How to Write a Small Business Financial Plan

Noah Parsons
3 min. read
Updated January 3, 2024
Creating a financial plan is often the most intimidating part of writing a business plan. It’s also one of the most vital. Businesses with well-structured and accurate financial statements in place are more prepared to pitch to investors, receive funding, and achieve long-term success.
Thankfully, you don’t need an accounting degree to successfully put your budget and forecasts together. Here is everything you need to include in your financial plan along with optional performance metrics, specifics for funding, and free templates.
- Key components of a financial plan
A sound financial plan is made up of six key components that help you easily track and forecast your business financials. They include your:

Sales forecast
What do you expect to sell in a given period? Segment and organize your sales projections with a personalized sales forecast based on your business type.
Subscription sales forecast
While not too different from traditional sales forecasts—there are a few specific terms and calculations you’ll need to know when forecasting sales for a subscription-based business.
Expense budget
Create, review, and revise your expense budget to keep your business on track and more easily predict future expenses.
How to forecast personnel costs
How much do your current, and future, employees’ pay, taxes, and benefits cost your business? Find out by forecasting your personnel costs.
Profit and loss forecast
Track how you make money and how much you spend by listing all of your revenue streams and expenses in your profit and loss statement.
Cash flow forecast
Manage and create projections for the inflow and outflow of cash by building a cash flow statement and forecast.
Balance sheet
Need a snapshot of your business’s financial position? Keep an eye on your assets, liabilities, and equity within the balance sheet.
What to include if you plan to pursue funding
Do you plan to pursue any form of funding or financing? If the answer is yes, then there are a few additional pieces of information that you’ll need to include as part of your financial plan.
Highlight any risks and assumptions
Every entrepreneur takes risks with the biggest being assumptions and guesses about the future. Just be sure to track and address these unknowns in your plan early on.
Plan your exit strategy
Investors will want to know your long-term plans as a business owner. While you don’t need to have all the details, it’s worth taking the time to think through how you eventually plan to leave your business.
- Financial ratios and metrics
With all of your financial statements and forecasts in place, you have all the numbers needed to calculate insightful financial ratios. While these metrics are entirely optional to include in your plan, having them easily accessible can be valuable for tracking your performance and overall financial situation.
Common business ratios
Unsure of which business ratios you should be using? Check out this list of key financial ratios that bankers, financial analysts, and investors will want to see.
Break-even analysis
Do you want to know when you’ll become profitable? Find out how much you need to sell to offset your production costs by conducting a break-even analysis.
How to calculate ROI
How much could a business decision be worth? Evaluate the efficiency or profitability by calculating the potential return on investment (ROI).
- Financial plan templates and tools
Download and use these free financial templates and calculators to easily create your own financial plan.

Sales forecast template
Download a free detailed sales forecast spreadsheet, with built-in formulas, to easily estimate your first full year of monthly sales.
Download Template

Accurate and easy financial forecasting
Get a full financial picture of your business with LivePlan's simple financial management tools.
Get Started
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- What to include for funding
Related Articles
6 Min. Read
How to create a business plan cover page

10 Min. Read
How to set milestones in your business plan

Show that you know the competition

3 Min. Read
What to include in your business plan appendix
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

Planning, Startups, Stories
Tim berry on business planning, starting and growing your business, and having a life in the meantime., what do business plan financials look like.
People often ask: What do business plan financials look like? You can get away with a sales forecast, spending budget, and cash flow plan. That’s enough for actually running your startup. It’s the essential numbers in a lean business plan.
If you want to do it right you take it further and present projected (also called Pro Forma) versions of the three main business plan financial statements: Income Statement (also called Profit & Loss), Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow. Here’s how they are related to each other:

And here’s another view:

Projected Profit and Loss (also called Income)
This is where you project sales, costs, and expenses; and what’s left over is profits. Here is a general summary , and you might also check out Your Profits are Way Too High , How to Forecast Sales and Profits Without Just Guessing . Profits are the performance of the business over a specified period of time, like a month, quarter, or year. You project sales , direct costs, and expenses .
Here’s what it looks like in a plan.

Projected Balance Sheet
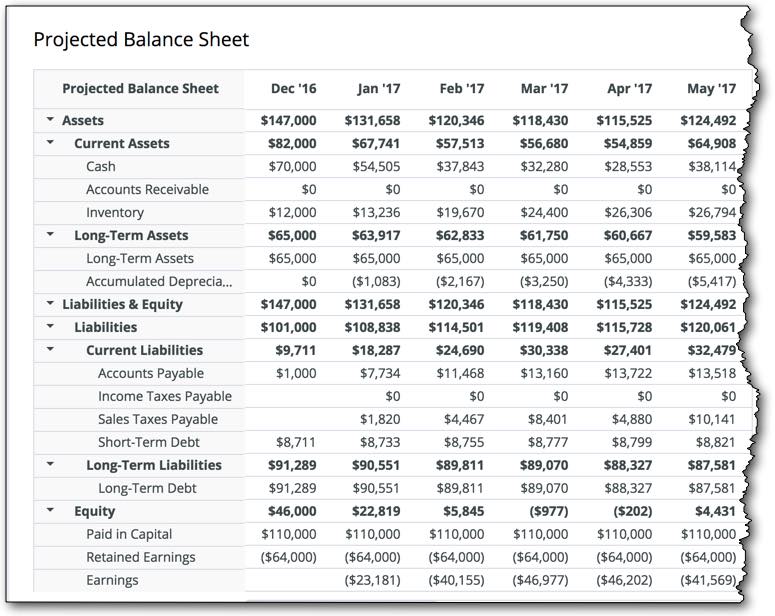
Projected Cash Flow
The cash flow is the most important, because your business lives on cash, not profits . You can project cash flow using the direct method , or the indirect method . Either way works if you do it right. Here’s an example of what an indirect cash flow projection looks like in a business plan.

Do It Right?
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
Key Financial Metrics for Your Business Plan
Posted september 6, 2018 by noah parsons.

Digging into your business’s financials can feel a bit like eating your fruits and vegetables, but what’s good for your business’s health is good for you.
When you’re putting a business plan together, the financial plan can feel like the most intimidating part. If you’re like most business owners, you probably didn’t go to business school or have a degree in accounting.
That’s O.K. This article will explain everything that you need to include in your financial plan so you get off to a good start.
All business plans, whether you’re just starting a business or building a plan for an existing business, should include the following:
Profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, sales forecast, personnel plan.
- and maybe some business ratios and/or a break-even analysis
Even if you’re in the very beginning stages of your business, these financial statements can still work for you.
The good news is that they don’t have to be difficult to create or hard to understand. With just a few educated guesses about how much you might sell and what your expenses will be, you’ll be well on your way to creating a complete financial plan.
A profit and loss statement is essentially an explanation of how your business made a profit (or incurred a loss) over a certain period of time. It’s a table that lists all of your revenue streams and all of your expenses—typically for a three-month period—and lists at the very bottom the total amount of net profit or loss.
This is a financial statement that goes by a few different names—profit and loss statement, income statement, pro forma income statement, P&L (short for “profit and loss”)—but no matter what you call it, it’s an essential report and very important to understand.

There are different formats for profit and loss statements, depending on the type of business you’re in and the structure of your business (nonprofit, LLC, C-Corp, etc.).
A typical profit and loss statement should include:
- Your revenue (also called sales)
- Your “cost of sale” or “cost of goods sold” (COGS)—keep in mind, some types of companies, such as a services firm, may not have COGS
- Your gross margin , which is your revenue less your COGS
These three components (revenue, COGS, and gross margin) are the backbone of your business model —i.e., how you make money.
You’ll also list your operating expenses, which are the expenses associated with running your business that aren’t incurred directly by making a sale. They’re the fixed expenses that don’t fluctuate depending on the strength or weakness of your revenue in a given month—think rent, utilities, and insurance.
Your gross margin less your operating expenses will give you your operating income:
Gross Margin – Operating Expenses = Operating Income
Depending on how you classify some of your expenses, your operating income will typically be equivalent to your “earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization” (EBITDA)—basically, how much money you made in profit before you take your accounting and tax obligations into consideration. This is also called your “profit before interest and taxes,” gross profit, and “contribution to overhead”—many names, but they all refer to the same number.
Your so-called “bottom line”—officially, your net income, which is found at the very end (or, bottom line) of your profit and loss statement—is your EBITDA less the “ITDA.” Just subtract your expenses for interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization from your EBITDA, and you have your net income:
Operating Income – Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization Expenses = Net Income
For further reading on profit and loss statements (a.k.a., income statements), including an example of what a profit and loss statement actually looks like, check out “ How to Read and Analyze an Income Statement.” And if you want to start building your own, download our free Income Statement Example .

A cash flow statement (also called a “statement of cash flows”) is an explanation of how much cash your business brought in, how much cash it paid out, and what its ending cash balance was, typically per-month.
That might sound like sales, expenses, and profits, but it’s not.
Consider this: What happens when you send out an invoice to a client, but they don’t pay it by the due date ? What happens when you pay your own bills late, or early? These kinds of things aren’t reflected in your profit and loss statement, but they are explained in your cash flow statement.
Your cash flow statement is just as important as your profit and loss statement. Businesses run on cash—there are no two ways around it.
Without a thorough understanding of how much cash you have, where your cash is coming from, where it’s going, and on what schedule, you’re going to have a hard time running a healthy business. And without the cash flow statement, which lays that information out neatly for lenders and investors, you’re not going to be able to raise funds. No business plan is complete without a cash flow plan.
The cash flow statement helps you understand the difference between what your profit and loss statement reports as income—your profit—and what your actual cash position is.
It is possible to be extremely profitable and still not have enough cash to pay your expenses and keep your business afloat, and it is also possible to be unprofitable but still have enough cash on hand to keep the doors open for several months and buy yourself time to turn things around—that’s why this financial statement is so important to understand.

How cash versus accrual accounting affects the cash flow statement
There are two methods of accounting—the cash method and the accrual method.
The cash method means that you just account for your sales and expenses as they happen, without worrying about matching up the expenses that are related to a particular sale or vice versa.
The accrual method means that you account for your sales and expenses at the same time—if you got a big preorder for a new product, for example, you’d wait to account for all of your preorder sales revenue until you’d actually started manufacturing and delivering the product. Matching revenue with the related expenses is what’s referred to as “the matching principle,” and is the basis of accrual accounting.
If you use the cash method of accounting in your business, your cash flow statement isn’t going to be very different from what you see in your profit and loss statement. That might seem like it makes things simpler, but I actually advise against it. I think that the accrual method of accounting gives you the best sense of how your business operates, and that you should consider switching to it if you aren’t using it already.
For the best sense of how your business operates, you should consider switching to accrual accounting if you aren’t using it already.
Here’s why: Let’s say you operate a summer camp business. You might receive payment from a camper in March, several months before camp actually starts in July—using the accrual method, you wouldn’t recognize the revenue until you’ve performed the service, so both the revenue and the expenses for the camp would be accounted for in the month of July.
With the cash method, you would have recognized the revenue back in March, but all of the expenses in July, which would have made it look like you were profitable in all of the months leading up to the camp, but unprofitable during the month that camp actually took place.
Cash accounting can get a little unwieldy when it comes time to evaluate how profitable an event or product was, and can make it harder to really understand the ins and outs of your business operations. For the best look at how your business works, accrual accounting is the way to go.
Your balance sheet is a snapshot of your business’s financial position—at a particular moment in time, how are you doing? How much cash do you have in the bank, how much do your customers owe you, and how much do you owe your vendors?
The balance sheet is standardized, and consists of three types of accounts:
- Assets (accounts receivable, money in the bank, inventory, etc.)
- Liabilities (accounts payable, credit card balances, loan repayments, etc.)
- Equity (for most small businesses, this is just the owner’s equity, but it could include investors’ shares, retained earnings, stock proceeds, etc.)
It’s called a balance sheet because it’s an equation that needs to balance out:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
The total of your liabilities plus your total equity always equals the total of your assets.
At the end of the accounting year, your total profit or loss adds to or subtracts from your retained earnings (a component of your equity). That makes your retained earnings your business’s cumulative profit and loss since the business’s inception.
However, if you are a sole proprietor or other pass-through tax entity, “retained earnings” doesn’t really apply to you—your retained earnings will always equal zero, as all profits and losses are passed through to the owners and not rolled over or retained like they are in a corporation.

If you’d like more help creating your balance sheet, check out our free downloadable Balance Sheet Template .
The sales forecast is exactly what it sounds like: your projections, or forecast, of what you think you will sell in a given period (typically, a year to three years). Your sales forecast is an incredibly important part of your business plan, especially when lenders or investors are involved, and should be an ongoing part of your business planning process.
Your sales forecast should be an ongoing part of your business planning process.
You should create a forecast that is consistent with the sales number you use in your profit and loss statement. In fact, in our business planning software , LivePlan, the sales forecast auto-fills the profit and loss statement.

There isn’t a one-size-fits-all kind of sales forecast—every business will have different needs. How you segment and organize your forecast depends on what kind of business you have and how thoroughly you want to track your sales.
Some helpful questions to ask yourself are:
- How many customers do you anticipate?
- How much will you charge them?
- How often will you charge them?
Your sales forecast can be as detailed as you want it to be, or you can simplify your forecast by summarizing it. However you choose to do a sales forecast, you should definitely have one.
Generally, you’ll want to break down your sales forecast into segments that are helpful to you for planning and marketing purposes. If you own a restaurant, for example, you’d probably want to separate your forecasts for dinner and lunch sales; if you own a gym, it might be helpful to differentiate between single memberships, family memberships, club shop sales, and extra services like personal training sessions. If you want to get really specific, you might even break your forecast down by product, with a separate line for every product you sell.
Along with each segment of forecasted sales, you’ll want to include that segment’s “cost of goods sold” (COGS). The difference between your forecasted revenue and your forecasted COGS is your forecasted gross margin .
The importance of the personnel plan depends largely on the type of business you have. If you are a sole proprietor with no employees, this might not be that important and could be summarized in a sentence of two. But if you are a larger business with high labor costs, you should spend the time necessary to figure out how your personnel affects your business.
Think of the personnel plan as a justification of each team member’s necessity to the business.
If you create a personnel plan, it should include a description of each member of your management team, explaining what they bring to the table in terms of training, expertise, and product or market knowledge. If you’re writing a business plan to present to lenders or investors, you could think of this as a justification of each team member’s necessity to the business, and a justification of their salary (and/or equity share, if applicable). This would fall in the company overview section of your business plan.
You can also choose to use this section to list entire departments if that is a better fit for your business and the intentions you have for your business plan . There’s no rule that says you have to list only individual members of the management team.
This is also where you would list team members or departments that you’ve budgeted for but haven’t hired yet. Describe who your ideal candidate(s) is/are, and justify your budgeted salary range(s).
Additional calculations you might find useful:
Business ratios.
If you have your profit and loss statement, your cash flow statement, and your balance sheet, you have all the numbers you need to calculate the standard business ratios . These ratios aren’t necessary to include in a business plan—especially for an internal plan—but knowing some key ratios is almost always a good idea.
You’d probably want some profitability ratios, like:
- Gross margin
- Return on sales
- Return on assets
- Return on investment
And you’d probably want some liquidity ratios, such as:
- Debt-to-equity
- Current ratio
- Working capital
Of these, the most common ratios used by business owners and requested by bankers are probably gross margin, return on investment (ROI), and debt-to-equity.
Break-even analysis
Your break-even analysis is a calculation of how much you will need to sell in order to “break-even” (i.e., how much you will need to sell in order to pay for all of your expenses).
Consider a restaurant: It has to be open, with the tables set and the menus printed and with the bartender and all of the cooks and servers working, in order to make even one sale. But if it only sold one dinner, the restaurant would be operating at a loss—even a $50 meal isn’t going to cover the night’s utility bills. So the restaurant owner might use a break-even analysis to get an idea of how many meals the restaurant needs to sell on a given night in order to cover its expenses.
In determining your break-even point, you’ll need to figure out the contribution margin of what you’re selling. In the case of a restaurant, the contribution margin will be the price of the meal less any associated costs. For example, the customer pays $50 for the meal. The food costs are $10 and the wages paid to prepare and serve the meal are $15. Your contribution margin is $25 ($50 – $10 – $15 = $25).
Using this model you can determine how high your sales revenue needs to be in order for you to break even. If your monthly fixed costs are $5,000 and you average a 50 percent contribution margin (like in our example with the restaurant), you’ll need to have sales of $10,000 in order to break even.
Your financial plan might feel overwhelming when you get started, but the truth is that this section of your business plan is absolutely essential to understand.
Even if you end up outsourcing your bookkeeping and regular financial analysis to an accounting firm, you—the business owner—should be able to read and understand these documents and make decisions based on what you learn from them. Using a business dashboard tool can help, so you’re not wading through spreadsheets to put your figures on the important details.
If you create and present financial statements that all work together to tell the story of your business, and if you can answer questions about where your numbers are coming from, your chances of securing funding from investors or lenders are much higher.
Further resources:
For more business financial concepts made simple, check out these articles on cash burn rate , direct costs , net profit , operating margin , accounts payable , accounts receivable , cash flow , profit and loss statement , balance sheet , and expense budgeting .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Noah Parsons
Posted in management, join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
4 Steps to Creating a Financial Plan for Your Small Business

