

How to Write an Effective Persuasive Speech Outline: 5 Key Elements
- The Speaker Lab
- April 14, 2024
Table of Contents
If you’re a speaker, you are probably well familiar with the path from initial speech drafts to the day you actually present. By its nature, speech delivery is a journey filled with obstacles, yet it’s simultaneously an adventure in persuasion. With a well-crafted persuasive speech outline , you can do more than just present facts and figures to your audience. You can weave them into a narrative that captivates, convinces, and converts.
A meticulously planned persuasive speech outline isn’t just helpful; it’s essential. Crafting this blueprint carefully lets you deliver your message more effectively, making sure each point lands with the impact you’re aiming for. To help you achieve this impact, we have some tips and tricks for you to try.
Writing an Effective Persuasive Speech Outline
When we talk about persuasive speeches , we’re diving into the art of convincing others to see things from a certain point of view. Your speech is your one shot to grab attention, build your case, and inspire action. Your secret weapon for achieving this is your speech outline. In your speech outline, you want to touch on several key elements.
- Pick your fight: Start by zeroing in on what you really want to change or influence with this speech.
- Support your claim with evidence: Identify those key points that back up your stance to appeal to your audience’s rational side .
- The emotional hook: Weave in stories or facts that hit home emotionally .
- Avoid the kitchen sink approach: Don’t throw everything at them hoping something sticks. Be selective and strategic with the info you share.
- Nail that closer: Your conclusion isn’t just goodbye; it’s where you charge your audience with a call to action.
These elements form the backbone of your persuasive speech. By including these in your talk’s outline, you can’t go wrong.
Free Download: 6 Proven Steps to Book More Paid Speaking Gigs in 2024
Download our 18-page guide and start booking more paid speaking gigs today!
Establishing Your Main Objective and Structuring Your Points
Now that you have a general idea of what goes into a persuasive speech outline, let’s break a couple of these pieces down and look at them a little more closely.
Identifying the Purpose of Your Persuasive Speech
When writing your speech, you first need to nail down why you’re doing this in the first place. In other words, identify your main objective. After all, choosing to speak up isn’t merely about the desire to express oneself; it’s deeply rooted in understanding the effect you hope your discourse will unleash. Do you hope to sway opinions towards the belief that animal experimentation is a relic of the past? Or perhaps persuade them that social media does more good than harm? Whatever your cause, identifying your main objective will help keep you on track and avoid rambling.
Organizing Key Points for Maximum Impact
Once you’ve determined what you want to persuade your audience of, you can start building your argument. Specifically, you can determine your key points. Key points support your position on a topic, proving to your audience that you have actual reasons for taking your position.
To pack the most punch, arrange these key points in a logical order. Consider how you might connect your key points. Are there some that can be grouped together? The flow of your argument matters just as much as the argument itself, and a disjointed argument won’t do anyone any favors. As you organize your key points, consider these tips:
- Lead with strength, but don’t throw all your cards out at once.
- Build upon each point; important transitions between them can make or break audience engagement.
- Finish strong by tying back everything to the emotional chord you struck at the beginning.
Nailing these steps will ensure that when you speak, your message doesn’t just echo—it resonates.
Selecting Compelling Topics for Your Persuasive Speeches
Let’s face it, picking the right topic for your persuasive speech outline is half the battle. But what makes a topic not just good, but great? First off, it needs to spark interest, both yours and your audience’s. If you’re not fired up about it, chances are they won’t be either. Second, make sure the topic is something relevant. It should resonate with your listeners’ experiences or touch on their concerns and aspirations. Lastly, your topic has to be something you can research and back up with solid facts and expert opinions.
For ideas to get you started, check out a variety of speech topics here .
Enhancing Persuasion Through Rhetorical Appeals
The art of persuasion is something that’s been studied since ancient Greece. Back then, Greek philosopher Aristotle came up with the three rhetorical appeals . Each one described a different way of convincing your audience of your position. Together, these appeals help you form a rock-strong argument, making them worth learning.
Building Credibility with Ethos
To get people on your side, you first need to win their trust. That’s where ethos comes into play. Demonstrating to your listeners that you’re both trustworthy and deserving of their attention hinges on transparency about your qualifications, genuine self, and the wisdom gained from occasional setbacks. Letting folks know why they should listen can make all the difference.
Connecting with the Audience Through Pathos
At some point, we’ve all been moved by a story or an ad because it hit right in the feels. That sort of emotional appeal is called pathos , and it’s powerful stuff. If you want people really invested in what you’re saying, then be sure to use this appeal in your presentation. To harness the power of pathos, try telling a story , especially one your audience can relate to. The key is authenticity—sharing true experiences resonates more than anything fabricated ever could.
Strengthening Arguments with Logos
Last but not least, we have logos, our logical appeal. Oftentimes, this logical appeal entails facts and data points, which are used to back up what you’re selling, turning skeptics into believers. But just because you’re listing facts and figures doesn’t mean this part has to be boring. To keep your audience engaged, craft persuasive narratives and then ground them in robust proof. Giving your story to go with your numbers doesn’t just help keep them engaged, it also helps the information stick.
The Importance of Supporting Evidence and Counterarguments
In your persuasive speech outline, you need to note compelling evidence for each key point. In addition, you’ll want to address opposing views.
Gathering and Presenting Convincing Evidence
No matter how trustworthy you seem, or how compelling your stories are, most people need tangible proof. That’s where concrete evidence steps into the spotlight. To fortify your argument and boost its believability, sprinkle in a mix of hard data, customer stories, numerical evidence, and endorsements from authorities. To illustrate this data for your audience, you may find it helpful to create a slideshow . Supporting every assertion with research is an essential part of any persuasive speech. Without it, arguments inevitably sound flimsy and unconvincing.
Addressing Opposing Views Effectively
Although it may seem counterintuitive, address counter-arguments head-on in your persuasive speech outline. It might feel like walking into enemy territory but it actually strengthens your own argument. By acknowledging opposing views, you’re showing that not only do you know what they are, but also that they don’t scare you.
When you address these counter-arguments, demonstrate your understanding. Again, this is where your good research skills are going to come in handy. Present the facts, and ditch biased explanations. In other words, don’t mock or belittle the other side’s viewpoint or you’ll undermine your own trustworthiness. Instead, explain opposing viewpoints with neutrality.
Adopting this strategy not only neutralizes possible objections but also enhances your stance. Plus, this makes for an engaging dialogue between both sides of any debate, which keeps audience members hooked from start to finish.
In essence, tackling counter-arguments is less about winning over naysayers and more about enriching discussions around hot-button issues. At its core, persuasion isn’t just convincing folks; it’s sparking conversations worth having.
Crafting a Captivating Introduction and Conclusion
Now that you have the body of your persuasive speech outline, it’s time to talk beginning and end. To really hit your message home, you want to grab your audience’s attention at the beginning and call them to action at the end.
Creating an Engaging Hook to Capture Attention
The opening of your speech is where you need a good first impression. To hook your audience, consider starting with an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or even a short story related to your topic. Whatever route you choose, keep it interesting and concise, so that you can transition into the rest of your persuasive speech outline.
Concluding with a Strong Call to Action
Crafting strong conclusions is about leaving your readers feeling pumped and ready to jump into action. After all, if you’ve argued convincingly enough, your audience should be ready to act. To channel this energy, urge listeners towards specific actions. Here are some strategies:
- Suggest clear next steps: Don’t leave your audience hanging wondering what’s next. Give them concrete steps they can take immediately after reading.
- Create urgency: Why wait? Let folks know why now is the perfect time to act.
- Show benefits: Paint vivid pictures of how taking action will positively impact their lives or solve their problems.
With that captivating hook and a decisive call-to-action, you are one step closer to presenting an unforgettable speech.
Utilizing Monroe’s Motivated Sequence for Persuasive Structure
As you finish off your persuasive speech outline, you may be wondering how best to structure your speech. If that’s you, then Purdue University professor Alan H. Monroe has some answers. In his book “Monroe’s Principles of Speech,” the professor outlines Monroe’s Motivated Sequence, the best structure for persuasive speeches. Each step is broken down below.
Attention: Grabbing the Audience’s Focus
You’ve got something important to say. But first, you need them to listen. Start with a bang. Throwing out a shocking truth, posing a thought-provoking query, or sharing an enthralling tale could work magic in grabbing their attention. It’s all about making heads turn and ears perk up.
Need: Highlighting the Issue at Hand
Now that they’re listening, show them there’s a gaping hole in their lives that only your message can fill. Paint a vivid picture of the problem your speech addresses.
Satisfaction: Proposing a Solution
This is where you come in as the hero with a plan. Introduce your solution clearly and convincingly. How does it patch things up? Why does it outshine merely applying quick fixes to deep-rooted issues? Give your audience hope.
Visualization: Helping the Audience Visualize Benefits
Show them life on the other side of adopting your idea or product—brighter, easier, better. Use vivid imagery and relatable scenarios so they can see themselves reaping those benefits firsthand.
Action: Encouraging Audience Action
Last step: nudge them from “maybe” to “yes.” Make this part irresistible by being clear about what action they should take next—and why now’s the time to act. Whether signing up, voting, or changing behavior, make sure they know how easy taking that first step can be.
Learn more about Monroe’s Motivated Sequence here .
What Type Of Speaker Are You?
Click below to discover your Speaker Archetype and how to start getting booked and paid to speak!
Overcoming Public Speaking Fears for Effective Delivery
Let’s face it, the thought of public speaking can turn even the most confident folks into a bundle of nerves. But hey, you’ve got this. Dive into these expert strategies and you’ll find yourself delivering speeches like a seasoned orator in no time.
Techniques to Build Confidence in Public Speaking
If you’re feeling nervous on the big day, these three techniques are perfect for you. Take a look!
- Breathe: Deep breathing is your secret weapon against those pesky nerves. It tells your brain that everything is going to be okay.
- Pose like a superhero: Stand tall and strike a power pose before you go on stage. This isn’t just fun; science backs it up as a confidence booster .
- Kick perfectionism to the curb: Aim for connection with your audience, not perfection. Mistakes make you human and more relatable.
The goal here is to calm yourself enough to be able to deliver your persuasive speech outline with confidence. Even if you still feel a little nervous, you can still present an awesome speech. You just don’t want those nerves running the show.
Practicing Your Speech for Perfect Execution
If you know that you tend to get nervous when public speaking, then you don’t want to be running through you speech for the first time on the big day. Instead, practice beforehand using these techniques.
- The mirror is your friend: Practice in front of a mirror to catch any odd gestures or facial expressions.
- Vary your voice: As you deliver your speech, let your voice rise and fall to match what you’re sharing. Avoid speaking in a monotone.
- Say no to memorization: Rather than memorizing every word, learn key points by heart. You want to sound natural out there.
Remembering these steps won’t just help you tackle public speaking fear, but will also polish those all-important public speaking skills .
Once you’ve honed the skills you need to write a persuasive speech outline, the only thing left to do is to get out there and practice them. So take the rhetorical appeals—ethos, logos, and pathos—and practice weaving each element into your speech. Or take Monroe’s Motivated Sequence and work on structuring your outline accordingly.
Prepare well and when you hit the stage, you have not just a well-prepared persuasive speech outline, but also the power to alter perspectives, challenge the status quo, or even change lives.
- Last Updated: April 11, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples
March 17, 2021 - Gini Beqiri
A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything – voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on.
A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing you come across as trustworthy and knowledgeable about the topic you’re discussing.
So, how do you start convincing a group of strangers to share your opinion? And how do you connect with them enough to earn their trust?
Topics for your persuasive speech
We’ve made a list of persuasive speech topics you could use next time you’re asked to give one. The topics are thought-provoking and things which many people have an opinion on.
When using any of our persuasive speech ideas, make sure you have a solid knowledge about the topic you’re speaking about – and make sure you discuss counter arguments too.
Here are a few ideas to get you started:
- All school children should wear a uniform
- Facebook is making people more socially anxious
- It should be illegal to drive over the age of 80
- Lying isn’t always wrong
- The case for organ donation
Read our full list of 75 persuasive speech topics and ideas .

Preparation: Consider your audience
As with any speech, preparation is crucial. Before you put pen to paper, think about what you want to achieve with your speech. This will help organise your thoughts as you realistically can only cover 2-4 main points before your audience get bored .
It’s also useful to think about who your audience are at this point. If they are unlikely to know much about your topic then you’ll need to factor in context of your topic when planning the structure and length of your speech. You should also consider their:
- Cultural or religious backgrounds
- Shared concerns, attitudes and problems
- Shared interests, beliefs and hopes
- Baseline attitude – are they hostile, neutral, or open to change?
The factors above will all determine the approach you take to writing your speech. For example, if your topic is about childhood obesity, you could begin with a story about your own children or a shared concern every parent has. This would suit an audience who are more likely to be parents than young professionals who have only just left college.
Remember the 3 main approaches to persuade others
There are three main approaches used to persuade others:
The ethos approach appeals to the audience’s ethics and morals, such as what is the ‘right thing’ to do for humanity, saving the environment, etc.
Pathos persuasion is when you appeal to the audience’s emotions, such as when you tell a story that makes them the main character in a difficult situation.
The logos approach to giving a persuasive speech is when you appeal to the audience’s logic – ie. your speech is essentially more driven by facts and logic. The benefit of this technique is that your point of view becomes virtually indisputable because you make the audience feel that only your view is the logical one.
- Ethos, Pathos, Logos: 3 Pillars of Public Speaking and Persuasion
Ideas for your persuasive speech outline
1. structure of your persuasive speech.
The opening and closing of speech are the most important. Consider these carefully when thinking about your persuasive speech outline. A strong opening ensures you have the audience’s attention from the start and gives them a positive first impression of you.
You’ll want to start with a strong opening such as an attention grabbing statement, statistic of fact. These are usually dramatic or shocking, such as:
Sadly, in the next 18 minutes when I do our chat, four Americans that are alive will be dead from the food that they eat – Jamie Oliver
Another good way of starting a persuasive speech is to include your audience in the picture you’re trying to paint. By making them part of the story, you’re embedding an emotional connection between them and your speech.
You could do this in a more toned-down way by talking about something you know that your audience has in common with you. It’s also helpful at this point to include your credentials in a persuasive speech to gain your audience’s trust.

Obama would spend hours with his team working on the opening and closing statements of his speech.
2. Stating your argument
You should pick between 2 and 4 themes to discuss during your speech so that you have enough time to explain your viewpoint and convince your audience to the same way of thinking.
It’s important that each of your points transitions seamlessly into the next one so that your speech has a logical flow. Work on your connecting sentences between each of your themes so that your speech is easy to listen to.
Your argument should be backed up by objective research and not purely your subjective opinion. Use examples, analogies, and stories so that the audience can relate more easily to your topic, and therefore are more likely to be persuaded to your point of view.
3. Addressing counter-arguments
Any balanced theory or thought addresses and disputes counter-arguments made against it. By addressing these, you’ll strengthen your persuasive speech by refuting your audience’s objections and you’ll show that you are knowledgeable to other thoughts on the topic.
When describing an opposing point of view, don’t explain it in a bias way – explain it in the same way someone who holds that view would describe it. That way, you won’t irritate members of your audience who disagree with you and you’ll show that you’ve reached your point of view through reasoned judgement. Simply identify any counter-argument and pose explanations against them.
- Complete Guide to Debating
4. Closing your speech
Your closing line of your speech is your last chance to convince your audience about what you’re saying. It’s also most likely to be the sentence they remember most about your entire speech so make sure it’s a good one!
The most effective persuasive speeches end with a call to action . For example, if you’ve been speaking about organ donation, your call to action might be asking the audience to register as donors.
Practice answering AI questions on your speech and get feedback on your performance .
If audience members ask you questions, make sure you listen carefully and respectfully to the full question. Don’t interject in the middle of a question or become defensive.
You should show that you have carefully considered their viewpoint and refute it in an objective way (if you have opposing opinions). Ensure you remain patient, friendly and polite at all times.
Example 1: Persuasive speech outline
This example is from the Kentucky Community and Technical College.
Specific purpose
To persuade my audience to start walking in order to improve their health.
Central idea
Regular walking can improve both your mental and physical health.
Introduction
Let’s be honest, we lead an easy life: automatic dishwashers, riding lawnmowers, T.V. remote controls, automatic garage door openers, power screwdrivers, bread machines, electric pencil sharpeners, etc., etc. etc. We live in a time-saving, energy-saving, convenient society. It’s a wonderful life. Or is it?
Continue reading
Example 2: Persuasive speech
Tips for delivering your persuasive speech
- Practice, practice, and practice some more . Record yourself speaking and listen for any nervous habits you have such as a nervous laugh, excessive use of filler words, or speaking too quickly.
- Show confident body language . Stand with your legs hip width apart with your shoulders centrally aligned. Ground your feet to the floor and place your hands beside your body so that hand gestures come freely. Your audience won’t be convinced about your argument if you don’t sound confident in it. Find out more about confident body language here .
- Don’t memorise your speech word-for-word or read off a script. If you memorise your persuasive speech, you’ll sound less authentic and panic if you lose your place. Similarly, if you read off a script you won’t sound genuine and you won’t be able to connect with the audience by making eye contact . In turn, you’ll come across as less trustworthy and knowledgeable. You could simply remember your key points instead, or learn your opening and closing sentences.
- Remember to use facial expressions when storytelling – they make you more relatable. By sharing a personal story you’ll more likely be speaking your truth which will help you build a connection with the audience too. Facial expressions help bring your story to life and transport the audience into your situation.
- Keep your speech as concise as possible . When practicing the delivery, see if you can edit it to have the same meaning but in a more succinct way. This will keep the audience engaged.
The best persuasive speech ideas are those that spark a level of controversy. However, a public speech is not the time to express an opinion that is considered outside the norm. If in doubt, play it safe and stick to topics that divide opinions about 50-50.
Bear in mind who your audience are and plan your persuasive speech outline accordingly, with researched evidence to support your argument. It’s important to consider counter-arguments to show that you are knowledgeable about the topic as a whole and not bias towards your own line of thought.
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
How to Write an Outline for a Persuasive Speech, with Examples

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

Persuasive speeches are one of the three most used speeches in our daily lives. Persuasive speech is used when presenters decide to convince their presentation or ideas to their listeners. A compelling speech aims to persuade the listener to believe in a particular point of view. One of the most iconic examples is Martin Luther King’s ‘I had a dream’ speech on the 28th of August 1963.
In this article:
What is Persuasive Speech?
Here are some steps to follow:, persuasive speech outline, final thoughts.

Persuasive speech is a written and delivered essay to convince people of the speaker’s viewpoint or ideas. Persuasive speaking is the type of speaking people engage in the most. This type of speech has a broad spectrum, from arguing about politics to talking about what to have for dinner. Persuasive speaking is highly connected to the audience, as in a sense, the speaker has to meet the audience halfway.
Persuasive Speech Preparation
Persuasive speech preparation doesn’t have to be difficult, as long as you select your topic wisely and prepare thoroughly.
1. Select a Topic and Angle
Come up with a controversial topic that will spark a heated debate, regardless of your position. This could be about anything. Choose a topic that you are passionate about. Select a particular angle to focus on to ensure that your topic isn’t too broad. Research the topic thoroughly, focussing on key facts, arguments for and against your angle, and background.
2. Define Your Persuasive Goal
Once you have chosen your topic, it’s time to decide what your goal is to persuade the audience. Are you trying to persuade them in favor of a certain position or issue? Are you hoping that they change their behavior or an opinion due to your speech? Do you want them to decide to purchase something or donate money to a cause? Knowing your goal will help you make wise decisions about approaching writing and presenting your speech.
3. Analyze the Audience
Understanding your audience’s perspective is critical anytime that you are writing a speech. This is even more important when it comes to a persuasive speech because not only are you wanting to get the audience to listen to you, but you are also hoping for them to take a particular action in response to your speech. First, consider who is in the audience. Consider how the audience members are likely to perceive the topic you are speaking on to better relate to them on the subject. Grasp the obstacles audience members face or have regarding the topic so you can build appropriate persuasive arguments to overcome these obstacles.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
4. Build an Effective Persuasive Argument
Once you have a clear goal, you are knowledgeable about the topic and, have insights regarding your audience, you will be ready to build an effective persuasive argument to deliver in the form of a persuasive speech.
Start by deciding what persuasive techniques are likely to help you persuade your audience. Would an emotional and psychological appeal to your audience help persuade them? Is there a good way to sway the audience with logic and reason? Is it possible that a bandwagon appeal might be effective?
5. Outline Your Speech
Once you know which persuasive strategies are most likely to be effective, your next step is to create a keyword outline to organize your main points and structure your persuasive speech for maximum impact on the audience.
Start strong, letting your audience know what your topic is, why it matters and, what you hope to achieve at the end of your speech. List your main points, thoroughly covering each point, being sure to build the argument for your position and overcome opposing perspectives. Conclude your speech by appealing to your audience to act in a way that will prove that you persuaded them successfully. Motivation is a big part of persuasion.
6. Deliver a Winning Speech
Select appropriate visual aids to share with your audiences, such as graphs, photos, or illustrations. Practice until you can deliver your speech confidently. Maintain eye contact, project your voice and, avoid using filler words or any form of vocal interference. Let your passion for the subject shine through. Your enthusiasm may be what sways the audience.

Topic: What topic are you trying to persuade your audience on?
Specific Purpose:
Central idea:
- Attention grabber – This is potentially the most crucial line. If the audience doesn’t like the opening line, they might be less inclined to listen to the rest of your speech.
- Thesis – This statement is used to inform the audience of the speaker’s mindset and try to get the audience to see the issue their way.
- Qualifications – Tell the audience why you are qualified to speak about the topic to persuade them.
After the introductory portion of the speech is over, the speaker starts presenting reasons to the audience to provide support for the statement. After each reason, the speaker will list examples to provide a factual argument to sway listeners’ opinions.
- Example 1 – Support for the reason given above.
- Example 2 – Support for the reason given above.
The most important part of a persuasive speech is the conclusion, second to the introduction and thesis statement. This is where the speaker must sum up and tie all of their arguments into an organized and solid point.
- Summary: Briefly remind the listeners why they should agree with your position.
- Memorable ending/ Audience challenge: End your speech with a powerful closing thought or recommend a course of action.
- Thank the audience for listening.
Persuasive Speech Outline Examples

