

ANA Nursing Resources Hub
Search Resources Hub
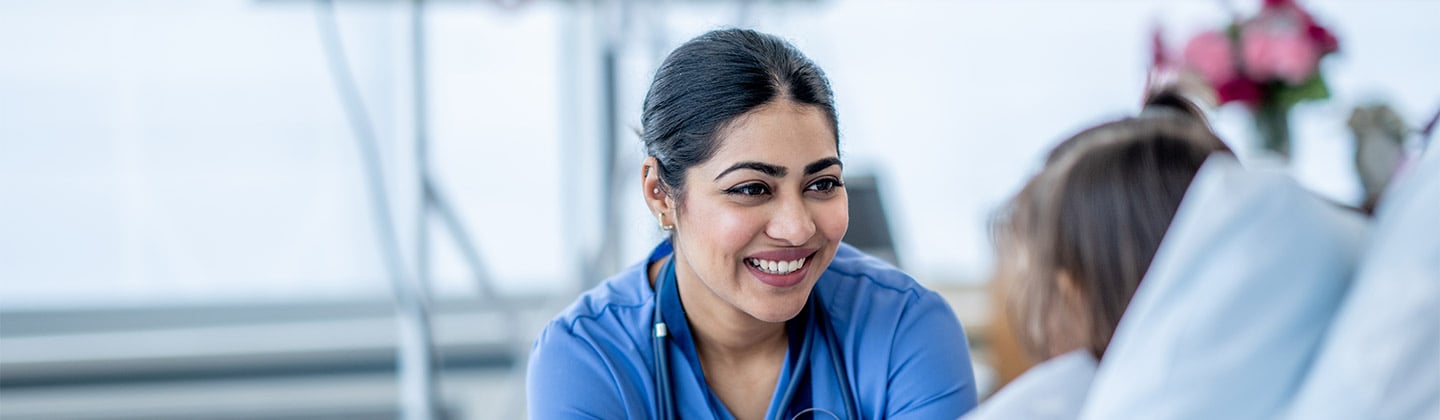

Critical Thinking in Nursing: Tips to Develop the Skill
4 min read • February, 09 2024
Critical thinking in nursing helps caregivers make decisions that lead to optimal patient care. In school, educators and clinical instructors introduced you to critical-thinking examples in nursing. These educators encouraged using learning tools for assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation.
Nurturing these invaluable skills continues once you begin practicing. Critical thinking is essential to providing quality patient care and should continue to grow throughout your nursing career until it becomes second nature.
What Is Critical Thinking in Nursing?
Critical thinking in nursing involves identifying a problem, determining the best solution, and implementing an effective method to resolve the issue using clinical decision-making skills.
Reflection comes next. Carefully consider whether your actions led to the right solution or if there may have been a better course of action.
Remember, there's no one-size-fits-all treatment method — you must determine what's best for each patient.
How Is Critical Thinking Important for Nurses?
As a patient's primary contact, a nurse is typically the first to notice changes in their status. One example of critical thinking in nursing is interpreting these changes with an open mind. Make impartial decisions based on evidence rather than opinions. By applying critical-thinking skills to anticipate and understand your patients' needs, you can positively impact their quality of care and outcomes.
Elements of Critical Thinking in Nursing
To assess situations and make informed decisions, nurses must integrate these specific elements into their practice:
- Clinical judgment. Prioritize a patient's care needs and make adjustments as changes occur. Gather the necessary information and determine what nursing intervention is needed. Keep in mind that there may be multiple options. Use your critical-thinking skills to interpret and understand the importance of test results and the patient’s clinical presentation, including their vital signs. Then prioritize interventions and anticipate potential complications.
- Patient safety. Recognize deviations from the norm and take action to prevent harm to the patient. Suppose you don't think a change in a patient's medication is appropriate for their treatment. Before giving the medication, question the physician's rationale for the modification to avoid a potential error.
- Communication and collaboration. Ask relevant questions and actively listen to others while avoiding judgment. Promoting a collaborative environment may lead to improved patient outcomes and interdisciplinary communication.
- Problem-solving skills. Practicing your problem-solving skills can improve your critical-thinking skills. Analyze the problem, consider alternate solutions, and implement the most appropriate one. Besides assessing patient conditions, you can apply these skills to other challenges, such as staffing issues .
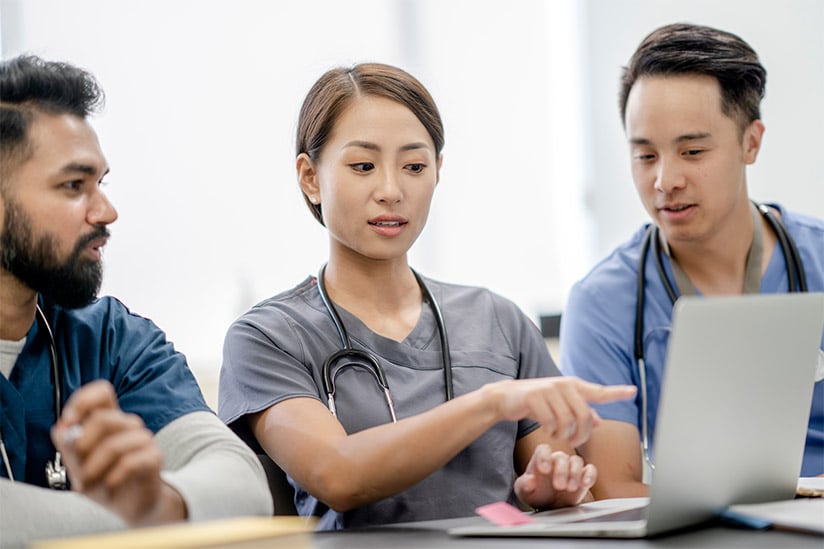

How to Develop and Apply Critical-Thinking Skills in Nursing
Critical-thinking skills develop as you gain experience and advance in your career. The ability to predict and respond to nursing challenges increases as you expand your knowledge and encounter real-life patient care scenarios outside of what you learned from a textbook.
Here are five ways to nurture your critical-thinking skills:
- Be a lifelong learner. Continuous learning through educational courses and professional development lets you stay current with evidence-based practice . That knowledge helps you make informed decisions in stressful moments.
- Practice reflection. Allow time each day to reflect on successes and areas for improvement. This self-awareness can help identify your strengths, weaknesses, and personal biases to guide your decision-making.
- Open your mind. Don't assume you're right. Ask for opinions and consider the viewpoints of other nurses, mentors , and interdisciplinary team members.
- Use critical-thinking tools. Structure your thinking by incorporating nursing process steps or a SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) to organize information, evaluate options, and identify underlying issues.
- Be curious. Challenge assumptions by asking questions to ensure current care methods are valid, relevant, and supported by evidence-based practice .
Critical thinking in nursing is invaluable for safe, effective, patient-centered care. You can successfully navigate challenges in the ever-changing health care environment by continually developing and applying these skills.
Images sourced from Getty Images
Related Resources

Item(s) added to cart
What is Critical Thinking in Nursing? (With Examples, Importance, & How to Improve)

Successful nursing requires learning several skills used to communicate with patients, families, and healthcare teams. One of the most essential skills nurses must develop is the ability to demonstrate critical thinking. If you are a nurse, perhaps you have asked if there is a way to know how to improve critical thinking in nursing? As you read this article, you will learn what critical thinking in nursing is and why it is important. You will also find 18 simple tips to improve critical thinking in nursing and sample scenarios about how to apply critical thinking in your nursing career.
What is Critical Thinking in Nursing?
4 reasons why critical thinking is so important in nursing, 1. critical thinking skills will help you anticipate and understand changes in your patient’s condition., 2. with strong critical thinking skills, you can make decisions about patient care that is most favorable for the patient and intended outcomes., 3. strong critical thinking skills in nursing can contribute to innovative improvements and professional development., 4. critical thinking skills in nursing contribute to rational decision-making, which improves patient outcomes., what are the 8 important attributes of excellent critical thinking in nursing, 1. the ability to interpret information:, 2. independent thought:, 3. impartiality:, 4. intuition:, 5. problem solving:, 6. flexibility:, 7. perseverance:, 8. integrity:, examples of poor critical thinking vs excellent critical thinking in nursing, 1. scenario: patient/caregiver interactions, poor critical thinking:, excellent critical thinking:, 2. scenario: improving patient care quality, 3. scenario: interdisciplinary collaboration, 4. scenario: precepting nursing students and other nurses, how to improve critical thinking in nursing, 1. demonstrate open-mindedness., 2. practice self-awareness., 3. avoid judgment., 4. eliminate personal biases., 5. do not be afraid to ask questions., 6. find an experienced mentor., 7. join professional nursing organizations., 8. establish a routine of self-reflection., 9. utilize the chain of command., 10. determine the significance of data and decide if it is sufficient for decision-making., 11. volunteer for leadership positions or opportunities., 12. use previous facts and experiences to help develop stronger critical thinking skills in nursing., 13. establish priorities., 14. trust your knowledge and be confident in your abilities., 15. be curious about everything., 16. practice fair-mindedness., 17. learn the value of intellectual humility., 18. never stop learning., 4 consequences of poor critical thinking in nursing, 1. the most significant risk associated with poor critical thinking in nursing is inadequate patient care., 2. failure to recognize changes in patient status:, 3. lack of effective critical thinking in nursing can impact the cost of healthcare., 4. lack of critical thinking skills in nursing can cause a breakdown in communication within the interdisciplinary team., useful resources to improve critical thinking in nursing, youtube videos, my final thoughts, frequently asked questions answered by our expert, 1. will lack of critical thinking impact my nursing career, 2. usually, how long does it take for a nurse to improve their critical thinking skills, 3. do all types of nurses require excellent critical thinking skills, 4. how can i assess my critical thinking skills in nursing.
• Ask relevant questions • Justify opinions • Address and evaluate multiple points of view • Explain assumptions and reasons related to your choice of patient care options
5. Can I Be a Nurse If I Cannot Think Critically?

The Value of Critical Thinking in Nursing

- How Nurses Use Critical Thinking
- How to Improve Critical Thinking
- Common Mistakes

Some experts describe a person’s ability to question belief systems, test previously held assumptions, and recognize ambiguity as evidence of critical thinking. Others identify specific skills that demonstrate critical thinking, such as the ability to identify problems and biases, infer and draw conclusions, and determine the relevance of information to a situation.
Nicholas McGowan, BSN, RN, CCRN, has been a critical care nurse for 10 years in neurological trauma nursing and cardiovascular and surgical intensive care. He defines critical thinking as “necessary for problem-solving and decision-making by healthcare providers. It is a process where people use a logical process to gather information and take purposeful action based on their evaluation.”
“This cognitive process is vital for excellent patient outcomes because it requires that nurses make clinical decisions utilizing a variety of different lenses, such as fairness, ethics, and evidence-based practice,” he says.
How Do Nurses Use Critical Thinking?
Successful nurses think beyond their assigned tasks to deliver excellent care for their patients. For example, a nurse might be tasked with changing a wound dressing, delivering medications, and monitoring vital signs during a shift. However, it requires critical thinking skills to understand how a difference in the wound may affect blood pressure and temperature and when those changes may require immediate medical intervention.
Nurses care for many patients during their shifts. Strong critical thinking skills are crucial when juggling various tasks so patient safety and care are not compromised.
Jenna Liphart Rhoads, Ph.D., RN, is a nurse educator with a clinical background in surgical-trauma adult critical care, where critical thinking and action were essential to the safety of her patients. She talks about examples of critical thinking in a healthcare environment, saying:
“Nurses must also critically think to determine which patient to see first, which medications to pass first, and the order in which to organize their day caring for patients. Patient conditions and environments are continually in flux, therefore nurses must constantly be evaluating and re-evaluating information they gather (assess) to keep their patients safe.”
The COVID-19 pandemic created hospital care situations where critical thinking was essential. It was expected of the nurses on the general floor and in intensive care units. Crystal Slaughter is an advanced practice nurse in the intensive care unit (ICU) and a nurse educator. She observed critical thinking throughout the pandemic as she watched intensive care nurses test the boundaries of previously held beliefs and master providing excellent care while preserving resources.
“Nurses are at the patient’s bedside and are often the first ones to detect issues. Then, the nurse needs to gather the appropriate subjective and objective data from the patient in order to frame a concise problem statement or question for the physician or advanced practice provider,” she explains.
Top 5 Ways Nurses Can Improve Critical Thinking Skills
We asked our experts for the top five strategies nurses can use to purposefully improve their critical thinking skills.
Case-Based Approach
Slaughter is a fan of the case-based approach to learning critical thinking skills.
In much the same way a detective would approach a mystery, she mentors her students to ask questions about the situation that help determine the information they have and the information they need. “What is going on? What information am I missing? Can I get that information? What does that information mean for the patient? How quickly do I need to act?”
Consider forming a group and working with a mentor who can guide you through case studies. This provides you with a learner-centered environment in which you can analyze data to reach conclusions and develop communication, analytical, and collaborative skills with your colleagues.
Practice Self-Reflection
Rhoads is an advocate for self-reflection. “Nurses should reflect upon what went well or did not go well in their workday and identify areas of improvement or situations in which they should have reached out for help.” Self-reflection is a form of personal analysis to observe and evaluate situations and how you responded.
This gives you the opportunity to discover mistakes you may have made and to establish new behavior patterns that may help you make better decisions. You likely already do this. For example, after a disagreement or contentious meeting, you may go over the conversation in your head and think about ways you could have responded.
It’s important to go through the decisions you made during your day and determine if you should have gotten more information before acting or if you could have asked better questions.
During self-reflection, you may try thinking about the problem in reverse. This may not give you an immediate answer, but can help you see the situation with fresh eyes and a new perspective. How would the outcome of the day be different if you planned the dressing change in reverse with the assumption you would find a wound infection? How does this information change your plan for the next dressing change?
Develop a Questioning Mind
McGowan has learned that “critical thinking is a self-driven process. It isn’t something that can simply be taught. Rather, it is something that you practice and cultivate with experience. To develop critical thinking skills, you have to be curious and inquisitive.”
To gain critical thinking skills, you must undergo a purposeful process of learning strategies and using them consistently so they become a habit. One of those strategies is developing a questioning mind. Meaningful questions lead to useful answers and are at the core of critical thinking .
However, learning to ask insightful questions is a skill you must develop. Faced with staff and nursing shortages , declining patient conditions, and a rising number of tasks to be completed, it may be difficult to do more than finish the task in front of you. Yet, questions drive active learning and train your brain to see the world differently and take nothing for granted.
It is easier to practice questioning in a non-stressful, quiet environment until it becomes a habit. Then, in the moment when your patient’s care depends on your ability to ask the right questions, you can be ready to rise to the occasion.
Practice Self-Awareness in the Moment
Critical thinking in nursing requires self-awareness and being present in the moment. During a hectic shift, it is easy to lose focus as you struggle to finish every task needed for your patients. Passing medication, changing dressings, and hanging intravenous lines all while trying to assess your patient’s mental and emotional status can affect your focus and how you manage stress as a nurse .
Staying present helps you to be proactive in your thinking and anticipate what might happen, such as bringing extra lubricant for a catheterization or extra gloves for a dressing change.
By staying present, you are also better able to practice active listening. This raises your assessment skills and gives you more information as a basis for your interventions and decisions.
Use a Process
As you are developing critical thinking skills, it can be helpful to use a process. For example:
- Ask questions.
- Gather information.
- Implement a strategy.
- Evaluate the results.
- Consider another point of view.
These are the fundamental steps of the nursing process (assess, diagnose, plan, implement, evaluate). The last step will help you overcome one of the common problems of critical thinking in nursing — personal bias.
Common Critical Thinking Pitfalls in Nursing
Your brain uses a set of processes to make inferences about what’s happening around you. In some cases, your unreliable biases can lead you down the wrong path. McGowan places personal biases at the top of his list of common pitfalls to critical thinking in nursing.
“We all form biases based on our own experiences. However, nurses have to learn to separate their own biases from each patient encounter to avoid making false assumptions that may interfere with their care,” he says. Successful critical thinkers accept they have personal biases and learn to look out for them. Awareness of your biases is the first step to understanding if your personal bias is contributing to the wrong decision.
New nurses may be overwhelmed by the transition from academics to clinical practice, leading to a task-oriented mindset and a common new nurse mistake ; this conflicts with critical thinking skills.
“Consider a patient whose blood pressure is low but who also needs to take a blood pressure medication at a scheduled time. A task-oriented nurse may provide the medication without regard for the patient’s blood pressure because medication administration is a task that must be completed,” Slaughter says. “A nurse employing critical thinking skills would address the low blood pressure, review the patient’s blood pressure history and trends, and potentially call the physician to discuss whether medication should be withheld.”
Fear and pride may also stand in the way of developing critical thinking skills. Your belief system and worldview provide comfort and guidance, but this can impede your judgment when you are faced with an individual whose belief system or cultural practices are not the same as yours. Fear or pride may prevent you from pursuing a line of questioning that would benefit the patient. Nurses with strong critical thinking skills exhibit:
- Learn from their mistakes and the mistakes of other nurses
- Look forward to integrating changes that improve patient care
- Treat each patient interaction as a part of a whole
- Evaluate new events based on past knowledge and adjust decision-making as needed
- Solve problems with their colleagues
- Are self-confident
- Acknowledge biases and seek to ensure these do not impact patient care
An Essential Skill for All Nurses
Critical thinking in nursing protects patient health and contributes to professional development and career advancement. Administrative and clinical nursing leaders are required to have strong critical thinking skills to be successful in their positions.
By using the strategies in this guide during your daily life and in your nursing role, you can intentionally improve your critical thinking abilities and be rewarded with better patient outcomes and potential career advancement.
Frequently Asked Questions About Critical Thinking in Nursing
How are critical thinking skills utilized in nursing practice.
Nursing practice utilizes critical thinking skills to provide the best care for patients. Often, the patient’s cause of pain or health issue is not immediately clear. Nursing professionals need to use their knowledge to determine what might be causing distress, collect vital information, and make quick decisions on how best to handle the situation.
How does nursing school develop critical thinking skills?
Nursing school gives students the knowledge professional nurses use to make important healthcare decisions for their patients. Students learn about diseases, anatomy, and physiology, and how to improve the patient’s overall well-being. Learners also participate in supervised clinical experiences, where they practice using their critical thinking skills to make decisions in professional settings.
Do only nurse managers use critical thinking?
Nurse managers certainly use critical thinking skills in their daily duties. But when working in a health setting, anyone giving care to patients uses their critical thinking skills. Everyone — including licensed practical nurses, registered nurses, and advanced nurse practitioners —needs to flex their critical thinking skills to make potentially life-saving decisions.
Meet Our Contributors

Crystal Slaughter, DNP, APRN, ACNS-BC, CNE
Crystal Slaughter is a core faculty member in Walden University’s RN-to-BSN program. She has worked as an advanced practice registered nurse with an intensivist/pulmonary service to provide care to hospitalized ICU patients and in inpatient palliative care. Slaughter’s clinical interests lie in nursing education and evidence-based practice initiatives to promote improving patient care.

Jenna Liphart Rhoads, Ph.D., RN
Jenna Liphart Rhoads is a nurse educator and freelance author and editor. She earned a BSN from Saint Francis Medical Center College of Nursing and an MS in nursing education from Northern Illinois University. Rhoads earned a Ph.D. in education with a concentration in nursing education from Capella University where she researched the moderation effects of emotional intelligence on the relationship of stress and GPA in military veteran nursing students. Her clinical background includes surgical-trauma adult critical care, interventional radiology procedures, and conscious sedation in adult and pediatric populations.

