- Skip to Nav
- Skip to Main
- Skip to Footer


What 9/11 Means for Me: There Is No Going Back to What Was Before
Please try again
e all carry some part of 9/11 with us.
There's raw memory, of course: what we recall about where we were, our experiences that day, the devastation as we saw what unfolded.
And there's something I'll call "considered memory": how we see that experience through the prism of all we've lived through, both privately as individuals and as a nation, since that date.
For me, honestly, I'm still puzzling over it. I've had an absorbing interest in our history for almost as long as I can remember, since a kids' Civil War book was put into my hands and I pronounced Potomac as "POT-oh-mack."
As I've gotten older, I've come to understand that one attraction of history, especially the history of war, of conflict, of tragedy, is the recounting of the battle and the exploit in much the same way the epic-singers of old traveled from court to court to relate "The Iliad." The battle and the exploit, the courage or failure of courage, themselves become the moral of the tale.
Often the recounting goes no further. The Light Brigade is forever charging the guns, always fulfilling a tragic destiny. But what then? What happens after Pickett's Charge is broken, after Appomattox, after the arms are stacked and the banners furled? What happens when we move beyond the sepia-tinted memories, the strains of elegiac strings, into the life that follows the battle?
The "what then?" is what I think about. To the extent I'm thinking about what Sept. 11 means, that's what's on my mind.
y brother John and his family lived in Brooklyn, a little more than 2 miles southeast of the World Trade Center, on Sept. 11, 2001. The attacks and their aftermath, things heard and seen, were intimate and immediate.
John's wife, Dawn, was just emerging from the subway when a jet screamed low overhead and vanished, followed by the sound of an explosion. Looking south from the corner, she could see the World Trade Center's North Tower had been hit.
John was at work in Brooklyn and watched from a rooftop as a second jet roared across the harbor and struck the South Tower. On the street below, New York Fire Department units sped toward the Brooklyn-Battery Tunnel to respond to the disaster across the river.
John and Dawn's neighborhood was downwind from the towers, and the blizzard of dust and paper unleashed when the buildings collapsed scattered scraps, documents and calendar pages everywhere. John told me later he would go around in the weeks after the attack and fill up sacks with the paper that had drifted to earth. At one point, he sent me a small bag with a few of the items he'd found.
I puzzle over these fragments. They're mundane: part of a financial firm's rules for handling trades. A blank visitor log for a government office. Design drawings for airport terminal signage. A page from a desk calendar (the date happens to be my birthday).
There's not a human mark on those scraps of paper. But they were handled by someone, somewhere, in a place we all saw destroyed. Touching them is like touching that place, touching that destruction, touching those who were lost.

o what's the "what then?" in our 9/11 story? One could say it's too early to tell and leave it at that.
But is anyone anywhere really satisfied with any of the outcomes we know about? Our ceaseless wars? Our embrace of assassination and torture as a means of making "the homeland" secure? The cost to our liberties through the adoption of such measures?
The climax of "The Odyssey" is the hero's return home after an epic of misfortune. But it's more than a homecoming — it's occasion for revenge. Odysseus, his son and their allies slaughter the young men who have been courting his wife, Penelope, and despoiling his estate. But that's not the end of it. The fathers and brothers of the murdered suitors are bent on vengeance themselves.
The goddess Athena, who has engineered Odysseus' return and his attack on the suitors, doesn't like what she sees brewing: an endless cycle of bloodshed and loss. She appeals to Zeus, her father, to stop it. He points out that she's distressed about her own handiwork, but says she's free to intervene.
"Do as your heart desires," he says. "But let me tell you how it should be done:
"Now that royal Odysseus has taken his revenge, let both sides seal their pacts that he shall reign for life, and let us purge their memories of the bloody slaughter of their brothers and their sons. Let them be friends, devoted as in the old days. Let peace and wealth come cresting through the land."
Would that it were so simple, or that we had gods so direct about pulling the strings. What 9/11 means for me, more than anything, is that there is no going back to what was before.
went up in the World Trade Center twice. Once during a visit in 1985, once in August 2001, about four weeks before the attacks. I was with my son, Thom, and John and his son, Sean. We were on top of the South Tower.
It was a high place with a view and some history: We talked about the guy who had climbed the tower, and the guy who had walked a high-wire between the towers.
Watching an airliner fly north over the Hudson, John recalled the story of an airline pilot who had, on a clear day, gotten off his flight path and flown his plane far too close to the towers and apparently lost his job over it. In fact, that conversation was the first thing that came to mind the morning of 9/11 when, standing in a San Francisco newsroom just before 6 a.m., I saw the first pictures of the North Tower after it had been hit.
One other memory.
I was at JFK airport, on a jet taxiing out to take off on a beautiful fall morning. The sun was just rising. I looked out my window and, far to the west, the towers caught that first stunning golden light. I still see them shining.
Editor's note: This is a revised version of an essay first written in 2011.
To learn more about how we use your information, please read our privacy policy.
The Meaning of 9/11
From my essay introducing The Atlantic's special coverage of the 10th anniversary of the 9/11 attacks:
What we saw on the morning of September 11, 2001 was evil made manifest. The terrorists who attacked the World Trade Center and the Pentagon (and tried to destroy the Capitol) claim to have been motivated by a theology of restoration -- a dream of restoring Islam to a position of global supremacy -- and by the politics of grievance. But something deeper undergirds these impulses: A compulsive need to murder one's way to glory. The stated goals of al Qaeda are flimsy excuses, meant to cover-up this ineluctable fact. The souls of men like Muhammad Atta and Khalid Sheikh Muhammad and Osama bin Laden are devoid of anything but hate, and murder is what erupted from these voids.

Self-criticism is necessary, even indispensable, for democracy to work. But this decade-long drama began with the unprovoked murder of 3,000 people, simply because they were American, or happened to be located in proximity to Americans. It is important to get our categories straight: The profound moral failures of the age of 9/11 belong to the murderers of al Qaeda, and those (especially in certain corners of the Muslim clerisy, along with a handful of bien-pensant Western intellectuals) who abet them, and excuse their actions. The mistakes we made were sometimes terrible (and sometimes, as at Abu Ghraib and in the CIA's torture rooms, criminal) but they came about in reaction to a crime without precedent.
9/11 was a test. The books of the last two decades show how America failed.

Deep within the catalogue of regrets that is the 9/11 Commission report — long after readers learn of the origins and objectives of al-Qaeda, past the warnings ignored by consecutive administrations, through the litany of institutional failures that allowed terrorists to hijack four commercial airliners — the authors pause to make a rousing case for the power of the nation’s character.
“The U.S. government must define what the message is, what it stands for,” the report asserts. “We should offer an example of moral leadership in the world, committed to treat people humanely, abide by the rule of law, and be generous and caring to our neighbors. . . . We need to defend our ideals abroad vigorously. America does stand up for its values.”
This affirmation of American idealism is one of the document’s more opinionated moments. Looking back, it’s also among the most ignored.
Rather than exemplify the nation’s highest values, the official response to 9/11 unleashed some of its worst qualities: deception, brutality, arrogance, ignorance, delusion, overreach and carelessness. This conclusion is laid bare in the sprawling literature to emerge from 9/11 over the past two decades — the works of investigation, memoir and narrative by journalists and former officials that have charted the path to that day, revealed the heroism and confusion of the early response, chronicled the battles in and about Afghanistan and Iraq, and uncovered the excesses of the war on terror. Reading or rereading a collection of such books today is like watching an old movie that feels more anguishing and frustrating than you remember. The anguish comes from knowing how the tale will unfold; the frustration from realizing that this was hardly the only possible outcome.
Whatever individual stories the 9/11 books tell, too many describe the repudiation of U.S. values, not by extremist outsiders but by our own hand. The betrayal of America’s professed principles was the friendly fire of the war on terror. In these works, indifference to the growing terrorist threat gives way to bloodlust and vengeance after the attacks. Official dissembling justifies wars, then prolongs them. In the name of counterterrorism, security is politicized, savagery legalized and patriotism weaponized.
It was an emergency, yes, that’s understood. But that state of exception became our new American exceptionalism.
It happened fast. By 2004, when the 9/11 Commission urged America to “engage the struggle of ideas,” it was already too late; the Justice Department’s initial torture memos were already signed, the Abu Ghraib images had already eviscerated U.S. claims to moral authority. And it has lasted long. The latest works on the legacy of 9/11 show how war-on-terror tactics were turned on religious groups, immigrants and protesters in the United States. The war on terror came home, and it walked in like it owned the place.
“It is for now far easier for a researcher to explain how and why September 11 happened than it is to explain the aftermath,” Steve Coll writes in “ Ghost Wars ,” his 2004 account of the CIA’s pre-9/11 involvement in Afghanistan. Throughout that aftermath, Washington fantasized about remaking the world in its image, only to reveal an ugly image of itself to the world.
The literature of 9/11 also considers Osama bin Laden’s varied aspirations for the attacks and his shifting visions of that aftermath. He originally imagined America as weak and easily panicked, retreating from the world — in particular from the Middle East — as soon as its troops began dying. But bin Laden also came to grasp, perhaps self-servingly, the benefits of luring Washington into imperial overreach, of “bleeding America to the point of bankruptcy,” as he put it in 2004, through endless military expansionism, thus beating back its global sway and undermining its internal unity. “We anticipate a black future for America,” bin Laden told ABC News more than three years before the 9/11 attacks. “Instead of remaining United States, it shall end up separated states and shall have to carry the bodies of its sons back to America.”
Bin Laden did not win the war of ideas. But neither did we. To an unnerving degree, the United States moved toward the enemy’s fantasies of what it might become — a nation divided in its sense of itself, exposed in its moral and political compromises, conflicted over wars it did not want but would not end. When President George W. Bush addressed the nation from the Oval Office on the evening of Sept. 11, 2001, he asserted that America was attacked because it is “the brightest beacon for freedom and opportunity in the world, and no one will keep that light from shining.” Bush was correct; al-Qaeda could not dim the promise of America. Only we could do that to ourselves.

“The most frightening aspect of this new threat . . . was the fact that almost no one took it seriously. It was too bizarre, too primitive and exotic.” That is how Lawrence Wright depicts the early impressions of bin Laden and his terrorist network among U.S. officials in “ The Looming Tower: Al-Qaeda and the Road to 9/11 .” For a country still basking in its post-Cold War glow, it all seemed so far away, even as al-Qaeda’s strikes — on the World Trade Center in 1993, on U.S. Embassies in 1998, on the USS Cole in 2000 — grew bolder. This was American complacency, mixed with denial.
The books traveling that road to 9/11 have an inexorable, almost suffocating feel to them, as though every turn invariably leads to the first crush of steel and glass. Their starting points vary. Wright dwells on the influence of Egyptian thinker Sayyid Qutb, whose mid-20th-century sojourn in the United States animated his vision of a clash between Islam and modernity, and whose work would inspire future jihadists. In “Ghost Wars,” Coll laments America’s abandonment of Afghanistan once it ceased serving as a proxy battlefield against Moscow. In “ The Rise and Fall of Osama bin Laden ,” Peter Bergen stresses the moment bin Laden arrived in Afghanistan from Sudan in 1996, when Khalid Sheikh Mohammed first pitched him on the planes plot. And the 9/11 Commission lingers on bin Laden’s declarations of war against the United States, particularly his 1998 fatwa calling it “the individual duty for every Muslim” to murder Americans “in any country in which it is possible.”
Yet these early works also make clear that the road to 9/11 featured plenty of billboards warning of the likely destination. A Presidential Daily Brief item on Aug. 6, 2001, titled “Bin Ladin Determined to Strike in US” became infamous in 9/11 lore, yet the commission report notes that it was the 36th PDB relating to bin Laden or al-Qaeda that year alone. (“All right. You’ve covered your ass now,” Bush reportedly sneered at the briefer.) Both the FBI and the CIA produced classified warnings on terrorist threats in the mid-1990s, Coll writes, including a particularly precise National Intelligence Estimate. “Several targets are especially at risk: national symbols such as the White House and the Capitol, and symbols of U.S. capitalism such as Wall Street,” it stated. “We assess that civil aviation will figure prominently among possible terrorist targets in the United States.” Some of the admonitions scattered throughout the 9/11 literature are too over-the-top even for a movie script: There’s the exasperated State Department official complaining about Defense Department inaction (“Does al Qaeda have to attack the Pentagon to get their attention?”), and the earnest FBI supervisor in Minneapolis warning a skeptical agent in Washington about suspected terrorism activity, insisting that he was “trying to keep someone from taking a plane and crashing it into the World Trade Center.”
In these books, everyone is warning everyone else. Bergen emphasizes that a young intelligence analyst in the State Department, Gina Bennett, wrote the first classified memo warning about bin Laden in 1993. Pockets within the FBI and the CIA obsess over bin Laden while regarding one another as rivals. On his way out, President Bill Clinton warns Bush. Outgoing national security adviser Sandy Berger warns his successor, Condoleezza Rice. And White House counterterrorism coordinator Richard Clarke, as he reminds incessantly in his 2004 memoir, “ Against All Enemies ,” warns anyone who will listen and many who will not.
With the system “blinking red,” as CIA Director George Tenet later told the 9/11 Commission, why were all these warnings not enough? Wright lingers on bureaucratic failings, emphasizing that intelligence collection on al-Qaeda was hampered by the “institutional warfare” between the CIA and the FBI, two agencies that by all accounts were not on speaking terms. Coll writes that Clinton regarded bin Laden as “an isolated fanatic, flailing dangerously but quixotically against the forces of global progress,” whereas the Bush team was fixated on great-power politics, missile defense and China.
Clarke’s conclusion is simple, and it highlights America’s we-know-better swagger, a national trait that often masquerades as courage or wisdom. “America, alas, seems only to respond well to disasters, to be undistracted by warnings,” he writes. “Our country seems unable to do all that must be done until there has been some awful calamity.”
The problem with responding only to calamity is that underestimation is usually replaced by overreaction. And we tell ourselves it is the right thing, maybe the only thing, to do.

