
- Request new password
- Create a new account

Research Methods and Statistics in Psychology
Student resources, multiple choice questions.
Revise your knowledge with these multiple choice quiz questions.
Chapter 2: Research in Psychology: Objectives and Ideals
Chapter 3: Research Methods
Chapter 4: Experimental Design
Chapter 5: Survey Design
Chapter 6: Descriptive Statistics
Chapter 7: Some Principles of Statistical Inference
Chapter 8: Examining Differences between Means: The t -test
Chapter 9: Examining Relationships between Variables: Correlation
Chapter 10: Comparing Two or More Means by Analysing Variances: ANOVA
Chapter 11: Analysing Other Forms of Data: Chi-square and Distribution-free Tests
Chapter 12: Classical Qualitative Methods
Chapter 13: Contextual Qualitative Methods
Chapter 14: Research Ethics
Chapter 15: Conclusion: Managing Uncertainty in Psychological Research
Research Methods In Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.

Hypotheses are statements about the prediction of the results, that can be verified or disproved by some investigation.
There are four types of hypotheses :
- Null Hypotheses (H0 ) – these predict that no difference will be found in the results between the conditions. Typically these are written ‘There will be no difference…’
- Alternative Hypotheses (Ha or H1) – these predict that there will be a significant difference in the results between the two conditions. This is also known as the experimental hypothesis.
- One-tailed (directional) hypotheses – these state the specific direction the researcher expects the results to move in, e.g. higher, lower, more, less. In a correlation study, the predicted direction of the correlation can be either positive or negative.
- Two-tailed (non-directional) hypotheses – these state that a difference will be found between the conditions of the independent variable but does not state the direction of a difference or relationship. Typically these are always written ‘There will be a difference ….’
All research has an alternative hypothesis (either a one-tailed or two-tailed) and a corresponding null hypothesis.
Once the research is conducted and results are found, psychologists must accept one hypothesis and reject the other.
So, if a difference is found, the Psychologist would accept the alternative hypothesis and reject the null. The opposite applies if no difference is found.
Sampling techniques
Sampling is the process of selecting a representative group from the population under study.
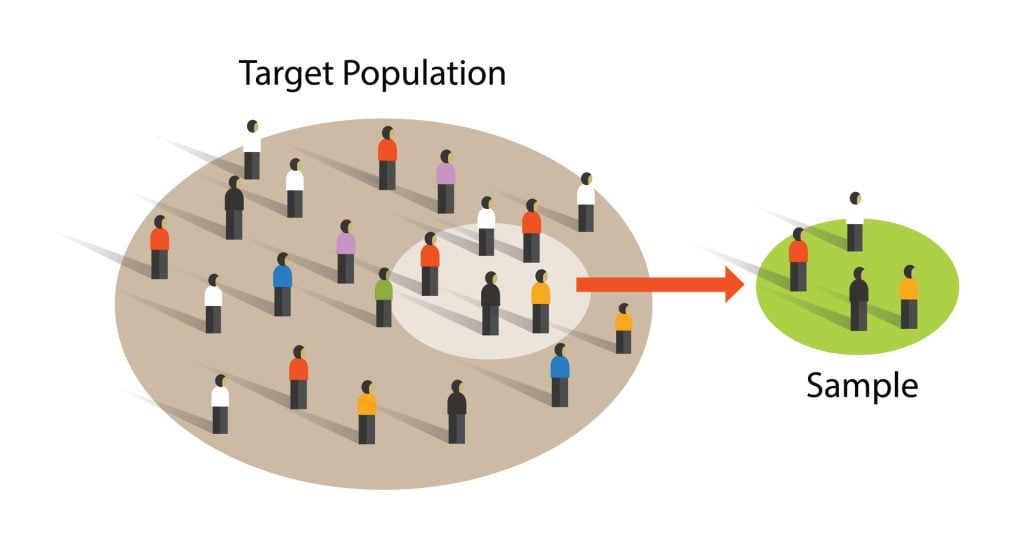
A sample is the participants you select from a target population (the group you are interested in) to make generalizations about.
Representative means the extent to which a sample mirrors a researcher’s target population and reflects its characteristics.
Generalisability means the extent to which their findings can be applied to the larger population of which their sample was a part.
- Volunteer sample : where participants pick themselves through newspaper adverts, noticeboards or online.
- Opportunity sampling : also known as convenience sampling , uses people who are available at the time the study is carried out and willing to take part. It is based on convenience.
- Random sampling : when every person in the target population has an equal chance of being selected. An example of random sampling would be picking names out of a hat.
- Systematic sampling : when a system is used to select participants. Picking every Nth person from all possible participants. N = the number of people in the research population / the number of people needed for the sample.
- Stratified sampling : when you identify the subgroups and select participants in proportion to their occurrences.
- Snowball sampling : when researchers find a few participants, and then ask them to find participants themselves and so on.
- Quota sampling : when researchers will be told to ensure the sample fits certain quotas, for example they might be told to find 90 participants, with 30 of them being unemployed.
