- Math Lessons Online

Lesson 3 Homework Practice Solve Equations with Rational Coefficients

You’re now diving into Lesson 3 , where your mission will be to tackle equations with rational coefficients. The term ‘rational coefficients’ is intimidating. But don’t worry! We’re here to break it down. A rational coefficient is a fancy term for a number that can be formulated as a ratio of two integers. It provides a logical framework to tackle complex equations.
Overview of solving equations with rational coefficients
First up, let’s take a clear look at equations. You can think about equations like balanced see-saws. Whatever you do on one side has to be balanced out on the other side. Equations with rational coefficients can be easily simplified by manipulating the fractional coefficients to isolate the variable.
Step 1: Identify the rational coefficient. The fraction in the equation is multiplied by the variable (e.g., 2/3x = 4).
Step 2: To isolate your variable, you will perform the inverse operation to eliminate the rational coefficient. You’ll multiply both sides of your equation by the reciprocal of your rational coefficient.
Example: Let’s use the equation above. If we multiply both sides of 2/3x = 4 by 3/2 (the reciprocal of 2/3), we get 1x = 6. And voila, you have your solution.
In just a few steps, you’ve tackled equations with rational coefficients. Don’t let challenges discourage you in mathematics. It involves estimation, trial and error, and practice. But you can master it. Keep practicing, be persistent, and continue to hone your problem-solving skills . Remember, every mathematician learns at their own pace. You got this!
Practice is the key here, so nail down these steps and tackle additional problems independently. Happy solving!
The Concept of Rational Coefficients
You’ve made it to Lesson 3 , where you’ll tackle problems including rational coefficients. It might seem daunting at first, but with a systematic approach and a little practice, you’ll quickly learn how to navigate this mathematical territory.
Explanation of rational coefficients and their role in equations
In algebra, a rational coefficient is a ratio of two integers with a zero denominator. It is important to remember that these coefficients, just like any number in an algebraic equation, can be manipulated through the usual multiplication, division, addition, and subtraction.
Now, you ask, how do rational coefficients affect the equation? These coefficients play a pivotal role in determining the solution to the equation.
Here is how you can approach it:
Step 1: Simplify the equation. If you have fractions in the equation, sometimes called rational numbers , making them whole numbers is easier. You can multiply every term with the least common denominator (LCD).
Step 2: The next step is to use simple math techniques to find the variable. It is fundamentally the same as solving any basic algebraic equation –addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are your friends.
Step 3: Remember to check if your solution is correct. Substitute the solution into the original equation and see if both sides balance.
Remember: The key to mastering equations with rational coefficients is understanding and accurately manipulating these coefficients to find your solution.
Remember, the key to success is consistent practice. Each equation you tackle improves your skill and confidence. Solving equations with rational coefficients will be easy. Good luck!
Let’s recap:
| Steps | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Step 1: Simplify the equation | Multiply every term with the least common denominator (LCD) to make them whole numbers. |
| Step 2: Solve for the variable | Use elementary operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) to solve for the variable. |
| Step 3: Check your solution | Substitute the solution back into the original equation to verify if both sides balance. |
Techniques for Solving Equations with Rational Coefficients
As an aspiring mathematician or someone trying to polish their math skills , navigating the world of equations with rational coefficients can sometimes seem daunting. Worry not! Let’s simplify the process into two easy-to-follow steps: clearing fractions and cross-multiplication.
Step-by-step methods for solving equations with rational coefficients
Step 1: Identify the equation with a rational coefficient. Rational coefficients are fractions expressed as a ratio of two integers.
Step 2: Apply one of the strategies below to solve the equation.
- Method 1: Clearing Fractions
Wherever you see fractions, simplify them!
Step 1: Multiply each term in the equation by the fraction’s denominator to clear the fractions.
Step 2: Carry out the arithmetic operations and solve the equation.
Step 3: Check your work by substituting the solution into the original equation. If it makes the equation true, then your solution is correct.
- Method 2: Cross-Multiplication
When your solution is a proportion, this method works well.
Step 1: Use cross-multiplication if two fractions are set equal.
Step 2: Multiply the terms diagonally and set the products equal.
Step 3: Solve for the variable.
Step 4: Verify your solution by plugging it into the original equation.
Please make no mistake: the key to mastering mathematical equations is through practice, and lots of it. Please don’t avoid making mistakes; use them to strengthen your understanding and sharpen your skills. Get your homework and apply the strategies you learned. You can solve these problems if you keep practicing. With unwavering dedication and practice, you can conquer any equation that comes your way.
Examples and Practice Problems
You’ll come across equations with rational terms as you learn math. At first, it might seem challenging, but after reading this blog, you can do it like a pro!
Solving equations with rational coefficients through examples and practice problems
As you embark on your mathematical journey, you are bound to encounter equations with rational coefficients. By the end of this guide, you will be a pro at solving these types of equations.
- Example 1: Clearing fractions and solving for the variable
Take this equation: 3/4x = 6. First, clear out the fraction by multiplying both sides of the equation by 4. You’ll get 3x = 24. Now, try solving for ‘x’ by dividing 24 by 3. Your answer will be x = 8.
Now let’s practice:
- Try solving 2/7y = 6.
- Keep in mind the steps followed in the example.
- Clear the fraction, isolate the variable, and solve for ‘y’.
- Example 2: Cross-multiplication to solve for the variable
Here’s our equation: 4/5 = x/10. Cross-multiplication involves multiplying the fraction’s numerator on the left by the fraction’s denominator on the right and vice versa. This gives us 4 10 = 5 x, which simplifies to 40 = 5x.
Proceed with the operation: Solve for ‘x’ by dividing both sides by 5, which leaves us with x = 8.
Time to practice: Try the same steps with the equation 3/4 = y/12. Follow this example above, and you can solve this equation effectively.
In both types of equations, remember always to check your answers. Substituting your calculated value into the original equation should give you a true statement. These tutorials can guide you in solving complex equations and hone your skills.
- Grade 1 Lessons
- Grade 2 Lessons
- Grade 3 Lessons
- Grade 4 Lessons
- Grade 5 Lessons
- Grade 6 Lessons
- Grade 7 Lessons
- Grade 8 Lessons
- Kindergarten
- Math Activities
- Math Tutorial
- Multiplication
- Subtraction
- #basic mathematic
- #Basic Mathematical Operation
- #best math online math tutor
- #Best Math OnlineTutor
- #dividing fractions
- #effective teaching
- #grade 8 math lessons
- #linear equation
- #Math Online Blog
- #mathematical rule
- #mutiplying fractions
- #odd and even numbers
- #Online Math Tutor
- #online teaching
- #order of math operations
- #pemdas rule
- #Point-Slope Form
- #Precalculus
- #Slope-Intercept Form
- #Tutoring Kids

