.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations

CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Business strategy |
- 7 strategic planning models, plus 8 fra ...
7 strategic planning models, plus 8 frameworks to help you get started
Strategic planning is vital in defining where your business is going in the next three to five years. With the right strategic planning models and frameworks, you can uncover opportunities, identify risks, and create a strategic plan to fuel your organization’s success. We list the most popular models and frameworks and explain how you can combine them to create a strategic plan that fits your business.
A strategic plan is a great tool to help you hit your business goals . But sometimes, this tool needs to be updated to reflect new business priorities or changing market conditions. If you decide to use a model that already exists, you can benefit from a roadmap that’s already created. The model you choose can improve your knowledge of what works best in your organization, uncover unknown strengths and weaknesses, or help you find out how you can outpace your competitors.
In this article, we cover the most common strategic planning models and frameworks and explain when to use which one. Plus, get tips on how to apply them and which models and frameworks work well together.
Strategic planning models vs. frameworks
First off: This is not a one-or-nothing scenario. You can use as many or as few strategic planning models and frameworks as you like.
When your organization undergoes a strategic planning phase, you should first pick a model or two that you want to apply. This will provide you with a basic outline of the steps to take during the strategic planning process.
![strategic business planning models [Inline illustration] Strategic planning models vs. frameworks (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/89236d14-1abf-4f49-8b91-4187147f1c63/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
During that process, think of strategic planning frameworks as the tools in your toolbox. Many models suggest starting with a SWOT analysis or defining your vision and mission statements first. Depending on your goals, though, you may want to apply several different frameworks throughout the strategic planning process.
For example, if you’re applying a scenario-based strategic plan, you could start with a SWOT and PEST(LE) analysis to get a better overview of your current standing. If one of the weaknesses you identify has to do with your manufacturing process, you could apply the theory of constraints to improve bottlenecks and mitigate risks.
Now that you know the difference between the two, learn more about the seven strategic planning models, as well as the eight most commonly used frameworks that go along with them.
![strategic business planning models [Inline illustration] The seven strategic planning models (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/23048ae4-8a18-4b9b-ad9e-33b0fc5d04ee/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
1. Basic model
The basic strategic planning model is ideal for establishing your company’s vision, mission, business objectives, and values. This model helps you outline the specific steps you need to take to reach your goals, monitor progress to keep everyone on target, and address issues as they arise.
If it’s your first strategic planning session, the basic model is the way to go. Later on, you can embellish it with other models to adjust or rewrite your business strategy as needed. Let’s take a look at what kinds of businesses can benefit from this strategic planning model and how to apply it.
Small businesses or organizations
Companies with little to no strategic planning experience
Organizations with few resources
Write your mission statement. Gather your planning team and have a brainstorming session. The more ideas you can collect early in this step, the more fun and rewarding the analysis phase will feel.
Identify your organization’s goals . Setting clear business goals will increase your team’s performance and positively impact their motivation.
Outline strategies that will help you reach your goals. Ask yourself what steps you have to take in order to reach these goals and break them down into long-term, mid-term, and short-term goals .
Create action plans to implement each of the strategies above. Action plans will keep teams motivated and your organization on target.
Monitor and revise the plan as you go . As with any strategic plan, it’s important to closely monitor if your company is implementing it successfully and how you can adjust it for a better outcome.
2. Issue-based model
Also called goal-based planning model, this is essentially an extension of the basic strategic planning model. It’s a bit more dynamic and very popular for companies that want to create a more comprehensive plan.
Organizations with basic strategic planning experience
Businesses that are looking for a more comprehensive plan
Conduct a SWOT analysis . Assess your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats with a SWOT analysis to get a better overview of what your strategic plan should focus on. We’ll give into how to conduct a SWOT analysis when we get into the strategic planning frameworks below.
Identify and prioritize major issues and/or goals. Based on your SWOT analysis, identify and prioritize what your strategic plan should focus on this time around.
Develop your main strategies that address these issues and/or goals. Aim to develop one overarching strategy that addresses your highest-priority goal and/or issue to keep this process as simple as possible.
Update or create a mission and vision statement . Make sure that your business’s statements align with your new or updated strategy. If you haven’t already, this is also a chance for you to define your organization’s values.
Create action plans. These will help you address your organization’s goals, resource needs, roles, and responsibilities.
Develop a yearly operational plan document. This model works best if your business repeats the strategic plan implementation process on an annual basis, so use a yearly operational plan to capture your goals, progress, and opportunities for next time.
Allocate resources for your year-one operational plan. Whether you need funding or dedicated team members to implement your first strategic plan, now is the time to allocate all the resources you’ll need.
Monitor and revise the strategic plan. Record your lessons learned in the operational plan so you can revisit and improve it for the next strategic planning phase.
The issue-based plan can repeat on an annual basis (or less often once you resolve the issues). It’s important to update the plan every time it’s in action to ensure it’s still doing the best it can for your organization.
You don’t have to repeat the full process every year—rather, focus on what’s a priority during this run.
3. Alignment model
This model is also called strategic alignment model (SAM) and is one of the most popular strategic planning models. It helps you align your business and IT strategies with your organization’s strategic goals.
You’ll have to consider four equally important, yet different perspectives when applying the alignment strategic planning model:
Strategy execution: The business strategy driving the model
Technology potential: The IT strategy supporting the business strategy
Competitive potential: Emerging IT capabilities that can create new products and services
Service level: Team members dedicated to creating the best IT system in the organization
Ideally, your strategy will check off all the criteria above—however, it’s more likely you’ll have to find a compromise.
Here’s how to create a strategic plan using the alignment model and what kinds of companies can benefit from it.
Organizations that need to fine-tune their strategies
Businesses that want to uncover issues that prevent them from aligning with their mission
Companies that want to reassess objectives or correct problem areas that prevent them from growing
Outline your organization’s mission, programs, resources, and where support is needed. Before you can improve your statements and approaches, you need to define what exactly they are.
Identify what internal processes are working and which ones aren’t. Pinpoint which processes are causing problems, creating bottlenecks , or could otherwise use improving. Then prioritize which internal processes will have the biggest positive impact on your business.
Identify solutions. Work with the respective teams when you’re creating a new strategy to benefit from their experience and perspective on the current situation.
Update your strategic plan with the solutions. Update your strategic plan and monitor if implementing it is setting your business up for improvement or growth. If not, you may have to return to the drawing board and update your strategic plan with new solutions.
4. Scenario model
The scenario model works great if you combine it with other models like the basic or issue-based model. This model is particularly helpful if you need to consider external factors as well. These can be government regulations, technical, or demographic changes that may impact your business.
Organizations trying to identify strategic issues and goals caused by external factors
Identify external factors that influence your organization. For example, you should consider demographic, regulation, or environmental factors.
Review the worst case scenario the above factors could have on your organization. If you know what the worst case scenario for your business looks like, it’ll be much easier to prepare for it. Besides, it’ll take some of the pressure and surprise out of the mix, should a scenario similar to the one you create actually occur.
Identify and discuss two additional hypothetical organizational scenarios. On top of your worst case scenario, you’ll also want to define the best case and average case scenarios. Keep in mind that the worst case scenario from the previous step can often provoke strong motivation to change your organization for the better. However, discussing the other two will allow you to focus on the positive—the opportunities your business may have ahead.
Identify and suggest potential strategies or solutions. Everyone on the team should now brainstorm different ways your business could potentially respond to each of the three scenarios. Discuss the proposed strategies as a team afterward.
Uncover common considerations or strategies for your organization. There’s a good chance that your teammates come up with similar solutions. Decide which ones you like best as a team or create a new one together.
Identify the most likely scenario and the most reasonable strategy. Finally, examine which of the three scenarios is most likely to occur in the next three to five years and how your business should respond to potential changes.
5. Self-organizing model
Also called the organic planning model, the self-organizing model is a bit different from the linear approaches of the other models. You’ll have to be very patient with this method.
This strategic planning model is all about focusing on the learning and growing process rather than achieving a specific goal. Since the organic model concentrates on continuous improvement , the process is never really over.
Large organizations that can afford to take their time
Businesses that prefer a more naturalistic, organic planning approach that revolves around common values, communication, and shared reflection
Companies that have a clear understanding of their vision
Define and communicate your organization’s cultural values . Your team can only think clearly and with solutions in mind when they have a clear understanding of your organization's values.
Communicate the planning group’s vision for the organization. Define and communicate the vision with everyone involved in the strategic planning process. This will align everyone’s ideas with your company’s vision.
Discuss what processes will help realize the organization’s vision on a regular basis. Meet every quarter to discuss strategies or tactics that will move your organization closer to realizing your vision.
6. Real-time model
This fluid model can help organizations that deal with rapid changes to their work environment. There are three levels of success in the real-time model:
Organizational: At the organizational level, you’re forming strategies in response to opportunities or trends.
Programmatic: At the programmatic level, you have to decide how to respond to specific outcomes or environmental changes.
Operational: On the operational level, you will study internal systems, policies, and people to develop a strategy for your company.
Figuring out your competitive advantage can be difficult, but this is absolutely crucial to ensure success. Whether it’s a unique asset or strength your organization has or an outstanding execution of services or programs—it’s important that you can set yourself apart from others in the industry to succeed.
Companies that need to react quickly to changing environments
Businesses that are seeking new tools to help them align with their organizational strategy
Define your mission and vision statement. If you ever feel stuck formulating your company’s mission or vision statement, take a look at those of others. Maybe Asana’s vision statement sparks some inspiration.
Research, understand, and learn from competitor strategy and market trends. Pick a handful of competitors in your industry and find out how they’ve created success for themselves. How did they handle setbacks or challenges? What kinds of challenges did they even encounter? Are these common scenarios in the market? Learn from your competitors by finding out as much as you can about them.
Study external environments. At this point, you can combine the real-time model with the scenario model to find solutions to threats and opportunities outside of your control.
Conduct a SWOT analysis of your internal processes, systems, and resources. Besides the external factors your team has to consider, it’s also important to look at your company’s internal environment and how well you’re prepared for different scenarios.
Develop a strategy. Discuss the results of your SWOT analysis to develop a business strategy that builds toward organizational, programmatic, and operational success.
Rinse and repeat. Monitor how well the new strategy is working for your organization and repeat the planning process as needed to ensure you’re on top or, perhaps, ahead of the game.
7. Inspirational model
This last strategic planning model is perfect to inspire and energize your team as they work toward your organization’s goals. It’s also a great way to introduce or reconnect your employees to your business strategy after a merger or acquisition.
Businesses with a dynamic and inspired start-up culture
Organizations looking for inspiration to reinvigorate the creative process
Companies looking for quick solutions and strategy shifts
Gather your team to discuss an inspirational vision for your organization. The more people you can gather for this process, the more input you will receive.
Brainstorm big, hairy audacious goals and ideas. Encouraging your team not to hold back with ideas that may seem ridiculous will do two things: for one, it will mitigate the fear of contributing bad ideas. But more importantly, it may lead to a genius idea or suggestion that your team wouldn’t have thought of if they felt like they had to think inside of the box.
Assess your organization’s resources. Find out if your company has the resources to implement your new ideas. If they don’t, you’ll have to either adjust your strategy or allocate more resources.
Develop a strategy balancing your resources and brainstorming ideas. Far-fetched ideas can grow into amazing opportunities but they can also bear great risk. Make sure to balance ideas with your strategic direction.
Now, let’s dive into the most commonly used strategic frameworks.
8. SWOT analysis framework
One of the most popular strategic planning frameworks is the SWOT analysis . A SWOT analysis is a great first step in identifying areas of opportunity and risk—which can help you create a strategic plan that accounts for growth and prepares for threats.
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Here’s an example:
![strategic business planning models [Inline illustration] SWOT analysis (Example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/cfab4ed2-46d1-4636-b801-14b3d86c8367/inline-project-management-SWOT-analysis-4-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
9. OKRs framework
A big part of strategic planning is setting goals for your company. That’s where OKRs come into play.
OKRs stand for objective and key results—this goal-setting framework helps your organization set and achieve goals. It provides a somewhat holistic approach that you can use to connect your team’s work to your organization’s big-picture goals. When team members understand how their individual work contributes to the organization’s success, they tend to be more motivated and produce better results
10. Balanced scorecard (BSC) framework
The balanced scorecard is a popular strategic framework for businesses that want to take a more holistic approach rather than just focus on their financial performance. It was designed by David Norton and Robert Kaplan in the 1990s, it’s used by companies around the globe to:
Communicate goals
Align their team’s daily work with their company’s strategy
Prioritize products, services, and projects
Monitor their progress toward their strategic goals
Your balanced scorecard will outline four main business perspectives:
Customers or clients , meaning their value, satisfaction, and/or retention
Financial , meaning your effectiveness in using resources and your financial performance
Internal process , meaning your business’s quality and efficiency
Organizational capacity , meaning your organizational culture, infrastructure and technology, and human resources
With the help of a strategy map, you can visualize and communicate how your company is creating value. A strategy map is a simple graphic that shows cause-and-effect connections between strategic objectives.
The balanced scorecard framework is an amazing tool to use from outlining your mission, vision, and values all the way to implementing your strategic plan .
You can use an integration like Lucidchart to create strategy maps for your business in Asana.
11. Porter’s Five Forces framework
If you’re using the real-time strategic planning model, Porter’s Five Forces are a great framework to apply. You can use it to find out what your product’s or service’s competitive advantage is before entering the market.
Developed by Michael E. Porter , the framework outlines five forces you have to be aware of and monitor:
![strategic business planning models [Inline illustration] Porter’s Five Forces framework (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d63265bc-23e2-4ce6-9b91-b3da5a756619/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Threat of new industry entrants: Any new entry into the market results in increased pressure on prices and costs.
Competition in the industry: The more competitors that exist, the more difficult it will be for you to create value in the market with your product or service.
Bargaining power of suppliers: Suppliers can wield more power if there are less alternatives for buyers or it’s expensive, time consuming, or difficult to switch to a different supplier.
Bargaining power of buyers: Buyers can wield more power if the same product or service is available elsewhere with little to no difference in quality.
Threat of substitutes: If another company already covers the market’s needs, you’ll have to create a better product or service or make it available for a lower price at the same quality in order to compete.
Remember, industry structures aren’t static. The more dynamic your strategic plan is, the better you’ll be able to compete in a market.
12. VRIO framework
The VRIO framework is another strategic planning tool designed to help you evaluate your competitive advantage. VRIO stands for value, rarity, imitability, and organization.
It’s a resource-based theory developed by Jay Barney. With this framework, you can study your firmed resources and find out whether or not your company can transform them into sustained competitive advantages.
Firmed resources can be tangible (e.g., cash, tools, inventory, etc.) or intangible (e.g., copyrights, trademarks, organizational culture, etc.). Whether these resources will actually help your business once you enter the market depends on four qualities:
Valuable : Will this resource either increase your revenue or decrease your costs and thereby create value for your business?
Rare : Are the resources you’re using rare or can others use your resources as well and therefore easily provide the same product or service?
Inimitable : Are your resources either inimitable or non-substitutable? In other words, how unique and complex are your resources?
Organizational: Are you organized enough to use your resources in a way that captures their value, rarity, and inimitability?
It’s important that your resources check all the boxes above so you can ensure that you have sustained competitive advantage over others in the industry.
13. Theory of Constraints (TOC) framework
If the reason you’re currently in a strategic planning process is because you’re trying to mitigate risks or uncover issues that could hurt your business—this framework should be in your toolkit.
The theory of constraints (TOC) is a problem-solving framework that can help you identify limiting factors or bottlenecks preventing your organization from hitting OKRs or KPIs .
Whether it’s a policy, market, or recourse constraint—you can apply the theory of constraints to solve potential problems, respond to issues, and empower your team to improve their work with the resources they have.
14. PEST/PESTLE analysis framework
The idea of the PEST analysis is similar to that of the SWOT analysis except that you’re focusing on external factors and solutions. It’s a great framework to combine with the scenario-based strategic planning model as it helps you define external factors connected to your business’s success.
PEST stands for political, economic, sociological, and technological factors. Depending on your business model, you may want to expand this framework to include legal and environmental factors as well (PESTLE). These are the most common factors you can include in a PESTLE analysis:
Political: Taxes, trade tariffs, conflicts
Economic: Interest and inflation rate, economic growth patterns, unemployment rate
Social: Demographics, education, media, health
Technological: Communication, information technology, research and development, patents
Legal: Regulatory bodies, environmental regulations, consumer protection
Environmental: Climate, geographical location, environmental offsets
15. Hoshin Kanri framework
Hoshin Kanri is a great tool to communicate and implement strategic goals. It’s a planning system that involves the entire organization in the strategic planning process. The term is Japanese and stands for “compass management” and is also known as policy management.
This strategic planning framework is a top-down approach that starts with your leadership team defining long-term goals which are then aligned and communicated with every team member in the company.
You should hold regular meetings to monitor progress and update the timeline to ensure that every teammate’s contributions are aligned with the overarching company goals.
Stick to your strategic goals
Whether you’re a small business just starting out or a nonprofit organization with decades of experience, strategic planning is a crucial step in your journey to success.
If you’re looking for a tool that can help you and your team define, organize, and implement your strategic goals, Asana is here to help. Our goal-setting software allows you to connect all of your team members in one place, visualize progress, and stay on target.
Related resources
Grant management: A nonprofit’s guide

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning

How Asana uses work management for organizational planning

Solve your tech overload with an intelligent transformation
9 Strategic Planning Models and Tools for the Customer-Focused Business
Published: July 11, 2023

As the economist and business strategy guru, Michael Porter, says, “The essence of strategy is choosing what not to do.”
With strategic planning, businesses identify their strengths and weaknesses, choose what not to do, and determine which opportunities should be pursued. In sales operations, having a clearly defined strategy will help your organization plan for the future, set viable goals, and achieve them.
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(53, '5f39f863-0316-486f-a5f3-849d76490a30', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
So, how do you get started with strategic planning? You‘ll begin with strategic planning models and tools. Let’s take a look at nine of the most prominent ones here.
.png)
Free Strategic Planning Template
Access a business strategic planning template to grow your business.
- Sales and Revenue Growth
- Growth of Customer Base
- Expansion into New Regions
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Fill out the form to access your business strategic planning template.
Strategic planning models.
Strategic planning is used to set up long-term goals and priorities for an organization. A strategic plan is a written document that outlines these goals.
Don't confuse strategic planning and tactical planning . Strategic planning is focused on long-term goals, while tactical planning is focused on the short-term.
Here are a few strategic planning models you can use to get started.
1. The Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard is one of the most prominent strategic planning models, tailored to give managers a comprehensive overview of their companies' operations on tight timelines. It considers both financial and operational metrics to provide valuable context about how a business has performed previously, is currently performing, and is likely to perform in the future.
The model plays on these concerns: time, quality, performance/service, and cost. The sum of those components amount to four specific reference points for goal-setting and performance measurement:
- Customer: How customers view your business
- Internal Process: How you can improve your internal processes
- Organizational Capacity: How your business can grow, adapt, and improve
- Financial: The potential profitability of your business
Those four categories can inform goals that are more thoughtful and focused while surfacing the most appropriate metrics with which you can use to track them. But the elements you choose to pursue and measure are ultimately up to you. As there's no definitive list, they will vary from organization to organization.
That being said, there‘s a universally applicable technique you can use when leveraging the model—creating a scorecard. This is a document that keeps track of your goals and how you apply them. Here’s an example of what a scorecard might look like:
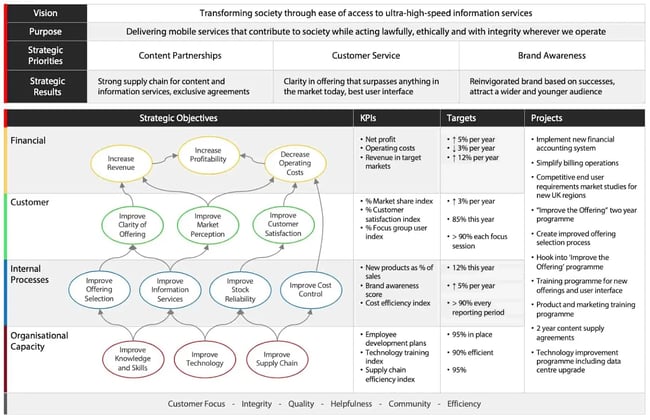
Image Source
The Balanced Scorecard is ideal for businesses looking to break up higher-level goals into more specific, measurable objectives. If you're interested in translating your big-picture ambitions into actionable projects, consider looking into it.
Example of the Balanced Scorecard
Let‘s imagine a B2B SaaS company that sells a construction management solution. It’s been running into trouble from virtually all angles. It‘s struggling with customer retention and, in turn, is hemorrhaging revenue. The company’s sales reps are working with very few qualified leads and the organization's tech stack is limiting growth and innovation.
The business decides to leverage a Balanced Scorecard approach to remedy its various issues. In this case, the full strategic plan—developed according to this model—might look like this:
- The company sets a broad financial goal of boosting revenue by 10% year over year.
- To help get there, it aims to improve its customer retention rate by 5% annually by investing in a more robust customer service infrastructure.
- Internally, leadership looks to improve the company's lead generation figures by 20% year over year by revamping its onboarding process for its pre-sales team.
- Finally, the business decides to move on from its legacy tech stack in favor of a virtualized operating system, making for at least 50% faster software delivery for consistent improvements to its product.
The elements listed above address key flaws in the company‘s customer perception, internal processes, financial situation, and organizational capacity. Every improvement the business is hoping to make involves a concrete goal with clearly outlined metrics and definitive figures to gauge each one’s success. Taken together, the organization's plan abides by the Balanced Scorecard model.
2. Objectives and Key Results
As its name implies, the OKR strategic planning model revolves around translating broader organizational goals into objectives and tracking their key results. The framework rests on identifying three to five attainable objectives and three to five results that should stem from each of them. Once you have those in place, you plan tactical initiatives around those results.
After you‘ve figured out those reference points, you determine the most appropriate metrics for measuring their success. And once you’ve carried out the projects informed by those ideal results, you gauge their success by giving a score on a scale from 0 to 1 or 0%-100%.
For instance, your goal might be developing relationships with 100 new targets or named accounts in a specific region. If you only were able to develop 95, you would have a score of .95 or 95%. Here's an example of what an OKR model might look like:
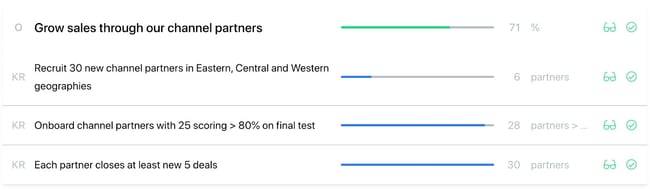
It's recommended that you structure your targets to land at a score of around 70% — taking some strain off workers while offering them a definitive ideal outcome. The OKR model is relatively straightforward and near-universally applicable. If your business is interested in a way to work towards firmly established, readily visible standards this model could work for you.
Example of the Objectives and Key Results
Let's consider a hypothetical company that makes educational curriculum and schedule planning for higher-education institutions. The company decides it would like to expand its presence in the community college system in California, something that constitutes an objective.
But what will it take to accomplish that? And how will the company know if it's successful? Well, in this instance, leadership within the business would get there by establishing three to five results they would like to see. Those could be:
- Generating qualified leads from 30 institutions
- Conducting demos at 10 colleges
- Closing deals at 5 campuses
Those results would lead to initiatives like setting standards for lead qualification and training reps at the top of the funnel on how to use them appropriately, revamping sales messaging for discovery calls, and conducting research to better tailor the demo process to the needs of community colleges.
Leveraging this model generally entails repeating that process between two and four more times, ultimately leading to a sizable crop of thorough, actionable, ambitious, measurable, realistic plans.
3. Theory of Change (TOC)
The Theory of Change (TOC) model revolves around organizations establishing long-term goals and essentially “working backward” to accomplish them. When leveraging the strategy, you start by setting a larger, big-picture goal.
Then, you identify the intermediate-term adjustments and plans you need to make to achieve your desired outcome. Finally, you work down a level and plan the various short-term changes you need to make to realize the intermediate ones. More specifically, you need to take these strides:
- Identify your long-term goals.
- Backward map the preconditions necessary to achieve your goal, and explain why they're necessary.
- Identify your basic assumptions about the situation.
- Determine the interventions your initiative will fulfill to achieve your goals.
- Come up with indicators to evaluate the performance of your initiative.
- Write an explanation of the logic behind your initiative.
Here's another visualization of what that looks like.
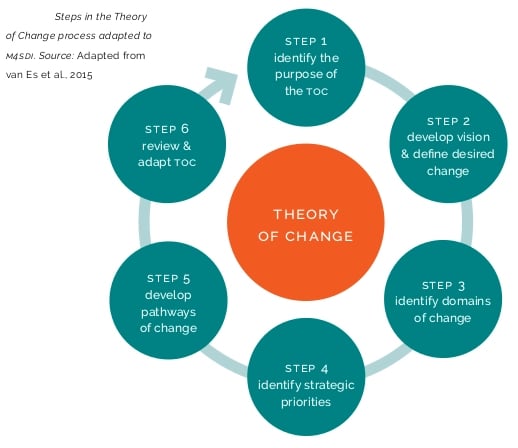
This planning model works best for organizations interested in taking on endeavors like building a team, planning an initiative, or developing an action plan. It's distinct from other models in its ability to help you differentiate between desired and actual outcomes. It also makes stakeholders more actively involved in the planning process by making them model exactly what they want out of a project.
It relies on more pointed detail than similar models. Stakeholders generally need to lay out several specifics, including information related to the company's target population, how success will be identified, and a definitive timeline for every action and intervention planned. Again, virtually any organization — be it public, corporate, nonprofit, or anything else — can get a lot out of this strategy model.
Example of the Theory of Change
For the sake of this example, imagine a business that makes HR Payroll Software , but hasn‘t been doing too well as of late. Leadership at the company feels directionless. They think it’s time to buckle down and put some firm plans in motion, but right now, they have some big picture outcomes in mind for the company without a feel for how they're going to get done.
In this case, the business might benefit from leveraging the Theory of Change model. Let‘s say its ultimate goal is to expand its market share. Leadership would then consider the preconditions that would ultimately lead to that goal and why they’re relevant.
For instance, one of those preconditions might be tapping into a new customer base without alienating its current one. The company could make an assumption like, “We currently cater to mid-size businesses almost exclusively, and we lack the resources to expand up-market to enterprise-level prospects. We need to find a way to more effectively appeal to small businesses.”
Now, the company can start looking into the specific initiatives it can take to remedy its overarching problem. Let's say it only sells its product at a fixed price point that suits midsize businesses much more than smaller ones. So the company decides that it should leverage a tiered pricing structure that offers a limited suite of features at a price that small businesses and startups can afford.
The factors the company elects to use as reference points for the plan's success are customer retention and new user acquisition. Once those have been established, leadership would explain why the goals, plans, and metrics it has outlined make sense.
If you track the process I‘ve just plotted, you’ll see the Theory of Change in motion. It starts with a big-picture goal and works its way down to specific initiatives and ways to gauge their effectiveness.
4. Hoshin Planning
The Hoshin Planning model is a process that aims to reduce friction and inefficiency by promoting active and open communication throughout an organization. In this model, everyone within an organization—regardless of department or seniority—is made aware of the company's goals.
Hoshin Planning rests on the notion that thorough communication creates cohesion, but that takes more than contributions from leadership. This model requires that results from every level be shared with management.
The ideal outcomes set according to this model are also conceived of by committee to a certain extent. Hoshin Planning involves management hearing and considering feedback from subordinates to come up with reasonable, realistic, and mutually understood goals.
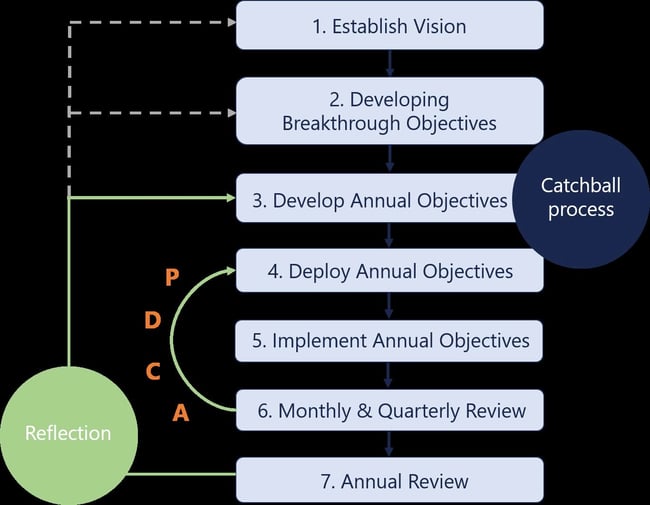
The model is typically partitioned into seven steps:
- establishing a vision
- developing breakthrough objectives
- developing annual objectives
- deploying annual objectives
- implementing annual objectives
- conducting monthly and quarterly reviews
- conducting an annual review.
Note: The first three steps are referred to as the “catchball process.” It's where company leadership sets goals and establishes strategic plans to send down the food chain for feedback and new ideas. That stage is what really separates Hoshin Planning from other models.
Example of Hoshin Planning
For this example, let‘s imagine a company that manufactures commercial screen printing machines. The business has seen success with smaller-scale, retail printing operations, but realizes that selling almost exclusively to that market won’t make for long-term, sustainable growth.
Leadership at the company decides that it's interested in making an aggressive push to move up-market towards larger enterprise companies. However, before they can establish that vision, they want to ensure that the entire company is willing and able to work with them to reach those goals.
Once they‘ve set a tentative vision, they begin to establish more concrete objectives and send them down the management hierarchy. One of the most pressing activities they’re interested in pursuing is a near-comprehensive product redesign to make their machines better suited for higher volume orders.
They communicate those goals throughout the organization and ask for feedback along the way. After the product team hears their ideal plans, it relays that the product overhaul that leadership is looking into isn‘t viable within the timeframe they’ve provided. Leadership hears this and adjusts their expectations before doling out any sort of demands for the redesign.
Once both parties agree on a feasible timeline, they begin to set more definitive objectives that suit both the company‘s ambitions and the product team’s capabilities.
Strategic Plan Example
The strategic plan above is for a fictitious shoe company and outlines the way in which it'll differentiate itself within the market. It effectively uses each step in the strategic planning model framework and is written in a way to give a brief overview of how the company will enter the market and sustain longevity.
If you're working on a strategic planning model for an existing business, your plan will look similar, but have a few tweaks to the goals, including more goals about improving sales and processes. When drafting the action plan and evaluation parts of the plan, be sure to think tactically about the actions that will help you achieve the goals, and use your mission, vision, and values to guide the choices you make.
Strategic Planning Tools
There are additional resources you can use to support whatever strategic planning model you put in place. Here are some of those:
1. SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool and acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It's used to identify each of these elements in relation to your business.
This strategic planning tool allows you to determine new opportunities and which areas of your business need improvement. You'll also identify any factors or threats that might negatively impact your business or success.