When it comes to long-term business success, preparation is the name of the game. And the key to that preparation is a solid financial plan that sets forth a business’s short- and long-term financial goals and how it intends to reach them. Used by company decision-makers and potential partners, investors and lenders, alike, a financial plan typically includes the company’s sales forecast, cash flow projection, expected expenses, key financial metrics and more. Here is what small businesses should understand to create a comprehensive financial plan of their own.
What Is a Financial Plan?
A financial plan is a document that businesses use to detail and manage their finances, ensure efficient allocation of resources and inform a plethora of decisions — everything from setting prices, to expanding the business, to optimizing operations, to name just a few. The financial plan provides a clear understanding of the company’s current financial standing; outlines its strategies, goals and projections; makes clear whether an idea is sustainable and worthy of investment; and monitors the business’s financial health as it grows and matures. Financial plans can be adjusted over time as forecasts become replaced with real-world results and market forces change.
A financial plan is an integral part of an overall business plan, ensuring financial objectives align with overall business goals. It typically contains a description of the business, financial statements, personnel plan, risk analysis and relevant key performance indicators (KPIs) and ratios. By providing a comprehensive view of the company’s finances and future goals, financial plans also assist in attracting investors and other sources of funding.
Key Takeaways
- A financial plan details a business’s current standing and helps business leaders make informed decisions about future endeavors and strategies.
- A financial plan includes three major financial statements: the income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement.
- A financial plan answers essential questions and helps track progress toward goals.
- Financial management software gives decision-makers the tools they need to make strategic decisions.
Why Is a Financial Plan Important to Your Small Business?
A financial plan can provide small businesses with greater confidence in their short- and long-term endeavors by helping them determine ways to best allocate and invest their resources. The process of creating the plan forces businesses to think through how different decisions could impact revenue and which occasions call for dipping into reserve funds. It’s also a helpful tool for monitoring performance, managing cash flow and tracking financial metrics.
Simply put, a financial plan shows where the business stands; over time, its analysis will reveal whether its investments were worthwhile and worth repeating. In addition, when a business is courting potential partners, investors and lenders, the financial plan spotlights the business’s commitment to spending wisely and meeting its financial obligations.
Benefits of a Financial Plan
A financial plan is only as effective as the data foundation it’s built on and the business’s flexibility to revisit it amid changing market forces and demand shifts. Done correctly, a financial plan helps small businesses stay on track so they can reach their short-term and long-term goals. Among the benefits that effective financial planning delivers:
- A clear view of goals and objectives: As with any type of business plan, it’s imperative that everyone in a company is on the same financial page. With clear responsibilities and expected results mapped out, every team member from the top down sees what needs to be done, when to do it and why.
- More accurate budgets and projections: A comprehensive financial plan leads to realistic budgets that allocate resources appropriately and plan for future revenue and expenses. Financial projections also help small businesses lay out steps to maintain business continuity during periods of cash flow volatility or market uncertainty.
- External funding opportunities: With a detailed financial plan in hand, potential partners, lenders and investors can see exactly where their money will go and how it will be used. The inclusion of stellar financial records, including past and current liabilities, can also assure external funding sources that they will be repaid.
- Performance monitoring and course correction: Small businesses can continue to benefit from their financial plans long after the plan has been created. By continuously monitoring results and comparing them with initial projections, businesses have the opportunity to adjust their plans as needed.
Components of a Small Business Financial Plan
A sound financial plan is instrumental to the success and stability of a small business. Whether the business is starting from scratch or modifying its plan, the best financial plans include the following elements:
Income statement: The income statement reports the business’s net profit or loss over a specific period of time, such a month, quarter or year. Also known as a profit-and-loss statement (P&L) or pro forma income statement, the income statement includes the following elements:
- Cost of goods sold (COGS): The direct costs involved in producing goods or services.
- Operating expenses: Rent, utilities and other costs involved in running the business.
- Revenue streams: Usually in the form of sales and subscription services, among other sources.
- Total net profit or loss: Derived from the total amount of sales less expenses and taxes.
Balance sheet: The balance sheet reports the business’s current financial standing, focusing on what it owns, what it owes and shareholder equity:
- Assets: Available cash, goods and other owned resources.
- Liabilities: Amounts owed to suppliers, personnel, landlords, creditors, etc.
Shareholder equity: Measures the company’s net worth, calculated with this formula:
Shareholder Equity = Assets – Liability
The balance sheet lists assets, liabilities and equity in chart format, with assets in the left column and liabilities and equity on the right. When complete — and as the name implies —the two sides should balance out to zero, as shown on the sample balance sheet below. The balance sheet is used with other financial statements to calculate business financial ratios (discussed soon).
Balance Sheet
Cash flow projection: Cash flow projection is a part of the cash flow statement , which is perhaps one of the most critical aspects of a financial plan. After all, businesses run on cash. The cash flow statement documents how much cash came in and went out of the business during a specific time period. This reveals its liquidity, meaning how much cash it has on hand. The cash flow projection should display how much cash a business currently has, where it’s going, where future cash will come from and a schedule for each activity.
Personnel plan: A business needs the right people to meet its goals and maintain a healthy cash flow. A personnel plan looks at existing positions, helps determine when it’s time to bring on more team members and determines whether new hires should be full-time, part-time or work on a contractual basis. It also examines compensation levels, including benefits, and forecasts those costs against potential business growth to gauge whether the potential benefits of new hires justify the expense.
Business ratios: In addition to a big-picture view of the business, decision-makers will need to drill down to specific aspects of the business to understand how individual areas are performing. Business ratios , such as net profit margin, return on equity, accounts payable turnover, assets to sales, working capital and total debt to total assets, help evaluate the business’s financial health. Data used to calculate these ratios come from the P&L statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement. Business ratios contextualize financial data — for example, net profit margin shows the profitability of a company’s operations in relation to its revenue. They are often used to help request funding from a bank or investor, as well.
Sales forecast: How much will you sell in a specific period? A sales forecast needs to be an ongoing part of any planning process since it helps predict cash flow and the organization’s overall health. A forecast needs to be consistent with the sales number within your P&L statement. Organizing and segmenting your sales forecast will depend on how thoroughly you want to track sales and the business you have. For example, if you own a hotel and giftshop, you may want to track separately sales from guests staying the night and sales from the shop.
Cash flow projection: Perhaps one of the most critical aspects of your financial plan is your cash flow statement . Your business runs on cash. Understanding how much cash is coming in and when to expect it shows the difference between your profit and cash position. It should display how much cash you have now, where it’s going, where it will come from and a schedule for each activity.
Income projections: Businesses can use their sales forecasts to estimate how much money they are on track to make in a given period, usually a year. This income projection is calculated by subtracting anticipated expenses from revenue. In some cases, the income projection is rolled into the P&L statement.
Assets and liabilities: Assets and liabilities appear on the business’s balance sheet. Assets are what a company owns and are typically divided into current and long-term assets. Current assets can be converted into cash within a year and include stocks, inventory and accounts receivable. Long-term assets are tangible or fixed assets designed for long-term use, such as furniture, fixtures, buildings, machinery and vehicles.
Liabilities are business obligations that are also classified as current and long-term. Current liabilities are due to be paid within a year and include accrued payroll, taxes payable and short-term loans. Long-term liabilities include shareholder loans or bank debt that mature more than a year later.
Break-even analysis: The break-even point is how much a business must sell to exactly cover all of its fixed and variable expenses, including COGS, salaries and rent. When revenue exceeds expenses, the business makes a profit. The break-even point is used to guide sales revenue and volume goals; determination requires first calculating contribution margin , which is the amount of sales revenue a company has, less its variable costs, to put toward paying its fixed costs. Businesses can use break-even analyses to better evaluate their expenses and calculate how much to mark up its goods and services to be able to turn a profit.
Four Steps to Create a Financial Plan for Your Small Business
Financial plans require deliberate planning and careful implementation. The following four steps can help small businesses get started and ensure their plans can help them achieve their goals.
Create a strategic plan
Before looking at any numbers, a strategic plan focuses on what the company wants to accomplish and what it needs to achieve its goals. Will it need to buy more equipment or hire additional staff? How will its goals affect cash flow? What other resources are needed to meet its goals? A strategic financial plan answers these questions and determines how the plan will impact the company’s finances. Creating a list of existing expenses and assets is also helpful and will inform the remaining financial planning steps.
Create financial projections
Financial projections should be based on anticipated expenses and sales forecasts . These projections look at the business’s goals and estimate the costs needed to reach them in the face of a variety of potential scenarios, such as best-case, worst-case and most likely to happen. Accountants may be brought in to review the plan with stakeholders and suggest how to explain the plan to external audiences, such as investors and lenders.
Plan for contingencies
Financial plans should use data from the cash flow statement and balance sheet to inform worst-case scenario plans, such as when incoming cash dries up or the business takes an unexpected turn. Some common contingencies include keeping cash reserves or a substantial line of credit for quick access to funds during slow periods. Another option is to produce a plan to sell off assets to help break even.
Monitor and compare goals
Actual results in the cash flow statement, income projections and relevant business ratios should be analyzed throughout the year to see how closely real-life results adhered to projections. Regular check-ins also help businesses spot potential problems before they can get worse and inform course corrections.
Three Questions Your Financial Plan Should Answer
A small business financial plan should be tailored to the needs and expectations of its intended audience, whether it is potential investors, lenders, partners or internal stakeholders. Once the plan is created, all parties should, at minimum, understand:
How will the business make money?
What does the business need to achieve its goals?
What is the business’s operating budget ?
Financial plans that don’t answer these questions will need more work. Otherwise, a business risks starting a new venture without a clear path forward, and decision-makers will lack the necessary insights that a detailed financial plan would have provided.
Improve Your Financial Planning With Financial Management Software
Using spreadsheets for financial planning may get the job done when a business is first getting started, but this approach can quickly become overwhelming, especially when collaborating with others and as the business grows.
NetSuite’s cloud-based financial management platform simplifies the labor-intensive process through automation. NetSuite Planning and Budgeting automatically consolidates real-time data for analysis, reporting and forecasting, thereby improving efficiency. With intuitive dashboards and sophisticated forecasting tools, businesses can create accurate financial plans, track progress and modify strategies in order to achieve and maintain long-term success. The solution also allows for scenario planning and workforce planning, plus prebuilt data synchronization with NetSuite ERP means the entire business is working with the same up-to-date information.
Whether a business is first getting started, looking to expand, trying to secure outside funding or monitoring its growth, it will need to create a financial plan. This plan lays out the business’s short- and long-term objectives, details its current and projected finances, specifies how it will invest its resources and helps track its progress. Not only does a financial plan guide the business along its way, but it is typically required by outside sources of funding that don’t invest or lend their money to just any company. Creating a financial plan may take some time, but successful small businesses know it is well worth the effort.
#1 Cloud Accounting Software
Small Business Financial Plan FAQs
How do I write a small business financial plan?
Writing a small business financial plan is a four-step process. It begins with creating a strategic plan, which covers the company’s goals and what it needs to achieve them. The next step is to create financial projections, which are dependent on anticipating sales and expenses. Step three plans for contingencies: For example, what if the business were to lose a significant client? Finally, the business must monitor its goals, comparing actual results to projections and adjusting as needed.
What is the best financial statement for a small business?
The income statement, also known as the profit and loss (P&L) statement, is often considered the most important financial statement for small businesses, as it summarizes profits and losses and the business’s bottom line over a specific financial period. For financial plans, the cash flow statement and the balance sheet are also critical financial statements.
How often should businesses update their financial plans?
Financial plans can be updated whenever a business deems appropriate. Many businesses create three- and five-year plans and adjust them annually. If a market experiences a large shift, such as a spike in demand or an economic downturn, a financial plan may need to be updated to reflect the new market.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a small business financial plan?
Some common mistakes to avoid when creating a small business financial plan include underestimating expenses, overestimating revenue, failing to plan for contingencies and adhering to plans too strictly when circumstances change. Plans should be regularly updated to reflect real-world results and current market trends.
How do I account for uncertainty and potential risks in my small business financial plan?
Small businesses can plan for uncertainty by maintaining cash reserves and opening lines of credit to cover periods of lower income or high expenses. Plans and projections should also take into account a variety of potential scenarios, from best case to worst case.
What is a typical business financial plan?
A typical business financial plan is a document that details a business’s goals, strategies and projections over a specific period of time. It is used as a roadmap for the organization’s financial activities and provides a framework for decision-making, resource allocation and performance evaluation.
What are the seven components of a financial plan?
Financial plans can vary to suit the business’s needs, but seven components to include are the income statement, operating income, net income, cash flow statement, balance sheet, financial projections and business ratios. Various financial key performance indicators and a break-even analysis are typically included as well.
What is an example of a financial plan?
A financial plan serves as a snapshot of the business’s current standing and how it plans to grow. For example, a restaurant looking to secure approval for a loan will be asked to provide a financial plan. This plan will include an executive summary of the business, a description and history of the company, market research into customer base and competition, sales and marketing strategies, key performance indicators and organizational structure. It will also include elements focusing on the future, such as financial projections, potential risks and funding requirements and strategies.
Financial Management

Small Business Financial Management: Tips, Importance and Challenges
It is remarkably difficult to start a small business. Only about half stay open for five years, and only a third make it to the 10-year mark. That’s why it’s vital to make every effort to succeed. And one of the most fundamental skills and tools for any small business owner is sound financial management.

Trending Articles

Learn How NetSuite Can Streamline Your Business
NetSuite has packaged the experience gained from tens of thousands of worldwide deployments over two decades into a set of leading practices that pave a clear path to success and are proven to deliver rapid business value. With NetSuite, you go live in a predictable timeframe — smart, stepped implementations begin with sales and span the entire customer lifecycle, so there’s continuity from sales to services to support.
Before you go...
Discover the products that 37,000+ customers depend on to fuel their growth.
Before you go. Talk with our team or check out these resources.
Want to set up a chat later? Let us do the lifting.
NetSuite ERP
Explore what NetSuite ERP can do for you.
Business Guide
Complete Guide to Cloud ERP Implementation
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Business consultants
Entrepreneurs and Small Business
Accelerators and Incubators
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai pitch deck generator
Stratrgic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
Small Business Tools
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Strategic Planning
How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)

Free Financial Statements Template
Ajay Jagtap
- December 7, 2023
13 Min Read

If someone were to ask you about your business financials, could you give them a detailed answer?
Let’s say they ask—how do you allocate your operating expenses? What is your cash flow situation like? What is your exit strategy? And a series of similar other questions.
Instead of mumbling what to answer or shooting in the dark, as a founder, you must prepare yourself to answer this line of questioning—and creating a financial plan for your startup is the best way to do it.
A business plan’s financial plan section is no easy task—we get that.
But, you know what—this in-depth guide and financial plan example can make forecasting as simple as counting on your fingertips.
Ready to get started? Let’s begin by discussing startup financial planning.
What is Startup Financial Planning?
Startup financial planning, in simple terms, is a process of planning the financial aspects of a new business. It’s an integral part of a business plan and comprises its three major components: balance sheet, income statement, and cash-flow statement.
Apart from these statements, your financial section may also include revenue and sales forecasts, assets & liabilities, break-even analysis , and more. Your first financial plan may not be very detailed, but you can tweak and update it as your company grows.
Key Takeaways
- Realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of the market are the key to reliable financial projections.
- Cash flow projection, balance sheet, and income statement are three major components of a financial plan.
- Preparing a financial plan is easier and faster when you use a financial planning tool.
- Exploring “what-if” scenarios is an ideal method to understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in the business operations.
Why is Financial Planning Important to Your Startup?
Poor financial planning is one of the biggest reasons why most startups fail. In fact, a recent CNBC study reported that running out of cash was the reason behind 44% of startup failures in 2022.
A well-prepared financial plan provides a clear financial direction for your business, helps you set realistic financial objectives, create accurate forecasts, and shows your business is committed to its financial objectives.
It’s a key element of your business plan for winning potential investors. In fact, YC considered recent financial statements and projections to be critical elements of their Series A due diligence checklist .
Your financial plan demonstrates how your business manages expenses and generates revenue and helps them understand where your business stands today and in 5 years.
Makes sense why financial planning is important to your startup, doesn’t it? Let’s cut to the chase and discuss the key components of a startup’s financial plan.
Say goodbye to old-school excel sheets & templates
Make accurate financial plan faster with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

Key Components of a Startup Financial Plan
Whether creating a financial plan from scratch for a business venture or just modifying it for an existing one, here are the key components to consider including in your startup’s financial planning process.
Income Statement
An Income statement , also known as a profit-and-loss statement(P&L), shows your company’s income and expenditures. It also demonstrates how your business experienced any profit or loss over a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of your business that shows the feasibility of your business idea. An income statement can be generated considering three scenarios: worst, expected, and best.
Your income or P&L statement must list the following:
- Cost of goods or cost of sale
- Gross margin
- Operating expenses
- Revenue streams
- EBITDA (Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation , & amortization )
Established businesses can prepare annual income statements, whereas new businesses and startups should consider preparing monthly statements.
Cash flow Statement
A cash flow statement is one of the most critical financial statements for startups that summarize your business’s cash in-and-out flows over a given time.
This section provides details on the cash position of your business and its ability to meet monetary commitments on a timely basis.
Your cash flow projection consists of the following three components:
✅ Cash revenue projection: Here, you must enter each month’s estimated or expected sales figures.
✅ Cash disbursements: List expenditures that you expect to pay in cash for each month over one year.
✅ Cash flow reconciliation: Cash flow reconciliation is a process used to ensure the accuracy of cash flow projections. The adjusted amount is the cash flow balance carried over to the next month.
Furthermore, a company’s cash flow projections can be crucial while assessing liquidity, its ability to generate positive cash flows and pay off debts, and invest in growth initiatives.
Balance Sheet
Your balance sheet is a financial statement that reports your company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of what your business owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by the shareholders.
This statement consists of three parts: assets , liabilities, and the balance calculated by the difference between the first two. The final numbers on this sheet reflect the business owner’s equity or value.
Balance sheets follow the following accounting equation with assets on one side and liabilities plus Owner’s equity on the other:
Here is what’s the core purpose of having a balance-sheet:
- Indicates the capital need of the business
- It helps to identify the allocation of resources
- It calculates the requirement of seed money you put up, and
- How much finance is required?
Since it helps investors understand the condition of your business on a given date, it’s a financial statement you can’t miss out on.
Break-even Analysis
Break-even analysis is a startup or small business accounting practice used to determine when a company, product, or service will become profitable.
For instance, a break-even analysis could help you understand how many candles you need to sell to cover your warehousing and manufacturing costs and start making profits.
Remember, anything you sell beyond the break-even point will result in profit.
You must be aware of your fixed and variable costs to accurately determine your startup’s break-even point.
- Fixed costs: fixed expenses that stay the same no matter what.
- Variable costs: expenses that fluctuate over time depending on production or sales.
A break-even point helps you smartly price your goods or services, cover fixed costs, catch missing expenses, and set sales targets while helping investors gain confidence in your business. No brainer—why it’s a key component of your startup’s financial plan.
Having covered all the key elements of a financial plan, let’s discuss how you can create a financial plan for your startup.
How to Create a Financial Section of a Startup Business Plan?
1. determine your financial needs.
You can’t start financial planning without understanding your financial requirements, can you? Get your notepad or simply open a notion doc; it’s time for some critical thinking.
Start by assessing your current situation by—calculating your income, expenses , assets, and liabilities, what the startup costs are, how much you have against them, and how much financing you need.
Assessing your current financial situation and health will help determine how much capital you need for your startup and help plan fundraising activities and outreach.
Furthermore, determining financial needs helps prioritize operational activities and expenses, effectively allocate resources, and increase the viability and sustainability of a business in the long run.
Having learned to determine financial needs, let’s head straight to setting financial goals.
2. Define Your Financial Goals
Setting realistic financial goals is fundamental in preparing an effective financial plan. So, it would help to outline your long-term strategies and goals at the beginning of your financial planning process.
Let’s understand it this way—if you are a SaaS startup pursuing VC financing rounds, you may ask investors about what matters to them the most and prepare your financial plan accordingly.
However, a coffee shop owner seeking a business loan may need to create a plan that appeals to banks, not investors. At the same time, an internal financial plan designed to offer financial direction and resource allocation may not be the same as previous examples, seeing its different use case.
Feeling overwhelmed? Just define your financial goals—you’ll be fine.
You can start by identifying your business KPIs (key performance indicators); it would be an ideal starting point.
3. Choose the Right Financial Planning Tool
Let’s face it—preparing a financial plan using Excel is no joke. One would only use this method if they had all the time in the world.
Having the right financial planning software will simplify and speed up the process and guide you through creating accurate financial forecasts.
Many financial planning software and tools claim to be the ideal solution, but it’s you who will identify and choose a tool that is best for your financial planning needs.

