Applying Ratios in Right Triangles

7.1: Tilted Triangle (5 minutes)
CCSS Standards
Routines and Materials
Required Materials
- Scientific calculators
Students are asked to calculate side lengths of a right triangle. They can apply their new understanding from the previous lesson and use trigonometry.
Student Facing
Calculate the lengths of sides \(AC\) and \(BC\) .

Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners .
Activity Synthesis
Remind students that \(\sin(20)\) is shorthand for “the length of the side opposite the 20 degree angle divided by the length of the hypotenuse for any right triangle with an acute angle of 20 degrees.” So when they ask the calculator to display \(\sin(20)\) , they are asking the calculator for the ratio that is constant for all the triangles similar to this one by the Angle-Angle Triangle Similarity Theorem.
7.2: Info Gap: Trigonometry (20 minutes)
Instructional Routines
- MLR4: Information Gap Cards
- Pre-printed cards, cut from copies of the blackline master
This info gap activity gives students an opportunity to determine and request the information needed to calculate side lengths of right triangles using trigonometry.
The info gap structure requires students to make sense of problems by determining what information is necessary, and then to ask for information they need to solve it. This may take several rounds of discussion if their first requests do not yield the information they need (MP1). It also allows them to refine the language they use and ask increasingly more precise questions until they get the information they need (MP6).
Here is the text of the cards for reference and planning:

Tell students they will continue to use trigonometry to solve for side lengths of right triangles. Explain the info gap structure, and consider demonstrating the protocol if students are unfamiliar with it.
Arrange students in groups of 2. In each group, distribute a problem card to one student and a data card to the other student. After reviewing their work on the first problem, give them the cards for a second problem and instruct them to switch roles.
Your teacher will give you either a problem card or a data card. Do not show or read your card to your partner.
If your teacher gives you the data card:
- Silently read the information on your card.
- Ask your partner, “What specific information do you need?” and wait for your partner to ask for information. Only give information that is on your card. (Do not figure out anything for your partner!)
- Before telling your partner the information, ask “Why do you need to know (that piece of information)?”
- Read the problem card, and solve the problem independently.
- Share the data card, and discuss your reasoning.
If your teacher gives you the problem card:
- Silently read your card and think about what information you need to answer the question.
- Ask your partner for the specific information that you need.
- Explain to your partner how you are using the information to solve the problem.
- When you have enough information, share the problem card with your partner, and solve the problem independently.
- Read the data card, and discuss your reasoning.
Pause here so your teacher can review your work. Ask your teacher for a new set of cards and repeat the activity, trading roles with your partner.
After students have completed their work, share the correct answers and ask students to discuss the process of solving the problems. Here are some questions for discussion:
- “What information did you need to ask for?” (What letters and where they go. An acute angle and a side length.)
- “What could you figure out once you knew angle \(C\) was the right angle?” (The legs of the right triangle both have the letter \(C\) and the hypotenuse uses the other two letters)
Highlight for students that drawing a diagram and labeling it with the information provided is an important strategy. It’s too easy to forget something or mix up information without a clear diagram to work from.
7.3: Tallest Tower (10 minutes)
- HSG-SRT.C.8
- MLR1: Stronger and Clearer Each Time
Students continue to use trigonometry to calculate side lengths of right triangles. In this case they apply that skill to a real world context and engage in some error analysis during the synthesis.
Consider showing where Dubai and Philadelphia are on a map and defining masonry.
The tallest building in the world is the Burj Khalifa in Dubai (as of April 2019).
If you’re standing on the bridge 250 meters from the bottom of the building, you have to look up at a 73 degree angle to see the top. How tall is the building? Explain or show your reasoning.

Attribution: dubai-tower-arab-khalifa-burj, by smarko. Public Domain.. Source .
The tallest masonry building in the world is City Hall in Philadelphia (as of April 2019). If you’re standing on the street 1,300 feet from the bottom of the building, you have to look up at a 23 degree angle to see the top. How tall is the building? Explain or show your reasoning.
Are you ready for more?
You’re sitting on a ledge 300 feet from a building. You have to look up 60 degrees to see the top of the building and down 15 degrees to see the bottom of the building. How tall is the building?
Anticipated Misconceptions
If students struggle with the city hall question prompt then to draw a diagram with the information they know.