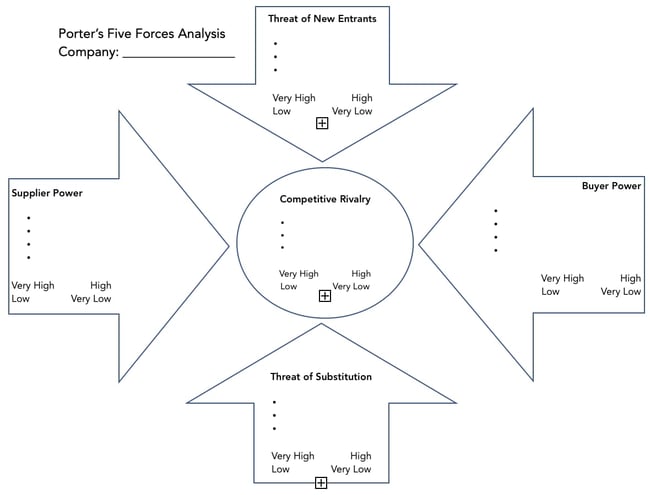
2. Porter's Five Forces
Use Porter‘s Five Forces as a strategic planning tool to identify the economic forces that impact your industry and determine your business’ competitive position. The five forces include:
- Competition in the industry
- Potential of new entrants into the industry
- Power of suppliers
- Power of customers
- Threat of substitute products
To learn more, check out this comprehensive guide to using Porter's Five Forces .
3. Visioning
Visioning is a goal-setting strategy used in strategic planning. It helps your organization develop a vision for the future and the outcomes you'd like to achieve.
Once you reflect on the goals you‘d like to reach within the next five years or more, you and your team can identify the steps you need to take to get where you’d like to be. From there, you can create your strategic plan.
4. PESTLE Analysis
The PESTLE analysis is another strategic planning tool you can use. It stands for:
- P: Political
- E: Economic
- T: Technological
- E: Environmental
Each of these elements allow an organization to take stock of the business environment they're operating in, which helps them develop a strategy for success. Use a PESTLE Analysis template to help you get started.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

S&OP: A Comprehensive Overview of Sales and Operations Planning

A Straightforward Guide to Qualitative Forecasting

4 Clever and Effective Ways to Simplify Your Sales Process From Seasoned Sales Experts
![strategic business planning models How to Develop a Strategic Plan for Business Development [Free Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Copy%20of%20Featured%20Image%20Template%20Backgrounds-2.png)
How to Develop a Strategic Plan for Business Development [Free Template]

Lead Distribution Methods and Best Practices

Lead Routing: How to Precisely Implement and Route Key Prospects

The 25 Best Lead Distribution Software in 2022

Return on Sales: How to Calculate It and What You Need to Know

30 Key Interview Questions and Answers for Sales Operations Role

How Using a Document Library Can Improve Your Sales Process
Plan your business's growth strategy with this free template.
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Strategic Planning Models, Tools & Frameworks (With Templates)

Organizations are always looking for ways to improve. It’s how they stay relevant and, more importantly, profitable. But you don’t get better just by desiring it. It takes strategy, and then a model to implement that strategy.
No surprise, there are models to accomplish this called strategic planning models. They’re great for businesses, big and small, and assist in project planning and implementing organizational goals in a thorough and structured manner. Once you have decided on an objective, then you must plan a model that will execute it successfully.
There are quite a few strategic planning models, and they can be very different from one another. Often the type of organization will dictate which strategic planning model is used. After a brief explanation, we’ll dig into five of the more popular ones. You’re sure to find a strategic planning model among them that works for you.
What Is a Strategic Planning Model?
It’s easy to define what a strategic planning model is because the definition is embedded in its name! A strategic planning model is how an organization takes its strategy and creates a plan to implement it to improve operations and better meet its goals.
How they get to this point requires identifying what the company wants, and how it hopes to achieve those goals in the near term. Once they have that target clearly defined, then it’s a matter of working backward to figure out how to get there.
This, of course, is easy to say and extremely difficult to do. Sometimes the complexity involved in trying to put together a plan to strategically meet your goals can feel like it needs a strategic planning model all its own! That’s why there are classic models already in place to help you accomplish your goals.
Get your free
Strategic Plan Template
Use this free Strategic Plan Template for Word to manage your projects better.
Do You Need a Strategic Planning Model?
If all this sounds like a fancy way of saying you need a plan to achieve your goals, well, you’re right. But that doesn’t dismiss its usefulness in achieving those objectives. No matter if you’re a startup or an established, market-dominant brand, if you don’t have a plan to reach your goals, you’re bound to fail. That could be losing market share or shuttering, neither of which is a path forward for a viable enterprise.
The benefits of having a strategic planning model are manyfold. For one, it provides a clear path that the organization uses for operational planning which determines what work will be done by everyone on the staff. Having all departments work together for a common goal is powerful. The opposite is disastrous. You can’t hit your target, whether it’s a year or five or 10 years in the future if everyone doesn’t know what it is and how you plan to get there.
Think of it as being focused. There are a lot of distractions that occur every day in every business. Knowing what your topline is helps you prioritize and keep your energies directed on the overall strategy for the company and the right strategic initiatives .
Another positive of having a strategic planning model is that it improves your knowledge of what works best in the organization. You know your strengths and weaknesses, as well as get a clear picture of where you are in the marketplace. It even helps you get a clear idea of who your competition is and how you can differentiate yourself from them.
Best Practices for Strategic Planning Models & Frameworks
We’ll get to the examples in a moment, but regardless of which you choose as most appropriate for your needs, there are best practices to make sure you succeed. When doing the research, assemble a group that is diverse but also appropriate for the goal. Diversity brings more ideas to the table. You’ll want between six and 10 people.
Once you start, give it time. The team needs to come up with creative solutions, and then season them, to make sure they’re the right course of action. You might want to remove the team from the work site. A change of environment, without the distractions of the office, can help them settle into a more contemplative state where they can come up with better ideas.
Of course, you need to get buy-in from the team or else your hard work will be for naught. Once you have them fully on board, build trust. You want everyone to participate, and to do so in a free and open discussion. That means from the boss on down. It might help to hire an outside facilitator to manage the process.
When you have a plan, it must be realistic. If you can’t execute it, then you’ve not done your job. Therefore, it must be actionable, with clearly defined goals , tasks, responsibilities outlined, accountability, deadlines—and all this must be clear to everyone involved. But that doesn’t mean you can’t be flexible. Plans change, so it’s best to not be rigid about it.
Finally, don’t think of creating a strategic planning model for your business as a one-and-done process. Not only must your plan be open to editing as internal and external forces demand, but these meetings should be regularly scheduled. Think of it as a process. Meet monthly if you can, or at least quarterly. You can discuss how the plan is being executed and hold people accountable for what they’ve been tasked to execute. This is how you ensure your plan becomes a reality.
Strategic Planning Models
As we said, there are many models that we encourage you to explore. You never know what you might find. For our purposes, let’s narrow the scope down to five with proven results.
Alignment Model
This strategic alignment model (SAM) is among the most used. It’s made up of two parts—strategic fit and functional integration. What that means is that the model aligns business and IT strategies . To do this requires identifying the key goals of an organization and then what the steps are to reach those goals. The plan must maximize the process to best achieve those goals.
There are four perspectives to guide you in this model:
- Strategy execution is when the business strategy is driving the model.
- Technology potential, which also sees the business strategy as the driver, but with an IT strategy to support it.
- Competitive potential deals with using emerging IT capabilities to create new products and services.
- Lastly, there’s the service level, which focuses on creating the best IT system in the organization.
Here, business strategy is important, but only the launching pad.
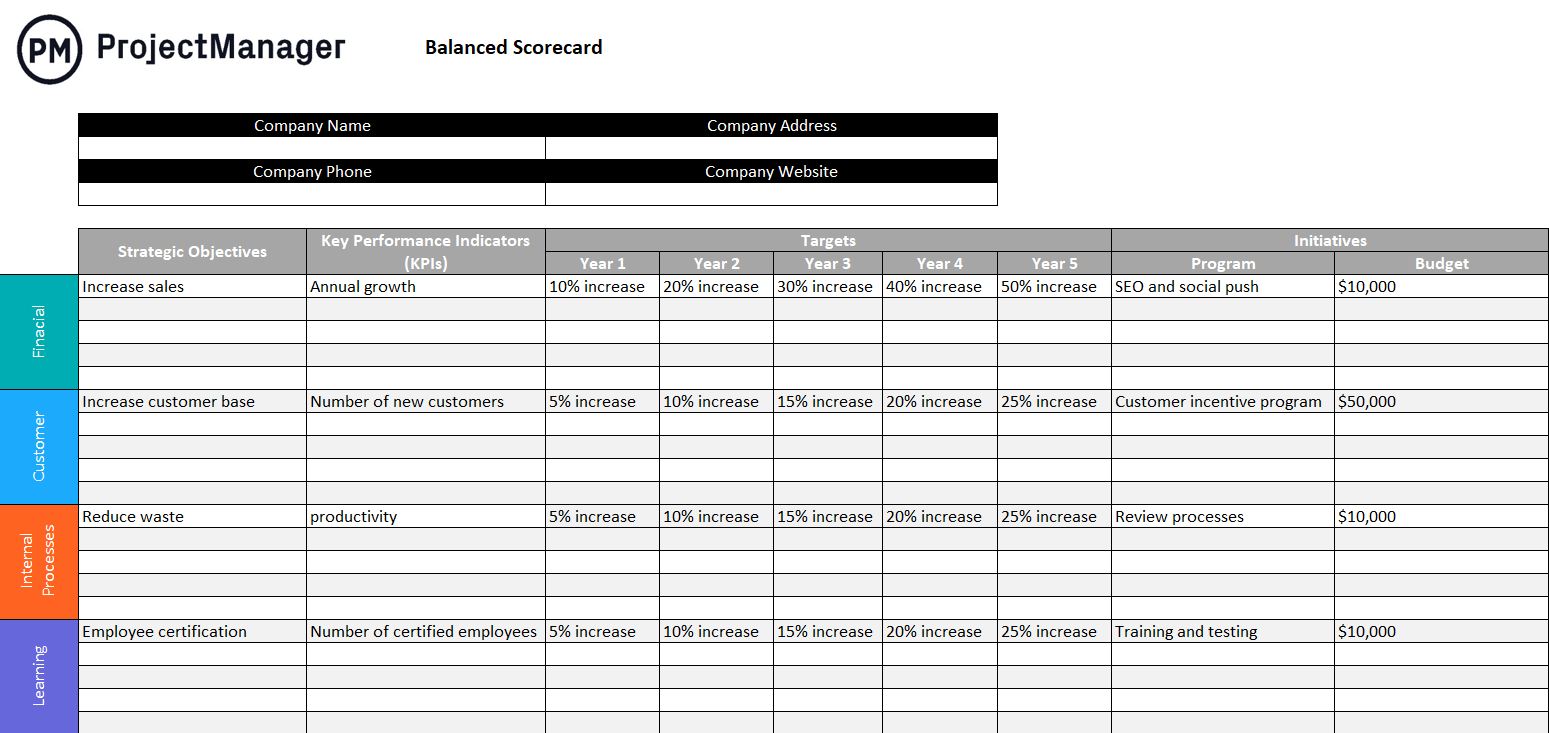
Balanced Scorecard
The balanced scorecard (BSC) is made up of clear communications on what is being accomplished. It aligns the work with the overall strategy and prioritizes, measures and monitors progress. The idea is that the model balances strategy with financial measurements. One of the reasons to use BSC is that it helps you see the connections between various parts of your strategic management and planning .
Using BSC means exploring four different aspects of your organization.
- One is the financial performance of the company and what financial resources have been most effective.
- You also want to gauge the performance of your stakeholders or customers and how you serve them.
- Internal processes should be judged on their efficiency, too, but also on quality.
- Then there’s the organizational capacity, which looks at your personnel, infrastructure, tech, culture and whatever else can be used to meet your goals.
We’ve created a free balanced scorecard template for Excel to help you get started with this tool.
Basic Model
Also called the simple model, this is often used by newer organizations that don’t have a history of strategic planning to help guide them in making decisions. But it’s also a fine model for any organization that doesn’t have the time or resources to spend on deep and extensive strategic planning .
First, you establish the mission statement for your organization, if you don’t already have one. That is a summary of your goals that are created to inspire and transform the organization. Next, you want to figure out what goals must be achieved to fulfill the mission statement. From that, break down the tasks that will reach those goals. Schedule, monitor and report on your progress.
Blue Ocean Strategy
The blue ocean strategy is designed to take your product to a market where there is no or little competition. Therefore, the research is heavily tilted towards finding a niche that can be exploited for profit, such as where few businesses are offering a product people have expressed an interest in, and there is little to no pricing pressure.
Unlike red ocean strategy, which describes a market that is saturated and products are threatened by pricing pressure that could threaten the business, blue ocean strategy looks for markets where there’s room to grow. You’re looking to capture new demand, where your product is either unique or so much better as to make competition irrelevant.
Issue (Or Goal) Based
The issue-based model (also called goal-based) is the next step up from the basic strategic planning model. It builds on the basic model and is intended for businesses that are more established. Thus, it’s more in-depth and possibly the most popular of all the models we’ve highlighted.
To begin, use a SWOT analysis, which is an acronym standing for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. It helps you identify and analyze internal and external factors that impact your business, product or service. Next comes the mission statement, then planning, creating a budget and a schedule to implement it. After a year, you’ll want to monitor the results and report on its progress , making adjustments as needed.
PEST Analysis
A PEST analysis consists of identifying any political, economic, social and technological factors that can affect a business. It’s especially useful for larger organizations, such as multinational companies whose strategic project management initiatives are the most affected by these types of issues.
It’s important to conduct a PEST analysis before or as you create a strategic plan, so you don’t fail to acknowledge any significant political, economic, social or technological risk that could affect your organization and its ability to achieve its goals.
Hoshin Kanri
This is a strategic planning model that ensures that all levels within an organization understand what the organization’s strategic objectives are. Then those strategic objectives are broken down into specific goals and action plans for employees at all levels of the organization, from executives to production floor employees.
Another important aspect of this strategic planning model is that it involves constant performance tracking and communication between employees and their supervisor which helps track the completion of strategic goals and evaluate their feasibility. This strategic planning model is mostly used by manufacturers who implement lean manufacturing best practices, but it can be used by any type of business.
Porter’s Five Forces Model
This is a fundamental strategic planning model that should be used by any business. It allows business owners, executives and other decision-makers to understand the competitive forces that shape an industry and what they mean for a business.
This model analyzes the rivalry among existing companies, the threat of substitute products, the threat of new competitors, the bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of buyers. Together, these five variables create the business environment to which your organization’s strategy should adapt.
Strategic Planning Tools
Now, here’s a quick overview of some tools that can help you as you go through the process of planning your organizational strategy.
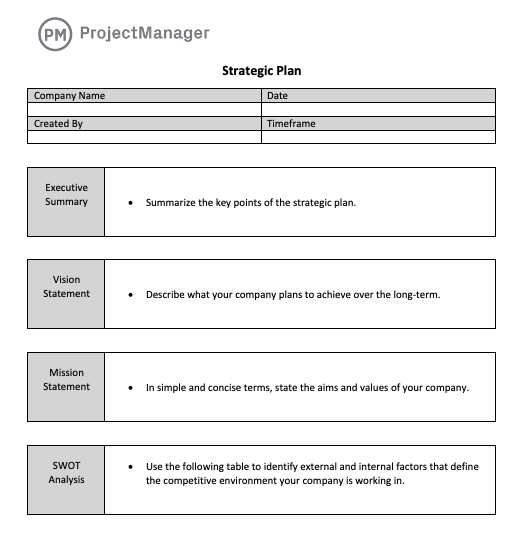
1. Strategic Plan
A strategic plan is a document that describes the strategic direction of an organization by outlining its vision, mission and long-term strategic objectives. It’s a fundamental tool when defining the strategy of your organization for the next three to five years.
The main purpose of a strategic plan is to provide high-level goals for the organization as a whole, known as strategic objectives, which will guide the efforts of the various departments within the organization.
This free strategic plan template for Word helps you capture some of the most important elements of your strategic plan such as your business goals, mission and vision statements, a SWOT analysis, and the operational actions that will be taken to achieve your objectives.
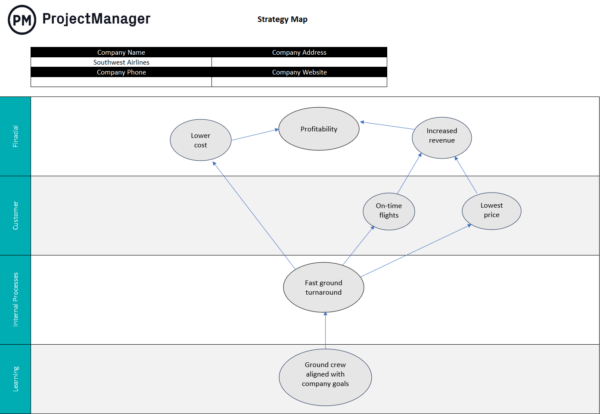
2. Strategy Map
A strategy map is a tool that can help you visualize the strategic objectives of your organization and the relationship between them and group them into the four balanced scorecard perspectives: financial, customer, internal business processes and learning and growth.
These four categories help you establish the relationship between strategic objectives. For example, a strategic objective that’s related to improving your internal business processes will have a positive impact on the customer and financial areas.
3. Strategic Roadmap
A strategic roadmap is a tool that can help you turn your strategic objectives into action plans. To create a strategic roadmap, you’ll need to think about all the different tasks that your team will need to execute to reach its strategic objectives.
Next, you’ll need to estimate the duration of each of those tasks and based on that information, create a timeline. Strategic roadmaps are usually created with Gantt charts, which allow you to create a visual timeline that shows all the different actions your organization will take to achieve its strategic objectives.
4. SWOT Matrix
A SWOT matrix is a simple yet effective strategic planning chart with four quadrants that allow you to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of your organization. These four categories describe the internal and external factors that may affect your business’s ability to compete in the market either positively or negatively. Here’s what they mean.
Strengths refer to the internal capabilities of your business which might give it an advantage over its competitors, such as, for example, lower production costs or intellectual property. Weaknesses on the other hand describe the areas of improvement for your business, which can be anything like having higher operational costs than your competitors or lack of brand awareness.
Opportunities refer to the positive external factors such as an underserved market niche or reduced costs of supplies and finally, threats are negative external conditions such as new technologies or new competitors that might replace your product. You must consider these factors before making the strategic plan of your organization so you don’t steer your business in the wrong direction. Our SWOT analysis template helps you document the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of your business or project.
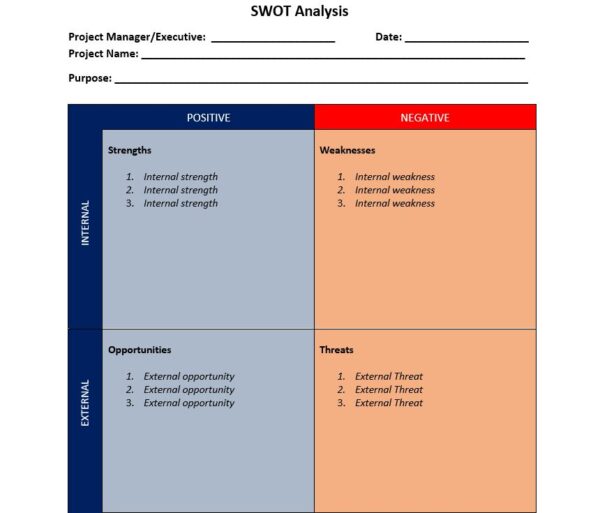
5. VRIO Framework
VRIO stands for value, rarity, imitability and organization, which are the four lenses the VRIO framework uses to determine whether your organization has a competitive organizational strategy. It can help you audit the competitiveness of your business and find weaknesses in your operational strategy .
By analyzing your organization from these four perspectives, you’ll be able to determine whether your business provides value to customers in a way that’s rare and costly to imitate for your competitors. If so, you have a competitive business strategy that can be sustained over time.
6. Ansoff Matrix
An Ansoff matrix or product-market expansion grid is a strategic planning tool that can help you gauge the risk-reward ratio of growth strategies that involve new products and new markets. It’s got four quadrants that show four different strategies: market penetration, product development, market development and diversification.
It’s a great tool to help you decide which of these strategies is the best for your business. You can create a separate Ansoff matrix for different business units or product lines.
7. GE Matrix
A GE matrix or McKinsey matrix is a tool that helps executives and other decision-makers prioritize which business units within an organization should be invested further and which should be divested based on the industry attractiveness and strength of each business unit. It can also be used for prioritizing what projects are approved and executed by an organization, which is a decision that’s made by executives and the board of directors, as advised by project managers and project management offices (PMOs), who are responsible for their success and ensuring they bring the benefits that are expected.
In simple terms, a GE matrix contrasts the potential benefits of an industry with the current positioning of a business unit to determine whether it will be profitable to invest in it. To do so, you’ll need to analyze variables such as the market size, growth rate, competition level and industry trends. It’s ideal for aligning your projects and business strategy .
How ProjectManager Executes Strategic Planning Models
Now that you know about strategic planning models, and have chosen one to reach your organization’s objective, you have a lot of work ahead of you. ProjectManager is an award-winning tool that organizes strategic plans, so you can execute, monitor and report on their progress.
Start Planning In-Depth With Gantt Charts
You have decided on your target, now you need to know how you get there. That’s as simple as breaking down the goal into realistic tasks, or steps, that end at your objective. You can use a work breakdown structure or collect them on a spreadsheet. Now the fun starts. Upload your tasks into our software, and you get to the planning part of your strategic planning model.
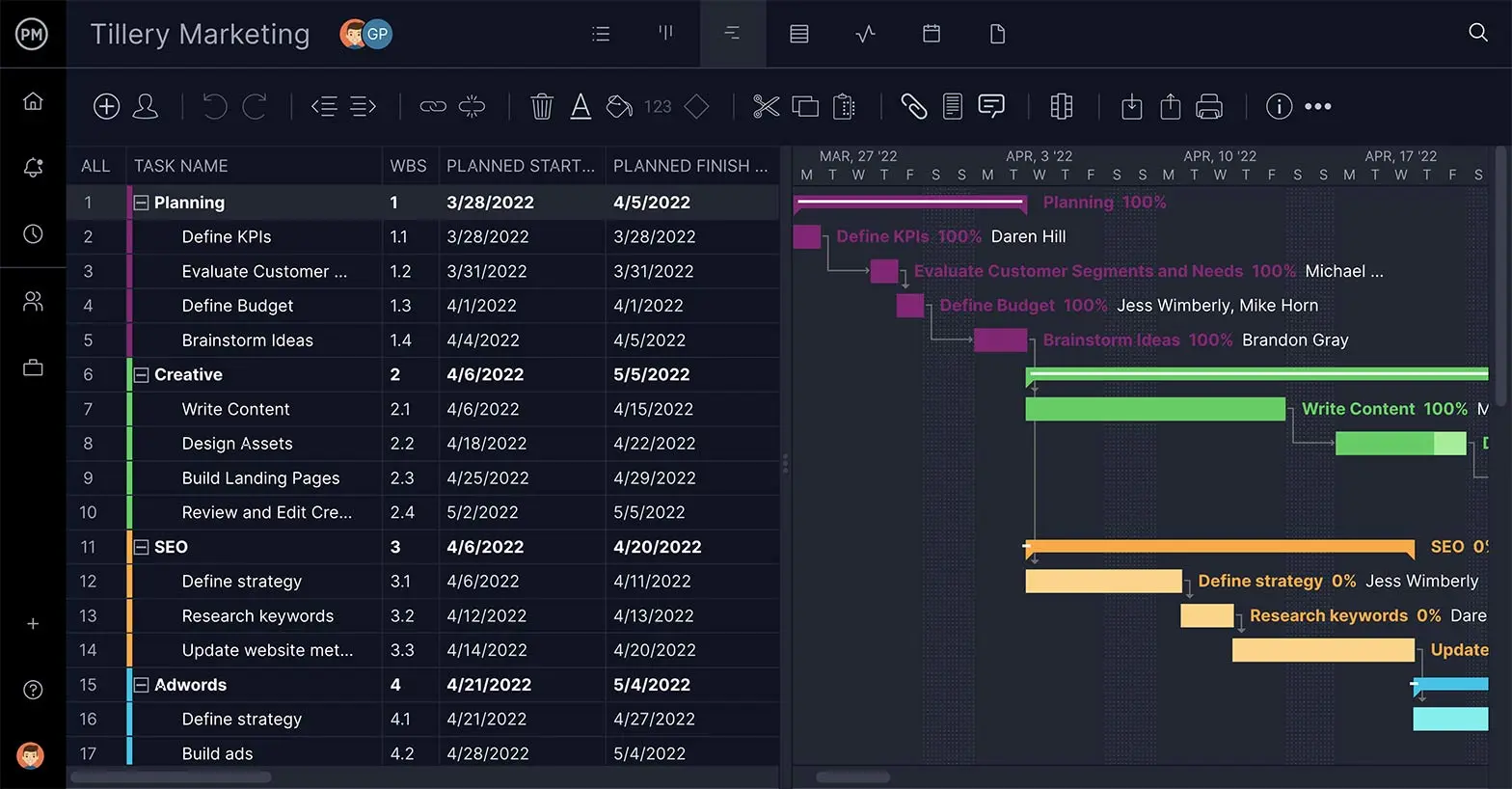
Add duration to your tasks, and they instantly populate the Gantt chart tool timeline. Now, you can see your whole project from start to finish. Add priorities, so your team knows what’s important, and break up the project into phases with our milestone feature. There’s a space on each task to write descriptions that guide your team, and they can collaborate by commenting with one another at the task level to facilitate productivity.
Multiple Views to Tackle Your Projects
There are many ways to work, and we have many tools to get that work done. Besides the Gantt, you can use a task list, calendar or kanban board to manage your work. The board view is especially helpful, as it breaks production into phases and provides transparency into the process, so you can keep traffic flowing and avoid costly bottlenecks.
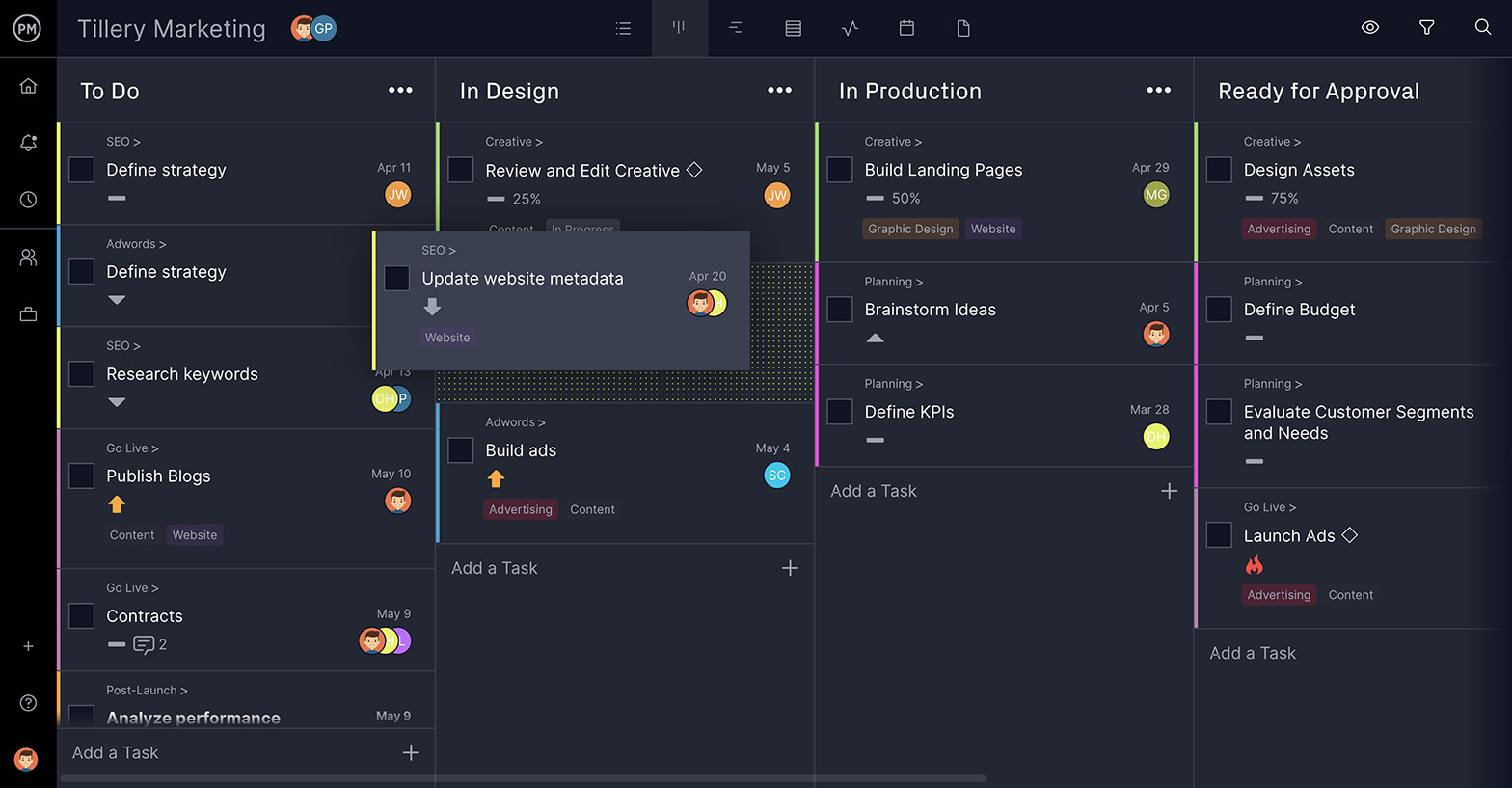
Monitor Your Progress With Real-Time Dashboards
Part of any strategic planning model isn’t just the planning and execution, but monitoring progress to make sure you’re hitting your targets. We have a real-time dashboard that tracks several project metrics, including project variance, which automatically calculates your planned vs. actual progress.

