- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus

Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
direct | indirect | reported clause | |
statement | ) I was tired. | -clause | |
question | . . | clause clause clause | |
command | . | -infinitive clause |
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
direct speech | indirect speech |
| not very happy at work.’ | not very happy at work. |
| going home.’ | going home. |
| be late.’ | be late. |
| been working,’ she said. | . |
| to make her so angry?’ he asked. | to make her so angry. |
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
direct | indirect | |
present simple | → | past simple |
present continuous | → | past continuous |
present perfect simple | → | past perfect simple |
present perfect continuous | → | past perfect continuous |
past simple | → | past perfect simple |
past continuous | → | past perfect continuous |
future (will) | → | future-in-the-past (would) |
past perfect | ↔ | past perfect (no change) |
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Direct speech | Indirect speech |
| already left. |
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
direct speech | indirect speech | change | |
| be there,’ he promised. | be there. | becomes |
| need more money.’ I open it?’ she asked. | need more money. open it. | usually becomes in reported questions, becomes |
| see you at 2.30,’ he added. | see me at 2.30. | becomes |
| be back later,’ she said. wait in the hallway,’ he said. | be back later. wait in the hallway. | (possibility) becomes (permission) becomes |
| pay by 30th April.’ be awful to live in such a noisy place,’ she said. | pay by 30th April. be awful to live in such a noisy place. | (obligation) usually becomes (speculation) does not change |
| sell it for about 2,000 euros,’ he said. | sell it for about 2,000 euros. | no change |
| go there immediately,’ she said. | go there immediately. | no change |
| buy it if I had the money,’ he said. | buy it if he had the money. | no change |
| snow tonight,’ he warned. | snow that night. | no change |
| come till six o’clock,’ he said. | come till six o’clock. | no change |
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
direct | indirect | |
| don’t want to shock people,’ Tom said. | said he didn’t want to shock people. | different speakers ( changes to ) |
| ’ll look after Toby,’ I said. | said I would look after Toby. | same speaker (no change) |
| need to be here at nine o’clock,’ George told Beatrice. | told Beatrice she needed to be there at nine o’clock. | different speakers ( changes to ) |
| hope you will join us tonight,’ I said to James. | told James I hoped he would join us that night. | same speaker (no change to ; changes to ) |
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
direct speech | indirect speech |
| .’ | the next/following day. |
| this moment in time.’ | . |
| .” | . |
| ,’ the boy protested. | . |
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
direct | indirect | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect speech: typical errors
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
skip out on something
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
to avoid doing something that you should do; to leave someone when they need your help

It’s not really my thing (How to say you don’t like something)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

Home / English Grammar / 19 Direct and Indirect Speech Rules Examples (Updated 2025)

19 Direct and Indirect Speech Rules Examples (Updated 2025)
Have you ever struggled with the rules of direct and indirect speech? You’re not alone. These forms of speech can be challenging, but mastering them is crucial for clear and effective communication, especially for school students, ESL learners, and those preparing for competitive exams.
Understanding direct and indirect speech conversion rules is crucial for clear and accurate communication and the conversion between direct and indirect speech will significantly enhance your language skills.
This informative article will explore these Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for Conversion with detailed examples.
Understanding Direct Speech
Direct speech is a form of reporting that presents someone’s exact words without any alterations. It is commonly enclosed in quotation marks, allowing readers to see the speaker’s statements precisely as they were uttered.
1. Key Elements of Direct Speech
a . Quotation Marks
Quotation marks are your best friends here. They compress the exact words spoken by a person.
b. Punctuation Placement
Punctuation is crucial. Commas , periods , question marks , and exclamation points all have their specific places within the quotation marks.
c. Speaker Tags
Speaker tags like “he said” or “she exclaimed” are often used to indicate who is speaking. These can be placed before , after , or even in the middle of the quoted speech.
2. E xamples of Direct Speech
a. Basic Examples
Consider this simple example:
- Ritu said, “I am going to the store.”
Here, the exact words of Ritu are presented within quotation marks.
b. Complex Examples
Now, let’s add more complexity:
- “I can’t believe it,” she whispered, “but I saw a unicorn in the garden.”
Notice how the sentence is split into two parts, but both are still within quotation marks.
For a better understanding of Direct Narration
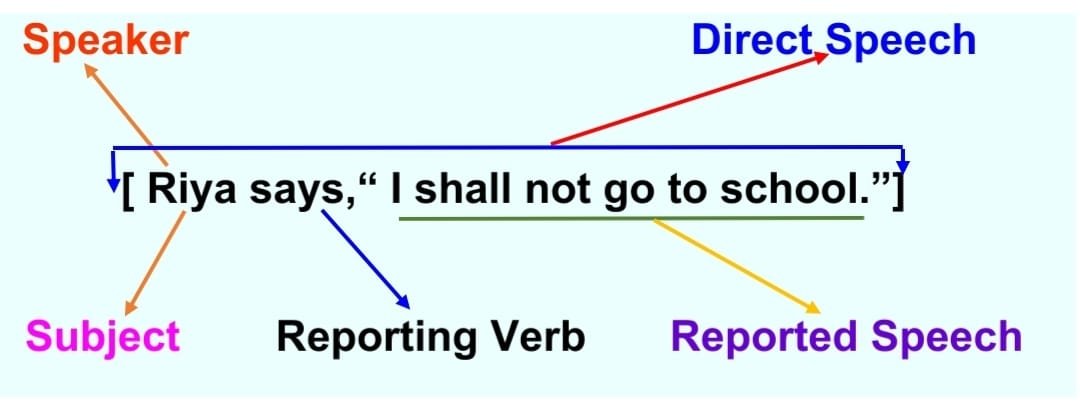
“I shall not go to school,” are the exact words of Riya, enclosed in quotation marks/inverted commas (“….”). This format, which uses commas and quotation marks/inverted commas, is called direct speech . In this sentence, ‘Riya’ is the subject or speaker, ‘says’ is the reporting verb, and ‘I shall not go to school’ is the reported speech.
Understanding Indirect Speech
Indirect speech , on the other hand, involves paraphrasing someone’s words and reporting them indirectly, without using quotation marks. It requires a few changes in structure, such as tense and pronoun shifts. Let’s convert the previous example of direct speech into indirect speech:
1. Key Elements of Indirect Speech
a. Removing Quotation Marks
Unlike direct speech, indirect speech doesn’t require quotation marks. You’re paraphrasing what was said.
b. Changing Pronouns
Pronouns often need to be changed to fit the new context. For instance, “I” becomes “he” or “she.”
c. Adjusting Tenses
Tenses usually shift back when converting to indirect speech. Present tense often turns into past tense.
d. Modifying Time Expressions
Time expressions like “today” or “tomorrow” also change to maintain the timeline consistency.
2. Examples of Indirect Speech
Basic Examples
Here’s a simple conversion:
- Direct: John said, “I am going to the store.”
- Indirect: John said that he was going to the store.
Complex Examples
For a more complex sentence:
- Direct: “I can’t believe it,” she whispered, “but I saw a unicorn in the garden.”
- Indirect: She whispered that she couldn’t believe it but that she had seen a unicorn in the garden.
For a clear concept of Indirect Narration
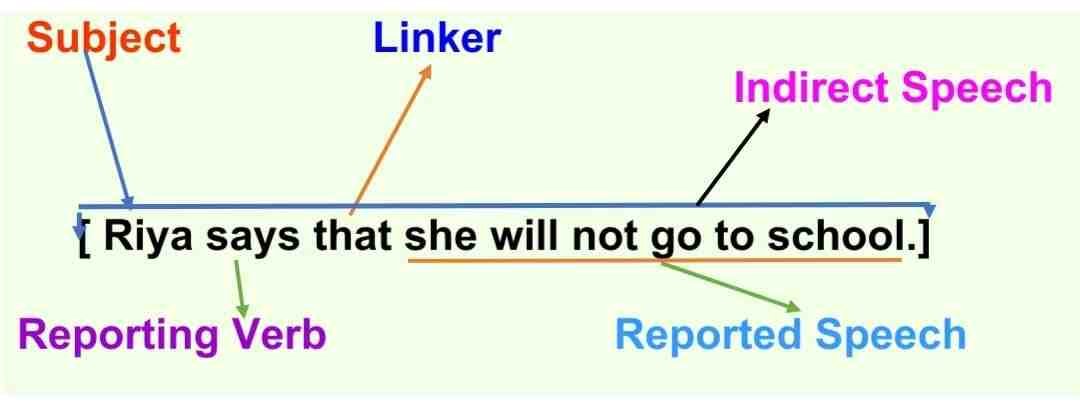
Similarly, we can report the above sentence without quoting Riya’s exact words while keeping the meaning the same. This format is called indirect speech. In this format, no commas or quotation marks/inverted commas are used; only a full stop (.) is used at the end of the sentence.
Difference between direct and indirect speech rules
The following comparison highlights the key differences between direct and indirect speech rules, including punctuation, tense changes, and adjustments to pronouns and time references.
| Quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker. | Reporting the essence of what the speaker said without quoting exactly. | |
| Uses quotation marks (“…”). | Does not use quotation marks. | |
| Follows the reporting verb with a comma. | Integrates the reporting verb without a comma. | |
| Tense remains as originally spoken. | Tense often shifts back (present to past, future to conditional, etc.). | |
| Pronouns remain as originally spoken. | Pronouns change to match the perspective of the reporting speaker. | |
| Time and place references remain as originally spoken. | Time and place references may change (e.g., “today” becomes “that day”). | |
| She said, “I am going to the store.” | She said that she was going to the store. | |
| John asked, “Can you help me?” | John asked if I could help him. | |
| “We will finish the project tomorrow,” they promised. | They promised that they would finish the project the next day. | |
| “I have never seen such a beautiful place,” he exclaimed. | He exclaimed that he had never seen such a beautiful place. |
People also ask
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules: Essential for Learners
Discover the essential rules of direct and indirect speech with a variety of examples to improve your language skills. Effortlessly understand the intricacies of converting statements, questions, and commands from one form to another.
Understanding direct and indirect speech is crucial for effective communication, for learners. Here, we have outlined the essential rules you need to know.
A. Reporting Verbs Rules B. Tenses Rules C. Pronouns Rules D. Punctuation Marks Rules E. Modals and Conditional Rules F. Modifying Words Rules
A. Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for Reporting Verbs
Different reporting verbs are used to introduce indirect speech. The choice of reporting verb can convey the speaker’s attitude towards the reported speech.
Changes in reporting verbs according to tense are one of the most important rules for converting direct speech into indirect speech.
Remember: If the reporting verbs are in the present or future tense, the tense of the verb in the reported speech is not changed .
Remember: If the reporting verbs are in the past tense , the tense of the verb in the reported speech will be in the corresponding past tense.
Here are some commonly used reporting verbs:
Rule 1: Reporting verbs rules for ‘ Say ‘ and ‘ Tell ‘.
“Say” and “tell” are two frequently used reporting verbs. “Say” is generally followed by the reported speech, while “tell” is followed by the indirect object (the person being addressed).
Direct: He says , “I am your friend.” Indirect: He says that he is your friend.
Direct: He said to me, “I’m going to the store.” Indirect: She told me that he was going to the store.
Reporting verbs ‘Say’ and ‘Tell’ Chart
| say | say |
| say to me | tell me |
| says to them | tells them |
| said | said |
| said to him | told him |
| shall/will say | shall/will say |
| shall/will say to her | shall/will tell her |
Rule 2: ‘ Ask ‘ and ‘ Inquire’ are used as reporting verbs.
When reporting questions , “ ask “ and “ inquire “ are commonly employed reporting verbs.
Direct: He said to me, “Where are you going?” Indirect: He asked where I was going.
Direct: She said , “When will the concert start?” Indirect: She inquired, “When will the concert start?”
Direct: Sarah said , “What time does the movie start?” Indirect: Sarah asked what time the movie started.
Direct: “Could you please provide more details?” she said to me. Indirect: She inquired politely if I could provide more details.
Direct: The customer said , “Do you have this item in stock?” Indirect: The customer i nquired if that item had in stock.
Rule 3: Reporting Verb rules for “ Request “, “ Advise “, “ Order “, and “ Beg “.
To report imperative sentences, “Request”, “Advise”, “Order”, and “beg” are often used.
Direct: “Please close the door,” she said . Indirect: She requested that the door be closed.
Direct: “You should study regularly,” he said. Indirect: He advised that regular studying should be done.
Direct: “Stand up straight,” the sergeant said . Indirect: The sergeant ordered that they stand up straight.
Direct: He said to me, “Go home at once” Indirect: He ordered me to go home at once.
Direct: She said , “Do not run in the sun” Indirect: She advised not to run in the sun.”
Direct: “Please forgive me,” she said. Indirect: She begged for forgiveness.
B. Tenses Rules for Direct and Indirect Speech
The second most important rule is the changes of Tenses for converting direct speech to indirect speech. When transforming direct speech into indirect speech, there are specific rules to follow regarding tense changes:
Rule 4: If the reporting verb is in the present tense ,
If the Reporting Verb is in the Present Tense , there is no change in the tense in the Reported Verb when Direct Speech is converted into Indirect Narration.
Direct: Arnab says , “The room is dark.” Indirect: Arnab says that the room is dark.
Direct: Arnab says , “The room was dark.” Indirect: Arnab says that the room was dark.
Direct: Arnab says , “I shall finish the work.” Indirect: Arnab says that he will finish the work.
Direct: Mary says , “I am going to the party.” Indirect: Mary says that she is going to the party.
Direct: He tells us, “I will finish the project by tomorrow.” Indirect: He tells us that he will finish the project by tomorrow.
Rule 5: If the reporting verb is in the future tense ,
If the Reporting Verb is in the Future Tense , there is no change in the tense in the Reported Verb when Direct Speech is converted into Indirect Narration.
Direct: Sarah will say , “I am going to the store.” Indirect: Sarah will say that she is going to the store.
Direct: John will say, “I have completed the assignment.” Indirect: John will say that he has completed the assignment.
Direct: Arnab will say, “The room is dark.” Indirect: Arnab will say that the room is dark.
Direct: Arnab will say , “The room was dark.” Indirect: Arnab will say that the room was dark.
Direct: Arnab will say, “I shall finish the work.” Indirect: Arnab will say that he will finish the work.
Rule 6: If the reporting verb is in the past tense ,
If the Reporting verb of the Direct Narration is in the Past Tense , the Present Tense of the Verb in the Reported Speech of Direct Narration is changed into the corresponding Past Tense in Indirect Narration .
| Past He , | Present Indefinite ” I you” | Past Indefinite He said that he me. |
| Past The teacher , | Universal Truth or Regular Habits ” The sun in the east.” | Remains Unchanged The teacher said that the sun in the east. |
| Past She , | Present Continuous ” I a song.” | Past Continuous She said that she . |
| Past Mother , | Present Perfect ” I cooking.” | Past Perfect Mother said that she cooking. |
| Past Maria , | Past Indefinite “You the work.” | Past Perfect Maria said that I the work. |
| Past Soumen , | Past Continuous ” I football.” | Soumen said that he football. |
| Past Ravvi , | Past Perfect ” You me.” | Remains Unchanged Ravi said that I him. |
| Past They said, | Shall/Will “We help him.” | Should/Would They said that they help him. |
| Past Doctor , | Can / May ” You do it.” | Could / Might The doctor said that I do it. |
Direct: Rohan said , “She works hard.” Indirect: Rohan said that she worked hard.
Direct: Rohan said, “She is singing a song.” Indirect: Rohan said that she was singing a song.
Direct: The guest said shouting, “We have arrived .” Indirect: The guest shouted that they had arrived.
Direct: My sister said , “It has been raining hard for 3 days”. Indirect: My sister said that it had been raining hard for 3 days.
Direct: Father said, “I visited the Taj yesterday.” Indirect: Father said that he had visited the Taj the previous day.
Direct: The boys said, “They were traveling in the park.” Indirect: The boys said that they had been traveling in the park.
Direct: The reporters commented , “The Kohinoor had been lost long ago”. Indirect: The reporters commented that the Kohinoor had been lost long ago.
Direct: Jyotsna said, “ She had been doing the work for 3 hours”. Indirect: Jyotsna said that she had been doing the work for 3 hours.
Rule: 7 If the reported speech implies Universal Truth or Habitual Fact or Scientific Truth ,
The Tense of the Verb remains unchanged in Indirect Narration in cases of General Statements of Facts , Universal Truths , Commonplace Occurrences , and Habitual or Repeated Actions . No real change occurs in these cases. Only there will be present Tense alone.
Direct: The boy said to his mother, “ The sun rises in the East”. Indirect: The boy told his mother that the sun rises in the East. [ Universal Truth ]
Direct: The monk answered , “ Man is mortal”. Indirect: The monk answered that man is mortal. [ Universal Truth ]
Direct: The teacher told the students, “ Perseverance always leads to success.” Indirect: The teacher told the students that perseverance always leads to success.
3. Direct and Indirect Speech R ules for Pronouns
There are certain rules to follow regarding the changes of pronouns from direct speech to indirect speech:
Rule 8: Personal Pronouns (I, We, You, He, She, They) Rules
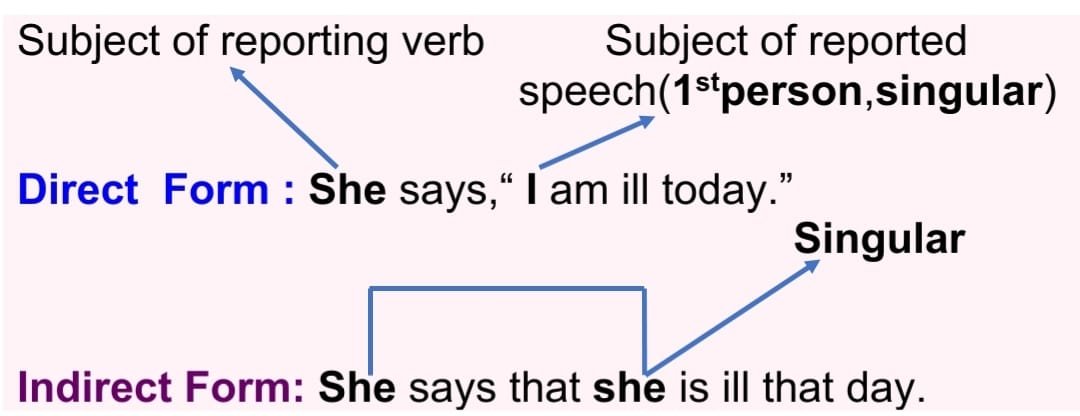
First person.
(a) If the subject of the reported speech of direct form is in the first person, the subject of the reported speech will be replaced by the subject of the reporting verb in indirect form, but the number must be the same. [ singular > singular and plural > plural ]
Direct: She says, “ I am ill today.” Indirect: She says that she is ill that day.
Second Person
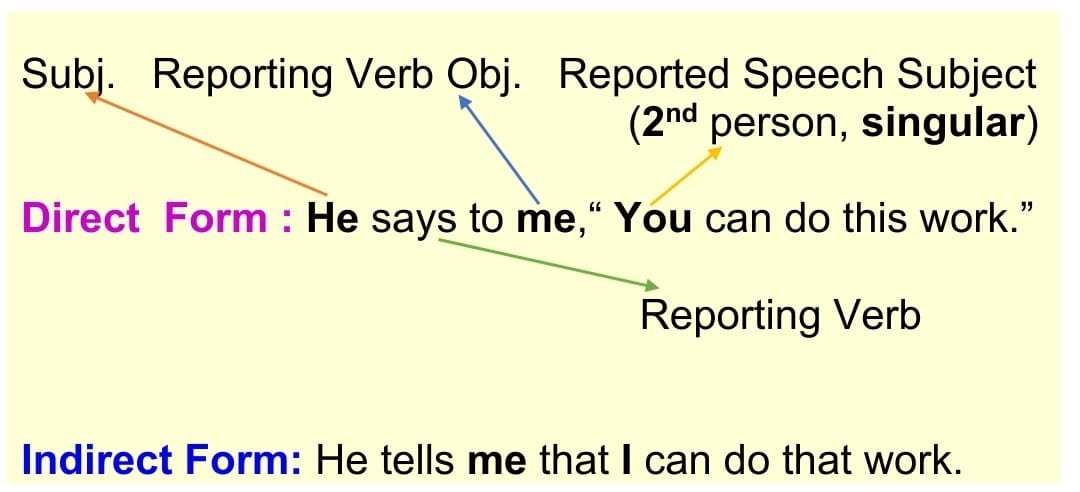
(b) If the subject of the reported speech in the Direct Form is in the second person, the subject of the reported speech will be replaced by the object of the reporting verb in the indirect form, but the number must be the same. [ singular > singular and plural > plural ]
Direct: He says to me , ” You can do this work.” Indirect: He tells me that I can do that work.
Third Person
(c) If the subject of the reported speech of Direct Form is in the third person, there will be no change in the person of the Indirect Form.
Direct: I said, “ He will not wait for his friend.” Indirect: I said that he would not wait for his friend.

