
Statistics Made Easy

What is a Directional Hypothesis? (Definition & Examples)
A statistical hypothesis is an assumption about a population parameter . For example, we may assume that the mean height of a male in the U.S. is 70 inches.
The assumption about the height is the statistical hypothesis and the true mean height of a male in the U.S. is the population parameter .
To test whether a statistical hypothesis about a population parameter is true, we obtain a random sample from the population and perform a hypothesis test on the sample data.
Whenever we perform a hypothesis test, we always write down a null and alternative hypothesis:
- Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The sample data occurs purely from chance.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H A ): The sample data is influenced by some non-random cause.
A hypothesis test can either contain a directional hypothesis or a non-directional hypothesis:
- Directional hypothesis: The alternative hypothesis contains the less than (“<“) or greater than (“>”) sign. This indicates that we’re testing whether or not there is a positive or negative effect.
- Non-directional hypothesis: The alternative hypothesis contains the not equal (“≠”) sign. This indicates that we’re testing whether or not there is some effect, without specifying the direction of the effect.
Note that directional hypothesis tests are also called “one-tailed” tests and non-directional hypothesis tests are also called “two-tailed” tests.
Check out the following examples to gain a better understanding of directional vs. non-directional hypothesis tests.
Example 1: Baseball Programs
A baseball coach believes a certain 4-week program will increase the mean hitting percentage of his players, which is currently 0.285.
To test this, he measures the hitting percentage of each of his players before and after participating in the program.
He then performs a hypothesis test using the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ = .285 (the program will have no effect on the mean hitting percentage)
- H A : μ > .285 (the program will cause mean hitting percentage to increase)
This is an example of a directional hypothesis because the alternative hypothesis contains the greater than “>” sign. The coach believes that the program will influence the mean hitting percentage of his players in a positive direction.
Example 2: Plant Growth
A biologist believes that a certain pesticide will cause plants to grow less during a one-month period than they normally do, which is currently 10 inches.
To test this, she applies the pesticide to each of the plants in her laboratory for one month.
She then performs a hypothesis test using the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ = 10 inches (the pesticide will have no effect on the mean plant growth)
- H A : μ < 10 inches (the pesticide will cause mean plant growth to decrease)
This is also an example of a directional hypothesis because the alternative hypothesis contains the less than “<” sign. The biologist believes that the pesticide will influence the mean plant growth in a negative direction.
Example 3: Studying Technique
A professor believes that a certain studying technique will influence the mean score that her students receive on a certain exam, but she’s unsure if it will increase or decrease the mean score, which is currently 82.
To test this, she lets each student use the studying technique for one month leading up to the exam and then administers the same exam to each of the students.
- H 0 : μ = 82 (the studying technique will have no effect on the mean exam score)
- H A : μ ≠ 82 (the studying technique will cause the mean exam score to be different than 82)
This is an example of a non-directional hypothesis because the alternative hypothesis contains the not equal “≠” sign. The professor believes that the studying technique will influence the mean exam score, but doesn’t specify whether it will cause the mean score to increase or decrease.
Additional Resources
Introduction to Hypothesis Testing Introduction to the One Sample t-test Introduction to the Two Sample t-test Introduction to the Paired Samples t-test
Featured Posts

Hey there. My name is Zach Bobbitt. I have a Masters of Science degree in Applied Statistics and I’ve worked on machine learning algorithms for professional businesses in both healthcare and retail. I’m passionate about statistics, machine learning, and data visualization and I created Statology to be a resource for both students and teachers alike. My goal with this site is to help you learn statistics through using simple terms, plenty of real-world examples, and helpful illustrations.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Join the Statology Community
Sign up to receive Statology's exclusive study resource: 100 practice problems with step-by-step solutions. Plus, get our latest insights, tutorials, and data analysis tips straight to your inbox!
By subscribing you accept Statology's Privacy Policy.
Directional Hypothesis: Definition and 10 Examples
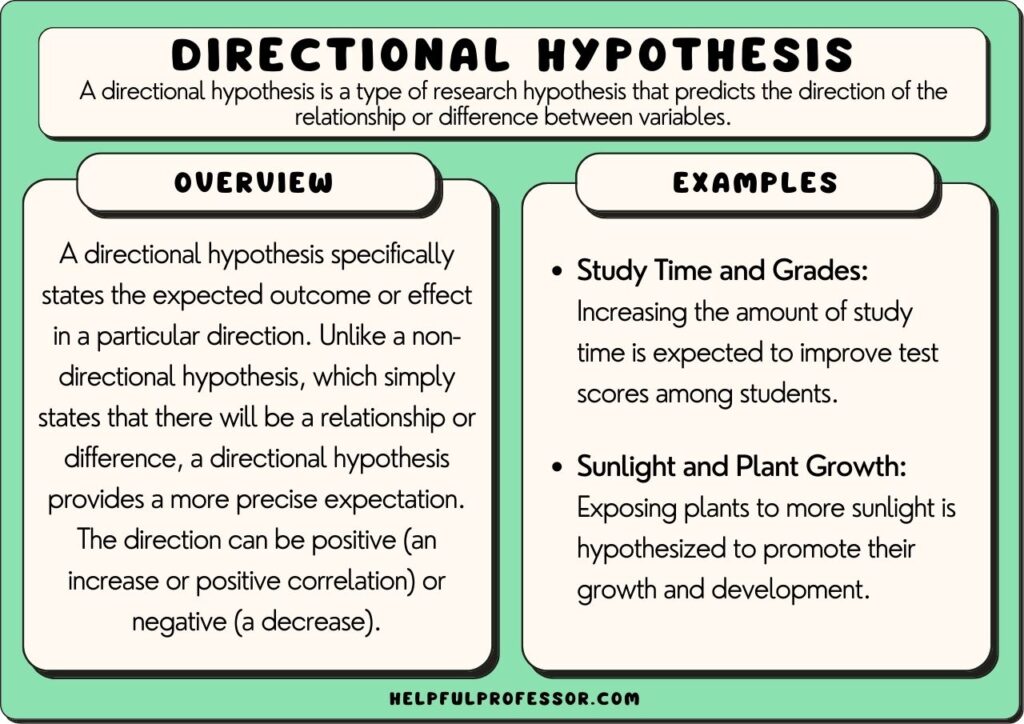
A directional hypothesis refers to a type of hypothesis used in statistical testing that predicts a particular direction of the expected relationship between two variables.
In simpler terms, a directional hypothesis is an educated, specific guess about the direction of an outcome—whether an increase, decrease, or a proclaimed difference in variable sets.
For example, in a study investigating the effects of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance, a directional hypothesis might state that as sleep deprivation (Independent Variable) increases, cognitive performance (Dependent Variable) decreases (Killgore, 2010). Such a hypothesis offers a clear, directional relationship whereby a specific increase or decrease is anticipated.
Global warming provides another notable example of a directional hypothesis. A researcher might hypothesize that as carbon dioxide (CO2) levels increase, global temperatures also increase (Thompson, 2010). In this instance, the hypothesis clearly articulates an upward trend for both variables.
In any given circumstance, it’s imperative that a directional hypothesis is grounded on solid evidence. For instance, the CO2 and global temperature relationship is based on substantial scientific evidence, and not on a random guess or mere speculation (Florides & Christodoulides, 2009).
Directional vs Non-Directional vs Null Hypotheses
A directional hypothesis is generally contrasted to a non-directional hypothesis. Here’s how they compare:
- Directional hypothesis: A directional hypothesis provides a perspective of the expected relationship between variables, predicting the direction of that relationship (either positive, negative, or a specific difference).
- Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis denotes the possibility of a relationship between two variables ( the independent and dependent variables ), although this hypothesis does not venture a prediction as to the direction of this relationship (Ali & Bhaskar, 2016). For example, a non-directional hypothesis might state that there exists a relationship between a person’s diet (independent variable) and their mood (dependent variable), without indicating whether improvement in diet enhances mood positively or negatively. Overall, the choice between a directional or non-directional hypothesis depends on the known or anticipated link between the variables under consideration in research studies.
Another very important type of hypothesis that we need to know about is a null hypothesis :
- Null hypothesis : The null hypothesis stands as a universality—the hypothesis that there is no observed effect in the population under study, meaning there is no association between variables (or that the differences are down to chance). For instance, a null hypothesis could be constructed around the idea that changing diet (independent variable) has no discernible effect on a person’s mood (dependent variable) (Yan & Su, 2016). This proposition is the one that we aim to disprove in an experiment.
While directional and non-directional hypotheses involve some integrated expectations about the outcomes (either distinct direction or a vague relationship), a null hypothesis operates on the premise of negating such relationships or effects.
The null hypotheses is typically proposed to be negated or disproved by statistical tests, paving way for the acceptance of an alternate hypothesis (either directional or non-directional).
Directional Hypothesis Examples
1. exercise and heart health.
Research suggests that as regular physical exercise (independent variable) increases, the risk of heart disease (dependent variable) decreases (Jakicic, Davis, Rogers, King, Marcus, Helsel, Rickman, Wahed, Belle, 2016). In this example, a directional hypothesis anticipates that the more individuals maintain routine workouts, the lesser would be their odds of developing heart-related disorders. This assumption is based on the underlying fact that routine exercise can help reduce harmful cholesterol levels, regulate blood pressure, and bring about overall health benefits. Thus, a direction – a decrease in heart disease – is expected in relation with an increase in exercise.
2. Screen Time and Sleep Quality
Another classic instance of a directional hypothesis can be seen in the relationship between the independent variable, screen time (especially before bed), and the dependent variable, sleep quality. This hypothesis predicts that as screen time before bed increases, sleep quality decreases (Chang, Aeschbach, Duffy, Czeisler, 2015). The reasoning behind this hypothesis is the disruptive effect of artificial light (especially blue light from screens) on melatonin production, a hormone needed to regulate sleep. As individuals spend more time exposed to screens before bed, it is predictably hypothesized that their sleep quality worsens.
3. Job Satisfaction and Employee Turnover
A typical scenario in organizational behavior research posits that as job satisfaction (independent variable) increases, the rate of employee turnover (dependent variable) decreases (Cheng, Jiang, & Riley, 2017). This directional hypothesis emphasizes that an increased level of job satisfaction would lead to a reduced rate of employees leaving the company. The theoretical basis for this hypothesis is that satisfied employees often tend to be more committed to the organization and are less likely to seek employment elsewhere, thus reducing turnover rates.
4. Healthy Eating and Body Weight
Healthy eating, as the independent variable, is commonly thought to influence body weight, the dependent variable, in a positive way. For example, the hypothesis might state that as consumption of healthy foods increases, an individual’s body weight decreases (Framson, Kristal, Schenk, Littman, Zeliadt, & Benitez, 2009). This projection is based on the premise that healthier foods, such as fruits and vegetables, are generally lower in calories than junk food, assisting in weight management.
5. Sun Exposure and Skin Health
The association between sun exposure (independent variable) and skin health (dependent variable) allows for a definitive hypothesis declaring that as sun exposure increases, the risk of skin damage or skin cancer increases (Whiteman, Whiteman, & Green, 2001). The premise aligns with the understanding that overexposure to the sun’s ultraviolet rays can deteriorate skin health, leading to conditions like sunburn or, in extreme cases, skin cancer.
6. Study Hours and Academic Performance
A regularly assessed relationship in academia suggests that as the number of study hours (independent variable) rises, so too does academic performance (dependent variable) (Nonis, Hudson, Logan, Ford, 2013). The hypothesis proposes a positive correlation , with an increase in study time expected to contribute to enhanced academic outcomes.
7. Screen Time and Eye Strain
It’s commonly hypothesized that as screen time (independent variable) increases, the likelihood of experiencing eye strain (dependent variable) also increases (Sheppard & Wolffsohn, 2018). This is based on the idea that prolonged engagement with digital screens—computers, tablets, or mobile phones—can cause discomfort or fatigue in the eyes, attributing to symptoms of eye strain.
8. Physical Activity and Stress Levels
In the sphere of mental health, it’s often proposed that as physical activity (independent variable) increases, levels of stress (dependent variable) decrease (Stonerock, Hoffman, Smith, Blumenthal, 2015). Regular exercise is known to stimulate the production of endorphins, the body’s natural mood elevators, helping to alleviate stress.
9. Water Consumption and Kidney Health
A common health-related hypothesis might predict that as water consumption (independent variable) increases, the risk of kidney stones (dependent variable) decreases (Curhan, Willett, Knight, & Stampfer, 2004). Here, an increase in water intake is inferred to reduce the risk of kidney stones by diluting the substances that lead to stone formation.
10. Traffic Noise and Sleep Quality
In urban planning research, it’s often supposed that as traffic noise (independent variable) increases, sleep quality (dependent variable) decreases (Muzet, 2007). Increased noise levels, particularly during the night, can result in sleep disruptions, thus, leading to poor sleep quality.
11. Sugar Consumption and Dental Health
In the field of dental health, an example might be stating as one’s sugar consumption (independent variable) increases, dental health (dependent variable) decreases (Sheiham, & James, 2014). This stems from the fact that sugar is a major factor in tooth decay, and increased consumption of sugary foods or drinks leads to a decline in dental health due to the high likelihood of cavities.
See 15 More Examples of Hypotheses Here
A directional hypothesis plays a critical role in research, paving the way for specific predicted outcomes based on the relationship between two variables. These hypotheses clearly illuminate the expected direction—the increase or decrease—of an effect. From predicting the impacts of healthy eating on body weight to forecasting the influence of screen time on sleep quality, directional hypotheses allow for targeted and strategic examination of phenomena. In essence, directional hypotheses provide the crucial path for inquiry, shaping the trajectory of research studies and ultimately aiding in the generation of insightful, relevant findings.
Ali, S., & Bhaskar, S. (2016). Basic statistical tools in research and data analysis. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia, 60 (9), 662-669. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103%2F0019-5049.190623
Chang, A. M., Aeschbach, D., Duffy, J. F., & Czeisler, C. A. (2015). Evening use of light-emitting eReaders negatively affects sleep, circadian timing, and next-morning alertness. Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences, 112 (4), 1232-1237. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1418490112
Cheng, G. H. L., Jiang, D., & Riley, J. H. (2017). Organizational commitment and intrinsic motivation of regular and contractual primary school teachers in China. New Psychology, 19 (3), 316-326. Doi: https://doi.org/10.4103%2F2249-4863.184631
Curhan, G. C., Willett, W. C., Knight, E. L., & Stampfer, M. J. (2004). Dietary factors and the risk of incident kidney stones in younger women: Nurses’ Health Study II. Archives of Internal Medicine, 164 (8), 885–891.
Florides, G. A., & Christodoulides, P. (2009). Global warming and carbon dioxide through sciences. Environment international , 35 (2), 390-401. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2008.07.007
Framson, C., Kristal, A. R., Schenk, J. M., Littman, A. J., Zeliadt, S., & Benitez, D. (2009). Development and validation of the mindful eating questionnaire. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 109 (8), 1439-1444. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2009.05.006
Jakicic, J. M., Davis, K. K., Rogers, R. J., King, W. C., Marcus, M. D., Helsel, D., … & Belle, S. H. (2016). Effect of wearable technology combined with a lifestyle intervention on long-term weight loss: The IDEA randomized clinical trial. JAMA, 316 (11), 1161-1171.
Khan, S., & Iqbal, N. (2013). Study of the relationship between study habits and academic achievement of students: A case of SPSS model. Higher Education Studies, 3 (1), 14-26.
Killgore, W. D. (2010). Effects of sleep deprivation on cognition. Progress in brain research , 185 , 105-129. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53702-7.00007-5
Marczinski, C. A., & Fillmore, M. T. (2014). Dissociative antagonistic effects of caffeine on alcohol-induced impairment of behavioral control. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 22 (4), 298–311. doi: https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/1064-1297.11.3.228
Muzet, A. (2007). Environmental Noise, Sleep and Health. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 11 (2), 135-142. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2006.09.001
Nonis, S. A., Hudson, G. I., Logan, L. B., & Ford, C. W. (2013). Influence of perceived control over time on college students’ stress and stress-related outcomes. Research in Higher Education, 54 (5), 536-552. doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018753706925
Sheiham, A., & James, W. P. (2014). A new understanding of the relationship between sugars, dental caries and fluoride use: implications for limits on sugars consumption. Public health nutrition, 17 (10), 2176-2184. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/S136898001400113X
Sheppard, A. L., & Wolffsohn, J. S. (2018). Digital eye strain: prevalence, measurement and amelioration. BMJ open ophthalmology , 3 (1), e000146. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjophth-2018-000146
Stonerock, G. L., Hoffman, B. M., Smith, P. J., & Blumenthal, J. A. (2015). Exercise as Treatment for Anxiety: Systematic Review and Analysis. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 49 (4), 542–556. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12160-014-9685-9
Thompson, L. G. (2010). Climate change: The evidence and our options. The Behavior Analyst , 33 , 153-170. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03392211
Whiteman, D. C., Whiteman, C. A., & Green, A. C. (2001). Childhood sun exposure as a risk factor for melanoma: a systematic review of epidemiologic studies. Cancer Causes & Control, 12 (1), 69-82. doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008980919928
Yan, X., & Su, X. (2009). Linear regression analysis: theory and computing . New Jersey: World Scientific.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Forest Schools Philosophy & Curriculum, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori's 4 Planes of Development, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori vs Reggio Emilia vs Steiner-Waldorf vs Froebel
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Parten’s 6 Stages of Play in Childhood, Explained!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Directional and non-directional hypothesis: A Comprehensive Guide
Karolina Konopka
Customer support manager
Want to talk with us?
In the world of research and statistical analysis, hypotheses play a crucial role in formulating and testing scientific claims. Understanding the differences between directional and non-directional hypothesis is essential for designing sound experiments and drawing accurate conclusions. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or simply curious about the foundations of hypothesis testing, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to navigate this fundamental aspect of scientific inquiry.
Understanding Directional Hypothesis
Understanding directional hypotheses is crucial for conducting hypothesis-driven research, as they guide the selection of appropriate statistical tests and aid in the interpretation of results. By incorporating directional hypotheses, researchers can make more precise predictions, contribute to scientific knowledge, and advance their fields of study.
Definition of directional hypothesis
Directional hypotheses, also known as one-tailed hypotheses, are statements in research that make specific predictions about the direction of a relationship or difference between variables. Unlike non-directional hypotheses, which simply state that there is a relationship or difference without specifying its direction, directional hypotheses provide a focused and precise expectation.
A directional hypothesis predicts either a positive or negative relationship between variables or predicts that one group will perform better than another. It asserts a specific direction of effect or outcome. For example, a directional hypothesis could state that “increased exposure to sunlight will lead to an improvement in mood” or “participants who receive the experimental treatment will exhibit higher levels of cognitive performance compared to the control group.”
Directional hypotheses are formulated based on existing theory, prior research, or logical reasoning, and they guide the researcher’s expectations and analysis. They allow for more targeted predictions and enable researchers to test specific hypotheses using appropriate statistical tests.
The role of directional hypothesis in research
Directional hypotheses also play a significant role in research surveys. Let’s explore their role specifically in the context of survey research:
- Objective-driven surveys : Directional hypotheses help align survey research with specific objectives. By formulating directional hypotheses, researchers can focus on gathering data that directly addresses the predicted relationship or difference between variables of interest.
- Question design and measurement : Directional hypotheses guide the design of survey question types and the selection of appropriate measurement scales. They ensure that the questions are tailored to capture the specific aspects related to the predicted direction, enabling researchers to obtain more targeted and relevant data from survey respondents.
- Data analysis and interpretation : Directional hypotheses assist in data analysis by directing researchers towards appropriate statistical tests and methods. Researchers can analyze the survey data to specifically test the predicted relationship or difference, enhancing the accuracy and reliability of their findings. The results can then be interpreted within the context of the directional hypothesis, providing more meaningful insights.
- Practical implications and decision-making : Directional hypotheses in surveys often have practical implications. When the predicted relationship or difference is confirmed, it informs decision-making processes, program development, or interventions. The survey findings based on directional hypotheses can guide organizations, policymakers, or practitioners in making informed choices to achieve desired outcomes.
- Replication and further research : Directional hypotheses in survey research contribute to the replication and extension of studies. Researchers can replicate the survey with different populations or contexts to assess the generalizability of the predicted relationships. Furthermore, if the directional hypothesis is supported, it encourages further research to explore underlying mechanisms or boundary conditions.
By incorporating directional hypotheses in survey research, researchers can align their objectives, design effective surveys, conduct focused data analysis, and derive practical insights. They provide a framework for organizing survey research and contribute to the accumulation of knowledge in the field.
Examples of research questions for directional hypothesis
Here are some examples of research questions that lend themselves to directional hypotheses:
- Does increased daily exercise lead to a decrease in body weight among sedentary adults?
- Is there a positive relationship between study hours and academic performance among college students?
- Does exposure to violent video games result in an increase in aggressive behavior among adolescents?
- Does the implementation of a mindfulness-based intervention lead to a reduction in stress levels among working professionals?
- Is there a difference in customer satisfaction between Product A and Product B, with Product A expected to have higher satisfaction ratings?
- Does the use of social media influence self-esteem levels, with higher social media usage associated with lower self-esteem?
- Is there a negative relationship between job satisfaction and employee turnover, indicating that lower job satisfaction leads to higher turnover rates?
- Does the administration of a specific medication result in a decrease in symptoms among individuals with a particular medical condition?
- Does increased access to early childhood education lead to improved cognitive development in preschool-aged children?
- Is there a difference in purchase intention between advertisements with celebrity endorsements and advertisements without, with celebrity endorsements expected to have a higher impact?
These research questions generate specific predictions about the direction of the relationship or difference between variables and can be tested using appropriate research methods and statistical analyses.
Definition of non-directional hypothesis
Non-directional hypotheses, also known as two-tailed hypotheses, are statements in research that indicate the presence of a relationship or difference between variables without specifying the direction of the effect. Instead of making predictions about the specific direction of the relationship or difference, non-directional hypotheses simply state that there is an association or distinction between the variables of interest.
Non-directional hypotheses are often used when there is no prior theoretical basis or clear expectation about the direction of the relationship. They leave the possibility open for either a positive or negative relationship, or for both groups to differ in some way without specifying which group will perform better or worse.
Advantages and utility of non-directional hypothesis
Non-directional hypotheses in survey s offer several advantages and utilities, providing flexibility and comprehensive analysis of survey data. Here are some of the key advantages and utilities of using non-directional hypotheses in surveys:
- Exploration of Relationships : Non-directional hypotheses allow researchers to explore and examine relationships between variables without assuming a specific direction. This is particularly useful in surveys where the relationship between variables may not be well-known or there may be conflicting evidence regarding the direction of the effect.
- Flexibility in Question Design : With non-directional hypotheses, survey questions can be designed to measure the relationship between variables without being biased towards a particular outcome. This flexibility allows researchers to collect data and analyze the results more objectively.
- Open to Unexpected Findings : Non-directional hypotheses enable researchers to be open to unexpected or surprising findings in survey data. By not committing to a specific direction of the effect, researchers can identify and explore relationships that may not have been initially anticipated, leading to new insights and discoveries.
- Comprehensive Analysis : Non-directional hypotheses promote comprehensive analysis of survey data by considering the possibility of an effect in either direction. Researchers can assess the magnitude and significance of relationships without limiting their analysis to only one possible outcome.
- S tatistical Validity : Non-directional hypotheses in surveys allow for the use of two-tailed statistical tests, which provide a more conservative and robust assessment of significance. Two-tailed tests consider both positive and negative deviations from the null hypothesis, ensuring accurate and reliable statistical analysis of survey data.
- Exploratory Research : Non-directional hypotheses are particularly useful in exploratory research, where the goal is to gather initial insights and generate hypotheses. Surveys with non-directional hypotheses can help researchers explore various relationships and identify patterns that can guide further research or hypothesis development.
It is worth noting that the choice between directional and non-directional hypotheses in surveys depends on the research objectives, existing knowledge, and the specific variables being investigated. Researchers should carefully consider the advantages and limitations of each approach and select the one that aligns best with their research goals and survey design.
- Share with others
- Twitter Twitter Icon
- LinkedIn LinkedIn Icon
Related posts
How to implement nps surveys: a step-by-step guide, 15 best website survey questions to ask your visitors, how to write a good survey introduction, 7 best ai survey generators, multiple choice questions: types, examples & samples, how to make a gdpr compliant survey, get answers today.
- No credit card required
- No time limit on Free plan
You can modify this template in every possible way.
All templates work great on every device.