Nicholas McGowan, BSN, RN, CCRN
Nicholas McGowan is a critical care nurse with 10 years of experience in cardiovascular, surgical intensive care, and neurological trauma nursing. McGowan also has a background in education, leadership, and public speaking. He is an online learner who builds on his foundation of critical care nursing, which he uses directly at the bedside where he still practices. In addition, McGowan hosts an online course at Critical Care Academy where he helps nurses achieve critical care (CCRN) certification.
The university of tulsa Online Blog
Trending topics in the tu online community
Why Critical Thinking Skills in Nursing Are Essential
Written by: university of tulsa • feb 29, 2024.
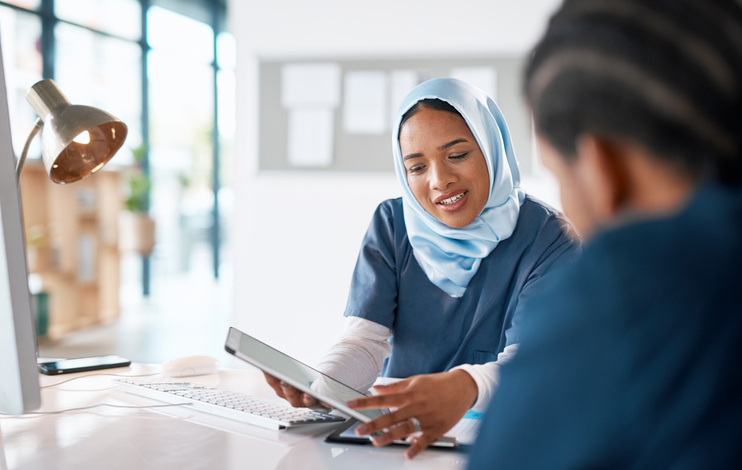

Why Critical Thinking Skills in Nursing Are Essential ¶
Working in health care requires quick thinking and confident decision-making to care for patients. While nurses use a broad range of technical skills to provide quality care, an essential skill that’s easy to overlook is critical thinking. Nursing professionals should explore the benefits of critical thinking skills in nursing, how to apply them, and the ways that advanced education can sharpen their ability to make precise decisions.
Critical Thinking Skills: A Definition ¶
Critical thinking is the process of evaluating facts, interpreting information, and analyzing situations to make informed decisions in various situations. Finding the correct answer to a complex problem isn’t easy. When situations don’t have clear answers and many factors to consider, critical thinking can help individuals move forward and make decisions.
Critical thinking competencies can be applied to a wide range of workplaces and personal situations. In nursing, critical thinking skills can help deliver effective care, handle a patient crisis, and assess the efficacy of treatment plans.
The Importance of Critical Thinking Skills in Nursing ¶
The fast-paced nursing environment requires prompt, data-driven decisions. Nurses use critical thinking daily, reviewing information and making decisions to promote quality care for patients. The following benefits of critical thinking highlight the importance of this skill in nursing careers:
Improves decision-making speed. A critical thinking mindset can help nurses make timely, effective decisions in difficult situations. A systematic method to evaluate decisions and move forward is a powerful tool for nurses.
Refines communication. Improving professional communication allows for factual, efficient, and empathetic conversations with patients and other health care professionals.
Promotes open-mindedness. It’s easy to overlook certain opinions or viewpoints in a high-pressure situation. Thankfully, critical thinking promotes open-mindedness in exploring solutions.
Combats bias. A critical look at different behaviors, contexts, and viewpoints can be helpful for identifying and addressing bias. Nurses must actively seek out ways to confront and remove bias in the workplace.
Critical Thinking in the Nursing Process ¶
There are many ways to apply critical thinking skills to nursing situations. The nursing process is a five-step process to assist nurses in applying critical thinking skills to their daily duties. Experienced nurses and professionals considering a career change to nursing should review the steps as part of their critical thinking process.
Step 1: Assessment ¶
Assessing a patient means far more than taking their vital signs. It also includes collecting sociocultural and psychological data. Lifestyle factors and experiences can affect the treatment process and approach, so skilled nurses review these areas before moving toward the next step, diagnosis.
For example, if a patient reports dizziness or shortness of breath, a nurse should not only check the patient’s temperature, blood pressure, and heart rate but also ask about their family history and recent events.
Step 2: Diagnosis ¶
During the second step, a nurse’s assessment and critical thinking skills produce a clinical judgment. Nurses need to carefully consider all the factors included in the first step. When necessary, consult with other health care professionals before reaching a diagnosis or communicating that diagnosis with the patient.
Discussing a patient’s assessment with other health care professionals requires critical thinking, as the information provided about vital signs, recent events, and family history are key components of this step.
Step 3: Planning ¶
A nurse may be responsible for setting goals and planning a treatment plan for patients. The third step can include setting measurable, achievable goals. Nurses also coordinate care with other health care professionals.
Goals can be simple or complex, depending on the assessment and diagnosis. For example, one patient’s goals may include eating three meals a day, while another’s may include having multiple medications, specialist visits, and physical therapy activities as part of their treatment plan.
Step 4: Implementation ¶
Critical thinking is needed to implement the nursing process, finding ways to carry out the plan with empathy. It’s also important for nurses to document care throughout the fourth step of the process.
For example, nurses should review patient history and consider symptoms before administering medication. Nursing professionals should also think critically about which patients to see first and how to prioritize patients who may need critical attention.
Step 5: Evaluation ¶
Nurses need to continue to evaluate and review the patient’s condition using critical thinking. Evaluation allows nursing professionals to review patient conditions, recommend care plan modification, and consider overall patient status.
For example, identifying whether patients may be ready for a care plan modification or another change in care requires critical thinking and a clear, focused evaluation of multiple patient factors.
How to Foster Critical Thinking Through Nursing Education ¶
Critical thinking is integral to success in the health care field. Thankfully, many ways are available for nurses to improve their critical thinking skills. Below are training, mentoring, and education options for fostering critical thinking.
On-the-Job Training ¶
Because critical thinking is so critical to the daily duties of nurses, experience in the field can improve their ability to evaluate situations and make data-driven decisions. Working firsthand with patients and alongside skilled professionals is a powerful way to see and apply critical thinking in real-world scenarios.
Mentoring Opportunities ¶
Nurses should seek mentorship opportunities for personalized, side-by-side instruction and inspiration from fellow professionals. Mentorships can be either formal or informal opportunities to learn from skilled nurses and health care professionals to promote critical thinking.
Further Education ¶
Many continuing education opportunities are available for nurses. Professionals looking to improve their critical thinking skills should consider enrolling in a course that promotes reflection, evaluation, and analytical thinking.
Review Critical Thinking Skills With The University of Tulsa ¶
Expand your critical thinking skills in nursing by enrolling in a program to earn a degree in the field. The University of Tulsa offers an accelerated online RN to Bachelor of Science in Nursing (RN to BSN) program for students to earn their BSN in as little as 12 months. Take 30 credits of online courses to expand your medical knowledge, general education, and critical thinking abilities. Review the features of this online opportunity to see if it’s the right decision for your career.
Recommended Readings:
The Benefits of Nurse Mentoring
Hospice Nurse: Job Description and Salary
Work-From-Home Safety Checklist: Securing Your Virtual Workspace
American Nurses Association, The Nursing Process
American Nurses Association, What Are the Qualities of a Good Nurse?
Forbes , “The Power of Critical Thinking: Enhancing Decision-Making and Problem-Solving”
Indeed, “Critical Thinking in Nursing (Definition and Vital Tips)”
Indeed, “Critical Thinking Skills in Nursing: Definition and Improvement Tips”
Indeed, “15 Essential Nursing Skills to Include on Your Resume”
StatPearls, “Nursing Process”
Recent Articles

Director of Nursing Education Career Overview
University of Tulsa
Jul 30, 2024

MSN vs. RN: Why Earn an Advanced Degree?

Nursing Peer Review: Definition and Example
Learn more about the benefits of receiving your degree from the university of tulsa.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Critical thinking in nursing clinical practice, education and research: From attitudes to virtue
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Fundamental Care and Medical Surgital Nursing, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, School of Nursing, Consolidated Research Group Quantitative Psychology (2017-SGR-269), University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain.
- 2 Department of Fundamental Care and Medical Surgital Nursing, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, School of Nursing, Consolidated Research Group on Gender, Identity and Diversity (2017-SGR-1091), University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain.
- 3 Department of Fundamental Care and Medical Surgital Nursing, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, School of Nursing, University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain.
- 4 Multidisciplinary Nursing Research Group, Vall d'Hebron Research Institute (VHIR), Vall d'Hebron Hospital, Barcelona, Spain.
- PMID: 33029860
- DOI: 10.1111/nup.12332
Critical thinking is a complex, dynamic process formed by attitudes and strategic skills, with the aim of achieving a specific goal or objective. The attitudes, including the critical thinking attitudes, constitute an important part of the idea of good care, of the good professional. It could be said that they become a virtue of the nursing profession. In this context, the ethics of virtue is a theoretical framework that becomes essential for analyse the critical thinking concept in nursing care and nursing science. Because the ethics of virtue consider how cultivating virtues are necessary to understand and justify the decisions and guide the actions. Based on selective analysis of the descriptive and empirical literature that addresses conceptual review of critical thinking, we conducted an analysis of this topic in the settings of clinical practice, training and research from the virtue ethical framework. Following JBI critical appraisal checklist for text and opinion papers, we argue the need for critical thinking as an essential element for true excellence in care and that it should be encouraged among professionals. The importance of developing critical thinking skills in education is well substantiated; however, greater efforts are required to implement educational strategies directed at developing critical thinking in students and professionals undergoing training, along with measures that demonstrate their success. Lastly, we show that critical thinking constitutes a fundamental component in the research process, and can improve research competencies in nursing. We conclude that future research and actions must go further in the search for new evidence and open new horizons, to ensure a positive effect on clinical practice, patient health, student education and the growth of nursing science.
Keywords: critical thinking; critical thinking attitudes; nurse education; nursing care; nursing research.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
PubMed Disclaimer
Similar articles
- Student and educator experiences of maternal-child simulation-based learning: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol. MacKinnon K, Marcellus L, Rivers J, Gordon C, Ryan M, Butcher D. MacKinnon K, et al. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):14-26. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1694. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447004
- Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature. Eddy K, Jordan Z, Stephenson M. Eddy K, et al. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314 Review.
- Strategies to overcome obstacles in the facilitation of critical thinking in nursing education. Mangena A, Chabeli MM. Mangena A, et al. Nurse Educ Today. 2005 May;25(4):291-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2005.01.012. Epub 2005 Apr 12. Nurse Educ Today. 2005. PMID: 15896414
- Ethics in nursing education: learning to reflect on care practices. Vanlaere L, Gastmans C. Vanlaere L, et al. Nurs Ethics. 2007 Nov;14(6):758-66. doi: 10.1177/0969733007082116. Nurs Ethics. 2007. PMID: 17901186 Review.
- Teaching strategies and outcome assessments targeting critical thinking in bachelor nursing students: a scoping review protocol. Westerdahl F, Carlson E, Wennick A, Borglin G. Westerdahl F, et al. BMJ Open. 2020 Feb 2;10(1):e033214. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033214. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32014875 Free PMC article. Review.
- Higher Vocational Nursing Students' Clinical Core Competence in China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Wang S, Huang S, Yan L. Wang S, et al. SAGE Open Nurs. 2024 Mar 1;10:23779608241233147. doi: 10.1177/23779608241233147. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. SAGE Open Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38435341 Free PMC article.
- Effect of the case-based learning method combined with virtual reality simulation technology on midwifery laboratory courses: A quasi-experimental study. Zhao L, Dai X, Chen S. Zhao L, et al. Int J Nurs Sci. 2023 Dec 16;11(1):76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnss.2023.12.009. eCollection 2024 Jan. Int J Nurs Sci. 2023. PMID: 38352279 Free PMC article.
- Translation, validation and psychometric properties of the Albanian version of the Nurses Professional Competence Scale Short form. Duka B, Stievano A, Caruso R, Prendi E, Ejupi V, Spada F, De Maria M, Rocco G, Notarnicola I. Duka B, et al. Acta Biomed. 2023 Aug 3;94(4):e2023197. doi: 10.23750/abm.v94i4.13575. Acta Biomed. 2023. PMID: 37539614 Free PMC article.
- A study of the effects of blended learning on university students' critical thinking: A systematic review. Haftador AM, Tehranineshat B, Keshtkaran Z, Mohebbi Z. Haftador AM, et al. J Educ Health Promot. 2023 Mar 31;12:95. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_665_22. eCollection 2023. J Educ Health Promot. 2023. PMID: 37288404 Free PMC article. Review.
- Multilevel Modeling of Individual and Group Level Influences on Critical Thinking and Clinical Decision-Making Skills among Registered Nurses: A Study Protocol. Zainal NH, Musa KI, Rasudin NS, Mamat Z. Zainal NH, et al. Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Apr 19;11(8):1169. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11081169. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37108003 Free PMC article.
- Alfaro-Lefevre, R. (2019). Critical thinking, clinical reasoning and clinical judgment. A practical approach, 7th ed. Elsevier.
- Armstrong, A. (2006). Towards a strong virtue ethics for nursing practice. Nursing Philosophy, 7(3), 110-124.
- Armstrong, A. (2007). Nursing ethics. A virtue-based approach. Palgrave Macmillian.
- Banks-Wallace, J., Despins, L., Adams-Leander, S., McBroom, L., & Tandy, L. (2008). Re/Affirming and re/conceptualizing disciplinary knowledge as the foundations for doctoral education. Advances in Nursing Sciencies, 31(1), 67-78. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ANS.0000311530.81188.88
- Banning, M. (2008). Clinical reasoning and its application to nursing: Concepts and research studies. Nurse Education in Practice, 8(3), 177-183.
- Search in MeSH
Grants and funding
- PREI-19-007-B/School of Nursing. Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences. University of Barcelona
LinkOut - more resources
Full text sources.
- Ovid Technologies, Inc.

- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.

Effective clinical learning for nursing students
Approaches that meet student and nurse needs..
- Direct care nurses serve as significant teachers and role models for nursing students in the clinical setting.
- Building critical thinking skills is one of the most important outcomes in the clinical setting for nursing students.
- Collaboration with nursing faculty during the clinical rotation can ease the burden on direct care nurses and facilitate a positive learning experience for the student.
The nursing profession continues to experience several challenges—some longstanding and exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. The shortage of nurses at the bedside and reports of nurses planning to leave the profession soon place stress on the workforce and the healthcare system. The situation has put even more pressure on nursing schools to recruit and retain students who enter the workforce well-prepared for practice and capable of filling these vacancies. However, concerns exist surrounding students’ critical thinking skills and their readiness for a demanding career.
The challenge
A longstanding shortage of nursing school faculty and a reliance on new graduate nurses to serve as preceptors create challenges to properly preparing nursing students for a demanding role that requires excellent critical thinking skills.
What-Why-How? Improving Clinical Judgement
New nurses and clinical judgment
Nurse faculty shortage
Lack of interest and incentives lead to difficulty recruiting nurses from the bedside or practice to education. Many 4-year schools require a terminal degree to teach full-time in their undergraduate programs, but only 1% of nurses hold a PhD. In addition, according to the National Advisory Council on Nurse Education and Practice (NACNEP), the average doctorally prepared nurse faculty member is in their 50s, which means they may soon retire. The surge in doctor of nursing practice programs has helped to bridge this gap, but attracting advanced practice nurses to academia from their more lucrative practice roles continues to prove difficult.
Concerns about the practice readiness of new graduate nurses have existed for several years. Missed clinical experiences and virtual learning during the COVID-19 pandemic heightened those concerns. The National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN) addressed the calls from nurse employers to make progress in this area by revamping the NCLEX-RN and NCLEX-PN exams to create Next Generation NCLEX (NGN), which includes more clinical judgment and critical thinking items. Nurse educators are working hard to prepare students for both practice and the new exam items by incorporating more active learning into classroom, clinical, and lab activities and emphasizing the importance of clinical judgment skills.
In most areas of the country, clinical student experiences have returned to pre-pandemic arrangements. State boards of nursing mandate maximum faculty-to-student ratios for clinical experiences. Schools can choose to have faculty supervise fewer students than the maximum, but faculty and clinical site shortages may eliminate that option. In many cases, preceptor-style experiences (such as capstone or practicum courses) have higher faculty-to-student ratios, and preceptors may have to meet specific criteria, such as a certain amount of experience.
Nursing faculty who facilitate on-site learning and supervise and teach students during their clinical experiences face several challenges. Some faculty supervise students across multiple units because unit size can’t accommodate 8 to 10 students at one time. Faculty may or may not have access to the organization’s electronic health records or other healthcare information technology, such as medication dispensing cabinets or glucometers.
In such instances, direct care nurses play an important role in the student’s experience at the clinical site. Their familiarity with the unit, the patient population, and the organization’s technology facilitates learning.
Direct care nurses
Allowing nursing students into the hospital can improve the patient care experience and potentially recruit students to work at the organization in the future. However, precepting a student or new employee creates an extra burden on an already overextended bedside nurse. NACNEP identifies several challenges for obtaining qualified preceptors, including lack of incentives and limited preparation in clinical teaching and learning strategies. Many hospitals have nursing students on the same unit several days a week to accommodate multiple area schools. This means that staff nurses are expected to teach students on most of their workdays during a typical school semester.
Unit nurse experience creates another barrier to effective precepting of nursing students. A study by Thayer and colleagues reported that the median length of experience for inpatient nurses working a 12-hour shift was less than 3 years at an organization. Without a better alternative, new graduate nurses frequently teach nursing students, although they may still be in what Benner describes as the advanced beginner stage of their career (still learning how to organize care, prioritize, and make clinical judgments). It’s difficult for someone who’s still learning and experiencing situations for the first time to teach complex concepts.
A guide to effective clinical site teaching
The following strategies promote critical thinking in students and collaboration with nurse faculty to ease direct care nurses’ teaching workload. Not every strategy is appropriate for all student clinical experiences. Consider them as multiple potential approaches to help facilitate meaningful learning opportunities.
Set the tone
Nursing students frequently feel anxious about clinical experiences, especially if they’ve been told or perceive that they’re a burden or unwanted on the unit. When meeting the student for the first time, welcome them and communicate willingness to have them on the unit.
If you feel that you can’t take on a student for the day, speak to the nurse faculty member and charge nurse to explore other arrangements. Nurse faculty recognize that work or personal concerns may require you to decline precepting a student. Faculty members want to find the best situation for everyone. If the charge nurse or supervisor determines that the student still needs to work with you, talk to the nurse faculty about how they can help ease the burden and facilitate the student’s learning experience for the day.
Begin your time with the student by asking about their experience level and any objectives for the day. Understanding what the student can or can’t do will help you make the most out of the clinical experience. You’ll want to know the content they’re learning in class and connect them with a patient who brings those concepts to life. A student may have assignments to complete, but their focus should be on patient care. Help the student identify the busiest parts of the day and the best time to review the electronic health record and complete assignments.
If a situation requires your full attention and limits training opportunities, briefly explain to the student what will happen. If you have time, provide the student with tasks or specific objectives to note during the observation. Involve the nursing faculty member to help facilitate the learning experience and make it meaningful.
Be a professional role model
Students like to hear about the benefits and rewards of being a nurse, and about each nurse’s unique path. Students also enjoy learning about the “real world” from nurses, but keep in mind that they’re impressionable. Speaking negatively about the unit, patients, organization, or profession may discourage the student. If you must deviate from standard care, such as performing a skill differently than it’s traditionally taught in school, provide the rationale or hospital policy behind the decision.
Feel free to discuss the student’s nursing school experience but don’t diminish the value of their education or assigned work. Keep in mind that school assignments, such as nursing care plans or concept maps, aren’t taught for job training but to deliberately and systematically promote critical thinking. These assignments allow a student to reflect on how a patient’s pathophysiology and nursing assessment and interventions relate to one another.
Reinforce how concepts students learn in school provide valuable knowledge in various settings. For example, if the student is on a medical-surgical unit but says that they want to work in obstetrics, engage the student by pointing out links between the two areas, such as managing diabetes and coagulation disorders. Provide encouragement and excitement about the student’s interest in joining the profession at a time of great need.
Build assessment skills
Explain to students your approach to performing assessments and organizing patient care. Most students learn comprehensive head-to-toe assessments but, in the clinical setting, need to focus on the most relevant assessments. To promote critical thinking, ask the student what data they should focus on gathering based on the patient’s condition. Many students focus on the psychomotor aspect of assessment (performing the assessment correctly); ask them about the subjective data they should gather.
Allow the student to perform an assessment and then compare findings. For example, a student may know that a patient’s lung sounds are abnormal but not remember what the sound is called or what it means. Provide them with the correct terminology to help connect the dots. Discuss with the student when reassessments are warranted. If appropriate, allow a student to reassess the patient (vital signs, output, pain, other physical findings) and then confirm their findings and discuss what any changes mean for the clinical situation. If you don’t have time for these types of discussions following a student’s patient assessment, ask nursing faculty to observe and discuss findings with the student.
Discuss care management
Take advantage of opportunities to discuss concepts such as prioritization, advocacy, delegation, collaboration, discharge planning, and other ways in which the nurse acts as a care manager. Pointing out what’s appropriate to delegate to unlicensed assistive personnel or a licensed practical nurse will prove valuable and help reinforce concepts frequently covered on the NGN exam.
Promote critical thinking
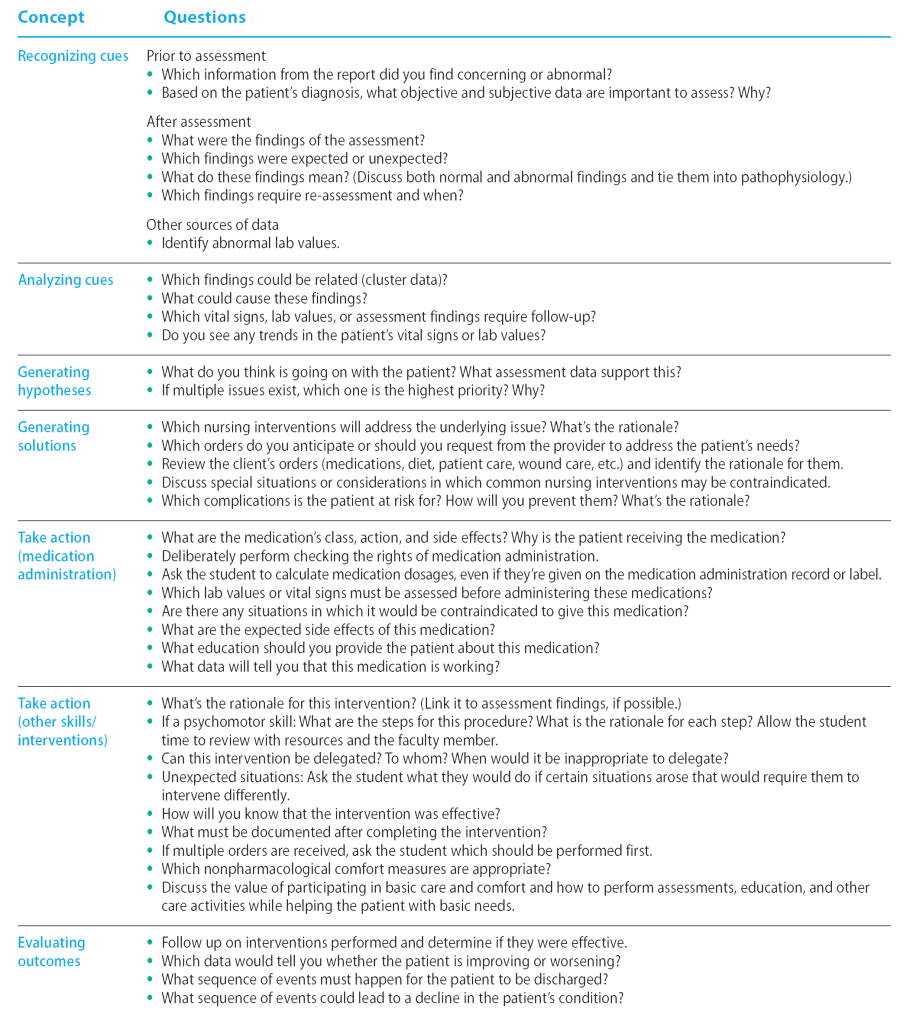
The NCBSN has introduced the Clinical Judgment Measurement Model (CJMM) as a framework for evaluating the NGN exam, which incorporates unfolding case studies that systematically address six steps: recognize cues, analyze cues, generate hypotheses, generate solutions, take action, and evaluate outcomes. Each candidate encounters three case studies, with six questions, one for each step of the CJMM. Nursing faculty incorporate this framework and language into the nursing curriculum to help students think systematically and critically and prepare them for the exam.
Nurses with practice experience use this type of framework to gather information, make judgments, and take action. As a nurse approaches Benner’s competent stage of nursing practice, this type of thinking becomes intuitive, and nurses may not even be aware of the conclusions they draw and decisions they make based on their clinical judgment skills. To help students understand why something is happening, they should continue to work through a process like this deliberately. For example, many students view medication administration as a simple task and may say in post-conference discussion, “All I did was give meds.” You perform many assessments and make various judgments while administering medications, but you may not think to discuss them with students. Asking questions of students while they’re performing what may seem like repetitive tasks can help prompt critical thinking. (See Critical questions .)
Critical questions
Enhance self-efficacy
Many nurses believe that the student must follow them to every patient. This can be overwhelming for the direct care nurse and a barrier to agreeing to work with students. Other approaches can better facilitate learning. Most students will complete an assignment focused on one or two patients. Encourage the student to spend time alone with those patients to perform a more comprehensive history and assessment, help patients with basic care, and provide education. Select a patient who might enjoy the extra attention to ensure a mutually beneficial experience.
Also, consider asking the student to find information using available resources. Such inquiry can benefit you and the student. For example, prompt a student to answer one or more critical thinking questions using their textbooks or resources available on the hospital’s intranet. If time prevents you from explaining complex topics or helping the student problem-solve, ask the student to take the information they find to their faculty member to review. Nurse faculty won’t be familiar with the specific details of all patients on the unit, so identify the most appropriate questions for the student to consider to help the nurse faculty facilitate learning.
Allowing the student time to find answers themselves builds self-efficacy and confidence and also relieves some of the stress and anxiety associated with being asked questions on the spot. This strategy also models the professional approach of using evidence-based resources to find information as needed in the clinical setting.
To ensure a positive learning experience and reduce anxiety, provide the student with ample time to prepare for performance-based skills. For example, identify an approximate time that medications will be administered to one patient and ask the student to independently look up the medication information by that time. This is more beneficial for the student than observing every patient’s medication administration or participating only in psychomotor tasks, such as scanning and giving injections. This also can free up your time by setting the expectation that the student will have the chance to prepare for and be directly involved in one medication pass.
Similarly, if an opportunity exists for practicing a psychomotor skill, such as inserting a urinary catheter or suctioning a tracheostomy, ask the student to review the procedure with their instructor using hospital policy and resources. If time doesn’t allow for a review, have the student observe to ensure provision of the best care and efficient use of time and resources.
Opportunities in education
Nurses who enjoy working with students or new staff members may want to consider academic roles. Many advanced nursing degrees, available in various formats, focus on education. For those who want to try teaching or have an interest in teaching only in the clinical setting, opportunities exist to work as adjunct faculty or to participate in hospital-based professional development activities. Adjunct faculty (part-time instructors) teach a variety of assignments and workloads, including in clinical, lab, or classroom settings. Many clinical adjunct faculty are nurses who also work in the organization with patients and may teach one group of students one day a week. Clinical and lab assignments vary from 4- or 6-hour experiences to 12-hour shifts.
According to NACNEP, most nursing programs require that adjunct faculty and clinical preceptors have the same or higher level of educational preparation as the program; for example, a nurse with a bachelor of science in nursing (BSN) may be able to teach clinicals for associate degree in nursing or BSN programs, depending on the state’s requirements and the school’s needs. Educational requirements to work in nursing programs vary by school. In some cases, adjunct faculty who don’t have a master’s degree may be supervised by full-time faculty with advanced degrees.
Benefits for adjunct faculty can include extra income, professional development, personal reward, tuition discounts or remissions, and giving back to the profession. Locate opportunities on nursing school websites or by talking to the nursing instructors or administrators in the local area.
Everyone benefits
Applying teaching approaches that benefit students and nurses can help ensure a positive clinical learning experience for everyone. When you graciously accept and teach students you help create positive encounters that enhance student critical thinking skill development, aid program retention, and support organizational recruitment.
Jennifer Miller is an assistant professor of nursing at the University of Louisville School of Nursing in Louisville, Kentucky .
American Nurse Journal. 2024; 19(4). Doi: 10.51256/ANJ042432
American Association of Colleges of Nursing. Nursing faculty shortage fact sheet. October 2022. aacnnursing.org/news-information/fact-sheets/nursing-faculty-shortage
Benner P. From Novice to Expert: Excellence and Power in Clinical Nursing Practice . Menlo Park, CA: Addison-Wesley; 1984.
National Advisory Council on Nurse Education and Practice. Preparing nurse faculty, and addressing the shortage of nurse faculty and clinical preceptors. January 2021. hrsa.gov/sites/default/files/hrsa/advisory-committees/nursing/reports/nacnep-17report-2021.pdf
National Council of State Boards of Nursing. Clinical Judgment Measurement Model. 2023. nclex.com/clinical-judgment-measurement-model.page
Thayer J, Zillmer J, Sandberg N, Miller AR, Nagel P, MacGibbon A. ‘The new nurse’ is the new normal. June 2, 2022. Epic Research. epicresearch.org/articles/the-new-nurse-is-the-new-normal
Key words: nursing students, nursing education, critical thinking, precepting
Let Us Know What You Think
1 comment . leave new.
All nursing programs need to put in more clinical time. Students do not get the time in clinicals so they do not have the opportunities to develop their clinical judgement and thinking skills. Clinical time is what glues concept and theory together if they don’t get the clinical time they are less likely to develop these skills which contributes to errors, burnout and nurses leaving the field.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

