
- Arts & Culture
- Civic Engagement
- Economic Development
- Environment
- Human Rights
- Social Services
- Water & Sanitation
- Foundations
- Nonprofits & NGOs
- Social Enterprise
- Collaboration
- Design Thinking
- Impact Investing
- Measurement & Evaluation
- Organizational Development
- Philanthropy & Funding
- Current Issue
- Sponsored Supplements
- Global Editions
- In-Depth Series
- Stanford PACS
- Submission Guidelines

A Better Education for All During—and After—the COVID-19 Pandemic
Research from the Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL) and its partners shows how to help children learn amid erratic access to schools during a pandemic, and how those solutions may make progress toward the Sustainable Development Goal of ensuring a quality education for all by 2030.
- order reprints
- related stories
By Radhika Bhula & John Floretta Oct. 16, 2020

Five years into the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the world is nowhere near to ensuring a quality education for all by 2030. Impressive gains in enrollment and attendance over recent decades have not translated into corresponding gains in learning. The World Bank’s metric of "learning poverty," which refers to children who cannot read and understand a simple text by age 10, is a staggering 80 percent in low-income countries .
The COVID-19 crisis is exacerbating this learning crisis. As many as 94 percent of children across the world have been out of school due to closures. Learning losses from school shutdowns are further compounded by inequities , particularly for students who were already left behind by education systems. Many countries and schools have shifted to online learning during school closures as a stop-gap measure. However, this is not possible in many places, as less than half of households in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) have internet access.

Many education systems around the world are now reopening fully, partially, or in a hybrid format, leaving millions of children to face a radically transformed educational experience. As COVID-19 cases rise and fall during the months ahead, the chaos will likely continue, with schools shutting down and reopening as needed to balance educational needs with protecting the health of students, teachers, and families. Parents, schools, and entire education systems—especially in LMICs—will need to play new roles to support student learning as the situation remains in flux, perhaps permanently. As they adjust to this new reality, research conducted by more than 220 professors affiliated with the Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL) and innovations from J-PAL's partners provide three insights into supporting immediate and long-term goals for educating children.
1. Support caregivers at home to help children learn while schools are closed . With nearly 1.6 billion children out of school at the peak of the pandemic, many parents or caregivers, especially with young children, have taken on new roles to help with at-home learning. To support them and remote education efforts, many LMICs have used SMS, phone calls, and other widely accessible, affordable, and low-technology methods of information delivery. While such methods are imperfect substitutes for schooling, research suggests they can help engage parents in their child’s education and contribute to learning , perhaps even after schools reopen.
Preliminary results from an ongoing program and randomized evaluation in Botswana show the promise of parental support combined with low-technology curriculum delivery. When the pandemic hit, the NGO Young 1ove was working with Botswana's Ministry of Education to scale up the Teaching at the Right Level approach to primary schools in multiple districts. After collecting student, parent, and teacher phone numbers, the NGO devised two strategies to deliver educational support. The first strategy sent SMS texts to households with a series of numeracy “problems of the week.” The second sent the same texts combined with 20-minute phone calls with Young 1ove staff members, who walked parents and students through the problems. Over four to five weeks, both interventions significantly improved learning . They halved the number of children who could not do basic mathematical operations like subtraction and division. Parents became more engaged with their children's education and had a better understanding of their learning levels. Young 1ove is now evaluating the impact of SMS texts and phone calls that are tailored to students’ numeracy levels.
In another example, the NGO Educate! reoriented its in-school youth skills model to be delivered through radio, SMS, and phone calls in response to school closures in East Africa. To encourage greater participation, Educate! called the students' caregivers to tell them about the program. Their internal analysis indicates that households that received such encouragement calls had a 29 percent increase in youth participation compared to those that did not receive the communication.
In several Latin American countries , researchers are evaluating the impact of sending SMS texts to parents on how to support their young children who have transitioned to distance-learning programs. Similar efforts to support parents and evaluate the effects are underway in Peru . Both will contribute to a better understanding of how to help caregivers support their child’s education using affordable and accessible technology.
Other governments and organizations in areas where internet access is limited are also experimenting with radio and TV to support parents and augment student learning. The Côte d’Ivoire government created a radio program on math and French for children in grades one to five. It involved hundreds of short lessons. The Indian NGO Pratham collaborated with the Bihar state government and a television channel to produce 10 hours of learning programming per week, creating more than 100 episodes to date. Past randomized evaluations of such “edutainment” programs from other sectors in Nigeria , Rwanda , and Uganda suggest the potential of delivering content and influencing behavior through mass media, though context is important, and more rigorous research is needed to understand the impact of such programs on learning.
2. As schools reopen, educators should use low-stakes assessments to identify learning gaps. As of September 1, schools in more than 75 countries were open to some degree. Many governments need to be prepared for the vast majority of children to be significantly behind in their educations as they return—a factor exacerbated by the low pre-pandemic learning levels, particularly in LMICs . Rather than jumping straight into grade-level curriculum, primary schools in LMICs should quickly assess learning levels to understand what children know (or don’t) and devise strategic responses. They can do so by using simple tools to frequently assess students, rather than focusing solely on high-stakes exams, which may significantly influence a child’s future by, for example, determining grade promotion.
Orally administered assessments—such as ASER , ICAN , and Uwezo —are simple, fast, inexpensive, and effective. The ASER math tool, for example, has just four elements: single-digit number recognition, double-digit number recognition, two-digit subtraction, and simple division. A similar tool exists for assessing foundational reading abilities. Tests like these don’t affect a child’s grades or promotion, help teachers to get frequent and clear views into learning levels, and can enable schools to devise plans to help children master the basics.
3. Tailor children's instruction to help them master foundational skills once learning gaps are identified. Given low learning levels before the pandemic and recent learning loss due to school disruptions, it is important to focus on basic skills as schools reopen to ensure children maintain and build a foundation for a lifetime of learning. Decades of research from Chile, India, Kenya, Ghana, and the United States shows that tailoring instruction to children’s’ education levels increases learning. For example, the Teaching at the Right Level (TaRL) approach, pioneered by Indian NGO Pratham and evaluated in partnership with J-PAL researchers through six randomized evaluations over the last 20 years, focuses on foundational literacy and numeracy skills through interactive activities for a portion of the day rather than solely on the curriculum. It involves regular assessments of students' progress and is reaching more than 60 million children in India and several African countries .
Toward Universal Quality Education
As countries rebuild and reinvent themselves in response to COVID-19, there is an opportunity to accelerate the thinking on how to best support quality education for all. In the months and years ahead, coalitions of evidence-to-policy organizations, implementation partners, researchers, donors, and governments should build on their experiences to develop education-for-all strategies that use expansive research from J-PAL and similar organizations. In the long term, evidence-informed decisions and programs that account for country-specific conditions have the potential to improve pedagogy, support teachers, motivate students, improve school governance, and address many other aspects of the learning experience. Perhaps one positive outcome of the pandemic is that it will push us to overcome the many remaining global educational challenges sooner than any of us expect. We hope that we do.
Support SSIR ’s coverage of cross-sector solutions to global challenges. Help us further the reach of innovative ideas. Donate today .
Read more stories by Radhika Bhula & John Floretta .
SSIR.org and/or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and to our better understanding of user needs. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to otherwise browse this site, you agree to the use of cookies.
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

Finding middle way out of Gaza war

Roadmap to Gaza peace may run through Oslo

Why Democrats, Republicans, who appear at war these days, really need each other
Rubén Rodriguez/Unsplash
Time to fix American education with race-for-space resolve
Harvard Staff Writer
Paul Reville says COVID-19 school closures have turned a spotlight on inequities and other shortcomings
This is part of our Coronavirus Update series in which Harvard specialists in epidemiology, infectious disease, economics, politics, and other disciplines offer insights into what the latest developments in the COVID-19 outbreak may bring.
As former secretary of education for Massachusetts, Paul Reville is keenly aware of the financial and resource disparities between districts, schools, and individual students. The school closings due to coronavirus concerns have turned a spotlight on those problems and how they contribute to educational and income inequality in the nation. The Gazette talked to Reville, the Francis Keppel Professor of Practice of Educational Policy and Administration at Harvard Graduate School of Education , about the effects of the pandemic on schools and how the experience may inspire an overhaul of the American education system.
Paul Reville
GAZETTE: Schools around the country have closed due to the coronavirus pandemic. Do these massive school closures have any precedent in the history of the United States?
REVILLE: We’ve certainly had school closures in particular jurisdictions after a natural disaster, like in New Orleans after the hurricane. But on this scale? No, certainly not in my lifetime. There were substantial closings in many places during the 1918 Spanish Flu, some as long as four months, but not as widespread as those we’re seeing today. We’re in uncharted territory.
GAZETTE: What lessons did school districts around the country learn from school closures in New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina, and other similar school closings?
REVILLE: I think the lessons we’ve learned are that it’s good [for school districts] to have a backup system, if they can afford it. I was talking recently with folks in a district in New Hampshire where, because of all the snow days they have in the wintertime, they had already developed a backup online learning system. That made the transition, in this period of school closure, a relatively easy one for them to undertake. They moved seamlessly to online instruction.
Most of our big systems don’t have this sort of backup. Now, however, we’re not only going to have to construct a backup to get through this crisis, but we’re going to have to develop new, permanent systems, redesigned to meet the needs which have been so glaringly exposed in this crisis. For example, we have always had large gaps in students’ learning opportunities after school, weekends, and in the summer. Disadvantaged students suffer the consequences of those gaps more than affluent children, who typically have lots of opportunities to fill in those gaps. I’m hoping that we can learn some things through this crisis about online delivery of not only instruction, but an array of opportunities for learning and support. In this way, we can make the most of the crisis to help redesign better systems of education and child development.
GAZETTE: Is that one of the silver linings of this public health crisis?
REVILLE: In politics we say, “Never lose the opportunity of a crisis.” And in this situation, we don’t simply want to frantically struggle to restore the status quo because the status quo wasn’t operating at an effective level and certainly wasn’t serving all of our children fairly. There are things we can learn in the messiness of adapting through this crisis, which has revealed profound disparities in children’s access to support and opportunities. We should be asking: How do we make our school, education, and child-development systems more individually responsive to the needs of our students? Why not construct a system that meets children where they are and gives them what they need inside and outside of school in order to be successful? Let’s take this opportunity to end the “one size fits all” factory model of education.
GAZETTE: How seriously are students going to be set back by not having formal instruction for at least two months, if not more?
“The best that can come of this is a new paradigm shift in terms of the way in which we look at education, because children’s well-being and success depend on more than just schooling,” Paul Reville said of the current situation. “We need to look holistically, at the entirety of children’s lives.”
Stephanie Mitchell/Harvard file photo
REVILLE: The first thing to consider is that it’s going to be a variable effect. We tend to regard our school systems uniformly, but actually schools are widely different in their operations and impact on children, just as our students themselves are very different from one another. Children come from very different backgrounds and have very different resources, opportunities, and support outside of school. Now that their entire learning lives, as well as their actual physical lives, are outside of school, those differences and disparities come into vivid view. Some students will be fine during this crisis because they’ll have high-quality learning opportunities, whether it’s formal schooling or informal homeschooling of some kind coupled with various enrichment opportunities. Conversely, other students won’t have access to anything of quality, and as a result will be at an enormous disadvantage. Generally speaking, the most economically challenged in our society will be the most vulnerable in this crisis, and the most advantaged are most likely to survive it without losing too much ground.
GAZETTE: Schools in Massachusetts are closed until May 4. Some people are saying they should remain closed through the end of the school year. What’s your take on this?
REVILLE: That should be a medically based judgment call that will be best made several weeks from now. If there’s evidence to suggest that students and teachers can safely return to school, then I’d say by all means. However, that seems unlikely.
GAZETTE: The digital divide between students has become apparent as schools have increasingly turned to online instruction. What can school systems do to address that gap?
REVILLE: Arguably, this is something that schools should have been doing a long time ago, opening up the whole frontier of out-of-school learning by virtue of making sure that all students have access to the technology and the internet they need in order to be connected in out-of-school hours. Students in certain school districts don’t have those affordances right now because often the school districts don’t have the budget to do this, but federal, state, and local taxpayers are starting to see the imperative for coming together to meet this need.
Twenty-first century learning absolutely requires technology and internet. We can’t leave this to chance or the accident of birth. All of our children should have the technology they need to learn outside of school. Some communities can take it for granted that their children will have such tools. Others who have been unable to afford to level the playing field are now finding ways to step up. Boston, for example, has bought 20,000 Chromebooks and is creating hotspots around the city where children and families can go to get internet access. That’s a great start but, in the long run, I think we can do better than that. At the same time, many communities still need help just to do what Boston has done for its students.
Communities and school districts are going to have to adapt to get students on a level playing field. Otherwise, many students will continue to be at a huge disadvantage. We can see this playing out now as our lower-income and more heterogeneous school districts struggle over whether to proceed with online instruction when not everyone can access it. Shutting down should not be an option. We have to find some middle ground, and that means the state and local school districts are going to have to act urgently and nimbly to fill in the gaps in technology and internet access.
GAZETTE : What can parents can do to help with the homeschooling of their children in the current crisis?
“In this situation, we don’t simply want to frantically struggle to restore the status quo because the status quo wasn’t operating at an effective level and certainly wasn’t serving all of our children fairly.”
More like this