A last-minute flight change. A new job at the Pentagon. A retirement from the fire station. The final tilt of a plane’s wings before impact. If the books about the lead-up to 9/11 are packed with unbearable inevitability, the volumes on the day itself highlight how randomness separated survival from death. “The ferocity of the attacks meant that innocent people lived or died because they stepped back from a doorway, or hopped onto a closing elevator, or simply shifted their weight from one foot to another,” Jim Dwyer and Kevin Flynn write in “ 102 Minutes ,” their narrative of events inside the World Trade Center from the moment the first plane hit through the collapse of both towers. Their detailed reporting on the human saga — such as a police officer asking a fire chaplain to hear his confession as they both flee a collapsing building — is excruciating and riveting at once.
Yet, as much as the people inside, the structures and history of the World Trade Center are key actors, too. They are not just symbols and targets but fully formed and deeply flawed characters in the day’s drama.
[ 9/11 has become all about New York — with D.C. and the Pentagon nearly forgotten ]
Had the World Trade Center, built in the late 1960s and early 1970s, been erected according to the city building code in effect since 1938, Dwyer and Flynn explain, “it is likely that a very different world trade center would have been built.” Instead, it was constructed according to a new code that the real estate industry had avidly promoted, a code that made it cheaper and more lucrative to build and own skyscrapers. “It increased the floor space available for rent . . . by cutting back on the areas that had been devoted, under the earlier law, to evacuation and exit,” the authors write. The result: Getting everybody out on 9/11 was virtually impossible.
Under the new rules, the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey was able to rent three-quarters of each floor of the World Trade Center, Dwyer and Flynn report, a 21 percent increase over the yield of older skyscrapers. The cost was dear. Some 1,000 people inside the North Tower who initially survived the impact of American Airlines Flight 11 could not reach an open staircase. “Their fate was sealed nearly four decades earlier, when the stairways were clustered in the core of the building, and fire stairs were eliminated as a wasteful use of valuable space.” (The authors write that “building code reform hardly makes for gripping drama,” an aside as modest as it is inaccurate.) The towers embodied the power of American capitalism, but their design embodied the folly of American greed. On that day, both conditions proved fatal.
The assault on the Pentagon, long treated as an undercard to New York’s main event, could have yielded even greater devastation, and again the details of the building played a role. In his oral history of 9/11, “ The Only Plane in the Sky ,” Garrett Graff quotes Defense Department officials marveling at how American Airlines Flight 77 struck a part of the Pentagon that, because of new anti-terrorism standards, had recently been reinforced and renovated. This meant it was not only stronger but, on that morning, also relatively unoccupied. “It was truly a miracle,” Army branch chief Philip Smith said. “In any other wedge of the Pentagon, there would have been 5,000 people, and the plane would have flown right through the middle of the building.” Instead, fewer than 200 people were killed in the attack on the Pentagon, including the passengers on the hijacked jet. Chance and preparedness came together.
The bravery of police and firefighters is the subject of countless 9/11 retrospectives, but these books also emphasize the selflessness of civilians who morphed into first responders. Port Authority workers Frank De Martini, Pablo Ortiz, Carlos da Costa and Peter Negron, for instance, saved at least 70 people in the World Trade Center’s North Tower by pulling apart elevator doors, busting walls and shining flashlights to find survivors, only to not make it out themselves. “With crowbar, flashlight, hardhat and big mouths, De Martini and Ortiz and their colleagues had pushed back the boundary line between life and death,” Dwyer and Flynn write. The authors also note how the double lines of people descending a World Trade Center staircase would automatically blend into single file when word came down that an injured person was behind them. And Graff cites a local assistant fire chief who recalls the “truly heroic” work of civilians and uniformed personnel at the Pentagon that day. “They were the ones who really got their comrades, got their workmates out,” he says.
The civilians aboard United Airlines Flight 93, whose resistance forced the plane to crash into a Pennsylvania field rather than the U.S. Capitol, were later lionized as emblems of swashbuckling Americana. But one offhand detail in the 9/11 Commission report underscores just how American their defiance was. The passengers had made phone calls when the hijacking began and had learned the fate of other aircraft that day. “According to one call, they voted on whether to rush the terrorists in an attempt to retake the plane,” the commission report states. “They decided, and acted.”
They voted on it. They voted. Even in that moment of unfathomable fear and distress, the passengers took a moment to engage in the great American tradition of popular consultation before deciding to become this new war’s earliest soldiers. Was there ever any doubt as to the outcome of that ballot?
Such episodes, led by ordinary civilians, embodied values that the 9/11 Commission called on the nation to display. Except those values would soon be dismantled, in the name of security, by those entrusted to uphold them.

Lawyering to death.
The phrase appears in multiple 9/11 volumes, usually uttered by top officials adamant that they were going to get things done , laws and rules be damned. Anti-terrorism efforts were always “lawyered to death” during the Clinton administration, Tenet complains in “ Bush at War ,” Bob Woodward’s 2002 book on the debates among the president and his national security team. In an interview with Woodward, Bush drops the phrase amid the machospeak — “dead or alive,” “bring ’em on” and the like — that became typical of his anti-terrorism rhetoric. “I had to show the American people the resolve of a commander in chief that was going to do whatever it took to win,” Bush explains. “No yielding. No equivocation. No, you know, lawyering this thing to death.” In “Against All Enemies,” Clarke recalls the evening of Sept. 11, 2001, when Bush snapped at an official who suggested that international law looked askance at military force as a tool of revenge. “I don’t care what the international lawyers say, we are going to kick some ass,” the president retorted.
The message was unmistakable: The law is an obstacle to effective counterterrorism. Worrying about procedural niceties is passe in a 9/11 world, an annoying impediment to the essential work of ass-kicking.
Except, they did lawyer this thing to death. Instead of disregarding the law, the Bush administration enlisted it. “Beginning almost immediately after September 11, 2001, [Vice President Dick] Cheney saw to it that some of the sharpest and best-trained lawyers in the country, working in secret in the White House and the United States Department of Justice, came up with legal justifications for a vast expansion of the government’s power in waging war on terror,” Jane Mayer writes in “ The Dark Side ,” her relentless 2008 compilation of the arguments and machinations of government lawyers after the attacks. Through public declarations and secret memos, the administration sought to remove limits on the president’s conduct of warfare and to deny terrorism suspects the protections of the Geneva Conventions by redefining them as unlawful enemy combatants. Nothing, Mayer argues of the latter effort, “more directly cleared the way for torture than this.”
To comprehend what our government can justify in the name of national security, consider the torture memos themselves, authored by the Justice Department’s Office of Legal Counsel between 2002 and 2005 to green-light CIA interrogation methods for terrorism suspects. Tactics such as cramped confinement, sleep deprivation and waterboarding were rebranded as “enhanced interrogation techniques,” legally and linguistically contorted to avoid the label of torture. Though the techniques could be cruel and inhuman, the OLC acknowledged in an August 2002 memo, they would constitute torture only if they produced pain equivalent to organ failure or death, and if the individual inflicting such pain really really meant to do so: “Even if the defendant knows that severe pain will result from his actions, if causing such harm is not his objective, he lacks the requisite specific intent.” It’s quite the sleight of hand, with torture moving from the body of the interrogated to the mind of the interrogator.
After devoting dozens of pages to the metaphysics of specific intent, the true meaning of “prolonged” mental harm or “imminent” death, and the elasticity of the Convention Against Torture, the memo concludes that none of it actually matters. Even if a particular interrogation method would cross some legal line, the relevant statute would be considered unconstitutional because it “impermissibly encroached” on the commander in chief’s authority to conduct warfare. Almost nowhere in these memos does the Justice Department curtail the power of the CIA to do as it pleases.
In fact, the OLC lawyers rely on assurances from the CIA itself to endorse such powers. In a second memo from August 2002, the lawyers ruminate on the use of cramped confinement boxes. “We have no information from the medical experts you have consulted that the limited duration for which the individual is kept in the boxes causes any substantial physical pain,” the memo states. Waterboarding likewise gets a pass. “You have informed us that this procedure does not inflict actual physical harm,” the memo states. “Based on your research . . . you do not anticipate that any prolonged mental harm would result from the use of the waterboard.”
You have informed us. Experts you have consulted. Based on your research. You do not anticipate . Such hand-washing words appear throughout the memos. The Justice Department relies on information provided by the CIA to reach its conclusions; the CIA then has the cover of the Justice Department to proceed with its interrogations. It’s a perfect circle of trust.
Yet the logic is itself tortured. In a May 2005 memo, the lawyers conclude that because no single technique inflicts “severe” pain amounting to torture, their combined use “would not be expected” to reach that level, either. As though embarrassed at such illogic, the memo attaches a triple-negative footnote: “We are not suggesting that combinations or repetitions of acts that do not individually cause severe physical pain could not result in severe physical pain.” Well, then, what exactly are you suggesting? Even when the OLC in 2004 officially withdrew its August 2002 memo following a public outcry and declared torture “abhorrent,” the lawyers added a footnote to the new memo assuring that they had reviewed the prior opinions on the treatment of detainees and “do not believe that any of their conclusions would be different under the standards set forth in this memorandum.”
In these documents, lawyers enable lawlessness. Another May 2005 memo concludes that, because the Convention Against Torture applies only to actions occurring under U.S. jurisdiction, the CIA’s creation of detention sites in other countries renders the convention “inapplicable.” Similarly, because the Eighth Amendment’s prohibition on cruel and unusual punishment is meant to protect people convicted of crimes, it should not apply to terrorism detainees — because they have not been officially convicted of anything. The lack of due process conveniently eliminates constitutional protections. In his introduction to “ The Torture Memos: Rationalizing the Unthinkable ,” David Cole describes the documents as “bad-faith lawyering,” which might be generous. It is another kind of lawyering to death, one in which the rule of law that the 9/11 Commission urged us to abide by becomes the victim.
Years later, the Senate Intelligence Committee would investigate the CIA’s post-9/11 interrogation program. Its massive report — the executive summary of which appeared as a 549-page book in 2014 — found that torture did not produce useful intelligence, that the interrogations were more brutal than the CIA let on, that the Justice Department did not independently verify the CIA’s information, and that the spy agency impeded oversight by Congress and the CIA inspector general. It explains that the CIA purported to oversee itself and, no surprise, that it deemed its interrogations effective and necessary, no matter the results. (If a detainee provided information, it meant the program worked; if he did not, it meant stricter applications of the techniques were needed; if still no information was forthcoming, the program had succeeded in proving he had none to give.)
“The CIA’s effectiveness representations were almost entirely inaccurate,” the Senate report concluded. It is one of the few lies of the war on terror unmasked by an official government investigation and public report, but just one of the many documented in the 9/11 literature.

Officials in the war on terror didn’t deceive or dissemble just with lawmakers or the public. In the recurring tragedy of war, they lied just as often to themselves.
In “ To Start a War: How the Bush Administration Took America Into Iraq ,” Robert Draper considers the influence of the president’s top aides. Deputy Defense Secretary Paul Wolfowitz (long obsessed with ousting Saddam Hussein), Pentagon chief Donald Rumsfeld (eager to test his theories of military transformation) and Cheney (fixated on apocalyptic visions of America’s vulnerability) all had their reasons. But Draper identifies a single responsible party: “The decision to invade Iraq was one made, finally and exclusively, by the president of the United States, George W. Bush,” he writes.
A president initially concerned about defending and preserving the nation’s moral goodness against terrorism found himself driven by darker impulses. “I’m having difficulty controlling my bloodlust,” Bush confessed to religious leaders in the Oval Office on Sept. 20, 2001, Draper reports. It was not a one-off comment; in Woodward’s “Bush at War,” the president admitted that before 9/11, “I didn’t feel that sense of urgency [about al-Qaeda], and my blood was not nearly as boiling.”
Bloodlust, moral certainty and sudden vulnerability make a dangerous combination. The belief that you are defending good against evil can lead to the belief that whatever you do to that end is good, too. Draper distills Bush’s worldview: “The terrorists’ primary objective was to destroy America’s freedom. Saddam hated America. Therefore, he hated freedom. Therefore, Saddam was himself a terrorist, bent on destroying America and its freedom.”
Note the asymmetry. The president assumed the worst about what Hussein had done or might do, yet embraced best-case scenarios of how an American invasion would proceed. “Iraqis would rejoice at the sight of their Western liberators,” Draper recaps. “Their newly shared sense of national purpose would overcome any sectarian allegiances. Their native cleverness would make up for their inexperience with self-government. They would welcome the stewardship of Iraqi expatriates who had not set foot in Baghdad in decades. And their oil would pay for everything.”

There are lies, and then there is self-delusion. The Americans did not have to anticipate the specifics of the civil war that would engulf the country after the invasion; they just had to realize that managing postwar Iraq would never be as simple as they imagined. It did not seem to occur to Bush and his advisers that Iraqis could simultaneously hate Hussein and resent the Americans — feelings that could have been discovered by speaking to Iraqis and hearing their concerns.
Anthony Shadid’s “ Night Draws Near: Iraq’s People in the Shadow of America’s War ,” published in 2005, is among the few books on the war that gets deep inside Iraqis’ aversion to the Americans in their midst. “What gives them the right to change something that’s not theirs in the first place?” a woman in a middle-class Baghdad neighborhood asks him. “I don’t like your house, so I’m going to bomb it and you can rebuild it again the way I want it, with your money?” In Fallujah, where Shadid hears early talk of the Americans as “kuffar” (heathens), a 51-year-old former teacher complains that “we’ve exchanged a tyrant for an occupier.” The occupation did not dissuade such impressions when it turned the former dictator’s seat of government into its own luxurious Green Zone, or when it retrofitted the Abu Ghraib prison (“the worst of Saddam’s hellholes,” Shadid calls it) into its own chamber of horrors.
Shadid understood that governmental legitimacy — who gets to rule, and by what right — was a matter of overriding importance for Iraqis. “The Americans never understood the question,” he writes; “Iraqis never agreed on the answer.” It’s hard to find a better summation of the trials of Iraq in the aftermath of America’s invasion. When the United States so quickly shifted from liberation to occupation, it lost whatever legitimacy it enjoyed. “Bush handed that enemy precisely what it wanted and needed, proof that America was at war with Islam, that we were the new Crusaders come to occupy Muslim land,” Clarke writes. “It was as if Usama bin Laden, hidden in some high mountain redoubt, were engaging in long-range mind control of George Bush, chanting ‘invade Iraq, you must invade Iraq.’ ”
[ The Pentagon's Obsession With Counterinsurgency ]
The foolishness and arrogance of the American occupation didn’t help. In “ Imperial Life in the Emerald City: Inside Iraq’s Green Zone ,” Rajiv Chandrasekaran explains how, even as daily security was Iraqis’ overwhelming concern, viceroy L. Paul Bremer, Bush’s man in Baghdad, was determined to turn the country into a model free-market economy, complete with new investment laws, bankruptcy courts and a state-of-the-art stock exchange. In charge of the new exchange was a 24-year-old American with no academic background in economics or finance. The man tasked with remaking Iraq’s sprawling university system had no experience in the Middle East — but did have connections to the Rumsfeld and Cheney families. A new traffic law for Iraq was partially cut and pasted from Maryland’s motor vehicle code. An antismoking campaign was led by a U.S. official who was a closet smoker. And a U.S. Army general, when asked by local journalists why American helicopters must fly so low at night, thus scaring Iraqi children, replied that the kids were simply hearing “the sound of freedom.”
Message: Freedom sounds terrifying.
For some Americans, inflicting that terror became part of the job, one more tool in the arsenal. In “ The Forever War ” by Dexter Filkins, a U.S. Army lieutenant colonel in Iraq assures the author that “with a heavy dose of fear and violence, and a lot of money for projects, I think we can convince these people that we are here to help them.” (Filkins asked him if he really meant it about fear and violence; the officer insisted that he did.) Of course, not all officials were so deluded and so forthright; some knew better but lied to the public. Chandrasekaran recalls the response of a top communications official under Bremer, when reporters asked about waves of violence hitting Baghdad in the spring of 2004. “Off the record: Paris is burning,” the official told the journalists. “On the record: Security and stability are returning to Iraq.”
In “The Rise and Fall of Osama bin Laden,” Bergen sums up how the Iraq War, conjured in part on the false connections between Iraq and al-Qaeda, ended up helping the terrorist network: It pulled resources from the war in Afghanistan, gave space for bin Laden’s men to regroup and spurred a new generation of terrorists in the Middle East. “A bigger gift to bin Laden was hard to imagine,” Bergen writes.
If Iraq was the war born of lies, Afghanistan was the one nurtured by them. Afghanistan was where al-Qaeda, supported by the Taliban, had made its base — it was supposed to be the good war, the right war, the war of necessity and not choice, the war endorsed at home and abroad. “U.S. officials had no need to lie or spin to justify the war,” Washington Post reporter Craig Whitlock writes in “ The Afghanistan Papers ,” a damning contrast of the war’s reality vs. its rhetoric. “Yet leaders at the White House, the Pentagon and the State Department soon began to make false assurances and to paper over setbacks on the battlefield.” As the years passed, the deceit became entrenched, what Whitlock calls “an unspoken conspiracy” to hide the truth.
Drawing from a “Lessons Learned” project that interviewed hundreds of military and civilian officials involved with Afghanistan, as well as from oral histories, government cables and reports, Whitlock finds commanding generals privately admitting that they long fought the war “without a functional strategy.” That, two years into the conflict, Rumsfeld complained that he had “no visibility into who the bad guys are.” That Army Lt. Gen. Douglas Lute, a former coordinator of Iraq and Afghanistan policy, acknowledged that “we didn’t have the foggiest idea of what we were undertaking.” That U.S. officials long wanted to withdraw American forces but feared — correctly so, it turns out — that the Afghan government might collapse. “Bin Laden had hoped for this exact scenario,” Whitlock observes. “To lure the U.S. superpower into an unwinnable guerrilla conflict that would deplete its national treasury and diminish its global influence.”
All along, top officials publicly contradicted these internal views, issuing favorable accounts of steady progress. Bad news was twisted into good: Rising suicide attacks in Kabul meant the Taliban was too weak for direct combat, for instance, while increased U.S. casualties meant America was taking the fight to the enemy. The skills and size of the Afghan security forces were frequently exaggerated; by the end of President Barack Obama’s second term, U.S. officials concluded that some 30,000 Afghan soldiers on the payroll didn’t actually exist; they were paper creations of local commanders who pocketed the fake soldiers’ salaries at U.S. taxpayer expense. American officials publicly lamented large-scale corruption in Afghanistan but enabled that corruption in practice, pouring massive contracts and projects into a country ill-equipped to absorb them. Such deceptions transpired across U.S. presidents, but the Obama administration, eager to show that its first-term troop surge was working, “took it to a new level, hyping figures that were misleading, spurious or downright false,” Whitlock writes. And then under President Donald Trump, he adds, the generals felt pressure to “speak more forcefully and boast that his war strategy was destined to succeed.”
Long before President Biden declared the end of the U.S. war in Afghanistan this summer, the United States twice made similar pronouncements, proclaiming the conclusion of combat operations in 2003 and again in 2014 — yet still the war endured. It did so in part because “in public, almost no senior government officials had the courage to admit that the United States was slowly losing,” Whitlock writes. “With their complicit silence, military and political leaders avoided accountability and dodged reappraisals that could have changed the outcome or shortened the conflict.”
It’s not like nobody warned them. In “Bush at War,” Woodward reports that CIA Counterterrorism Center Director Cofer Black and Deputy Secretary of State Richard Armitage traveled to Moscow shortly after 9/11 to give officials a heads up about the coming hostilities in Afghanistan. The Russians, recent visitors to the graveyard of empires, cautioned that Afghanistan was an “ambush heaven” and that, in the words of one of them, “you’re really going to get the hell kicked out of you.” Cofer responded confidently: “We’re going to kill them. . . . We’re going to rock their world.”
Now, with U.S. forces gone and the Taliban having reclaimed power in Afghanistan, Washington is wrestling with the legacy of the nation’s longest war. Why and how did America lose? Should we have stayed longer? Was it worth its price in blood and billions? How does the United States repay the courage of Afghans who worked alongside U.S. military and civilian authorities? What if Afghanistan again becomes a haven for terrorists attacking U.S. interests and allies, as the airport suicide bombing in Kabul that killed 13 U.S. service members last month may signal? Biden has asserted that “the war in Afghanistan is now over” but has also pledged to continue the fight against terrorists there — so what are the limits and the means of future U.S. military and intelligence action in the country?
These are essential debates, but a war should not be measured only by the timing and the competence of its end. We still face an equally consequential appraisal: How good was this good war if it could be sustained only by lies?