Topic: Walking frequently can improve both your mental and physical health.
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to start walking to improve their health.
Central idea: Regular walking can improve your mental and physical health.
Life has become all about convenience and ease lately. We have dishwashers, so we don’t have to wash dishes by hand with electric scooters, so we don’t have to paddle while riding. I mean, isn’t it ridiculous?
Today’s luxuries have been welcomed by the masses. They have also been accused of turning us into passive, lethargic sloths. As a reformed sloth, I know how easy it can be to slip into the convenience of things and not want to move off the couch. I want to persuade you to start walking.
Americans lead a passive lifestyle at the expense of their own health.
- This means that we spend approximately 40% of our leisure time in front of the TV.
- Ironically, it is also reported that Americans don’t like many of the shows that they watch.
- Today’s studies indicate that people were experiencing higher bouts of depression than in the 18th and 19th centuries, when work and life were considered problematic.
- The article reports that 12.6% of Americans suffer from anxiety, and 9.5% suffer from severe depression.
- Present the opposition’s claim and refute an argument.
- Nutritionist Phyllis Hall stated that we tend to eat foods high in fat, which produces high levels of cholesterol in our blood, which leads to plaque build-up in our arteries.
- While modifying our diet can help us decrease our risk for heart disease, studies have indicated that people who don’t exercise are at an even greater risk.
In closing, I urge you to start walking more. Walking is a simple, easy activity. Park further away from stores and walk. Walk instead of driving to your nearest convenience store. Take 20 minutes and enjoy a walk around your neighborhood. Hide the TV remote, move off the couch and, walk. Do it for your heart.
Thank you for listening!
Topic: Less screen time can improve your sleep.
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to stop using their screens two hours before bed.
Central idea: Ceasing electronics before bed will help you achieve better sleep.
Who doesn’t love to sleep? I don’t think I have ever met anyone who doesn’t like getting a good night’s sleep. Sleep is essential for our bodies to rest and repair themselves.
I love sleeping and, there is no way that I would be able to miss out on a good night’s sleep.
As someone who has had trouble sleeping due to taking my phone into bed with me and laying in bed while entertaining myself on my phone till I fall asleep, I can say that it’s not the healthiest habit, and we should do whatever we can to change it.
- Our natural blue light source is the sun.
- Bluelight is designed to keep us awake.
- Bluelight makes our brain waves more active.
- We find it harder to sleep when our brain waves are more active.
- Having a good night’s rest will improve your mood.
- Being fully rested will increase your productivity.
Using electronics before bed will stimulate your brainwaves and make it more difficult for you to sleep. Bluelight tricks our brains into a false sense of daytime and, in turn, makes it more difficult for us to sleep. So, put down those screens if you love your sleep!
Thank the audience for listening
A persuasive speech is used to convince the audience of the speaker standing on a certain subject. To have a successful persuasive speech, doing the proper planning and executing your speech with confidence will help persuade the audience of your standing on the topic you chose. Persuasive speeches are used every day in the world around us, from planning what’s for dinner to arguing about politics. It is one of the most widely used forms of speech and, with proper planning and execution, you can sway any audience.
How to Write the Most Informative Essay
How to Craft a Masterful Outline of Speech
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
How To Write A Persuasive Speech: 7 Steps
Table of contents
- 1 Guidance on Selecting an Effective and Relevant Topic
- 2 Strategies for Connecting With Different Types of Audiences
- 3 Developing Your Thesis Statement
- 4.1 Writing the Introduction
- 4.2 Body of Your Speech
- 4.3 Concluding Effectively
- 5 Techniques for Creating a Coherent Flow of Ideas
- 6 Importance of Transitions Between Points
- 7 Importance of Tone and Style Adjustments Based on the Audience
- 8 Prepare for Rebuttals
- 9 Use Simple Statistics
- 10 Practicing Your Speech
- 11 Additional Resources to Master Your Speech
- 12 Master the Art of Persuasion With PapersOwl
Are you about to perform a persuasive speech and have no idea how to do it? No need to worry; PapersOwl is here to guide you through this journey!
What is persuasive speaking? Persuasive speaking is a form of communication where the speaker aims to influence or convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or belief or take specific actions. The goal is to sway the listeners’ opinions, attitudes, or behaviors by presenting compelling arguments and supporting evidence while appealing to their emotions.
Today, we prepared a guide to help you write a persuasive speech and succeed in your performance, which will surprise your audience. We will:
- Understand how to connect with your audience.
- Give you persuasive speech tips.
- Provide you with the best structure for a persuasive speech outline.
- Prepare yourself for rebuttals!
- Talk about the importance of flow in your speech.
- Discover additional resources for continuous improvement.
Let’s begin this journey together!
Guidance on Selecting an Effective and Relevant Topic
The most important thing in convincing speeches is the topic. Indeed, you must understand the purpose of your speech to succeed. Before preparing for your performance, you should understand what you want to discuss! To do that, you can:
- Choose a compelling speech topic relevant to your audience’s interests and concerns.
- Find common interests or problems to form a genuine relationship.
- Remember that a persuasive speech format should be adapted to your audience’s needs and ideals. Make your content relevant and appealing.
And if you are struggling on this step, PapersOwl is already here to help you! Opt to choose persuasive speech topics and find the one that feels perfect for you.
Strategies for Connecting With Different Types of Audiences
A successful persuasive speech connects you with your audience. To do that, you should really know how to connect yourself to people.
Thus, the speaker connects with and persuades the audience by using emotions such as sympathy or fear. Therefore, you can successfully connect with different types of audiences through different emotions. You can do it by showing that you have something in common with the audience. For example, demonstrate that you have a comparable history or an emotional connection. Additionally, include personal stories or even make a part of a speech about yourself to allow your audience to relate to your story.
Developing Your Thesis Statement
When you give a persuasive speech, there should be a thesis statement demonstrating that your goal is to enlighten the audience rather than convince them.
A thesis statement in persuasive speaking serves as the central argument or main point, guiding the entire presentation. A successful thesis anchors your speech and briefly expresses your position on the subject, giving a road map for both you and your audience.
For instance, in pushing for renewable energy, a thesis may be: “Transitioning to renewable sources is imperative for a sustainable future, mitigating environmental impact and fostering energy independence.” This statement summarizes the argument and foreshadows the supporting points.
Overview of speech structure (introduction, body, conclusion)
The key elements of a persuasive speech are:
- introduction (hook, thesis, preview);
- body (main points with supporting details and transitions);
- conclusion (summary, restated thesis, closing statement).
Let’s look closer at how to structure them to write a good persuasive speech.
Writing the Introduction
The introduction to persuasive speech is crucial. The very beginning of your discourse determines your whole performance, drawing in your audience and creating a foundation for trust and engagement. Remember, it’s your opportunity to make a memorable first impression, ensuring your listeners are intrigued and receptive to your message.
Start off a persuasive speech with an enticing quotation, image, video, or engaging tale; it can entice people to listen. As we mentioned before, you may connect your speech to the audience and what they are interested in. Establish credibility by showcasing your expertise or connecting with shared values. Ultimately, ensure your thesis is clear and outline which specific purpose statement is most important in your persuasive speech.
Body of Your Speech
After choosing the topic and writing an intro, it’s time to concentrate on one of the most critical parts of a persuasive speech: the body.
The main body of your speech should provide the audience with several convincing reasons to support your viewpoint. In this part of your speech, create engaging primary points by offering strong supporting evidence — use statistics, illustrations, or expert quotations to strengthen each argument. Also, don’t forget to include storytelling for an emotional connection with your audience. If you follow this combination, it will for sure make a speech persuasive!
Concluding Effectively
After succeeding in writing the main points, it is time to end a persuasive speech! Indeed, a call to action in persuasive speech is vital, so we recommend you end your performance with it. After listening to your argument and proof, you want the audience to make a move. Restate your purpose statement, summarize the topic, and reinforce your points by restating the logical evidence you’ve provided.
Techniques for Creating a Coherent Flow of Ideas
Your ideas should flow smoothly and naturally connect to strengthen the persuasive speech structure . You can do this by employing transitional words and organizing your thoughts methodically, ensuring that each point flows effortlessly into the next.
Importance of Transitions Between Points
No one can underestimate the importance of transition. They are important persuasive speech elements. Thus, each idea must flow smoothly into the following one with linking phrases so your speech has a logical flow. Effective transitions signal shifts, aiding audience comprehension and improving the overall structure of the speech.
Importance of Tone and Style Adjustments Based on the Audience
To be persuasive in a speech, don’t forget to analyze your audience in advance, if possible. Customizing your approach to specific listeners encourages their engagement. A thorough awareness of your target audience’s tastes, expectations, and cultural subtleties ensures that your message connects, making it more approachable and appealing to the people you seek to reach.
Prepare for Rebuttals
Still, be aware that there may be different people in the audience. The main point of persuasive speaking is to convince people of your ideas. Be prepared for rebuttals and that they might attack you. Extensively research opposing points of view to prove yours. You may manage any objections with elegance by being prepared and polite, reaffirming the strength of your argument.
Use Simple Statistics
We’ve already discussed that different techniques may reach different audiences. You could also incorporate simple data to lend credibility to your persuasive talk. Balance emotional appeal with plain numerical statistics to create a captivating blend that will appeal to a wide audience.
Practicing Your Speech
We all have heard Benjamin Franklin’s famous quote, “Practice makes perfect.” Even though he said it hundreds of years ago, it still works for everything, including persuasive public speaking! Consequently, you can improve your text with these pieces of advice:
- Go through and edit your persuasive speech sample.
- Practice your speech with body language and voice variation to find the perfect way to perform it.
- Reduce anxiety by practicing in front of a mirror or telling it to someone ready to provide you with valuable feedback.
- Embrace pauses for emphasis, and work on regulating your pace.
It will help you to know your content well, increase confidence, and promote a polished delivery, resulting in a dynamic and engaging speech to persuade your audience.
Additional Resources to Master Your Speech
PapersOwl wants you to ace your speech! We recommend using additional sources to help master your persuasive speech presentation!
- For inspiration, study any example of persuasive speech from a famous speaker, such as Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” or Steve Jobs’ Stanford commencement address. Analyzing these speeches can provide valuable insights into effective communication techniques.
- Explore Coursera’s course “Speaking to Persuade: Motivating Audiences With Solid Arguments and Moving Language” by the University of Washington.
- Go through different persuasive speech examples for students around the internet, for instance, “Talk Like TED” by Carmine Gallo.
Make your persuasive speech successful by continuously learning and drawing inspiration from accomplished speakers!
Master the Art of Persuasion With PapersOwl
In conclusion, speaking to persuade is an art that helps convince with words . You can craft it by following our tips: include a well-structured persuasive speech introduction, a compelling body, and memorable conclusion. To ace your speech, practice it in advance, be ready for rebuttals, and confidently state your message. The secret lies in blending both for a nuanced and compelling communication style, ensuring your message resonates with diverse audiences in various contexts.
Nevertheless, writing a persuasive speech that can hold your audience’s attention might be difficult. You do not need to step on this path alone. You may quickly construct a persuasive speech that is both successful and well-organized by working with PapersOwl.com . We’ll be there for you every step, from developing a convincing argument to confidently giving the speech. Just send us a message, “ write a speech for me ,” and enjoy the results!
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Persuasive Speech
Persuasive Speech Outline
Last updated on: Apr 9, 2024
A Comprehensive Guide to Crafting an Effective Persuasive Speech Outline
By: Nova A.
10 min read
Reviewed By: Rylee W.
Published on: Jun 19, 2023

Persuasive speeches are a type of speech that aim to convince and persuade an audience to take some action or change their attitudes.
When preparing a persuasive speech , making an outline is an essential step that can really make a difference and bring you closer to success.
So how can you create an excellent outline for your persuasive speech?
Read on to find the answer. In this blog, you’ll get a step-by-step guide on creating an outline, along with some helpful tips and a practical example.

On this Page
How to Write a Persuasive Speech Outline - 7 Easy Steps
Let’s go through the step-by-step process of creating a perfect structure for your persuasive speech.
Step 1: Identify Your Topic & Objective
Begin by clearly identifying the topic and main objective of your persuasive speech. Your persuasive speech topic should be something you feel passionate about and have a strong stance on.
In addition, ask yourself what do you want to achieve with your speech? For instance, you could aim to:
- Change common attitudes
- Motivate your audience
- Inspire specific action
Defining your objective will shape the content and direction of your speech outline.
Step 2: Write the Hook for an Engaging Introduction
Think about how you are going to start your speech. Remember, the hook is the most critical part of your speech's introduction—it's what grabs your audience's attention and compels them to listen.
It could either be:
- A surprising fact or statistic
- A compelling story
- A provocative question
- Or an engaging quote
So write down your hook statement in your outline. Apart from that, you should also add points about the background information or context in your outline.
Step 3: Determine Your Key Points & Arguments
Next, determine the key points or arguments that support your objective. These are the main ideas or concepts you want to convey to your audience.
Consider the key reasons or evidence that support your core message. These supporting points should be clear, relevant, and persuasive. Typically, three to five key points work well for a persuasive speech.
Ensure that each key point supports your overall objective and is logically connected to the others. In addition, you should also address any counter arguments to make your central point stronger.
Step 4: Add Supporting Evidence for Each Key Point
For each key point in your persuasive speech outline, gather supporting evidence that strengthens your argument. This can include:
- Relevant statistics
- Research findings
- Expert opinions
- Anecdotes or examples
Ensure that your evidence is reliable, up-to-date, and directly supports the specific purpose you're addressing.
Step 5: Arrange Your Points in a Logical Order
Once you have identified your key points and their supporting evidence, arrange them in a logical order within your speech outline.
Consider organizing them in a way that builds upon one another, enhancing the flow of your argument and building momentum toward your conclusion.
You can choose to arrange them in the following ways:
- Chronologically
- By order of importance
- Problem-to-solution model
Step 6: Write Call-to-Action for an Impactful Conclusion
The conclusion of your persuasive speech is your final opportunity to leave a lasting impression on your audience. Depending on your topic, you can end with a specific call to action or a thought-provoking question for a memorable ending.
Use strong verbs and emotionally resonant language to compel your audience to think, change, or take action.
Step 7: Revise & Improve
The final step in creating a persuasive speech outline is to thoroughly revise and improve your draft. Here's how to ensure your speech is polished and impactful:
- Review for clarity and coherence. Ensure that your arguments are concise, coherent, and easy to understand.
- Double-check the accuracy and relevance of the supporting evidence you've included for each key point. Make sure they are taken from credible sources and effectively strengthen your arguments.
- Refine your language to make it more persuasive and impactful. Use vivid imagery, strong verbs, and rhetorical devices to engage your audience and evoke emotion.
- Review the length of your speech outline to ensure it aligns with your allotted speaking time. Trim any unnecessary content and streamline your arguments for maximum impact.
Persuasive Speech Format: Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
When it comes to outlining and delivering persuasive speeches, one effective format that has stood the test of time is Monroe's Motivated Sequence. Developed by Alan H. Monroe, this framework provides a structured way to engage and influence your audience.
This format also complements the outline writing steps mentioned above. Let’s break down how you can apply Monroe's motivated sequence format to make your persuasive speech more effective.

Step 1: Attention
The first step in Monroe's Motivated Sequence is to grab the attention of your audience.
You can do it with a captivating hook. As mentioned above, you can use several techniques for capturing attention at the start, such as a compelling story or rhetorical question. The goal is to make your audience sit up, take notice, and become invested in what you have to say.
Step 2: Need
Once you have their attention, it's time to highlight the need for change or action.
Paint a vivid picture that evokes emotions and demonstrates why the need for change, understanding, or action is urgent and important. Use compelling evidence and relatable anecdotes to make the issue tangible to your audience.
Step 3: Satisfaction
After establishing the need, present your proposed solution or action step. Demonstrate how your solution directly addresses the identified problem and fulfills the needs of your audience.
For this, you should provide a clear and detailed explanation of how your solution works and why it is the most effective approach. In addition, back up your claims with evidence, expert opinions, and success stories to strengthen your argument and build credibility.
Step 4: Visualization
To make your persuasive speech more impactful, help your audience visualize the potential outcomes.
For instance, you could paint a compelling picture of what the future could look like if your solution is implemented. Again, try using descriptive language, vivid imagery, and storytelling techniques to engage and evoke their imaginations.
Step 5: Action
The final step in Monroe's Motivated Sequence is to call your audience to action.
In simple words, clearly and explicitly state what you want them to do and how they can take action. Whether it's making a donation or changing their behavior, provide specific steps they can take to contribute to the cause.
Sample Persuasive Speech Outlines
Now that you know how to make your outline using our 7-step guide and the Monroe framework, check out some outline templates and examples. It’ll help you get a better understanding of how it looks in practice.
Problem-Cause-Solution Persuasive Speech Template
Death penalty persuasive speech template, more persuasive speech outline examples.
Want to have a look at more outline samples for a better idea? We've got you covered. Here are some more examples for you:
Pro Choice Persuasive Speech Outline
Universal Healthcare Persuasive Speech Outline
Recycling Persuasive Speech Outline
Persuasive Speech Outline On Mental Health
Tips for Creating an Outstanding Persuasive Speech Outline
Here are some brief tips for creating an engaging persuasive speech outline:
- Choose a Compelling Topic : Select a topic that you are passionate about and that resonates with your audience. A topic that is relevant, timely, and sparks interest will captivate your listeners from the beginning.
- Conduct Thorough Research : Gather credible sources, statistics, examples, and expert opinions to support your arguments. A well-researched speech adds credibility and strengthens your persuasive case.
- Use Persuasive Language : Utilize persuasion techniques including ethos, pathos, and logos to make it compelling, persuasive, and engaging. Choose rhetorical devices such as metaphors, analogies, and powerful imagery to enhance your message and make it memorable.
In conclusion,
By following the outlined steps and examples provided, you can effectively structure your speech and craft persuasive arguments. Remember, you should always make an outline before writing your speech to make it organized and powerful from the start.
However, if you need further help with your speech, then consider hiring a professional service such as MyPerfectPaper.net.
At MyPerfectPaper.net , we have a team of experienced writers that is dedicated to delivering high-quality, custom-written essays.
If you need our help, then just say ' write my paper fast ' and we will make sure to deliver a high-quality paper on time.
Don't hesitate to contact us for expert assistance and take your academic success to the next level.

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- A Complete Guide to Crafting an Effective Persuasive Speech

- 200+ Engaging Persuasive Speech Topics & Ideas for 2024
-11765.jpg)
- 15+ Persuasive Speech Examples to Engage and Persuade

People Also Read
- compare and contrast essay examples
- research proposal writing
- how to write a speech
- narrative essay outline
- thesis topics
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- LEGAL Privacy Policy
© 2024 - All rights reserved
How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you.
You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular problem is important to them, and then you must convince them that you have the solution to make things better.
Note: You don't have to address a real problem. Any need can work as the problem. For example, you could consider the lack of a pet, the need to wash one's hands, or the need to pick a particular sport to play as the "problem."
As an example, let's imagine that you have chosen "Getting Up Early" as your persuasion topic. Your goal will be to persuade classmates to get themselves out of bed an hour earlier every morning. In this instance, the problem could be summed up as "morning chaos."
A standard speech format has an introduction with a great hook statement, three main points, and a summary. Your persuasive speech will be a tailored version of this format.
Before you write the text of your speech, you should sketch an outline that includes your hook statement and three main points.
Writing the Text
The introduction of your speech must be compelling because your audience will make up their minds within a few minutes whether or not they are interested in your topic.
Before you write the full body you should come up with a greeting. Your greeting can be as simple as "Good morning everyone. My name is Frank."
After your greeting, you will offer a hook to capture attention. A hook sentence for the "morning chaos" speech could be a question:
- How many times have you been late for school?
- Does your day begin with shouts and arguments?
- Have you ever missed the bus?
Or your hook could be a statistic or surprising statement:
- More than 50 percent of high school students skip breakfast because they just don't have time to eat.
- Tardy kids drop out of school more often than punctual kids.
Once you have the attention of your audience, follow through to define the topic/problem and introduce your solution. Here's an example of what you might have so far:
Good afternoon, class. Some of you know me, but some of you may not. My name is Frank Godfrey, and I have a question for you. Does your day begin with shouts and arguments? Do you go to school in a bad mood because you've been yelled at, or because you argued with your parent? The chaos you experience in the morning can bring you down and affect your performance at school.
Add the solution:
You can improve your mood and your school performance by adding more time to your morning schedule. You can accomplish this by setting your alarm clock to go off one hour earlier.
Your next task will be to write the body, which will contain the three main points you've come up with to argue your position. Each point will be followed by supporting evidence or anecdotes, and each body paragraph will need to end with a transition statement that leads to the next segment. Here is a sample of three main statements:
- Bad moods caused by morning chaos will affect your workday performance.
- If you skip breakfast to buy time, you're making a harmful health decision.
- (Ending on a cheerful note) You'll enjoy a boost to your self-esteem when you reduce the morning chaos.
After you write three body paragraphs with strong transition statements that make your speech flow, you are ready to work on your summary.
Your summary will re-emphasize your argument and restate your points in slightly different language. This can be a little tricky. You don't want to sound repetitive but will need to repeat what you have said. Find a way to reword the same main points.
Finally, you must make sure to write a clear final sentence or passage to keep yourself from stammering at the end or fading off in an awkward moment. A few examples of graceful exits:
- We all like to sleep. It's hard to get up some mornings, but rest assured that the reward is well worth the effort.
- If you follow these guidelines and make the effort to get up a little bit earlier every day, you'll reap rewards in your home life and on your report card.
Tips for Writing Your Speech
- Don't be confrontational in your argument. You don't need to put down the other side; just convince your audience that your position is correct by using positive assertions.
- Use simple statistics. Don't overwhelm your audience with confusing numbers.
- Don't complicate your speech by going outside the standard "three points" format. While it might seem simplistic, it is a tried and true method for presenting to an audience who is listening as opposed to reading.
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- 5 Tips on How to Write a Speech Essay
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- Writing an Opinion Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- 5 Steps to Writing a Position Paper
- How to Structure an Essay
- Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Audience Analysis in Speech and Composition
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- How to Write a Graduation Speech as Valedictorian
PHILADELPHIA, MAY 9-10 PUBLIC SPEAKING CLASS IS ALMOST FULL! RESERVE YOUR SPOT NOW

- Public Speaking Classes
- Corporate Presentation Training
- Online Public Speaking Course
- Northeast Region
- Midwest Region
- Southeast Region
- Central Region
- Western Region
- Presentation Skills
- 101 Public Speaking Tips
- Fear of Public Speaking
Persuasive Speech: How to Write an Effective Persuasive Speech

Most often, it actually causes the other person to want to play “Devil’s advocate” and argue with you. In this article, we are going to show you a simple way to win people to your way of thinking without raising resentment. If you use this technique, your audience will actually WANT to agree with you! The process starts with putting yourself in the shoes of your listener and looking at things from their point of view.
Background About How to Write a Persuasive Speech. Facts Aren’t Very Persuasive.

Most people think that a single fact is good, additional facts are better, and too many facts are just right. So, the more facts you can use to prove your point, the better chance you have of convincing the other person that you are right. The HUGE error in this logic, though, is that if you prove that you are right, you are also proving that the other person is wrong. People don’t like it when someone proves that they are wrong. So, we prove our point, the other person is likely to feel resentment. When resentment builds, it leads to anger. Once anger enters the equation, logic goes right out the window.
In addition, when people use a “fact” or “Statistic” to prove a point, the audience has a natural reaction to take a contrary side of the argument. For instance, if I started a statement with, “I can prove to you beyond a doubt that…” before I even finish the statement, there is a good chance that you are already trying to think of a single instance where the statement is NOT true. This is a natural response. As a result, the thing that we need to realize about being persuasive is that the best way to persuade another person is to make the person want to agree with us. We do this by showing the audience how they can get what they want if they do what we want.
You may also like How to Design and Deliver a Memorable Speech .
A Simple 3-Step Process to Create a Persuasive Presentation

The process below is a good way to do both.
Step One: Start Your Persuasive Speech with an Example or Story
When you write an effective persuasive speech, stories are vital. Stories and examples have a powerful way to capture an audience’s attention and set them at ease. They get the audience interested in the presentation. Stories also help your audience see the concepts you are trying to explain in a visual way and make an emotional connection. The more details that you put into your story, the more vivid the images being created in the minds of your audience members.
This concept isn’t mystical or anything. It is science. When we communicate effectively with another person, the purpose is to help the listener picture a concept in his/her mind that is similar to the concept in the speaker’s mind. The old adage is that a “picture is worth 1000 words.” Well, an example or a story is a series of moving pictures. So, a well-told story is worth thousands of words (facts).
By the way, there are a few additional benefits of telling a story. Stories help you reduce nervousness, make better eye contact, and make for a strong opening. For additional details, see Storytelling in Speeches .
I’ll give you an example.
Factual Argument: Seatbelts Save Lives

- 53% of all motor vehicle fatalities from last years were people who weren’t wearing seatbelts.
- People not wearing seatbelts are 30 times more likely to be ejected from the vehicle.
- In a single year, crash deaths and injuries cost us over $70 billion dollars.
These are actual statistics. However, when you read each bullet point, you are likely to be a little skeptical. For instance, when you see the 53% statistic, you might have had the same reaction that I did. You might be thinking something like, “Isn’t that right at half? Doesn’t that mean that the other half WERE wearing seatbelts?” When you see the “30 times more likely” statistic, you might be thinking, “That sounds a little exaggerated. What are the actual numbers?” Looking at the last statistic, we’d likely want to know exactly how the reporter came to that conclusion.
As you can see, if you are a believer that seatbelts save lives, you will likely take the numbers at face value. If you don’t like seatbelts, you will likely nitpick the finer points of each statistic. The facts will not likely persuade you.
Example Argument: Seatbelts Save Lives

When I came to, I tried to open my door. The accident sealed it shut. The windshield was gone. So I took my seatbelt off and scrambled out the hole. The driver of the truck was a bloody mess. His leg was pinned under the steering wheel.
The firefighters came a few minutes later, and it took them over 30 minutes to cut the metal from around his body to free him.
A Sheriff’s Deputy saw a cut on my face and asked if I had been in the accident. I pointed to my truck. His eyes became like saucers. “You were in that vehicle?”
I nodded. He rushed me to an ambulance. I had actually ruptured my colon, and I had to have surgery. I was down for a month or so, but I survived. In fact, I survived with very few long-term challenges from the accident.
The guy who hit me wasn’t so lucky. He wasn’t wearing a seatbelt. The initial impact of the accident was his head on the steering wheel and then the windshield. He had to have a number of facial surgeries. The only reason he remained in the truck was his pinned leg. For me, the accident was a temporary trauma. For him, it was a life-long tragedy.
The Emotional Difference is the Key
As you can see, there are major differences between the two techniques. The story gives lots of memorable details along with an emotion that captures the audience. If you read both examples, let me ask you a couple of questions. Without looking back up higher on the page, how long did it take the firefighters to cut the other driver from the car? How many CDs did I have? There is a good chance that these two pieces of data came to you really quickly. You likely remembered this data, even though, the data wasn’t exactly important to the story.
However, if I asked you how much money was lost last year as a result of traffic accidents, you might struggle to remember that statistic. The CDs and the firefighters were a part of a compelling story that made you pay attention. The money lost to accidents was just a statistic thrown at you to try to prove that a point was true.
The main benefit of using a story, though, is that when we give statistics (without a story to back them up,) the audience becomes argumentative. However, when we tell a story, the audience can’t argue with us. The audience can’t come to me after I told that story and say, “It didn’t take 30 minutes to cut the guy out of the car. He didn’t have to have a bunch of reconstructive surgeries. The Deputy didn’t say those things to you! The audience can’t argue with the details of the story, because they weren’t there.
Step 2: After the Story, Now, Give Your Advice
When most people write a persuasive presentation, they start with their opinion. Again, this makes the listener want to play Devil’s advocate. By starting with the example, we give the listener a simple way to agree with us. They can agree that the story that we told was true. So, now, finish the story with your point or your opinion. “So, in my opinion, if you wear a seatbelt, you’re more likely to avoid serious injury in a severe crash.”
By the way, this technique is not new. It has been around for thousands of years. Aesop was a Greek slave over 500 years before Christ. His stories were passed down verbally for hundreds of years before anyone ever wrote them down in a collection. Today, when you read an Aesop fable, you will get 30 seconds to two minutes of the story first. Then, at the conclusion, almost as a post-script, you will get the advice. Most often, this advice comes in the form of, “The moral of the story is…” You want to do the same in your persuasive presentations. Spend most of the time on the details of the story. Then, spend just a few seconds in the end with your morale.
Step 3: End with the Benefit to the Audience