NurseLine Newsletter
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- Hidden Referrer
*By submitting your e-mail, you are opting in to receiving information from Healthcom Media and Affiliates. The details, including your email address/mobile number, may be used to keep you informed about future products and services.
Test Your Knowledge
Recent posts.

Hypnosis and pain

Measuring nurses’ health

From Retirement to Preferment: Crafting Your Next Chapter

Leadership in changing times

Valuing nursing

Promoting health literacy

Mentorship: A strategy for nursing retention

Anatomy of Writing for Publication for Nurses: The writing guide you’ve been looking for

Nurse leadership: Pitfalls and solutions

It’s time embrace AI in nursing

CMS establishes minimum LTC staffing standards

Mental health matters

Connecting the dots with cannabis care

Wellness challenges

Writing retreats for nurses: Inspiration to share
Miller J. Effective clinical learning for nursing students. American Nurse Journal. 2024;19(4):32-37. doi:10.51256/anj042432 https://www.myamericannurse.com/effective-clinical-learning-for-nursing-students/
#1 Duquesne University Graduate School of Nursing is Ranked #1 for Veterans by Militaryfriendly.com for 7 years running

- Adult-Gerontology Acute Care Nurse Practitioner
- Executive Nurse Leadership and Health Care Management
- Family Nurse Practitioner
- Forensic Nursing
- Nursing Education and Faculty Role
- Psychiatric-Mental Health Nurse Practitioner
- Clinical Leadership
- Admissions & Aid
- About Duquesne
- Why Duquesne Online?

Developing Critical-Thinking Skills in Student Nurses
April 8, 2020
View all blog posts under Articles | View all blog posts under Master of Science in Nursing

Critical thinking skills for nurses include problem-solving and the ability to evaluate situations and make recommendations. Done correctly, critical thinking results in positive patient outcomes, Srinidhi Lakhanigam, an RN-BSN, said in a Minority Nurse article.
“Critical thinking is the result of a combination of innate curiosity; a strong foundation of theoretical knowledge of human anatomy and physiology, disease processes, and normal and abnormal lab values; and an orientation for thinking on your feet,” Lakhanigam said in “Critical Thinking: A Vital Trait for Nurses.” “Combining this with a strong passion for patient care will produce positive patient outcomes. The critical thinking nurse has an open mind and draws heavily upon evidence-based research and past clinical experiences to solve patient problems.”
Since the 1980s, critical thinking has become a widely discussed component of nurse education, and a significant factor for National League for Nursing (NLN) nursing school accreditation. Nursing school curriculum is expected to teach students how to analyze situations and develop solutions based on high-order thinking skills. For nurse educators who are responsible for undergraduate and graduate learners , teaching critical thinking skills is crucial to the future of healthcare.
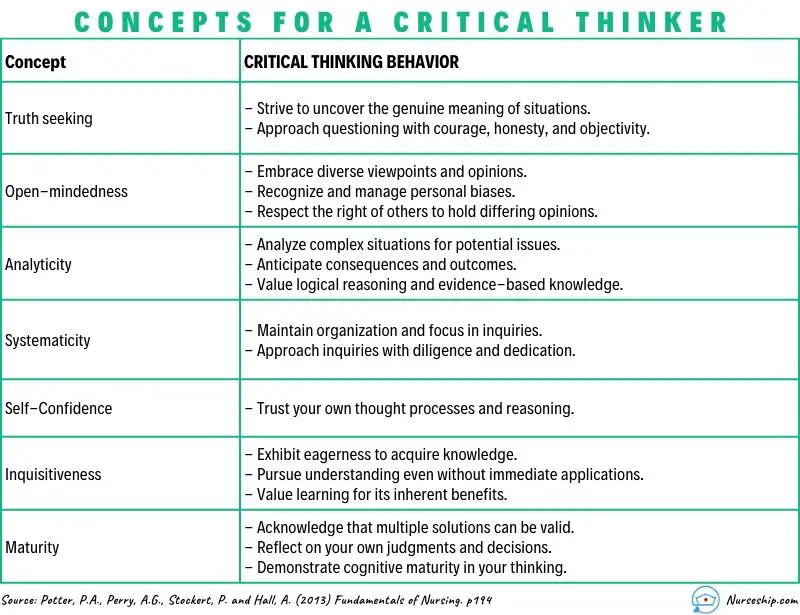
Characteristics of Critical Thinkers
A landmark 1990 study found critical thinkers demonstrate similar characteristics. The Delphi Report by the American Philosophical Association (APA) identified these cognitive skills common to critical thinkers:
Interpretation
Critical thinkers are able to categorize and decode the significance and meaning of experiences, situations, data, events, and rules, among others.
Critical thinkers can examine varying ideas, statements, questions, descriptions and concepts and analyze the reasoning.
Critical thinkers consider relevant information from evidence to draw conclusions.
Explanation
Critical thinkers state the results of their reasoning through sound arguments.
Self-regulation
Critical thinkers monitor their cognitive abilities to reflect on their motivations and correct their mistakes.
In addition, critical thinkers are well-informed and concerned about a wide variety of topics. They are flexible to alternative ideas and opinions and are honest when facing personal biases. They have a willingness to reconsider their views when change is warranted.
In nursing, critical thinking and clinical reasoning are inextricably linked, columnist Margaret McCartney said in the BMJ . While experienced nurses are able to make sound clinical judgements quickly and accurately, novice nurses find the process more difficult, McCartney said in “Nurses must be allowed to exercise professional judgment.”
“Therefore, education must begin at the undergraduate level to develop students’ critical thinking and clinical reasoning skills,” McCartney said. “Clinical reasoning is a learnt skill requiring determination and active engagement in deliberate practice design to improve performance. In order to acquire such skills, students need to develop critical thinking ability, as well as an understanding of how judgments and decisions are reached in complex healthcare environments.”
Teaching Critical Thinking to Nurses
In 2015, a study in the Journal of College Teaching & Learning found a positive correlation between critical thinking skills and success in nursing school. The study said, “It is the responsibility of nurse educators to ensure that nursing graduates have developed the critical thinking abilities necessary to practice the profession of nursing.”
To help new nurses develop critical-thinking skills, the professional development resources provider Lippincott Solutions recommended nurse educators focus on the following in the classroom:
Promoting interactions
Collaboration and learning in group settings help nursing students achieve a greater understanding of the content.
Asking open-ended questions
Open-ended questions encourage students to think about possible answers and respond without fear of giving a “wrong” answer.
Providing time for students to reflect on questions
Student nurses should be encouraged to deliberate and ponder questions and possible responses and understand that perhaps the immediate answer is not always the best answer.
Teaching for skills to transfer
Educators should provide opportunities for student nurses to see how their skills can apply to various situations and experiences.
In the Minority Nurse article, Lakhanigam also said students who thirst for knowledge and understanding make the best critical thinkers. The author said novice nurses who are open to constructive criticism can learn valuable lessons that will translate into successful practice.
At the same time, however, critical thinking skills alone will not ensure success in the profession , Lakhanigam said in the article. Other factors count as well.
“A combination of open-mindedness, a solid foundational knowledge of disease processes, and continuous learning, coupled with a compassionate heart and great clinical preceptors, can ensure that every new nurse will be a critical thinker positively affecting outcomes at the bedside,” Lakhanigam said.
Another element that ensures success as both an educator and student is earning a nursing degree from a school that focuses on student accomplishments. At Duquesne University’s School of Nursing, students learn best practices in healthcare. The online master’s in nursing program prepares educators to train the next generation of nurses.
About Duquesne University’s online Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) Program
Duquesne University’s MSN curriculum for the Nursing Education and Faculty Role program focuses on preparing registered nurses (RNs) for careers as nurse educators. Students enrolled in the online master’s in nursing program learn the skills needed in the classroom and for clinical training. RNs learn how to empower student nurses to work to their fullest potential.
The MSN program is presented entirely online, so RNs can pursue their career goals and continue personal responsibilities simultaneously. Duquesne University has been recognized for excellence in education as a U.S. News & World Report Best Online Graduate Nursing Program and best among Roman Catholic universities in the nation.
For more information, contact Duquesne University today.
Critical Thinking: A Vital Trait for Nurses: Minority Nurse
Consensus Descriptions of Core CT Skills And Sub-Skills: Delphi
Margaret McCartney: Nurses must be allowed to exercise professional judgment: BMJ
Predicting Success in Nursing Programs: Journal of College Teaching & Learning
Turning New Nurses Into Critical Thinkers: Wolters Kluwer
| 1. | What is your highest level of education? |
| 2. | Do you currently hold an unencumbered RN license? |
| 3. | Which are you interested in? |
| 4. | Who is this brochure for? |

What is Critical Thinking in Nursing? (Explained W/ Examples)

Last updated on August 23rd, 2023
Critical thinking is a foundational skill applicable across various domains, including education, problem-solving, decision-making, and professional fields such as science, business, healthcare, and more.
It plays a crucial role in promoting logical and rational thinking, fostering informed decision-making, and enabling individuals to navigate complex and rapidly changing environments.
In this article, we will look at what is critical thinking in nursing practice, its importance, and how it enables nurses to excel in their roles while also positively impacting patient outcomes.
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is a cognitive process that involves analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to make reasoned and informed decisions.
It’s a mental activity that goes beyond simple memorization or acceptance of information at face value.
Critical thinking involves careful, reflective, and logical thinking to understand complex problems, consider various perspectives, and arrive at well-reasoned conclusions or solutions.
Key aspects of critical thinking include:
- Analysis: Critical thinking begins with the thorough examination of information, ideas, or situations. It involves breaking down complex concepts into smaller parts to better understand their components and relationships.
- Evaluation: Critical thinkers assess the quality and reliability of information or arguments. They weigh evidence, identify strengths and weaknesses, and determine the credibility of sources.
- Synthesis: Critical thinking involves combining different pieces of information or ideas to create a new understanding or perspective. This involves connecting the dots between various sources and integrating them into a coherent whole.
- Inference: Critical thinkers draw logical and well-supported conclusions based on the information and evidence available. They use reasoning to make educated guesses about situations where complete information might be lacking.
- Problem-Solving: Critical thinking is essential in solving complex problems. It allows individuals to identify and define problems, generate potential solutions, evaluate the pros and cons of each solution, and choose the most appropriate course of action.
- Creativity: Critical thinking involves thinking outside the box and considering alternative viewpoints or approaches. It encourages the exploration of new ideas and solutions beyond conventional thinking.
- Reflection: Critical thinkers engage in self-assessment and reflection on their thought processes. They consider their own biases, assumptions, and potential errors in reasoning, aiming to improve their thinking skills over time.
- Open-Mindedness: Critical thinkers approach ideas and information with an open mind, willing to consider different viewpoints and perspectives even if they challenge their own beliefs.
- Effective Communication: Critical thinkers can articulate their thoughts and reasoning clearly and persuasively to others. They can express complex ideas in a coherent and understandable manner.
- Continuous Learning: Critical thinking encourages a commitment to ongoing learning and intellectual growth. It involves seeking out new knowledge, refining thinking skills, and staying receptive to new information.