Thank you for signing up!
GET IN TOUCH WITH US
- Toggle navigation
Mathematics Department Course Hub
- Project Profile
- Course Outline
- Official Textbooks
- Video resources
- Faculty Announcements
- Course Coordination
- WeBWorK – Faculty Resources
- Training and Support
- STEM Applications
- Lesson 3: Solving Rational Equations
Hi Everyone!
On this page you will find some material about Lesson 3. Read through the material below, watch the videos, and follow up with your instructor if you have questions.
Table of Contents
In this section you will find some important information about the specific resources related to this lesson:
- the learning outcomes,
- the section in the textbook,
- the WeBWorK homework sets,
- a link to the pdf of the lesson notes,
- a link to a video lesson.
Learning Outcomes.
- Solve a rational equation.
- Check the potential solutions.
Topic . This lesson covers Section 5.5: Solving Rational Equations.
WeBWorK . There is one WeBWorK assignment on today’s material:
FractionalEquations
Lesson Notes.
Video Lesson.
Video Lesson 3 (based on Lesson 3 Notes)
Warmup Questions
These are questions on fundamental concepts that you need to know before you can embark on this lesson. Don’t skip them! Take your time to do them, and check your answer by clicking on the “Show Answer” tab.
Warmup Question 1
Solve $$\dfrac{3x+5}{x}=2,$$ and check your answer.
Show Answer 1
$$\dfrac{3x+5}{x}=2$$
Multiplying both sides by $x$ gives
$$3x+5 = 2x$$
Check : $$\dfrac{3(-5)+5}{-5}=\dfrac{-10}{-5} =2$$
Warmup Question 2
What is the LCD (least common denominator) of
$$\dfrac{1}{x^4}, \dfrac{x^3}{x^2-1}, \quad\text{and}\quad\dfrac{x-1}{2x(x+1)}?$$