So, the moral of the story is to wear your seatbelt. If you do that, you will avoid being cut out of your car and endless reconstructive surgeries .
Now, instead of leaving your audience wanting to argue with you, they are more likely to be thinking, “Man, I don’t want to be cut out of my car or have a bunch of facial surgeries.”
The process is very simple. However, it is also very powerful.
How to Write a Successful Persuasive Speech Using the “Breadcrumb” Approach
Once you understand the concept above, you can create very powerful persuasive speeches by linking a series of these persuasive stories together. I call this the breadcrumb strategy. Basically, you use each story as a way to move the audience closer to the ultimate conclusion that you want them to draw. Each story gains a little more agreement.
So, first, just give a simple story about an easy to agree with concept. You will gain agreement fairly easily and begin to also create an emotional appeal. Next, use an additional story to gain additional agreement. If you use this process three to five times, you are more likely to get the audience to agree with your final conclusion. If this is a formal presentation, just make your main points into the persuasive statements and use stories to reinforce the points.
Here are a few persuasive speech examples using this approach.
An Example of a Persuasive Public Speaking Using Breadcrumbs
Marijuana Legalization is Causing Huge Problems in Our Biggest Cities Homelessness is Out of Control in First States to Legalize Marijuana Last year, my family and I took a mini-vacation to Colorado Springs. I had spent a summer in Colorado when I was in college, so I wanted my family to experience the great time that I had had there as a youth. We were only there for four days, but we noticed something dramatic had happened. There were homeless people everywhere. Keep in mind, this wasn’t Denver, this was Colorado City. The picturesque landscape was clouded by ripped sleeping bags on street corners, and trash spread everywhere. We were downtown, and my wife and daughter wanted to do some shopping. My son and I found a comic book store across the street to browse in. As we came out, we almost bumped into a dirty man in torn close. He smiled at us, walked a few feet away from the door, and lit up a joint. He sat on the corner smoking it. As my son and I walked the 1/4 mile back to the store where we left my wife and daughter, we stepped over and walked around over a dozen homeless people camped out right in the middle of the town. This was not the Colorado that I remembered. From what I’ve heard, it has gotten even worse in the last year. So, if you don’t want to dramatically increase your homelessness population, don’t make marijuana legal in your state. DUI Instances and Traffic Accidents Have Increased in Marijuana States I was at the airport waiting for a flight last week, and the guy next to me offered me his newspaper. I haven’t read a newspaper in years, but he seemed so nice that I accepted. It was a copy of the USA Today, and it was open to an article about the rise in unintended consequences from legalizing marijuana. Safety officials and police in Colorado, Nevada, Washington, and Oregon, the first four state to legalize recreational marijuana, have reported a 6% increase in traffic accidents in the last few years. Although the increase (6%) doesn’t seem very dramatic, it was notable because the rate of accidents had been decreasing in each of the states for decades prior to the law change. Assuming that only one of the two parties involved in these new accidents was under the influence, that means that people who aren’t smoking marijuana are being negatively affected by the legalization. So, if you don’t want to increase your chances of being involved in a DUI incident, don’t legalize marijuana. (Notice how I just used an article as my evidence, but to make it more memorable, I told the story about how I came across the article. It is also easier to deliver this type of data because you are just relating what you remember about the data, not trying to be an expert on the data itself.) Marijuana is Still Largely Unregulated Just before my dad went into hospice care, he was in a lot of pain. He would take a prescription painkiller before bed to sleep. One night, my mom called frantically. Dad was in a catatonic state and wasn’t responsive. I rushed over. The hospital found that Dad had an unusually high amount of painkillers in his bloodstream. His regular doctor had been on vacation, and the fill-in doctor had prescribed a much higher dosage of the painkiller by accident. His original prescription was 2.5 mg, and the new prescription was 10 mg. Since dad was in a lot of pain most nights, he almost always took two tablets. He was also on dialysis, so his kidneys weren’t filtering out the excess narcotic each day. He had actually taken 20 MG (instead of 5 MG) on Friday night and another 20 mg on Saturday. Ordinarily, he would have had, at max, 15 mg of the narcotic in his system. Because of the mistake, though, he had 60 MGs. My point is that the narcotics that my dad was prescribed were highly regulated medicines under a doctor’s care, and a mistake was still made that almost killed him. With marijuana, there is really no way of knowing how much narcotic is in each dosage. So, mistakes like this are much more likely. So, in conclusion, legalizing marijuana can increase homelessness, increase the number of impaired drivers, and cause accidental overdoses.
If you use this breadcrumb approach, you are more likely to get at least some agreement. Even if the person disagrees with your conclusion, they are still likely to at least see your side. So, the person may say something like, I still disagree with you, but I totally see your point. That is still a step in the right direction.
For Real-World Practice in How to Design Persuasive Presentations Join Us for a Class
Our instructors are experts at helping presenters design persuasive speeches. We offer the Fearless Presentations ® classes in cities all over the world about every three to four months. In addition to helping you reduce nervousness, your instructor will also show you secrets to creating a great speech. For details about any of the classes, go to our Presentation Skills Class web page.
For additional details, see Persuasive Speech Outline Example .

Podcasts , presentation skills
View More Posts By Category: Free Public Speaking Tips | leadership tips | Online Courses | Past Fearless Presentations ® Classes | Podcasts | presentation skills | Uncategorized

15 Persuasive Speeches
Speeches that Make a Change
In this chapter . . .
For many public speeches, the specific purpose is to convince the audience of a particular opinion or claim or to convince them to take some action in response to the speech. When your intention is to affect change in your audience (not just the acquisition of knowledge) then you are delivering a persuasive speech. In this chapter you will learn about the elements of persuasion, why persuasion is difficult, and how to overcome people’s resistance to change by using effective and ethical methods.
Although a persuasive speech involves information—even as much as an informative speech—the key difference is that a persuasive speech is designed for “creating, reinforcing, or changing people’s beliefs or actions” (Lucas, 2015. p. 306). A persuasive speech makes something happen. In other words, it performs a job.
Traditional Views of Persuasion
In the fourth century BCE, the classic philosopher Aristotle took up the study of the public practices of the ruling class in Athenian society. For two years he observed the rhetoric (the art of persuasion) of the men who spoke in the assembly and the courts. In the end, he developed a theory about persuasiveness that has come down to us in history as a treatise called Rhetoric. Among his many ideas was the identification of three elements essential to persuasion: ethos, logos, and pathos. In short, they mean credibility, reasonability, and emotion.
Ethos has come to mean speaker character and credentials. It is the element that establishes the audience’s trust in you as a speaker. A speaker’s credibility is based on who the speaker is and what they know: experience, education, expertise, and background. If you’re delivering a persuasive speech about adopting a pet from a shelter and you have raised several shelter dogs, then you have credibility through experience and should share that fact about yourself with the audience to enhance their trust in your persuasive argument. Another way to establish your credibility is through research sources. You may not be an expert in climate change, but if you were giving a persuasive speech about it, you can cite reliable authoritative sources.
The word ethos looks very much like the word “ethics,” and there are many close parallels to the trust an audience has in a speaker and their honesty and ethical stance. In terms of ethics, it goes without saying that your speech will be truthful.
In addition to expertise and truthfulness is your personal involvement in the topic. Ideally you have chosen the topic because it means something to you personally. Audiences will have more trust in you if they feel you have something as stake or something personal in the subject. For example, perhaps your speech is designed to motivate audience members to take action against bullying in schools, and it’s important to you because you work with the Boys and Girls Club organization and have seen how anti-bullying programs can have positive results. Sharing your own involvement and commitment is key to establishing your credibility on this topic.
Logos is the second key element in Aristotle’s theory of rhetoric. Related to our word “logic,” the Greek term logos in persuasion means presenting ideas that appeal to logic or reason. Logos in a speech pertain to arguments that the audience would find acceptable. Imagine a speech, for example, which has the goal of persuading an audience to adopt healthier eating habits. Would the speech be effective if the arguments focused on how expensive organic foods are? Of course not.
Logic and reason are persuasive not only as matters of content. Logos pertains to organization, as well. An effective persuasive speech presents arguments in an organized fashion.
In words like “empathy,” “sympathy,” and “compassion” we see the root word behind the Greek word pathos. Pathos, for Aristotle, meant exciting emotions such as anger, joy, hate, love, and desire to persuade the audience of the rightness of a proposition. In a positive sense, appealing to the emotions of the audience is a highly effective persuasive tool. In the earlier example of a speech designed to encourage an audience to take action against bullying in schools, including a touching story about a student experiencing bullying would make the audience more likely to support your call for action.
However, we recognize that pathos can be used in a negative way. Emotional appeals that use anger, guilt, hatred, inflammatory language like name-calling, or that try to frighten the audience with horrible images, are counter-productive and even unethical. They might incite emotion in the audience, but they are poor uses of pathos.
One negative emotion used frequently by persuasive speakers is fear. Candidates for political office, for example, often try to provoke fear to move us to vote for them. Intense, over-the-top fear appeals, based on factual falsehoods or cherry-picking, and/or including shocking photos, are not ethical and are often dismissed by discerning audience members. Appealing to the emotion of fear can be ethical if it’s managed carefully. This means being strictly factual and avoiding extremes.
Persuasion and the Audience
It makes sense that if a speaker wants to affect the audience’s beliefs or actions, then the speaker must be perfectly clear about their expectations. If you were listening to a persuasive speech call for your audience to support animals, wouldn’t you want to know exactly what “support” the speaker was talking about? Giving money to charities? Volunteering at an animal shelter? Writing state legislators and urging them to change laws? Your job as a persuasive speaker is to be clear about what you want to create, reinforce, or change in your audience.
For your speech to have persuasive power, you must also consider your audience and choose a goal that is feasible for them. Persuasion isn’t an on/off switch. It’s more like a thermometer. Skillful persuasive speakers respect and identify a persuasive goal that is calibrated to the audience. Think of persuasion as a continuum or line going both directions. At one end is strong disagreement. At the other end is strong agreement. Your audience members, either as a group or individually, are sitting somewhere on that line in relation to your central idea statement, or what we are going to call a proposition in this chapter.
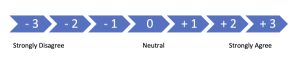
For example, your speech proposition might be something like “The main cause of climate change is human activity.” You are claiming that climate change is due to the harmful things that humans have done to the environment. To be an effective persuasive speaker, one of your first jobs after choosing this topic would be to determine where your audience “sits” on the continuum.
+ 3 means strongly agree to the point of making lifestyle choices to lessen climate change (such as riding a bike instead of driving a car, recycling, eating certain kinds of foods, and advocating for government policy changes). + 2 means agree but not to the point of acting upon it or only acting on it in small ways. + 1 as mildly agrees with your proposition; that is, they think it’s probably true, but the issue doesn’t affect them personally. 0 means neutral, no opinion, or feeling too uninformed to decide. – 1 means mildly opposed to the proposition but willing to listen to those with whom they disagree. – 2 means disagreement to the point of dismissing the idea pretty quickly. – 3 means strong opposition to the point that the concept of climate change itself isn’t even listened to or acknowledged as a valid subject.
Since everyone in the audience is somewhere on this line or continuum, you can accept the fact that any movement toward +3 or to the right is a win. Trying to change an audience from -3 (strong disagreement) to +3 (strong agreement) in a single speech would be quite impossible. When you understand this, you can make strategic choices about the content of your speech.
In this example, if you knew that most of the audience was at -2 or -3, your speech could focus on opening their minds to the possibility of climate change and provide the science behind human causes. On the other hand, if you knew your audience was at +1 or +2, you could focus on urging them to take bold steps, like giving up their gasoline-powered vehicles.
A proposition is assumed to be in some way controversial, or a “stretch” for the audience. Some people in the audience will disagree with your proposition or at least have no opinion; they are not “on your side.”
There will be those in the audience who disagree with your proposition but who are willing to listen. Some members of the audience may already agree with you, although they don’t know why. Both groups could be called the target audience . At the same time, another cluster of your audience may be extremely opposed to your position to the degree that they probably will not give you a fair hearing. They probably can’t be persuaded. Focus on your target audience, they are the one you can persuade.
Why is Persuasion Hard?
Persuasion is hard mainly because we have a bias against change. We go out of our way to protect our beliefs, attitudes, and values. We selectively expose ourselves to messages that we already agree with, rather than those that confront or challenge us. We find it uncomfortable to be confronted with conflicting information or viewpoints.
Additionally, during a persuasive speech the audience members are holding a mental dialogue with the speaker or at least the speaker’s content. The processes that the human mind goes through while it listens to a persuasive message is like a silent conversation. In their minds, audience members are producing doubts or reservations about your proposal. If we could listen in on one of these conversations, it might go something like this:
Speaker: Switching to a plant-based diet is the best action you can take to support a reduction in the CO-2 emissions harming the climate. Audience Member Mind: Yeah, I hear what you’re saying, but eating like that won’t give me enough protein.
The audience member has a doubt or reservation about the speaker’s proposal. We can call these doubts “yeah, buts” because the audience members are thinking, “Yeah, but what about—?” It’s a skill of good persuasion speechwriting to anticipate reservations.
Solutions to the Difficulty of Persuasion
With these reasons for the resistance audience members have to persuasion, what is a speaker to do? Here are some strategies.
First, choose a feasible goal for the persuasive action you want the audience to take. Going back to our continuum, trying to move an audience from -3 to +2 or +3 is too big a move. Having reasonable persuasive goals is the first way to meet resistance. Even moving someone from -3 to -2 is progress, and over time these small shifts can eventually result in a significant amount of persuasion.
Secondly, as speakers we must address reservations. While speechwriters aren’t mind-readers, we can easily imagine reservations about our proposition and build a response to those reservations into the speech. Using the example above, a speaker might say:
Switching to a plant-based diet is the best action you can take to support a reduction in the CO-2 emissions harming the climate. I urge all of you to consider this important dietary change. Perhaps you are thinking that a plant-based diet won’t provide enough protein. That is a common concern. Nutritionists at the website Forks Over Knives explain how the staples of a PB diet—whole grains, legumes, and nuts—provide ample protein.
Here, the speaker acknowledges a valid reservation and then offers a rebuttal. This is called a two-tailed argument. The speaker articulates a possible argument against their proposition and then refutes it.
The third strategy is to keep in mind that since you are asking the audience to change something, they must view the benefits of the change as worth the stress of the change. In effect, audiences want to know: “What’s in it for me?” (WIIFM). As a speaker, you should give thought to that question and in your speech address the benefit, advantage, or improvement that the audience will gain by taking the action you propose.
Structure of a Persuasive Speech
A persuasive speech shares with an informational speech the same four elements for a strongly structured speech: introduction, body, conclusion, and connectors. Like informative speeches, preparation requires thoughtful attention to the given circumstances of the speech occasion, as well as audience analysis in terms of demographic and psychographic features. That said, there are some elements unique to a persuasive speech.
General and Specific Purpose General Purpose: To Persuade Specific Purpose: To motivate my audience of campus administrators to provide LGBTQ+ safe spaces on campus.
This looks familiar up to this point. The general purpose is one of the three broad speech goals (to instruct, to persuade, to inspire or entertain). The specific purpose statement follows a clear T.W.A.C. pattern:
T o + W ord: To convince A udience: campus administrators C ontent: LGBTQ+ safe spaces
What is unique to persuasive speeches is what comes next, the proposition.
Propositions
Informational speeches require a thesis. This is the central idea of the speech; its “takeaway.” Persuasive speeches equally require a strong focus on the main idea, but we call this something else: a proposition . A proposition is a statement that expresses a judgement or opinion about which you want audience in agreement. Remember that propositions must be something that can be argued. To say, “The earth is round” isn’t a proposition. “The earth is flat” is a proposition.
- Converting to solar energy saves homeowners money.
- A vegan diet is the most ethical way to eat.
- Universities should provide on-line learning options for all classes.
- The Constitution’s Second Amendment does not include possession of automatic weapons for private use.
Like a thesis statement for an informative speech, a proposition statement is best when it not only clearly states the judgment or opinion for which you seek audience agreement, but also provides a succinct preview of the reasons for that judgement.
Universities should provide LGBTQ+ safe spaces on campus to promote visibility, build community, and protect well-being for LGBTQ+ students and their allies.
Types of Propositions
If you take a closer look at the propositions above, you’ll notice that they suggest several types of persuasion. In fact, there are several broad categories of propositions, determined by their primary goal. These are: a) propositions of fact, b) propositions of value, c) propositions of policy, and d) propositions of definition.
Proposition of Fact
Speeches with this type of proposition attempt to establish the truth of a statement. The core of the proposition isn’t whether something is morally right or wrong, only that a statement is supported by evidence or not. These propositions are not facts such as “the chemical symbol for water is H20.” Rather, propositions of fact are statements over which people disagree and there is evidence on both sides. Some examples of propositions of fact are:
- Experiments using animals are essential to the development of many life-saving medical procedures.
- Climate change has been caused by human activity.
Notice that in none of these are any values—good or bad—mentioned. The point of these propositions is to prove with evidence the truth of a statement.
Proposition of Value
Propositions of fact have the primary purpose of arguing that something exists in a particular way. Propositions of value, on the other hand, have as their primary purpose to argue that one thing is better than another. When the proposition has a word such as “good,” “bad,” “best,” “worst,” “just,” “unjust,” “ethical,” “unethical,” “moral,” “immoral,” “beneficial,” “harmful,” “advantageous,” or “disadvantageous,” then it’s a proposition of value. Some examples include:
- Hybrid cars are the best form of automobile transportation available today.
- Mascots that involve Native American names, characters, and symbols are unjust.
Propositions of value require a first step: defining the “value” word. If you are trying to convince your audience that something is “unjust,” you will have to make clear what you mean by that term. For different people, “best” might mean “safest,” “least expensive,” “most environmentally responsible,” “stylish,” “powerful,” or “prestigious.” Obviously, in the case of the first proposition above, it means “environmentally responsible.” It’s the first job of the speaker, after introducing the speech and stating the proposition, to explain what “best form of automobile transportation” means. Then the proposition would be defended with separate arguments.
Proposition of Policy
These propositions are easy to identify because they almost always have the word “should” in them. These propositions call for a change in policy or practice (including those in a government, community, or school), or they can call for the audience to adopt a certain behavior.
- The federal government should act to ensure clean water standards for all citizens.
- Universities should eliminate attendance requirements.
- States should lower taxes on food.
The proposition determines the approach to the speech, especially the organization. The exact phrasing of the proposition should be carefully done to be reasonable, positive, and appropriate for the context and audience.
Propositions of Definition
Propositions of definitions argue that a word, phrase, or concept has a particular meaning. Lawyers, legislators, and scholars often write briefs, present persuasive speeches, or compose articles to define terms that are vital to defendants, citizens, or disciplines. Some examples might be:
- The Second Amendment to the Constitution does not include possession of automatic weapons for private use.
- Alcoholism should be considered a disease because…
- Thomas Jefferson’s definition of inalienable rights did not include a right to privacy.
In each of these examples, the proposition is that the definition of these things needs to be changed or viewed differently, but the audience isn’t asked to change an attitude or action.
These are not strict categories. A proposition of value most likely contains elements of facts and definitions, for example. However, identifying the primary category for a persuasive speech focuses the speaker on the ultimate purpose of the speech.
Pro-Arguments
Once you know your proposition, the next step is to make your case for your judgement or opinion through clear and distinct points. These are the main points of the body of your persuasive speech. We call these the “pro” or “for” arguments. You should present at least three distinct arguments in favor of your proposition. Expanding on the example above,
General Purpose: To Persuade Specific Purpose: To motivate my audience of campus administrators to provide LGBTQ+ safe spaces on campus. Proposition: Universities should provide LGBTQ+ safe spaces on campus in order to promote visibility, build community, and protect well-being for LGBTQ+ students and their allies.
Three pro-arguments for the proposition are:
Pro-Argument #1: Creating a safe space makes LGBTQ+ community more visible and central to campus life, instead of marginalized. Pro-Argument #2: Safe spaces create a place where LGBTQ+ and their allies learn to build networks, friendship, and support circles. Pro-Argument #3: With a safe and centralized space bringing together this community, instances of bias or harassment can be brought to counselors, making for a safer community.
Two-Tailed Arguments
There is one more crucial element following pro-arguments. These are unique to persuasive speeches. As discussed above, it’s essential to anticipate and address audience reservations about your propositions. These are the two-tailed arguments that articulate the reservation and then address it or refute it. In the example we’re using, such a statement might look like this:
“Perhaps you are thinking that an LGBTQ+ safe space isn’t necessary on campus because there are already places on campus that provide this function. I understand that concern. However, a space that is officially provided by the University provides access to resources with trained personnel. The national organization CampusPride provides training to university facilitators for exactly this reason.”
There are some techniques for rebuttal or refutation that work better than others. You would not want to say, “If you are one of the people who believe this about my proposition, you are wrong.” It’s better to say that their reservations are “misconceptions,” “myths,” or “mistaken ideas” that are commonly held about the proposition.
Building Upon Your Persuasive Speech’s Arguments
Once you have constructed the key arguments, it’s time to be sure the main points are well supported with evidence.
First, your evidence should be from sources that the audience will find credible. If you can find the same essential information from two sources but know that the audience will find the information more credible from one source than another, use and cite the information from the more credible one. For example, if you find the same statistical data on Wikipedia and the US Department of Labor’s website, cite the US Department of Labor. Audiences also accept information from sources they consider unbiased or indifferent. Gallup polls, for example, have been considered reliable sources of survey data because unlike some organizations, Gallup does not have a cause (political or otherwise) it’s supporting.
Secondly, your evidence should be new to the audience. New evidence is more attention-getting, and you will appear more credible if you tell the audience something new (as long as you cite it well) than if you use the “same old, same old” evidence they have heard before.
Third, in order to be effective and ethical, your supporting evidence should be relevant and not used out of context, manipulated, or edited to change its meaning.
After choosing the evidence and apportioning it to the correct parts of the speech, you will want to consider the use of metaphors, quotations, rhetorical devices, and narratives that will enhance the language and “listenability” of your speech. Narratives are especially good for introduction and conclusions, to get attention and to leave the audience with something dramatic. You might refer to the narrative in the introduction again in the conclusion to give the speech a sense of finality.
Lastly, you will want to decide if you should use any type of presentation aid for the speech. The decision to use visuals such as PowerPoint slides or a video clip in a persuasive speech should take into consideration the effect of the visuals on the audience and the time allotted for the speech. The charts, graphs, or photographs you use should be focused and credibly done.
Organization of a Persuasive Speech
You can see that the overall structure of a persuasive speech follows a common model: introduction, body (arguments and support), two-tailed arguments, and conclusion. Study the example at the end of this chapter to see this structure in action.
In speechwriting, you can think of a speech structure like the building of a house and organization like the arrangement of the rooms within it. As with other speeches, persuasive speeches can be organized topically, chronologically, or spatially. However, persuasive speeches often follow a problem-solution or problem-cause-solution pattern.
Organization for a proposition of fact
If your proposition is one of fact or definition, it will be best to use a topical organization for the body of your speech. That means that you will have two to four discrete, separate topics in support of the proposition.
Proposition: Converting to solar energy saves homeowners money.
- (Pro-Argument 1) Solar energy can be economical to install.
- (Pro-Argument 2) The government awards grants for solar.
- (Pro-Argument 3) Solar energy reduces power bills.
- (Pro-Argument 4) Solar energy requires less money for maintenance.
Organization for a proposition of value
A persuasive speech that incorporates a proposition of value will have a slightly different structure. A proposition of value must first define the “value” word for clarity and provide a basis for the other arguments of the speech. Then the pro-arguments for the proposition based on the definition.
Proposition: Hybrid cars are the best form of automotive transportation available today.
- (Definition of value) Automotive transportation that is best meets three standards: dependable, economical, and environmentally responsible.
- (Pro-Argument 1) Studies show that hybrid cars are durable and dependable.
- (Pro-Argument 2) Hybrid cars are fuel-efficient.
- (Pro-Argument 3) Hybrid cars are environmentally responsible.
Organization for a propositions of policy
The most common type of outline organizations for speeches with propositions of policy is problem-solution or problem-cause-solution. Typically, we don’t feel any motivation to change unless we are convinced that some harm, problem, need, or deficiency exists, and even more, that it affects us personally. Therefore, the organization of a speech about policy needs to first explain the problem and its cause, followed by the solution in the form of 3-5 pro-arguments.
Proposition: Universities should provide on-line learning options for all classes.
- (Problem) Regular attendance in a physical classroom is no longer possible for all students.
- (Cause) Changes brought about by the COVID pandemic have made guaranteed classroom attendance difficult.
- (Pro-Argument 1) Providing on-line learning options protects the health of students.
- (Pro-Argument 2) On-line learning serves students who cannot come to campus.
- (Pro-Argument 3) Access to on-line learning allows students to maintain employment while still going to school.
To complete this outline, along with introduction and conclusion, your pro-arguments should be supported with fact, quotations, and statistics.
Your persuasive speech in class, as well as in real life, is an opportunity to share a passion or cause that you believe will matter to society and help the audience live a better life. Even if you are initially uncomfortable with the idea of persuasion, we use it all the time in diverse ways. Choose your topic based on your commitment and experience, look for quality evidence, craft your proposition so that it will be clear and audience appropriate, and put the finishing touches on it with an eye toward enhancing your logos , ethos , and pathos .
Media Attributions
- Persuasion Scale © Mechele Leon is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
Public Speaking as Performance Copyright © 2023 by Mechele Leon is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
How to Write a Persuasive Speech | Tips for Crafting an Effective One in 2024
Leah Nguyen • 08 Apr 2024 • 7 min read
A persuasive speech doesn’t make you talk till your throat’s dry.
In today’s discussion, we’ll break down the proven formula successful orators use to move minds and hearts.
Whether you’re running for office, pitching new product, or advocating for an important cause, let’s check out how to write a persuasive speech .
Table of Contents
What is a persuasive speech, #1. research the subject, #2. cut down the fluff, #3. craft a persuasive speech structure, #4. tell a story, short persuasive speech examples, persuasive speech topics, bottom line, frequently asked questions, tips for audience engagement.
- Eye Contact in Communication
- Persuasive Speech Outline
- Use live word clouds or live Q&A to survey your audience easier!
- Use brainstorming tool effectively by AhaSlides idea board

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
Have you ever been truly moved by a speaker who had you hanging on their every word? Who took you on such an inspiring journey that you left wanting to take action? Those are the hallmarks of a master persuader at work.
A persuasive speech is a type of public speaking designed to literally change minds and motivate behaviour. It’s part communication magic, part psychology hack – and with the right tools, anyone can learn to do it.
At its core, a persuasive speech aims to convince an audience of a specific idea or course of action by appealing to both logic and emotion. It lays out clear arguments while also tapping into passions and values.