How to Write a Directional Hypothesis: A Step-by-Step Guide

In research, hypotheses play a crucial role in guiding investigations and making predictions about relationships between variables.
One type of hypothesis that researchers often encounter is the directional hypothesis, also known as a one-tailed hypothesis.
In this blog post, we’ll explore what a directional hypothesis is, why it’s important, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to write one effectively.
Table of Contents
What is a Directional Hypothesis?
A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between two variables. Unlike non-directional hypotheses, which simply state that there is a relationship between variables without specifying the direction, directional hypotheses make a clear prediction about the expected outcome.
For example, a directional hypothesis might predict that an increase in one variable will lead to a decrease in another.
Examples of Directional Hypotheses
- Increasing the amount of sunlight exposure will lead to higher levels of vitamin D in the body.
- Decreasing the amount of sugar consumption will result in lower body weight among participants.
- Introducing mindfulness meditation techniques will reduce symptoms of anxiety in patients with generalized anxiety disorder.
Why to Write a Directional Hypothesis?
Directional hypotheses offer several advantages in research. They provide researchers with a more focused prediction, allowing them to test specific hypotheses rather than exploring all possible relationships between variables.
This can help streamline research efforts and increase the likelihood of finding meaningful results. Additionally, directional hypotheses are often used in experimental research, where researchers manipulate variables to observe their effects on outcomes.
Step 1: Identify the Variables
Start by identifying the independent variable (the variable you are manipulating) and the dependent variable (the variable you are measuring). Understanding the relationship between these variables is essential for writing a directional hypothesis.
Step 2: Predict the Direction
Based on your understanding of the relationship between the variables, predict the direction of the effect.
Will an increase in the independent variable lead to an increase or decrease in the dependent variable?
Be specific in your prediction.
Step 3: Use Clear Language
Write your directional hypothesis using clear and concise language. Avoid technical jargon or terms that may be difficult for readers to understand. Your hypothesis should be easily understood by both researchers and non-experts.
Step 4: Ensure Testability
Ensure that your hypothesis is testable by collecting data and conducting statistical analysis. You should be able to measure the variables and determine whether the observed results support or refute your hypothesis.
Step 5: Revise and Refine
Review your directional hypothesis to ensure that it accurately reflects your research question and predictions. Make any necessary revisions to improve clarity and specificity.
Writing a directional hypothesis is an essential skill for researchers conducting experiments and investigations.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can effectively formulate hypotheses that make clear predictions about the relationship between variables.
Whether you’re a researcher or just starting out in the field, mastering the art of writing directional hypotheses will enhance the quality and rigor of your research endeavors.
Related Posts
How to write a conclusion for research paper | examples, six useful tips for finding research gap, example of abstract for your research paper: tips, dos, and don’ts, survey sampling: what it is, types & tips, cluster sampling | method and examples, advantages and disadvantages of snowball sampling, exploring qualitative researcher skills: what they are and how to develop them, difference between quota sampling and stratified sampling, what is purposive sampling | examples, quota sampling in research.
Comments are closed.
Research Hypothesis In Psychology: Types, & Examples
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A research hypothesis, in its plural form “hypotheses,” is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method .
Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding
Some key points about hypotheses:
- A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
- It is stated in clear, precise terms before any data collection or analysis occurs. This makes the hypothesis testable.
- A hypothesis must be falsifiable. It should be possible, even if unlikely in practice, to collect data that disconfirms rather than supports the hypothesis.
- Hypotheses guide research. Scientists design studies to explicitly evaluate hypotheses about how nature works.
- For a hypothesis to be valid, it must be testable against empirical evidence. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
- Hypotheses are informed by background knowledge and observation, but go beyond what is already known to propose an explanation of how or why something occurs.
Predictions typically arise from a thorough knowledge of the research literature, curiosity about real-world problems or implications, and integrating this to advance theory. They build on existing literature while providing new insight.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Alternative hypothesis.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative or experimental hypothesis in experimental research.
It typically suggests a potential relationship between two key variables: the independent variable, which the researcher manipulates, and the dependent variable, which is measured based on those changes.
The alternative hypothesis states a relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable affects the other).
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses:
- Important hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested empirically. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
In summary, a hypothesis is a precise, testable statement of what researchers expect to happen in a study and why. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and are significant in supporting the theory being investigated.
The alternative hypothesis can be directional, indicating a specific direction of the effect, or non-directional, suggesting a difference without specifying its nature. It’s what researchers aim to support or demonstrate through their study.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable.
It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The null hypothesis, positing no effect or relationship, is a foundational contrast to the research hypothesis in scientific inquiry. It establishes a baseline for statistical testing, promoting objectivity by initiating research from a neutral stance.
Many statistical methods are tailored to test the null hypothesis, determining the likelihood of observed results if no true effect exists.
This dual-hypothesis approach provides clarity, ensuring that research intentions are explicit, and fosters consistency across scientific studies, enhancing the standardization and interpretability of research outcomes.
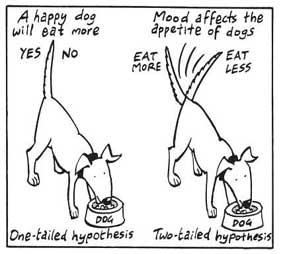
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of this relationship.
It merely indicates that a change or effect will occur without predicting which group will have higher or lower values.
For example, “There is a difference in performance between Group A and Group B” is a non-directional hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional (one-tailed) hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It predicts in which direction the change will take place. (i.e., greater, smaller, less, more)
It specifies whether one variable is greater, lesser, or different from another, rather than just indicating that there’s a difference without specifying its nature.
For example, “Exercise increases weight loss” is a directional hypothesis.
Falsifiability
The Falsification Principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory or hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable and irrefutable.
Falsifiability emphasizes that scientific claims shouldn’t just be confirmable but should also have the potential to be proven wrong.
It means that there should exist some potential evidence or experiment that could prove the proposition false.
However many confirming instances exist for a theory, it only takes one counter observation to falsify it. For example, the hypothesis that “all swans are white,” can be falsified by observing a black swan.
For Popper, science should attempt to disprove a theory rather than attempt to continually provide evidence to support a research hypothesis.
Can a Hypothesis be Proven?
Hypotheses make probabilistic predictions. They state the expected outcome if a particular relationship exists. However, a study result supporting a hypothesis does not definitively prove it is true.
All studies have limitations. There may be unknown confounding factors or issues that limit the certainty of conclusions. Additional studies may yield different results.
In science, hypotheses can realistically only be supported with some degree of confidence, not proven. The process of science is to incrementally accumulate evidence for and against hypothesized relationships in an ongoing pursuit of better models and explanations that best fit the empirical data. But hypotheses remain open to revision and rejection if that is where the evidence leads.
- Disproving a hypothesis is definitive. Solid disconfirmatory evidence will falsify a hypothesis and require altering or discarding it based on the evidence.
- However, confirming evidence is always open to revision. Other explanations may account for the same results, and additional or contradictory evidence may emerge over time.
We can never 100% prove the alternative hypothesis. Instead, we see if we can disprove, or reject the null hypothesis.
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct but does support the alternative/experimental hypothesis.
Upon analysis of the results, an alternative hypothesis can be rejected or supported, but it can never be proven to be correct. We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist which could refute a theory.
How to Write a Hypothesis
- Identify variables . The researcher manipulates the independent variable and the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
- Operationalized the variables being investigated . Operationalization of a hypothesis refers to the process of making the variables physically measurable or testable, e.g. if you are about to study aggression, you might count the number of punches given by participants.
- Decide on a direction for your prediction . If there is evidence in the literature to support a specific effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a directional (one-tailed) hypothesis. If there are limited or ambiguous findings in the literature regarding the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.
- Make it Testable : Ensure your hypothesis can be tested through experimentation or observation. It should be possible to prove it false (principle of falsifiability).
- Clear & concise language . A strong hypothesis is concise (typically one to two sentences long), and formulated using clear and straightforward language, ensuring it’s easily understood and testable.
Consider a hypothesis many teachers might subscribe to: students work better on Monday morning than on Friday afternoon (IV=Day, DV= Standard of work).
Now, if we decide to study this by giving the same group of students a lesson on a Monday morning and a Friday afternoon and then measuring their immediate recall of the material covered in each session, we would end up with the following:
- The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
- The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors.
More Examples
- Memory : Participants exposed to classical music during study sessions will recall more items from a list than those who studied in silence.
- Social Psychology : Individuals who frequently engage in social media use will report higher levels of perceived social isolation compared to those who use it infrequently.
- Developmental Psychology : Children who engage in regular imaginative play have better problem-solving skills than those who don’t.
- Clinical Psychology : Cognitive-behavioral therapy will be more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety over a 6-month period compared to traditional talk therapy.
- Cognitive Psychology : Individuals who multitask between various electronic devices will have shorter attention spans on focused tasks than those who single-task.
- Health Psychology : Patients who practice mindfulness meditation will experience lower levels of chronic pain compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Organizational Psychology : Employees in open-plan offices will report higher levels of stress than those in private offices.
- Behavioral Psychology : Rats rewarded with food after pressing a lever will press it more frequently than rats who receive no reward.
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
The Research Hypothesis: Role and Construction
- First Online: 01 January 2012
Cite this chapter

- Phyllis G. Supino EdD 3
6024 Accesses
A hypothesis is a logical construct, interposed between a problem and its solution, which represents a proposed answer to a research question. It gives direction to the investigator’s thinking about the problem and, therefore, facilitates a solution. There are three primary modes of inference by which hypotheses are developed: deduction (reasoning from a general propositions to specific instances), induction (reasoning from specific instances to a general proposition), and abduction (formulation/acceptance on probation of a hypothesis to explain a surprising observation).
A research hypothesis should reflect an inference about variables; be stated as a grammatically complete, declarative sentence; be expressed simply and unambiguously; provide an adequate answer to the research problem; and be testable. Hypotheses can be classified as conceptual versus operational, single versus bi- or multivariable, causal or not causal, mechanistic versus nonmechanistic, and null or alternative. Hypotheses most commonly entail statements about “variables” which, in turn, can be classified according to their level of measurement (scaling characteristics) or according to their role in the hypothesis (independent, dependent, moderator, control, or intervening).
A hypothesis is rendered operational when its broadly (conceptually) stated variables are replaced by operational definitions of those variables. Hypotheses stated in this manner are called operational hypotheses, specific hypotheses, or predictions and facilitate testing.
Wrong hypotheses, rightly worked from, have produced more results than unguided observation
—Augustus De Morgan, 1872[ 1 ]—
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
De Morgan A, De Morgan S. A budget of paradoxes. London: Longmans Green; 1872.
Google Scholar
Leedy Paul D. Practical research. Planning and design. 2nd ed. New York: Macmillan; 1960.
Bernard C. Introduction to the study of experimental medicine. New York: Dover; 1957.
Erren TC. The quest for questions—on the logical force of science. Med Hypotheses. 2004;62:635–40.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Peirce CS. Collected papers of Charles Sanders Peirce, vol. 7. In: Hartshorne C, Weiss P, editors. Boston: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press; 1966.
Aristotle. The complete works of Aristotle: the revised Oxford Translation. In: Barnes J, editor. vol. 2. Princeton/New Jersey: Princeton University Press; 1984.
Polit D, Beck CT. Conceptualizing a study to generate evidence for nursing. In: Polit D, Beck CT, editors. Nursing research: generating and assessing evidence for nursing practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2008. Chapter 4.
Jenicek M, Hitchcock DL. Evidence-based practice. Logic and critical thinking in medicine. Chicago: AMA Press; 2005.
Bacon F. The novum organon or a true guide to the interpretation of nature. A new translation by the Rev G.W. Kitchin. Oxford: The University Press; 1855.
Popper KR. Objective knowledge: an evolutionary approach (revised edition). New York: Oxford University Press; 1979.
Morgan AJ, Parker S. Translational mini-review series on vaccines: the Edward Jenner Museum and the history of vaccination. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007;147:389–94.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Pead PJ. Benjamin Jesty: new light in the dawn of vaccination. Lancet. 2003;362:2104–9.
Lee JA. The scientific endeavor: a primer on scientific principles and practice. San Francisco: Addison-Wesley Longman; 2000.
Allchin D. Lawson’s shoehorn, or should the philosophy of science be rated, ‘X’? Science and Education. 2003;12:315–29.
Article Google Scholar
Lawson AE. What is the role of induction and deduction in reasoning and scientific inquiry? J Res Sci Teach. 2005;42:716–40.
Peirce CS. Collected papers of Charles Sanders Peirce, vol. 2. In: Hartshorne C, Weiss P, editors. Boston: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press; 1965.
Bonfantini MA, Proni G. To guess or not to guess? In: Eco U, Sebeok T, editors. The sign of three: Dupin, Holmes, Peirce. Bloomington: Indiana University Press; 1983. Chapter 5.
Peirce CS. Collected papers of Charles Sanders Peirce, vol. 5. In: Hartshorne C, Weiss P, editors. Boston: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press; 1965.
Flach PA, Kakas AC. Abductive and inductive reasoning: background issues. In: Flach PA, Kakas AC, editors. Abduction and induction. Essays on their relation and integration. The Netherlands: Klewer; 2000. Chapter 1.
Murray JF. Voltaire, Walpole and Pasteur: variations on the theme of discovery. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172:423–6.
Danemark B, Ekstrom M, Jakobsen L, Karlsson JC. Methodological implications, generalization, scientific inference, models (Part II) In: explaining society. Critical realism in the social sciences. New York: Routledge; 2002.
Pasteur L. Inaugural lecture as professor and dean of the faculty of sciences. In: Peterson H, editor. A treasury of the world’s greatest speeches. Douai, France: University of Lille 7 Dec 1954.
Swineburne R. Simplicity as evidence for truth. Milwaukee: Marquette University Press; 1997.
Sakar S, editor. Logical empiricism at its peak: Schlick, Carnap and Neurath. New York: Garland; 1996.
Popper K. The logic of scientific discovery. New York: Basic Books; 1959. 1934, trans. 1959.
Caws P. The philosophy of science. Princeton: D. Van Nostrand Company; 1965.
Popper K. Conjectures and refutations. The growth of scientific knowledge. 4th ed. London: Routledge and Keegan Paul; 1972.
Feyerabend PK. Against method, outline of an anarchistic theory of knowledge. London, UK: Verso; 1978.
Smith PG. Popper: conjectures and refutations (Chapter IV). In: Theory and reality: an introduction to the philosophy of science. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 2003.
Blystone RV, Blodgett K. WWW: the scientific method. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2006;5:7–11.
Kleinbaum DG, Kupper LL, Morgenstern H. Epidemiological research. Principles and quantitative methods. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold; 1982.
Fortune AE, Reid WJ. Research in social work. 3rd ed. New York: Columbia University Press; 1999.
Kerlinger FN. Foundations of behavioral research. 1st ed. New York: Hold, Reinhart and Winston; 1970.
Hoskins CN, Mariano C. Research in nursing and health. Understanding and using quantitative and qualitative methods. New York: Springer; 2004.
Tuckman BW. Conducting educational research. New York: Harcourt, Brace, Jovanovich; 1972.
Wang C, Chiari PC, Weihrauch D, Krolikowski JG, Warltier DC, Kersten JR, Pratt Jr PF, Pagel PS. Gender-specificity of delayed preconditioning by isoflurane in rabbits: potential role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Anesth Analg. 2006;103:274–80.
Beyer ME, Slesak G, Nerz S, Kazmaier S, Hoffmeister HM. Effects of endothelin-1 and IRL 1620 on myocardial contractility and myocardial energy metabolism. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1995;26(Suppl 3):S150–2.
PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Stone J, Sharpe M. Amnesia for childhood in patients with unexplained neurological symptoms. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002;72:416–7.
Naughton BJ, Moran M, Ghaly Y, Michalakes C. Computer tomography scanning and delirium in elder patients. Acad Emerg Med. 1997;4:1107–10.
Easterbrook PJ, Berlin JA, Gopalan R, Matthews DR. Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet. 1991;337:867–72.
Stern JM, Simes RJ. Publication bias: evidence of delayed publication in a cohort study of clinical research projects. BMJ. 1997;315:640–5.
Stevens SS. On the theory of scales and measurement. Science. 1946;103:677–80.
Knapp TR. Treating ordinal scales as interval scales: an attempt to resolve the controversy. Nurs Res. 1990;39:121–3.
The Cochrane Collaboration. Open Learning Material. www.cochrane-net.org/openlearning/html/mod14-3.htm . Accessed 12 Oct 2009.
MacCorquodale K, Meehl PE. On a distinction between hypothetical constructs and intervening variables. Psychol Rev. 1948;55:95–107.
Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1986;51:1173–82.
Williamson GM, Schultz R. Activity restriction mediates the association between pain and depressed affect: a study of younger and older adult cancer patients. Psychol Aging. 1995;10:369–78.
Song M, Lee EO. Development of a functional capacity model for the elderly. Res Nurs Health. 1998;21:189–98.
MacKinnon DP. Introduction to statistical mediation analysis. New York: Routledge; 2008.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Medicine, College of Medicine, SUNY Downstate Medical Center, 450 Clarkson Avenue, 1199, Brooklyn, NY, 11203, USA
Phyllis G. Supino EdD
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Phyllis G. Supino EdD .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
, Cardiovascular Medicine, SUNY Downstate Medical Center, Clarkson Avenue, box 1199 450, Brooklyn, 11203, USA
Phyllis G. Supino
, Cardiovascualr Medicine, SUNY Downstate Medical Center, Clarkson Avenue 450, Brooklyn, 11203, USA
Jeffrey S. Borer
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Supino, P.G. (2012). The Research Hypothesis: Role and Construction. In: Supino, P., Borer, J. (eds) Principles of Research Methodology. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3360-6_3
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3360-6_3
Published : 18 April 2012
Publisher Name : Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN : 978-1-4614-3359-0
Online ISBN : 978-1-4614-3360-6
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
5.2 - writing hypotheses.
The first step in conducting a hypothesis test is to write the hypothesis statements that are going to be tested. For each test you will have a null hypothesis (\(H_0\)) and an alternative hypothesis (\(H_a\)).
When writing hypotheses there are three things that we need to know: (1) the parameter that we are testing (2) the direction of the test (non-directional, right-tailed or left-tailed), and (3) the value of the hypothesized parameter.
- At this point we can write hypotheses for a single mean (\(\mu\)), paired means(\(\mu_d\)), a single proportion (\(p\)), the difference between two independent means (\(\mu_1-\mu_2\)), the difference between two proportions (\(p_1-p_2\)), a simple linear regression slope (\(\beta\)), and a correlation (\(\rho\)).
- The research question will give us the information necessary to determine if the test is two-tailed (e.g., "different from," "not equal to"), right-tailed (e.g., "greater than," "more than"), or left-tailed (e.g., "less than," "fewer than").
- The research question will also give us the hypothesized parameter value. This is the number that goes in the hypothesis statements (i.e., \(\mu_0\) and \(p_0\)). For the difference between two groups, regression, and correlation, this value is typically 0.
Hypotheses are always written in terms of population parameters (e.g., \(p\) and \(\mu\)). The tables below display all of the possible hypotheses for the parameters that we have learned thus far. Note that the null hypothesis always includes the equality (i.e., =).

