

What this handout is about
This handout will provide a broad overview of gathering and using evidence. It will help you decide what counts as evidence, put evidence to work in your writing, and determine whether you have enough evidence. It will also offer links to additional resources.
Introduction
Many papers that you write in college will require you to make an argument ; this means that you must take a position on the subject you are discussing and support that position with evidence. It’s important that you use the right kind of evidence, that you use it effectively, and that you have an appropriate amount of it. If, for example, your philosophy professor didn’t like it that you used a survey of public opinion as your primary evidence in your ethics paper, you need to find out more about what philosophers count as good evidence. If your instructor has told you that you need more analysis, suggested that you’re “just listing” points or giving a “laundry list,” or asked you how certain points are related to your argument, it may mean that you can do more to fully incorporate your evidence into your argument. Comments like “for example?,” “proof?,” “go deeper,” or “expand” in the margins of your graded paper suggest that you may need more evidence. Let’s take a look at each of these issues—understanding what counts as evidence, using evidence in your argument, and deciding whether you need more evidence.
What counts as evidence?
Before you begin gathering information for possible use as evidence in your argument, you need to be sure that you understand the purpose of your assignment. If you are working on a project for a class, look carefully at the assignment prompt. It may give you clues about what sorts of evidence you will need. Does the instructor mention any particular books you should use in writing your paper or the names of any authors who have written about your topic? How long should your paper be (longer works may require more, or more varied, evidence)? What themes or topics come up in the text of the prompt? Our handout on understanding writing assignments can help you interpret your assignment. It’s also a good idea to think over what has been said about the assignment in class and to talk with your instructor if you need clarification or guidance.
What matters to instructors?
Instructors in different academic fields expect different kinds of arguments and evidence—your chemistry paper might include graphs, charts, statistics, and other quantitative data as evidence, whereas your English paper might include passages from a novel, examples of recurring symbols, or discussions of characterization in the novel. Consider what kinds of sources and evidence you have seen in course readings and lectures. You may wish to see whether the Writing Center has a handout regarding the specific academic field you’re working in—for example, literature , sociology , or history .
What are primary and secondary sources?
A note on terminology: many researchers distinguish between primary and secondary sources of evidence (in this case, “primary” means “first” or “original,” not “most important”). Primary sources include original documents, photographs, interviews, and so forth. Secondary sources present information that has already been processed or interpreted by someone else. For example, if you are writing a paper about the movie “The Matrix,” the movie itself, an interview with the director, and production photos could serve as primary sources of evidence. A movie review from a magazine or a collection of essays about the film would be secondary sources. Depending on the context, the same item could be either a primary or a secondary source: if I am writing about people’s relationships with animals, a collection of stories about animals might be a secondary source; if I am writing about how editors gather diverse stories into collections, the same book might now function as a primary source.
Where can I find evidence?
Here are some examples of sources of information and tips about how to use them in gathering evidence. Ask your instructor if you aren’t sure whether a certain source would be appropriate for your paper.
Print and electronic sources
Books, journals, websites, newspapers, magazines, and documentary films are some of the most common sources of evidence for academic writing. Our handout on evaluating print sources will help you choose your print sources wisely, and the library has a tutorial on evaluating both print sources and websites. A librarian can help you find sources that are appropriate for the type of assignment you are completing. Just visit the reference desk at Davis or the Undergraduate Library or chat with a librarian online (the library’s IM screen name is undergradref).
Observation
Sometimes you can directly observe the thing you are interested in, by watching, listening to, touching, tasting, or smelling it. For example, if you were asked to write about Mozart’s music, you could listen to it; if your topic was how businesses attract traffic, you might go and look at window displays at the mall.
An interview is a good way to collect information that you can’t find through any other type of research. An interview can provide an expert’s opinion, biographical or first-hand experiences, and suggestions for further research.
Surveys allow you to find out some of what a group of people thinks about a topic. Designing an effective survey and interpreting the data you get can be challenging, so it’s a good idea to check with your instructor before creating or administering a survey.
Experiments
Experimental data serve as the primary form of scientific evidence. For scientific experiments, you should follow the specific guidelines of the discipline you are studying. For writing in other fields, more informal experiments might be acceptable as evidence. For example, if you want to prove that food choices in a cafeteria are affected by gender norms, you might ask classmates to undermine those norms on purpose and observe how others react. What would happen if a football player were eating dinner with his teammates and he brought a small salad and diet drink to the table, all the while murmuring about his waistline and wondering how many fat grams the salad dressing contained?
Personal experience
Using your own experiences can be a powerful way to appeal to your readers. You should, however, use personal experience only when it is appropriate to your topic, your writing goals, and your audience. Personal experience should not be your only form of evidence in most papers, and some disciplines frown on using personal experience at all. For example, a story about the microscope you received as a Christmas gift when you were nine years old is probably not applicable to your biology lab report.
Using evidence in an argument
Does evidence speak for itself.
Absolutely not. After you introduce evidence into your writing, you must say why and how this evidence supports your argument. In other words, you have to explain the significance of the evidence and its function in your paper. What turns a fact or piece of information into evidence is the connection it has with a larger claim or argument: evidence is always evidence for or against something, and you have to make that link clear.
As writers, we sometimes assume that our readers already know what we are talking about; we may be wary of elaborating too much because we think the point is obvious. But readers can’t read our minds: although they may be familiar with many of the ideas we are discussing, they don’t know what we are trying to do with those ideas unless we indicate it through explanations, organization, transitions, and so forth. Try to spell out the connections that you were making in your mind when you chose your evidence, decided where to place it in your paper, and drew conclusions based on it. Remember, you can always cut prose from your paper later if you decide that you are stating the obvious.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself about a particular bit of evidence:
- OK, I’ve just stated this point, but so what? Why is it interesting? Why should anyone care?
- What does this information imply?
- What are the consequences of thinking this way or looking at a problem this way?
- I’ve just described what something is like or how I see it, but why is it like that?
- I’ve just said that something happens—so how does it happen? How does it come to be the way it is?
- Why is this information important? Why does it matter?
- How is this idea related to my thesis? What connections exist between them? Does it support my thesis? If so, how does it do that?
- Can I give an example to illustrate this point?
Answering these questions may help you explain how your evidence is related to your overall argument.
How can I incorporate evidence into my paper?
There are many ways to present your evidence. Often, your evidence will be included as text in the body of your paper, as a quotation, paraphrase, or summary. Sometimes you might include graphs, charts, or tables; excerpts from an interview; or photographs or illustrations with accompanying captions.
When you quote, you are reproducing another writer’s words exactly as they appear on the page. Here are some tips to help you decide when to use quotations:
- Quote if you can’t say it any better and the author’s words are particularly brilliant, witty, edgy, distinctive, a good illustration of a point you’re making, or otherwise interesting.
- Quote if you are using a particularly authoritative source and you need the author’s expertise to back up your point.
- Quote if you are analyzing diction, tone, or a writer’s use of a specific word or phrase.
- Quote if you are taking a position that relies on the reader’s understanding exactly what another writer says about the topic.
Be sure to introduce each quotation you use, and always cite your sources. See our handout on quotations for more details on when to quote and how to format quotations.
Like all pieces of evidence, a quotation can’t speak for itself. If you end a paragraph with a quotation, that may be a sign that you have neglected to discuss the importance of the quotation in terms of your argument. It’s important to avoid “plop quotations,” that is, quotations that are just dropped into your paper without any introduction, discussion, or follow-up.
Paraphrasing
When you paraphrase, you take a specific section of a text and put it into your own words. Putting it into your own words doesn’t mean just changing or rearranging a few of the author’s words: to paraphrase well and avoid plagiarism, try setting your source aside and restating the sentence or paragraph you have just read, as though you were describing it to another person. Paraphrasing is different than summary because a paraphrase focuses on a particular, fairly short bit of text (like a phrase, sentence, or paragraph). You’ll need to indicate when you are paraphrasing someone else’s text by citing your source correctly, just as you would with a quotation.
When might you want to paraphrase?
- Paraphrase when you want to introduce a writer’s position, but their original words aren’t special enough to quote.
- Paraphrase when you are supporting a particular point and need to draw on a certain place in a text that supports your point—for example, when one paragraph in a source is especially relevant.
- Paraphrase when you want to present a writer’s view on a topic that differs from your position or that of another writer; you can then refute writer’s specific points in your own words after you paraphrase.
- Paraphrase when you want to comment on a particular example that another writer uses.
- Paraphrase when you need to present information that’s unlikely to be questioned.
When you summarize, you are offering an overview of an entire text, or at least a lengthy section of a text. Summary is useful when you are providing background information, grounding your own argument, or mentioning a source as a counter-argument. A summary is less nuanced than paraphrased material. It can be the most effective way to incorporate a large number of sources when you don’t have a lot of space. When you are summarizing someone else’s argument or ideas, be sure this is clear to the reader and cite your source appropriately.
Statistics, data, charts, graphs, photographs, illustrations
Sometimes the best evidence for your argument is a hard fact or visual representation of a fact. This type of evidence can be a solid backbone for your argument, but you still need to create context for your reader and draw the connections you want them to make. Remember that statistics, data, charts, graph, photographs, and illustrations are all open to interpretation. Guide the reader through the interpretation process. Again, always, cite the origin of your evidence if you didn’t produce the material you are using yourself.
Do I need more evidence?
Let’s say that you’ve identified some appropriate sources, found some evidence, explained to the reader how it fits into your overall argument, incorporated it into your draft effectively, and cited your sources. How do you tell whether you’ve got enough evidence and whether it’s working well in the service of a strong argument or analysis? Here are some techniques you can use to review your draft and assess your use of evidence.
Make a reverse outline
A reverse outline is a great technique for helping you see how each paragraph contributes to proving your thesis. When you make a reverse outline, you record the main ideas in each paragraph in a shorter (outline-like) form so that you can see at a glance what is in your paper. The reverse outline is helpful in at least three ways. First, it lets you see where you have dealt with too many topics in one paragraph (in general, you should have one main idea per paragraph). Second, the reverse outline can help you see where you need more evidence to prove your point or more analysis of that evidence. Third, the reverse outline can help you write your topic sentences: once you have decided what you want each paragraph to be about, you can write topic sentences that explain the topics of the paragraphs and state the relationship of each topic to the overall thesis of the paper.
For tips on making a reverse outline, see our handout on organization .
Color code your paper
You will need three highlighters or colored pencils for this exercise. Use one color to highlight general assertions. These will typically be the topic sentences in your paper. Next, use another color to highlight the specific evidence you provide for each assertion (including quotations, paraphrased or summarized material, statistics, examples, and your own ideas). Lastly, use another color to highlight analysis of your evidence. Which assertions are key to your overall argument? Which ones are especially contestable? How much evidence do you have for each assertion? How much analysis? In general, you should have at least as much analysis as you do evidence, or your paper runs the risk of being more summary than argument. The more controversial an assertion is, the more evidence you may need to provide in order to persuade your reader.
Play devil’s advocate, act like a child, or doubt everything
This technique may be easiest to use with a partner. Ask your friend to take on one of the roles above, then read your paper aloud to them. After each section, pause and let your friend interrogate you. If your friend is playing devil’s advocate, they will always take the opposing viewpoint and force you to keep defending yourself. If your friend is acting like a child, they will question every sentence, even seemingly self-explanatory ones. If your friend is a doubter, they won’t believe anything you say. Justifying your position verbally or explaining yourself will force you to strengthen the evidence in your paper. If you already have enough evidence but haven’t connected it clearly enough to your main argument, explaining to your friend how the evidence is relevant or what it proves may help you to do so.
Common questions and additional resources
- I have a general topic in mind; how can I develop it so I’ll know what evidence I need? And how can I get ideas for more evidence? See our handout on brainstorming .
- Who can help me find evidence on my topic? Check out UNC Libraries .
- I’m writing for a specific purpose; how can I tell what kind of evidence my audience wants? See our handouts on audience , writing for specific disciplines , and particular writing assignments .
- How should I read materials to gather evidence? See our handout on reading to write .
- How can I make a good argument? Check out our handouts on argument and thesis statements .
- How do I tell if my paragraphs and my paper are well-organized? Review our handouts on paragraph development , transitions , and reorganizing drafts .
- How do I quote my sources and incorporate those quotes into my text? Our handouts on quotations and avoiding plagiarism offer useful tips.
- How do I cite my evidence? See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
- I think that I’m giving evidence, but my instructor says I’m using too much summary. How can I tell? Check out our handout on using summary wisely.
- I want to use personal experience as evidence, but can I say “I”? We have a handout on when to use “I.”
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Lunsford, Andrea A., and John J. Ruszkiewicz. 2016. Everything’s an Argument , 7th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Miller, Richard E., and Kurt Spellmeyer. 2016. The New Humanities Reader , 5th ed. Boston: Cengage.
University of Maryland. 2019. “Research Using Primary Sources.” Research Guides. Last updated October 28, 2019. https://lib.guides.umd.edu/researchusingprimarysources .
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Finance and Business
- Legal Matters
- Contracts and Legal Agreements
How to Introduce Evidence in an Essay
Last Updated: May 5, 2024
This article was co-authored by Tristen Bonacci . Tristen Bonacci is a Licensed English Teacher with more than 20 years of experience. Tristen has taught in both the United States and overseas. She specializes in teaching in a secondary education environment and sharing wisdom with others, no matter the environment. Tristen holds a BA in English Literature from The University of Colorado and an MEd from The University of Phoenix. This article has been viewed 242,880 times.
When well integrated into your argument, evidence helps prove that you've done your research and thought critically about your topic. But what's the best way to introduce evidence so it feels seamless and has the highest impact? There are actually quite a few effective strategies you can use, and we've rounded up the best ones for you here. Try some of the tips below to introduce evidence in your essay and make a persuasive argument.
Things You Should Know
- "According to..."
- "The text says..."
- "Researchers have learned..."
- "For example..."
- "[Author's name] writes..."
Setting up the Evidence