Create a Financial Plan with Upmetrics in no time
Enter your Financial Assumptions, and we’ll calculate your monthly/quarterly and yearly financial projections.
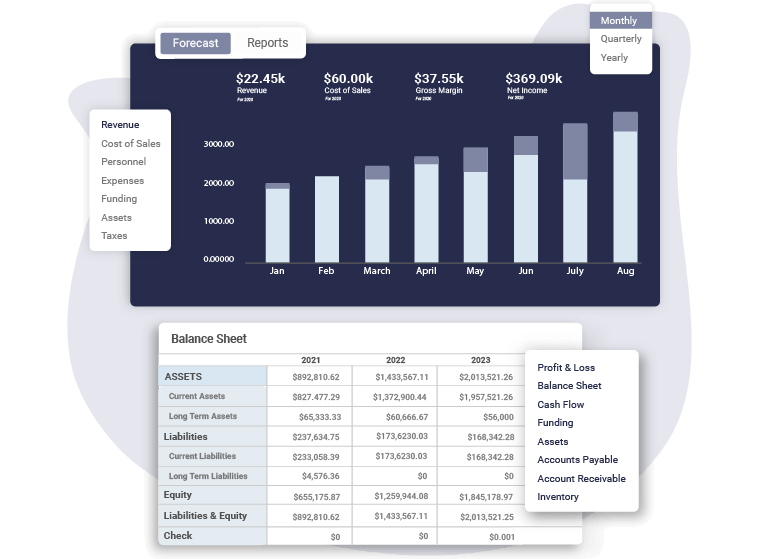
Start Forecasting
4. Make Assumptions Before Projecting Financials
Once you have a financial planning tool, you can move forward to the next step— making financial assumptions for your plan based on your company’s current performance and past financial records.
You’re just making predictions about your company’s financial future, so there’s no need to overthink or complicate the process.
You can gather your business’ historical financial data, market trends, and other relevant documents to help create a base for accurate financial projections.
After you have developed rough assumptions and a good understanding of your business finances, you can move forward to the next step—projecting financials.
5. Prepare Realistic Financial Projections
It’s a no-brainer—financial forecasting is the most critical yet challenging aspect of financial planning. However, it’s effortless if you’re using a financial planning software.
Upmetrics’ forecasting feature can help you project financials for up to 7 years. However, new startups usually consider planning for the next five years. Although it can be contradictory considering your financial goals and investor specifications.
Following are the two key aspects of your financial projections:
Revenue Projections
In simple terms, revenue projections help investors determine how much revenue your business plans to generate in years to come.
It generally involves conducting market research, determining pricing strategy , and cash flow analysis—which we’ve already discussed in the previous steps.
The following are the key components of an accurate revenue projection report:
- Market analysis
- Sales forecast
- Pricing strategy
- Growth assumptions
- Seasonal variations
This is a critical section for pre-revenue startups, so ensure your projections accurately align with your startup’s financial model and revenue goals.
Expense Projections
Both revenue and expense projections are correlated to each other. As revenue forecasts projected revenue assumptions, expense projections will estimate expenses associated with operating your business.
Accurately estimating your expenses will help in effective cash flow analysis and proper resource allocation.
These are the most common costs to consider while projecting expenses:
- Fixed costs
- Variable costs
- Employee costs or payroll expenses
- Operational expenses
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Emergency fund
Remember, realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of your market are the key to reliable financial projections.
6. Consider “What if” Scenarios
After you project your financials, it’s time to test your assumptions with what-if analysis, also known as sensitivity analysis.
Using what-if analysis with different scenarios while projecting your financials will increase transparency and help investors better understand your startup’s future with its best, expected, and worst-case scenarios.
Exploring “what-if” scenarios is the best way to better understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in business operations. This proactive exercise will help you make strategic decisions and necessary adjustments to your financial plan.
7. Build a Visual Report
If you’ve closely followed the steps leading to this, you know how to research for financial projections, create a financial plan, and test assumptions using “what-if” scenarios.
Now, we’ll prepare visual reports to present your numbers in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
Don’t worry—it’s no extra effort. You’ve already made a visual report while creating your financial plan and forecasting financials.
Check the dashboard to see the visual presentation of your projections and reports, and use the necessary financial data, diagrams, and graphs in the final draft of your financial plan.
Here’s what Upmetrics’ dashboard looks like:
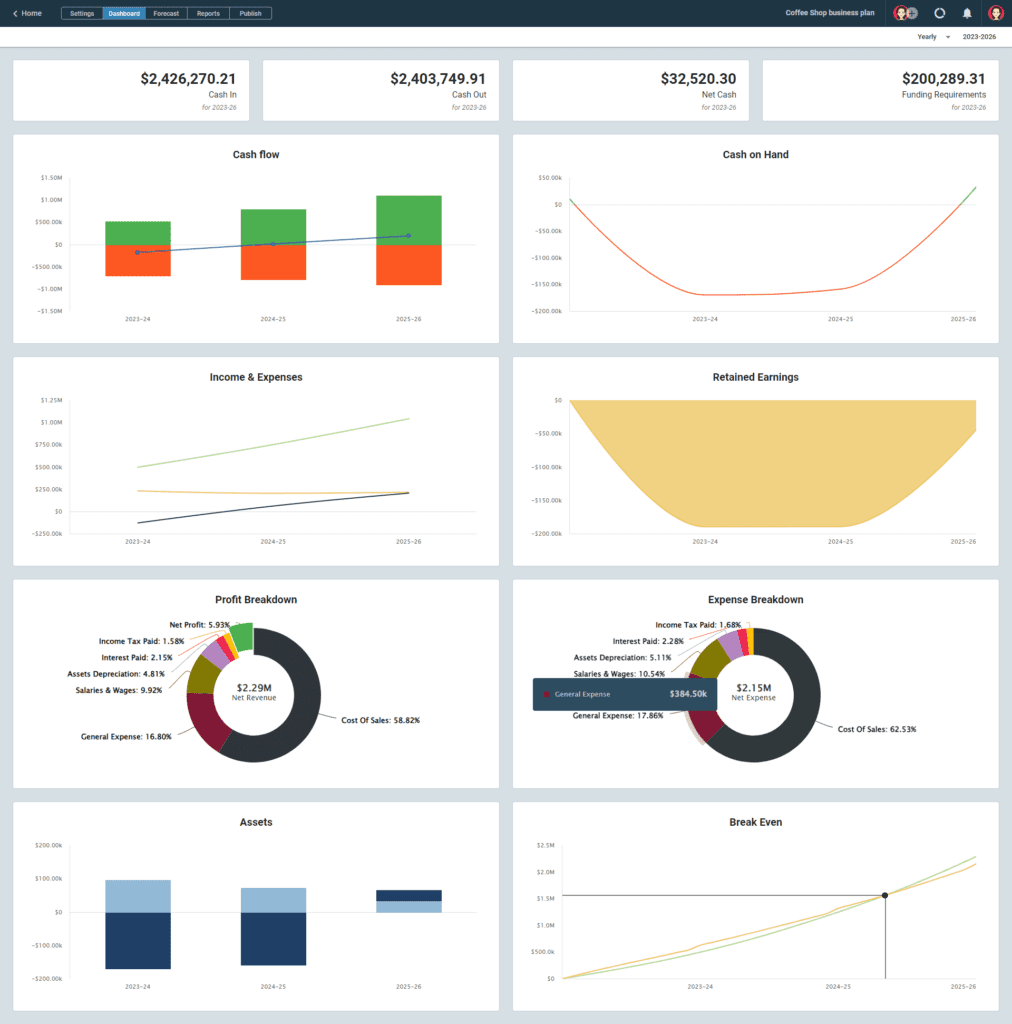
8. Monitor and Adjust Your Financial Plan
Even though it’s not a primary step in creating a good financial plan, it’s quite essential to regularly monitor and adjust your financial plan to ensure the assumptions you made are still relevant, and you are heading in the right direction.
There are multiple ways to monitor your financial plan.
For instance, you can compare your assumptions with actual results to ensure accurate projections based on metrics like new customers acquired and acquisition costs, net profit, and gross margin.
Consider making necessary adjustments if your assumptions are not resonating with actual numbers.
Also, keep an eye on whether the changes you’ve identified are having the desired effect by monitoring their implementation.
And that was the last step in our financial planning guide. However, it’s not the end. Have a look at this financial plan example.
Startup Financial Plan Example
Having learned about financial planning, let’s quickly discuss a coffee shop startup financial plan example prepared using Upmetrics.
Important Assumptions
- The sales forecast is conservative and assumes a 5% increase in Year 2 and a 10% in Year 3.
- The analysis accounts for economic seasonality – wherein some months revenues peak (such as holidays ) and wanes in slower months.
- The analysis assumes the owner will not withdraw any salary till the 3rd year; at any time it is assumed that the owner’s withdrawal is available at his discretion.
- Sales are cash basis – nonaccrual accounting
- Moderate ramp- up in staff over the 5 years forecast
- Barista salary in the forecast is $36,000 in 2023.
- In general, most cafes have an 85% gross profit margin
- In general, most cafes have a 3% net profit margin
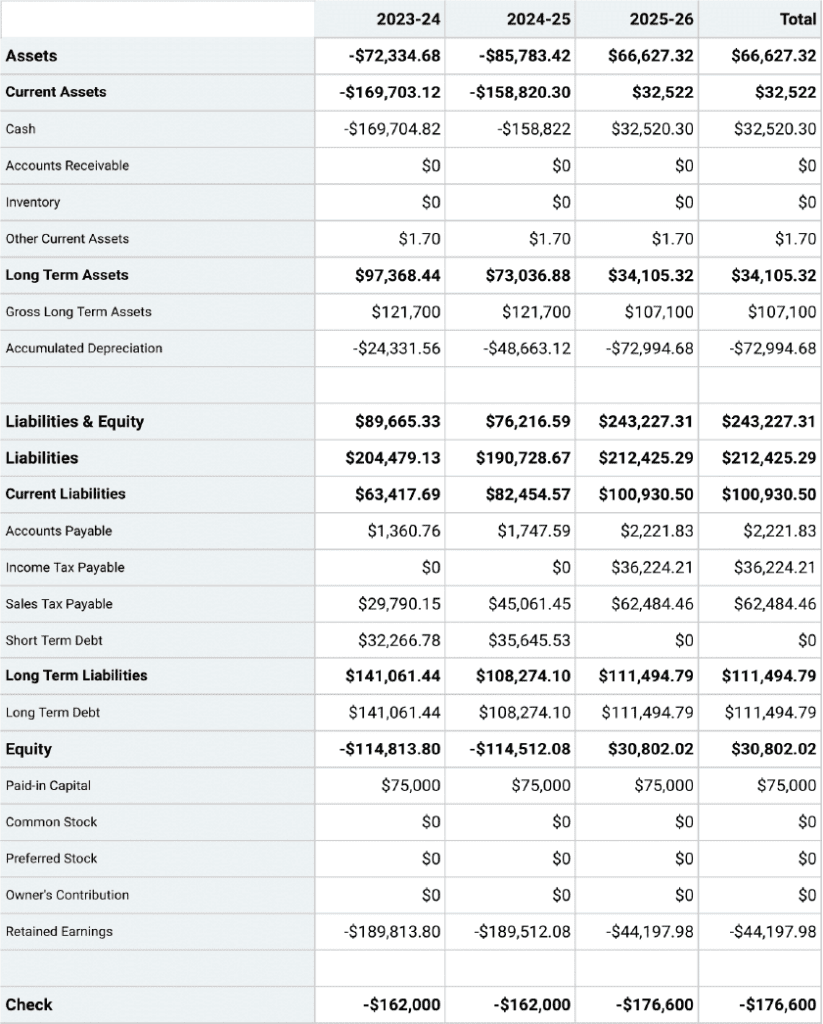
Projected Balance Sheet
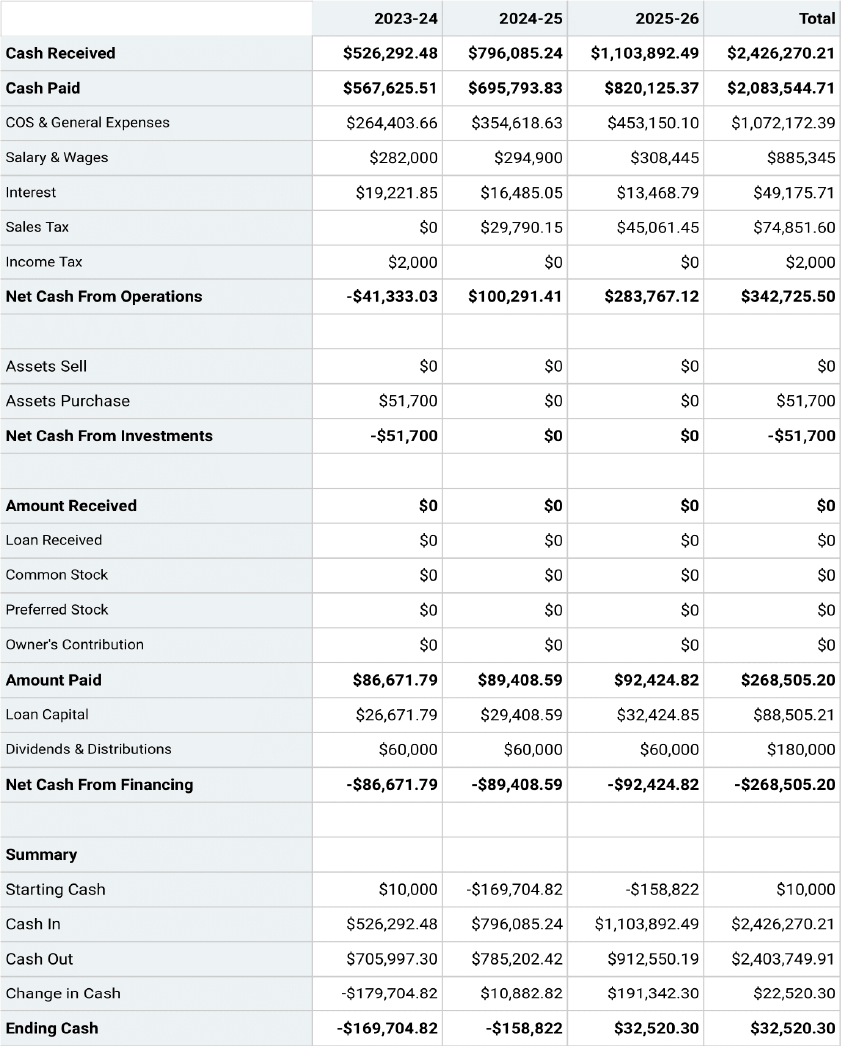
Projected Cash-Flow Statement
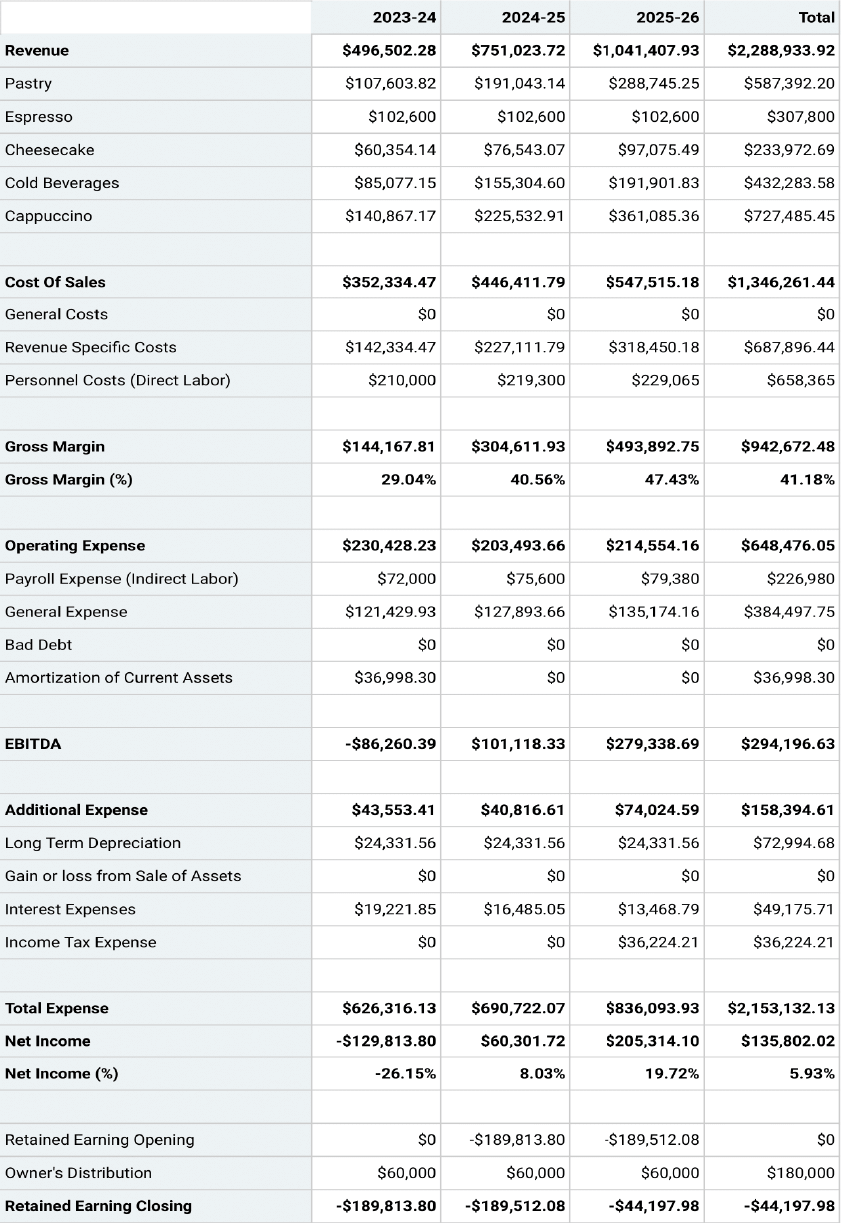
Projected Profit & Loss Statement
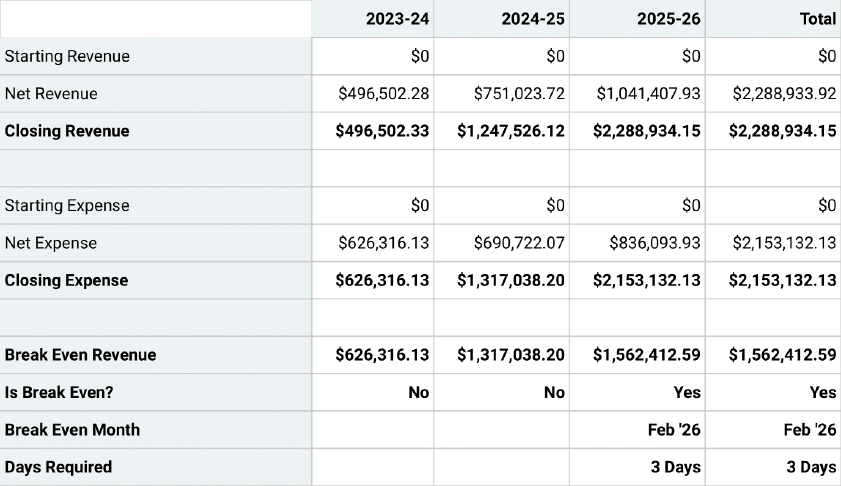
Break Even Analysis
Start Preparing Your Financial Plan
We covered everything about financial planning in this guide, didn’t we? Although it doesn’t fulfill our objective to the fullest—we want you to finish your financial plan.
Sounds like a tough job? We have an easy way out for you—Upmetrics’ financial forecasting feature. Simply enter your financial assumptions, and let it do the rest.
So what are you waiting for? Try Upmetrics and create your financial plan in a snap.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

Frequently Asked Questions
How often should i update my financial projections.
Well, there is no particular rule about it. However, reviewing and updating your financial plan once a year is considered an ideal practice as it ensures that the financial aspirations you started and the projections you made are still relevant.
How do I estimate startup costs accurately?
You can estimate your startup costs by identifying and factoring various one-time, recurring, and hidden expenses. However, using a financial forecasting tool like Upmetrics will ensure accurate costs while speeding up the process.
What financial ratios should startups pay attention to?
Here’s a list of financial ratios every startup owner should keep an eye on:
- Net profit margin
- Current ratio
- Quick ratio
- Working capital
- Return on equity
- Debt-to-equity ratio
- Return on assets
- Debt-to-asset ratio
What are the 3 different scenarios in scenario analysis?
As discussed earlier, Scenario analysis is the process of ascertaining and analyzing possible events that can occur in the future. Startups or businesses often consider analyzing these three scenarios:
- base-case (expected) scenario
- Worst-case scenario
- best case scenario.
About the Author

Ajay is a SaaS writer and personal finance blogger who has been active in the space for over three years, writing about startups, business planning, budgeting, credit cards, and other topics related to personal finance. If not writing, he’s probably having a power nap. Read more
Related Articles