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

7.3: The Research Hypothesis and the Null Hypothesis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 18038

- Michelle Oja
- Taft College
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Hypotheses are predictions of expected findings.
The Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is a mathematical way of stating a research question. A research hypothesis names the groups (we'll start with a sample and a population), what was measured, and which we think will have a higher mean. The last one gives the research hypothesis a direction. In other words, a research hypothesis should include:
- The name of the groups being compared. This is sometimes considered the IV.
- What was measured. This is the DV.
- Which group are we predicting will have the higher mean.
There are two types of research hypotheses related to sample means and population means: Directional Research Hypotheses and Non-Directional Research Hypotheses
Directional Research Hypothesis
If we expect our obtained sample mean to be above or below the other group's mean (the population mean, for example), we have a directional hypothesis. There are two options:
- Symbol: \( \displaystyle \bar{X} > \mu \)
- (The mean of the sample is greater than than the mean of the population.)
- Symbol: \( \displaystyle \bar{X} < \mu \)
- (The mean of the sample is less than than mean of the population.)
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
A study by Blackwell, Trzesniewski, and Dweck (2007) measured growth mindset and how long the junior high student participants spent on their math homework. What’s a directional hypothesis for how scoring higher on growth mindset (compared to the population of junior high students) would be related to how long students spent on their homework? Write this out in words and symbols.
Answer in Words: Students who scored high on growth mindset would spend more time on their homework than the population of junior high students.
Answer in Symbols: \( \displaystyle \bar{X} > \mu \)
Non-Directional Research Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis states that the means will be different, but does not specify which will be higher. In reality, there is rarely a situation in which we actually don't want one group to be higher than the other, so we will focus on directional research hypotheses. There is only one option for a non-directional research hypothesis: "The sample mean differs from the population mean." These types of research hypotheses don’t give a direction, the hypothesis doesn’t say which will be higher or lower.
A non-directional research hypothesis in symbols should look like this: \( \displaystyle \bar{X} \neq \mu \) (The mean of the sample is not equal to the mean of the population).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
What’s a non-directional hypothesis for how scoring higher on growth mindset higher on growth mindset (compared to the population of junior high students) would be related to how long students spent on their homework (Blackwell, Trzesniewski, & Dweck, 2007)? Write this out in words and symbols.
Answer in Words: Students who scored high on growth mindset would spend a different amount of time on their homework than the population of junior high students.
Answer in Symbols: \( \displaystyle \bar{X} \neq \mu \)
See how a non-directional research hypothesis doesn't really make sense? The big issue is not if the two groups differ, but if one group seems to improve what was measured (if having a growth mindset leads to more time spent on math homework). This textbook will only use directional research hypotheses because researchers almost always have a predicted direction (meaning that we almost always know which group we think will score higher).
The Null Hypothesis
The hypothesis that an apparent effect is due to chance is called the null hypothesis, written \(H_0\) (“H-naught”). We usually test this through comparing an experimental group to a comparison (control) group. This null hypothesis can be written as:
\[\mathrm{H}_{0}: \bar{X} = \mu \nonumber \]
For most of this textbook, the null hypothesis is that the means of the two groups are similar. Much later, the null hypothesis will be that there is no relationship between the two groups. Either way, remember that a null hypothesis is always saying that nothing is different.
This is where descriptive statistics diverge from inferential statistics. We know what the value of \(\overline{\mathrm{X}}\) is – it’s not a mystery or a question, it is what we observed from the sample. What we are using inferential statistics to do is infer whether this sample's descriptive statistics probably represents the population's descriptive statistics. This is the null hypothesis, that the two groups are similar.
Keep in mind that the null hypothesis is typically the opposite of the research hypothesis. A research hypothesis for the ESP example is that those in my sample who say that they have ESP would get more correct answers than the population would get correct, while the null hypothesis is that the average number correct for the two groups will be similar.
In general, the null hypothesis is the idea that nothing is going on: there is no effect of our treatment, no relation between our variables, and no difference in our sample mean from what we expected about the population mean. This is always our baseline starting assumption, and it is what we seek to reject. If we are trying to treat depression, we want to find a difference in average symptoms between our treatment and control groups. If we are trying to predict job performance, we want to find a relation between conscientiousness and evaluation scores. However, until we have evidence against it, we must use the null hypothesis as our starting point.
In sum, the null hypothesis is always : There is no difference between the groups’ means OR There is no relationship between the variables .
In the next chapter, the null hypothesis is that there’s no difference between the sample mean and population mean. In other words:
- There is no mean difference between the sample and population.
- The mean of the sample is the same as the mean of a specific population.
- \(\mathrm{H}_{0}: \bar{X} = \mu \nonumber \)
- We expect our sample’s mean to be same as the population mean.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
A study by Blackwell, Trzesniewski, and Dweck (2007) measured growth mindset and how long the junior high student participants spent on their math homework. What’s the null hypothesis for scoring higher on growth mindset (compared to the population of junior high students) and how long students spent on their homework? Write this out in words and symbols.
Answer in Words: Students who scored high on growth mindset would spend a similar amount of time on their homework as the population of junior high students.
Answer in Symbols: \( \bar{X} = \mu \)
Contributors and Attributions
Foster et al. (University of Missouri-St. Louis, Rice University, & University of Houston, Downtown Campus)
Dr. MO ( Taft College )
psychologyrocks
Hypotheses; directional and non-directional, what is the difference between an experimental and an alternative hypothesis.
Nothing much! If the study is a laboratory experiment then we can call the hypothesis “an experimental hypothesis”, where we make a prediction about how the IV causes an effect on the DV. If we have a non-experimental design, i.e. we are not able to manipulate the IV as in a natural or quasi-experiment , or if some other research method has been used, then we call it an “alternativehypothesis”, alternative to the null.
Directional hypothesis: A directional (or one tailed hypothesis) states which way you think the results are going to go, for example in an experimental study we might say…”Participants who have been deprived of sleep for 24 hours will have more cold symptoms in the following week after exposure to a virus than participants who have not been sleep deprived”; the hypothesis compares the two groups/conditions and states which one will ….have more/less, be quicker/slower, etc.
If we had a correlational study, the directional hypothesis would state whether we expect a positive or a negative correlation, we are stating how the two variables will be related to each other, e.g. there will be a positive correlation between the number of stressful life events experienced in the last year and the number of coughs and colds suffered, whereby the more life events you have suffered the more coughs and cold you will have had”. The directional hypothesis can also state a negative correlation, e.g. the higher the number of face-book friends, the lower the life satisfaction score “
Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional (or two tailed hypothesis) simply states that there will be a difference between the two groups/conditions but does not say which will be greater/smaller, quicker/slower etc. Using our example above we would say “There will be a difference between the number of cold symptoms experienced in the following week after exposure to a virus for those participants who have been sleep deprived for 24 hours compared with those who have not been sleep deprived for 24 hours.”
When the study is correlational, we simply state that variables will be correlated but do not state whether the relationship will be positive or negative, e.g. there will be a significant correlation between variable A and variable B.
Null hypothesis The null hypothesis states that the alternative or experimental hypothesis is NOT the case, if your experimental hypothesis was directional you would say…
Participants who have been deprived of sleep for 24 hours will NOT have more cold symptoms in the following week after exposure to a virus than participants who have not been sleep deprived and any difference that does arise will be due to chance alone.
or with a directional correlational hypothesis….
There will NOT be a positive correlation between the number of stress life events experienced in the last year and the number of coughs and colds suffered, whereby the more life events you have suffered the more coughs and cold you will have had”
With a non-directional or two tailed hypothesis…
There will be NO difference between the number of cold symptoms experienced in the following week after exposure to a virus for those participants who have been sleep deprived for 24 hours compared with those who have not been sleep deprived for 24 hours.
or for a correlational …
there will be NO correlation between variable A and variable B.
When it comes to conducting an inferential stats test, if you have a directional hypothesis , you must do a one tailed test to find out whether your observed value is significant. If you have a non-directional hypothesis , you must do a two tailed test .
Exam Techniques/Advice
- Remember, a decent hypothesis will contain two variables, in the case of an experimental hypothesis there will be an IV and a DV; in a correlational hypothesis there will be two co-variables
- both variables need to be fully operationalised to score the marks, that is you need to be very clear and specific about what you mean by your IV and your DV; if someone wanted to repeat your study, they should be able to look at your hypothesis and know exactly what to change between the two groups/conditions and exactly what to measure (including any units/explanation of rating scales etc, e.g. “where 1 is low and 7 is high”)
- double check the question, did it ask for a directional or non-directional hypothesis?
- if you were asked for a null hypothesis, make sure you always include the phrase “and any difference/correlation (is your study experimental or correlational?) that does arise will be due to chance alone”
Practice Questions:
- Mr Faraz wants to compare the levels of attendance between his psychology group and those of Mr Simon, who teaches a different psychology group. Which of the following is a suitable directional (one tailed) hypothesis for Mr Faraz’s investigation?
A There will be a difference in the levels of attendance between the two psychology groups.
B Students’ level of attendance will be higher in Mr Faraz’s group than Mr Simon’s group.
C Any difference in the levels of attendance between the two psychology groups is due to chance.
D The level of attendance of the students will depend upon who is teaching the groups.
2. Tracy works for the local council. The council is thinking about reducing the number of people it employs to pick up litter from the street. Tracy has been asked to carry out a study to see if having the streets cleaned at less regular intervals will affect the amount of litter the public will drop. She studies a street to compare how much litter is dropped at two different times, once when it has just been cleaned and once after it has not been cleaned for a month.
Write a fully operationalised non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis for Tracy’s study. (2)
3. Jamila is conducting a practical investigation to look at gender differences in carrying out visuo-spatial tasks. She decides to give males and females a jigsaw puzzle and will time them to see who completes it the fastest. She uses a random sample of pupils from a local school to get her participants.
(a) Write a fully operationalised directional (one tailed) hypothesis for Jamila’s study. (2) (b) Outline one strength and one weakness of the random sampling method. You may refer to Jamila’s use of this type of sampling in your answer. (4)
4. Which of the following is a non-directional (two tailed) hypothesis?
A There is a difference in driving ability with men being better drivers than women
B Women are better at concentrating on more than one thing at a time than men
C Women spend more time doing the cooking and cleaning than men
D There is a difference in the number of men and women who participate in sports
Revision Activity
writing-hypotheses-revision-sheet
Quizizz link for teachers: https://quizizz.com/admin/quiz/5bf03f51add785001bc5a09e
Share this:

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
- Privacy Policy

Home » What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation.
Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments and the collection and analysis of data. It is an essential element of the scientific method, as it allows researchers to make predictions about the outcome of their experiments and to test those predictions to determine their accuracy.
Types of Hypothesis
Types of Hypothesis are as follows:
Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is a statement that predicts a relationship between variables. It is usually formulated as a specific statement that can be tested through research, and it is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is no significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as a starting point for testing the research hypothesis, and if the results of the study reject the null hypothesis, it suggests that there is a significant difference or relationship between variables.
Alternative Hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is a significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as an alternative to the null hypothesis and is tested against the null hypothesis to determine which statement is more accurate.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. For example, a researcher might predict that increasing the amount of exercise will result in a decrease in body weight.
Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables but does not specify the direction. For example, a researcher might predict that there is a relationship between the amount of exercise and body weight, but they do not specify whether increasing or decreasing exercise will affect body weight.
Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement that assumes a particular statistical model or distribution for the data. It is often used in statistical analysis to test the significance of a particular result.
Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis is a statement that assumes more than one condition or outcome. It can be divided into several sub-hypotheses, each of which represents a different possible outcome.
Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement that is based on observed phenomena or data. It is often used in scientific research to develop theories or models that explain the observed phenomena.
Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement that assumes only one outcome or condition. It is often used in scientific research to test a single variable or factor.
Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is a statement that assumes multiple outcomes or conditions. It is often used in scientific research to test the effects of multiple variables or factors on a particular outcome.
Applications of Hypothesis
Hypotheses are used in various fields to guide research and make predictions about the outcomes of experiments or observations. Here are some examples of how hypotheses are applied in different fields:
- Science : In scientific research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain natural phenomena. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular variable on a natural system, such as the effects of climate change on an ecosystem.
- Medicine : In medical research, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of treatments and therapies for specific conditions. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new drug on a particular disease.
- Psychology : In psychology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of human behavior and cognition. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular stimulus on the brain or behavior.
- Sociology : In sociology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of social phenomena, such as the effects of social structures or institutions on human behavior. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of income inequality on crime rates.
- Business : In business research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain business phenomena, such as consumer behavior or market trends. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new marketing campaign on consumer buying behavior.
- Engineering : In engineering, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of new technologies or designs. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the efficiency of a new solar panel design.
How to write a Hypothesis
Here are the steps to follow when writing a hypothesis:
Identify the Research Question
The first step is to identify the research question that you want to answer through your study. This question should be clear, specific, and focused. It should be something that can be investigated empirically and that has some relevance or significance in the field.
Conduct a Literature Review
Before writing your hypothesis, it’s essential to conduct a thorough literature review to understand what is already known about the topic. This will help you to identify the research gap and formulate a hypothesis that builds on existing knowledge.
Determine the Variables
The next step is to identify the variables involved in the research question. A variable is any characteristic or factor that can vary or change. There are two types of variables: independent and dependent. The independent variable is the one that is manipulated or changed by the researcher, while the dependent variable is the one that is measured or observed as a result of the independent variable.
Formulate the Hypothesis
Based on the research question and the variables involved, you can now formulate your hypothesis. A hypothesis should be a clear and concise statement that predicts the relationship between the variables. It should be testable through empirical research and based on existing theory or evidence.
Write the Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is the opposite of the alternative hypothesis, which is the hypothesis that you are testing. The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference or relationship between the variables. It is important to write the null hypothesis because it allows you to compare your results with what would be expected by chance.
Refine the Hypothesis
After formulating the hypothesis, it’s important to refine it and make it more precise. This may involve clarifying the variables, specifying the direction of the relationship, or making the hypothesis more testable.
Examples of Hypothesis
Here are a few examples of hypotheses in different fields:
- Psychology : “Increased exposure to violent video games leads to increased aggressive behavior in adolescents.”
- Biology : “Higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will lead to increased plant growth.”
- Sociology : “Individuals who grow up in households with higher socioeconomic status will have higher levels of education and income as adults.”
- Education : “Implementing a new teaching method will result in higher student achievement scores.”
- Marketing : “Customers who receive a personalized email will be more likely to make a purchase than those who receive a generic email.”
- Physics : “An increase in temperature will cause an increase in the volume of a gas, assuming all other variables remain constant.”
- Medicine : “Consuming a diet high in saturated fats will increase the risk of developing heart disease.”
Purpose of Hypothesis
The purpose of a hypothesis is to provide a testable explanation for an observed phenomenon or a prediction of a future outcome based on existing knowledge or theories. A hypothesis is an essential part of the scientific method and helps to guide the research process by providing a clear focus for investigation. It enables scientists to design experiments or studies to gather evidence and data that can support or refute the proposed explanation or prediction.
The formulation of a hypothesis is based on existing knowledge, observations, and theories, and it should be specific, testable, and falsifiable. A specific hypothesis helps to define the research question, which is important in the research process as it guides the selection of an appropriate research design and methodology. Testability of the hypothesis means that it can be proven or disproven through empirical data collection and analysis. Falsifiability means that the hypothesis should be formulated in such a way that it can be proven wrong if it is incorrect.
In addition to guiding the research process, the testing of hypotheses can lead to new discoveries and advancements in scientific knowledge. When a hypothesis is supported by the data, it can be used to develop new theories or models to explain the observed phenomenon. When a hypothesis is not supported by the data, it can help to refine existing theories or prompt the development of new hypotheses to explain the phenomenon.
When to use Hypothesis
Here are some common situations in which hypotheses are used:
- In scientific research , hypotheses are used to guide the design of experiments and to help researchers make predictions about the outcomes of those experiments.
- In social science research , hypotheses are used to test theories about human behavior, social relationships, and other phenomena.
- I n business , hypotheses can be used to guide decisions about marketing, product development, and other areas. For example, a hypothesis might be that a new product will sell well in a particular market, and this hypothesis can be tested through market research.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some common characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable : A hypothesis must be able to be tested through observation or experimentation. This means that it must be possible to collect data that will either support or refute the hypothesis.
- Falsifiable : A hypothesis must be able to be proven false if it is not supported by the data. If a hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a scientific hypothesis.
- Clear and concise : A hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner so that it can be easily understood and tested.
- Based on existing knowledge : A hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and research in the field. It should not be based on personal beliefs or opinions.
- Specific : A hypothesis should be specific in terms of the variables being tested and the predicted outcome. This will help to ensure that the research is focused and well-designed.
- Tentative: A hypothesis is a tentative statement or assumption that requires further testing and evidence to be confirmed or refuted. It is not a final conclusion or assertion.
- Relevant : A hypothesis should be relevant to the research question or problem being studied. It should address a gap in knowledge or provide a new perspective on the issue.
Advantages of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have several advantages in scientific research and experimentation:
- Guides research: A hypothesis provides a clear and specific direction for research. It helps to focus the research question, select appropriate methods and variables, and interpret the results.
- Predictive powe r: A hypothesis makes predictions about the outcome of research, which can be tested through experimentation. This allows researchers to evaluate the validity of the hypothesis and make new discoveries.
- Facilitates communication: A hypothesis provides a common language and framework for scientists to communicate with one another about their research. This helps to facilitate the exchange of ideas and promotes collaboration.
- Efficient use of resources: A hypothesis helps researchers to use their time, resources, and funding efficiently by directing them towards specific research questions and methods that are most likely to yield results.
- Provides a basis for further research: A hypothesis that is supported by data provides a basis for further research and exploration. It can lead to new hypotheses, theories, and discoveries.
- Increases objectivity: A hypothesis can help to increase objectivity in research by providing a clear and specific framework for testing and interpreting results. This can reduce bias and increase the reliability of research findings.
Limitations of Hypothesis
Some Limitations of the Hypothesis are as follows:
- Limited to observable phenomena: Hypotheses are limited to observable phenomena and cannot account for unobservable or intangible factors. This means that some research questions may not be amenable to hypothesis testing.
- May be inaccurate or incomplete: Hypotheses are based on existing knowledge and research, which may be incomplete or inaccurate. This can lead to flawed hypotheses and erroneous conclusions.
- May be biased: Hypotheses may be biased by the researcher’s own beliefs, values, or assumptions. This can lead to selective interpretation of data and a lack of objectivity in research.
- Cannot prove causation: A hypothesis can only show a correlation between variables, but it cannot prove causation. This requires further experimentation and analysis.
- Limited to specific contexts: Hypotheses are limited to specific contexts and may not be generalizable to other situations or populations. This means that results may not be applicable in other contexts or may require further testing.
- May be affected by chance : Hypotheses may be affected by chance or random variation, which can obscure or distort the true relationship between variables.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like


Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
How to write a research hypothesis
Last updated
19 January 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
Start with a broad subject matter that excites you, so your curiosity will motivate your work. Conduct a literature search to determine the range of questions already addressed and spot any holes in the existing research.
Narrow the topics that interest you and determine your research question. Rather than focusing on a hole in the research, you might choose to challenge an existing assumption, a process called problematization. You may also find yourself with a short list of questions or related topics.
Use the FINER method to determine the single problem you'll address with your research. FINER stands for:
I nteresting
You need a feasible research question, meaning that there is a way to address the question. You should find it interesting, but so should a larger audience. Rather than repeating research that others have already conducted, your research hypothesis should test something novel or unique.
The research must fall into accepted ethical parameters as defined by the government of your country and your university or college if you're an academic. You'll also need to come up with a relevant question since your research should provide a contribution to the existing research area.
This process typically narrows your shortlist down to a single problem you'd like to study and the variable you want to test. You're ready to write your hypothesis statements.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- Types of research hypotheses
It is important to narrow your topic down to one idea before trying to write your research hypothesis. You'll only test one problem at a time. To do this, you'll write two hypotheses – a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (Ha).
You'll come across many terms related to developing a research hypothesis or referring to a specific type of hypothesis. Let's take a quick look at these terms.
Null hypothesis
The term null hypothesis refers to a research hypothesis type that assumes no statistically significant relationship exists within a set of observations or data. It represents a claim that assumes that any observed relationship is due to chance. Represented as H0, the null represents the conjecture of the research.
Alternative hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis accompanies the null hypothesis. It states that the situation presented in the null hypothesis is false or untrue, and claims an observed effect in your test. This is typically denoted by Ha or H(n), where “n” stands for the number of alternative hypotheses. You can have more than one alternative hypothesis.
Simple hypothesis
The term simple hypothesis refers to a hypothesis or theory that predicts the relationship between two variables - the independent (predictor) and the dependent (predicted).
Complex hypothesis
The term complex hypothesis refers to a model – either quantitative (mathematical) or qualitative . A complex hypothesis states the surmised relationship between two or more potentially related variables.
Directional hypothesis
When creating a statistical hypothesis, the directional hypothesis (the null hypothesis) states an assumption regarding one parameter of a population. Some academics call this the “one-sided” hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis indicates whether the researcher tests for a positive or negative effect by including either the greater than (">") or less than ("<") sign.
Non-directional hypothesis
We refer to the alternative hypothesis in a statistical research question as a non-directional hypothesis. It includes the not equal ("≠") sign to show that the research tests whether or not an effect exists without specifying the effect's direction (positive or negative).
Associative hypothesis
The term associative hypothesis assumes a link between two variables but stops short of stating that one variable impacts the other. Academic statistical literature asserts in this sense that correlation does not imply causation. So, although the hypothesis notes the correlation between two variables – the independent and dependent - it does not predict how the two interact.
Logical hypothesis
Typically used in philosophy rather than science, researchers can't test a logical hypothesis because the technology or data set doesn't yet exist. A logical hypothesis uses logic as the basis of its assumptions.
In some cases, a logical hypothesis can become an empirical hypothesis once technology provides an opportunity for testing. Until that time, the question remains too expensive or complex to address. Note that a logical hypothesis is not a statistical hypothesis.
Empirical hypothesis
When we consider the opposite of a logical hypothesis, we call this an empirical or working hypothesis. This type of hypothesis considers a scientifically measurable question. A researcher can consider and test an empirical hypothesis through replicable tests, observations, and measurements.
Statistical hypothesis
The term statistical hypothesis refers to a test of a theory that uses representative statistical models to test relationships between variables to draw conclusions regarding a large population. This requires an existing large data set, commonly referred to as big data, or implementing a survey to obtain original statistical information to form a data set for the study.
Testing this type of hypothesis requires the use of random samples. Note that the null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing.
Causal hypothesis
The term causal hypothesis refers to a research hypothesis that tests a cause-and-effect relationship. A causal hypothesis is utilized when conducting experimental or quasi-experimental research.
Descriptive hypothesis
The term descriptive hypothesis refers to a research hypothesis used in non-experimental research, specifying an influence in the relationship between two variables.
- What makes an effective research hypothesis?
An effective research hypothesis offers a clearly defined, specific statement, using simple wording that contains no assumptions or generalizations, and that you can test. A well-written hypothesis should predict the tested relationship and its outcome. It contains zero ambiguity and offers results you can observe and test.
The research hypothesis should address a question relevant to a research area. Overall, your research hypothesis needs the following essentials:
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
- How to develop a good research hypothesis
In developing your hypothesis statements, you must pre-plan some of your statistical analysis. Once you decide on your problem to examine, determine three aspects:
the parameter you'll test
the test's direction (left-tailed, right-tailed, or non-directional)
the hypothesized parameter value
Any quantitative research includes a hypothesized parameter value of a mean, a proportion, or the difference between two proportions. Here's how to note each parameter:
Single mean (μ)
Paired means (μd)
Single proportion (p)
Difference between two independent means (μ1−μ2)
Difference between two proportions (p1−p2)
Simple linear regression slope (β)
Correlation (ρ)
Defining these parameters and determining whether you want to test the mean, proportion, or differences helps you determine the statistical tests you'll conduct to analyze your data. When writing your hypothesis, you only need to decide which parameter to test and in what overarching way.
The null research hypothesis must include everyday language, in a single sentence, stating the problem you want to solve. Write it as an if-then statement with defined variables. Write an alternative research hypothesis that states the opposite.
- What is the correct format for writing a hypothesis?
The following example shows the proper format and textual content of a hypothesis. It follows commonly accepted academic standards.
Null hypothesis (H0): High school students who participate in varsity sports as opposed to those who do not, fail to score higher on leadership tests than students who do not participate.
Alternative hypothesis (H1): High school students who play a varsity sport as opposed to those who do not participate in team athletics will score higher on leadership tests than students who do not participate in athletics.
The research question tests the correlation between varsity sports participation and leadership qualities expressed as a score on leadership tests. It compares the population of athletes to non-athletes.
- What are the five steps of a hypothesis?
Once you decide on the specific problem or question you want to address, you can write your research hypothesis. Use this five-step system to hone your null hypothesis and generate your alternative hypothesis.
Step 1 : Create your research question. This topic should interest and excite you; answering it provides relevant information to an industry or academic area.
Step 2 : Conduct a literature review to gather essential existing research.
Step 3 : Write a clear, strong, simply worded sentence that explains your test parameter, test direction, and hypothesized parameter.
Step 4 : Read it a few times. Have others read it and ask them what they think it means. Refine your statement accordingly until it becomes understandable to everyone. While not everyone can or will comprehend every research study conducted, any person from the general population should be able to read your hypothesis and alternative hypothesis and understand the essential question you want to answer.
Step 5 : Re-write your null hypothesis until it reads simply and understandably. Write your alternative hypothesis.
What is the Red Queen hypothesis?
Some hypotheses are well-known, such as the Red Queen hypothesis. Choose your wording carefully, since you could become like the famed scientist Dr. Leigh Van Valen. In 1973, Dr. Van Valen proposed the Red Queen hypothesis to describe coevolutionary activity, specifically reciprocal evolutionary effects between species to explain extinction rates in the fossil record.
Essentially, Van Valen theorized that to survive, each species remains in a constant state of adaptation, evolution, and proliferation, and constantly competes for survival alongside other species doing the same. Only by doing this can a species avoid extinction. Van Valen took the hypothesis title from the Lewis Carroll book, "Through the Looking Glass," which contains a key character named the Red Queen who explains to Alice that for all of her running, she's merely running in place.
- Getting started with your research
In conclusion, once you write your null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (Ha), you’ve essentially authored the elevator pitch of your research. These two one-sentence statements describe your topic in simple, understandable terms that both professionals and laymen can understand. They provide the starting point of your research project.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 13 April 2023
Last updated: 14 February 2024
Last updated: 27 January 2024
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 8 February 2023
Last updated: 23 January 2024
Last updated: 30 January 2024
Last updated: 7 February 2023
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 31 January 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free

How to Develop a Good Research Hypothesis
The story of a research study begins by asking a question. Researchers all around the globe are asking curious questions and formulating research hypothesis. However, whether the research study provides an effective conclusion depends on how well one develops a good research hypothesis. Research hypothesis examples could help researchers get an idea as to how to write a good research hypothesis.
This blog will help you understand what is a research hypothesis, its characteristics and, how to formulate a research hypothesis
Table of Contents
What is Hypothesis?
Hypothesis is an assumption or an idea proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested. It is a precise, testable statement of what the researchers predict will be outcome of the study. Hypothesis usually involves proposing a relationship between two variables: the independent variable (what the researchers change) and the dependent variable (what the research measures).
What is a Research Hypothesis?
Research hypothesis is a statement that introduces a research question and proposes an expected result. It is an integral part of the scientific method that forms the basis of scientific experiments. Therefore, you need to be careful and thorough when building your research hypothesis. A minor flaw in the construction of your hypothesis could have an adverse effect on your experiment. In research, there is a convention that the hypothesis is written in two forms, the null hypothesis, and the alternative hypothesis (called the experimental hypothesis when the method of investigation is an experiment).
Characteristics of a Good Research Hypothesis
As the hypothesis is specific, there is a testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. You may consider drawing hypothesis from previously published research based on the theory.
A good research hypothesis involves more effort than just a guess. In particular, your hypothesis may begin with a question that could be further explored through background research.
To help you formulate a promising research hypothesis, you should ask yourself the following questions:
- Is the language clear and focused?
- What is the relationship between your hypothesis and your research topic?
- Is your hypothesis testable? If yes, then how?
- What are the possible explanations that you might want to explore?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate your variables without hampering the ethical standards?
- Does your research predict the relationship and outcome?
- Is your research simple and concise (avoids wordiness)?
- Is it clear with no ambiguity or assumptions about the readers’ knowledge
- Is your research observable and testable results?
- Is it relevant and specific to the research question or problem?

The questions listed above can be used as a checklist to make sure your hypothesis is based on a solid foundation. Furthermore, it can help you identify weaknesses in your hypothesis and revise it if necessary.
Source: Educational Hub
How to formulate a research hypothesis.
A testable hypothesis is not a simple statement. It is rather an intricate statement that needs to offer a clear introduction to a scientific experiment, its intentions, and the possible outcomes. However, there are some important things to consider when building a compelling hypothesis.
1. State the problem that you are trying to solve.
Make sure that the hypothesis clearly defines the topic and the focus of the experiment.
2. Try to write the hypothesis as an if-then statement.
Follow this template: If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.
3. Define the variables
Independent variables are the ones that are manipulated, controlled, or changed. Independent variables are isolated from other factors of the study.
Dependent variables , as the name suggests are dependent on other factors of the study. They are influenced by the change in independent variable.
4. Scrutinize the hypothesis
Evaluate assumptions, predictions, and evidence rigorously to refine your understanding.
Types of Research Hypothesis
The types of research hypothesis are stated below:
1. Simple Hypothesis
It predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable.
2. Complex Hypothesis
It predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables.
3. Directional Hypothesis
It specifies the expected direction to be followed to determine the relationship between variables and is derived from theory. Furthermore, it implies the researcher’s intellectual commitment to a particular outcome.
4. Non-directional Hypothesis
It does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables. The non-directional hypothesis is used when there is no theory involved or when findings contradict previous research.
5. Associative and Causal Hypothesis
The associative hypothesis defines interdependency between variables. A change in one variable results in the change of the other variable. On the other hand, the causal hypothesis proposes an effect on the dependent due to manipulation of the independent variable.
6. Null Hypothesis
Null hypothesis states a negative statement to support the researcher’s findings that there is no relationship between two variables. There will be no changes in the dependent variable due the manipulation of the independent variable. Furthermore, it states results are due to chance and are not significant in terms of supporting the idea being investigated.
7. Alternative Hypothesis
It states that there is a relationship between the two variables of the study and that the results are significant to the research topic. An experimental hypothesis predicts what changes will take place in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated. Also, it states that the results are not due to chance and that they are significant in terms of supporting the theory being investigated.
Research Hypothesis Examples of Independent and Dependent Variables
Research Hypothesis Example 1 The greater number of coal plants in a region (independent variable) increases water pollution (dependent variable). If you change the independent variable (building more coal factories), it will change the dependent variable (amount of water pollution).
Research Hypothesis Example 2 What is the effect of diet or regular soda (independent variable) on blood sugar levels (dependent variable)? If you change the independent variable (the type of soda you consume), it will change the dependent variable (blood sugar levels)
You should not ignore the importance of the above steps. The validity of your experiment and its results rely on a robust testable hypothesis. Developing a strong testable hypothesis has few advantages, it compels us to think intensely and specifically about the outcomes of a study. Consequently, it enables us to understand the implication of the question and the different variables involved in the study. Furthermore, it helps us to make precise predictions based on prior research. Hence, forming a hypothesis would be of great value to the research. Here are some good examples of testable hypotheses.
More importantly, you need to build a robust testable research hypothesis for your scientific experiments. A testable hypothesis is a hypothesis that can be proved or disproved as a result of experimentation.
Importance of a Testable Hypothesis
To devise and perform an experiment using scientific method, you need to make sure that your hypothesis is testable. To be considered testable, some essential criteria must be met:
- There must be a possibility to prove that the hypothesis is true.
- There must be a possibility to prove that the hypothesis is false.
- The results of the hypothesis must be reproducible.
Without these criteria, the hypothesis and the results will be vague. As a result, the experiment will not prove or disprove anything significant.
What are your experiences with building hypotheses for scientific experiments? What challenges did you face? How did you overcome these challenges? Please share your thoughts with us in the comments section.
Frequently Asked Questions
The steps to write a research hypothesis are: 1. Stating the problem: Ensure that the hypothesis defines the research problem 2. Writing a hypothesis as an 'if-then' statement: Include the action and the expected outcome of your study by following a ‘if-then’ structure. 3. Defining the variables: Define the variables as Dependent or Independent based on their dependency to other factors. 4. Scrutinizing the hypothesis: Identify the type of your hypothesis
Hypothesis testing is a statistical tool which is used to make inferences about a population data to draw conclusions for a particular hypothesis.
Hypothesis in statistics is a formal statement about the nature of a population within a structured framework of a statistical model. It is used to test an existing hypothesis by studying a population.
Research hypothesis is a statement that introduces a research question and proposes an expected result. It forms the basis of scientific experiments.
The different types of hypothesis in research are: • Null hypothesis: Null hypothesis is a negative statement to support the researcher’s findings that there is no relationship between two variables. • Alternate hypothesis: Alternate hypothesis predicts the relationship between the two variables of the study. • Directional hypothesis: Directional hypothesis specifies the expected direction to be followed to determine the relationship between variables. • Non-directional hypothesis: Non-directional hypothesis does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables. • Simple hypothesis: Simple hypothesis predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable. • Complex hypothesis: Complex hypothesis predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables. • Associative and casual hypothesis: Associative and casual hypothesis predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables. • Empirical hypothesis: Empirical hypothesis can be tested via experiments and observation. • Statistical hypothesis: A statistical hypothesis utilizes statistical models to draw conclusions about broader populations.
Wow! You really simplified your explanation that even dummies would find it easy to comprehend. Thank you so much.
Thanks a lot for your valuable guidance.
I enjoy reading the post. Hypotheses are actually an intrinsic part in a study. It bridges the research question and the methodology of the study.
Useful piece!
This is awesome.Wow.
It very interesting to read the topic, can you guide me any specific example of hypothesis process establish throw the Demand and supply of the specific product in market
Nicely explained
It is really a useful for me Kindly give some examples of hypothesis
It was a well explained content ,can you please give me an example with the null and alternative hypothesis illustrated
clear and concise. thanks.
So Good so Amazing
Good to learn
Thanks a lot for explaining to my level of understanding
Explained well and in simple terms. Quick read! Thank you
It awesome. It has really positioned me in my research project
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Industry News
COPE Forum Discussion Highlights Challenges and Urges Clarity in Institutional Authorship Standards
The COPE forum discussion held in December 2023 initiated with a fundamental question — is…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
Developing the research hypothesis
Affiliation.
- 1 Division of Abdominal Transplantation, Department of Surgery, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, USA. [email protected]
- PMID: 21867386
- DOI: 10.3109/08941939.2011.609449
The research hypothesis is needed for a sound and well-developed research study. The research hypothesis contributes to the solution of the research problem. Types of research hypotheses include inductive and deductive, directional and non-directional, and null and alternative hypotheses. Rejecting the null hypothesis and accepting the alternative hypothesis is the basis for building a good research study. This work reviews the most important aspects of organizing and establishing an efficient and complete hypothesis.
- Biomedical Research / methods*
- Data Interpretation, Statistical
- Research Design*
How to Write a Research Hypothesis
- Research Process
- Peer Review
Since grade school, we've all been familiar with hypotheses. The hypothesis is an essential step of the scientific method. But what makes an effective research hypothesis, how do you create one, and what types of hypotheses are there? We answer these questions and more.
Updated on April 27, 2022

What is a research hypothesis?
General hypothesis.
Since grade school, we've all been familiar with the term “hypothesis.” A hypothesis is a fact-based guess or prediction that has not been proven. It is an essential step of the scientific method. The hypothesis of a study is a drive for experimentation to either prove the hypothesis or dispute it.
Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is more specific than a general hypothesis. It is an educated, expected prediction of the outcome of a study that is testable.
What makes an effective research hypothesis?
A good research hypothesis is a clear statement of the relationship between a dependent variable(s) and independent variable(s) relevant to the study that can be disproven.
Research hypothesis checklist
Once you've written a possible hypothesis, make sure it checks the following boxes:
- It must be testable: You need a means to prove your hypothesis. If you can't test it, it's not a hypothesis.
- It must include a dependent and independent variable: At least one independent variable ( cause ) and one dependent variable ( effect ) must be included.
- The language must be easy to understand: Be as clear and concise as possible. Nothing should be left to interpretation.
- It must be relevant to your research topic: You probably shouldn't be talking about cats and dogs if your research topic is outer space. Stay relevant to your topic.
How to create an effective research hypothesis
Pose it as a question first.
Start your research hypothesis from a journalistic approach. Ask one of the five W's: Who, what, when, where, or why.
A possible initial question could be: Why is the sky blue?
Do the preliminary research
Once you have a question in mind, read research around your topic. Collect research from academic journals.
If you're looking for information about the sky and why it is blue, research information about the atmosphere, weather, space, the sun, etc.
Write a draft hypothesis
Once you're comfortable with your subject and have preliminary knowledge, create a working hypothesis. Don't stress much over this. Your first hypothesis is not permanent. Look at it as a draft.
Your first draft of a hypothesis could be: Certain molecules in the Earth's atmosphere are responsive to the sky being the color blue.
Make your working draft perfect
Take your working hypothesis and make it perfect. Narrow it down to include only the information listed in the “Research hypothesis checklist” above.
Now that you've written your working hypothesis, narrow it down. Your new hypothesis could be: Light from the sun hitting oxygen molecules in the sky makes the color of the sky appear blue.
Write a null hypothesis
Your null hypothesis should be the opposite of your research hypothesis. It should be able to be disproven by your research.
In this example, your null hypothesis would be: Light from the sun hitting oxygen molecules in the sky does not make the color of the sky appear blue.
Why is it important to have a clear, testable hypothesis?
One of the main reasons a manuscript can be rejected from a journal is because of a weak hypothesis. “Poor hypothesis, study design, methodology, and improper use of statistics are other reasons for rejection of a manuscript,” says Dr. Ish Kumar Dhammi and Dr. Rehan-Ul-Haq in Indian Journal of Orthopaedics.
According to Dr. James M. Provenzale in American Journal of Roentgenology , “The clear declaration of a research question (or hypothesis) in the Introduction is critical for reviewers to understand the intent of the research study. It is best to clearly state the study goal in plain language (for example, “We set out to determine whether condition x produces condition y.”) An insufficient problem statement is one of the more common reasons for manuscript rejection.”
Characteristics that make a hypothesis weak include:
- Unclear variables
- Unoriginality
- Too general
- Too specific
A weak hypothesis leads to weak research and methods . The goal of a paper is to prove or disprove a hypothesis - or to prove or disprove a null hypothesis. If the hypothesis is not a dependent variable of what is being studied, the paper's methods should come into question.
A strong hypothesis is essential to the scientific method. A hypothesis states an assumed relationship between at least two variables and the experiment then proves or disproves that relationship with statistical significance. Without a proven and reproducible relationship, the paper feeds into the reproducibility crisis. Learn more about writing for reproducibility .
In a study published in The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India by Dr. Suvarna Satish Khadilkar, she reviewed 400 rejected manuscripts to see why they were rejected. Her studies revealed that poor methodology was a top reason for the submission having a final disposition of rejection.
Aside from publication chances, Dr. Gareth Dyke believes a clear hypothesis helps efficiency.
“Developing a clear and testable hypothesis for your research project means that you will not waste time, energy, and money with your work,” said Dyke. “Refining a hypothesis that is both meaningful, interesting, attainable, and testable is the goal of all effective research.”
Types of research hypotheses
There can be overlap in these types of hypotheses.
Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a hypothesis at its most basic form. It shows the relationship of one independent and one independent variable.
Example: Drinking soda (independent variable) every day leads to obesity (dependent variable).
Complex hypothesis
A complex hypothesis shows the relationship of two or more independent and dependent variables.
Example: Drinking soda (independent variable) every day leads to obesity (dependent variable) and heart disease (dependent variable).
Directional hypothesis
A directional hypothesis guesses which way the results of an experiment will go. It uses words like increase, decrease, higher, lower, positive, negative, more, or less. It is also frequently used in statistics.
Example: Humans exposed to radiation have a higher risk of cancer than humans not exposed to radiation.
Non-directional hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis says there will be an effect on the dependent variable, but it does not say which direction.
Associative hypothesis
An associative hypothesis says that when one variable changes, so does the other variable.
Alternative hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis states that the variables have a relationship.
- The opposite of a null hypothesis
Example: An apple a day keeps the doctor away.
Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis states that there is no relationship between the two variables. It is posed as the opposite of what the alternative hypothesis states.
Researchers use a null hypothesis to work to be able to reject it. A null hypothesis:
- Can never be proven
- Can only be rejected
- Is the opposite of an alternative hypothesis
Example: An apple a day does not keep the doctor away.
Logical hypothesis
A logical hypothesis is a suggested explanation while using limited evidence.
Example: Bats can navigate in the dark better than tigers.
In this hypothesis, the researcher knows that tigers cannot see in the dark, and bats mostly live in darkness.
Empirical hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is also called a “working hypothesis.” It uses the trial and error method and changes around the independent variables.
- An apple a day keeps the doctor away.
- Two apples a day keep the doctor away.
- Three apples a day keep the doctor away.
In this case, the research changes the hypothesis as the researcher learns more about his/her research.
Statistical hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a look of a part of a population or statistical model. This type of hypothesis is especially useful if you are making a statement about a large population. Instead of having to test the entire population of Illinois, you could just use a smaller sample of people who live there.
Example: 70% of people who live in Illinois are iron deficient.
Causal hypothesis
A causal hypothesis states that the independent variable will have an effect on the dependent variable.
Example: Using tobacco products causes cancer.
Final thoughts
Make sure your research is error-free before you send it to your preferred journal . Check our our English Editing services to avoid your chances of desk rejection.