Related Strategic Planning Content
We’ve created dozens of blogs, templates and guides on project management, operational management and strategic planning. Here’s some content that relates to the strategic planning models and tools we explored above.
- How to Create a Strategic Roadmap for Your Organization
- Operational Strategy: A Quick Guide
- Strategic Project Management: Planning Strategic Projects
- A Quick Guide to Strategic Initiatives
ProjectManager is online software made to help teams and projects get better organized. We help you deliver on your strategic plan with tools to help you through every phase of the project. See why tens of thousands of teams are already using our software and take our free 30-day trial today.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.

Top frameworks for strategic planning
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 8 min
If you want to stay ahead in business, you need to constantly be improving. It’s how you stay relevant and remain profitable. But improvement and success don’t come just because you want them enough—you need to develop a strategic plan that details:
Where you are right now: Look at your current strategic position relative to your competition. Describe your current problems keeping you from progressing. Define your mission, vision, and values.
Where you want to go: Describe your competitive advantage and understand where your organization is currently headed. Look for ways to solve your current problems.
How you will get there: Define your goals, objectives, and the steps you will need to take to achieve your goals.
This is an oversimplification of the strategic planning process. There are many different strategic planning models you can use that expand on these three basic elements.
Let’s look at some strategic planning frameworks that will help you to see where you can improve, define your goals, and map out the processes and procedures you will use to keep achieving your goals.
Strategic planning models vs. strategic planning frameworks
A strategic planning model maps out how your company plans to implement a strategy for improving operations, delivering quality, and meeting specific goals. It is like a template or a tool you use at the beginning of the planning process. It helps you flesh out the ideas that will take you where you want to go.
A strategic planning framework outlines how you will conceptually approach your strategic plan. Frameworks tend to be visual and detail the activities that are performed in your organization’s strategy plan. Think of the framework as a blueprint or the foundation for your messaging and brand narrative. The idea is to communicate to internal and external stakeholders the aspirations of your strategic plan.
Common strategic planning models
Why is a planning model important? Because it’s hard to achieve your company’s goals if your employees don’t know what the goals are or how you plan to reach them.
Strategic planning models are the roadmaps that keep your team focused on what needs to be completed to reach your goals. And you will need to constantly monitor and review your plans to ensure that you quickly address issues and realign processes as necessary to keep your production working as smoothly as possible.
The following are a few strategic planning process models that can help you to create the roadmap your team will follow to success.

Basic model
Sometimes called the simple model, the basic model is often used by companies that:
- Are new and don’t have a lot of experience with or are new to strategic planning
- Are small and don’t have the resources to develop complex plans
- Don’t have too many serious problems to solve
- Don’t have a lot of time to create an extensive plan
This model focuses on establishing your company vision and mission statement, setting goals to make the vision a reality, outlining specific steps to take to reach the goals, and monitoring progress to keep everybody on track and to address issues when they come up.

Issue-based model
This model is also known as the goal-based model. It’s essentially an extension of the basic model. The issue-based model is more dynamic and popular with established companies to develop more comprehensive plans.

Alignment model
The goal of this model is to align your business and IT strategies with the company’s strategic goals. This model is good for organizations that need to reassess objectives or correct problem areas that impede progress.
Like the issue-based model, this model has you look at your internal operations to develop a strategy. The model involves the following steps:
- Review your vision, mission statement, and company goals.
- Determine what is currently working well and what needs to be realigned.
- Make suggestions for improving the problem areas.
- Implement changes to improve or eliminate weak areas.

Scenario model
This model looks at different outside influences that could have an impact on your organization. For example, government regulations can have a big impact on a manufacturer, such as what materials can be used to make their products.
The idea is to look at how outside influences might impact your operations from the following perspectives: best-case scenario, worst-case scenario, and reasonable-case scenario.
These scenarios help you to figure out the best way to respond to each. Determine which would be the most likely scenario and determine how you will address it. Then add it to your strategic plan.

Organic model
This model is not linear or structured like the other models. Its focus is on your company’s shared vision and values instead of plans and processes. The idea is that a company’s vision is achieved more organically when teams are able to openly and continuously discuss what steps to take. This requires a clear understanding of the vision, frequent and consistent communication, and dialogue among various stakeholders.
The model might include the following three basic steps:
- Clarify shared vision and values.
- Based on shared values, determine the actions and responsibilities for each person so they can work toward the vision.
- Stakeholders report the results of the action plans.
The organic model can work in large organizations that can afford to take a long time to achieve their vision and who can work well in a less structured environment.
Real-time model
This model is fluid and designed for organizations that need to react quickly to a rapidly changing work environment. Long-term, detailed plans quickly become irrelevant because of rapid changes.
Real-time strategic planning involves the following:
- Organizational strategy: Define your mission and vision, understand your competitors, and know what the current market trends are.
- Programmatic strategy: Research external environments, list opportunities and threats, and brainstorm the best ways to approach each.
- Operational strategy: Analyze internal processes, resources, and systems. Develop a strategy that addresses internal strengths and weaknesses.
Inspirational model
This model is designed to inspire your people to energize them as they work toward goals. People come together to discuss an inspirational vision for your company. Then, participants are encouraged to brainstorm far-reaching, exciting goals to realize your company vision.
The inspirational model works well for organizations looking to lift the spirits of its staff or quickly produce a plan.
Types of strategic planning frameworks
Without a strategic framework, you risk inconsistent messaging that can confuse customers and stakeholders. If your message and purpose are not completely understood, you can alienate stakeholders and lose employee motivation.
Here are some of the different types of strategic planning frameworks that you can use:
Balanced scorecards: Works as a strategic planning and management system. The balanced scorecard helps companies to align daily tasks with long-term strategy, communicate progress, set priorities, monitor progress, and measure success.

Strategy mapping: Provides a visual document to communicate your strategic plan. A strategy map make it easy to show relationships among various takes and objectives.

Porter’s Five Forces: Helps you to assess how competitive the market is. Porter’s Five Forces focuses on your company’s ability to enter a market, similar products customers can buy instead of yours, buyer power, supplier power, and the effect a competitor’s change in strategy would have on your company.

SWOT analysis: With this strategic planning framework, you analyze your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
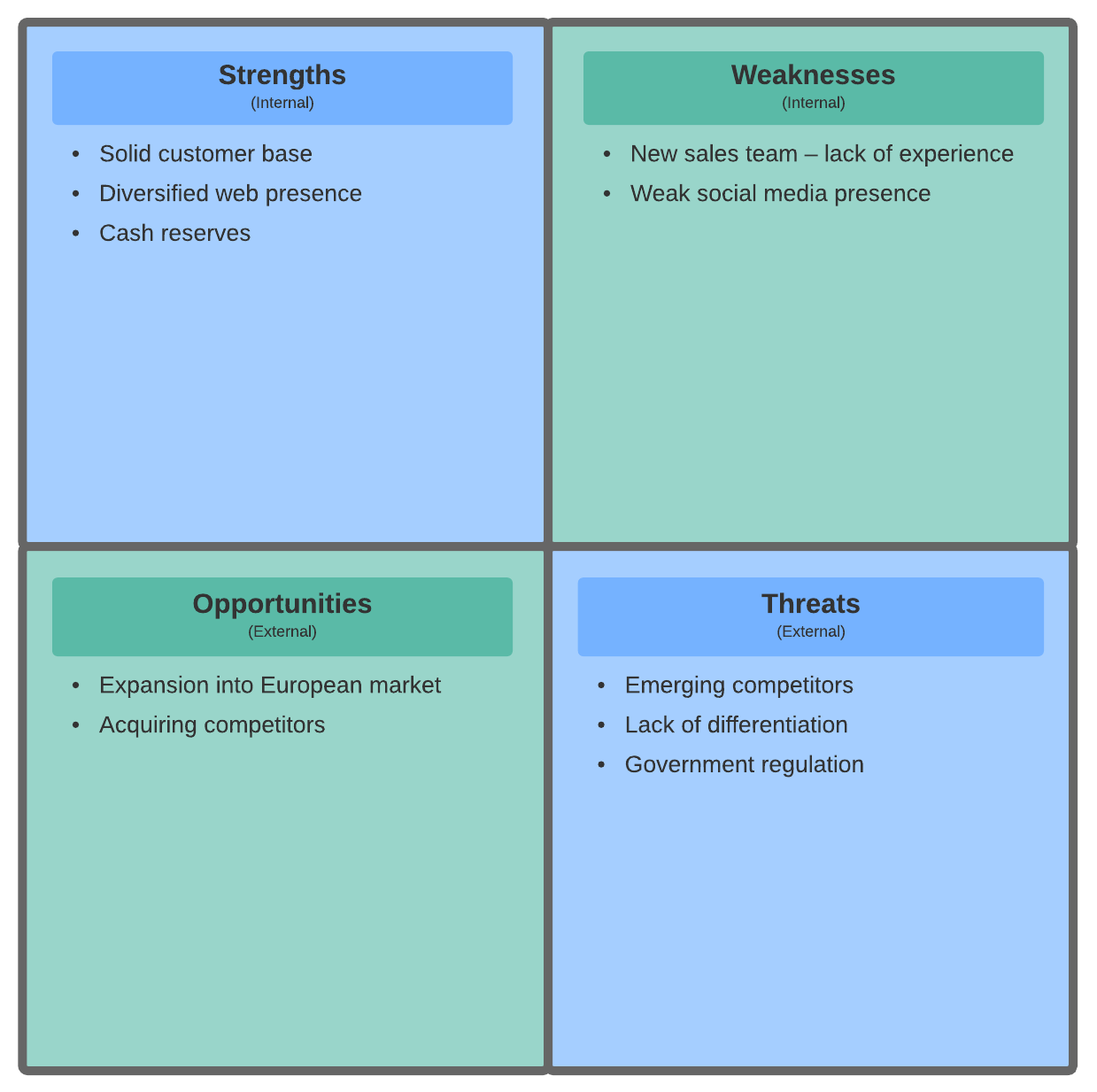
PEST/PESTLE analysis: This framework looks at a business environment to see if there are any factors that could impact your organization’s health. PEST analysis includes political, economic, sociocultural, and technological factors.

Ansoff matrix: This strategic planning framework analyzes four potential opportunities for growth: market penetration, product development, market development, and diversification. Try the Ansoff matrix when seeking out new opportunities.

Objectives and key results ( OKRs ): In The objectives refer to what you want to achieve. The key results indicate how you’ll measure your progress toward your objectives.

Blue Ocean Strategy: With this framework, your company creates demand for products in an uncontested market space. You focus on differentiating your product from the competition rather than trying to beat them.
Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organization (VRIO): This strategic planning framework answers questions concerning your product’s value, the amount of competition in your market, how easily your product can be imitated, and how well-organized your company is.
Hoshin Kanri: This framework is used to align goals with tasks, keeping everything coordinated and ensuring that everybody is working toward the same end result.
If strategic planning models and frameworks seem similar, it’s because they are. While strategic planning models outline the high-level structure of your plan, the strategic framework describes the design concepts and the plan’s details.
It doesn’t matter which model and framework you choose to use. You can even combine aspects of several models or frameworks to meet your needs. The important thing to remember is that strategic models and frameworks are vital to creating and communicating a clear strategic plan that will keep your company relevant and competitive.

See how Lucidchart can help you through the strategic planning process, especially when it comes time to take action.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
How to Use Strategic Planning Frameworks and Models
By Joe Weller | April 12, 2019 (updated July 26, 2021)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Strategic planning models and frameworks can help guide you through the strategic planning process. In this article, seasoned industry experts explain the models and frameworks to help you identify which is best for you.
Included on this page, you'll find different types of models and frameworks , tools to help you decide which models and frameworks to use , and details on how to use strategic planning models .
Strategic Planning Basics
Strategic planning is a team process that sets up how your company will accomplish its goals. When you deploy it correctly, strategic planning highlights problems, helps find solutions, and monitors progress. To learn more about the basics of strategic planning, read this article.
A strategic plan includes many sections. When done well, a strategic plan can help you prioritize your company’s functions and stay in line with your mission and vision.
There are different ways to present a strategic plan — for example, it can be a written document, a spreadsheet, or an animated presentation. To learn how to write a strategic plan, read this article.
Strategic Planning Frameworks and Models
Just as there are many approaches to presenting a strategic plan, you have several ways to frame or model your plan.
The terms strategic planning framework and strategic framing models are often used interchangeably, but some say they are different.