How to Write a Business Plan Complete Guide

How to Calculate Business Startup Costs

How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Small Business?
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
How To Create Financial Projections for Your Business
Learn how to anticipate your business’s financial performance
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ScreenShot2020-03-26at1.24.14PM-16d178cb2ee74d71946d658ab027e210.png)
- Understanding Financial Projections & Forecasting
Why Forecasting Is Critical for Your Business
Key financial statements for forecasting, how to create your financial projections, frequently asked questions (faqs).
Maskot / Getty Images
Just like a weather forecast lets you know that wearing closed-toe shoes will be important for that afternoon downpour later, a good financial forecast allows you to better anticipate financial highs and lows for your business.
Neglecting to compile financial projections for your business may signal to investors that you’re unprepared for the future, which may cause you to lose out on funding opportunities.
Read on to learn more about financial projections, how to compile and use them in a business plan, and why they can be crucial for every business owner.
Key Takeaways
- Financial forecasting is a projection of your business's future revenues and expenses based on comparative data analysis, industry research, and more.
- Financial projections are a valuable tool for entrepreneurs as they offer insight into a business's ability to generate profit, increase cash flow, and repay debts, which can be attractive to investors.
- Some of the key components to include in a financial projection include a sales projection, break-even analysis, and pro forma balance sheet and income statement.
- A financial projection can not only attract investors, but helps business owners anticipate fixed costs, find a break-even point, and prepare for the unexpected.
Understanding Financial Projections and Forecasting
Financial forecasting is an educated estimate of future revenues and expenses that involves comparative analysis to get a snapshot of what could happen in your business’s future.
This process helps in making predictions about future business performance based on current financial information, industry trends, and economic conditions. Financial forecasting also helps businesses make decisions about investments, financing sources, inventory management, cost control strategies, and even whether to move into another market.
Developing both short- and mid-term projections is usually necessary to help you determine immediate production and personnel needs as well as future resource requirements for raw materials, equipment, and machinery.
Financial projections are a valuable tool for entrepreneurs as they offer insight into a business's ability to generate profit, increase cash flow, and repay debts. They can also be used to make informed decisions about the business’s plans. Creating an accurate, adaptive financial projection for your business offers many benefits, including:
- Attracting investors and convincing them to fund your business
- Anticipating problems before they arise
- Visualizing your small-business objectives and budgets
- Demonstrating how you will repay small-business loans
- Planning for more significant business expenses
- Showing business growth potential
- Helping with proper pricing and production planning
Financial forecasting is essentially predicting the revenue and expenses for a business venture. Whether your business is new or established, forecasting can play a vital role in helping you plan for the future and budget your funds.
Creating financial projections may be a necessary exercise for many businesses, particularly those that do not have sufficient cash flow or need to rely on customer credit to maintain operations. Compiling financial information, knowing your market, and understanding what your potential investors are looking for can enable you to make intelligent decisions about your assets and resources.
The income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flow are three key financial reports needed for forecasting that can also provide analysts with crucial information about a business's financial health. Here is a closer look at each.
Income Statement
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement or P&L, is a financial document that provides an overview of an organization's revenues, expenses, and net income.
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a snapshot of the business's assets and liabilities at a certain point in time. Sometimes referred to as the “financial portrait” of a business, the balance sheet provides an overview of how much money the business has, what it owes, and its net worth.
The assets side of the balance sheet includes what the business owns as well as future ownership items. The other side of the sheet includes liabilities and equity, which represent what it owes or what others owe to the business.
A balance sheet that shows hypothetical calculations and future financial projections is also referred to as a “pro forma” balance sheet.
Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement monitors the business’s inflows and outflows—both cash and non-cash. Cash flow is the business’s projected earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization ( EBITDA ) minus capital investments.
Here's how to compile your financial projections and fit the results into the three above statements.
A financial projections spreadsheet for your business should include these metrics and figures:
- Sales forecast
- Balance sheet
- Operating expenses
- Payroll expenses (if applicable)
- Amortization and depreciation
- Cash flow statement
- Income statement
- Cost of goods sold (COGS)
- Break-even analysis
Here are key steps to account for creating your financial projections.
Projecting Sales
The first step for a financial forecast starts with projecting your business’s sales, which are typically derived from past revenue as well as industry research. These projections allow businesses to understand what their risks are and how much they will need in terms of staffing, resources, and funding.
Sales forecasts also enable businesses to decide on important levels such as product variety, price points, and inventory capacity.
Income Statement Calculations
A projected income statement shows how much you expect in revenue and profit—as well as your estimated expenses and losses—over a specific time in the future. Like a standard income statement, elements on a projection include revenue, COGS, and expenses that you’ll calculate to determine figures such as the business’s gross profit margin and net income.
If you’re developing a hypothetical, or pro forma, income statement, you can use historical data from previous years’ income statements. You can also do a comparative analysis of two different income statement periods to come up with your figures.
Anticipate Fixed Costs
Fixed business costs are expenses that do not change based on the number of products sold. The best way to anticipate fixed business costs is to research your industry and prepare a budget using actual numbers from competitors in the industry. Anticipating fixed costs ensures your business doesn’t overpay for its needs and balances out its variable costs. A few examples of fixed business costs include:
- Rent or mortgage payments
- Operating expenses (also called selling, general and administrative expenses or SG&A)
- Utility bills
- Insurance premiums
Unfortunately, it might not be possible to predict accurately how much your fixed costs will change in a year due to variables such as inflation, property, and interest rates. It’s best to slightly overestimate fixed costs just in case you need to account for these potential fluctuations.
Find Your Break-Even Point
The break-even point (BEP) is the number at which a business has the same expenses as its revenue. In other words, it occurs when your operations generate enough revenue to cover all of your business’s costs and expenses. The BEP will differ depending on the type of business, market conditions, and other factors.
To find this number, you need to determine two things: your fixed costs and variable costs. Once you have these figures, you can find your BEP using this formula:
Break-even point = fixed expenses ➗ 1 – (variable expenses ➗ sales)
The BEP is an essential consideration for any projection because it is the point at which total revenue from a project equals total cost. This makes it the point of either profit or loss.
Plan for the Unexpected
It is necessary to have the proper financial safeguards in place to prepare for any unanticipated costs. A sudden vehicle repair, a leaky roof, or broken equipment can quickly derail your budget if you aren't prepared. Cash management is a financial management plan that ensures a business has enough cash on hand to maintain operations and meet short-term obligations.
To maintain cash reserves, you can apply for overdraft protection or an overdraft line of credit. Overdraft protection can be set up by a bank or credit card business and provides short-term loans if the account balance falls below zero. On the other hand, a line of credit is an agreement with a lending institution in which they provide you with an unsecured loan at any time until your balance reaches zero again.
How do you make financial projections for startups?
Financial projections for startups can be hard to complete. Historical financial data may not be available. Find someone with financial projections experience to give insight on risks and outcomes.
Consider business forecasting, too, which incorporates assumptions about the exponential growth of your business.
Startups can also benefit from using EBITDA to get a better look at potential cash flow.
What are the benefits associated with forecasting business finances?
Forecasting can be beneficial for businesses in many ways, including:
- Providing better understanding of your business cash flow
- Easing the process of planning and budgeting for the future based on income
- Improving decision-making
- Providing valuable insight into what's in their future
- Making decisions on how to best allocate resources for success
How many years should your financial forecast be?
Your financial forecast should either be projected over a specific time period or projected into perpetuity. There are various methods for determining how long a financial forecasting projection should go out, but many businesses use one to five years as a standard timeframe.
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Market Research and Competitive Analysis ."
Score. " Financial Projections Template ."
How to Develop a Small Business Financial Plan
By Andy Marker | April 29, 2022
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Financial planning is critical for any successful small business, but the process can be complicated. To help you get started, we’ve created a step-by-step guide and rounded up top tips from experts.
Included on this page, you’ll find what to include in a financial plan , steps to develop one , and a downloadable starter kit .
What Is a Small Business Financial Plan?
A small business financial plan is an outline of the financial status of your business, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow information. A financial plan can help guide a small business toward sustainable growth.

Financial plans can aid in business goal setting and metrics tracking, as well as provide proof of profitable ideas. Craig Hewitt, Founder of Castos , shares that “creating a financial plan will show you if your business ideas are sustainable. A financial plan will show you where your business stands and help you make better decisions about resource allocation. It will also help you plan growth, survive cash flow shortages, and pitch to investors.”
Why Is It Important for a Small Business to Have a Financial Plan?
All small businesses should create a financial plan. This allows you to assess your business’s financial needs, recognize areas of opportunity, and project your growth over time. A strong financial plan is also a bonus for potential investors.

Mark Daoust , the President and CEO of Quiet Light Brokerage, Inc., explains why a financial plan is important for small businesses: “It can sometimes be difficult for business owners to evaluate their own progress, especially when starting a new company. A financial plan can be helpful in showing increased revenues, cash flow growth, and overall profit in quantifiable data. It's very encouraging for small business owners who are often working long hours and dealing with so many stressful decisions to know that they are on the right track.”
To learn more about other important considerations for a small business, peruse our list of free startup plan, budget, and cost templates .
What Does a Small Business Financial Plan Include?
All small businesses should include an income statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement in their financial plan. You may also include other documents, such as personnel plans, break-even points, and sales forecasts, depending on the business and industry.

- Balance Sheet: A balance sheet determines the difference between your liabilities and assets to determine your equity. “A balance sheet is a snapshot of a business’s financial position at a particular moment in time,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “It adds up everything your business owns and subtracts all debts — the difference reflects the net worth of the business, also referred to as equity .” Yüzbaşıoğlu explains that this statement consists of three parts: assets, liabilities, and equity. “Assets include your money in the bank, accounts receivable, inventories, and more. Liabilities can include your accounts payables, credit card balances, and loan repayments, for example. Equity for most small businesses is just the owner’s equity, but it could also include investors’ shares, retained earnings, or stock proceeds,” he says.
- Cash Flow Statement: A cash flow statement shows where the money is coming from and where it is going. For existing businesses, this will include bank statements that list deposits and expenditures. A new business may not have much cash flow information, but it can include all startup costs and funding sources. “A cash flow statement shows how much cash is generated and used during a given period of time. It documents all the money flowing in and out of your business,” explains Yüzbaşıoğlu.
- Break-Even Analysis: A break-even analysis is a projection of how long it will take you to recoup your investments, such as expenses from startup costs or ongoing projects. In order to perform this analysis, Yüzbaşıoğlu explains, “You need to know the difference between fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs are the expenses that stay the same, regardless of how much you sell or don't sell. For example, expenses such as rent, wages, and accounting fees are typically fixed. Variable costs are the expenses that change in accordance with production or sales volume. “In other words, [a break-even analysis] determines the units of products or services you need to sell at least to cover your production costs. Generally, to calculate the break-even point in business, divide fixed costs by the gross profit margin. This produces a dollar figure that a company needs to break even,” Yüzbaşıoğlu shares.
- Personnel Plan: A personnel plan is an outline of various positions or departments that states what they do, why they are necessary, and how much they cost. This document is generally more useful for large businesses, or those that find themselves spending a large percentage of their budget on labor.
- Sales Forecast: A sales forecast can help determine how many sales and how much money you expect to make in a given time period. To learn more about various methods of predicting these figures, check out our guide to sales forecasting .
How to Write a Small Business Financial Plan
Writing a financial plan begins with collecting financial information from your small business. Create income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, and any other documents you need using that information. Then share those documents with relevant stakeholders.
“Creating a financial plan is key to any business and essential for success: It provides protection and an opportunity to grow,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “You can use [the financial plan] to make better-informed decisions about things like resource allocation on future projects and to help shape the success of your company.”
1. Create a Plan
Create a strategic business plan that includes your business strategy and goals, and define their financial impact. Your financial plan will inform decisions for every aspect of your business, so it is important to know what is important and what is at stake.
2. Gather Financial Information
Collect all of the available financial information about your business. Organize bank statements, loan information, sales numbers, inventory costs, payroll information, and any other income and expenses your business has incurred. If you have not already started to do so, regularly record all of this information and store it in an easily accessible place.
3. Create an Income Statement
Your income statement should display revenue, expenses, and profit for a given time period. Your revenue minus your expenses equals your profit or loss. Many businesses create a new statement yearly or quarterly, but small businesses with less cash flow may benefit from creating statements for shorter time frames.
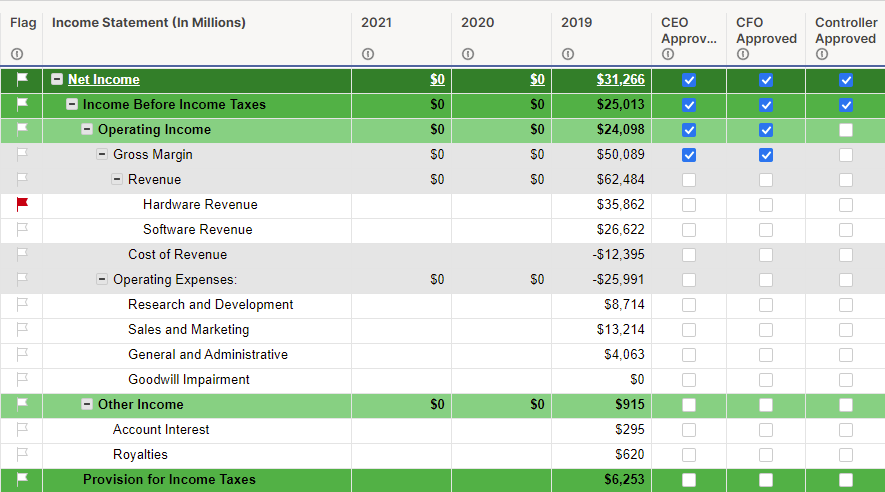
4. Create a Balance Sheet
Your balance sheet is a snapshot of your business’s financial status at a particular moment in time. You should update it on the same schedule as your income statement. To determine your equity, calculate all of your assets minus your liabilities.
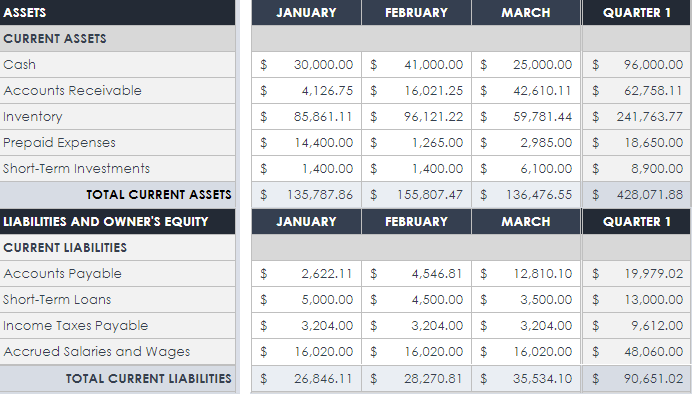
5. Create a Cash Flow Statement
As mentioned above, the cash flow statement shows all past and projected cash flow for your business. “Your cash flow statement needs to cover three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities,” suggests Hewitt. “Operating activities are the movement of cash from the sale or purchase of goods or services. Investing activities are the sale or purchase of long-term assets. Financing activities are transactions with creditors and investments.”
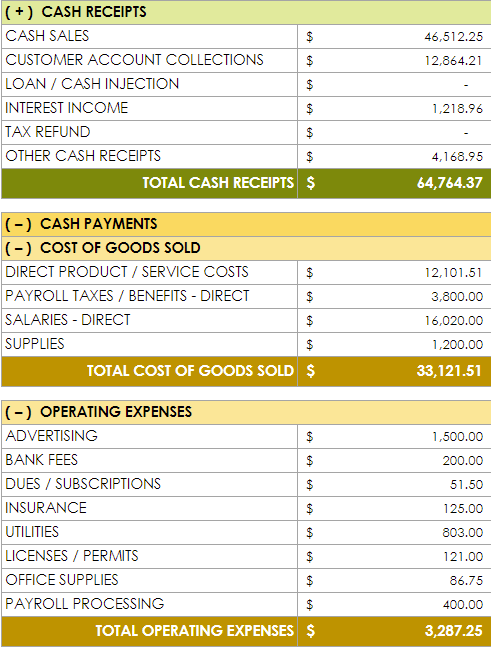
6. Create Other Documents as Needed
Depending on the age, size, and industry of your business, you may find it useful to include these other documents in your financial plan as well.
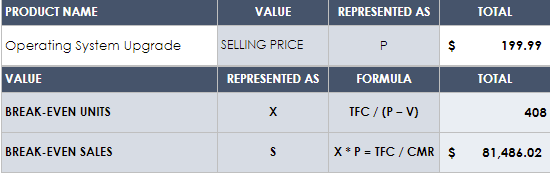
- Sales Forecast: Your sales forecast should reference sales numbers from your past to estimate sales numbers for your future. Sales forecasts may be more useful for established companies with historical numbers to compare to, but small businesses can use forecasts to set goals and break records month over month. “To make future financial projections, start with a sales forecast,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “Project your sales over the course of 12 months. After projecting sales, calculate your cost of sales (also called cost of goods or direct costs). This will let you calculate gross margin. Gross margin is sales less the cost of sales, and it's a useful number for comparing with different standard industry ratios.”
7. Save the Plan for Reference and Share as Needed
The most important part of a financial plan is sharing it with stakeholders. You can also use much of the same information in your financial plan to create a budget for your small business.