Jonny Rhein, BA
See our "Privacy Policy"

Directional vs Non-Directional Hypothesis – Collect Feedback More Effectively
To conduct a perfect survey, you should know the basics of good research . That’s why in Startquestion we would like to share with you our knowledge about basic terms connected to online surveys and feedback gathering . Knowing the basis you can create surveys and conduct research in more effective ways and thanks to this get meaningful feedback from your customers, employees, and users. That’s enough for the introduction – let’s get to work. This time we will tell you about the hypothesis .
What is a Hypothesis?
A Hypothesis can be described as a theoretical statement built upon some evidence so that it can be tested as if it is true or false. In other words, a hypothesis is a speculation or an idea, based on insufficient evidence that allows it further analysis and experimentation.
The purpose of a hypothetical statement is to work like a prediction based on studied research and to provide some estimated results before it ha happens in a real position. There can be more than one hypothesis statement involved in a research study, where you need to question and explore different aspects of a proposed research topic. Before putting your research into directional vs non-directional hypotheses, let’s have some basic knowledge.
Most often, a hypothesis describes a relation between two or more variables. It includes:
An Independent variable – One that is controlled by the researcher
Dependent Variable – The variable that the researcher observes in association with the Independent variable.
Try one of the best survey tools for free!
Start trial period without any credit card or subscription. Easily conduct your research and gather feedback via link, social media, email, and more.
Create first survey
No credit card required · Cancel any time · GDRP Compilant
How to write an effective Hypothesis?
To write an effective hypothesis follow these essential steps.
- Inquire a Question
The very first step in writing an effective hypothesis is raising a question. Outline the research question very carefully keeping your research purpose in mind. Build it in a precise and targeted way. Here you must be clear about the research question vs hypothesis. A research question is the very beginning point of writing an effective hypothesis.
Do Literature Review
Once you are done with constructing your research question, you can start the literature review. A literature review is a collection of preliminary research studies done on the same or relevant topics. There is a diversified range of literature reviews. The most common ones are academic journals but it is not confined to that. It can be anything including your research, data collection, and observation.
At this point, you can build a conceptual framework. It can be defined as a visual representation of the estimated relationship between two variables subjected to research.
Frame an Answer
After a collection of literature reviews, you can find ways how to answer the question. Expect this stage as a point where you will be able to make a stand upon what you believe might have the exact outcome of your research. You must formulate this answer statement clearly and concisely.
Build a Hypothesis
At this point, you can firmly build your hypothesis. By now, you knew the answer to your question so make a hypothesis that includes:
- Applicable Variables
- Particular Group being Studied (Who/What)
- Probable Outcome of the Experiment
Remember, your hypothesis is a calculated assumption, it has to be constructed as a sentence, not a question. This is where research question vs hypothesis starts making sense.
Refine a Hypothesis
Make necessary amendments to the constructed hypothesis keeping in mind that it has to be targeted and provable. Moreover, you might encounter certain circumstances where you will be studying the difference between one or more groups. It can be correlational research. In such instances, you must have to testify the relationships that you believe you will find in the subject variables and through this research.
Build Null Hypothesis
Certain research studies require some statistical investigation to perform a data collection. Whenever applying any scientific method to construct a hypothesis, you must have adequate knowledge of the Null Hypothesis and an Alternative hypothesis.
Null Hypothesis:
A null Hypothesis denotes that there is no statistical relationship between the subject variables. It is applicable for a single group of variables or two groups of variables. A Null Hypothesis is denoted as an H0. This is the type of hypothesis that the researcher tries to invalidate. Some of the examples of null hypotheses are:
– Hyperactivity is not associated with eating sugar.
– All roses have an equal amount of petals.
– A person’s preference for a dress is not linked to its color.
Alternative Hypothesis:
An alternative hypothesis is a statement that is simply inverse or opposite of the null hypothesis and denoted as H1. Simply saying, it is an alternative statement for the null hypothesis. The same examples will go this way as an alternative hypothesis:
– Hyperactivity is associated with eating sugar.
– All roses do not have an equal amount of petals.
– A person’s preference for a dress is linked to its color.
Start your research right now: use professional survey templates
- Brand Awareness Survey
- Survey for the thesis
- Website Evaluation Survey
See more templates
Types of Hypothesis
Apart from null and alternative hypotheses, research hypotheses can be categorized into different types. Let’s have a look at them:
Simple Hypothesis:
This type of hypothesis is used to state a relationship between a particular independent variable and only a dependent variable.
Complex Hypothesis:
A statement that states the relationship between two or more independent variables and two or more dependent variables, is termed a complex hypothesis.
Associative and Causal Hypothesis:
This type of hypothesis involves predicting that there is a point of interdependency between two variables. It says that any kind of change in one variable will cause a change in the other one. Similarly, a casual hypothesis says that a change in the dependent variable is due to some variations in the independent variable.
Directional vs non-directional hypothesis
Directional hypothesis:.
A hypothesis that is built upon a certain directional relationship between two variables and constructed upon an already existing theory, is called a directional hypothesis. To understand more about what is directional hypothesis here is an example, Girls perform better than boys (‘better than’ shows the direction predicted)
Non-directional Hypothesis:
It involves an open-ended non-directional hypothesis that predicts that the independent variable will influence the dependent variable; however, the nature or direction of a relationship between two subject variables is not defined or clear.
For Example, there will be a difference in the performance of girls & boys (Not defining what kind of difference)
As a professional, we suggest you apply a non-directional alternative hypothesis when you are not sure of the direction of the relationship. Maybe you’re observing potential gender differences on some psychological test, but you don’t know whether men or women would have the higher ratio. Normally, this would say that you are lacking practical knowledge about the proposed variables. A directional test should be more common for tests.

Author: Ula Kamburov-Niepewna
Updated: 18 November 2022
Eleven Useful ChatGPT Alternatives
ChatGPT has made quite a splash in the world of generative AI, but it's not the only game in town. Let's take a look at some of the best alternatives that could become your new go-to.

Top 10 Useful Employee Pulse Survey Tools
This guide explores the goal of pulse surveys, reviews the top tools available for conducting them, and contrasts their benefits with traditional survey methods.