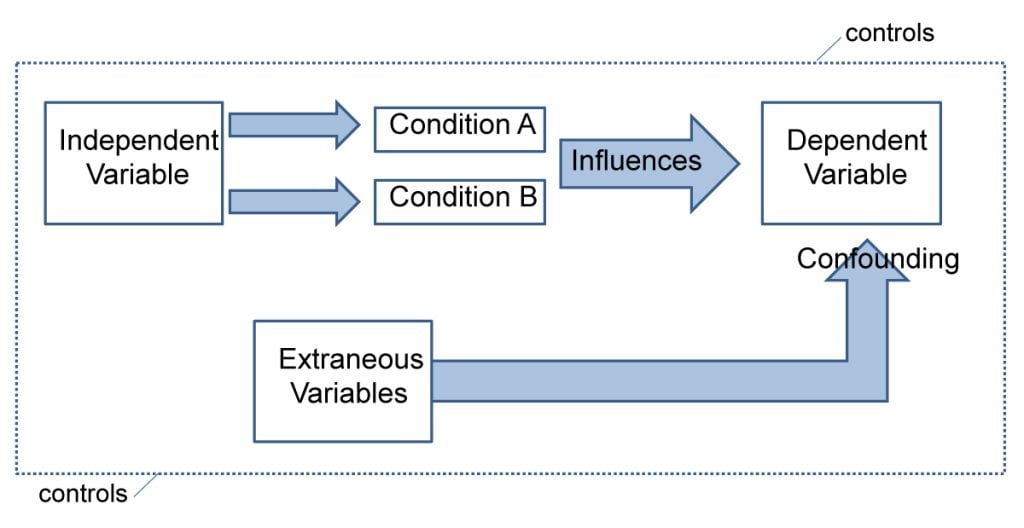
Experiments always have an independent and dependent variable .
- The independent variable is the one the experimenter manipulates (the thing that changes between the conditions the participants are placed into). It is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable.
- The dependent variable is the thing being measured, or the results of the experiment.
Operationalization of variables means making them measurable/quantifiable. We must use operationalization to ensure that variables are in a form that can be easily tested.
For instance, we can’t really measure ‘happiness’, but we can measure how many times a person smiles within a two-hour period.
By operationalizing variables, we make it easy for someone else to replicate our research. Remember, this is important because we can check if our findings are reliable.
Extraneous variables are all variables which are not independent variable but could affect the results of the experiment.
It can be a natural characteristic of the participant, such as intelligence levels, gender, or age for example, or it could be a situational feature of the environment such as lighting or noise.
Demand characteristics are a type of extraneous variable that occurs if the participants work out the aims of the research study, they may begin to behave in a certain way.
For example, in Milgram’s research , critics argued that participants worked out that the shocks were not real and they administered them as they thought this was what was required of them.
Extraneous variables must be controlled so that they do not affect (confound) the results.
Randomly allocating participants to their conditions or using a matched pairs experimental design can help to reduce participant variables.
Situational variables are controlled by using standardized procedures, ensuring every participant in a given condition is treated in the same way
Experimental Design
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to each condition of the independent variable, such as a control or experimental group.
- Independent design ( between-groups design ): each participant is selected for only one group. With the independent design, the most common way of deciding which participants go into which group is by means of randomization.
- Matched participants design : each participant is selected for only one group, but the participants in the two groups are matched for some relevant factor or factors (e.g. ability; sex; age).
- Repeated measures design ( within groups) : each participant appears in both groups, so that there are exactly the same participants in each group.
- The main problem with the repeated measures design is that there may well be order effects. Their experiences during the experiment may change the participants in various ways.
- They may perform better when they appear in the second group because they have gained useful information about the experiment or about the task. On the other hand, they may perform less well on the second occasion because of tiredness or boredom.
- Counterbalancing is the best way of preventing order effects from disrupting the findings of an experiment, and involves ensuring that each condition is equally likely to be used first and second by the participants.
If we wish to compare two groups with respect to a given independent variable, it is essential to make sure that the two groups do not differ in any other important way.
Experimental Methods
All experimental methods involve an iv (independent variable) and dv (dependent variable)..
- Field experiments are conducted in the everyday (natural) environment of the participants. The experimenter still manipulates the IV, but in a real-life setting. It may be possible to control extraneous variables, though such control is more difficult than in a lab experiment.
- Natural experiments are when a naturally occurring IV is investigated that isn’t deliberately manipulated, it exists anyway. Participants are not randomly allocated, and the natural event may only occur rarely.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. It uses information from a range of sources, such as from the person concerned and also from their family and friends.
Many techniques may be used such as interviews, psychological tests, observations and experiments. Case studies are generally longitudinal: in other words, they follow the individual or group over an extended period of time.
Case studies are widely used in psychology and among the best-known ones carried out were by Sigmund Freud . He conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
Case studies provide rich qualitative data and have high levels of ecological validity. However, it is difficult to generalize from individual cases as each one has unique characteristics.