A successful persuasive structure will introduce the topic, outline key points, address counterarguments, and conclude with a memorable call to action. Visual aids, stories, rhetorical devices and enthusiastic delivery all enhance the experience.
Although meant to be convincing, quality persuaders never resort to manipulation. Rather, they present solid facts with empathy and honour other perspectives along the journey.
From campaign speeches to PTA fundraisers , the ability to strategically rally support around a viewpoint through oration alone is a talent worth cultivating. So whether you aspire to inspire social change or simply motivate mindsets in your circle, adding persuasion to your public speaking playbook is sure to magnify your impact.
How to Write a Persuasive Speech
Crafting the perfect persuasive address requires thoughtful planning. But fear not, with the right framework you’ll be well on your way to masterfully motivating any audience.

They say knowing is half the battle. When you’re doing research on the topic, you’ll unconsciously remember every detail and information along the way. And because of that, smooth information will flow out of your mouth before you know it.
Get familiarised with reputational research papers, peer-reviewed journals and expert opinions to craft a concrete foundation for your speech. They also present different views and counterarguments so you can address them on the day.
You can map each point with a respective counterargument using a mind-mapping tool for a structured and more organised approach.
🎊 Check out: 2024 Updated | Online Quiz Makers | Top 5 Free Options to Energise your Crowd

This is no time to flex your wealth of ultra-complicated technical words. The idea of a persuasive speech is to get your point across verbally.
Make it sound natural so that you have no trouble spewing it out loud and your tongue doesn’t linger trying to pronounce something like anthropomorphism.
Avoid lengthy constructions that cause you to stumble. Chop the sentences down to short and concise pieces of information.
See this example:
- It could be said that in light of the presently existing circumstances which are currently surrounding us at this moment in time, there may potentially exist certain conditions that might feasibly be conducive toward potentially providing an optimum environment for potentially achieving desired outcomes.
Sounds unnecessarily long and complex, isn’t it? You can just bring this down to something like this:
- The current circumstances could create conditions conducive to achieving desired outcomes.
The clearer version gets the same point across in a more direct and succinct way by removing extra words, simplifying the phrasing and structure, and using more active rather than passive construction.

The general outline for a speech needs to be clear and logical. Here are some tips on how to craft one:
- Start with a compelling hook. Capture attention instantly with a surprising stat, intriguing anecdote or open question. Pique curiosity about the issue.
- Clearly state your thesis up front. Distil your central argument and goal into a concise, memorable statement. Paint the picture of what you aim to achieve.
- Support your thesis with well-chosen facts. Cite respected sources and data-driven evidence to rationally reinforce key talking points. Appeal to logic as well as emotion.
- Anticipate objections and address counterarguments respectfully. Show you understand opposing viewpoints yet position why yours is most sound.
- Weave in illustrative stories and examples. Relate concepts to people’s lives through a compelling narrative. Paint a vivid mental image they’ll never forget.
- Close powerfully with a call to action. Inspire audiences to take a specific next step that furthers your cause. Motivate minds and spark an enduring commitment to your vision.
🎊 Persuasive speech tips: Survey and feedback better with the write tools, to make sure that your structure is appealing to the participants!

While logic and facts are important, truly moving an audience to act requires connecting on a deeper human level through emotion.
Persuasive speeches that only present dry statistics and reasoning, no matter how sound, will fail to inspire.
To craft a speech that sways hearts as well as minds, strategically incorporate stories, anecdotes and value-based language tailored to your listeners.
Describe how the issue personally impacts real people in a way the audience can relate to and feel empathetic towards. Share a short, engaging narrative that puts a vivid face to the topic.
Appeal to your crowd’s core beliefs and priorities by framing your argument in terms of principles they cherish such as justice, empathy or progress.
Tap into emotions like pride, hope or outrage to energise their conviction to support your solution. With targeted emotional insights paired with rational appeals, you’ll guide your audience along a far more persuasive journey of the heart and soul.

Here are examples of short persuasive speeches. A convincing one should have a specific purpose, as well as central arguments built on it.
Persuasive Speech Example 1: Title: Why Recycling Should Be Mandatory Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that recycling should be required by law in all communities. Central Idea: Recycling helps the environment, conserves natural resources and saves money; therefore, all communities should pass laws to mandate recycling programs.
Persuasive Speech Example 2: Title: Why Social Media Is Detrimental to Teen Mental Health Specific Purpose: To persuade parents to monitor and limit their teen’s social media usage. Central Idea: Excessive social media use has been linked to increased anxiety, depression and loneliness in teens by promoting social comparison and FOMO. Implementing reasonable limits can help protect mental well-being.
Persuasive Speech Example 3: Title: Why School Lunches Need Improvement Specific Purpose: To persuade the PTA to lobby for healthier cafeteria food options. Central Idea: The current lunch offerings at our school are often overly processed and lack nutrients, leading to obesity risks. Upgrading to fresher, whole foods will boost student health and focus.

Practising a chosen speech topic can increase your persuasion skills tremendously. Here are some topics to kickstart:
- Year-round schooling, later start times, homework policies, funding for arts/sports, dress codes
- Immigration reform, gun control laws, LGBTQ+ rights, abortion, marijuana legalisation
- Sugar/food taxes, banning plastic straws, GMO labelling, smoking bans, green energy initiatives
- Social media regulations, driverless cars, surveillance laws, video game restrictions
- Minimum wage increases, universal basic income, trade policies, taxes
- Prison/sentencing reform, police use of force, drug decriminalisation, private prisons
- Foreign aid, refugees/asylum, trade agreements, military budget
- Gender roles, body positivity, social media/TV influence, work-life balance
- Free will vs. determinism, ethical consumption, technology’s impact, social justice
- Ratings systems, content restrictions, media bias, streaming vs. cable
In closing, an effective persuasive speech has the power to inspire change and bring people together behind important causes. If you understand audience psychology and craft your message strategically with passion and precision, you too can sway minds on issues you care about.
How do I start a persuasive speech?
Start your persuasive speech with a startling statistic, fact or emotional story to hook the audience instantly.
What makes a good persuasive speech?
A good persuasive speech often comprises logic, emotion and credibility. Satisfying all three criteria will enhance your argument.
Leah Nguyen
Words that convert, stories that stick. I turn complex ideas into engaging narratives - helping audiences learn, remember, and take action.
More from AhaSlides

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
- Speechwriting
How to Write a Persuasive Speech
Last Updated: December 10, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Patrick Muñoz . Patrick is an internationally recognized Voice & Speech Coach, focusing on public speaking, vocal power, accent and dialects, accent reduction, voiceover, acting and speech therapy. He has worked with clients such as Penelope Cruz, Eva Longoria, and Roselyn Sanchez. He was voted LA's Favorite Voice and Dialect Coach by BACKSTAGE, is the voice and speech coach for Disney and Turner Classic Movies, and is a member of Voice and Speech Trainers Association. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,525,722 times.
A persuasive speech is a speech intended to convince the audience to do something. Whether you want to get people to vote, stop littering, or change their minds about an important issue, persuasive speeches are an effective way to sway an audience. There are many elements that go into a successful persuasive speech. But, with some preparation and practice, you can deliver a powerful speech.
Preparing to Write

- Especially if your topic is a controversial one, it's a good idea to know the arguments on all sides of the issue. [1] X Research source Whatever argument you are making, you'll be more persuasive if you can address the views of the opposing side.
- Spend some time reading books or articles about your topic. You can go to the library and ask a librarian for help finding books, or just go online and find some articles. Make sure to use reliable sources, like major news organizations, or academic books or articles.
- Opinion-oriented sources, like editorials, talk radio, or partisan cable news, can be valuable for finding out what other people think about your topic. But, don't rely on them as your only source of information. They can be very biased. If you use them at all, make sure to read a variety of viewpoints on the matter, not just one side.

- For example, if your topic is recycling, it's important to know a lot about recycling. But, your speech will need to reflect exactly what you hope the audience will do. Are you trying to get people to vote in favor of a citywide recycling program? Or are you trying to convince them to sort out their glass and cans and put them in a separate bin? These will be different speeches, so having the goal spelled out early will help you craft your message.

- An audience that knows little about your topic will need more background information and simpler language. An audience made up of experts on the topic would likely find such a simple speech boring.
- Likewise, an audience that already supports your view on a topic will be easier to persuade to take some action. You won't need to convince them you are right, but only that they need to do something. By contrast, an audience that does not agree with you will need persuasion to even consider your point of view.
- For example, imagine you want to convince your audience to support a city-wide recycling program. If they already think recycling is important, you only need to convince them of the value of this specific program. But, if they don't care about recycling or oppose it, you will need to first convince them that recycling is worthwhile.

- Ethos. These are appeals to the audience's ethics or morals. For example: "Recycling is the right thing to do. Wasting our limited resources steals from future generations, which is immoral."
- Pathos. These are appeals to the audience's emotions. For example: "Think of the animals that lose their homes every day because of trees being chopped down. If we recycled more, we could save these beautiful forests."
- Logos. These are appeals to the audiences logic or intellect. For example: "We know that there is a limited supply of natural resources. We can make this supply last longer by recycling."
- You can rely on any one or some combination.

- The number of points you can make to support your position will be determined by how much time you have to speak.
- As a rule of thumb, three to four supporting points is usually a good number. [2] X Research source
- For example, in the speech about recycling, your three main points might be: 1. Recycling saves resources, 2. Recycling reduces the amount of garbage, and 3. Recycling is cost-effective.
Writing your Speech

- An attention grabber. This could be a statement (or sometimes a visual) that gets your audience's attention. It can be a good idea to be a little startling or dramatic at the opening of your speech. For example, you might start with information (or pictures) showing how a nearby landfill is nearly full to capacity.
- A link to the audience. This is a means of showing that you have something in common with the audience. Show that you have a similar background or share an emotional connection of some kind. This will really depend on knowing your audience. For example, if you are a parent, speaking to other parents, you might emphasize the concern for your own children's future. If you share a common interest or ideological position with your audience, you can emphasize that.
- Your credentials. This is a means of showing that you are knowledgeable or an authority on the topic of the speech. Highlight the research you've done on your topic. If you have any personal or professional experience with the topic, be sure to emphasize that, too. In the recycling example, you might say "I've invested many hours studying the recycling issue and the types of programs available in other cities."
- Your goal. Explain to the audience what you hope the speech will accomplish. For example: "I hope by the end of my talk that you will agree that we need a city wide recycling program."
- A road map. Finally, tell the audience what the main points of the speech will be. For example, "I believe we must start a recycling program for these three reasons...."

- Arrange these points logically. Don't jump from one point to the next, and then back again. Instead, complete an argument, then move on to another that flows logically from it. [4] X Research source
- Use credible sources from your research to back the points you are making. Even if your point is more emotional (pathos), introducing some factual information will make your argument stronger. For example "Each year, 40,000 acres of beautiful forests are destroyed to make paper, according to a study from the American Recycling Institute."
- Use real life examples that the audience can relate to. Even an argument based on facts and logic (logos) should relate to the audience's lives and interests. For example: "In these hard economic times, I know many of you are afraid that a recycling program will mean a costly increase in taxes. But, the city of Springfield started a program like this one three years ago. So far they've seen an increase in revenue as a result of the program. Many residents have seen a decrease in their taxes as a result."

- Make sure that you describe opposing views fairly and objectively. Consider whether someone who actually holds that view would approve of the way you are describing their position. If you aren't sure, find someone who thinks that way and ask!
- For example, you would not want to say: "opponents of recycling just don't care if we waste our precious resources, or our money." That's not a fair description of their opinion.
- Instead, you might say: "opponents of recycling are concerned that the cost might be much higher than just using new materials," and then go on to offer an argument about why recycling might be the more cost-effective option.

- Don't just restate, verbatim, what you've already said. Instead, use this as an opportunity to reinforce the way your main points support your call to action. For example: "To sum up, I've shown you (points a, b, and c). These three undeniable facts point to a city-wide recycling program as the most sensible and ethical step we can take in helping create a more sustainable future. Please, join me in voting 'yes' on this program in November."
Delivering your Speech

- Try practicing in front of a mirror, so that you can see how you are delivering the speech. This can help you notice your facial expressions and body language. These can help or hinder your ability to get your message across.
- For example, you might notice you are slouching, or that that you fidget with your collar. These actions suggest to an audience that you aren't confident.
- Better still, record yourself with a video camera and watch the tape afterwards. This can help you see (and hear) where your delivery needs improvement. [5] X Research source It has the benefit of providing audio, and also won't distract you as much as a mirror when you're speaking.
- Once you've practiced on your own a few times, try giving the speech to a small group of friends or family members. Ask for their feedback on your message and delivery.

- Generally speaking, this will mean dressing professionally. But, the degree of formality will vary. A speech to a film club to convince them to show your film won't require the same degree of formality as speaking to the executives of a movie distribution company. For the executives, you would want to wear a suit. For the film club, that might be overdoing it.

- Be friendly and make eye contact with the audience.
- Move around, where appropriate, but don't fidget or pick at your clothes or hair.
- Don't read the speech. It's okay to use a few notes to keep yourself on track, but your speech should be mostly memorized.
- Roll with the punches. If you make a mistake, don't let it derail your whole speech. This might be an opportunity to use a little humor. Then, move on.

- For example, if you want them to contact the mayor, demanding a recycling program, don't just ask them to do it. Give them stamped, addressed envelopes to send a letter, or cards with the mayor's phone number and email address. If you do this, many more people are likely to follow through.
Patrick Muñoz
Speak from your heart and connect with your audience. Look them in the eyes and really talk to them. Make sure you're comfortable delivering your speech and that you use a warm, confident tone.
Sample Template

Community Q&A
- Look around at the audience, making eye contact, especially during pauses in your speech. If you're feeling nervous about this, pick out a single person in the audience and pretend you are speaking only to them. After a little while, pick someone else, and repeat. [6] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Speak forward, projecting your voice toward the audience with confidence. Do not speak down toward the floor. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Try to cite sources for statistics and use credible, non-biased sources. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Avoid being confrontational, when possible. Don't be sarcastic or mocking when discussing viewpoints other than your own. This can be alienating to your audience, even those who may agree with you. Thanks Helpful 55 Not Helpful 17
- Don't be pompous or arrogant during your speech. Be humble, and be open to questions, suggestions, and feedback. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://grammar.yourdictionary.com/style-and-usage/steps-for-writing-a-persuasive-speech.html
- ↑ http://www.best-speech-topics.com/writing-a-persuasive-speech.html
- ↑ https://www.speechanddebate.org/wp-content/uploads/Tips-for-Writing-a-Persuasive-Speech.pdf
- ↑ https://www.comm.pitt.edu/structuring-speech
- ↑ https://www.leonardoenglish.com/blog/recording-yourself-in-english
- ↑ https://www.zenbusiness.com/blog/eyecontact/
About This Article

To write a persuasive speech, start with a strong opening that will make your reader want to pay attention, including an attention grabber, your credentials, the essay's goal, and a road map for the essay. Next, offer persuasive evidence or reasons why the reader should support your viewpoint. Arrange these points logically, use credible sources, and employ some real life examples. Additionally, address counter-arguments to show that you’re looking at the topic from all sides. Finally, conclude by clearly letting the audience know how to put your ideas into action. To learn how to involve your audience when you deliver your speech, keep reading. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Evan Murphree
Feb 8, 2022
Did this article help you?

Dianka Pradhan
Jun 28, 2019
Brittany Grech
Mar 27, 2017
Mavis Agyeiwaa Kyei
Oct 27, 2020
Jun 5, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles


Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Module 10: Persuasive Speaking
Structure of a persuasive speech, learning objectives.
Identify characteristic structures of a persuasive speech.
In many ways, a persuasive speech is structured like an informative speech. It has an introduction with an attention-getter and a clear thesis statement. It also has a body where the speaker presents their main points and it ends with a conclusion that sums up the main point of the speech.
The biggest difference is that the primary purpose of an informative speech is to explain whereas the primary purpose of a persuasive speech is to advocate the audience adopt a point of view or take a course of action. A persuasive speech, in other words, is an argument supported by well-thought-out reasons and relevant, appropriate, and credible supporting evidence.
We can classify persuasive speeches into three broad categories:
- The widely used pesticide Atrazine is extremely harmful to amphibians.
- All house-cats should be kept indoors to protect the songbird population.
- Offshore tax havens, while legal, are immoral and unpatriotic .
The organizational pattern we select and the type of supporting material we use should support the overall argument we are making.
The informative speech organizational patterns we covered earlier can work for a persuasive speech as well. In addition, the following organization patterns are especially suited to persuasive speeches (these are covered in more detail in Module 6: Organizing and Outlining Your Speech):
- Causal : Also known as cause-effect, the causal pattern describes some cause and then identifies what effects resulted from the cause. This can be a useful pattern to use when you are speaking about the positive or negative consequences of taking a particular action.
- Problem-solution : With this organizational pattern, you provide two main points. The first main point focuses on a problem that exists and the second details your proposed solution to the problem. This is an especially good organization pattern for speeches arguing for policy changes.
- Problem-cause-solution: This is a variation of the problem-solution organizational pattern. A three-step organizational pattern where the speaker starts by explaining the problem, then explains the causes of the problem, and lastly proposes a solution to the problem.
- Comparative advantage : A speaker compares two or more things or ideas and explains why one of the things or ideas has more advantages or is better than the other.
- Monroe’s motivated sequence : An organizational pattern that is a more elaborate variation of the problem-cause-solution pattern. We’ll go into more depth on Monroe’s motivated sequence on the next page.
- Structure of a Persuasive Speech. Authored by : Mike Randolph with Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution

Persuasive Speeches — Types, Topics, and Examples

What is a persuasive speech?
In a persuasive speech, the speaker aims to convince the audience to accept a particular perspective on a person, place, object, idea, etc. The speaker strives to cause the audience to accept the point of view presented in the speech.
The success of a persuasive speech often relies on the speaker’s use of ethos, pathos, and logos.

Ethos is the speaker’s credibility. Audiences are more likely to accept an argument if they find the speaker trustworthy. To establish credibility during a persuasive speech, speakers can do the following:
Use familiar language.
Select examples that connect to the specific audience.
Utilize credible and well-known sources.
Logically structure the speech in an audience-friendly way.
Use appropriate eye contact, volume, pacing, and inflection.
Pathos appeals to the audience’s emotions. Speakers who create an emotional bond with their audience are typically more convincing. Tapping into the audience’s emotions can be accomplished through the following:
Select evidence that can elicit an emotional response.
Use emotionally-charged words. (The city has a problem … vs. The city has a disease …)
Incorporate analogies and metaphors that connect to a specific emotion to draw a parallel between the reference and topic.
Utilize vivid imagery and sensory words, allowing the audience to visualize the information.
Employ an appropriate tone, inflection, and pace to reflect the emotion.
Logos appeals to the audience’s logic by offering supporting evidence. Speakers can improve their logical appeal in the following ways:
Use comprehensive evidence the audience can understand.
Confirm the evidence logically supports the argument’s claims and stems from credible sources.
Ensure that evidence is specific and avoid any vague or questionable information.
Types of persuasive speeches
The three main types of persuasive speeches are factual, value, and policy.

A factual persuasive speech focuses solely on factual information to prove the existence or absence of something through substantial proof. This is the only type of persuasive speech that exclusively uses objective information rather than subjective. As such, the argument does not rely on the speaker’s interpretation of the information. Essentially, a factual persuasive speech includes historical controversy, a question of current existence, or a prediction:
Historical controversy concerns whether an event happened or whether an object actually existed.
Questions of current existence involve the knowledge that something is currently happening.
Predictions incorporate the analysis of patterns to convince the audience that an event will happen again.
A value persuasive speech concerns the morality of a certain topic. Speakers incorporate facts within these speeches; however, the speaker’s interpretation of those facts creates the argument. These speeches are highly subjective, so the argument cannot be proven to be absolutely true or false.
A policy persuasive speech centers around the speaker’s support or rejection of a public policy, rule, or law. Much like a value speech, speakers provide evidence supporting their viewpoint; however, they provide subjective conclusions based on the facts they provide.
How to write a persuasive speech
Incorporate the following steps when writing a persuasive speech:
Step 1 – Identify the type of persuasive speech (factual, value, or policy) that will help accomplish the goal of the presentation.
Step 2 – Select a good persuasive speech topic to accomplish the goal and choose a position .

Step 3 – Locate credible and reliable sources and identify evidence in support of the topic/position. Revisit Step 2 if there is a lack of relevant resources.
Step 4 – Identify the audience and understand their baseline attitude about the topic.
Step 5 – When constructing an introduction , keep the following questions in mind:
What’s the topic of the speech?
What’s the occasion?
Who’s the audience?
What’s the purpose of the speech?
Step 6 – Utilize the evidence within the previously identified sources to construct the body of the speech. Keeping the audience in mind, determine which pieces of evidence can best help develop the argument. Discuss each point in detail, allowing the audience to understand how the facts support the perspective.
Step 7 – Addressing counterarguments can help speakers build their credibility, as it highlights their breadth of knowledge.
Step 8 – Conclude the speech with an overview of the central purpose and how the main ideas identified in the body support the overall argument.

Persuasive speech outline
One of the best ways to prepare a great persuasive speech is by using an outline. When structuring an outline, include an introduction, body, and conclusion:
Introduction
Attention Grabbers
Ask a question that allows the audience to respond in a non-verbal way; ask a rhetorical question that makes the audience think of the topic without requiring a response.
Incorporate a well-known quote that introduces the topic. Using the words of a celebrated individual gives credibility and authority to the information in the speech.
Offer a startling statement or information about the topic, typically done using data or statistics.
Provide a brief anecdote or story that relates to the topic.
Starting a speech with a humorous statement often makes the audience more comfortable with the speaker.
Provide information on how the selected topic may impact the audience .
Include any background information pertinent to the topic that the audience needs to know to understand the speech in its entirety.
Give the thesis statement in connection to the main topic and identify the main ideas that will help accomplish the central purpose.
Identify evidence
Summarize its meaning
Explain how it helps prove the support/main claim
Evidence 3 (Continue as needed)
Support 3 (Continue as needed)
Restate thesis
Review main supports
Concluding statement
Give the audience a call to action to do something specific.
Identify the overall importan ce of the topic and position.
Persuasive speech topics
The following table identifies some common or interesting persuasive speech topics for high school and college students:
Persuasive speech examples
The following list identifies some of history’s most famous persuasive speeches:
John F. Kennedy’s Inaugural Address: “Ask Not What Your Country Can Do for You”
Lyndon B. Johnson: “We Shall Overcome”
Marc Antony: “Friends, Romans, Countrymen…” in William Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar
Ronald Reagan: “Tear Down this Wall”
Sojourner Truth: “Ain’t I a Woman?”