Definition of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is an intellectual process of analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to make reasoned and informed decisions.
What is Critical Thinking in Nursing?
Critical thinking in nursing is a vital cognitive skill that involves analyzing, evaluating, and making reasoned decisions about patient care.
It’s an essential aspect of a nurse’s professional practice as it enables them to provide safe and effective care to patients.
Critical thinking involves a careful and deliberate thought process to gather and assess information, consider alternative solutions, and make informed decisions based on evidence and sound judgment.
This skill helps nurses to:
- Assess Information: Critical thinking allows nurses to thoroughly assess patient information, including medical history, symptoms, and test results. By analyzing this data, nurses can identify patterns, discrepancies, and potential issues that may require further investigation.
- Diagnose: Nurses use critical thinking to analyze patient data and collaboratively work with other healthcare professionals to formulate accurate nursing diagnoses. This is crucial for developing appropriate care plans that address the unique needs of each patient.
- Plan and Implement Care: Once a nursing diagnosis is established, critical thinking helps nurses develop effective care plans. They consider various interventions and treatment options, considering the patient’s preferences, medical history, and evidence-based practices.
- Evaluate Outcomes: After implementing interventions, critical thinking enables nurses to evaluate the outcomes of their actions. If the desired outcomes are not achieved, nurses can adapt their approach and make necessary changes to the care plan.
- Prioritize Care: In busy healthcare environments, nurses often face situations where they must prioritize patient care. Critical thinking helps them determine which patients require immediate attention and which interventions are most essential.
- Communicate Effectively: Critical thinking skills allow nurses to communicate clearly and confidently with patients, their families, and other members of the healthcare team. They can explain complex medical information and treatment plans in a way that is easily understood by all parties involved.
- Identify Problems: Nurses use critical thinking to identify potential complications or problems in a patient’s condition. This early recognition can lead to timely interventions and prevent further deterioration.
- Collaborate: Healthcare is a collaborative effort involving various professionals. Critical thinking enables nurses to actively participate in interdisciplinary discussions, share their insights, and contribute to holistic patient care.
- Ethical Decision-Making: Critical thinking helps nurses navigate ethical dilemmas that can arise in patient care. They can analyze different perspectives, consider ethical principles, and make morally sound decisions.
- Continual Learning: Critical thinking encourages nurses to seek out new knowledge, stay up-to-date with the latest research and medical advancements, and incorporate evidence-based practices into their care.
In summary, critical thinking is an integral skill for nurses, allowing them to provide high-quality, patient-centered care by analyzing information, making informed decisions, and adapting their approaches as needed.
It’s a dynamic process that enhances clinical reasoning , problem-solving, and overall patient outcomes.
What are the Levels of Critical Thinking in Nursing?
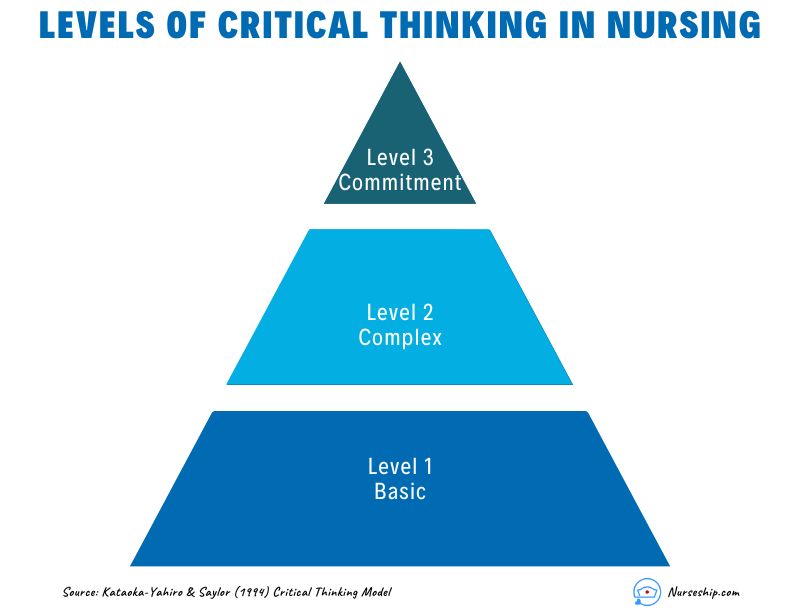
The development of critical thinking in nursing practice involves progressing through three levels: basic, complex, and commitment.
The Kataoka-Yahiro and Saylor model outlines this progression.
1. Basic Critical Thinking:
At this level, learners trust experts for solutions. Thinking is based on rules and principles. For instance, nursing students may strictly follow a procedure manual without personalization, as they lack experience. Answers are seen as right or wrong, and the opinions of experts are accepted.
2. Complex Critical Thinking:
Learners start to analyze choices independently and think creatively. They recognize conflicting solutions and weigh benefits and risks. Thinking becomes innovative, with a willingness to consider various approaches in complex situations.
3. Commitment:
At this level, individuals anticipate decision points without external help and take responsibility for their choices. They choose actions or beliefs based on available alternatives, considering consequences and accountability.
As nurses gain knowledge and experience, their critical thinking evolves from relying on experts to independent analysis and decision-making, ultimately leading to committed and accountable choices in patient care.
Why Critical Thinking is Important in Nursing?
Critical thinking is important in nursing for several crucial reasons:
Patient Safety:
Nursing decisions directly impact patient well-being. Critical thinking helps nurses identify potential risks, make informed choices, and prevent errors.
Clinical Judgment:
Nursing decisions often involve evaluating information from various sources, such as patient history, lab results, and medical literature.
Critical thinking assists nurses in critically appraising this information, distinguishing credible sources, and making rational judgments that align with evidence-based practices.
Enhances Decision-Making:
In nursing, critical thinking allows nurses to gather relevant patient information, assess it objectively, and weigh different options based on evidence and analysis.
This process empowers them to make informed decisions about patient care, treatment plans, and interventions, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
Promotes Problem-Solving:
Nurses encounter complex patient issues that require effective problem-solving.
Critical thinking equips them to break down problems into manageable parts, analyze root causes, and explore creative solutions that consider the unique needs of each patient.
Drives Creativity:
Nursing care is not always straightforward. Critical thinking encourages nurses to think creatively and explore innovative approaches to challenges, especially when standard protocols might not suffice for unique patient situations.
Fosters Effective Communication:
Communication is central to nursing. Critical thinking enables nurses to clearly express their thoughts, provide logical explanations for their decisions, and engage in meaningful dialogues with patients, families, and other healthcare professionals.
Aids Learning:
Nursing is a field of continuous learning. Critical thinking encourages nurses to engage in ongoing self-directed education, seeking out new knowledge, embracing new techniques, and staying current with the latest research and developments.
Improves Relationships:
Open-mindedness and empathy are essential in nursing relationships.
Critical thinking encourages nurses to consider diverse viewpoints, understand patients’ perspectives, and communicate compassionately, leading to stronger therapeutic relationships.
Empowers Independence:
Nursing often requires autonomous decision-making. Critical thinking empowers nurses to analyze situations independently, make judgments without undue influence, and take responsibility for their actions.
Facilitates Adaptability:
Healthcare environments are ever-changing. Critical thinking equips nurses with the ability to quickly assess new information, adjust care plans, and navigate unexpected situations while maintaining patient safety and well-being.
Strengthens Critical Analysis:
In the era of vast information, nurses must discern reliable data from misinformation.
Critical thinking helps them scrutinize sources, question assumptions, and make well-founded choices based on credible information.
How to Apply Critical Thinking in Nursing? (With Examples)
Here are some examples of how nurses can apply critical thinking.
Assess Patient Data:
Critical Thinking Action: Carefully review patient history, symptoms, and test results.
Example: A nurse notices a change in a diabetic patient’s blood sugar levels. Instead of just administering insulin, the nurse considers recent dietary changes, activity levels, and possible medication interactions before adjusting the treatment plan.
Diagnose Patient Needs:
Critical Thinking Action: Analyze patient data to identify potential nursing diagnoses.
Example: After reviewing a patient’s lab results, vital signs, and observations, a nurse identifies “ Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity ” due to the patient’s limited mobility.
Plan and Implement Care:
Critical Thinking Action: Develop a care plan based on patient needs and evidence-based practices.
Example: For a patient at risk of falls, the nurse plans interventions such as hourly rounding, non-slip footwear, and bed alarms to ensure patient safety.
Evaluate Interventions:
Critical Thinking Action: Assess the effectiveness of interventions and modify the care plan as needed.
Example: After administering pain medication, the nurse evaluates its impact on the patient’s comfort level and considers adjusting the dosage or trying an alternative pain management approach.
Prioritize Care:
Critical Thinking Action: Determine the order of interventions based on patient acuity and needs.
Example: In a busy emergency department, the nurse triages patients by considering the severity of their conditions, ensuring that critical cases receive immediate attention.
Collaborate with the Healthcare Team:
Critical Thinking Action: Participate in interdisciplinary discussions and share insights.
Example: During rounds, a nurse provides input on a patient’s response to treatment, which prompts the team to adjust the care plan for better outcomes.
Ethical Decision-Making:
Critical Thinking Action: Analyze ethical dilemmas and make morally sound choices.
Example: When a terminally ill patient expresses a desire to stop treatment, the nurse engages in ethical discussions, respecting the patient’s autonomy and ensuring proper end-of-life care.
Patient Education:
Critical Thinking Action: Tailor patient education to individual needs and comprehension levels.
Example: A nurse uses visual aids and simplified language to explain medication administration to a patient with limited literacy skills.
Adapt to Changes:
Critical Thinking Action: Quickly adjust care plans when patient conditions change.
Example: During post-operative recovery, a nurse notices signs of infection and promptly informs the healthcare team to initiate appropriate treatment adjustments.
Critical Analysis of Information:
Critical Thinking Action: Evaluate information sources for reliability and relevance.
Example: When presented with conflicting research studies, a nurse critically examines the methodologies and sample sizes to determine which study is more credible.
Making Sense of Critical Thinking Skills
What is the purpose of critical thinking in nursing.
The purpose of critical thinking in nursing is to enable nurses to effectively analyze, interpret, and evaluate patient information, make informed clinical judgments, develop appropriate care plans, prioritize interventions, and adapt their approaches as needed, thereby ensuring safe, evidence-based, and patient-centered care.
Why critical thinking is important in nursing?
Critical thinking is important in nursing because it promotes safe decision-making, accurate clinical judgment, problem-solving, evidence-based practice, holistic patient care, ethical reasoning, collaboration, and adapting to dynamic healthcare environments.
Critical thinking skill also enhances patient safety, improves outcomes, and supports nurses’ professional growth.
How is critical thinking used in the nursing process?
Critical thinking is integral to the nursing process as it guides nurses through the systematic approach of assessing, diagnosing, planning, implementing, and evaluating patient care. It involves:
- Assessment: Critical thinking enables nurses to gather and interpret patient data accurately, recognizing relevant patterns and cues.
- Diagnosis: Nurses use critical thinking to analyze patient data, identify nursing diagnoses, and differentiate actual issues from potential complications.
- Planning: Critical thinking helps nurses develop tailored care plans, selecting appropriate interventions based on patient needs and evidence.
- Implementation: Nurses make informed decisions during interventions, considering patient responses and adjusting plans as needed.
- Evaluation: Critical thinking supports the assessment of patient outcomes, determining the effectiveness of intervention, and adapting care accordingly.
Throughout the nursing process , critical thinking ensures comprehensive, patient-centered care and fosters continuous improvement in clinical judgment and decision-making.
What is an example of the critical thinking attitude of independent thinking in nursing practice?
An example of the critical thinking attitude of independent thinking in nursing practice could be:
A nurse is caring for a patient with a complex medical history who is experiencing a new set of symptoms. The nurse carefully reviews the patient’s history, recent test results, and medication list.
While discussing the case with the healthcare team, the nurse realizes that the current treatment plan might not be addressing all aspects of the patient’s condition.
Instead of simply following the established protocol, the nurse independently considers alternative approaches based on their assessment.
The nurse proposes a modification to the treatment plan, citing the rationale and evidence supporting the change.
This demonstrates independent thinking by critically evaluating the situation, challenging assumptions, and advocating for a more personalized and effective patient care approach.
How to use Costa’s level of questioning for critical thinking in nursing?
Costa’s levels of questioning can be applied in nursing to facilitate critical thinking and stimulate a deeper understanding of patient situations. The levels of questioning are as follows:
| Level 1: Gathering | 1. What are the common side effects of the prescribed medication? 2. When was the patient’s last bowel movement? 3. Who is the patient’s emergency contact person? 4. Describe the patient’s current level of pain. 5. What information is in the patient’s medical record? |
| 1. What would happen if the patient’s blood pressure falls further? 2. Compare the patient’s oxygen saturation levels before and after administering oxygen. 3. What other nursing interventions could be considered for wound care? 4. Infer the potential reasons behind the patient’s increased heart rate. 5. Analyze the relationship between the patient’s diet and blood glucose levels. | |
| 1. What do you think will be the patient’s response to the new pain management strategy? 2. Could the patient’s current symptoms be indicative of an underlying complication? 3. How would you prioritize care for patients with varying acuity levels in the emergency department? 4. What evidence supports your choice of administering the medication at this time? 5. Create a care plan for a patient with complex needs requiring multiple interventions. |
- 15 Attitudes of Critical Thinking in Nursing (Explained W/ Examples)
- Nursing Concept Map (FREE Template)
- Clinical Reasoning In Nursing (Explained W/ Example)
- 8 Stages Of The Clinical Reasoning Cycle
- How To Improve Critical Thinking Skills In Nursing? 24 Strategies With Examples
- What is the “5 Whys” Technique?
- What Are Socratic Questions?
Critical thinking in nursing is the foundation that underpins safe, effective, and patient-centered care.
Critical thinking skills empower nurses to navigate the complexities of their profession while consistently providing high-quality care to diverse patient populations.
Reading Recommendation
Potter, P.A., Perry, A.G., Stockert, P. and Hall, A. (2013) Fundamentals of Nursing
Comments are closed.
Medical & Legal Disclaimer
All the contents on this site are for entertainment, informational, educational, and example purposes ONLY. These contents are not intended to be used as a substitute for professional medical advice or practice guidelines. However, we aim to publish precise and current information. By using any content on this website, you agree never to hold us legally liable for damages, harm, loss, or misinformation. Read the privacy policy and terms and conditions.
Privacy Policy
Terms & Conditions
© 2024 nurseship.com. All rights reserved.
We use cookies on our website to support technical features that enhance your user experience, and to help us improve our website. By continuing to use this website, you accept our privacy policy .
- Student Login
- Call Us: 888-549-6755
- 888-559-6763
- Search site Search our site Search Now Close
- Request Info
Skip to Content (Press Enter)
Why Critical Thinking Skills in Nursing Matter (And What You Can Do to Develop Them)
By Hannah Meinke on 07/05/2021

The nursing profession tends to attract those who have natural nurturing abilities, a desire to help others, and a knack for science or anatomy. But there is another important skill that successful nurses share, and it's often overlooked: the ability to think critically.
Identifying a problem, determining the best solution and choosing the most effective method to solve the program are all parts of the critical thinking process. After executing the plan, critical thinkers reflect on the situation to figure out if it was effective and if it could have been done better. As you can see, critical thinking is a transferable skill that can be leveraged in several facets of your life.
But why is it so important for nurses to use? We spoke with several experts to learn why critical thinking skills in nursing are so crucial to the field, the patients and the success of a nurse. Keep reading to learn why and to see how you can improve this skill.
Why are critical thinking skills in nursing important?
You learn all sorts of practical skills in nursing school, like flawlessly dressing a wound, taking vitals like a pro or starting an IV without flinching. But without the ability to think clearly and make rational decisions, those skills alone won’t get you very far—you need to think critically as well.
“Nurses are faced with decision-making situations in patient care, and each decision they make impacts patient outcomes. Nursing critical thinking skills drive the decision-making process and impact the quality of care provided,” says Georgia Vest, DNP, RN and senior dean of nursing at the Rasmussen University School of Nursing.
For example, nurses often have to make triage decisions in the emergency room. With an overflow of patients and limited staff, they must evaluate which patients should be treated first. While they rely on their training to measure vital signs and level of consciousness, they must use critical thinking to analyze the consequences of delaying treatment in each case.
No matter which department they work in, nurses use critical thinking in their everyday routines. When you’re faced with decisions that could ultimately mean life or death, the ability to analyze a situation and come to a solution separates the good nurses from the great ones.
How are critical thinking skills acquired in nursing school?
Nursing school offers a multitude of material to master and upholds high expectations for your performance. But in order to learn in a way that will actually equip you to become an excellent nurse, you have to go beyond just memorizing terms. You need to apply an analytical mindset to understanding course material.
One way for students to begin implementing critical thinking is by applying the nursing process to their line of thought, according to Vest. The process includes five steps: assessment, diagnosis, outcomes/planning, implementation and evaluation.
“One of the fundamental principles for developing critical thinking is the nursing process,” Vest says. “It needs to be a lived experience in the learning environment.”
Nursing students often find that there are multiple correct solutions to a problem. The key to nursing is to select the “the most correct” solution—one that will be the most efficient and best fit for that particular situation. Using the nursing process, students can narrow down their options to select the best one.
When answering questions in class or on exams, challenge yourself to go beyond simply selecting an answer. Start to think about why that answer is correct and what the possible consequences might be. Simply memorizing the material won’t translate well into a real-life nursing setting.
How can you develop your critical thinking skills as a nurse?
As you know, learning doesn’t stop with graduation from nursing school. Good nurses continue to soak up knowledge and continually improve throughout their careers. Likewise, they can continue to build their critical thinking skills in the workplace with each shift.
“To improve your critical thinking, pick the brains of the experienced nurses around you to help you get the mindset,” suggests Eileen Sollars, RN ADN, AAS. Understanding how a seasoned nurse came to a conclusion will provide you with insights you may not have considered and help you develop your own approach.
The chain of command can also help nurses develop critical thinking skills in the workplace.
“Another aid in the development of critical thinking I cannot stress enough is the utilization of the chain of command,” Vest says. “In the chain of command, the nurse always reports up to the nurse manager and down to the patient care aide. Peers and fellow healthcare professionals are not in the chain of command. Clear understanding and proper utilization of the chain of command is essential in the workplace.”
How are critical thinking skills applied in nursing?
“Nurses use critical thinking in every single shift,” Sollars says. “Critical thinking in nursing is a paramount skill necessary in the care of your patients. Nowadays there is more emphasis on machines and technical aspects of nursing, but critical thinking plays an important role. You need it to understand and anticipate changes in your patient's condition.”
As a nurse, you will inevitably encounter a situation in which there are multiple solutions or treatments, and you'll be tasked with determining the solution that will provide the best possible outcome for your patient. You must be able to quickly and confidently assess situations and make the best care decision in each unique scenario. It is in situations like these that your critical thinking skills will direct your decision-making.
Do critical thinking skills matter more for nursing leadership and management positions?
While critical thinking skills are essential at every level of nursing, leadership and management positions require a new level of this ability.
When it comes to managing other nurses, working with hospital administration, and dealing with budgets, schedules or policies, critical thinking can make the difference between a smooth-running or struggling department. At the leadership level, nurses need to see the big picture and understand how each part works together.
A nurse manager , for example, might have to deal with being short-staffed. This could require coaching nurses on how to prioritize their workload, organize their tasks and rely on strategies to keep from burning out. A lead nurse with strong critical thinking skills knows how to fully understand the problem and all its implications.
- How will patient care be affected by having fewer staff?
- What kind of strain will be on the nurses?
Their solutions will take into account all their resources and possible roadblocks.
- What work can be delegated to nursing aids?
- Are there any nurses willing to come in on their day off?
- Are nurses from other departments available to provide coverage?
They’ll weigh the pros and cons of each solution and choose those with the greatest potential.
- Will calling in an off-duty nurse contribute to burnout?
- Was this situation a one-off occurrence or something that could require an additional hire in the long term?
Finally, they will look back on the issue and evaluate what worked and what didn’t. With critical thinking skills like this, a lead nurse can affect their entire staff, patient population and department for the better.
Beyond thinking
You’re now well aware of the importance of critical thinking skills in nursing. Even if you already use critical thinking skills every day, you can still work toward strengthening that skill. The more you practice it, the better you will become and the more naturally it will come to you.
If you’re interested in critical thinking because you’d like to move up in your current nursing job, consider how a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) could help you develop the necessary leadership skills.
EDITOR’S NOTE: This article was originally published in July 2012. It has since been updated to include information relevant to 2021.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Pinterest
- Share on LinkedIn
Request More Information
Talk with an admissions advisor today.
Fill out the form to receive information about:
- Program Details and Applying for Classes
- Financial Aid (for those who qualify)
- Customized Support Services
- Detailed Program Plans
There are some errors in the form. Please correct the errors and submit again.
Please enter your first name.
Please enter your last name.
There is an error in email. Make sure your answer has:
- An "@" symbol
- A suffix such as ".com", ".edu", etc.
There is an error in phone number. Make sure your answer has:
- 10 digits with no dashes or spaces
- No country code (e.g. "1" for USA)
There is an error in ZIP code. Make sure your answer has only 5 digits.
We offer tuition savings for many employers—see if yours is one of them.
Please enter Corporate Employer.
Can’t find your employer? Select "Other Employer Not In List" or "Not Employed".
Please choose a School of study.
Please choose a program.
Please choose a degree.
The program you have selected is not available in your ZIP code. Please select another program or contact an Admissions Advisor (877.530.9600) for help.
The program you have selected requires a nursing license. Please select another program or contact an Admissions Advisor (877.530.9600) for help.
Rasmussen University is not enrolling students in your state at this time.
By selecting "Submit," I authorize Rasmussen University to contact me by email, phone or text message at the number provided. There is no obligation to enroll. This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
About the author
Hannah Meinke