Correlational Studies
Correlation means association; it is a measure of the extent to which two variables are related. One of the variables can be regarded as the predictor variable with the other one as the outcome variable.
Correlational studies typically involve obtaining two different measures from a group of participants, and then assessing the degree of association between the measures.
The predictor variable can be seen as occurring before the outcome variable in some sense. It is called the predictor variable, because it forms the basis for predicting the value of the outcome variable.
Relationships between variables can be displayed on a graph or as a numerical score called a correlation coefficient.
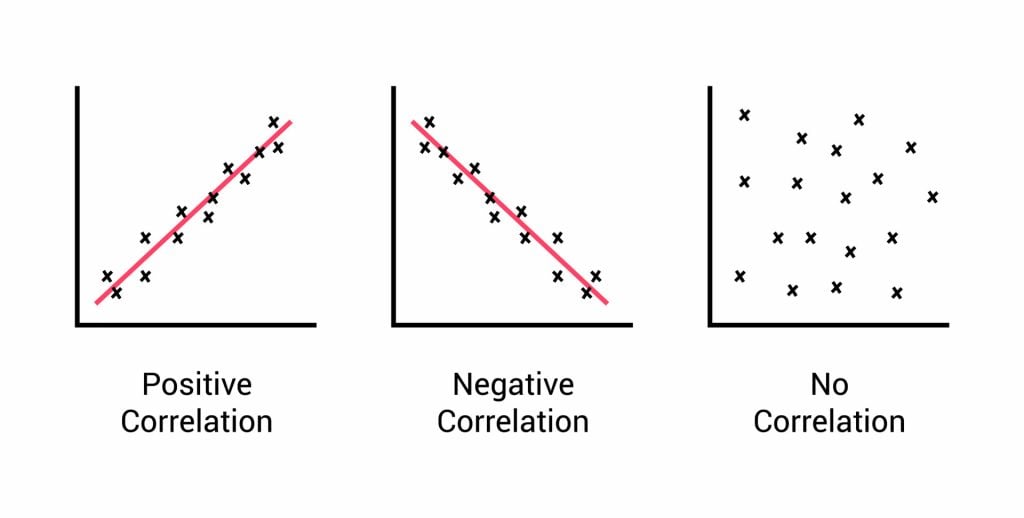
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with an increase in the other, then this is known as a positive correlation .
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with a decrease in the other, then this is known as a negative correlation .
- A zero correlation occurs when there is no relationship between variables.
After looking at the scattergraph, if we want to be sure that a significant relationship does exist between the two variables, a statistical test of correlation can be conducted, such as Spearman’s rho.
The test will give us a score, called a correlation coefficient . This is a value between 0 and 1, and the closer to 1 the score is, the stronger the relationship between the variables. This value can be both positive e.g. 0.63, or negative -0.63.
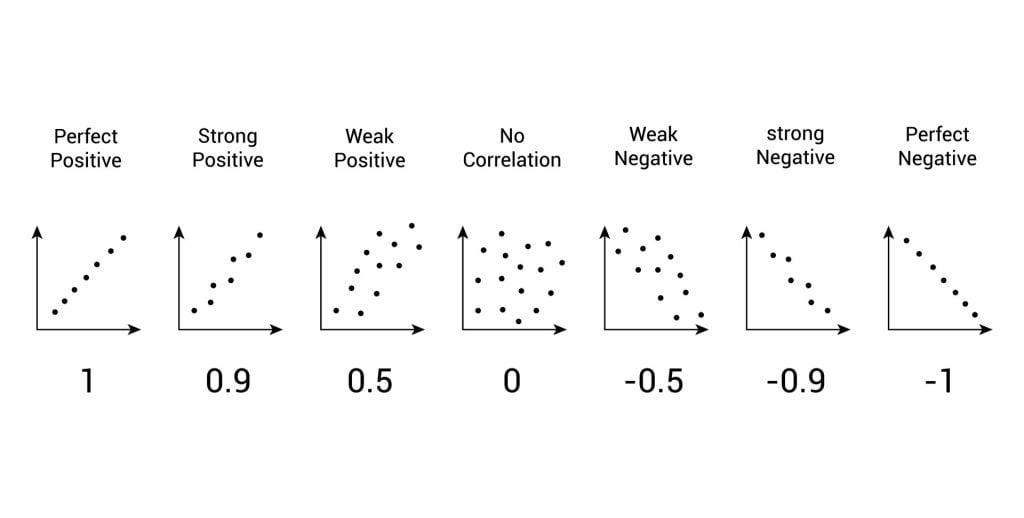
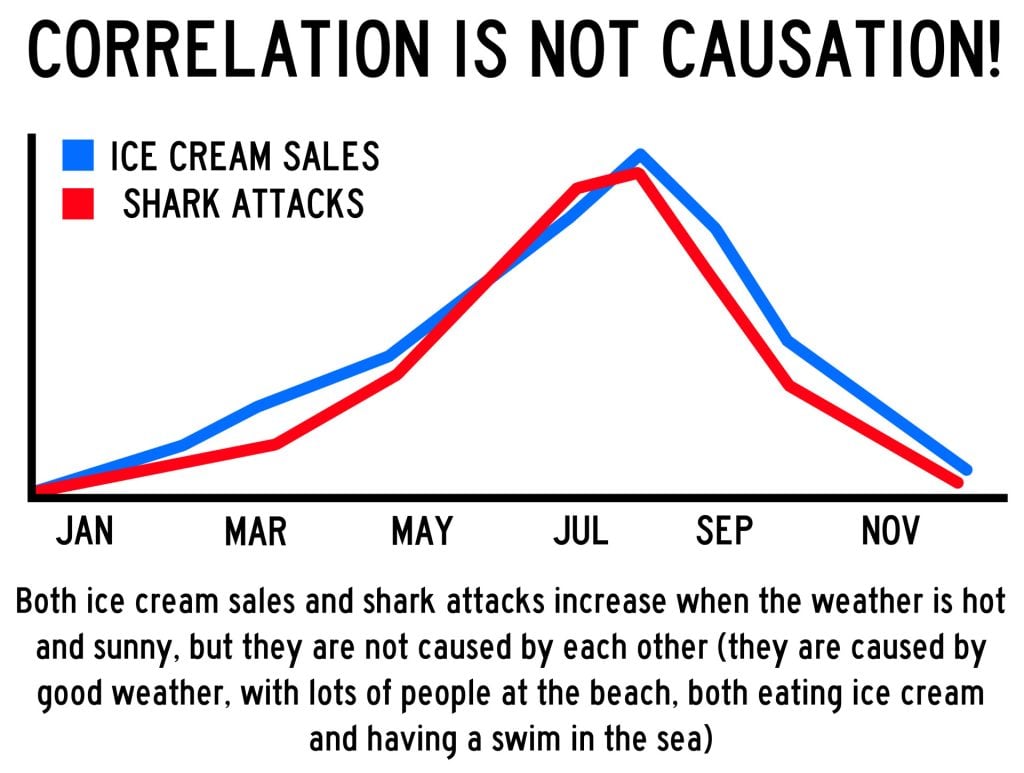
A correlation between variables, however, does not automatically mean that the change in one variable is the cause of the change in the values of the other variable. A correlation only shows if there is a relationship between variables.
Correlation does not always prove causation, as a third variable may be involved.
Interview Methods
Interviews are commonly divided into two types: structured and unstructured.
A fixed, predetermined set of questions is put to every participant in the same order and in the same way.
Responses are recorded on a questionnaire, and the researcher presets the order and wording of questions, and sometimes the range of alternative answers.
The interviewer stays within their role and maintains social distance from the interviewee.
There are no set questions, and the participant can raise whatever topics he/she feels are relevant and ask them in their own way. Questions are posed about participants’ answers to the subject
Unstructured interviews are most useful in qualitative research to analyze attitudes and values.