Pronouns Chart : direct and indirect speech rules
| I (1st person, singular) | me (1st person, singular) |
| We (1st person, plural) | us (1st person, plural) |
| You (2nd person, singular / plural) | You (2nd person, |
| He (3rd person, singular) | him (3rd person, singular) |
| She (3rd person, singular) | her (3rd person, singular) |
| They (3rd person, plural) | them (3rd person, plural) |
Rule 9: Demonstrative Pronouns ( This, That ) Rules
In the case of demonstrative pronouns, replace them with appropriate pronouns in indirect speech.
Direct: “ This is my book,” she said. Indirect: She said that this was her book.
4. Direct and Indirect Speech ( Punctuation and Quotation Marks ) Rules
Understanding how to punctuate and use quotation marks correctly is crucial when dealing with direct and indirect speech. Here are some guidelines:
Rule 10: Comma with Reporting Verb Rules
When introducing indirect speech with a reporting verb, use a comma to separate the reporting verb from the reported speech.
Example: She said, “I’ll be there on time.”
Rule 11: Question Mark to Full Stop Rules
If the direct speech is a question, change the question mark to a full stop when converting to indirect speech.
Direct: He asked, “Are you coming to the party?” Indirect: He asked if I was coming to the party.
Rule 12: Exclamation Mark to Full Stop Rules
In cases where the direct speech has an exclamation mark, replace it with a full stop in indirect speech.
Direct: She exclaimed, “What a beautiful day!” Indirect: She exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
E. Direct to Indirect Speech Conversion Rules : Modals and Conditional Sentences
Indirect speech involving modals and conditional sentences requires careful attention to maintain accuracy:
Rule 13: Rules of Modals in Indirect Speech
When dealing with modals like can, could, will, would, may, might, shall, should, must, etc., use the appropriate past form in indirect speech.
Direct: She said, “You should respect your elders. Indirect: She said that I should respect my elders.
Direct: She said, “I can speak French fluently. Indirect: She said that she could speak French fluently.
Direct: May I borrow your pen?” she asked. Indirect: She asked if she might borrow my pen.
Direct: He said, “You must complete the assignment by tomorrow. Indirect: He said that I must complete the assignment by the next day.
Rule 14: Conditional Sentences in Indirect Speech Rules
In indirect speech, conditional sentences undergo specific changes, especially when they involve “will” or “would.”
Direct: He said, “I will help you.” Indirect: He said that he would help me.
Direct: He said, “I will help you with your project Indirect: He said that he would help me with my project.
F. Direct and Indirect Speech Rules: ( Modifying Words – Time, Place, Manner )
Adding modifying words or phrases can alter the meaning of the reported speech:
Rule 15: Reporting with Adverbs of Time
When using adverbs of time in indirect speech, adjust them to match the new timeframe.
Direct: “I will come tomorrow,” she said. Indirect: She said that she would come the next day.
Rule 16: Reporting with Adverbs of Place
Similar to adverbs of time, adverbs of place need modification in indirect speech.
Direct: ” I live here,” he said. Indirect: He said that he lived there.
Rule 17: Reporting with Adverbs of Manner
We can also use Adverbs of manner in indirect speech, requiring appropriate adjustments.
Direct: “He ran quickly,” she said. Indirect: She said that he ran quickly.
Time, Place, Manner, Distance, Direction Chart: Direct and Indirect Speech Rules
In Indirect Narration, words denoting Time, Place, Manner, Distance, and Direction used in the quoted speech are correspondingly changed to conform to the point of view of the Reporter. Thus, the sense of nearness is changed into that of Distance, and so on.
| now | then /at that time |
| ago | before |
| henceforth | thenceforth |
| long ago | long before |
| henceforward | thenceforward |
| today | That day /the same day |
| tonight | that night /the same night |
| tomorrow | the next day /the following day |
| yesterday | the previous day /the day before |
| yesterday night | the previous night /the night before |
| last night | the previous night /the night before |
| last evening | the previous evening /the evening before |
| last week | the previous week /the week before |
| last fortnight | the previous fortnight /the fortnight before |
| last month | the previous month /the month before |
| last year | the previous year /the year before |
| last occasion | the previous occasion |
| next day | the following day /the day after |
| next week | the following week /the week after |
| next fortnight | the following fortnight /the fortnight after |
| next month | the following month /the month after |
| next year | the following year /the year after |
| on the next occasion | on the following occasion |
Place Chart
| here | there |
| at this place | at that place |
Manner Chart
| thus | so /in that way |
| in this way | in that way |
| in this manner | in that manner |
| hereby | thereby |
Distance Chart
| this | that |
| these | those |
Direction Chart
| hither | thither |
| hence | thence |
| From here | From there |
Direct and Indirect Speech Advanced Rules
It is necessary to know about the Direct Indirect Speech Advanced Rules to change the mode of narration from direct to indirect speech of different sentences. All five sentences of Direct Indirect Speech Conversion Rules are shown with proper examples below.
A. Assertive Sentence Conversion Rules
To convert Assertive sentences into indirect speech the following rules are applied.
(a) No comma and Inverted comma in Indirect Speech, only full stop at the end. (b) Reporting Verbs changed from Direct Speech to Indirect Speech ; ‘say – say’, ‘says – says’, ‘said – said’, ‘said to – told’, ‘say to – tell’, ‘says to – tells’. (c) Connective ‘that’ added before Reported Speech in indirect Narration.
Direct: He said to me, “I am ill.” Indirect: He told me that he was ill.
Direct: Mary said, “I am happy with my results.” Indirect: Mary said that she was happy with her results.
Direct: Tom said, “I will attend the meeting tomorrow.” Indirect: Tom said that he would attend the meeting the next day.
Direct: Alice said, “I have finished my homework.” Indirect: Alice said that she had finished her homework.
Direct: David said, “We are planning a trip to the mountains.” Indirect: David said that they were planning a trip to the mountains.
B. Interrogative sentences Conversion rules
Forming indirect speech with questions necessitates some adjustments:
a. Reporting Yes/No Questions rules
When reporting yes/no questions, use “if” or “whether” and invert the subject and auxiliary verb in indirect speech.
Direct: John asked, “Are you coming to the party?” Indirect: John asked if I was coming to the party.
Direct: Sarah asked, “Do you like chocolate?” Indirect: Sarah asked if I liked chocolate.
Direct: Mike asked, “Have you finished your project?” Indirect: Mike asked if I had finished my project.
Direct: Emma asked, “Will you help me with my homework?” Indirect: Emma asked if I would help her with her homework.
Direct: “Will you be there?” he asked. Indirect: He asked if I would be there.
b. Reporting Wh-Questions rules
For reporting wh-questions, maintain the question word and adjust the word order in indirect speech.
(a) ‘Tell’ and ‘say’ in Direct Narration are changed to ‘ask’, ‘enquire of’, ‘question’, ‘want to know’ etc. in Indirect Narration. (b) In place of introductory ‘that’. ‘if’ or ‘whether’ should be used. (c) In Indirect Narration a full stop (.) must be put in place of a question mark(?) at the end of the sentence. (d) In Direct Narration the Reported Speech begins with W-word or how, in Indirect Narration the same Wh-word or how is retained.
Direct: Lisa asked, “Where are you going?” Indirect: Lisa asked where I was going.
Direct: Mark asked, “What time does the movie start?” Indirect: Mark asked what time the movie started.
Direct: Jennifer asked, “Why did you leave early?” Indirect: Jennifer asked why I had left early.
Direct: Tom asked, “How do you solve this problem?” Indirect: Tom asked how I solved that problem.
Direct: “Where are you going?” she asked. Indirect: She asked where I was going.
Direct: The teacher said to me, “Why are you late?” Indirect: The teacher asked me why I was late.
C. Imperative Sentences Conversion rules
The indirect speech also involves reporting imperatives, which are commands, requests, or advice:
Reporting Commands
When reporting commands, use the reporting verb “tell” and change the imperative verb to the corresponding infinitive.
Direct: The teacher said, “Open your books.” Indirect: The teacher told the students to open their books.
Reporting Requests
For reporting requests, employ the reporting verb “ask” and convert the imperative verb to the corresponding infinitive.
Direct: She said, “Please help me with this.” Indirect: She asked for help with that.
(a) Reporting verbs of Direct Speech changed into order or command, advise, or request according to sense in Indirect Speech. (b) ‘To’ is placed before Reported speech in Indirect Narration; for the negative imperative sentence ‘not to’ is used. (c) ‘not to’ can also be replaced by ‘forbid’, or ‘prohibit’. (d) ‘Let’ implies ‘suggestion’ or ‘proposal’; Reporting verb will be ‘suggest’ or ‘propose’ in Indirect Speech. ‘that’ is used before Reported speech in Indirect Narration (e) ‘Let’ without ‘suggestion’ or ‘proposal’; Reporting verb will be ‘tell’, or ‘wish’ according to sense in Indirect Speech. ‘that’ is used before Reported speech in Indirect Narration.
Direct: Mother said to me, “Don’t run in the sun.” Indirect: Mother advised me not to run in the sun.
Direct: She said to me, “Let us go for a picnic.” Indirect: She suggested that we should go for a picnic.
D. Optative Sentence Conversion rules
The following rules are used to change an optative sentence from direct speech to indirect speech
(a) Reporting verbs changed to ‘ wish ’, ‘ pray’ , and ‘ bless ’ in Indirect Speech. (b) Linker, ‘ that ’ is placed before Reported speech in Indirect Narration.
Direct: The monk said to me, “ May God bless you.” Indirect: The monk wished that God might bless me.
E. Exclamatory Sentences Conversion rules
(a) The reporting verb is changed into exclaim (in joy), exclaim (in grief), cried out (in sorrow), pray, wish, etc. (b) Examinations are turned into statements. (c) Interjections (Alas, Oh, Hurrah) are omitted. (d) ‘What’, and ‘How’ used in exclamation should be replaced by great, great, very, very much, and big.
Direct: The boys said, “Hurrah! we have won the match.” Indirect: The boy exclaimed in joy that they had won the match.
Solved Exercises Direct and Indirect Speech
Change the following sentences into indirect speech.
Q: Ratan said to Anita, “I don’t like your brother”.
Ans: Ratan told Anita that she did not like her brother.
Q: The hermit said to the boys, “God is present everywhere.”
Ans: The hermit told the boys that God is present everywhere.
Q: :He said to you, “You shouldn’t play in my garden.”
Ans: He told you that you should not play in his garden.
Q: The class teacher said to the students. “The inspector will visit our school today.”
Ans: The class teacher told the students that the inspector would visit their school that day.
Q: He said to me, “I don’t believe you.”
Ans: He told me that he didn’t believe me.
Q: She said to her son, “I’ve often told you not to play with fire.”
Ans: She told her son that she had often told him not to play with fire.
Q: Sitesh said to Lina, “I want you to go to Patna with me.”
Ans: Sitesh told Lina that he wanted her to go to Patna with him.
Q: “We can’t be quite happy in life,” he said.
Ans: He said that they couldn’t be quite happy in life.
Q: He said, “The Muslims bury their dead.”
He said that the Muslims bury their dead.
Q: “You’ve overcooked the steak again, Mary”, he said.
Ans: He told Mary that she had overcooked the steak again.
Q: Ramen said to Bina, “I’m going to your house this, week.”
Ans: Ramen told Bina that he was going to her house that week.
Q: He said, “We will discuss this tomorrow.”
Ans: He said that they would discuss that the next day
Turn the following sentences into direct speech.
Q: He said to me, “You are wicked; so I shall not mix with you.”
Ans: He told me that I was wicked; so he would not mix with me.
Q: He said to you, “I was much struck by your eloquence.”
Ans: He told you that he had been much struck by your eloquence.
Q: We remarked, “God is gracious.”
Ans: We remarked that God is gracious.
Q: I said to my mother, “I shall always obey you.”
Ans: I told my mother that I should always obey her.
Q: He said to Gopal, “You were a mere boy when I saw you last.”
Ans: He told Gopal that he was a mere boy when he had seen him last.
Q: I said to him, “The sky is blue.”
Ans: I told him that the sky is blue.
Q: He said to me, “You will feel the consequences.”
Ans: He told me that I should feel the consequences.
Q: She said to you, “I am not angry with you.”
Ans: She told you that she was not angry with you.
Q: I said to them, “You have done wrong.”
Ans: I told them that they had done wrong.
Q: He said, “I visit the temple every day.”
Ans: He said that he visited the temple every day.
Direct and Indirect Speech Sample MCQ Questions Answers
Fill in the blanks with proper direct and indirect speech rules.
- d) had been
- Answer: a) was
- c) will like
- d) had liked
- Answer: a) liked
- a) will visit
- b) would visit
- d) had visited
- Answer: b) would visit
- Answer: c) was
- c) will have
- Answer: b) had
- Answer: b) could
- a) revolves
- c) revolved
- d) is revolving
- Answer: a) revolves
- b) had been
- Answer: b) had been
- Answer: b) would
FAQs : Direct and Indirect Speech Rules
Q : what is the key difference between direct and indirect speech.
Ans: The main difference lies in the quoting style. Direct speech involves repeating someone’s exact words, while indirect speech reports what was said without quoting verbatim.
FAQ 2: Is it always necessary to backshift the tense in indirect speech?
Ans: While backshifting is common, some exceptions exist, especially in cases where the statement’s truth remains constant.
FAQ 3: How do I handle multiple speakers in indirect speech?
Ans: When reporting multiple speakers, use appropriate reporting verbs and introduce each person’s dialogue in a logical sequence.
FAQ 4: Can I mix direct and indirect speech in the same sentence?
Ans: Combining direct and indirect speech in a sentence is possible, but it requires precision to avoid confusion.
FAQ 5: What are some reporting verbs commonly used in indirect speech?
Ans: Reporting verbs like “said,” “told,” “asked,” “claimed,” and “explained” are frequently employed.
FAQ 6: How can I ensure my writing maintains a natural flow when switching between direct and indirect speech?
Ans: Focus on maintaining consistency in style and verb tense to ensure a smooth transition between direct and indirect speech.
FAQ 7: How do I identify direct and indirect speech in a sentence?
Ans: Direct speech is usually enclosed within quotation marks and directly quotes someone’s words. Indirect speech, on the other hand, reports those words without quotation marks, often using reporting verbs like “said,” “told,” “asked,” etc.
FAQ 8: Can reporting verbs change the meaning of indirect speech?
Ans: Yes, the choice of reporting verbs can convey the speaker’s attitude or emotions towards the reported speech. Different reporting verbs can modify the meaning slightly.
FAQ 9: What are the common reporting verbs for indirect speech?
Ans: Common reporting verbs for indirect speech include “say,” “tell,” “ask,” “inquire,” “explain,” “describe,” and more.
FAQ 10: How do I change tenses in indirect speech?
Ans: The tense in indirect speech is generally shifted back one step. For example, present simple becomes past simple, present continuous becomes past continuous, and so on.
FAQ 11: Is it essential to use quotation marks in indirect speech?
Ans: No, quotation marks are not used in indirect speech as they report the speech without directly quoting it.
FAQ 12: Can you give an example of indirect speech in narratives?
Ans: Certainly! In the story, he said, “I love you,” to which she replied that she loved him too.
FAQ 14: Can we omit the reporting verb in indirect speech?
Ans: It is possible to omit the reporting verb in some cases, especially in informal contexts, but including it adds clarity and structure to the reported speech.
FAQ 15: Do all tenses change in indirect speech?
Ans: Most tenses change in indirect speech, but the changes depend on the context and the tense of the original statement.
FAQ 16: Can you provide more examples of direct and indirect speech transformations?
Ans: Certainly! Here are a few more examples:
Direct: “I am reading a book,” she said. Indirect: She said that she was reading a book.
Direct: “We have completed the project,” they exclaimed. Indirect: They exclaimed that they had completed the project.
FAQ 17: How can I practice using direct and indirect speech effectively?
Ans: Practice by converting direct speech to indirect speech and vice versa using various reporting verbs, tenses, and pronouns. Additionally, read books or articles and identify the reported speech used by the authors.
Related Posts:

100 Reported Speech Examples: How To Change Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of communicating what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. For example, if your friend said, “ I am going to the store ,” in reported speech, you might convey this as, “ My friend said he was going to the store. ” Reported speech is common in both spoken and written language, especially in storytelling, news reporting, and everyday conversations.
Reported speech can be quite challenging for English language learners because in order to change direct speech into reported speech, one must change the perspective and tense of what was said by the original speaker or writer. In this guide, we will explain in detail how to change direct speech into indirect speech and provide lots of examples of reported speech to help you understand. Here are the key aspects of converting direct speech into reported speech.
Reported Speech: Changing Pronouns
Pronouns are usually changed to match the perspective of the person reporting the speech. For example, “I” in direct speech may become “he” or “she” in reported speech, depending on the context. Here are some example sentences:
Reported Speech: Reporting Verbs
Reported speech: tense shifts.
When converting direct speech into reported speech, the verb tense is often shifted back one step in time. This is known as the “backshift” of tenses. It’s essential to adjust the tense to reflect the time elapsed between the original speech and the reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how different tenses in direct speech are transformed in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Changing Time and Place References
Reported speech: question format.
When converting questions from direct speech into reported speech, the format changes significantly. Unlike statements, questions require rephrasing into a statement format and often involve the use of introductory verbs like ‘asked’ or ‘inquired’. Here are some examples to demonstrate how questions in direct speech are converted into statements in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Omitting Quotation Marks
Reported speech quiz.
Transformation of Sentence: Direct & Indirect Speech
A direct speech can be transformed into an indirect speech and vice versa using a suitable reporting verb and a linker depending on the sentence. Let’s have an example first.
Direct Speech
| Tina | said | “Are you busy now?” |
Indirect Speech
| Tina | asked | whether | I was busy then. |
List of Reporting verbs and linkers (list 1)
| Said, told | That | |
| 1. Yes-no question 2. Wh-question | Asked, wanted to know, enquired | If / whether |
| Asked, wanted to know, enquired | wh-word | |
| 1. Without ‘Let’ 2. With ‘Let’ | Told, ordered, advised, requested, asked | to / not to |
| Suggested, proposed | that | |
| Wished, prayed | that | |
| Exclaimed in joy / sorrow / wonder / fear / disgust etc. | that |
Verbs of Reported speech (if the reporting verb is in past tense) (list 2) Direct speech → Indirect speech Am / is / are → was / were Was / were → had been Has / have → had Had → had had Shall / will → would Can → could May → might Must, should → must, should Verb1 → verb2 Verb2 → had + verb3
Change of time and place expressions in past tense (list 3) now → then ago → before today → that day yesterday → the previous day tomorrow → the next day last night → the previous night here → there this → that these → those
Narration change of Assertive sentence
Narration change of interrogative sentence, narration change of imperative sentence, narration change of optative sentence, narration change of exclamatory sentence, narration change of vocatives, narration change of question tag.
We serve cookies on this site to offer, protect and improve our services. KNOW MORE OK
Reported Speech
Perfect english grammar.

Reported Statements
Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: I like ice cream.
- Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'. (As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you don't use 'that'.)
But , if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
| present simple | I like ice cream | She said (that) she liked ice cream. |
| present continuous | I am living in London | She said (that) she was living in London. |
| past simple | I bought a car | She said (that) she had bought a car OR She said (that) she bought a car. |
| past continuous | I was walking along the street | She said (that) she had been walking along the street. |
| present perfect | I haven't seen Julie | She said (that) she hadn't seen Julie. |
| past perfect* | I had taken English lessons before | She said (that) she had taken English lessons before. |
| will | I'll see you later | She said (that) she would see me later. |
| would* | I would help, but... | She said (that) she would help but... |
| can | I can speak perfect English | She said (that) she could speak perfect English. |
| could* | I could swim when I was four | She said (that) she could swim when she was four. |
| shall | I shall come later | She said (that) she would come later. |
| should* | I should call my mother | She said (that) she should call her mother |
| might* | I might be late | She said (that) she might be late |
| must | I must study at the weekend | She said (that) she must study at the weekend OR She said she had to study at the weekend |
* doesn't change.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
Click here for a mixed tense exercise about practise reported statements. Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.
Reported Questions
So now you have no problem with making reported speech from positive and negative sentences. But how about questions?
- Direct speech: Where do you live?
- Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
- Direct speech: Where is Julie?
- Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
| Where is the Post Office, please? | She asked me where the Post Office was. |
| What are you doing? | She asked me what I was doing. |
| Who was that fantastic man? | She asked me who that fantastic man had been. |
- Direct speech: Do you like chocolate?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
| Do you love me? | He asked me if I loved him. |
| Have you ever been to Mexico? | She asked me if I had ever been to Mexico. |
| Are you living here? | She asked me if I was living here. |
Click here to practise reported 'wh' questions. Click here to practise reported 'yes / no' questions. Reported Requests
There's more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
- Direct speech: Close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
| Please help me. | She asked me to help her. |
| Please don't smoke. | She asked me not to smoke. |
| Could you bring my book tonight? | She asked me to bring her book that night. |
| Could you pass the milk, please? | She asked me to pass the milk. |
| Would you mind coming early tomorrow? | She asked me to come early the next day. |
- Direct speech: Please don't be late.
- Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
Reported Orders
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
| Go to bed! | He told the child to go to bed. |
| Don't worry! | He told her not to worry. |
| Be on time! | He told me to be on time. |
| Don't smoke! | He told us not to smoke. |
- Click here for an exercise to practise reported requests and orders.
| now | then / at that time |
| today | yesterday / that day / Tuesday / the 27th of June |
| yesterday | the day before yesterday / the day before / Wednesday / the 5th of December |
| last night | the night before, Thursday night |
| last week | the week before / the previous week |
| tomorrow | today / the next day / the following day / Friday |
- Click here for an exercise about using 'say' and 'tell'.
- Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
Reported Speech in English Grammar
What is reported speech, changing direct speech to reported speech, changing the tense (backshifting), no change of tenses, questions in reported speech, demands/requests, expressions with who/what/how + infinitive, typical changes to time and place markers.
- Exercises – Reported Speech
Reported speech is when we repeat what another person has said but instead of using their exact words in quotation marks (direct speech), we use subordinate clause introduced by a reporting verb like the ones below:
Often, we have to change the tense, pronouns and time markers in reported speech.
Learn the rules for writing indirect speech in English with Lingolia’s simple explanation. In the exercises, you can test your grammar skills.
| “I’ve prepared a presentation about the product, if you’re interested?” “I would love to see it. … This product is exactly what my company has been looking for! Is there any room to negotiate on price?” “I’m happy to hear that. Unfortunately, pricing is fixed.” “That’s a shame, but I appreciate your transparency. Could you send me a written offer?” “Yes, I will contact you tomorrow to finalise the details.” |
| I had an appointment with a new client yesterday. I told him that and he said . |
When turning direct speech into reported speech, we may have to change all or some of the following:
- the pronouns
- information about time and place (see the table at the end of this page)
- the tense (backshift)
If the reporting verb is in the simple past (e.g. said, told, asked, replied … ), the tense has to be set back by one degree (see the table below). This is known as backshifting .
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech | |
|---|---|---|
| simple present | → | simple past |
| present progressive | → | past progressive |
| simple past | → | past perfect simple |
| present perfect simple | ||
| past perfect simple | ||
| past progressive | → | past perfect progressive |
| present perfect progressive | ||
| past perfect progressive | ||
| future with going to | → | was / were going to |
| future with will | → | conditional (would) |
| would |
The verbs could, should, would, might, must, needn’t, ought to, used to normally do not change.
If the reporting verb is in the simple present (e.g. says, tells, asks, replies … ), then the tense remains unchanged.
While the tense remains unchanged, we often still have to change the verb form to match the new pronouns.
that after a reporting verb
We often omit the word that after a reporting verb, especially in spoken language and informal contexts.
When turning questions into reported speech, we follow the same rules as for declarative sentences: we change the pronouns as well as the time and place markers and backshift the tense as needed.
In addition, we also have to bear in mind the following:
- instead of that , we use a question word after the reporting verb; if there is no question word, we use whether / if instead
- questions in reported speech follow declarative sentence word order (subject + verb)
- we don’t use the auxiliary verb do/did for questions in reported speech; instead, the main verb appears in the simple past without an auxiliary verb
- put the verb directly after who or what in subject questions.
Questions in reported speech do not end in a question mark.
When turning orders, demands and requests into reported speech, we only need to change the pronouns and the time and place information.
We don’t have to pay attention to the tense – we simply use an infinitive rather than a conjugated verb.
If the imperative is negated, then we use not + infinitive .
To express what someone should or can do in reported speech, we leave out the subject and the modal verb and instead we use the construction who/what/where/how + infinitive .
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
| today | that day |
| now | then at that moment/time |
| yesterday | the day before |
| … days ago | … days before |
| last week | the week before |
| next year | the following year |
| tomorrow | the next day the following day |
| here | there |
| this | that |
| these | those |
say vs. tell
The words say and tell are not interchangeable.
- say = say something
- tell = say something to someone
Head over to the vocabulary section to learn more about the difference between say and tell .
How good is your English?
Find out with Lingolia’s free grammar test
Take the test!
Maybe later
My English Grammar
Ultimate English Grammar, Vocabulary, and Names Database
Indirect Speech
Introduction.
Communicating effectively requires us to master a variety of grammatical rules. One such critical element is the appropriate use of ‘Indirect Speech’, also known as reported speech. Indirect speech allows us to convey what another person has said without quoting them directly.
Table of Contents
What is Indirect Speech?
Indirect Speech is a way of expressing the words or utterances of a speaker in a reported manner. In contrast to direct speech, where the original speaker’s words are quoted verbatim, indirect speech is more about reporting the essence or meaning of what the speaker said rather than quoting them exactly.
For example:
Direct Speech: Lisa said, “I am going shopping.”
Indirect Speech: Lisa said that she was going shopping.
Changes in Verb Tenses
Tense shifts.
When you transform sentences from direct to indirect speech, the verb tenses typically shift back a step in time. This phenomenon is often referred to as ‘sequence of tenses’ or ‘backshift’. However, the backshift is not applied if the spoken words still apply at the time of reporting or the words express a universal truth.
Here are the typical conversions:
- Present Simple changes to Past Simple. E.g., “I like pizza” becomes “She said that she liked pizza.”
- Present Continuous changes to Past Continuous. E.g., “I am eating pizza” becomes “She said that she was eating pizza.”
- Will changes to would. E.g., “I will go” becomes “He said that he would go.”
- Past Simple changes to Past Perfect. E.g., “I ate lunch” becomes “She said that she had eaten lunch.”
Exceptions to Tense Shifts
There are exceptions to these rules, such as when the direct speech element is a universal truth or a fact. Consider the below examples:
- John said, “The sun rises in the east” becomes “John said that the sun rises in the east.”
- She said, “Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius” becomes “She said that water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.”
Changes in Pronouns and Time Expressions
Pronoun changes.
When changing from direct to indirect speech, it’s often necessary to modify the pronouns to match the speaker and listener’s point of view. For example:
- “I love you,” he said. (Direct)
- He said he loved me. (Indirect)
Time Expression Changes
Time expressions often undergo necessary modifications when moving from direct to indirect speech. Here are some examples:
- “Today” becomes “That day.”
- “Now” becomes “Then.”
- “Tomorrow” becomes “The next day” or “the following day.”
- “Next week” becomes “The following week.”
Indirect Commands and Requests
We can also convey commands and requests indirectly. For indirect commands, we use “to” + base verb and for indirect requests we use “if” or “whether” + subject + could/would, followed by the base verb.
- Direct: “Close the window!” – Indirect: He told me to close the window.
- Direct: “Can you lend me the book?” – Indirect: She asked if I could lend her the book.
Indirect Questions
When posing indirect questions, we need to ensure that the word order follows the structure of a standard statement, rather than a direct question.
Direct: “Where are you going?” – Indirect: He asked me where I was going.
Mastering indirect speech is essential but can be challenging because of the need to adjust verb tenses, pronouns, and time expressions. However, with practice, it becomes easier, and steadily, you find yourself communicating more effectively and efficiently, especially in formal and written contexts. Keep practicing, and soon converting direct speech to indirect speech will become second nature.
Related Posts:

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Search form
- Highest rated
- Verb phrase generator
- Test your grammar
Changes in indirect speech
In order to understand changes in indirect speech, we must bear in mind that words are always spoken in context: somebody says something to someone at a specific place and time. When we report something, changes are made to the original words if there are changes in the context (people, place or time).
- Changes in place, time and person in indirect speech
- Tense changes in indirect speech
- Modal changes in indirect speech
- Conditionals and unreal tenses in indirect speech
Rate this page

For timeline diagrams, quotes and exercises, check out our e-book The Grammaring Guide to English Grammar

About | Copyright
Grammaring – A guide to English grammar | Copyright © 2009-2024
Direct and Indirect Speech: Useful Rules and Examples
Are you having trouble understanding the difference between direct and indirect speech? Direct speech is when you quote someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. This can be a tricky concept to grasp, but with a little practice, you’ll be able to use both forms of speech with ease.


Direct and Indirect Speech
When someone speaks, we can report what they said in two ways: direct speech and indirect speech. Direct speech is when we quote the exact words that were spoken, while indirect speech is when we report what was said without using the speaker’s exact words. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I love pizza,” said John. Indirect speech: John said that he loved pizza.
Using direct speech can make your writing more engaging and can help to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion. However, indirect speech can be useful when you want to summarize what someone said or when you don’t have the exact words that were spoken.
To change direct speech to indirect speech, you need to follow some rules. Firstly, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb. Secondly, you need to change the pronouns and adverbs in the reported speech to match the new speaker. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will go to the park,” said Sarah. Indirect speech: Sarah said that she would go to the park.
It’s important to note that when you use indirect speech, you need to use reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked” to indicate who is speaking. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is it?” asked Tom. Indirect speech: Tom asked what time it was.
In summary, understanding direct and indirect speech is crucial for effective communication and writing. Direct speech can be used to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion, while indirect speech can be useful when summarizing what someone said. By following the rules for changing direct speech to indirect speech, you can accurately report what was said while maintaining clarity and readability in your writing.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech
When it comes to reporting speech, there are two ways to go about it: direct and indirect speech. Direct speech is when you report someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. Here are some of the key differences between direct and indirect speech:
Change of Pronouns
In direct speech, the pronouns used are those of the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the pronouns have to be changed to reflect the perspective of the reporter. For example:
- Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” said John.
- Indirect speech: John said he was going to the store.
In the above example, the pronoun “I” changes to “he” in indirect speech.
Change of Tenses
Another major difference between direct and indirect speech is the change of tenses. In direct speech, the verb tense used is the same as that used by the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the verb tense may change depending on the context. For example:
- Direct speech: “I am studying for my exams,” said Sarah.
- Indirect speech: Sarah said she was studying for her exams.
In the above example, the present continuous tense “am studying” changes to the past continuous tense “was studying” in indirect speech.
Change of Time and Place References
When reporting indirect speech, the time and place references may also change. For example:
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” said Tom.
- Indirect speech: Tom said he would meet you at the park the next day.
In the above example, “tomorrow” changes to “the next day” in indirect speech.
Overall, it is important to understand the differences between direct and indirect speech to report speech accurately and effectively. By following the rules of direct and indirect speech, you can convey the intended message of the original speaker.
Converting Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
When you need to report what someone said in your own words, you can use indirect speech. To convert direct speech into indirect speech, you need to follow a few rules.
Step 1: Remove the Quotation Marks
The first step is to remove the quotation marks that enclose the relayed text. This is because indirect speech does not use the exact words of the speaker.
Step 2: Use a Reporting Verb and a Linker
To indicate that you are reporting what someone said, you need to use a reporting verb such as “said,” “asked,” “told,” or “exclaimed.” You also need to use a linker such as “that” or “whether” to connect the reporting verb to the reported speech.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I love ice cream,” said Mary.
- Indirect speech: Mary said that she loved ice cream.
Step 3: Change the Tense of the Verb
When you use indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb.
- Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store.
Step 4: Change the Pronouns
You also need to change the pronouns in the reported speech to match the subject of the reporting verb.
- Direct speech: “Are you busy now?” Tina asked me.
- Indirect speech: Tina asked whether I was busy then.
By following these rules, you can convert direct speech into indirect speech and report what someone said in your own words.
Converting Indirect Speech Into Direct Speech
Converting indirect speech into direct speech involves changing the reported speech to its original form as spoken by the speaker. Here are the steps to follow when converting indirect speech into direct speech:
- Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb used in the indirect speech. This will help you determine the tense of the direct speech.
- Change the pronouns: The next step is to change the pronouns in the indirect speech to match the person speaking in the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “She said that she was going to the store,” the direct speech would be “I am going to the store,” if you are the person speaking.
- Change the tense: Change the tense of the verbs in the indirect speech to match the tense of the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “He said that he would visit tomorrow,” the direct speech would be “He says he will visit tomorrow.”
- Remove the reporting verb and conjunction: In direct speech, there is no need for a reporting verb or conjunction. Simply remove them from the indirect speech to get the direct speech.
Here is an example to illustrate the process:
Indirect Speech: John said that he was tired and wanted to go home.
Direct Speech: “I am tired and want to go home,” John said.
By following these steps, you can easily convert indirect speech into direct speech.
Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct and indirect speech are two ways to report what someone has said. Direct speech reports the exact words spoken by a person, while indirect speech reports the meaning of what was said. Here are some examples of both types of speech:
Direct Speech Examples
Direct speech is used when you want to report the exact words spoken by someone. It is usually enclosed in quotation marks and is often used in dialogue.
- “I am going to the store,” said Sarah.
- “It’s a beautiful day,” exclaimed John.
- “Please turn off the lights,” Mom told me.
- “I will meet you at the library,” said Tom.
- “We are going to the beach tomorrow,” announced Mary.
Indirect Speech Examples
Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, is used to report what someone said without using their exact words. It is often used in news reports, academic writing, and in situations where you want to paraphrase what someone said.
Here are some examples of indirect speech:
- Sarah said that she was going to the store.
- John exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
- Mom told me to turn off the lights.
- Tom said that he would meet me at the library.
- Mary announced that they were going to the beach tomorrow.
In indirect speech, the verb tense may change to reflect the time of the reported speech. For example, “I am going to the store” becomes “Sarah said that she was going to the store.” Additionally, the pronouns and possessive adjectives may also change to reflect the speaker and the person being spoken about.
Overall, both direct and indirect speech are important tools for reporting what someone has said. By using these techniques, you can accurately convey the meaning of what was said while also adding your own interpretation and analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is direct and indirect speech?
Direct and indirect speech refer to the ways in which we communicate what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, using quotation marks to indicate that you are quoting someone. Indirect speech, on the other hand, involves reporting what someone has said without using their exact words.
How do you convert direct speech to indirect speech?
To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb, such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.” For example, “I love ice cream,” said Mary (direct speech) can be converted to “Mary said that she loved ice cream” (indirect speech).
What is the difference between direct speech and indirect speech?
The main difference between direct speech and indirect speech is that direct speech uses the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. Direct speech is usually enclosed in quotation marks, while indirect speech is not.
What are some examples of direct and indirect speech?
Some examples of direct speech include “I am going to the store,” said John and “I love pizza,” exclaimed Sarah. Some examples of indirect speech include John said that he was going to the store and Sarah exclaimed that she loved pizza .
What are the rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech?
The rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech include changing the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb and use appropriate reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.”
What is a summary of direct and indirect speech?
Direct and indirect speech are two ways of reporting what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions and introduce a reporting verb.
You might also like:
- List of Adjectives
- Predicate Adjective
- Superlative Adjectives
This website is AMNAZING
MY NAAMEE IS KISHU AND I WANTED TO TELL THERE ARE NO EXERCISES AVAILLABLEE BY YOUR WEBSITE PLEASE ADD THEM SSOON FOR OUR STUDENTS CONVIENCE IM A EIGHT GRADER LOVED YOUR EXPLABATIO
sure cries l miss my friend
he saiad,” we are all sinners”. convert into indirect speech
He said that they were all sinners.
- Grammar Exercises
- Grammar Lessons
- Grammar Quizzes
- Mixed Tests
- PDF Worksheets
- Beginners Lessons
- Easy Worksheets
- Beginners Tests
- Reading Exercises
- Drag & Drop Grammar
- English For Kids
- Kids Word Games
- Picture Vocabulary
- Reading Tests
- Short Dialogues
- Short Sentences
- Closest in Meaning
- Irrelevant Sentence
- ESL Paragraphs
- GRE Reading
- Text Completion
- GRE Equivalence
- SAT Sentence
- Essay Writing
- Vocabulary Exercises
- Study Skills Tips
- Drag & Drop Vocab
Reported Speech / Indirect Speech
Direct speech:, indirect speech / reported speech:, convert direct speech to indirect speech.
| Pronouns and possessive adjectives | We usually change from first or second to third person except when the speaker is reporting his own words. | that day |
| the day before (the previous day) | |
| Tomorrow / the next day | The following day |
| The day before yesterday | Two days before / earlier |
| Yesterday morning | The previous morning |
| A year / month / week ago | A year before / earlier |
| The day after tomorrow | In two days' time |
| Next week / month / year | The following week / month / year |
| now | then |
| tonight | that night |
| here | here / there |
| this | that, it |
| these | those |
| can | could |
| would | |
| could | |
| might | |
| might | might |
| have to / has to | had to |
| must | must |
| ought to / should | ought to / should |
Indirect Speech Statements
Mixed types, common verbs used with reported speech.
| Add boast | complain observe reply Announce deny | point out scream Answer grumble promise | shout Argue inform | Assure + Object murmur remark |
Try our latest video exercises?

Latest Video Exercises


Reported Speech
Learn how to use reported speech in English. Reported speech is also known as indirect speech and is used to tell somebody else what another person said. Using reported speech in English can sometimes be difficult for non-native speakers as we (usually) change the verbs, pronouns and specific times.
Keep reading to understand how to use reported speech and download this free English lesson!