The collective effort

Notes from the new normal

‘If you remain mostly upright, you are doing it well enough’
REVILLE: School districts can be helpful by giving parents guidance about how to constructively use this time. The default in our education system is now homeschooling. Virtually all parents are doing some form of homeschooling, whether they want to or not. And the question is: What resources, support, or capacity do they have to do homeschooling effectively? A lot of parents are struggling with that.
And again, we have widely variable capacity in our families and school systems. Some families have parents home all day, while other parents have to go to work. Some school systems are doing online classes all day long, and the students are fully engaged and have lots of homework, and the parents don’t need to do much. In other cases, there is virtually nothing going on at the school level, and everything falls to the parents. In the meantime, lots of organizations are springing up, offering different kinds of resources such as handbooks and curriculum outlines, while many school systems are coming up with guidance documents to help parents create a positive learning environment in their homes by engaging children in challenging activities so they keep learning.
There are lots of creative things that can be done at home. But the challenge, of course, for parents is that they are contending with working from home, and in other cases, having to leave home to do their jobs. We have to be aware that families are facing myriad challenges right now. If we’re not careful, we risk overloading families. We have to strike a balance between what children need and what families can do, and how you maintain some kind of work-life balance in the home environment. Finally, we must recognize the equity issues in the forced overreliance on homeschooling so that we avoid further disadvantaging the already disadvantaged.
GAZETTE: What has been the biggest surprise for you thus far?
REVILLE: One that’s most striking to me is that because schools are closed, parents and the general public have become more aware than at any time in my memory of the inequities in children’s lives outside of school. Suddenly we see front-page coverage about food deficits, inadequate access to health and mental health, problems with housing stability, and access to educational technology and internet. Those of us in education know these problems have existed forever. What has happened is like a giant tidal wave that came and sucked the water off the ocean floor, revealing all these uncomfortable realities that had been beneath the water from time immemorial. This newfound public awareness of pervasive inequities, I hope, will create a sense of urgency in the public domain. We need to correct for these inequities in order for education to realize its ambitious goals. We need to redesign our systems of child development and education. The most obvious place to start for schools is working on equitable access to educational technology as a way to close the digital-learning gap.
GAZETTE: You’ve talked about some concrete changes that should be considered to level the playing field. But should we be thinking broadly about education in some new way?
REVILLE: The best that can come of this is a new paradigm shift in terms of the way in which we look at education, because children’s well-being and success depend on more than just schooling. We need to look holistically, at the entirety of children’s lives. In order for children to come to school ready to learn, they need a wide array of essential supports and opportunities outside of school. And we haven’t done a very good job of providing these. These education prerequisites go far beyond the purview of school systems, but rather are the responsibility of communities and society at large. In order to learn, children need equal access to health care, food, clean water, stable housing, and out-of-school enrichment opportunities, to name just a few preconditions. We have to reconceptualize the whole job of child development and education, and construct systems that meet children where they are and give them what they need, both inside and outside of school, in order for all of them to have a genuine opportunity to be successful.
Within this coronavirus crisis there is an opportunity to reshape American education. The only precedent in our field was when the Sputnik went up in 1957, and suddenly, Americans became very worried that their educational system wasn’t competitive with that of the Soviet Union. We felt vulnerable, like our defenses were down, like a nation at risk. And we decided to dramatically boost the involvement of the federal government in schooling and to increase and improve our scientific curriculum. We decided to look at education as an important factor in human capital development in this country. Again, in 1983, the report “Nation at Risk” warned of a similar risk: Our education system wasn’t up to the demands of a high-skills/high-knowledge economy.
We tried with our education reforms to build a 21st-century education system, but the results of that movement have been modest. We are still a nation at risk. We need another paradigm shift, where we look at our goals and aspirations for education, which are summed up in phrases like “No Child Left Behind,” “Every Student Succeeds,” and “All Means All,” and figure out how to build a system that has the capacity to deliver on that promise of equity and excellence in education for all of our students, and all means all. We’ve got that opportunity now. I hope we don’t fail to take advantage of it in a misguided rush to restore the status quo.
This interview has been condensed and edited for length and clarity.
Share this article
You might like.
Educators, activists explore peacebuilding based on shared desires for ‘freedom and equality and independence’ at Weatherhead panel

Former Palestinian Authority prime minister says strengthening execution of 1993 accords could lead to two-state solution

Political philosopher Harvey C. Mansfield says it all goes back to Aristotle, balance of competing ideas about common good
College accepts 1,937 to Class of 2028
Students represent 94 countries, all 50 states
Pushing back on DEI ‘orthodoxy’
Panelists support diversity efforts but worry that current model is too narrow, denying institutions the benefit of other voices, ideas
So what exactly makes Taylor Swift so great?
Experts weigh in on pop superstar's cultural and financial impact as her tours and albums continue to break records.
The COVID-19 pandemic has changed education forever. This is how

With schools shut across the world, millions of children have had to adapt to new types of learning. Image: REUTERS/Gonzalo Fuentes
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Cathy Li
Farah lalani.

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} COVID-19 is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:.
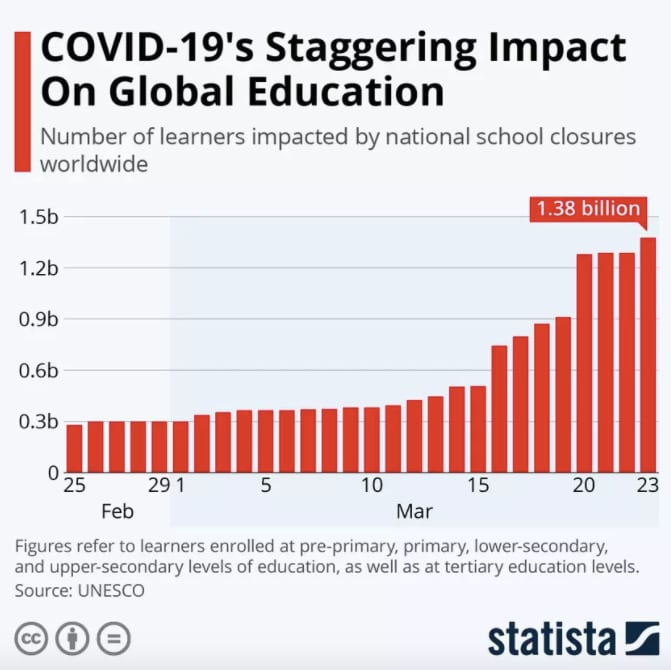
- The COVID-19 has resulted in schools shut all across the world. Globally, over 1.2 billion children are out of the classroom.
- As a result, education has changed dramatically, with the distinctive rise of e-learning, whereby teaching is undertaken remotely and on digital platforms.
- Research suggests that online learning has been shown to increase retention of information, and take less time, meaning the changes coronavirus have caused might be here to stay.
While countries are at different points in their COVID-19 infection rates, worldwide there are currently more than 1.2 billion children in 186 countries affected by school closures due to the pandemic. In Denmark, children up to the age of 11 are returning to nurseries and schools after initially closing on 12 March , but in South Korea students are responding to roll calls from their teachers online .
With this sudden shift away from the classroom in many parts of the globe, some are wondering whether the adoption of online learning will continue to persist post-pandemic, and how such a shift would impact the worldwide education market.