Show Answer 2
The LCD is $2x^4(x^2-1)$.
If you are not comfortable with the Warmup Questions, don’t give up! Click on the indicated lesson for a quick catchup. A brief review will help you boost your confidence to start the new lesson, and that’s perfectly fine.
Need a review? Check Lesson 1 .
Quick Intro
This is like a mini-lesson with an overview of the main objects of study. It will often contain a list of key words, definitions and properties – all that is new in this lesson. We will use this opportunity to make connections with other concepts. It can be also used as a review of the lesson.
A Quick Intro to Solving Rational Equations
Key Words. Solution to an equation, rational equation, LCD (least common denominator), checking potential solutions.
The first step in solving a rational equation is to clear the denominators. For example, in the equation
$$\dfrac{2}{x}=\dfrac{x}{2}$$
the LCD is $2x$. Multiplying both sides by $2x$ clears the denominators.
\begin{align*} \dfrac{2}{x}\cdot 2x&=\dfrac{x}{2}\cdot 2x\\2\cdot 2& = x\cdot x\\4 &=x^2\\x^2&=4\\x&=\pm 2\end{align*}
The potential solutions are $x=\pm 2$. We now need to check them.
$\bullet$ Check: $x=-2$
\begin{align*}\dfrac{2}{-2} &\stackrel{?}{=}\dfrac{-2}{2} \\-1 &= -1 \quad\checkmark \end{align*}
$\bullet$ Check: $x=2$
\begin{align*}\dfrac{2}{2} &\stackrel{?}{=}\dfrac{2}{2}\\1&=1 \quad\checkmark \end{align*}
The solution set is $\{-2,2\}$.
Now watch the video lesson to see that, depending on the equation, another approach can be taken. You will see that it is important to always check the solutions.
Video Lesson
Many times the mini-lesson will not be enough for you to start working on the problems. You need to see someone explaining the material to you. In the video you will find a variety of examples, solved step-by-step – starting from a simple one to a more complex one. Feel free to play them as many times as you need. Pause, rewind, replay, stop… follow your pace!
A description of the video
In the video you will see how to solve
$$\dfrac{x}{x-1}-\dfrac{1}{x} = \dfrac{3}{2}$$
in two ways.
Try Questions
Now that you have read the material and watched the video, it is your turn to put in practice what you have learned. We encourage you to try the Try Questions on your own. When you are done, click on the “Show answer” tab to see if you got the correct answer.
Try Question 1
$$\dfrac{12}{x}-\dfrac{12}{x-5}=\dfrac{2}{x}.$$
$$\dfrac{12}{x}-\dfrac{12}{x-5}=\dfrac{2}{x} $$
The LCD is $x(x-5)$. We multiply both sides of the equation by $x(x-5)$.
\begin{align*}\dfrac{12x(x-5)}{x}-\dfrac{12x(x-5)}{x-5} &=\dfrac{2x(x-5)}{x} \\12(x-5) – 12x&= 2(x-5) \\12x-60-12x& = 2x-10 \\-60& =2x-10 \\-50 &= 2x\\2x &= -50\\x&=-25\end{align*}
The potential solution is $x=-25$. The next step is to check it.
$\bullet$ Check: $x=-25$
\begin{align*}\dfrac{12}{x}-\dfrac{12}{x-5}&=\dfrac{2}{x} \\\dfrac{12}{-25}-\dfrac{12}{-25-5} & \stackrel{?}{=}\dfrac{2}{-25} \\ -\dfrac{12}{25} + \dfrac{12}{30} &\stackrel{?}{=} – \dfrac{2}{25} \\-\dfrac{12\cdot 6}{150} + \dfrac{12\cdot 5}{150} &\stackrel{?}{=} – \dfrac{2}{25} \\ \dfrac{-72+60}{150} &\stackrel{?}{=} – \dfrac{2}{25}\\\dfrac{-12}{150} &\stackrel{?}{=} – \dfrac{2}{25} \\-\dfrac{2}{25} &\stackrel{?}{=} – \dfrac{2}{25} \quad\checkmark \end{align*}
Therefore the solution set is $\{-25\}$.
You should now be ready to start working on the WeBWorK problems. Doing the homework is an essential part of learning. It will help you practice the lesson and reinforce your knowledge.