- You can use 1-2 sentences to set up the evidence, if needed, but usually more concise you are, the better.

- For example, you may make an argument like, “Desire is a complicated, confusing emotion that causes pain to others.”
- Or you may make an assertion like, “The treatment of addiction must consider root cause issues like mental health and poor living conditions.”

- For example, you may write, “The novel explores the theme of adolescent love and desire.”
- Or you may write, “Many studies show that addiction is a mental health issue.”
Putting in the Evidence

- For example, you may use an introductory clause like, “According to Anne Carson…”, "In the following chart...," “The author states…," "The survey shows...." or “The study argues…”
- Place a comma after the introductory clause if you are using a quote. For example, “According to Anne Carson, ‘Desire is no light thing" or "The study notes, 'levels of addiction rise as levels of poverty and homelessness also rise.'"
- A list of introductory clauses can be found here: https://student.unsw.edu.au/introducing-quotations-and-paraphrases .

- For example, you may write, “In the novel, Carson is never shy about how her characters express desire for each other: ‘When they made love/ Geryon liked to touch in slow succession each of the bones of Herakles' back…’”
- Or you may write, "The study charts the rise in addiction levels, concluding: 'There is a higher level of addiction in specific areas of the United States.'"

- For example, you may write, “Carson views events as inevitable, as man moving through time like “a harpoon,” much like the fates of her characters.”
- Or you may write, "The chart indicates the rising levels of addiction in young people, an "epidemic" that shows no sign of slowing down."

- For example, you may write in the first mention, “In Anne Carson’s The Autobiography of Red , the color red signifies desire, love, and monstrosity.” Or you may write, "In the study Addiction Rates conducted by the Harvard Review...".
- After the first mention, you can write, “Carson states…” or “The study explores…”.
- If you are citing the author’s name in-text as part of your citation style, you do not need to note their name in the text. You can just use the quote and then place the citation at the end.

- If you are paraphrasing a source, you may still use quotation marks around any text you are lifting directly from the source.

- For example, you may write, “In the novel, the characters express desire for each other: ‘When they made love/ Geryon liked to touch in slow succession each of the bones of Herakles' back (Carson, 48).”
- Or you may write, "Based on the data in the graph below, the study shows the 'intersection between opioid addiction and income' (Branson, 10)."
- If you are using footnotes or endnotes, make sure you use the appropriate citation for each piece of evidence you place in your essay.

- You may also mention the title of the work or source you are paraphrasing or summarizing and the author's name in the paraphrase or summary.
- For example, you may write a paraphrase like, "As noted in various studies, the correlation between addiction and mental illness is often ignored by medical health professionals (Deder, 10)."
- Or you may write a summary like, " The Autobiography of Red is an exploration of desire and love between strange beings, what critics have called a hybrid work that combines ancient meter with modern language (Zambreno, 15)."

- The only time you should place 2 pieces of evidence together is when you want to directly compare 2 short quotes (each less than 1 line long).
- Your analysis should then include a complete compare and contrast of the 2 quotes to show you have thought critically about them both.
Analyzing the Evidence

- For example, you may write, “In the novel, Carson is never shy about how her characters express desire for each other: ‘When they made love/ Geryon liked to touch in slow succession each of the bones of Herakles' back (Carson, 48). The connection between Geryon and Herakles is intimate and gentle, a love that connects the two characters in a physical and emotional way.”
- Or you may write, "In the study Addiction Rates conducted by the Harvard Review, the data shows a 50% rise in addiction levels in specific areas across the United States. The study illustrates a clear connection between addiction levels and communities where income falls below the poverty line and there is a housing shortage or crisis."

- For example, you may write, “Carson’s treatment of the relationship between Geryon and Herakles can be linked back to her approach to desire as a whole in the novel, which acts as both a catalyst and an impediment for her characters.”
- Or you may write, "The survey conducted by Dr. Paula Bronson, accompanied by a detailed academic dissertation, supports the argument that addiction is not a stand alone issue that can be addressed in isolation."