Let’s study reported speech !
Reported speech vs. direct speech.
When we want to tell somebody else what another person said, we can use either direct speech or reported speech .
When we use d irect speech, we use the same words but use quotation marks, “_”. For example:
Scott said, “I am coming to work. I will be late because there is a lot of traffic now.”
When we use r eported speech, we usually change the verbs, specific times, and pronouns. For example:
Scott said that he was coming to work. He said that he would be late because there was a lot of traffic at that time.
How do we use reported speech ?
Since reported speech is usually talking about the past, we usually change the verbs into the past. It is always necessary to change the verbs when the action has finished or is untrue.
We do not always change the verbs. When you are reporting an action that is still current or true, it is not necessary to change the verb tense. For example:
How old are you? “ I am twenty-seven years old .” She said she is twenty-seven years old.
We usually follow the rules below. When we are reporting speech, we are usually talking about the past; therefore, we change the verbs into the past.
|
|
“I eat pizza.” | He said (that) he ate pizza. |
“I am eating pizza.” | He said (that) he was eating pizza. |
“I will eat pizza.” | He said (that) he would eat pizza. |
“I am going to eat pizza.” | He said (that) he was going to eat pizza. |
When we are reporting past actions, it is not always necessary to change the verb tense. We can usually leave the verbs in the same tense and just change the pronouns. However, we sometimes need to use the to clarify the time order of events. the never changes in . | |
“I ate pizza.” “I ate pizza, so I am not hungry.” | He said (that) he ate pizza. He said (that) he had eaten pizza, so he wasn’t hungry.” |
“I was eating pizza.” “I was eating pizza when she called.” | He said (that) he was eating pizza. He said (that) he had been eating pizza when she called. |
Reporting Questions
We use a special form when we report questions:
WH-Questions:
Where is + Tom’s house ? He asked where Tom’s house + was.
Where does Tom live? He asked where Tom lived.
Yes/No Questions:
Does Tom live in Miami? She asked if Tom lived in Miami.
Is Tom happy? She asked if Tom was happy.
Say vs. Tell
Say Something
June: “I love English .”
June said (that) she loved English.
Tell Someone Something
June: “I love English.”
June told me (that) she loved English.
Modal Verbs and Reported Speech
Must, might, could, would, should , and ought to stay the same in re ported s peech . We usually change may to might .
Infinitives and Reported Speech
Infinitives stay the same in reported speech:
“ I am going to the store to buy milk.” He said he was going to the store to buy milk.
We also use infinitives when reporting orders and commands, especially when using tell .
“ Do your homework. Don’t use a dictionary!!” He told me to do to my homework and not to use a dictionary.
Reporting Suggestions
When we are reporting another speakers suggestions, we can use a special form with suggest, recommend, or propose .
SUGGEST/ RECOMMEND/PROPOSE + (*THAT) + SUBJECT PRONOUN + **V1
SUGGEST/ RECOMMEND/PROPOSE + V1 + ING
“I think you should visit Viscaya.” → He suggested we visit Viscaya. He suggested visiting Viscaya.
“Try to get there early to get good seats.” → He recommended we get there early to get good seats.
*That is often omitted in speech.
**The verb is always in the base form. We do not use third person.
Reporting Statements
A reported statement begins with an introductory clause and is followed by the ‘information’ clause. The speaker may choose different words, but the meaning remains unchanged. Some formal words to introduce a reported statement or response are: declared, stated, informed, responded, replied, etc.
“I don’t agree with these new rules. I am not going to accept this change!” → He declared that he was in disagreement with the new rules and stated that he would not accept the changes.
Free English Lesson PDF Download
Reported Speech ~ Exercises and Practice
A. Change each direct speech example into the reported speech . The first one has been done for you.
- Michelle said, “I love my Chihuahua, Daisy.”
Michelle said that she loved her Chihuahua, Daisy.
2. Republicans said, “We don’t support Obama’s plan to raise taxes.”
__________________________________________________________.
3.With her mouth full, Sarah said, “I am eating mashed potatoes.”
4. John Lee said, “This year, I will not pay my taxes.”
5. Lebron said, “I am going to win the championship next year.”
6. Patty said, “I can’t stomach another hamburger. I ate one yesterday.”
B. Rewrite the sentences/questions below using reported / indirect speech . Always change the tense, even though it is not always necessary. You can use ‘said’, ‘told me’ , or ‘asked’ .
1. Sarah: “I am in the shower right now.”
_____________________________________________________________________________
2. John: “I dropped my son off at school this morning.”
3. Samuel: “I am going to the beach with my sister this afternoon.”
4. John: “Jessica will call you later.”
5. The girls: “Who does John live with?”
6. Our classmate: “Did we have any homework last night?”
7. Sarah: “I am moving to Tokyo because I want to learn Japanese.”
8. John: “Why do you have an umbrella?”
9. The students: “Our teacher can’t find her books anywhere.”
10. Sarah and Jillian: “Is John British?”
11. Steve: “I’m going to the beach so that I can play volleyball.”
__________________________________________________________________________________
12. Ann: “Where is the bathroom?”
13. My parents: “What are you going to do with your life?”
14. Sarah: “I ate breakfast before I came to school.”
C. Your friend Megan is very nosy (she always wants to know what’s going on) so she constantly asks questions about your life and the lives of your friends. Rewrite her questions using the reported questions form. The first one has been done for you .
1. Why do you date Ryan?
She asked me why I dated Ryan.
2. How much money do you make at your new job?
________________________________________________________________________________
3. Does Ryan think I’m pretty?
4. Where is your favorite restaurant?
5. Do I look good in these jeans?
6. Can I borrow some twenty bucks?
D. Your American grandfather is telling you about how things used to be. Using the reported speech , tell your friends what he said.
“In the 1930s, people were very poor. They ate watery soup and hard bread. Many people lost their jobs. To make matters worse, a horrible drought ruined most of the farmland in the American midwest. People went to California to look for a better life. They picked strawberries in the hot California sun.”
Did you download this lesson? If not, don’t forget to download this free English lesson.
If you have any questions about English grammar, please contact us via email us or just comment below. I hope this lesson helped you understand how to use reported speech in English.
Click here to subscribe to our newsletter! #TurnYourLanguageOn
Do you need to improve your English? See the locations of our English language schools in the United States.

Take our FREE Proficiency Test and
Discover your English Proficiency Level!

Proud partners with National Geographic Learning

Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Type | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ajs_anonymous_id | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| ajs_group_id | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| ajs_user_id | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| centerVisitorId | persistent | 7981 years | Description unavailable. |
| fr | persistent | 3 months | Description unavailable. |
| hblid | persistent | 2 years | Description unavailable. |
| NID | persistent | 6 months | Description unavailable. |
| olfsk | persistent | 2 years | Description unavailable. |
| test_cookie | persistent | 15 minutes | Description unavailable. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | persistent | 1 hour | Description unavailable. |
| wcsid | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| wordpress_test_cookie | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| _fbp | persistent | 2 hours | Description unavailable. |
| _ga | persistent | 2 year | Description unavailable. |
| _gat | session | 1 minute | Description unavailable. |
| _gid | persistent | 1 day | Description unavailable. |
| _hjIncludedInSample | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| _ok | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| _okbk | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| _okdetect | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| _oklv | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| __cfduid | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
Home of English Grammar
Direct and indirect speech
Change into indirect speech
1. John said, ‘I am trying to find a new job.’
2. He said, ‘I wrote a letter.’
3. The girl said, ‘I want something to eat.’
4. The teacher said, ‘Stop writing.’
5. The man said, ‘I have nowhere to go.’
6. The girl said, ‘I have been practicing the violin for six months.’
7. Mother said, ‘I have laid the table.’
8. He said, ‘Who are you?’
9. He said, ‘Are you happy here?’
10. The father said to his son, ‘Go and pay your fee at once.’
11. He said, ‘Let’s go for a drive.’
1. John said that he was trying to find a new job.
2. He said that he had written a letter.
3. The girl said that she wanted something to eat.
4. The teacher asked them to stop writing.
5. The man said that he had nowhere to go. / The man lamented that he had nowhere to go.
6. The girl said that she had been practicing the violin for six months.
7. Mother said that she had laid the table.
8. He asked who I was.
9. He enquired if I was happy there?’
10. The father told his son to go and pay his fee at once.
11. He suggested going for a drive. / He suggested that we should go for a drive.


Your way to the top of Grammar...
Indirect Speech: Formula and Rules
- July 3, 2021
We are talking about a very important and interesting topic. We are talking about direct and indirect speech in English and what is the correct formula of the usage.
Remember to read How to learn English with audiobooks for FREE
This topic can seem complicated at the beginning, but necessary to learn. Having this topic solved, you improve your English to a new level, so let’s start to deal with it.
What are Direct and Indirect speech?
In English, there are two ways how we can tell what another person said. Two ways you can say what someone else has said before.
- Direct Speech
- Indirect (Reported) Speech
Note : Indirect speech in different textbooks can be called differently: Indirect Speech or Reported Speech . But these two names mean the same.
Indirect Speech = Reported Speech

Direct speech in English is a type of speech when we retell someone’s speech as it was. We don’t change anything.
John says: I’m a good boy.
To tell what John said, we will say:
We say: John said, “I’m a good boy.”
Indirect speech differs from direct speech in that we DO NOT tell exactly what another person said. We are NOT repeating what someone else said. Indirect speech is when we tell the MEANING of what someone else said.
We say: John said he was a good boy.
Pay attention to what this sentence looks like. Earlier, when John said this, the sentence looked like this:
I am a good boy.
But after WE retell John’s words, in the indirect speech, this sentence looks like this:
John said he was a good boy.
The Quotes and the comma that stood after the name John, separating the speaker from his direct speech, disappeared from this sentence.
In indirect speech, we do not use the separating comma and quotation marks. Because now it is WE are retelling the meaning of what the other person (John) said.

In direct speech, the speaker most often speaks in the first person. That is, the speaker speaks from his person.
John will not talk about himself: John is a good boy . John will say it on his behalf: I am a good boy.
But when we retell the words of John (indirect speech), we cannot speak on his behalf. We cannot say “I am a good boy” because those are not our words. This is John a good boy.
Therefore, in indirect speech, we change “I” to the third person.
He says: I hate you but I need your help.
I retell: He said that he hated me but he needed my help.
To translate direct speech into indirect speech, we use certain rules that you should know.
Let’s take a look at these rules and formulas in order.
Quotation marks and comma
In direct speech, we use a comma to separate the speaker from what he is saying. Direct speech (what the speaker says) is in quotation marks.
When we translate direct speech into indirect speech, we remove quotes and commas.
Jessica says , “I’m from the future.”
We retell Jessica’s words: She said that she was from the future.
Personal and possessive pronouns
When translating direct speech into indirect speech, we change personal and possessive pronouns to third-person pronouns.
Direct Speech : He says, “ I couldn’t stay” Indirect Speech : He said that he couldn’t stay. Direct Speech : Tom says, “ I am deeply disturbed” Indirect Speech : Tom said that he was deeply disturbed.
Note: If in direct speech the speaker tells his own words, then we do not change personal and possessive pronouns.
Direct Speech: I said, “ I will do that” Indirect Speech: I said that I would do that.
Adverbs in direct speech
When we translate adverbs from direct speech to indirect, adverbs change their form.
You can see how adverbs look in direct speech and how adverbs look in indirect speech in this table:
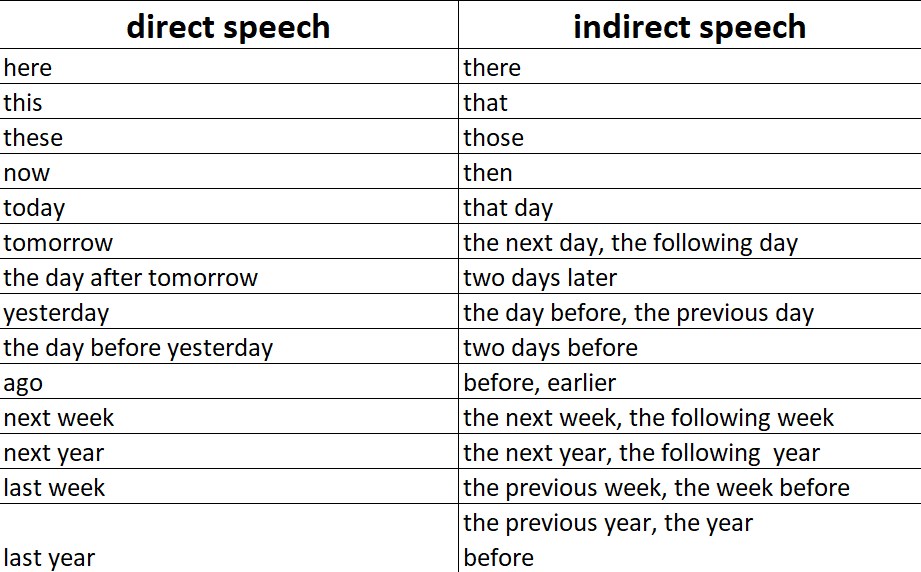
But we don’t always change adverbs this way. We change adverbs only if, when translating from direct speech into indirect speech adverbs cannot express the same meaning as in direct speech.
Take a look at an example:
Mom says, “ Tomorrow we will go to Uncle John’s.” Mom said that the next day we would go to Uncle John’s.
In these examples, we have replaced the adverb tomorrow with the next day . Because we retell Mom’s words on another day. We cannot say tomorrow anymore.
Now look at another example:
Mom says, “We went to visit Uncle John yesterday .”
Now imagine that we are retelling this the next day. We have to say:
Mom said that we went to visit Uncle John the day before yesterday .
If we said “ yesterday “, it would change the meaning of what we want to tell.
If in direct speech in the main sentence the predicate is in Past Simple, then in indirect speech we use the agreement rules.
We put the conjunction “ that ” in front of indirect speech.
Note: We may not use the conjunction that after verbs such as:
He said he found it on the island. He thought he was better than me. He knew he could call you anytime.

Prepositional object
If in direct speech after the verb to say there is a prepositional object, then in order to translate such a sentence into indirect speech, we change the verb to say to tell . In this case, tell is used without the preposition to .
Incorrect : to tell Correct : tell
This means:
She said to me … changes to She told me that …
Note : Remember that in this case we also change the adverbs of place and time and demonstrative pronouns, if they are in direct speech.
Modal verbs
For modals, we use several important rules.
We change modal verbs as well as main verbs when moving from direct to indirect speech.
But we do not change all modal verbs. We leave some verbs in their original form.
Let’s talk about modals in more detail.
Modal verb must
If in direct speech the verb must means an obligation or command, then in the subordinate clause in indirect speech must does NOT change and looks like must .
The teacher says, “You must behave well in class.” The teacher said that we must behave well in class.
If in direct speech the verb must expresses the need, then in the subordinate clause in indirect speech we change the verb must to had to .
Mom says, “You must visit the doctor.” Mom said that I had to visit the doctor.
The past form of Modal verbs in indirect speech
Can and could..
We change the modal verb can in direct speech to could in indirect speech. Could is the past form of the modal verb can .
She says, “I can swim.” She said that she could swim.
May and might.
We change the modal verb may in direct speech to might in indirect speech. Might is the past form of the modal verb may .
John says, “I may propose to Maria.” John said that he might propose to Maria.
Must and had to.
We change the modal verb must in direct speech to had to in indirect speech (if the verb must expresses the need). Had to is the past analog of the modal verb must .