“Think of models as a way of ideating strategy. [A model is] a template: You use it at the beginning of the planning process. The idea behind a model is to tease out the ideas,” says Tom Wright, CEO and Co-Founder of Cascade Strategy , a software company based in Sydney, Australia, with offices all over the world. “Frameworks are like a lens to help you see different perspectives, whereas the model is a process you would use from the beginning. You add a framework on top of the [strategic plan] to slice and dice the model.”
There are many strategic planning models and frameworks — some are tried and true, others are newer and more adaptive, and planners and managers may be more familiar with some methods than others. There is no one right or wrong way to create a strategic plan, and you can modify models and frameworks based on your company culture, your current situation, and the purpose behind your planning.
“The major driver [for picking a model or framework] is what type of business you are and what you want to accomplish,” Wright explains.
Strategic planners often utilize different frameworks or customize particular models as they move through the planning process. But be careful; customizing models or frameworks too much might confuse people who are familiar with a particular planning process.
Below is a list of some of the most common frameworks and models:
Alignment Model: This model helps align your mission statement with available resources. It is particularly effective for businesses facing internal struggles.
Balanced Scorecard (BSC): The balanced scorecard system strives to connect big-picture elements with operational elements. BSC is well-known and works for companies of varying sizes.
The Basic Model: Sometimes called a simple strategic planning model , the basic model involves creating a mission statement, goals, and strategies.
Blue Ocean Strategy: This framework emphasizes new markets and uncontested space.
Gap Planning: A strategy gap is the distance between how a company is currently performing and its desired goal. Gap planning is the analysis and evaluation of that difference.
Inspirational Model: This is a somewhat quick method of strategic planning that begins by coming up with a highly inspirational vision for the organization and the goals to match.
Issue-Based or Goal-Based Model: A step up from the basic model, this model is better for more established businesses. It incorporates SWOT or other types of assessments to determine goals, mission statements, action plans, and other steps.
Organic Model: As the name implies, this model does not necessarily follow a set plan, instead evolving and changing as conditions warrant.
PEST Model: The PEST (political, economic, social, and technological) approach looks at elements of the external environment, including the forces in its name.
Porter’s Five Forces: This model looks at five competitive forces that are present in every industry and helps to determine strengths and weaknesses: competition in the industry, the potential of new entrants into the industry, the power of suppliers, the power of customers, and the threat of substitute products.
Real-Time Model: This a fluid process that works best for companies that operate in a rapidly changing environment.
Scenario Model: When used in conjunction with other models, the scenario model can help you identify goals, as well as issues around them, by using scenarios that might arise. Some experts say this is more of a technique than a model.
Strategy Mapping: This approach helps organizations design and communicate their strategies. Strategy mapping often falls under the umbrella of a BSC, but strategy maps can also stand alone.
SWOT Analysis or SWOT Matrix: SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) offers a way to examine both internal and external forces impacting your company.
VRIO Framework: This approach looks at the questions of value, rarity, imitability, and organization concerning the competitive potential of a company.
Using Strategic Planning Models
In this section, you’ll learn the specifics of the different strategic planning models and frameworks. Sometimes, models can serve as a visual guide. In contrast, frameworks function as an overlay to a model that helps clarify particular items, such as goals.
The Basic Model
The basic model of strategic planning is the most common and simplistic approach. The basic model works well for companies that are small, do not have much time to plan, don’t need to address many serious issues, or operate in stable external environments. It also works for companies that are new to strategic planning.
The basic model is not meant for organizations with significant resources to pursue ambitious visions and goals.
The basic model centers on the mission and vision statements. The vision statement identifies your company’s purpose on a higher level, and the mission statement outlines what happens within the organization to achieve that vision. It makes sense to build the rest of your plan from these statements.
The next step is to come up with goals you must achieve to live up to your mission and make it a reality, then outline what must happen to achieve those goals. Next, list the specific activities you must implement and who will participate in those activities. Lastly, create a simple monitoring plan to make sure your organization stays on track.
The Issue-Based or Goal-Based Model
The issue- or goal-based model evolves from the basic model and results in a more comprehensive plan. The steps vary.
This approach is dynamic and fluid, and it works well for businesses that want to go deeper into strategic planning but have the following concerns:
Limited resources for planning
Several issues to address
Limited past success reaching ambitious goals
No buy-in for the strategic planning process
The issue-based model requires organizations to identify their most important current issues, suggest action plans to address those issues, and include that information in the strategic plan.
The goal-based model often includes the following:
A way to monitor and amend the plan
Action plans, including objectives, resources, and implementation roles
Core values
Major issues and goals, along with ways to address them
Mission statement
SWOT analysis
Vision statement
Yearly operating plan, including a budget
The Alignment Model
The alignment model focuses on making sure an organization’s actions align with its vision. In the plan, you outline the mission, resources, programs, and support your organization needs to ensure it fulfills its vision.
The alignment model works well for organizations that are trying to figure out what is and isn’t working well, along with what needs adjusting. The process can help identify issues, such as internal inefficiencies and productivity problems. However, some critics of this model say it functions more like an internal development plan than a strategic plan.
The Scenario Model
The scenario model looks at what is happening outside of an organization, including regulatory, demographic, or political forces, to determine how they can impact what is happening inside of a company.
The scenario model works best when used in combination with other models and is more of a technique than a model.
For each change in an external force, discuss how it could impact the future of your organization in the following three ways:
A best-case scenario
A worst-case scenario
A reasonable-case scenario
After looking at the three potential impacts, figure out how to best respond to each. Then pick the most likely scenario and discuss strategies to address it.
The scenario model works well for businesses that need help planning for several potential situations.
The Organic Model
If your company wants to stay away from strict and formal strategic planning, the organic model might be a good fit. As the name implies, the organic model of strategic planning is more of a free-spirited conversation, rather than a set process. It emphasizes the journey over the destination.
The organic model relies on everyone having a shared vision and being willing to openly discuss how to get there using common values. This less systematic model requires patience since it involves constant dialogue and is never really finished.
The organic model works well for organizations where traditional methods feel static and obsolete. If you are looking for a set plan outlining steps to follow, the organic model is not for you.
Storyboarding techniques and open dialogue are often a part of the organic model, and everyone is encouraged to participate openly. The focus is more on learning and less about the method of strategic planning.
Real-Time Strategic Planning
The real-time method of strategic planning is even more fluid than the organic model. It helps articulate an organization’s mission and, sometimes, its vision and values. Real-time strategic planning often involves presenting lists to board members or management for further discussion.
Like the organic model, real-time strategic planning is a continuous process and works best for rapidly changing organizations that might not have the need for set, detailed, or traditional strategic planning.
Inspirational Model
Like the name implies, the inspirational model can be energizing to participants, but also have less of a strategic impact on an organization than other, more formal models.
The process works by gathering people to talk about a highly inspirational vision for the company. Leaders encourage participants to brainstorm exciting and far-reaching goals, then capture the details using powerful and poignant wording.
The inspirational model works well for organizations looking to lift the spirits of a staff or to quickly produce a plan.
Strategic Planning Frameworks
Like models, strategic planning frameworks help an organization through the strategic planning process. Most frameworks cover the basics of strategic planning (mission, vision, goals), but include additional sections and have more specific focus areas.
Balanced Scorecard Framework
One of the more popular strategic planning frameworks is the balanced scorecard. It functions as both a strategic planning and management system, and it helps connect a company’s plan to the operational elements that make it happen. The balanced scorecard takes more than financial profits into account when measuring success.
Companies use the balanced scorecard to do the following:
Align the daily work to the longer-term strategy.
Communicate where they are doing and why.
Set priorities.
Monitor progress and measure success.
When Drs. Robert Kaplan and David Norton created the balanced scorecard in the 1990s, it changed the way many companies do their strategic planning because it focused on more than one performance metric.
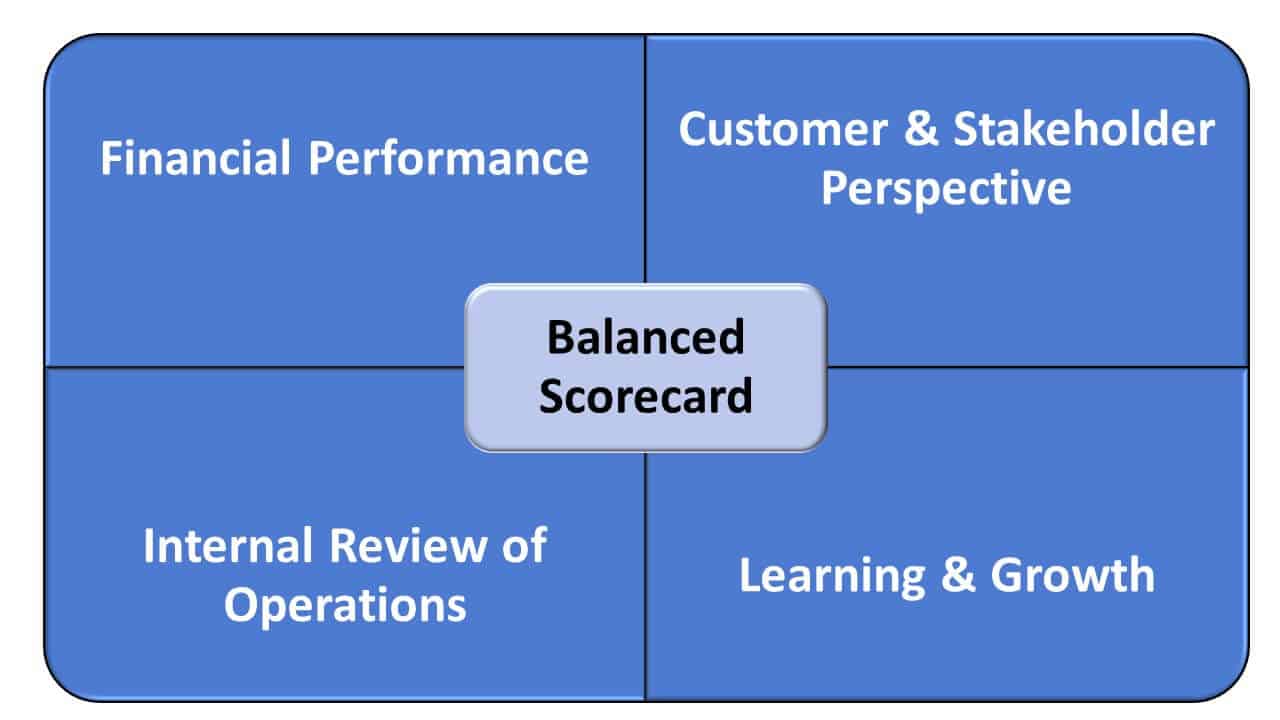
Companies that use the balanced scorecard try to look at themselves using four unique perspectives to get a better understanding of their planning:
Financial performance
Stakeholders and customers the company is serving
An internal review of how the company is operating
Learning and growth (including capacity, infrastructure, technology, and culture)
The key to the balanced scorecard is that a business should be a balance of the four quadrants.
Cascade’s Wright says the balanced scorecard works well for medium and large companies that don’t change very quickly or don’t need to make radical changes.
To learn more about the balanced scorecard and find free templates and examples, read this article .
Strategy Mapping
Strategy mapping can help an organization reach its goals by providing a visual tool to communicate a strategic plan. Strategy mapping is often part of (but is not exclusive to) the balanced scorecard framework.
Because the graphic is visual and simple, it is an easy way to show how one objective impacts others.
Strategy mapping helps you identify key goals and unify those goals into strategies. People can refer back to it in order to stick to the overall plan when working on tasks or making decisions.
The map shows how different items interact with each other in various ways, including a cause-and-effect relationship.
Strategy maps are often set up in the following manner:
List the four perspectives (financial, customer, process and learning, and growth) horizontally.
Place objectives within those perspectives.
Write sets of linked objectives across different perspectives (these are called strategic themes ).
Show cause-and-effect impacts between objectives and across perspectives.
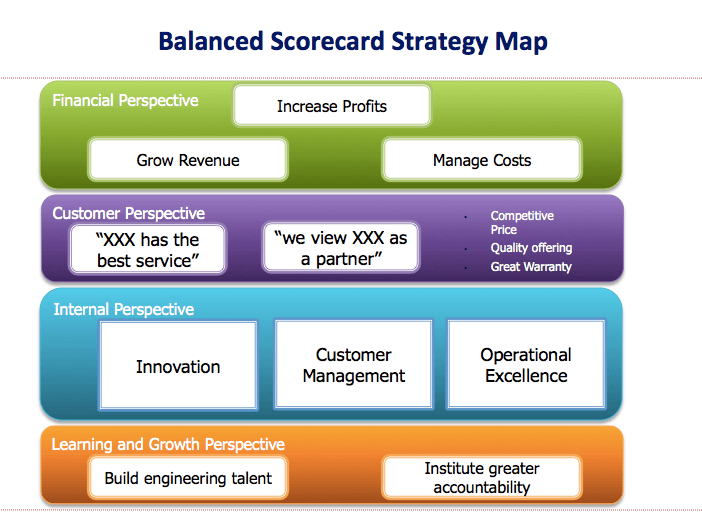
Image credit: Clearpoint Strategy
Use this template to help you organize your thoughts visually. By thinking of how different perspectives relate to each other, you can come up with your objectives.
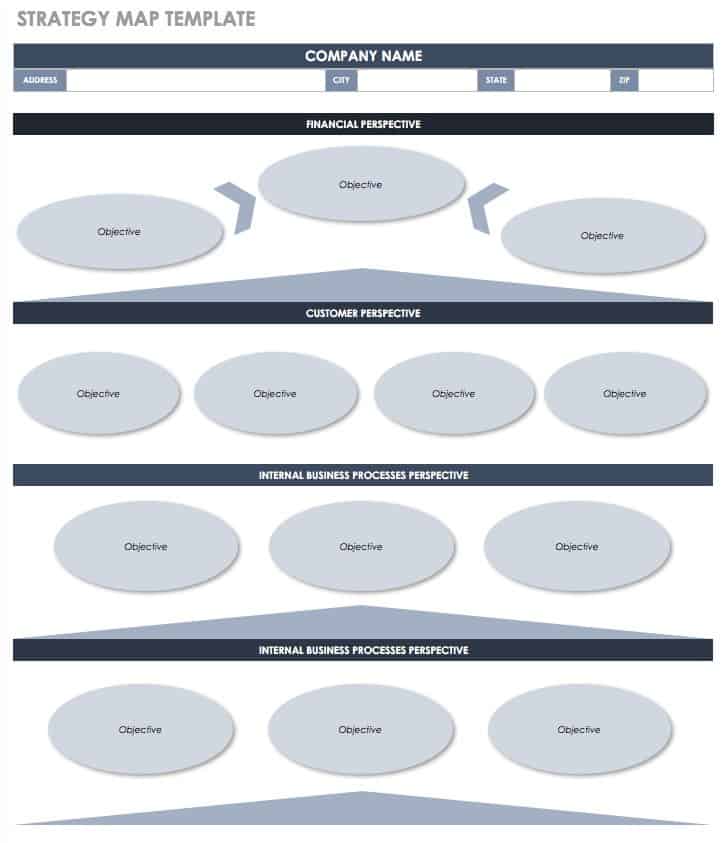
Download Strategy Map Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces approach helps companies assess the competitiveness of the market. Introduced in 1979, it is one of the oldest strategic planning frameworks.
This approach focuses on the five forces that can impact the profitability of an organization:
The Threat of Entry: Can new companies enter the market?
The Threat of Other Substitute Products or Services: Is there a competitor on the market that your customers could use instead of your product or service?
Customers’ Bargaining Power: Can customers pressure you to react to their demands?
Suppliers’ Bargaining Power: Can suppliers apply pressure to your company?
Competitive Rivalry Among Companies: If a rival company changes its strategy, will it impact yours?
The key is to look at the amount of pressure each force applies to a company in order to determine that company’s future.
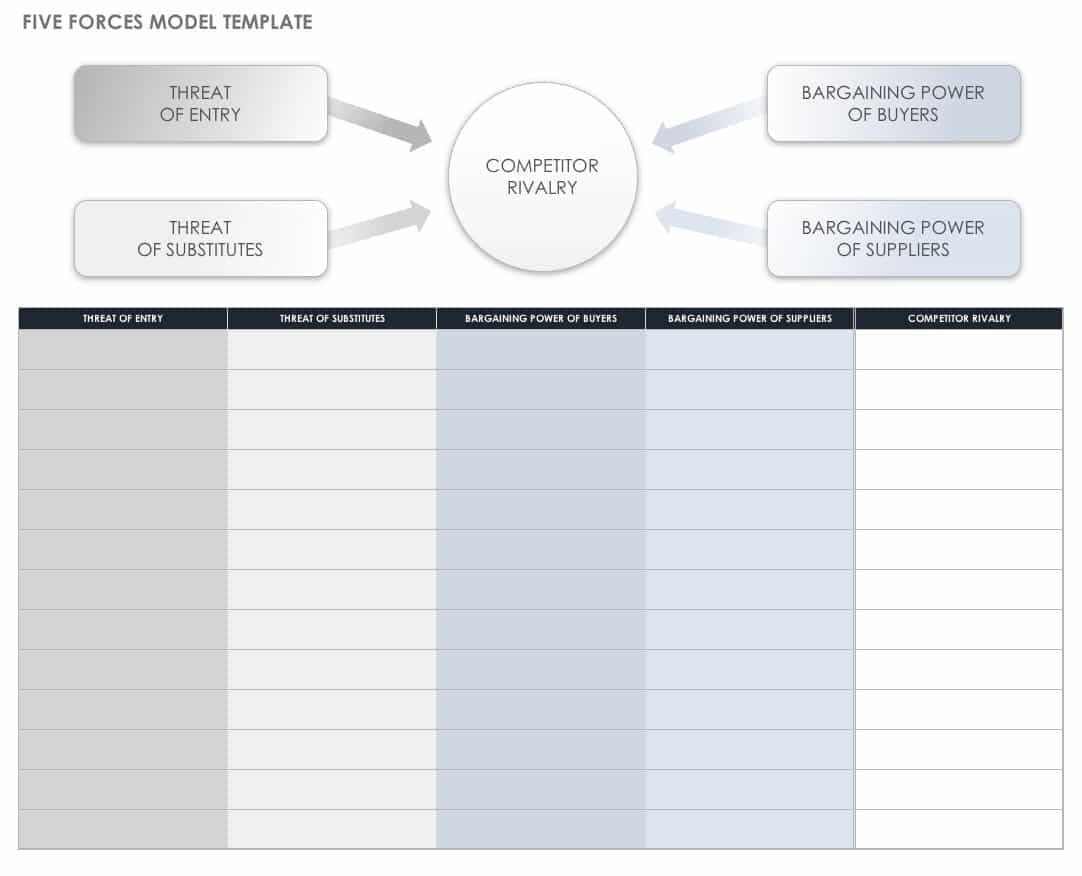
Download Five Forces Model Template
Excel | PDF
SWOT Analysis
Most strategic planning processes include a SWOT analysis. Many companies perform a SWOT analysis at the beginning of the strategic planning process, as it offers them a look at what they are doing well and where they can improve.
A SWOT analysis examines the following:
Strengths: What the business does well to achieve its objectives
Weaknesses: What activities could keep a business from achieving its objectives
Opportunities: The external factors that could help achieve its objectives
Threats: Possible external factors that could keep the company from achieving its objectives
Strengths and weaknesses are internal characteristics, while opportunities and threats are external.
You've seen how the four quadrants of a SWOT analysis work. Use this template to write down each factor, so you can view your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
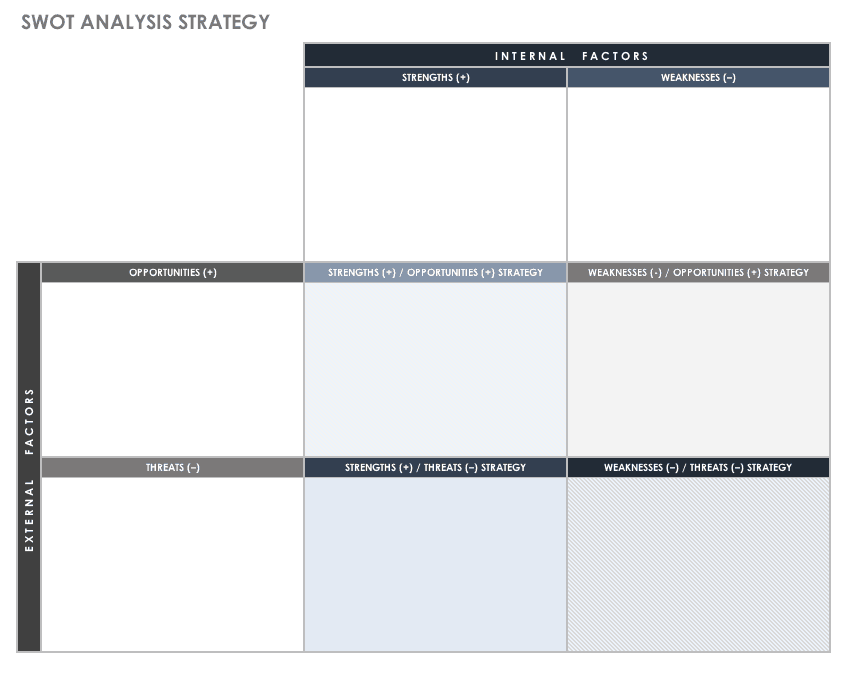
Download SWOT Analysis Strategy
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
PEST/PESTEL Planning
PEST stands for political, economic, sociocultural, and technological factors. There are several variations based on the idea, including PESTEL or PESTLE (when you also consider environmental and legal factors) or STEEPLED, where you consider sociocultural, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, education, and demographic information.
These frameworks look at an industry or business environment and see what factors could impact an organization’s overall health and well-being. These do not stand alone and often go along with a SWOT analysis and other frameworks.
Below are some possible examples of these factors:
Political: Changes in tax laws, trading relationships, grant changes
Economic: Interest rate changes, inflation, consumer demand
Social: Changing lifestyle trends, demographic shifts
Technological: Competing technologies, productivity changes
Legal: Changes in regulations, employment laws
Environmental: Changes in customer expectations or regulations
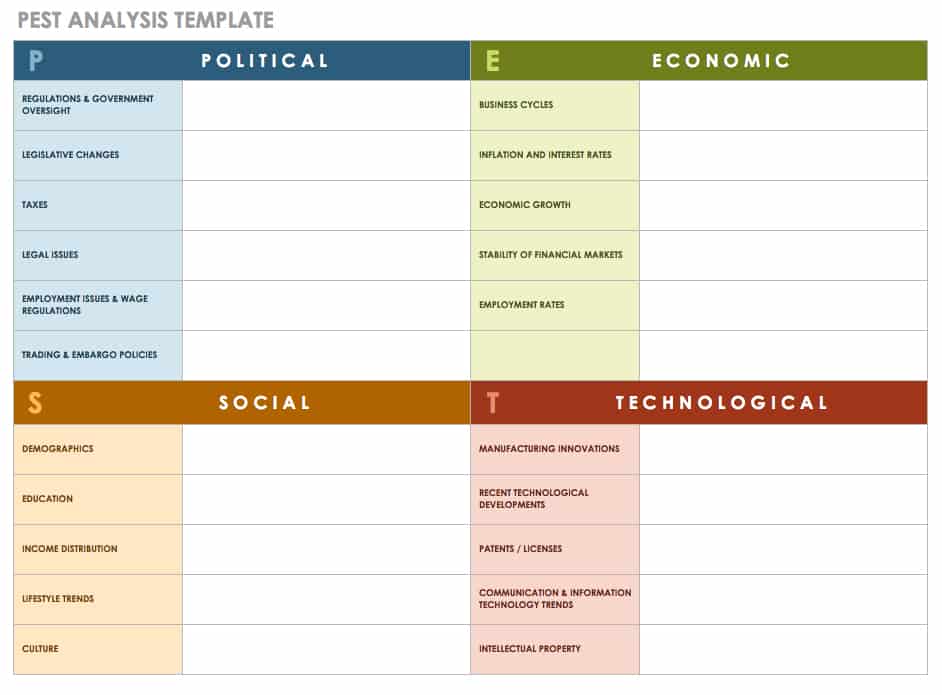
Download PEST Analysis Template
Gap Planning
Gap planning allows you to compare an organization’s current position to its goal, then identify ways to bridge that gap. Gap planning can also help you identify internal deficiencies. Gap planning is sometimes known as gap analysis, needs assessment, or a strategic planning gap.
For a more detailed look at gap planning, read this article .
Blue Ocean Strategy
Created by professors W. Chan Kim and Renee Mauborgne in 2005, the blue ocean strategy is a relatively new planning framework. The idea of a blue ocean is to create an uncontested market space for your company. By contrast, a red ocean is a market space that is already developed and saturated.
A blue ocean is the unknown. A company creates demand for a product or service instead of fighting over it, so there is plenty of opportunity for everyone. The idea is to pursue differentiation, thereby creating market share instead of trying to beat competitors.
A red ocean is the known market space. Industries in that space define and accept the boundaries that exist, and they play by the rules. The only way to get ahead is to outperform rivals to claim a bigger share of the market. The competition can be bloody, which leads to the term red ocean .
An example of an organization that found a blue ocean is Cirque du Soleil. Instead of operating as a typical circus, it found and expanded on a niche. The key to the blue ocean strategy is to make the competition irrelevant because you are doing something the others are not.
VRIO Framework
VRIO (value, rarity, imitability, and organization) is a framework that deals primarily with the vision statement, rather than the entire strategy for a company. By answering four main questions, an organization should be able to create a vision statement to take it through the rest of the planning process. This results in a competitive advantage in your marketplace.
Below are the four main questions:
Value: Using a particular resource, can you exploit an opportunity or get rid of a threat?
Rarity: Is there a lot of competition in your market, or do a few entities control most of the market?
Imitability: Can anyone else do what you do?
Organization: Are you organized enough as a company to adequately exploit your product or service?
Companies can use the VRIO framework to evaluate its resources and capabilities as part of the overall strategic planning process. VRIO comes into play after a company creates a vision statement, but before the rest of the planning process. The advantages you identify help determine what you need to do in order to achieve them.
McKinsey’s Strategic Horizons
McKinsey’s Strategic Horizons framework focuses on growth and innovation by categorizing goals into three categories: the core business, emerging opportunities, and new business.
Image credit: CASCADE
“McKinsey’s is one of my favorites because it applies to businesses small to large and generates excitement,” says Wright. He adds that it is an easy model because it does not involve much jargon and focuses on the future.
The first horizon deals mostly with core activities in which a company is already engaged. Existing revenue is placed here, so goals mostly deal with improving margins and processes, as well as maintaining incoming cash flow. The second horizon involves taking what is already happening and expanding it into new areas. The third horizon involves new directions, possibly including research and new programs. Wright recommends a 70/20/10 split between the three horizons.
Fast-growing and startup organizations might find McKinsey’s framework helpful.
The Ansoff Matrix
Sometimes called the product-market matrix , the Ansoff matrix looks at market penetration and potential future growth. It helps companies that want to try to grow sales volumes or have it as a major focus area.
In this matrix, market development concerns selling more of an existing product or service to a new group of people. Market penetration focuses on selling even more of a current product or service to the same people. Product development focuses on developing new products for current customers. Diversification is all about new products and services and new markets; this carries the most risk, but potentially offers large gains.
Wright says this framework helps companies think deeply about how they will achieve growth instead of merely saying they want to grow.
The Bryson Model or Strategy Change Cycle
John M. Bryson, McKnight Presidential Professor of Planning and Public Affairs at the Hubert H. Humphrey School of Public Affairs, University of Minnesota and author of Strategic Planning for Public and Nonprofit Organizations: A Guide to Strengthening and Sustaining Organizational Achievement , created the Bryson model. Some people, himself included, call it the Strategy Change Cycle.

“It’s a framework, not a recipe. It’s a reference point, the logic does not go step by step from one to 10,” Bryson says. “You start with purposes in mind and then figure out how to get there.”
There are 10 standard steps in the cycle, but Bryson stresses they are not sequential and often happen simultaneously.
Initiate and agree on a strategic planning process
Identify organizational mandates
Clarify organizational mission and values
Assess the external and internal environment to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT)
Identify the issues facing the organization
Formulate strategies to manage the issues
Review and adopt the strategies or strategic plan
Establish an effective organizational vision
Develop an effective implementation process
Reassess the strategies and the strategic planning process
Using this cycle, changes to the norm often happen. “You might think you know what your mission and goals are, and after you go through the process, you might need to change your mission and goals,” Bryson explains. “We try to let the mission and goals emerge from the conversations rather than starting there.”
Other Planning Models and Frameworks
In addition to the models and frameworks listed above, there are several other types, including the following:
The Stakeholder Theory: This approach focuses on adding value to specific groups of people, including employees, customers, the community, shareholders, and society. Organizations can add groups as necessary since the model is very flexible.
Kaufman Model: Also called mega planning, the Kaufman Model relies on a needs assessment. This model focuses on the impact an organization can have on society and clients.
Global Model: As the name implies, global strategic planning includes what is necessary to compete in an international marketplace. It involves looking at both the internal and external environments of multinational organizations.
Maturity Model: The maturity model assesses how strategic management is working within an organization and how it stands up to other organizations.
Diamond-E Framework: The Diamond-E framework helps identify possible gaps in an organization to decide whether or not to pursue an opportunity.
Value Migration: This model helps companies plan ahead of the competition. Its creator, Adrian Slywotzky, defines value migration as the shifting of forces that create value, and that shift goes from an outdated business model to a better-designed model that satisfies customers.
Value Disciplines: This flexible framework focuses on what an organization is already good at and builds on it. Three areas of focus are operational excellence, customer intimacy, and product leadership.
Agile Strategic Planning Model: The flexibility of Agile planning allows for growth and change in strategic planning. The cornerstone of Agile is being able to respond quickly to change, which seems like the antithesis of strategic planning. The Agile approach to strategic planning involves reviewing and adapting your strategic plan at regular intervals and whenever conditions warrant it.
General Electric Model: Also known as the McKinsey Matrix, this model looks at the industry externally versus the internal forces. Since it helps to identify the attractiveness of an industry and a firm’s strengths, the grid can help evaluate market share and identify areas for development.
How to Decide Which Strategic Planning Model or Framework to Use
Though strategic planning has changed over the years, the need remains for organizations to have some kind of vision and mission, as well as an outline about how to achieve them.
There is no right or wrong way to decide which model or framework to use for your strategic planning process. The key is to figure out which one best applies to your company and its needs — for example, VRIO can help you create a vision statement, and BSC can help keep plans on track. Additionally, some methods work well together.
“The perfect plan is the one that actually gets done,” says Wright. “A poor plan well executed is worth more than a great plan that never gets off the ground. Most people know what they need to do; it’s getting the traction and about democratizing the process. Constantly, people undervalue the role of buy-in with strategic planning. People need to be involved.”