- For example, you may write, “The value of love between two people is not romanticized, but it is still considered essential, similar to the feeling of belonging, another key theme in the novel.”
- Or you may write, "There is clearly a need to reassess the current thinking around addiction and mental illness so the health and sciences community can better study these pressing issues."
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ Tristen Bonacci. Licensed English Teacher. Expert Interview. 21 December 2021.
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/quoliterature/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/evidence/
- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/using-evidence.html
About This Article

Before you introduce evidence into your essay, begin the paragraph with a topic sentence. This sentence should give the reader an overview of the point you’ll be arguing or making with the evidence. When you get to citing the evidence, begin the sentence with a clause like, “The study finds” or “According to Anne Carson.” You can also include a short quotation in the middle of a sentence without introducing it with a clause. Remember to introduce the author’s first and last name when you use the evidence for the first time. Afterwards, you can just mention their last name. Once you’ve presented the evidence, take time to explain in your own words how it backs up the point you’re making. For tips on how to reference your evidence correctly, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Apr 15, 2022
Did this article help you?

Mar 2, 2019

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
- Free Interview Course
Home > Blog > Essay Writing Guide – Using Evidence In Your Arguments
Essay Writing Guide – Using Evidence In Your Arguments

Essay Writing Guide – Introduction
If you want to write a good essay, you need strong evidence to support your ideas. No matter how good your ideas are, you need to support them with evidence. Strong evidence is vital for achieving high grades in essay-based assessments. If you make a claim, you must always give evidence for it. In this essay writing guide, we’re going to take a look at how to incorporate evidence into your argument.
Essay Writing Guide – What is Evidence?
One dictionary defines evidence as follows:
“The available body of facts or information indicating whether a belief or proposition is true or valid.”
This means that evidence is material which can be used to support an argument, claim, belief, or proposition. For example, fossils and bones are evidence to support the accepted theory that dinosaurs once walked the earth.

Essay Writing Guide – Different Kinds of Evidence
The definition of evidence that we’ve given is quite broad. In essence, any kind of facts or information can be regarded as evidence. The thing to make note of is that not all evidence is good evidence! What determines whether evidence is good or bad will depend on the subject you’re writing an essay for. This is because different academic disciplines, such as History and English Literature, care more about different types of evidence. Let’s take a look at different kinds of evidence now.
- Sciences such as Physics, Biology, Chemistry and Psychology, value peer-reviewed results of scientific studies.This means that, when making scientific arguments, you need to find results from well-received studies to support your argument.
- In contrast, History accepts a wider range of kinds of evidence. Historical statistics are welcome, but historical interpretation is also important.Strong theories written by historians can be used to support your own argument.
- In a subject such as English Literature, evidence will usually come in the form of quotations. For example, you might be asked to discuss the themes of a play.
To support your argument, you should find relevant quotations from the play. Like History, interpretations are also accepted as evidence. Try to find writers in the field of literary criticism which present theories about the play, book, or poem that you’re writing about.
Essay Writing Guide – How to Use Evidence in an Essay
When writing an essay, it is essential that you provide evidence. As we’ve discussed, evidence takes many forms. Make sure your type of evidence is appropriate for the subject you’re writing about.
So, if you’re writing a Psychology essay, don’t fill it with historical interpretation. Hard facts are necessary to sell your hypothesis in a scientific essay. Likewise, don’t bring hard statistics into an English Literature essay. This subject is all about interpretation, and so scientific studies won’t be particularly useful.
Evidence is always used to support a point that you’re trying to make.
- So, you make your point first. This is the claim of your argument: “Dinosaurs walked the earth tens of millions of years ago.”
- Once you’ve made your point, move on to your evidence: “Fossils found in Central America show that creatures used to live there.”
- Then you need to link the evidence back to your point by explaining it: “We can use radiocarbon dating to estimate how old the fossils are. Some of these fossils are over a hundred million years old.”

Essay Writing Guide – Key Phrases for Introducing Evidence
When incorporating evidence into an essay, you need to make sure it flows well. Try using some of these key phrases in your essay to help you introduce your evidence:
“The evidence clearly reveals…” “Analysis of the data suggests…” “This graph shows that…” “As shown by the information…” “This claim is supported by several authors, including…” “There seems to be a consensus regarding this…” “Popular opinion supports this idea…” “Popular opinion does not support this idea…” “Most experts agree…” “According to this study, we can deduce that…” “Over many years, this interpretation has developed…”
Essay Writing Guide – Key Phrases for Explaining Evidence
Once you’ve given your evidence, you need to be able explain it. Try using these phrases when explaining evidence in your essay:
“This means that…” “This evidence supports the claim that…” “This evidence supports this proposition because…” “It’s clear then, that this argument is supported by the evidence. This is because…” “If this evidence is true, then…” “This interpretation clearly supports the view that…” “This evidence suggests that…”
Essay Writing Guide – Key Phrases for Linking Evidence
Finally, you need to link your proposition, evidence, and explanation back to your main argument. Here are some phrases you can use to do this:
“Therefore, this analysis supports the central thesis of this essay…” “If followed to its logical conclusion, then this claim plays in favour of this essay’s core argument…” “The evidence and analysis presented here shows that…” “Due to this, it seems plausible that…” “In summary, it is shown that…” “While there are still many other ideas to consider, this proposition alone supports the view that…”
Essay Writing Guide – Key Phrases for Opposing Evidence
While most of the evidence you provide will support your argument, some essays will require you to examine counter-examples and evidence which opposes your central idea. So, make sure you clearly show that this evidence doesn’t damage your argument with the following phrases:
“While this evidence appears compelling, it doesn’t apply to these circumstances because…” “This counter-argument fails to acknowledge the following points: …” “While this is a popular counter-argument, it isn’t relevant to the focus of this essay, and therefore will not be discussed further.” “This claim relies on the premise that _____. The focus now will be to demonstrate that this premise is false.” “While this data appears to contradict the argument of this essay, this isn’t the case because…”
Essay Writing Guide – Key Phrases for Moving on to the Next Point
Eventually, you’ll need to move on to your next point. Here are some key phrases you can use to move from one point to another so that your essay flows better:
“Now that this claim has been suitably supported, the focus needs to shift to…” “The truth of this proposition has been clarified. Therefore, it is now appropriate to move to the next key argument in this essay: …” “This conclusion naturally leads to the next claim that…” “While this is compelling evidence, it is still not enough to logically reach the conclusion of this argument. It’s important to now discuss…” “While this theme is prominent in the text, others must also be considered, such as…” (Most relevant for English Literature essays)

Essay Writing Guide – Handy Phrases for Discussing Evidence
Finally, here are a few phrases that you can make use of to flesh out your arguments so that they read better:
“According to…” “Also…” “As well as…” “Based on…” “Clearly…” “Closely…” “Confirmed by…” “Evidently…” “For example…” “For instance…” “In addition…” “Therefore…” “This indicates that…” “This suggests…”
Essay Writing Guide – Conclusion
Whenever you make a new claim, support it with evidence. Evidence takes many different forms – find evidence that is appropriate to your subject or topic.
Start by introducing your argument. Then, give evidence. After that, explain your evidence. Finally, link your evidence back to your central argument.
Evidence is the fuel for your argument. Make sure you have enough of it to get you across the finish line!
Andy Bosworth
One thought on “ essay writing guide – using evidence in your arguments ”.
Clearly explained.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Free Aptitude Tests

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
Welcome to the new OASIS website! We have academic skills, library skills, math and statistics support, and writing resources all together in one new home.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Using Evidence: Analysis
Beyond introducing and integrating your paraphrases and quotations, you also need to analyze the evidence in your paragraphs. Analysis is your opportunity to contextualize and explain the evidence for your reader. Your analysis might tell the reader why the evidence is important, what it means, or how it connects to other ideas in your writing.
Note that analysis often leads to synthesis , an extension and more complicated form of analysis. See our synthesis page for more information.
Example 1 of Analysis
Without analysis.
Embryonic stem cell research uses the stem cells from an embryo, causing much ethical debate in the scientific and political communities (Robinson, 2011). "Politicians don't know science" (James, 2010, p. 24). Academic discussion of both should continue (Robinson, 2011).
With Analysis (Added in Bold)
Embryonic stem cell research uses the stem cells from an embryo, causing much ethical debate in the scientific and political communities (Robinson, 2011). However, many politicians use the issue to stir up unnecessary emotion on both sides of the issues. James (2010) explained that "politicians don't know science," (p. 24) so scientists should not be listening to politics. Instead, Robinson (2011) suggested that academic discussion of both embryonic and adult stem cell research should continue in order for scientists to best utilize their resources while being mindful of ethical challenges.
Note that in the first example, the reader cannot know how the quotation fits into the paragraph. Also, note that the word both was unclear. In the revision, however, that the writer clearly (a) explained the quotations as well as the source material, (b) introduced the information sufficiently, and (c) integrated the ideas into the paragraph.
Example 2 of Analysis
Trow (1939) measured the effects of emotional responses on learning and found that student memorization dropped greatly with the introduction of a clock. Errors increased even more when intellectual inferiority regarding grades became a factor (Trow, 1939). The group that was allowed to learn free of restrictions from grades and time limits performed better on all tasks (Trow, 1939).
In this example, the author has successfully paraphrased the key findings from a study. However, there is no conclusion being drawn about those findings. Readers have a difficult time processing the evidence without some sort of ending explanation, an answer to the question so what? So what about this study? Why does it even matter?
Trow (1939) measured the effects of emotional responses on learning and found that student memorization dropped greatly with the introduction of a clock. Errors increased even more when intellectual inferiority regarding grades became a factor (Trow, 1939). The group that was allowed to learn free of restrictions from grades and time limits performed better on all tasks (Trow, 1939). Therefore, negative learning environments and students' emotional reactions can indeed hinder achievement.
Here the meaning becomes clear. The study’s findings support the claim the reader is making: that school environment affects achievement.
Analysis Video Playlist
Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.

Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Quotation
- Next Page: Synthesis
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills

Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Cost of Attendance
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

- Departments and Units
- Majors and Minors
- LSA Course Guide
- LSA Gateway
Search: {{$root.lsaSearchQuery.q}}, Page {{$root.page}}
| {{item.snippet}} |
- Accessibility
- Undergraduates
- Instructors
- Alums & Friends

- ★ Writing Support
- Minor in Writing
- First-Year Writing Requirement
- Transfer Students
- Writing Guides
- Peer Writing Consultant Program
- Upper-Level Writing Requirement
- Writing Prizes
- International Students
- ★ The Writing Workshop
- Dissertation ECoach
- Fellows Seminar
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Rackham / Sweetland Workshops
- Dissertation Writing Institute
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- Teaching Support and Services
- Support for FYWR Courses
- Support for ULWR Courses
- Writing Prize Nominating
- Alums Gallery
- Commencement
- Giving Opportunities
- How Do I Effectively Integrate Textual Evidence?
- How Do I Make Sure I Understand an Assignment?
- How Do I Decide What I Should Argue?
- How Can I Create Stronger Analysis?
- How Do I Write a Great Title?
- What Exactly is an Abstract?
- How Do I Present Findings From My Experiment in a Report?
- What is a Run-on Sentence & How Do I Fix It?
- How Do I Check the Structure of My Argument?
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph?
- How Do I Incorporate Quotes?
- How Can I Create a More Successful Powerpoint?
- How Can I Create a Strong Thesis?
- How Can I Write More Descriptively?
- How Do I Incorporate a Counterargument?
- How Do I Check My Citations?
See the bottom of the main Writing Guides page for licensing information.
Academic writing often requires students to use evidence, and learning how to use evidence effectively is an important skill for college writers to master. Often, the evidence college writers are asked to use comes from their textbooks, course readings, or other written work by professional scholars. It is important to learn how to use these writings responsibly and accurately.
General Considerations
There are three methods of incorporating the writing of others into your paper as evidence:
- quotation , which is anything from a word to several sentences taken word-for-word from the original source and enclosed in quotation marks
- paraphrase , which is a rephrasing in your own voice and sentence structure of one portion of the original source and is about the same length as the original sentence or sentences you are paraphrasing
- summary , which is shorter than the original source and gives the text’s central idea in your own words
Some words to use in signal phrases are argues, asserts, contends, emphasizes, explains, observes, suggests, writes.
In what follows, you will learn some strategies for using these methods of incorporating evidence into your paper.
In Practice
When you use a quotation as evidence, you should integrate it into your own writing using a “signal phrase.” Take, for example, this quotation, taken from page 418 of the essay “Prejudice and the Individual” by Gordon Allport: “Much prejudice is caught rather than directly taught.” Here are three ways to integrate Allport’s quotation into a sentence of your own with a signal phrase:
Allport claims that “prejudice is caught rather than directly taught” (418). “Much prejudice is caught rather than directly taught,” claims Allport (418). “Much prejudice,” Allport claims, “is caught rather than directly taught” (418).
You can adapt a quotation to fit your own paragraph and sentence structure by making small changes to words and indicating those changes with square brackets. Say, for example, you liked this quotation from Allport:
“It should be added that overgeneralized prejudgments of this sort are prejudices only if they are not reversible when exposed to new knowledge” (417).
However, you want to apply Allport’s words to a specific example of your own. You could adapt the quotation like this:
The young man in my example was not prejudiced, according to Allport’s definition; his opinion was “reversible when [he was] exposed to new knowledge” (417).
You can also use ellipses to indicate that you have left irrelevant words out of a quotation. Again, say you wanted to use this quotation from Allport:
“The best opinion today says that if we eliminate discrimination, then—as people become acquainted with one another on equal terms—attitudes are likely to change, perhaps more rapidly than through the continued preaching or teaching of tolerance” (417).
But the middle part is less important to your paper than what Allport says at the start and the end. You could modify the quotation like this:
“The best opinion today says that if we eliminate discrimination . . . attitudes are likely to change, perhaps more rapidly than through the continued preaching or teaching of tolerance” (417).
Longer quotations must be formatted in a special way; usually, they are indented from the left margin and/or single-spaced. Depending on what citation style you use, guidelines differ regarding what defines a long quotation and how a long quotation should be formatted. Typically, a quotation of four or five lines is considered long.
Paraphrasing
To paraphrase a source for use as evidence, you should use as little of the original language as possible and put the passage in your own voice and sentence structure. Also, because paraphrasing involves wrapping your words around someone else’s idea, people often forget to give credit to the author. Even though a paraphrase is in your words, it is not your idea. Remember to cite your source when you paraphrase. Here is another quotation from Allport and an example of weak and strong paraphrase:
“Education combats easy overgeneralizations, and as the educational level rises we find a reduction in stereotyped thinking” (Allport 422).
WEAK PARAPHRASE: Learning fights against stereotypes, and as more people are more educated we notice a decrease in prejudice (422).
STRONG PARAPHRASE: Allport explains that the more we learn, the harder we will find it to make unfair assumptions about groups of people, which means as more people pursue more education, prejudice decreases (422).
In the weak example above, you can see the sentence structure in the paraphrase is very similar to the quotation—notice, for instance, the use in both the original sentence and the weak paraphrase of a comma plus the conjunction “and.” Also, the replacement of Allport’s words with synonyms makes the paraphrase too close to the original—Allport’s “education” is replaced with “learning” in the paraphrase; his “combats” is exchanged for “fights”; “overgeneralizations” becomes “stereotypes.” The strong example above does a better job of restating Allport’s idea in a new sentence structure and without simple word substitution. Also, notice the weak paraphrase does not give Allport credit by mentioning him, but the strong one does.
Summarizing
When you summarize another writer’s idea to use as evidence in a paper of your own, you are taking the essence of the writer’s idea and stating it more briefly, with less detail and explanation, than in the original. You may summarize an article or a chapter, or even a book, in a sentence, a paragraph, a page, or more—the purpose of your summary should dictate how specific you are. Summaries should be mostly in your own words, but often summaries include quotations or paraphrases when it is necessary to highlight a certain key point. When you are writing a summary, you need to be very careful not to use the original writer’s words without putting those words in quotation marks. You also need to be sure that when you summarize, you are fairly representing the original writer’s main idea. Here is a paragraph from Allport and examples of weak and strong summary:
“While discrimination ultimately rests on prejudice, the two processes are not identical. Discrimination denies people their natural or legal rights because of their membership in some unfavored group. Many people discriminate automatically without being prejudiced; and others, the “gentle people of prejudice,” feel irrational aversion, but are careful not to show it in discriminatory behavior. Yet in general, discrimination reinforces prejudices, and prejudices provide rationalizations for discrimination. The two concepts are most distinct when it comes to seeking remedies. The corrections for discrimination are legal, or lie in a direct change of social practices; whereas the remedy for prejudice lies in education and the conversion of attitudes. The best opinion today says that if we eliminate discrimination, then—as people become acquainted with one another on equal terms—attitudes are likely to change, perhaps more rapidly than through the continued preaching or teaching of tolerance.” (Allport 417)
WEAK SUMMARY: Discrimination is when people are denied their rights because they belong to some unfavored group, and it is addressed with legal action or a change in social practices. Eliminating discrimination from society would have a drastic effect on social attitudes overall, according to Allport (417).
STRONG SUMMARY: Allport explains that discrimination occurs when an individual is refused rights because he or she belongs to a group which is the object of prejudice. In this way, discrimination reinforces prejudice, but if instances of discrimination are ruled illegal or seen as socially unacceptable, prejudice will likely decrease along with discrimination (417).
You will notice that the weak summary above uses exact words and phrases from the source (“unfavored group,” “social practices”) and also some words and phrases very close to the original (“when people are denied,” “eliminating discrimination”). It does not effectively restate the original in different language. It also does not fairly represent the complete idea of the source paragraph: it does not explain the relationship between discrimination and prejudice, an important part of what Allport says. The strong example does a better job using independent language and fairly conveying Allport’s point.
How to choose which method of incorporating evidence to use
These methods of incorporating evidence into your paper are helpful in different ways. Think carefully about what you need each piece of evidence to do for you in your paper, then choose the method that most suits your needs.
You should use a quotation if
- you are relying on the reputation of the writer of the original source to give authority or credibility to your paper.
- the original wording is so remarkable that paraphrasing would diminish it.
A paraphrase is a good choice if
- you need to provide a supporting fact or detail but the original writer’s exact words are not important.
- you need to use just one specific idea from a source and the rest of the source is not as important.
Summary is useful when
- you need to give an overview of a source to orient your reader.
- you want to provide background that leads up to the point of your paper.
Last but certainly not least, remember that anytime you use another person’s ideas or language, you must give credit to that person. If you do not know the name of the person whose idea or language you are using, you must still give credit by referring to a title or any such available information. You should always check with your instructor to see what method of citing and documenting sources you should use. The examples on this handout are cited using MLA style.
The sample text in these exercises is Holly Devor’s “Gender Role Behaviors and Attitudes.”
1. Read the paragraph from Devor below, then identify which summary of it is weak and which is strong.
“Body postures and demeanors which communicate subordinate status and vulnerability to trespass through a message of "no threat" make people appear to be feminine. They demonstrate subordination through a minimizing of spatial use: people appear to be feminine when they keep their arms closer to their bodies, their legs closer together, and their torsos and heads less vertical than do masculine-looking individuals. People also look feminine when they point their toes inward and use their hands in small or childlike gestures.” (486)
A. Devor argues that body language suggests a great deal about gender and power in our society. People who minimize the body space they occupy and whose physical gestures are minimal and unobtrusive appear inferior and feminine (486).
B. Devor says that body postures and demeanors that imply weakness make people look feminine. Minimizing the space one takes up and using infantile gestures also makes one appear feminine (486).
2. Read the sentence from Devor below, then identify which paraphrase of it is weak and which is strong.
“They demonstrate subordination through a minimizing of spatial use: people appear to be feminine when they keep their arms closer to their bodies, their legs closer together, and their torsos and heads less vertical than do masculine-looking individuals.” (486)
A. Devor explains that people demonstrate a lesser position by using less space, keeping arms close, legs together, and head less upright (486).
B. According to Devor, taking up less space with one’s body—keeping arms and legs close and hunching to reduce height—makes one appear inferior and implies femininity (486).
3. The quotations of Devor below, taken from the paragraph in exercise 1, contain technical errors. Identify and correct them.
A. Devor argues that “[b]ody postures and demeanors which communicate subordinate status and vulnerability make people appear to be feminine” (486).
B. The actress looked particularly feminine because she “point their toes inward and use their hands in small or childlike gestures” (486).
C. Devor claims that “using their hands in small or childlike gestures” makes people look feminine (486).
Answers: 1. A. STRONG B. WEAK – This example uses too many exact words and phrases from the original.
2. A. WEAK – This example uses too many exact words and phrases from the source, and its sentence structure is also too close to the original. B. STRONG
3. A. Devor argues that “[b]ody postures and demeanors which communicate subordinate status and vulnerability . . . make people appear to be feminine.” B. The actress looked particularly feminine because she “point[s her] toes inward and use[s her] hands in small or childlike gestures.” C. Devor claims that “us[ing] their hands in small or childlike gestures” makes people look feminine.
Allport, Gordon, “Prejudice and the Individual,” in The Borozoi College Reader , 6th ed. Eds. Charles Muscatine and Marlene Griffith (New York: Alfred A Knopf, 1988): 416-22.
Devor, Holly, “Gender Role Behaviors and Attitudes,” in Signs of Life in the USA: Readings on Popular Culture for Writers , 4th ed. Eds. Sonia Maasik and Jack Solomon (New York: Bedford / St Martin's, 2003): 484-89.

- Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Faculty and Staff
- Alumni and Friends
- More about LSA
- How Do I Apply?
- LSA Magazine
- Student Resources
- Academic Advising
- Global Studies
- LSA Opportunity Hub
- Social Media
- Update Contact Info
- Privacy Statement
- Report Feedback
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Introduce Evidence: 41 Effective Phrases & Examples
Research requires us to scrutinize information and assess its credibility. Accordingly, when we think about various phenomena, we examine empirical data and craft detailed explanations justifying our interpretations. An essential component of constructing our research narratives is thus providing supporting evidence and examples.
The type of proof we provide can either bolster our claims or leave readers confused or skeptical of our analysis. Therefore, it’s crucial that we use appropriate, logical phrases that guide readers clearly from one idea to the next. In this article, we explain how evidence and examples should be introduced according to different contexts in academic writing and catalog effective language you can use to support your arguments, examples included.
When to Introduce Evidence and Examples in a Paper
Evidence and examples create the foundation upon which your claims can stand firm. Without proof, your arguments lack credibility and teeth. However, laundry listing evidence is as bad as failing to provide any materials or information that can substantiate your conclusions. Therefore, when you introduce examples, make sure to judiciously provide evidence when needed and use phrases that will appropriately and clearly explain how the proof supports your argument.
There are different types of claims and different types of evidence in writing. You should introduce and link your arguments to evidence when you
- state information that is not “common knowledge”;
- draw conclusions, make inferences, or suggest implications based on specific data;
- need to clarify a prior statement, and it would be more effectively done with an illustration;
- need to identify representative examples of a category;
- desire to distinguish concepts; and
- emphasize a point by highlighting a specific situation.
Introductory Phrases to Use and Their Contexts
To assist you with effectively supporting your statements, we have organized the introductory phrases below according to their function. This list is not exhaustive but will provide you with ideas of the types of phrases you can use.
| stating information that is not “common knowledge” | ] | |
| drawing conclusions, making inferences, or suggesting implications based on specific data | ||
| clarifying a prior statement | ||
| identifying representative examples of a category |
*NOTE: “such as” and “like” have two different uses. “Such as” introduces a specific example that is part of a category. “Like” suggests the listed items are similar to, but not included in, the topic discussed. | |
| distinguishing concepts | ||
| emphasizing a point by highlighting a specific situation |
Although any research author can make use of these helpful phrases and bolster their academic writing by entering them into their work, before submitting to a journal, it is a good idea to let a professional English editing service take a look to ensure that all terms and phrases make sense in the given research context. Wordvice offers paper editing , thesis editing , and dissertation editing services that help elevate your academic language and make your writing more compelling to journal authors and researchers alike.
For more examples of strong verbs for research writing , effective transition words for academic papers , or commonly confused words , head over to the Wordvice Academic Resources website.
- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code
Gen ed writes, writing across the disciplines at harvard college.
- Evidence and Analysis
Why It Matters
An assignment prompt’s guidance on evidence and analysis sets parameters for the content and form of a writing assignment: What kinds of sources should you be working with? Where should you find those sources? How should you be working with them?
More on "Evidence and Analysis"
The evidence and analysis you're asked to use (or not use) for a writing assignment often reflect the genre and size of the assignment at hand. With any writing assignment prompt, it’s important to step back and make sure you’re clear about the scope of evidence and analysis you’ll be working with. For example:
In terms of evidence,
- what kinds of evidence should be used (peer-reviewed articles versus op-ed pieces),
- which evidence in particular and how much (3–5 readings from class versus independent research), and
- why (because op-ed pieces capture a kind of public discourse better than peer-reviewed articles, or because 3–5 readings from class is manageable for a 4-page essay and also reinforces the readings assigned for the course, etc.).
In terms of analysis,
- is the assignment asking you to make an argument? If so, what kind of argument? (e.g., a rhetorical analysis weighing the pros and cons of a think piece, or a policy memo making normative claims about recommended courses of action, or a test a theory essay assessing the applicability of a framework to real-world cases?)
- if not, what is it asking you to do with evidence? (e.g., summarize a source’s argument, or draft a research question based on an annotated bibliography or data set)
- why? (because it’s important to establish other thinkers’ positions accurately before taking your own position, or because asking questions before moving on to a thesis or conclusion will make the research process more compelling).
What It Looks Like
- Science & Technology in Society
- Ethics & Civics
- Histories, Societies, Individuals
- Aesthetics & Culture
STEP 1: PROPOSAL WITH ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY
Length: 250–500 words, not including annotated bibliography. The annotated bibliography must have at least 5 different references from outside the course and 5 different references from the syllabus.
Source requirements:
- Minimum 5 different references from outside the course (at least 3 must be peer-reviewed scholarly sources) [1]
- Minimum 5 different references from Gen Ed 1093 reading assignments listed on the syllabus; lectures do not count toward the reference requirement, and Reimagining Global Health will only count as one reference [2]
- Citation format either AAA or APA [3] , consistent throughout the paper
- Careful attention to academic integrity and appropriate citation practices
- The annotated bibliography does not count toward your word count, but in-text citations do. [4]
__________ [1] Explicit guidance about what kinds of sources and how many sources to include [2] Clarification about what does / doesn't count toward the required number of sources [3] Clear guidance about citation format [4] Clarification about what does / doesn't count toward the required word count
Adapted from Gen Ed 1093 : Who Lives, Who Dies, Who Cares? Reimagining Global Health | Fall 2020
On p 13 of Why not Socialism?, G. A. Cohen states that the principle of “socialist equality of opportunity” is a principle of justice. What is the principle of “socialist equality of opportunity,” why does Cohen think it is a principle of justice, why does he think it is a desirable principle, and why does he think it is feasible? Which part of his argument do you think is most vulnerable to objections? Formulate some objections and explore how Cohen could respond. Do you think the objections succeed, or is Cohen’s view correct?
Proceed as follows: [1] State what socialist equality of opportunity is, by way of contrast with the two other kinds of equality of opportunity identified by Cohen. Explain why Cohen thinks, as a matter of justice, socialist equality of opportunity is preferable to the other two, and explain why an additional principle of community is needed to supplement that principle of justice. Then assess whether Cohen offers additional reasons (beyond the superiority of his principle over the alternatives) as to why equality and community are desirable, both for the camping trip and society at large. In a next step briefly summarize what he says about the feasibility of the principle. Devote about two thirds of your discussion to the tasks sketched so far, and then devote the remaining third to your exploration of the objections to parts of Cohen’s argument and an exploration of their success.
General Guidance
In section, your TF will discuss general guidelines to writing a philosophy paper. [2] Please also consult the “Advice on Written Assignments” posted on Canvas before writing the paper. Recall that you will write three papers in this course. The assignments get progressively more demanding. In the first paper, the emphasis is on reconstructing arguments, allowing you to develop the skill of logical reconstruction rather than narrative summary of a text. …The second paper goes beyond reconstruction, putting more emphasis on the critically evaluating arguments. The third paper gives you an opportunity to develop a well-reasoned defense in support of your own view regarding one of the central issues of the class. [3]
__________ [1] Students are given clear advice about how to use evidence differently at different points in their assignment. [2] Students are assured that they will learn guidelines for working with evidence and analysis in a more disciplinary kind of writing (with which many of them will likely be unfamiliar). [3] The move from “reconstruction” to “critically evaluating” to “well-reasoned defense” signals a scaffolded development of ways to work with evidence, along with reasons why students are being are being asked to work with evidence in a certain way for this first essay, viz., “ to develop the skill of logical reconstruction."
Adapted from Gen Ed 1121 : Economic Justice | Spring 2020 Professor Mathias Risse
Research Requirements
All projects, regardless of which modality you adopt, will need to include [1]
- an annotated bibliography that includes at least 5 scholarly sources. These sources can include scholarly articles, books, or websites. For a website, please check with the TFs to confirm the viability of it as a source. [2] There are legitimately scholarly websites, but many content-related sites are not scholarly.
- a 1-page artist statement.
See “How tos_Annotated Bibliography_your Artist Statement” for specific instructions for both the annotated bibliography and the artist statement. [3]
__________ [1] Explicit guidance about what kinds of sources and how many to include [2] Advice on how to get help evaluating whether a source counts as viable evidence [3] Additional resources (tied to guidelines and process) that help explain the roles of evidence and analysis in the assignment
Adapted from Gen Ed 1099 : Pyramid Schemes: What Can Ancient Egyptian Civilization Teach Us? Professor Peter der Manuelian
Introduce yourself to another student in the class by making a virtual mixtape for them. ⋮ Your tape should contain the following (in any order): [1]
- The greeting on the Golden Record that best describes you (or record your own)
- One piece of music included on the Golden Record
- Your personal summer hit of 2020
- A “found sound” (recorded in your environment that seems characteristic or interesting)
- A piece of music that best describes you
- Your favorite piece/song by a musician outside the US/Canada
Use these guidelines as a starting point for your mixtape. Feel free to get creative. The mixtape should say something important about YOU. (There will be no written text accompanying your file. The sounds have to say it all.) [2]
__________ [1] Students are given a clear checklist of what to include in their assignment. [2] In this assignment, the evidence makes its argument through curation, rather than additional written analysis. Making sure students understand that particular relationship of evidence to analysis ahead of time frames the assignment’s purpose and genre.
Adapted from Gen Ed 1006 : Music from Earth | Fall 2020 Professor Alex Rehding
- DIY Guides for Analytical Writing Assignments