Display this image of the Philadelphia City Hall:

Attribution: By jgcalifornia. Public Domain. Pixabay. Source .
“The exact heights are 829.8 meters for the Burj Khalifa and 548 feet for City Hall. Why don’t those numbers match your calculations?” (Rounding or measurement error. The difference between \(\tan(23)\) and \(\tan(23.2)\) makes a big difference when you work with large numbers.) "Is it reasonable to assume you are accurate to the nearest tenth in this case?" (No, the provided measurements were rounded to the nearest ten meters or hundred feet so our usual rounding scheme doesn't apply.)
Lesson Synthesis
Tell students, “In addition to measuring the heights of objects that are too tall to reach, professionals also use trigonometry to calculate the heights of objects they are designing. For example, here is some information a billboard designer knows about a new site.”
Display this information:
- The local law says the maximum height from the ground to the top of any billboard is 50 feet.
- To see over the trees from the highway people need to look up at least 40 degrees.
- The highway is 47 feet from the billboard.
Invite students to discuss what they can do with this information. (How tall—from bottom to top of the image—can the billboard be?) Then invite students to answer the questions they generated. (To be above the trees the bottom of the billboard must be 39.4 feet off the ground, so the billboard can be up to 10.6 feet tall.)
7.4: Cool-down - Tallest Tree (5 minutes)
Building On
Student Lesson Summary
Using trigonometry and properties of right triangles, we can calculate and estimate measures in different right triangles. We can use these skills to estimate unknown heights of objects that are too tall to measure directly. For example, we can't reach the top of this tree with a measuring tape.

To calculate the height of the tree, we could stand where the angle between the top and bottom of the tree is 10 degrees. Since we know the distance to the tree (the adjacent leg) and would like to know the height (the opposite leg), we need to use tangent. So \(\tan(10)=\frac{h}{100}\) . In the calculator we can look up that \(\tan(10)\) is 0.176. Then we can calculate that \(h\) is about 17.6. That means the tree is 17.6 feet tall.


Home > CC3 > Chapter 4 > Lesson 4.1.7
Lesson 4.1.1, lesson 4.1.2, lesson 4.1.3, lesson 4.1.4, lesson 4.1.5, lesson 4.1.6, lesson 4.1.7.
© 2022 CPM Educational Program. All rights reserved.
- For Parents
- For Teachers
- Teaching Topics

- Kindergarten
- End of the Year
- Grade Level Goals
- Family Letters
- Student Gallery
- Understanding EM
- Algorithms/ Computation
- Student Links

Everyday Mathematics for Parents: What You Need to Know to Help Your Child Succeed
The University of Chicago School Mathematics Project
University of Chicago Press
Learn more >>
Related Links
Help with algorithms.
Access video tutorials, practice exercises, and information on the research basis and development of various algorithms.
Everyday Mathematics Online
With a login provided by your child's teacher, access resources to help your child with homework or brush up on your math skills.
Parent Connections on Publisher's site
McGraw-Hill Education offers many resources for parents, including tips, activities, and helpful links.
Parent Resources on EverydayMath.com
EverydayMath.com features activity ideas, literature lists, and family resources for the EM curriculum.
Understanding Everyday Mathematics for Parents
Learn more about the EM curriculum and how to assist your child.

- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 7 Lesson 5 Answer Key
Engage ny eureka math 4th grade module 7 lesson 5 answer key, eureka math grade 4 module 7 lesson 5 sprint answer key.