Even before COVID-19, there was already high growth and adoption in education technology, with global edtech investments reaching US$18.66 billion in 2019 and the overall market for online education projected to reach $350 Billion by 2025 . Whether it is language apps , virtual tutoring , video conferencing tools, or online learning software , there has been a significant surge in usage since COVID-19.
How is the education sector responding to COVID-19?
In response to significant demand, many online learning platforms are offering free access to their services, including platforms like BYJU’S , a Bangalore-based educational technology and online tutoring firm founded in 2011, which is now the world’s most highly valued edtech company . Since announcing free live classes on its Think and Learn app, BYJU’s has seen a 200% increase in the number of new students using its product, according to Mrinal Mohit, the company's Chief Operating Officer.
Tencent classroom, meanwhile, has been used extensively since mid-February after the Chinese government instructed a quarter of a billion full-time students to resume their studies through online platforms. This resulted in the largest “online movement” in the history of education with approximately 730,000 , or 81% of K-12 students, attending classes via the Tencent K-12 Online School in Wuhan.
Have you read?
The future of jobs report 2023, how to follow the growth summit 2023.
Other companies are bolstering capabilities to provide a one-stop shop for teachers and students. For example, Lark, a Singapore-based collaboration suite initially developed by ByteDance as an internal tool to meet its own exponential growth, began offering teachers and students unlimited video conferencing time, auto-translation capabilities, real-time co-editing of project work, and smart calendar scheduling, amongst other features. To do so quickly and in a time of crisis, Lark ramped up its global server infrastructure and engineering capabilities to ensure reliable connectivity.
Alibaba’s distance learning solution, DingTalk, had to prepare for a similar influx: “To support large-scale remote work, the platform tapped Alibaba Cloud to deploy more than 100,000 new cloud servers in just two hours last month – setting a new record for rapid capacity expansion,” according to DingTalk CEO, Chen Hang.
Some school districts are forming unique partnerships, like the one between The Los Angeles Unified School District and PBS SoCal/KCET to offer local educational broadcasts, with separate channels focused on different ages, and a range of digital options. Media organizations such as the BBC are also powering virtual learning; Bitesize Daily , launched on 20 April, is offering 14 weeks of curriculum-based learning for kids across the UK with celebrities like Manchester City footballer Sergio Aguero teaching some of the content.
What does this mean for the future of learning?
While some believe that the unplanned and rapid move to online learning – with no training, insufficient bandwidth, and little preparation – will result in a poor user experience that is unconducive to sustained growth, others believe that a new hybrid model of education will emerge, with significant benefits. “I believe that the integration of information technology in education will be further accelerated and that online education will eventually become an integral component of school education,“ says Wang Tao, Vice President of Tencent Cloud and Vice President of Tencent Education.
There have already been successful transitions amongst many universities. For example, Zhejiang University managed to get more than 5,000 courses online just two weeks into the transition using “DingTalk ZJU”. The Imperial College London started offering a course on the science of coronavirus, which is now the most enrolled class launched in 2020 on Coursera .
Many are already touting the benefits: Dr Amjad, a Professor at The University of Jordan who has been using Lark to teach his students says, “It has changed the way of teaching. It enables me to reach out to my students more efficiently and effectively through chat groups, video meetings, voting and also document sharing, especially during this pandemic. My students also find it is easier to communicate on Lark. I will stick to Lark even after coronavirus, I believe traditional offline learning and e-learning can go hand by hand."
These 3 charts show the global growth in online learning
The challenges of online learning.
There are, however, challenges to overcome. Some students without reliable internet access and/or technology struggle to participate in digital learning; this gap is seen across countries and between income brackets within countries. For example, whilst 95% of students in Switzerland, Norway, and Austria have a computer to use for their schoolwork, only 34% in Indonesia do, according to OECD data .
In the US, there is a significant gap between those from privileged and disadvantaged backgrounds: whilst virtually all 15-year-olds from a privileged background said they had a computer to work on, nearly 25% of those from disadvantaged backgrounds did not. While some schools and governments have been providing digital equipment to students in need, such as in New South Wales , Australia, many are still concerned that the pandemic will widenthe digital divide .
Is learning online as effective?
For those who do have access to the right technology, there is evidence that learning online can be more effective in a number of ways. Some research shows that on average, students retain 25-60% more material when learning online compared to only 8-10% in a classroom. This is mostly due to the students being able to learn faster online; e-learning requires 40-60% less time to learn than in a traditional classroom setting because students can learn at their own pace, going back and re-reading, skipping, or accelerating through concepts as they choose.
Nevertheless, the effectiveness of online learning varies amongst age groups. The general consensus on children, especially younger ones, is that a structured environment is required , because kids are more easily distracted. To get the full benefit of online learning, there needs to be a concerted effort to provide this structure and go beyond replicating a physical class/lecture through video capabilities, instead, using a range of collaboration tools and engagement methods that promote “inclusion, personalization and intelligence”, according to Dowson Tong, Senior Executive Vice President of Tencent and President of its Cloud and Smart Industries Group.
Since studies have shown that children extensively use their senses to learn, making learning fun and effective through use of technology is crucial, according to BYJU's Mrinal Mohit. “Over a period, we have observed that clever integration of games has demonstrated higher engagement and increased motivation towards learning especially among younger students, making them truly fall in love with learning”, he says.
A changing education imperative
It is clear that this pandemic has utterly disrupted an education system that many assert was already losing its relevance . In his book, 21 Lessons for the 21st Century , scholar Yuval Noah Harari outlines how schools continue to focus on traditional academic skills and rote learning , rather than on skills such as critical thinking and adaptability, which will be more important for success in the future. Could the move to online learning be the catalyst to create a new, more effective method of educating students? While some worry that the hasty nature of the transition online may have hindered this goal, others plan to make e-learning part of their ‘new normal’ after experiencing the benefits first-hand.
The importance of disseminating knowledge is highlighted through COVID-19
Major world events are often an inflection point for rapid innovation – a clear example is the rise of e-commerce post-SARS . While we have yet to see whether this will apply to e-learning post-COVID-19, it is one of the few sectors where investment has not dried up . What has been made clear through this pandemic is the importance of disseminating knowledge across borders, companies, and all parts of society. If online learning technology can play a role here, it is incumbent upon all of us to explore its full potential.
Our education system is losing relevance. Here's how to unleash its potential
3 ways the coronavirus pandemic could reshape education, celebrities are helping the uk's schoolchildren learn during lockdown, don't miss any update on this topic.
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on COVID-19 .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all
Winding down COVAX – lessons learnt from delivering 2 billion COVID-19 vaccinations to lower-income countries
Charlotte Edmond
January 8, 2024
Here’s what to know about the new COVID-19 Pirola variant
October 11, 2023

How the cost of living crisis affects young people around the world
Douglas Broom
August 8, 2023
From smallpox to COVID: the medical inventions that have seen off infectious diseases over the past century
Andrea Willige
May 11, 2023

COVID-19 is no longer a global health emergency. Here's what it means
Simon Nicholas Williams
May 9, 2023

New research shows the significant health harms of the pandemic
Philip Clarke, Jack Pollard and Mara Violato
April 17, 2023
Centre for Social Research & Methods

- Education & training
- Programs & research
- Working papers
- Methods research papers
- COVID-19 publications
- Other publications
Related Sites
- ANU College of Arts & Social Sciences
- Research School of Social Sciences
- Australian National Internships Program
You are here
Experience and views on education during the COVID-19 pandemic

COVID-19 has resulted in disruptions to schooling for the vast majority of Australian school children. Universities and other post-secondary education providers have also seen widespread shifts to remote learning, and considerable impacts on school funding. While there have undoubtedly been negative impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on education institutions, students and their families, the crisis has at the same time created an opportunity to reflect on the role of education in a society like Australia’s. In this paper we provide a summary of survey data on the experiences of students and their families during the pandemic, as well as attitudes of the entire Australian population to the role of schools and universities. We found 47.8 per cent, or almost one-in-two Australians were very satisfied with their child’s educational institution, while 40.2 per cent were somewhat satisfied. Only a small percentage of the population were not satisfied with their child’s education, with a slightly higher per cent of adult learners not being satisfied with their own education. Despite this high level of satisfaction, the paper also shows that a large number parents or adult learners were concerned about their own learning or their children’s learning.
- Experience_and_views_on_education_during_the_COVID-19_pandemic.pdf ( PDF , 642.49 KB )
Tweets by @WhatAustThinks
There were no tweets found.
Connect with us

Updated: 17 December 2020 / Responsible Officer: Centre Director / Page Contact: CASS Marketing & Communications
- Contact ANU
- Freedom of Information
+61 2 6125 5111 The Australian National University, Canberra TEQSA Provider ID: PRV12002 (Australian University) CRICOS Provider : 00120C ABN : 52 234 063 906