In the two decades since the 9/11 attacks, the United States has often attempted to reconsider its response. Take two documents from late 2006: the report from the Iraq Study Group, co-chaired by James A. Baker III and Lee H. Hamilton, which argued that Washington needed to radically rethink its diplomatic and political strategy for Iraq; and “ The U.S. Army/Marine Corps Counterinsurgency Field Manual ,” written by a team led by then-Army Lt. Gen. David H. Petraeus, which argued that U.S. officials needed to radically rethink military tactics for insurgency wars of the kind it faced in Iraq and Afghanistan.
They are written as though intending to solve problems. But they can be read as proof that the problems have no realistic solution, or that the only solution is to never have created them.
“There is no magic formula to solve the problems of Iraq,” the ISG report begins, yet its proposed fixes would have required plenty of fairy dust. The report calls for a “diplomatic offensive” to gain international support for Iraq, to persuade Iran and Syria to respect Iraq’s territory and sovereignty, and to commit to “a comprehensive Arab-Israeli peace on all fronts.” Simple! Iraq, meanwhile, needed to make progress on national reconciliation (in a country already awash in sectarian bloodletting), boost domestic security (even though the report deems the Iraqi army a mess and the Iraqi police worse) and deliver social services (even as the report concludes that the government was failing to adequately provide electricity, drinking water, sewage services and education).
The recommendations seem written in the knowledge that they will never happen. “Miracles cannot be expected,” the report states — twice. Absent divine intervention, the next step is obvious. If the Iraqi government can’t demonstrate “substantial progress” toward its goals, the report asserts, “the United States should reduce its political, military, or economic support” for Iraq. Indeed, the report sets the bar for staying so high that an exit strategy appears to be its primary purpose.
The counterinsurgency manual is an extraordinary document. Implicitly repudiating notions such as “shock and awe” and “overwhelming force,” it argues that the key to battling an insurgency in countries such as Iraq and Afghanistan is to provide security for the local population and to win its support through effective governance. It also attempts to grasp the nature of America’s foes. “Most enemies either do not try to defeat the United States with conventional operations or do not limit themselves to purely military means,” the manual states. “They know that they cannot compete with U.S. forces on those terms. Instead, they try to exhaust U.S. national will.” Exhausting America’s will is an objective that al-Qaeda understood well.
“Soldiers and Marines are expected to be nation builders as well as warriors,” the manual proclaims, but the arduous tasks involved — reestablishing government institutions, rebuilding infrastructure, strengthening local security forces, enforcing the rule of law — reveal the tension at the heart of the new doctrine. “Counterinsurgents should prepare for a long-term commitment,” the manual states. Yet, just a few pages later, it admits that “eventually all foreign armies are seen as interlopers or occupiers.” How to accomplish the former without descending into the latter? No wonder so many of the historical examples of counterinsurgency that the manual highlights, including accounts from the Vietnam War, are stories of failure.

The manual seems aware of its importance. The 2007 edition contains a foreword, followed by an introduction, then another foreword, a preface, then some brief acknowledgments and finally one more introduction. (Just reaching Chapter 1 feels like defeating an insurgency.) But the throat-clearing is clarifying. In his foreword, Army Lt. Col. John Nagl writes that the document’s most lasting impact may be as a catalyst not for remaking Iraq or Afghanistan, but for transforming the Army and Marine Corps into “more effective learning organizations,” better able to adapt to changing warfare. And in her introduction, Sarah Sewall, then director of Harvard’s Carr Center for Human Rights Policy, concludes that its “ultimate value” may be in warning civilian officials to think hard before engaging in a counterinsurgency campaign.
At best, then, the manual helps us rethink future conflicts — how we fight and whether we should. It’s no coincidence that Biden, in his Aug. 16 remarks defending the decision to withdraw American troops from Afghanistan, specifically repudiated counterinsurgency as an objective of U.S. policy. “I’ve argued for many years that our mission should be narrowly focused on counterterrorism, not counterinsurgency or nation-building,” the president affirmed. Even the longest war was not long enough for a counterinsurgency effort to succeed.
In his 2009 book, “ The Good Soldiers ,” David Finkel chronicles the experiences of an Army battalion deployed in Iraq during the U.S. troop surge in 2007 and 2008, a period of the war ostensibly informed by the new counterinsurgency doctrine. In his 2013 sequel, “ Thank You for Your Service ,” the author witnesses these men when they come home and try to make sense of their military experience and adapt to their new lives. “The thing that got to everyone,” Finkel explains in the latter book, “was not having a defined front line. It was a war in 360 degrees, no front to advance toward, no enemy in uniform, no predictable patterns, no relief.” It’s a powerful summation of battling an insurgency.
Adam Schumann returns from war because of post-traumatic stress disorder and traumatic brain injury, “the result of a mortar round that dropped without warning out of a blue sky,” Finkel explains. Schumann suffers from nightmares, headaches and guilt; he wishes he needed bandages or crutches, anything to visibly justify his absence from the front. His wife endures his treatments, his anger, his ambivalence toward life. “He’s still a good guy,” she decides. “He’s just a broken good guy.” Another returning soldier, Nic DeNinno, struggles to tell his wife about the time he and his fellow soldiers burst into an Iraqi home in search of a high-value target. He threw a man down the stairs and held another by the throat. After they left, the lieutenant told him it was the wrong house. “The wrong f---ing house,” Nic says to his wife. “One of the things I want to remember is how many times we hit the wrong house.”
Hitting the wrong house is what counterinsurgency doctrine is supposed to avoid. Even successfully capturing or killing a high-value target can be counterproductive if in the process you terrorize a community and create more enemies. In Iraq, the whole country was the wrong house. America’s leaders knew it was the wrong house. They hit it anyway.

In the 11th chapter of the 9/11 Commission report, just before all the recommendations for reforms in domestic and foreign policy, the authors get philosophical, pondering how hindsight had affected their views of Sept. 11, 2001. “As time passes, more documents become available, and the bare facts of what happened become still clearer,” the report states. “Yet the picture of how those things happened becomes harder to reimagine, as that past world, with its preoccupations and uncertainty, recedes.” Before making definitive judgments, then, they ask themselves “whether the insights that seem apparent now would really have been meaningful at the time.”
It’s a commendable attitude, one that helps readers understand what the attacks felt like in real time and why authorities responded as they did. But that approach also keeps the day trapped in the past, safely distant. Two of the latest additions to the canon, “ Reign of Terror ” by Spencer Ackerman and “ Subtle Tools ” by Karen Greenberg, draw straight, stark lines between the earliest days of the war on terror and its mutations in our current time, between conflicts abroad and divisions at home. These works show how 9/11 remains with us, and how we are still living in the ruins.
When Trump declared that “we don’t have victories anymore” in his 2015 speech announcing his presidential candidacy, he was both belittling the legacy of 9/11 and harnessing it to his ends. “His great insight was that the jingoistic politics of the War on Terror did not have to be tied to the War on Terror itself,” Ackerman writes. “That enabled him to tell a tale of lost greatness.” And if greatness is lost, someone must have taken it. The backlash against Muslims, against immigrants crossing the southern border and against protesters rallying for racial justice was strengthened by the open-ended nature of the global war on terror. In Ackerman’s vivid telling — his prose can be hyperbolic, even if his arguments are not — the war is not just far away in Iraq or Afghanistan, in Yemen or Syria, but it’s happening here, with mass surveillance, militarized law enforcement and the rebranding of immigration as a threat to the nation’s security rather than a cornerstone of its identity. “Trump had learned the foremost lesson of 9/11,” Ackerman writes, “that the terrorists were whomever you said they were.”
Both Ackerman and Greenberg point to the Authorization for Use of Military Force , drafted by administration lawyers and approved by Congress just days after the attacks, as the moment when America’s response began to go awry. The brief joint resolution allowed the president to use “all necessary and appropriate force” against any nation, organization or person who committed the attacks, and to prevent any future ones. It was the “Ur document in the war on terror and its legacy,” Greenberg writes. “Riddled with imprecision, its terminology was geared to codify expansive powers.” Where the battlefield, the enemy and the definition of victory all remain vague, war becomes endlessly expansive, “with neither temporal nor geographical boundaries.”
This was the moment the war on terror was “conceptually doomed,” Ackerman concludes. This is how you get a forever war.
There were moments when an off-ramp was visible. The killing of bin Laden in 2011 was one such instance, Ackerman argues, but “Obama squandered the best chance anyone could ever have to end the 9/11 era.” The author assails Obama for making the war on terror more “sustainable” through a veneer of legality — banning torture yet failing to close the detention camp at Guantánamo Bay and relying on drone strikes that “perversely incentivized the military and the CIA to kill instead of capture.” There would always be more targets, more battlefields, regardless of president or party. Failures became the reason to double down, never wind down.
The longer the war went on, the more that what Ackerman calls its “grotesque subtext” of nativism and racism would move to the foreground of American politics. Absent the war on terror, it is harder to imagine a presidential candidate decrying a sitting commander in chief as foreign, Muslim, illegitimate — and using that lie as a successful political platform. Absent the war on terror, it is harder to imagine a travel ban against people from Muslim-majority countries. Absent the war on terror, it is harder to imagine American protesters labeled terrorists, or a secretary of defense describing the nation’s urban streets as a “battle space” to be dominated. Trump was a disruptive force in American life, but there was much continuity there, too. “A vastly different America has taken root” in the two decades since 9/11, Greenberg writes. “In the name of retaliation, ‘justice,’ and prevention, fundamental values have been cast aside.”
In his latest book on bin Laden, Bergen argues that 9/11 was a major tactical success but a long-term strategic failure for the terrorist leader. Yes, he struck a vicious blow against “the head of the snake,” as he called the United States, but “rather than ending American influence in the Muslim world, the 9/11 attacks greatly amplified it,” with two lengthy, large-scale invasions and new bases established throughout the region.
Yet the legacy of the 9/11 era is found not just in Afghanistan or Iraq, but also in an America that drew out and heightened some of its ugliest impulses — a nation that is deeply divided (like those “separated states” bin Laden imagined); that bypasses inconvenient facts and embraces conspiracy theories; that demonizes outsiders; and that, after failing to spread freedom and democracy around the world, seems less inclined to uphold them here. More Americans today are concerned about domestic extremism than foreign terrorism, and on Jan. 6, 2021, our own citizens assaulted the Capitol building that al-Qaeda hoped to strike on Sept. 11, 2001. Seventeen years after the 9/11 Commission called on the United States to offer moral leadership to the world and to be generous and caring to our neighbors, our moral leadership is in question, and we can barely be generous and caring to ourselves.
In “The Forever War,” Dexter Filkins describes a nation in which “something had broken fundamentally after so many years of war . . . there had been some kind of primal dislocation between cause and effect, a numbness wholly understandable, necessary even, given the pain.” He was writing of Afghanistan, but his words could double as an interpretation of the United States over the past two decades. Still reeling from an attack that dropped out of a blue sky, America is suffering from a sort of post-traumatic stress democracy. It remains in recovery, still a good country, even if a broken good country.
About this story
Copy editing by Jennifer Morehead. Design and development by Andrew Braford.

Never Forget: The Lasting Psychological Impact of 9/11
We’re all survivors, but we’re all scarred..
Posted September 11, 2016 | Reviewed by Jessica Schrader

“Nietzsche said, ‘Whatever doesn’t kill you makes you stronger,’ but, of course, whatever doesn’t kill you leaves scars.”
–Joe Frank, At the Border
Somewhere in my closet, I have a VHS tape, recorded off a CRT television with rabbit-ear antennae, with grainy footage from the morning of Sept. 11, 2001. The footage features the World Trade Center set ablaze, the second airplane flying into the South Tower, people jumping one after another to their death a hundred stories below, and plumes of dust and smoke billowing after the towers finally came down. I’ve never watched that tape and I probably never will, but the images are burned into my memory nonetheless.
The morning of 9/11, I was on the West Coast. A friend called, waking me from sleep and telling me to turn on the television. I spent the next few hours glued to the screen while scrambling to get in touch with friends who were working in Lower Manhattan. Later, when a third plane flew into the Pentagon, I tried tracking down my father, who was working across the street at the time.
Thankfully, I didn’t lose anyone on 9/11. My friends in Manhattan made it out of Ground Zero unscathed, eventually making a long sojourn across the Brooklyn Bridge to get back home later in the day. My father likewise walked several miles in a daze, but in time, made his way back home. By the evening, all my friends and family were accounted for.
As far as my own experience, watching 9/11 unfold on television from the safety of my living room couch, I remember feeling shocked, confused, and frightened. Living underneath the flight path of a nearby airport at the time, things were eerily quiet as air travel was suspended for the next week or so. But when flights started up again, I distinctly remember that the sound of jet engines overhead set me on edge.
For my generation, 9/11 was the pivotal event of our adulthood, having only experienced the shooting of President Reagan and the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster as children. Fifteen years removed, we now have a new generation that wasn’t around to witness 9/11, having only been born in its aftermath. And yet, all of us—regardless of where we were, who we lost, and whether we were alive at the time—feel the psychological repercussions of our national trauma, taking for granted the effects that are deeply embedded in the realities of today.
The U.S. is at war with no clear end in sight. We think nothing of taking off our shoes and belts in long lines at the airport, despite evidence that TSA screening doesn’t work. Most of us readily give up any semblance of electronic privacy in the name of Homeland Security. We’re mistrustful of foreigners, even though the U.S. has always been a country of foreigners. We worry incessantly about the threat of more terrorist attacks. And now, in the midst of a presidential race, we’re a nation divided, squabbling between perspectives that reflect a kind of post-9/11 humility and the desperate hope that we can “make American great again.”
If the historically low ratings of our current presidential candidates is any reflection of the state of the union, it would appear that we live in a time of maximal pessimism about government. Perhaps that was an inevitable outcome for a country that lived through the deadliest attack on homeland soil in the history of our existence. If our leaders were unable to keep us safe then, is it any wonder that some took their skepticism to the point of conspiracy theory, coming up with 9/11 denialism and the so-called “ Truth Movement "? Is it any wonder that some level of skepticism has taken root in the mainstream, reflected in the backing of political outsiders like Bernie Sanders or Donald Trump who we hope might take our country in a different direction?
Of course, if the legacy of the 9/11 terrorist attacks is mistrust of government, a palpable awareness of Middle East politics and Islamic terrorist groups, and a pervasive culture of fear , it’s worth reminding ourselves that this was presumably the exact intent of 9/11’s perpetrators. From their perspective, mission accomplished.
But what about the perspective of the 9/11’s survivors? No doubt, some of us have deeper scars than others. But regardless of how the events of 9/11 touched us individually on that day, we’ve been traumatized as a nation. We’re all children of 9/11 and we’re all survivors, one way or another.
In my experience as a psychiatrist working with patients who have endured trauma, it’s not unusual for friends and family to find themselves wondering why a survivor, years later, can’t “get over it.” The answer is simple—if the traumatic experience isn’t transformed, it retains the immediacy of the original experience.