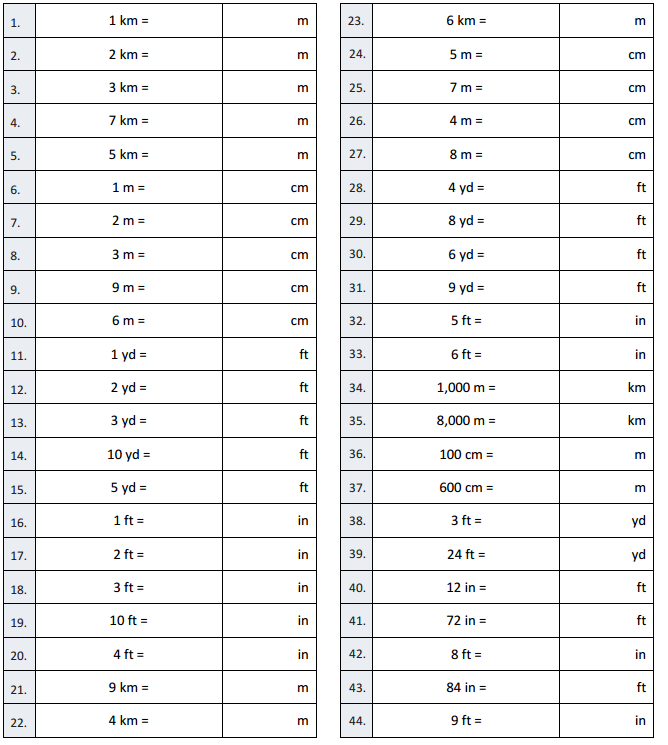
Question 2. 2 km = Answer: 2000 m
Question 3. 3 km = Answer: 3000 m
Question 4. 7 km = Answer: 7000 m
Question 5. 5 km = Answer: 5000 m
Question 6. 1 m = Answer: 100 cm
Question 7. 2 m = Answer: 200 cm
Question 8. 3 m = Answer: 300 cm
Question 9. 9 m = Answer: 900 cm
Question 10. 6 m = Answer: 600 cm
Question 11. 1 yd = Answer: 3 ft
Question 12. 2 yd = Answer: 6 ft
Question 13. 3 yd = Answer: 9 ft
Question 14. 10 yd = Answer: 30 ft
Question 15. 5 yd = Answer: 15 ft
Question 16. 1 ft = Answer: 12 in
Question 17. 2 ft = Answer: 24 in
Question 18. 3 ft = Answer: 36 in
Question 19. 10 ft = Answer: 120 in
Question 20. 4 ft = Answer: 48 in
Question 21. 9 km = Answer: 9000 m
Question 22. 4 km = Answer: 4000 m
Question 23. 6 km = Answer: 6000 m
Question 24. 5 m = Answer: 500 cm
Question 25. 7 m = Answer: 700 cm
Question 26. 4 m = Answer: 400 cm
Question 27. 8 m = Answer: 800 cm
Question 28. 4 yd = Answer: 12 ft
Question 29. 8 yd = Answer: 24 ft
Question 30. 6 yd = Answer: 18 ft
Question 31. 9 yd = Answer: 27 ft
Question 32. 5 ft = Answer: 60 in
Question 33. 6 ft = Answer: 72 in
Question 34. 1,000 m = Answer: 1 km
Question 35. 8,000 m = Answer: 8 km
Question 36. 100 cm = Answer: 1 m
Question 37. 600 cm = Answer: 6 m
Question 38. 3 ft = Answer: 1 yd
Question 39. 24 ft = Answer: 8 yd
Question 40. 12 in = Answer: 1 ft
Question 41. 72 in = Answer: 6 ft
Question 42. 8 ft = Answer: 96 in
Question 43. 84 in = Answer: 7 ft
Question 44. 9 ft = Answer: 108 in
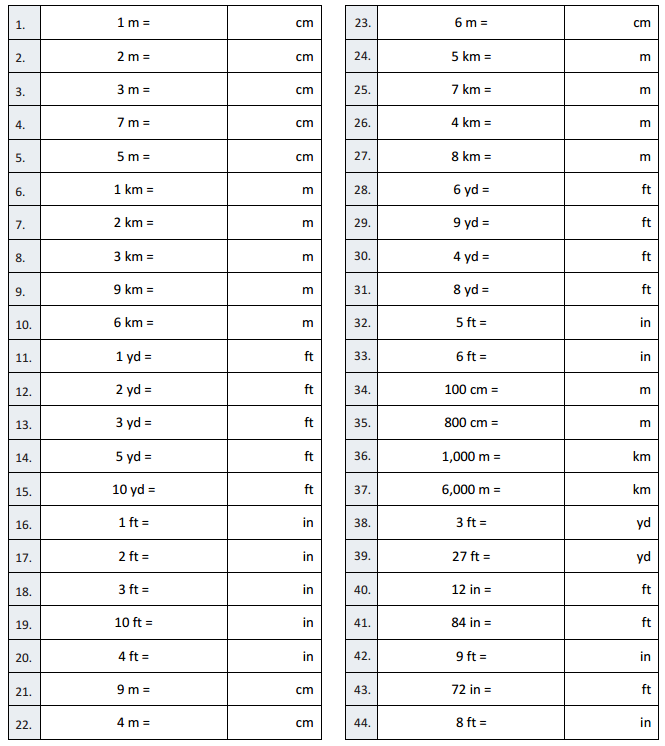
Question 2. 2 m = Answer: 200 cm
Question 3. 3 m = Answer: 300 cm
Question 4. 7 m = Answer: 700 cm
Question 5. 5 m = Answer: 500 cm
Question 6. 1 km = Answer: 1000 m
Question 7. 2 km = Answer: 2000 m
Question 8. 3 km = Answer: 3000 m
Question 9. 9 km = Answer: 9000 m
Question 10. 6 km = Answer: 6000 m
Question 14. 5 yd = Answer: 15 ft
Question 15. 10 yd = Answer: 30 ft
Question 21. 9 m = Answer: 900 cm