It is time to do the homework on WeBWork:
When you are done, come back to this page for the Exit Questions.
Exit Questions
After doing the WeBWorK problems, come back to this page. The Exit Questions include vocabulary checking and conceptual questions. Knowing the vocabulary accurately is important for us to communicate. You will also find one last problem. All these questions will give you an idea as to whether or not you have mastered the material. Remember: the “Show Answer” tab is there for you to check your work!
- What is the difference between an expression and an equation?
- What does it mean to solve an equation?
- Is it necessary to check your answer if you know you have not made a mistake? Explain.
$\bigstar$ Solve $$\quad\dfrac{y}{y+3}+\dfrac{3}{y-3} = \dfrac{18}{y^2-9}.$$
Show Answer
The LCD is $y^2-9$ or $(y-3)(y+3)$.
\begin{align*}\dfrac{y}{y+3}+\dfrac{3}{y-3} & = \dfrac{18}{y^2-9}\\(y-3)(y+3)\left(\dfrac{y}{y+3}+\dfrac{3}{y-3}\right) &= (y-3)(y+3)\dfrac{18}{y^2-9}\\\dfrac{y(y-3)(y+3)}{y+3}+\dfrac{3(y-3)(y+3)}{y-3}& =\dfrac{18(y-3)(y+3)}{y^2-9} \\y(y-3)+3(y+3) & = 18 \\y^2-3y+3y+9 & = 18\\y^2 &= 9\\y& = \pm\sqrt 9\\ y & = \pm 3\end{align*}
The potential solutions are $y=\pm 3$. We will now check them.
$\bullet$ Check: $y=3$
$$\dfrac{3}{3+3}+\dfrac{3}{3-3} \stackrel{?}{=} \dfrac{18}{3^2-9}$$
Two denominators are zero for the value of $y=3$.
$\bullet$ Check: $y=-3$
\[\dfrac{-3}{-3+3}+\dfrac{3}{-3-3} \stackrel{?}{=} \dfrac{18}{(-3)^2-9}\]
Two denominators are zero for the value of $y=-3$.
The solution set is the empty set, $\{\}$.
Need more help?
Don’t wait too long to do the following.
- Watch the additional video resources.
- Talk to your instructor.
- Form a study group.
- Visit a tutor. For more information, check the tutoring page .
Lessons Menu
- Lesson 1: Properties of Integer Exponents & Addition and Subtraction of Rational Expressions
- Lesson 2: Complex Fractions
- Lesson 4: Roots and Rational Exponents
- Lesson 5: Simplifying Radical Expressions & Addition and Subtraction of Radicals
- Lesson 6: Multiplication of Radicals
- Lesson 7: Division of Radicals and Rationalization
- Lesson 8: Solving Radical Equations
- Lesson 9: Complex Numbers
- Lesson 10: Solving Equations by Using the Zero Product Rule
- Lesson 11: Square Root Property and Completing the Square & Quadratic Formula
- Lesson 12: Applications of Quadratic Equations
- Lesson 13: Graphs of Quadratic Functions & Vertex of a Parabola
- Lesson 14: Distance Formula, Midpoint Formula, and Circles & Perpendicular Bisector
- Lesson 1: Systems of Linear Equations With Three Variables
- Lesson 16: Nonlinear Systems of Equations in Two Variables
- Lesson 17: Angle Measure and Special Triangles & The Trigonometry of Right Triangles
- Lesson 18: Solving Right Triangles & Applications of Static Trigonometry
- Lesson 19: Angle Measure in Radian & Trigonometry and the Coordinate Plane
- Lesson 20: Unit Circles
- Lesson 21: Graphs of Sine and Cosine
- Lesson 22: Fundamental Identities and Families of Identities
- Lesson 23: Trigonometric Equations
- Lesson 24: Oblique Triangles and The Law of Sines & The Law of Cosines
- Lesson 25: Exponential Expressions
- Lesson 26: Logarithmic Expressions
- Lesson 27: Properties of Logarithms & Compound Interest
- Lesson 28: Logarithmic and Exponential Equations