Modal verbs that do not change in indirect speech
The following verbs move from direct to indirect speech in their original form. They don’t change in any way.
- must (if the verb must means an obligation or command)
He says, “I could do this.” He said he could do that.
Let’s take a closer look at these verbs:
The modal verb would in direct speech remains in the form would in indirect speech too.
Mom says, “I would bake a cake.” Mom said she would bake a cake.
If we use the modal verb could in direct speech, then we do not change this verb in any way in indirect speech. Because could is a past form already (It’s the past form of the modal verb can ).
John says, “I could learn to swim” John said he could learn to swim.
The modal verb might does not change its form when we translate this verb from direct to indirect speech. Because the modal might is the past form of the modal may .
He says, “I might ask the same question again”. He said that he might ask the same question again.
We do not change should when switching to indirect speech. Because should is considered the past form of the modal verb shall .
He says, “We should see Mr. Gannon” He said that we should see Mr. Gannon.
We do not change the modal verb OUGHT TO when translating this verb into indirect speech.
She says, “You ought to be angry with John” She said that I ought to be angry with John
Exceptions to the rules
Let’s talk about the important exceptions to the rules of this lesson.
- We can exclude the word that out of affirmative sentences in indirect speech. Because in indirect speech in affirmative sentences, the meaning of the sentence does not change, regardless of whether we use that or not.
He said ( that ) he thought you seemed depressed. He said ( that ) there was no need. He said ( that ) he had many friends.
- If in direct speech we are talking about a specific event that happened at exactly the specified time and did not happen anymore, then we translate the sentence into indirect speech without the agreement.
He says, “Gagarin went to space in 1961.” He said that Gagarin went to space in 1961.
The event that we are talking about in this example happened at exactly the specified time and did not happen anymore.

- If in direct speech we use verbs such as:
then when translating into indirect speech, we do not change the form of these verbs. These verbs remain in their form.
She says, “We might find some treasure” She said that we might find some treasure.
He says, “I should do it”. He said that he should do it.
- If indirect speech begins with the verb say or tell which is used in the form:
- Present Simple
- Present Perfect
- Future Simple
then we translate such a sentence into indirect speech without changing the tense to the past:
She says, “I cook deliciously.” She says that she cooks deliciously. He says, “I have a new smartphone.” He says that he has a new smartphone. She will say, “I didn’t know it.” He will say (that) he didn’t know it.
- If in direct speech we are talking about a well-known fact or law of nature, then we do not transfer to the past such a fact or the law of nature when translating from direct speech to indirect.
He says, “After winter comes spring.” He said that after winter comes spring. She says, “Lions don’t hunt camels.” She said that lions don’t hunt camels.
- If in direct speech we use tenses:
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
then when translating into indirect speech, we do not change the sentence, we do not translate the sentence into the past.
He says, “I had fixed my car.” He said he had fixed his car. He says, “I was skiing .” He said he was skiing . He says, “I had been all alone for a very long time”. He said that he had been all alone for a very long time.
Interrogative (question) sentences in indirect speech
Look at the following rules and nuances to know how to correctly translate interrogative (question) sentences from direct speech to indirect speech:
- When we translate a general question into indirect speech, we put one of the conjunctions between the main sentence and the question:
He asks, “Do you play dominoes?” He asked if I played dominoes. He asked whether I played dominoes.

- If we translate an interrogative sentence from direct speech to indirect speech, then we change the interrogative word order to direct word order.
We remove the auxiliary verb that was used in the interrogative sentence. We put the subject before the predicate as it should be for the direct word order.
He asks, “Where are you going?” He asked where I was going.
- If in an indirect sentence we ask a question using the verb say and if there is no indirect object in the main sentence, then we change the verb say to one of these words:
- want to know
She asks, “Where you are?” She wanted to know where you were.
- When translating an interrogative sentence from direct speech into indirect speech, we change all pronouns, verbs, adverbs of place, adverbs of time.
She asks, “What do these letters mean?” She asked what those letters mean.
Special questions in indirect speech
Special questions (or Wh-questions) are questions that begin with an additional, question word.
In indirect speech, such a question should also begin with a question word.
This question word also serves as conjunction. This word attaches the question part to the main sentence.
In the question part, we use direct word order.
At the same time, we comply with all the rules for the Sequence of tenses.
My dad asks, “What do you plan to do with yourself?” My dad asked what I planned to do with myself.
Imperative sentences in indirect speech
When translating imperative sentences from direct to indirect speech, we must take into account several nuances:
- Orders in indirect speech look like this:
He said, “ Go now!” He said to go then. She says, “ Carry my bag” She asked to carry her bag.
We use the verb to say when we translate an ordinary sentence into indirect speech. But in imperative sentences, we change the verb to say to a verb that expresses an order or request:
She says , “Carry my bag” She asked to carry her bag.

- In direct speech in the imperative mood, we often use:
let’s (let us)
let’s encourage the speaker and the person to do something together.
In indirect speech, we change let’s to to suggest . For example:
She says, “ let’s do that!” She suggested to do that.
- In indirect speech, we put a noun after the verb that expresses an order or request. The noun is the one to whom this request or order is addressed. Then we use the infinitive.
She says, “Replace him, John “ She asked John to replace him.
- We can strengthen the request or order in indirect speech if we add verbs such as:
- to recommend
- to urge etc.
She says , “Read this book” She ordered ( advised, recommend ) me to read that book.
- In order to make a negative imperative sentence in direct speech, we need:
not + infinitive
He says, “Don’t cry.” He said to me not to cry.
- In direct speech, we often do not name the person to whom the order or request is addressed. But when translating an imperative sentence from direct speech to indirect speech, we must indicate the one to whom the order or request is addressed.
For this, we use a noun or a pronoun.
She says, “Speak to him!” She asked me to speak to you.
Present and future tense in indirect speech
Most often, we translate the future and the present into the past.
He says, “I have two brothers” He says that he had two brothers She says, “I do this every time” She says that he did that every day. He says, “I write books” He says that he wrote books. She says, “I am reading” She said that she was reading. He says, “I can swim” He said that he could swim. He says, “I will help you” He said that he would help me.
Past tense in indirect speech
When we translate a sentence written in the past into indirect speech, we can leave it unchanged or we can change the past to the Past Perfect.
He says, “I saw this movie” He said that he saw that movie. He said that he had seen that movie.
What if in direct speech the main verb is already in Past Perfect?
In this case, the verb in Past Perfect remains unchanged. The verb in Past Perfect in direct speech remains in Past Perfect in indirect speech too.
He says, “I had bought I new house” He said that he had bought a new house.
Hello! If you would like to thank me for the articles I wrote, you can click Buy me a coffee . Thank you! ❤❤❤
Recommended reading: Complex Sentence in English.
Related Posts

Prepositions of Place in English Grammar

Prepositions of Reason and Purpose

Direct Word Order in English Sentences

Word Order in Interrogative Sentence

Conditional Sentences Types in English

Apostrophe in English: All you need to know
Trending now.


- English fluency
- English writing
- Practical Tips
- Spoken English

Direct To Indirect Speech: Complete Rules With Examples

Direct and indirect speech is often a confusing topic for English learners. The basic idea is this:
- In direct speech, we quote a person’s exact words. For example, Meera said, “I can speak English fluently.”
- In indirect speech, we do not quote the person’s exact words but provide a summary of what was said. For example, Meera said that she could speak English fluently.
The critical difference is that direct speech uses the exact words spoken by a person, while indirect speech summarizes what was said. While the definition is simple, the challenge for English language learners is using the proper tenses when converting a phrase from direct to indirect and vice versa.
Why Should You Learn Direct To Indirect Speech Rules?
There are several occasions – in your professional and personal – where you might need to describe an action or event to others. For example, you might have to repeat the team leader’s instructions to your teammates at the workplace. In this scenario, you convert your team leader’s direct to indirect speech.
Knowing conversion rules can help you present or describe the event correctly without making any grammatical errors or spoken English blunders.
In this post, we walk you through the rules of converting direct to indirect speech, helping you speak English fluently online and offline.
How To Use Direct Speech?
The rule is simple: Use direct speech when you want to repeat what someone says as it is, and ensure that the spoken text is sandwiched between quotation (speech) marks.
John said, “I want to learn to speak English fluently.”
It’s common to see the direct speech in newspaper articles and books. For example,
The District Collector announced, “The Chief Minister will inaugurate the city centre next week.”
As you can notice, in direct speech, we use the verb say (said in the past tense) to denote what was spoken. You can also use related verbs like ‘asked,’ ‘replied,’ ‘told,’ ‘informed,’ ‘shouted,’ etc.
How To Use Indirect Speech?
Indirect speech is also reported speech, as we use it to inform/repeat what someone else said. Using the two examples above, we can convert it into indirect speech as follows:
John said that he wanted to learn to speak English fluently.
The District Collector announced that the Chief Minister would inaugurate the city centre the week after.
Another example,
Direct Speech: “I feel cold.”
Indirect Speech: She says that she feels cold.
If you notice these examples carefully, you can see that the tense changes when converting from direct to indirect speech. To illustrate this point, in the following example, direct speech is in the present simple tense, while indirect speech is written in the simple past tense.
Direct Speech: “I live in the city centre.”
Indirect Speech: He said he lived in the city centre.
Tense Change Rules: Direct To Indirect Speech
Similarly, other tenses follow similar rules when changing from direct to indirect speech. Use the following table to help you better understand the tense change rules:
| Direct Speech | Tense | Indirect Speech | Tense |
| The kids said, “We play football.” | Present Simple | The kids said that they played football. | Past Simple |
| He said, “I’m having lunch.” | Present Continuous | He said that he was having lunch. | Past Continuous |
| She said, “I have bought a new home.” | Present Perfect | She said that she had bought a new home. | Past Perfect |
| The teacher said, “I have been teaching English for the last five years.” | Present Perfect Continuous | The teacher said she had been teaching English for the last five years. | Past Perfect Continuous |
| The students exclaimed, “We won a prize.” | Past Simple | The students exclaimed that they had won a prize. | Past Perfect |
| Jenifer said, “I was watching a movie.” | Past Continuous | Jenifer said that she had been watching a movie. | Past Perfect Continuous |
| The project manager said, “We had resolved the issue.” | Past Perfect | The project manager said they had resolved the issue. | Past Perfect (Remains the same) |
| The chef said, “I had been peeling onions since morning.” | Past Perfect Continuous | The chef said that he had been peeling onions since morning. | Past Perfect Continuous (Remains the same) |
| Rahul said, “I will celebrate New Year’s Eve in Chennai.” | Future Simple | Rahul said he would celebrate New Year’s Eve in Chennai. | Note that “will” changes to “would” |
| Neha said, “We will be waiting for you.” | Future Continuous | Neha said that they would be waiting for me. | Note that “will” changes to “would be” |
| The scientist said, “We will have completed the mission in 2023.” | Future Perfect Continuous | The scientist said that they would have completed the mission in 2023. | Note that “will” changes to “would have” |
Modal Verbs: Direct To Indirect Speech
When converting direct to indirect speech, you must change modal verbs accordingly. Here are a few examples to help you understand better:
| Direct Speech | Modal Verbs | Indirect Speech | Modal Verbs |
| The kid said, “I can swim.” | Can | The kid said that she could swim. | “Can” changes to “could” |
| Priya said, “I must go.” | Must | Priya said that she had to go. | “Must” changes to “had” |
| Dad asked, “Shall we start?” | Shall | Dad asked if we should start. | “Shall” becomes “should” |
Changing Time Expressions: Direct To Indirect Speech
Sometimes it becomes necessary to change the time expressions when converting from direct to indirect speech. A few examples,
- Direct speech: Sheila said, “I am meeting my brother tomorrow.”
- Indirect speech: Sheila said that she was meeting her brother the following day.
Here are a few examples of other typical time expressions and how they change:
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| Yesterday | The day before |
| Now | At that time, then |
| Today | That day, on Sunday/Monday, etc. |
| Tonight | That night |
| Last night | The night before |
| Last month | The previous month |
| This week | That week, last week |
| Five minutes ago | Five minutes before |
| In one hour | One hour later |
Changing Place Expressions: Direct To Indirect Speech
Like time expressions, you might also have to change words representing places when reporting indirect speech. For example,
- Direct speech: “It’s raining here.”
- Indirect speech: She said that it was raining there.
Here are a few examples of other common place expressions and how they change:
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| here | There (or) the place |
| this | that |
| This pen | That pen |
| In this room | In that room |
However, the place words only change when you report something from a different location.
Over To You
Now that you’ve seen the rules to convert direct to indirect speech, it’s time to put them into practice. The most efficient way to improve English speaking is to practice what you’ve learned. Join online English-speaking practice classes to gain confidence and mastery in your daily conversations.
Recent Posts
However, whenever, whatever, and more, popular slang words, “what time is it”: how to ask the time, cooking vocabulary: master the language of the kitchen, annoying habits in english.
- August 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- August 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
Related Posts

Top 10 English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoi...

Challenge Your English! Can you answer these qu...

Interesting English Idioms | Everyday Phrases t...

“GET OUR FREE ENGLISH COURSE BY SUBSCRIBING TO OUR BLOG FOR FREE”
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise
Turn the following sentences into indirect speech.
1. John said, ‘I am very busy now.’ 2. He said, ‘The horse has been fed.’ 3. ‘I know her name and address,’ said John. 4. ‘German is easy to learn,’ she said. 5. He said, ‘I am writing letters.’ 6. ‘It is too late to go out,’ Alice said. 7. He said to me, ‘I don’t believe you.’ 8. He says, ‘I am glad to be here this evening.’ 9. He said to me, ‘What are you doing?’ 10. ‘Where is the post office?’ asked the stranger. 11. He said, ‘Will you listen to me?’ 12. John said to Peter, ‘Go away.’ 13. She said to me, ‘Please wait here till I return.’ 14. ‘Call the witness,’ said the judge. 15. The speaker said, ‘Be quiet and listen to my words.’
1. John said that he was very busy then. 2. He said that the horse had been fed. 3. John said that he knew/knows her name and address. (Note that the tenses may not change if the statement is still relevant or if it is a universal truth.) 4. She said that German is/was easy to learn. 5. He said that he was writing letters. 6. Alice said that it was too late to go out. 7. He told me that he didn’t believe me. OR He said he didn’t believe me. 8. He says that he is glad to be here this evening. (When the reporting verb is in the present tense, adverbs of time and place do not normally change in indirect speech.) 9. He asked me what I was doing. 10. The stranger asked where the post office is/was. 11. He asked me if I would listen to him. 12. John ordered Peter to go away. 13. She asked me to wait there till she returned. 14. The judge commanded them to call the first witness. 15. He urged them to be quiet and listen to them.

Search Articles
Recent articles.
- Prepositions Quiz
- General Grammar Exercise
- Pronouns Exercise
- Proper Nouns Exercise
- General Vocabulary Exercise
- Identify the Adverbs Exercise
- Grammar Exercise (Intermediate Level)
- Intermediate Level Grammar Exercise
- General Grammar Worksheet
- Vocabulary Exercise
- Gap Filling Tenses Exercise
- Gap Filling Grammar Exercise
- More resources
EnglishPractice.com © 2024 - All rights Reserved.