Question 22. 4 m = Answer: 400 cm
Question 23. 6 m = Answer: 600 cm
Question 24. 5 km = Answer: 5000 m
Question 25. 7 km = Answer: 7000 m
Question 26. 4 km = Answer: 4000 m
Question 27. 8 km = Answer: 8000 m
Question 28. 6 yd = Answer: 18 ft
Question 29. 9 yd = Answer: 27 ft
Question 30. 4 yd = Answer: 12 ft
Question 31. 8 yd = Answer: 24 ft
Question 34. 100 cm = Answer: 1 m
Question 35. 800 cm = Answer: 8 m
Question 36. 1000 m = Answer: 1 km
Question 37. 6000 m = Answer: 6 km
Question 39. 27 ft = Answer: 9 yd
Question 41. 84 in = Answer: 7 ft
Question 42. 9 ft = Answer: 108 in
Question 43. 72 in = Answer: 6 ft
Question 44. 8 ft = Answer: 96 in
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 7 Lesson 5 Problem Set Answer Key
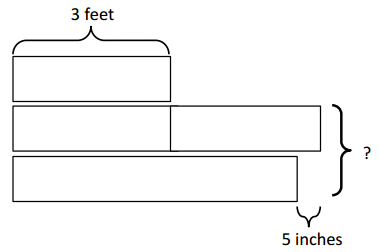
3 feet + 3 feet = 6 feet 1 feet = 12 inches 6 feet = 6 x 12 = 72 inches 72 inches – 5 inches = 67 inches
b. Write a problem of your own that could be solved using the diagram above. Answer: Maria, knitted a cloth of length 3 feet. Mark knitted a cloth as twice as long as Maria. Jacob knitted a cloth which is 5 inches shorter than Mark. Calculate the length of Mark and Jacob altogether
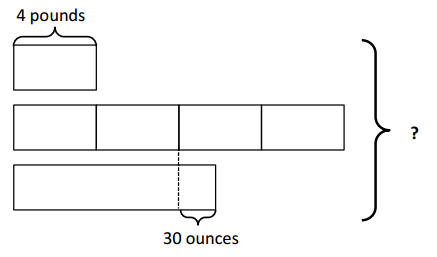
Harry have 3 dogs. First dog weighs 4 pounds. Second dog weighs 4 times more than the first dog and the third dog weighs 30 ounces more than the half of second dog. Calculate the total weight of three dogs. 4 pounds x 7 = 28 pounds 30 ounces = 1 pound 14 ounces Total : 28 pounds + 1 pound 14 ounces = 29 pounds 14 ounces
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 7 Lesson 5 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Caitlin ran 1,680 feet on Monday and 2,340 feet on Tuesday. How many yards did she run in those two days? Answer: The total distance Caitlin ran on Monday = 1680 The total distance she ran on Tuesday = 2, 340 Total : 1680 + 2340 = 4,020 We know that, 1 yard = 3 feet Now, 4020 / 3 = 1340 Therefore, Caitlin ran 1340 yards in two days.