Additionally, be sure to conduct regular reviews, as things will inevitably change. “My best tip for small businesses when creating a financial plan is to schedule reviews. Once you have your plan in place, it is essential that you review it often and compare how well the strategy fits with the actual monthly expenses. This will help you adjust your plan accordingly and prepare for the year ahead,” suggests Janet Patterson, Loan and Finance Expert at Highway Title Loans.
Small Business Financial Plan Example
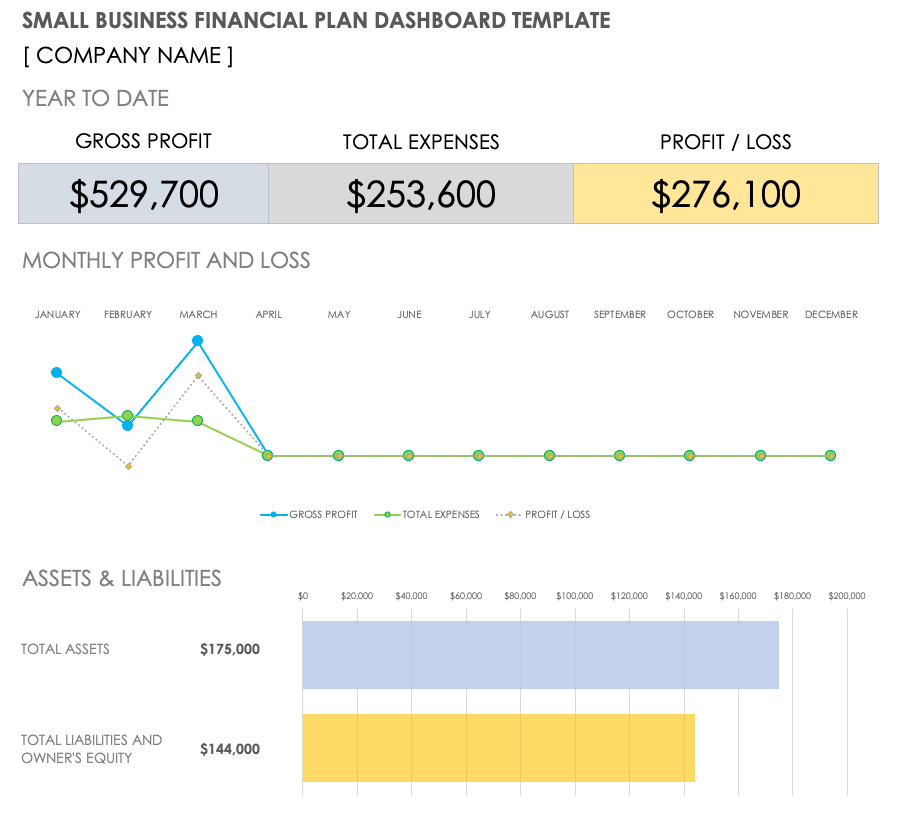
Download Small Business Financial Plan Example Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Here is an example of what a completed small business financial plan dashboard might look like. Once you have completed your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statements, use a template to create visual graphs to display the information to make it easier to read and share. In this example, this small business plots its income and cash flow statements quarterly, but you may find it valuable to update yours more often.
Small Business Financial Plan Starter Kit
Download Small Business Financial Plan Starter Kit
We’ve created this small business financial plan starter kit to help you get organized and complete your financial plan. In this kit, you will find a fully customizable income statement template, a balance sheet template, a cash flow statement template, and a dashboard template to display results. We have also included templates for break-even analysis, a personnel plan, and sales forecasts to meet your ongoing financial planning needs.
Small Business Income Statement Template
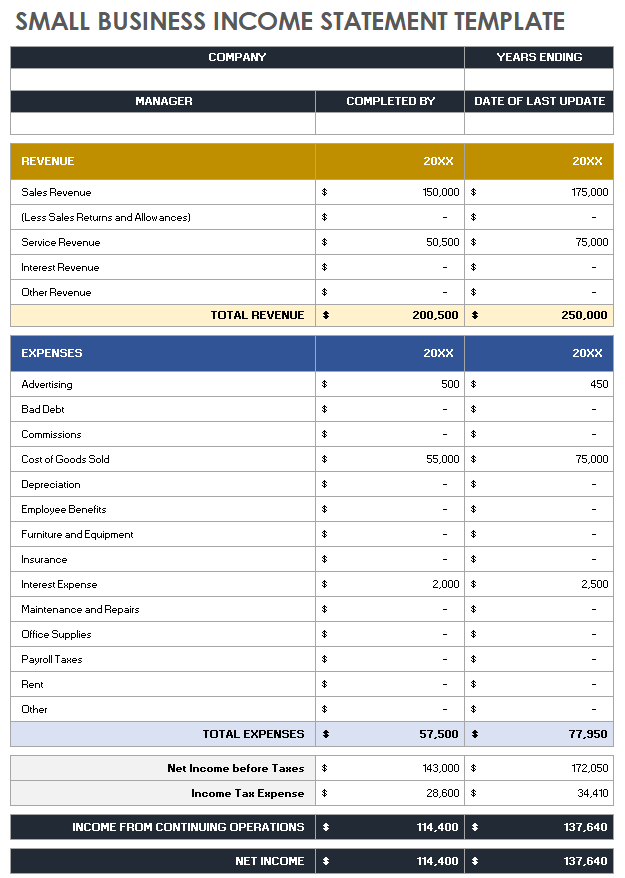
Download Small Business Income Statement Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this small business income statement template to input your income information and track your growth over time. This template is filled to track by the year, but you can also track by months or quarters. The template is fully customizable to suit your business needs.
Small Business Balance Sheet Template
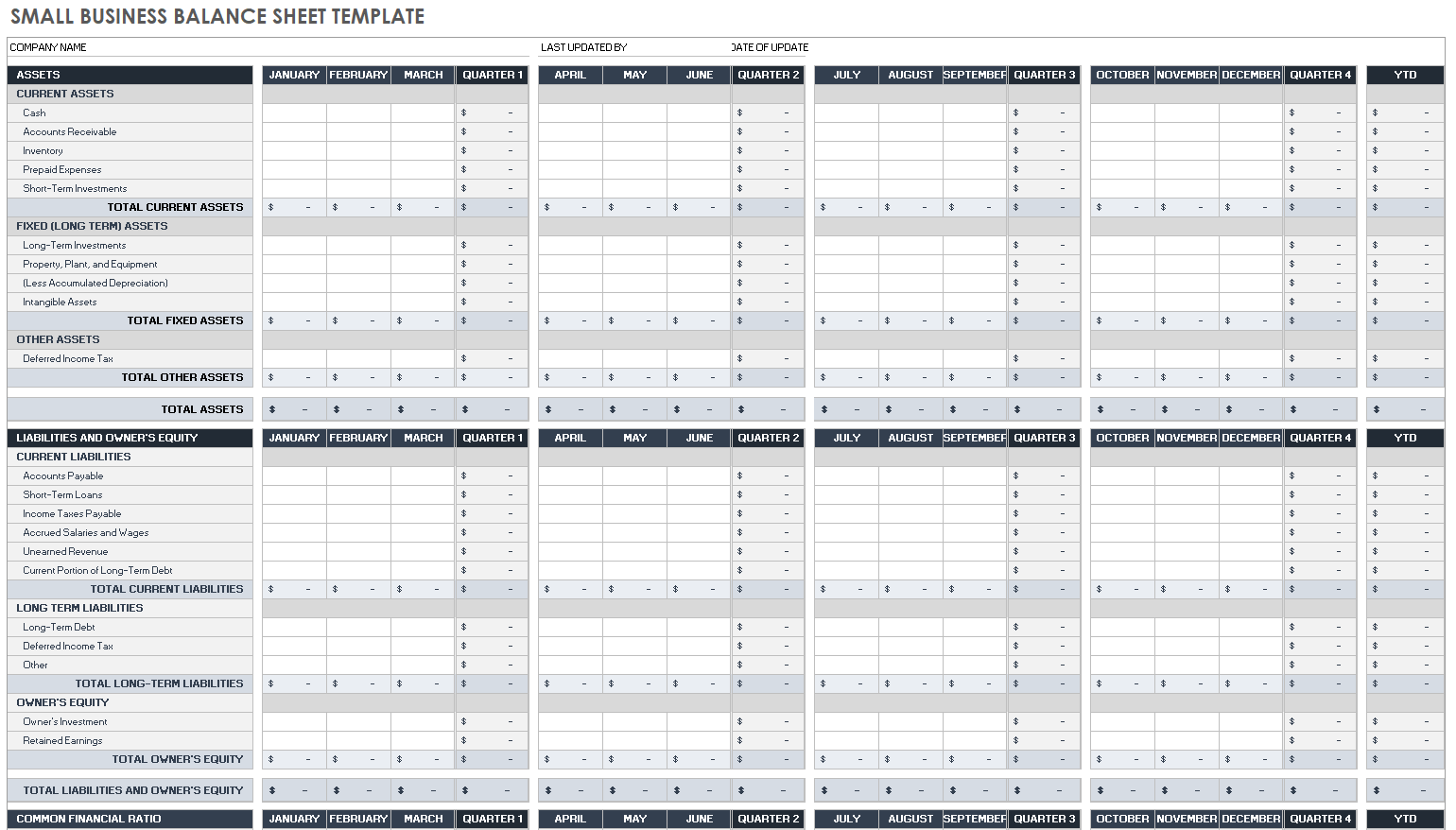
Download Small Business Balance Sheet Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
This customizable balance sheet template was created with small businesses in mind. Use it to create a snapshot of your company’s assets, liabilities, and equity quarter over quarter.
Small Business Cash Flow Statement Template
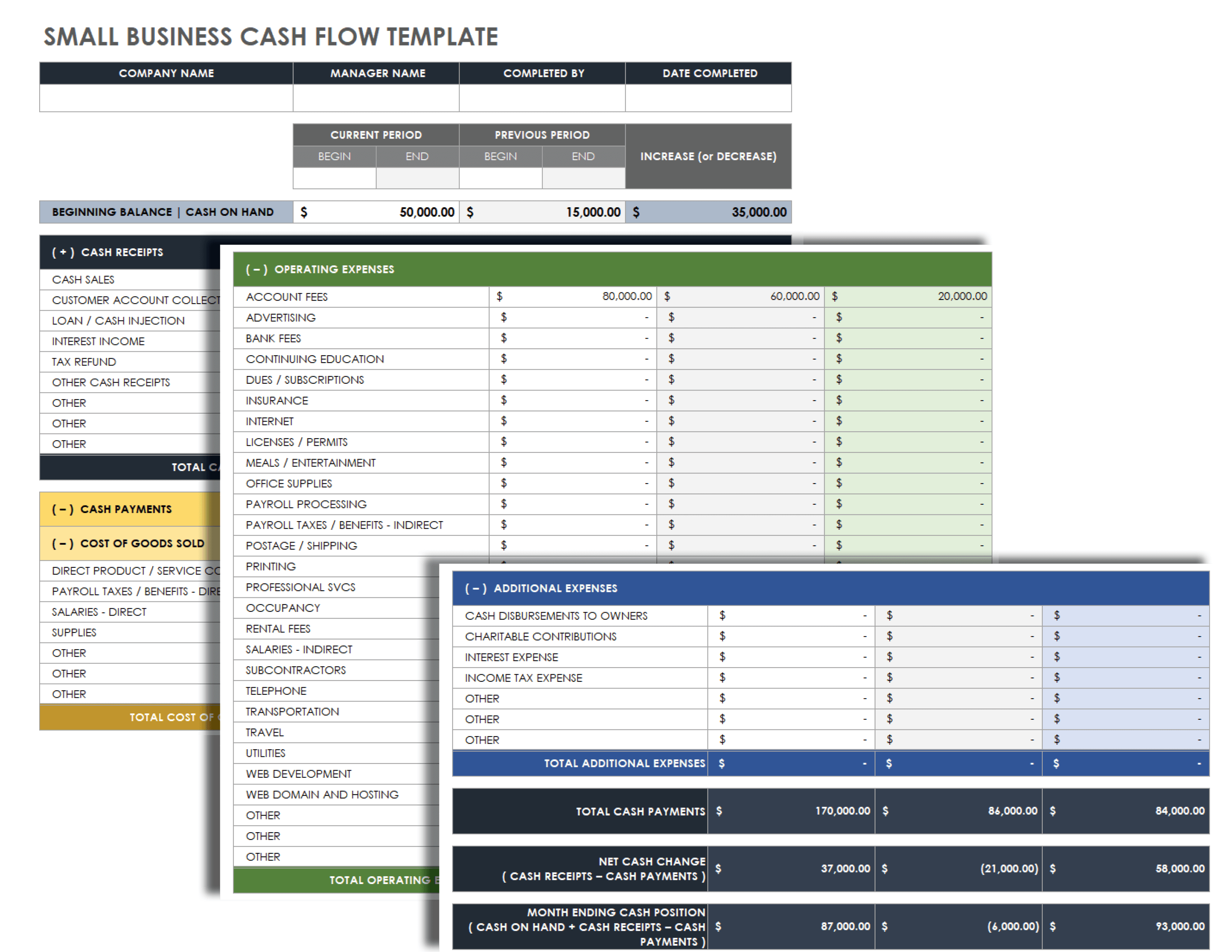
Download Small Business Cash Flow Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this customizable cash flow statement template to stay organized when documenting your cash flow. Note the time frame and input all of your financial data in the appropriate cell. With this information, the template will automatically generate your total cash payments, net cash change, and ending cash position.
Break-Even Analysis Template
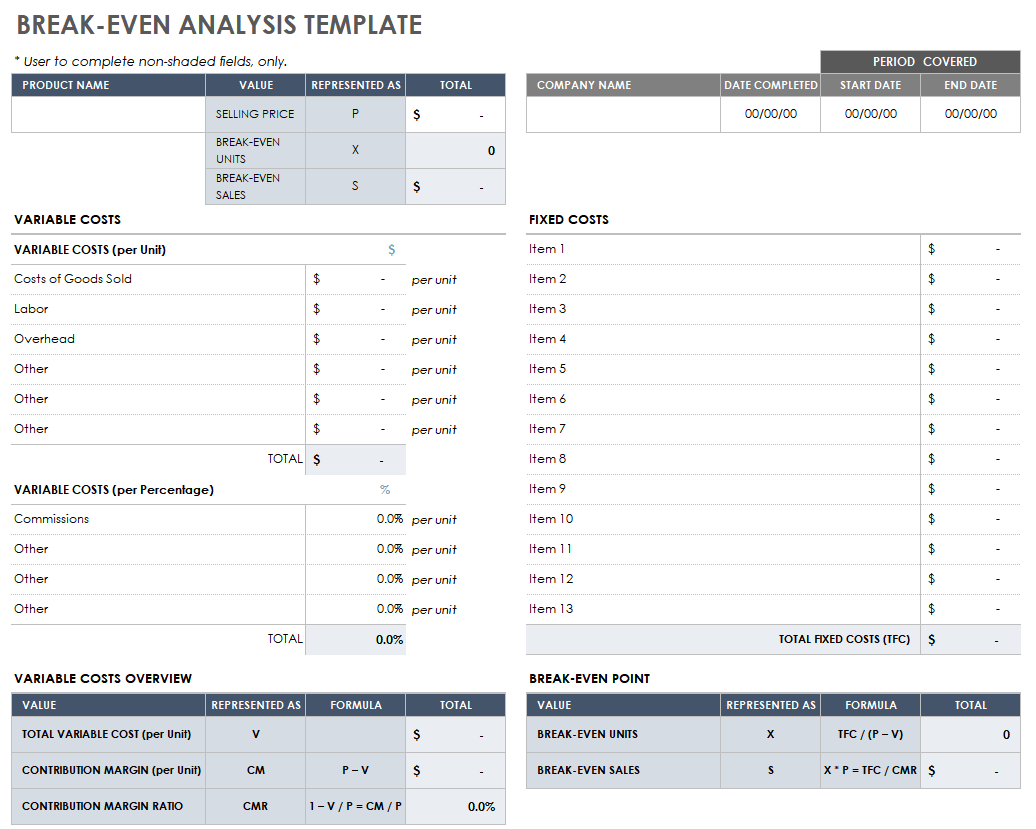
Download Break-Even Analysis Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
This powerful template can help you determine the point at which you will break even on product investment. Input the sale price of the product, as well as its various associated costs, and this template will display the number of units needed to break even on your initial costs.
Personnel Plan Template
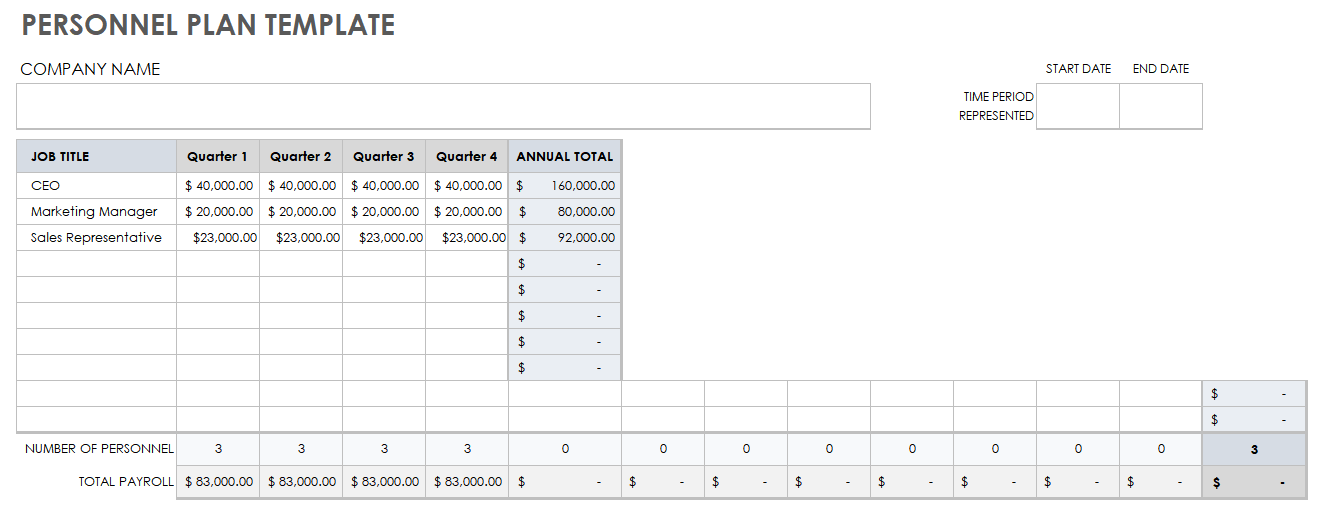
Download Personnel Plan Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this simple personnel plan template to help organize and define the monetary cost of the various roles or departments within your company. This template will generate a labor cost total that you can use to compare roles and determine whether you need to make cuts or identify areas for growth.

Sales Forecast Template
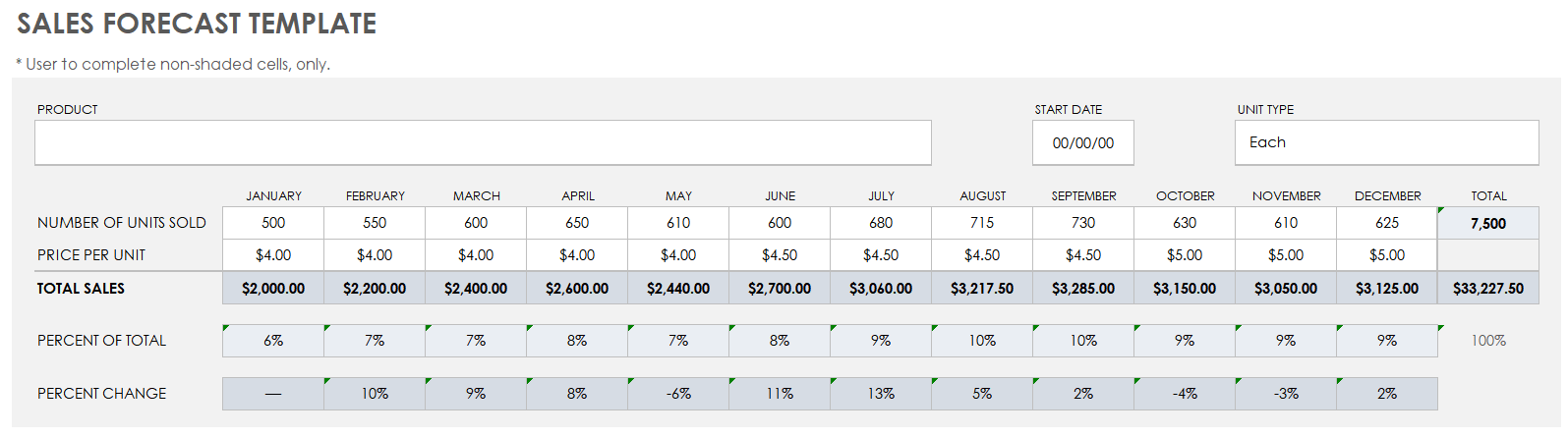
Download Sales Forecast Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this customizable template to forecast your sales month over month and determine the percentage changes. You can use this template to set goals and track sales history as well.
Small Business Financial Plan Dashboard Template
Download Small Business Financial Plan Dashboard Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
This dashboard template provides a visual example of a small business financial plan. It presents the information from your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in a graphical form that is easy to read and share.
Tips for Completing a Financial Plan for a Small Business
You can simplify the development of your small business financial plan in many ways, from outlining your goals to considering where you may need help. We’ve outlined a few tips from our experts below:

- Outline Your Business Goals: Before you create a financial plan, outline your business goals. This will help you determine where money is being well spent to achieve those goals and where it may not be. “Before applying for financing or investment, list the expected business goals for the next three to five years. You can ask a certified public accountant for help in this regard,” says Thé. The U.S. Small Business Administration or a local small business development center can also help you to understand the local market and important factors for business success. For more help, check out our quick how-to guide on writing a business plan .
- Make Sure You Have the Right Permits and Insurance: One of the best ways to keep your financial plan on track is to anticipate large expenditures. Double- and triple-check that you have the permits and insurances you need so that you do not incur any fines or surprise expenses down the line. “If you own your own business, you're no longer able to count on your employer for your insurance needs. It's important to have a plan for how you're going to pay for this additional expense and make sure that you know what specific insurance you need to cover your business,” suggests Daost.
- Separate Personal Goals from Business Goals: Be as unbiased as possible when creating and laying out your business’s financial goals. Your financial and prestige goals as a business owner may be loftier than what your business can currently achieve in the present. Inflating sales forecasts or income numbers will only come back to bite you in the end.
- Consider Hiring Help: You don’t know what you don’t know, but fortunately, many financial experts are ready to help you. “Hiring financial advisors can help you make sound financial decisions for your business and create a financial roadmap to follow. Many businesses fail in the first few years due to poor planning, which leads to costly mistakes. Having a financial advisor can help keep your business alive, make a profit, and thrive,” says Hewitt.
- Include Less Obvious Expenses: No income or expense is too small to consider — it all matters when you are creating your financial plan. “I wish I had known that you’re supposed to incorporate anticipated internal hidden expenses in the plan as well,” Patterson shares. “I formulated my first financial plan myself and didn’t have enough knowledge back then. Hence, I missed out on essential expenses, like office maintenance, that are less common.”
Do Small Business Owners Need a Financial Planner?
Not all small business owners need a designated financial planner, but you should understand the documents and information that make up a financial plan. If you do not hire an advisor, you must be informed about your own finances.
Small business owners tend to wear many hats, but Powell says, “it depends on the organization of the owner and their experience with the financial side of operating businesses.” Hiring a financial advisor can take some tasks off your plate and save you time to focus on the many other details that need your attention. Financial planners are experts in their field and may have more intimate knowledge of market trends and changing tax information that can end up saving you money in the long run.
Yüzbaşıoğlu adds, “Small business owners can greatly benefit from working with a financial advisor. A successful small business often requires more than just the skills of an entrepreneur; a financial advisor can help the company effectively manage risks and maximize opportunities.”
For more examples of the tasks a financial planner might be able to help with, check through our list of free financial planning templates .
Drive Small Business Success with Financial Planning in Smartsheet
Discover a better way to connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform that empowers your team to get more done, faster.
With Smartsheet, you can align your team on strategic initiatives, improve collaboration efforts, and automate repetitive processes, giving you the ability to make better business decisions and boost effectiveness as you scale.
When you wear a lot of hats, you need a tool that empowers you to get more done in less time. Smartsheet helps you achieve that. Try free for 30 days, today .
Connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform.