If survivors are to heal from trauma, they must first acknowledge that it happened. They must remember. They must appreciate that it has shaped them in profound and irreversible ways. And then they must set about doing the hard work—reorienting themselves to the present, rewriting the wrongheaded lessons that trauma has taught them, and figuring out how to escape the past and forge a path into a new future.
"Never forget." Though I’m in no hurry to dig out my old VHS tape of the day, one of my favorite remembrances of 9/11 is Tom Junod’s article from Esquire , “ Falling Man. ” Originally published in 2003, it attempts to reconstruct the identity of a man (captured in a series of photographs by Richard Drew) who, having jumped from the World Trade Center, is seen suspended in air, in one long, tumbling, downward plummet . Junod finishes his essay conceding that the Falling Man’s identity remains elusive, but concludes:
Richard Drew's photograph is all we know of [the Falling Man], and yet all we know of him becomes a measure of what we know of ourselves. The picture is his cenotaph, and like the monuments dedicated to the memory of unknown soldiers everywhere, it asks that we look at it, and make one simple acknowledgment. That we have known who the Falling Man is all along.
Junod seems to suggest that the Falling Man represents all of us, symbolizing someone or something we lost 15 years ago. As individuals and as a nation, let’s all remember what we lost in 9/11. Let’s think about how it’s shaped the country that we live in today. And if we’re unhappy with the state of things now, let’s not get mired in finger-pointing and an all too common externalization of blame as we cling to the familiarity of our injured bodies and lives. If we are to recover from trauma, let’s instead ponder about how we can all get on the same page, becoming part of the solution to heal our national scars, in an effort to retrieve a part of what was lost.
Follow me on Facebook and Twitter .

Joseph M. Pierre, M.D., is a Health Sciences Clinical Professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at University of California, San Francisco and the Unit Chief of the Langley Porter Psychiatric Hospital Adult Inpatient Unit.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Essays revisited: Reflecting on 9/11
- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
In the days and weeks after Sept. 11, 2001, the Times ran dozens of analysis and opinion pieces examining how the events of that day might change the United States and the world. We asked some of the writers who contributed their thoughts after the tragedy to look back at what they wrote then and reflect on it from the vantage point of today.
Richard Rodriguez works at New America Media. His book on the influence of the desert on the Abrahmic religions will be published next year.
On the Sunday after 9/11, Rodriguez wrote eloquently that “it was a week when words failed us. We sensed ourselves entering some terrible epoch, but we did not have sufficient nouns and verbs.” Ten years later, the words are clearer, as is the extent of what was lost.
I believe the time has come to put away the ceremonies of 9/11—the politicians’ speeches at Ground Zero, the parade of children holding the photos of their dead fathers and mothers, the bag-pipes, the tolling bell, the roll call of the dead.
Those of us who were alive that day will always dread the annual alignment of those two numbers — nine, eleven -- the blue September sky; our thoughts will return to the ashes. Let that be the way of it. There is no moratorium on grief.
The dreadful mnemonic date has formed a seal over our minds. Something is wrong. It will not be fixed.
In generations past, America used wounds to form armies. Remember the Alamo! Remember the Maine! After the attack on Pearl Harbor, President Franklin Delano Roosevelt bore witness to December 7, “a date which will live in infamy.”
In the decade since the attacks of September 11th, Americans have turned inward. We have become a nation obsessed with guarding our borders, particularly the Mexican border, even as ghostly TSA images of our naked bodies reach upward, as though under arrest.
We eschew the international, except for the deserts from which the terrorists came. Under the banner of 9/11, President George W. Bush sent Americans to war against Iraq. We were crazed. Osama bin Laden was the leering genie within the explosions. We toppled Saddam Hussein. We ended up fighting Taliban tribesmen in Kandahar.
When American special forces killed Osama bin Laden in May (we do not remember the date), there was no pervading sense in America that the era of 9/11 was finished. Some Americans danced in the street, waved flags, honked their horns. The fighting in Iraq and Afghanistan went on.
What is maddening us is that the wars of 9/11 can have no ending, because we have no clear purpose, because they have no clear adversary. We are not fighting nations; we are fighting peasants and mercenaries and religious ideologues and millionaires. In the war against terrorism, there will never be an “eleventh hour of the eleventh day of the eleventh month”; it will always be 9/11.
But an America that only guards against a dangerous world diminishes its power in the world. In the last ten years, China has usurped the noun Americans thought we held the patent to—the “future.”
While we have deployed troops backward, into the Bible, China has built dams in Africa and made trade agreements with South America. The Chinese have welcomed young men and women from the Third World to Chinese universities. While U.S. troops are killed building roads between tribal villages in Afghanistan, the Chinese sign mineral contracts in Kabul.
The “Arab spring” that began in Tunisia and spread throughout the Middle East has toppled dictators with whom our government maintained “relationships.” We want to feel encouraged by the youthful rebellions. We want to conflate rebellion with American democracy in the designs of the crowd. All the while, we worry the stage is being set for a coming Islamist revival.
Some in our national media have advanced the hope that American technology is liberating the young of the Middle East. Are Apple, Facebook and Twitter democratizing the region? My suspicion is that Americans are confusing conveyance with content. We credit the iPhone with ideological apps that the rest of the world does not necessarily buy.
Hemmed in by an adversarial world, we turn on each other: President Bush was, in the eyes of his critics on the left, a fool wound up by big business. President Barack Obama, according to his critics on the right, is a socialist and a Muslim. Our Congress has become an international scandal. Conservatives versus progressives.
About the only thing that Washington and the nation can seem to manage these days are monuments—we are monument mad, anniversary obsessed. Which leads us to Ground Zero, the tenth anniversary.
This year, put your hand on your heart for all who were lost, for all we have lost, then turn from this place and look at it no more, and see what our nation has become.
Geraldine Brooks, former Mideast correspondent and author, most recently, of the novel Caleb’s Crossing.
In a December 2001 essay titled “ Iraqi people deserve to be liberated ,” Brooks wrote: “Iraq is a far richer country than Afghanistan, gifted with oil, water, good farmland, scenic beauty, rare antiquities. Were it were not for the bleak and terrible regime of Hussein, it could be the showplace of the region. Now is the time to make some belated amends for a tragic mistake. Some in the Bush Cabinet want to strike Iraq to safeguard the West from future terrorism. That is a reason. But there is an even better one. It should be done for the sake of the Iraqis.”
When I wrote those words, I thought I knew Iraq pretty much as well as any non-Iraqi at that time could know it. I’d traveled there many times, in war and peace, visited its cities under oppression and during their brief liberation, in 1980s prosperity and 1990s decline. I’d met with dissidents and torture victims in Europe, Australia and the Mideast. I had seen the effects of Saddam’s brutal terror, but I hadn’t understood that it also acted as a vise, holding that nation together.
It might be possible to plead that in the run up to the war none of us could foresee the depth of fecklessness of the Bush/Cheney administration, or know just how profoundly the plan for the peace had been neglected. So ideological blindness begat the grim fiesta of lawlessness and looting, squandered Iraqi trust, inspired and enabled insurgency.
But the truth and the lessons of Iraq are more compelling and far simpler. Augustine knew them when he set out the basis of just war theory in the fourth century: One should never resort to war unless the threat is existential and there is no other way to answer it; success should be likely and the suffering created less than the suffering averted. Neither of the first two criteria applied to the Iraq war, and the others remain debatable.
Iraqis have had to endure a decade of fear and continue to live with a ravaged infrastructure. The birth pains of their freedom have been unnecessarily agonizing and their future remains uncertain. For us, meanwhile, the costs of war are everywhere apparent: in the shattered bodies of soldiers, in a glinting prosperity dulled by crushing debt, and in a national psyche coarsened by a war whose unequal sacrifice has demanded so much from a few and little more than jingoistic platitudes from the rest.
Peter Tomsen, U.S. special envoy and ambassador on Afghanistan from 1989 to 1992 and author of the just-published “The Wars of Afghanistan.”
In his October 2001 essay “ Past Provides Lessons for Afghanistan’s Future ,” Tomsen warned that: “If the U.S. military offensive is drawn out, and Washington lacks an overarching strategic vision for the region, Pakistan could unravel. Islamic militants would take to the streets, the already wobbly economy could fall and the army splinter into rival factions.” Today Tomsen is still worried.
We entered Afghanistan with the best of intentions, but 10 years later, it is clear that American policy toward Afghanistan and Pakistan has not succeeded.
There are those who will say we should have pressed the war harder, that we should have committed more forces. That was not the problem. Even 500,000 U.S. troops in Afghanistan could not bring peace as long as Pakistan’s army and military intelligence service, the ISI, continue to foster sanctuaries for international terrorist groups inside Pakistan.
Today, American and Afghan troops are under constant attack from a variety of Pakistan-supported organizations, including the Afghan Taliban, the Afghan Haqqani and Gulbuddin Hekmatyar networks, and three ISI-created Pakistani religio-terrorist organizations. Since 9/11, numerous international terrorists, including Faizal Shahzad, the would-be Times Square bomber, have been trained in Pakistani sanctuaries for extremists.
It is clear that Pakistan’s generals have no more intention of dismantling these safe havens now than they had before 9/11. If Washington does not finally deal with Pakistan’s duplicity, our stabilization efforts in Afghanistan will fail and the country will slip into yet another cycle of warfare.
American policy-makers must realize that the risk of taking a tougher approach to Pakistan is less, in the long run, than the risk of continuing the status quo. Ten years of inaction have not paid off. More troops and money are not the answer; nor is continuing to hope that Islamabad’s episodic cooperation with the CIA in eliminating specific terrorists will blossom into a productive working relationship. The United States needs an overarching, long-term policy toward Pakistan that would focus geo-strategic and bilateral pressure on Pakistan’s military leaders to end the Afghan war and stop international terrorism emanating from Pakistan. America and the international community could then focus on helping Afghanistan to once again become a neutral crossroads for Eurasian commerce rather than a proxy battlefield for predatory neighbors.
Naomi Klein, author most recently of “The Shock Doctrine: The Rise of Disaster Capitalism”
In a September 2001 essay titled “ Game Over: The End of Warfare as Play ,” Klein noted that the United States had fought a series of wars in which it had experienced few casualties. “This is a country that has come to believe in the ultimate oxymoron: a safe war,” she wrote. The attacks of 9/11 would change that, she believed. “The illusion of war without casualties has been forever shattered.” Today, she’s not so sure.
I suppose it was wishful thinking. As I watched footage of New Yorkers fleeing from the attacks, their terrified faces covered in dust from the collapsing towers, I was overwhelmed by how different these images were from the people-free videogame wars that my friends and I had grown up watching on CNN. Now that we were finally getting an unsanitized look at what it meant to be attacked from the air, I was sure it would change our hearts forever.
But the Bush Administration was determined to tightly police what we saw of the invasions of Afghanistan and Iraq, introducing “embedded” reporting, and banning photographs of returning caskets. They also let it be known that reporters who embedded themselves with local populations instead of with allied troops were acceptable military targets -- as attacks on Al Jazeera reporters in Afghanistan and Iraq made clear.
The wars being waged by our governments in our names are today more distant to us than ever before. . Some of the fighting is carried out by mercenaries, who die without so much as a mention in the papers. And drone attacks have ushered in something even more dangerous than the “safe war” -- the idea of “no touch” warfare. This sends a clear message to the civilians on the other side of our weapons that we consider our lives so much more valuable than theirs that we will no longer even bother showing up to kill them in person.
As we should have learned ten years ago, this is an extraordinarily dangerous message to send.
Doyle McManus, op-ed columnist
In March 2002, in a front page analysis piece titled “ U.S. Gets Back to Normal ,” McManus, then the paper’s Washington bureau chief, concluded that the news wasn’t how much the attacks had changed America, but how little.
“Six months after Sept. 11,” he wrote, “here’s what’s changed:
“The federal government, its budget and its public image. The focus of American foreign policy. Security measures at airports, seaports and border crossings. The nation’s sense of patriotism, cohesion and vulnerability. The lives of almost 1.4 million people in the armed services…. [and] the victims, their families and friends.
“Here’s what hasn’t changed much: Everything else.” Today, he says, that’s still mostly true.
Since Sept. 11, the federal government has continued to grow. Spending has mushroomed on war-fighting, intelligence-gathering and homeland security. Security measures at airports and seaports are even tighter than before – although the government promises we’ll be allowed to keep our shoes on some day.
But that hasn’t made us love the federal government more. In the frightened months after Sept. 11, polls found that Americans’ trust in the government’s ability to do the right thing soared; in the years since, that same measure has plummeted.
That’s largely because the issue that concerns Americans most is no longer terrorism, but economic stagnation – and the federal government hasn’t succeeded in overcoming that threat.
As for “the nation’s sense of patriotism [and] cohesion,” the patriotism is still there, but the cohesion we discovered in 2001 was evanescent. A divisive war in Iraq and a virtual civil war over fiscal policy quickly turned politics nasty again.
In 2002, I asked Harvard social scientist Robert D. Putnam if 9/11 could have a lasting positive effect on our sense of community, and he was skeptical – appropriately, as it turned out.
“After almost any crisis, calamity or natural disaster, there’s a sudden spike in community-mindedness, whether it’s an earthquake, a flood or a snowstorm in Buffalo,” he said. “But these spikes don’t last. Over time, the community feeling dissipates.”
The only exception, Putnam noted, was Pearl Harbor – because World War II called on every citizen to sacrifice. This time, only a few were called on; the rest of us were encouraged to go shopping.
The focus of American policy has shifted, too. Immediately after 9/11, it was stopping further terrorism; then it was managing the consequences of our Global War on Terror, especially in Iraq and Afghanistan. But now the focus is broader – and, increasingly, economic. As the just-retired chairman of the joint chiefs of staff, Adm. Mike Mullen, often said, “The single biggest threat to our national security is our debt.”
The war on terror isn’t over, even though it’s no longer called by that name. There are still almost 100,000 U.S. troops in Afghanistan, almost 50,000 in Iraq. The real cost of those wars – more than 5000 killed in action, more than 45,000 injured – changed many lives irrevocably.
But for most Americans, the most striking fact remains not how much 9/11 changed, but how little.
Graham Allison is director of the Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs at Harvard’s Kennedy School of Government and a former assistant secretary of Defense.
In November 2001, Allison wrote that “After Sept. 11, a nuclear terrorist attack can no longer be dismissed as an analyst’s fantasy. … As the international noose tightens around Al Qaeda’s neck, the group will become more desperate and audacious.” Ten years later, he says we have made some progress in keeping nuclear weapons out of terrorist groups’ hands.
On 9/11, 19 terrorists killed more Americans than the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. If the terrorists had been in possession of a nuclear weapon, the attack might have killed 300,000.
Post 9/11, President Bush, and now President Obama, have declared nuclear terrorism the biggest threat to American national security.
The United States has taken the lead in investing more than $10 billion and countless hours in securing and eliminating nuclear weapons and material worldwide. President Obama’s Nuclear Security Summit in 2010 focused exclusively on the threat. As a result of these efforts, thousands of weapons and material that could have produced thousands more weapons are better secured today than they were a decade ago. In Russia, which has the world’s largest stockpile of nuclear weapons and material, hundreds of sensitive sites have been secured; 17 countries have eliminated their weapons-usable material stockpiles entirely.
But to prevent a nuclear 9/11, all nuclear weapons and weapons-usable material everywhere must be secured to a “gold standard” — beyond the reach of terrorists or thieves.
On that agenda, much remains to be done. The ever-more fragile state of Pakistan has the world’s most rapidly expanding nuclear arsenal. North Korea today has enough material for about 10 nuclear bombs. And Iran now has enough low enriched uranium, if further processed, for four nuclear weapons. One of these weapons in the hands of terrorists could mean an “American Hiroshima”
The price of success in preventing a nuclear 9/11 remains eternal vigilance.
James Fallows is a national correspondent for the Atlantic and an author.
In September 2001, Fallows wrote in his essay “ Step One: Station a Marshal Outside Every Cockpit Door ” that: “There may not be a next time, as everything involving air travel becomes more constrained. The tightening of security, while necessary, almost certainly will have aspects of fighting the last war. We may spend years refining passenger-screening processes, only to have the next terrorist explosive arrive by barge.
… Any system careful enough to eliminate sophisticated terrorists also would be cumbersome enough to negate the speed advantage of traveling by air.”
I wish my fears had had turned out to be wholly unfounded. And when it comes to the specific scenario of bombs aboard barges, I’m glad to say that they have been, at least so far.
Unfortunately, there was a much broader challenge that many people, including me, foresaw from the very beginning of the push toward a sweeping emphasis on “homeland security” and the “global war on terror.” This was the risk that, in the name of “protecting” ourselves against future threats, we might ultimately give up, distort or sacrifice the values that made a free society most worth defending. I am sorry to say that this fear has largely been realized.
We can’t be sure of much when it comes to future acts of terrorism, but one certainty is that there will never be “another 9/11.” That attack depended for its shocking success on people not imagining that airliners would be used as large-scale urban bombs. Everyone in the world now understands that possibility, which is why a “9/11-style” attack simply cannot be pulled off again. If the passengers and crew on a plane did not stop future hijackers from flying a fuel-laden plane into a city, the Air Force would.
We also know that our reflexive response to threats has given tremendous leverage to any handful of people who conceive of a new means of attack. Because of one foiled shoe-bombing attempt, hundreds of millions of air passengers worldwide continue removing their shoes before boarding planes. Osama bin Laden’s associates spent hundreds of thousands of dollars on their attacks. America’s chosen response has cost the nation trillions of dollars in direct military and security expenditures, not to mention the other costs.
The long-standing truth about terrorism is that the worst damage it inflicts is not through the initial attack but rather through the self-defeating and extreme response it often evokes. It is past time for America to consider a security response that does more damage to potential attackers and less to ourselves.
Shireen T. Hunter is a visiting professor at Georgetown University’s School of Foreign Service .
In her September 2001 OpEd (“ Wake-Up Call for the Islamic World ”), Hunter argued that Muslims themselves have been the ones most adversely affected by the extremist ideas and groups that have sprung up amid them, “giving credence to the worst perceptions of Islam as a rigid, aggressive, reactionary and xenophobic creed.” She recommended that Muslim nations “stop using Islam as an instrument of foreign policy” and to “abandon outdated utopian and expansionist schemes.”
Unfortunately, in the intervening years, Muslim nations have continued this behavior. Thus, in their bids to expand their regional influence, countries such as Saudi Arabia, Iran and Pakistan have stoked the fires of sectarianism in Iraq, Bahrain, Afghanistan, Pakistan and Yemen. Saudi Arabia has even resorted to manipulating sectarian divisions in Lebanon and Syria in its attempt to eliminate the Iranian influence. Meanwhile, Iran has continued to support its Shiite co-religionists in Lebanon.
The upshot of this situation is that in the Muslim world today, sectarian divisions and hatreds are even deeper. This seriously hampers the establishment of peace and even a modicum of stability, and dims the prospect of consensual politics. Instead, the manipulation of sectarian divides and rivalries for power and influence, notably between Iran and Saudi Arabia, has led to new tragedies such as that in Bahrain where the Shiite majority is being brutally repressed by the Sunni rulership.
Meanwhile, Al Qaeda Inc. branches have sprung up in Iraq, Yemen and elsewhere, and remain strong, despite the deaths of Osama bin Laden and other top leaders; the Taliban are resurgent in Afghanistan; and the ultra-conservative Salafists have developed strong footholds in Egypt, Tunisia and Jordan.
All this time, the needs and aspirations of the people have been ignored, leading them to revolt as we have seen during the “Arab spring.” Yet revolts and revolutions seldom lead to democracy. Generally they result in politics of revenge, chaos and eventually another form of dictatorship. Muslim countries have missed an opportunity.
Alexander Cockburn coedits the CounterPunch website and writes for the Nation and other publications.
“The lust for retaliation traditionally outstrips precision in identifying the actual assailant,” Cockburn wrote in September 2001 (“ The Next Casualty: Bill of Rights? ”). “The targets abroad will be all the usual suspects -- the Taliban or Saddam Hussein, who started off as creatures of U.S. intelligence. The target at home will be the Bill of Rights.”
It was maybe an hour after the north tower of the World Trade Center collapsed that I heard the first of a thousand pundits that day saying that America might soon have to sacrifice “some of those freedoms we have taken for granted.” They said this with grave relish, as though the Bill of Rights – the first 10 amendments to the U.S. Constitution — was somehow responsible for the onslaught, and should join the rubble of the towers, carted off to New Jersey and exported to China for recycling into abutments for the Three Gorges Dam.
Of course it didn’t take 9/11 to give the Bill of Rights a battering. It is always under duress and erosion. Where there’s emergency, there’s opportunity for the enemies of freedom. The Patriot Act, passed in October 2001 and periodically renewed in most of its essentials in the Bush and Obama years, kicked new holes in at least six of our Bill of Rights protections.
The government can search and seize citizens’ papers and effects without probable cause, spy on their electronic communications, and has, amid ongoing court battles on the issue, eavesdropped on their conversations without a warrant. Goodbye to the right to a speedy public trial with assistance of counsel. Welcome indefinite incarceration without charges, denial of the assistance of legal counsel and of the right to confront witnesses or even have a trial. Until beaten back by the courts, the Patriot Act gave a sound whack at the 1st Amendment, too, since the government could now prosecute librarians or keepers of any records if they told anyone the government had subpoenaed information related to a terror investigation.
Let’s not forget that a suspect may be in no position to do any confronting or waiting for trial since American citizens deemed a threat to their country can be extrajudicially and summarily executed by order of the president, with the reasons for the order shielded from the light of day as “state secrets”. That takes us back to the bills of attainder the Framers expressly banned in Article One of the U.S. Constitution, about as far from the Bill of Rights as you can get. We can thank the War on Terror, launched after 9/11, for it.
Jonathan Turley is a law professor at George Washington University.
In his September 13 Op Ed (“ Cries of “war” stumble over the law ”), Turley warned against the government seeking “greater flexibility” in responding to terrorists by treating criminal attacks “as a matter of war.” “Our system,” he wrote, “requires that legal means be used to achieve legal ends. We decide those means and ends within the general confines of the Constitution.” How has the founding document fared?
As the smoke was still rising from the Pentagon and World Trade Center, it became quickly evident that some of the greatest damage from the September 11th attacks would not come from without but from within our nation.
There was an almost immediate effort by Bush officials to change the definition of war. Rather than declare war on Afghanistan (where Bin Laden was sheltered), President George W. Bush wanted to declare war on terrorism. It was no rhetorical triviality. Bush decided to invoke the heightened constitutional powers of a wartime president by declaring war on what was a category of crime. Because there could never be a total, final defeat of terrorism, this “war” would become permanent – as would the heightened powers of the president.
Ten years later, the country remains “at war,” with President Barack Obama expanding many of the national security powers of his predecessor and, in the Libyan war, claiming his own re-definition of war: “a time-limited, scope-limited military action.”
Of course, the ominous signs in 2001 were realized in a myriad of other ways, from the establishment of the first American torture program to the widespread use of targeted assassinations, including operations killing American citizens. Ironically, I wrote then of the possibility of a new law that could govern the use of assassination, one that would deny a president unilateral authority to kill individuals and would reduce the need to invoke war powers. Instead, the Bush administration claimed full wartime authority as well as radically expanding the use of assassination as an unchecked presidential power. The claim of unilateral presidential authority to kill even United States citizens has been embraced by Obama.
What ultimately fell on that terrible day proved to be some of our most important constitutional structures. Tragically, it is a degree of damage that cannot be claimed by Al Qaeda alone.
Laila Al-Marayati, Los Angeles physician
In a January 2002 essay titled “ An Identity Reduced to a Burka ,” Al-Marayati wrote: “It should be obvious that the critical element Muslim women need is freedom, especially the freedom to make choices that enable them to be independent agents of positive change.”
After the tragic events of 9/11, there were some genuine attempts to improve understanding and awareness between peoples. But that good will has given way in recent years to increased anti-Muslim sentiment in the U.S. and around the world, prejudices that were reflected in a recent Gallup poll. Muslim women who choose to wear hijab take the brunt of the hostility. They are subject to verbal assault and to misdirected legal actions such as in the ban on the headscarf imposed in France. For centuries, Muslim women have been in the crosshairs of the supposed conflict between Islam and the West. Shortly before the invasion of Afghanistan, we saw images, almost daily, of burqa-clad women who had been suffering under the Taliban. But what most people forget is that they were suffering long before 9/11 and that they continue to experience hardship today in most parts of the country. In 2001, their plight was exploited for political expediency, to help drum up support among freedom-loving Americans for a war that has yet to make life better for the common Afghan woman. Over the past decade, Muslim women around the world have continued to demand their rights and claim their position alongside their Muslim brothers by advocating for changes in legal systems that discriminate against them, by educating their daughters, and by challenging harmful traditions that have no basis in Islam. Many of them are now engaged in the struggle of their lives to achieve the kind of freedom that Muslims living in the U.S. appreciate. It is too soon to predict the outcome, but we should have no doubt that women will be at the forefront of positive change. We should support their efforts, not for political expediency, but because it is the right thing to do.
More to Read