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Students’ online learning challenges during the pandemic and how they cope with them: The case of the Philippines
Jessie s. barrot.
College of Education, Arts and Sciences, National University, Manila, Philippines
Ian I. Llenares
Leo s. del rosario, associated data.
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Recently, the education system has faced an unprecedented health crisis that has shaken up its foundation. Given today’s uncertainties, it is vital to gain a nuanced understanding of students’ online learning experience in times of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although many studies have investigated this area, limited information is available regarding the challenges and the specific strategies that students employ to overcome them. Thus, this study attempts to fill in the void. Using a mixed-methods approach, the findings revealed that the online learning challenges of college students varied in terms of type and extent. Their greatest challenge was linked to their learning environment at home, while their least challenge was technological literacy and competency. The findings further revealed that the COVID-19 pandemic had the greatest impact on the quality of the learning experience and students’ mental health. In terms of strategies employed by students, the most frequently used were resource management and utilization, help-seeking, technical aptitude enhancement, time management, and learning environment control. Implications for classroom practice, policy-making, and future research are discussed.
Introduction
Since the 1990s, the world has seen significant changes in the landscape of education as a result of the ever-expanding influence of technology. One such development is the adoption of online learning across different learning contexts, whether formal or informal, academic and non-academic, and residential or remotely. We began to witness schools, teachers, and students increasingly adopt e-learning technologies that allow teachers to deliver instruction interactively, share resources seamlessly, and facilitate student collaboration and interaction (Elaish et al., 2019 ; Garcia et al., 2018 ). Although the efficacy of online learning has long been acknowledged by the education community (Barrot, 2020 , 2021 ; Cavanaugh et al., 2009 ; Kebritchi et al., 2017 ; Tallent-Runnels et al., 2006 ; Wallace, 2003 ), evidence on the challenges in its implementation continues to build up (e.g., Boelens et al., 2017 ; Rasheed et al., 2020 ).
Recently, the education system has faced an unprecedented health crisis (i.e., COVID-19 pandemic) that has shaken up its foundation. Thus, various governments across the globe have launched a crisis response to mitigate the adverse impact of the pandemic on education. This response includes, but is not limited to, curriculum revisions, provision for technological resources and infrastructure, shifts in the academic calendar, and policies on instructional delivery and assessment. Inevitably, these developments compelled educational institutions to migrate to full online learning until face-to-face instruction is allowed. The current circumstance is unique as it could aggravate the challenges experienced during online learning due to restrictions in movement and health protocols (Gonzales et al., 2020 ; Kapasia et al., 2020 ). Given today’s uncertainties, it is vital to gain a nuanced understanding of students’ online learning experience in times of the COVID-19 pandemic. To date, many studies have investigated this area with a focus on students’ mental health (Copeland et al., 2021 ; Fawaz et al., 2021 ), home learning (Suryaman et al., 2020 ), self-regulation (Carter et al., 2020 ), virtual learning environment (Almaiah et al., 2020 ; Hew et al., 2020 ; Tang et al., 2020 ), and students’ overall learning experience (e.g., Adarkwah, 2021 ; Day et al., 2021 ; Khalil et al., 2020 ; Singh et al., 2020 ). There are two key differences that set the current study apart from the previous studies. First, it sheds light on the direct impact of the pandemic on the challenges that students experience in an online learning space. Second, the current study explores students’ coping strategies in this new learning setup. Addressing these areas would shed light on the extent of challenges that students experience in a full online learning space, particularly within the context of the pandemic. Meanwhile, our nuanced understanding of the strategies that students use to overcome their challenges would provide relevant information to school administrators and teachers to better support the online learning needs of students. This information would also be critical in revisiting the typology of strategies in an online learning environment.
Literature review
Education and the covid-19 pandemic.
In December 2019, an outbreak of a novel coronavirus, known as COVID-19, occurred in China and has spread rapidly across the globe within a few months. COVID-19 is an infectious disease caused by a new strain of coronavirus that attacks the respiratory system (World Health Organization, 2020 ). As of January 2021, COVID-19 has infected 94 million people and has caused 2 million deaths in 191 countries and territories (John Hopkins University, 2021 ). This pandemic has created a massive disruption of the educational systems, affecting over 1.5 billion students. It has forced the government to cancel national examinations and the schools to temporarily close, cease face-to-face instruction, and strictly observe physical distancing. These events have sparked the digital transformation of higher education and challenged its ability to respond promptly and effectively. Schools adopted relevant technologies, prepared learning and staff resources, set systems and infrastructure, established new teaching protocols, and adjusted their curricula. However, the transition was smooth for some schools but rough for others, particularly those from developing countries with limited infrastructure (Pham & Nguyen, 2020 ; Simbulan, 2020 ).
Inevitably, schools and other learning spaces were forced to migrate to full online learning as the world continues the battle to control the vicious spread of the virus. Online learning refers to a learning environment that uses the Internet and other technological devices and tools for synchronous and asynchronous instructional delivery and management of academic programs (Usher & Barak, 2020 ; Huang, 2019 ). Synchronous online learning involves real-time interactions between the teacher and the students, while asynchronous online learning occurs without a strict schedule for different students (Singh & Thurman, 2019 ). Within the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, online learning has taken the status of interim remote teaching that serves as a response to an exigency. However, the migration to a new learning space has faced several major concerns relating to policy, pedagogy, logistics, socioeconomic factors, technology, and psychosocial factors (Donitsa-Schmidt & Ramot, 2020 ; Khalil et al., 2020 ; Varea & González-Calvo, 2020 ). With reference to policies, government education agencies and schools scrambled to create fool-proof policies on governance structure, teacher management, and student management. Teachers, who were used to conventional teaching delivery, were also obliged to embrace technology despite their lack of technological literacy. To address this problem, online learning webinars and peer support systems were launched. On the part of the students, dropout rates increased due to economic, psychological, and academic reasons. Academically, although it is virtually possible for students to learn anything online, learning may perhaps be less than optimal, especially in courses that require face-to-face contact and direct interactions (Franchi, 2020 ).
Related studies
Recently, there has been an explosion of studies relating to the new normal in education. While many focused on national policies, professional development, and curriculum, others zeroed in on the specific learning experience of students during the pandemic. Among these are Copeland et al. ( 2021 ) and Fawaz et al. ( 2021 ) who examined the impact of COVID-19 on college students’ mental health and their coping mechanisms. Copeland et al. ( 2021 ) reported that the pandemic adversely affected students’ behavioral and emotional functioning, particularly attention and externalizing problems (i.e., mood and wellness behavior), which were caused by isolation, economic/health effects, and uncertainties. In Fawaz et al.’s ( 2021 ) study, students raised their concerns on learning and evaluation methods, overwhelming task load, technical difficulties, and confinement. To cope with these problems, students actively dealt with the situation by seeking help from their teachers and relatives and engaging in recreational activities. These active-oriented coping mechanisms of students were aligned with Carter et al.’s ( 2020 ), who explored students’ self-regulation strategies.
In another study, Tang et al. ( 2020 ) examined the efficacy of different online teaching modes among engineering students. Using a questionnaire, the results revealed that students were dissatisfied with online learning in general, particularly in the aspect of communication and question-and-answer modes. Nonetheless, the combined model of online teaching with flipped classrooms improved students’ attention, academic performance, and course evaluation. A parallel study was undertaken by Hew et al. ( 2020 ), who transformed conventional flipped classrooms into fully online flipped classes through a cloud-based video conferencing app. Their findings suggested that these two types of learning environments were equally effective. They also offered ways on how to effectively adopt videoconferencing-assisted online flipped classrooms. Unlike the two studies, Suryaman et al. ( 2020 ) looked into how learning occurred at home during the pandemic. Their findings showed that students faced many obstacles in a home learning environment, such as lack of mastery of technology, high Internet cost, and limited interaction/socialization between and among students. In a related study, Kapasia et al. ( 2020 ) investigated how lockdown impacts students’ learning performance. Their findings revealed that the lockdown made significant disruptions in students’ learning experience. The students also reported some challenges that they faced during their online classes. These include anxiety, depression, poor Internet service, and unfavorable home learning environment, which were aggravated when students are marginalized and from remote areas. Contrary to Kapasia et al.’s ( 2020 ) findings, Gonzales et al. ( 2020 ) found that confinement of students during the pandemic had significant positive effects on their performance. They attributed these results to students’ continuous use of learning strategies which, in turn, improved their learning efficiency.
Finally, there are those that focused on students’ overall online learning experience during the COVID-19 pandemic. One such study was that of Singh et al. ( 2020 ), who examined students’ experience during the COVID-19 pandemic using a quantitative descriptive approach. Their findings indicated that students appreciated the use of online learning during the pandemic. However, half of them believed that the traditional classroom setting was more effective than the online learning platform. Methodologically, the researchers acknowledge that the quantitative nature of their study restricts a deeper interpretation of the findings. Unlike the above study, Khalil et al. ( 2020 ) qualitatively explored the efficacy of synchronized online learning in a medical school in Saudi Arabia. The results indicated that students generally perceive synchronous online learning positively, particularly in terms of time management and efficacy. However, they also reported technical (internet connectivity and poor utility of tools), methodological (content delivery), and behavioral (individual personality) challenges. Their findings also highlighted the failure of the online learning environment to address the needs of courses that require hands-on practice despite efforts to adopt virtual laboratories. In a parallel study, Adarkwah ( 2021 ) examined students’ online learning experience during the pandemic using a narrative inquiry approach. The findings indicated that Ghanaian students considered online learning as ineffective due to several challenges that they encountered. Among these were lack of social interaction among students, poor communication, lack of ICT resources, and poor learning outcomes. More recently, Day et al. ( 2021 ) examined the immediate impact of COVID-19 on students’ learning experience. Evidence from six institutions across three countries revealed some positive experiences and pre-existing inequities. Among the reported challenges are lack of appropriate devices, poor learning space at home, stress among students, and lack of fieldwork and access to laboratories.
Although there are few studies that report the online learning challenges that higher education students experience during the pandemic, limited information is available regarding the specific strategies that they use to overcome them. It is in this context that the current study was undertaken. This mixed-methods study investigates students’ online learning experience in higher education. Specifically, the following research questions are addressed: (1) What is the extent of challenges that students experience in an online learning environment? (2) How did the COVID-19 pandemic impact the online learning challenges that students experience? (3) What strategies did students use to overcome the challenges?
Conceptual framework
The typology of challenges examined in this study is largely based on Rasheed et al.’s ( 2020 ) review of students’ experience in an online learning environment. These challenges are grouped into five general clusters, namely self-regulation (SRC), technological literacy and competency (TLCC), student isolation (SIC), technological sufficiency (TSC), and technological complexity (TCC) challenges (Rasheed et al., 2020 , p. 5). SRC refers to a set of behavior by which students exercise control over their emotions, actions, and thoughts to achieve learning objectives. TLCC relates to a set of challenges about students’ ability to effectively use technology for learning purposes. SIC relates to the emotional discomfort that students experience as a result of being lonely and secluded from their peers. TSC refers to a set of challenges that students experience when accessing available online technologies for learning. Finally, there is TCC which involves challenges that students experience when exposed to complex and over-sufficient technologies for online learning.
To extend Rasheed et al. ( 2020 ) categories and to cover other potential challenges during online classes, two more clusters were added, namely learning resource challenges (LRC) and learning environment challenges (LEC) (Buehler, 2004 ; Recker et al., 2004 ; Seplaki et al., 2014 ; Xue et al., 2020 ). LRC refers to a set of challenges that students face relating to their use of library resources and instructional materials, whereas LEC is a set of challenges that students experience related to the condition of their learning space that shapes their learning experiences, beliefs, and attitudes. Since learning environment at home and learning resources available to students has been reported to significantly impact the quality of learning and their achievement of learning outcomes (Drane et al., 2020 ; Suryaman et al., 2020 ), the inclusion of LRC and LEC would allow us to capture other important challenges that students experience during the pandemic, particularly those from developing regions. This comprehensive list would provide us a clearer and detailed picture of students’ experiences when engaged in online learning in an emergency. Given the restrictions in mobility at macro and micro levels during the pandemic, it is also expected that such conditions would aggravate these challenges. Therefore, this paper intends to understand these challenges from students’ perspectives since they are the ones that are ultimately impacted when the issue is about the learning experience. We also seek to explore areas that provide inconclusive findings, thereby setting the path for future research.
Material and methods
The present study adopted a descriptive, mixed-methods approach to address the research questions. This approach allowed the researchers to collect complex data about students’ experience in an online learning environment and to clearly understand the phenomena from their perspective.