What You Need to Know About Calculating Financial Ratios for Your Business Plan
By henry sheykin, introduction.
Financial ratios are variables used to measure a company's financial performance. They provide valuable insight into a business's liquidity, debt, profitability and other essential aspects. A business plan is a strategic document prepared by entrepreneurs to secure funding or other resources. It is a critical document that outlines the goals and objectives of the business, and how it will achieve them. Introducing financial ratios into a business plan could help to emphasize the viability of the project in the eyes of a potential investor.
What is a Financial Ratio?
Financial ratios are mathematical calculations of a company’s financial performance that provide insight into the company's performance. By comparing financial ratios such as profitability, liquidity, and solvency, investors and business owners can understand better how their business operates financially.
Types of Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are broken down into five main categories: profitability, liquidity, solvency, efficiency, and coverage. They can be further divided into various types of ratios, such as gross profit margin, cash flow, debt-equity ratio, and asset turnover.
Examples of Most Popular Financial Ratios
- Profitability ratios assess how profitable a company is, such as gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin.
- Liquidity ratios assess how easily a company can access cash and pay off liabilities, such as the current ratio and quick ratio.
- Solvency ratios measure a company’s ability to repay debt, such as the debt-equity ratio and interest coverage ratio.
- Efficiency ratios assess how well a company is able to manage assets and liabilities, such as asset turnover and inventory turnover.
- Coverage ratios measure the ability to meet financial obligations, such as the debt service coverage ratio.
Preparing Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are an important part of a business plan as they help in tracking company performance and predicting future performance. Preparation of financial ratios requires certain steps, data, and knowledge. It is also beneficial in understanding well the financial position of a company and designing strategies accordingly.
Steps on How to Calculate Financial Ratios
Calculating financial ratios is a tool to measure a business entity’s performance, liquidity, solvency, profitability, efficiency, and capital structure. The following steps are involved in calculating financial ratios:
- Step 1: Set Objective: It is important to have clear objective and purpose before starting the process by considering factors like time and resources that are available.
- Step 2: Select Ratios: Having an idea about the financial performance gives an indication about the kind of ratio to be selected for measurement. Ratios can be selected based on industry benchmark or on the basis of the company goals.
- Step 3: Collect Data: Data collection is one of the most important steps in determining financial ratios. The accuracy of the ratios depends on the accuracy and availability of the data.
- Step 4: Calculate Ratios: The actual calculation is the next step, where the relevant two or three financial variables are related for achieving the desired ratio.
- Step 5: Analyze Ratios: After calculating the ratios, the results are hyperlinked with the goals and results are analyzed and discussed.
Data Needed to Prepare Ratios
The data required for calculating financial ratios include certain financial variables such as profit margin, asset turnover, liquidity ratios, and debt ratio. The financial variables depend on the ratio being computed.
For example, for computing liquidity ratios such as current ratio and quick ratio, the data required will include current assets, current liabilities, and quick assets. Likewise, for computing profitability ratios such as gross profit margin, the required data will include gross sales, gross profit and total operating costs.
Benefits of Preparing Financial Ratios
Financial ratios offer useful information that can be used to improve different aspects in a business such as expense management and product pricing. The benefits of preparing financial ratios include:
- Better Understanding of Financial Performance: Preparing financial ratios helps in understanding the financial performance better and making future financial goals.
- Easy Comparison with Competitors: Financial ratios help in measuring the financial position of one’s company in comparison to its competitors.
- Achievement of Goals: Ratios help in understanding the degree of financial success achieved or needs to be achieved.
- Identification of Problems: Preparing financial ratios helps in early identification of problems such as inventory control, liquidity, and high expenses.
Calculating Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios are used to evaluate the financial health of a business by showing the return on investments. They provide a valuable insight into the business performance and offer important metrics that are essential to understanding the business plan.
Definition of Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios measure a company’s ability to generate income from its operations and investments. They capture the ability of a company to increase its sales and decrease its costs by providing a quantitative analysis of how efficiently the company is using its resources to generate the desired income.
Examples of Profitability Ratios
- Gross Profit Margin
- Net Profit Margin
- Operating Profit Margin
- Return on Assets
Guide on How to Calculate Profitability Ratios
In order to calculate profitability ratios, it is essential to have accurate financial information such as sales, expenses, and capital. Further, companies may require different ratios to be calculated based on their specific goals and objectives.
To calculate profitability ratios, first, determine the sales and expenses associated with the business plan. This includes all costs directly related to the business, such as direct materials, direct labor, and marketing expenses. Next, calculate the gross profit margin, by subtracting the direct costs from sales and dividing the result by sales. Net profit margin is then calculated by subtracting all indirect costs, such as administrative and general expenses, from the gross profit margin and dividing the result by the sales.
Operating profit margin is calculated by subtracting operating expenses from net profit margin. Finally, the return on assets ratio is calculated by dividing the net profit margin by the company’s total assets and multiplying the result by 100.
Assessing Liquidity Ratios
Businesses can use liquidity ratios to assess the short-term ability to pay off immediate debts, such as business taxes, loan payments and invoice payments. These liquidity ratios measure whether a company's assets are quickly converted into cash, so management can fulfill its current liabilities.
Definition of Liquidity Ratios
Liquidity ratios measure a company's ability to pay off short-term debts and obligations. Higher liquidity ratios indicate that a company is better able to pay off its liabilities and lower liquidity ratios indicate that a company may be at risk of not being able to pay its obligations. Common liquidity ratios include current ratio, quick ratio and cash ratio.
Examples of Liquidity Ratios
- Current Ratio: This ratio is used to measure the ability of a company to pay its liabilities using its most liquid assets, such as cash, inventory and accounts receivable. Current ratio is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities.
- Quick Ratio: This ratio measures the capability of a company to pay its liabilities using only its most liquid assets. Quick ratio is calculated by dividing quick assets (cash, marketable securities and accounts receivable) by current liabilities.
- Cash Ratio: This ratio is used to measure the ability of a company to pay its liabilities using its most liquid asset, cash. Cash ratio is calculated by dividing cash by current liabilities.
Guide on how to Calculate Liquidity Ratios
- Current Ratio: To calculate current ratio, divide total current assets by total current liabilities.
- Quick Ratio: To calculate quick ratio, divide total quick assets (cash, marketable securities and accounts receivable) by total current liabilities.
- Cash Ratio: To calculate cash ratio, divide total cash by total current liabilities.
By examining these ratios, company management can assess the company's ability to meet its short-term demands, adjust pricing and production decisions, increase or decrease the size of the company's inventory and plan accordingly.
Demonstrating Feasibility Ratios
Feasibility ratios are an important part of a business plan, as they provide an accurate assessment of the potential financial stability of a project and its potential for success. By analyzing these ratios, investors and lenders can quickly identify whether or not the project is worth their investment.
Definition of Feasibility Ratios
Feasibility ratios are a type of financial ratio used to analyze the financial stability of a project by assessing the amount of risk it may pose. These ratios measure the project's ability to generate cash, repay debt, and cover its ongoing expenses. They are used to determine if the project is feasible and if it can meet the expected goals and objectives.
Examples of Feasibility Ratios
Some of the most common feasibility ratios include:
- Cash Ratio: This measures the company’s ability to cover its short-term liabilities with cash.
- Debt Coverage Ratio: This ratio is used to identify how much of a company’s cash flow is used to cover its debt obligations.
- Return on Investment Ratio: This ratio measures the profitability of a project by comparing the project’s net profits to the amount of money invested.
Guide on How to Calculate Feasibility Ratios
To calculate these feasibility ratios, you will need to have certain financial documents, like a cash flow statement and balance sheet. You will then use this information to analyze the project’s current financial standing and its potential for success. Here are some tips on calculating feasibility ratios:
- Find the figures that you will need to calculate the ratios, such as cash flow, net income, and debt levels.
- Calculate the cash ratio by dividing the total cash available by the current liabilities. This will tell you how much cash is available to cover the short-term liabilities.
- Calculate the debt coverage ratio by dividing the net income available by the total debt. This will tell you how much of the net income is used to cover debt obligations.
- Calculate the return on investment ratio by subtracting total fixed costs from the net profits available and then dividing the result by the total amount invested. This provides an estimation of the project’s profitability.
Feasibility ratios are a great way to assess the financial viability of a project and its potential for success. By carefully analyzing these ratios, you can come up with an accurate assessment of the project’s feasibility and decide if it is worth investing in.
In this blog post, we discussed the importance of financial ratios in constructing a successful business plan. We discussed the common types of financial ratios and their utility in measuring the financial standing of a business, such as solvency, profitability, and efficiency. Additionally, we discussed the steps to integrating financial ratios into the business planning process, such as collecting the financial documents, being aware of benchmarks, and creating a strategy based on the analysis.
Summary of Information Presented
Financial ratios are analytic tools used to measure the performance of a company and aid in business planning. Common and useful types of financial ratios can include a debt-to-assets ratio (for solvency measurements), a current or operating ratio (for liquidity measurements), or a return on assets ratio (for profitability measurements). To effectively use financial ratios in a business plan, a company must gather financial documents, be aware of industry benchmarks, and use the analytics to create a strategy.
Benefits of Using Financial Ratios in a Business Plan
Using financial ratios can be immensely beneficial for businesses of any size. These measurables tell the story of a business's performance over time and provide owners and managers with data to guide the direction of the business. Additionally, they can help investors assess the risk of a certain business venture while also gauging the profitability of said venture.
What to do Next for Further Guidance on the Topic
For further guidance on using financial ratios in a business plan, we recommend consulting your business advisor or financial adviser. Additionally, we suggest researching accepted benchmarks in your industry and researching top performing companies to glean useful insights from their processes. You can also find useful information on online resources related to business planning and best practices.

$169.00 $99.00 Get Template
Related Blogs
- Private Equity and its Role in Startup Funding
- Increase Collection Efficiency & minimise Financial Impact:Knowing How to Manage Debtors
- Harness The Power of Angel Investing For Optimal Portfolio Diversification
- The Basics of Single Entry Bookkeeping - Start Tracking Your Business' Finances Now!
- Unlock the Power of Annual Contract Value (ACV) for Your Business
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Please note, comments must be approved before they are published

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

- Frequently Asked Questions
- Business Credit Cards
- Talk to Us 1-800-496-1056

How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan
When you are starting a small business or a startup, you will need to make financial projections for your business.
What is Financial Plan in Business Plan?
How to write a business plan financial section, profit and loss statement.
- Cash Flow Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Sales Forecast
- Personnel Plan
Breakeven Analysis and Business Ratios
Frequently asked questions (faqs).
Financial plan in business plan helps understand the chances of your business becoming a financial success. Investors want to see a financial plan to know how much money they’ll invest and what the expected return over investment is for them.
We have briefly discussed the process of writing a financial plan in business plan. One thing that can make or break your financial plan in business plan is your honesty about numbers.
Try not to be over-optimistic. See the growth pattern of similar businesses and project closely to them. Don’t overestimate the effects of your competitive advantage.

Want to write a business plan?
Hire our top business plan writers now!
A financial plan in business plan is an overview of your business financial projections.
Business plan financial projections include financial reports including Profit & Loss, cash flow statement, and balance sheet.
A financial plan will also discuss sales forecast, employees’ salaries and other expenses forecast, business breakeven analysis, and important business rations that help measure growth.
A business plan financial section is about making simple forecasts and creating a few financial reports. You don’t need to know accounting, nor is it necessary for creating financial projections.
We have outlined and simplified the process of creating a financial plan for business plan. Simply follow the process and take help from our examples and templates to write an excellent financial plan section of a business plan.

Review your Business Goals and Strategic Plan
You have set business goals in your business plan. A strategic plan is how you will navigate to financial success.
Everything in a business plan that contributes toward your business goals. Before writing financial projections, consider these goals and milestones:
- Expansion plans
- Adding more people to your team
- Resources required to meet your business goals
- Cash flow needs of your business in the short and long term
- Financing needs to meet business goals
Create Financial Projections
Financial projections in a business plan will include the following:
- Profit and loss statement
Cash Flow Statement
Sales forecast .
- Business Ratios and Breakeven Analysis
We will explore each in detail in the following section. By the end of the article, you will fully understand how to create financial plan in business plan.
A profit and loss statement is the first financial report you will create when writing financial plan in business plan.
A profit and loss statement reports your business income or loss over a certain period of time.
Profit and loss statement is also known by other names including its short form i.e., P & L statement, income statement, and pro forma income statement.
A profit and loss statement includes total revenues, expenses, and costs. A P&L statement is made for different time intervals like quarterly, bi-annual and annual. It shows net income after the cost of goods sold, expenses, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
Before creating a P&L statement for your business, you may need to look for the right format for your business structure. For example, you will need a different format for a profit and loss statement for a sole proprietorship and a different one for an LLC.
Check income statement examples to understand and create one yourself.
Profit and Loss Statement Template
Download our free profit and loss statement templates & examples, and make a professional income statement for financial plan in business plan.
Parts of a Profit and Loss Statement
Every profit and loss statement includes the following elements:
- Total Revenues
- Cost of Sales or Cost of Goods Sold
- Gross Margin
Depending on the business type, a P&L statement may include insurance, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Make sure to include a forecast for all heads in financial plan in business plan.
Calculate Operating Income
Start your profit and loss statement by calculating operating income; use this formula.
Gross Margin – Operating Expenses = Operating Income
Typically, operating income is equal to EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization).
Operating income is also called the gross profit and it does not deduce taxes or other accounting adjustments from the income.
Calculate Net Income
Use this formula to calculate net income.
Operating Income – (Interest + Taxes + Depreciation + Amortization Expenses) = Net Income
Access our free sample business plans now!
A cash flow statement is typically prepared every month. You can create monthly and quarterly cash flow statement in financial plan in business plan.
A cash flow statement informs about the cash your business brought income, the cash it paid out, and how much is still available with the bank.
A cash flow statement gives an understanding of your income sources and expenses. When you forecast your financial reports, a cash flow statement will show your expected income sources and expenses.
A cash flow statement will help potential lenders and investors understand how you plan to make money. It provides reliable data about cash in and cash out. Keep it realistic and in line with the industry number for the most part. An exception may be an innovation or a breakthrough you bring to the market.
Your profit and cash flow are not the same. It is possible to have a cashless, profitable business or a business in loss with plenty of cash. A good cash flow helps you keep your business open and turn things around.
A cash flow statement also reflects your behavior with money. It shows if you spend on spur of the moment or think strategically. When creating a cash flow statement in a business plan, you will need to understand two basic concepts of accounting; cash accounting and accrual accounting.
Professional Business Templates for Small Businesses
Check our extensive library of business templates for small businesses and make use of the templates and examples in writing your business plan.
Difference between Cash and Accrual Accounting
The difference between cash and accrual accounting is Accrual accounting records revenues/income and expenses when they occur while cash accounting records income/revenue and expenses when the money actually changes hands.
You will need to decide if you will use cash accounting or accrual accounting. However, the final choice will depend on your business type and product.
For example, you are selling tickets to a show or you are taking preorders for your new product. Under cash accounting, you will record all income now and expenses when you have actually shipped the product or organized the show.
However, with accrual accounting, you will record both income and expenses when you have shipped the product or held the show.
Here, cash accounting will show the months with cash abundance as profitable and the months of spending, like shipping of the products of event organization, as a loss. It is hard to see a pattern and get actionable insight with cash accounting.
It is a good time to decide about the accounting method you will use when you are writing a financial plan in business plan.
Check with your accounting consultant and discuss accrual and cash accounting to select the one most suitable for your business.
Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is a summary of the financial position of your business.
A balance sheet includes assets, liabilities, and equity. A balance sheet is based on this formula and it is always equal on both sides of the equation.
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Here, Assets include your inventory, cash at hand and bank, property, vehicles, accounts receivables, etc. Liabilities are debts, loans and account payables. Equity includes shares proceeds, retained earnings, and owner’s money.
Download Balance Sheet Template from WiseBusinessPlan and make a balance sheet easy.
A sales forecast is your projection about the sales you will make in a certain time. Investors and lenders will be interested in seeing your sales forecast. They will estimate your chances of meeting the forecast and projections.
Keep your sales forecast consistent with the financial reports like the cash flow statement and profit & loss statement.
How To Make A Sales Forecast For A Business Plan?
First, decide the period for the sales forecast, like one month or a quarter. Then, do the following steps to make a sales forecast for that period.
- List goods or services your business sells
- Forecast sales for each product or service
- Set per unit price for your goods or services
- Find sales volume by multiplying units sold with unit price
- Calculate the cost of goods sold
- Multiply the cost of goods sold by the number of units sold, this is your total cost
- Take the total cost amount from the total sales amount
Need Business Plan Cover Page?
Download our business plan cover page now!
Personnel Plan
A personnel plan shows the costs and value of the employees you will hire.
Very small businesses, startups, or solopreneurs may not need a personnel plan but any business with employees, or plans to hire employees, will need this.
Forecast the cost of each employee and the value they will provide. You don’t need to discuss everything about employees, just do a short cost-benefit analysis for each position or employee.
Breakeven analysis tells you the number of sales you need to bring in to cover all of your business expenses.
Use this formula to calculate the breakeven point for your business.
Break-Even Point (units) = Fixed Costs / (Sales price per unit – Variable costs per unit)
Business ratios are like signals for your business. You can quickly spot a growth or fall with a ratio. Some business ratios also help you see business health.
You are not required to include business ratio forecasts however, it is good to know about them when writing a business plan.
Here are some of the most used business ratios.
- Gross margin
- Return on sales
- Return on assets
- Return on investment
- Debt-to-equity
- Current ratio
- Working capital
- gross margin
- return on investment (ROI)
- Debt-to-equity.
Use Financial Plan as a Tool for Business Management
One mistake that most people make is thinking that building a business plan is a one time thing.
Your business plan and your financial projections can help you measure your business growth. You can use these numbers as a yard stick to see if you are meeting your projections or not.
Here is how you can your business plan as a management tool for your business.
Schedule monthly and quarterly business review meetings. Compare your actual data for that period with your forecast data and see how you are moving towards your business goals. Adjust your forecast or projections with the help of actual data to keep your growth trajectory in the right direction.
Hire our professional who can help write a business plan !
The financial section of a business plan should include key financial statements such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. It should also provide details on projected sales, expenses, and profitability, along with any assumptions or financial ratios used.
Forecasting sales and revenue involves analyzing market research, understanding your target audience, and considering factors such as pricing, competition, and marketing strategies. Utilize historical data, industry benchmarks, and realistic growth assumptions to estimate future sales figures.
In addition to sales and revenue projections, the financial section should include projected expenses, such as operational costs, marketing expenses, and overheads. It should also outline anticipated profits, cash flow projections, and return on investment (ROI) calculations.
Yes, including a break-even analysis is important as it helps determine the point at which your business will start generating profits. It identifies the sales volume needed to cover all expenses and provides insights into the viability of your business.
Supporting documents may include historical financial statements, tax returns, cash flow statements, balance sheets, and any other relevant financial records. Additionally, include details about any loans, investments, or funding sources that contribute to the financial projections.
Loving the information on this web site, you have done great job on the content.
I thought of the same thing before reading this blog that a business plan is a one-time thing but now I know that a business plan and financial projections can really help you measure business growth. Let me just change my stance from now onward.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
7 Financial Forecasting Methods to Predict Business Performance