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Reported Speech /
How to Change Sentences into Indirect Speech
- Updated on
- May 10, 2024

Change sentences into indirect speech: Indirect Speech often known as reported speech is a linguistic tool . It helps to quote someone else words that are not the actual words of the speaker. In this blog article, we learn about the meaning of indirect speech , examples of indirect speech, and practice exercises to master the art of changing sentences to indirect speech.
This Blog Includes:
Understanding indirect speech, examples of indirect speech, rules for changing sentences to indirect speech, simple present changes to simple past , present continuous changes to past continuous, present perfect changes to past perfect, present perfect continuous changes to past perfect continuous, , simple past changes to past perfect, past continuous changes to past perfect continuous, changes in the pronouns, changes in the adverbs of time and place, exercise to change sentences from direct to indirect speech.
MUST READ! Reported Speech: Definition, Rules, Usage with Examples, Tips, Exercises for Students
Indirect Speech includes paraphrasing speakers’ words instead of defining the actual words of the speaker. This linguistic device is used to maintain politeness of tone and social dynamics. It is an important concept that allows a speaker to convey information tactfully while maintaining the meaning of the words spoken by the speaker.
Let us comprehend the few examples of Indirect Speech for the proper understanding of the concept.
| He said to him,” Do you live in Chandigarh?” | He asked him if he lived in Chandigarh. |
| She said to her mother “Are you going to school tomorrow?” | She asked her mother if she was going to school the next day. |
| The professor said to me “ Did you come late today?” | The professor asked me if I came late the same day. |
| My mother said to me,” What do you want?” | My mother asked me what I wanted. |
| The teacher said to Ram,” Where are you going?” | The teacher asked Ram where he was going. |
| She said to my sister,” Will you take tea?” | She asked my sister if she would take tea. |
Here are the key rules for converting sentences from direct speech to indirect speech. These rules include changes in verb tense, pronouns, and other elements to maintain the meaning of the original statement.
Changes in Tenses
For example, He said,” I like chocolates”.
He said that he liked chocolates.
For example, He said,” We are studying”.
He said that they were studying.
For example, He said,” They have finished”
He said that they had finished.
For example, She said, “ They have been living in Canada since 1970.”
She said that they had been living in Canada since 1970.
For example, He said, “ They played in the garden”.
He said that they had played in the garden.
For example, He said,” They had grown vegetables.”
He said that they had been growing vegetables.
Future Indefinite Changes will and shall and should accordingly
For example, He said,” He will go to the market.”
He said that he would go to the market.
Pronouns in the direct speech change according to the perspective of the speaker.
- First-person changes according to subject
- Second-person changes according to the object
- Third-person pronoun there is no change.
- Follows the SON rule that is easy to remember
For Example She said, ” I love her job .” (direct speech)
She said that she loved her job . (indirect speech)
Also Read Tenses Rules: Charts, Examples, Types [PDF Available]
Adverbs change according to the context
- Now to then,
- Here to there,
- Today to the same day,
- Yesterday to the last day, etc.
For example: He said,” I will go to school tomorrow .” (Direct Speech)
He said that he would go to the school the next day. (Indirect Speech)
Must Read: Subject-Verb Agreement: Definition, 12 Rules & Examples
Let’s check your understanding of the sentences that have been changed from direct to indirect speech:
- “I can’t believe you did that!” exclaimed Sonali.
- “What time is the meeting?” asked the teacher.
- “I love this song!” shouted Mohit
- “Where did you find that book?” inquired the teacher
- “I’ll be there by 3 PM,” promised Alia
- “Stop right there!” commanded the officer
- “Would you like some coffee?” offered James
- “Let’s go to the beach this weekend,” suggested Rohit
- “I don’t want to go to the dentist,” complained Tina.
- “Congratulations on your promotion!” cheered Mary.
Answers
Match your answers with the solved exercises to analyze the understanding of the concept.
- Sonali exclaimed with surprise that she couldn’t believe he had done that.
- The teacher asked about the time of the meeting.
- Mohit enthusiastically shouted that he loved that song.
- The teacher inquired where the book had been found.
- Alia promised that she would be there by 3 PM.
- The officer commanded me to stop right there.
- James offered coffee.
- Rohit suggested going to the beach that weekend.
- Tina complained that she didn’t want to go to the dentist.
- Mary cheered and congratulated on the promotion.
Must Read: Figures of Speech: Types, Usage & Examples [Download PDF]
Direct speech is the actual words spoken by a person and is written in quotation marks, while indirect speech defines the meaning of the original statement without quoting the actual words of the speaker. Indirect speech involves various changes in verb tense, pronouns, and other elements.
Pronouns change according to the SON Rule where SON stands for: First-person changes according to (S-Subject) Second-person changes according to(O- Object) A third-person there is (N- No Change)
A few reporting verbs used in indirect speech are “said,” “told,” “asked,” “explained,” inquired, commanded, requested, exclaimed with joy, etc.” The choice of reporting verb reflects the tone and meaning of the reported speech.
Direct Speech: It’s been raining since this afternoon. Indirect Speech: He said it’d been raining since that afternoon.
To advance your grammar knowledge and read more informative blogs, check out our Learn English page and don’t forget to follow Leverage Edu .
Amanpreet Kaur
📚✨ From Classroom Chats Entered Into The Wordy World ….. Yes , If you all Remember that teacher who kept you on your toes with pop quizzes and endless homework? YEP! THAT WAS Me ! 🌟 But with the blessings of almighty and the key motivation of my husband who came across the spark of writing in me has insisted me to pave my way away from chalk dust to creative burst!💫 Being in this new world of writing I can compose pun-tastic content, poetry full of emotions and humorous articles that can even make Shakespeare envious of me 📝🎭.Yippee! from teaching young minds to educating worldwide readers it's an epic career switch. From teaching grammar lessons to grammatically flawless copy, I'm todays' wordsmith on a mission! Let me spin literary magic all around and conquer my exact destination of proving myself as The Best Writer in The World.🚀🏆 My promise is to provide you with valuable insights, solutions to your questions, and a momentary escape from the routine. I believe in the power of words to create connections, provoke thought, and foster growth. Woods are lovely dark and deep But I have promises to keep and Miles to go before I sleep ……..🌳✨🌌
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
| Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said) |
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
| I | He, she |
| Me | Him, her |
| We | They |
| Us | Them |
| You | He, she, they |
| You | Him, her, them |
| My | His, her |
| Mine | His, hers |
| Our | Their |
| Ours | Theirs |
| Your | His, her, their |
| Yours | His, hers, theirs |
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Here | There |
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Tomorrow | The next day / The following day |
| Yesterday | The previous day |
| Tonight | That night |
| Last week | The week before |
| Next week | The week after |
| Last month | The previous month |
| Next month | The following month |
| Last year | The previous year |
| Next year | The following year |
| Ago | Before |
| Thus | So |
| Simple Present Example: Preethi said, “I cook pasta.” | Simple Past Example: Preethi said that she cooked pasta. |
| Present Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I am cooking pasta.” | Past Continuous Example: Preethi said that she was cooking pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Simple Past Example: Preethi said, “I cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I was cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Past Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I had cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I had been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Will | Would |
| May | Might |
| Can | Could |
| Shall | Should |
| Has/Have | Had |
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Reported speech
Changing time and place in reported speech
Time and place must often change when going from direct to reported speech (indirect speech).
| Phrase in direct speech | Equivalent in reported speech |
|---|---|
| "I saw him ", she said. | She said that she had seen him . |
| "I saw him ", she said. | She said that she had seen him . |
| "I met her ", he said. | He said that he had met her . |
| "I'll see you ", he said | He said that he would see me . |
| "We'll come ", they said. | They said that they would come . |
| "I have an appointment ", she said. | She said that she had an appointment . |
| "I was on holiday ", he told us. | He told us that he had been on holiday . |
| "I saw her ," he said. | He said he had seen her . |
| "I'm getting a new car ", she said. | She said she was getting a new car . |
| "Do you like ?" he asked | He asked if I liked . |
| He said, "I live ". | He told me he lived . |
In general, personal pronouns change to the third person singular or plural, except when the speaker reports his own words: I/me/my/mine, you/your/yours = him/his/her/hers we/us/our/ours, you/your/yours = they/their/theirs
He said: "I like your new car." = He told her that he liked her new car. I said: "I'm going to my friend's house." = I said that I was going to my friend's house.
If we are in the same place when we report something, then we do not need to make any changes to place words . But if we are in a different place when we report something, then we need to change the place words. Look at these example sentences:
- He said: "It is cold in here ." → He said that it was cold in there .
- He said: "How much is this book ?" → He asked how much the book was.
Here are some common place words, showing how you change them for reported speech:
| direct speech | indirect speech |
|---|---|
| here | there, in Starbucks |
| this | that |
| this book | the book, that book, |
| in this room | in the room, in that room, in the kitchen |
Course Curriculum
- Changing time and place in reported speech 20 mins
- Direct and indirect speech 15 mins
- Tense changes in reported speech 20 mins
- Reported questions 20 mins
- Reporting verbs 20 mins
- Reporting orders and requests 15 mins
- Reporting hopes, intentions and promises 20 mins
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech: Whenever you are quoting someone else’s words , you use two kinds of speeches – Direct or Indirect speech . In this chapter, we will learn all about Direct and Indirect speech and how to convert one into another.
Suggested Videos
Reported speech- how does it work.