Though they rarely provide a valid basis for generalization, their main advantage is that they enable the researcher to probe social actors’ subjective point of view.
Questionnaire Method
Questionnaires can be thought of as a kind of written interview. They can be carried out face to face, by telephone, or post.
The choice of questions is important because of the need to avoid bias or ambiguity in the questions, ‘leading’ the respondent or causing offense.
- Open questions are designed to encourage a full, meaningful answer using the subject’s own knowledge and feelings. They provide insights into feelings, opinions, and understanding. Example: “How do you feel about that situation?”
- Closed questions can be answered with a simple “yes” or “no” or specific information, limiting the depth of response. They are useful for gathering specific facts or confirming details. Example: “Do you feel anxious in crowds?”
Its other practical advantages are that it is cheaper than face-to-face interviews and can be used to contact many respondents scattered over a wide area relatively quickly.
Observations
There are different types of observation methods :
- Covert observation is where the researcher doesn’t tell the participants they are being observed until after the study is complete. There could be ethical problems or deception and consent with this particular observation method.
- Overt observation is where a researcher tells the participants they are being observed and what they are being observed for.
- Controlled : behavior is observed under controlled laboratory conditions (e.g., Bandura’s Bobo doll study).
- Natural : Here, spontaneous behavior is recorded in a natural setting.
- Participant : Here, the observer has direct contact with the group of people they are observing. The researcher becomes a member of the group they are researching.
- Non-participant (aka “fly on the wall): The researcher does not have direct contact with the people being observed. The observation of participants’ behavior is from a distance
Pilot Study
A pilot study is a small scale preliminary study conducted in order to evaluate the feasibility of the key s teps in a future, full-scale project.
A pilot study is an initial run-through of the procedures to be used in an investigation; it involves selecting a few people and trying out the study on them. It is possible to save time, and in some cases, money, by identifying any flaws in the procedures designed by the researcher.
A pilot study can help the researcher spot any ambiguities (i.e. unusual things) or confusion in the information given to participants or problems with the task devised.