“The framework you choose would have to deal with the sophistication of your business,” says Ted Jackson, founder and managing partner of ClearPoint Strategy . He recommends adapting a model or framework to meet your needs, rather than attempting to stick to hard and fast rules that might come from a book or a similar source. “I think if you read a book and try to implement it exactly [as the book outlines it] to your organization, you will fail,” he says.
Jackson advises simplifying some frameworks and adapting them, but he has some cautionary advice about trying to combine parts of different frameworks. “One mistake is not picking one framework. You can’t be so flexible that you’re implementing multiple frameworks together. People within an organization get really confused,” Jackson says, adding that people who have some knowledge of specific models or frameworks will not understand different terms and ideas, and they’ll probably be afraid to ask.
Some organizations might not get to choose the framework they use. For example, governmental organizations or companies that receive grant funding might need to produce a strategic plan that fits into a formula the government dictates.
Even though you should not use a strategic plan solely because a similar company does, it might help to look at their preferred framework to pick the one that is right for you.
Below are other criteria to help you decide:
Check the size of your organization and the resources you can devote to planning.
If your organization is in trouble, you might want to focus on a framework or model that addresses immediate issues rather than tackles the longer term.
Look at the health of your organization and its developmental stage.
See who is excited about the planning process.
“If you have a cultural challenge in your organization about getting excited about planning, the model you pick is important. Some models are sexier than others,” Wright explains.
Wright does not recommend changing models during the planning process. “[The model] is a template you use to get your ideas on paper. The model is just a vehicle. If you’re struggling with the model, it might be you.”
It isn’t the same for frameworks, according to Wright. “There is a ton of value in changing frameworks and using multiple frameworks at the same time [to view things differently],” he says. Though Wright encourages using different frameworks, he echoes Jackson’s warning to not use different models at the same time.
In certain cases, strategic planning is not an immediate need — for instance, when a company is failing financially or is autocratic, or when a major upheaval is occurring.
Strategic Planning for Specific Areas
Strategic planning for specific departments is a bit different than planning for a company as a whole. In this section, we’ll explain the basics of how some departments typically approach strategic planning.
IT Strategic Planning
A strategic plan for the IT department details how technology will help a company succeed in reaching its goals and objectives. You can think of it as a technology roadmap that outlines where IT can do its part to implement a company’s strategies.
The IT plan must align with the company’s overall mission and vision statements, but it has a secondary mission statement that states how the IT strategy relates to the overall plans for the organization.
The IT plan should also include a SWOT analysis, goals, and objectives. The plan will help make sure you purchase the right assets and work with existing technology effectively. Use the template below to draft a strong, comprehensive IT strategic plan.

Download IT Strategic Planning Template - Excel
Strategic Human Capital Planning
Strategic human capital planning refers to when a company looks at how people — and how to manage them — go along with the organization’s strategic goals. The end result is a plan to help attract and maintain the talent necessary to achieve the company’s mission and vision.
You can use the following HR strategic plan to list, assess, and plan for future program strategies.
Download HR Strategic Planning Template - Excel
Succession Planning
At its core, succession planning relies on developing and identifying new leaders. Because employees move on or retire, a company needs to have a plan in place to assume new and important roles.
Often, succession planning happens as a part of the overarching strategic planning process — for example, when you look at the resources available to a company and their productivity.
Note that available human resources can be both strengths and weaknesses. The planning process can help companies identify specific hiring needs.
For more about human resources management, this article can help. Additionally, you can find templates for succession planning here .
Healthcare Strategic Planning
The world of healthcare is changing, and healthcare organizations have to adapt. Still, the following general ideas persist:
There will be a continued need to provide quality patient care.
Operating costs and government regulations will impact the bottom line.
The volume and demographics of patients will change.
There will be a change in the labor supply, especially in the number of primary care physicians available.
Wellness and prevention will gain importance.
New technologies will continue to emerge.
Even with the ever-changing healthcare industry, strategic plans will continue to help organizations stay focused on their goals and objectives. By having a structured planning process, rather than following models that are more organic and reactionary, healthcare entities can survive and succeed.
But be careful with metrics that only consider financial success — there is much more to healthcare than profit.
Improve Strategic Planning with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

Strategic Planning Models: The 5 Best Strategy Models

New business models, global disruptions, and a need for rapid changes inspired various approaches to strategic planning, also known as strategic planning models.
What all planning models have in common is that they help you translate strategies into action and aim to provide you with structure in the process of creating a strategic plan. But there are now countless frameworks, each with its own approach.
We summarized the 5 most popular strategic planning models in one place so you can start building your own strategic plan in no time.
To get there, let’s explore:
- What is a Strategic Planning Model?
- Planning or strategy: Where to start?
The Cascade Model
The hoshin kanri model, balanced scorecard, strategic planning process model vs strategic frameworks.
- Strategy Model: Which One Is Right For You?

What is a Strategic Planning Model?
A strategic planning model is a collective term for several elements contributing to the strategic planning process . The core components of a strategic planning model include:
- A templated structure for creating strategic goals.
- A loose structure of governance to help you manage and track your strategy.
You can think of strategic planning models as “templates” into which you can drop your own ideas. In the end, you'll come out with a strategic plan which is sensibly structured and gives you a clear strategic roadmap to hit your business goals.
Now that we've defined what a strategic planning model actually is, let's look a bit deeper into each element that one should contain.
2 essential elements of any effective strategic planning model
- Structure refers to the different elements of your strategic plan and how they all fit together. For example, your structure may start with a Vision and Mission Statement, then flow into Values, Focus Areas, and any number of Goal levels.
- Governance refers to how you'll go about actually tracking and reporting on the execution of your strategy.
Planning or strategy: Where to start?
Before we move into the planning section of this article, let’s clarify a common confusion around strategy and strategic planning. What’s the difference and what comes first?
First, do not mistake strategy for a plan. In short, strategy is the act of making strategic choices, while a plan is a roadmap with timelines, owners, and deliverables.
Before laying out your plan, you should get a better understanding of your internal and external business environment so you can make strategic choices and prioritize initiatives.
“ The heart of the strategy is the matched pair of Where-to-Play and How-to-Win. ” - Roger Martin , Bestselling Author and Strategy Advisor
You should always start with strategic analysis. Through this process, you will be able to identify competitive advantage, assess organizational capacity, analyze external factors that might impact your strategy, and find other opportunities you could exploit.
Feel free to use multiple strategic analysis tools since each has its own purpose.
📚Here’s a list of the most popular strategic tools and frameworks that can help you brainstorm your strategy:
- VRIO Framework
- SWOT Analysis
- PESTLE Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Ansoff Matrix
- McKinsey 7S Model
- Blue Ocean Strategy
Once you have a clear picture of where you want your organization to be in the short-term and long-term future (and where you do NOT want it to be), you can start building a strategic plan that will take you to your destination. And this is where strategic planning models come into play.
Note: Every organization is unique and has different stakeholder needs. Thus, every strategic plan is unique. The goal here is to give you perspective on how you can approach your planning before you dive into the details.
Below, you’ll find examples of strategic planning models that include both Structure & Governance since both are critical to implementing your strategic plan. Because, what's the point in having an awesome strategy on paper if you have no effective way to actually execute it?
The Cascade model is hands-down the most effective example of a strategic planning model that you can find.
It is simple to understand and easy to implement, facilitating the execution of your strategy. Its straightforward structure is suitable for organizations and teams of any size and industry.
Here's a snippet of the structure:

Let's dive into the key elements of the Cascade Strategic Planning Model, its structure and governance.
The structural elements of the Cascade strategic model:
- Identify your vision statement . This statement(s) describes why the organization exists, i.e., its basic purpose.
- Define your company’s values . Describe how you want your organization to behave as it strives towards its Vision.
- Craft your focus areas . They articulate the key areas on which you'll be focusing your efforts to help deliver your Vision.
- Create your objectives . Your strategic objectives define more specifically the outcomes you want to achieve under each of your Focus Areas.
- Define your KPIs . Each of your Objectives should contain at least one or two KPIs to help you measure whether or not you're close to reaching your desired outcomes (Objectives).
- Create your projects . These are one of the most critical elements in your strategic planning model, as they state exactly what actions you will take to deliver against your Objectives.
The governance elements of the Cascade strategic model:
- Monthly Strategic Reports . Team members can create reports at the objective, team, individual, KPI, and action levels. Using Cascade, users can add text, charts, and tables to their reports to provide more context for the reader.
- Project Updates. These are ad hoc updates made against the Project level of the plan and include general project management updates and progress.
- KPI Dashboards. In addition to providing real-time data, they allow users to look back and understand what happened over time using data sources that are available. Live dashboards are essential for identifying deviations from KPI tolerance levels, explaining the difference, and setting an action plan to resolve the issue.
-1.png)
When you combine the goal and the governance elements of this strategic planning model, you get a comprehensive set of tools that you can use not just for creating your plan but also for executing it.
📚 Recommened reading:
- How To Write A Strategic Plan + Example
- 18 Free Strategic Plan Templates (Excel & Cascade) 2023
The Hoshin Kanri model is a strategic planning model that organizations use to drive a consistent focus throughout many levels of their structure.
This makes it ideal for large organizations with different layers of management, including “top-level” executive management, “middle managers,” and “front-line” staff.
Much of the work we did to create the Cascade Strategic Model was inspired by Hoshin Kanri.
So it's certainly a strategic planning model that we respect and admire here at Cascade. Let's dive into the detail of the Hoshin strategic planning model with a quick visual:
.jpeg)
The structural elements of the Hoshin Kanri strategic model:
- The first level of the Hoshin Kanri strategic planning model refers to your vision . A distant horizon that will guide everything that sits beneath.
- Then you move on to your 3-5 Year Strategies . These are high-level summaries of what you want to achieve (qualitatively and quantitatively).
- Beneath that, you define Annual Objectives , which will be split between different departments.
- Finally, you determine your Action Items . They are specific things you are going to do to reach your Annual Objectives.
The governance elements of the Hoshin Kanri strategic model:
- Monthly Reviews . These are done against the Annual Objectives and require the goals' owners to provide descriptive progress updates.
- Annual Reviews . These are also done against the Annual Objectives. However, they happen at the end of the time period and encompass a decision point on whether to mark the Annual Objective as complete or roll it over into another year.
There are many different ways to implement the Hoshin Kanri strategic planning model. Above is a simplified explanation that covers most of the core elements.
- Hoshin Kanri: Close Strategy Execution Gap In 7 Steps
OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)
The OKR model is a goal-setting and planning framework that focuses on quarterly sets of OKRs and is reviewed by every management level in the organization.
The basic structure of the OKR strategic planning model looks something like this:
.jpeg)
As with the Cascade Strategic Planning Model and Hoshin Kanri, the OKR strategy model has the following key elements.
The structural elements of the OKRs strategic model:
- Objectives. These describe the outcome you are looking for in the current quarter.
- Key Results. These are specific metrics that describe your progress toward your Objective in numerical terms.
- Initiatives. These are tasks or projects that sit against each of your Key Results. Once completed, they should help you reach your Key Results.
The governance elements of the OKRs strategic model:
- Weekly Check-Ins. Each Key Result should have a weekly check-in that covers your confidence level in achieving that OKR, action plan, and general progress updates.
- Quarterly Review. For each Objective, a formal quarterly review should be undertaken where that OKR is given a “score” (usually from 0 to 1) and a decision is made on what to do with that OKR in the next quarter.
- OKRs: How To Avoid The Trap That Kills Performance
- The OKR Framework: How To Implement It & Mistakes To Avoid
- Using Cascade as your OKR Software
Balanced scorecard (also known as BSC) helps organizations drive and assess business performance by organizing key performance indicators (KPIs) into four focus areas: Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning & Growth.
Here is an example of a basic Balanced Scorecard structure:

The structural elements of the Balanced Scorecard:
- Four perspectives that act as your focus areas.
- Strategic objectives where you define your desired outcomes.
- Projects that outline specific initiatives, timelines, and resources.
- KPIs that measure progress and success.
The governance elements of Balanced Scorecard:
- Strategy dashboards where you should see the real-time status of each perspective and a summary of your key objectives, projects, and KPIs.
- Weekly or Monthly reports where each owner provides progress updates and short-term action plans.
- The strategy map shows how are four perspectives layered and cause-and-effect connections between strategic objectives.
📚Recommended reading:
How To Implement The Balanced Scorecard Framework (With Examples)
- Balanced Scorecard Template (Free)
V2MOM is one of the most simple strategic planning and alignment models out there. Developed by Salesforce's cofounder, Marc Benioff, it helps you implement and drive alignment across your organization.
The model can be used in a variety of organizations, including small businesses, startups, and nonprofits.
As a top-down approach, V2MOM scales across your organization at all levels, including the business unit, department, team, or individual. However, this model won't work if your organization is siloed, as each V2MOM document should be aligned with the top-level V2MOM plan.
An example of a basic V2MOM structure would look like this:

The structural elements of the V2MOM:
- Vision. Like with the Cascade Model, this is where you define your vision of the future.
- Values. A set of values that drive your company’s culture.
- Methods . Strategic objectives, projects, or other strategic initiatives that will help your organization get one step closer to its vision.
- Obstacles. Compared to other models, this is a unique element. It should identify all possible obstacles and risks that can prevent you execute the plan.
- Measures. A set of KPIs that will measure your performance and progress.
The governance elements of V2MOM:
The original V2MOM approach only outlines the structure, but it does not offer a solution to track and measure performance. To meet the needs of our clients, we leveled up V2MOM to help teams measure their performance against set goals in a strategy execution platform :
- Customizable strategy dashboards where leadership teams and team members can get insight into what’s happening across the organization or with specific initiatives.
- Reports that analyze in-depth raw data of the past, and turns it into actionable narratives for regular review meetings and faster decision-making.
📚 Recommended reading:
- The V2MOM: Overview, How To Use It, Examples (2022)
It's important to distinguish between strategy frameworks and strategic planning models before you jump into the strategic planning process. Online resources use these terms interchangeably, but they are in fact quite different.
Strategic planning models provide a way to structure the information of your strategy and the content of your strategic plan.
Strategic frameworks , including analysis tools, provide the context that surrounds your strategic plan, and the information that helps you define your strategy.
There are a few different views on this subject, but here is what we think makes the most sense:
- A strategic framework is a general term that covers different types of frameworks, including strategic analysis frameworks, goal-based frameworks, and strategic planning frameworks (in this case, also called strategic planning models).
- A strategic planning model refers to the overall structure you apply to your strategic planning process. It roughly describes the various components and how they interact with one another. For example, imagine an architect building an airport.
A model of the airport would show you at a high level how the approach roads connect to the departure hall and how the departure hall connects to immigration, which then connects to the terminals, the runways, etc.
A strategic planning model functions much the same way in that it describes each of the elements of a coherent strategy: what they do, how they fit together, and in what order.
Strategy Model: Which One Is Right For You? 👀
The examples of strategic planning models we've picked have a lot in common. There's a good reason for it.
The best strategic planning models are simple, contain all the right elements, and combine goal setting with governance.
As a result, they serve you well when it comes to building a highly effective strategic management process and executing your strategy.
You can't really go wrong with any of the strategic planning model examples we've outlined above: Cascade Model, Balanced Scorecard, V2MOM, Hoshin Kanri, or OKRs.
In the Cascade strategy execution platform , you can import or create a strategic plan no matter the model you use since our strategic planning tool is sophisticated enough to customize it to your way of doing strategy.
Interested in seeing Cascade in action? Start building your strategic plan for free or book a demo with a Cascade expert.
What is the difference between strategic planning and strategic management?
The main difference between strategic planning and strategic management is that strategic planning is just a stage within the strategic management process.
What are the 5 models of strategic management?
There are more than five models of strategic management. A strategic management process involves multiple stages, including strategic analysis, strategy formulation, strategy execution, and strategy evaluation. There are multiple models and frameworks suitable for each stage of the strategic process.
Popular articles

Viva Goals Vs. Cascade: Goal Management Vs. Strategy Execution

What Is A Maturity Model? Overview, Examples + Free Assessment
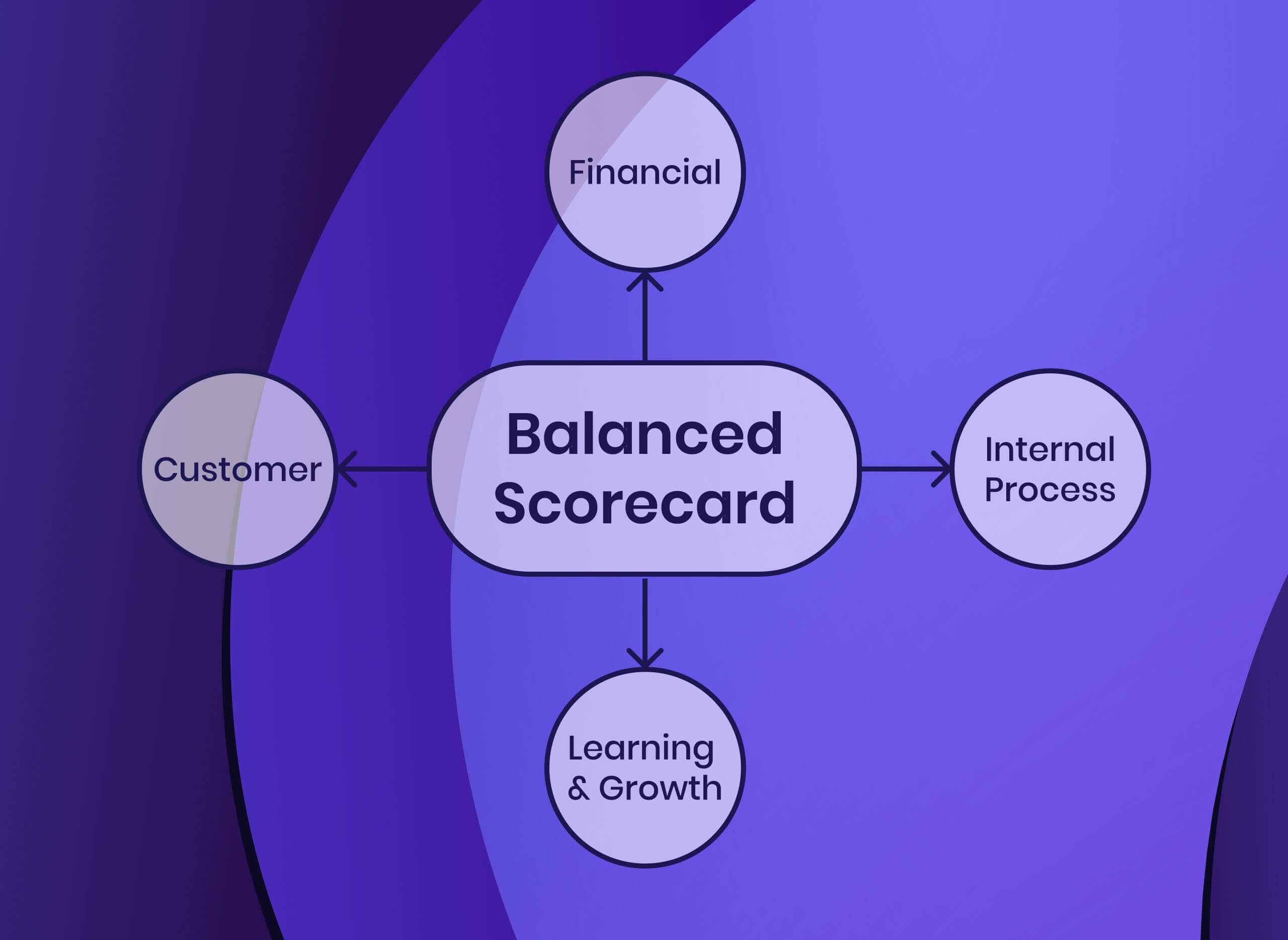
The Best Management Reporting Software For Strategy Officers (2024 Guide)
Your toolkit for strategy success.


Prefer a self-guided tour?
In just 5 minutes (no strings attached!), learn how market leaders use Leapsome to build high-performing teams, enable managers and retain their best talent.
9 effective strategic planning models for your business
Strategic planning models can make a big difference to your organization. That remains true whether you’re a startup developing an overall strategy or an established business fine-tuning internal processes.
But there are many strategic planning models, and it’s vital to pick one that suits your purpose and needs. The right framework will help you streamline processes, drive alignment, and propel your business.
To help your research process, we’ve compiled a list of the most effective strategic planning models and their top use cases. Let’s take a look.
🧐 Looking for a flexible framework to help you reach your business objectives? Leapsome’s goal management tools fit any strategic planning process. 👉 Learn more
What is a strategic planning model?
A strategic planning model is a framework that allows organizations to map out their short- and long-term business plans. They can help:
- Identify and overcome obstacles
- Improve and streamline operations
- Reach overarching business goals
- Create alignment between different departments
- Track progress over time
And you don’t have to limit your organization to one strategic planning model. Businesses can benefit from using multiple approaches, even simultaneously. But different strategic planning models are best suited for different situations, so make your choice based on your business type, growth stage, priorities, and goals.
9 models for strategic planning
These are some of the most popular strategic planning models. Our list covers a definition of each model, an example of it in action, and which use cases it works best for.
1. Objectives & key results (OKRs)
OKRs are a popular goal-setting framework that organizations, teams, and individuals use to define long-term objectives and track progress. To better understand the meaning of OKRs , let’s unpack the acronym:
- Objectives — ambitious but achievable long-term goals
- Key results — milestones used to measure progress toward each objective
When establishing your OKRs, create quarterly objectives for all company levels — Leapsome has a free OKR template to help you get started. Then, revisit your OKRs regularly to monitor your progress and make adjustments if necessary. You can also introduce regular OKR meetings to your organization’s internal processes.
OKR example
Here’s an example of an OKR for a B2B SaaS company:
Objective | Significantly scale our customer base and deliver our great product to more people
- Key results:
- Increase sales conversion rate from 25% to 30%
- Reduce user churn from 5% to 3%
- Publish a successful case study on our website every quarter
- Achieve a minimum of 4.7 out of 5 rating across all major review sites
OKRs work best for organizations that want to create more alignment behind their goals. By breaking down company-wide objectives into smaller, more manageable tasks, OKRs ensure everyone works toward a common purpose.
OKRs also show employees how their work contributes to the big picture, giving them a sense of purpose and boosting employee engagement . Research by Gallup links engaged employees to lower turnover rates, better work performance, and a thriving work culture. Consequently, OKRs help companies build successful workplaces.
.png)
💡 Wondering how to introduce OKRs to your organization? Use Leapsome’s flexible framework to set company-wide objectives and track them in one intuitive place. 👉 Learn more
2. SWOT analysis
SWOT stands for strengths , weaknesses , opportunities , and threats . Use the SWOT model to define internal and external factors affecting your business. Then, compare the different factors to assess the risk of a potential strategy.
For example, if your organization’s strengths match opportunities in the market — say, you have a lot of capital, and your competitors don’t — you know you have a competitive advantage. In that scenario, you can take an offensive business strategy with relatively low risk.
SWOT example
Here’s a SWOT example for a sales-based organization:
- Strengths — We have an excellent rapport with our customers and a loyal customer base.
- Weaknesses — Our current supply chain is inadequate.
- Opportunities — There’s high customer demand for one of our products.
- Threat — Our main competitor is developing a similar product.
Based on this SWOT analysis, our example organization isn’t in a strong strategic position. There’s a risk they won’t produce or distribute enough of their product to meet demand, and their competitor has the potential to outperform them. They should prioritize optimizing their product offering and solving supply chain issues over generating leads or working on an aggressive marketing campaign.
Any business can benefit from SWOT analysis. However, it’s best to use it at the beginning stages of a new strategy and with a specific goal in mind. You could try a SWOT approach when deciding priorities, like implementing new technology or restructuring your organization.
3. PEST or PESTLE analysis
PEST analysis focuses on external factors that can affect your organization. The letters stand for:
- Socio-cultural
- Technological
And depending on your industry, you might add legal and environmental factors to make PESTLE.
PEST or PESTLE example
Here’s an example of a PESTLE analysis for a multinational confectionery company:
- Political factors — The government of a country where we sell many products is planning to raise import tariffs.
- Economic factors — Our target demographic (13 to 21-year-olds) has more disposable income now that Covid-19 restrictions have been lifted.
- Socio-cultural factors — Surveys report that customers consider our products healthy.
- Technological factors — Engineers devised a more efficient way to farm the main ingredient in half our products.
- Legal factors — The FDA approved our latest chocolate bar.
- Environmental factors — NGOs are pressuring us to use more environmentally friendly processes.
PEST analysis lets you assess the business environment for a product or service, so it’s best used during the beginning stages of a project.
4. The Balanced Scorecard framework
The Balanced Scorecard framework lets you take a holistic approach to business planning that doesn’t just focus on economic performance. Instead, you look at four perspectives:
- Financial perspective — how well your organization is performing economically
- Customer perspective — your customer satisfaction and retention levels
- Internal business perspective — the quality and efficiency of your internal operations
- Innovation and learning perspective — your ability to improve, pivot, and grow your business
Then, create objectives and define measures to track your progress for each perspective. Those measures will support you in planning and executing initiatives to achieve your goals. And as you carry out this strategy, you can update your scorecard to show your progress.
Balanced Scorecard example
The management at ECI (Electronic Circuits Inc.) wanted to improve their delivery times. But when they talked to customers about the issue, the organization received unreliable feedback — different people had different definitions of being ‘on time.’
Using the Balanced Scorecard framework, managers shifted focus to their operations and checked the efficiency of their manufacturing process. They discovered ways to optimize the business’s cycle time, yield, and costs.
Despite not having a reliable customer perspective, the Balanced Scorecard’s comprehensive overview of the ECI organization provided a versatile solution for reducing delivery times and streamlining the business’s overall operations.
The Balanced Scorecard framework is best for understanding your business health and creating alignment across your company.
5. Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces is an approach that lets you assess your product or service’s competitive advantage in the market. Identifying potential threats can guide your organization in developing a more dynamic strategic plan.
The ‘Five Forces’ that may affect your product are:
- The threat of new competitors — Are many new businesses popping up in your industry? How easy is it for new companies to develop a product or service similar to yours?
- The number of existing competitors — How many direct competitors are you contending with? What about adjacent competitors? Are any of them growing quickly?
- The bargaining power of suppliers — Could suppliers put pressure on you to lower costs or change your business model?
- The bargaining power of customers — Are your products or services available elsewhere? Is there a demand for them? Do people have issues with your pricing or quality?
- The threat of a substitute — How likely is a similar product or service to enter the market?
Porter’s Five Forces example
Let’s take the example of a cosmetics company planning to release a shampoo with SPF 50:
- The threat of new competitors — The shampoo requires expertise to develop, which is an obstacle for competitors entering the market.
- The number of existing competitors — Two companies with similar products are poised to grow. They could create an almost identical product and pressure them to lower costs.
- The bargaining power of suppliers — There’s a large number of suppliers, so they have little bargaining power.
- The bargaining power of customers — Depending on where customers live, they’ll consider the shampoo a seasonal product. As it’s almost winter in the countries with the largest customer base, demand is lower.
- The threat of a substitute — Research suggests that no products currently in development could fill the same need (protecting the scalp from sunburn).
Porter’s Five Forces are best for evaluating your product or service after development but before entering the market. It’s also helpful for assessing an organization’s overall competitive position.
6. The VRIO framework
The VRIO framework helps organizations determine whether they can turn a resource into a competitive advantage. These can be physical resources like inventory, tools, and technology, or nonphysical ones like patents, skills, and work culture.
Let’s break down the VRIO acronym to understand how to evaluate each resource:
- Valuable — The resource increases revenue or decreases operational costs.
- Rare — The resource is limited or you control the supply.
- Inimitable — The resource is unique or complex, meaning it’s difficult for competitors to copy.
- Organizational — Your organization can exploit the full potential of the resource.
VRIO example
Here’s an example of a delivery company determining whether they can exploit their resource — distribution centers — to gain a competitive advantage:
- Valuable — All the distribution centers are in strategic positions, which makes them a valuable resource as the company can use their location to create more efficient delivery routes.
- Rare — The distribution network is a scarce resource because there are only a few ports for international delivery.
- Inimitable — Competitors could build distribution centers in nearby locations.
- Organizational — Delivery drivers aren’t using the most efficient routes between distribution centers.
The delivery company could have a temporary competitive advantage, but they’re not exploiting this resource. Management needs to address whatever stops delivery drivers from using the fastest route before rival delivery companies copy and control the same resource.