17.6 Constructing a Persuasive Speech

In a sense, constructing your persuasive speech is the culmination of the skills you have learned already. In another sense, you are challenged to think somewhat differently. While the steps of analyzing your audience, formulating your purpose and central idea, applying evidence, considering ethics, framing the ideas in appropriate language, and then practicing delivery will of course apply, you will need to consider some expanded options about each of these steps.
Formulating a Proposition
As mentioned before, when thinking about a central idea statement in a persuasive speech, we use the terms “proposition” or claim. Persuasive speeches have one of four types of propositions or claims, which determine your overall approach. Before you move on, you need to determine what type of proposition you should have (based on the audience, context, issues involved in the topic, and assignment for the class).
Proposition of Fact
Speeches with this type of proposition attempt to establish the truth of a statement. The core of the proposition (or claim) is not whether something is morally right and wrong or what should be done about the topic, only that a statement is supported by evidence or not. These propositions are not facts such as “the chemical symbol for water is H20” or “Barack Obama won the presidency in 2008 with 53% of the vote.” Propositions or claims of fact are statements over which persons disagree and there is evidence on both sides, although probably more on one than the other. Some examples of propositions of fact are:
Converting to solar energy can save homeowners money. John F. Kennedy was assassinated by Lee Harvey Oswald working alone. Experiments using animals are essential to the development of many life-saving medical procedures. Climate change has been caused by human activity. Granting tuition tax credits to the parents of children who attend private schools will perpetuate educational inequality. Watching violence on television causes violent behavior in children. William Shakespeare did not write most of the plays attributed to him. John Doe committed the crime of which he is accused.
Notice that in none of these are any values—good or bad—mentioned. Perpetuating segregation is not portrayed as good or bad, only as an effect of a policy. Of course, most people view educational inequality negatively, just as they view life-saving medical procedures positively. But the point of these propositions is to prove with evidence the truth of a statement, not its inherent value or what the audience should do about it. In fact, in some propositions of fact no action response would even be possible, such as the proposition listed above that Lee Harvey Oswald acted alone in the assassination of President Kennedy.
Propositions of Definition
This is probably not one that you will use in your class, but it bears mentioning here because it is used in legal and scholarly arguments. Propositions of definitions argue that a word, phrase, or concept has a particular meaning. There are various ways to define words, such as by negation, operationalizing, and classification and division. It may be important for you to define your terms, especially if you have a value proposition. Lawyers, legislators, and scholars often write briefs, present speeches, or compose articles to define terms that are vital to defendants, citizens, or disciplines. We saw a proposition of definition defended in the Supreme Court’s 2015 decision to redefine marriage laws as applying to same-sex couples, based on arguments presented in court. Other examples might be:
The Second Amendment to the Constitution does not include possession of automatic weapons for private use. Alcoholism should be considered a disease because… The action committed by Mary Smith did not meet the standard for first-degree murder. Thomas Jefferson’s definition of inalienable rights did not include a right to privacy.
In each of these examples, the proposition is that the definition of these things (the Second Amendment, alcoholism, crime, and inalienable rights) needs to be changed or viewed differently, but the audience is not asked to change an attitude or action.
Propositions of Value
It is likely that you or some of your classmates will give speeches with propositions of value. When the proposition has a word such as “good,” “bad,” “best,” “worst,” “just,” “unjust,” “ethical,” “unethical,” “moral,” “immoral,” “beneficial,” “harmful,” “advantageous,” or “disadvantageous,” it is a proposition of value. Some examples include:
Hybrid cars are the best form of automobile transportation available today. Homeschooling is more beneficial for children than traditional schooling. The War in Iraq was not justified. Capital punishment is morally wrong. Mascots that involve Native American names, characters, and symbols are demeaning. A vegan diet is the healthiest one for adults.
Propositions of value require a first step: defining the “value” word. If a war is unjustified, what makes a war “just” or “justified” in the first place? That is a fairly philosophical question. What makes a form of transportation “best” or “better” than another? Isn’t that a matter of personal approach? For different people, “best” might mean “safest,” “least expensive,” “most environmentally responsible,” “stylish,” “powerful,” or “prestigious.” Obviously, in the case of the first proposition above, it means “environmentally responsible.” It would be the first job of the speaker, after introducing the speech and stating the proposition, to explain what “best form of automobile transportation” means. Then the proposition would be defended with separate arguments.
Propositions of Policy
These propositions are easy to identify because they almost always have the word “should” in them. These propositions call for a change in policy or practice (including those in a government, community, or school), or they can call for the audience to adopt a certain behavior. Speeches with propositions of policy can be those that call for passive acceptance and agreement from the audience and those that try to instigate the audience to action, to actually do something immediately or in the long-term.
Our state should require mandatory recertification of lawyers every ten years. The federal government should act to ensure clean water standards for all citizens. The federal government should not allow the use of technology to choose the sex of an unborn child. The state of Georgia should require drivers over the age of 75 to take a vision test and present a certificate of good health from a doctor before renewing their licenses. Wyeth Daniels should be the next governor of the state. Young people should monitor their blood pressure regularly to avoid health problems later in life.
As mentioned before, the proposition determines the approach to the speech, especially the organization. Also as mentioned earlier in this chapter, the exact phrasing of the proposition should be carefully done to be reasonable, positive, and appropriate for the context and audience. In the next section we will examine organizational factors for speeches with propositions of fact, value, and policy.
Organization Based on Type of Proposition
Organization for a proposition of fact.
If your proposition is one of fact, you will do best to use a topical organization. Essentially that means that you will have two to four discrete, separate arguments in support of the proposition. For example:
Proposition: Converting to solar energy can save homeowners money I. Solar energy can be economical to install.
A. The government awards grants.
B. The government gives tax credits.
II. Solar energy reduces power bills.
III. Solar energy requires less money for maintenance.
IV. S olar energy works when the power grid goes down.
Here is a first draft of another outline for a proposition of fact:
Proposition: Experiments using animals are essential to the development of many life-saving medical procedures.
- Research of the past shows many successes from animal experimentation.
- Research on humans is limited for ethical and legal reasons.
- Computer models for research have limitations.
However, these outlines are just preliminary drafts because preparing a speech of fact requires a great deal of research and understanding of the issues. A speech with a proposition of fact will almost always need an argument or section related to the “reservations,” refuting the arguments that the audience may be preparing in their minds, their mental dialogue. So the second example needs revision, such as:
I. The first argument in favor of animal experimentation is the record of successful discoveries from animal research. II. A second reason to support animal experimentation is that research on humans is limited for ethical and legal reasons. III. Animal experimentation is needed because computer models for research have limitations. IV. Many people today have concerns about animal experimentation. A. Some believe that all experimentation is equal. 1. There is experimentation for legitimate medical research. 2. There is experimentation for cosmetics or shampoos. B. Others argue that the animals are mistreated. 1. There are protocols for the treatment of animals in experimentation. 2. Legitimate medical experimentation follows the protocols. C. Some believe the persuasion of certain advocacy groups like PETA. 1. Many of the groups that protest animal experimentation have extreme views. 2. Some give untrue representations.
To complete this outline, along with introduction and conclusion, there would need to be quotations, statistics, and facts with sources provided to support both the pro-arguments in Main Points I-III and the refutation to the misconceptions about animal experimentation in Subpoints A-C under Point IV.
Organization for a Proposition of Value
A persuasive speech that incorporates a proposition of value will have a slightly different structure. As mentioned earlier, a proposition of value must first define the “value” word for clarity and provide a basis for the other arguments of the speech. The second or middle section would present the defense or “pro” arguments for the proposition based on the definition. The third section would include refutation of the counter arguments or “reservations.” The following outline draft shows a student trying to structure a speech with a value proposition. Keep in mind it is abbreviated for illustrative purposes, and thus incomplete as an example of what you would submit to your instructor, who will expect more detailed outlines for your speeches.
Proposition: Hybrid cars are the best form of automotive transportation available today. I. Automotive transportation that is best meets three standards. (Definition) A. It is reliable and durable. B. It is fuel efficient and thus cost efficient. C. It is therefore environmentally responsible. II. Studies show that hybrid cars are durable and reliable. (Pro-Argument 1) A. Hybrid cars have 99 problems per 100 cars versus 133 problem per 100 conventional cars, according to TrueDelta, a car analysis website much like Consumer Reports. B. J.D. Powers reports hybrids also experience 11 fewer engine and transmission issues than gas-powered vehicles, per 100 vehicles. III. Hybrid cars are fuel-efficient. (Pro-Argument 2) A. The Toyota Prius gets 48 mpg on the highway and 51 mpg in the city. B. The Ford Fusion hybrid gets 47 mpg in the city and in the country. IV. Hybrid cars are environmentally responsible. (Pro-Argument 3) A. They only emit 51.6 gallons of carbon dioxide every 100 miles. B. Conventional cars emit 74.9 gallons of carbon dioxide every 100 miles. C. The hybrid produces 69% of the harmful gas exhaust that a conventional car does. V. Of course, hybrid cars are relatively new to the market and some have questions about them. (Reservations) A. Don’t the batteries wear out and aren’t they expensive to replace? 1. Evidence to address this misconception. 2. Evidence to address this misconception. B. Aren’t hybrid cars only good for certain types of driving and drivers? 1. Evidence to address this misconception. 2. Evidence to address this misconception. C. Aren’t electric cars better? 1. Evidence to address this misconception. 2. Evidence to address this misconception.
Organization for a Proposition of Policy
The most common type of outline organizations for speeches with propositions of policy is problem-solution or problem-cause-solution. Typically we do not feel any motivation to change unless we are convinced that some harm, problem, need, or deficiency exists, and even more, that it affects us personally. As the saying goes, “If it ain’t broke, why fix it?” As mentioned before, some policy speeches look for passive agreement or acceptance of the proposition. Some instructors call this type of policy speech a “think” speech since the persuasion is just about changing the way your audience thinks about a policy.
On the other hand, other policy speeches seek to move the audience to do something to change a situation or to get involved in a cause, and these are sometimes called a “do” speech since the audience is asked to do something. This second type of policy speech (the “do” speech) is sometimes called a “speech to actuate.” Although a simple problem-solution organization with only two main points is permissible for a speech of actuation, you will probably do well to utilize the more detailed format called Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
This format, designed by Alan Monroe (1951), who wrote a popular speaking textbook for many years, is based on John Dewey’s reflective thinking process. It seeks to go in-depth with the many questions an audience would have in the process of listening to a persuasive speech. Monroe’s Motivated Sequence involves five steps, which should not be confused with the main points of the outline. Some steps in Monroe’s Motivated Sequence may take two points.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
- Attention . This is the introduction, where the speaker brings attention to the importance of the topic as well as his or her own credibility and connection to the topic. This step will include the thesis and preview. More specifically, sub steps under “Attention” are: the attention getter, the orientation (which includes background information, self introduction, and thesis), the establishment of credibility, and the preview statement. The attention getter should be just that, a statement that pulls the audience into the presentation and makes them want to listen. The orientation serves to establish the topic and tone of the presentation. It includes any relevant background information, a self introduction, and a thesis statement. Establishing credibility can be done verbally or nonverbally. If the speaker has specific credentials or experience with the topic, they should tell the audience about it in the introduction. If they do not have specific credentials, speakers may establish credibility by dressing nice, making good eye contact, properly citing sources, and demonstrating confidence. The preview statement is the roadmap for the presentation. The preview will indicate the problem, that it has negative impacts, and the speaker has a solution. It is not recommended for speakers to give away the solution in most cases in the preview statement. Usually it’s best to let the curiosity build in the audience and introduce it for the first time in the Satisfaction step.
- Need . Here, the problem is defined and established with evidence. It is important to make the audience see the severity of the problem, and how it affects them, their family, or their community. The harm or need can be physical, financial, psychological, legal, emotional, educational, social, or a combination. Specific sub steps for “Need” are: problem statement, illustration, ramifications (side effects), pointing, and establishing clear criteria (features that should be in an acceptable solution). The problem statement should be a direct statement that focuses on a specific concern or problem that exists. The illustration is a real life instance of the problem’s existence. Ramifications are the side effects and harms of the problem. Ramifications may be a variety of supporting materials that underscore the significance of the problem and its effects. Pointing is a clear, direct statement that draws a clear connection between the audience and the topic. As obvious as it may be, speakers need to explicitly tell the audience why they should care about this problem. Establishing criteria is a persuasive tactic. Speakers outline a few vital features that must be in a solution in order for it to be effective. The speaker does not give away the solution yet, but outlines criteria that a good solution should meet.
- Satisfaction . A need calls for satisfaction in the same way a problem requires a solution. Not only does the speaker present the solution and describe it, but they must also defend that it works and will address the causes of the problem as well as the symptoms. Sub steps required for “Satisfaction” are: solution statement, explanation, theoretical demonstration, practical experience, and meeting objections. The solution statement is when the solution or advocated behavior is introduced. The explanation will detail the solution and how it will work. The theoretical demonstration shows or explains how the solution meets the criteria from the Need step or has the necessary features. Practical experience presents an opportunity to show where the solution has proven successful. This may be in the form of a success story or specific instance where the solution made a difference. Meeting objections gives speakers an opportunity to respond to the potential reservations the audience may ben thinking while listening. It gives the speaker an opportunity to acknowledge what critics might be thinking and refute those concerns.
- Visualization . This step looks to the future either positively or negatively. The speaker creates a hypothetical scenario that places each audience member in their own future. If positive, the benefits from enacting or choosing the solution are shown. If negative, the disadvantages of not doing anything to solve the problem are shown. There may be times when it is acceptable to skip this step, especially if time is limited. If a speaker wishes to use both positive and negative scenarios, it is known as the method of contrast. The purpose of visualization is to motivate the audience by revealing future benefits or through fear appeals by showing future harms. The conditions in this situation should be probable and must be a personalized scenario for the audience members. This step requires imagery and vivid language.
- Action . The action step serves as the conclusion. In the action step, the goal is to give specific steps for the audience to take as soon as possible to move toward solving the problem. Whereas the satisfaction step explains the solution overall, the action step gives concrete, individual ways to begin making the solution happen. The sub steps of the “Action” step are: brakelight, summary, challenge/appeal, and note of finality. The brake light is the indication that a speaker is nearing the end. It is usually demonstrated by phrases like, “In conclusion,…” or “In summary,…” The summary statement should be a restatement of the preview statement, but in past tense. Instead of being vague about the solution, it is emphasized in the summary statement. The challenge or appeal is why this step is called Action. Speakers tell the audience what they should do individually as a result of hearing the speech. The note of finality serves as a strong closing statement. It leaves the audience reflecting on the presentation.
The more concrete you can make the action step, the better. Research shows that people are more likely to act if they know how accessible the action can be. For example, if you want students to be vaccinated against the chicken pox virus (which can cause a serious disease called shingles in adults), you can give them directions to and hours for a clinic or health center where vaccinations at a free or discounted price can be obtained.
In some cases for speeches of policy, no huge problem needs solving. Or, there is a problem, but the audience already knows about it and is convinced that the problem exists and is important. In those cases, a format called “comparative advantages” is used, which focuses on how one possible solution is better than other possible ones. The organizational pattern for this kind of proposition might be topical:
I. This policy is better because… II. This policy is better because… III. This policy is better because…
If this sounds a little like a commercial that is because advertisements often use comparative advantages to show that one product is better than another. Here is an example:
Proposition : Owning the Barnes and Noble Nook is more advantageous than owning the Amazon Kindle. I. The Nook allows owners to trade and loan books to other owners or people who have downloaded the Nook software, while the Kindle does not. II. The Nook has a color-touch screen, while the Kindle’s screen is black and grey and non-interactive. III. The Nook’s memory can be expanded through microSD, while the Kindle’s memory cannot be upgraded.
Building Upon Your Persuasive Speech’s Arguments
Once you have constructed the key arguments and order of points (remembering that if you use topical order, to put your strongest or most persuasive point last), it is time to be sure your points are well supported. In a persuasive speech, there are some things to consider about evidence.
First, your evidence should be from sources that the audience will find credible. If you can find the same essential information from two sources but know that the audience will find the information more credible from one source than another, use and cite the information from the more credible one. For example, if you find the same statistical data on Wikipedia and the U.S. Department of Labor’s website, cite the U.S. Department of Labor (your instructor will probably not accept the Wikipedia site anyway). Audiences also accept information from sources they consider unbiased or indifferent. Gallup polls, for example, have been considered reliable sources of survey data because unlike some organizations, Gallup does not have a cause (political or otherwise) it is supporting.
Secondly, your evidence should be new to the audience. In other words, the best evidence is that which is from credible sources and the audience has not heard before (Reinard, 1988; McCroskey, 1969). If they have heard it before and discounted it, they will not consider your argument well supported. An example is telling people who smoke that smoking will cause lung cancer. Everyone in the U.S. has heard that thousands of times, but 14% of the population still smokes, which is about one in seven (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2017)). Many of those who smoke have not heard the information that really motivates them to quit yet, and of course quitting is very difficult. Additionally, new evidence is more attention-getting, and you will appear more credible if you tell the audience something new (as long as you cite it well) than if you use the “same old, same old” evidence they have heard before.
Third, in order to be effective and ethical, your supporting evidence should be relevant and not used out of context, and fourth, it should be timely and not out of date.
After choosing the evidence and apportioning it to the correct parts of the speech, you will want to consider use of metaphors, quotations, rhetorical devices, and narratives that will enhance the language and “listenability” of your speech. Narratives are especially good for introduction and conclusions, to get attention and to leave the audience with something dramatic. You might refer to the narrative in the introduction again in the conclusion to give the speech a sense of finality.
Next you will want to decide if you should use any type of presentation aid for the speech. The decision to use visuals such as PowerPoint slides or a video clip in a persuasive speech should take into consideration the effect of the visuals on the audience and the time allotted for the speech (as well as your instructor’s specifications). The charts, graphs, or photographs you use should be focused and credibly done.
One of your authors remembers a speech by a student about using seat belts (which is, by the way, an overdone topic). What made the speech effective in this case were photographs of two totaled cars, both of which the student had been driving when they crashed. The devastation of the wrecks and his ability to stand before us and give the speech because he had worn his seat belt was effective (although it didn’t say much for his driving ability). If you wanted an audience to donate to disaster relief after an earthquake in a foreign country, a few photographs of the destruction would be effective, and perhaps a map of the area would be helpful. But in this case, less is more. Too many visual aids will likely distract from your overall speech claim.
Finally, since you’ve already had experience in class giving at least one major speech prior to this one, your delivery for the persuasive speech should be especially strong. Since delivery does affect credibility (Burgoon, Birk, & Pfau, 1990), you want to be able to connect visually as you make your appeals. You want to be physically involved and have vocal variety when you tell dramatic narratives that emphasize the human angle on your topic. If you do use presentation slides, you want them to work in seamlessly, using black screens when the visuals are not necessary.
Your persuasive speech in class, as well as in real life, is an opportunity to share a passion or cause that you believe will matter to society and help the audience live a better life. Even if you are initially uncomfortable with the idea of persuasion, we use it all the time in different ways. Choose your topic based on your own commitment and experience, look for quality evidence, craft your proposition so that it will be clear and audience appropriate, and put the finishing touches on it with an eye toward enhancing your logos, ethos, and pathos.
organizational pattern used for persuasive speeches involving five steps: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action
Introduction to Speech Communication Copyright © 2021 by Individual authors retain copyright of their work. is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Persuasive Speech

Learn How to Write a Perfect Persuasive Speech
13 min read
Published on: May 24, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

People also read
Interesting Persuasive Speech Topics & Ideas for Students
Know About the 3 Types of Persuasive Speeches
Demonstration Speech Ideas for an Effective Speech
Share this article
Do you ever feel like you have a great idea or a strong opinion, but struggle to get others on board? That's where persuasive speech comes in.
Persuasive speech is a powerful tool for influencing people's beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. But how do you write a persuasive speech that is effective and impactful?
In this blog post, we'll walk you through the key elements of writing a persuasive speech, from types to techniques. Whether you're a seasoned speaker or just getting started, these tips will help you craft a persuasive speech that achieves your desired outcome.
So, if you're ready to become a more persuasive speaker, read on and discover the power of persuasive speech.
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Persuasive Speech?
A persuasive speech is aimed at convincing the audience to adopt or agree with the speaker's viewpoint or call to action. It involves presenting a well-reasoned argument with supporting evidence and appeals to emotions.
Importance: Persuasive speeches can influence people's beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors towards a goal or cause, making them important. They inspire action and bring change.
Types of Persuasive Speeches
There are several different types of persuasive speech you can choose from depending on your goals and audience. Let's take a closer look at some of the most common types.
Policy Persuasion
This type of persuasive speech aims to convince the audience to support a specific policy or action. It can be delivered by politicians, activists, or anyone who wants to change public policy. A policy persuasive speech often involves outlining the benefits of the proposed policy and addressing potential concerns or objections.
Example: Why we need to implement a carbon tax to combat climate change
Value Persuasion
Value persuasive speeches aim to persuade the audience to adopt a particular set of values or beliefs. This type of speech can be used to promote a certain worldview or to challenge an existing belief system.
This type often uses emotional appeals to connect with the audience and encourage them to see things from a different perspective.
Example: Why volunteering is important for building a sense of community
Factual Persuasion
Factual persuasive speeches focus on presenting evidence and logical arguments to convince the audience of a particular point of view.
This type of speech is often used in academic or professional settings. The goal is to persuade an audience based on facts and evidence.
Example: The benefits of a plant-based diet for human health and the environment
Motivational Persuasion
Motivational persuasive speeches aim to inspire the audience to take action or make a change. This type of speech is often used by coaches, motivational speakers, and leaders to encourage their audience to achieve their goals.
Example: How to overcome fear and achieve your dreams
Need to deliver a motivational speech but stuck on what to talk about? Our blog offers an abundance of motivational speech topics to help you create a memorable speech.
Comparative Persuasion
Comparative persuasive speeches involve comparing two or more options to persuade the audience to choose one over the other. This type of speech can be used to compare products, services, or ideas.
Comparative persuasion can be particularly effective when the audience is already familiar with both options being compared.
Example: Why our product is better than our competitors' products
Problem-Solution Persuasion
Problem-solution persuasive speeches aim to persuade the audience to take action to solve a particular problem. This type of speech often involves identifying a problem that the audience cares about and presenting a viable solution.
This type can be particularly effective when the audience is already aware of the problem and is looking for a solution.
Example: How we can reduce plastic waste and preserve the environment by adopting a circular economy model
Want to become a well-rounded speaker? Our blog can help you understand the various types of speeches and how to deliver them effectively.
Elements of a Persuasive Speech
Here's a detailed table outlining the key elements of a persuasive speech with examples:

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How to Write a Persuasive Speech?
To write a persuasive speech, follow these essential steps:
Step#1: Choose A Compelling Topic
Select a subject that is relevant, interesting, and aligns with your audience's interests and values.
Step#2: Understand Your Audience
Research and analyze your target audience's demographics, beliefs, and concerns. This knowledge will help you tailor your speech to resonate with them effectively.
Step#3: Define Your Goal
Determine the specific outcome you want to achieve with your speech. Is it to persuade, inspire, or motivate your audience? Clarify your objective early on.
Step#4: Develop A Strong Thesis Statement
Craft a clear and concise thesis statement that presents your main argument or position. This statement will serve as the foundation for your persuasive speech.
Step#5: Gather Supporting Evidence
Conduct thorough research to find credible and compelling evidence, examples, statistics, and expert opinions that support your thesis. This evidence will strengthen your arguments and make them more persuasive.
Step#6: Structure Your Speech
Organize your speech into an introduction, body, and conclusion.
The introduction should grab your audience's attention, introduce the topic, and present your thesis statement. The body should present your main points and supporting evidence. The conclusion should summarize your key arguments and end with a strong call to action.
Step#7: Use Persuasive Language And Rhetorical Devices
Employ rhetorical devices such as anecdotes, metaphors, analogies, and emotional appeals to engage your audience and make your arguments more persuasive. Use strong and convincing language throughout your speech.
Step#8: Anticipate And Address Counterarguments
Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and counterarguments. Present them respectfully and then refute them with logical reasoning and evidence. This demonstrates your credibility and strengthens your persuasive case.
Step#9: Practice And Refine Your Delivery
Rehearse your speech multiple times to improve your delivery and timing. Pay attention to your body language, voice modulation, and overall confidence. Practice in front of a mirror or seek feedback from a trusted friend or colleague.
Step#10: Engage Your Audience
During your actual speech, connect with your audience by maintaining eye contact, using gestures, and speaking with passion and conviction. Encourage audience participation through questions, stories, or interactive elements.
Techniques for Persuasive Speaking
To deliver a persuasive speech that truly resonates with your audience, it's important to use a variety of techniques.
Here are five techniques you can use to make your speech more persuasive and effective:
1- Emotional Appeal
One of the most powerful techniques for persuasive speaking is emotional appeal. This involves using language and stories that evoke strong emotions in your audience, such as fear, anger, or compassion.
By connecting with your audience on an emotional level, you can make your message more memorable and impactful.
2- Logical Appeal
Another effective technique is logical appeal, which involves using reasoning and evidence to support your argument. This can include statistics, facts, and expert opinions. It helps to bolster your case and convince your audience that your position is the right one.
3- Ethical Appeal
The ethical appeal involves appealing to your audience's sense of morality and values. This can include using examples of right and wrong behavior. By framing your argument in ethical terms, you can make it more persuasive and compelling.
4- Repetition
Repetition involves repeating key ideas throughout your speech to emphasize their importance and make them more memorable. This can be especially effective for driving home your main points and making a lasting impression on your audience.
5- Rhetorical Questions
Rhetorical questions can be an effective way to engage your audience and encourage them to think deeply about your message. By asking questions that lead your audience to draw their own conclusions, you can make your speech more interactive.
Delivering a Persuasive Speech
Delivering a persuasive speech requires more than just having a well-written script. Here are some tips to help you deliver your speech effectively:
- Using body language effectively: Your body language can convey confidence, enthusiasm, and sincerity. Use gestures, facial expressions, and posture to emphasize key points and connect with your audience.
- Maintaining eye contact: Eye contact is essential to establishing trust and credibility with your audience. Make eye contact with different members of your audience to engage them and maintain their attention.
- Speaking confidently and clearly: Your voice should be clear, strong, and articulate. Use pauses and inflection to emphasize key points and vary your tone and pace to keep your audience engaged.
- Handling audience questions and objections: Be prepared to answer questions and address objections from your audience. Listen carefully, acknowledge their concerns, and provide thoughtful responses that reinforce your key points.
Read our blog on speech writing for practical strategies to make your speechwriting process smoother!
How to Choose a Topic For Persuasive Speech?
To effectively brainstorm persuasive speech ideas, it is vital to consider the "who, what, when, where, and why" approach.
- Who: Who is my intended audience for this speech? What are their interests and beliefs? How can I connect with them on a personal level?
- What: What topics am I knowledgeable about and passionate about? What topics are relevant and timely to my audience? What topics can I research and present with credibility?
- When: How much time do I have to present? Should I choose a broad topic or a niche topic based on the time frame? Is my topic appropriate for the time of day or the event schedule?
- Where: Where will I be delivering this speech? What is the setting and environment? What tools and resources will be available to me?
- Why: What is the purpose of my speech? Do I want to inform, persuade, or motivate my audience? Why is my topic important and why should my audience care about it? How can I make my audience feel connected to my topic and invested in my message?
By using this approach, you can pick a topic that you are interested in and effectively capture the attention of your audience.
Persuasive Speech Topics
Here are some persuasive speech topics that may inspire you to create a successful persuasive speech:
- Should the Supreme Court have term limits?
- What makes a good persuasive speech topic and how to pick one?
- Should schools be required to teach financial literacy as a mandatory subject?
- Should mental health treatment be covered by health insurance?
- The key elements of a successful persuasive speech and how to deliver it.
- Should art and music therapy be considered a legitimate form of treatment?
- At what age should children be allowed to use social media and why?
- How high school students can prepare and deliver persuasive speeches that flow logically.
- Should the minimum wage be increased to a living wage?
- Do video games contribute to increased aggression and should they be regulated accordingly?
Check out our blog on interesting persuasive speech topics to get plenty of ideas and get inspired!
Examples of Persuasive Speeches
Here are some examples of powerful and influential persuasive speeches from both historical and contemporary figures:
Historical Examples:
- Martin Luther King Jr.'s " I Have a Dream " speech
- Winston Churchill's " We Shall Fight on the Beaches " speech
- Abraham Lincoln's " Gettysburg Address " speech
- Susan B. Anthony's " Women's Right to Vote " speech
Contemporary Examples:
- Greta Thunberg's speech on climate change at the United Nations
- Barack Obama's " Yes We Can " speech
- Malala Yousafzai's speech at the United Nations on education for girls
- Elon Musk's speech on space exploration and colonization
Tips for Delivering an Effective Persuasive Speech
Here are some tips for delivering a successful persuasive speech:
- Practice, practice, practice: Rehearse your speech to improve your delivery and confidence.
- Be passionate about your topic: Emphasize your enthusiasm to engage and persuade your audience.
- Connect with your audience: Build a rapport with your audience by showing empathy and relating to their experiences.
- Use visuals if appropriate: Use visual aids, such as images or charts, to reinforce your message and improve comprehension.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Giving a Persuasive Speech
You should avoid these mistakes when giving a persuasive speech:
- Not knowing the audience
- Lack of preparation
- Failing to establish credibility
- Overwhelming the audience with information
- Ignoring counterarguments
- Using weak or irrelevant evidence
- Lack of enthusiasm or passion
- Reading directly from notes or slides
- Going off-topic or rambling
- Ignoring time constraints.
The Bottom Line!
We have covered everything you need to know about writing a persuasive speech. We have discussed the different types, essential elements, and techniques for writing a compelling persuasive speech.
Additionally, we have provided some persuasive speech topics and tips that you can use to make your speech more engaging. We hope this guide has been helpful to you in crafting a persuasive speech that will impress your audience.
Looking for an essay helper to guide you through your academic journey? Look no further! Our team of experienced writers is here to assist you in crafting top-notch essays that will impress your professors.
But that's not all, if you're looking for an extra boost in productivity, don't forget to check out our AI essay generator .
Caleb S. (Education, Marketing)
Caleb S. has extensive experience in writing and holds a Masters from Oxford University. He takes great satisfaction in helping students exceed their academic goals. Caleb always puts the needs of his clients first and is dedicated to providing quality service.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

Ace the Presentation

9 Basic Elements of a Great Persuasive Speech
As human beings, we commonly face debates, sales pitch, or even casual conversations, where we discuss with an audience (that can be familiar or not) about a subject that we want to convince, to think in a similar or same perspective that we do.
If we are playing the speaker role, we need to bring arguments that will acknowledge our audience and use techniques to make them see why they should be there buying our ideas.
Persuasion is the ability to convince a social group by coming up with factual statements, great posture making people doubt, reconsider, and feel the need to know more about the arguments we affirm.
Only a few of most speakers have a great persuasive speech, which is a quality that allows us to convince and influence people more than others.
So now we know that changing people’s mindsets takes a lot more than merely coming out with good arguments. Some skills need to be learned or enhanced; it requires passion, confidence, accuracy in our words, involving the audience, many more skills than the knowledge itself.
Hang on with us a little more to find out how to develop them in the next steps; let us find out more about what it takes to produce the public speaking skills (elements) that a great persuasive speech compose.
The 9 Basic Elements of a Great Persuasive Speech:
- Credibility and Passion!
- Evolvement.
- Connection with the audience.
- Conversational Presentation.
- Rhetoric Game (Pathos, Logos, Ethos).
- Markable Analysis.
- Good Posture.
- Visual Impact.
- Voice Tone.
Every element on the list complements each other, making our delivery more appealing to be heard and seen and helps with our goal, which is to persuade our audience.
Highly Recommended Next Articles:
15 Ideas to Make a Speech Unique, Memorable, and Inspiring
8 THINGS YOU CAN DO TO ACE ANY JOB INTERVIEW

The happiness when receiving a call marking the job interview gives rise to endless anxiety. After all, it’s only a few minutes to prove your worth, impress the recruiter and seize the opportunity. However, to do well at the job interview, you need to think about what you will say, how you will present yourself,…
TOP 7 Core Interpersonal Skills in Leadership

At any time, a leader is seen as one who guides one or more people to fulfill something stipulated; today, however, we understand that this journey comprises the achievement of results and the evolution, in some way, of all who participate in the process. Leaders are people with high power to inspire those around them,…
An Easy Guide to All 15 Types of Speech

We keep learning that there are three types of speeches, informative speeches, persuasive speeches and special occasion speeches. However, I believe and know that there are many more such as debates, motivational speeches, forensic speeches, impromptu speeches, eulogy, and so on. Here’s a growing list of over 13 types of speech and tips on how…
Understanding the nine Essential Elements of a Great Persuasive Speech
The audience may not hear every time we speak because we are not confident enough. As we form an idea or argument, we must have some background knowledge about the subject we want to talk about.
If we don’t own the subject we want to pitch about, our audience will discard our message right away and for that is vital that we study it, know-how it formed, and preview the doubts that our audience can have if we want to influence them.
If we want to deliver a great persuasive speech, it is essential to talk about a subject that inspires us to do better, to talk about something we know or have a certain familiarity with.
Passion will come out naturally because of it, and the audience will be more and more open to what we are saying, raising the odds of them buying our arguments.
When we bring facts, which can happen by giving examples of real-life situations that expose our speech, scientific proofs of that phenomenon;
We are also showing that the subject we are out coming is credible and not only conveys to us as individuals but also a group of people that make them believe in that will be our primary duty.
A) PASSION: We can accomplish this step by
- Watching a few documentaries, tv shows, or reading could help us find some good subjects to be passionate about (if we don’t);
- Reading articles, video reviews about these subjects, especially the ones that think the other way around;
- Taking notes of day-to-day problems people face and then google it;
- Talk with different people about their opinion about it and mostly listen;
- Ask yourself what do you think and write it down.
- Involvement.
Our goal is to sell our pitch, make people or a particular group understand, and buy our perspective. For that, we need to be straight forward as possible with the main question we want to raise influence our audience.
We want them to engage with us and vibrate as we bring this new idea; we want to blow their minds and make them want to have more of us, more of what we have to say.
We are raising our voice about this subject we chose because we have an opinion about, even if we don’t know what reaction to expect from the audience we did our research about this subject. We are giving the audience something that will be impactful to their lives.
We are here because we are trying to bring to people something new that we think is hidden. What drives us an altruist felt that we would not say but show them by organizing a structure, storytelling, and being polite intimate but not intrusive.
We must take in place enough information such as: what the main question is ( the subject), how it is a problem for everybody, and how we can interpret it.
B) CREDIBILITY: We can accomplish this step by:
- Connecting with the audience
To make our presentation memorable, we need to engage our audience from the beginning, since the word ONE, so they can understand our message. For that, we need to act as we mean it, and being positive is one way to make the audience feel a part of our speech.
Imagine that we are talking about social inequalities. Sharing pictures of people in degrading situations would be the obvious way but may leave the audience a little bit uncomfortable.
Instead, we could share examples of how this problem could reverse actual live issues; let us take by example, volunteering.
Making them visualize how people belonging from distinct social structures can make at least dozens of them, that could be robbing or killing having the opportunity to do better.
It can force the audience without violence to create petitions, for example, that will benefit these groups in need, making them feel helpful and productive in some way.
Our audience has to feel that they are accomplishing a worthwhile thing, supporting our arguments. Ideas are increasing them to do something that is not selfish, making our message valuable to the audience.
- Start to list the pros of the activities we could be doing to help solve the problem;
- Telling the audience them the consequences of groups who are not of these activities we are suggesting that could help;
- Conversational Presentation
In a conversational presentation, the subject on the table has to be concerning the audience, worthy of listening, and useful to others.
We can make our speech a conversational presentation if we deliver the message with the care to use a language that embraces subjects such as “We” and “Us.” It can make them feel we are having an actual conversation and have an opinion about it.
Even though we have a persuasive speech and our goals are to influence and persuade people to adopt our argument, we should not make them feel under pressure or attack. It should feel as natural as possible.
- Rhetorical Game ( Pathos, Logos, Ethos)
Rhetoric is the art of persuasion that appeals to people to action through visual, verbal, or written language, using one or multiple means of spreading the message.
When we want to call people to action, we need to have something besides the story, and we need to happen to say that will justify why that subject is concerning and for that becoming a problem.
A presentation can use one primary technique, namely by calling out values that broke. These proofs show how particular behavior is degrading people’s lives, or even how we are accepting things that have no credibility at all.
Here are some Examples of Ethos, Logos, and Pathos for saciating your own curiosity.
- Markable Analysis
So we already agreed that we want to make our discourse memorable and for that is essential that we choose the simplest way to explain to people the logic we want them to follow.
Having a structure that organizes what we should introduce first to have the audience step by step with us engaged and receiving the message.
People may not remember every word we say. Still, we give them examples, bullets, or keynotes about our idea that can be an organized way to start pitching by imprinting with the audience.
A markable analysis is precise notwithstanding being polite, explicative, and making people feel confused or in the wrong place. Rather than that, it has a mode of persuasion that guides the presentation.
It may seem weird, but our body language speaks and is quite loud. We may have an excellent speech delivery by articulating thoughts, engaging the audience, and making them feel like part of the process but guess what? Our stance is curvy.
To avoid that, keeping up a good posture is a big sign of confidence and will make the audience feel that we own the presentation and for that worthy of being listened to.
We want to ace the speech and pass the audience’s first impression judgment, so ensure that you are not wearing colors that will overshadow our listeners’ eyes because, by doing that, we keep them focused on our message and less on our body.
To make eye contact with the audience from the first very moment we meet can be a useful thing that we know very well. That is why we do it while looking at them, creating a connected environment to the audience to make questions and not feel misplaced.
Highly Recommended Article on the topic: 11 Best Body Language Tips for Engaging Presentations .
- Makes a Visual Impact
Visual stimulation and emotions are connected to the same part of the human brain that processes and creates memories. If we want to influence the audience, we want them to recall our speech and spread our word to as many people as possible.
By showing slides, for example, images related to our subject, graphics can make people visualize our words and create their interpretation aside from ours about our speech.
That will make our audience better comprehend the information we are giving and make them collaborative by developing their perception of the content and synthesizing our analysis quickly.
Lastly, but not least important, the voice tone, how we speak is as essential as not saying anything. The body language and tone of voice are two crucial parts critical to ace non-verbal communication.
The tone of voice is how we sound when we talk about how we think or feel out loud, so if we do it very loud or quickly, some of the words can be misunderstood or take a different meaning from the one we want to share.
“A firm, confident tone of voice makes other people think that we are distinguished and important. Talking in a quiet tone of voice makes us look like someone who has major weaknesses or is awkward. People who have a high tone of voice don’t convey much credibility.” Maria Pellicano
Here, we want our voice to look assertive and sure about what is we are going to say. For that, we need to take little breaks to breathe. Let’s do it in parts that we know the audience needs a few seconds to digest and analyze the message.
Being able to persuade different people doesn’t have to be a quality of a few if we prepare and properly educate ourselves.
The body language control, the voice tone, knowing a bit of rhetoric , using vivid examples, and visuals to engage the audience can improve a persuasive speech.
In the persuasive speech, we have to be the tour guide of the audience who plays the role of tourists. Our goal is to enlighten them about a subject or issue that they haven’t seen yet. If you read this far, thank you so much, and I hope you enjoyed it.
References and Further Reading
Ace The Presentation . Amadebai, E. 11 Best Body Language Tips for Engaging Presentations.
Ace The Presentation . Amadebai, E., 120 Persuasive Speech Topics.
Ace The Presentation. Amadebai, E. 8. Awesome Persuasive Speech Techniques.
Ezine Articles . Toney, B (2011). Key Elements of a Persuasive Speech.
The Knowledge Project FS. Parrish, S (2020). Ethos, Logos, and Pathos: The Structure of a Great Speech.
Similar Posts

Diction – A Key Rhetorical Device and Staple for Speakers
Language is quite a peculiar thing, don’t you feel? We all use it every single day for one thing or the other, but we’re pretty sure few of you stop and ponder about what kind of words you use, how you use them, and whether they’re having any impact on your audience. This is where…

21 Social Skills Competency Questions Examples
This article will discuss how we can use our social abilities to pass a competency-based interview with these 21 relatable examples successfully. We will be sharing the full list of social skills competency questions, at the end of this article. You can download them for free. But before we get to list and discuss them,…

A 9-Step Practical Guide On How To Analyze A Speech – Speech Analysis of I have A Dream Speech as an Example
A speech, as we all know, is a vocal opinion of a speaker’s stand. Speeches are usually used as an effective tool for rallying support, conveying opinion, as well as influencing the thoughts of others (usually the audience) to accept or agree with the thoughts of the Speaker. For a speech to achieve its goal,…

Smooth Transition in a Speech – 69 Transition Statements
There are times when you listen to a speech and you wonder, how does the speaker relate these two things, or if he jumped topics and you felt completely lost. Knowing how to make a smooth transition in a speech will help you as a speaker to keep your audience engaged and on topic. Any…

7 ORATORY SECRETS: HOW TO GIVE AN EFFECTIVE ORATORICAL SPEECH?
What is oratory and why most of the greatest speeches ever are oratorical in nature? Oratory can be summarized as the art of informing and persuading people through the use of public speaking skills. It generally means speaking in front of an audience and using high level language skills to inform, educate and persuade the…

How to Improve your Communication Skills – 7 Essential Tips
Before we delve into how to improve your communication skills, let us first address the basic definition of communication. Communication in simple terms can simply be defined as the act of transferring information from one place to another or, from one person to another. There are many forms of communication, such as verbal (words of…

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
17.3 Organizing Persuasive Speeches
Learning objectives.
- Understand three common organizational patterns for persuasive speeches.
- Explain the steps utilized in Monroe’s motivated sequence.
- Explain the parts of a problem-cause-solution speech.
- Explain the process utilized in a comparative advantage persuasive speech.

Steven Lilley – Engaged – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Previously in this text we discussed general guidelines for organizing speeches. In this section, we are going to look at three organizational patterns ideally suited for persuasive speeches: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantages.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
One of the most commonly cited and discussed organizational patterns for persuasive speeches is Alan H. Monroe’s motivated sequence. The purpose of Monroe’s motivated sequence is to help speakers “sequence supporting materials and motivational appeals to form a useful organizational pattern for speeches as a whole” (German et al., 2010).
While Monroe’s motivated sequence is commonly discussed in most public speaking textbooks, we do want to provide one minor caution. Thus far, almost no research has been conducted that has demonstrated that Monroe’s motivated sequence is any more persuasive than other structural patterns. In the only study conducted experimentally examining Monroe’s motivated sequence, the researchers did not find the method more persuasive, but did note that audience members found the pattern more organized than other methods (Micciche, Pryor, & Butler, 2000). We wanted to add this sidenote because we don’t want you to think that Monroe’s motivated sequence is a kind of magic persuasive bullet; the research simply doesn’t support this notion. At the same time, research does support that organized messages are perceived as more persuasive as a whole, so using Monroe’s motivated sequence to think through one’s persuasive argument could still be very beneficial.
Table 17.1 “Monroe’s Motivated Sequence” lists the basic steps of Monroe’s motivated sequence and the subsequent reaction a speaker desires from his or her audience.
Table 17.1 Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
The first step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the attention step , in which a speaker attempts to get the audience’s attention. To gain an audience’s attention, we recommend that you think through three specific parts of the attention step. First, you need to have a strong attention-getting device. As previously discussed in Chapter 9 “Introductions Matter: How to Begin a Speech Effectively” , a strong attention getter at the beginning of your speech is very important. Second, you need to make sure you introduce your topic clearly. If your audience doesn’t know what your topic is quickly, they are more likely to stop listening. Lastly, you need to explain to your audience why they should care about your topic.
In the need step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. In Monroe’s conceptualization of need, he talks about four specific parts of the need: statement, illustration, ramification, and pointing. First, a speaker needs to give a clear and concise statement of the problem. This part of a speech should be crystal clear for an audience. Second, the speaker needs to provide one or more examples to illustrate the need. The illustration is an attempt to make the problem concrete for the audience. Next, a speaker needs to provide some kind of evidence (e.g., statistics, examples, testimony) that shows the ramifications or consequences of the problem. Lastly, a speaker needs to point to the audience and show exactly how the problem relates to them personally.
Satisfaction
In the third step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the satisfaction step , the speaker sets out to satisfy the need or solve the problem. Within this step, Monroe (1935) proposed a five-step plan for satisfying a need:
- Explanation
- Theoretical demonstration
- Reference to practical experience
- Meeting objections
First, you need to clearly state the attitude, value, belief, or action you want your audience to accept. The purpose of this statement is to clearly tell your audience what your ultimate goal is.
Second, you want to make sure that you clearly explain to your audience why they should accept the attitude, value, belief, or action you proposed. Just telling your audience they should do something isn’t strong enough to actually get them to change. Instead, you really need to provide a solid argument for why they should accept your proposed solution.
Third, you need to show how the solution you have proposed meets the need or problem. Monroe calls this link between your solution and the need a theoretical demonstration because you cannot prove that your solution will work. Instead, you theorize based on research and good judgment that your solution will meet the need or solve the problem.
Fourth, to help with this theoretical demonstration, you need to reference practical experience, which should include examples demonstrating that your proposal has worked elsewhere. Research, statistics, and expert testimony are all great ways of referencing practical experience.
Lastly, Monroe recommends that a speaker respond to possible objections. As a persuasive speaker, one of your jobs is to think through your speech and see what counterarguments could be made against your speech and then rebut those arguments within your speech. When you offer rebuttals for arguments against your speech, it shows your audience that you’ve done your homework and educated yourself about multiple sides of the issue.
Visualization
The next step of Monroe’s motivated sequence is the visualization step , in which you ask the audience to visualize a future where the need has been met or the problem solved. In essence, the visualization stage is where a speaker can show the audience why accepting a specific attitude, value, belief, or behavior can positively affect the future. When helping people to picture the future, the more concrete your visualization is, the easier it will be for your audience to see the possible future and be persuaded by it. You also need to make sure that you clearly show how accepting your solution will directly benefit your audience.
According to Monroe, visualization can be conducted in one of three ways: positive, negative, or contrast (Monroe, 1935). The positive method of visualization is where a speaker shows how adopting a proposal leads to a better future (e.g., recycle, and we’ll have a cleaner and safer planet). Conversely, the negative method of visualization is where a speaker shows how not adopting the proposal will lead to a worse future (e.g., don’t recycle, and our world will become polluted and uninhabitable). Monroe also acknowledged that visualization can include a combination of both positive and negative visualization. In essence, you show your audience both possible outcomes and have them decide which one they would rather have.
The final step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the action step , in which a speaker asks an audience to approve the speaker’s proposal. For understanding purposes, we break action into two distinct parts: audience action and approval. Audience action refers to direct physical behaviors a speaker wants from an audience (e.g., flossing their teeth twice a day, signing a petition, wearing seat belts). Approval, on the other hand, involves an audience’s consent or agreement with a speaker’s proposed attitude, value, or belief.
When preparing an action step, it is important to make sure that the action, whether audience action or approval, is realistic for your audience. Asking your peers in a college classroom to donate one thousand dollars to charity isn’t realistic. Asking your peers to donate one dollar is considerably more realistic. In a persuasive speech based on Monroe’s motivated sequence, the action step will end with the speech’s concluding device. As discussed elsewhere in this text, you need to make sure that you conclude in a vivid way so that the speech ends on a high point and the audience has a sense of energy as well as a sense of closure.
Now that we’ve walked through Monroe’s motivated sequence, let’s look at how you could use Monroe’s motivated sequence to outline a persuasive speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that the United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments.
Main Points:
- Attention: Want to make nine thousand dollars for just three weeks of work lying around and not doing much? Then be a human guinea pig. Admittedly, you’ll have to have a tube down your throat most of those three weeks, but you’ll earn three thousand dollars a week.
- Need: Every day many uneducated and lower socioeconomic-status citizens are preyed on by medical and pharmaceutical companies for use in for-profit medical and drug experiments. Do you want one of your family members to fall prey to this evil scheme?
- Satisfaction: The United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments to ensure that uneducated and lower-socioeconomic-status citizens are protected.
- Visualization: If we enact tougher experiment oversight, we can ensure that medical and pharmaceutical research is conducted in a way that adheres to basic values of American decency. If we do not enact tougher experiment oversight, we could find ourselves in a world where the lines between research subject, guinea pig, and patient become increasingly blurred.
- Action: In order to prevent the atrocities associated with for-profit medical and pharmaceutical experiments, please sign this petition asking the US Department of Health and Human Services to pass stricter regulations on this preying industry that is out of control.
This example shows how you can take a basic speech topic and use Monroe’s motivated sequence to clearly and easily outline your speech efficiently and effectively.
Table 17.2 “Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Checklist” also contains a simple checklist to help you make sure you hit all the important components of Monroe’s motivated sequence.
Table 17.2 Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Checklist
Problem-Cause-Solution
Another format for organizing a persuasive speech is the problem-cause-solution format. In this specific format, you discuss what a problem is, what you believe is causing the problem, and then what the solution should be to correct the problem.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that our campus should adopt a zero-tolerance policy for hate speech.
- Demonstrate that there is distrust among different groups on campus that has led to unnecessary confrontations and violence.
- Show that the confrontations and violence are a result of hate speech that occurred prior to the events.
- Explain how instituting a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy against hate speech could stop the unnecessary confrontations and violence.
In this speech, you want to persuade people to support a new campus-wide policy calling for zero-tolerance of hate speech. Once you have shown the problem, you then explain to your audience that the cause of the unnecessary confrontations and violence is prior incidents of hate speech. Lastly, you argue that a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy could help prevent future unnecessary confrontations and violence. Again, this method of organizing a speech is as simple as its name: problem-cause-solution.
Comparative Advantages
The final method for organizing a persuasive speech is called the comparative advantages speech format. The goal of this speech is to compare items side-by-side and show why one of them is more advantageous than the other. For example, let’s say that you’re giving a speech on which e-book reader is better: Amazon.com’s Kindle or Barnes and Nobles’ Nook. Here’s how you could organize this speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that the Nook is more advantageous than the Kindle.
- The Nook allows owners to trade and loan books to other owners or people who have downloaded the Nook software, while the Kindle does not.
- The Nook has a color-touch screen, while the Kindle’s screen is black and grey and noninteractive.
- The Nook’s memory can be expanded through microSD, while the Kindle’s memory cannot be upgraded.
As you can see from this speech’s organization, the simple goal of this speech is to show why one thing has more positives than something else. Obviously, when you are demonstrating comparative advantages, the items you are comparing need to be functional equivalents—or, as the saying goes, you cannot compare apples to oranges.
Key Takeaways
- There are three common patterns that persuaders can utilize to help organize their speeches effectively: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantage. Each of these patterns can effectively help a speaker think through his or her thoughts and organize them in a manner that will be more likely to persuade an audience.
- Alan H. Monroe’s (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience’s attention. In the second stage, the speaker shows an audience that a need exists. In the third stage, the speaker shows how his or her persuasive proposal could satisfy the need. The fourth stage shows how the future could be if the persuasive proposal is or is not adopted. Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker’s persuasive proposal.
- The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem. Lastly, the speaker proposes a solution to the problem that corrects the underlying causes.
- The comparative advantages speech format is utilized when a speaker is comparing two or more things or ideas and shows why one of the things or ideas has more advantages than the other(s).
- Create a speech using Monroe’s motivated sequence to persuade people to recycle.
- Create a speech using the problem-cause-solution method for a problem you see on your college or university campus.
- Create a comparative advantages speech comparing two brands of toothpaste.
German, K. M., Gronbeck, B. E., Ehninger, D., & Monroe, A. H. (2010). Principles of public speaking (17th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon, p. 236.
Micciche, T., Pryor, B., & Butler, J. (2000). A test of Monroe’s motivated sequence for its effects on ratings of message organization and attitude change. Psychological Reports, 86 , 1135–1138.
Monroe, A. H. (1935). Principles and types of speech . Chicago, IL: Scott Foresman.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- All Insights
- Top-Rated Articles
- How-to Guides
- For Parents
The Art of Persuasion: Writing a Compelling Speech
Discover the art of persuasion and learn how to write a compelling speech that captivates your audience. This blog post provides expert insights and practical tips for crafting an impactful persuasive speech.
Understanding the Power of Persuasion
Understanding the power of persuasion is crucial when it comes to writing a persuasive speech. Persuasion is the art of influencing and convincing others to adopt your point of view or take a specific action. By understanding the principles behind persuasion, you can effectively communicate your ideas and sway your audience.
One key aspect of persuasion is understanding the psychological factors that influence decision-making. People are often motivated by emotions, personal beliefs, and social influences. By tapping into these factors, you can tailor your speech to resonate with your audience and increase the likelihood of them being persuaded by your arguments.
Additionally, understanding the power dynamics at play can also enhance your persuasive abilities. Recognizing the authority or expertise you possess on the topic can lend credibility to your arguments, while acknowledging and addressing counterarguments can help you anticipate and overcome potential objections.
In summary, understanding the power of persuasion involves recognizing the psychological factors and power dynamics that influence decision-making. By leveraging these insights, you can effectively craft a persuasive speech that resonates with your audience and achieves your intended goals.
Analyzing Your Audience
Analyzing your audience is a crucial step in writing a persuasive speech. By understanding who your audience is, their beliefs, values, and attitudes, you can tailor your arguments to appeal to their specific needs and interests.
Start by conducting research or surveys to gather information about your audience. Consider their demographics, such as age, gender, education, and socioeconomic background. This information can provide valuable insights into their preferences and perspectives.
Furthermore, analyze your audience's psychographics, which include their interests, values, and motivations. What are their concerns and aspirations? What do they care about? By understanding their psychographics, you can identify common ground and frame your arguments in a way that resonates with their values.
Remember, effective persuasion requires connecting with your audience on an emotional level. By tailoring your speech to address their specific concerns and interests, you can create a compelling case that is more likely to persuade them.
In conclusion, analyzing your audience is essential for writing a persuasive speech. By understanding their demographics and psychographics, you can tailor your arguments to resonate with their needs and interests, increasing the chances of persuading them.
Selecting a Relevant and Timely Topic
Selecting a relevant and timely topic is crucial for capturing your audience's attention and maintaining their interest throughout your persuasive speech.
Firstly, consider the current issues and trends that are relevant to your audience. What are the pressing concerns or debates in their lives? By choosing a topic that is timely, you can tap into their existing interests and create a sense of urgency.
Additionally, selecting a topic that is relevant to your audience's lives or experiences can make your speech more relatable and engaging. Consider their needs, challenges, and aspirations. How can your speech address these aspects and provide valuable insights or solutions?
Furthermore, it is important to choose a topic that aligns with your own expertise and interests. By selecting a topic that you are passionate about and knowledgeable in, you can deliver a more authentic and compelling speech.
In summary, selecting a relevant and timely topic involves considering the current issues and trends that are relevant to your audience, as well as their needs and interests. By choosing a topic that aligns with your expertise and resonates with your audience, you can create a persuasive speech that captures their attention and maintains their interest.
Crafting a Strong Thesis Statement
Crafting a strong thesis statement is essential for creating a persuasive speech that effectively communicates your main argument or point of view.
A thesis statement serves as the foundation of your speech, providing a clear and concise statement of your main idea. It should be specific, debatable, and focused on the main argument you want to make.
To craft a strong thesis statement, start by clearly stating your position on the topic. Avoid vague or general statements and strive for clarity and precision. Additionally, ensure that your thesis statement is debatable, meaning that there are valid arguments on both sides of the issue.
Furthermore, consider the structure of your thesis statement. It should be concise and to the point, capturing the essence of your argument in a single sentence or two.
In conclusion, crafting a strong thesis statement involves clearly stating your position on the topic, ensuring that it is debatable, and structuring it in a concise and focused manner. A strong thesis statement sets the tone for your persuasive speech and guides your audience in understanding your main argument.
Using Emotional Appeals
Using emotional appeals is a powerful technique for persuading your audience and eliciting a strong response to your persuasive speech.
Emotions play a significant role in decision-making, and by tapping into your audience's emotions, you can create a deeper connection and increase the likelihood of them being persuaded.
To effectively use emotional appeals, start by identifying the emotions that are relevant to your topic and your audience. Consider the desired emotional response you want to evoke, whether it's empathy, excitement, fear, or hope. By understanding your audience's emotional triggers, you can tailor your speech to generate the desired emotional response.
Additionally, use storytelling and personal anecdotes to make your speech more relatable and emotionally engaging. Humanizing your arguments and connecting them to real-life experiences can create a powerful emotional impact.
However, it is important to use emotional appeals ethically and responsibly. Avoid manipulating or exploiting your audience's emotions, and ensure that your emotional appeals are supported by logical arguments and evidence.
In summary, using emotional appeals involves identifying the relevant emotions for your topic and audience, using storytelling and personal anecdotes to make your speech more relatable, and maintaining ethical standards in your use of emotional appeals. By effectively using emotional appeals, you can create a persuasive speech that resonates with your audience on an emotional level.
Supporting Your Arguments with Evidence
Supporting your arguments with evidence is essential for building credibility and persuasiveness in your speech.
Evidence can take various forms, including statistics, research findings, expert opinions, and real-life examples. By incorporating relevant and reliable evidence, you can strengthen your arguments and make them more convincing.
When selecting evidence, ensure that it is up-to-date, accurate, and relevant to your topic. Use credible sources and cite them appropriately to maintain credibility.
Additionally, consider the counterarguments and potential objections that your audience may have. Anticipate these objections and address them with counter-evidence or logical reasoning. By acknowledging and refuting opposing viewpoints, you can strengthen your overall argument.
Furthermore, use clear and concise language when presenting your evidence. Avoid jargon or complex terminology that may confuse or alienate your audience. Present the evidence in a logical and organized manner, making it easy for your audience to follow and understand.
In conclusion, supporting your arguments with evidence involves incorporating relevant, reliable, and up-to-date evidence to strengthen your persuasive speech. By addressing potential objections and presenting the evidence in a clear and organized manner, you can build credibility and persuade your audience effectively.
Structuring an Engaging Speech
Structuring your speech in an engaging manner is crucial for capturing and maintaining your audience's attention throughout your persuasive speech.
Start by organizing your speech into a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should grab your audience's attention, provide a brief overview of your topic, and present your thesis statement. The body should be structured logically, with each main point supported by evidence and examples. The conclusion should summarize your main arguments and leave a lasting impression on your audience.
Additionally, consider incorporating storytelling, anecdotes, or rhetorical questions to make your speech more engaging and interactive. These techniques can help create a connection with your audience and enhance their overall experience.
Furthermore, use transitions and signposts to guide your audience through your speech. Clear and concise transitions help your audience follow your thoughts and maintain a sense of flow.
Lastly, consider the use of visual aids, such as slides or props, to enhance your speech and make it more visually appealing. Visual aids can help illustrate your points and make complex ideas more accessible to your audience.
In summary, structuring an engaging speech involves organizing it into a clear introduction, body, and conclusion, incorporating storytelling and rhetorical techniques, using transitions to guide your audience, and considering the use of visual aids. By structuring your speech effectively, you can capture and maintain your audience's attention throughout your persuasive speech.
Related Insights
Mastering the art of extemporaneous speech, using stage movements and gestures as foundations of persuasion: learn these 3 ways (part 2), learn to create a persuasive speech: how to apply these tools to investigate your topic (part 2).