Sometimes the task is too hard, and the researcher may get a floor effect, because none of the participants can score at all or can complete the task – all performances are low.
The opposite effect is a ceiling effect, when the task is so easy that all achieve virtually full marks or top performances and are “hitting the ceiling”.
Research Design
In cross-sectional research , a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at the same time
Sometimes, we want to see how people change over time, as in studies of human development and lifespan. Longitudinal research is a research design in which data-gathering is administered repeatedly over an extended period of time.
In cohort studies , the participants must share a common factor or characteristic such as age, demographic, or occupation. A cohort study is a type of longitudinal study in which researchers monitor and observe a chosen population over an extended period.
Triangulation means using more than one research method to improve the study’s validity.
Reliability
Reliability is a measure of consistency, if a particular measurement is repeated and the same result is obtained then it is described as being reliable.
- Test-retest reliability : assessing the same person on two different occasions which shows the extent to which the test produces the same answers.
- Inter-observer reliability : the extent to which there is an agreement between two or more observers.
Meta-Analysis
A meta-analysis is a systematic review that involves identifying an aim and then searching for research studies that have addressed similar aims/hypotheses.
This is done by looking through various databases, and then decisions are made about what studies are to be included/excluded.
Strengths: Increases the conclusions’ validity as they’re based on a wider range.
Weaknesses: Research designs in studies can vary, so they are not truly comparable.
Peer Review
A researcher submits an article to a journal. The choice of the journal may be determined by the journal’s audience or prestige.
The journal selects two or more appropriate experts (psychologists working in a similar field) to peer review the article without payment. The peer reviewers assess: the methods and designs used, originality of the findings, the validity of the original research findings and its content, structure and language.
Feedback from the reviewer determines whether the article is accepted. The article may be: Accepted as it is, accepted with revisions, sent back to the author to revise and re-submit or rejected without the possibility of submission.
The editor makes the final decision whether to accept or reject the research report based on the reviewers comments/ recommendations.
Peer review is important because it prevent faulty data from entering the public domain, it provides a way of checking the validity of findings and the quality of the methodology and is used to assess the research rating of university departments.
Peer reviews may be an ideal, whereas in practice there are lots of problems. For example, it slows publication down and may prevent unusual, new work being published. Some reviewers might use it as an opportunity to prevent competing researchers from publishing work.
Some people doubt whether peer review can really prevent the publication of fraudulent research.
The advent of the internet means that a lot of research and academic comment is being published without official peer reviews than before, though systems are evolving on the internet where everyone really has a chance to offer their opinions and police the quality of research.

Types of Data
- Quantitative data is numerical data e.g. reaction time or number of mistakes. It represents how much or how long, how many there are of something. A tally of behavioral categories and closed questions in a questionnaire collect quantitative data.
- Qualitative data is virtually any type of information that can be observed and recorded that is not numerical in nature and can be in the form of written or verbal communication. Open questions in questionnaires and accounts from observational studies collect qualitative data.
- Primary data is first-hand data collected for the purpose of the investigation.
- Secondary data is information that has been collected by someone other than the person who is conducting the research e.g. taken from journals, books or articles.
Validity means how well a piece of research actually measures what it sets out to, or how well it reflects the reality it claims to represent.
Validity is whether the observed effect is genuine and represents what is actually out there in the world.
- Concurrent validity is the extent to which a psychological measure relates to an existing similar measure and obtains close results. For example, a new intelligence test compared to an established test.
- Face validity : does the test measure what it’s supposed to measure ‘on the face of it’. This is done by ‘eyeballing’ the measuring or by passing it to an expert to check.
- Ecological validit y is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other settings / real life.
- Temporal validity is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other historical times.
Features of Science
- Paradigm – A set of shared assumptions and agreed methods within a scientific discipline.
- Paradigm shift – The result of the scientific revolution: a significant change in the dominant unifying theory within a scientific discipline.
- Objectivity – When all sources of personal bias are minimised so not to distort or influence the research process.
- Empirical method – Scientific approaches that are based on the gathering of evidence through direct observation and experience.
- Replicability – The extent to which scientific procedures and findings can be repeated by other researchers.
- Falsifiability – The principle that a theory cannot be considered scientific unless it admits the possibility of being proved untrue.
Statistical Testing
A significant result is one where there is a low probability that chance factors were responsible for any observed difference, correlation, or association in the variables tested.
If our test is significant, we can reject our null hypothesis and accept our alternative hypothesis.
If our test is not significant, we can accept our null hypothesis and reject our alternative hypothesis. A null hypothesis is a statement of no effect.
In Psychology, we use p < 0.05 (as it strikes a balance between making a type I and II error) but p < 0.01 is used in tests that could cause harm like introducing a new drug.
A type I error is when the null hypothesis is rejected when it should have been accepted (happens when a lenient significance level is used, an error of optimism).
A type II error is when the null hypothesis is accepted when it should have been rejected (happens when a stringent significance level is used, an error of pessimism).