The VRIO framework works best for businesses deciding how to launch a new product or service or determining how to improve their existing business model.
Specifically, the organizational metric shows how efficiently your organization uses its resources. If you have a high score for the first three metrics but consistently fail to capture the value of your resources, it’s a sign you need to improve your internal processes.
Combine the VRIO framework with Porter’s Five Forces for a clear strategic direction when launching a new product.
7. The Hoshin Planning framework
The Hoshin Planning framework is mainly a top-down approach. This method outlines seven strategic planning stages, which are:
- Define your vision to clarify your organization’s primary purpose.
- Develop your main objectives to give your organization a competitive advantage.
- Break down objectives into smaller annual goals.
- Set goals across your entire organization — at C-level, managerial, departmental, and individual levels.
- Implement your plans.
- Perform monthly reviews to reflect and monitor progress.
- Do an annual review to determine if you’ve achieved your goals and what to work on next.
It’s worth noting that the Hoshin Planning framework doesn’t have to be strictly top-down. Another core idea behind this method is that managers should ‘play catch ball’ — that is, bounce ideas between management, department heads, and team members during the first four stages.

Hoshin Planning example
Here’s how a car manufacturer might implement the Hoshin Planning framework:
- Management shares their vision of developing the most innovative technology on the market.
- They decide their main goal is to develop the first self-driving car by the end of 2025. But when leadership talks to the head of engineering, they say this breakthrough won’t be possible by 2025. They collectively adjust the deadline to 2027.
- Management breaks this goal down into smaller targets. One of them is mapping out what the self-driving car should be able to do in every scenario. The engineering department agrees with this plan.
- Those targets inform detailed initiatives, like observing real-life driving incidents and collecting data on traffic and accidents.
- All parties carry out the agreed-upon initiatives. After a month, management conducts a meeting to check everyone’s progress.
- A year later, the engineering department has data on most scenarios the self-driving car would encounter on the road.
Companies with complex processes — like manufacturing and tech businesses — are more likely to use the Hoshin Planning framework. Their operations benefit from the ‘catch ball’ idea because it’s easier to spot problems when you filter them through diverse teams.
The Hoshin Planning Framework is also ideal for creating alignment within your company. Consider it for a larger organization that’s experienced project issues and bottlenecks.
8. The Theory of Change model
The Theory of Change model involves establishing long-term goals and working backward. Start with your desired outcome and go through all preconditions necessary for it to become a reality. During this process, you determine what needs to change to reach your objectives.
Theory of Change example
Nonprofit organizations with specific missions often use the Theory of Change model. Take adult literacy, for example. The project team would start with an ideal situation — like their country having a 100% literacy rate — and work backward to find out what’s preventing them from achieving that aim. The issues might range from a lack of funding to a need to increase awareness about resources that are already available. Then, the nonprofit team could start addressing the issues they identified.
Any organization can benefit from the Theory of Change framework. Still, it works best for specific projects, like expanding your company abroad or opening a new department, as it involves scenario planning.
9. The Blue Ocean strategy
The Blue Ocean strategy is a strategic planning model that’s become popular recently. Developed in 2004, this method assesses whether your organization operates in a saturated market. If so, the underlying assumption of the Blue Ocean strategy is that it’s better to create new demand.
In the strategy, the ‘ocean’ is a metaphor for the market. The ‘red ocean’ is full of predators (large companies) competing for food (customers) and turning the water red, whereas the ‘blue ocean’ is deep, unexplored water that’s full of potential (uncontested market space). Here’s a list of indicators that you’re in a ‘blue ocean’:
- You’ve found uncontested market space
- You’ve made the competition irrelevant
- You’re creating and capturing new demand
- You’re breaking the value-cost trade-off
Blue Ocean example
Apple is a famous example of a business that operates in a ‘blue ocean.’ Although it’s one of the leading technology companies in the world, the Apple team still prefers to innovate new products rather than beat the competition.
The Blue Ocean strategy is ideal for small businesses and start-ups trying to establish themselves among larger organizations. Established companies in dynamic industries like tech can also use it to stay ahead of their competition.
How to implement a strategic planning model
Once you’ve set up your strategic plan, you’ll want to utilize it to its full potential. Here are some tips to make sure your strategy goes into action.
Align your approach to strategic planning with your values
There are many strategic planning models to choose from, and your organization can only implement so many. Although all of them have pros and cons, none are necessarily better than the others. So, choose the strategic planning models that reflect your organization’s values. That way, it’ll be easier to introduce your strategy and get all team members on board.
If you’re a people-first organization, OKRs are an ideal choice. OKRs involve your employees in company initiatives, make internal decisions more transparent, and give everyone a sense of purpose.
Allocate resources to the strategic planning process
Strategic planning is like any other task: It requires resources like funding, time, and research. You should have a budget and schedule for every part of the process.
The employees helping you with strategic planning and implementation are also vital assets — offer them training and consistent support. Free up their schedule for strategic planning and create a timeline for the entire process to set your team up for success.

Review your progress
Aside from planning and implementing your strategy, you’ll need to check on your progress regularly. That means monthly and annual reviews at all levels.
Many strategic planning models already have reviews built into their stages. But even if they don’t, you should reevaluate at regular intervals. You can define some key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of your initiatives and your overall business health. Popular KPIs include revenue growth, client retention rate, and employee satisfaction.
Be ready to adjust your strategic plan
As the saying goes, even the best-laid plans often go awry. You may find that conditions change as you implement your strategic plan or that you didn’t predict certain issues. The key isn’t necessarily to strategize better, but to have a dynamic strategy. This will allow you to adjust your plan and deal with problems as they arise.
For instance, you might opt for the PEST analysis, but be open to considering important legal and environmental factors when they come up. You can try to predict what new legislation or world events may affect your industry. Then, if any conditions arise that affect your business, you’ll be able to pivot your strategy without too much additional effort.
Boost your organization’s performance with strategic planning models
Strategic planning models help you assess the current state of your organization, decide which direction to take in the future, and communicate your plans to your employees. They can be the difference between your business merely sustaining itself and thriving.
If you’re wondering how to implement a new strategic planning model, Leapsome can offer professional support. Our Goals and OKR Management Software provides an adaptable framework for your chosen strategic model.
🚀 Kickstart your strategic plan with Leapsome Our goals and OKR management tools make it easy to implement your strategy of choice. 👉 Book a demo
Leapsome Team
.png)
Related Articles

OKRs vs. SMART goals | Comparison & use cases

A step-by-step guide to starting with OKRs from an OKR expert

How to write OKRs | Our step-by-step guide
Ready to upgrade your people enablement strategy.
Exlpore our performance reviews, goals & OKRs, engagement surveys, onboarding and more.
.webp)
The #1 rated HR platform for people enablement
Schedule a demo to find out why leading companies choose Leapsome, the intelligent HR platform that empowers managers to develop, align, and engage their teams.
- Get AI-powered recommendations 🪄
- Save countless hours with automations ⏱️
- Learn from industry best-practices and benchmarks 📊
1,600+ forward-thinking companies choose Leapsome

Schedule a demo
Our friendly team will be in touch right away!
.png)
Mitarbeiter entwickeln mit Leapsome
Stärken Sie Mitarbeiter-Engagement und Erfolg Ihres Unternehmens - wie andere führende Marken.
Interesse an Leapsome?
Unsere Produktexperten zeigen Ihnen gerne unsere Plattform oder eröffnen einen Account.
Transform teamwork with Confluence. See why Confluence is the content collaboration hub for all teams. Get it free
- The Workstream
- Strategic planning
How a strategic planning framework can help you achieve your big goals
Don’t worry — it’s not nearly as complex as it sounds
Browse topics
A strategic planning framework is a tool you and your team will use to focus on and fill in a specific element of your strategic plan.
You’ve got big ideas and bigger goals for your company. Maybe you’re set on making the world a better place (hey, aren’t we all?). Or maybe you want to be known for unmatched customer care. Regardless of your specific aim, your whole team is gung-ho about your mission.
But now’s the hard part: How do you transform that idea into an actionable strategy?
The strategic planning process can be daunting, but a strategic planning framework can help. You’ll use your framework (or frameworks) to tackle a specific piece of the strategic planning process with zero confusion and eyerolls, and plenty of energy and enthusiasm.
Who needs a strategic planning framework?
Here’s the short answer: Anyone who’s completing a strategic plan, whether it’s a strategic plan for a single project or an entire organization.
The good news is that these frameworks are way more straightforward than you think. Anyone from your grandma to your dog will be able to use them.
Alright, maybe not your dog…but you get it.
What is a strategic planning framework?
A strategic planning framework is a tool you and your team will use to focus on a specific element of your strategic plan.
Your entire strategic plan needs to cover a lot, including:
- Where you are now
- Where you want to go
- How you’ll achieve those goals
Pulling all of that together can be overwhelming, but a strategic planning framework will help you chip away at that iceberg.
For example, you could use the objectives and key results (OKRs) framework to iron out the goals included in your strategic plan. Or, you might use the framework called Porter’s five forces (we’ll cover this later) to dig into your competition and understand how competitive factors will impact the future of your organization.
Strategic planning frameworks help you dig deep into a specific section of your plan, so you can create something comprehensive that actually helps you turn ideas into action.
Strategic planning frameworks vs. models: One of these things is not like the other
Many people use the terms “strategic planning framework” and “strategic planning models” interchangeably. However, the terms represent two parts of a whole.
Your strategic planning model provides a high-level overview of all of the elements of your strategic plan. Your model comes first, as it dictates the structure of your entire plan.
Tom Wright, CEO and co-founder of Cascade Strategy, a strategy execution platform, likens it to building an airport. “A model of the airport would show you at a high-level how the approach roads connect to the departure hall, and how the departure hall connects to immigration, which then connects to the terminals, the runways, etc.,” he writes in a blog post .
In contrast, frameworks help you fill in different elements with specific information.
“In our airport example, we might apply a building framework that is designed to maximize the speed at which people move through the airport for efficiency,” Wright adds. “Or alternatively, we might apply a framework which is designed not to maximize speed, but rather to maximize the amount of time people spend in the airport shops.”
The model encompasses all pieces of your strategic plan, but your framework is your approach for a specific piece. Think of your model as the forest, and your different frameworks as the trees. You’ll only use one strategic planning model, but you can use numerous frameworks.
8 strategic planning frameworks to hash out your strategy with confidence
You’ll use different frameworks for different aspects of your strategic plan, from developing your action items to evaluating your competitors.
Here are eight of the most common strategic planning frameworks, and which piece of your strategy they can help you with.
1. SWOT analysis
Use this framework: To grasp what internal and external factors can impact your strategy
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors (meaning you have some control over them), while opportunities and threats are external factors (and you have little to no control).
Get your team together for a brainstorming session where you can tackle each category. Using our customer service example, you might determine:
- Strengths: We have a new and innovative product that people love.
- Weaknesses: Our customer ticketing system is outdated and ineffective.
- Opportunities: Customers have a growing interest in chat support, which we could roll out relatively easily.
- Threats: All of our competitors are prioritizing customer service.
You’ll use this framework at the beginning of your strategic planning process, as it helps you understand where things are going well for your company — as well as where you need to improve. That’s important information as you hash out your strategy.
2. Issue-based strategic planning
Use this framework: To build a strategic plan that addresses your organization’s biggest problems
While most of the strategic planning frameworks start with objectives (where you look to the future), this one starts with problems (where you look to the present). You’ll identify the challenges your organization is facing right now and create action plans to address them.
This is another framework that you’ll use at the very beginning of the strategic planning process, as it will shape your entire plan.
Start by asking: What are the biggest problems our organization is dealing with?
Perhaps you’ll realize that your customer feedback scores are plummeting. From there, your strategic plan should detail the steps you’ll take to resolve that issue.
3. Balanced scorecard
Use this framework: To define your goals and the steps you’ll take to get there
A balanced scorecard (BSC) outlines what your team or organization is trying to accomplish, as well as what work everybody needs to do in order to make it happen. It’s helpful for understanding objectives, connecting and prioritizing day-to-day work, and monitoring progress using established metrics.
With this framework, you’ll need to identify:
- Objectives: The goal you want to achieve (i.e. be looked to as the industry standard for quality customer care)
- Measures: How you’ll define success (i.e. average customer feedback score of B+)
- Initiatives: Programs established to achieve objectives (i.e. launch a new customer ticketing system to manage your customer support cases)
- Action items: Individual steps one person or a small team will take (i.e. Rico will research ticketing software, Sarah will complete the migration from our current platform, etc.)
See how you move from the big, seemingly unattainable goal all the way down to bite-sized actions you can take? That’s the beauty of a balanced scorecard — it connects your organization-wide goals to the daily tasks of everybody on the team.
4. Strategy mapping
Use this framework: To understand how all of your company’s objectives fit together
A strategy map is often used as a supplement to your balanced scorecard. You’ll list every objective from your balanced scorecard on your strategy map. It should be represented by a shape.
Next, you’ll group objectives into different perspectives. Think of these as buckets or themes for similar goals. The most common perspectives are:
- Internal business processes
- Learning and growth
Once all of your ovals are drawn out, you’ll draw arrows between them to show cause and effect. Does one objective have a direct impact on another?
For example, perhaps boosting the expertise of your customer service team (perspective: learning and growth) directly impacts your ability to provide top-notch customer care (perspective: customer).
Your strategy map can become a living resource, and you can color-code your objective bubbles (green, yellow, and red) to show your progress toward that objective.
5. Objectives and key results (OKRs)
Use this framework: To keep a close eye on progress
Objectives and key results (OKRs) is a popular goal setting methodology to help teams go after audacious goals. With this framework, you’ll identify:
- Objectives: What you want to achieve
- Key results: How you’ll measure your progress
Keep in mind that your key results need to be quantitative, measurable outcomes and not tasks or to-dos. So, sticking with our example of world-class customer service, a key result could be, “Secure 25+ five-star reviews by the end of Q2.”
OKRs are designed to be ambitious, and you don’t want to overdo it and overwhelm your team. Set only three to five at a time ( this template can help ) to make sure they’re motivating, and not anxiety-inducing.
6. Porter’s five forces
Use this framework: To understand the ins and outs of your existing and prospective competitors
Most strategic plans include a section for competitive analysis, and Porter’s five forces is a framework you’ll use to fill in that section. The five competitive forces you’ll identify are:
- Competition in the industry: Are your competitors growing rapidly?
- Potential of new entrants into the industry: Are a lot of new players able to easily enter your market and thrive? Or is it tough to get going?
- Power of suppliers: How much bargaining power do your suppliers have to pressure you to lower costs?
- Power of customers: How much bargaining power do your customers have to pressure you to lower costs?
- Threat of substitute products: Is your product easily replaced with another product? Or are you one-of-a-kind?
Your competition will shape your strategy, and this framework will help you understand how. If you realize that there’s a high threat of substitute products, then maybe differentiating yourself needs to be a key piece of your strategic plan.
7. Gap planning
Use this framework: To determine how you’ll close the gap between where you are and where you want to be
You have a strong vision for your organization. Maybe that vision feels like it’s within arm’s reach, or maybe it feels like it’s still miles and miles away.
Either way, bridging the gap between where you are now and where you want to be is no easy task. That messy middle is where all of the hard work happens.
That’s where gap planning (also called a needs assessment) comes in. It zeros in on everything you need to do to move from your current state to your vision. When you analyze a gap, you need to challenge yourself to think about why you haven’t achieved your ideal state. What’s the root cause?
Here’s a very simple example of what this could look like:
Vision: Reputation for industry-leading customer service
Current state: Good customer service, but not great (average feedback score of B-)
Gap: Customer service representatives are using outdated software
Improvement: Implement a new ticketing system to support the customer service team
This framework is another way to break your vision down into more tactical steps and improvements.
8. PEST analysis
Use this framework: To understand the external factors that can impact your company
When drafting your strategic plan, you can’t just think about what’s happening internally — you also need to think about what’s happening externally. A PEST analysis will help you take a holistic look at the environment your company is operating in.
PEST stands for political, economic, sociocultural, and technological, and this framework requires that you determine how each of those factors could impact your company’s overall health. Here are a few (of many) examples:
- Political: Are there a lot of government regulations that dictate how your industry can correspond with customers?
- Economic: Are customers in your industry watching their wallets closely?
- Sociocultural: Do customers expect an increasingly fast response?
- Technological: Are you operating with outdated customer ticketing software?
These are important considerations to make, so you avoid hashing out a strategy that doesn’t align with what’s happening around you.
There are plenty of strategic planning frameworks to choose from, and one isn’t inherently better than the others. They all serve different purposes.
So, when you need to choose a framework, start with your goal and work backward from there.
Do you need to identify clear action items? Then gap planning or a balanced scorecard are your best bets. Do you want to understand the impact of outside forces? Look at a PEST or SWOT analysis.
Keep in mind that you don’t have to choose only one. You can use different frameworks for different stages and elements of your strategic planning process. Plus, strategic plans are often revisited and reevaluated. You might require a different framework as your plan and company evolve over time.
Regardless of which framework(s) you use, you’ll want to keep your strategic plan and all of your supporting documentation somewhere organized and accessible. Your strategic plan doesn’t do any good if it sits and collects digital dust. A collaborative workspace like Confluence makes it easy for your entire team to reference that information whenever they need it.
Goals require strategy (and action)
Coming up with goals is easy. The hard part is figuring out how you’ll achieve them.
Your strategic plan takes your high-level vision and breaks it down into actionable steps you’ll take to make it happen.
The strategic planning process itself can sound dry and daunting, but a strategic planning framework makes it way easier to dig into the details of every element of your strategic plan.
Use one (or even a few) of the eight frameworks we discussed here, and you’ll be ready to take action on your company’s most ambitious goals.
Document all of your company’s goals, plans, challenges, and more. Check out the Confluence template gallery to make knowledge sharing even easier.
You may also like
Strategic planning template.
Capture and present your business strategy to the executive team and board of directors.
OKRs Template
Use this goal-setting template to set measurable, ambitious milestones.
Enable faster content collaboration for every team with Confluence
Copyright © 2024 Atlassian
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
How to Develop a Business Strategy: 6 Steps

- 25 Oct 2022
Business strategy can seem daunting, and for good reason: It can make or break an organization. Yet, developing a strong strategy doesn’t need to be overwhelming.
In the online course Business Strategy , Harvard Business School Professor Felix Oberholzer-Gee posits that strategy is simple. His secret? Focus on your organization’s value creation.
“Strategy often sounds like a lofty concept that only the most senior executives can develop,” Oberholzer-Gee says. “But actually, anyone can think and act strategically. It doesn’t need to be difficult; all you need is a proven framework.”
Here’s a breakdown of why business strategy is important, the basics of value-based strategy, and six steps for developing your own.
Why Do You Need a Business Strategy?
Business strategy is the development, alignment, and integration of an organization’s strategic initiatives to give it a competitive edge in the market. Devising a business strategy can ensure you have a clear plan for reaching organizational goals and continue to survive and thrive.
According to a study by Bridges Business Consultancy , 48 percent of organizations fail to meet half of their strategic targets and 85 percent fail to meet two-thirds, highlighting why dedication to the business strategy process is crucial.
One type of business strategy is called value-based strategy, which simplifies the process by leveraging the value stick framework to focus on the advantage your business creates.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Value-Based Strategy?
Value-based strategy , also called value-based pricing, is a pricing method in which an organization relies on the perceived value of its goods and services to determine its pricing structure and resource allocation.
The value stick framework can be used to visualize how various factors impact each other and determine which initiatives to pursue to increase value for all parties.

The value stick has four factors:
- Willingness to pay (WTP) : The highest price a customer is willing to pay for your product or service
- Price : The amount customers have to pay for goods or services
- Cost : The amount a company spends on producing goods or services
- Willingness to sell (WTS) : The lowest amount suppliers are willing to accept for the materials required to produce goods or services
To determine how to best create value, you can toggle each factor on the value stick to see how the others are affected. For instance, lowering price increases customer delight.
"As strategists, we really ask three questions,” Oberholzer-Gee says in Business Strategy. “How can my business best create value for customers? How can my business create value for employees? And how can my business create value by collaborating with suppliers? Think of a company's strategy as an answer to these three questions."
Related: 4 Business Strategy Skills Every Business Leader Needs
6 Steps to Develop a Value-Based Business Strategy
1. define your purpose.
When approaching business strategy, defining your organization’s purpose can be a useful starting point.
This is vital in creating customer and employee value, especially if your organization’s purpose is linked to a cause such as environmental protection or alleviating specific social issues.
A recent survey conducted by clean energy company Swytch found that nearly 75 percent of millennials would take a decrease in salary if it meant working for an environmentally responsible company. Nearly 40 percent selected one job over another because of an organization’s sustainability practices.
Additionally, research in the Harvard Business Review shows that consumers’ motivation to buy from sustainable brands is on the rise. Sales of products marked as sustainable grew more than five times faster than those that weren’t.
By starting with purpose, your organization can create more value down the line.
2. Assess Market Opportunity
Next, understand your market’s competitive landscape. Which companies own shares of the market? What differentiates your competitors’ products from yours? Are there any unmet needs your organization could take advantage of?
Conducting this research before planning a strategy is critical in identifying how your organization provides unique customer value and opportunities to create even more.
3. Create Value for Customers
With an understanding of the market and your company’s purpose, you can determine how your organization provides unique or greater value and strategize ways to improve.
On the value stick, the value captured by customers is called “customer delight.” It can be increased by raising their willingness to pay and decreasing the product’s price. If lowering the price isn’t an option, brainstorm how you could make the product more valuable to customers, thus increasing their willingness to pay.
Some ways to create customer value include:
- Lowering the product’s price
- Increasing the product’s physical quality and longevity
- Providing quick, high-quality customer service and a smooth shopping experience
- Leveraging network effects , if applicable, to create a community of users
- Incorporating an environmental or social cause into processes, packaging, and branding
4. Create Value for Suppliers
In addition to creating value for customers, you also need to provide value for suppliers. Suppliers can include any company that provides raw materials, labor, and transportation to help your organization produce goods or deliver services.
Supplier surplus, also called supplier delight, is created when the cost of materials increases or their willingness to sell decreases. The relationship between a firm and its suppliers can be contentious, given that both want to increase their margins. Yet, there are ways to create value for both parties.
Some ways to create value for suppliers include:
- Agreeing to pay more for higher quality materials : While this increases the supplier surplus, it may also increase customer delight by raising willingness to pay, or increase the firm’s margin by allowing you to raise prices.
- Working with the supplier to increase efficiency : This strategy can increase supplier surplus by lowering the overall cost of the supplier’s labor and their willingness to sell.

5. Create Value for Employees
Creating value for employees is a critical part of an effective business strategy and can be assessed using the value stick. Think of your employees as the “supplier” of labor and the supplier margin as employee satisfaction.
Employee satisfaction can be increased by raising wages or lowering the minimum salary they’re willing to receive by delivering value in other ways. Satisfied employees may provide a better customer experience, resulting in increased customer delight.
The value you provide employees ensures they’re motivated to do their best work, develop their skills, and stay with your company long-term.
Some examples of ways to create value for your employees include:
- Offering competitive salaries and bonuses
- Offering benefits like ample paid vacation and sick days, generous parental leave, and wellness budgets
- Providing flexibility of work location, whether your team is fully remote or hybrid
- Aiding in professional development
- Creating a workplace rich with a diversity of experiences, identities, and ideas
- Fostering a supportive organizational culture
One example from Business Strategy is that of a call center for a diagnostics company. The employees were being paid minimum wage and expressed that the analytical nature of their phone calls with customers warranted higher pay. They also expressed pain points about cumbersome tasks and work conditions.
When a pay increase was implemented for all employees, along with operational changes to make processes smoother, employee productivity increased to the point that it balanced out the higher cost of salaries.
Because the employees’ satisfaction increased, they also began providing better experiences on the phone with customers. This increased the customers’ willingness to pay, directly impacting customer delight.
6. Map Strategy to Actionable Tasks and KPIs
Amidst creating value for each of the three groups, don’t forget the fourth party that needs value: your company. By creating value for employees, suppliers, and customers, you’re creating value for your firm, too.
To ensure you’re tracking to goals, determine your key performance indicators, what metrics constitute success, and how you’ll report results over time. Then, break each of the above value-creation goals into action items. For instance, what steps can you take to increase your employees’ compensation? Who will be responsible for each task?
Having actionable assignments and clear metrics for success will allow for a smooth transition from strategy formulation to execution.

