass, and sucrose (table sugar) is always 42.11% carbon, 6.48% hydrogen, and 51.41% oxygen by mass.
Whereas a law states only what happens, a theory attempts to explain why nature behaves as it does. Laws are unlikely to change greatly over time unless a major experimental error is discovered. In contrast, a theory, by definition, is incomplete and imperfect, evolving with time to explain new facts as they are discovered.
Because scientists can enter the cycle shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) at any point, the actual application of the scientific method to different topics can take many different forms. For example, a scientist may start with a hypothesis formed by reading about work done by others in the field, rather than by making direct observations.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Classify each statement as a law, a theory, an experiment, a hypothesis, an observation.
- Ice always floats on liquid water.
- Birds evolved from dinosaurs.
- Hot air is less dense than cold air, probably because the components of hot air are moving more rapidly.
- When 10 g of ice were added to 100 mL of water at 25°C, the temperature of the water decreased to 15.5°C after the ice melted.
- The ingredients of Ivory soap were analyzed to see whether it really is 99.44% pure, as advertised.
- This is a general statement of a relationship between the properties of liquid and solid water, so it is a law.
- This is a possible explanation for the origin of birds, so it is a hypothesis.
- This is a statement that tries to explain the relationship between the temperature and the density of air based on fundamental principles, so it is a theory.
- The temperature is measured before and after a change is made in a system, so these are observations.
- This is an analysis designed to test a hypothesis (in this case, the manufacturer’s claim of purity), so it is an experiment.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Classify each statement as a law, a theory, an experiment, a hypothesis, a qualitative observation, or a quantitative observation.
- Measured amounts of acid were added to a Rolaids tablet to see whether it really “consumes 47 times its weight in excess stomach acid.”
- Heat always flows from hot objects to cooler ones, not in the opposite direction.
- The universe was formed by a massive explosion that propelled matter into a vacuum.
- Michael Jordan is the greatest pure shooter to ever play professional basketball.
- Limestone is relatively insoluble in water, but dissolves readily in dilute acid with the evolution of a gas.
The scientific method is a method of investigation involving experimentation and observation to acquire new knowledge, solve problems, and answer questions. The key steps in the scientific method include the following:
- Step 1: Make observations.
- Step 2: Formulate a hypothesis.
- Step 3: Test the hypothesis through experimentation.
- Step 4: Accept or modify the hypothesis.
- Step 5: Develop into a law and/or a theory.
Contributions & Attributions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The scientific method. At the core of biology and other sciences lies a problem-solving approach called the scientific method. The scientific method has five basic steps, plus one feedback step: Make an observation. Ask a question. Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation. Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
The scientific method is a process used to explore observations and answer questions. Originally used by scientists looking to prove new theories, its use has spread into many other areas, including that of problem-solving and decision-making. The scientific method is designed to eliminate the influences of bias, prejudice and personal beliefs ...
The number of steps varies, but the process begins with an observation, progresses through an experiment, and concludes with analysis and sharing data. One of the most important pieces to the scientific method is skepticism —the goal is to find truth, not to confirm a particular thought. That requires reevaluation and repeated experimentation ...
The six steps of the scientific method include: 1) asking a question about something you observe, 2) doing background research to learn what is already known about the topic, 3) constructing a hypothesis, 4) experimenting to test the hypothesis, 5) analyzing the data from the experiment and drawing conclusions, and 6) communicating the results ...
The Six Steps. The number of steps can vary from one description to another (which mainly happens when data and analysis are separated into separate steps), however, this is a fairly standard list of the six scientific method steps that you are expected to know for any science class: Purpose/Question Ask a question.
The scientific method is critical to the development of scientific theories, which explain empirical (experiential) laws in a scientifically rational manner. In a typical application of the scientific method, a researcher develops a hypothesis, tests it through various means, and then modifies the hypothesis on the basis of the outcome of the ...
The scientific method is a method of investigation involving experimentation and observation to acquire new knowledge, solve problems, and answer questions. The key steps in the scientific method include the following: Step 1: Make observations. Step 2: Formulate a hypothesis. Step 3: Test the hypothesis through experimentation.