Opinion: Why did Israel miss so many warnings of the Hamas attack? Here’s one answer
Dec. 11, 2023

Opinion: We were one nation, united in mourning, when President Kennedy died. Not anymore
Nov. 25, 2023

Opinion: 9/11 offers awful lessons for what could happen with a Gaza ground invasion
Oct. 16, 2023
A cure for the common opinion
Get thought-provoking perspectives with our weekly newsletter.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Granderson: A football player said something stupid about women. Let it go
May 17, 2024

Opinion: Will California’s new tax on gun sales reduce firearm violence?

Editorial: China embraced electric vehicles. The U.S. didn’t. Now we’re paying the price

Letters to the Editor
Letters to the Editor: A modest proposal for transit safety: Every rider gets a gun
Lesson Plan
Sept. 10, 2023, 7:45 p.m.
Lesson plan: 9/11 — Ways to reflect on the day’s legacy

September 11th will remain a day that shaped the course of the nation’s — and the world’s — history. Students in high school and middle school who were not yet born on September 11, 2001, have still grown up in a cultural and political environment that owes much to the actions of the United States in response to 9/11.
The purpose of this lesson is to invite participants to generate and share their own questions about both the day of 9/11 and the larger context of the response that followed, including the U.S. occupation of Afghanistan that is just now ending after two decades.
You can see more stories from the NewsHour examining how this recent history has shaped the nation and the world. These NewsHour pieces will become optional components of the lesson.
Click here for a series of slides that can supplement this lesson (note: you will be prompted to make a copy).
- Understand the history and impact of the 9/11 attacks
- Construct critical questions around the anniversary of 9/11 and its present-day context
- Evaluate & reflect on personal understanding of 9/11 through critical questions
Grade Levels
Supplemental links.
- GOOGLE DOC VERSION
- SUPPLEMENTAL SLIDES
CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RI.9-10.1: Cite strong and thorough textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.9-10.2: Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of how key events or ideas develop over the course of the text. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.11-12.7: Integrate and evaluate multiple sources of information presented in diverse formats and media (e.g., visually, quantitatively, as well as in words) in order to address a question or solve a problem. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.9-10.9: Compare and contrast treatments of the same topic in several primary and secondary sources.
Original lesson appeared Sept. 11, 2021.

Sun setting behind Twin Towers. (Photo by Robert Pirillo/Ovoworks/Time Life Pictures/Getty Images) For a Google version of this lesson click here . A note on teaching hard history: Most educators can recall exactly where they were and what they were doing when 9/11 unfolded. Today’s generation of students does not share this collective memory, with today’s high school seniors being born a few years after 2001.
Teaching 9/11 on its anniversary has its merits, as does teaching 9/11 within the curricular context of American and global history. We encourage educators to explore the wealth of resources provided in this lesson plan, to examine their own unanswered questions and biases, and to reflect on pedagogical practice before bringing in traumatic and provocative images of 9/11. Check out “Trauma-Informed Teaching Strategies” and consider how you might design lessons that engage with hard history with a trauma-informed lens. Read Learning for Justice's article “Debunking Stereotypes About Muslims and Islam” and incorporate media literacy education as you confront misinformation.
In addition, consider doing the following:
- Preview your expectations or reminding your class about norms
- Name clearly the topics; create time for participants to reflect and process
- Teach with a trauma-informed lens
- Consider the emotional response of your participants and yourself
Warm up activities (5-10 mins):
Note for instructors: Whether you’re teaching about 9/11 on the anniversary of the attacks or as a part of your broader curriculum, starting with the questions participants have can set up an anchor and circular flow (returning to those questions to close out or build upon them in the end). Remind participants to be and stay curious and to practice the skill of writing and developing strong questions.
- Generate: Participants write as many questions as they can about the September 11 attacks — without stopping to revise, edit, evaluate or answer their questions.
- Reflect: Then, participants circle or mark their three most important questions — and briefly reflect on why they selected these three.
- Turn & Talk: Participants turn and share their three questions, noting what may overlap or be different, and have partners share out questions to gauge what participants are curious about. This is also an opportunity to note any misinformation or incorrect assumptions participants may have to clarify & revisit. Read “Debunking Stereotypes About Muslims and Islam” by Learning for Justice to learn more.
Main activities (30-45 mins)
Directions: Choose one or more activity best suited to your class based on the many factors your role as a teacher requires you to know.
- Watch the 9/11 Memorial Museum’s short film (3 minutes): This video outlines the events on the morning of 9/11. As participants listen, instruct them to watch for any answers to the questions they just constructed. CONTENT WARNING : This video contains images of the Twin Towers and the Pentagon after they are hit.
- Optional: Take a detour into a robust timeline of the 9/11 attacks using this interactive guide at the 9/11 Memorial & Museum and pair it with this “Historical Timeline of Afghanistan” from PBS NewsHour . Focus on context-building, asking participants to investigate questions, connections and narratives they see represented.
- Clarify and reflect (5-10 mins): Turning to talk with their partners again (or return to their notebook to write), what did participants notice about the short clip or (timelines) that answered some of their questions?
- Together with their partner, what new questions can they create? Note: If a participant replies with “I don’t have any questions,” encourage them to practice the skill of questioning and examining what they think, why they think it and what they wonder. Encourage curiosity.
- Share this infographic with participants. After reviewing, ask participants: What surprises them? Does anything connect to the questions they crafted?