- Types of Assignments
- Style and Conventions
- Specific Guidelines
- Advice on Process
- Receiving Feedback
Assignment Decoder
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- Mission, Vision, and Inclusive Language Statement
- Locations & Hours
- Undergraduate Employment
- Graduate Employment
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Newsletter Archive
- Support WTS
- Schedule an Appointment
- Online Tutoring
- Before your Appointment
- WTS Policies
- Group Tutoring
- Students Referred by Instructors
- Paid External Editing Services
- Writing Guides
- Scholarly Write-in
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Journal Article Writing Groups
- Early Career Graduate Student Writing Workshop
- Workshops for Graduate Students
- Teaching Resources
- Syllabus Information
- Course-specific Tutoring
- Nominate a Peer Tutor
- Tutoring Feedback
- Schedule Appointment
- Campus Writing Program
Writing Tutorial Services
Using evidence.
Like a lawyer in a jury trial, a writer must convince her audience of the validity of her argument by using evidence effectively. As a writer, you must also use evidence to persuade your readers to accept your claims. But how do you use evidence to your advantage? By leading your reader through your reasoning.
The types of evidence you use change from discipline to discipline--you might use quotations from a poem or a literary critic, for example, in a literature paper; you might use data from an experiment in a lab report.
The process of putting together your argument is called analysis --it interprets evidence in order to support, test, and/or refine a claim . The chief claim in an analytical essay is called the thesis . A thesis provides the controlling idea for a paper and should be original (that is, not completely obvious), assertive, and arguable. A strong thesis also requires solid evidence to support and develop it because without evidence, a claim is merely an unsubstantiated idea or opinion.
This Web page will cover these basic issues (you can click or scroll down to a particular topic):
- Incorporating evidence effectively.
- Integrating quotations smoothly.
- Citing your sources.
Incorporating Evidence Into Your Essay
When should you incorporate evidence.
Once you have formulated your claim, your thesis (see the WTS pamphlet, " How to Write a Thesis Statement ," for ideas and tips), you should use evidence to help strengthen your thesis and any assertion you make that relates to your thesis. Here are some ways to work evidence into your writing:
- Offer evidence that agrees with your stance up to a point, then add to it with ideas of your own.
- Present evidence that contradicts your stance, and then argue against (refute) that evidence and therefore strengthen your position.
- Use sources against each other, as if they were experts on a panel discussing your proposition.
- Use quotations to support your assertion, not merely to state or restate your claim.
Weak and Strong Uses of Evidence
In order to use evidence effectively, you need to integrate it smoothly into your essay by following this pattern:
- State your claim.
- Give your evidence, remembering to relate it to the claim.
- Comment on the evidence to show how it supports the claim.
To see the differences between strong and weak uses of evidence, here are two paragraphs.
Weak use of evidence
Today, we are too self-centered. Most families no longer sit down to eat together, preferring instead to eat on the go while rushing to the next appointment (Gleick 148). Everything is about what we want.
This is a weak example of evidence because the evidence is not related to the claim. What does the claim about self-centeredness have to do with families eating together? The writer doesn't explain the connection.
The same evidence can be used to support the same claim, but only with the addition of a clear connection between claim and evidence, and some analysis of the evidence cited.
Stronger use of evidence
Today, Americans are too self-centered. Even our families don't matter as much anymore as they once did. Other people and activities take precedence. In fact, the evidence shows that most American families no longer eat together, preferring instead to eat on the go while rushing to the next appointment (Gleick 148). Sit-down meals are a time to share and connect with others; however, that connection has become less valued, as families begin to prize individual activities over shared time, promoting self-centeredness over group identity.
This is a far better example, as the evidence is more smoothly integrated into the text, the link between the claim and the evidence is strengthened, and the evidence itself is analyzed to provide support for the claim.
Using Quotations: A Special Type of Evidence
One effective way to support your claim is to use quotations. However, because quotations involve someone else's words, you need to take special care to integrate this kind of evidence into your essay. Here are two examples using quotations, one less effective and one more so.
Ineffective Use of Quotation
Today, we are too self-centered. "We are consumers-on-the-run . . . the very notion of the family meal as a sit-down occasion is vanishing. Adults and children alike eat . . . on the way to their next activity" (Gleick 148). Everything is about what we want.
This example is ineffective because the quotation is not integrated with the writer's ideas. Notice how the writer has dropped the quotation into the paragraph without making any connection between it and the claim. Furthermore, she has not discussed the quotation's significance, which makes it difficult for the reader to see the relationship between the evidence and the writer's point.
A More Effective Use of Quotation
Today, Americans are too self-centered. Even our families don't matter as much any more as they once did. Other people and activities take precedence, as James Gleick says in his book, Faster . "We are consumers-on-the-run . . . the very notion of the family meal as a sit-down occasion is vanishing. Adults and children alike eat . . . on the way to their next activity" (148). Sit-down meals are a time to share and connect with others; however, that connection has become less valued, as families begin to prize individual activities over shared time, promoting self-centeredness over group identity.
The second example is more effective because it follows the guidelines for incorporating evidence into an essay. Notice, too, that it uses a lead-in phrase (". . . as James Gleick says in his book, Faster ") to introduce the direct quotation. This lead-in phrase helps to integrate the quotation with the writer's ideas. Also notice that the writer discusses and comments upon the quotation immediately afterwards, which allows the reader to see the quotation's connection to the writer's point.
REMEMBER: Discussing the significance of your evidence develops and expands your paper!
Citing Your Sources
Evidence appears in essays in the form of quotations and paraphrasing. Both forms of evidence must be cited in your text. Citing evidence means distinguishing other writers' information from your own ideas and giving credit to your sources. There are plenty of general ways to do citations. Note both the lead-in phrases and the punctuation (except the brackets) in the following examples:
Quoting: According to Source X, "[direct quotation]" ([date or page #]).
Paraphrasing: Although Source Z argues that [his/her point in your own words], a better way to view the issue is [your own point] ([citation]).
Summarizing: In her book, Source P's main points are Q, R, and S [citation].
Your job during the course of your essay is to persuade your readers that your claims are feasible and are the most effective way of interpreting the evidence.
Questions to Ask Yourself When Revising Your Paper
- Have I offered my reader evidence to substantiate each assertion I make in my paper?
- Do I thoroughly explain why/how my evidence backs up my ideas?
- Do I avoid generalizing in my paper by specifically explaining how my evidence is representative?
- Do I provide evidence that not only confirms but also qualifies my paper's main claims?
- Do I use evidence to test and evolve my ideas, rather than to just confirm them?
- Do I cite my sources thoroughly and correctly?
Produced by Writing Tutorial Services, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN
Writing Tutorial Services social media channels