Whenever you report a speech there’s a reporting verb used like “say” or “tell”. For example:
Direct speech: I love to play football .
Reported speech: She said that she loves to play football. (Note 1 : Assume a gender if not mentioned already. Note 2: Using “that” is optional. This sentence could also have been written as “She said she loves to play football.”)
The tense doesn’t have to be changed in this case of reported speech. But of the reporting verb is in the past tense , we do change the tense of the sentence.
Browse more Topics under Transformation Sentences
- Active and Passive Voice
- Parts of Speech
- Types of Sentences
Reported speech- Play of the tenses:
| Simple present | simple past |
| present continous | past continuous |
| simple past | past perfect |
| past continuous | past perfect continuous |
| present perfect tense | past perfect tense |
| past perfect tense | past perfect tense |
Learn more about Parts of Speech here in detail
This is a summary table that will be crystal clear to you as you read further. Just come back to this table after this section and use this as a summary table:
| Simple present | I like to swim in the ocean | She said she liked to swim in the ocean | Simpe past |
| Simple present | I live in New Orleans | He said he lived in New Orleans | Simpe past |
| Past simple | I went to school in the morning | She said she had gone to school that morning | Past perfect |
| Present continuous | I was going to the Himalayas | He said he was going to the Himalayas | Past continuous |
| Past continuous | I was walking near the beach | She said that she had been walking near the beach | past perfect continuous |
| Present perfect | I have caught a few fishes | She said she had caught a few fishes | past perfect |
| Past perfect | I had trekked the Himalayas this time last year | He said he had trekked the Himalayas this time last year | Past perfect |
Some word transitions from direct to reported speech that will come in handy:
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- would stays would
- should stays should
- must stays must or had to(matter of choice)
- shall becomes should
Exception : A present tense in direct speech may not become a past tense in the reported speech if it’s a fact or something generic we are talking about in the sentence. For example-
Direct speech: The sun rises from the East.
Reported speech: She said that the sun rises/rose from the East.
Reported speech- Handling questions:
What happens when the sentence we are trying to report was actually a question? That’s something we are going to deal with in this section. Reported questions- It’s quite interesting. let’s get into it:
Well the good news is that the tense change you learnt above stays the same in reported speech for questions. The only difference is that when you report a question, you no more report it in the form of a question but in the form of a statement. For example:
Direct speech: Where do you want to eat?
Reported speech: She asked me where I wanted to eat.
Notice how the question mark is gone from the reported speech. The reported speech is a statement now. Keep that in mind as you read further.
Remember the tense change? Let’s apply that to a few questions now.
| Are you going to my house? | She asked me if I was going to her house. |
| Where were you going? | He asked me where I was going. |
| Where have you been? | She asked me where had i been. |
Now these are questions that have wordy answers to them. What about the questions that has yes/no answers to them? In these type of questions just add “if” before asking the question. For example:
- Direct speech: Would you like to eat some cupcakes?
- Reported speech: He asked me if i would like to eat some cupcakes.
- Direct speech: Have you ever seen the Van Gogh paintings?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I had ever seen the Van Gogh paintings.
- Direct speech: Are you eating your vegetables?
- Reported speech: She asked if I was eating my vegetables.
Reported speech- Reported requests:
Well not all questions require answers. Some questions are polite requests. Remember? Could you please try to remember? And then there are request statements. Let’s see how do we convert these into reported speech.
Reported request = ask me + to + verb or requested me + to +verb
Just add this rule to your reported speech and you have what is called a reported request.
| Could you please shut the door? | She asked me to shut the door. |
| Can you please help me? | She requested me to help her. |
Reported speech- Reported orders:
Well, not everyone is going to be polite. Sometimes, we get orders. Now how will you report them? Unlike the request, the reporting verb isn’t ask but told or tell. Also, when in orders, sometimes subjects are omitted but while reporting we have to revive the subjects. Let’s see a few examples:
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
- Direct speech: don’t worry!
- Reported speech: She told me not to worry.
Reported speech- Time transitions:
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| now | then / at that time |
| today | yesterday / that day / Tuesday / the 27th of June |
| yesterday | the day before yesterday / the day before / Wednesday / the 5th of December |
| last night | the night before, Thursday night |
| last week | the week before / the previous week |
| tomorrow | today / the next day / the following day / Friday |
With that, you have everything it takes to understand reported speech. you are all se to change the direct to reported speech. Go ahead and try a few examples. All the best!
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Transformation of Sentences
- Active and Passive voice
37 responses to “Active and Passive voice”
Simple but very nice explanation and helpfull too.
What is the voice change of ” I have endeavoured to understand the fundamental truths.”
ENDEAVOUR HAS BEEN MADE BY ME TO UNDERSTAND THE FUNDAMENTAL TRUTH.
The fundamental truths have been endeavoured to be understood by me
The fundamental truths to understand had been endeavoured by him
The fundamental truths have endeavoured to be understood by me
The fundamental truths has been understood endeavoured to by me
How to change the voice for the following sentence – the books will be received by tomorrow
By whom? We need a subject. If the subject was for example “The library”, then the sentence in active voice would read “The library will receive the books by tomorrow”.
You will receive the books by tomorrow.
Tomorrow you will receive the book
You will receive the books (by) tomorrow.
Someone will receive the books by tomorrow
Tomorrow will be receive the books
HE WILL RECEIVE THE BOOKS BY TOMORROW.
By tomorrow the books will be received.
By tomorrow, you will receive the books
Tomorrow received the book
Change this “take right and turn left” into passive voice
Let the right be taken amd left be turned
‘amd’ is “and” 😅
You are advised to take right and turn left
Very helpful information thanks
Very well explained all basics that can lead to gain further knowledge very easily
What is in this box change into passive
what is the voice change of,” some people think nuclear is the best, because it doesnt add to global warming “….
Brilliant stuff!! – Rishabh
A kite was made by Ravi . What is the active form of this statement???
how to change into passive this sentence “when they were shifting the patient to the I.C.U.,he died
change into passive voice this sentence “when they were shifting the patient to I.C.U.,he died .
May you tell us tense conversion in voice.
Sentences without action like…. Jim is a doctor . Is it active or passive and if any how would you decide without having a main verb ?
It is named after the name of its principal tree ‘sundari'(passive)
how can ocean be object 🙄???
They made a bag
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Narration / Direct and Indirect Speech
The art of reporting the words of a speaker is called Narration.
There are two main ways of reporting the words of a speaker.
1. Direct Speech
2. Indirect Speech
Direct Speech
In this form, the actual words of the speaker are put in quotes “”. Ex:-
- Rama said,” I am very busy now.”
- In the above example the Speaker i.e
- Rama is known as Reporter ,
- said is known as Reporting verb and
- “I am very busy now.” is known as Reported Speech.
Indirect Speech
In this form, the actual words of the speaker are transformed and said/written in a simple manner.
- Rama said that he was very busy then.
Basic rules to convert a Direct Speech to Indirect Speech.
There are five basic things that have to be changed while converting a Direct speech to an I ndirect speech.
- To change the reporting verb according to the reported speech.
- To remove the inverted comma’s from the direct speech and replace them with an appropriate conjunction.
- To change the pronoun of reported speech accordingly.
- Change the adverbs of the Direct Speech.
Active - Rajiv said to me,” I shall go to the picture today” Passive - Rajiv told me that he would go to the picture that day.
In the above example
Reporting verb said to is changed into told. Inverted Commas are replaced by the conjunction that Reported speech’s pronoun I is changed into He. Reported speech’s verb shall go is changed into would go. As another change today is changed with the word that day.
Rules of change of Pronouns
| I | My | Me | Myself |
| We | Our | Us | Ourselves |
| You | Yours | You | Yourself |
| He | His | Him | Himself |
| She | Her | Her | Herself |
| They | Their | Them | Themselves |
Pronouns are changed according to a rule designated as SON where
- S stands for Subject
- O stands for Object
- N stands for No change.
- First person changes to subject of Reporting Verb
- Second person changes to Object of Reporting Verb
- There is no change if it is a Third person.
Rule No 1. 1 st Person pronoun of Reported speech is changed according to the Subject of Reporting verb.
Direct: She says, “I am in tenth class.” Indirect: She says that she is in tenth class.
Direct: I say, “I am an honest man.” Indirect: I say that I am an honest man.
Rule No 2. 2 nd Person pronoun of Reported speech is changed according to Object of Reporting verb.
Direct: She says to me, “you have done your work” Indirect: She tells me that I have done my work.
Direct: She says to her, “You have done your work” Indirect: She tells her that she has done her work.
Direct: I say to them, “you have done your work.” Indirect: I tell them that they have done their work.
Rule No 3. 3 rd Person Pronoun of Reported speech is not changed.
Direct: He says, “He does not work hard” Indirect: He says that he does not work hard.
Direct: Everybody says, “They have spoken the truth” Indirect: Everybody says that they have spoken the truth.
Rules of change of verb or Tense
If reporting verb is given in Present or Future tense then there will be no change in the verb or tense of Reported speech
Direct: The teacher says, “Gayatri performs on the stage” Indirect: The teacher says that Gayatri performs on the stage.
Direct: The teacher is saying, “Gayatri performs on the stage” Indirect: The teacher is saying that Gayatri performs on the stage.
Direct: The teacher will say, “Gayatri is performing on the stage” Indirect: The teacher will say that Gayatri is performing on the stage.
If reporting verb is given in Past tense then the tense of the verb of Reported Speech will change into corresponding Past tense.
Direct: The teacher said, “I am suffering from fever.” Indirect: The teacher said that she was suffering from fever.
Direct: She said to me, “I took the breakfast in the morning”. Indirect: She told me that she had taken the breakfast in the morning.
Corresponding Changes to past form in an indirect speech from the verb in Reported speech.
- Simple present changes to Simple Past
- Present Continuous changes to Past Continuous
- Present Perfect changes to Past Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous changes to Past Perfect Continuous
- Simple Past changes to Past Perfect
- Past Continuous changes to Past Perfect Continuous
- In Future Tense will/Shall changes to would
- Can changes to Could
- May changes to Might
Some of the exceptional cases of Rule 2
Exception 1:
If Reporting speech has Universal Truth or Habitual fact then there is no change in the Tense.
Direct: Our teacher said, “The earth is round” Indirect: Our teacher said that the earth is round.( Universal Truth)
Direct: Rajiv said to me, “He plays with right hand” Indirect: Rajiv told me that he plays with the right hand.(Habitual fact)
Exception 2: If reporting speech has Past Historical Fact then there is no change in the Tense.
Direct: Our teacher said, “Asoka left war after the conquest of Kalinga”. Indirect: Our teacher said that Asoka left war after the conquest of Kalinga.
Exception 3: If Reporting speech has two actions to be happening at a time when there is no change in the Tense.
Direct: She said “My wife was making lunch when I was studying” Indirect: She said that her wife was making lunch when she was studying.
Exception 4: If Reporting speech has some Imagined Condition then there is no change in the Tense.
Direct: She said, “If I were rich, I would help him.” Indirect: She said that if she were rich she would help her.
Exception 5: If Reporting speech contains had 3 rd form, to-infinitive and would, could, should, must, might, ought to etc. then there is no change in the Tense.
Direct: She said to me, “You should obey your elders.” Indirect: She told me that I should obey my elders.
Some other small changes that used to take place while changing Direct Speech to Indirect Speech.
| Here | Changes to | There |
| Now | Changes to | Then |
| This | Changes to | That |
| These | Changes to | Those |
| Today | Changes to | That day |
| To-night | Changes to | That night |
| Yesterday | Changes to | The previous day |
| Last night | Changes to | The previous night |
| Last week | Changes to | The previous week |
| Tomorrow | Changes to | The next day |
| Next Week | Changes to | The following week |
| Ago | Changes to | Before |
| Thus | Changes to | so |
| Hence | Changes to | Thence |
| Hither | Changes to | Thither |
| Come | Changes to | Go |
Note:- An in indirect speech we talk about such incidents that are after the time of reporting and had happened away from the place of reporting therefore the words that show nearness has to be replaced by the words that show distance.
Some exception in these changes
1. Come is changed to go if there is some word given after come that shows nearness.
2. If this , here and now points to such a thing, place or time that is in front of the speaker then no change takes place in Indirect Narration.
Rules for Change in Narration of different type of sentences
Type No 1. Assertive Sentences
- If there is no object after Reporting verb there it should not be changed.
- If there is some object after Reporting verb then say is changed to tell , says to tells and said to told.
- According to the context said to can be replaced by replied, informed, stated, added, remarked, asserted, assured, pleaded, reminded, reported or complained etc.
- Put conjunction that in place of “ ”.
- Change the pronouns of the Reported speech as enlisted earlier.
Examples showing some Assertive Sentences Changed into Indirect form
Direct: She said to me, “I shall sleep now” Indirect: She told me that she would play then.
Direct: He said, “My brother’s marriage comes off next month.” Indirect : He said that his brother’s marriage would come off the following month.
Type No 2. Interrogative Sentences
- An interrogative sentence is meant to ask questions, therefore, Reporting verb said/said to is changed to asked.
- Said to can also be changed into enquired or demanded
- If question is formed with the help of any of the helping verbs like is/are/am, was/were, has/have, do/does, will/would etc then “ __” are to be replaced by if or whether
- If the question is formed with the help of words starting with “Wh” like who, whose, what, whom, when etc (also known as W family) or How then to replace “___” no conjunction is used.
- In these sentences question form of the sentence is removed and full-stop is put at the end of the sentence.
- Helping verb is /are/am, was/were etc should be put after the subject.
- If the interrogative sentence is expressing positive feeling then do/does of the Direct speech is removed while converting it into Indirect speech.
- If the interrogative sentence is expressing negative feeling then do/does of the Direct speech is changed into did while converting it into Indirect speech.
- Did or has/have the interrogative sentence is changed to had.
- Pronouns and verbs are changed according to the set rule of Narration.
English Related Links
Various skills of the english language, components of the english language, english grammar, words/parts of speech, forms of verbs.
Composition : Parts of composition
Analysis, Transformation and Synthesis of sentence
- Analysis of Simple Sentence
- Punctuation
- Spelling Rules
- Question Tag
- Analysis of Complex Sentence
- Analysis of Compound Sentence
- Transformation of Sentence
- Active and Passive Voice
- Direct and Indirect Speech
Written Composition
Page Views: 1398706
Updated On: 13-Feb-2018
Education India, Colleges, Universities, Courses, Exams, Schools
Don't have an account? Sign Up .
New to Target Study? Sign Up to get started.
Already have an account? Sign In .
Forgot password? Submit your email address and we'll send you a link to reset your password.
Already registered? Sign In
Modal title
Confirm Password *
By registering, you agree to the Terms of Service and Privacy Policy . *
Username or email *
Forgot Password
Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive a link and will create a new password via email.
Sorry, you do not have permission to ask a question, You must login to ask a question.
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.

English Notes
English notes latest questions, she said, “i am reading a book.” change into indirect speech.
Indirect Speech: She said that she was reading a book.
Explanation: When the reporting verb is in the past (said) and the direct speech is in the present continuous tense, then the indirect (reported) speech will change into the past continuous tense.
Present Continuous Tense > Past Continuous Tense.
Learn Narration
- Share on WhatsApp
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Select as best answer
Indirect Speech : She said that she was reading a book.
You must login to add an answer.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Indirect: He said that he would do it the next day. Direct: She said, "I was here." Indirect: She said that she was there. Changes in Modals. Modals also change when transforming direct speech into indirect speech. Here are some common changes: 'Can' changes to 'could'. 'May' changes to 'might'. 'Will' changes to ...
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
The following rules are used to change an optative sentence from direct speech to indirect speech. (a) Reporting verbs changed to ' wish ', ' pray', and ' bless ' in Indirect Speech. (b) Linker, ' that ' is placed before Reported speech in Indirect Narration. Example: Direct: The monk said to me, " May God bless you.".
Direct: "I will help you," she promised. Reported: She promised that she would help me. Direct: "You should study harder," he advised. Reported: He advised that I should study harder. Direct: "I didn't take your book," he denied. Reported: He denied taking my book. Direct: "Let's go to the cinema," she suggested.
Verbs of Reported speech (if the reporting verb is in past tense) (list 2) Direct speech → Indirect speech Am / is / are → was / were Was / were → had been Has / have → had Had → had had Shall / will → would Can → could May → might Must, should → must, should Verb1 → verb2 Verb2 → had + verb3 Change of time and place expressions in past tense (list 3) now → then ago → ...
Watch my reported speech video: Here's how it works: We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
Changing direct speech to reported speech. When turning direct speech into reported speech, we may have to change all or some of the following: the pronouns; Example: "I would love to see it." → He said (that) he would love to see it. 1st person singular I → 3rd person singular he. information about time and place (see the table at the ...
Rule 1: Change the verb tense in the quoted speech. With past tense reporting verbs, shift the tense back. For example, if the direct speech is in the present simple, shift it to the past simple in the reported speech. Hence, "He says, 'I am busy'" will change to "He said he was busy." Rule 2: Adjust pronouns and time/place words as necessary.
Direct Speech: Lisa said, "I am going shopping." Indirect Speech: Lisa said that she was going shopping. Changes in Verb Tenses Tense Shifts. When you transform sentences from direct to indirect speech, the verb tenses typically shift back a step in time. This phenomenon is often referred to as 'sequence of tenses' or 'backshift'.
In order to understand changes in indirect speech, we must bear in mind that words are always spoken in context: somebody says something to someone at a specific place and time. When we report something, changes are made to the original words if there are changes in the context (people, place or time). Changes in place, time and person in ...
Direct speech: "I love ice cream," said Mary. Indirect speech: Mary said that she loved ice cream. Step 3: Change the Tense of the Verb. When you use indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb. For example: Direct speech: "I am going to the store," said John.
Indirect : He said that I didn't know his language. Direct : I said, "I sold my book." Indirect : I said that I had sold my book. Direct : She said to me, "Your brother is bothering me." Indirect : She told me that my brother was bothering her. Indirect Speech Statements We join the indirect and the direct parts of a sentence with that.
Reported Speech ~ Exercises and Practice. A. Change each direct speech example into the reported speech. The first one has been done for you. Michelle said, "I love my Chihuahua, Daisy." Michelle said that she loved her Chihuahua, Daisy. 2. Republicans said, "We don't support Obama's plan to raise taxes."
Change into indirect speech. 1. John said, 'I am trying to find a new job.' 2. He said, 'I wrote a letter.' 3. The girl said, 'I want something to eat.' 4. The teacher said, 'Stop writing.' 5. The man said, 'I have nowhere to go.' 6. The girl said, 'I have been practicing the violin for six months.' 7.
When we translate direct speech into indirect speech, we remove quotes and commas. Jessica says, "I'm from the future." We retell Jessica's words: She said that she was from the future. Personal and possessive pronouns. When translating direct speech into indirect speech, we change personal and possessive pronouns to third-person pronouns.
When we tell people what another person said or thought, we often use reported speech or indirect speech. To do that, we need to change verb tenses (present, past, etc.) and pronouns ( I, you, my, your, etc .) if the time and speaker are different. Sally: 'I don't have time.' ⇒ Sally said that she didn't have time.
Direct speech: Sheila said, "I am meeting my brother tomorrow.". Indirect speech: Sheila said that she was meeting her brother the following day. Here are a few examples of other typical time expressions and how they change: Direct Speech. Indirect Speech. Yesterday. The day before. Now.
The speaker said, 'Be quiet and listen to my words.'. Answers. 1. John said that he was very busy then. 2. He said that the horse had been fed. 3. John said that he knew/knows her name and address. (Note that the tenses may not change if the statement is still relevant or if it is a universal truth.)
4.2. ( 20) Change sentences into indirect speech: Indirect Speech often known as reported speech is a linguistic tool. It helps to quote someone else words that are not the actual words of the speaker. In this blog article, we learn about the meaning of indirect speech, examples of indirect speech, and practice exercises to master the art of ...
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
Place. If we are in the same place when we report something, then we do not need to make any changes to place words. But if we are in a different place when we report something, then we need to change the place words. Look at these example sentences: He said: "It is cold in here ." → He said that it was cold in there.
Whenever you report a speech there's a reporting verb used like "say" or "tell". For example: Direct speech: I love to play football. Reported speech: She said that she loves to play football. (Note 1 : Assume a gender if not mentioned already. Note 2: Using "that" is optional.
Indirect: She said that if she were rich she would help her. Exception 5: If Reporting speech contains had 3 rd form, to-infinitive and would, could, should, must, might, ought to etc. then there is no change in the Tense. Direct: She said to me, "You should obey your elders." Indirect: She told me that I should obey my elders.
Added an answer on November 25, 2021 at 11:27 am. Indirect Speech: She said that she was reading a book. Explanation: When the reporting verb is in the past (said) and the direct speech is in the present continuous tense, then the indirect (reported) speech will change into the past continuous tense. Present Continuous Tense > Past Continuous ...