Posted in General Nursing
- nursing education
Related Content

Brianna Flavin | 05.07.2024

Brianna Flavin | 03.19.2024

Robbie Gould | 11.14.2023

Noelle Hartt | 11.09.2023
This piece of ad content was created by Rasmussen University to support its educational programs. Rasmussen University may not prepare students for all positions featured within this content. Please visit www.rasmussen.edu/degrees for a list of programs offered. External links provided on rasmussen.edu are for reference only. Rasmussen University does not guarantee, approve, control, or specifically endorse the information or products available on websites linked to, and is not endorsed by website owners, authors and/or organizations referenced. Rasmussen University is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission, an institutional accreditation agency recognized by the U.S. Department of Education.
- Open access
- Published: 26 August 2024
Using a flipped teaching strategy in undergraduate nursing education: students’ perceptions and performance
- Shaherah Yousef Andargeery 1 ,
- Hibah Abdulrahim Bahri 2 ,
- Rania Ali Alhalwani 1 ,
- Shorok Hamed Alahmedi 1 &
- Waad Hasan Ali 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 926 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
81 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Flipped teaching is an interactive learning strategy that actively engages students in the learning process. Students have an active role in flipped teaching as they independently prepare for the class. Class time is dedicated to discussion and learning activities. Thus, it is believed that flipped teaching promotes students’ critical thinking, communication, application of knowledge in real-life situations, and becoming lifelong learners. The aim of this study was to describe the students’ perception of flipped teaching as an innovative learning strategy. And to assess if there was a difference in students’ academic performance between those who participated in a traditional teaching strategy compared to those who participated in flipped teaching intervention.
A quasi-experimental design with intervention and control groups. A purposive sampling technique of undergraduate nursing students was used.
A total of 355 students participated in both groups, and 70 out of 182 students in the intervention group completed the survey. The students perceived a moderate level of effectiveness of the flipped teaching classroom as a teaching strategy. The result revealed that there is a statistically significant difference in the mean students’ scores for the intervention group (M = 83.34, SD = 9.81) and control group (M = 75.57, SD = 9.82).
Flipped teaching proves its effectiveness in improving students’ learning experience and academic performance. Also, students had a positive perception about flipped teaching as it allowed them to develop essential nursing competencies. Future studies must consider measuring the influence of flipped teaching on students’ ability to acquire nursing competencies, such as critical thinking and clinical reasoning.
Peer Review reports
The successful outcome of individualized nursing care of each patient depends on effective communication between nurses and patients. Therapeutic communication consists of an exchange of verbal and non-verbal cues. It is a process in which the professional nurse uses specific techniques to help patients better understand their conditions and promote patients’ open communication of their thoughts and feelings in an environment of mutual respect and acceptance [ 1 ]. Effective educational preparation, continuing practice, and self-reflection about one’s communication skills are all necessary for becoming proficient in therapeutic communication. Teaching therapeutic communication to nursing students explains the principles of verbal and non-verbal communication that can be emphasized through classroom presentation, discussion, case studies and role-play. It also helps them develop their ability to communicate effectively with patients, families, and other health care professionals. Nursing students should be able to critically think, conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and evaluating information generated by observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, and communication. Utilizing a traditional teaching strategy can be a challenge to meet the previously stated requirements [ 2 ]. Therefore, nurse educators should adapt unique teaching methods to help students learn and participate in their own education.
The “flipped classroom” is a pedagogical approach that has gained popularity worldwide to foster active learning. Active learning is defined as instructional strategies that actively engage students in their learning. It requires them to do meaningful learning activities and reflect on their actions [ 3 ]. Flipped teaching is a teaching strategy that promotes critical thinking and the application of information learned outside of the classroom to real-world situations and solves problems within the classroom. It is used in a way that allows educators to deliver lectures by using technologies such as video, audio files, PowerPoint or other media. Thus, the students can read or study those materials on their own at home before attending the class. As a result, discussions and debates about the materials take place throughout the lecture time. Some of the main principles of flipped teaching are increasing interaction and communication between students and educators, allocating more time for content mastery and understanding, granting opportunities for closing gaps and development, creating opportunities for active engagement, and providing immediate feedback [ 4 , 5 ]. This teaching/learning methodology is supported by constructivism learning theory. A “problem-solving approach to learning” is how constructivism is frequently described. In which, it requires a shift in the nurse educator’s epistemic assumptions about the teaching-learning process. Constructivism requires nursing educators to take on the role of a learning facilitator who encourages collaboration and teamwork as well as guides the students in building their knowledge. The underlying assumptions of constructivism include the idea that learning occurs as a result of social interaction in which the student actively creates their own knowledge, while prior experiences serve as the foundation for the learning process. The “flipping classroom” reflects that approach, which integrates student-centered learning [ 6 ].
Flipped teaching approach has students learning before lectures, teaching the material to better use classroom time for cooperative learning. The discussed herein represents studies and case studies from primary through graduate schools. The literature indicated students did see value in this pedagogical approach. Most of the studies found that flipped teaching was associated with better understanding of the material learned, higher academic achievement/performance, and potentially improved psychosocial factors (self-esteem, self-efficacy) that are associated with learning. Interestingly, one article pointed out that non-didactic material used in flipped-teaching lead to an increase in performance and this did not happen with didactic material.
According to Jordan et al. [ 7 ], a flipped teaching is a methodology that was developed as a response to advancements and changes in society, pedagogical approaches, and rapid growth and advancement of technology; The flipped teaching was evolved from the peer instruction and just in time teaching approaches. Jordan and colleagues [ 7 ] state that independent learning happens outside the classroom prior to the lesson through instructional materials while classroom time is maximized to fosters an environment of collaborative learning. Qutob [ 8 ] states that flipped teaching enhances student learning and engagement and promotes greater independence for students.
Jordan et al. [ 7 ] studied the use of flipped teaching on the teaching of first- and fourth-year students’ discrete mathematics and graphs, models, and applications. Across all the classes studied (pilot, graph, model and application, practices, computer and business administration), students preferred flipped teaching compared to traditional teaching. According to Jordan et al. [ 7 ], the quality of the materials and exercises, and perceived difficulty of the course and material are important to student satisfaction with this method. Additionally, it was found that interactions with teachers and collaborative learning were positive. Likewise, Nguyen et al. [ 9 ] found students favorably perceive flipped teaching. This is especially true for those students who have an understanding that the method involves preparation and interaction and how these affect the outcomes. Vazquez and Chiang [ 10 ] discuss the lessons learned from observing two large Principles of Economics Classes at the University of Illinois; each class held 900 students. Vazquez and Chiang [ 10 ] found that the students preferred watching videos over reading the textbook. Secondly, students were better prepared after they watched pre-lecture videos compared to reading the textbook beforehand. The third finding involved the length of time pre-lecture work should take; the authors state pre-lecture work should be approximately 15 to 20 min of work ahead of each in-class session. The fourth finding is that the flipped teaching is a costly endeavor. Finally, it was found that having the students watch videos before the lectures reduced the time spent in class covering the material; the end result of this is students spend more time engaging in active learning than reviewing the material.
Qutob [ 8 ] studied the effects of flip teaching using two hematology courses. One of the courses was delivered using traditional teaching and the other course was flipped teaching. Qutob [ 8 ] found that students in the flipped course not only performed better on academic tasks, but also they had more knowledge and understanding of the material covered compared to those in the traditional format class. Additionally, Qutob [ 8 ] revealed that students in the flipped classroom found this style of learning is more beneficial than traditional teaching. Moreover, Florence and Kolski [ 11 ] found an improvement in high school students’ writing post-intervention. The authors further found that students were more engaged with the material and had a positive perception of the flipped model. Bahadur and Akhtar [ 12 ] conducted a meta-analysis of twelve research articles on flipped teaching; the studies demonstrated that students taught in the flip teaching classroom performed better academically and were more interactive and engaged in the material than students taught through traditional methods. Galindo-Dominguez [ 13 ] conducted a systematic review using 61 studies and found evidence for the effectiveness of this approach compared to other pedagogical approaches with regards to academic achievement, improved self-efficacy, motivation, engagement, and cooperativeness. Webb et al. [ 14 ] studied 127 students taking microeconomics and found the delivery of flipped material (didactic vs. non-didactic) influenced students’ improvements. They further found performance improvements for the students who attended flipped classes using non-didactic pre-class material. At the same time, Webb et al. [ 14 ] further found non-improvement associated with flipped classes that used didactic pre-class materials; these materials are akin to traditional lectures.
In the context of nursing education, flipped teaching strategy has demonstrated promising and effective results in enhancing student motivation, performance, critical thinking skills, and learning quality. The flipped teaching classrooms were associated with high ratings in teaching evaluations, increased course satisfaction, improved critical thinking skills [ 15 ], improved exam results and learning quality [ 16 ] and high levels of personal, teaching, and pedagogical readiness [ 17 ]. Another study showed that student performance motivation scores especially in extrinsic goal orientation, control beliefs, and self-efficacy for learning and performance were significantly higher in the flipped teaching classroom when compared to the traditional classroom strategy [ 16 ].
Regardless of these important findings, there have been limited studies published about the flipped teaching strategy in Saudi Arabia, particularly among nursing students. Therefore, implementing the flipped teaching strategy in a therapeutic communication course would be effective in academic performance and retention of knowledge. The flipped teaching method will fit best with the goals of a therapeutic communication course as both focus on active learning and student engagement. This approach is well-matched for a therapeutic communication course as it allows students to apply and practice the communication techniques and strategies, they have learned outside of class from the flipped teaching materials and freeing up class time for interactive and experiential activities. The filliped teaching method can provide opportunities for students to apply effective interpersonal communication skills in classes, provide more time to observe students practicing therapeutic communication techniques through role-play, group discussions, and case studies. It also allows instructors to refine and provide individualized feedback and offer real-time guidance to help students improve their interpersonal communication skills.
The current study aims to examine the students’ perception of a teaching innovation based on the use of the flipped teaching strategy in the therapeutic communication course. Further, to compare if there is a difference in students’ academic performance of students who participate in a traditional teaching strategy when compared with students who participate in flipped teaching intervention.
Students who participated in the intervention group perceived a high level of effectiveness of the flipped teaching classroom as a teaching/learning strategy.
There is a significant difference in the mean scores of students’ academic performance between students who participate in a traditional teaching strategy (control group) when compared with those students who participate in flipped teaching classroom (intervention group).
Design of the study
Quantitative method, quasi-experimental design was used in this study. This research study involves implementing a flipped teaching strategy (intervention) to examine the effectiveness of the flipped teaching among the participants in the intervention group and to examine the significant difference in the mean scores of the students’ performance between the intervention and control group.
College of Nursing at one of the educational universities located in Saudi Arabia.
A purposive sampling technique was conducted in this study. This sampling technique allows the researcher to target specific participants who have certain characteristics that are most relevant and informative for addressing the research questions. The advantages of the purposive sampling lie in gathering in-depth, detailed and contextual data from the most appropriate sources and ensure that the study captures a more comprehensive understanding of the concept of interest by considering different viewpoints [ 18 ]. Participants were eligible to participate in this study if they were (1) Enrolled in the undergraduate nursing programs (Nursing or Midwifery Programs) in the College Nursing; (2) Enrolled in Therapeutic Communication Course; (3) at least 18 years old or older. Participant’s data was excluded if 50% of the responses were incomplete. The sample size was calculated using G-Power. The required participants for recruitment to implement this study is 152 participants to reach a confidence level of 95% and a margin error of 5%.
Measurement
Demographic data including the participants’ age and GPA were collected from all the participants. Educational characteristics related to the flipped teaching were collected from the participants in the intervention group including the level of English proficiency, program enrollment, attending previous, attending previous course(s) that used flipped teaching strategy, time spent each week preparing for the lectures, time spent preparing for the course exams, and recommendation for applying flipped teaching in other classes.
The student’s perception of the effectiveness of the flipped teaching strategy was measured by a survey that focused on the effectiveness of flipped teaching. This data was collected only from the participants in the intervention group. The survey involves 14 items that used 5-point Likert-type scale (5 = strongly agree, 4 = agree, 3 = neutral, 2 = disagree and 1 = strongly disagree). The sum of the scores was calculated for the item, a high score indicates a high effectiveness of flipped teaching. The survey was developed by Neeli et al. [ 19 ] and the author was contacted to obtain permission to use the survey. The reliability of the scale was tested using Cronbach alpha, which was 0.91, indicating that the scale has an excellent reliability.
Also, student academic performance was measured for both the intervention and control groups though the average cumulative scores of the assessment methods of students who were enrolled in the Therapeutic Communication Course, given a total of 100. The students’ grades obtained in the course were calculated based grading structure of the Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia (The Rules and Regulations of Undergraduate Study and Examination).
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval (No. 22-0860) was received before conducting the study. Participants were provided with information about the study and informed about the consent process. Informed consent to participate was obtained from all the participants in the study.
Intervention
Therapeutic communication course was taught face-to-face for students enrolled in the second year in the Bachelor of Science in Midwifery and Bachelor of Science in Nursing Programs. There were eight sections for the therapeutic communication course, two of them were under the midwifery program and the remaining (six sections) were under the nursing program. Each section was held once a week in a two-hour length for 10 weeks during the second semester of 2022. Students in all sections received the same materials, contents, and assessment methods, which is considered the traditional teaching strategy. The contents of the course included the following topics: introduction of communication, verbal and written communication, listening skills, non-verbal communication, nurse-patient relationship, professional boundaries, communication styles, effective communication skills for small groups, communication through nursing process, communication with special needs patient, health education and principles for empowering individuals, communication through technology, and trends and issues in therapeutic communication. The course materials, course objectives and learning outcomes, learning resources, and other supporting materials were uploaded to the electronic platform “Blackboard” (A Learning Management System) for all sections to facilitate students’ preparation during classes. The assessment methods include written mid-term examination, case studies, group presentation, and final written examination. The grading scores for each assessment method were also the same for all sections.
The eight course sections were randomly assigned into traditional teaching strategy (control group) or flipped teaching strategy (intervention group). Figure 1 shows random distribution of the course sections. The intervention group ( n = 182) included one section of the Bachelor of Science in Midwifery program ( n = 55 students) and three sections of Bachelor of Science in Nursing program ( n = 127 students). The control group ( n = 173) included one section of the Bachelor of Science in Midwifery program ( n = 50 students) and three sections of Bachelor of Science in Nursing program ( n = 123 students). Although randomization of the participants is not possible, we were able to create comparison groups between participants who received the flipped teaching and traditional teaching strategy. To ensure the consistency of the information given to the students and reduce the variability, the instructors were meeting periodically and reviewed the materials together. More importantly, all students received the same topics and assessment methods as stated in the course syllabus and as mentioned above. The instructors in all sections were required to answer students’ questions, provide clarification to the points raised throughout the semester, and give constructive feedback after the evaluation of each assessment method. Students were encouraged to freely express their opinions on the issues discussed and to share their thoughts when the opinions were inconsistent.

Random Distribution of the Course Sections
The intervention group were taught the course contents by using the flipped teaching strategy. The participants in the intervention group were asked to read the lectures and watch short videos from online sources before coming to classes. Similar materials and links were uploaded by the course instructors into the Blackboard system. During the classes, participants were divided into groups and were given time to appraise research articles and case scenarios related to the topics of the course. During the discussion time, each group presented their answers, and the course instructors encouraged the students to share their thoughts and provided constructive feedback. Questions corresponded to the intended objectives and learning outcomes were posted during the class time in Kahoot and Nearpod platforms as a competition to enhance students’ engagement. By the end of the semester, the flipped teaching survey was electronically distributed to students who were involved in the intervention group to examine the educational characteristics and assess the students’ perceptions about the flipped teaching.
Data collection procedure
After obtaining the IRB approval, the PI sent invitation letters to the potential participants using their official university email accounts. The invitation letter included a Microsoft Forms’ link with the description about the study, aim, research question, and sample size required to conduct the study. All students gave their permission to participate, and informed consent was obtained from them ( N = 355). The link also included questions related to age, GPA, and approval to use their scores from assessment methods for research purposes. The first part of data collection was obtained immediately after the therapeutic communication course was over. The average cumulative scores of all the assessment methods (out of 100) were calculated to measure the students’ academic performance for both the intervention and control groups.
The second part of data collection was conducted after the final exam of the therapeutic communication course ( n = 182). A Microsoft Forms link was sent to the participants in the intervention group only. It included questions related to educational characteristics and students’ perception of the effectiveness of flipped teaching. Students needed a maximum of 10 min to complete the study survey.
Data analysis
Data was analyzed using the SPSS version 27. Descriptive analysis was used to analyze the demographic and educational characteristics and perception of flipped teaching strategy. An independent t-test was implemented to compare the mean scores of the intervention and control groups to examine whether there is a statistically significance difference between both groups. A significance level of p < 0.05 was determined as statistical significance in this study.
The total number of students who enrolled in therapeutic communication course was 355 students. The intervention group included 182 students and the control group included 173 students. The mean age of all participants in the study was 19 years old (M = 19.56, SD = 1.19). The mean GPA was 3.53 (SD = 1.43). Of those enrolled in the intervention group, only 70 out of 182 students completed the survey. Table 1 represents the description of the educational characteristics of the participants in intervention group ( n = 70). Around 65% of the participants reported that their level of English proficiency is intermediate, and they were enrolled in the nursing program. Half of the students had precious courses that used flipped teaching strategy. About one-third of the students indicated that they spent less than 15 min each week preparing for lectures. Around 65% of the students stated that they spent more than 120 min preparing for the course exam. Half of the students gave their recommendation for applying flipped teaching strategy in other courses. The mean score of the students’ performance in Therapeutic Communication course who enrolled in the intervention group is 83.34 (SD = 9.81) and for those who were enrolled in the control group is 75.57 (SD = 9.82).
The students perceived a moderate level of effectiveness of the flipped teaching classroom as a teaching strategy (M = 3.49, SD = 0.69) (Table 2 ). The three highest items that improved students’ perception about the flipped teaching strategy were: flipped classroom session develops logical thinking (M = 3.77, SD = 0.99), followed by flipped classroom session provides extra information (M = 3.68, SD = 1.02), then flipped classroom session improves the application of knowledge (M = 3.64, SD = 1.04). The three lowest items perceived by the students were: Flipped classroom session should have allotted more time for each topic (M = 3.11, SD = 1.07), flipped classroom session requires a long time for preparation and conduction (M = 3.23, SD = 1.04), and flipped classroom session reduces the amount of time needed for study when compared to lectures (M = 3.26, SD = 1.07).
An independent sample T-test was implemented to compare the mean scores of the students’ academic performance between the intervention group ( n = 182) and control group ( n = 173) (Table 3 ). The results of Levene’s test for equality of variances ( p = 0.801) indicated that equal variances assumed, and the assumption of equal variances has not been violated. The significant level value (2-tailed) is p ≤ 0.001, indicating that there is a statistically significant difference in the mean scores of students’ academic performance for the intervention group (M = 83.34, SD = 9.81) and control group (M = 75.57, SD = 9.82). The magnitude of the differences in the means (Mean difference= -7.77%, CI: -10.02 to -5.52) is very small (Eta squared = 0.00035).
Flipped teaching is a learning strategy that engages students in the learning process allowing them to improve their academic performance and develop cognitive skills [ 20 ]. This study investigated the effect of implementing flipped teaching as an interactive learning strategy on nursing students’ performance. Also, the study examined students’ perceptions of integrating flipped teaching into their learning process. Flipped teaching is identified as an interactive teaching strategy that provides an engaging learning environment with immediate feedback allowing students to master the learning content [ 4 , 5 ]. Improvement in the student’s academic performance and development of learning competencies were expected outcomes. The flipped classroom approach aligns with the constructivist theory of education, which posits that students actively construct their own knowledge and understanding through engaging with the content and applying it in meaningful contexts. By providing pre-class materials (e.g., videos, readings) for students to engage with independently, the flipped classroom allows them to build a foundational understanding of the concepts before class, enabling them to actively participate in discussions, problem-solving, and collaborative activities during the class. By shifting the passive acquisition of knowledge to the pre-class phase and dedicating in-class time to active, collaborative, and problem-based learning, the flipped classroom approach creates an environment that fosters deeper understanding, the development of critical thinking and clinical reasoning skills as well as the ability to apply knowledge in clinical practice [ 21 ].
Effectiveness of the flipped teaching on students’ academic performance
The influence of flipped teaching on students’ academic performance was identified by evaluating students’ examination scores. The results of this study indicated that flipped teaching had a significant influence on students’ academic performance ( p = 0.000). This significant influence implies the positive effectiveness of flipped teaching on students’ academic performance (M = 83.34, SD = 9.81) compared to traditional classroom (M = 75.57, SD = 9.82). These results are in line with other researchers regarding improving students’ academic performance [ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Qutob’s [ 8 ] study shows that flipped teaching positively influences students’ performance. Preparation for class positively influenced students’ academic performance. The flipped classroom approach is underpinned by the principles of constructivism. These principles emphasize the active role of students in constructing their own understanding of concepts and ideas, rather than passively receiving information [ 21 ].
In a traditional classroom, the teacher typically delivers content through lectures, and students are tasked with applying that knowledge through homework or in-class activities. However, this model often fails to engage students actively in the learning process. In contract,
Flipped classroom requires students to prepare for the class which allows them to be exposed to the learning material before the class. During class time, students are giving opportunities to interact with their classmates and instructors to discuss the learning topic which can positively influencing their academic performance later [ 7 , 9 ]. Furthermore, the flipped classroom approach aligns perfectly with the core tenets of constructivism. Its adherence to the constructivist 5E Instructional Model further demonstrates its grounding in this learning theory. The 5E model, which includes the phases of engagement, exploration, explanation, elaboration, and evaluation, provides a framework for facilitating the active construction of knowledge [ 22 ].
It first sparks student interest and curiosity about the concepts (engagement), then enables students to investigate and experiment with the ideas through hands-on activities and investigations (exploration). This is followed by opportunities for students to make sense of their explorations and construct their own explanations (explanation). The flipped classroom then allows students to apply their knowledge in new contexts, deepening their understanding (elaboration). Finally, the evaluation phase assesses student learning and provides feedback, completing the cycle of constructivist learning [ 22 ]. This alignment with the 5E model, along with the flipped classroom’s emphasis on active learning and create environment that nurtures deeper understanding, the development of higher-order thinking skills, and the ability to transfer learning to real-world contexts.
In this study, one third of the students indicated that the preparation time was less than fifteen minutes a week. According to Vazquez and Chiang [ 10 ], preparation time for classroom should be about 15 to 20 min for each topic. Preparation for class did not take much time but positively influenced students’ academic performance. Furthermore, preparation for class allows students to develop the skills to be independent learners [ 8 ]. Independence in learning develops continuous learning skills, such as long-life learning which is a required competency for nursing. Garcia et al. [ 22 ] found out that focusing on shifting teachers’ practices towards active learning approaches, such as the 5E Instructional Model, can have lasting, positive impacts on students’ conceptual understanding and learning.
Students’ perception of flipped teaching as a teaching strategy
Students’ perception of flipped teaching as a learning strategy was examined using a survey developed by Neeli et al. [ 19 ]. Students recognize flipped teaching as an effective teaching strategy (M = 3.49, SD = 0.69) that had a positive influence on their learning processes and outcomes. Several studies identified the positive influence of flipped teaching on students’ learning process and learning outcomes [ 8 , 19 ]. Flipped teaching provides a problem-based learning environment allowing students to develop clinical reasoning, critical thinking, and a deeper understanding of the subject [ 5 , 8 , 19 , 23 ]. The flipped teaching approach introduces students to the learning materials before class. Class time is then utilized for discussion, hands-on, and problem-solving activities to foster a deeper understanding of the studied subject [ 5 ]. Consequently, flipped teaching provides a problem-based learning environment as it encourages students to be actively engaged in the learning process, work collaboratively with their classmates, and apply previously learned knowledge and skills to solve a problem. The result of this study is consistent with the results from a systematic review conducted by Youhasan et al. [ 5 ]. Implementing flipped teaching in undergraduate nursing education provides positive outcomes on students’ learning experiences and outcomes and prepares them to deal with future challenges in their academic and professional activities [ 5 ].
Implications
The results from this study identified that flipped teaching has a significant influence on students’ academic performance. The results also indicated that students have positive perception of flipped teaching as an interactive learning strategy. Flipped teaching pedagogy could be integrated in nursing curriculum to improve the quality of education process and outcomes which will result in improving the students’ performance. Flipped teaching provides an interactive learning environment that enhances the development of essential nursing competencies, such as communication, teamwork, collaboration, life-long learning, clinical reasoning, and critical thinking. For example, flipped teaching allows students to develop communication skills throughout discussion in the classroom, and collaboration skills by working with their classmate and instructor. In this study, flipped teaching was implemented in a theoretical course (therapeutic communication course). This interactive learning strategy could also be applied in clinical and practice setting for effective and meaningful learning process and outcomes.
Strengths and limitations
This research study reveals the effectiveness of flipped teaching on students’ academic performance. This study used a quasi-experimental design with control and intervention groups to investigate the influence of flipped teaching on nursing education. Nevertheless, this study has limitations. One of the study’s limitations is the lack of randomization, thus causal association between the variables cannot be investigated. In addition, this study used a self-administered survey which may include respondents’ bias; thus, it may affect the results. Also, this study investigated students’ perceptions of flipped teaching as a learning strategy. The results from examining students’ perceptions indicated that students had a positive perception of flipped teaching as it allowed them to develop essential nursing competencies. This study did not focus on identifying and measuring competencies. Therefore, future studies must consider measuring the influence of flipped teaching on students’ ability to acquire nursing competencies, such as critical thinking and clinical reasoning.
Flipped teaching is an interactive learning strategy that depends on students’ preparation of the topic to be interactive learners in the learning environment. Interactive learning environment improves learning process and outcomes. This study indicated that flipped teaching has significant influence on students’ academic performance. Students perceived flipped teaching as a learning strategy that allowed them to acquire learning skills, such as logical thinking and application of knowledge. These skills allow students to have meaningful learning experience. Also, students could apply these skills in other learning content and/or environments, for example, in clinical. Thus, we believe that flipped teaching is an effective learning approach to be integrated in the nursing curriculum to enhance students’ learning experience.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to data privacy but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Institutional Review Board
Standard deviation
The level of marginal significance within a statistical test
Confidence Interval of the Difference
Figueiredo AR, Potra TS. Effective communication transitions in nursing care: a scoping review. Ann Med. 2019;51(sup1):201–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2018.1560159 .
Article Google Scholar
O’Rae A, Ferreira C, Hnatyshyn T, Krut B. Family nursing telesimulation: teaching therapeutic communication in an authentic way. Teach Learn Nurs. 2021;16(4):404–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teln.2021.06.013 .
Thai NTT, De Wever B, Valcke M. The impact of a flipped classroom design on learning performance in higher education: looking for the best blend of lectures and guiding questions with feedback. Computers Educ. 2017;107:113–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2017.01.003 .
Özbay Ö, Çınar S. Effectiveness of flipped classroom teaching models in nursing education: a systematic review. Nurse Educ Today. 2021;104922–104922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2021.104922 . 102 (n. Issue).
Youhasan P, Chen Y, Lyndon M, Henning MA. Exploring the pedagogical design features of the flipped classroom in undergraduate nursing education: a systematic review. BMC Nurs. 2021;20(1):50–50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-021-00555-w .
Barbour C, Schuessler JB. A preliminary framework to guide implementation of the flipped classroom method in nursing education. Nurse Educ Pract. 2019;34:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2018.11.001 .
Jordan C, Magrenan A, Orcos L. Considerations about flip education in the teaching of advanced mathematics. Educational Sci. 2019;9(3):227.
Qutob H. Effect of flipped classroom approach in the teaching of a hematology course. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(4):1–8.
Nguyen B, Yu X, Japutra A, Chen C. Reverse teaching: exploring student perceptions of flip teaching. Act Learn High Educ. 2016;17(1):51–61.
Vazquez J, Chiang E. Flipping out! A case study on how to flip the principles of economics classroom. Int Adv Econ Res. 2015;21(4):379–90.
Florence E, Kolski T. Investigating the flipped classroom model in a high school writing course: action research to impact student writing achievement and engagement. TechTrends: Link Res Pract Improve Learn. 2021;65(6):1042–52.
Bahadur G, Akhtar Z. Effect of teaching with flipped classroom model: a meta-analysis. Adv Social Sci Educ Humanit Res. 2021;15(3):191–7.
Google Scholar
Galindo-Dominguez H. Flipped classroom in the educational system: Trend or effective pedagogical model compared to other methodologies? J Educational Technol Soc. 2021;24(3):44–60.
Webb R, Watson D, Shepherd C, Cook S. Flipping the classroom: is it the type of flipping that adds value? Stud High Educ. 2021;46(8):1649–63.
Barranquero-Herbosa M, Abajas-Bustillo R, Ortego-Maté C. Effectiveness of flipped classroom in nursing education: a systematic review of systematic and integrative reviews. Int J Nurs Stud. 2022;135:104327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2022.104327 .
Lelean H, Edwards F. The impact of flipped classrooms in nurse education. Waikato J Educ. 2020;25:145–57.
Youhasan P, Chen Y, Lyndon M, Henning MA. Assess the feasibility of flipped classroom pedagogy in undergraduate nursing education in Sri Lanka: a mixed-methods study. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(11):e0259003. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0259003 .
Harris AD, McGregor JC, Perencevich EN, Furuno JP, Zhu J, Peterson DE, Finkelstein J. The use and interpretation of quasi-experimental studies in medical informatics. J Am Med Inf Association: JAMIA. 2006;13(1):16–23. https://doi.org/10.1197/jamia.M1749 .
Neeli D, Prasad U, Atla B, Kukkala SSS, Konuku VBS, Mohammad A. (2019). Integrated teaching in medical education: undergraduate student’s perception.
Baloch MH, Shahid S, Saeed S, Nasir A, Mansoor S. Does the implementation of flipped Classroom Model improve the Learning Outcomes of Medical College Students? A single centre analysis. J Coll Physicians Surgeons–pakistan: JCPSP. 2022;32(12):1544–7.
Robertson WH. The Constructivist flipped Classroom. J Coll Sci Teach. 2022;52(2):17–22.
Garcia I, Grau F, Valls C, Piqué N, Ruiz-Martín H. The long-term effects of introducing the 5E model of instruction on students’ conceptual learning. Int J Sci Educ. 2021;43(9):1441–58.
Chu TL, Wang J, Monrouxe L, Sung YC, Kuo CL, Ho LH, Lin YE. The effects of the flipped classroom in teaching evidence based nursing: a quasi-experimental study. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(1):e0210606.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the facilities and other support given by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2024R447), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
This research was funded by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2024R447), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Nursing Management and Education Department, College of Nursing, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, P.O. Box 84428, Riyadh, 11671, Saudi Arabia
Shaherah Yousef Andargeery, Rania Ali Alhalwani, Shorok Hamed Alahmedi & Waad Hasan Ali
Medical-Surgical Nursing Department, College of Nursing, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, P.O. Box 84428, Riyadh, 11671, Saudi Arabia
Hibah Abdulrahim Bahri
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization, H.B, S.Y.A, W.A.; methodology, S.Y.A., S.H.A.; validation, S.Y.A.; formal analysis, S.Y.A.; resources, H.B, S.Y.A, W.A, R. A.; data curation, S.Y.A, S.H.A.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A, H.B, S.Y.A., S.H.A, W.A; writing—review and editing, R.A, H.B, S.Y.A, S.H.A, W.A; supervision, R.A, H.B, S.Y.A, S.H.A.; project administration, R.A, S.Y.A, S.H.A.; funding acquisition, S.Y.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hibah Abdulrahim Bahri .
Ethics declarations
Institutional review board.
Institutional Review Board (IRB) in Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, approval No. (22-0860).
Informed consent
Informed consents were obtained from all study participants.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Andargeery, S.Y., Bahri, H.A., Alhalwani, R.A. et al. Using a flipped teaching strategy in undergraduate nursing education: students’ perceptions and performance. BMC Med Educ 24 , 926 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05749-9
Download citation
Received : 26 February 2024
Accepted : 05 July 2024
Published : 26 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05749-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Flipped teaching
- Active learning
- Teaching strategy
- Nursing education
- Undergraduate nursing education
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Critical thinking definition

Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement.
Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process, which is why it's often used in education and academics.
Some even may view it as a backbone of modern thought.
However, it's a skill, and skills must be trained and encouraged to be used at its full potential.
People turn up to various approaches in improving their critical thinking, like:
- Developing technical and problem-solving skills
- Engaging in more active listening
- Actively questioning their assumptions and beliefs
- Seeking out more diversity of thought
- Opening up their curiosity in an intellectual way etc.
Is critical thinking useful in writing?
Critical thinking can help in planning your paper and making it more concise, but it's not obvious at first. We carefully pinpointed some the questions you should ask yourself when boosting critical thinking in writing:
- What information should be included?
- Which information resources should the author look to?
- What degree of technical knowledge should the report assume its audience has?
- What is the most effective way to show information?
- How should the report be organized?
- How should it be designed?
- What tone and level of language difficulty should the document have?
Usage of critical thinking comes down not only to the outline of your paper, it also begs the question: How can we use critical thinking solving problems in our writing's topic?
Let's say, you have a Powerpoint on how critical thinking can reduce poverty in the United States. You'll primarily have to define critical thinking for the viewers, as well as use a lot of critical thinking questions and synonyms to get them to be familiar with your methods and start the thinking process behind it.
Are there any services that can help me use more critical thinking?
We understand that it's difficult to learn how to use critical thinking more effectively in just one article, but our service is here to help.
We are a team specializing in writing essays and other assignments for college students and all other types of customers who need a helping hand in its making. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
- Select the topic and the deadline of your essay.
- Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the essay writing process you struggle with.
- Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
- Select your prefered payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed essay writers , online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.
Teachers' knowledge of soft skills and flipped classrooms: Nursing and health technologies
- Elkhalladi, Jaouad
- Sefrioui, Amal
Soft skills and flipped classrooms are important in the fields of education, nursing, and health techniques. This study determined nursing teachers' knowledge of soft skills and flipped classrooms. This was a descriptive cross-sectional study with an analytical focus involving 100 teachers. The study was conducted at the Higher Institute of Nursing Professions and Health Techniques (ISPITS) at Agadir and its annex in Tiznit. One hundred permanent and temporary teachers (with an equal distribution of male and female teachers) participated in the survey. A five-part questionnaire was used to collect data. The independent variable was the use of a flipped classroom and dependent variable was the development of soft skills. SPSS version 25 software was used to process the data. Chi-square test, Ficher's test, binary logistic regression test, and multivariate logistic regression model were employed for data analysis. In total, 80 % participants had knowledge of soft skills, and 75 % knew about flipped classrooms. The most important soft skills were considered to be communication, stress management, teamwork, conflict management, problem-solving, time management, critical thinking, autonomy, adaptability, and decision-making. The five soft skills considered most likely to be developed by flipped classrooms were autonomy, analysis, teamwork, communication, and time management. Furthermore, the development of soft skills through the flipped classrooms was independently associated with soft skills training (p = 0.008) and use of flipped classrooms (p = 0.042). Teachers have knowledge of soft skills and flipped classrooms despite a lack of training, and flipped classrooms contribute to the development of soft skills.
- Health science;
- Soft skills;
- Medical education
Digital University For All
- Shared Values
- Pro-Chancellor
- Board of Governors
- Executive Management Committee
- METEOR Board of Directors
Administration
- President/VC's Office
- VP/DVC's Office
- - Academic & Research
- - Learner Experience & Technology
- - Business Development
- - Registrar's Office
Achievements
- Awards & Recognition
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Faculty of Business & Management
- Faculty of Technology & Applied Sciences
- Faculty of Education
- Faculty of Social Sciences & Humanities
- Research Hub
- Digital Library
- Recognition & Accreditation
- Request Info
- Visit Learning Centre
55 Programmes Available
Future Learners
- Learning Centres
Current Learners
- Online Score Entry System
- Support & Guidance
- Financial Aid
- PsyQiQ plus
- Alumni Portal
- Convocation
- Verify Graduates
Malaysian Learners
- How To Apply
- Requirements
- Programmes Offered
International Learners
- Financial Assistance
- Online Application
Top Searches:
- TSDAS Digital Library
- Scholarships
- Application
NPCP 7003 CONCEPT PAPERNPND 7100-1 DISSERTATION PROPOSAL WRITING /DEFENSE
NPND 7100-2 DISSERTATION PROPOSAL WRITING/DEFENCE/ETHICS
NPND7100-3 DATA COLLECTION , DATA ANALYSIS
NPND7100-4 DISCUSSION & PRELIMINARY FINDINGS PRESENTATION (SUPERVISOR) CONCLUSION
NPND7100-5 SUBMISSION
NPND7100-6 FINAL SUBMISSION /VIVA
Malaysian Learner Fees
| Year 1 | RM4,590 (Sem 1) | RM4,590 (Sem 2) | RM4,590 (Sem 3) |
| Year 2 | RM4,590 (Sem 4) | RM7,650 (Sem 5) | RM4,590 (Sem 6) |
| Year 3 | RM2,110 (Sem 7) | RM2,110 (Sem 8) | RM2,110 (Sem 9) |
| Year 4 | RM2,110 (Sem 10) | RM2,110 (Sem 11) | RM2,110 (Sem 12) |
| TOTAL | RM43,260 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Discount for the Physically Challenged Learners (OKU) and Senior Citizens
* Fees applicable to Malaysians and Permanent Residents only. * The University reserves the right to revise the fees without prior notice.
The University offers 50% discount for: 1. Senior citizens aged 60 and above on registration date; and 2. Physically challenged learners – a valid Orang Kelainan Upaya (OKU) is required. The discounts are not valid for second time registration and repeating of subjects. Learners who receive this discount are not entitled to other discounts and promotions.
Note Processing fee: RM50 Re-registration fee of RM220 per semester is chargeable for extension of the Research Thesis/Dissertation
| EPF (Account 2); or | JomPAY |
| Education or Personal Loan from commercial banks; or | Internet Banking |
| HRDF (subject to employer’s eligibility); or | Debit/Credit Card. |
International Learner Fees
| Year 1 | RM5,508 (Sem 1) | RM5,508 (Sem 2) | RM5,508 (Sem 3) |
| Year 2 | RM5,508 (Sem 4) | RM9,180 (Sem 5) | RM5,508 (Sem 6) |
| Year 3 | RM2,110 (Sem 7) | RM2,110 (Sem 8) | RM2,110 (Sem 9) |
| Year 4 | RM2,110 (Sem 10) | RM2,110 (Sem 11) | RM2,110 (Sem 12) |
| TOTAL | RM49,380 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Notes: 1 – Fees applicable to International applicants 2 – The fee above excludes registration fee, processing fee and resource fee. Fee imposed first semester only-non refundable . (Diploma RM2,700; Bachelor RM3,200, Master RM3,700, PhD/Doctorate RM4,200). 3 – Financial method: Telegraphic Transfer , PayPal (Invoice will be prepared in MYR and will be added 6% to cover PayPal transaction fees.) 4 – The fees are for subject fees only and are not applicable for research, registration, repeating of subjects and other fees. 5 – 60% payment of the semester fees must be made before the semester starts, 40% payment before the examination week.
* The University reserves the right to revise the fees without prior notice. **LATEST UPDATE: 30 August 2022
Entry Requirements
Program educational objectives (peo).
PEO 1 – Demonstrate a critical understanding of the most advanced health knowledge in the field of professional nursing practice. ( PLO 1, 2 )
PEO 2 – Collaborate with health care teams to deliver health to a diverse population in complex health care environments using evidence-based practice. ( PLO 3, 4, 5, 6 )
PEO 3 – Evaluate health care policy to innovate and influence change using appropriate professional communication and leadership skills. ( PLO 8 )
PEO 4 – Apply research, information technology and entrepreneurial skills legally and ethically in personal and professional development. ( PLO 7, 9, 10, 11 )
Program Learning Objectives (PLO)
| Demonstrate a critical understanding of the most advanced knowledge in a field of study or professional nursing practice | Cluster 1 |
| Evaluate current critical issues with complex abstract ideas into a comprehensive systematic, integrated new nursing knowledge. | Cluster 2 |
| Demonstrate mastery of practical/ technical/scientific skills at all levels of complexities in one or more areas of specialization and resolve new emerging problems within the context of the nurse practitioner | Cluster 3a |
| Influence peers, scholarly community and society in the field of expertise to bring effective collaboration within a diversity of partners | Cluster 3b |
| Display advanced/sophisticated leadership skills in ethically and professionally conveying information, insights, ideas, and problems to other groups and networks. (A5, P5) | Cluster 3c |
| Perform existing or develop lifelong learning skills with new appropriate tools/methodologies to support and enhance research activities | Cluster 3d |
| Use numeracy skills for research and lifelong learning activities ( | Cluster 3e |
| Work with full autonomy using leadership, professionalism, and accountable managerial capabilities in solving problems in a complex setting, for own work and significant others within the organization, as well as contribute to society at large in technological, social, and cultural progress | Cluster 3f |
| Integrate knowledge for lifelong learning to enhance personal and professional development in the nursing field. | Cluster 4(i) |
| Initiate and lead entrepreneurial ventures and projects locally and globally ( | Cluster 4(ii) |
| Display attitudes and professionalism ethically in providing care to meet the needs of the diverse population with its complexities and implication while upholding the professional and ethical code of nursing practice | Cluster 5 |
- What is a Doctor of Nursing (DN)? The DN is a one of two terminal doctoral degrees in the field of nursing. While its counterpart, the PhD, is more research-oriented, those who earn a DN have completed the highest level of nursing academic through course work -oriented designed. The program is for nurses to pursue their career pathway in clinical, education and research. This terminal degree for nurses will prepare them for their future challenging roles in healthcare delivery.
- How do I qualify to join this DN program ? Requirement for joining this program is Master of Nursing , Master in Health Science or other health related qualification at level 7 Malaysian Qualification Framework. Other qualifications equivalent with Masters which is accepted by Senate.
- What is the duration of the course? This is a 12-semesters course (4 years). A specific set of doctoral-level coursework required in all DN programs for two years , and two years of dissertation. This is a 4-year coursework and dissertation based program offered via the distance and open learning mode.
- What are the requirements for International students to join this program? A minimum score of 500 in Test for English as a Foreign language (TOEFL). A minimum score of 5.0 in International English Language Testing System(IELTS)
- What is total credit to complete the duration of the course? A total of 80 credits as approved by Malaysian Qualification Framework
- What is the nomenclature of post graduate degree awarded after completion of DN? Doctoral degree according to the field of specialisation e.g DBA, DEd , DN
- What is the impact of DN program to your career? Nurses with DN degree are in an important position to serve as leaders in the continuing articulation of the discipline, as well as contributors on multiple levels to the development of the knowledge base of nursing.
- How does DN program contribute to the community in general? They continue to lead, share and contribute new knowledge/innovations/practices in the related field and its emerging issues, and towards the social, technological and cultural progress in the academic and professional contexts.
- Is the program accredited? The program has been accredited and approved by MQA – The assessment of required accreditation of DN program no is MQA/FA 0839
- What are the course subjects in DN program? DN curriculum coursework include subjects health care policy and politics , and evidence-based practice. Philosophy of science, nursing informatics , research methods and statistics and health economics , risk management and law and ethics in nursing. All DN students are required to fulfil 40 credits of course work and 40 credits of dissertation.The dissertation is meant to demonstrate students’ mastery of the theories and practices learned throughout the DN
- What will be the career progression from entry into nursing and the DN? Multiple routes and mechanisms for career progression will be possible and ultimately decided by each educational institution. The proposed model allows for progression from the BS or MS or to the DN.
- How many institutions currently offer the DN through online ? Currently Open University Malaysia is the only university in Malaysia offering the course via online.
- How will the DN differ from the PhD in terms of curriculum content, research competencies, outcomes and roles occupied? The DN focuses on providing leadership for evidence-based practice. This requires competence in translating research in practice, evaluating evidence, applying research in decision-making, and implementing viable clinical innovations to change practice. Considerable emphasis is placed on a population perspective, how to obtain assessment data on populations or cohorts, how to use data to make programmatic decisions, and program evaluation.
How to Apply
Request information, financing your education, do you have more questions.
Here some common types of career fields for graduates with a Doctor of nursing degree, along with examples of career opportunities in each field
| Career Field | Examples of Career Opportunities |
|---|---|
| Advanced Practice Nursing | 1. Nurse Practitioner 2. Certified Nurse Midwife 3. Clinical Nurse Specialist 4. Nurse Anesthetist |
| Nursing Education | 1. Nurse Educator 2. Clinical Instructor 3. Nursing Program Director 4. Academic Dean |
| Nursing Administration | 1. Nurse Manager 2. Nursing Director 3. Chief Nursing Officer (CNO) 4. Healthcare Administrator |
| Health Policy and Advocacy | 1. Health Policy Analyst 2. Nurse Advocate 3. Lobbyist 4. Government Health Advisor |
| Public Health Nursing | 1. Public Health Nurse 2. Epidemiologist 3. Community Health Specialist 4. Occupational Health Nurse |
| Telehealth Nursing | 1. Telehealth Nurse Practitioner 2. Telehealth Program Manager 3. Remote Patient Monitoring Specialist 4. Virtual Care Coordinator |
| Research and Innovation | 1. Nurse Researcher 2. Clinical Trials Coordinator 3. Nursing Informatician 4. Healthcare Innovations Manager |
| Gerontology Nursing | 1. Geriatric Nurse Practitioner 2. Gerontological Clinical Nurse Specialist 3. Director of Geriatric Services 4. Aging-in-Place Coordinator |