Unless otherwise noted, this site by Ariane Masuda and Jonas Reitz has a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA) license. Learn more.
© 2024 MAT 1275 Course Hub
Theme by Anders Noren — Up ↑
The OpenLab at City Tech: A place to learn, work, and share
The OpenLab is an open-source, digital platform designed to support teaching and learning at City Tech (New York City College of Technology), and to promote student and faculty engagement in the intellectual and social life of the college community.

New York City College of Technology | City University of New York
Accessibility
Our goal is to make the OpenLab accessible for all users.
Learn more about accessibility on the OpenLab
Creative Commons
- - Attribution
- - NonCommercial
- - ShareAlike

© New York City College of Technology | City University of New York
- Notifications 0

- Add Friend ($5)

As a registered member you can:
- View all solutions for free
- Request more in-depth explanations for free
- Ask our tutors any math-related question for free
- Email your homework to your parent or tutor for free
- Grade 7 McGraw Hill Glencoe - Answer Keys
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
| \(-5w = -24.5\) | ||||

Explanation:
\(-22.8 = 6n\)
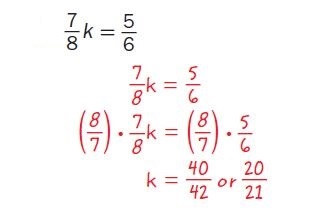
\(-6\cfrac{1}{4}=\cfrac{3}{5}c\)
\(-\frac{4}{7}v = -8\frac{2}{3}\)
The Mammoth Cave Discovery Tour includes an elevation change of 140 feet. This is \(\frac{7}{15}\) of the elevation change on the Wild Cave Tour. What is the elevation change on the Wild Cave Tour? Use a bar diagram to solve arithmetically. Then use an equation to solve algebraically.

| feet |
Model with Mathematics Refer to the graphic novel frame below. Write and solve an equation to find how many movies they have time to show. Equation: Solution:

| movies |
Yes, email page to my online tutor. ( if you didn't add a tutor yet, you can add one here )
Thank you for doing your homework!
Submit Your Question