via slideshow -- see link at top of lesson
via slideshow — see link at top of lesson
- Ask participants: What stories do these numbers tell? What stories don’t these numbers tell? (Can invite participants to update their list of questions here, pushing into open-ended questions vs. closed questions.)
- Watch The 9/11 Memorial & Museum has a trailer (3 minutes) for one of their programs featuring some personal connections individuals have to 9/11.
- What did you notice, what surprised you, or what do you now wonder after hearing from some individuals who have a personal connection to that day?
- Now that you’ve reviewed or learned some of the historical context of 9/11, what do you know or wonder about the legacy of 9/11? What impact has the 9/11 terrorist attacks had on the United States? Other countries? Ordinary and everyday people in the United States?
- Turn & talk: Have participants share some of their ideas, questions and reflections with their partner.
- Whole group: Invite participants to share any ideas, encourage questions and discuss together.
Part 3 (Choose one or more of the following activities)
Each night this week, PBS NewsHour features stories that examine some of the ways 9/11 transformed the nation and world. Choose one or more of the following available stories to discuss.
- What do you notice?
- What do you wonder?
- Does your community share anything in common with the communities of the speakers? How so?
- How does (or did) 9/11 impact different communities? How so?
- What other connections or questions can you craft?
- NewsHour's Amna Nawaz says: “20 years later, there is now an entire generation of young American adults, including American Muslims, who don’t have firsthand memories of [9/11], who did not live through the trauma, as all of us did.”
- How do you think the impact of 9/11 varies from generation to generation? What similarities or differences do you notice among your generation versus your parent’s generation? And older generations?
- What are some of the ways these students' lives have been directly impacted by the legacy of 9/11?
- What are some ways these students sees their generation's experience as different from past generations?
- What is Middletown’s connection to the 9/11 attacks?
- What were the different perspectives shared on how families coped with the loss of loved ones in the attacks?
- How does this feature story expand or inform what you already know about 9/11?
- Why is it important to understand the emotional reaction of U.S. citizens on the day of 9/11, according to Graff?
- What is the connection that Graff makes between 9/11 and political polarization?
- What do you think Graff means when he says 9/11 is slipping “from memory into history”? What are your first memories of learning about 9/11 or understanding the day’s events and legacy?
- As a generation, what has shaped your view and understanding of 9/11? How so? How might this differ from other generations or communities?
- What perspectives and narratives are you seeing and hearing surrounding the 20th anniversary of 9/11?
- How do you think the legacy of 9/11 will continue to evolve?
- Whose stories are being told? Is anyone’s voice missing?
Closing (10-15 mins)
Circle back to warm up questions for clarifying and answering the unanswered questions. (Could be collected as an exit ticket or final turn and talk.)
- Look back over the questions you created at the start of class.
- What’s one question that has been answered today?
- What’s a new question you have or are thinking about? What’s left unanswered for you? What are you wondering about?
- What’s the impact of 9/11 on your generation? What do you predict will be the legacy of 9/11 for future generations?
Extension activities
Extension 1, Poetry Focus: Days before 9/11, poet Lucille Clifton welcomed a granddaughter into the world and remembers eating lunch on the day itself as she “watched on television the devastation of the Twin Towers.” In her poem “September’s Song: A Poem in Seven Days,” she examines “love and continuing and fear and hope.”
Share this excerpt of Tuesday and Sunday from the longer poem with students , reading aloud together or ask participants to annotate a copy of the poem (or digitally with a partner using this Google Doc). [Note: September 11, 2001 was a Tuesday]
Write in response:
- Ask participants to write their own day poem connecting to the themes of hope and fear, of love and continuing, mimicking some of Clifton’s style.
- Do not require participants to write specifically about 9/11. Instead leave the invitation open for them to write about what they choose.
- Or invite participants to identify vivid imagery, metaphors or symbols in the poem.
- Compare Clifton’s poem with excerpts from “ With Their Eyes: September 11th — The View From A High School at Ground Zero. ” What word choice evokes an emotional response in the reader? How does the physical structure of the poems impact the way it is read aloud? As writers, what writing moves might participants employ in their own writing?
Extension 2 : Just over a year ago, more than 123,000 Afghan refugees, many fearing for their lives, were evacuated from Afghanistan and were resettled all over the world, including the United States. Thousands of Afghans did not make it out of the country before the U.S. military's departure on Aug. 30. Explore who, what, when, where and how of the refugees arriving in the U.S., and what local community organizations are still working to provide assistance. Read this NewsHour article for more information.
- Inquire: What do trustworthy and credible charities and organizations look like?
- Explore: What is being done locally in your area or state?
- Understand: What don’t you know? What questions do you have?
- Apply: How could your class, school, or community support and welcome refugees?
- What are the latest updates as to the Afghan refugees welfare and status in the U.S. and around the world?

U.S. Air Force loadmasters and pilots assigned to the 816th Expeditionary Airlift Squadron, load passengers aboard a U.S. Air Force C-17 Globemaster III in support of the Afghanistan evacuation at Hamid Karzai International Airport in Kabul, Afghanistan, August 24, 2021. Picture taken August 24, 2021. U.S. Air Force/Master Sgt. Donald R. Allen/Handout via REUTERS
Kate Stevens, M.S. in Curriculum & Instruction, is an instructional coach and educator with more than a decade of experience in online, hybrid, and blended learning. In 2015, Kate was honored with Colorado Department of Education’s Online & Blended Teacher of the Year. Connect with Kate on Twitter @KateTeaching.
Fill out this form to share your thoughts on Classroom’s resources. Sign up for NewsHour Classroom’s ready-to-go Daily News Lessons delivered to your inbox each morning.
Recent Lesson Plans

Lesson Plan: Using robotics to support rural communities
A short project-based lesson that weaves arts & sciences together

Lesson plan: Watergate and the limits of presidential power
On August 9, 1974, President Richard M. Nixon resigned from the Oval Office. Use this resource to teach young people about this period in U.S. history.

How2Internet: Use media literacy skills to navigate the misinformation highway
Learn to produce a fact-check video using media literacy skills

Lesson plan: Understand the UN Declaration of Rights of Indigenous Peoples through oral history
Learn about the United Nations human rights principles for indigenous peoples through the lens of oral history storytelling
- September 11th anniversary
- government-civics
- social-studies
- lesson-plan
- news-media-literacy
- Misinformation
- trauma-informed practices
SUPPORTED BY VIEWERS LIKE YOU. ADDITIONAL SUPPORT PROVIDED BY:

Copyright © 2023 NewsHour Production LLC. All Rights Reserved
Illustrations by Annamaria Ward

Nearby Communities
- Greater Hartford, CT
- Farmington, CT
- Newington, CT
- Wethersfield, CT
- Simsbury, CT
- Windsor, CT
- Rocky Hill, CT
- South Windsor, CT
State Edition
- Connecticut
National Edition
- Top National News
- See All Communities
Community Corner
What 9/11 means to me: an essay from a west hartford firefighter, battalion chief matthew j. stuart of the west hartford fire department shares his his thoughts about sept. 11..

Ronni Newton , Patch Staff

The anniversary of 9/11 is firefighter memorial day.
I understand for others it’s about a day of great loss for our nation, and for some people they look at the thousands of people killed that day.
But for me, it’s about the sacrifice that the members of the FDNY (Fire Department, City of New York) made on that date. They lost 343 members in the collapse of the towers, and these were people who willingly advanced into the danger rather than retreat from it.
Find out what's happening in West Hartford with free, real-time updates from Patch.
Anybody who is a firefighter has a unique perspective on life, and how fragile it can be. Every time you go to work you might be involved on an intimate level with people who are probably having the worst day of their lives. It’s up close and personal. The things you see and experience during a career as a firefighter are constant reminders of how lucky you are. These experiences change you forever.
What made these members of the FDNY go so willingly into a situation where they knew they might not come out? Why would anyone do this for his or her fellow man?
Firefighting is not a job to us. When asked, we will all say we were “just doing our job,” but that’s not really the whole story.
Being a firefighter is who we are. It’s a deep held belief that with other firefighters we can help people because we are willing to step up. We are willing to put ourselves between danger and the people who need help. We do not need to know who they are, nor do we care about all the things that society looks at as “important.” We just know somebody needs help, and as firefighters we are the last line of defense. People know when they call us for help that we are going to show up, and make things better. It’s what we do.
Firefighters are stubborn. We don’t give up easily when faced with a tough situation. We respond to calls in teams (known as companies), which in turn reinforces our efforts as individuals because no one wants to let the “team” down. That team effort on our part makes us stronger than as individuals. When a firefighter is recognized for his or her achievements, they always give credit to their fellow firefighters.
On Sept. 11, 2001, what you really saw was the dedication of a group of firefighters to the cause of protecting the public. They walked into the World Trade center and went to work. I read reports of some firefighters saying to each other, “It’s been nice knowin’ ya,” as they advanced in. They knew full well the dangers they were facing, and they went in – willingly.
To me 9/11/01 was the day the public saw just how extraordinary those members of the FDNY were. It showed how a group of “ordinary” firefighters, faced with an extraordinary task, did not flinch in the course of their duty.
The sad part was that 343 of my brother firefighters lost their lives when the towers came down. It is sad that so many families of these guys had to give up a family member that day. And don’t forget the loss to the FDNY itself. These guys were part of that family too.
We knew that even after the towers came down, that the FDNY would regroup, and continue to do the job they were tasked with.
Everybody on our job felt that we needed to do something to show support for our FDNY brothers. A task force was organized of people willing to go to New York and help. The International Association of Firefighters organized a “fill the boot” campaign to raise money for the families, and we were able to help with that. Public support of the fill the boot drive was tremendous.
The hardest thing we did as firefighters was to attend as many funerals and memorial services as we could – just to show our support for the families and the FDNY. This went on for over a year.
While 9/11 was the largest loss of firefighters on a single day in American fire service history, the loss of even a single firefighter in the line of duty is a tragedy. And I can assure you through personal experience that even the loss of that one person in the line of duty affects that fire department immensely.
So for me, I remember the sacrifices of all firefighters who have died in the line of duty on 9/11, every year. Appreciating the extraordinary bravery and courage of those who made the “ultimate sacrifice” does not require ceremony, just reflection and remembrance. I also remember how lucky I am to work with the greatest “ordinary” people in any profession – firefighters.
Get more local news delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for free Patch newsletters and alerts.
More from West Hartford
Safety improvements mulled at west hartford school.

Hidden Gems Of Hartford And Tolland Counties

Tour West Hartford's Arboretum This Spring

Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:

Two Decades Later, the Enduring Legacy of 9/11
Table of contents, a devastating emotional toll, a lasting historical legacy, 9/11 transformed u.s. public opinion, but many of its impacts were short-lived, u.s. military response: afghanistan and iraq, the ‘new normal’: the threat of terrorism after 9/11, addressing the threat of terrorism at home and abroad, views of muslims, islam grew more partisan in years after 9/11.
Americans watched in horror as the terrorist attacks of Sept. 11, 2001, left nearly 3,000 people dead in New York City, Washington, D.C., and Shanksville, Pennsylvania. Nearly 20 years later, they watched in sorrow as the nation’s military mission in Afghanistan – which began less than a month after 9/11 – came to a bloody and chaotic conclusion.
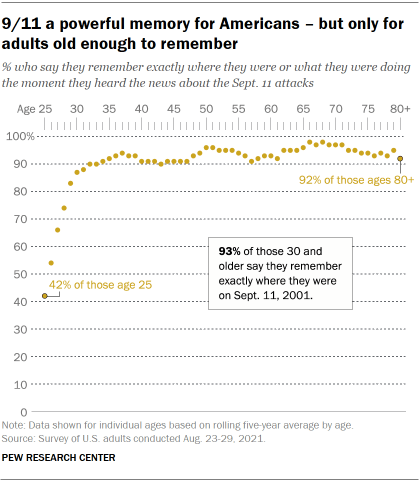
The enduring power of the Sept. 11 attacks is clear: An overwhelming share of Americans who are old enough to recall the day remember where they were and what they were doing when they heard the news. Yet an ever-growing number of Americans have no personal memory of that day, either because they were too young or not yet born.
A review of U.S. public opinion in the two decades since 9/11 reveals how a badly shaken nation came together, briefly, in a spirit of sadness and patriotism; how the public initially rallied behind the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, though support waned over time; and how Americans viewed the threat of terrorism at home and the steps the government took to combat it.
As the country comes to grips with the tumultuous exit of U.S. military forces from Afghanistan, the departure has raised long-term questions about U.S. foreign policy and America’s place in the world. Yet the public’s initial judgments on that mission are clear: A majority endorses the decision to withdraw from Afghanistan, even as it criticizes the Biden administration’s handling of the situation. And after a war that cost thousands of lives – including more than 2,000 American service members – and trillions of dollars in military spending, a new Pew Research Center survey finds that 69% of U.S. adults say the United States has mostly failed to achieve its goals in Afghanistan.
This examination of how the United States changed in the two decades following the Sept. 11 terrorist attacks is based on an analysis of past public opinion survey data from Pew Research Center, news reports and other sources.
Current data is from a Pew Research Center survey of 10,348 U.S. adults conducted Aug. 23-29, 2021. Most of the interviewing was conducted before the Aug. 26 suicide bombing at Kabul airport, and all of it was conducted before the completion of the evacuation. Everyone who took part is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for the report, along with responses, and its methodology .
Shock, sadness, fear, anger: The 9/11 attacks inflicted a devastating emotional toll on Americans. But as horrible as the events of that day were, a 63% majority of Americans said they couldn’t stop watching news coverage of the attacks.
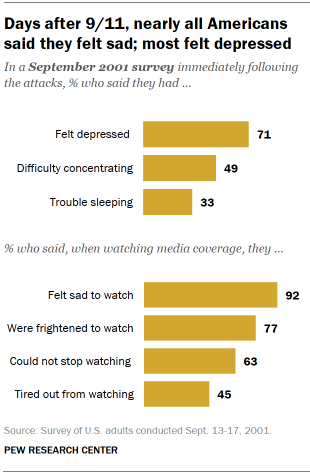
Our first survey following the attacks went into the field just days after 9/11, from Sept. 13-17, 2001. A sizable majority of adults (71%) said they felt depressed, nearly half (49%) had difficulty concentrating and a third said they had trouble sleeping.
It was an era in which television was still the public’s dominant news source – 90% said they got most of their news about the attacks from television, compared with just 5% who got news online – and the televised images of death and destruction had a powerful impact. Around nine-in-ten Americans (92%) agreed with the statement, “I feel sad when watching TV coverage of the terrorist attacks.” A sizable majority (77%) also found it frightening to watch – but most did so anyway.
Americans were enraged by the attacks, too. Three weeks after 9/11 , even as the psychological stress began to ease somewhat, 87% said they felt angry about the attacks on the World Trade Center and Pentagon.
Fear was widespread, not just in the days immediately after the attacks, but throughout the fall of 2001. Most Americans said they were very (28%) or somewhat (45%) worried about another attack . When asked a year later to describe how their lives changed in a major way, about half of adults said they felt more afraid, more careful, more distrustful or more vulnerable as a result of the attacks.

Even after the immediate shock of 9/11 had subsided, concerns over terrorism remained at higher levels in major cities – especially New York and Washington – than in small towns and rural areas. The personal impact of the attacks also was felt more keenly in the cities directly targeted: Nearly a year after 9/11, about six-in-ten adults in the New York (61%) and Washington (63%) areas said the attacks had changed their lives at least a little, compared with 49% nationwide. This sentiment was shared by residents of other large cities. A quarter of people who lived in large cities nationwide said their lives had changed in a major way – twice the rate found in small towns and rural areas.
The impacts of the Sept. 11 attacks were deeply felt and slow to dissipate. By the following August, half of U.S. adults said the country “had changed in a major way” – a number that actually increased , to 61%, 10 years after the event .
A year after the attacks, in an open-ended question, most Americans – 80% – cited 9/11 as the most important event that had occurred in the country during the previous year. Strikingly, a larger share also volunteered it as the most important thing that happened to them personally in the prior year (38%) than mentioned other typical life events, such as births or deaths. Again, the personal impact was much greater in New York and Washington, where 51% and 44%, respectively, pointed to the attacks as the most significant personal event over the prior year.
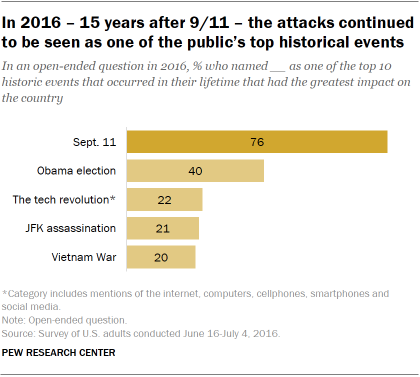
Just as memories of 9/11 are firmly embedded in the minds of most Americans old enough to recall the attacks, their historical importance far surpasses other events in people’s lifetimes. In a survey conducted by Pew Research Center in association with A+E Networks’ HISTORY in 2016 – 15 years after 9/11 – 76% of adults named the Sept. 11 attacks as one of the 10 historical events of their lifetime that had the greatest impact on the country. The election of Barack Obama as the first Black president was a distant second, at 40%.
The importance of 9/11 transcended age, gender, geographic and even political differences. The 2016 study noted that while partisans agreed on little else that election cycle, more than seven-in-ten Republicans and Democrats named the attacks as one of their top 10 historic events.