- 21 Jun 2022
Much of accounting involves evaluating past performance. Financial results demonstrate business success to both shareholders and the public. Planning and preparing for the future, however, is just as important.
Shareholders must be reassured that a business has been, and will continue to be, successful. This requires financial forecasting.
Here's an overview of how to use pro forma statements to conduct financial forecasting, along with seven methods you can leverage to predict a business's future performance.
What Is Financial Forecasting?
Financial forecasting is predicting a company’s financial future by examining historical performance data, such as revenue, cash flow, expenses, or sales. This involves guesswork and assumptions, as many unforeseen factors can influence business performance.
Financial forecasting is important because it informs business decision-making regarding hiring, budgeting, predicting revenue, and strategic planning . It also helps you maintain a forward-focused mindset.
Each financial forecast plays a major role in determining how much attention is given to individual expense items. For example, if you forecast high-level trends for general planning purposes, you can rely more on broad assumptions than specific details. However, if your forecast is concerned with a business’s future, such as a pending merger or acquisition, it's important to be thorough and detailed.
Access your free e-book today.
Forecasting with Pro Forma Statements
A common type of forecasting in financial accounting involves using pro forma statements . Pro forma statements focus on a business's future reports, which are highly dependent on assumptions made during preparation, such as expected market conditions.
Because the term "pro forma" refers to projections or forecasts, pro forma statements apply to any financial document, including:
- Income statements
- Balance sheets
- Cash flow statements
These statements serve both internal and external purposes. Internally, you can use them for strategic planning. Identifying future revenues and expenses can greatly impact business decisions related to hiring and budgeting. Pro forma statements can also inform endeavors by creating multiple statements and interchanging variables to conduct side-by-side comparisons of potential outcomes.
Externally, pro forma statements can demonstrate the risk of investing in a business. While this is an effective form of forecasting, investors should know that pro forma statements don't typically comply with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) . This is because pro forma statements don't include one-time expenses—such as equipment purchases or company relocations—which allows for greater accuracy because those expenses don't reflect a company’s ongoing operations.
7 Financial Forecasting Methods
Pro forma statements are incredibly valuable when forecasting revenue, expenses, and sales. These findings are often further supported by one of seven financial forecasting methods that determine future income and growth rates.
There are two primary categories of forecasting: quantitative and qualitative.
Quantitative Methods
When producing accurate forecasts, business leaders typically turn to quantitative forecasts , or assumptions about the future based on historical data.
1. Percent of Sales
Internal pro forma statements are often created using percent of sales forecasting . This method calculates future metrics of financial line items as a percentage of sales. For example, the cost of goods sold is likely to increase proportionally with sales; therefore, it’s logical to apply the same growth rate estimate to each.
To forecast the percent of sales, examine the percentage of each account’s historical profits related to sales. To calculate this, divide each account by its sales, assuming the numbers will remain steady. For example, if the cost of goods sold has historically been 30 percent of sales, assume that trend will continue.
2. Straight Line
The straight-line method assumes a company's historical growth rate will remain constant. Forecasting future revenue involves multiplying a company’s previous year's revenue by its growth rate. For example, if the previous year's growth rate was 12 percent, straight-line forecasting assumes it'll continue to grow by 12 percent next year.
Although straight-line forecasting is an excellent starting point, it doesn't account for market fluctuations or supply chain issues.
3. Moving Average
Moving average involves taking the average—or weighted average—of previous periods to forecast the future. This method involves more closely examining a business’s high or low demands, so it’s often beneficial for short-term forecasting. For example, you can use it to forecast next month’s sales by averaging the previous quarter.
Moving average forecasting can help estimate several metrics. While it’s most commonly applied to future stock prices, it’s also used to estimate future revenue.
To calculate a moving average, use the following formula:
A1 + A2 + A3 … / N
Formula breakdown:
A = Average for a period
N = Total number of periods
Using weighted averages to emphasize recent periods can increase the accuracy of moving average forecasts.
4. Simple Linear Regression
Simple linear regression forecasts metrics based on a relationship between two variables: dependent and independent. The dependent variable represents the forecasted amount, while the independent variable is the factor that influences the dependent variable.
The equation for simple linear regression is:
Y = Dependent variable (the forecasted number)
B = Regression line's slope
X = Independent variable
A = Y-intercept
5. Multiple Linear Regression
If two or more variables directly impact a company's performance, business leaders might turn to multiple linear regression . This allows for a more accurate forecast, as it accounts for several variables that ultimately influence performance.
To forecast using multiple linear regression, a linear relationship must exist between the dependent and independent variables. Additionally, the independent variables can’t be so closely correlated that it’s impossible to tell which impacts the dependent variable.

Qualitative Methods
When it comes to forecasting, numbers don't always tell the whole story. There are additional factors that influence performance and can't be quantified. Qualitative forecasting relies on experts’ knowledge and experience to predict performance rather than historical numerical data.
These forecasting methods are often called into question, as they're more subjective than quantitative methods. Yet, they can provide valuable insight into forecasts and account for factors that can’t be predicted using historical data.
6. Delphi Method
The Delphi method of forecasting involves consulting experts who analyze market conditions to predict a company's performance.
A facilitator reaches out to those experts with questionnaires, requesting forecasts of business performance based on their experience and knowledge. The facilitator then compiles their analyses and sends them to other experts for comments. The goal is to continue circulating them until a consensus is reached.
7. Market Research
Market research is essential for organizational planning. It helps business leaders obtain a holistic market view based on competition, fluctuating conditions, and consumer patterns. It’s also critical for startups when historical data isn’t available. New businesses can benefit from financial forecasting because it’s essential for recruiting investors and budgeting during the first few months of operation.
When conducting market research, begin with a hypothesis and determine what methods are needed. Sending out consumer surveys is an excellent way to better understand consumer behavior when you don’t have numerical data to inform decisions.

Improve Your Forecasting Skills
Financial forecasting is never a guarantee, but it’s critical for decision-making. Regardless of your business’s industry or stage, it’s important to maintain a forward-thinking mindset—learning from past patterns is an excellent way to plan for the future.
If you’re interested in further exploring financial forecasting and its role in business, consider taking an online course, such as Financial Accounting , to discover how to use it alongside other financial tools to shape your business.
Do you want to take your financial accounting skills to the next level? Consider enrolling in Financial Accounting —one of three courses comprising our Credential of Readiness (CORe) program —to learn how to use financial principles to inform business decisions. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author
- Entrepreneurship

How to Calculate Financials for Business Plan?
Creating a business plan is essential for any entrepreneur who wants to start a new business venture. A business plan outlines the business’s objectives and strategies, including the financial projections, which play a vital role in the success of the business. Financial projections help entrepreneurs to understand how much money they need to start and run their business, how much they can expect to earn, and how long it will take to break even. In this article, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to calculate financials for a business plan.
1. Calculate Start-up Costs
The first step in calculating financials for a business plan is to determine the start-up costs. Start-up costs refer to the expenses that an entrepreneur will incur before the business starts generating revenue. These costs may include market research, legal fees, equipment, office rent, and other expenses. Once you have identified all the start-up costs, you can add them up to determine the total start-up cost.
The start-up cost will give you an idea of how much money you need to start your business. It will also help you determine how much you need to borrow if you plan to secure funding from investors or lenders.
2. Estimate Monthly Operating Expenses
After determining the start-up costs, the next step is to estimate the monthly operating expenses. These expenses include rent, utilities, salaries, marketing, and other costs associated with running the business. It is essential to be as accurate as possible when estimating these expenses to avoid underestimating or overestimating the monthly operating costs.
Once you have estimated the monthly operating expenses, you can multiply them by the number of months in your financial projection to determine the total operating expenses for the period.
3. Project Revenue
The next step in calculating financials for a business plan is to project revenue. Revenue refers to the money the business will earn from the sale of products or services. To project revenue, you need to estimate the number of units that you will sell and the price per unit.
It is crucial to be realistic when projecting revenue. You can use market research to determine the demand for your product or service and how much customers are willing to pay for it.
4. Calculate Gross Profit
After projecting revenue, the next step is to calculate gross profit. Gross profit refers to the money left over after deducting the cost of goods sold from the revenue. Cost of goods sold includes the direct costs associated with producing the product or service, such as materials, labor, and overhead costs.
To calculate gross profit, you can subtract the cost of goods sold from the projected revenue.
5. Determine Net Income
Once you have calculated the gross profit, the next step is to determine the net income. Net income refers to the profit after deducting all the expenses, including operating expenses, taxes, and interest.
To calculate net income, you can subtract the total expenses from the gross profit.
6. Create Cash Flow Statement
Creating a cash flow statement is essential to understanding the cash flow of the business. A cash flow statement shows the inflow and outflow of cash in the business over a period. It helps entrepreneurs to determine how much cash they need to keep the business running and when they will need it.
A cash flow statement includes three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities.
7. Calculate Break-Even Point
Calculating the break-even point is essential for entrepreneurs to understand when the business will start making a profit. The break-even point is the point at which the revenue equals the total expenses. To calculate the break-even point, you need to divide the total fixed costs by the contribution margin.
The contribution margin is the difference between the price of the product or service and the variable costs associated with producing it.
8. Analyze Financial Ratios
Analyzing financial ratios is essential to understand the financial health of the business. Financial ratios help entrepreneurs to compare their business’s performance with other businesses in the same industry.
Some of the critical financial ratios include liquidity ratios, profitability ratios, and debt ratios.
9. Benefits of Calculating Financials
Calculating financials for a business plan has several benefits. It helps entrepreneurs to understand how much money they need to start and run their business. It also helps them to determine the profitability of the business and when they can expect to break even.
Financial projections also help entrepreneurs to secure funding from investors or lenders. Investors and lenders want to see a well-thought-out financial projection before investing in a business.
10. Conclusion: Calculating Financials for Business Plan
Calculating financials for a business plan is essential for entrepreneurs who want to start a new business venture. Financial projections help entrepreneurs to understand the financial health of the business and how much money they need to start and run the business.
By following the steps outlined in this article, entrepreneurs can create a well-thought-out financial projection that will help them secure funding from investors or lenders and make informed business decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are the financial statements required for a business plan.
Financial statements required for a business plan include the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. The income statement outlines the revenues and expenses of the business, while the balance sheet shows the assets, liabilities, and equity. The cash flow statement shows the cash inflows and outflows of the business.
These financial statements help potential investors and lenders understand the financial health of the business and make informed decisions about investing or lending money.
How do I calculate revenue projections for my business plan?
To calculate revenue projections for your business plan, start by estimating the number of units or services you expect to sell. Then, determine the price per unit or service and multiply that by the estimated number of sales. Be sure to consider any factors that may impact sales, such as seasonality or competition.
It’s important to be realistic in your revenue projections and to base them on market research and industry benchmarks. Investors and lenders will be looking for realistic and achievable revenue projections in your business plan.
How do I calculate my business’ break-even point?
The break-even point is the point at which your business’s total revenue equals its total expenses. To calculate the break-even point, you need to know your fixed costs, variable costs, and the price per unit or service.
Once you have these numbers, you can use a break-even formula to calculate the number of units or services you need to sell to break even. This information can help you make informed decisions about pricing and sales strategies.
What is a cash flow statement, and how do I create one?
A cash flow statement shows the cash inflows and outflows of your business over a specific period. It helps you understand how much cash your business has on hand and how it is being used. To create a cash flow statement, you’ll need to start with the beginning cash balance, add cash inflows, subtract cash outflows, and end with the ending cash balance.
It’s important to keep accurate records of all cash transactions in your business to create an accurate cash flow statement. This information is important for investors and lenders who want to understand how your business uses cash.
What is the difference between net income and cash flow?
Net income is the profit your business makes after all expenses have been deducted from revenue. Cash flow, on the other hand, is the amount of cash that is coming in and going out of your business.
While net income is important, cash flow is critical to the success of your business. Your business needs cash to pay bills, invest in growth, and survive unexpected challenges. It’s important to carefully manage your cash flow and plan for contingencies to ensure the long-term success of your business.
In conclusion, mastering the art of calculating financials for a business plan is crucial for the success of any business venture. It involves a thorough understanding of the different financial statements, such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement, and how they interrelate. By accurately forecasting revenues, expenses, and profits, you can make informed decisions that will drive your business forward.
However, it’s important to note that financial projections are just that: projections. They are based on assumptions and estimates, and the actual results may vary. Therefore, it’s essential to regularly monitor and adjust your financials as needed to stay on track and achieve your business goals.
In the end, the key to successful financial planning is to take the time to do it right. Don’t rush through the process or cut corners. Instead, invest the time and effort to develop a solid financial plan that will serve as a roadmap for your business’s success. With the right financials in place, you can confidently move forward, knowing that you have a clear understanding of your business’s financial health and a plan for achieving your goals.
RELATED ARTICLES
Cash flow budgeting: allocating funds and prioritizing expenses, 7 tools and software for financial modeling and analysis, what is the role of inventory management in working capital management, what is a project budget, how much of my budget for business should be advertising, performance management vs employee development: what generator fuel is best in 2023, what is free cash flow in a business, can employers refuse to hire smokers, how can transposition errors impact cash flow at your business, how important is marketing for small business, 10 benefits of investing in money market instruments for businesses, 10 common business goals and how to set them, 10 common financial risks faced by businesses and how to manage them, 10 common types of bonds for business financing and investments, 10 customer retention techniques to foster long-term loyalty, how can trust be gained between the business and development, software startup ideas, the dummies guide to starting your own business, how to find new businesses before they open, what must an entrepreneur assume when starting a business, editor’s choice, how a business works cash flow, what is the success rate from research to market, how much does a product developer make, how effective communication in business motivates employees and customers, how can i create a compelling elevator pitch for my business, stay in touch.
To be updated with all the latest news, offers and special announcements.
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use

Search Product category Any value Sample Label 1 Sample Label 2 Sample Label 3
How To Build A Financial Model For a Bar
- January 3, 2023
- Food & Beverage

Every business needs a financial model. Whether you want to understand what’s your breakeven , your valuation or create a budget for your bar business plan, you’ve come the right way.
In this article we’ll explain you how to create powerful and accurate financial projections for a typical 80 seats bar.
1. Forecast Customers
The first thing you must do to create a financial model for your bar is to forecast the number of customers you will serve over time.
Forecasting customers can be done as follows. You must set the number of:
- Customers you expect to serve on average on a weekday
- Customers on a weekend day instead
- Days you are open in a week on average (for example 3 weekdays and 2 weekend days if you are open Wednesday to Sunday)
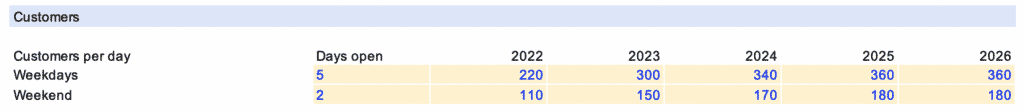
That way, you will be able to forecast accurately the number of customers you can serve over time, and so the revenues which we will now see.
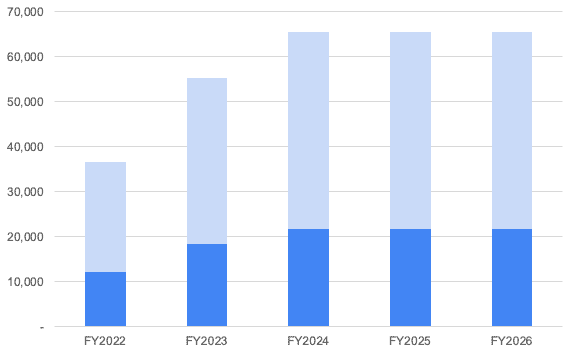
2. Forecast Revenue
Now that we have the number of customers, we can calculate revenue easily.
Yet, before we do so, we must break down the number of customers into the different products they may buy. Indeed, most of you customers may buy a beer at an average price of $5.50, yet some may instead buy pricier products such as cocktails for a average price of $11.00, etc.
It’s very important to break it down right. Indeed, as you know all these products have very different unit economics (prices and profit margins) you need to forecast accurately. Let’s see now how.
First, break down the products into a percentage of your total customers. For example:
- 35% of the customers may choose to buy a beer at an average price of $5.50;
- another 20% buy cocktails to go at an average price of $11.011
- 15% buy a wine glass for $6.50, and so on..
That way, you can now multiply the number of customers for each product by their respective price to obtain revenue.
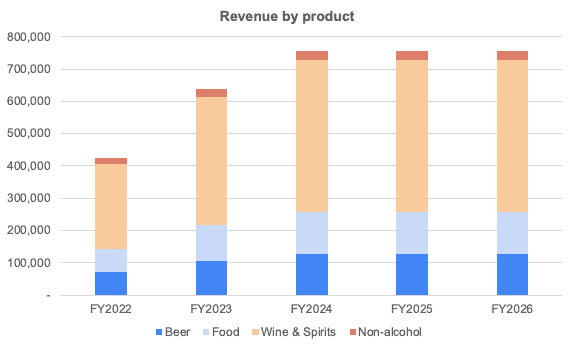
3. Forecast Expenses
In addition to the one-off startup costs discussed here , you must also budget for all the operating costs of running a bar.
We have laid out below the key expenses you can expect as well as their amount. Please note that these costs are for illustrative purposes, correspond to a hypothetical 80-seats bar and depend on a number of factors which may not be fully relevant to you.
Bar Financial Model
Download an expert-built 5-year Excel financial model for your business plan
Let’s break down the key costs incurred by all bar businesses below:
Unless you own the space, you need to pay rent to the landlord. The rent price depends on the property’s location, size, and condition.
Assuming an average $40 per square foot per year in a premium location of a city like Portland , you would be paying $4,600 approximately per month in rent for a 1,400 square foot space.
You need staff to keep your bar operational. The day-to-day tasks include greeting customers, creating a welcoming atmosphere, taking orders and payments from patrons, handling cash, serving drinks and meals at the table, and other essential operations.
The number of staff depends on the size of your bar and what you plan to sell. The average annual gross salary for a bartender is around $28,000 . Assuming you only offer drinks and need 3 full time bartenders, the total monthly cost can go up to $7,000 per month, excluding the manager (add another $3,000 if full time).
Inventory (COGS)
One of the most important expense for bars is inventory itself: alcohol and any other consumable used in the drinks (and potentially food) you serve. Expect to pay on average 18% to 24% in your revenues in COGS.
Assuming an average monthly revenue of $27,500 , you will have to incur approximately $5,500 in COGS each month.
Utility Bills
You have to keep water, lights, gas, and music in a bar. Therefore, you have to budget for the utility bills appropriately. You can expect to pay approximately $2,500 per month on utility bills , depending on the size of your bar.
Admin & other
In addition to the expenses above, you will have to incur expenses for support and administrative tasks such as bookkeeping and human resources (payroll).
As a reference point, accountants will likely cost anywhere from $1,000 to $2,000 per month in fees (as you will likely have a lot of small receipts to deal with, which takes more time to process).

4. Build your P&L And Cash flow
Once we have forecasted revenues and expenses, we can easily build the profit-and-loss (P&L) from revenues down to net profit . This will help you to visualise key financial metrics such as Gross Profit or EBITDA margin as shown below:
The cash flow statement, in comparison, needs to include all cash items from the P&L and other cash movements such as capital investments (also referred as “Capex”), fundraising, debt, etc.
Cash flow is vital as it will help you understand how much funding you should get, either from investors or the bank (SBA loan for example) to start and run your own bar.