- 5 Prep Tips for BP
- Top Speech Introductions
- Public Speaking and Debate Competitions
- Incorporating Humor
- Logical Fallacies
- How-To: Prepare for Debate Tournaments
- How-To: Judge a Debate
- How-To: Win a BP Debate
- How-To: Win An Argument
- How-To: Improve at Home
- Team China Wins World Championship
- Ariel Wins Tournament
- Jaxon Speaks Up
- Tina Improves
- Self Confidence
- Public Speaking
- Communication
- Communication Skills
LEARNER STORIES
- Kanhaiya Sharma
- Ashfaq Sorathia
- Prateek Chawla
OTHER TOOLS
- Comparative Analysis
On This Page
Imagine standing before an audience, your heart pounding like a drum, and a critical decision hanging in the balance. Your ability to make a persuasive speech and to communicate effectively has never been more critical. From the hallowed halls of historic speeches to the humble corridors of everyday conversations, persuasive communication is the unspoken power behind change, influence, and success.
In this blog post, we’re embarking on a journey to uncover the art of persuasive speech. Are you ready to discover the secrets that have inspired leaders, swayed opinions, and changed lives throughout history? Let’s begin by demystifying persuasive speech and unlocking its transformative potential, one word at a time.
Understanding Persuasion
Persuasion is the subtle art of influencing the audience to thoughts, decisions, and actions through effective communication. It’s the skill that allows you to win hearts, change minds, and motivate others to your cause.
Whether you’re delivering a persuasive speech in front of a packed auditorium or crafting a persuasive email to your boss, this ability to persuade is a potent tool that can help you navigate life’s challenges with finesse.
Persuasive speech matters because it’s not just about convincing others; it’s about building trust and credibility. When you communicate persuasively, you demonstrate your expertise, sincerity, and empathy. This, in turn, fosters trust and credibility with your audience. People are more likely to listen to, respect, and follow those they trust.
While persuasive speeches often come to mind when we think of persuasion, this skill extends far beyond formal presentations. It’s embedded in conversations, negotiations, marketing messages, and social media posts.
Mastering your persuasive speech means becoming a more effective communicator in all aspects of life, from convincing a friend to join a new adventure to negotiating a critical business deal.
Persuasive communication isn’t something you either have or don’t have; it’s a skill that can be learned, honed, and improved throughout your life. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your career, the audience to whom you’re communicating is always key. There’s always room for growth. Becoming a persuasive communicator is an ongoing process that involves continually honing your skills to engage the audience to convey your message effectively.
In the upcoming sections, we’ll dive into the essential elements of a persuasive speech topic to enhance your skills as a speaker and writer in any situation. Let’s get started in uncovering these secrets.
Elements Of Persuasive Speech
These elements serve as the foundation upon which your persuasive speech skills are built, whether you’re speaking or writing. Let’s uncover the secrets that will empower you to craft your speech and sway hearts and minds effectively.

1. Building Credibility
Credibility is the cornerstone of a persuasive speech, representing the trust your audience invests in you as a communicator. Without it, your words may lack impact. To build credibility, authenticity is key; by sharing your genuine thoughts, emotions, and intentions, you establish trust rapidly.
Additionally, positioning yourself as an authority on the subject through your speech knowledge, experience, and qualifications enhances your persuasiveness. Moreover, recognizing and managing emotions, a trait linked to emotional intelligence is vital for effective persuasive communication.
2. Understanding Your Audience
Understanding your audience is a fundamental component of a persuasive speech, emphasizing the importance of tailoring your message to address their specific needs, desires, and pain points. Demonstrating your consideration of their perspective and showing empathy, by understanding their emotions and feelings, paves the way for a deeper connection with your audience.
Furthermore, adaptability in your communication style is key; recognizing that different individuals may respond better to various approaches, some driven by logic and data, while emotional stories sway others, ensures a more successful and resonant persuasive speech.
3. Communicating Effectively
Effective communication is the linchpin of a persuasive speech topic , demanding a harmonious blend of clarity, engagement, and active listening to create a deeply resonating message. Clarity is of utmost importance; your message must be free from diluting ambiguity. Use straightforward language and logical arguments to eliminate doubts in your audience .
Beyond words, effective communication thrives on constant audience engagement for your audience , using anecdotes, examples, and rhetorical questions to sustain their interest and heighten receptivity. Active listening is equally vital, enabling real-time message adjustments by keenly observing your audience responses and non-verbal cues, ensuring your words continually align with their needs and concerns. Your persuasive speech hinges on this interplay, fostering a connection that resonates and influences the audience.
In the following sections, we’ll apply these elements to your persuasive speech , offering practical tips to enhance your persuasive communication skills in different contexts. Let’s continue our journey to unveil the secrets of persuasion.
Developing Persuasive Speaking
In this subsection, we journey into persuasive speaking, uncovering the techniques and strategies that empower you to speak with confidence, clarity, and persuasiveness. Let’s embark on the path to mastering the art of spoken persuasion.

1. Crafting A Compelling Narrative
Imagine you’re about to give a speech on environmental conservation. To start strong, you might begin with a vivid example of the devastating effects of climate change. Perhaps you paint a picture of a future where our children won’t be able to enjoy the beauty of a lush, green Earth. That’s the power of crafting a compelling narrative – it grips the audience right from the beginning.
As you continue, you structure your speech with clear signposts, guiding the audience through your message, and conclude with a memorable call to action. It’s like weaving a story that takes your listeners on a journey.
2. Mastering Persuasive Techniques
Persuasive speaking is all about using the right tools. Think of it like a master craftsman wielding various instruments to create a masterpiece. In your speech, you can employ rhetorical devices, such as using parallelism to emphasize your points, just like Martin Luther King Jr. did in his iconic “I Have a Dream” speech.
Or, you might use persuasive language that taps into your audience emotions. For instance, if you’re advocating for animal welfare, you could describe the suffering of a specific animal, making the audience feel a personal connection. It’s like using different brushes and colors to paint a compelling picture.
3. Use Of Visual Aids in the Persuasive Speech
In the digital age, persuasive speaking should be integrated with visual aids and technology. Imagine you’re giving a speech on the latest technological innovations. To engage the audience , you could incorporate dynamic visuals, like charts, videos, or interactive graphics, that illustrate the impact of these innovations.
You should be using real-time data to support your points. Consider Steve Jobs’ iconic iPhone launch presentations – he used visuals and technology to make complex ideas simple and captivating.
This is about using the power of visuals and tech to enhance your speech , making it more impactful and memorable.
Impact Of Persuasive Speech
In this section, we delve into your speech , witnessing the real-world impact of persuasive communication—how it transforms lives, shapes careers, and influences societies. Here, we explore compelling examples and delve into the personal and societal growth that comes with mastering the art of persuasion.
1. Professional Advancement
Mastering persuasive communication skills should be considered like having a Swiss Army knife for your career. It’s not just about crafting fancy words; it’s about being the captain of your professional ship.
Imagine you’re leading a team, and you want them to tackle a challenging project. With persuasive communication, your speech can inspire and guide them to collaborate effectively, resulting in outstanding results.
But it’s not just about leadership; it also should be your secret weapon for navigating those tricky workplace conflicts and sealing the deal in negotiations. For instance, picture a scenario where you’re resolving an issue with a colleague.
Instead of just fixing the problem, you both end up with a win-win solution that advances your careers.
That’s the magic of persuasive speech – it unlocks your career’s full potential, making your goals achievable and your journey fulfilling.
2. Personal Empowerment
Now, let’s talk about how persuasive thinking and communication should be able to empower you personally. It’s like having your point of view as your superpower, boosting your self-confidence and enriching your relationships.
When you can articulate your speech effectively, you don’t just talk the talk; you walk the walk with confidence.
Picture this: You’re in a group, and you have an idea to share. With a persuasive speech , you express it so well that everyone listens, and you leave a lasting impression. It’s not just about talking to others; it’s also about connecting with them on a deeper level.
Think about how understanding and persuading with empathy should be utilized to create trust and make your personal relationships more fulfilling.
Moreover, in everyday life, persuasive thinking should be a tool that helps you make clear decisions and solve problems with finesse and purpose. It’s like having a guiding light in your pocket for navigating life’s twists and turns.
3. Societal Influence and Change
Now, let’s journey into the world of persuasive speeches and their incredible impact on society. Think about history – about how a persuasive speech is litting the flames of transformative movements across the globe.
Whether it’s the words of influential leaders rallying for change and justice or persuasive communication fueling social activism, their influence is undeniable.
Imagine standing in a crowd, listening to a speech that stirs your soul and inspires you to take action for a cause you deeply believe in. That’s the power of persuasive advocacy. And that leads to the question: What are the key elements that make advocacy truly compelling and influential?
These speeches aren’t just words; they’re catalysts for action and beacons of hope, uniting people and driving positive change on a societal scale from your point of view .
Corporate Influence
In the corporate world, a persuasive speech is not just a tool; it’s the dynamo that powers business growth and innovation. Imagine you’re a corporate leader addressing your team. Your persuasive speech aligns them with a shared vision, igniting their motivation and driving remarkable results.
But it’s not just about the employees; it’s also about stakeholders, investors, and partners. With your point of view on persuasive communication, you can build trust, inspire confidence, and secure vital partnerships that shape corporate influence.
It’s like painting a masterpiece with words, creating a narrative that captivates and influences everyone in your business ecosystem.
Civic Engagement
The impact of a persuasive speech on civic engagement is like a rallying cry for community betterment and democratic participation. Imagine you’re listening to a speech that should be compelling you to vote, engage in public discourse, and address critical social and political issues.
It’s not just words; it’s a call to action in your speech.
Historically, persuasive speeches have ignited social movements, united people in shared causes, and inspired civic action. They nurture collective responsibility, foster civic-mindedness, and empower individuals to advocate for your point of view on positive community change.
Your speech acts like a wave of change, driven by persuasive messages, enhancing democracy and pursuing a more equitable and just society.
In the upcoming sections, we’ll uncover how these facets of personal and societal impact intersect, showcasing the transformative potential of a persuasive speech .
Famous Examples of the Persuasive Speech
Here, we’ll explore five iconic and influential persuasive speeches throughout history that have demonstrated the power of persuasive speech . By analysing these famous examples, you should be able to gain valuable insights into the art of compelling persuasion.

1. Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream”
Martin Luther King Jr.’s “ I Have a Dream ” speech epitomizes persuasive speech with its rhetorical brilliance, emotional depth, and historical significance.
Dr. King’s power lay in his vision, as he painted a vivid picture of a world where racial equality should be not a mere dream but a shared reality, instilling hope and motivation.
He harnessed rhetorical devices such as repeating phrases like “I have a dream” and “Let freedom ring,” creating a rhythmic, memorable quality reinforcing key messages.
Furthermore, his words tapped into the deep-seated emotions of the audience , stirring a profound sense of urgency and a shared mission, making this speech an enduring testament to the art of your persuasive speech .
2. Winston Churchill’s “We Shall Fight on the Beaches”
Winston Churchill’s “ We Shall Fight on the Beaches ” is a testament to his unwavering resolve and powerful rhetoric, which rallied a nation during a critical historical moment.
Churchill’s words conveyed a spirit of defiance that deeply resonated with a nation facing formidable challenges, highlighting mental health . His speech left no room for ambiguity, articulating a clear path forward and the unwavering commitment required.
Through mobilizing language, Churchill should be galvanizing citizens to come together, confront adversity head-on, and work collectively toward a common objective, making this speech a remarkable example of persuasive leadership.
3. John F. Kennedy’s “Ich bin ein Berliner”
John F. Kennedy’s “ Ich bin ein Berliner ” speech went beyond political boundaries to convey a powerful message of unity. Kennedy’s words expressed unwavering support and a sense of shared identity with the people of Berlin, fostering solidarity.
Through symbolic gestures and a choice of language that demonstrated a deep understanding of the local context, he effectively connected with the audience .
Furthermore, his words resonated with Berliners by highlighting the shared values and ideals they held dear, making this speech a poignant example of international persuasive speech and solidarity.
4. Malala Yousafzai’s United Nations Address
Malala Yousafzai’s United Nations Address established her as a global symbol for education and girls’ rights through her courage and eloquence. Her remarkable courage in the face of adversity should be highlighted as a powerful testament to her unwavering commitment to the girls’ education.
Malala’s youthful perspective and unwavering determination captured the hearts of people worldwide, underscoring the urgency of her message.
Her speech not only inspired but also catalyzed a global movement dedicated to addressing the barriers to the education that girls face worldwide, making her a remarkable advocate for change and the power of a persuasive speech .
5. Ronald Reagan’s “Tear Down This Wall!”
Ronald Reagan’s “ Tear Down This Wall! ” speech became synonymous with the fall of the Berlin Wall and the end of the Cold War. His words conveyed a powerful and symbolic demand, boldly challenging the division of the city and offering a vision of a united, free Berlin.
Reagan’s clarity of message resonated deeply with those yearning for liberty behind the Iron Curtain, addressing not only political freedom but also impacting the mental health of those living in oppressive circumstances.
The historical significance of his speech should be undeniable, as it played a pivotal role in shaping the course of history and ushering in a new era of freedom and cooperation, making it a prime example of persuasive speech with profound global implications.
Persuasive Speech Topics
In this section, we delve into various persuasive speech topics, each carefully curated to captivate the audience , stimulate critical thinking, and drive discussions that matter.
1. Good Persuasive Speech Topics in Arts
The Role of Art in Promoting Mental Health and Well-being
The Impact of Digital Art on Traditional Art Forms
Censorship in the Arts: Balancing Creative Freedom and Societal Values
Art as a Tool for Social Change and Activism
The Importance of Arts Education in K-12 Schools
2. Best Persuasive Speech Topics for High School Students
The Benefits of Mandatory Volunteering for High School Students
Social Media and its Impact on Teen Mental Health
The Importance of Financial Literacy Education in High Schools
Should High School Students Have a Say in Curriculum Development?
The Pros and Cons of Standardised Testing in High Schools
3. Best Persuasive Speech Topics for College Students
Addressing Student Loan Debt: Strategies for College Affordability
The Role of Technology in Modern Education
Campus Free Speech and its Limits: Balancing Freedom and Inclusivity
Promoting Mental Health Awareness and Support on College Campuses
The Impact of Climate Change: What Can College Students Do?
4. Good Persuasive Speech Topics on Academics
The Future of Remote Learning and its Impact on Academic Achievement
Reevaluating Grading Systems: Is Pass/Fail a Better Option?
The Role of Critical Thinking in Modern Education
Promoting Multilingual Education for a Globalised World
The Ethics of AI and Automation in Education
5. Good Persuasive Speech Topics on the Economy
Universal Basic Income: A Solution to the Economic Inequality?
Green Jobs and the Transition to a Sustainable Economy
The Gig Economy: Flexibility vs. Workers’ Rights
The Pros and Cons of Cryptocurrency and Digital Money
Economic Impacts of the Aging Population: Preparing for the Silver Tsunami
6. Good Persuasive Speech Topics on Entertainment
The Influence of Streaming Services on Traditional Television and Film
Celebrity Culture and its Effects on Society
The Ethics of Cancel Culture in the Entertainment Industry
The Representation of Diversity in Media and Entertainment
The Future of Live Events and Performances in a Post-Pandemic World
7. Interesting Persuasive Speech Topics on Politics and Government
The Role of Social Media in Shaping Political Discourse
Campaign Finance Reform: Reducing the Influence of Big Money in Politics
Voting Rights and Access: Ensuring a Fair and Inclusive Democracy
The Pros and Cons of Term Limits for Elected Officials
Addressing Cybersecurity Threats to the Election Integrity
8. Good Persuasive Speech Topics on Sports
The Impact of Athletes’ Activism on Social and Political Issues
Gender Equality in Sports: Closing the Pay Gap
The Ethics of Performance-Enhancing Drugs in Professional Sports
Should College Athletes Be Paid for Their Performance?
The Environmental Impact of Major Sporting Events
9. Good Persuasive Speech Topics on Education
The Digital Divide: Bridging the Gap in Access to the Education
Inclusive Education: Supporting Students with Disabilities
The Importance of the Arts and Physical Education in Schools
Homeschooling vs. Traditional Schooling: Pros and Cons
Reimagining Teacher Training and Professional Development
10. Good Persuasive Speech Topics for Social Media
Online Privacy and Data Security: Protecting Your Digital Identity
Social Media Addiction: Recognising the Signs and Finding Balance
The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health and Self-Esteem
Social Media and Cyberbullying: Strategies for Prevention
The Role of Social Media in Political Movements and Activism
11. Good Persuasive Speech Topics for 2023 on Technology
Ethical Considerations in AI and Machine Learning
The Future of the Space Exploration: Private vs. Government Initiatives
Cybersecurity in the Age of IoT: Protecting Our Digital Lives
The Role of Technology in Healthcare: Advancements and Challenges
The Environmental Impact of the E-Waste and Technology Disposal
Empower Yourself With Persuasion
In an era of information overload and constant communication, the ability to wield persuasive speech is a powerful tool that can transform your personal and professional life before your audience , so empower yourself with persuasion.
Acquire the skills to express your ideas effectively, build authentic connections, and drive positive change. With the art of persuasion in your toolkit, you hold the key to leaving a lasting mark on the world and shaping your unique history, all while considering the impact on mental health .
By Rishabh Bhandari
How to give a persuasive presentation: techniques and proven framework, influence vs persuasion: what’s the real difference, what is persuasion: meaning, skills and examples.
Kapable © 2024
- TERMS OF USE
- PRIVACY POLICY
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
Persuasive-Speech-and-Outline
- Communications