Ethical Issues
- Informed consent is when participants are able to make an informed judgment about whether to take part. It causes them to guess the aims of the study and change their behavior.
- To deal with it, we can gain presumptive consent or ask them to formally indicate their agreement to participate but it may invalidate the purpose of the study and it is not guaranteed that the participants would understand.
- Deception should only be used when it is approved by an ethics committee, as it involves deliberately misleading or withholding information. Participants should be fully debriefed after the study but debriefing can’t turn the clock back.
- All participants should be informed at the beginning that they have the right to withdraw if they ever feel distressed or uncomfortable.
- It causes bias as the ones that stayed are obedient and some may not withdraw as they may have been given incentives or feel like they’re spoiling the study. Researchers can offer the right to withdraw data after participation.
- Participants should all have protection from harm . The researcher should avoid risks greater than those experienced in everyday life and they should stop the study if any harm is suspected. However, the harm may not be apparent at the time of the study.
- Confidentiality concerns the communication of personal information. The researchers should not record any names but use numbers or false names though it may not be possible as it is sometimes possible to work out who the researchers were.
Chapter 3: Research Ethics
Chapter 3: introduction.
In 1998 a medical journal called The Lancet published an article of interest to many psychologists. The researchers claimed to have shown a statistical relationship between receiving the combined measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and the development of autism—suggesting furthermore that the vaccine might even cause autism. One result of this report was that many parents decided not to have their children vaccinated (becoming a cultural phenomenon known as “anti-vaxxers”), which of course put them at higher risk for measles, mumps, and rubella. However, follow-up studies by other researchers consistently failed to find a statistical relationship between the MMR vaccine and autism—and it is generally accepted now that there is no relationship. In addition, several more serious problems with the original research were uncovered. Among them were that the lead researcher stood to gain financially from his conclusions because he had patented a competing measles vaccine. He had also used biased methods to select and test his research participants and had used unapproved and medically unnecessary procedures on them. In 2010 The Lancet retracted the article, and the lead researcher’s right to practice medicine was revoked (Burns, 2010) [1] .
In 2011 Diederik Stapel, a prominent and well-regarded social psychologist at Tilburg University in the Netherlands, was found to have perpetrated an audacious academic crime – fabricating data [2] . Following a multi-university investigation, Stapel confessed to having made-up the data for at least 55 studies that he published in scientific journals since 2004. This revelation came as a shock to researchers, including some of his colleagues who had spent time and valuable resources designing and conducting studies that built on some of Stapel’s fraudulently published findings. Even more tragically, Stapel revealed that he had perpetrated the same fraud in 10 doctoral dissertations he oversaw, actions that caused harm to the academic careers of his former students. At a more general level, however, Stapel’s actions inflicted a serious blow to the honour code that scientists abide by. Science is, after all, a shared process of discovery that requires researchers to be honest about their work and findings – whether or not their research hypotheses are supported by the data they collect. Breaching this trust as seriously as Stapel did undermines the entire foundation of this process. Needless to say, Stapel was suspended from his position at Tilburg University. In addition, the American Psychological Association retracted a Career Trajectory Award it had presented to Stapel in 2009, and the Dutch government launched an investigation into his misuse of research funding. Stapel has since returned the doctorate he received from the University of Amsterdam, noting that his “behaviour of the past years are inconsistent with the duties associated with the doctorate.” Stapel also apologized to his colleagues, saying, “I have failed as a scientist and researcher. I feel ashamed for it and have great regret.” [3]
In political psychology, a contentious case of fraudulent data has resulted in a retracted paper from the prestigious journal, Science , as well as a rescinded job offer from Princeton University. Michael LaCour, a graduate student in political science published a surprising result with Donald Green, an established professor at Columbia University: interacting with a gay canvasser can change a voter’s opinion of gay equality. The myriad of LaCour’s fabricated information includes grants, awards, and ethical approval. Although Green requested the retraction of the Science article without consulting his co-author, LaCour stands by the data [4] .
In this chapter we explore the ethics of scientific research in psychology. We begin with a general framework for thinking about the ethics of scientific research in psychology. Then we look at some specific ethical codes for biomedical and behavioural researchers—focusing on the Ethics Code of the American Psychological Association and the Tri-Council Policy Statement (TCPS 2). Finally, we consider some practical tips for conducting ethical research in psychology.