12 Post Event Survey Questions to Ask
After your meticulously planned event concludes, there’s one crucial step left: gathering feedback. Post-event surveys are invaluable tools for understanding attendee experiences, identifying areas for improvement, and maintaining attendee satisfaction.
- Open access
- Published: 27 May 2024
Current status of community resources and priorities for weed genomics research
- Jacob Montgomery 1 ,
- Sarah Morran 1 ,
- Dana R. MacGregor ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0543-0408 2 ,
- J. Scott McElroy ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0331-3697 3 ,
- Paul Neve ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3136-5286 4 ,
- Célia Neto ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3256-5228 4 ,
- Martin M. Vila-Aiub ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2118-290X 5 ,
- Maria Victoria Sandoval 5 ,
- Analia I. Menéndez ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9681-0280 6 ,
- Julia M. Kreiner ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8593-1394 7 ,
- Longjiang Fan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4846-0500 8 ,
- Ana L. Caicedo ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0378-6374 9 ,
- Peter J. Maughan 10 ,
- Bianca Assis Barbosa Martins 11 ,
- Jagoda Mika 11 ,
- Alberto Collavo 11 ,
- Aldo Merotto Jr. ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1581-0669 12 ,
- Nithya K. Subramanian ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1659-7396 13 ,
- Muthukumar V. Bagavathiannan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1107-7148 13 ,
- Luan Cutti ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2867-7158 14 ,
- Md. Mazharul Islam 15 ,
- Bikram S. Gill ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4510-9459 16 ,
- Robert Cicchillo 17 ,
- Roger Gast 17 ,
- Neeta Soni ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4647-8355 17 ,
- Terry R. Wright ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3969-2812 18 ,
- Gina Zastrow-Hayes 18 ,
- Gregory May 18 ,
- Jenna M. Malone ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9637-2073 19 ,
- Deepmala Sehgal ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4141-1784 20 ,
- Shiv Shankhar Kaundun ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7249-2046 20 ,
- Richard P. Dale 20 ,
- Barend Juan Vorster ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3518-3508 21 ,
- Bodo Peters 11 ,
- Jens Lerchl ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9633-2653 22 ,
- Patrick J. Tranel ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0666-4564 23 ,
- Roland Beffa ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3109-388X 24 ,
- Alexandre Fournier-Level ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6047-7164 25 ,
- Mithila Jugulam ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2065-9067 15 ,
- Kevin Fengler 18 ,
- Victor Llaca ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4822-2924 18 ,
- Eric L. Patterson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7111-6287 14 &
- Todd A. Gaines ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1485-7665 1
Genome Biology volume 25 , Article number: 139 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
469 Accesses
5 Altmetric
Metrics details
Weeds are attractive models for basic and applied research due to their impacts on agricultural systems and capacity to swiftly adapt in response to anthropogenic selection pressures. Currently, a lack of genomic information precludes research to elucidate the genetic basis of rapid adaptation for important traits like herbicide resistance and stress tolerance and the effect of evolutionary mechanisms on wild populations. The International Weed Genomics Consortium is a collaborative group of scientists focused on developing genomic resources to impact research into sustainable, effective weed control methods and to provide insights about stress tolerance and adaptation to assist crop breeding.
Each year globally, agricultural producers and landscape managers spend billions of US dollars [ 1 , 2 ] and countless hours attempting to control weedy plants and reduce their adverse effects. These management methods range from low-tech (e.g., pulling plants from the soil by hand) to extremely high-tech (e.g., computer vision-controlled spraying of herbicides). Regardless of technology level, effective control methods serve as strong selection pressures on weedy plants and often result in rapid evolution of weed populations resistant to such methods [ 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]. Thus, humans and weeds have been locked in an arms race, where humans develop new or improved control methods and weeds adapt and evolve to circumvent such methods.
Applying genomics to weed science offers a unique opportunity to study rapid adaptation, epigenetic responses, and examples of evolutionary rescue of diverse weedy species in the face of widespread and powerful selective pressures. Furthermore, lessons learned from these studies may also help to develop more sustainable control methods and to improve crop breeding efforts in the face of our ever-changing climate. While other research fields have used genetics and genomics to uncover the basis of many biological traits [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ] and to understand how ecological factors affect evolution [ 12 , 13 ], the field of weed science has lagged behind in the development of genomic tools essential for such studies [ 14 ]. As research in human and crop genetics pushes into the era of pangenomics (i.e., multiple chromosome scale genome assemblies for a single species [ 15 , 16 ]), publicly available genomic information is still lacking or severely limited for the majority of weed species. Recent reviews of current weed genomes identified 26 [ 17 ] and 32 weed species with sequenced genomes [ 18 ]—many assembled to a sub-chromosome level.
Here, we summarize the current state of weed genomics, highlighting cases where genomics approaches have successfully provided insights on topics such as population genetic dynamics, genome evolution, and the genetic basis of herbicide resistance, rapid adaptation, and crop dedomestication. These highlighted investigations all relied upon genomic resources that are relatively rare for weedy species. Throughout, we identify additional resources that would advance the field of weed science and enable further progress in weed genomics. We then introduce the International Weed Genomics Consortium (IWGC), an open collaboration among researchers, and describe current efforts to generate these additional resources.
Evolution of weediness: potential research utilizing weed genomics tools
Weeds can evolve from non-weed progenitors through wild colonization, crop de-domestication, or crop-wild hybridization [ 19 ]. Because the time span in which weeds have evolved is necessarily limited by the origins of agriculture, these non-weed relatives often still exist and can be leveraged through population genomic and comparative genomic approaches to identify the adaptive changes that have driven the evolution of weediness. The ability to rapidly adapt, persist, and spread in agroecosystems are defining features of weedy plants, leading many to advocate agricultural weeds as ideal candidates for studying rapid plant adaptation [ 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 ]. The insights gained from applying plant ecological approaches to the study of rapid weed adaptation will move us towards the ultimate goals of mitigating such adaptation and increasing the efficacy of crop breeding and biotechnology [ 14 ].
Biology and ecological genomics of weeds
The impressive community effort to create and maintain resources for Arabidopsis thaliana ecological genomics provides a motivating example for the emerging study of weed genomics [ 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 ]. Arabidopsis thaliana was the first flowering plant species to have its genome fully sequenced [ 28 ] and rapidly became a model organism for plant molecular biology. As weedy genomes become available, collection, maintenance, and resequencing of globally distributed accessions of these species will help to replicate the success found in ecological studies of A. thaliana [ 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 ]. Evaluation of these accessions for traits of interest to produce large phenomics data sets (as in [ 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 ]) enables genome-wide association studies and population genomics analyses aimed at dissecting the genetic basis of variation in such traits [ 41 ]. Increasingly, these resources (e.g. the 1001 genomes project [ 29 ]) have enabled A. thaliana to be utilized as a model species to explore the eco-evolutionary basis of plant adaptation in a more realistic ecological context. Weedy species should supplement lessons in eco-evolutionary genomics learned from these experiments in A. thaliana .
Untargeted genomic approaches for understanding the evolutionary trajectories of populations and the genetic basis of traits as described above rely on the collection of genotypic information from across the genome of many individuals. While whole-genome resequencing accomplishes this requirement and requires no custom methodology, this approach provides more information than is necessary and is prohibitively expensive in species with large genomes. Development and optimization of genotype-by-sequencing methods for capturing reduced representations of newly sequence genomes like those described by [ 42 , 43 , 44 ] will reduce the cost and computational requirements of genetic mapping and population genetic experiments. Most major weed species do not currently have protocols for stable transformation, a key development in the popularity of A. thaliana as a model organism and a requirement for many functional genomic approaches. Functional validation of genes/variants believed to be responsible for traits of interest in weeds has thus far relied on transiently manipulating endogenous gene expression [ 45 , 46 ] or ectopic expression of a transgene in a model system [ 47 , 48 , 49 ]. While these methods have been successful, few weed species have well-studied viral vectors to adapt for use in virus induced gene silencing. Spray induced gene silencing is another potential option for functional investigation of candidate genes in weeds, but more research is needed to establish reliable delivery and gene knockdown [ 50 ]. Furthermore, traits with complex genetic architecture divergent between the researched and model species may not be amenable to functional genomic approaches using transgenesis techniques in model systems. Developing protocols for reduced representation sequencing, stable transformation, and gene editing/silencing in weeds will allow for more thorough characterization of candidate genetic variants underlying traits of interest.
Beyond rapid adaptation, some weedy species offer an opportunity to better understand co-evolution, like that between plants and pollinators and how their interaction leads to the spread of weedy alleles (Additional File 1 : Table S1). A suite of plant–insect traits has co-evolved to maximize the attraction of the insect pollinator community and the efficiency of pollen deposition between flowers ensuring fruit and seed production in many weeds [ 51 , 52 ]. Genetic mapping experiments have identified genes and genetic variants responsible for many floral traits affecting pollinator interaction including petal color [ 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 ], flower symmetry and size [ 57 , 58 , 59 ], and production of volatile organic compounds [ 60 , 61 , 62 ] and nectar [ 63 , 64 , 65 ]. While these studies reveal candidate genes for selection under co-evolution, herbicide resistance alleles may also have pleiotropic effects on the ecology of weeds [ 66 ], altering plant-pollinator interactions [ 67 ]. Discovery of genes and genetic variants involved in weed-pollinator interaction and their molecular and environmental control may create opportunities for better management of weeds with insect-mediated pollination. For example, if management can disrupt pollinator attraction/interaction with these weeds, the efficiency of reproduction may be reduced.
A more complete understanding of weed ecological genomics will undoubtedly elucidate many unresolved questions regarding the genetic basis of various aspects of weediness. For instance, when comparing populations of a species from agricultural and non-agricultural environments, is there evidence for contemporary evolution of weedy traits selected by agricultural management or were “natural” populations pre-adapted to agroecosystems? Where there is differentiation between weedy and natural populations, which traits are under selection and what is the genetic basis of variation in those traits? When comparing between weedy populations, is there evidence for parallel versus non-parallel evolution of weediness at the phenotypic and genotypic levels? Such studies may uncover fundamental truths about weediness. For example, is there a common phenotypic and/or genotypic basis for aspects of weediness among diverse weed species? The availability of characterized accessions and reference genomes for species of interest are required for such studies but only a few weedy species have these resources developed.
Population genomics
Weed species are certainly fierce competitors, able to outcompete crops and endemic species in their native environment, but they are also remarkable colonizers of perturbed habitats. Weeds achieve this through high fecundity, often producing tens of thousands of seeds per individual plant [ 68 , 69 , 70 ]. These large numbers in terms of demographic population size often combine with outcrossing reproduction to generate high levels of diversity with local effective population sizes in the hundreds of thousands [ 71 , 72 ]. This has two important consequences: weed populations retain standing genetic variation and generate many new mutations, supporting weed success in the face of harsh control. The generation of genomic tools to monitor weed populations at the molecular level is a game-changer to understanding weed dynamics and precisely testing the effect of artificial selection (i.e., management) and other evolutionary mechanisms on the genetic make-up of populations.
Population genomic data, without any environmental or phenotypic information, can be used to scan the genomes of weed and non-weed relatives to identify selective sweeps, pointing at loci supporting weed adaptation on micro- or macro-evolutionary scales. Two recent within-species examples include weedy rice, where population differentiation between weedy and domesticated populations was used to identify the genetic basis of weedy de-domestication [ 73 ], and common waterhemp, where consistent allelic differences among natural and agricultural collections resolved a complex set of agriculturally adaptive alleles [ 74 , 75 ]. A recent comparative population genomic study of weedy barnyardgrass and crop millet species has demonstrated how inter-specific investigations can resolve the signatures of crop and weed evolution [ 76 ] (also see [ 77 ] for a non-weed climate adaptation example). Multiple sequence alignments across numerous species provide complementary insight into adaptive convergence over deeper timescales, even with just one genomic sample per species (e.g., [ 78 , 79 ]). Thus, newly sequenced weed genomes combined with genomes available for closely related crops (outlined by [ 14 , 80 ]) and an effort to identify other non-weed wild relatives will be invaluable in characterizing the genetic architecture of weed adaptation and evolution across diverse species.
Weeds experience high levels of genetic selection, both artificial in response to agricultural practices and particularly herbicides, and natural in response to the environmental conditions they encounter [ 81 , 82 ]. Using genomic analysis to identify loci that are the targets of selection, whether natural or artificial, would point at vulnerabilities that could be leveraged against weeds to develop new and more sustainable management strategies [ 83 ]. This is a key motivation to develop genotype-by-environment association (GEA) and selective sweep scan approaches, which allow researchers to resolve the molecular basis of multi-dimensional adaptation [ 84 , 85 ]. GEA approaches, in particular, have been widely used on landscape-wide resequencing collections to determine the genetic basis of climate adaptation (e.g., [ 27 , 86 , 87 ]), but have yet to be fully exploited to diagnose the genetic basis of the various aspects of weediness [ 88 ]. Armed with data on environmental dimensions of agricultural settings, such as focal crop, soil quality, herbicide use, and climate, GEA approaches can help disentangle how discrete farming practices have influenced the evolution of weediness and resolve broader patterns of local adaptation across a weed’s range. Although non-weedy relatives are not technically required for GEA analyses, inclusion of environmental and genomic data from weed progenitors can further distinguish genetic variants underpinning weed origins from those involved in local adaptation.
New weeds emerge frequently [ 89 ], either through hybridization between species as documented for sea beet ( Beta vulgaris ssp. maritima) hybridizing with crop beet to produce progeny that are well adapted to agricultural conditions [ 90 , 91 , 92 ], or through the invasion of alien species that find a new range to colonize. Biosecurity measures are often in place to stop the introduction of new weeds; however, the vast scale of global agricultural commodity trade precludes the possibility of total control. Population genomic analysis is now able to measure gene flow between populations [ 74 , 93 , 94 , 95 ] and identify populations of origin for invasive species including weeds [ 96 , 97 , 98 ]. For example, the invasion route of the pest fruitfly Drosophila suzukii from Eastern Asia to North America and Europe through Hawaii was deciphered using Approximate Bayesian Computation on high-throughput sequencing data from a global sample of multiple populations [ 99 ]. Genomics can also be leveraged to predict invasion rather than explain it. The resequencing of a global sample of common ragweed ( Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.) elucidated a complex invasion route whereby Europe was invaded by multiple introductions of American ragweed that hybridized in Europe prior to a subsequent introduction to Australia [ 100 , 101 ]. In this context, the use of genomically informed species distribution models helps assess the risk associated with different source populations, which in the case of common ragweed, suggests that a source population from Florida would allow ragweed to invade most of northern Australia [ 102 ]. Globally coordinated research efforts to understand potential distribution models could support the transformation of biosecurity from perspective analysis towards predictive risk assessment.
Herbicide resistance and weed management
Herbicide resistance is among the numerous weedy traits that can evolve in plant populations exposed to agricultural selection pressures. Over-reliance on herbicides to control weeds, along with low diversity and lack of redundancy in weed management strategies, has resulted in globally widespread herbicide resistance [ 103 ]. To date, 272 herbicide-resistant weed species have been reported worldwide, and at least one resistance case exists for 21 of the 31 existing herbicide sites of action [ 104 ]—significantly limiting chemical weed control options available to agriculturalists. This limitation of control options is exacerbated by the recent lack of discovery of herbicides with new sites of action [ 105 ].
Herbicide resistance may result from several different physiological mechanisms. Such mechanisms have been classified into two main groups, target-site resistance (TSR) [ 4 , 106 ] and non-target-site resistance (NTSR) [ 4 , 107 ]. The first group encompasses changes that reduce binding affinity between a herbicide and its target [ 108 ]. These changes may provide resistance to multiple herbicides that have a common biochemical target [ 109 ] and can be effectively managed through mixture and/or rotation of herbicides targeting different sites of action [ 110 ]. The second group (NTSR), includes alterations in herbicide absorption, translocation, sequestration, and/or metabolism that may lead to unpredictable pleotropic cross-resistance profiles where structurally and functionally diverse herbicides are rendered ineffective by one or more genetic variant(s) [ 47 ]. This mechanism of resistance threatens not only the efficacy of existing herbicidal chemistries, but also ones yet to be discovered. While TSR is well understood because of the ease of identification and molecular characterization of target site variants, NTSR mechanisms are significantly more challenging to research because they are often polygenic, and the resistance causing element(s) are not well understood [ 111 ].
Improving the current understanding of metabolic NTSR mechanisms is not an easy task, since genes of diverse biochemical functions are involved, many of which exist as extensive gene families [ 109 , 112 ]. Expression changes of NTSR genes have been implicated in several resistance cases where the protein products of the genes are functionally equivalent across sensitive and resistant plants, but their relative abundance leads to resistance. Thus, regulatory elements of NTSR genes have been scrutinized to understand their role in NTSR mechanisms [ 113 ]. Similarly, epigenetic modifications have been hypothesized to play a role in NTSR, with much remaining to be explored [ 114 , 115 , 116 ]. Untargeted approaches such as genome-wide association, selective sweep scans, linkage mapping, RNA-sequencing, and metabolomic profiling have proven helpful to complement more specific biochemical- and chemo-characterization studies towards the elucidation of NTSR mechanisms as well as their regulation and evolution [ 47 , 117 , 118 , 119 , 120 , 121 , 122 , 123 , 124 ]. Even in cases where resistance has been attributed to TSR, genetic mapping approaches can detect other NTSR loci contributing to resistance (as shown by [ 123 ]) and provide further evidence for the role of TSR mutations across populations. Knowledge of the genetic basis of NTSR will aid the rational design of herbicides by screening new compounds for interaction with newly discovered NTSR proteins during early research phases and by identifying conserved chemical structures that interact with these proteins that should be avoided in small molecule design.
Genomic resources can also be used to predict the protein structure for novel herbicide target site and metabolism genes. This will allow for prediction of efficacy and selectivity for new candidate herbicides in silico to increase herbicide discovery throughput as well as aid in the design and development of next-generation technologies for sustainable weed management. Proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) have the potential to bind desired targets with great selectivity and degrade proteins by utilizing natural protein ubiquitination and degradation pathways within plants [ 125 ]. Spray-induced gene silencing in weeds using oligonucleotides has potential as a new, innovative, and sustainable method for weed management, but improved methods for design and delivery of oligonucleotides are needed to make this technique a viable management option [ 50 ]. Additionally, success in the field of pharmaceutical drug discovery in the development of molecules modulating protein–protein interactions offers another potential avenue towards the development of herbicides with novel targets [ 126 , 127 ]. High-quality reference genomes allow for the design of new weed management technologies like the ones listed here that are specific to—and effective across—weed species but have a null effect on non-target organisms.
Comparative genomics and genome biology
The genomes of weed species are as diverse as weed species themselves. Weeds are found across highly diverged plant families and often have no phylogenetically close model or crop species relatives for comparison. On all measurable metrics, weed genomes run the gamut. Some have smaller genomes like Cyperus spp. (~ 0.26 Gb) while others are larger, such as Avena fatua (~ 11.1 Gb) (Table 1 ). Some have high heterozygosity in terms of single-nucleotide polymorphisms, such as the Amaranthus spp., while others are primarily self-pollinated and quite homozygous, such as Poa annua [ 128 , 129 ]. Some are diploid such as Conyza canadensis and Echinochloa haploclada while others are polyploid such as C. sumetrensis , E. crus-galli , and E. colona [ 76 ]. The availability of genomic resources in these diverse, unexplored branches of the tree of life allows us to identify consistencies and anomalies in the field of genome biology.
The weed genomes published so far have focused mainly on weeds of agronomic crops, and studies have revolved around their ability to resist key herbicides. For example, genomic resources were vital in the elucidation of herbicide resistance cases involving target site gene copy number variants (CNVs). Gene CNVs of 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase ( EPSPS ) have been found to confer resistance to the herbicide glyphosate in diverse weed species. To date, nine species have independently evolved EPSPS CNVs, and species achieve increased EPSPS copy number via different mechanisms [ 153 ]. For instance, the EPSPS CNV in Bassia scoparia is caused by tandem duplication, which is accredited to transposable element insertions flanking EPSPS and subsequent unequal crossing over events [ 154 , 155 ]. In Eleusine indica , a EPSPS CNV was caused by translocation of the EPSPS locus into the subtelomere followed by telomeric sequence exchange [ 156 ]. One of the most fascinating genome biology discoveries in weed science has been that of extra-chromosomal circular DNAs (eccDNAs) that harbor the EPSPS gene in the weed species Amaranthus palmeri [ 157 , 158 ]. In this case, the eccDNAs autonomously replicate separately from the nuclear genome and do not reintegrate into chromosomes, which has implications for inheritance, fitness, and genome structure [ 159 ]. These discoveries would not have been possible without reference assemblies of weed genomes, next-generation sequencing, and collaboration with experts in plant genomics and bioinformatics.
Another question that is often explored with weedy genomes is the nature and composition of gene families that are associated with NTSR. Gene families under consideration often include cytochrome P450s (CYPs), glutathione- S -transferases (GSTs), ABC transporters, etc. Some questions commonly considered with new weed genomes include how many genes are in each of these gene families, where are they located, and which weed accessions and species have an over-abundance of them that might explain their ability to evolve resistance so rapidly [ 76 , 146 , 160 , 161 ]? Weed genome resources are necessary to answer questions about gene family expansion or contraction during the evolution of weediness, including the role of polyploidy in NTSR gene family expansion as explored by [ 162 ].
Translational research and communication with weed management stakeholders
Whereas genomics of model plants is typically aimed at addressing fundamental questions in plant biology, and genomics of crop species has the obvious goal of crop improvement, goals of genomics of weedy plants also include the development of more effective and sustainable strategies for their management. Weed genomic resources assist with these objectives by providing novel molecular ecological and evolutionary insights from the context of intensive anthropogenic management (which is lacking in model plants), and offer knowledge and resources for trait discovery for crop improvement, especially given that many wild crop relatives are also important agronomic weeds (e.g., [ 163 ]). For instance, crop-wild relatives are valuable for improving crop breeding for marginal environments [ 164 ]. Thus, weed genomics presents unique opportunities and challenges relative to plant genomics more broadly. It should also be noted that although weed science at its core is an applied discipline, it draws broadly from many scientific disciplines such as, plant physiology, chemistry, ecology, and evolutionary biology, to name a few. The successful integration of weed-management strategies, therefore, requires extensive collaboration among individuals collectively possessing the necessary expertise [ 165 ].
With the growing complexity of herbicide resistance management, practitioners are beginning to recognize the importance of understanding resistance mechanisms to inform appropriate management tactics [ 14 ]. Although weed science practitioners do not need to understand the technical details of weed genomics, their appreciation of the power of weed genomics—together with their unique insights from field observations—will yield novel opportunities for applications of weed genomics to weed management. In particular, combining field management history with information on weed resistance mechanisms is expected to provide novel insights into evolutionary trajectories (e.g. [ 6 , 166 ]), which can be utilized for disrupting evolutionary adaptation. It can be difficult to obtain field history information from practitioners, but developing an understanding among them of the importance of such information can be invaluable.
Development of weed genomics resources by the IWGC
Weed genomics is a fast-growing field of research with many recent breakthroughs and many unexplored areas of study. The International Weed Genomics Consortium (IWGC) started in 2021 to address the roadblocks listed above and to promote the study of weedy plants. The IWGC is an open collaboration among academic, government, and industry researchers focused on producing genomic tools for weedy species from around the world. Through this collaboration, our initial aim is to provide chromosome-level reference genome assemblies for at least 50 important weedy species from across the globe that are chosen based on member input, economic impact, and global prevalence (Fig. 1 ). Each genome will include annotation of gene models and repetitive elements and will be freely available through public databases with no intellectual property restrictions. Additionally, future funding of the IWGC will focus on improving gene annotations and supplementing these reference genomes with tools that increase their utility.
The International Weed Genomics Consortium (IWGC) collected input from the weed genomics community to develop plans for weed genome sequencing, annotation, user-friendly genome analysis tools, and community engagement
Reference genomes and data analysis tools
The first objective of the IWGC is to provide high-quality genomic resources for agriculturally important weeds. The IWGC therefore created two main resources for information about, access to, or analysis of weed genomic data (Fig. 1 ). The IWGC website (available at [ 167 ]) communicates the status and results of genome sequencing projects, information on training and funding opportunities, upcoming events, and news in weed genomics. It also contains details of all sequenced species including genome size, ploidy, chromosome number, herbicide resistance status, and reference genome assembly statistics. The IWGC either compiles existing data on genome size, ploidy, and chromosome number, or obtains the data using flow cytometry and cytogenetics (Fig. 1 ; Additional File 2 : Fig S1-S4). Through this website, users can request an account to access our second main resource, an online genome database called WeedPedia (accessible at [ 168 ]), with an account that is created within 3–5 working days of an account request submission. WeedPedia hosts IWGC-generated and other relevant publicly accessible genomic data as well as a suite of bioinformatic tools. Unlike what is available for other fields, weed science did not have a centralized hub for genomics information, data, and analysis prior to the IWGC. Our intention in creating WeedPedia is to encourage collaboration and equity of access to information across the research community. Importantly, all genome assemblies and annotations from the IWGC (Table 1 ), along with the raw data used to produce them, will be made available through NCBI GenBank. Upon completion of a 1-year sponsoring member data confidentiality period for each species (dates listed in Table 1 ), scientific teams within the IWGC produce the first genome-wide investigation to submit for publication including whole genome level analyses on genes, gene families, and repetitive sequences as well as comparative analysis with other species. Genome assemblies and data will be publicly available through NCBI as part of these initial publications for each species.
WeedPedia is a cloud-based omics database management platform built from the software “CropPedia” and licensed from KeyGene (Wageningen, The Netherlands). The interface allows users to access, visualize, and download genome assemblies along with structural and functional annotation. The platform includes a genome browser, comparative map viewer, pangenome tools, RNA-sequencing data visualization tools, genetic mapping and marker analysis tools, and alignment capabilities that allow searches by keyword or sequence. Additionally, genes encoding known target sites of herbicides have been specially annotated, allowing users to quickly identify and compare these genes of interest. The platform is flexible, making it compatible with future integration of other data types such as epigenetic or proteomic information. As an online platform with a graphical user interface, WeedPedia provides user-friendly, intuitive tools that encourage users to integrate genomics into their research while also allowing more advanced users to download genomic data to be used in custom analysis pipelines. We aspire for WeedPedia to mimic the success of other public genomic databases such as NCBI, CoGe, Phytozome, InsectBase, and Mycocosm to name a few. WeedPedia currently hosts reference genomes for 40 species (some of which are currently in their 1-year confidentiality period) with additional genomes in the pipeline to reach a currently planned total of 55 species (Table 1 ). These genomes include both de novo reference genomes generated or in progress by the IWGC (31 species; Table 1 ), and publicly available genome assemblies of 24 weedy or related species that were generated by independent research groups (Table 2 ). As of May 2024, WeedPedia has over 370 registered users from more than 27 countries spread across 6 continents.
The IWGC reference genomes are generated in partnership with the Corteva Agriscience Genome Center of Excellence (Johnston, Iowa) using a combination of single-molecule long-read sequencing, optical genome maps, and chromosome conformation mapping. This strategy has already yielded highly contiguous, phased, chromosome-level assemblies for 26 weed species, with additional assemblies currently in progress (Table 1 ). The IWGC assemblies have been completed as single or haplotype-resolved double-haplotype pseudomolecules in inbreeding and outbreeding species, respectively, with multiple genomes being near gapless. For example, the de novo assemblies of the allohexaploids Conyza sumatrensis and Chenopodium album have all chromosomes captured in single scaffolds and most chromosomes being gapless from telomere to telomere. Complementary full-length isoform (IsoSeq) sequencing of RNA collected from diverse tissue types and developmental stages assists in the development of gene models during annotation.
As with accessibility of data, a core objective of the IWGC is to facilitate open access to sequenced germplasm when possible for featured species. Historically, the weed science community has rarely shared or adopted standard germplasm (e.g., specific weed accessions). The IWGC has selected a specific accession of each species for reference genome assembly (typically susceptible to herbicides). In collaboration with a parallel effort by the Herbicide Resistant Plants committee of the Weed Science Society of America, seeds of the sequenced weed accessions will be deposited in the United States Department of Agriculture Germplasm Resources Information Network [ 186 ] for broad access by the scientific community and their accession numbers will be listed on the IWGC website. In some cases, it is not possible to generate enough seed to deposit into a public repository (e.g., plants that typically reproduce vegetatively, that are self-incompatible, or that produce very few seeds from a single individual). In these cases, the location of collection for sequenced accessions will at least inform the community where the sequenced individual came from and where they may expect to collect individuals with similar genotypes. The IWGC ensures that sequenced accessions are collected and documented to comply with the Nagoya Protocol on access to genetic resources and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from their utilization under the Convention on Biological Diversity and related Access and Benefit Sharing Legislation [ 187 ]. As additional accessions of weed species are sequenced (e.g., pangenomes are obtained), the IWGC will facilitate germplasm sharing protocols to support collaboration. Further, to simplify the investigation of herbicide resistance, the IWGC will link WeedPedia with the International Herbicide-Resistant Weed Database [ 104 ], an already widely known and utilized database for weed scientists.
Training and collaboration in weed genomics
Beyond producing genomic tools and resources, a priority of the IWGC is to enable the utilization of these resources across a wide range of stakeholders. A holistic approach to training is required for weed science generally [ 188 ], and we would argue even more so for weed genomics. To accomplish our training goals, the IWGC is developing and delivering programs aimed at the full range of IWGC stakeholders and covering a breadth of relevant topics. We have taken care to ensure our approaches are diverse as to provide training to researchers with all levels of existing experience and differing reasons for engaging with these tools. Throughout, the focus is on ensuring that our training and outreach result in impacts that benefit a wide range of stakeholders.
Although recently developed tools are incredibly enabling and have great potential to replace antiquated methodology [ 189 ] and to solve pressing weed science problems [ 14 ], specialized computational skills are required to fully explore and unlock meaning from these highly complex datasets. Collaboration with, or training of, computational biologists equipped with these skills and resources developed by the IWGC will enable weed scientists to expand research programs and better understand the genetic underpinnings of weed evolution and herbicide resistance. To fill existing skill gaps, the IWGC is developing summer bootcamps and online modules directed specifically at weed scientists that will provide training on computational skills (Fig. 1 ). Because successful utilization of the IWGC resources requires more than general computational skills, we have created three targeted workshops that teach practical skills related to genomics databases, molecular biology, and population genomics (available at [ 190 ]). The IWGC has also hosted two official conference meetings, one in September of 2021 and one in January of 2023, with more conferences planned. These conferences have included invited speakers to present successful implementations of weed genomics, educational workshops to build computational skills, and networking opportunities for research to connect and collaborate.
Engagement opportunities during undergraduate degrees have been shown to improve academic outcomes [ 191 , 192 ]. As one activity to help achieve this goal, the IWGC has sponsored opportunities for US undergraduates to undertake a 10-week research experience, which includes an introduction to bioinformatics, a plant genomics research project that results in a presentation, and access to career building opportunities in diverse workplace environments. To increase equitable access to conferences and professional communities, we supported early career researchers to attend the first two IWGC conferences in the USA as well as workshops and bootcamps in Europe, South America, and Australia. These hybrid or in-person travel grants are intentionally designed to remove barriers and increase participation of individuals from backgrounds and experiences currently underrepresented within weed/plant science or genomics [ 193 ]. Recipients of these travel awards gave presentations and gained the measurable benefits that come from either virtual or in-person participation in conferences [ 194 ]. Moving forward, weed scientists must amass skills associated with genomic analyses and collaborate with other area experts to fully leverage resources developed by the IWGC.
The tools generated through the IWGC will enable many new research projects with diverse objectives like those listed above. In summary, contiguous genome assemblies and complete annotation information will allow weed scientists to join plant breeders in the use of genetic mapping for many traits including stress tolerance, plant architecture, and herbicide resistance (especially important for cases of NTSR). These assemblies will also allow for investigations of population structure, gene flow, and responses to evolutionary mechanisms like genetic bottlenecking and artificial selection. Understanding gene sequences across diverse weed species will be vital in modeling new herbicide target site proteins and designing novel effective herbicides with minimal off-target effects. The IWGC website will improve accessibility to weed genomics data by providing a single hub for reference genomes as well as phenotypic and genotypic information for accessions shared with the IWGC. Deposition of sequenced germplasm into public repositories will ensure that researchers are able to access and utilize these accessions in their own research to make the field more standardized and equitable. WeedPedia allows users of all backgrounds to quickly access information of interest such as herbicide target site gene sequence or subcellular localization of protein products for different genes. Users can also utilize server-based tools such as BLAST and genome browsing similar to other public genomic databases. Finally, the IWGC is committed to training and connecting weed genomicists through hosting trainings, workshops, and conferences.
Conclusions