Building Your Strategic Skill Set
By leveraging the value stick, you can create a business strategy that provides value to employees, customers, suppliers, and your firm.
To develop your strategies further and dig deeper into how to navigate value creation, consider taking an online course like Business Strategy . Professor Oberholzer-Gee walks through real-world examples of business challenges, prompts you to consider how you’d create value, and then reveals what those business leaders did and how you can apply the lessons to your organization.
Want to learn more about how to craft a successful strategy for your organization? Explore Business Strategy , one of our online strategy courses , to learn how to create organizational value. Not sure which course is the right fit? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Strategic planning
- Strategy formulation
Five Questions to Identify Key Stakeholders
- Graham Kenny
- March 06, 2014

The Former CEO of Guardian on Using Values to Drive Strategic Planning
- Deanna Mulligan
- From the January–February 2021 Issue
Marketing Malpractice: The Cause and the Cure
- Clayton M. Christensen
- From the December 2005 Issue
How One Family Business Found Its Sweet Spot
- George Stalk, Jr.
- April 05, 2013
Give My Regrets to Wall Street (HBR Case Study and Commentary)
- Mark L. Frigo
- Joel Litman
- Tom Copeland
- John J. Mulherin
- From the February 2004 Issue
Making Planning Strategic
- Richard G. Hamermesh
- From the July 1986 Issue
Living in the Futures
- Angela Wilkinson
- Roland Kupers
- From the May 2013 Issue
Today's Innovation Can Rise from Yesterday's Failure
- Vijay Govindarajan
- March 29, 2011
Every CEO Should Write an Annual Memo to the Board
- Anthony K. Tjan
- November 12, 2009
Fast Heat: How Korea Won the Microwave War
- Ira C. Magaziner
- Mark Patinkin
- From the January–February 1989 Issue

What Strategists Can Learn from Architecture
- Andrew Campbell
- Mark Lancelott
- November 13, 2013
Coupling Strategy to Operating Plans
- John M. Hobbs
- Donald F. Heany
- From the May 1977 Issue
Measuring the Strategic Readiness of Intangible Assets
- Robert S. Kaplan
- David P. Norton
- February 01, 2004
The World Bank’s Innovation Market
- Robert Chapman Wood
- From the November 2002 Issue
Link Manufacturing Process and Product Life Cycles
- Robert H. Hayes
- Steven C. Wheelwright
- From the January 1979 Issue

Right Tech, Wrong Time
- Rahul Kapoor
- From the November 2016 Issue
How to Avoid Catastrophe
- Catherine H. Tinsley
- Robin L. Dillon
- Peter M. Madsen
- From the April 2011 Issue

The Best Strategies Don't Just Take a Long View. They Take a Broad View.
- Richard Whittington
- May 23, 2022
Can We Simplify Financial Regulation?
- Ron Ashkenas
- November 06, 2009
If Brands Are Built over Years, Why Are They Managed over Quarters?
- Leonard M. Lodish
- Carl F. Mela
- From the July–August 2007 Issue

Merck Latin America (D): Mexico
- Michael Beer
- James Weber
- March 12, 2001
The Merger of UCSF Medical Center and Stanford Health Services
- Susan L. Madden
- Nancy M. Kane
- May 01, 2015
Franco Bernabe at ENI (A)
- Linda A. Hill
- Jennifer M. Suesse
- Mara Willard
- December 17, 1997
RKO Warner Video, Inc.: Incentive Compensation Plan
- George P. Baker
- Samuel L. Shimer
- October 20, 1989
Strategy Planning Sequence
- L. J. Bourgeois III
- November 06, 2013
iLinko: Enterprise Systems Implementation All Over Again
- January 11, 2013
Polaroid-Kodak (B4)
- Michael E. Porter
- January 01, 1978
GroupM India: The Human Dimension of Digital Transformation (A)
- Anand Narasimhan
- November 07, 2017
Swoop in the Era of Coronavirus
- Susan S. Harmeling
- October 30, 2020
GroupM India: The Human Dimension of Digital Transformation (B)
Colorado growth policy - sequel.
- Charles Kireker
- L. M. Cater
- Carol Edmonds Sullivan
- January 01, 1983
New Balance: Developing an Integrated CSR Strategy
- Vesela Veleva
- January 28, 2010
Polaroid-Kodak (B5)

Marketing as Strategy: Understanding the CEO's Agenda for Driving Growth and Innovation
- Nirmalya Kumar
- May 05, 2004
Parks and Partnership in New York City (A): Adrian Benepe's Challenge
- John D. Donahue
- June 01, 2004
Competitive Strategy in International Construction
- John D. Macomber
- Emrah Ergelen
- March 08, 2021
Leader-as-Architect: Alignment
- Ethan S. Bernstein
- Ryan L. Raffaelli
- Joshua D. Margolis
- October 22, 2014
Bill Riddick and the Durham S.O.S. Charrette
- Francesca Gino
- Jeff Huizinga
- February 08, 2020
General Electric's 20th Century CEOs (Abridged)
- Nitin Nohria
- Anthony J. Mayo
- Mark Benson
- May 30, 2006
Experiment in Public Procurement: Italy Buys in Bulk
- Pamela Varley
- September 30, 2008

Reversing the AMD Fusion Launch, Teaching Plan
- Ryan Johnson
- June 28, 2011
Playa Dorada Tennis Club: Expansion Strategy, Teaching Note
- W. Earl Sasser Jr.
- Brent Kazan
- June 28, 2010
Museum XYZ, Major City, USA, Teaching Note
- Anne Cohn Donnelly
- July 01, 2010
Popular Topics
Partner center.
- What is i-nexus
- Why i-nexus
- Strategy Execution
- Hoshin Kanri
- Operational excellence
- Case studies
- i-nexus reviews
- Strategy execution guide
- Hoshin Kanri guide
- Operational excellence guide
- Book a demo
- Demo on-demand
- Plan to practice
- Buy or build
- Customer success overview
- Customer success journey
- Customer services
- Customer support
- News & Press
8 types of strategic planning models you should be using
While classical strategic planning models are effective in traditional markets and environments, we no longer live in this world. to thrive here requires planners to evolve and adapt their practices. find out why one strategic planning model - hybrid - stands head and shoulders above the rest..
Agile has pushed beyond its roots in software development and into other functions in the business. With it comes a fresh workstream or project management approach, the promise of “continuous” delivery, and greater responsiveness to change.
But can agile principles also be applied to strategy and strategic planning?
In this age of uncertainty and volatility, strategic planning surely would benefit from increased responsiveness.
This blog explores eight strategic planning models to find those that will support your organization to be continuous - and adaptive - when it comes to a continuous approach to strategy.
Classic types of strategic planning
Three classical strategic planning models are rational, incremental, and organic.
1. The rational model of strategic planning
The rational model is a top-down, step-by-step process in which a company analyzes its industry, competitors, and environment to identify opportunities and threats.
It then develops strategies to take advantage of the opportunities and address the threats.
The benefits of a rational model
This rational model is beneficial because it allows for a systematic and analytical approach to decision-making in your organization.
It also helps to ensure that all possible outcomes are considered and that the best course of action is chosen based on available information.
Additionally, a rational model encourages planners to think ahead and anticipate potential problems or challenges.
The challenges of a rational model
However, the rational theoretical framework assumes that managers are fully informed, able to calculate the best course of action, and motivated to act in the best interests of their firm.
While this may be a reasonable assumption in some cases, it does not reflect the reality of many business environments.
Managerial decision-making is often influenced by biases, emotions, and personal agendas, which can lead to suboptimal outcomes.
In addition, complex systems cannot be accurately modeled using rational analysis alone, so managers must rely on their intuition and experience to make decisions in uncertain situations.
2. The incremental model of strategic planning
The incremental model is also a top-down process but is more flexible than the rational model.
The company begins by identifying its goals and objectives and developing strategies to achieve them.
The benefits of an incremental model
An incremental strategic planning model is beneficial because it allows for continuous refinement and adjustment to the plan as new information arises.
This helps ensure that the plan is always aligned with the current reality and can be adapted as necessary.
Additionally, an incremental model allows for a more participatory planning process, leading to a better understanding and buy-in from all stakeholders.
The challenges of an incremental model
A few challenges are associated with using an incremental strategic planning model.
One is that it can be difficult to maintain momentum and keep all stakeholders aligned and committed to the plan if changes are made incrementally.
Another challenge is that it can be difficult to accurately forecast future needs and trends if changes are too slow.
Finally, it can be difficult to get buy-in from all stakeholders for a constantly evolving plan; therefore, it's crucial to take stakeholders through the continuous strategy manifesto .
3. The organic model of strategic planning
The organic model is a bottom-up process in which the company allows employees to develop ideas for improving the business.
Employees then develop strategies to implement these ideas.
An organic strategic planning model is beneficial because it allows for a flexible and adaptable plan to grow and change along with the organization.
It also allows for input and feedback from employees at all levels, which can help ensure that the plan meets the organization's and its employees' needs.
The challenges of an organic model of strategic planning are many.
One key challenge is that organic planning models rely on accurate and timely information, which can be difficult to obtain and process.
Additionally, the decision-making process in an organic model is often slower than in a traditional top-down model, which can lead to missed opportunities.
Furthermore, the lack of a clear hierarchy can make it difficult to assign responsibility and accountability for strategic decisions.
Finally, the participatory nature of organic planning can lead to conflict and gridlock if stakeholders have different visions for the organization's future.
4. Strategic alignment model
The strategic alignment model is a tool that can be used to help your organization ensure its strategies align closely with operational goals. This is often seen through the Hoshin Kanri model.
The four steps of the strategic alignment model are to: 1. Establish the organization's mission and vision. 2. Determine the organization's strategic goals and objectives. 3. Develop strategies to achieve the strategic goals and objectives. 4. Evaluate the effectiveness of the strategies and make necessary adjustments.
The benefits of the strategic alignment model
The benefits of the strategic alignment model are that it helps organizations to identify and focus on their critical success factors and also allows them to measure their progress in achieving these factors.
Additionally, the model can help organizations identify and manage any gaps between their actual and desired states.
The challenges of the strategic alignment model
Because the strategic alignment model aims to get the enterprise working towards the same goal, by its very essence, this is challenging as different areas may have different goals. This can make it hard to agree on what the goal should be.
To this end, strategic planners can use the catchball goal-setting method , and supplement it with the "W" process for strategic planning
Additionally, the strategic alignment model can be difficult to implement because it requires cooperation between all departments. If one department is not working together with the others, it can disrupt the entire plan. Culture hacking is a key means to overcome a silo, tribal mentality in your organization.

Testing the degree to which your business is strategically aligned (and therefore an early indicator of how this model may or may not work for you) is HBR's two-part question :
“1. How well does your business strategy support the fulfillment of your company’s purpose? 2. How well does your organization support the achievement of your business strategy?" Trevor and Varcoe, "A simple way to test your company's strategic alignment", Harvard Business Review 2016
5. The basic strategic planning model
The basic (or simple) model is the right place to start for organizations that are novices or new to structured strategic planning.
While it is best suited to those planners working in businesses with little to no history of strategic planning, it is also an effective framework for any organization that doesn’t have the time or resources to spend on deep and extensive strategic planning.
The basic strategic planning model provides structure and guidance for developing and implementing a successful strategy.
The model consists of four steps:
1. Situation analysis 2. Goal setting 3. Strategy creation, and 4. Implementation and monitoring. Situational analysis
The first step, situation analysis, involves conducting a thorough assessment of the current environment and identifying the key factors that will impact the organization's success.
This step is important because it provides a foundation for setting realistic goals and developing effective strategies. Goal setting
The second step, goal setting, involves establishing specific objectives the organization hopes to achieve.
These objectives should be SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Strategy creation
The third step, strategy development, involves crafting a plan of action to help the organization reach its objectives.
This step requires careful consideration of the resources available and the constraints faced by the organization and could be any of these strategies . Implementation and monitoring
The fourth step, implementation and monitoring involve putting the strategy into action and tracking progress toward the objectives.
This step requires ongoing communication and coordination among all members of the organization.
The benefits of the basic strategic planning model
A basic strategic planning model can help a company or organization clarify its purpose, identify its strengths and weaknesses, and determine its goals and strategies.
Creating a strategic plan can help management better understand the business, identify potential opportunities and threats, and assess the company's current position in the market.
Having a clear and well-defined strategy can help a company focus its resources and improve its chances of success.
The challenges of the basic strategic planning model
Basic strategic planning models can be challenging to implement, especially for organizations that have never attempted formal strategic planning.
Creating a mission statement , outlining objectives and strategies, and developing action plans can be overwhelming for some groups.
Additionally, it can be difficult to focus on the strategic planning process and resist the temptation to rush into implementation. Another challenge is ensuring that everyone in the organization buys into the plan.
This involves getting input from all levels of the company and ensuring that everyone understands and agrees with the objectives and strategies. It can also be difficult to keep everyone on track once the plan is implemented.
Finally, it is important to regularly review and update the plan to remain relevant and effective.

Three continuous types of strategic planning
While classical types of strategic planning are advantageous in their ability to align your business around goals, inspire belief in achieving them, and give structure to strategic implementation - they're static.
These common strategic planning models, bar the incremental approach, fail to help you successfully adapt to your surroundings.
That is why your organization's best approach to strategic planning lies in continuous strategic models like those we'll outline now.
What does continuous strategic planning mean?
In many senses, it means incremental planning and delivery.
Traditionally, annual strategic planning involves considerable upfront planning followed by a 12-month program of delivery.
Any reviews during delivery are focused on performance against this plan.
A more agile approach to strategic planning advocates a continuous approach to planning and delivery.
Such an agile approach negates the need to plan a year’s worth of strategic activity while creating regular opportunities to review progress and plan the next activity increment.
What’s attractive about this approach is the ability to course correct or even pivot to respond to changing internal or external environmental factors.
What are the three models of continuous strategic planning?
To help answer that question, let’s explore three models:
1. Annual planning
This is the traditional approach to strategic planning.
Strategic plans are developed in cadence with the financial year.
Strategic objectives and their supporting workstreams are determined and planned before embarking on the plan.
The “planning cycle” is the same as the “delivery cycle.” Battle-tested, this model is reliable and well-understood.
However, it lacks that responsiveness to uncertainty and might sometimes feel like a blind race to the finish line.
The benefits of annual planning
There are many benefits to annual planning.
One of the biggest benefits is that it allows you to track your progress over the year. You can see what goals you have accomplished and what needs to be done. This can help you stay on track and ensure you reach your goals.
Annual planning can also help you identify areas of your business that need improvement. You can then take steps to improve these areas. Additionally, annual planning can help you budget for the year ahead.
This will help you make sure you have enough money to accomplish your goals. Lastly, annual planning can help you stay organized and on top of everything that needs to be done.
The challenges of annual planning
One of the challenges of annual planning is ensuring that all stakeholders are on the same page.
This cannot be easy, as different departments may have different priorities.
It is important to ensure that everyone understands the organization's goals and works towards achieving them.
Another challenge is ensuring that the plan is realistic and achievable. This means setting realistic goals and ensuring enough time to accomplish them.
Finally, it is important to evaluate the plan regularly and make changes as needed. This helps ensure that the plan remains effective and relevant.
2. Agile planning
Agile Planning is an iterative and incremental process of planning and monitoring the work that needs to be done to deliver a product or service. It enables teams to respond quickly to changes in customer demand and business conditions.
Applied to strategy, agile means that strategic decisions are made on a much more frequent basis than annual, and any future strategic activity exists in the form of a prioritized list (or backlog) of strategic priorities.
The benefits of agile planning
The benefits of agile planning are that it enables you to respond quickly to changes in the market or customer demands.
It also allows you to prioritize tasks and ensure that the most important tasks are completed first.
Additionally, agile planning helps you to track progress and ensure that you are on track to meet your goals.
The challenges of agile planning
The challenges of agile planning stem from the need to balance the need for predictability and the need for flexibility.
Agile planning requires regular adjustments to plans to account for requirements changes and stakeholders' feedback.
This can be difficult to manage, particularly when stakeholders are unavailable or changes occur rapidly.
There is also a risk that agile planning can lead to over-optimism and unrealistic expectations.
3. Hybrid planning
In a hybrid model, the planning cycle remains annual, but its delivery is managed in a more agile way.
In this model, the annual plan acts as a “north star” for activity, but in-between delivery cycles, priorities for the next delivery cycle are calibrated before the activity proceeds.
The benefits of hybrid planning
Hybrid planning can provide a company with the ability to have a more streamlined and efficient process for both long-term and short-term planning.
By combining the strengths of each approach, a company can develop a plan tailored specifically to its needs.
Additionally, a hybrid plan can help a company stay agile and responsive to changes in the market or industry.
The challenges of hybrid planning
One challenge of hybrid planning is that it can be difficult to strike the right balance between long-term and short-term planning.
Another challenge is that it can be difficult to keep all of the different aspects of the plan organized and coordinated. This, in turn, can lead to challenges around reviewing strategy and adapting to the environment.

What goes into a strategic planning cycle?
With our understanding of continuous strategic planning models in mind, we can now better understand their similarities and differences. To achieve that, we will consider five planning elements:
1. Planning horizons
A long-term future view of an organization’s strategic direction.
A planning horizon might include overarching breakthrough objectives that an organization aspires to achieve over that timeframe.
Planning horizons might vary significantly between industries.
2. Planning cycles
The period over which strategic activity is planned ahead of delivery.
Traditionally, planning cycles have been aligned with budget cycles.
3. Delivery cycles
An incremental delivery within the planning cycle.
Historically, delivery cycles have been aligned directly with planning cycles.
An annual strategic plan has a twelve-month delivery cycle.
4. Strategic sprints
A short, time-boxed period during which a team works to complete strategic work.
Multiple sprints are delivered throughout a delivery cycle.
5. Strategic reviews
Regular reviews of strategy, progress against strategic plan, and performance to targets.
How do continuous strategic planning models compare?
The comparison below shows that all three models share the same planning horizon element, typically 2-5 years in duration.
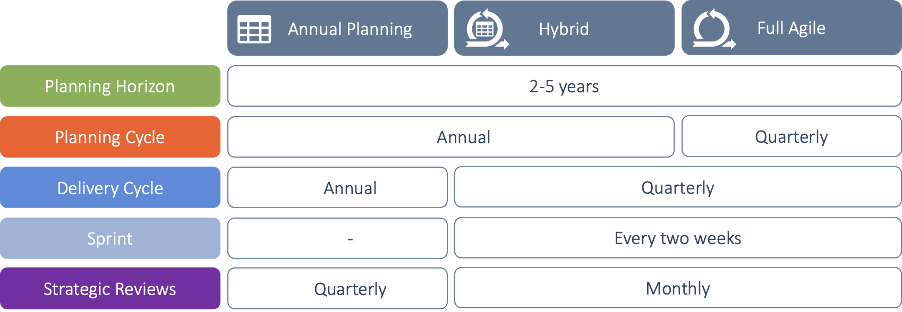
When considering the planning cycle, differences start to appear.
Annual planning is built on an annual planning cycle, and the same is true for the hybrid model.
However, full agile would likely adopt quarterly planning cycles.
Why quarterly? Any longer and responsiveness are compromised. Any shorter and an organization risks introducing the very thing we’re trying to avoid: uncertainty.
Arguably exposing the first key weakness of annual planning, the annual cycle is adopted for both planning and delivery cycles, unlike hybrid and full agile models that adopt unified quarterly delivery cycles.
Annual planning today invariably relies more on traditional project management than agile methods. Once again, both hybrid and full agile models advocate two weekly sprints.
Finally, annual planning might typically hold quarterly strategic reviews.
Here lies another key weakness – not only are these strategic reviews too infrequent, but they also invariably focus on performance against the strategic plan rather than ensuring ongoing relevance of the strategy itself.

How do you pick the right strategic planning model?
Simple. Your organization cannot afford to continue with traditional strategic planning.
It is simply too rigid and unresponsive.
Nor can organizations afford to pick their strategic direction every quarter, regardless of how well their planning horizon and breakthrough objectives are defined.
The answer is hybrid which leans on both annual planning and full hybrid to emerge with a pragmatic new – and more continuous – approach to strategic planning.
And in a future blog, we’ll explore equally pragmatic steps toward hybrid strategic planning.
Learn more about continuous strategy
Take the next steps in your journey to embracing continuous strategy by exploring our strategy execution resource hub .
About the author
James Davies is i-nexus’ Chief Product Officer. As an experienced software executive with 20 years of experience working in Silicon Valley, USA, James has held senior leadership roles in three venture capital-backed software start-ups (including CEO, CPO, and Chairman). He has delivered management consulting services to some of the world’s largest technology companies. If you’d like to talk more about the future of strategy execution, reach out to him on [email protected] or connect with James on LinkedIn for the latest insights

How Porter's Five Forces supports strategic planning

Why you should use the x matrix strategic planning tool

Top-down vs. bottom-up strategic and operational planning explained
The 5 steps of the strategic planning process
.jpg)
Starting a project without a strategy is like trying to bake a cake without a recipe — you might have all the ingredients you need, but without a plan for how to combine them, or a vision for what the finished product will look like, you’re likely to end up with a mess. This is especially true when working with a team — it’s crucial to have a shared plan that can serve as a map on the pathway to success.
Creating a strategic plan not only provides a useful document for the future, but also helps you define what you have right now, and think through and outline all of the steps and considerations you’ll need to succeed.
What is strategic planning?
While there is no single approach to creating a strategic plan, most approaches can be boiled down to five overarching steps:
- Define your vision
- Assess where you are
- Determine your priorities and objectives
- Define responsibilities
- Measure and evaluate results
Each step requires close collaboration as you build a shared vision, strategy for implementation, and system for understanding performance.
Related: Learn how to hold an effective strategic planning meeting
Why do I need a strategic plan?
Building a strategic plan is the best way to ensure that your whole team is on the same page, from the initial vision and the metrics for success to evaluating outcomes and adjusting (if necessary) for the future. Even if you’re an expert baker, working with a team to bake a cake means having a collaborative approach and clearly defined steps so that the result reflects the strategic goals you laid out at the beginning.
The benefits of strategic planning also permeate into the general efficiency and productivity of your organization as a whole. They include:
- Greater attention to potential biases or flaws, improving decision-making
- Clear direction and focus, motivating and engaging employees
- Better resource management, improving project outcomes
- Improved employee performance, increasing profitability
- Enhanced communication and collaboration, fostering team efficiency
Next, let’s dive into how to build and structure your strategic plan, complete with templates and assets to help you along the way.
Before you begin: Pick a brainstorming method
There are many brainstorming methods you can use to come up with, outline, and rank your priorities. When it comes to strategy planning, it’s important to get everyone’s thoughts and ideas out before committing to any one strategy. With the right facilitation , brainstorming helps make this process fair and transparent for everyone involved.
First, decide if you want to run a real-time rapid ideation session or a structured brainstorming . In a rapid ideation session, you encourage sharing half-baked or silly ideas, typically within a set time frame. The key is to just get out all your ideas quickly and then edit the best ones. Examples of rapid ideation methods include round robin , brainwriting , mind mapping , and crazy eights .
In a structured brainstorming session, you allow for more time to prepare and edit your thoughts before getting together to share and discuss those more polished ideas. This might involve brainstorming methods that entail unconventional ways of thinking, such as reverse brainstorming or rolestorming .
Using a platform like Mural, you can easily capture and organize your team’s ideas through sticky notes, diagrams, text, or even images and videos. These features allow you to build actionable next steps immediately (and in the same place) through color coding and tagging.
Whichever method you choose, the ideal outcome is that you avoid groupthink by giving everyone a voice and a say. Once you’ve reached a consensus on your top priorities, add specific objectives tied to each of those priorities.
Related: Brainstorming and ideation template
1. Define your vision
Whether it’s for your business as a whole, or a specific initiative, successful strategic planning involves alignment with a vision for success. You can think of it as a project-specific mission statement or a north star to guide employees toward fulfilling organizational goals.
To create a vision statement that explicitly states the ideal results of your project or company transformation, follow these four key steps:
- Engage and involve the entire team . Inclusivity like this helps bring diverse perspectives to the table.
- Align the vision with your core values and purpose . This will make it familiar and easy to follow through.
- Stay grounded . The vision should be ambitious enough to motivate and inspire yet grounded enough to be achievable and relevant.
- Think long-term flexibility . Consider future trends and how your vision can be flexible in the face of challenges or opportunities.
For example, say your vision is to revolutionize customer success by streamlining and optimizing your process for handling support tickets. It’s important to have a strategy map that allows stakeholders (like the support team, marketing team, and engineering team) to know the overall objective and understand the roles they will play in realizing the goals.
This can be done in real time or asynchronously , whether in person, hybrid, or remote. By leveraging a shared digital space , everyone has a voice in the process and room to add their thoughts, comments, and feedback.
Related: Vision board template
2. Assess where you are
The next step in creating a strategic plan is to conduct an assessment of where you stand in terms of your own initiatives, as well as the greater marketplace. Start by conducting a resource assessment. Figure out which financial, human, and/or technological resources you have available and if there are any limitations. You can do this using a SWOT analysis.
What is SWOT analysis?
SWOT analysis is an exercise where you define:
- Strengths: What are your unique strengths for this initiative or this product? In what ways are you a leader?
- Weaknesses: What weaknesses can you identify in your offering? How does your product compare to others in the marketplace?
- Opportunities: Are there areas for improvement that'd help differentiate your business?
- Threats: Beyond weaknesses, are there existing potential threats to your idea that could limit or prevent its success? How can those be anticipated?
For example, say you have an eco-friendly tech company and your vision is to launch a new service in the next year. Here’s what the SWOT analysis might look like:
- Strengths : Strong brand reputation, loyal customer base, and a talented team focused on innovation
- Weaknesses : Limited bandwidth to work on new projects, which might impact the scope of its strategy formulation
- Opportunities : How to leverage and experiment with existing customers when goal-setting
- Threats : Factors in the external environment out of its control, like the state of the economy and supply chain shortages
This SWOT analysis will guide the company in setting strategic objectives and formulating a robust plan to navigate the challenges it might face.
Related: SWOT analysis template
3. Determine your priorities and objectives
Once you've identified your organization’s mission and current standing, start a preliminary plan document that outlines your priorities and their corresponding objectives. Priorities and objectives should be set based on what is achievable with your available resources. The SMART framework is a great way to ensure you set effective goals . It looks like this:
- Specific: Set clear objectives, leaving no room for ambiguity about the desired outcomes.
- Measurable : Choose quantifiable criteria to make it easier to track progress.
- Achievable : Ensure it is realistic and attainable within the constraints of your resources and environment.
- Relevant : Develop objectives that are relevant to the direction your organization seeks to move.
- Time-bound : Set a clear timeline for achieving each objective to maintain a sense of urgency and focus.
For instance, going back to the eco-friendly tech company, the SMART goals might be:
- Specific : Target residential customers and small businesses to increase the sales of its solar-powered device line by 25%.
- Measurable : Track monthly sales and monitor customer feedback and reviews.
- Achievable : Allocate more resources to the marketing, sales, and customer service departments.
- Relevant : Supports the company's growth goals in a growing market of eco-conscious consumers.
- Time-bound : Conduct quarterly reviews and achieve this 25% increase in sales over the next 12 months.
With strategic objectives like this, you’ll be ready to put the work into action.
Related: Project kickoff template
4. Define tactics and responsibilities
In this stage, individuals or units within your team can get granular about how to achieve your goals and who'll be accountable for each step. For example, the senior leadership team might be in charge of assigning specific tasks to their team members, while human resources works on recruiting new talent.
It’s important to note that everyone’s responsibilities may shift over time as you launch and gather initial data about your project. For this reason, it’s key to define responsibilities with clear short-term metrics for success. This way, you can make sure that your plan is adaptable to changing circumstances.
One of the more common ways to define tactics and metrics is to use the OKR (Objectives and Key Results) method. By outlining your OKRs, you’ll know exactly what key performance indicators (KPIs) to track and have a framework for analyzing the results once you begin to accumulate relevant data.
For instance, if our eco-friendly tech company has a goal of increasing sales, one objective might be to expand market reach for its solar-powered products. The sales team lead would be in charge of developing an outreach strategy. The key result would be to successfully launch its products in two new regions by Q2. The KPI would be a 60% conversation rate in those targeted markets.
Related: OKR planning template
5. Manage, measure, and evaluate
Once your plan is set into motion, it’s important to actively manage (and measure) progress. Before launching your plan, settle on a management process that allows you to measure success or failure. In this way, everyone is aligned on progress and can come together to evaluate your strategy execution at regular intervals.
Determine the milestones at which you’ll come together and go over results — this can take place weekly, monthly, or quarterly, depending on the nature of the project.
One of the best ways to evaluate progress is through agile retrospectives (or retros) , which can be done in real time or asynchronously. During this process, gather and organize feedback about the key elements that played a role in your strategy.
Related: Retrospective radar template
Retrospectives are typically divided into three parts:
- What went well.
- What didn’t go well.
- New opportunities for improvement.
This structure is also sometimes called the “ rose, thorn, bud ” framework. By using this approach, team members can collectively brainstorm and categorize their feedback, making the next steps clear and actionable. Creating an action plan during a post-mortem meeting is a crucial step in ensuring that lessons learned from past projects or events are effectively translated into tangible improvements.
Another method for reviewing progress is the quarterly business review (QBR). Like the agile retrospective, it allows you to collect feedback and adjust accordingly. In the case of QBRs, however, we recommend dividing your feedback into four categories:
- Start (what new items should be launched?).
- Stop (what items need to be paused?).
- Continue (what is going well?).
- Change (what could be modified to perform better?).
Strategic planners know that planning activities continue even after a project is complete. There’s always room for improvement and an action plan waiting to be implemented. Using the above approaches, your team can make room for new ideas within the existing strategic framework in order to track better to your long-term goals.
Related: Quarterly business review template
Conclusions
The beauty of the strategic plan is that it can be applied from the campaign level all the way up to organizational vision. Using the strategic planning framework, you build buy-in , trust, and transparency by collaboratively creating a vision for success, and mapping out the steps together on the road to your goals.
Also, in so doing, you build in an ability to adapt effectively on the fly in response to data through measurement and evaluation, making your plan both flexible and resilient.
Related: 5 Tips for Holding Effective Post-mortems
Why Mural for strategic planning
Mural unlocks collaborative strategic planning through a shared digital space with an intuitive interface, a library of pre-fab templates, and methodologies based on design thinking principles.
Outline goals, identify key metrics, and track progress with a platform built for any enterprise.
Learn more about strategic planning with Mural.
About the authors

Bryan Kitch
Tagged Topics
Related blog posts
%20(2).jpg)
How to hold effective strategic planning meetings
%20(2).jpg)
Tactical vs. strategic planning: Why you need both
%20(2).jpg)
5 effective strategic planning models for your business
Related blog posts.