- Burns, J. F. (2010, May 24). British medical council bars doctor who linked vaccine to autism. The New York Times . Retrieved from http://www.nytimes.com/2010/05/25/health/policy/25autism.html?ref=andrew_wakefield ↵
- Jump, P. (2011, November 28). A star’s collapse. Inside Higher Ed . Retrieved from http://www.insidehighered.com/news/2011/11/28/scholars-analyze-case-massive-research-fraud ↵
- Carey, B. (2011, November 2). Fraud case seen as a red flag for psychology research. The New York Times . Retrieved from http://www.nytimes.com/2011/11/03/health/research/noted-dutch-psychologist-stapel-accused-of-research-fraud.html ↵
- Singal, J. (2015, May 29). The Case of the Amazing Gay-Marriage Data: How a Graduate Student Reluctantly Uncovered a Huge Scientific Fraud. New York Magazine . Retrieved from http://nymag.com/scienceofus/2015/05/how-a-grad-student-uncovered-a-huge-fraud.html ↵
- Research Methods in Psychology. Authored by : Paul C. Price, Rajiv S. Jhangiani, and I-Chant A. Chiang. Provided by : BCCampus. Located at : https://opentextbc.ca/researchmethods/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike

Privacy Policy
Final dates! Join the tutor2u subject teams in London for a day of exam technique and revision at the cinema. Learn more →
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Psychology news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Psychology Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
- Quizzes & Activities
A Level Psychology Topic Quiz - Research Methods
Last updated 5 May 2017
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
Here is an overall topic quiz on research methods as featured in the AQA A Level Psychology specification.
Each time you take this quiz you will get 10 MCQs drawn at random from over 100 questions relevant to research methods. Try the first ten, see how you get on, and then try again with 10 different questions!

Core Topics Revision Flashcards for AQA A-Level Psychology
Printed Resource
- Research Methods
- Laboratory Experiment
- Correlation Coefficient
- Coding: Content Analysis
You might also like

Delaying Gratification: Could you? Can your students?
18th February 2016
Content Analysis
Study Notes
Investigator Effects
Operationalisation, case studies, laboratory experiments, natural experiments, our subjects.
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.
Have an account?

Psychology Research Methods
11th - 12th grade, social studies.
18 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
- 1. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt This research method is a descriptive technique in which one individual or group is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles Case Study Survey Observational Correlational Experiments
- 2. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt This research method is a technique for ascertaining the self – reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of the group. Survey Observational Correlational Experiments Case Study
- 3. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt This is a method of research where the researcher carefully and systematically observes and records behavior without interfering Observational Correlational Experiments Case Study Survey
- 4. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt This research method is a measure of the extent to which two variables change together, and thus of how well either variable predicts the other Correlational Experiments Case Study Survey Observational
- 5. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt This is a method of research where an investigator manipulates one or more factors (independent variables) to observe the effect on some behavior or mental process (the dependent variable). Experiments Case Study Survey Observational Correlational
- 6. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt The advantage of this descriptive method of research is that it yields a great deal of detailed descriptive information and they are very useful in forming a hypothesis Case Study Survey Observational Correlational Experiments
- 7. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt The advantage of this descriptive method of research is that it creates an immense amount of data to be gathered quickly and inexpensively. Survey Observational Correlational Experiments Case Study
- 8. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt The advantage of this method of research is that the behavior observed in the subject(s) natural environment to be more natural, spontaneous, and varied than that observed in a laboratory. Observational Correlational Experiments Case Study Survey
- 9. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt The advantage of this method of research is that it can help to clarify relationships between variable that cannot be explained by other research methods, in other words- predictions. Correlational Experiments Case Study Survey Observational
- 10. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt The advantage of this descriptive method of research is that the strict control of variables offers researchers the opportunity to draw conclusions about cause and effect relationships. Experiments Case Study Survey Observational Correlational
- 11. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt The disadvantage of this method of descriptive research is that the research may not be a representative sample of the general population and doesn’t yield reliable conclusions about behavior. Case Study Survey Observational Correlational Experiments
- 12. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt The disadvantage of this method of descriptive research is that the data is limited to only answering the question(s) asked. These limitations lead to biases, ambiguous conclusions, and low participation rates among research populations. Survey Observational Correlational Experiments Case Study
- 13. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt The disadvantage of this method of descriptive research is the behaviors could be only one-time occurrences. Observational Correlational Experiments Case Study Survey
- 14. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt The disadvantage of this method of descriptive research is that it does not permit researchers to draw conclusions regarding cause-and-effect relationships Correlational Experiments Case Study Survey Observational
- 15. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt The disadvantage of this method of descriptive research is the artificiality of the lab doesn’t lend itself to real unexpected results. Experiments Case Study Survey Observational Correlational
- 16. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt Most notable examples of this method of descriptive research are cross-sectional studies and longitudinal studies. Case Study Survey Observational Correlational Experiments
- 17. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt The disadvantage of this method of descriptive research is questions must be asked “just right” to get reliable answers and a considerable amount of honesty and trust is given in the answers. Survey Observational Correlational Experiments Case Study
- 18. Multiple Choice Edit 45 seconds 1 pt The disadvantage of this method of descriptive research is that some variables are too challenging to manipulate in an experiment (emotions, other cognitive behavior). Results may not be reflective of the general population. Experiments Case Study Survey Observational Correlational
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Psychology. Research Methods in Psychology Exam 3. One group, pretest/posttest design. Click the card to flip 👆. Design in which a researcher recruits one group of participants, measures them on a pretest, exposes them to a treatment or change, and then measures them on a posttest; an ineffective experimental design.