Participants
This study involved 200 (66 male and 134 female) students from a private higher education institution in the Philippines. These participants were Psychology, Physical Education, and Sports Management majors whose ages ranged from 17 to 25 ( x ̅ = 19.81; SD = 1.80). The students have been engaged in online learning for at least two terms in both synchronous and asynchronous modes. The students belonged to low- and middle-income groups but were equipped with the basic online learning equipment (e.g., computer, headset, speakers) and computer skills necessary for their participation in online classes. Table Table1 1 shows the primary and secondary platforms that students used during their online classes. The primary platforms are those that are formally adopted by teachers and students in a structured academic context, whereas the secondary platforms are those that are informally and spontaneously used by students and teachers for informal learning and to supplement instructional delivery. Note that almost all students identified MS Teams as their primary platform because it is the official learning management system of the university.
Participants’ Online Learning Platforms
Informed consent was sought from the participants prior to their involvement. Before students signed the informed consent form, they were oriented about the objectives of the study and the extent of their involvement. They were also briefed about the confidentiality of information, their anonymity, and their right to refuse to participate in the investigation. Finally, the participants were informed that they would incur no additional cost from their participation.
Instrument and data collection
The data were collected using a retrospective self-report questionnaire and a focused group discussion (FGD). A self-report questionnaire was considered appropriate because the indicators relate to affective responses and attitude (Araujo et al., 2017 ; Barrot, 2016 ; Spector, 1994 ). Although the participants may tell more than what they know or do in a self-report survey (Matsumoto, 1994 ), this challenge was addressed by explaining to them in detail each of the indicators and using methodological triangulation through FGD. The questionnaire was divided into four sections: (1) participant’s personal information section, (2) the background information on the online learning environment, (3) the rating scale section for the online learning challenges, (4) the open-ended section. The personal information section asked about the students’ personal information (name, school, course, age, and sex), while the background information section explored the online learning mode and platforms (primary and secondary) used in class, and students’ length of engagement in online classes. The rating scale section contained 37 items that relate to SRC (6 items), TLCC (10 items), SIC (4 items), TSC (6 items), TCC (3 items), LRC (4 items), and LEC (4 items). The Likert scale uses six scores (i.e., 5– to a very great extent , 4– to a great extent , 3– to a moderate extent , 2– to some extent , 1– to a small extent , and 0 –not at all/negligible ) assigned to each of the 37 items. Finally, the open-ended questions asked about other challenges that students experienced, the impact of the pandemic on the intensity or extent of the challenges they experienced, and the strategies that the participants employed to overcome the eight different types of challenges during online learning. Two experienced educators and researchers reviewed the questionnaire for clarity, accuracy, and content and face validity. The piloting of the instrument revealed that the tool had good internal consistency (Cronbach’s α = 0.96).
The FGD protocol contains two major sections: the participants’ background information and the main questions. The background information section asked about the students’ names, age, courses being taken, online learning mode used in class. The items in the main questions section covered questions relating to the students’ overall attitude toward online learning during the pandemic, the reasons for the scores they assigned to each of the challenges they experienced, the impact of the pandemic on students’ challenges, and the strategies they employed to address the challenges. The same experts identified above validated the FGD protocol.
Both the questionnaire and the FGD were conducted online via Google survey and MS Teams, respectively. It took approximately 20 min to complete the questionnaire, while the FGD lasted for about 90 min. Students were allowed to ask for clarification and additional explanations relating to the questionnaire content, FGD, and procedure. Online surveys and interview were used because of the ongoing lockdown in the city. For the purpose of triangulation, 20 (10 from Psychology and 10 from Physical Education and Sports Management) randomly selected students were invited to participate in the FGD. Two separate FGDs were scheduled for each group and were facilitated by researcher 2 and researcher 3, respectively. The interviewers ensured that the participants were comfortable and open to talk freely during the FGD to avoid social desirability biases (Bergen & Labonté, 2020 ). These were done by informing the participants that there are no wrong responses and that their identity and responses would be handled with the utmost confidentiality. With the permission of the participants, the FGD was recorded to ensure that all relevant information was accurately captured for transcription and analysis.
Data analysis
To address the research questions, we used both quantitative and qualitative analyses. For the quantitative analysis, we entered all the data into an excel spreadsheet. Then, we computed the mean scores ( M ) and standard deviations ( SD ) to determine the level of challenges experienced by students during online learning. The mean score for each descriptor was interpreted using the following scheme: 4.18 to 5.00 ( to a very great extent ), 3.34 to 4.17 ( to a great extent ), 2.51 to 3.33 ( to a moderate extent ), 1.68 to 2.50 ( to some extent ), 0.84 to 1.67 ( to a small extent ), and 0 to 0.83 ( not at all/negligible ). The equal interval was adopted because it produces more reliable and valid information than other types of scales (Cicchetti et al., 2006 ).
For the qualitative data, we analyzed the students’ responses in the open-ended questions and the transcribed FGD using the predetermined categories in the conceptual framework. Specifically, we used multilevel coding in classifying the codes from the transcripts (Birks & Mills, 2011 ). To do this, we identified the relevant codes from the responses of the participants and categorized these codes based on the similarities or relatedness of their properties and dimensions. Then, we performed a constant comparative and progressive analysis of cases to allow the initially identified subcategories to emerge and take shape. To ensure the reliability of the analysis, two coders independently analyzed the qualitative data. Both coders familiarize themselves with the purpose, research questions, research method, and codes and coding scheme of the study. They also had a calibration session and discussed ways on how they could consistently analyze the qualitative data. Percent of agreement between the two coders was 86 percent. Any disagreements in the analysis were discussed by the coders until an agreement was achieved.
This study investigated students’ online learning experience in higher education within the context of the pandemic. Specifically, we identified the extent of challenges that students experienced, how the COVID-19 pandemic impacted their online learning experience, and the strategies that they used to confront these challenges.
The extent of students’ online learning challenges
Table Table2 2 presents the mean scores and SD for the extent of challenges that students’ experienced during online learning. Overall, the students experienced the identified challenges to a moderate extent ( x ̅ = 2.62, SD = 1.03) with scores ranging from x ̅ = 1.72 ( to some extent ) to x ̅ = 3.58 ( to a great extent ). More specifically, the greatest challenge that students experienced was related to the learning environment ( x ̅ = 3.49, SD = 1.27), particularly on distractions at home, limitations in completing the requirements for certain subjects, and difficulties in selecting the learning areas and study schedule. It is, however, found that the least challenge was on technological literacy and competency ( x ̅ = 2.10, SD = 1.13), particularly on knowledge and training in the use of technology, technological intimidation, and resistance to learning technologies. Other areas that students experienced the least challenge are Internet access under TSC and procrastination under SRC. Nonetheless, nearly half of the students’ responses per indicator rated the challenges they experienced as moderate (14 of the 37 indicators), particularly in TCC ( x ̅ = 2.51, SD = 1.31), SIC ( x ̅ = 2.77, SD = 1.34), and LRC ( x ̅ = 2.93, SD = 1.31).
The Extent of Students’ Challenges during the Interim Online Learning
Out of 200 students, 181 responded to the question about other challenges that they experienced. Most of their responses were already covered by the seven predetermined categories, except for 18 responses related to physical discomfort ( N = 5) and financial challenges ( N = 13). For instance, S108 commented that “when it comes to eyes and head, my eyes and head get ache if the session of class was 3 h straight in front of my gadget.” In the same vein, S194 reported that “the long exposure to gadgets especially laptop, resulting in body pain & headaches.” With reference to physical financial challenges, S66 noted that “not all the time I have money to load”, while S121 claimed that “I don't know until when are we going to afford budgeting our money instead of buying essentials.”
Impact of the pandemic on students’ online learning challenges
Another objective of this study was to identify how COVID-19 influenced the online learning challenges that students experienced. As shown in Table Table3, 3 , most of the students’ responses were related to teaching and learning quality ( N = 86) and anxiety and other mental health issues ( N = 52). Regarding the adverse impact on teaching and learning quality, most of the comments relate to the lack of preparation for the transition to online platforms (e.g., S23, S64), limited infrastructure (e.g., S13, S65, S99, S117), and poor Internet service (e.g., S3, S9, S17, S41, S65, S99). For the anxiety and mental health issues, most students reported that the anxiety, boredom, sadness, and isolation they experienced had adversely impacted the way they learn (e.g., S11, S130), completing their tasks/activities (e.g., S56, S156), and their motivation to continue studying (e.g., S122, S192). The data also reveal that COVID-19 aggravated the financial difficulties experienced by some students ( N = 16), consequently affecting their online learning experience. This financial impact mainly revolved around the lack of funding for their online classes as a result of their parents’ unemployment and the high cost of Internet data (e.g., S18, S113, S167). Meanwhile, few concerns were raised in relation to COVID-19’s impact on mobility ( N = 7) and face-to-face interactions ( N = 7). For instance, some commented that the lack of face-to-face interaction with her classmates had a detrimental effect on her learning (S46) and socialization skills (S36), while others reported that restrictions in mobility limited their learning experience (S78, S110). Very few comments were related to no effect ( N = 4) and positive effect ( N = 2). The above findings suggest the pandemic had additive adverse effects on students’ online learning experience.
Summary of students’ responses on the impact of COVID-19 on their online learning experience
Students’ strategies to overcome challenges in an online learning environment
The third objective of this study is to identify the strategies that students employed to overcome the different online learning challenges they experienced. Table Table4 4 presents that the most commonly used strategies used by students were resource management and utilization ( N = 181), help-seeking ( N = 155), technical aptitude enhancement ( N = 122), time management ( N = 98), and learning environment control ( N = 73). Not surprisingly, the top two strategies were also the most consistently used across different challenges. However, looking closely at each of the seven challenges, the frequency of using a particular strategy varies. For TSC and LRC, the most frequently used strategy was resource management and utilization ( N = 52, N = 89, respectively), whereas technical aptitude enhancement was the students’ most preferred strategy to address TLCC ( N = 77) and TCC ( N = 38). In the case of SRC, SIC, and LEC, the most frequently employed strategies were time management ( N = 71), psychological support ( N = 53), and learning environment control ( N = 60). In terms of consistency, help-seeking appears to be the most consistent across the different challenges in an online learning environment. Table Table4 4 further reveals that strategies used by students within a specific type of challenge vary.
Students’ Strategies to Overcome Online Learning Challenges
Discussion and conclusions
The current study explores the challenges that students experienced in an online learning environment and how the pandemic impacted their online learning experience. The findings revealed that the online learning challenges of students varied in terms of type and extent. Their greatest challenge was linked to their learning environment at home, while their least challenge was technological literacy and competency. Based on the students’ responses, their challenges were also found to be aggravated by the pandemic, especially in terms of quality of learning experience, mental health, finances, interaction, and mobility. With reference to previous studies (i.e., Adarkwah, 2021 ; Copeland et al., 2021 ; Day et al., 2021 ; Fawaz et al., 2021 ; Kapasia et al., 2020 ; Khalil et al., 2020 ; Singh et al., 2020 ), the current study has complemented their findings on the pedagogical, logistical, socioeconomic, technological, and psychosocial online learning challenges that students experience within the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Further, this study extended previous studies and our understanding of students’ online learning experience by identifying both the presence and extent of online learning challenges and by shedding light on the specific strategies they employed to overcome them.
Overall findings indicate that the extent of challenges and strategies varied from one student to another. Hence, they should be viewed as a consequence of interaction several many factors. Students’ responses suggest that their online learning challenges and strategies were mediated by the resources available to them, their interaction with their teachers and peers, and the school’s existing policies and guidelines for online learning. In the context of the pandemic, the imposed lockdowns and students’ socioeconomic condition aggravated the challenges that students experience.
While most studies revealed that technology use and competency were the most common challenges that students face during the online classes (see Rasheed et al., 2020 ), the case is a bit different in developing countries in times of pandemic. As the findings have shown, the learning environment is the greatest challenge that students needed to hurdle, particularly distractions at home (e.g., noise) and limitations in learning space and facilities. This data suggests that online learning challenges during the pandemic somehow vary from the typical challenges that students experience in a pre-pandemic online learning environment. One possible explanation for this result is that restriction in mobility may have aggravated this challenge since they could not go to the school or other learning spaces beyond the vicinity of their respective houses. As shown in the data, the imposition of lockdown restricted students’ learning experience (e.g., internship and laboratory experiments), limited their interaction with peers and teachers, caused depression, stress, and anxiety among students, and depleted the financial resources of those who belong to lower-income group. All of these adversely impacted students’ learning experience. This finding complemented earlier reports on the adverse impact of lockdown on students’ learning experience and the challenges posed by the home learning environment (e.g., Day et al., 2021 ; Kapasia et al., 2020 ). Nonetheless, further studies are required to validate the impact of restrictions on mobility on students’ online learning experience. The second reason that may explain the findings relates to students’ socioeconomic profile. Consistent with the findings of Adarkwah ( 2021 ) and Day et al. ( 2021 ), the current study reveals that the pandemic somehow exposed the many inequities in the educational systems within and across countries. In the case of a developing country, families from lower socioeconomic strata (as in the case of the students in this study) have limited learning space at home, access to quality Internet service, and online learning resources. This is the reason the learning environment and learning resources recorded the highest level of challenges. The socioeconomic profile of the students (i.e., low and middle-income group) is the same reason financial problems frequently surfaced from their responses. These students frequently linked the lack of financial resources to their access to the Internet, educational materials, and equipment necessary for online learning. Therefore, caution should be made when interpreting and extending the findings of this study to other contexts, particularly those from higher socioeconomic strata.