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step-by-step methods for solving equations with rational coefficients. Step 1: Identify the equation with a rational coefficient. Rational coefficients are fractions expressed as a ratio of two integers. Step 2: Apply one of the strategies below to solve the equation. Method 1: Clearing Fractions.
Lesson 3 Homework Practice Solve Equations with Rational Coefficients Solve each equation. Check your solution. ... If this represented −−9 of the volunteers at the shelter, write and solve an 16 equation to determine how many volunteers helped at the local shelter.
Email your homework to your parent or tutor for free; ... Chapter 6: Equations and Inequalities; Lesson 3: Solve Equations with rational Coefficients. ... Guided Practice. Solve each equation. Check your solution. Question 1 (request help) \(1.6k = 3.2\) (show solution) ...
Learn to solve equations with rational coefficients.Example problems include one with a positive coefficient and one with a negative coefficient.-2/3x =81/4x...
Twenty-four students brought their permission slips to attend the class field trip to the local art museum. If this represented eight tenths of the class, how many students are in the class? Use a bar diagram to solve arithmetically. Then use an equation to solve algebraically. Equation: Solution:
Lesson 1 Reteach Solve Equations with Rational Coefficients To solve an equation when the coefficient is a rational number, multiply each side by the multiplicative inverse of the fraction. Example Solve Check your solution. Write the equation. ( ) ( ) Multiply each side by the multiplicative inverse of , 1 1 4 Write . Divide out common factors ...
3 a 6. 9 = 0.3n 7. −−15 7 y = 3 8. 21 = 0.75a 9. −−14 3 = - −7 9 b Lesson 3 - Solve Equations with Rational Coefficents Multiplicative inverses, or reciprocals, are two numbers whose product is 1. To solve an equation in which the coefficient is a fraction, multiply each side of the equation by the reciprocal of the coefficient.
Course 3 • Chapter 2 Equations in One Variable 23 Define a variable. Then write and solve an equation for each situation. 13. COOKING Simone peeled 14 potatoes in hour. At this rate, how many potatoes can Simone peel in one hour? 14. VOTING In the eighth grade, 322 students voted for the new mascot to be a tiger. This was $ of the total number
Steps and process used to solve equations with rational coefficients.
Step 2 Subtract 5x from both sides. 6 2 5. x. L13: Solve Linear Equations with Rational Coefficients. Part 2: Guided Instruction. Connect It. Now you will analyze how each student solved the equation. 2 Look at Elise's solution method. She took three steps to solve the equation.
Title: 087_104_CC_A_RSPC2_C06_662331.indd Author: A042 Created Date: 7/13/2011 3:56:59 AM
Need an engaging practice activity for solving equations with variables on both side? With this worksheet, each solution reveals a fun cactus fact. All equations have variables on both sides. Students must use the distributive property, collect like terms, and work with rational coefficients.This worksheet works great for engaging classwork, homework, sub plans, or after a test.
A Quick Intro to Solving Rational Equations. Key Words. Solution to an equation, rational equation, LCD (least common denominator), checking potential solutions. The first step in solving a rational equation is to clear the denominators. For example, in the equation. 2 x = x 2. the LCD is 2 x. Multiplying both sides by 2 x clears the denominators.
Email your homework to your parent or tutor for free; ... Lesson 3: Solve Equations with rational Coefficients. ... Extra Practice. Solve each equation. Check your solution. Question 15 (request help) Question 16 (request help) \(-5w = -24.5\) (show solution) ...
8. $0.50. PDF. This is a packet for Solving One-Step Equations with Rational Coefficients (Fractions and Decimals). It includes all of the following: Warm-up Exercise (Solving One-Step Equations), a "I/We/You" practice exercise, Cornell Notes, summary space, and Extra Practice Problems. The key is included!
An interactive video tutorial about how to solve one-step equations with rational coefficients.
PDF. This worksheet will provide your student with review of solving one step equations with rational coefficients. This includes printable and Google Slides™ versions of the worksheet, which makes this perfect for in the classroom, stations, or distance learning.Solving One Step Equations Worksheet includes: 1 worksheet with 12 equations 4 ...
Our resource for Glencoe Math Course 3, Volume 1 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and move forward with confidence. Find step-by-step solutions and answers to ...
These Solving Equations with Rational Coefficients notes and practice are differentiated based on some common needs found in the middle school math classroom. Modifications are considered for both struggling learners and high flyers. In these activities, students practice solving equations involving fractions and decimals. Students learn how to use the least common denominator to clear ...
curriculum teaching and learning of yesterday do not meet the needs of today s students Algebra 2, Homework Practice Workbook McGraw-Hill Education,2008-12-10 The Homework Practice Workbook contains two worksheets for every lesson in the Student Edition This workbook helps students Practice the skills of the lesson Use their skills to solve
Lesson 3 Homework Practice Solve Equations With Rational Coefficients: Math, Grade 3 Homework, Practice, Problem Solving Workbook Hsp,2009 Math Connects, Grade 3, Homework Practice Workbook McGraw-Hill Education,2008-01-17 The Homework Practice Workbook helps students practice problems learned in each of the lessons Prealgebra 2e Lynn Marecek ...