120 Strong Persuasive Speech Topics to Captivate Your Audience
The information on this website should not be considered medical advice. This website contains affiliate links, and we may be compensated for referrals.
Introduction
Persuasive speech is an art form that combines rhetoric, passion, and logic to sway an audience. It has been a crucial aspect of human communication, playing a pivotal role in history, politics, and personal relations. This comprehensive guide aims to dissect the elements of a persuasive speech, providing insight into crafting a message that is not only heard but also acted upon.
The power of persuasive speech lies in its ability to mold opinions and drive action. From Socrates to Steve Jobs, great speakers have always known how to appeal to their audiences’ hearts and minds. This article will explore the strategies and techniques that make a speech not just memorable but effective in persuasion.
Understanding Persuasion
At its core, persuasion is about more than just presenting facts and figures; it’s about creating a narrative that resonates with the audience on a deeper level. Aristotle’s three modes of persuasion—ethos, pathos, and logos—offer a time-tested framework for building a convincing argument. Ethos appeals to the speaker’s credibility, pathos to the audience’s emotions, and logos to logical reasoning.
Understanding these elements is fundamental to crafting a speech that persuades. A speaker’s ability to combine these elements effectively determines how well they can connect with their audience and sway them to their point of view. The right mix can make the difference between a speech that is forgettable and one that inspires and motivates.
Knowing Your Audience
The first step in effective persuasion is to understand the audience. Who are they? What do they value? What are their beliefs and biases? Tailoring your message to the audience’s expectations and knowledge level is critical. This involves researching the demographic, cultural, and psychographic characteristics of your audience.
Once you understand your audience, you can craft a message that resonates with them. This means using language that they understand, addressing their concerns, and connecting your message to their values and beliefs. The better you know your audience, the more effectively you can persuade them.
Choosing the Right Topic
Choosing a relevant and engaging topic is crucial for a persuasive speech. It should be a subject you are passionate about and one that resonates with your audience. Relevance is key; the topic should be timely and of interest to your audience.
When selecting a topic, consider the currentness of the issue and its potential impact on your audience. It should be broad enough to allow for a comprehensive discussion but focused enough to be addressed within the constraints of your speech time. Balancing these aspects will help ensure that your topic is not only interesting but also persuasive.
Skip to the list of 120 persuasive speech topics below.
Structuring Your Speech
A clear and logical structure is the backbone of a persuasive speech. Start with a strong introduction that captures the audience’s attention and states your thesis. The introduction should be compelling, setting the tone for the rest of the speech.
The body of your speech should contain well-researched arguments supported by evidence. Each point should be clearly stated and flow logically from one to the next. Addressing counterarguments and refuting them strengthens your position. Finally, conclude your speech with a summary of your key points and a strong call to action or concluding thought.
Crafting Your Arguments
The arguments you present are the crux of your persuasive speech. They should be logical, well-structured, and supported by evidence. Start by stating your argument clearly, then back it up with facts, statistics, expert opinions, or anecdotes.
Balancing emotional appeal with logical reasoning is crucial. While logical arguments provide the foundation of your persuasion, emotional appeal can drive your point home, making your speech more memorable and impactful. It’s about striking the right balance to engage both the minds and hearts of your audience.
Using Persuasive Language and Rhetorical Devices
The language you use in your speech can significantly impact its persuasiveness. Rhetorical devices such as metaphors, similes, and analogies can make complex ideas more relatable and memorable. Repetition can reinforce key points, while rhetorical questions can engage the audience and provoke thought.
Your tone and body language also play vital roles in delivery. Confidence, enthusiasm, and sincerity in your voice and posture can greatly enhance the persuasiveness of your speech. The goal is to engage your audience not just intellectually, but also emotionally.
Compelling Words for a Persuasive Speech
In a persuasive speech, the choice of words can significantly impact its effectiveness. Strong, compelling words create an emotional response and emphasize the importance of your message. Words like “unprecedented,” “revolutionary,” and “transformative” suggest significant impact and innovation. Terms such as “crucial,” “vital,” and “essential” underline the importance of an issue. Using words like “empower,” “inspire,” and “motivate” can encourage positive action. Phrases such as “imagine a world where” or “picture this” help paint a vivid picture, engaging the audience’s imagination and empathy.
Language to Avoid in a Persuasive Speech
Conversely, certain types of language can weaken a persuasive speech. Overly complex or jargon-heavy language can alienate or confuse the audience, so it’s best to use clear, straightforward language. Avoiding generalizations, absolutes, and hyperbolic statements like “always,” “never,” or “the best/worst ever” is crucial as they can undermine your credibility. Passive voice can also make your statements less direct and impactful. Additionally, negative language or attacking an opposing viewpoint too aggressively can be off-putting to the audience and detract from the persuasiveness of your argument.
Dealing with Counterarguments
Addressing counterarguments head-on can greatly enhance the credibility of your speech. It shows that you have considered different perspectives and are confident enough in your position to openly discuss opposing views.
Acknowledge the counterarguments fairly and then use evidence and logic to refute them. This not only strengthens your argument but also shows respect for your audience’s intelligence, enhancing your ethos.
Practicing and Delivering Your Speech
Effective delivery can make or break a persuasive speech. Practice is key to delivering your speech confidently and fluidly. Rehearse your speech multiple times, focusing on your tone, pace, and body language.
During delivery, engage with your audience. Make eye contact and use gestures to engage them effectively. Non-verbal cues like smiling, nodding, and appropriate hand gestures can make your speech more dynamic and relatable. Remember, how you deliver your message can be just as important as the message itself.
Time yourself. It’s important to make sure your speech doesn’t go over your allotted time, and speaking for too long can lose your audience’s attention.
120 Compelling Persuasive Speech Topics
Art & Culture
- The importance of preserving indigenous art
- Street art: Vandalism or valuable culture?
- The role of social media in contemporary art promotion
- Should art education be mandatory in schools?
- The impact of digitalization on the music industry
- The relevance of classical music in modern society
- How do movies influence our cultural perceptions?
- The role of museums in preserving history
- Cultural appropriation in fashion
- The decline of traditional theaters in the digital age
Business & Entrepreneurship
- The role of ethics in business
- Is the customer always right in business?
- The rise of social entrepreneurship
- The future of retail in the digital era
- The impact of AI on business decision-making
- Crowdfunding: Changing the landscape of business funding
- The role of leadership in business success
- The gig economy and the future of work
- Corporate social responsibility: A necessity or a trend?
- The impact of globalization on small businesses
Economy & Work
- Universal Basic Income: Solution or problem?
- The gig economy: Freedom or exploitation?
- Cryptocurrency: The future of finance or a passing fad?
- Should minimum wage be a living wage?
- The impact of automation on job markets
- The role of women in the corporate world
- Globalization: Pros and cons for the average worker
- The ethics of advertising in children’s media
- The future of remote work post-pandemic
- Consumerism and its impact on the global economy
- The benefits of bilingual education
- Standardized testing: Does it help or hinder students?
- Online vs. traditional education: Which is better?
- The importance of teaching financial literacy in schools
- Should college education be free?
- The role of technology in modern classrooms
- The impact of school uniforms on student behavior
- The necessity of sex education in schools
- The influence of social media on student productivity
- The importance of arts in education
Environment & Sustainability
- The impact of climate change on global agriculture
- Plastic pollution: A global crisis
- The importance of protecting endangered species
- Urban gardening as a tool for sustainability
- The future of clean energy
- Water scarcity: The next global crisis?
- The impact of fast fashion on the environment
- Sustainable tourism: A paradox?
- The importance of green spaces in urban areas
- Climate change: What is the solution?
Ethics & Morality
- The ethics of cloning
- Animal rights: Ethical obligations or personal choice?
- The moral implications of euthanasia
- The ethics of surveillance in modern society
- Moral relativism in a globalized world
- The importance of ethical consumption
- The role of religion in ethical decision-making
- The impact of technology on moral values
- The ethics of whistleblowing
- The morality of war in the modern world
Health & Medicine
- The benefits of a plant-based diet
- Vaccinations: Rights vs. public health
- The impact of mental health on physical well-being
- Should alternative medicine be more mainstream?
- The obesity epidemic: Society’s responsibility?
- The ethics of animal testing in medicine
- The importance of sleep for health
- The impact of social media on body image
- The future of telemedicine
- The role of exercise in mental health
Personal Development & Lifestyle
- The power of positive thinking
- The importance of work-life balance
- The role of meditation in stress reduction
- The impact of self-help books on personal growth
- The importance of goal setting for success
- The effects of social media on self-esteem
- Minimalism as a lifestyle choice
- The benefits of lifelong learning
- The importance of time management
- The role of travel in personal development
Politics & Governance
- The role of the United Nations in modern conflicts
- Should voting be mandatory?
- The impact of lobbying on democracy
- The future of the European Union
- National security vs. individual privacy
- The role of social media in political campaigns
- The effectiveness of the criminal justice system
- The impact of global trade agreements on local economies
- Political correctness: Freedom of speech vs. respect
- The role of youth in political change
Science & Technology
- Should genetic engineering be more regulated?
- The ethical implications of artificial intelligence
- Space exploration: Is it worth the cost?
- The impact of smartphones on mental health
- Renewable energy: The path to a sustainable future
- The role of technology in modern education
- Cybersecurity: The new global battleground
- The future of transportation: Electric vehicles
- Is technology making us less human?
- The impact of social media on interpersonal communication
Social Issues & Ethics
- The death penalty: Justice or inhumanity?
- Gun control: Rights vs. safety
- The impact of media on public opinion
- Racial profiling in law enforcement
- LGBTQ+ rights in modern society
- The role of protest in democracy
- The ethics of drone warfare
- The refugee crisis: A global responsibility
- The impact of social networks on privacy
- Fake news: A threat to democracy?
Sports & Recreation
- The importance of physical education in schools
- Should eSports be considered real sports?
- The impact of commercialization on professional sports
- The role of sports in promoting global peace
- Performance-enhancing drugs in sports
- The benefits of outdoor activities for mental health
- The importance of team sports for personal development
- Gender equality in sports
- The impact of technology on sports performance
- The future of the Olympics in a changing world
The art of persuasive speech is a powerful tool that can shape opinions, influence decisions, and inspire change. A well-crafted speech, grounded in solid research and delivered with conviction, can resonate deeply with an audience. Whether you’re aiming to persuade a small group or a large assembly, the principles of effective persuasion remain the same. By understanding your audience, carefully selecting your topic, structuring your speech for clarity and impact, crafting strong arguments, using persuasive language and rhetorical devices, addressing counterarguments, and practicing confident delivery, you can elevate your persuasive speech from merely good to truly compelling.
Facebook Comments

How to Download Add-Ons for Anki

Step 1 Resources – Boards and Beyond Review
Privacy overview.
More From Forbes
How to look for all the possibilities to be successful in conflict.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Colleagues arguing in a meeting
In the face of truly competing needs and the polarizing conflicts on both local and global scales, it’s become incredibly difficult to bring people together in most situations. But in a recent conversation, William Ury , expert negotiator and author of Possible: How We Survive (and Thrive) in an Age of Conflict , describes several approaches to help us navigate conflict skillfully and achieve the best resolution for all parties.
Operate From Your Most Effective Zone
The biggest obstacle to getting what you want in a conflict is not your difficult opponent, Ury says. Rather, it’s “our own very human, very natural tendency to react, to act without thinking, to act out of fear, out of anger.” He explains: “In conflict, we tend to get hyperactivated with fear and anxiety; or, after a while, we burn out and we get hypoactivated, which is despair and depression. We’re at our most effective in that optimal zone which psychologists call the ‘window of tolerance,’ where we feel the emotions but we’re in control of our own emotions rather than our emotions being in control of us. That is the most effective place to be when it comes to dealing with conflicts, organizational conflicts, interpersonal conflicts, conflicts of any kind.”
When we’re outside our window of tolerance, we can’t think well, which makes it difficult to respond creatively and generate pertinent alternatives. Ury notes that we’re all subject to a lot of stress, which tends to over-activate us and then burn us out. When negotiations are difficult, he suggests taking time to breathe or even asking for a moment of silence so everyone can calm themselves. Once we’ve stabilized, we can consider which resources we need to motivate ourselves to refocus, including exercise, being in nature or reaching out to a friend. These kinds of interventions permit us to return to our window of tolerance.
Get The Right People’s Opinions In The Room
Stakeholders who are not at the table are “often the ones who actually control or can block any agreement made at the table,” Ury warns. If people are not involved in the decision-making process, then no matter what their actual interests are, they may block a resolution simply because they weren’t involved in creating it.
“Negotiation is not just about reaching agreements, it’s about getting to an agreement that gets implemented,” he notes. Even if you think you’ve drafted a great resolution and gotten agreement from your colleagues around the negotiating table, when you return to your respective sides, you may find out about other considerations that weren’t addressed.
Billionaire Mark Cuban Issues Post Halving Bitcoin Warning Amid Unprecedented Crypto Fee Price Chaos
Aew dynasty 2024 results winners and grades as swerve makes history, who is david pecker why he s testifying against trump in hush money trial.
“If you have resistance or people not understanding, or there’s no buy-in, or we drag the implementation out for a long time, it will never happen at all,” says Ury. “And so that initial phase of getting buy-in actually makes it go much faster.”
Be A Persuasive And Empathetic Listener
It’s surprising how often you don’t actually have to fix the problems that people bring to you. If they see that their views and concerns are included, you may still be able to get them to agree to what you want to do. By practicing empathetic listening, says Ury, you can find “the cheapest concession you can make. It signals empathy. It signals respect. It says, ‘I hear you, even if I can’t fix your problem.’” No matter how things go, he adds, “Acknowledge how hard it is, and then ask, ‘Okay, what can we do to move forward here?’”
Most participants in a conflict view the other participants as adversaries, but “it’s in your interest to put yourself in the other person’s shoes because negotiation is an exercise in influence,” Ury notes. “You’re trying to change someone’s mind. How could you possibly change someone’s mind or their heart if you don’t know where they are?”
Manage Power Imbalances
In conflicts where someone has more hierarchical power or authority than we do, we’re likely to operate at a disadvantage. Ury’s advice for dealing with power asymmetry is to “prepare, prepare, prepare: really think about what you want, but also think about what they want.” For example, Ury suggests “trying to write your opponent or boss’s victory speech as a thought experiment to understand what that person needs to accomplish to feel successful. That person wants to be a hero. They want to look good to their boss, to their board of directors, to their shareholders”—just as you want to look good to your constituents.
Ury recommends getting ready for negotiations by considering, “What are their three key talking points? What’s the push-back they’re gonna get? What’s the best counterargument they could deliver?” By thinking through what the other participants are trying to accomplish, you can be more creative and targeted in the way you make your case and the options you present.
This exercise also helps you identify your best alternative actions if you don’t get the negotiated agreement you want. When you’ve identified your best alternative, Ury points out, “it gives you more confidence. You’re actually more likely to negotiate in a way that you’re likely to get what you want.” He explains: “You’ve got to be flexible and opportunistic to see, ‘Oh, there’s a barrier; there’s a block here.’ If I just hit the block, I’m just gonna keep on hitting that block—not gonna go anywhere.”
Also consider how else to gather some additional power for your side. Ury suggests coalition building or finding allies who can help educate the person in power and show them your strength in numbers.
Be A Possibilist
When it comes to negotiating conflicts, Ury describes himself as a “possibilist” rather than an optimist or pessimist. Having helped people resolve boardroom battles, labor strikes and even end civil wars, he recommends three stances to encourage reluctant participants see the possibilities: meet animosity with curiosity, apply your natural creativity and unleash your instinctive collaborativeness. “The choice isn’t about ending conflict,” he says. “It’s about transforming it from the destructive form of these vicious fights that go nowhere, where everybody ends up losing arguments, to constructive listening, dialog, conversation, negotiation and joint problem-solving. That’s the real opportunity and that’s the message: always keep on looking for the possibilities.”
It takes self-awareness, inclusiveness and empathy as well as savvy to advance your interests in a conflict: Sometimes ensuring that the other side gets what it wants makes it more likely that you’ll get your desired outcome too.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

Click here for our new feature on Presidents & the First Amendment
An examination of all 46 presidents and their engagement with the First Amendment
- ENCYCLOPEDIA
- IN THE CLASSROOM
Home » News » 6 key points on book bans from new PEN America report
6 key points on book bans from new PEN America report
By Ken Paulson, published on April 22, 2024

Photo courtesy iStock
The pace at which books are being banned in America continues to accelerate, according to a new study by PEN America.
More books were banned in the first six months of the current school year of 2023-2024 than in the entire 2022-2023 school year, according to the report released this week.
“This escalation follows two years of coordinated efforts to censor books in libraries and classrooms across the country, restricting young people’s freedom to read and learn,” noted PEN America, a nonprofit center that advocates on behalf of authors and publishers.
Six takeaways from the report:
- Targeted content: Most banned books fall into one of three categories: Books that refer to sexual violence or activity; books about LGBTQ+ experiences, and books that involve themes of race or racism.
- States differ: Book bans are common, but not universal among states. Since July 2021, PEN America has documented book bans in 42 states.
- Censorship and geography: Book bans are most common in the South and Midwest. Florida had the largest number of bans, totaling 3,135, with Wisconsin, Iowa, Texas, Kentucky and Virginia following in frequency.
- Concentration of censorship: Book bans tend to be concentrated in a few communities in each state. In Florida, more than half of the state’s banning incidents occurred in Escambia County. Wisconsin’s bans came overwhelmingly from the Elkhorn Area School District.
- Ambiguous legislation: Many books are banned because of fear of violating poorly drafted laws. Florida’s “Don’t Say Gay” law barring classroom discussion of gender identity and sexual orientation became a template in multiple states, leaving teachers unsure of legal limits. Books featuring gay and transgender characters were widely removed from shelves. The Florida law was challenged in a lawsuit, which was settled in March 2024 after the state and plaintiffs agreed on clarification of the statute’s language.
- Targeting race: More than a third of the book bans recorded by PEN America involved books with characters of color or themes of racism: Politically charged efforts to remove books with these subjects were justified as a bar on critical race theory or diversity, equity and inclusion practices.
As disconcerting as the findings may be, PEN America cites an encouraging development.
“A broad coalition of students and advocates has heeded the call: Even in the face of extreme state laws, hateful rhetoric, and an extraordinary number of bans, the fight for the freedom to read has never been stronger,” according to the report.
Related: Banned Books Week: Book bans reflect outdated beliefs about how children read
Ken Paulson is the director of the Free Speech Center at Middle Tennessee State University.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE
April 22, 2024
Judge in Trump case orders press not to report where potential jurors work
April 19, 2024
Perspective
School mom traces development of book bans
Supreme court’s questions about first amendment cases show support for ‘free trade in ideas’.
March 21, 2024
Explore The First Amendment Encyclopedia
More than 1,700 articles on First Amendment topics, court cases and history

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In your speech outline, you want to touch on several key elements. Pick your fight: Start by zeroing in on what you really want to change or influence with this speech. Support your claim with evidence: Identify those key points that back up your stance to appeal to your audience's rational side. The emotional hook: Weave in stories or facts ...
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples. A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything - voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on. A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing ...
Research the topic thoroughly, focussing on key facts, arguments for and against your angle, and background. 2. Define Your Persuasive Goal ... your next step is to create a keyword outline to organize your main points and structure your persuasive speech for maximum impact on the audience. Start strong, letting your audience know what your ...
following outlines the basic format of a persuasive speech, but speeches may take alternative forms. INTRODUCTION There are four key components to an introduction: the attention getting device (AGD), common ground, thesis, and preview. For the sake of this speech, you'll want to keep your introduction around 20 seconds (give or take).
The key elements of a persuasive speech are: introduction (hook, thesis, preview); body (main points with supporting details and transitions); conclusion (summary, restated thesis, closing statement). Let's look closer at how to structure them to write a good persuasive speech. Writing the Introduction. The introduction to persuasive speech ...
Typically, three to five key points work well for a persuasive speech. Ensure that each key point supports your overall objective and is logically connected to the others. In addition, you should also address any counter arguments to make your central point stronger. Step 4: Add Supporting Evidence for Each Key Point.
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you. You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your ...
Step 2: After the Story, Now, Give Your Advice. When most people write a persuasive presentation, they start with their opinion. Again, this makes the listener want to play Devil's advocate. By starting with the example, we give the listener a simple way to agree with us.
Although a persuasive speech involves information—even as much as an informative speech—the key difference is that a persuasive speech is designed for "creating, reinforcing, or changing people's beliefs or actions" (Lucas, 2015. p. 306). ... These are the main points of the body of your persuasive speech. We call these the "pro ...
Close powerfully with a call to action. Inspire audiences to take a specific next step that furthers your cause. Motivate minds and spark an enduring commitment to your vision. 🎊 Persuasive speech tips: Survey and feedback better with the write tools, to make sure that your structure is appealing to the participants! #4.
3. Address the counter-argument. Although it is not strictly necessary, your argument may be stronger if one or more of your supporting points addresses the views of the opposing side. This gives you a chance to address your audience's possible objections and make your argument stronger.
Identify characteristic structures of a persuasive speech. In many ways, a persuasive speech is structured like an informative speech. It has an introduction with an attention-getter and a clear thesis statement. It also has a body where the speaker presents their main points and it ends with a conclusion that sums up the main point of the speech.
Step 2 - Select a good persuasive speech topic to accomplish the goal and choose a position. How to write a persuasive speech. Step 3 - Locate credible and reliable sources and identify evidence in support of the topic/position. Revisit Step 2 if there is a lack of relevant resources. Step 4 - Identify the audience and understand their ...
The main points of your persuasive speech and the supporting material you include serve as evidence. For example, a speaker may make the following claim: "There should be a national law against texting while driving." The speaker could then support the claim by providing the following evidence: "Research from the US Department of ...
Building Upon Your Persuasive Speech's Arguments. Once you have constructed the key arguments and order of points (remembering that if you use topical order, to put your strongest or most persuasive point last), it is time to be sure your points are well supported. In a persuasive speech, there are some things to consider about evidence.
Here are five techniques you can use to make your speech more persuasive and effective: 1- Emotional Appeal. One of the most powerful techniques for persuasive speaking is emotional appeal. This involves using language and stories that evoke strong emotions in your audience, such as fear, anger, or compassion.
In the persuasive speech, we have to be the tour guide of the audience who plays the role of tourists. Our goal is to enlighten them about a subject or issue that they haven't seen yet. If you read this far, thank you so much, and I hope you enjoyed it. References and Further Reading Ace The Presentation. Amadebai, E. 11 Best Body Language ...
Alan H. Monroe's (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience's attention.
3 components of a persuasive speech structure. Make sure your persuasive speech structure includes some aspect of the three below elements. They are a huge tool for ensuring your persuasive presentation is a success. Ethos: establishing credibility. Establishing credibility as a speaker is crucial to winning over an audience.
Understanding the power of persuasion is crucial when it comes to writing a persuasive speech. Persuasion is the art of influencing and convincing others to adopt your point of view or take a specific action. By understanding the principles behind persuasion, you can effectively communicate your ideas and sway your audience.
1. Building Credibility. Credibility is the cornerstone of a persuasive speech, representing the trust your audience invests in you as a communicator. Without it, your words may lack impact. To build credibility, authenticity is key; by sharing your genuine thoughts, emotions, and intentions, you establish trust rapidly.
APSU Writing Center Persuasive Speech A persuasive speech aims to convince the audience to believe a certain viewpoint, opinion, or idea. The end goal is to change the mind of your audience and to persuade them into action or thought. A persuasive speech often describes facts, values, and policies. You can also use the ethos (ethical, moral), logos (logical, intellectual), or pathos (emotional ...
Persuasive speech is an art form that combines rhetoric, passion, and logic to sway an audience. It has been a crucial aspect of human communication, playing a pivotal role in history, politics, and personal relations. ... Finally, conclude your speech with a summary of your key points and a strong call to action or concluding thought. Crafting ...
If they see that their views and concerns are included, you may still be able to get them to agree to what you want to do. By practicing empathetic listening, says Ury, you can find "the ...
6 key points on book bans from new PEN America report. The pace at which books are being banned in America continues to accelerate, according to a by. More books were banned in the first six months of the current school year of 2023-2024 than in the entire 2022-2023 school year, according to the report released this week.