It is difficult to think of an event that so profoundly transformed U.S. public opinion across so many dimensions as the 9/11 attacks. While Americans had a shared sense of anguish after Sept. 11, the months that followed also were marked by rare spirit of public unity.

Patriotic sentiment surged in the aftermath of 9/11. After the U.S. and its allies launched airstrikes against Taliban and al-Qaida forces in early October 2001, 79% of adults said they had displayed an American flag. A year later, a 62% majority said they had often felt patriotic as a result of the 9/11 attacks.
Moreover, the public largely set aside political differences and rallied in support of the nation’s major institutions, as well as its political leadership. In October 2001, 60% of adults expressed trust in the federal government – a level not reached in the previous three decades, nor approached in the two decades since then.
George W. Bush, who had become president nine months earlier after a fiercely contested election, saw his job approval rise 35 percentage points in the space of three weeks. In late September 2001, 86% of adults – including nearly all Republicans (96%) and a sizable majority of Democrats (78%) – approved of the way Bush was handling his job as president.
Americans also turned to religion and faith in large numbers. In the days and weeks after 9/11, most Americans said they were praying more often. In November 2001, 78% said religion’s influence in American life was increasing, more than double the share who said that eight months earlier and – like public trust in the federal government – the highest level in four decades .
Public esteem rose even for some institutions that usually are not that popular with Americans. For example, in November 2001, news organizations received record-high ratings for professionalism. Around seven-in-ten adults (69%) said they “stand up for America,” while 60% said they protected democracy.
Yet in many ways, the “9/11 effect” on public opinion was short-lived. Public trust in government, as well as confidence in other institutions, declined throughout the 2000s. By 2005, following another major national tragedy – the government’s mishandling of the relief effort for victims of Hurricane Katrina – just 31% said they trusted the federal government, half the share who said so in the months after 9/11. Trust has remained relatively low for the past two decades: In April of this year, only 24% said they trusted the government just about always or most of the time.
Bush’s approval ratings, meanwhile, never again reached the lofty heights they did shortly after 9/11. By the end of his presidency, in December 2008, just 24% approved of his job performance.

With the U.S. now formally out of Afghanistan – and with the Taliban firmly in control of the country – most Americans (69%) say the U.S. failed in achieving its goals in Afghanistan.
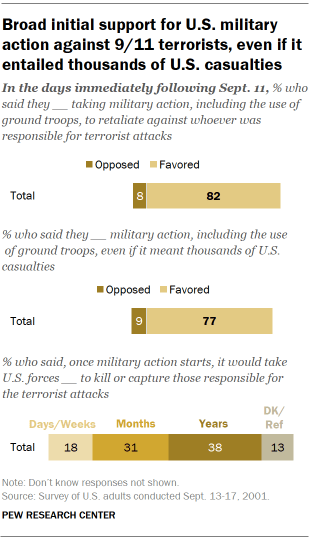
But 20 years ago, in the days and weeks following 9/11, Americans overwhelmingly supported military action against those responsible for the attacks. In mid-September 2001, 77% favored U.S. military action, including the deployment of ground forces, “to retaliate against whoever is responsible for the terrorist attacks, even if that means U.S. armed forces might suffer thousands of casualties.”
Many Americans were impatient for the Bush administration to give the go-ahead for military action. In a late September 2001 survey, nearly half the public (49%) said their larger concern was that the Bush administration would not strike quickly enough against the terrorists; just 34% said they worried the administration would move too quickly.
Even in the early stages of the U.S. military response, few adults expected a military operation to produce quick results: 69% said it would take months or years to dismantle terrorist networks, including 38% who said it would take years and 31% who said it would take several months. Just 18% said it would take days or weeks.
The public’s support for military intervention was evident in other ways as well. Throughout the fall of 2001, more Americans said the best way to prevent future terrorism was to take military action abroad rather than build up defenses at home. In early October 2001, 45% prioritized military action to destroy terrorist networks around the world, while 36% said the priority should be to build terrorism defenses at home.

Initially, the public was confident that the U.S. military effort to destroy terrorist networks would succeed. A sizable majority (76%) was confident in the success of this mission, with 39% saying they were very confident.
Support for the war in Afghanistan continued at a high level for several years to come. In a survey conducted in early 2002, a few months after the start of the war, 83% of Americans said they approved of the U.S.-led military campaign against the Taliban and al-Qaida in Afghanistan. In 2006, several years after the United States began combat operations in Afghanistan, 69% of adults said the U.S. made the right decision in using military force in Afghanistan. Only two-in-ten said it was the wrong decision.
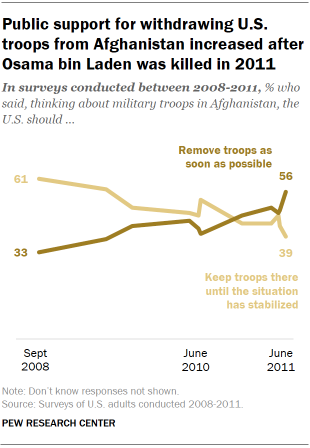
But as the conflict dragged on, first through Bush’s presidency and then through Obama’s administration, support wavered and a growing share of Americans favored the withdrawal of U.S. forces from Afghanistan. In June 2009, during Obama’s first year in office, 38% of Americans said U.S. troops should be removed from Afghanistan as soon as possible. The share favoring a speedy troop withdrawal increased over the next few years. A turning point came in May 2011, when U.S. Navy SEALs launched a risky operation against Osama bin Laden’s compound in Pakistan and killed the al-Qaida leader.
The public reacted to bin Laden’s death with more of a sense of relief than jubilation . A month later, for the first time , a majority of Americans (56%) said that U.S. forces should be brought home as soon as possible, while 39% favored U.S. forces in the country until the situation had stabilized.
Over the next decade, U.S. forces in Afghanistan were gradually drawn down, in fits and starts, over the administrations of three presidents – Obama, Donald Trump and Joe Biden. Meanwhile, public support for the decision to use force in Afghanistan, which had been widespread at the start of the conflict, declined . Today, after the tumultuous exit of U.S. troops from Afghanistan, a slim majority of adults (54%) say the decision to withdraw troops from the country was the right decision; 42% say it was the wrong decision.
There was a similar trajectory in public attitudes toward a much more expansive conflict that was part of what Bush termed the “war on terror”: the U.S. war in Iraq. Throughout the contentious, yearlong debate before the U.S. invasion of Iraq, Americans widely supported the use of military force to end Saddam Hussein’s rule in Iraq.
Importantly, most Americans thought – erroneously, as it turned out – there was a direct connection between Saddam Hussein and the 9/11 attacks. In October 2002, 66% said that Saddam helped the terrorists involved in the 9/11 attacks on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon.
In April 2003, during the first month of the Iraq War, 71% said the U.S. made the right decision to go to war in Iraq. On the 15th anniversary of the war in 2018, just 43% said it was the right decision. As with the case with U.S. involvement in Afghanistan, more Americans said that the U.S. had failed (53%) than succeeded (39%) in achieving its goals in Iraq.

There have been no terrorist attacks on the scale of 9/11 in two decades, but from the public’s perspective, the threat has never fully gone away. Defending the country from future terrorist attacks has been at or near the top of Pew Research Center’s annual survey on policy priorities since 2002.
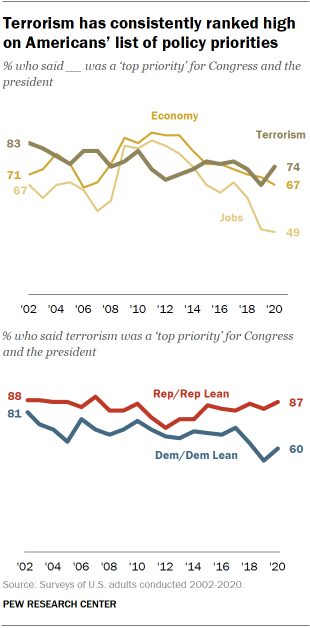
In January 2002, just months after the 2001 attacks, 83% of Americans said “defending the country from future terrorist attacks” was a top priority for the president and Congress, the highest for any issue. Since then, sizable majorities have continued to cite that as a top policy priority.
Majorities of both Republicans and Democrats have consistently ranked terrorism as a top priority over the past two decades, with some exceptions. Republicans and Republican-leaning independents have remained more likely than Democrats and Democratic leaners to say defending the country from future attacks should be a top priority. In recent years, the partisan gap has grown larger as Democrats began to rank the issue lower relative to other domestic concerns. The public’s concerns about another attack also remained fairly steady in the years after 9/11, through near-misses and the federal government’s numerous “Orange Alerts” – the second-most serious threat level on its color-coded terrorism warning system.
A 2010 analysis of the public’s terrorism concerns found that the share of Americans who said they were very concerned about another attack had ranged from about 15% to roughly 25% since 2002. The only time when concerns were elevated was in February 2003, shortly before the start of the U.S. war in Iraq.
In recent years, the share of Americans who point to terrorism as a major national problem has declined sharply as issues such as the economy, the COVID-19 pandemic and racism have emerged as more pressing problems in the public’s eyes.
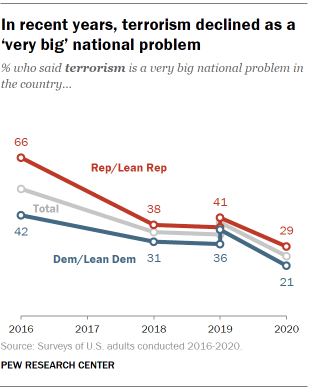
In 2016, about half of the public (53%) said terrorism was a very big national problem in the country. This declined to about four-in-ten from 2017 to 2019. Last year, only a quarter of Americans said that terrorism was a very big problem.
This year, prior to the U.S. withdrawal of forces from Afghanistan and the subsequent Taliban takeover of the country, a somewhat larger share of adults said domestic terrorism was a very big national problem (35%) than said the same about international terrorism . But much larger shares cited concerns such as the affordability of health care (56%) and the federal budget deficit (49%) as major problems than said that about either domestic or international terrorism.
Still, recent events in Afghanistan raise the possibility that opinion could be changing, at least in the short term. In a late August survey, 89% of Americans said the Taliban takeover of Afghanistan was a threat to the security of the U.S., including 46% who said it was a major threat.

Just as Americans largely endorsed the use of U.S. military force as a response to the 9/11 attacks, they were initially open to a variety of other far-reaching measures to combat terrorism at home and abroad. In the days following the attack, for example, majorities favored a requirement that all citizens carry national ID cards, allowing the CIA to contract with criminals in pursuing suspected terrorists and permitting the CIA to conduct assassinations overseas when pursuing suspected terrorists.
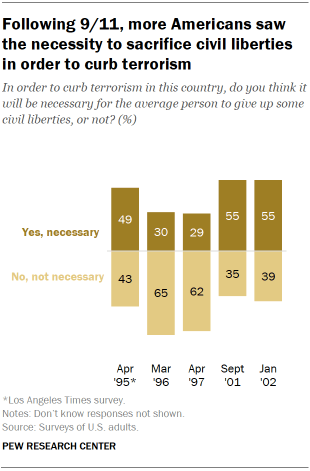
However, most people drew the line against allowing the government to monitor their own emails and phone calls (77% opposed this). And while 29% supported the establishment of internment camps for legal immigrants from unfriendly countries during times of tension or crisis – along the lines of those in which thousands of Japanese American citizens were confined during World War II – 57% opposed such a measure.
It was clear that from the public’s perspective, the balance between protecting civil liberties and protecting the country from terrorism had shifted. In September 2001 and January 2002, 55% majorities said that, in order to curb terrorism in the U.S., it was necessary for the average citizen to give up some civil liberties. In 1997, just 29% said this would be necessary while 62% said it would not.
For most of the next two decades, more Americans said their bigger concern was that the government had not gone far enough in protecting the country from terrorism than said it went too far in restricting civil liberties.
The public also did not rule out the use of torture to extract information from terrorist suspects. In a 2015 survey of 40 nations, the U.S. was one of only 12 where a majority of the public said the use of torture against terrorists could be justified to gain information about a possible attack.

Concerned about a possible backlash against Muslims in the U.S. in the days after 9/11, then-President George W. Bush gave a speech to the Islamic Center in Washington, D.C., in which he declared: “Islam is peace.” For a brief period, a large segment of Americans agreed. In November 2001, 59% of U.S. adults had a favorable view of Muslim Americans, up from 45% in March 2001, with comparable majorities of Democrats and Republicans expressing a favorable opinion.
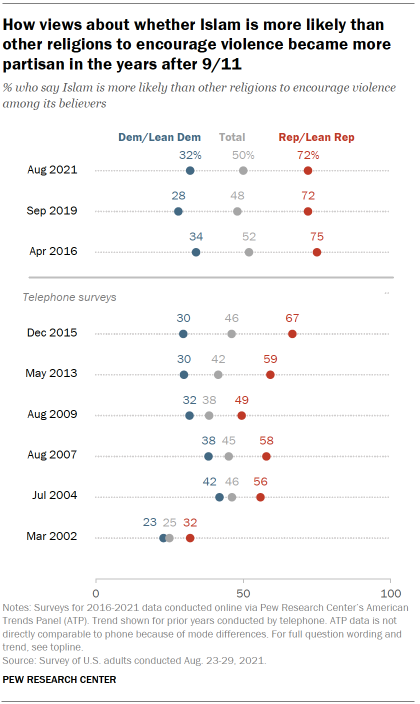
This spirit of unity and comity was not to last. In a September 2001 survey, 28% of adults said they had grown more suspicious of people of Middle Eastern descent; that grew to 36% less than a year later.
Republicans, in particular, increasingly came to associate Muslims and Islam with violence. In 2002, just a quarter of Americans – including 32% of Republicans and 23% of Democrats – said Islam was more likely than other religions to encourage violence among its believers. About twice as many (51%) said it was not.
But within the next few years, most Republicans and GOP leaners said Islam was more likely than other religions to encourage violence. Today, 72% of Republicans express this view, according to an August 2021 survey.
Democrats consistently have been far less likely than Republicans to associate Islam with violence. In the Center’s latest survey, 32% of Democrats say this. Still, Democrats are somewhat more likely to say this today than they have been in recent years: In 2019, 28% of Democrats said Islam was more likely than other religions to encourage violence among its believers than other religions.
The partisan gap in views of Muslims and Islam in the U.S. is evident in other meaningful ways. For example, a 2017 survey found that half of U.S. adults said that “Islam is not part of mainstream American society” – a view held by nearly seven-in-ten Republicans (68%) but only 37% of Democrats. In a separate survey conducted in 2017, 56% of Republicans said there was a great deal or fair amount of extremism among U.S. Muslims, with fewer than half as many Democrats (22%) saying the same.
The rise of anti-Muslim sentiment in the aftermath of 9/11 has had a profound effect on the growing number of Muslims living in the United States. Surveys of U.S. Muslims from 2007-2017 found increasing shares saying they have personally experienced discrimination and received public expression of support.