Weeds are unique and fascinating plants, having significant impacts on agriculture and ecosystems; and yet, aspects of their biology, ecology, and genetics remain poorly understood. Weeds represent a unique area within plant biology, given their repeated rapid adaptation to sudden and severe shifts in the selective landscape of anthropogenic management practices. The production of a public genomics database with reference genomes and annotations for over 50 weed species represents a substantial step forward towards research goals that improve our understanding of the biology and evolution of weeds. Future work is needed to improve annotations, particularly for complex gene families involved in herbicide detoxification, structural variants, and mobile genetic elements. As reference genome assemblies become available; standard, affordable methods for gathering genotype information will allow for the identification of genetic variants underlying traits of interest. Further, methods for functional validation and hypothesis testing are needed in weeds to validate the effect of genetic variants detected through such experiments, including systems for transformation, gene editing, and transient gene silencing and expression. Future research should focus on utilizing weed genomes to investigate questions about evolutionary biology, ecology, genetics of weedy traits, and weed population dynamics. The IWGC plans to continue the public–private partnership model to host the WeedPedia database over time, integrate new datasets such as genome resequencing and transcriptomes, conduct trainings, and serve as a research coordination network to ensure that advances in weed science from around the world are shared across the research community (Fig. 1 ). Bridging basic plant genomics with translational applications in weeds is needed to deliver on the potential of weed genomics to improve weed management and crop breeding.
Availability of data and materials
All genome assemblies and related sequencing data produced by the IWGC will be available through NCBI as part of publications reporting the first genome-wide analysis for each species.
Gianessi LP, Nathan PR. The value of herbicides in U.S. crop production. Weed Technol. 2007;21(2):559–66.
Article Google Scholar
Pimentel D, Lach L, Zuniga R, Morrison D. Environmental and economic costs of nonindigenous species in the United States. Bioscience. 2000;50(1):53–65.
Barrett SH. Crop mimicry in weeds. Econ Bot. 1983;37(3):255–82.
Powles SB, Yu Q. Evolution in action: plants resistant to herbicides. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2010;61:317–47.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Thurber CS, Reagon M, Gross BL, Olsen KM, Jia Y, Caicedo AL. Molecular evolution of shattering loci in U.S. weedy rice. Mol Ecol. 2010;19(16):3271–84.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Comont D, Lowe C, Hull R, Crook L, Hicks HL, Onkokesung N, et al. Evolution of generalist resistance to herbicide mixtures reveals a trade-off in resistance management. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3086.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ashworth MB, Walsh MJ, Flower KC, Vila-Aiub MM, Powles SB. Directional selection for flowering time leads to adaptive evolution in Raphanus raphanistrum (wild radish). Evol Appl. 2016;9(4):619–29.
Chan EK, Rowe HC, Kliebenstein DJ. Understanding the evolution of defense metabolites in Arabidopsis thaliana using genome-wide association mapping. Genetics. 2010;185(3):991–1007.
Frayling TM, Timpson NJ, Weedon MN, Zeggini E, Freathy RM, Lindgren CM, et al. A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity. Science. 2007;316(5826):889–94.
Harkess A, Zhou J, Xu C, Bowers JE, Van der Hulst R, Ayyampalayam S, et al. The asparagus genome sheds light on the origin and evolution of a young Y chromosome. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1279.
Periyannan S, Moore J, Ayliffe M, Bansal U, Wang X, Huang L, et al. The gene Sr33 , an ortholog of barley Mla genes, encodes resistance to wheat stem rust race Ug99. Science. 2013;341(6147):786–8.
Ågren J, Oakley CG, McKay JK, Lovell JT, Schemske DW. Genetic mapping of adaptation reveals fitness tradeoffs in Arabidopsis thaliana . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(52):21077–82.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Schartl M, Walter RB, Shen Y, Garcia T, Catchen J, Amores A, et al. The genome of the platyfish, Xiphophorus maculatus , provides insights into evolutionary adaptation and several complex traits. Nat Genet. 2013;45(5):567–72.
Ravet K, Patterson EL, Krähmer H, Hamouzová K, Fan L, Jasieniuk M, et al. The power and potential of genomics in weed biology and management. Pest Manag Sci. 2018;74(10):2216–25.
Hufford MB, Seetharam AS, Woodhouse MR, Chougule KM, Ou S, Liu J, et al. De novo assembly, annotation, and comparative analysis of 26 diverse maize genomes. Science. 2021;373(6555):655–62.
Liao W-W, Asri M, Ebler J, Doerr D, Haukness M, Hickey G, et al. A draft human pangenome reference. Nature. 2023;617(7960):312–24.
Huang Y, Wu D, Huang Z, Li X, Merotto A, Bai L, et al. Weed genomics: yielding insights into the genetics of weedy traits for crop improvement. aBIOTECH. 2023;4:20–30.
Chen K, Yang H, Wu D, Peng Y, Lian L, Bai L, et al. Weed biology and management in the multi-omics era: progress and perspectives. Plant Commun. 2024;5(4):100816.
De Wet JMJ, Harlan JR. Weeds and domesticates: evolution in the man-made habitat. Econ Bot. 1975;29(2):99–108.
Mahaut L, Cheptou PO, Fried G, Munoz F, Storkey J, Vasseur F, et al. Weeds: against the rules? Trends Plant Sci. 2020;25(11):1107–16.
Neve P, Vila-Aiub M, Roux F. Evolutionary-thinking in agricultural weed management. New Phytol. 2009;184(4):783–93.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Sharma G, Barney JN, Westwood JH, Haak DC. Into the weeds: new insights in plant stress. Trends Plant Sci. 2021;26(10):1050–60.
Vigueira CC, Olsen KM, Caicedo AL. The red queen in the corn: agricultural weeds as models of rapid adaptive evolution. Heredity (Edinb). 2013;110(4):303–11.
Donohue K, Dorn L, Griffith C, Kim E, Aguilera A, Polisetty CR, et al. Niche construction through germination cueing: life-history responses to timing of germination in Arabidopsis thaliana . Evolution. 2005;59(4):771–85.
PubMed Google Scholar
Exposito-Alonso M. Seasonal timing adaptation across the geographic range of Arabidopsis thaliana . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(18):9665–7.
Fournier-Level A, Korte A, Cooper MD, Nordborg M, Schmitt J, Wilczek AM. A map of local adaptation in Arabidopsis thaliana . Science. 2011;334(6052):86–9.
Hancock AM, Brachi B, Faure N, Horton MW, Jarymowycz LB, Sperone FG, et al. Adaptation to climate across the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. Science. 2011;334(6052):83–6.
Initiative TAG. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana . Nature. 2000;408(6814):796–815.
Alonso-Blanco C, Andrade J, Becker C, Bemm F, Bergelson J, Borgwardt KM, et al. 1,135 genomes reveal the global pattern of polymorphism in Arabidopsis thaliana . Cell. 2016;166(2):481–91.
Durvasula A, Fulgione A, Gutaker RM, Alacakaptan SI, Flood PJ, Neto C, et al. African genomes illuminate the early history and transition to selfing in Arabidopsis thaliana . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(20):5213–8.
Frachon L, Mayjonade B, Bartoli C, Hautekèete N-C, Roux F. Adaptation to plant communities across the genome of Arabidopsis thaliana . Mol Biol Evol. 2019;36(7):1442–56.
Fulgione A, Koornneef M, Roux F, Hermisson J, Hancock AM. Madeiran Arabidopsis thaliana reveals ancient long-range colonization and clarifies demography in Eurasia. Mol Biol Evol. 2018;35(3):564–74.
Fulgione A, Neto C, Elfarargi AF, Tergemina E, Ansari S, Göktay M, et al. Parallel reduction in flowering time from de novo mutations enable evolutionary rescue in colonizing lineages. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):1461.
Kasulin L, Rowan BA, León RJC, Schuenemann VJ, Weigel D, Botto JF. A single haplotype hyposensitive to light and requiring strong vernalization dominates Arabidopsis thaliana populations in Patagonia. Argentina Mol Ecol. 2017;26(13):3389–404.
Picó FX, Méndez-Vigo B, Martínez-Zapater JM, Alonso-Blanco C. Natural genetic variation of Arabidopsis thaliana is geographically structured in the Iberian peninsula. Genetics. 2008;180(2):1009–21.
Atwell S, Huang YS, Vilhjálmsson BJ, Willems G, Horton M, Li Y, et al. Genome-wide association study of 107 phenotypes in Arabidopsis thaliana inbred lines. Nature. 2010;465(7298):627–31.
Flood PJ, Kruijer W, Schnabel SK, van der Schoor R, Jalink H, Snel JFH, et al. Phenomics for photosynthesis, growth and reflectance in Arabidopsis thaliana reveals circadian and long-term fluctuations in heritability. Plant Methods. 2016;12(1):14.
Marchadier E, Hanemian M, Tisné S, Bach L, Bazakos C, Gilbault E, et al. The complex genetic architecture of shoot growth natural variation in Arabidopsis thaliana . PLoS Genet. 2019;15(4):e1007954.
Tisné S, Serrand Y, Bach L, Gilbault E, Ben Ameur R, Balasse H, et al. Phenoscope: an automated large-scale phenotyping platform offering high spatial homogeneity. Plant J. 2013;74(3):534–44.
Tschiersch H, Junker A, Meyer RC, Altmann T. Establishment of integrated protocols for automated high throughput kinetic chlorophyll fluorescence analyses. Plant Methods. 2017;13:54.
Chen X, MacGregor DR, Stefanato FL, Zhang N, Barros-Galvão T, Penfield S. A VEL3 histone deacetylase complex establishes a maternal epigenetic state controlling progeny seed dormancy. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):2220.
Choi M, Scholl UI, Ji W, Liu T, Tikhonova IR, Zumbo P, et al. Genetic diagnosis by whole exome capture and massively parallel DNA sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(45):19096–101.
Davey JW, Blaxter ML. RADSeq: next-generation population genetics. Brief Funct Genomics. 2010;9(5–6):416–23.
Elshire RJ, Glaubitz JC, Sun Q, Poland JA, Kawamoto K, Buckler ES, et al. A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(5):e19379.
MacGregor DR. What makes a weed a weed? How virus-mediated reverse genetics can help to explore the genetics of weediness. Outlooks Pest Manag. 2020;31(5):224–9.
Mellado-Sánchez M, McDiarmid F, Cardoso V, Kanyuka K, MacGregor DR. Virus-mediated transient expression techniques enable gene function studies in blackgrass. Plant Physiol. 2020;183(2):455–9.
Dimaano NG, Yamaguchi T, Fukunishi K, Tominaga T, Iwakami S. Functional characterization of Cytochrome P450 CYP81A subfamily to disclose the pattern of cross-resistance in Echinochloa phyllopogon . Plant Mol Biol. 2020;102(4–5):403–16.
de Figueiredo MRA, Küpper A, Malone JM, Petrovic T, de Figueiredo ABTB, Campagnola G, et al. An in-frame deletion mutation in the degron tail of auxin coreceptor IAA2 confers resistance to the herbicide 2,4-D in Sisymbrium orientale . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(9):e2105819119.
Patzoldt WL, Hager AG, McCormick JS, Tranel PJ. A codon deletion confers resistance to herbicides inhibiting protoporphyrinogen oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(33):12329–34.
Zabala-Pardo D, Gaines T, Lamego FP, Avila LA. RNAi as a tool for weed management: challenges and opportunities. Adv Weed Sci. 2022;40(spe1):e020220096.
Fattorini R, Glover BJ. Molecular mechanisms of pollination biology. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2020;71:487–515.
Rollin O, Benelli G, Benvenuti S, Decourtye A, Wratten SD, Canale A, et al. Weed-insect pollinator networks as bio-indicators of ecological sustainability in agriculture. A review Agron Sustain Dev. 2016;36(1):8.
Irwin RE, Strauss SY. Flower color microevolution in wild radish: evolutionary response to pollinator-mediated selection. Am Nat. 2005;165(2):225–37.
Ma B, Wu J, Shi T-L, Yang Y-Y, Wang W-B, Zheng Y, et al. Lilac ( Syringa oblata ) genome provides insights into its evolution and molecular mechanism of petal color change. Commun Biol. 2022;5(1):686.
Xing A, Wang X, Nazir MF, Zhang X, Wang X, Yang R, et al. Transcriptomic and metabolomic profiling of flavonoid biosynthesis provides novel insights into petals coloration in Asian cotton ( Gossypium arboreum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2022;22(1):416.
Zheng Y, Chen Y, Liu Z, Wu H, Jiao F, Xin H, et al. Important roles of key genes and transcription factors in flower color differences of Nicotiana alata . Genes (Basel). 2021;12(12):1976.
Krizek BA, Anderson JT. Control of flower size. J Exp Bot. 2013;64(6):1427–37.
Powell AE, Lenhard M. Control of organ size in plants. Curr Biol. 2012;22(9):R360–7.
Spencer V, Kim M. Re"CYC"ling molecular regulators in the evolution and development of flower symmetry. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018;79:16–26.
Amrad A, Moser M, Mandel T, de Vries M, Schuurink RC, Freitas L, et al. Gain and loss of floral scent production through changes in structural genes during pollinator-mediated speciation. Curr Biol. 2016;26(24):3303–12.
Delle-Vedove R, Schatz B, Dufay M. Understanding intraspecific variation of floral scent in light of evolutionary ecology. Ann Bot. 2017;120(1):1–20.
Pichersky E, Gershenzon J. The formation and function of plant volatiles: perfumes for pollinator attraction and defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2002;5(3):237–43.
Ballerini ES, Kramer EM, Hodges SA. Comparative transcriptomics of early petal development across four diverse species of Aquilegia reveal few genes consistently associated with nectar spur development. BMC Genom. 2019;20(1):668.
Corbet SA, Willmer PG, Beament JWL, Unwin DM, Prys-Jones OE. Post-secretory determinants of sugar concentration in nectar. Plant Cell Environ. 1979;2(4):293–308.
Galliot C, Hoballah ME, Kuhlemeier C, Stuurman J. Genetics of flower size and nectar volume in Petunia pollination syndromes. Planta. 2006;225(1):203–12.
Vila-Aiub MM, Neve P, Powles SB. Fitness costs associated with evolved herbicide resistance alleles in plants. New Phytol. 2009;184(4):751–67.
Baucom RS. Evolutionary and ecological insights from herbicide-resistant weeds: what have we learned about plant adaptation, and what is left to uncover? New Phytol. 2019;223(1):68–82.
Bajwa AA, Latif S, Borger C, Iqbal N, Asaduzzaman M, Wu H, et al. The remarkable journey of a weed: biology and management of annual ryegrass ( Lolium rigidum ) in conservation cropping systems of Australia. Plants (Basel). 2021;10(8):1505.
Bitarafan Z, Andreasen C. Fecundity allocation in some european weed species competing with crops. Agronomy. 2022;12(5):1196.
Costea M, Weaver SE, Tardif FJ. The biology of Canadian weeds. 130. Amaranthus retroflexus L., A. powellii , A. powellii S. Watson, and A. hybridus L. Can J Plant Sci. 2004;84(2):631–68.
Dixon A, Comont D, Slavov GT, Neve P. Population genomics of selectively neutral genetic structure and herbicide resistance in UK populations of Alopecurus myosuroides . Pest Manag Sci. 2021;77(3):1520–9.
Kersten S, Chang J, Huber CD, Voichek Y, Lanz C, Hagmaier T, et al. Standing genetic variation fuels rapid evolution of herbicide resistance in blackgrass. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023;120(16):e2206808120.
Qiu J, Zhou Y, Mao L, Ye C, Wang W, Zhang J, et al. Genomic variation associated with local adaptation of weedy rice during de-domestication. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):15323.
Kreiner JM, Caballero A, Wright SI, Stinchcombe JR. Selective ancestral sorting and de novo evolution in the agricultural invasion of Amaranthus tuberculatus . Evolution. 2022;76(1):70–85.
Kreiner JM, Latorre SM, Burbano HA, Stinchcombe JR, Otto SP, Weigel D, et al. Rapid weed adaptation and range expansion in response to agriculture over the past two centuries. Science. 2022;378(6624):1079–85.
Wu D, Shen E, Jiang B, Feng Y, Tang W, Lao S, et al. Genomic insights into the evolution of Echinochloa species as weed and orphan crop. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):689.
Yeaman S, Hodgins KA, Lotterhos KE, Suren H, Nadeau S, Degner JC, et al. Convergent local adaptation to climate in distantly related conifers. Science. 2016;353(6306):1431–3.
Haudry A, Platts AE, Vello E, Hoen DR, Leclercq M, Williamson RJ, et al. An atlas of over 90,000 conserved noncoding sequences provides insight into crucifer regulatory regions. Nat Genet. 2013;45(8):891–8.
Sackton TB, Grayson P, Cloutier A, Hu Z, Liu JS, Wheeler NE, et al. Convergent regulatory evolution and loss of flight in paleognathous birds. Science. 2019;364(6435):74–8.
Ye CY, Fan L. Orphan crops and their wild relatives in the genomic era. Mol Plant. 2021;14(1):27–39.
Clements DR, Jones VL. Ten ways that weed evolution defies human management efforts amidst a changing climate. Agronomy. 2021;11(2):284.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Weinig C. Rapid evolutionary responses to selection in heterogeneous environments among agricultural and nonagricultural weeds. Int J Plant Sci. 2005;166(4):641–7.
Cousens RD, Fournier-Level A. Herbicide resistance costs: what are we actually measuring and why? Pest Manag Sci. 2018;74(7):1539–46.
Lasky JR, Josephs EB, Morris GP. Genotype–environment associations to reveal the molecular basis of environmental adaptation. Plant Cell. 2023;35(1):125–38.
Lotterhos KE. The effect of neutral recombination variation on genome scans for selection. G3-Genes Genom Genet. 2019;9(6):1851–67.
Lovell JT, MacQueen AH, Mamidi S, Bonnette J, Jenkins J, Napier JD, et al. Genomic mechanisms of climate adaptation in polyploid bioenergy switchgrass. Nature. 2021;590(7846):438–44.
Todesco M, Owens GL, Bercovich N, Légaré J-S, Soudi S, Burge DO, et al. Massive haplotypes underlie ecotypic differentiation in sunflowers. Nature. 2020;584(7822):602–7.
Revolinski SR, Maughan PJ, Coleman CE, Burke IC. Preadapted to adapt: Underpinnings of adaptive plasticity revealed by the downy brome genome. Commun Biol. 2023;6(1):326.
Kuester A, Conner JK, Culley T, Baucom RS. How weeds emerge: a taxonomic and trait-based examination using United States data. New Phytol. 2014;202(3):1055–68.
Arnaud JF, Fénart S, Cordellier M, Cuguen J. Populations of weedy crop-wild hybrid beets show contrasting variation in mating system and population genetic structure. Evol Appl. 2010;3(3):305–18.
Ellstrand NC, Schierenbeck KA. Hybridization as a stimulus for the evolution of invasiveness in plants? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(13):7043–50.
Nakabayashi K, Leubner-Metzger G. Seed dormancy and weed emergence: from simulating environmental change to understanding trait plasticity, adaptive evolution, and population fitness. J Exp Bot. 2021;72(12):4181–5.
Busi R, Yu Q, Barrett-Lennard R, Powles S. Long distance pollen-mediated flow of herbicide resistance genes in Lolium rigidum . Theor Appl Genet. 2008;117(8):1281–90.
Délye C, Clément JAJ, Pernin F, Chauvel B, Le Corre V. High gene flow promotes the genetic homogeneity of arable weed populations at the landscape level. Basic Appl Ecol. 2010;11(6):504–12.
Roumet M, Noilhan C, Latreille M, David J, Muller MH. How to escape from crop-to-weed gene flow: phenological variation and isolation-by-time within weedy sunflower populations. New Phytol. 2013;197(2):642–54.
Moghadam SH, Alebrahim MT, Mohebodini M, MacGregor DR. Genetic variation of Amaranthus retroflexus L. and Chenopodium album L. (Amaranthaceae) suggests multiple independent introductions into Iran. Front Plant Sci. 2023;13:1024555.
Muller M-H, Latreille M, Tollon C. The origin and evolution of a recent agricultural weed: population genetic diversity of weedy populations of sunflower ( Helianthus annuus L.) in Spain and France. Evol Appl. 2011;4(3):499–514.
Wesse C, Welk E, Hurka H, Neuffer B. Geographical pattern of genetic diversity in Capsella bursa-pastoris (Brassicaceae) -A global perspective. Ecol Evol. 2021;11(1):199–213.
Fraimout A, Debat V, Fellous S, Hufbauer RA, Foucaud J, Pudlo P, et al. Deciphering the routes of invasion of Drosophila suzukii by means of ABC random forest. Mol Biol Evol. 2017;34(4):980–96.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Battlay P, Wilson J, Bieker VC, Lee C, Prapas D, Petersen B, et al. Large haploblocks underlie rapid adaptation in the invasive weed Ambrosia artemisiifolia . Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):1717.
van Boheemen LA, Hodgins KA. Rapid repeatable phenotypic and genomic adaptation following multiple introductions. Mol Ecol. 2020;29(21):4102–17.
Putra A, Hodgins K, Fournier-Level A. Assessing the invasive potential of different source populations of ragweed ( Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.) through genomically-informed species distribution modelling. Authorea. 2023;17(1):e13632.
Google Scholar
Bourguet D, Delmotte F, Franck P, Guillemaud T, Reboud X, Vacher C, et al. Heterogeneity of selection and the evolution of resistance. Trends Ecol Evol. 2013;28(2):110–8.
The International Herbicide-Resistant Weed Database. www.weedscience.org . Accessed 20 June 2023.
Powles S. Herbicide discovery through innovation and diversity. Adv Weed Sci. 2022;40(spe1):e020220074.
Murphy BP, Tranel PJ. Target-site mutations conferring herbicide resistance. Plants (Basel). 2019;8(10):382.
Gaines TA, Duke SO, Morran S, Rigon CAG, Tranel PJ, Küpper A, et al. Mechanisms of evolved herbicide resistance. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(30):10307–30.
Lonhienne T, Cheng Y, Garcia MD, Hu SH, Low YS, Schenk G, et al. Structural basis of resistance to herbicides that target acetohydroxyacid synthase. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):3368.
Comont D, MacGregor DR, Crook L, Hull R, Nguyen L, Freckleton RP, et al. Dissecting weed adaptation: fitness and trait correlations in herbicide-resistant Alopecurus myosuroides . Pest Manag Sci. 2022;78(7):3039–50.
Neve P. Simulation modelling to understand the evolution and management of glyphosate resistance in weeds. Pest Manag Sci. 2008;64(4):392–401.
Torra J, Alcántara-de la Cruz R. Molecular mechanisms of herbicide resistance in weeds. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(11):2025.
Délye C, Gardin JAC, Boucansaud K, Chauvel B, Petit C. Non-target-site-based resistance should be the centre of attention for herbicide resistance research: Alopecurus myosuroides as an illustration. Weed Res. 2011;51(5):433–7.
Chandra S, Leon RG. Genome-wide evolutionary analysis of putative non-specific herbicide resistance genes and compilation of core promoters between monocots and dicots. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(7):1171.
Margaritopoulou T, Tani E, Chachalis D, Travlos I. Involvement of epigenetic mechanisms in herbicide resistance: the case of Conyza canadensis . Agriculture. 2018;8(1):17.
Pan L, Guo Q, Wang J, Shi L, Yang X, Zhou Y, et al. CYP81A68 confers metabolic resistance to ALS and ACCase-inhibiting herbicides and its epigenetic regulation in Echinochloa crus-galli . J Hazard Mater. 2022;428:128225.
Sen MK, Hamouzová K, Košnarová P, Roy A, Soukup J. Herbicide resistance in grass weeds: Epigenetic regulation matters too. Front Plant Sci. 2022;13:1040958.
Han H, Yu Q, Beffa R, González S, Maiwald F, Wang J, et al. Cytochrome P450 CYP81A10v7 in Lolium rigidum confers metabolic resistance to herbicides across at least five modes of action. Plant J. 2021;105(1):79–92.
Kubis GC, Marques RZ, Kitamura RS, Barroso AA, Juneau P, Gomes MP. Antioxidant enzyme and Cytochrome P450 activities are involved in horseweed ( Conyza sumatrensis ) resistance to glyphosate. Stress. 2023;3(1):47–57.
Qiao Y, Zhang N, Liu J, Yang H. Interpretation of ametryn biodegradation in rice based on joint analyses of transcriptome, metabolome and chemo-characterization. J Hazard Mater. 2023;445:130526.
Rouse CE, Roma-Burgos N, Barbosa Martins BA. Physiological assessment of non–target site restistance in multiple-resistant junglerice ( Echinochloa colona ). Weed Sci. 2019;67(6):622–32.
Abou-Khater L, Maalouf F, Jighly A, Alsamman AM, Rubiales D, Rispail N, et al. Genomic regions associated with herbicide tolerance in a worldwide faba bean ( Vicia faba L.) collection. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):158.
Gupta S, Harkess A, Soble A, Van Etten M, Leebens-Mack J, Baucom RS. Interchromosomal linkage disequilibrium and linked fitness cost loci associated with selection for herbicide resistance. New Phytol. 2023;238(3):1263–77.
Kreiner JM, Tranel PJ, Weigel D, Stinchcombe JR, Wright SI. The genetic architecture and population genomic signatures of glyphosate resistance in Amaranthus tuberculatus . Mol Ecol. 2021;30(21):5373–89.
Parcharidou E, Dücker R, Zöllner P, Ries S, Orru R, Beffa R. Recombinant glutathione transferases from flufenacet-resistant black-grass ( Alopecurus myosuroides Huds.) form different flufenacet metabolites and differ in their interaction with pre- and post-emergence herbicides. Pest Manag Sci. 2023;79(9):3376–86.
Békés M, Langley DR, Crews CM. PROTAC targeted protein degraders: the past is prologue. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022;21(3):181–200.
Acuner Ozbabacan SE, Engin HB, Gursoy A, Keskin O. Transient protein-protein interactions. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2011;24(9):635–48.
Lu H, Zhou Q, He J, Jiang Z, Peng C, Tong R, et al. Recent advances in the development of protein–protein interactions modulators: mechanisms and clinical trials. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):213.
Benson CW, Sheltra MR, Maughan PJ, Jellen EN, Robbins MD, Bushman BS, et al. Homoeologous evolution of the allotetraploid genome of Poa annua L. BMC Genom. 2023;24(1):350.
Robbins MD, Bushman BS, Huff DR, Benson CW, Warnke SE, Maughan CA, et al. Chromosome-scale genome assembly and annotation of allotetraploid annual bluegrass ( Poa annua L.). Genome Biol Evol. 2022;15(1):evac180.
Montgomery JS, Giacomini D, Waithaka B, Lanz C, Murphy BP, Campe R, et al. Draft genomes of Amaranthus tuberculatus , Amaranthus hybridus and Amaranthus palmeri . Genome Biol Evol. 2020;12(11):1988–93.
Jeschke MR, Tranel PJ, Rayburn AL. DNA content analysis of smooth pigweed ( Amaranthus hybridus ) and tall waterhemp ( A. tuberculatus ): implications for hybrid detection. Weed Sci. 2003;51(1):1–3.
Rayburn AL, McCloskey R, Tatum TC, Bollero GA, Jeschke MR, Tranel PJ. Genome size analysis of weedy Amaranthus species. Crop Sci. 2005;45(6):2557–62.
Laforest M, Martin SL, Bisaillon K, Soufiane B, Meloche S, Tardif FJ, et al. The ancestral karyotype of the Heliantheae Alliance, herbicide resistance, and human allergens: Insights from the genomes of common and giant ragweed. Plant Genome . 2024;e20442. https://doi.org/10.1002/tpg2.20442 .
Mulligan GA. Chromosome numbers of Canadian weeds. I Canad J Bot. 1957;35(5):779–89.
Meyer L, Causse R, Pernin F, Scalone R, Bailly G, Chauvel B, et al. New gSSR and EST-SSR markers reveal high genetic diversity in the invasive plant Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. and can be transferred to other invasive Ambrosia species. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0176197.
Pustahija F, Brown SC, Bogunić F, Bašić N, Muratović E, Ollier S, et al. Small genomes dominate in plants growing on serpentine soils in West Balkans, an exhaustive study of 8 habitats covering 308 taxa. Plant Soil. 2013;373(1):427–53.
Kubešová M, Moravcova L, Suda J, Jarošík V, Pyšek P. Naturalized plants have smaller genomes than their non-invading relatives: a flow cytometric analysis of the Czech alien flora. Preslia. 2010;82(1):81–96.
Thébaud C, Abbott RJ. Characterization of invasive Conyza species (Asteraceae) in Europe: quantitative trait and isozyme analysis. Am J Bot. 1995;82(3):360–8.
Garcia S, Hidalgo O, Jakovljević I, Siljak-Yakovlev S, Vigo J, Garnatje T, et al. New data on genome size in 128 Asteraceae species and subspecies, with first assessments for 40 genera, 3 tribes and 2 subfamilies. Plant Biosyst. 2013;147(4):1219–27.
Zhao X, Yi L, Ren Y, Li J, Ren W, Hou Z, et al. Chromosome-scale genome assembly of the yellow nutsedge ( Cyperus esculentus ). Genome Biol Evol. 2023;15(3):evad027.
Bennett MD, Leitch IJ, Hanson L. DNA amounts in two samples of angiosperm weeds. Ann Bot. 1998;82:121–34.
Schulz-Schaeffer J, Gerhardt S. Cytotaxonomic analysis of the Euphorbia spp. (leafy spurge) complex. II: Comparative study of the chromosome morphology. Biol Zentralbl. 1989;108(1):69–76.
Schaeffer JR, Gerhardt S. The impact of introgressive hybridization on the weediness of leafy spurge. Leafy Spurge Symposium. 1989;1989:97–105.
Bai C, Alverson WS, Follansbee A, Waller DM. New reports of nuclear DNA content for 407 vascular plant taxa from the United States. Ann Bot. 2012;110(8):1623–9.
Aarestrup JR, Karam D, Fernandes GW. Chromosome number and cytogenetics of Euphorbia heterophylla L. Genet Mol Res. 2008;7(1):217–22.
Wang L, Sun X, Peng Y, Chen K, Wu S, Guo Y, et al. Genomic insights into the origin, adaptive evolution, and herbicide resistance of Leptochloa chinensis , a devastating tetraploid weedy grass in rice fields. Mol Plant. 2022;15(6):1045–58.
Paril J, Pandey G, Barnett EM, Rane RV, Court L, Walsh T, et al. Rounding up the annual ryegrass genome: high-quality reference genome of Lolium rigidum . Front Genet. 2022;13:1012694.
Weiss-Schneeweiss H, Greilhuber J, Schneeweiss GM. Genome size evolution in holoparasitic Orobanche (Orobanchaceae) and related genera. Am J Bot. 2006;93(1):148–56.
Towers G, Mitchell J, Rodriguez E, Bennett F, Subba Rao P. Biology & chemistry of Parthenium hysterophorus L., a problem weed in India. Biol Rev. 1977;48:65–74.
CAS Google Scholar
Moghe GD, Hufnagel DE, Tang H, Xiao Y, Dworkin I, Town CD, et al. Consequences of whole-genome triplication as revealed by comparative genomic analyses of the wild radish ( Raphanus raphanistrum ) and three other Brassicaceae species. Plant Cell. 2014;26(5):1925–37.
Zhang X, Liu T, Wang J, Wang P, Qiu Y, Zhao W, et al. Pan-genome of Raphanus highlights genetic variation and introgression among domesticated, wild, and weedy radishes. Mol Plant. 2021;14(12):2032–55.
Chytrý M, Danihelka J, Kaplan Z, Wild J, Holubová D, Novotný P, et al. Pladias database of the Czech flora and vegetation. Preslia. 2021;93(1):1–87.
Patterson EL, Pettinga DJ, Ravet K, Neve P, Gaines TA. Glyphosate resistance and EPSPS gene duplication: Convergent evolution in multiple plant species. J Hered. 2018;109(2):117–25.
Jugulam M, Niehues K, Godar AS, Koo DH, Danilova T, Friebe B, et al. Tandem amplification of a chromosomal segment harboring 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase locus confers glyphosate resistance in Kochia scoparia . Plant Physiol. 2014;166(3):1200–7.
Patterson EL, Saski CA, Sloan DB, Tranel PJ, Westra P, Gaines TA. The draft genome of Kochia scoparia and the mechanism of glyphosate resistance via transposon-mediated EPSPS tandem gene duplication. Genome Biol Evol. 2019;11(10):2927–40.
Zhang C, Johnson N, Hall N, Tian X, Yu Q, Patterson E. Subtelomeric 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase ( EPSPS ) copy number variation confers glyphosate resistance in Eleusine indica . Nat Commun. 2023;14:4865.
Koo D-H, Molin WT, Saski CA, Jiang J, Putta K, Jugulam M, et al. Extrachromosomal circular DNA-based amplification and transmission of herbicide resistance in crop weed Amaranthus palmeri . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(13):3332–7.
Molin WT, Yaguchi A, Blenner M, Saski CA. The eccDNA Replicon: A heritable, extranuclear vehicle that enables gene amplification and glyphosate resistance in Amaranthus palmeri . Plant Cell. 2020;32(7):2132–40.
Jugulam M. Can non-Mendelian inheritance of extrachromosomal circular DNA-mediated EPSPS gene amplification provide an opportunity to reverse resistance to glyphosate? Weed Res. 2021;61(2):100–5.
Kreiner JM, Giacomini DA, Bemm F, Waithaka B, Regalado J, Lanz C, et al. Multiple modes of convergent adaptation in the spread of glyphosate-resistant Amaranthus tuberculatus . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(42):21076–84.
Cai L, Comont D, MacGregor D, Lowe C, Beffa R, Neve P, et al. The blackgrass genome reveals patterns of non-parallel evolution of polygenic herbicide resistance. New Phytol. 2023;237(5):1891–907.
Chen K, Yang H, Peng Y, Liu D, Zhang J, Zhao Z, et al. Genomic analyses provide insights into the polyploidization-driven herbicide adaptation in Leptochloa weeds. Plant Biotechnol J. 2023;21(8):1642–58.
Ohadi S, Hodnett G, Rooney W, Bagavathiannan M. Gene flow and its consequences in Sorghum spp. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2017;36(5–6):367–85.
Renzi JP, Coyne CJ, Berger J, von Wettberg E, Nelson M, Ureta S, et al. How could the use of crop wild relatives in breeding increase the adaptation of crops to marginal environments? Front Plant Sci. 2022;13:886162.
Ward SM, Cousens RD, Bagavathiannan MV, Barney JN, Beckie HJ, Busi R, et al. Agricultural weed research: a critique and two proposals. Weed Sci. 2014;62(4):672–8.
Evans JA, Tranel PJ, Hager AG, Schutte B, Wu C, Chatham LA, et al. Managing the evolution of herbicide resistance. Pest Manag Sci. 2016;72(1):74–80.
International Weed Genomics Consortium Website. https://www.weedgenomics.org . Accessed 20 June 2023.
WeedPedia Database. https://weedpedia.weedgenomics.org/ . Accessed 20 June 2023.
Hall N, Chen J, Matzrafi M, Saski CA, Westra P, Gaines TA, et al. FHY3/FAR1 transposable elements generate adaptive genetic variation in the Bassia scoparia genome. bioRxiv . 2023; DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.05.26.542497 .
Jarvis DE, Sproul JS, Navarro-Domínguez B, Krak K, Jaggi K, Huang Y-F, et al. Chromosome-scale genome assembly of the hexaploid Taiwanese goosefoot “Djulis” ( Chenopodium formosanum ). Genome Biol Evol. 2022;14(8):evac120.
Ferreira LAI, de Oliveira RS, Jr., Constantin J, Brunharo C. Evolution of ACCase-inhibitor resistance in Chloris virgata is conferred by a Trp2027Cys mutation in the herbicide target site. Pest Manag Sci. 2023;79(12):5220–9.
Laforest M, Martin SL, Bisaillon K, Soufiane B, Meloche S, Page E. A chromosome-scale draft sequence of the Canada fleabane genome. Pest Manag Sci. 2020;76(6):2158–69.
Guo L, Qiu J, Ye C, Jin G, Mao L, Zhang H, et al. Echinochloa crus-galli genome analysis provides insight into its adaptation and invasiveness as a weed. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1031.
Sato MP, Iwakami S, Fukunishi K, Sugiura K, Yasuda K, Isobe S, et al. Telomere-to-telomere genome assembly of an allotetraploid pernicious weed, Echinochloa phyllopogon . DNA Res. 2023;30(5):dsad023.
Stein JC, Yu Y, Copetti D, Zwickl DJ, Zhang L, Zhang C, et al. Genomes of 13 domesticated and wild rice relatives highlight genetic conservation, turnover and innovation across the genus Oryza . Nat Genet. 2018;50(2):285–96.
Wu D, Xie L, Sun Y, Huang Y, Jia L, Dong C, et al. A syntelog-based pan-genome provides insights into rice domestication and de-domestication. Genome Biol. 2023;24(1):179.
Wang Z, Huang S, Yang Z, Lai J, Gao X, Shi J. A high-quality, phased genome assembly of broomcorn millet reveals the features of its subgenome evolution and 3D chromatin organization. Plant Commun. 2023;4(3):100557.
Mao Q, Huff DR. The evolutionary origin of Poa annua L. Crop Sci. 2012;52(4):1910–22.
Benson CW, Sheltra MR, Maughan JP, Jellen EN, Robbins MD, Bushman BS, et al. Homoeologous evolution of the allotetraploid genome of Poa annua L. Res Sq. 2023. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2729084/v1 .
Brunharo C, Benson CW, Huff DR, Lasky JR. Chromosome-scale genome assembly of Poa trivialis and population genomics reveal widespread gene flow in a cool-season grass seed production system. Plant Direct. 2024;8(3):e575.
Mo C, Wu Z, Shang X, Shi P, Wei M, Wang H, et al. Chromosome-level and graphic genomes provide insights into metabolism of bioactive metabolites and cold-adaption of Pueraria lobata var. montana . DNA Research. 2022;29(5):dsac030.
Thielen PM, Pendleton AL, Player RA, Bowden KV, Lawton TJ, Wisecaver JH. Reference genome for the highly transformable Setaria viridis ME034V. G3 (Bethesda, Md). 2020;10(10):3467–78.
Yoshida S, Kim S, Wafula EK, Tanskanen J, Kim Y-M, Honaas L, et al. Genome sequence of Striga asiatica provides insight into the evolution of plant parasitism. Curr Biol. 2019;29(18):3041–52.
Qiu S, Bradley JM, Zhang P, Chaudhuri R, Blaxter M, Butlin RK, et al. Genome-enabled discovery of candidate virulence loci in Striga hermonthica , a devastating parasite of African cereal crops. New Phytol. 2022;236(2):622–38.
Nunn A, Rodríguez-Arévalo I, Tandukar Z, Frels K, Contreras-Garrido A, Carbonell-Bejerano P, et al. Chromosome-level Thlaspi arvense genome provides new tools for translational research and for a newly domesticated cash cover crop of the cooler climates. Plant Biotechnol J. 2022;20(5):944–63.
USDA-ARS Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). https://www.ars-grin.gov/ . Accessed 20 June 2023.
Buck M, Hamilton C. The Nagoya Protocol on access to genetic resources and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from their utilization to the convention on biological diversity. RECIEL. 2011;20(1):47–61.
Chauhan BS, Matloob A, Mahajan G, Aslam F, Florentine SK, Jha P. Emerging challenges and opportunities for education and research in weed science. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:1537.
Shah S, Lonhienne T, Murray CE, Chen Y, Dougan KE, Low YS, et al. Genome-guided analysis of seven weed species reveals conserved sequence and structural features of key gene targets for herbicide development. Front Plant Sci. 2022;13:909073.
International Weed Genomics Consortium Training Resources. https://www.weedgenomics.org/training-resources/ . Accessed 20 June 2023.
Blackford S. Harnessing the power of communities: career networking strategies for bioscience PhD students and postdoctoral researchers. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018;365(8):fny033.
Pender M, Marcotte DE, Sto Domingo MR, Maton KI. The STEM pipeline: The role of summer research experience in minority students’ Ph.D. aspirations. Educ Policy Anal Arch. 2010;18(30):1–36.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Burke A, Okrent A, Hale K. The state of U.S. science and engineering 2022. Foundation NS. https://ncses.nsf.gov/pubs/nsb20221 . 2022.
Wu J-Y, Liao C-H, Cheng T, Nian M-W. Using data analytics to investigate attendees’ behaviors and psychological states in a virtual academic conference. Educ Technol Soc. 2021;24(1):75–91.
Download references
Peer review information
Wenjing She was the primary editor of this article and managed its editorial process and peer review in collaboration with the rest of the editorial team.
The International Weed Genomics Consortium is supported by BASF SE, Bayer AG, Syngenta Ltd, Corteva Agriscience, CropLife International (Global Herbicide Resistance Action Committee), the Foundation for Food and Agriculture Research (Award DSnew-0000000024), and two conference grants from USDA-NIFA (Award numbers 2021–67013-33570 and 2023-67013-38785).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Agricultural Biology, Colorado State University, 1177 Campus Delivery, Fort Collins, CO, 80523, USA
Jacob Montgomery, Sarah Morran & Todd A. Gaines
Protecting Crops and the Environment, Rothamsted Research, Harpenden, Hertfordshire, UK
Dana R. MacGregor
Department of Crop, Soil, and Environmental Sciences, Auburn University, Auburn, AL, USA
J. Scott McElroy
Department of Plant and Environmental Sciences, University of Copenhagen, Taastrup, Denmark
Paul Neve & Célia Neto
IFEVA-Conicet-Department of Ecology, University of Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina
Martin M. Vila-Aiub & Maria Victoria Sandoval
Department of Ecology, Faculty of Agronomy, University of Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina
Analia I. Menéndez
Department of Botany, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
Julia M. Kreiner
Institute of Crop Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Longjiang Fan
Department of Biology, University of Massachusetts Amherst, Amherst, MA, USA
Ana L. Caicedo
Department of Plant and Wildlife Sciences, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT, USA
Peter J. Maughan
Bayer AG, Weed Control Research, Frankfurt, Germany
Bianca Assis Barbosa Martins, Jagoda Mika, Alberto Collavo & Bodo Peters
Department of Crop Sciences, Federal University of Rio Grande Do Sul, Porto Alegre, Rio Grande Do Sul, Brazil
Aldo Merotto Jr.
Department of Soil and Crop Sciences, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA
Nithya K. Subramanian & Muthukumar V. Bagavathiannan
Department of Plant, Soil and Microbial Sciences, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, USA
Luan Cutti & Eric L. Patterson
Department of Agronomy, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS, USA
Md. Mazharul Islam & Mithila Jugulam
Department of Plant Pathology, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS, USA
Bikram S. Gill
Crop Protection Discovery and Development, Corteva Agriscience, Indianapolis, IN, USA
Robert Cicchillo, Roger Gast & Neeta Soni
Genome Center of Excellence, Corteva Agriscience, Johnston, IA, USA
Terry R. Wright, Gina Zastrow-Hayes, Gregory May, Kevin Fengler & Victor Llaca
School of Agriculture, Food and Wine, University of Adelaide, Glen Osmond, South Australia, Australia
Jenna M. Malone
Jealott’s Hill International Research Centre, Syngenta Ltd, Bracknell, Berkshire, UK
Deepmala Sehgal, Shiv Shankhar Kaundun & Richard P. Dale
Department of Plant and Soil Sciences, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa
Barend Juan Vorster
BASF SE, Ludwigshafen Am Rhein, Germany
Jens Lerchl
Department of Crop Sciences, University of Illinois, Urbana, IL, USA
Patrick J. Tranel
Senior Scientist Consultant, Herbicide Resistance Action Committee / CropLife International, Liederbach, Germany
Roland Beffa
School of BioSciences, University of Melbourne, Parkville, VIC, Australia
Alexandre Fournier-Level
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JMo and TG conceived and outlined the article. TG, DM, EP, RB, JSM, PJT, MJ wrote grants to obtain funding. MMI, BSG, and MJ performed mitotic chromosome visualization. VL performed sequencing. VL and KF assembled the genomes. LC and ELP annotated the genomes. JMo, SM, DRM, JSM, PN, CN, MV, MVS, AIM, JMK, LF, ALC, PJM, BABM, JMi, AC, MVB, LC, AFL, and ELP wrote the first draft of the article. All authors edited the article and improved the final version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Todd A. Gaines .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical approval is not applicable for this article.
Competing interests
Some authors work for commercial agricultural companies (BASF, Bayer, Corteva Agriscience, or Syngenta) that develop and sell weed control products.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
13059_2024_3274_moesm1_esm.docx.
Additional file 1. List of completed and in-progress genome assemblies of weed species pollinated by insects (Table S1).
13059_2024_3274_MOESM2_ESM.docx
Additional file 2. Methods and results for visualizing and counting the metaphase chromosomes of hexaploid Avena fatua (Fig S1); diploid Lolium rigidum (Fig S2); tetraploid Phalaris minor (Fig S3); and tetraploid Salsola tragus (Fig S4).
Additional file 3. Review history.
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Montgomery, J., Morran, S., MacGregor, D.R. et al. Current status of community resources and priorities for weed genomics research. Genome Biol 25 , 139 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-024-03274-y
Download citation
Received : 11 July 2023
Accepted : 13 May 2024
Published : 27 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-024-03274-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Weed science
- Reference genomes
- Rapid adaptation
- Herbicide resistance
- Public resources
Genome Biology
ISSN: 1474-760X
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