The struggle to balance study and work gave me better insight into productivity and efficiency. I was able to apply the lessons learned to my occupation. My study at OUM was my progress in development. The encouragement and guidance from OUM gave me the platform and confidence to succeed in my studies. Today, my degree has given me generous employment recognition, added edge in promotion, and salary advances.
Look for other programmes that you might be interested:
- Bachelor of Information Technology (Honours)
- Bachelor of Manufacturing Management (Honours)
- Bachelor of Occupational Safety & Health Management (Honours)
- Bachelor of Science Project and Facility Management (Honours)
- Bachelor of Medical and Health Sciences (Honours)
- Bachelor of Nursing Science (Honours)
- Bachelor of Digital Media and Design (Honours)
- Diploma in Information Technology
- Doctor of Philosophy (Information Technology)
- Doctor of Philosophy (Science)
- Master of Information Technology
- Master in Data Science
- Master of Nursing
- Master of Project Management
- Master of Quality Management
- Master of Facility Management
- Master of Occupational Safety and Health Risk Management
- OUM Graduates
- Staff Portal
- Centre for Teaching & Learning Management
- Vendor Registration
- Procurement Notices
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Rev Lat Am Enfermagem
Language: English | Portuguese | Spanish
Reflective and critical thinking in nursing curriculum
O pensamento crítico-reflexivo nos currículos de enfermagem, el pensamiento reflexivo y crítico en los currículos de enfermería, maría antonia jiménez-gómez.
1 Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Facultad de Enfermería, Bogotá, Colombia.
Lucila Cárdenas-Becerril
2 Universidad Autónoma del Estado de México, Facultad de Enfermería, Toluca, México.
Margarita Betzabé Velásquez-Oyola
3 Universidad Nacional José Faustino Sánchez Carrión, Facultad de Medicina Humana, Huacho, Lima, Peru.
Marcela Carrillo-Pineda
4 Universidad de Antioquia, Facultad de Enfermería, Medellín, Colombia.
Leyvi Yamile Barón-Díaz
5 Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Facultad de Medicina, Bogotá, Colombia.
to evaluate the teaching of transversal competence of the Reflective and Critical Thinking that is fundamental in the decision-making and solution of nursing problems, in degree programs of public and private institutions in the Andean region.
multi-center, cross-sectional, exploratory-descriptive study, with mixed approach in 5 countries.
76 nursing programs participated in the study. The Reflective and Critical Thinking was found as a subject, subject content and didactic strategies. Of the 562 subjects reviewed, this type of thinking is found in 46% of the humanities area and 42% in the area of research and professional discipline. It is important to train teachers to achieve coherence between the pedagogical model approach, teaching strategies and evaluations.
Conclusion:
nursing programs in the Andean region contemplate the critical thinking as cognitive and personals skills of communication. They also use real situations analysis, supervised practice, simulation labs and specifically learning based in problems to develop the capacity to solve them, decision-making and develop communication skills, including analysis, synthesis and evaluation.
avaliar o ensino da competência transversal do pensamento crítico-reflexivo, fundamental na tomada de decisões e solução de problemas de enfermagem, nos programas de graduação de instituições públicas e privadas da região Andina.
Método:
estudo multicêntrico, transversal, exploratório-descritivo, com abordagem mista em cinco países.
Resultados:
76 programas de Enfermagem participaram do estudo. O pensamento crítico-reflexivo foi constatado como disciplina, conteúdo de disciplina e estratégias didáticas. Das 562 disciplinas revisadas, este tipo de pensamento se encontra em 46% da área de humanidades e 42% na área de pesquisa e profissional-disciplinar. Existe a necessidade de capacitar os docentes para obter coerência entre a proposta do modelo pedagógico, as estratégias didáticas e a avaliação.
Conclusão:
os programas de enfermagem da região Andina contemplam o pensamento crítico como habilidades cognitivas, de comunicação e pessoais. Da mesma forma, utilizam a análise de situações reais, estágio supervisionado, laboratórios de simulação e, principalmente, a aprendizagem baseada em problemas, com a finalidade de desenvolver a capacidade para solucionar problemas, tomar decisões e desenvolver habilidades comunicativas, incluindo análise, síntese e avaliação.
evaluar la enseñanza de la competencia transversal del Pensamiento Reflexivo y Crítico, fundamental en la toma de decisiones y en la solución de problemas de enfermería, en los programas de grado de instituciones públicas y privadas de la región Andina.
estudio multicéntrico, transversal, exploratorio-descriptivo, con abordaje mixto en 5 países.
76 programas de Enfermería participaron en el estudio. El Pensamiento Reflexivo y Crítico se encontró como asignatura, contenido de asignatura y estrategias didácticas. De las 562 asignaturas que han sido revisadas, este tipo de pensamiento se encuentra en el 46% del área de humanidades y el 42% en el área de investigación y profesional disciplinar. Está la necesidad de capacitar a los docentes para lograr coherencia entre el planteamiento del modelo pedagógico, las estrategias didácticas y la evaluación.
Conclusión:
los programas de enfermería de la región Andina contemplan el pensamiento crítico como habilidades cognitivas, de comunicación y personales. Asimismo, utilizan el análisis de situaciones reales, la práctica supervisada, los laboratorios de simulación y, principalmente, el aprendizaje basado en problemas, con la finalidad de desarrollar la capacidad para solucionar los problemas, tomar decisiones y desarrollar habilidades comunicativas, incluyendo el análisis, la síntesis y la evaluación.
Introduction
Globalization brought with it changes in all aspects of life: social, political, economic and cultural. Moreover, the nursing profession is evolving, so that it is increasingly moving away from the biomedical model of care, focused on the instrumental, to focus on people’s health care, with primacy of dialogue and agreements between the professional and the person under care. As part of a multiprofessional team, this requires changes in the curricular proposal and, in turn, a qualifying teacher for a new profile of graduate, whereby reflection, self-criticism and professional responsibility are developed ( 1 ) .
Therefore, it is necessary to work intensely to reduce the dichotomies that are present in nursing programs, namely: between theory-practice; training and the reality of professional practice; and the student as a passive part of the teaching-learning process and the professional who is required, active, proactive, creative, analytical, with contextual perspective, flexible, with logical thinking, able to carry out a permanent and continuous search for information, able to contribute with his profession to the solution of health problems.
The General Conference of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), at its 38th session, held in Paris from 3 to 18 November 2015, “Recommendation about Adult Learning and Education” states in one of its objectives the need to develop people’s capacity to think critically and to act with autonomy and a sense of responsibility ( 2 ) .
Critical thinking (CT) is a process and a learning outcome ( 3 - 4 ) and the clinical judgment is the result of this process. The development of the clinical judgment (clinical reasoning skills) is one of the most important and challenging tasks of being a nurse. Clinical reasoning precedes clinical judgment and the decision-making that is important in professional and personal life.
In order to achieve professionals with reflective and critical thinking (RACT), it is necessary to make deep changes in the educational dynamics, in the teaching and student roles, in the use of pedagogy and didactics to transmit knowledge, the curricular structure, the strategies of teaching-learning. These changes are expected to be centered on the student, who must actively participate in the learning process in order to achieve greater development of his or her capacities for reasoning, self-learning, self-evaluation, self-management and self-regulation. Likewise, it is expected that teachers to be critical and creative, attending to individual ways of learning, encouraging the development of good thinking in the student ( 3 ) .
Literature points out that critical thinking is the “essential foundation for education, since it is the basis for adaptation to the individual, social and professional demands of daily life in the 21st century and beyond” ( 4 ) . The world changes fast and new realities arise, so there is a fundamental need of people to develop capabilities that allow them to respond and adapt themselves to these changes.
Critical thinking is “the process of seeking, obtaining, evaluating, analyzing, synthesizing and conceptualizing information as a guide, to develop self-conscious thinking and the ability to use this information by adding creativity and taking risks” ( 4 ) .
Authors pointed out one of the first definitions of critical thinking: “knowledge, skills and attitudes” ( 5 ) and, since the end of 1980, various strategies for its teaching have been discussed at all school levels ( 4 ) . On the other hand, authors point out the importance of generating opportunities to develop RACT in students. Therefore, some authors emphasize the importance of developing it in all health situations in favor of the patient ( 4 , 6 - 7 ) . The nursing professional developing RACT will know where, when and how to use their knowledge, skills, values and attitudes.
The motivation for nurse training in the Andean region became evident in the 1960s. In particular, Colombia generated the first degree program in 1958, which was approved in 1961. In the same period, Venezuela, Ecuador, and Peru initiated undergraduate programs; in the case of Bolivia, it happened only until 1970 ( 8 ) .
The 1980s were marked by the rise of postgraduate programs, increased development of research and the generation of knowledge. The 1990s saw a boom in graduate, specialization, masters, and doctoral programs, the latter especially in education. However, there were also more options for the qualification of nursing professionals for the teaching role. On the other hand, the Higher Education Quality Assurance System ( Sistema de Aseguramiento de la Calidad de la Educación Superior ) was implemented, as well as the Accreditation of the programs and the own regulations or nursing law emerged in each country of the region.
The first decade of the 21st century brought the development of the highest level of nursing education, the doctorate, and, with it, the generation of nursing knowledge in the region and its progress towards consolidation as a discipline ( 8 ) .
Throughout this journey, there was a permanent motivation for balance and congruence between the graduation profiles and the reality of the job, based on the permanent motivation for the adaptation of the curriculum, the teaching-learning strategies, the evaluation processes, and the teacher qualification to respond to this constantly changing context.
The literature ( 9 - 11 ) shows the need to expand the research in the area of education, to achieve greater development of research and to work in education and nursing policies and practices. On the other hand, the latter shows the need to implement and evaluate pedagogical and didactic strategies that help the student to develop a critical judgment, justified decision making, comprehensive memory and communicative competence ( 11 ) .
For its part, the Ibero-American Network for Research in Nursing Education ( Red Iberoamericana de Investigación en Educación en Enfermería - RIIEE), in 2011, identified as a research priority, “The development of RACT in nursing students”, within the tree of the problems detected in its research line Higher Education and Nursing. For the development of this research purpose, the Network suggested a multicenter macroproject with the theme “Strategies to develop the RACT in nursing students: situation in Latin America”. In fact, the conceptual paradigm refers to “critical theory and constructivism, since RACT is an analytical, cyclical, broad and systematic process, but not rigid; its analysis and interpretation allows to have elements for decision-making, as well as to make informed choices” ( 8 - 12 ) .
The project involves five of the six regions that make up the RIIEE: the Andean region (Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru and Venezuela), Brazil, the Southern Cone, Europe, and Mexico and the Caribbean. The investigation is planned in three stages: 1. Diagnose; 2. Planning and implementation of interventions; and 3. Evaluation. The diagnostic stage includes: 1. The state of the art on scientific production in RACT and teaching strategies for its development; 2. Characterization of educational strategies for teaching the RACT collected in nursing literature; 3. To determine the development of the RACT competence in the different nursing curriculum; 4. To identify the educational strategies used by teachers to develop the competence of reflective critical thinking in nursing students; 5. To identify levels of critical thinking in nursing students according to the classification of Paul and Elder (unreflective thinker - master thinker). Objectives 4 and 5 are currently being developed.
The analysis of the “Scientific Production in RACT in Nursing in 1990-2012 in Ibero-America” produced among others the following conclusion: the formation of a critical reader and the investigative process are strategies that help university students to be critical and autonomous and to access more critically to the knowledge of the disciplinary area. For this, teachers are required to make of each moment and situation in the teaching-learning relationship an open forum for reflection, debate, questioning and contrasting of the different perspectives around the area of professional training and society’s problems ( 8 ) .
After reviewing the literature on the web of science by using the descriptors critical thinking and nursing, education and curriculum, it was not possible to find studies that analyzed the presence of RACT in the curriculum of nursing degree programs. However, it is very striking the motivation to analyze the importance of its development and studies that demonstrate its value, as well as the use of different and combined teaching-learning strategies to achieve the formation of RACT in nursing students.
This study was done with the purpose of to evaluate the teaching of transversal competence of the Reflective and Critical Thinking that is fundamental in the decision-making and solution of nursing problems, in degree programs of public and private institutions in the Andean region.
The coordinating group of RIIEE developed the research project from which the research groups of each country and region of the Network were made up, integrated by members of the Network and researchers in education and nursing, who are also teachers in Higher Education Institutions (HEI), and mostly with PhD academic level. The HEI in Nursing (HEIN) were identified through the Ministries of Education, the Associations of Schools and Universities of Nursing of each country and the Latin American Association of Schools and Universities of Nursing ( Asociación Latinoamericana de Escuelas y Facultades de Enfermería - ALADEFE).
The project was benefited from the Declaration of Helsinki (Ethical principles for medical research on human subjects) and the current ethics legislation in each country, was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Antioquia, Colombia, by Act No. CEI-FE 2015-25 on July 31, 2015. The respect for privacy and confidentiality were ensured to each Program Director, with the informed consent signed by each participant. The project was also sent to them and their understanding was guaranteed. In turn, we conceded the right to choose what information they wanted to share. Confidentiality was maintained by institutional coding. Finally, was given a deadline of 15 days to obtain the response of acceptance to participate.
The target population of this research were 187 undergraduate nursing programs in the Andean region: Bolivia (47), Colombia (47), Ecuador (21), Peru (62) and Venezuela (10). We considered only the nursing curriculum of the HEI, recognized by the Associations of Schools and Colleges of Nursing of each country or its counterpart, regardless of whether they were public or private. Resulting in the nursing curriculum of 76 Institutions that correspond to the 40.64% HEIN that teach undergraduate nursing in the Andean region: Bolivia (7), Colombia (38), Ecuador (11), Peru (14), and Venezuela (6). Due to the difficulty in obtaining the information, we checked web pages, contacted HEIN members, made contacts by telephone, in some cases, we made personal visits and, finally, the complete program was requested in PDF format for the complete the instrument of the research group. In addition, the HEIN did not refused to participate, but some institutions did not respond to the invitation. The result of this process: 30 institutions accepted to participate and provided the complete information, and out of 46 partial results were obtained. An HEIN database of the names, telephone numbers and e-mail addresses of the authorities in charge of managing the programs was created in order to follow up on their responses.
After identifying, during 2011 and 2012, the theoretical and conceptual framework of RACT from different authors and different perspectives (education, pedagogy, psychology and nursing), despite the abundance of literature about the subject, we concluded that the concept is very unclear from a nursing point of view ( 13 - 14 ) .
However, it was necessary to establish a concept that was accepted by the research group of the Network, that allowed to determine a starting point or consensus to carry out this work and, without detriment to seek some level of fidelity to the multiple approaches of the scholars of this research object, that was understandable for the group and reflected what was intended to be done in its research phases and stages.
The Network took as a theoretical framework the approaches made by Paul ( 15 ) and Paul; Elder ( 16 ) , the elements of the CT and the attitudes of the Critical Thinker proposed by these authors. With the material analyzed, RIIEE constructed the following concept: “Reflective and critical thinking is a complex, systematic and deliberate process of reasoning, self-directed and action-oriented. It is primary purpose to choose, based on intellectual and affective processes (cognitive, experiential and intuitive), the best response options that favor the solution of nursing problems, in well-defined contexts and in accordance with the ethical postulates of the profession that allow it to act with rationality and professional autonomy” ( 8 ) .
The research process included the conceptual and theoretical analysis of the curriculum, the updating of the context of research development in nursing education in each country of the region, the characterization of the HEIN and, finally, the results of the state of the art on teaching strategies for the development of the RACT 1990-2012, Andean region.
Once the exhaustive bibliographic review was carried out, the instrument was designed based on the concept of Stenhouse ( 17 ) , the curriculum as a macro concept that encompasses the socializing function of the school is at the same time pedagogical ideas, structure of contents in a particular form, precision of them, reflection of educational aspirations more difficult to translate in concrete terms and skills to promote in the students ( 16 ) . In Posner ( 18 ) , who raised the great number of phenomena involved in the curriculum; Gimeno-Sacristán; Pérez-Gómez ( 19 ) , there is five categories in which the definitions of curriculum can be articulated: as an organized knowledge structure, production technology system, instructional plan, set of learning experiences and problems solution.
Based on the aforementioned, the specific instrument for this investigation was constructed with three parts. The first with 10 items, with general information from the HEI or University. Each University is subdivided into Centers that are parted into Colleges and these are divided into programs: name, geographic location, type of institution, accreditation data, mission, vision, objectives, curricular guidelines for degree programs, web page, and data about who completed the instrument. The second, 28 items, for the College, School, Department or Nursing Program (typology to identify HEIN in the region), with the following subsections: general aspects of the nursing program, character within the institution, number of sites where the program is offered, accreditation data (date, resolution, and time of accreditation), program justification, mission, vision and objectives of the program, evaluation process, graduation profile, pedagogical model, number of hours and credits, curricular structure (nursing program subjects that correspond to each area or component). Finally, the general characteristics of the teachers: kind of affiliation with the institution, time worked, and maximum educational level achieved. The third, 9 items, for specific information about each of the subjects: name, component or area to which it belongs, number of hours and credits, type of subject (theoretical, practical and theoretical-practical), contents, teaching-learning methodologies and evaluation process.
The members of the research group carried out an analysis of the validity of the content of the instrument. Afterwards, the pilot test was conducted, starting with its implementation in each of the HEI in which the researchers worked; the results were analyzed and the corresponding adjustments were made in its structure. Subsequently, the adjusted instrument was tested with five members from the region, one from each country, but different from the research group. Because of this test, we decided to design a guide to facilitate the completion of the instrument and ensure objectivity in the collection of information, because of the language differences. It is possible to obtain the final version of the instrument from the authors of the project.
Each participant received the letter of invitation, the project, the informed consent, the instrument to collect the information and the corresponding guide for its completion in hands and by e-mail.
The information obtained was reviewed and, in some cases, it was necessary to request the complementation of some aspects of the instrument. Then we proceeded to codify the HEI or Universities and the HEIN. The information was included in Excel tables designed with the predetermined categories and subcategories, which were later incorporated into the SPSS statistical analysis program, version 19. The information was processed using descriptive statistics, with frequency distributions and average analysis, and analyzed by institution, by country and as an Andean region, according to the categories and subcategories determined, allowing comparisons between countries and conclusions to be drawn as a region.
The analysis of the information was carried out using the deductive-inductive method, considering the objectives of the project and the revised conceptual theoretical framework, with the aim of determining the presence of the RACT, explicit and implicit, in each categories, the coherence of the approaches between University-College-Program, the coherence between the objectives, contents, teaching-learning strategies and the evaluation process in each subject. In this sense, we analyzed the linearity or coherence with respect to what was proposed, developed and evaluated in relation to the RACT and, finally, the contradictions and inconsistencies found in the aforementioned approaches were pointed out. We considered national and international studies about the subject for the analysis and discussion of the results obtained, in addition to the documents mentioned above.
According to the information obtained by the research group, the Andean region has 2,552 HEI; 410 with character of universities and 160 are public, 220 are private and 14 are in special regime. There are 167 universities with nursing programs, 146 affiliated and recognized by the respective Associations of Schools and Colleges of Nursing in each country. The number of accredited nursing programs in the Andean region is 43: Colombia (20), Peru (20) and Bolivia (3). Precisely, of the 20 accredited institutions in Colombia, 11 already have their certifications renewed, which are of 8, 6 and 4 years; 5 and 6 years for Ecuador and 3 years for Peru. Bolivia is just beginning the process and Venezuela has no information about it.
The total population of HEIN by country was Bolivia 47, Colombia 42, Ecuador 21, Peru 62 and Venezuela 10. A total of 76 HEIN answered: Bolivia 7; Colombia 38; Ecuador 11; Peru 14 and Venezuela, 6. These institutions constituted the sample of the study.
Twenty-one of these institutions are certified: in Colombia 20 and in Bolivia 1; 12 did not include this information and 41 were not yet certificated. Of the total number of institutions that provided the information, 47 are public, 26 private and three do not know the information. Administratively, 36 are programs; 22 Colleges; 21 Schools and one Department.
The number of hours and credits of the programs showed considerable heterogeneity: the average number of hours was 5,552.3, corresponding on average to 232.11 credits. Regarding the number of hours per credit, the lowest is in Peru, which has 13 hours per credit, and the highest is in Colombia, with 48 hours corresponding to one credit. There are institutions that do not work with credits, especially in Bolivia; others did not included this information, among them Ecuador and Venezuela.
The main characteristics of the 912 teachers developing nursing programs in the Andean region are: 501 (54.9%) with a Specialist degree; 634 (69.51%) with a Master’s degree and 58 (6.35%) with a PhD; 249 (27.3%) with a postgraduate degree in Education.
From a general perspective, it should be noted that of the five countries in the region only Venezuela and Peru explicitly present the RACT in their Organic Law (OL) or Higher Education Law in terms of integral and permanent formation of reflective critical citizens (LOE, 2009, or Organic Law of Education, in Venezuela) ( 20 ) and (Law 30220, 2014, or University Law, in Peru) ( 21 ) .
The results of RACT’s presence are presented below: Universities or HEI; in Colleges, Programs, Schools and Departments, that is, in HEIN; and in the subjects.
When analyzing the information of the Universities or HEI, we found the RACT as direct mention, indirect mention and evidence of traditional positions was found. Directly, it was found as a training purpose in Bolivia, Colombia and Peru: receptor and analytical constructor, with critical conscience; as methodology to achieve it, in Colombia and Peru: “ promoting reasoning, the CT and creative”; as a result of learning in Ecuador and Venezuela: capable of solving problems, CT promoter.
The indirect mention was found as result in the five countries of the Region, as a strategy in Bolivia, Ecuador, Peru and Venezuela: integral formation, relation practical theory; and as objective in Colombia: future graduates with ethical conscience, autonomy, democratic spirit and highly qualified.
There are still traditional postures: teaching, evaluation as a final product, training in instrumental action, the educational process as providing knowledge.
By going a little deeper into the HEI, we found that 88% (38) consider the RACT: 63% (27) in the mission; 7% (3) in the vision; 51% (22) in the objectives and 30% (13) in the curricular guidelines. Among these, three defining categories were identified. The first, as a training purpose: prepare professionals and leaders with CT and social conscience . The second, as a methodological strategy to achieve its development: to develop and implement pedagogical methods that encourage reasoning, CT and creativity, and that encourage habits of discipline and productive work . And the third, as a result of the formation process that includes the subject: Training of critical, self-managed, creative and proactive men and women; and, moreover, refers to the projection and utility: with the promotion of CT and the generation of knowledge, thanks to the strengthening of critical analysis, anticipation and vision of the future and development of viable alternatives to the problems.
At HEIN, RACT is expressed in the graduation profile, objectives, curricular guidelines and mission. Table 1 shows the data summarized in relation to the number and percentage in which the RACT is presented in the subcategories and with regard to the total. The information recovered allows us to identify that the RACT ranks first with 38.3% in the graduation profile, followed by 35% both in the curricular guidelines and in the objectives; thirdly, is in the mission, 26.7%, and finally, with 11.7% it is in the vision. Bolivia has the highest percentage of presence in its curricular guidelines, followed by Colombia in its graduation profile, objectives, and mission, while Venezuela is in one before the last place with a 28% of presence in its mission and is not present in the profile or in the curricular guidelines. Peru has the last place and presents it only in the objectives of the programs.
| Countries | Institutions | Mission | Vision | Objectives | P. Graduation | Curricular guidelines | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RACT | % RACT | RACT | % RACT | RACT | % RACT | RACT | % RACT | RACT | %RACT | ||
| Venezuela | 7 | 2 | 28.6 | 1 | 14.3 | 1 | 14.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Peru | 15 | 2 | 13.3 | 1 | 6.7 | 4 | 26.7 | 3 | 20.0 | 3 | 20.0 |
| Ecuador | 13 | 1 | 7.7 | 3 | 23.1 | 3 | 23.1 | 3 | 23.1 | 10 | 76.9 |
| Bolivia | 7 | 3 | 42.9 | 2 | 28.6 | 3 | 42.9 | 2 | 28.6 | 7 | 100.0 |
| Colombia | 18 | 8 | 44.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 10 | 55.6 | 15 | 83.3 | 1 | 5.6 |
| Andean Region | 60 | 16 | 26.7 | 7 | 11.7 | 21 | 35.0 | 23 | 38.3 | 21 | 35.0 |
In a cross-sectional view of what is proposed by curricular programs, three categories were identified to be highlighted. The first, the development of cognitive and personal skills, expressed as the training of professionals with scientific, technical, critical, analytical and reflective knowledge, as well as communication, oral and written expression skills; and referred to a critical, creative, participative, supportive, innovative and sensitive attitude towards social change.
The second, the way in which its development could be achieved, among which the research stands out: promote and develop research, generating knowledge in the different areas of nursing that contribute to universal science and the solution of health problems; and the use of technologies: learns permanently developing the capacity of abstraction, analysis, synthesis and using information technologies . The third, its finality, related to the ability of individuals, families and community groups to interfere and make decisions in the solution of health problems, to provide comprehensive care with the capacity to solve health problems in changing and emerging environments.
Concerning the pedagogical models expressed in the HEIN, a variety was found in the denomination. First of all, the constructivist approaches are highlighted in eight (8) Institutions, with some connotations as the model social-critical-constructivist and second, the cognitive - humanistic in four (4). Other models or approaches were also identified, among them: dialectic, technological, psychological, the problematic schools, the Active, Reflective, Dialectic, Innovative and Critical . Finally one institution works with the model based on the pillars of education , in which learning to know, learning to do, learning to be and learning to live together, which includes, educating for life, educating for life, educating for work, educating in society and for society ( 22 ) .
The RACT in the subjects of the programs of Nursing in the Andean region
Only 29 of the 76 HEIN participants in the study were able to obtain information on subjects (38.15%), and 22 (75.86%) of these in nursing programs, RACT was present in different elements of the subjects. 562 subjects were reviewed, 159 (29%) of which have no information about teaching strategies or evaluation. Moreover, some programs record the same teaching and assessment strategies for all subjects in the program, 45 (8%).
Table 2 presents the results by subcategory and the total presence of RACT in the different groups of subjects, basic area or foundation subjects (which introduce and contextualize the student in the field of knowledge), Research, Humanities (the study of the behavior, conditions and performance of the human being), disciplinary professional area (gives the basic grammar of the profession and discipline) and those of the flexible area (the student chooses them according to personal interests, allow to the learner to approach, contextualize and study in depth aspects of the profession and discipline, allowing to learn tools and other kinds of knowledge, leading to develop interdisciplinarity, flexibility and diversity).
| Countries | Basic or Foundation | Research | Humanities | Disciplinary or Professional | Flexible Area | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub | RACT | % | Sub | RACT | % | Sub | RACT | % | Sub | RACT | % | Sub | RACT | % | |
| Peru | 21 | 7 | 33 | 12 | 6 | 50 | 2 | 1 | 50 | 53 | 29 | 55 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Ecuador | 56 | 6 | 11 | 13 | 1 | 8 | 27 | 6 | 22 | 96 | 24 | 25 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Bolivia | 17 | 4 | 24 | 7 | 3 | 43 | 6 | 4 | 67 | 64 | 27 | 42 | |||
| Colombia | 50 | 17 | 34 | 9 | 7 | 78 | 20 | 14 | 70 | 94 | 49 | 52 | 8 | 4 | 50 |
| Total | 144 | 34 | 24 | 41 | 17 | 42 | 55 | 25 | 47 | 307 | 129 | 42 | 15 | 4 | 27 |
The information provided makes it possible to indicate RACT as a subject: Workshop of Critical Thinking and Introduction to CT ; second, as a subject content: CT in Nursing, and, third, RACT is evidenced in teaching-learning strategies.
The highest percentage of subjects in which RACT is evident correspond to the area of humanities, with 46% (55), in which analysis of real situations, group work, concept maps, role playing and seminars are predominant.
In second place, it is in the professional-disciplinary area with 42% (307) subjects with the predominance of the following strategies: supervised clinical practice, clinical case, problem-based learning, simulation laboratories, and the nursing process. The research is in the same place, 42% (41) subjects. The most commonly used strategies are: critical discussions of research reports and articles, project development, workshops, and problem-based learning.
In the last place, subjects from the basic or foundation area 144 (24%). Including discussion workshops, concept maps and case studies.
A great variety of strategies have been identified, among them are: presentation and discussion of clinical case, group work, clinical practice, flipchart, observation guides, debates, discussion about specific topics, resolution of case studies, support of the nursing care plan, investigative reports , workshop development.
What is evaluated: the development of competencies, the acquisition of skills, the development of superior cognitive processes, the professional spirit and the development of processes and independence.
Finally, in some of the subjects, the intentionality of the evaluation of the RACT is explicitly presented: written works about the topics of each seminar in which the proper handling of the bibliography is evidenced, the capacity for criticism, analysis and synthesis, evidence of problem solving, case analysis and Nursing Based in Evidences , didactic relationship analysis and fundamental elements of the RACT, conceptual knowledge, written and oral reflections, group work, practical reflections and group discussions.
It is evident that traditional evaluation techniques still exist: evaluating procedural aspects, dexterity, motivation and initiative in the procedures, memory evaluation, participation in class, oral and written interventions and, finally, the replication of the topics studied in classes.
Therefore, the analyzed programs show interest in including as an important element in their future graduates the development of the RACT. This aspect is vanishing in the development of the subjects. It is evident in the pedagogical strategies, but it is lost until disappearing in most of the evaluative processes.
The analysis results of the plans and programs of the HEI and HEIN allow to conclude that the proposes of the Law of Higher Education to develop the RACT in the students does not guarantee that it is included in the subjects and evaluations.
What is stated in HEI and HEIN allows us to infer that epistemological and theoretical contradictions are present in the Institutions and among them. It makes necessary an epistemological, theoretical and methodological consideration in order to achieve alignment and coherence between the purposes in the curricular guidelines and what is programmed in the curricular plans for the concrete work with the students. This matter goes against comprehensive training, since it is demonstrated that critical and reflective skills contribute to train professionals with greater ability to care for patients ( 23 ) .
It should be noted that it is the University or HEI that determines the philosophical bases that will guide the academic units that compose it, so that they, in turn, incorporate these principles into their academic programs. The results show that there is no linearity between the proposals of the university with respect to its mission, vision, objectives, graduation profile, curricular guidelines, and what is proposed in the nursing degree programs. There is more linearity in Institutions with a longer trajectory and development, private and public ones.
The analysis of the areas in which the subjects are grouped made it possible to identify that the subjects of the humanities area have the highest percentage of presence of the RACT. This result can be explained by the strategies used, but even more by the subjects under study, since it has been demonstrated that the teaching-learning strategies based on the humanities have a significant impact on the development of skills such as clinical reasoning ( 24 ) . The subjects in the professional area use strategies such as case study, supervised clinical practice and other relatively new ones as problem-based learning and simulation laboratories. Strategies that, by involving simulation or potential practical actions, contribute to enhance critical skills and make decisions that lead to the future professional committing fewer errors during the care of patients ( 25 - 26 ) .
By contrast, it is not the same with the subjects of the foundation or basic area in which it is necessary to return to some knowledge aspects that already exists, such as anatomy, physiology, anthropology, psychology, statistics, among many others. For some students these topics are very difficult and involve, on several occasions, an excellent dose of memory. However, the teaching strategies that develop the RACT are not so frequent. It is important doing more research on this point to sustain if it is true.
On the other hand, for the majority of HEIN, training is conceived as qualification and progress achieved by people and as a principle of theories, concepts, methods, models, strategies and courses of pedagogical action that aim to understand and qualify the teaching. In some cases, the transfer of knowledge is approached, but it still underlies the concept of learning as acquisition of knowledge built and finished; the teacher is the one who has the knowledge and the student is who learns what teacher knows.
The curricula of the Andean region include explicit elements that contribute to the development of the RACT, such as reading, writing and reasoning, allowing to the future professional to know how to learn, reason, think creatively, generate and evaluate ideas, make decisions and solve problems ( 24 ) . It includes as proposals the development of social skills, with emphasis on oral and written communication, cognitive skills including problem solving, establish different alternatives, understand the consequences of actions, make decisions and critical thinking ( 16 ) . Also, intend to achieve in the student some characteristics of the critical thinker like to be creative, innovative, proactive, analytical, participatory, entrepreneurial, self-critical, supportive, humanistic, ethical and scientific ( 27 ) .
Regarding the pedagogical models proposed by the HEIN, inconsistencies between the approach of constructivist approach and meaningful learning are evident. The axis is the student and the repetitive approach in the subjects with master class methodology, reading guides and analysis made by teacher, but not by the student. It shows a traditional model centered on the teacher, with an emphasis on memory, comprehension and the application of concepts. Some subjects focus learning on the acquisition of concepts, despite using the integrating project as a teaching-learning strategy, workshops and practice as evaluation. The pretense for the development of the RACT is not in line with the evaluation, with the examination, in the application of contents, since it is centralized in aspects of memory and knowledge, in an asymmetric theory-practice relationship.
Although significant learning is intended and the importance of integrating it into the formation of learning approaches with the intention of promoting critical thinking, added with successful learning experiences ( 28 ) , it is not really concrete how it could be achieved. Strategies such as simple repetition and teaching for the acquisition of concepts show the persistence of the traditional educational models.
This study found there is no a clear structure to operationalize the theories of the proposed pedagogical models, even though there are expressions that point to RACT. Thus, the elements important for its development are presented in the teaching and learning strategies in a more remarkable way.
The curricular guidelines express the intention to transcend technical rationality and behavioral objectives ( 29 ) , from the positivist, rationalist or empirical analyst paradigm, to the humanist and critical curriculum ( 30 ) to the socio-critical paradigm and critical thinking based on hermeneutic processes ( 31 ) . The social and contextual (political, economic and cultural) aspects that influence and determine the health behaviors of the people are still incipient in the curricula ( 32 ) .
According to what has been demonstrated, it is possible to state that there is no predominance of a pedagogical model, but a mixture of several models in the same program with varied influences. The presence of the following models was identified: Traditional Pedagogical, Behavioral, Cognitive, and Social Pedagogical, the latter being very tenuous ( 33 ) .
There are four fundamental elements to forming critical thinkers: first, the question; second, the creation of continuous opportunities to participate in dialogue, debate, research, and critique; third, self-evaluation and hetero-evaluation; and fourth, teachers as models of critical thinkers ( 32 ) . Considering these elements, we can assure that the creation of opportunities is present with more intensity in some curricula, and self-evaluation and hetero-evaluation have begun to be implemented especially in public institutions.
Mentioning the subjects, it is not evident that the thought is motivated by complex kind of questions that encourage exploration, generate evaluation, create concepts and knowledge ( 33 ) .
The literature points out that the Socratic questions stimulate the student to use existing knowledge, since they promote a greater understanding and integration of new knowledge, they foment the habit of thinking critically ( 8 , 34 ) . Other authors suggest, for the reports, questions about the purpose, information, concepts, assumptions, implications, points of view and the questions, as elements that favor analysis, the evaluation of ideas and reasoning ( 24 , 35 ) .
Like other researches, this study found that the most used strategies in the progress of the professional area that promote the development of RACT are the case study ( 24 , 36 ) , problem-based learning ( 24 ) , supervised clinical practice ( 37 ) , the nursing process ( 4 , 38 ) and simulation laboratories ( 34 , 37 - 38 ) . In this article, we only refer to two of these strategies, which were selected because of the great advance of information and communications technologies. The growing need to access this kind of infrastructure as a fundamental part in the training of future professionals and as an example of a single teaching and learning strategy is not sufficient to achieve the RACT, rather, the use of different techniques enhance its development, as we will see below.
We agree with the conclusion of authors who suggest that Problem-Based Learning and simulation labs are active strategies that develop RACT in nursing students ( 37 ) .
The case study, moreover, promotes active learning, helps to solve clinical problems, promotes the development of critical thinking skills ( 34 - 35 ) , in addition, it allows to integrate knowledge, to think as a professional, to analyze individual situations in specific contexts from different angles, to use theoretical concepts in the delimitation of a concrete problem ( 36 ) . It also stimulates collaborative and team work, the work with different points of view. The question-problem is the motivator in the search for alternative solutions, is useful in simple and complex situations, allows to apply theory in practice, promotes the exchange of ideas, teaches students to learn to control their own thinking and promote the exchange of ideas and intellect ( 37 ) . In addition, it helps to incorporate time management and take responsibility. It also facilitates the integration of the four elements of the Nursing metaparadigm: the person receiving the care, health as purpose, the nature of the nursing and the context or environment.
The case study allows the simultaneous implementation of other strategies that further enhance the development of RACT, such as concept maps, the analysis and selection of scientific evidence, the nursing process, nursing history, role-playing, argued discussion and debate.
In contradiction to all the positive aspects of the case study in the development of RACT, the dichotomy between theory and practice in a large number of the curricula reviewed is an obstacle to achieving all the benefits pointed out. Since some teachers are in charge of the development of the theoretical subject in the classroom, others are in charge of their practical part in other spaces that require this care.
Regarding the practice based on simulation models, a study ( 38 ) shows how the promotion of RACT is relevant. In this connection, it highlights the importance of including simulation as a key element in curricula, because it ensures skills in this kind of thinking ( 38 ) and gives students the opportunity to show their ability in decision-making, critical thinking and other skills ( 39 ) . Other authors emphasize its importance when students reflect it on their thinking process and show how it guided their actions ( 34 ) .
There is efficiency of simulation laboratories when accompanied by active strategies, such as the conceptual map before each laboratory session, a visual aid that allows the concepts, objectives, justification, expected results and possible complications to be described in a logical manner if the procedure is not carried out in the appropriate manner ( 34 ) . The same author suggests the use of high-level questions to stimulate reason more than memory. He also suggests assigning an observer, who will ensure analysis and reflection on patient safety, communication, teamwork and leadership, among others ( 34 ) . The reflection of the group around the whole process carried out will be the end of the laboratory ( 15 , 34 ) .
Another study concluded that simulation as a pedagogical method allows students to recognize, interpret and integrate new information with previous knowledge in order to make decisions about the best direction to follow. The authors state that simulation, as an educational method, provides an opportunity to systematically structure learning to help students acquire deep content knowledge and to facilitate the development of thought processes; that simulation experiences stimulate students’ RACT skills and help them become more competent in caring for patients in complex conditions ( 37 ) .
We agree with what has been found in other studies emphasizing that simulation laboratories by themselves do not guarantee the development of RACT skills, but if combined with other strategies and implemented with adequate pedagogy, the results will be much more effective in terms of CT skills ( 34 , 37 - 38 ) .
It is also possible to find correspondence with that was discovered in the State of the Art of scientific production in RACT in the Andean region. The students perceive that “Clinical simulation is a valuable strategy for the acquisition, complementation and integration of the theoretical part with the practical part, because it seeks to make decisions according to the CT” ( 38 ) .
The evaluation of the subjects is cumulative and formative. In some cases, a diagnosis of the level of the student’s participation in the subject is made; it is evaluated in the intermediate and at the end with the objective of promotion to another level. In other cases, a teaching-learning balance is done to verify the fulfillment of the objectives and competences. Self-evaluation and heteroevaluation are increasingly used, implying a process of reflection, analysis and self-criticism.
Precisely, evaluation appears as one of the weakest points when analyzing the presence of RACT in curricula. Therefore, we agree that the “best teaching practice begins by establishing learning outcomes and continues with a focus on helping the student to achieve satisfactory results”. If the proposal is to achieve a higher order thinking, the evaluation will be oriented towards the synthesis, analysis and evaluation of knowledge ( 40 ) .
Overall, the strong approaches to RACT training formulated at HEI, HEIN, as evidenced by some of the teaching and learning strategies presented in the subjects, become much weaker in the evaluation process, with predominance of traditional evaluation models, and in some cases, the intention to evaluate RACT is outlined.
The curricula of Colleges and Schools of Nursing in the Andean region explicitly contemplate reflective and critical thinking in their mission, vision, objectives, graduation profile and didactic strategies, and implicitly as integral formation. However, there is a tension between what is proposed by the HEI and HEIN and what is implemented and evaluated in the subjects. The presence of RACT in the proposed didactic strategies is much more evident, but it is not sufficiently objective or explicit in the evaluation processes.
Despite the great diversity of pedagogical models, there is a clear intention to facilitate the development of RACT. In addition, although a constructivist model is proposed centered on the student, dialogical, active, reflexive, innovative and critical, this model is more centered on the teacher than on the student; on knowledge over a relationship between equals; more on results than on the learning process. Likewise, knowledge is considered as something finished, fixed and the ultimate truth.
In order to be able to teach the RACT to the nursing student it is necessary to include it in the nursing curriculum, teachers who are professionals in the areas of Education and Nursing and with RACT in their training. Teachers should create spaces for the development of RACT, know and implement the different and complementary didactic strategies that facilitate its learning and that analyze the students in relation to the level of RACT achieved.
The authors of this article suggest that the projects currently developed with teachers and students in Ibero-America should be finalized and retaken with the implementation and evaluation of strategies that value the development of RACT.
RACT is considered an indispensable element in personal and professional development, in order to have autonomy, confidence, the ability to make decisions, reach clinical judgment and, the most important, provide individualized, comprehensive and human nursing care. In summary, graduates should be able to work as members of the health team with sufficient clarity of the role and identity they should have, because they have to integrate and experience the four paradigms of the Nursing.
The limitations of the study are
The complexity of the project due to the number of participating countries and the different research groups;
The large number of public and private nursing schools and colleges in the Andean region;
The limitation in accessibility to the complete information of the curricula of each institution;
The minimal presence of information on the official web pages of each institution, school or nursing college;
No response and lack of interest from different schools and nursing colleges, public and private, to participate of this project;
Limited access of current and recent updates of the curricula of nursing colleges to develop this project.
The research group made efforts to reduce these limitations and devised multiple options that were proposed to the institutions, in order to facilitate the provision of information and its complementation when necessary.
Applications for practice
The innovation and contributions expected with this research are based fundamentally on documenting and analyzing of the diverse existing evidences about if RACT is contemplated in the nursing curricula or not, the strategies used by teachers to create and promote it in nursing students and the evaluation processes employed. It provides insights about how RACT’s competence in nursing is addressed in the context of the Andean region and other regions of Ibero-America, its weaknesses and strengths, as well as the improvements that can be made. The final intention of the research is to offer, as a network and collegial body, proposals for teaching, learning and evaluation that will enable the empowerment of new generations of nurses, using RACT as a center of innovation and development.