How to plan and organize a workshop
%20(3).jpg)
How to run efficient Agile meetings [+ templates]

The best use cases of AI in project management
Thinking strategically
In the late 1970s, Fred Gluck led an effort to revitalize McKinsey’s thinking on strategy while, in parallel, Tom Peters and Robert Waterman were leading a similar effort to reinvent the Firm’s thinking on organization. The first published product of Gluck’s strategy initiative was a 1978 staff paper, "The evolution of strategic management."
The ostensible purpose of Gluck’s article was to throw light on the then-popular but ill-defined term "strategic management," using data from a recent McKinsey study of formal strategic planning in corporations. The authors concluded that such planning routinely evolves through four distinct phases of development, rising in sophistication from simple year-to-year budgeting to strategic management, in which strategic planning and everyday management are inextricably intertwined.
But the power of the article comes from the authors’ insights into the true nature of strategy and what constitutes high-quality strategic thinking. The article is also noteworthy for setting forth McKinsey’s original definition of strategy as "an integrated set of actions designed to create a sustainable advantage over competitors" and includes a description of the well-known "nine-box" matrix that formed the basis of McKinsey’s approach to business portfolio analysis.
Ten years later, a team from the Firm’s Australian office took portfolio analysis a step further. Rather than basing portfolio strategy only on metrics of a business unit’s absolute attractiveness, as suggested by the nine-box matrix, John Stuckey and Ken McLeod recommended adding a key new decision variable: how well-suited is the parent company to run the business unit as compared with other possible owners? If the parent is best suited to extract value from a unit, it often makes no sense to sell, even if that unit doesn’t compete in a particularly profitable industry. Conversely, if a parent company determines that it is not the best possible owner of a business unit, the parent maximizes value by selling it to the most appropriate owner, even if the unit happens to be in a business that is fundamentally attractive. In short, the "market-activated corporate strategy framework" prompts managers to view their portfolios with an investor’s value-maximizing eye.
The evolution of strategic management
Frederick W. Gluck, Stephen P. Kaufman, and A. Steven Walleck
A minor but pervasive frustration that seems to be unique to management as a profession is the rapid obsolescence of its jargon. As soon as a new management concept emerges, it becomes popularized as a buzzword, generalized, overused, and misused until its underlying substance has been blunted past recognition. The same fate could easily befall one of the brightest new concepts to come along lately: strategic management.
In seeking to understand what strategic management is, we have conducted a major study of the planning systems at large corporations. This study is unique in that it attempts to pass judgment on the quality of the business plans produced rather than only on the planning process.
We found that planning routinely progresses through four discrete phases of development. The first phase, financial planning, is the most basic and can be found at all companies. It is simply the process of setting annual budgets and using them to monitor progress. As financial planners extend their time horizons beyond the current year, they often cross into forecast-based planning, which is the second phase. A few companies have advanced beyond forecast-based planning by entering the third phase, which entails a profound leap forward in the effectiveness of strategic planning. We call this phase externally oriented planning, since it derives many of its advantages from more thorough and creative analyses of market trends, customers, and the competition. Only phase four—which is really a systematic, company-wide embodiment of externally oriented planning—earns the appellation strategic management, and its practitioners are very few indeed.
It doesn’t appear possible to skip a step in the process, because at each phase a company adopts attitudes and gains capabilities needed in the phases to come. Many companies have enjoyed considerable success without advancing beyond the rudimentary levels of strategic development. Some large, successful enterprises, for instance, are still firmly embedded in the forecast-based planning phase. You might well ask, are these companies somehow slipping behind, or are they simply responding appropriately to an environment that changes more slowly? The answer must be determined on a case-by-case basis.
Phase one: Financial planning
Financial planning, as we have said, is nothing more than the familiar annual budgeting process. Managers forecast revenue, costs, and capital needs a year in advance and use these numbers to benchmark performance. In well over half of the companies McKinsey studied—including some highly successful ones—formal planning was still at this most basic phase.
Note the word formal. Many firms that lack a sophisticated formal planning process make up for it with an informal "implicit strategy" worked out by the chief executive officer and a few top managers. Formal strategic planning, in fact, is just one of the possible sources of sound strategy development. There are at least two others: strategic thinking and opportunistic strategic decision making (Exhibit 1). All three routes can result in an effective strategy, which we define as "an integrated set of actions designed to create a sustainable advantage over competitors."
Phase-one companies, then, do have strategies, even though such companies often lack a formal system for planning them. The quality of the strategy of such a company depends largely on the entrepreneurial vigor of its CEO and other top executives. Do they have a good feel for the competition? Do they know their own cost structures? If the answer to such questions is yes, there may be little advantage to formal strategic planning. Ad-hoc studies by task forces and systematic communication of the essence of the strategy to those who need to know may suffice.
Phase two: Forecast-based planning
Still, most large enterprises are too complex to be managed with only an implicit strategy. Companies usually learn the shortcomings of phase-one planning as their treasurers struggle to estimate capital needs and make trade-offs among various financing plans, based on no more than a one-year budget. Ultimately, the burden becomes unbearable, and the company evolves toward phase two. At first, phase-two planning differs little from annual budgeting except that it covers a longer period of time. Very soon, however, planners become frustrated because the real world does not behave as their extrapolations predict. Their first response is usually to develop more sophisticated forecasting tools: trend analysis, regression models, and, finally, simulation models.
This initial response brings some improvement, but sooner or later all extrapolative models fail. At this point, a creative spark stirs the imaginations of the planners. They suddenly realize that their responsibility is not to chart the future—which is, in fact, impossible—but, rather, to lay out for managers the key issues facing the company. We call this spark "issue orientation."
The tough strategic issue that most often triggers the move to issue orientation is the problem of resource allocation: how to set up a flow of capital and other resources among the business units of a diversified company. The technique most commonly applied to this problem is portfolio analysis, a means of depicting a diversified company’s business units in a way that suggests which units should be kept and which sold off and how financial resources should be allocated among them. McKinsey’s standard portfolio analysis tool is the nine-box matrix (Exhibit 2), in which each business unit is plotted along two dimensions: the attractiveness of the relevant industry and the unit’s competitive strength within that industry. Units below the diagonal of the matrix are sold, liquidated, or run purely for cash, and they are allowed to consume little in the way of new capital. Those on the diagonal—marked "Selectivity, earnings"—can be candidates for selective investment. And business units above the diagonal, as the label suggests, should pursue strategies of either selective or aggressive investment and growth.
Phase three: Externally oriented planning
Once planners see their main role as identifying issues, they shift their attention from the details of their companies’ activities to the outside world, where the most profound issues reside. The planners’ in-depth analyses, previously reserved for inwardly focused financial projections, are now turned outward, to customers, potential customers, competitors, suppliers, and others. This outward focus is the chief characteristic of phase three: externally oriented planning.
The process can be time-consuming and rigorous—scrutinizing the outside world is a much larger undertaking than studying the operations of a single company—but it can also pay off dramatically. Take the example of a heavy-equipment maker that spent nine person-months reverse engineering its competitor’s product, reconstructing that competitor’s manufacturing facilities on paper, and estimating its production costs. The result: the company decided that no achievable level of cost reduction could meet the competition and that it therefore made no sense to seek a competitive advantage on price.
Phase-three plans can sometimes achieve this kind of dramatic impact because they are very different from the kind of static, deterministic, sterile plans that result from phase-two efforts. In particular, they share the following features:
Phase-three resource allocation is dynamic rather than static. The planner looks for opportunities to "shift the dot" of a business into a more attractive region of the portfolio matrix. This can be done by creating new capabilities that will help the company meet the most important prerequisite for success within a market, by redefining the market itself, or by changing the customers’ buying criteria to correspond to the company’s strengths.
Phase-three plans are adaptive rather than deterministic. They do not work from a standard strategy, such as "invest for growth." Instead, they continually aim to uncover new ways of defining and satisfying customer needs, new ways of competing more effectively, and new products or services.
Phase-three strategies are often surprise strategies. The competition often does not even recognize them as a threat until after they have taken effect.
Phase-three plans often recommend not one course of action but several, acknowledging the trade-offs among them. This multitude of possibilities is precisely what makes phase three very uncomfortable for top managers. As in-depth dynamic planning spreads through the organization, top managers realize that they cannot control every important decision. Of course, lower-level staff members often make key decisions under phase-one and phase-two regimes, but because phase three makes this process explicit, it is more unsettling for top managers and spurs them to invest even more in the strategic-planning process.
Phase Four: Strategic management
When this investment is successful, the result is strategic management: the melding of strategic planning and everyday management into a single, seamless process. In phase four, it is not that planning techniques have become more sophisticated than they were in phase three but that they have become inseparable from the process of management itself. No longer is planning a yearly, or even quarterly, activity. Instead, it is woven into the fabric of operational decision making.
No more than a few of the world’s companies—mainly diversified multinationals that manufacture electrical and electronic products—have reached this fourth phase. Perhaps the need to plan for hundreds of fast-evolving businesses serving thousands of product markets in dozens of nations has accelerated evolution at these companies. Observing them can teach executives much about strategic management.
The key factor that distinguishes strategically managed companies from their counterparts in phase three is not the sophistication of their planning techniques but rather the care and thoroughness with which they link strategic planning to operational decision making. This often boils down to the following five attributes:
A well-understood conceptual framework that sorts out the many interrelated types of strategic issues. This framework is defined by tomorrow’s strategic issues rather than by today’s organizational structure. Strategic issues are hung on the framework like ornaments on a Christmas tree. Top management supervises the process and decides which issues it must address and which should be assigned to operating managers.
Strategic thinking capabilities that are widespread throughout the company, not limited to the top echelons.
A process for negotiating trade-offs among competing objectives that involves a series of feedback loops rather than a sequence of planning submissions. A well-conceived strategy plans for the resources required and, where resources are constrained, seeks alternatives.
A performance review system that focuses the attention of top managers on key problem and opportunity areas, without forcing those managers to struggle through an in-depth review of each business unit’s strategy every year.
A motivational system and management values that reward and promote the exercise of strategic thinking.
Although it is not possible to make everyone at a company into a brilliant strategic thinker, it is possible to achieve widespread recognition of what strategic thinking is. This understanding is based on some relatively simple rules.
Strategic thinking seeks hard, fact-based, logical information. Strategists are acutely uncomfortable with vague concepts like "synergy." They do not accept generalized theories of economic behavior but look for underlying market mechanisms and action plans that will accomplish the end they seek.
Strategic thinking questions everyone’s unquestioned assumptions. Most business executives, for example, regard government regulation as a bothersome interference in their affairs. But a few companies appear to have revised that assumption and may be trying to participate actively in the formation of regulatory policies to gain a competitive edge.
Strategic thinking is characterized by an all-pervasive unwillingness to expend resources. A strategist is always looking for opportunities to win at low or, better yet, no cost.
Strategic thinking is usually indirect and unexpected rather than head-on and predictable. Basil Henry Liddell Hart, probably the foremost thinker on military strategy in the 20th century, has written, "To move along the line of natural expectation consolidates the opponent’s balance and thus his resisting power." "In strategy," says Liddell Hart, "the longest way around is often the shortest way home." 1 1. See B. H. Liddell Hart, Strategy , second edition, Columbus, Ohio: Meridian Books, 1991.
It appears likely that strategic management will improve a company’s long-term business success. Top executives in strategically managed companies point with pride to many effective business strategies supported by coherent functional plans. In every case, they can identify individual successes that have repaid many times over the company’s increased investment in planning.
About the Authors
Frederick Gluck was the managing director of McKinsey from 1988 to 1994; Stephen Kaufman and Steven Walleck are alumni of McKinsey’s Cleveland office. This article is adapted from a McKinsey staff paper dated October 1978.
MACS: The market-activated corporate strategy framework
Ken McLeod and John Stuckey
McKinsey’s nine-box strategy matrix, prevalent in the 1970s, plotted the attractiveness of a given industry along one axis and the competitive position of a particular business unit in that industry along the other. Thus, the matrix could reduce the value-creation potential of a company’s many business units to a single, digestible chart.
However, the nine-box matrix applied only to product markets: those in which companies sell goods and services to customers. Because a comprehensive strategy must also help a parent company win in the market for corporate control—where business units themselves are bought, sold, spun off, and taken private—we have developed an analytical tool called the market-activated corporate strategy (MACS) framework.
MACS represents much of McKinsey’s most recent thinking in strategy and finance. Like the old nine-box matrix, MACS includes a measure of each business unit’s stand-alone value within the corporation, but it adds a measure of a business unit’s fitness for sale to other companies. This new measure is what makes MACS especially useful.
The key insight of MACS is that a corporation’s ability to extract value from a business unit relative to other potential owners should determine whether the corporation ought to hold onto the unit in question. In particular, this issue should not be decided by the value of the business unit viewed in isolation. Thus, decisions about whether to sell off a business unit may have less to do with how unattractive it really is (the main concern of the nine-box matrix) and more to do with whether a company is, for whatever reason, particularly well suited to run it.
In the MACS matrix, the axes from the old nine-box framework measuring the industry’s attractiveness and the business unit’s ability to compete have been collapsed into a single horizontal axis, representing a business unit’s potential for creating value as a stand-alone enterprise (Exhibit 3). The vertical axis in MACS represents a parent company’s ability, relative to other potential owners, to extract value from a business unit. And it is this second measure that makes MACS unique.
Managers can use MACS just as they used the nine-box tool, by representing each business unit as a bubble whose radius is proportional to the sales, the funds employed, or the value added by that unit. The resulting chart can be used to plan acquisitions or divestitures and to identify the sorts of institutional skill-building efforts that the parent corporation should be engaged in.
The horizontal dimension: The potential to create value
The horizontal dimension of a MACS matrix shows a business unit’s potential value as an optimally managed stand-alone enterprise. Sometimes, this measure can be qualitative. When precision is needed, though, you can calculate the maximum potential net present value (NPV) of the business unit and then scale that NPV by some factor—such as sales, value added, or funds employed—to make it comparable to the values of the other business units. If the business unit might be better run under different managers, its value is appraised as if they already do manage it, since the goal is to estimate optimal, not actual, value.
That optimal value depends on three basic factors:
Industry attractiveness is a function of the structure of an industry and the conduct of its players, both of which can be assessed using the structure-conduct-performance (SCP) model. Start by considering the external forces impinging on an industry, such as new technologies, government policies, and lifestyle changes. Then consider the industry’s structure, including the economics of supply, demand, and the industry chain. Finally, look at the conduct and the financial performance of the industry’s players. The feedback loops shown in Exhibit 4 interact over time to determine the attractiveness of the industry at any given moment.
The position of your business unit within its industry depends on its ability to sustain higher prices or lower costs than the competition does. Assess this ability by considering the business unit as a value delivery system, where "value" means benefits to buyers minus price. 2 2. See Michael J. Lanning and Edward G. Michaels, 'A business is a value delivery system,' on page 53 of this anthology.
Chances to improve the attractiveness of the industry or the business unit’s competitive position within it come in two forms: opportunities to do a better job of managing internally and possible ways of shaping the structure of the industry or the conduct of its participants.
The vertical dimension: The ability to extract value
The vertical axis of the MACS matrix measures a corporation’s relative ability to extract value from each business unit in its portfolio. The parent can be classified as "in the pack," if it is no better suited than other companies to extract value from a particular business unit, or as a "natural owner," if it is uniquely suited for the job. The strength of this vertical dimension is that it makes explicit the true requirement for corporate performance: extracting more value from assets than anyone else can.
Many qualities can make a corporation the natural owner of a certain business unit. The parent corporation may be able to envision the future shape of the industry—and therefore to buy, sell, and manipulate assets in a way that anticipates a new equilibrium. It may excel at internal control: cutting costs, squeezing suppliers, and so on. It may have other businesses that can share resources with the new unit or transfer intermediate products or services to and from it. (In our experience, corporations tend to overvalue synergies that fall into this latter category. Believing that the internal transfer of goods and services is always a good thing, these companies never consider the advantages of arm’s-length market transactions.) Finally, there may be financial or technical factors that determine, to one extent or other, the natural owner of a business unit. These can include taxation, owners’ incentives, imperfect information, and differing valuation techniques.
Using the framework
Once a company’s business units have been located on the MACS matrix, the chart can be used to plan preliminary strategies for each of them. The main principle guiding this process should be the primary one behind MACS itself: the decision about whether a unit ought to be part of a company’s portfolio hangs more on that company’s relative ability to extract value from the unit than on its intrinsic value viewed in isolation.
The matrix itself can suggest some powerful strategic prescriptions—for example:
Divest structurally attractive businesses if they are worth more to someone else.
Retain structurally mediocre (or even poor) businesses if you can coax more value out of them than other owners could.
Give top priority to business units that lie toward the far left of the matrix—either by developing them internally if you are their natural owner or by selling them as soon as possible if someone else is.
Consider improving a business unit and selling it to its natural owner if you are well equipped to increase the value of the business unit through internal improvements but not in the best position to run it once it is in top shape.
Of course, the MACS matrix is just a snapshot. Sometimes, a parent company can change the way it extracts value, and in so doing it can become the natural owner of a business even if it wasn’t previously. But such a change will come at a cost to the parent and to other units in its portfolio. The manager’s objective is to find the combination of corporate capabilities and business units that provides the best overall scope for creating value.
MACS, a descendent of the old nine-box matrix, packages much of McKinsey’s thinking on strategy and finance. We have found that it serves well as a means of assessing strategy along the critical dimensions of value creation potential and relative ability to extract value.
Ken McLeod is an alumnus of McKinsey’s Melbourne office, and John Stuckey is a director in the Sydney office. This article is adapted from a McKinsey staff paper dated July 1989. Copyright © 1989, 2000 McKinsey & Company. All rights reserved.
Explore a career with us

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Now that you know the difference between the two, learn more about the seven strategic planning models, as well as the eight most commonly used frameworks that go along with them. 1. Basic model. The basic strategic planning model is ideal for establishing your company's vision, mission, business objectives, and values.
20 Strategic Frameworks & Models Every Business Leader MUST Know in 2024 1. The Balanced Scorecard. The Balanced Scorecard is a strategy management framework created by Drs. Robert Kaplan and David Norton.. It takes into account your: Objectives, which are high-level organizational goals.; Measures, which help you understand if you're accomplishing your objective strategically.
Here are a few strategic planning models you can use to get started. 1. The Balanced Scorecard. The Balanced Scorecard is one of the most prominent strategic planning models, tailored to give managers a comprehensive overview of their companies' operations on tight timelines.
This strategic planning model is mostly used by manufacturers who implement lean manufacturing best practices, but it can be used by any type of business. Porter's Five Forces Model This is a fundamental strategic planning model that should be used by any business.
Create an action plan to implement the strategy: Break down your strategy into tasks and milestones. Create a clear roadmap for implementation by assigning responsibilities and deadlines to team members. Related: The 5 steps of the strategic planning process. 2. Goal-based strategic planning model.
A strategic planning model maps out how your company plans to implement a strategy for improving operations, delivering quality, and meeting specific goals. It is like a template or a tool you use at the beginning of the planning process. ... The goal of this model is to align your business and IT strategies with the company's strategic goals ...
Inspirational Model: This is a somewhat quick method of strategic planning that begins by coming up with a highly inspirational vision for the organization and the goals to match. Issue-Based or Goal-Based Model: A step up from the basic model, this model is better for more established businesses.
New business models, global disruptions, and a need for rapid changes inspired various approaches to strategic planning, also known as strategic planning models. What all planning models have in common is that they help you translate strategies into action and aim to provide you with structure in the process of creating a strategic plan.
Businesses can benefit from using multiple approaches, even simultaneously. But different strategic planning models are best suited for different situations, so make your choice based on your business type, growth stage, priorities, and goals. 9 models for strategic planning. These are some of the most popular strategic planning models.
Many people use the terms "strategic planning framework" and "strategic planning models" interchangeably. However, the terms represent two parts of a whole. Your strategic planning model provides a high-level overview of all of the elements of your strategic plan. Your model comes first, as it dictates the structure of your entire plan.
Strategic planning is an essential component of business management. It involves analyzing the current situation of an organization, identifying its strengths and weaknesses, and developing a plan for its future. A range of strategic planning models are available to help organizations achieve their goals.
Strategy Frameworks and Tools You Should Know. 1. Jobs to Be Done Framework. The Jobs to Be Done (JTBD) framework, developed by Harvard Business School Professor Clayton Christensen, is a way to validate a consumer's need for a product. The basis of Christensen's theory is that, when people purchase products, they "hire" them to do a ...
Here are some examples of strategic planning models to help you understand the options available to you: 1. Hoshin Planning. The Hoshin Planning model involves a top-down approach to creating and reviewing a few goals at a time. First, upper management determines objectives for the company and creates some plans.
Strategy and strategic plans: How they are different and why it matters. Strategy creates a common understanding of what an organization wants to achieve and what it needs to do to meet its goals. Strategic plans bridge the gap from overall direction to specific projects and day-to-day actions that ultimately execute the strategy. Job No. 1 is ...
Devising a business strategy can ensure you have a clear plan for reaching organizational goals and continue to survive and thrive. According to a study by Bridges Business Consultancy , 48 percent of organizations fail to meet half of their strategic targets and 85 percent fail to meet two-thirds, highlighting why dedication to the business ...
Strategic planning Magazine Article. Cheryl A. Bachelder. Behind the Popeyes turnaround was a conscious decision to treat leadership as stewardship—and to put the interests of franchisees above ...
Classic types of strategic planning. Three classical strategic planning models are rational, incremental, and organic. 1. The rational model of strategic planning. The rational model is a top-down, step-by-step process in which a company analyzes its industry, competitors, and environment to identify opportunities and threats.
00:00. Audio. How to improve strategic planning. This sense of disappointment was captured in a recent McKinsey Quarterly survey of nearly 800 executives: just 45 percent of the respondents said they were satisfied with the strategic-planning process. 1 Moreover, only 23 percent indicated that major strategic decisions were made within its ...
Overcoming Challenges and Pitfalls. Challenge of consensus over clarity. Challenge of who provides input versus who decides. Preparing a long, ambitious, 5 year plan that sits on a shelf. Finding a balance between process and a final product. Communicating and executing the plan. Lack of alignment between mission, action, and finances.
Strategic planning is a process designed to conduct robust planning and make informed decisions. These are the steps involved in strategic planning. ... Whether it's for your business as a whole, or a specific initiative, successful strategic planning involves alignment with a vision for success. ... 5 effective strategic planning models for ...
The first published product of Gluck's strategy initiative was a 1978 staff paper, "The evolution of strategic management." The ostensible purpose of Gluck's article was to throw light on the then-popular but ill-defined term "strategic management," using data from a recent McKinsey study of formal strategic planning in corporations.
A strategic plan is more than just a business tool, it also plays a key role in defining operational, cultural, and workplace ethics. Here are some of the key aspects of the importance of strategic planning: 1. Provides a unified goal . A strategic plan is like a unified action plan for the whole company in order to achieve common outcomes.