- Argumentative Writing / Articles
Help Student Writers Find the Best Evidence
by MiddleWeb · Published 02/23/2016 · Updated 11/17/2019

No matter what grade or subject you teach, sooner or later you find yourself trying to help students write more clearly and convincingly. In one of my most-read posts for MiddleWeb, written in the early days of the Common Core implementation, I said:
One of the things students struggle with the most — and it’s relevant to every grade and subject — is distinguishing between argument and evidence. This problem manifests itself in both reading and writing…
In reading, students often cannot pick topic sentences or thesis arguments out of a lineup; and when writing, they tend to construct paragraphs and essays that lack arguments.
I went on to describe roughly six steps we can use to move students from “What’s the difference between arguments and evidence?” to “How can I write an effective research paper?” That’s such an important journey, and I want to share more thoughts about it, now that we’ve spent some years in “Common Core” classrooms. But first, here’s a quick refresher about those six steps for students:

Moving students through the steps
Lately, I’ve been working with teachers on how to help students write more effective paragraphs and essays. We have found that students can quickly master Step 1—applying the three rules for determining if a statement is an argument or not (it includes debatable/arguable words; it includes cause/effect language, or it raises “How” or “Why” questions). But they need more scaffolding to move from Step 2 to Step 3.
We are starting to think there may be a “Step 2.5.”

Step 3 gives students an argument and asks them to support it with relevant evidence and explanation. Breaking this down, it means they need to know what “relevant” means, how to select that evidence, and how and why to explain. It becomes more challenging to select relevant evidence when it appears not as a few isolated sentences but immersed somewhere in a complete text. You have to know what to look for and what to rule out.
Step 2.5 – Zeroing in on good evidence
Students have a tendency to look simply for words or phrases that seem related, and often their quest for evidence is too superficial, which causes them to select evidence that is not helpful.
As part of the new Step 2.5, therefore, we’re teaching students what to rule out – the ineffective evidence . “Ineffective” evidence manifests one of three problems: 1) it opposes the argument, 2) it’s irrelevant, or 3) it’s true but not as relevant.

Directions : Put a star next to the evidence from the choices below that BEST supports the argument. For each choice, tell why you would or would not use it. THEN write a logical sentence that would follow from your choice, explaining how the evidence supports the argument.
ARGUMENT: Eating too much candy causes stomach aches.
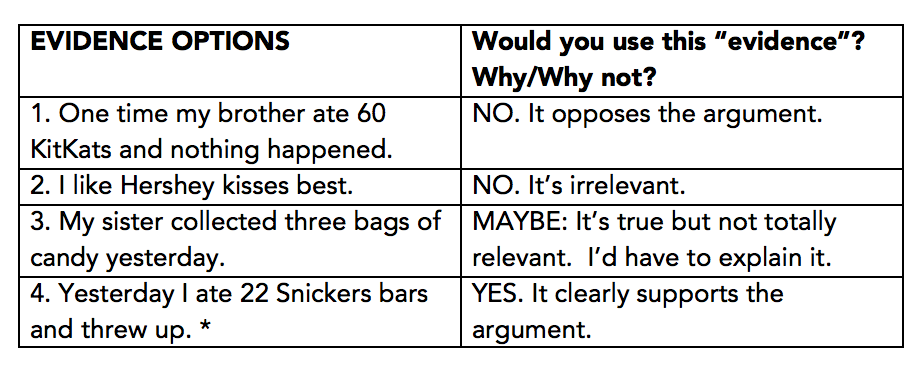
Here’s a template for practice ( it’s part of the Word doc download ):
ARGUMENT: [Teacher provides this.] ____________________________________
[In early practice, at least one evidence option should oppose, one should be irrelevant, and one should be true but not totally relevant. In later practice, you can mix/double up the options so that students won’t simply use a process of elimination.]
Good enough evidence

Share this:
Tags: argument argumentative writing evidence explanation Sarah Tantillo scaffolding the literacy cookbook
MiddleWeb is all about the middle grades, with great 4-8 resources, book reviews, and guest posts by educators who support the success of young adolescents. And be sure to subscribe to MiddleWeb SmartBrief for the latest middle grades news & commentary from around the USA.
4 Responses
- Pingbacks 0
Please provide a list of the statements, arguments, and evidence that you used.
Please see Part 2 here at MiddleWeb for an extended example of this “Best Evidence” strategy.
Hi, Tiffany–In addition to the other post MiddleWeb referred you to, I also have more explanations of the Argument vs. Evidence Steps 1-6 on my Website, The Literacy Cookbook. See under “Writing,” there’s a category called “Argument vs. Evidence,” here: https://www.literacycookbook.com/page.php?id=159 Also, please feel free to email me directly if you have additional questions. Thanks, ST
This was extremely helpful. I am an art teacher and my students are writing an argumentative essay.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Popular Posts
- Recent Posts
- Recent Comments

Book Reviews / Writing
Engaging All Students with Imaginative Writing

Articles / Literacy
2 Questions Help Move Kids Deeper into Texts

Articles / Mathematics
Do Less This Year to Let Kids Do More in Math

Book Reviews / Teaching Insights
Reflections on Teachers’ Life-Shaping Power

Articles / Coteaching
How to Create a Co-Teaching Power Zone

Artificial Intelligence / New Teacher Tips
What Will You Teach Your Students About AI?

Book Reviews / mathematics
Engage All Students with Offbeat Math Problems

First Days of Math Class / Meaningful Math
Low Prep Math Activities to Start the Year Right!

Articles / Group Work
4 Tips to Support Group Work in Middle School

Book Reviews / Leadership
Use Emotional IQ Skills to Navigate Turbulence

Articles / Back to School
3 Ways to Relieve Back to School ‘Overwhelm’

Articles / Reading
Welcome Students with New Fiction for Fall

Book Reviews / Reading
How Reader’s Theater Builds Reading Fluency

Start 24/25 with Super Ideas from MiddleWeb

Articles / New Teacher Advice
New to Teaching Grades 4-6? Try These Ideas
- Anne Jolly says: Thanks, Daniel, for your insight. I agree with you wholeheartedly. Business...
- Daniel Bassett says: Thanks for providing a wealth of knowledge for new STEM teachers.
- Matthew Kinney says: As a middle school reading intervention teacher, I find MiddleWeb’s resources...
- Tricia Buonacore says: Thanks for sharing this. As I prepare to head back to...
- Cynthia Delacruz says: Laurie and Patti, I just finished a course and your book,...
Sign Up & Receive the Latest News about Our Content…
Email address:
First Name:
Read our Privacy Policy
BOOK REVIEWS