Among all the different online learning challenges, the students experienced the least challenge on technological literacy and competency. This is not surprising considering a plethora of research confirming Gen Z students’ (born since 1996) high technological and digital literacy (Barrot, 2018 ; Ng, 2012 ; Roblek et al., 2019 ). Regarding the impact of COVID-19 on students’ online learning experience, the findings reveal that teaching and learning quality and students’ mental health were the most affected. The anxiety that students experienced does not only come from the threats of COVID-19 itself but also from social and physical restrictions, unfamiliarity with new learning platforms, technical issues, and concerns about financial resources. These findings are consistent with that of Copeland et al. ( 2021 ) and Fawaz et al. ( 2021 ), who reported the adverse effects of the pandemic on students’ mental and emotional well-being. This data highlights the need to provide serious attention to the mediating effects of mental health, restrictions in mobility, and preparedness in delivering online learning.
Nonetheless, students employed a variety of strategies to overcome the challenges they faced during online learning. For instance, to address the home learning environment problems, students talked to their family (e.g., S12, S24), transferred to a quieter place (e.g., S7, S 26), studied at late night where all family members are sleeping already (e.g., S51), and consulted with their classmates and teachers (e.g., S3, S9, S156, S193). To overcome the challenges in learning resources, students used the Internet (e.g., S20, S27, S54, S91), joined Facebook groups that share free resources (e.g., S5), asked help from family members (e.g., S16), used resources available at home (e.g., S32), and consulted with the teachers (e.g., S124). The varying strategies of students confirmed earlier reports on the active orientation that students take when faced with academic- and non-academic-related issues in an online learning space (see Fawaz et al., 2021 ). The specific strategies that each student adopted may have been shaped by different factors surrounding him/her, such as available resources, student personality, family structure, relationship with peers and teacher, and aptitude. To expand this study, researchers may further investigate this area and explore how and why different factors shape their use of certain strategies.
Several implications can be drawn from the findings of this study. First, this study highlighted the importance of emergency response capability and readiness of higher education institutions in case another crisis strikes again. Critical areas that need utmost attention include (but not limited to) national and institutional policies, protocol and guidelines, technological infrastructure and resources, instructional delivery, staff development, potential inequalities, and collaboration among key stakeholders (i.e., parents, students, teachers, school leaders, industry, government education agencies, and community). Second, the findings have expanded our understanding of the different challenges that students might confront when we abruptly shift to full online learning, particularly those from countries with limited resources, poor Internet infrastructure, and poor home learning environment. Schools with a similar learning context could use the findings of this study in developing and enhancing their respective learning continuity plans to mitigate the adverse impact of the pandemic. This study would also provide students relevant information needed to reflect on the possible strategies that they may employ to overcome the challenges. These are critical information necessary for effective policymaking, decision-making, and future implementation of online learning. Third, teachers may find the results useful in providing proper interventions to address the reported challenges, particularly in the most critical areas. Finally, the findings provided us a nuanced understanding of the interdependence of learning tools, learners, and learning outcomes within an online learning environment; thus, giving us a multiperspective of hows and whys of a successful migration to full online learning.
Some limitations in this study need to be acknowledged and addressed in future studies. One limitation of this study is that it exclusively focused on students’ perspectives. Future studies may widen the sample by including all other actors taking part in the teaching–learning process. Researchers may go deeper by investigating teachers’ views and experience to have a complete view of the situation and how different elements interact between them or affect the others. Future studies may also identify some teacher-related factors that could influence students’ online learning experience. In the case of students, their age, sex, and degree programs may be examined in relation to the specific challenges and strategies they experience. Although the study involved a relatively large sample size, the participants were limited to college students from a Philippine university. To increase the robustness of the findings, future studies may expand the learning context to K-12 and several higher education institutions from different geographical regions. As a final note, this pandemic has undoubtedly reshaped and pushed the education system to its limits. However, this unprecedented event is the same thing that will make the education system stronger and survive future threats.
Authors’ contributions
Jessie Barrot led the planning, prepared the instrument, wrote the report, and processed and analyzed data. Ian Llenares participated in the planning, fielded the instrument, processed and analyzed data, reviewed the instrument, and contributed to report writing. Leo del Rosario participated in the planning, fielded the instrument, processed and analyzed data, reviewed the instrument, and contributed to report writing.
No funding was received in the conduct of this study.
Availability of data and materials
Declarations.
The study has undergone appropriate ethics protocol.
Informed consent was sought from the participants.
Authors consented the publication. Participants consented to publication as long as confidentiality is observed.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Adarkwah MA. “I’m not against online teaching, but what about us?”: ICT in Ghana post Covid-19. Education and Information Technologies. 2021; 26 (2):1665–1685. doi: 10.1007/s10639-020-10331-z. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Almaiah MA, Al-Khasawneh A, Althunibat A. Exploring the critical challenges and factors influencing the E-learning system usage during COVID-19 pandemic. Education and Information Technologies. 2020; 25 :5261–5280. doi: 10.1007/s10639-020-10219-y. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Araujo T, Wonneberger A, Neijens P, de Vreese C. How much time do you spend online? Understanding and improving the accuracy of self-reported measures of Internet use. Communication Methods and Measures. 2017; 11 (3):173–190. doi: 10.1080/19312458.2017.1317337. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barrot, J. S. (2016). Using Facebook-based e-portfolio in ESL writing classrooms: Impact and challenges. Language, Culture and Curriculum, 29 (3), 286–301.
- Barrot, J. S. (2018). Facebook as a learning environment for language teaching and learning: A critical analysis of the literature from 2010 to 2017. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 34 (6), 863–875.
- Barrot, J. S. (2020). Scientific mapping of social media in education: A decade of exponential growth. Journal of Educational Computing Research . 10.1177/0735633120972010.
- Barrot, J. S. (2021). Social media as a language learning environment: A systematic review of the literature (2008–2019). Computer Assisted Language Learning . 10.1080/09588221.2021.1883673.
- Bergen N, Labonté R. “Everything is perfect, and we have no problems”: Detecting and limiting social desirability bias in qualitative research. Qualitative Health Research. 2020; 30 (5):783–792. doi: 10.1177/1049732319889354. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Birks, M., & Mills, J. (2011). Grounded theory: A practical guide . Sage.
- Boelens R, De Wever B, Voet M. Four key challenges to the design of blended learning: A systematic literature review. Educational Research Review. 2017; 22 :1–18. doi: 10.1016/j.edurev.2017.06.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Buehler MA. Where is the library in course management software? Journal of Library Administration. 2004; 41 (1–2):75–84. doi: 10.1300/J111v41n01_07. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carter RA, Jr, Rice M, Yang S, Jackson HA. Self-regulated learning in online learning environments: Strategies for remote learning. Information and Learning Sciences. 2020; 121 (5/6):321–329. doi: 10.1108/ILS-04-2020-0114. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cavanaugh CS, Barbour MK, Clark T. Research and practice in K-12 online learning: A review of open access literature. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning. 2009; 10 (1):1–22. doi: 10.19173/irrodl.v10i1.607. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cicchetti D, Bronen R, Spencer S, Haut S, Berg A, Oliver P, Tyrer P. Rating scales, scales of measurement, issues of reliability: Resolving some critical issues for clinicians and researchers. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease. 2006; 194 (8):557–564. doi: 10.1097/01.nmd.0000230392.83607.c5. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Copeland WE, McGinnis E, Bai Y, Adams Z, Nardone H, Devadanam V, Hudziak JJ. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on college student mental health and wellness. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 2021; 60 (1):134–141. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2020.08.466. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Day T, Chang ICC, Chung CKL, Doolittle WE, Housel J, McDaniel PN. The immediate impact of COVID-19 on postsecondary teaching and learning. The Professional Geographer. 2021; 73 (1):1–13. doi: 10.1080/00330124.2020.1823864. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Donitsa-Schmidt S, Ramot R. Opportunities and challenges: Teacher education in Israel in the Covid-19 pandemic. Journal of Education for Teaching. 2020; 46 (4):586–595. doi: 10.1080/02607476.2020.1799708. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Drane, C., Vernon, L., & O’Shea, S. (2020). The impact of ‘learning at home’on the educational outcomes of vulnerable children in Australia during the COVID-19 pandemic. Literature Review Prepared by the National Centre for Student Equity in Higher Education. Curtin University, Australia.
- Elaish M, Shuib L, Ghani N, Yadegaridehkordi E. Mobile English language learning (MELL): A literature review. Educational Review. 2019; 71 (2):257–276. doi: 10.1080/00131911.2017.1382445. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fawaz, M., Al Nakhal, M., & Itani, M. (2021). COVID-19 quarantine stressors and management among Lebanese students: A qualitative study. Current Psychology , 1–8. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Franchi T. The impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on current anatomy education and future careers: A student’s perspective. Anatomical Sciences Education. 2020; 13 (3):312–315. doi: 10.1002/ase.1966. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garcia R, Falkner K, Vivian R. Systematic literature review: Self-regulated learning strategies using e-learning tools for computer science. Computers & Education. 2018; 123 :150–163. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2018.05.006. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gonzalez T, De La Rubia MA, Hincz KP, Comas-Lopez M, Subirats L, Fort S, Sacha GM. Influence of COVID-19 confinement on students’ performance in higher education. PLoS ONE. 2020; 15 (10):e0239490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239490. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hew KF, Jia C, Gonda DE, Bai S. Transitioning to the “new normal” of learning in unpredictable times: Pedagogical practices and learning performance in fully online flipped classrooms. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education. 2020; 17 (1):1–22. doi: 10.1186/s41239-020-00234-x. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang Q. Comparing teacher’s roles of F2F learning and online learning in a blended English course. Computer Assisted Language Learning. 2019; 32 (3):190–209. doi: 10.1080/09588221.2018.1540434. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- John Hopkins University. (2021). Global map . https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/
- Kapasia N, Paul P, Roy A, Saha J, Zaveri A, Mallick R, Chouhan P. Impact of lockdown on learning status of undergraduate and postgraduate students during COVID-19 pandemic in West Bengal. India. Children and Youth Services Review. 2020; 116 :105194. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105194. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kebritchi M, Lipschuetz A, Santiague L. Issues and challenges for teaching successful online courses in higher education: A literature review. Journal of Educational Technology Systems. 2017; 46 (1):4–29. doi: 10.1177/0047239516661713. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Khalil R, Mansour AE, Fadda WA, Almisnid K, Aldamegh M, Al-Nafeesah A, Al-Wutayd O. The sudden transition to synchronized online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia: A qualitative study exploring medical students’ perspectives. BMC Medical Education. 2020; 20 (1):1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02208-z. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Matsumoto K. Introspection, verbal reports and second language learning strategy research. Canadian Modern Language Review. 1994; 50 (2):363–386. doi: 10.3138/cmlr.50.2.363. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ng W. Can we teach digital natives digital literacy? Computers & Education. 2012; 59 (3):1065–1078. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2012.04.016. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pham T, Nguyen H. COVID-19: Challenges and opportunities for Vietnamese higher education. Higher Education in Southeast Asia and beyond. 2020; 8 :22–24. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rasheed RA, Kamsin A, Abdullah NA. Challenges in the online component of blended learning: A systematic review. Computers & Education. 2020; 144 :103701. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103701. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Recker MM, Dorward J, Nelson LM. Discovery and use of online learning resources: Case study findings. Educational Technology & Society. 2004; 7 (2):93–104. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roblek V, Mesko M, Dimovski V, Peterlin J. Smart technologies as social innovation and complex social issues of the Z generation. Kybernetes. 2019; 48 (1):91–107. doi: 10.1108/K-09-2017-0356. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Seplaki CL, Agree EM, Weiss CO, Szanton SL, Bandeen-Roche K, Fried LP. Assistive devices in context: Cross-sectional association between challenges in the home environment and use of assistive devices for mobility. The Gerontologist. 2014; 54 (4):651–660. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnt030. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Simbulan N. COVID-19 and its impact on higher education in the Philippines. Higher Education in Southeast Asia and beyond. 2020; 8 :15–18. [ Google Scholar ]
- Singh K, Srivastav S, Bhardwaj A, Dixit A, Misra S. Medical education during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single institution experience. Indian Pediatrics. 2020; 57 (7):678–679. doi: 10.1007/s13312-020-1899-2. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Singh V, Thurman A. How many ways can we define online learning? A systematic literature review of definitions of online learning (1988–2018) American Journal of Distance Education. 2019; 33 (4):289–306. doi: 10.1080/08923647.2019.1663082. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Spector P. Using self-report questionnaires in OB research: A comment on the use of a controversial method. Journal of Organizational Behavior. 1994; 15 (5):385–392. doi: 10.1002/job.4030150503. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suryaman M, Cahyono Y, Muliansyah D, Bustani O, Suryani P, Fahlevi M, Munthe AP. COVID-19 pandemic and home online learning system: Does it affect the quality of pharmacy school learning? Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy. 2020; 11 :524–530. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tallent-Runnels MK, Thomas JA, Lan WY, Cooper S, Ahern TC, Shaw SM, Liu X. Teaching courses online: A review of the research. Review of Educational Research. 2006; 76 (1):93–135. doi: 10.3102/00346543076001093. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tang, T., Abuhmaid, A. M., Olaimat, M., Oudat, D. M., Aldhaeebi, M., & Bamanger, E. (2020). Efficiency of flipped classroom with online-based teaching under COVID-19. Interactive Learning Environments , 1–12.
- Usher M, Barak M. Team diversity as a predictor of innovation in team projects of face-to-face and online learners. Computers & Education. 2020; 144 :103702. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103702. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Varea, V., & González-Calvo, G. (2020). Touchless classes and absent bodies: Teaching physical education in times of Covid-19. Sport, Education and Society , 1–15.
- Wallace RM. Online learning in higher education: A review of research on interactions among teachers and students. Education, Communication & Information. 2003; 3 (2):241–280. doi: 10.1080/14636310303143. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World Health Organization (2020). Coronavirus . https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_1
- Xue, E., Li, J., Li, T., & Shang, W. (2020). China’s education response to COVID-19: A perspective of policy analysis. Educational Philosophy and Theory , 1–13.
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, teaching and learning continuity amid and beyond the pandemic.