Research Methods in psychology Exam 3. Get a hint. Sleeper Effect. Click the card to flip 👆. - No main effect of discounting cue presentation (before vs. after message) - Main effect for delay (rating becomes more positive with time) - The cross over interaction of delay by cue presentation. Click the card to flip 👆. 1 / 39.
Research Methods in Psychology Exam 3. Internal validity means you can? Click card to see definition 👆. make a casual relationship. Click again to see term 👆. 1/97. Previous.
experiment. systematic research study in which one factor is manipulated and one factor is measured. independent variable. the factor whose effect is being studied, the manipulated variable. There must be at least two levels. types of independent variables. 1. situational variables (environmental) 2. task variables. 3. instructional variables.
8. Which of the following is a research method that allows a researcher to get information about a large number of subjects relatively inexpensively and easily? Naturalistic observation. Case study. Laboratory observation. Survey. 9. What is a common way of controlling extraneous variables in an experiment?
Revise your knowledge with these multiple choice quiz questions. Chapter 2: Research in Psychology: Objectives and Ideals. Chapter 3: Research Methods. Chapter 4: Experimental Design. Chapter 5: Survey Design. Chapter 6: Descriptive Statistics. Chapter 7: Some Principles of Statistical Inference. Chapter 8: Examining Differences between Means ...
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc. Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.
The following video includes 10 practice multiple choice questions related to research methods and statistics in psychology. I hope that these can help you to test and assess your own knowledge and provide practice retrieving the terms, ideas, and concepts that you've learned. You can also find a PDF with the practice questions and an answer ...
Research Methods Exam 3 Study Guide. 5 pages 2019/2020 100% (3) 2019/2020 ... 1 page 2022/2023 None. 2022/2023 None. Save. Lab assignment #3 - Research methods lab materials. 2 pages 2022/2023 None. 2022/2023 None. Save. Research chap 7 sampling definitions chart. 3 pages ... Research Methods in Psychology: Evaluating a World of Information ...
Research Methods Exam 3 Study Guide. Chapter 9 Pattern and Parsimony- using a variety of correlational studies that all point in a single, causal direction o Allows researchers to examine a problem in a variety of ways, the diversity of the predictions/findings makes it hard to argue for the 3rd variable problem. . Moderators- explains/inlfuences the strength of a relationship Mediators ...
1. organize phenomena to help people think clearly and efficiently. 2. allows researchers to make future predictions. 3. generate new research by raising new questions. True of False: replication refers to conducting the same research again without making any modifications.
Chapter 3: Introduction. In 1998 a medical journal called The Lancet published an article of interest to many psychologists. The researchers claimed to have shown a statistical relationship between receiving the combined measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and the development of autism—suggesting furthermore that the vaccine might even ...
Study Flashcards On Research Methods in Psychology Test 3 at Cram.com. Quickly memorize the terms, phrases and much more. Cram.com makes it easy to get the grade you want!
-Showing major changes in beliefs and how the beliefs relate to other variables -(e., Gilbert, 1951; Karlins, Coffman, & Walters, 1969; Katz & Braly, 1933; Philogene, 2001) -Survey research used -To collect data used to test theoretical models constructed by researchers based on past literature, experimental results, and other factors (e ...
Describe correlational research. Use to examine relationships between 2 variables. It can also be used to predict behavior or performance. Describe descriptive research. Use to describe the characteristics of a phenomenon. T or F: In descriptive research, the experimenter does not manipulate independent variables.
A Level Psychology Topic Quiz - Research Methods. Here is an overall topic quiz on research methods as featured in the AQA A Level Psychology specification. Each time you take this quiz you will get 10 MCQs drawn at random from over 100 questions relevant to research methods. Try the first ten, see how you get on, and then try again with 10 ...
1.provides a way of checking the validity of the research. 2. making a judgement about the credibility of the research. 3. assessingthe quality and appropriateness of the design and method. 4. peers can assess the significance of the research in a wider context. 5. can judge originality and relevance to other research.
Psych 303 Exam 1 Study Guide a set of observations representing the values of some variables, collected from one or more research methods when a claim can be rejected, it is possible to collect data that will prove the theory wrong Hypothesis: statement of the specific relationship between a variables that the researcher expects to observe if a theory is accurate Journal: monthly or quarterly ...
RESEARCH REPORT (Last Name) 1 Research Report (Student) PSYC 300 Research Methods in Psychology Professor 13 December 2021 fRESEARCH REPORT (Last Name) 2 Abstract The Stroop Effect is the slight delay in a person's reaction time when switching between aut. PSYC 300. University of Maryland, University College. 157 views.
Survey. Observational. Correlational. Experiments. 2. Multiple Choice. 45 seconds. 1 pt. This research method is a technique for ascertaining the self - reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of the group.
give incentives for participating, enroll new participants in the study. Cram has partnered with the National Tutoring Association Claim your access. Study Flashcards On Research Methods Exam 2 at Cram.com. Quickly memorize the terms, phrases and much more. Cram.com makes it easy to get the grade you want!