Privacy Overview
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- March Madness
- AP Top 25 Poll
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
What to know about the SAVE plan, the income-driven plan to repay student loans
FILE - Wheaton College students stop to chat on the Norton, Mass. campus, Feb. 13, 2024 as snow falls. More than 75 million student loan borrowers have enrolled in the U.S. government’s newest repayment plan since it launched in August. (Mark Stockwell/The Sun Chronicle via AP, File)
- Copy Link copied
NEW YORK (AP) — More than 7.5 million student loan borrowers have enrolled in the U.S. government’s newest repayment plan since it launched in August.
President Joe Biden recently announced that he was canceling federal student loans for nearly 153,000 borrowers enrolled in the plan, known as the SAVE plan . Forgiveness was granted to borrowers who had made payments for at least 10 years and originally borrowed $12,000 or less.
The SAVE plan was created last year to replace other existing income-based repayment plans offered by the federal government. More borrowers are now eligible to have their monthly payments reduced to $0, and many will qualify for lower payments compared to other repayment plans.
For Lauran Michael and her husband, the SAVE plan has reduced student loan payments by half.
Since getting married, they’ve both been paying off her husband’s student loans, which would have amounted to about $1,000 a month when payments resumed after a pause during the pandemic. Under the SAVE plan, their payments are now $530 a month.
“We don’t want our loans dictating our life choices, and us not being able to do other things because we’re paying so much money. The SAVE plan is definitely a game changer for us,” said Michael, a 34-year-old interior designer in Raleigh, North Carolina.
Michael’s family is paying for daycare for their two children using the money they saved from not making payments during the pandemic and the reduced payments under the SAVE plan.
If you are interested in applying for the SAVE plan, here’s what you need to know:
WHAT IS AN INCOME-DRIVEN REPAYMENT PLAN?
The U.S. Education Department offers several plans for repaying federal student loans. Under the standard plan, borrowers are charged a fixed monthly amount that ensures all their debt will be repaid after 10 years. But if borrowers have difficulty paying that amount, they can enroll in one of several plans that offer lower monthly payments based on income and family size. Those are known as income-driven repayment plans.
Income-driven options have been offered for years and generally cap monthly payments at 10% of a borrower’s discretionary income. If a borrower’s earnings are low enough, their bill is reduced to $0. And after 20 or 25 years, any remaining debt gets erased.
HOW IS THE SAVE PLAN DIFFERENT?
More borrowers in the SAVE plan are eligible for $0 payments. This plan won’t require borrowers to make payments if they earn less than 225% of the federal poverty line — $32,800 a year for a single person. The cutoff for other plans, by contrast, is 150% of the poverty line, or $22,000 a year for a single person.
Also, the SAVE plan prevents interest from piling up. As long as borrowers make their monthly payments, their overall balance won’t increase. Once they cover their adjusted monthly payment — even if it’s $0 — any remaining interest is waived.
Other major changes will take effect in July 2024. Payments on undergraduate loans will be capped at 5% of discretionary income, down from 10% now. Those with graduate and undergraduate loans will pay between 5% and 10%, depending on their original loan balance.
The maximum repayment period is capped at 20 years for those with only undergraduate loans and 25 years for those with any graduate school loans.
WHO QUALIFIES FOR THE SAVE PLAN?
The SAVE plan is available to all student loan borrowers in the Direct Loan Program who are in good standing on their loans.
Read more about the SAVE plan here .
HOW DO I APPLY FOR THE SAVE PLAN?
Borrowers can apply to the SAVE plan using the Income-Driven Repayment Plan request through the Education Department’s website.
HOW WILL I KNOW THAT MY DEBT HAS BEEN CANCELED?
If you are one of the borrowers who is benefitting from forgiveness under the SAVE plan, you will receive an email from the Education Department.
WHAT ARE OTHER PROGRAMS THAT CAN HELP WITH STUDENT LOAN DEBT?
If you’ve worked for a government agency or a nonprofit , the Public Service Loan Forgiveness program offers cancellation after 10 years of regular payments, and some income-driven repayment plans cancel the remainder of a borrower’s debt after 20 to 25 years.
Borrowers should make sure they’re signed up for the best possible income-driven repayment plan to qualify for these programs.
Borrowers who have been defrauded by for-profit colleges may also apply for relief through a program known as Borrower Defense.
If you’d like to repay your federal student loans under an income-driven plan, the first step is to fill out an application through the Federal Student Aid website .
WILL THERE BE FUTURE FORGIVENESS?
Several categories of borrowers would be eligible for relief under Biden’s second try at widespread cancellation after the Supreme Court rejected his first plan last year.
The proposed plan includes relief for borrowers who have been paying their loans for at least 20 or 25 years, automatic forgiveness for borrowers who are eligible for income-driven repayment plans but are not enrolled, and loan cancellation for borrowers who attended a for-profit college that left them unable to pay their student loans, among others.
Whether any of the relief will materialize is a looming question as conservatives vow to challenge any attempt at mass student loan cancellation. The new proposal is narrower, focusing on several categories of borrowers who could get some or all of their loans canceled, but legal challenge is almost certain.
Currently, borrowers who are eligible for forgiveness under the SAVE program will get their loans discharged on a rolling basis, according to the Education Department.
This story was first published on March 10, 2024. It was updated on March 18, 2024, to correct the number of borrowers who have enrolled in the government’s newest repayment plan.
The Associated Press receives support from Charles Schwab Foundation for educational and explanatory reporting to improve financial literacy. The independent foundation is separate from Charles Schwab and Co. Inc. The AP is solely responsible for its journalism.

- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
As Car Incentives Return, Here’s How to Find Them and Save Money

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
Car incentives nearly vanished during the past several years, thanks to pandemic-driven supply chain issues for auto manufacturers. As vehicle inventories dwindled and consumer demand outweighed supply, automakers had no reason to offer incentives like rebates or low-rate financing. The good news is that auto incentives, while still below prepandemic levels, are starting to return.
According to Kelley Blue Book, a Cox Automotive company, auto incentives — as a percentage of the average new-vehicle price buyers paid — reached 5.9% in February 2024. That’s compared with a general range of 10% to 11% before COVID-19 hit and 2% in fall 2022. In February, auto manufacturers spent an average of $2,808 per vehicle in incentives, up 88% from a year ago.
With inventories returning to normal and some auto manufacturers again sweetening deals to move vehicles, here’s how you can find and possibly save with car incentives.
Tips for saving with auto incentives
Although new car prices have declined since peaking in late 2022, the average price a buyer pays remains around $47,000. Incentives are one way to whittle down that price tag, and certain strategies can help maximize savings.
Be flexible about the vehicle you buy
Traditionally, auto dealers strive to have 60 selling days' worth of cars in stock. As auto production has returned, some manufacturers — like Toyota — remain well below the 60-day mark, while others — including Ford, Nissan and Buick — are overstocked and more likely to offer incentives and discounts to move cars.
"The key right now is to be flexible about which vehicle you consider," says Sean Tucker, senior editor for data company Cox Automotive. "If you had your heart set on something from Toyota, you're probably not going to find a great deal. They just don't have trouble selling cars right now."
Auto manufacturer websites are a good place to research auto deals and incentives — including cash rebates, low-rate financing and lease deals — that are available for various makes and models. Such incentives often vary regionally, so you can usually narrow a search by ZIP code. Also, auto research companies like Edmunds maintain webpages with current car deals and incentives by carmaker.
Tucker suggests that incentives for leasing and electric vehicles are both good sources for saving in the current market. Auto dealerships are trying to restore the leasing cycle that feeds the used car market, so many dealerships are offering lease deals.
"It's actually relatively easy right now to get a good lease on an EV," Tucker says. "And that might even be a good idea just from a technology standpoint, because three years from now, when your lease is likely coming up, there may be far better EVs on the market."
Know what incentives you qualify for
To ensure you receive every incentive available to you, know exactly which incentives you qualify for before engaging with a car dealer. Joseph Yoon, consumer insights analyst at Edmunds, recommends telling the dealer upfront what you expect in the way of incentives.
"The dealer is not going to offer it to you unless they’re deeply desperate to get the deal done," Yoon says.
As part of your research, be aware of the different types of incentives available, because in some cases they can be combined.
Auto rebates provide a certain dollar amount to reduce your overall cost of buying, financing or leasing a vehicle. The rebate reduction should be on top of any other discount you’ve negotiated.
Low-rate financing is an incentive offered by automaker captive lenders — although you’ll need to have good or excellent credit to qualify and may be limited on loan length. As of March 5, 2024, Cox Automotive reported that 14.2% of new vehicle financing transactions had an APR of 3% or less. Only 3.2% of transactions had a 0% APR. While low-rate offers are available, they aren’t plentiful.
Loyalty incentives may be available if you have a certain car brand and want to buy or lease another one from the same manufacturer.
Demographic-focused incentives — for example, if you’re a recent college graduate, military member or educator — are also offered by some auto manufacturers and dealers.
Stacking more than one incentive, when possible, can help you take advantage of every dollar available to you. If you have to choose between multiple incentives, for example, either a rebate or low rate from the same manufacturer, use an auto loan calculator to run each scenario and see which will save you the most money in the long run. Also, consider whether taking a cash rebate at the dealer and financing elsewhere could save you even more.
When you buy or lease an EV, stacking manufacturer and other incentives can result in major savings. If you and the vehicle qualify, you can claim the federal EV tax credit of up to $7,500. On top of that, you may find EV incentives from your electric company or state and local governments. The Energy Department's Alternative Fuels Data Center enables users to search and filter by state and utility/private incentives.
About EVs, Yoon says auto manufacturers and dealers are motivated right now to offer savings on top of the federal incentive, because “there's still a little bit of inventory left from 2023 that they really, really, really want to get rid of as the 2024 models [are starting to] hit.”
Plan to negotiate and comparison shop
If you know you qualify for a $1,500 car rebate, don’t assume that’s the best you can do — even if the dealer tells you it is. The ability to negotiate car prices for some models has also reappeared, and incentives should be in addition to any amount you negotiate off the manufacturer’s suggested retail price. You can use valuation tools on car-buying sites to see what people are paying for the car you want and whether negotiating a lower price is realistic.
Finally, if you can find more than one dealership with the vehicle you want, present the deal you expect to each and let them compete for your business. Dealers receive factory-to-dealer discounts to help move certain vehicles, usually slower-selling ones. They can choose whether to pass these savings on to you and may be more motivated to do so if they know you’re shopping for the same car elsewhere.
Yoon says if a dealership isn’t willing to “play ball,” you shouldn’t hesitate to walk away. “Cars cost literally more than they have ever cost the consumer, and so you should, rightfully so, fight for every dollar that you can save.”
On a similar note...
Find your next new or used car with ease
Compare prices, models, and more from over 1,000,000 cars nationwide. Shop and compare before visiting the dealer, and get a trade-in offer for your current car in minutes.

Vehicle imagery licensed by EVOX

Types of mortgage rate buydowns
How mortgage rate buydowns work, benefits of mortgage rate buydowns, considerations before opting for a buydown, how to get a mortgage rate buydown, understanding mortgage rate buydowns.
Affiliate links for the products on this page are from partners that compensate us (see our advertiser disclosure with our list of partners for more details). However, our opinions are our own. See how we rate mortgages to write unbiased product reviews.
- In an interest rate buydown, the seller pays mortgage points on the buyer's mortgage, lowering the interest rate.
- Permanent buydowns are more beneficial than price reductions for the buyer and the seller.
- Also called seller buydowns, they're better for buyers who plan on living in the same house for a long time.
Higher mortgage rates and home prices can prohibit many consumers from getting a mortgage and buying a house.
An interest rate buydown, though, could help. These allow buyers or other involved parties — like the lender or seller — to pay for a lower interest rate. This can reduce the amount of interest the buyer pays, both monthly and over the long haul, considerably.
An interest rate buydown is where one party — the buyer, lender, or seller — agrees to pay an upfront fee to lower the buyer's interest rate.
Temporary vs. permanent buydowns
Buydowns can be permanent for the life of the loan or temporary, lasting only the first few years.
The choice between temporary vs. permanent rate buydown options depends on your budget, what the lender or seller is offering, the market, and other factors, but in recent years, buydowns are more often temporary, offering a short reprieve from high interest rates.
Many people opt for a 2-1 buydown. This lowers interest by two points during the first year and one point during the second year. After that, interest returns to the original rate.
"Homebuyers can have a lower payment for two years and ideally be able to refinance right as rates are coming down in the future," says Steve Hill, lead mortgage broker for SBC Lending .
Point-based buydowns
Permanent buydowns are typically done by buyers, agreeing to pay their mortgage lender money upfront in exchange for a lower rate.
This practice is often referred to as buying mortgage points, as you'll pay one "point" and, in return, get an incrementally lower interest rate. The more points you buy, the lower your rate goes. (Though lenders may put a cap on how many points you can purchase).
How mortgage buydowns work depend on the type you're using. See below for details on buyer-paid buydowns and those paid for by other parties.
The process of buying down a rate
If you're buying down your rate yourself, you'll buy mortgage points. Each point costs 1% of the loan amount and usually lowers the interest rate by about 0.25%. You'll hand these fees over along with your down payment at the closing table.
Other parties can purchase buydowns, too. When a seller or lender does it, the buydown is reflected in the closing costs as "seller credits" or "lender credits." These are usually a tool used to secure a buyer in a competitive market. In lieu of taking a lower offer or making other concessions, a seller can offer a buydown, which will lower the buyer's monthly mortgage payment — either temporarily or permanently — making the purchase more attractive.
Calculating the cost and savings
If a lender or seller offers you a buydown, that's a win-win, even if it's temporary (as long as you can handle the higher payment later on).
If you hope to buy points yourself, though, you'll need to do some math. Specifically, you'll want to calculate the breakeven point — which is the point at which you'll break even on the costs of the buydown. We'll go into this math more later on.
The benefits of buying down a mortgage rate primarily pertain to affordability.
Lower monthly payments
First, lower rates mean buyers get a lower monthly payment. This could help them afford a home more easily and without stretching their budget.
Potential long-term interest savings
It can also save you significantly on long-term interest costs.
See an example of calculating savings from mortgage buydowns below (this one is a permanent rate buydown that takes the rate from 7% to 6% on a $400,000 loan):
If you hope to buy points yourself, though, you'll need to do some math. Specifically, you'll want to calculate the breakeven point — which is the point at which you'll break even on the costs of the buydown.
Analyzing the break-even point and your long-term vs. short-term homeownership plans
Think of this as a cost analysis of mortgage rate buydowns. To calculate yours, take the total cost of the points and divide it by the monthly savings you'd get from it. This will tell you how many months it will take to break even.
From here, you'll need a good idea of how long you plan to be in the home. If you think you'll still be there to reach the breakeven point, then the buydown is probably a good idea. If you're not sure, the move could be risky.
Current and future financial situation
Keep in mind that if you're getting a temporary buydown, you'll need to be confident in your future finances. Once your rate buydown expires, your rate and payment will revert to the original ones quoted by your lender. You'll want to be sure you have the cash to cover this increased payment when the time comes, or you could risk foreclosure.
Buying down your rate yourself is pretty simple, but if you want someone else to cover the costs, you'll need to work for it. Use the following strategies for negotiating rate buydowns with lenders and sellers.
Negotiating with lenders and exploring lender credits
Shop around with lenders, and see if any are offering promotions. If rates are high, lenders may offer buydown promos to tempt buyers away from other companies. If you're not finding any, get loan quotes from several lenders and use those estimates to negotiate with others. There's a chance some will offer temporary buydowns to remain competitive.
Seller contributions
To get a home seller to cover your buydown, work with your real estate agent. Sellers are more likely to pay for buydowns in a buyer's market — when there are more properties for sale than buyers. They also may prefer to offer a buydown than lower the price of the home (the math usually works out better in the long run).
And if you do secure a seller buydown, make sure it's clearly outlined in your purchase contract. That's a legally binding document that both buyer and seller must adhere to.
A mortgage rate buydown allows a borrower or other party, like a lender or seller, to pay an upfront fee to reduce the interest rate on a mortgage. This leads to lower monthly payments, either for a a few years or the life of the loan.
Temporary buydowns reduce the interest rate and monthly payments for a few years at the beginning of the loan. Permanent buydowns lower the rate and payment for the entirety of the loan's term.
If you're paying for the buydown yourself, you'll need to calculate the breakeven point and make sure you'll be in the home long enough the save more than the buydown cost. With temporary buydowns paid for by other parties, you'll need to consider your financial situation and make sure you'll have the funds to cover a higher rate and payment later on.
Yes, you can negotiate a rate buydown with your lender. Lenders may also offer buydown options as part of their loan products, which can be discussed during the loan application process. Lenders are more likely to offer this in high-rate environments to entice buyers.
You may be able to reduce your payment by taking out a smaller loan, making a larger down payment, or exploring low-rate government-backed loan programs. Having a good credit score can also help you get a lower interest rate and payment.
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For your business plan, you should create a pro forma balance sheet that summarizes the information in the income statement and cash flow projections. A business typically prepares a balance sheet once a year. Download the Sample Balance Sheet Template. Once your balance sheet is complete, write a brief analysis for each of the three financial ...
There are a number of ways to calculate your sales but the following approach can be useful: List each of your products or services. Work out the price for each of those products or services. Think about the market and how many sales you may achieve each month. This might be as a percentage of capacity (e.g. available hours or tables occupied ...
Financial plan templates and tools. Download and use these free financial templates and calculators to easily create your own financial plan. Download a free detailed sales forecast spreadsheet, with built-in formulas, to easily estimate your first full year of monthly sales. Get a full financial picture of your business with LivePlan's simple ...
Use the numbers that you put in your sales forecast, expense projections, and cash flow statement. "Sales, lest cost of sales, is gross margin," Berry says. "Gross margin, less expenses, interest ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
This financial plan projections template comes as a set of pro forma templates designed to help startups. The template set includes a 12-month profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement for you to detail the current and projected financial position of a business. Download Startup Financial Projections Template.
Balance Sheet. The balance sheet portion of the financial plan aims to give an idea of what the business will be worth, considering all its assets and liabilities, at a future date. To do this, it uses figures from the income statement and cash flow statement. The essence of a balance sheet is found in the equation: Liabilities + Equity = Assets.
That's enough for actually running your startup. It's the essential numbers in a lean business plan. If you want to do it right you take it further and present projected (also called Pro Forma) versions of the three main business plan financial statements: Income Statement (also called Profit & Loss), Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow.
For example, the customer pays $50 for the meal. The food costs are $10 and the wages paid to prepare and serve the meal are $15. Your contribution margin is $25 ($50 - $10 - $15 = $25). Using this model you can determine how high your sales revenue needs to be in order for you to break even.
Whether the business is starting from scratch or modifying its plan, the best financial plans include the following elements: Income statement: The income statement reports the business's net profit or loss over a specific period of time, such a month, quarter or year.
7. Build a Visual Report. If you've closely followed the steps leading to this, you know how to research for financial projections, create a financial plan, and test assumptions using "what-if" scenarios. Now, we'll prepare visual reports to present your numbers in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
1. Start with a Sales Projection. A sales forecast is the first step in creating your income statement. You can start with a one, three, or five-year projection, but keep in mind that, without historical financial data, accuracy may decrease over time.
The first step for a financial forecast starts with projecting your business's sales, which are typically derived from past revenue as well as industry research. These projections allow businesses to understand what their risks are and how much they will need in terms of staffing, resources, and funding.
Step 4: Create an income statement projection. Current business owners can easily create an income statement projection by using your current income statement to estimate your projected numbers ...
A small business financial plan is an outline of the financial status of your business, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow information. A financial plan can help guide a small business toward sustainable growth. Financial plans can aid in business goal setting and metrics tracking, as well as provide proof of profitable ...
Step 4: Calculate Ratios: The actual calculation is the next step, where the relevant two or three financial variables are related for achieving the desired ratio. Step 5: Analyze Ratios: After calculating the ratios, the results are hyperlinked with the goals and results are analyzed and discussed.
A financial plan in business plan is an overview of your business financial projections. Business plan financial projections include financial reports including Profit & Loss, cash flow statement, and balance sheet. A financial plan will also discuss sales forecast, employees' salaries and other expenses forecast, business breakeven analysis ...
6. Delphi Method. The Delphi method of forecasting involves consulting experts who analyze market conditions to predict a company's performance. A facilitator reaches out to those experts with questionnaires, requesting forecasts of business performance based on their experience and knowledge.
Determine the impact on your company's finances and create a list of existing expenses and assets to help with your next steps. Create financial projections: This should be based on anticipated expenses and sales forecasts. Look at your goals and plug in the costs needed to achieve them.
COGS = Starting inventory costs + additional inventory costs - ending inventory. For example, say your business' inventory costs at the start of the year add up to $200,000. You make $500,000 worth of additional inventory purchases throughout the year and finish with $100,000 worth of inventory at the end of the year.
Here is what you typically find in a basic business plan: 1. Executive Summary. A snapshot of your business plan as a whole, touching on your company's profile, mission, and the main points of ...
Calculating financials for a business plan involves several steps. First, determine your startup costs and projected revenue for the first year. Next, create a projected income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Use realistic assumptions and data to estimate expenses, sales, and profits.
1. Forecast Customers. The first thing you must do to create a financial model for your bar is to forecast the number of customers you will serve over time. Forecasting customers can be done as follows. You must set the number of: Customers you expect to serve on average on a weekday.
1. Start with a Sales Projection. A sales forecast is the first step in creating your income statement. You can start with a one, three, or five-year projection, but keep in mind that, without historical financial data, accuracy may decrease over time.
It's no secret that investing in the financial markets is one of the surest ways to build wealth over time. The S&P 500 — an index typically used as a benchmark for the overall US stock market ...
HOW IS THE SAVE PLAN DIFFERENT? More borrowers in the SAVE plan are eligible for $0 payments. This plan won't require borrowers to make payments if they earn less than 225% of the federal poverty line — $32,800 a year for a single person. The cutoff for other plans, by contrast, is 150% of the poverty line, or $22,000 a year for a single ...
Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does ...
Investors approved a plan to take Donald Trump's struggling social-media company public, putting him one step closer to a roughly $3 billion windfall that could end a financial squeeze that is ...
As a small-business owner, it is critical to create a plan for your digital assets after you are gone to prevent any financial and sentimental harm. The first step is to create a list of all the ...
Specifically, you'll want to calculate the breakeven point — which is the point at which you'll break even on the costs of the buydown. buydown. Analyzing the break-even point and your long-term ...