COMMENTS
A hypothesis test can either contain a directional hypothesis or a non-directional hypothesis: Directional hypothesis: The alternative hypothesis contains the less than ("<") or greater than (">") sign. This indicates that we're testing whether or not there is a positive or negative effect. Non-directional hypothesis: The alternative ...
Directional Hypothesis Examples. 1. Exercise and Heart Health. Research suggests that as regular physical exercise (independent variable) increases, the risk of heart disease (dependent variable) decreases (Jakicic, Davis, Rogers, King, Marcus, Helsel, Rickman, Wahed, Belle, 2016). In this example, a directional hypothesis anticipates that the ...
Directional hypotheses, also known as one-tailed hypotheses, are statements in research that make specific predictions about the direction of a relationship or difference between variables. Unlike non-directional hypotheses, which simply state that there is a relationship or difference without specifying its direction, directional hypotheses ...
A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between two variables. Unlike non-directional hypotheses, which simply state that there is a relationship between variables without specifying the direction, directional hypotheses make a clear prediction about the expected outcome.
A research hypothesis, in its plural form "hypotheses," is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. ... A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of ...
There are seven different types of research hypotheses. Simple Hypothesis. A simple hypothesis predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable. Complex Hypothesis. A complex hypothesis predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables. Directional Hypothesis.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
A research hypothesis is an assumption or a tentative explanation for a specific process observed during research. Unlike a guess, research hypothesis is a calculated, educated guess proven or disproven through research methods. ... Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis only claims an effect on the dependent variable. It does ...
Abstract. Statistical hypothesis testing is common in research, but a conventional understanding sometimes leads to mistaken application and misinterpretation. The logic of hypothesis testing presented in this article provides for a clearer understanding, application, and interpretation. Key conclusions are that (a) the magnitude of an estimate ...
A hypothesis (from the Greek, foundation) is a logical construct, interposed between a problem and its solution, which represents a proposed answer to a research question. It gives direction to the investigator's thinking about the problem and, therefore, facilitates a solution. Unlike facts and assumptions (presumed true and, therefore, not ...
5.2 - Writing Hypotheses. The first step in conducting a hypothesis test is to write the hypothesis statements that are going to be tested. For each test you will have a null hypothesis (\ (H_0\)) and an alternative hypothesis (\ (H_a\)). Null Hypothesis. The statement that there is not a difference in the population (s), denoted as \ (H_0\)
It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis. 7.
Non-Directional Research Hypothesis. A non-directional hypothesis states that the means will be different, but does not specify which will be higher. In reality, there is rarely a situation in which we actually don't want one group to be higher than the other, so we will focus on directional research hypotheses.
Research Questions and Hypotheses. I. nvestigators place signposts to carry the reader through a plan for a study. The first signpost is the purpose statement, which establishes the central direction for the study. From the broad, general purpose state- ment, the researcher narrows the focus to specific questions to be answered or predictions ...
The directional hypothesis can also state a negative correlation, e.g. the higher the number of face-book friends, the lower the life satisfaction score ". Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional (or two tailed hypothesis) simply states that there will be a difference between the two groups/conditions but does not say which will be ...
The research hypothesis is needed for a sound and well-developed research study. The research hypothesis contributes to the solution of the research problem. Types of research hypotheses include inductive and deductive, directional and non-directional, and null and alternative hypotheses. Rejecting the null hypothesis and accepting the ...
Directional Hypothesis. A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. For example, a researcher might predict that increasing the amount of exercise will result in a decrease in body weight. ... Guides research: A hypothesis provides a clear and specific direction for research. It ...
Developing a hypothesis (with example) Step 1. Ask a question. Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project. Example: Research question.
A research hypothesis defines the theory or problem your research intends to test. It is the "educated guess" of what the final results of your research or experiment will be. ... Directional hypothesis. When creating a statistical hypothesis, the directional hypothesis (the null hypothesis) states an assumption regarding one parameter of a ...
The steps to write a research hypothesis are: 1. Stating the problem: Ensure that the hypothesis defines the research problem. 2. Writing a hypothesis as an 'if-then' statement: Include the action and the expected outcome of your study by following a 'if-then' structure. 3.
Abstract. The research hypothesis is needed for a sound and well-developed research study. The research hypothesis contributes to the solution of the research problem. Types of research hypotheses include inductive and deductive, directional and non-directional, and null and alternative hypotheses. Rejecting the null hypothesis and accepting ...
Research hypothesis checklist. Once you've written a possible hypothesis, make sure it checks the following boxes: It must be testable: You need a means to prove your hypothesis. If you can't test it, it's not a hypothesis. It must include a dependent and independent variable: At least one independent variable ( cause) and one dependent ...
Here you must be clear about the research question vs hypothesis. A research question is the very beginning point of writing an effective hypothesis. ... Non-directional Hypothesis: It involves an open-ended non-directional hypothesis that predicts that the independent variable will influence the dependent variable; however, the nature or ...
Ad testing, surveys, fake door tests, and unmoderated testing can help provide helpful directional input, but at an early stage, nothing beats qualitative interviews for deeply understanding ...
Weeds are attractive models for basic and applied research due to their impacts on agricultural systems and capacity to swiftly adapt in response to anthropogenic selection pressures. Currently, a lack of genomic information precludes research to elucidate the genetic basis of rapid adaptation for important traits like herbicide resistance and stress tolerance and the effect of evolutionary ...