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 7 Lesson 5 Homework Answer Key
Draw a tape diagram to solve the following problems. Question 1. Timmy drank 2 quarts of water yesterday. He drank twice as much water today as he drank yesterday. How many cups of water did Timmy drink in the two days? Answer: The amount of water he drank today = 2 quarts 1 quart = 4 cups So, 2 quarts = 2 x 4 = 8 cups Also given, he drank twice as much water today as he drank yesterday Now, 4 quarts = 4 x 4 = 16 Total : 8 cups + 16 cups = 24 cups Therefore, Timmy drank 24 cups of water in two days altogether.
Question 2. Lisa recorded a 2-hour television show. When she watched it, she skipped the commercials. It took her 84 minutes to watch the show. How many minutes did she save by skipping the commercials? Answer: The time period of television show = 2 hours We know that, 1 hour = 60 minutes 2 hours = 2 x 60 = 120 minutes The time period of commercials Lisa skipped= 84 minutes Now, 120 minutes – 84 minutes = 36 minutes Therefore, Lisa saved 36 minutes.
Question 3. Jason bought 2 pounds of cashews. Sarah ate 9 ounces. David ate 2 ounces more than Sarah. How many ounces were left in Jason’s bag of cashews? Answer: The amount of cashews Jason bought = 2 pounds 2 pounds = 2 x 16 = 32 ounces The amount of cashews Sarah ate = 9 The amount of cashews David ate is 2 ounces more than Sarah That is 9 + 2 = 11 Total cashews they ate all together = 9 + 11 = 20 Now, 32 – 20 = 12 Therefore, 12 ounces of cashews were left in Jason bag
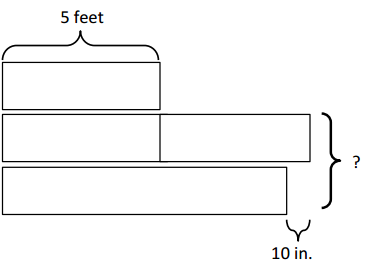
5 feet + 5 feet = 10 feet 1 feet = 12 inches 10 feet = 10 x 12 = 120 inches Now, 120 – 10 = 110 inches.
b. Write a problem of your own that could be solved using the diagram above. Answer: Harry, Henry and Ron each throw a stone. Harry stone flies 5 feet. Henry’s stone flies twice as far as Harry’s stone. Ron’s stone flies 10 inches shorter than Henry. Calculate the total distance flown by Henry and Ron?
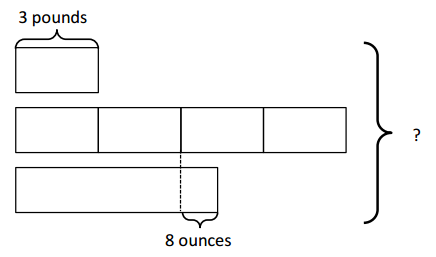
Leo weight = 3 pounds Bailey weight = 4 x 3 = 12 pounds Rio weight = 6 pounds 8 ounces Total : 3 pounds + 12 pounds + 6 pounds 8 ounces = 21 pounds 8 ounces . I have 3 cats. Leo weighs 3 pounds. Bailey weighs 4 times as much as Leo. Rio weighs 10 ounces more than the half of Bailey. Calculate the total weight of the three cats.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Lesson 7: Solve problems involving mixed units of length. Lesson 7 Homework 4• 7 Name Date 1. Determine the following sums and differences. Show your work. a. 2 yd 2 ft + 1 ft = _____ yd b.
Special thanks go to the Gordon A. Cain Center and to the Department of Mathematics at Louisiana State University for their support in the development of
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 4 Lesson 7 Homework Answer Key. Construct angles that measure the given number of degrees. For Problems 1-4, use the ray shown as one of the rays of the angle with its endpoint as the vertex of the angle. Draw an arc to indicate the angle that was measured. Question 1. 25° Answer: The 25° angle is an acute angle ...
Grade 4 - School District U-46 / Homepage
Answer: a. Given , the parameter of quadrilateral = 18 feet 2 inches or 17 feet 14 inches. The sum of three of the sides = 12 feet 4 inches. The length of fourth side = 18 ft 2 in - 12 ft 4 in = 5 ft 10 in. Therefore, the length of forth side = 5 ft 10 in. b. The perimeter of triangle =. 3 x (5 ft 10 in)
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 7 Lesson 1 Answer Key; Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 7 Lesson 2 Answer Key; Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 7 Lesson 3 Answer Key; Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 7 Lesson 4 Answer Key; Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 7 Lesson 5 Answer Key; Eureka Math 4th Grade Module 7 Topic B Problem Solving with Measurement. Eureka Math Grade 4 ...