- Office of the University President, Palompon - Office of the Vice-President for Academic Affairs, Garcia-Center for Research and Development, Olvido - Office of the Board and University Secretary, Cebu, Philippines
The study explored the challenges and issues in teaching and learning continuity of public higher education in the Philippines as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. The study employed the exploratory mixed-method triangulation design and analyzed the data gathered from 3, 989 respondents composed of students and faculty members. It was found out that during school lockdowns, the teachers made adjustments in teaching and learning designs guided by the policies implemented by the institution. Most of the students had difficulty complying with the learning activities and requirements due to limited or no internet connectivity. Emerging themes were identified from the qualitative responses to include the trajectory for flexible learning delivery, the role of technology, the teaching and learning environment, and the prioritization of safety and security. Scenario analysis provided the contextual basis for strategic actions amid and beyond the pandemic. To ensure teaching and learning continuity, it is concluded that higher education institutions have to migrate to flexible teaching and learning modality recalibrate the curriculum, capacitate the faculty, upgrade the infrastructure, implement a strategic plan and assess all aspects of the plan.
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has created unprecedented challenges economically, socially, and politically across the globe. More than just a health crisis, it has resulted in an educational crisis. During lockdowns and quarantines, 87% of the world’s student population was affected and 1.52 billion learners were out of school and related educational institutions ( UNESCO Learning Portal, 2020 ). The suddenness, uncertainty, and volatility of COVID-19 left the education system in a rush of addressing the changing learning landscape.
The disruption of COVID-19 in the educational system is of great magnitude that universities have to cope with at the soonest possible time. The call is for higher education institutions to develop a resilient learning system using evidence-based and needs-based information so that responsive and proactive measures can be instituted. Coping with the effects of COVID-19 in higher education institutions demands a variety of perspectives among stakeholders. Consultation needs to include the administration who supports the teaching-learning processes, the students who are the core of the system, the faculty members or teachers who perform various academic roles, parents, and guardians who share the responsibility of learning continuity, the community, and the external partners who contribute to the completion of the educational requirements of the students. These complicated identities show that an institution of higher learning has a large number of stakeholders ( Illanes et al., 2020 ; Smalley, 2020 ). In the context of the pandemic, universities have to start understanding and identifying medium-term and long-term implications of this phenomenon on teaching, learning, student experience, infrastructure, operation, and staff. Scenario analysis and understanding of the context of each university are necessary to the current challenges they are confronted with (Frankki et al., 2020). Universities have to be resilient in times of crisis. Resiliency in the educational system is the ability to overcome challenges of all kinds–trauma, tragedy, crises, and bounce back stronger, wiser, and more personally powerful ( Henderson, 2012 ). The educational system must prepare to develop plans to move forward and address the new normal after the crisis. To be resilient, higher education needs to address teaching and learning continuity amid and beyond the pandemic.
Teaching and Learning in Times of Crisis
The teaching and learning process assumes a different shape in times of crisis. When disasters and crises (man-made and natural) occur, schools and colleges need to be resilient and find new ways to continue the teaching–learning activities ( Chang-Richards et al., 2013 ). One emerging reality as a result of the world health crisis is the migration to online learning modalities to mitigate the risk of face-to-face interaction. Universities are forced to migrate from face-to-face delivery to online modality as a result of the pandemic. In the Philippines, most universities including Cebu Normal University have resorted to online learning during school lockdowns. However, this sudden shift has resulted in problems especially for learners without access to technology. When online learning modality is used as a result of the pandemic, the gap between those who have connectivity and those without widened. The continuing academic engagement has been a challenge for teachers and students due to access and internet connectivity.
Considering the limitation on connectivity, the concept of flexible learning emerged as an option for online learning especially in higher institutions in the Philippines. Flexible learning focuses on giving students choice in the pace, place, and mode of students’ learning which can be promoted through appropriate pedagogical practice ( Gordon, 2014 ). The learners are provided with the option on how he/she will continue with his/her studies, where and when he/she can proceed, and in what ways can the learners comply with the requirements and show evidences of learning outcomes. Flexible learning and teaching span a multitude of approaches that can meet the varied needs of diverse learners. These include “independence in terms of time and location of learning, and the availability of some degree of choice in the curriculum (including content, learning strategies, and assessment) and the use of contemporary information and communication technologies to support a range of learning strategies” ( Alexander, 2010 ).
One key component in migrating to flexible modality is to consider how flexibility is integrated into the key dimensions of teaching and learning. One major consideration is leveraging flexibility in the curriculum. The curriculum encompasses the recommended, written, taught or implemented, assessed, and learned curriculum ( Glatthorn, 2000 ). Curriculum pertains to the curricular programs, the teaching, and learning design, learning resources as assessment, and teaching and learning environment. Adjustment on the types of assessment measures is a major factor amid the pandemic. There is a need to limit requirements and focus on the major essential projects that measure the enduring learning outcomes like case scenarios, problem-based activities, and capstone projects. Authentic assessments have to be intensified to ensure that competencies are acquired by the learners. In the process of modifying the curriculum amid the pandemic, it must be remembered that initiatives and evaluation tasks must be anchored on what the learners need including their safety and well-being.
Curriculum recalibration is not just about the content of what is to be learned and taught but how it is to be learned, taught, and assessed in the context of the challenges brought about by the pandemic. A flexible curriculum design should be learner-centered; take into account the demographic profile and circumstances of learners–such as access to technology, technological literacies, different learning styles and capabilities, different knowledge backgrounds and experiences - and ensure varied and flexible forms of assessment ( Ryan and Tilbury, 2013 ; Gachago et al., 2018 ). The challenge during the pandemic is how to create a balance between relevant basic competencies for the students to acquire and the teachers’ desire to achieve the intended outcomes of the curriculum.
The learners’ engagement in the teaching-learning process needs to be taken into consideration in the context of flexibility. This is about the design and development of productive learning experiences so that each learner is exposed to most of the learning opportunities. Considering that face-to-face modality is not feasible during the pandemic, teachers may consider flexible distant learning options like correspondence teaching, module-based learning, project-based, and television broadcast. For learners with internet connectivity, computer-assisted instruction, synchronous online learning, asynchronous online learning, collaborative e-learning may be considered.
The Role of Technology in Learning Continuity
Technology provides innovative and resilient solutions in times of crisis to combat disruption and helps people to communicate and even work virtually without the need for face-to-face interaction. This leads to many system changes in organizations as they adopt new technology for interacting and working ( Mark and Semaan, 2008 ). However, technological challenges like internet connectivity especially for places without signals can be the greatest obstacle in teaching and learning continuity especially for academic institutions who have opted for online learning as a teaching modality. Thus, the alternative models of learning during the pandemic should be supported by a well-designed technical and logistical implementation plan ( Edizon, 2020 ).
The nationwide closure of educational institutions in an attempt to contain the spread of the virus has impacted 90% of the world’s student population ( UNESCO, 2020 ). It is the intent of this study to look into the challenges in teaching and learning continuity amidst the pandemic. The need to mitigate the immediate impact of school closures on the continuity of learning among learners from their perspectives is an important consideration ( Edizon, 2020 ; Hijazi, 2020 ; UNESCO, 2020 ). Moreover, the teachers' perspectives are equally as important as the learners since they are the ones providing and sustaining the learning process. Teachers should effectively approach these current challenges to facilitate learning among learners, learner differentiation, and learner-centeredness and be ready to assume the role of facilitators on the remote learning platforms ( Chi-Kin Lee, 2020 ; Edizon, 2020 ; Hijazi, 2020 ).
Statement of Objective
This study explores the issues and challenges in teaching and learning amid the pandemic from the lenses of the faculty members and students of a public university in the Philippines as the basis for the development of strategic actions for teaching and learning continuity. Specifically, this study aimed to:
a.1. Preferred flexible learning activities.
a.2. Problems completing Requirements due to ICT Limitation
a.3. Provision of alternative/additional requirement.
a.4. Receipt of learning feedback.
a.5. Learning environment.
Objective 2: determine the profile of faculty and students in terms of online capacity as categorized into:
b.1. Access to Information Technology.
b.2. Access to Internet/Wi-fi.
b.3. Stability of internet connection.
Objective 3: develop emerging themes from the experiences and challenges of teaching and learning amidst the pandemic.
Methodology
The design used in the study is an exploratory mixed-method triangulation design. It was utilized to obtain different information but complementary data on a common topic or intent of the study, bringing together the differing strengths non-overlapping weaknesses of quantitative methods with those of qualitative methods ( Creswell, 2006 ). The use of the mixed method provided the data used as a basis for the analysis and planning perspective of the study.
This study was conducted in the context of a state university funded by the Philippine government whose location was once identified as having one of the highest COVID19 cases in the country. With this incidence, the sudden suspension of classes and the immediate need to shift the learning platform responsive to the needs of the learners lend a significant consideration in this study. This explored the perspectives of the learners in terms of their current capacity and its implications in the learning continuity using online learning. These were explored based on the availability of gadgets, internet connectivity, and their learning experiences with their teachers. These perspectives were also explored on the part of the teachers as they were the ones who provided learning inputs to the students. These are necessary information to identify strategic actions for the teaching and learning continuity plan of the university.
After getting the quantitative and qualitative findings, these data were reviewed to provide a clear understanding of teachers’ and learners’ context and their experiences. From this information, a scenario analysis through scenario building was conducted which led to the development of the strategic actions for teaching and learning continuity. Scenario analysis is a method used in predicting the possible occurrences of consequences of a situation assuming the phenomenon will be continued in the future ( Kishita et al., 2016 ). This approach is considered a useful way for exploring plausible events that may or may not happen in the future ( Bekessy and Selinske, 2017 ). This approach was used to analyze the behavior of both teachers and students as part of the whole system in response to an unexpected event such as the pandemic which creates a theoretical scenario of best -case (optimistic) or worse case (pessimistic) scenario to enable the university to develop a holistic strategic plan for the teaching and learning continuity ( Balaman, 2019 ).
Both quantitative and qualitative approaches were used simultaneously. In this study, objectives 1 and 2 require data on the profile of the teachers and learners which can best be acquired using a descriptive quantitative design. This was done through an online structured survey was conducted to identify the challenges in teaching and learning using google forms. Choices were provided in the Google form which the respondents can choose from. The surveys were done by the Cebu Normal University - Center for Research and Development and Federation of Supreme Student Council.
The qualitative approach was utilized to answer objective number 3 which looked into the experiences and challenges of the teachers and the learners. The narratives which the respondents submitted were done through online open-ended questions to allow them to share their experiences and challenges. These were analyzed using a thematic approach to best provide a clear description of the experiences and challenges.
After the analysis of the quantitative and qualitative data, the team of researchers developed the possible scenarios that will take place as the basis for the flexible strategic actions that the university will adapt depending on the classification of community quarantine and the health situation of the locale where the university is located. In the analysis of the current status of Cebu Normal University, parameters are reviewed and outcomes are utilized through scenario building. Scenario building provides the contextual basis for the development of the new normal in the university. Scenario building as explained by Wilkinson (1995) is a good strategy to use on how current observations play their role in future situations. Each scenario is constructed about the future, modeling a distinct, plausible world. Scenarios are plausible alternative futures of what might happen under particular assumptions by focusing on key drivers, complex interactions, and irreducible uncertainties ( Polcyznski, 2009 ).
The prospective scenarios created are the best, probable scenarios, and worse scenarios. Current or existing situations/conditions of CNU served as the probable scenario, while the ideal case situation served as the best scenario. From the scenario built, key problems and challenges are developed as a basis for the model developed ( Imperial, 2020 ). This provided the strategic long-term and short-term strategies for CNU’s academic operations. The best scenario is based on the perspective that the university allows limited face-to-face classes in the remaining months of the semester. The probable scenario is with the current enhanced community quarantine (ECQ) status of the city or province where the university is located, at least six (6) months, after, face-to-face interactions will be allowed with the opening of the new school year will. Worse Scenario happens when the locale is placed under sustained community quarantine and face-to-face classes will never be allowed at the start of the new school year. The strategic actions of the university are inclusive of the three (3) scenarios to allow flexibility of the responses of the university in this pandemic.
There were 3,646 student respondents (85% of the student population) and 252 (97% of the teaching personnel) teaching personnel who responded to the survey. To determine accessibility and reach of communication transmission related to the teaching-learning process, the location of the respondents was also identified. The majority of the student respondents (67%) are located in Cebu province; 17% in Cebu City, and 12% in other provinces. The 63% or 157 faculty members are residing in Cebu province while 32% or 81 of them reside in Cebu City; other provinces 5%. Qualitative feedback was also gathered to explore further the challenges experienced and clarify information about open-ended online messaging. Data was gathered from March-April 2020 in a state-funded university in the Philippines with the campus located in the center of the city. To comply with the ethical guidelines, strict adherence to data privacy protocols and data use restrictions were followed. The data were analyzed and were considered in identifying emerging themes scenarios in teaching and learning.
The data gathered were reviewed and analyzed by looking into the challenges that need to be addressed and the ideal perspectives that should have been implemented to generate different scenarios. Scenario building provides the contextual basis for the development of the new normal in the university. Scenario building as explained by Wilkinson (1995) is a good strategy to use on how current observations play their role in future situations. Each scenario is constructed about the future modeling a distinct, plausible world. Scenarios are plausible alternative futures of what might happen under particular assumptions by focusing on key drivers, complex interactions, and irreducible uncertainties ( Polcyznski, 2009 ). The prospective scenarios created are the best and probable scenarios. Current or existing situations/conditions of the university served as the probable scenario, while the ideal case situation served as the best scenario. From the scenario built, key problems and challenges are developed as a basis for the model developed ( Imperial, 2020 ). The model will provide the strategic long-term and short-term strategies for the university’s academic operations Figure 1 .
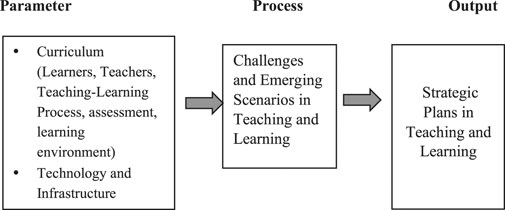
FIGURE 1 . Schematic diagram of the conceptual analysis.
Results and Discussion
Challenges on teaching and learning amid the pandemic.
In the quantitative data gathered through an online survey, the students reported their concerns related to their learning experiences during the suspension of physical classes. Most of the student respondents reported that adjustments were made by the teachers in terms of course outcomes and syllabi. However, most of them claimed that the learning activities were not flexible enough to be done either offline or online as they could not as shown in Table 1 comply with the requirements within the expected schedule.