Use the scientific method and your problem solving abilities to get out. While you are in the escape room see what else you might uncover as you test your escape skills.To learn more, visit Using the Scientific Method to Solve Mysteries. ... Method: following a certain set of steps to make something, or find an answer to a question. Like baking ...
Steps in the scientific method. While the scientific method is versatile in form and function, it encompasses a collection of principles that create a logical progression to the process of problem solving: Define a question: Constructing a clear and precise problem statement that identifies the main question or goal of the investigation is the ...
The scientific method is the process by which scientists of all fields attempt to explain the phenomena in the world. It is how science is conducted--through experimentation. Generally, the scientific method refers to a set of steps whereby a scientist can form a conjecture (the hypothesis) for why something functions the way it does and then test their hypothesis. It is an empirical process ...
In doing so, they are using the scientific method. 1.2: Scientific Approach for Solving Problems is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Chemists expand their knowledge by making observations, carrying out experiments, and testing hypotheses to develop laws to summarize their results and ...
The scientific method. At the core of physics and other sciences lies a problem-solving approach called the scientific method. The scientific method has five basic steps, plus one feedback step: Make an observation. Ask a question. Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation. Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
In the example below, the scientific method is used to solve an everyday problem. Order the scientific method steps (numbered items) with the process of solving the everyday problem (lettered items). Based on the results of the experiment, is the hypothesis correct? If it is incorrect, propose some alternative hypotheses.
The scientific method is a step-by-step problem-solving process. These steps include: ... It's a step-by-step problem-solving process that involves: (1) observation, (2) asking questions, (3 ...
A brief history of the scientific method. The scientific method has its roots in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. Philosophers Francis Bacon and René Descartes are often credited with formalizing the scientific method because they contrasted the idea that research should be guided by metaphysical pre-conceived concepts of the nature of reality—a position that, at the time, was ...
Here are the seven steps of the scientific method illustrated by an example scientific hypothesis: 1. Ask a question. The first step in the scientific method is asking a question you want to answer. This question will include one of the key starters: how, what, when, why, where, who or which. The question you ask should also be measurable and ...
Chapter 6: Scientific Problem Solving. Science is a method to discover empirical truths and patterns. Roughly speaking, the scientific method consists of. 4) Interpreting the data to confirm or disconfirm the hypothesis. The beauty of science is that any scientific claim can be tested if you have the proper knowledge and equipment.
The scientific method, as developed by Bacon and others, involves several steps: Ask a question - identify the problem to be considered. Make observations - gather data that pertains to the question. Propose an explanation (a hypothesis) for the observations. Make new observations to test the hypothesis further.
The scientific method is a method of research with defined steps that include experiments and careful observation. The scientific method was used even in ancient times, but it was first documented by England's Sir Francis Bacon (1561-1626; Figure 1.1.1.2 1.1.1. 2 ), who set up inductive methods for scientific inquiry.
The scientific method is a method of investigation involving experimentation and observation to acquire new knowledge, solve problems, and answer questions. The key steps in the scientific method include the following: Step 1: Make observations. Step 2: Formulate a hypothesis. Step 3: Test the hypothesis through experimentation.
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century. (For notable practitioners in previous centuries, see history of scientific method.). The scientific method involves careful observation coupled with rigorous scepticism, because cognitive assumptions can distort the interpretation of the ...
Formulate student's ideas into a chart of steps in the scientific method. Determine with the students how a scientist solves problems. • Arrange students in working groups of 3 or 4. Students are to attempt to discover what is in their mystery box. • The group must decide on a procedure to determine the contents of their box and formulate ...
Step 1. DEFINE THE SPECIFIC PROBLEM. -The starting point is recognizing and stating a very specific question/. Step 2. COLLECT INFORMATION BY MAKING OBSERVATIONS. -Gather background information on the problem, and make many observations, information obtained by using the senses. Step 3. FORM A HYPOTHESIS.