COMMENTS
Critical thinking in nursing is invaluable for safe, effective, patient-centered care. You can successfully navigate challenges in the ever-changing health care environment by continually developing and applying these skills. Images sourced from Getty Images. Critical thinking in nursing is essential to providing high-quality patient care.
The following are examples of attributes of excellent critical thinking skills in nursing. 1. The ability to interpret information: In nursing, the interpretation of patient data is an essential part of critical thinking. Nurses must determine the significance of vital signs, lab values, and data associated with physical assessment.
Critical thinking is applied by nurses in the process of solving problems of patients and decision-making process with creativity to enhance the effect. It is an essential process for a safe, efficient and skillful nursing intervention. Critical thinking according to Scriven and Paul is the mental active process and subtle perception, analysis ...
Strategies to overcome obstacles in the facilitation of critical thinking in nursing education. Nurse Education Today, 25 (4), 291-298. 10.1016/j.nedt ... Concept mapping can help both newly registered staff and nursing students develop the critical thinking skills they lack. Nursing Management (Harrow), 14, 28-31. 10.7748/nm2008.02.14 ...
To investigate the impact of web-based concept mapping education on nursing students' critical-thinking and concept-mapping skills. 34: Zarshenas et al., 2019 : n = 90: 2 h for 6 days: Problem-solving: To investigate how training problem-solving skills affected the rate of self-handicapping among nursing students. 33: Svellingen et al., 2021 ...
For example, a nurse might be tasked with changing a wound dressing, delivering medications, and monitoring vital signs during a shift. However, it requires critical thinking skills to understand how a difference in the wound may affect blood pressure and temperature and when those changes may require immediate medical intervention.
The following benefits of critical thinking highlight the importance of this skill in nursing careers: Improves decision-making speed. A critical thinking mindset can help nurses make timely, effective decisions in difficult situations. A systematic method to evaluate decisions and move forward is a powerful tool for nurses.
A popular strategy to teach critical thinking skills in nursing education is simulation. Both live and virtual simulation can be implemented to improve critical thinking skills and clinical outcomes. Shin et al. (2015) studied the effects of multiple simulation exposures on critical thinking skills.
The concepts from an escape room are a great way to deliver opportunities for students to practice this skill and can be provided economically and easily. Being creative in managing these concepts will offer an exciting chance to introduce critical thinking for your students. Nursing Education Perspectives42 (6):E145-E146, November/December 2021.
It has been emphasized that critical thinking and decision-making skills are at the center of all nursing curricula in nursing education (Lee et al., 2017; Reji & Saini, 2022). The literature has studies generally conducted with senior nursing students ( Durmaz Edeer & Sarıkaya, 2015 ; Günerigök et al., 2020 ).
Critical thinking is a complex, dynamic process formed by attitudes and strategic skills, with the aim of achieving a specific goal or objective. The attitudes, including the critical thinking attitudes, constitute an important part of the idea of good care, of the good professional. It could be said that they become a virtue of the nursing ...
Building critical thinking skills is one of the most important outcomes in the clinical setting for nursing students. Collaboration with nursing faculty during the clinical rotation can ease the burden on direct care nurses and facilitate a positive learning experience for the student. The nursing profession continues to experience several ...
Critical thinking skills cannot be taught by rote learning and relying on traditional lecture-based education only. Therefore, innovative active learning strategies are demanded as critical thinking skills in nursing students are crucial and should be started with early acquisition to equip nursing students' capacities to become critical thinkers.
Although previous literature reviews have been conducted relative to CT in nursing education, few recent systematic reviews have been conducted. This systematic review aims to review qualitative studies from 2002 to 2011, in order to explore how critical thinking is perceived in the studies of nursing education, and the obstacles and strategies ...
Since the 1980s, critical thinking has become a widely discussed component of nurse education, and a significant factor for National League for Nursing (NLN) nursing school accreditation. Nursing school curriculum is expected to teach students how to analyze situations and develop solutions based on high-order thinking skills.
Studies have shown that critical thinking skills in nurses are linked to lower hospital costs to patients, as well as to the facility thanks to lower in-hospital complications (3). ... Zhang C, Jin C. The effectiveness of concept mapping on development of critical thinking in nursing education: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nurse Educ ...
In summary, critical thinking is an integral skill for nurses, allowing them to provide high-quality, patient-centered care by analyzing information, making informed decisions, and adapting their approaches as needed. It's a dynamic process that enhances clinical reasoning, problem-solving, and overall patient outcomes.
The main critical thinking skills in which nursing students should be exercised during their studies are critical analysis, introductory and concluding justification, valid conclusion, distinguish of facts and ... Key Words: critical thinking, nursing education, clinical nurse education, clinical nursing practice doi: 10.5455/aim.2014.22.283 ...
Nursing critical thinking skills drive the decision-making process and impact the quality of care provided," says Georgia Vest, DNP, RN and senior dean of nursing at the Rasmussen University School of Nursing. For example, nurses often have to make triage decisions in the emergency room. With an overflow of patients and limited staff, they ...
Critical thinking is a complex, dynamic process formed by attitudes and strategic skills, with the aim of achieving a specific goal or objective. The attitudes, including the critical thinking attitudes, constitute an important part of the idea of good care, of the good professional.
Flipped teaching is an interactive learning strategy that actively engages students in the learning process. Students have an active role in flipped teaching as they independently prepare for the class. Class time is dedicated to discussion and learning activities. Thus, it is believed that flipped teaching promotes students' critical thinking, communication, application of knowledge in real ...
Critical Thinking. Nursing education has emphasized critical thinking as an essential nursing skill for more than 50 years. 1 The definitions of critical thinking have evolved over the years. There are several key definitions for critical thinking to consider. ... and complexity of care demand higher-order thinking skills. Critical thinking ...
Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement. Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process ...
In everyday life, critical thinking might involve analyzing news reports to identify potential biases or considering the long-term implications of a major financial decision. How to build critical thinking skills for better decision-making. Building critical thinking skills requires practice and a deliberate approach.
This underscores the pressing need to enhance their critical thinking skills to a higher level, enabling them to effectively process a variety of media information. ... Journal of Nursing Education, 33(8), 345 - 350. doi: 10.3928/0148-4834-19941001-05 Facione, P. A. (1990). Critical Thinking: A Statement of Expert Consensus for Purposes of ...
Given the crucial role critical thinking bears in education, it is time for the Higher Educational Institutions (HEIs) to prioritize its cultivation in the teaching-learning processes by promoting a culture of questioning, epistemic curiosity, joyous exploration, and open-mindedness. ... While generic critical thinking skills may cut across ...
Incorporating Critical Thinking Skills in Medical Education July 22, 2024 Clinicians today need strong critical thinking skills in order to properly diagnose and treat…
Soft skills and flipped classrooms are important in the fields of education, nursing, and health techniques. This study determined nursing teachers' knowledge of soft skills and flipped classrooms. This was a descriptive cross-sectional study with an analytical focus involving 100 teachers. The study was conducted at the Higher Institute of Nursing Professions and Health Techniques (ISPITS) at ...
The Doctor of Nursing is a 4 year coursework and dissertation based program offered via the distance and open learning mode. The program is for nurses to pursue their career pathway in clinical, education and research, while honing their critical and analytical thinking and decision making skills.
76 nursing programs participated in the study. The Reflective and Critical Thinking was found as a subject, subject content and didactic strategies. Of the 562 subjects reviewed, this type of thinking is found in 46% of the humanities area and 42% in the area of research and professional discipline. It is important to train teachers to achieve ...