Reach Past the Timeline with Thematic History

Literacy Instruction Can Promote Social Justice

Centering Love, Justice & Liberation in Schools

Routines for Creating Reading Communities

All the Tools You’ll Need for Differentiation

What MATH-ish Can Add to Your Math Classes

Coaching That Builds GT Teacher Capacity

Building Skills in the World Language Class

Mapping Out Diverse Gifted Programs

Using 100-Word Stories for Expansive Writing

What to Expect from AI in Class and Beyond

Strategies for Teaching Against Disinformation

The Democratic Roots Essential to Literacy

How to Reclaim Your Energy, Passion, & Time

A Leadership Blueprint for Growth and Success
While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays.
You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question.
The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make.
Argumentative writing at college level
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts.
In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise.
Examples of argumentative essay prompts
At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response.
Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
- Don’t just list all the effects you can think of.
- Do develop a focused argument about the overall effect and why it matters, backed up by evidence from sources.
- Don’t just provide a selection of data on the measures’ effectiveness.
- Do build up your own argument about which kinds of measures have been most or least effective, and why.
- Don’t just analyze a random selection of doppelgänger characters.
- Do form an argument about specific texts, comparing and contrasting how they express their thematic concerns through doppelgänger characters.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion.
There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
Toulmin arguments
The Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
- Make a claim
- Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim
- Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim)
- Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay.
Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
- Claim that unconscious bias training does not have the desired results, and resources would be better spent on other approaches
- Cite data to support your claim
- Explain how the data indicates that the method is ineffective
- Anticipate objections to your claim based on other data, indicating whether these objections are valid, and if not, why not.
Rogerian arguments
The Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
- Discuss what the opposing position gets right and why people might hold this position
- Highlight the problems with this position
- Present your own position , showing how it addresses these problems
- Suggest a possible compromise —what elements of your position would proponents of the opposing position benefit from adopting?
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith.
Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
- Acknowledge that students rely too much on websites like Wikipedia
- Argue that teachers view Wikipedia as more unreliable than it really is
- Suggest that Wikipedia’s system of citations can actually teach students about referencing
- Suggest critical engagement with Wikipedia as a possible assignment for teachers who are skeptical of its usefulness.
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments.
Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion .
Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true.
In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings.
Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information.
This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position.
Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body.
No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument.
Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved August 29, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
How to Find Evidence to Support Every Claim in a Student Paper

Writing papers is one of the most important skills anyone should master in their life, but students especially benefit from it. Good essay writing skills are not important only in high school or college , but can also lead to good presentation skills throughout one’s professional career. It’s well known that a student has to write at least a few hundred essays in his life, so the sooner he can master the skill, the better. While there are lots of features that separate good papers from bad ones, there’s one skill that’s critical to successful paper writing: learning to find and use evidence.
What is Evidence?
Although the question might seem very straightforward, there are lots of students out there who confuse arguments and evidence. Textbooks are very often the reason why students confuse these two terms – they don’t offer great examples of writing and more often than not just list facts, rather them putting them together into an argument. To put it simply, scientific, cold facts with no opinions or personal insights count as evidence – what you do with them, how you build them up to support your case, is an argument. When writing an essay, you typically need anywhere between 3 and 5 clearly structured arguments to support your cause. These will all be founded upon clear, trustworthy pieces of evidence.
Where to Find Evidence?

Finished papers
Customer reviews

Here are some of the most important pieces of information you need about finding and using evidence:
- Don’t be afraid to change your opinion. Finding evidence to support each and every stream of thought might be very hard, but if you do stumble upon mountains of proof that dictate the exact opposite of what you believe, don’t be afraid to change your beliefs. This is a sign of maturity, not weakness, and your final paper will thank you.
- Look for evidence near key people from the field. More often than not, key resources or influencers from a certain field have already looked into the domain you’re writing about and have a thing or two to say about it. It’s very important to remember to check the background and previous opinions of these people so that you’re certain to be using credible sources, not just someone with a big mouth.
- Use google scholar. It’s a great resource to find serious scientific papers, statistical data and much, much more. The great benefit of this is that every google scholar article sends you towards other studies, data or even opinion pieces written by professional who disagree with the opinions stated. There is really way to underestimate the value of this tool.
- Talk to people directly. If you’re finding trouble with the sources above, there’s no better way to come up with evidence that contacting a serious professional directly. If their time allows them, they’re usually very eager to share their experience.
- Avoid argument-softeners. Sometimes, bad evidence (logical fallacies, opinion from less-respected professionals, data curated only to support a certain part of your argument) can hinder the overall power of an essay. Only keep the best evidence you can find and leave the rest behind.

If you follow the above guidelines for finding evidence, essay writing will be a breeze and a pleasure. Your arguments will be much more structured and anchored in reality – which means your grades and relationship with your teacher will skyrocket.
Related posts:
- ESL Essay: Unboxing an ESL Essay with Topics and Examples
- How to Write a Book Review
- How to Create Expository Essay Outline
- Secret Weapon of Essay Writing: Stasis Theory
Improve your writing with our guides

Writing a Great Research Summary and where to Get Help on it
How to Write a Synthesis Essay
How To Write A Process Essay: Essay Outline, Tips, Topics and Essay Help
Get 15% off your first order with edusson.
Connect with a professional writer within minutes by placing your first order. No matter the subject, difficulty, academic level or document type, our writers have the skills to complete it.
100% privacy. No spam ever.


COMMENTS
Books, journals, websites, newspapers, magazines, and documentary films are some of the most common sources of evidence for academic writing. Our handout on evaluating print sources will help you choose your print sources wisely, and the library has a tutorial on evaluating both print sources and websites. A librarian can help you find sources ...
Choosing the Best Sources and Evidence. The sources and evidence you select to use in an academic paper should be of a higher caliber than what you use in your daily life and need to be verifiable, accurate, objective and authoritative. Before integrating research into your paper, follow these guidelines to select the best sources and evidence ...
Setting up the Evidence. Download Article. 1. Set up the evidence in the first sentence of the paragraph. The first sentence in the paragraph or section of your essay is called the topic sentence. It should let the reader know what is going to be discussed in the paragraph or section. If the paragraph is one of many in the body of your essay ...
find points of tension: • You may read a published view that doesn't seem convincing to you, and you may want to ask a question about what's missing or about how the evidence might be reconsidered. • You may notice an inconsistency, gap, or ambiguity in the evidence, and you may want to explore how that changes your understanding of ...
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
When incorporating evidence into an essay, you need to make sure it flows well. Try using some of these key phrases in your essay to help you introduce your evidence: "The evidence clearly reveals…". "Analysis of the data suggests…". "This graph shows that…". "As shown by the information…". "This claim is supported by ...
Research databases. You can search for scholarly sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar. These provide a range of search functions that can help you to find the most relevant sources. If you are searching for a specific article or book, include the title or the author's name. Alternatively, if you're just ...
Analysis is your opportunity to contextualize and explain the evidence for your reader. Your analysis might tell the reader why the evidence is important, what it means, or how it connects to other ideas in your writing. Note that analysis often leads to synthesis, an extension and more complicated form of analysis.
There are three methods of incorporating the writing of others into your paper as evidence: Some words to use in signal phrases are argues, asserts, contends, emphasizes, explains, observes, suggests, writes. In what follows, you will learn some strategies for using these methods of incorporating evidence into your paper.
Wordvice KH. Research requires us to scrutinize information and assess its credibility. Accordingly, when we think about various phenomena, we examine empirical data and craft detailed explanations justifying our interpretations. An essential component of constructing our research narratives is thus providing supporting evidence and examples.
which evidence in particular and how much (3-5 readings from class versus independent research), and why (because op-ed pieces capture a kind of public discourse better than peer-reviewed articles, or because 3-5 readings from class is manageable for a 4-page essay and also reinforces the readings assigned for the course, etc.).
In order to use evidence effectively, you need to integrate it smoothly into your essay by following this pattern: State your claim. Give your evidence, remembering to relate it to the claim. Comment on the evidence to show how it supports the claim. To see the differences between strong and weak uses of evidence, here are two paragraphs.
Basic essay structure: the 3 main parts of an essay. Almost every single essay that's ever been written follows the same basic structure: Introduction. Body paragraphs. Conclusion. This structure has stood the test of time for one simple reason: It works. It clearly presents the writer's position, supports that position with relevant ...
Here's a tool we're using to teach this point ( download a Word doc ): Directions: Put a star next to the evidence from the choices below that BEST supports the argument. For each choice, tell why you would or would not use it. THEN write a logical sentence that would follow from your choice, explaining how the evidence supports the argument.
Come up with a thesis. Create an essay outline. Write the introduction. Write the main body, organized into paragraphs. Write the conclusion. Evaluate the overall organization. Revise the content of each paragraph. Proofread your essay or use a Grammar Checker for language errors. Use a plagiarism checker.
Here's a helpful approach to evaluating a source: First, read the abstract or introduction of the source to decide if it's useful for your work . Then, take a look at the citations and references at the end of the source. You can also check the publication date to ensure the information is current.
They give coherence by providing an overarching theme and position towards which the entire essay is directed. 3. Use evidence, reasoning and scholarship. To convince your audience of your argument, you must use evidence and reasoning, which involves referring to and evaluating relevant scholarship.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement, a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas. The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ...
Revised on May 9, 2024. A credible source is free from bias and backed up with evidence. It is written by a trustworthy author or organization. There are a lot of sources out there, and it can be hard to tell what's credible and what isn't at first glance. Evaluating source credibility is an important information literacy skill.
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
Finding evidence to support each and every stream of thought might be very hard, but if you do stumble upon mountains of proof that dictate the exact opposite of what you believe, don't be afraid to change your beliefs. This is a sign of maturity, not weakness, and your final paper will thank you. Look for evidence near key people from the field.
An important strategy in finding evidence in a reading passage is understanding what makes the evidence ''strong.'' Supporting evidence is strong when it clearly connects to the question and the ...