It has now been two decades since the terrorist attacks on the World Trade Center and Pentagon and the crash of Flight 93 – where only the courage of passengers and crew possibly prevented an even deadlier terror attack.
For most who are old enough to remember, it is a day that is impossible to forget. In many ways, 9/11 reshaped how Americans think of war and peace, their own personal safety and their fellow citizens. And today, the violence and chaos in a country half a world away brings with it the opening of an uncertain new chapter in the post-9/11 era.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Language selector
Don't have an account? Create an account today and support the 9/11 Memorial & Museum.
Log in with Google , Facebook or Twitter .
- Create new account
- Forgot your password?
Students Reflect on 9/11 in Essay Contest

First responders and supporters from the city of Palm Beach Gardens, Fla. have once again sponsored an essay contest in which local students can reflect on their understanding of the terrorist attacks of Sept. 11.
The second annual September 11th remembrance essay contest, which is open to Palm Beach Gardens residents and the dependents of city employees, requests that students in grades nine to 12 "reflect on how the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001 affected our nation and the future of the world."
Building on their successful 2015 contest , the contest is being sponsored by the Palm Beach Gardens Police Foundation, Fire Chief’s Association of Palm Beach County and Palm Beach Gardens Fire-Rescue, according to the Palm Beach Post .
Essay submissions should be between 500 to 700 words and applications are due Aug. 15, 2016. Three winners will be chosen.
By 9/11 Memorial Staff
Previous Post
The lens: capturing life and events at the 9/11 memorial and museum.

The Lens: Capturing Life and Events at the 9/11 Memorial and Museum is a photography series devoted to documenting moments big and small that unfold at the 9/11 Memorial and Museum.
9/11 Museum Honors Legacy of New York Yankees
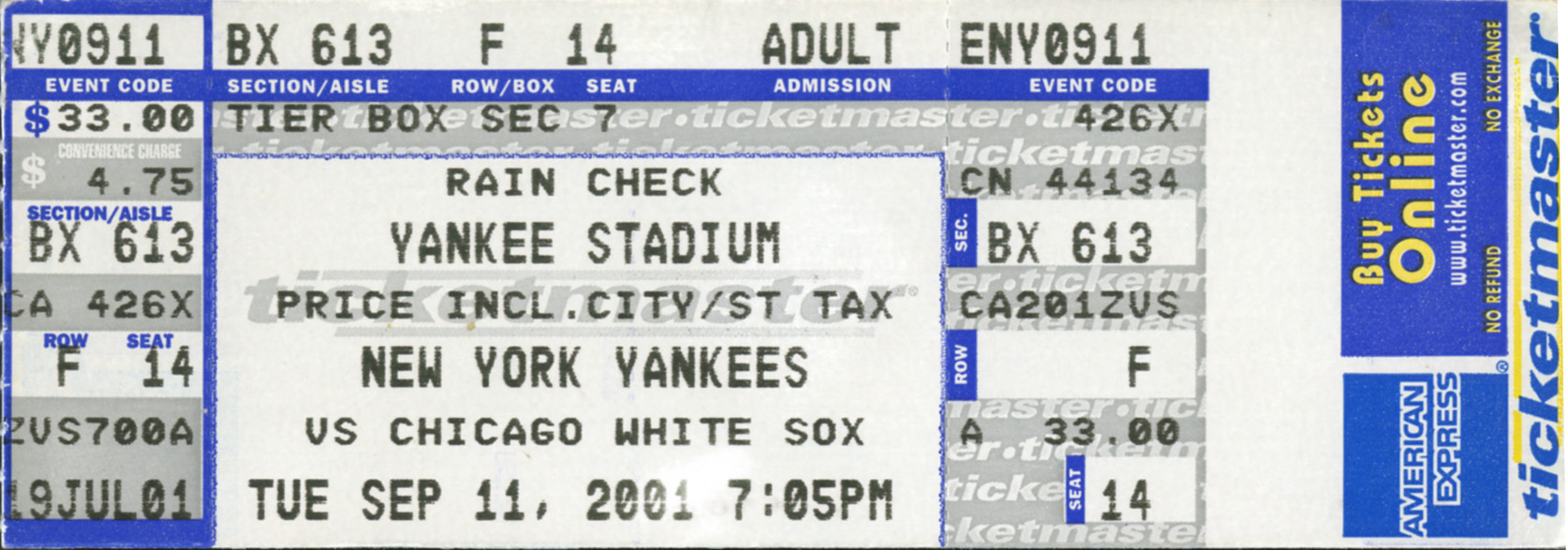
With the Bronx Bombers opening their season yesterday at Yankee Stadium, the 9/11 Memorial and Museum honors the connection between the Yankees and legacy of Sept. 11.
- Group Visits
- Museum Admission Discounts
- New York First Mondays
- Health and Safety
- Visitor Guidelines
- Getting Here
- Accessibility
- Exhibitions
- The Collection
- Programs and Events
- Find a Name
- Outdoor Memorial Audio Guide
- 9/11 Memorial Glade
- The Survivor Tree
- Past Public Programs
- School Programs
- Lesson Plans
- Anniversary Digital Learning Experience
- Digital Learning Experience Archives
- Teacher Professional Development
- Activities at Home
- Youth and Family Tours
- Talking to Children about Terrorism
- Digital Exhibitions
- Interactive Timelines
- 9/11 Primer
- Oral Histories
- Visiting Information
- Rescue and Recovery Workers
- Witnesses and Survivors
- Service Members and Veterans
- September 11, 2001
- Remember the Sky
- February 26, 1993
- May 30, 2002
- The MEMO Blog
- Sponsor a Cobblestone
- Other Ways to Give
- Member Login
- 5K Run/Walk
- Benefit Dinner
- Summit on Security
- Corporate Membership
- The Never Forget Fund
- Visionary Network
- Give to the Collection
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Solar Storm Intensifies, Filling Skies With Northern Lights
Officials warned of potential blackouts or interference with navigation and communication systems this weekend, as well as auroras as far south as Southern California or Texas.

By Katrina Miller and Judson Jones
Katrina Miller reports on space and astronomy and Judson Jones is a meteorologist.
A dramatic blast from the sun set off the highest-level geomagnetic storm in Earth’s atmosphere on Friday that is expected to make the northern lights visible as far south as Florida and Southern California and could interfere with power grids, communications and navigations system.
It is the strongest such storm to reach Earth since Halloween of 2003. That one was strong enough to create power outages in Sweden and damage transformers in South Africa.
The effects could continue through the weekend as a steady stream of emissions from the sun continues to bombard the planet’s magnetic field.
The solar activity is so powerful that the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, which monitors space weather, issued an unusual storm watch for the first time in 19 years, which was then upgraded to a warning. The agency began observing outbursts on the sun’s surface on Wednesday, with at least five heading in the direction of Earth.
“What we’re expecting over the next couple of days should be more significant than what we’ve seen certainly so far,” Mike Bettwy, the operations chief at NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center, said at a news conference on Friday morning.
For people in many places, the most visible part of the storm will be the northern lights, known also as auroras. But authorities and companies will also be on the lookout for the event’s effects on infrastructure, like global positioning systems, radio communications and even electrical power.
While the northern lights are most often seen in higher latitudes closer to the North Pole, people in many more parts of the world are already getting a show this weekend that could last through the early part of next week.

As Friday turned to Saturday in Europe, people across the continent described skies hued in a mottling of colors.
Alfredo Carpineti , an astrophysicist, journalist and author in North London, saw them with his husband from the rooftop of their apartment building.
“It is incredible to be able to see the aurora directly from one’s own backyard,” he said. “I was hoping to maybe catch a glimpse of green on the horizon, but it was all across the sky in both green and purple.”
Here’s what you need to know about this weekend’s solar event.
How will the storm affect people on Earth?
A geomagnetic storm watch or warning indicates that space weather may affect critical infrastructure on or orbiting near Earth. It may introduce additional current into systems, which could damage pipelines, railroad tracks and power lines.
According to Joe Llama, an astronomer at Lowell Observatory, communications that rely on high frequency radio waves, such as ham radio and commercial aviation , are most likely to suffer. That means it is unlikely that your cellphone or car radio, which depend on much higher frequency radio waves, will conk out.
Still, it is possible for blackouts to occur. As with any power outage, you can prepare by keeping your devices charged and having access to backup batteries, generators and radio.
The most notable solar storm recorded in history occurred in 1859. Known as the Carrington Event, it lasted for nearly a week, creating aurora that stretched down to Hawaii and Central America and impacting hundreds of thousands of miles of telegraph lines.
But that was technology of the 19th century, used before scientists fully understood how solar activity disrupted Earth’s atmosphere and communication systems.
“That was an extreme level event,” said Shawn Dahl, a forecaster at NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center. “We are not anticipating that.”
Unlike tornado watches and warnings, the target audience for NOAA’s announcements is not the public.
“For most people here on planet Earth, they won’t have to do anything,” said Rob Steenburgh, a space scientist at NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center.
The goal of the announcements is to give agencies and companies that operate this infrastructure time to put protection measures in place to mitigate any effects.
“If everything is working like it should, the grid will be stable and they’ll be able to go about their daily lives,” Mr. Steenburgh said.

Will I be able to see the northern lights?
It is possible that the northern lights may grace the skies this week over places that don’t usually see them. The best visibility is outside the bright lights of cities.
Clouds or stormy weather could pose a problem in some places. But if the skies are clear, even well south of where the aurora is forecast to take place, snap a picture or record a video with your cellphone. The sensor on the camera is more sensitive to the wavelengths produced by the aurora and may produce an image you can’t see with the naked eye.
Another opportunity could be viewing sunspots during the daytime, if your skies are clear. As always, do not look directly at the sun without protection. But if you still have your eclipse glasses lying around from the April 8 event, you may try to use them to try to spot the cluster of sunspots causing the activity.
How strong is the current geomagnetic storm?
Giant explosions on the surface of the sun, known as coronal mass ejections, send streams of energetic particles into space. But the sun is large, and such outbursts may not cross our planet as it travels around the star. But when these particles create a disturbance in Earth’s magnetic field, it is known as a geomagnetic storm.
NOAA classifies these storms on a “G” scale of 1 to 5, with G1 being minor and G5 being extreme. The most extreme storms can cause widespread blackouts and damage to infrastructure on Earth. Satellites may also have trouble orienting themselves or sending or receiving information during these events.
The current storm is classified as G5, or “extreme.” It is caused by a cluster of sunspots — dark, cool regions on the solar surface — that is about 16 times the diameter of Earth. The cluster is flaring and ejecting material every six to 12 hours.
“We anticipate that we’re going to get one shock after another through the weekend,” said Brent Gordon, chief of the space weather services branch at NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center.
Why is this happening now?
The sun’s activity ebbs and flows on an 11-year cycle, and right now, it is approaching a solar maximum. Three other severe geomagnetic storms have been observed so far in the current activity cycle, which began in December 2019, but none were predicted to cause effects strong enough on Earth to warrant a watch or warning announcement.
The cluster of sunspots generating the current storm is the largest seen in this solar cycle, NOAA officials said. They added that the activity in this cycle has outperformed initial predictions .
More flares and expulsions from this cluster are expected, but because of the sun’s rotation the cluster will be oriented in a position less likely to affect Earth. In the coming weeks, the sunspots may appear again on the left side of the sun, but it is difficult for scientists to predict whether this will cause another bout of activity.
“Usually, these don’t come around packing as much of a punch as they did originally,” Mr. Dahl said. “But time will tell on that.”
Jonathan O’Callaghan contributed reporting from London.
An earlier version of this article misstated the radio frequencies used by cellphones and car radios. They are higher frequencies, not low.
How we handle corrections
Katrina Miller is a science reporting fellow for The Times. She recently earned her Ph.D. in particle physics from the University of Chicago. More about Katrina Miller
Judson Jones is a meteorologist and reporter for The Times who forecasts and covers extreme weather. More about Judson Jones
What’s Up in Space and Astronomy
Keep track of things going on in our solar system and all around the universe..
Never miss an eclipse, a meteor shower, a rocket launch or any other 2024 event that’s out of this world with our space and astronomy calendar .
A dramatic blast from the sun set off the highest-level geomagnetic storm in Earth’s atmosphere, making the northern lights visible around the world .
With the help of Google Cloud, scientists who hunt killer asteroids churned through hundreds of thousands of images of the night sky to reveal 27,500 overlooked space rocks in the solar system .
A celestial image, an Impressionistic swirl of color in the center of the Milky Way, represents a first step toward understanding the role of magnetic fields in the cycle of stellar death and rebirth.
Scientists may have discovered a major flaw in their understanding of dark energy, a mysterious cosmic force . That could be good news for the fate of the universe.
Is Pluto a planet? And what is a planet, anyway? Test your knowledge here .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Mills gave Zack, then 9, a vague reply like, "It's to keep us safe.". Unsatisfied, he persisted, and eventually, the conversation wove around to the Sept. 11 attacks, which happened before ...
Note: This essay is the introduction to The Atlantic's special report on the 10th anniversary of 9/11.See more articles and videos here. What we saw on the morning of September 11, 2001 was evil ...
What 9/11 means for me, more than anything, is that there is no going back to what was before. I. went up in the World Trade Center twice. Once during a visit in 1985, once in August 2001, about four weeks before the attacks. I was with my son, Thom, and John and his son, Sean. We were on top of the South Tower.
In the space of less than 90 minutes on a late summer morning, the world changed. Nearly 3,000 people were killed that day and the United States soon found itself mired in what would become the longest war in its history, a war that cost an estimated $8 trillion.The events of 9/11 not only reshaped the global response to terrorism, but raised new and troubling questions about security, privacy ...
Ahead of the 20th anniversary of the September 11 terrorist attacks on the World Trade Center and Pentagon, we asked students, staff, and faculty members to reflect on what the day means to them. Here are their answers. "My son was only three weeks old when I watched in horror the tragedy of 9/11. I was scared for my son and what the future ...
Looking back at those heady times, Packer concludes that 9/11 pricked the illusion that somehow Americans stood outside of time. "September 11 wasn't a sui generis event coming out of a clear ...
At the same time, U.S. foreign policy was "remilitarized," said Berkeley political scientist George Breslauer, a scholar in U.S. foreign affairs. "After 9/11, with the neoconservatives in power, you get this notion: 'We are the most powerful country in the world, and it's about time to show our adversaries what that means.'".
The Meaning of 9/11. From my essay introducing The Atlantic's special coverage of the 10th anniversary of the 9/11 attacks: What we saw on the morning of September 11, 2001 was evil made manifest ...
It happened fast. By 2004, when the 9/11 Commission urged America to "engage the struggle of ideas," it was already too late; the Justice Department's initial torture memos were already ...
A decade has passed since the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001. Most of us remember where we were when we learned of the attacks, although our memories of the event and of our feelings that day may not be as accurate as we suspect (Hirst et al., 2009). The attacks of 9/11 did far more than destroy buildings and kill thousands of innocent ...
The morning of 9/11, I was on the West Coast. A friend called, waking me from sleep and telling me to turn on the television. I spent the next few hours glued to the screen while scrambling to get ...
Essays revisited: Reflecting on 9/11. In the days and weeks after Sept. 11, 2001, the Times ran dozens of analysis and opinion pieces examining how the events of that day might change the United ...
September 11 attacks • The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist suicide terrorist attacks carried out by Al-Qaeda against the United States on September ...
On Sept. 11, 2001, what you really saw was the dedication of a group of firefighters to the cause of protecting the public. They walked into the World Trade center and went to work. I read reports ...
9/11 transformed U.S. public opinion, but many of its impacts were short-lived. It is difficult to think of an event that so profoundly transformed U.S. public opinion across so many dimensions as the 9/11 attacks. While Americans had a shared sense of anguish after Sept. 11, the months that followed also were marked by rare spirit of public unity.
The 9/11 attack of 2001 was a shock to most individuals across the globe. It was a Wednesday that was marked as one of the most tragic events in the US and other governments across the globe. The impacts of the attack were long-lasting economically, emotionally, and politically. However, despite the challenge, the US government's reaction to ...
Cite this essay. Download. September 11th, 2001 would be remembered as the worst tragedy to ever happen to the United States. On the morning of 9/11, four planes would be hijacked in hopes of crippling the American economy. Two of the four planes would then crash into the World Trade Center in New York City leaving the twin towers destroyed.
The second annual September 11th remembrance essay contest, which is open to Palm Beach Gardens residents and the dependents of city employees, requests that students in grades nine to 12 "reflect on how the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001 affected our nation and the future of the world." Building on their successful 2015 contest, the ...
Barenboim: What Beethoven's Ninth Teaches Us. Mr. Barenboim is a pianist and conductor. Ludwig van Beethoven's Ninth Symphony was first performed exactly 200 years ago Tuesday and has since ...
For people in many places, the most visible part of the storm will be the northern lights, known also as auroras. But authorities and companies will also be on the lookout for the event's ...