Answer Key Lesson 4.7 Practice Level C 1. x 5 9, y 5 11 2. x 5 6, y 5 13 3. x 5 3.5, y 5 9 4. x 5 12, y 5 5 5. x 5 6, y 5 7 6. x 5 3, y 5 9.5 7. x 5 20.5, y 5 6 8. x 5 8, y 5 3 9. x 5 7, cannot determine y; could findy if it was given that 9y 2 10 is equal to 5y 2 8. 10. 98 in. 11. 72.5 m 12. 149.25 ft
Chapter 4 • Lesson 7 237. MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES .0%&- t 3&"40/ t M",& 4&/4&. Unlock l t the Problem l. 7. SMARTER. A new playground will be 108 feet long. Builders need to allow 9 feet of space for each piece of climbing equipment. They want to put as many climbers along the length of the playground as possible.
Draw a model. Lesson 7.4 COMMON CORE STANDARD CC.5.NF.4b Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to multiply and divide fractions. , or — Check students' models. 5. , or or 24' 4. or 12' 25 Problem Solving REAL WORLD 7. Nora has a piece of ribbon that is yard long. She will use of it to make a bow.
Tell students they will continue to use trigonometry to solve for side lengths of right triangles. Explain the info gap structure, and consider demonstrating the protocol if students are unfamiliar with it. Arrange students in groups of 2. In each group, distribute a problem card to one student and a data card to the other student.
Answer: Angle a is 140°. Explanation: The smallest angle given is 38 and the largest angle is 160°. 160 × 38 = 4808 = 60. 160 + 60 = 220. 360-220= 140. Hence the value of angle a is 140°. c. Abbie spent 58 of her money and saved the rest.
CPM Education Program proudly works to offer more and better math education to more students.
Lesson. Vocabulary. Home Link Help. Games. 7-1. Converting Liquid Measures: U.S. Customary Units. cup. pint. ... Selected Answers. 7-2. Exploring Fraction Multiplication Situations. Home Link 7-2 English Español Selected Answers. 7-3. A Fraction as a Multiple of a Unit Fraction ... access resources to help your child with homework or brush up ...
Unit 4.7 Handout 1 TEACHER ANSWER KEY Page 1 A. 1. A 2. C 3. D 4. B B. Answers will vary: An example: Genetic modification is controversial and people would be more offended by changes in animals than in plants. Page 2 A. Same 1. They are both controlled by people 2. They both change organisms' traits. Different 1.
Our resource for Math Makes Sense 7 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and move forward with confidence. Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Math Makes ...
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 7 Lesson 12 Problem Set Answer Key. Question 1. Draw a tape diagram to show 1 yard divided into 3 equal parts. Question 2. Draw a tape diagram to show 2 23 yards = 8 feet. Question 3. Draw a tape diagram to show 3 4 gallon = 3 quarts. Question 4.
Lesson. Vocabulary. Study Link Help Games. 7-1. Review of Basic Fraction Concepts ... For problems 4-7: Student Reference Book pages 32-37. Selected Answers. 7-5. Fraction and Mixed ... Selected Answers. 7-12a. Multiplying Fractions by Whole Numbers (CCSS Ed. Only)
Engage NY Eureka Math 4th Grade Module 7 Lesson 13 Answer Key Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 7 Lesson 13 Problem Set Answer Key Question 1. Solve. a. pound = _______ ounce b. pound =
Overall, the answer key for practice and homework lesson 4 7 is an essential resource for both students and teachers in promoting a successful learning experience. Lesson 4.7: Practice and Homework Answer Key. In this lesson, we will go over the answer key for the practice and homework questions in Lesson 4.7. This will help you check your work ...
Engage NY Eureka Math 4th Grade Module 7 Lesson 5 Answer Key Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 7 Lesson 5 Sprint Answer Key. A Convert Length Units Question 1. 1 km = Answer: 1000 m. Question 2. 2 km = Answer: 2000 m. Question 3. 3 km = Answer: 3000 m. Question 4. 7 km = Answer: 7000 m. Question 5. 5 km = Answer: 5000 m. Question 6. 1 m = Answer: 100 ...