TABLE 1 . The profile of flexibility of the learning activities for offline or online learning among students (n = 1,689).
Moreover, as shown in Table 2 , students reported that the majority of them were unable to accomplish the tasks assigned by the teachers due to their inability to access the internet or use suitable gadgets to finish the tasks.
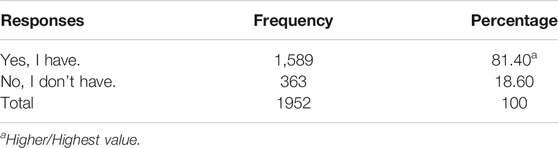
TABLE 2 . Number of students who reported if they have problems. Completing requirements due to ICT limitation (n = 1952).
Part of the survey for students focused on how students reacted to home-based tasks assigned to them to complete the learning competencies of the course. Teachers provided alternative tasks online through electronic mails and an online portal Table 3 .
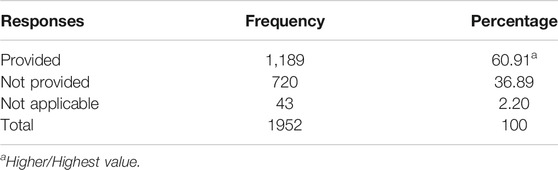
TABLE 3 . Provision of alternative/additional requirement (n=1952).
Students confirmed that some online classes and additional requirements were still provided to them by the faculty ( Table 4 ) The majority of the students responded that the alternative tasks were adequate. The nature and content of the alternative tasks provided were suited to the remaining concepts to be addressed in their coursework ( Table 4 ). Despite that, several students still reported that these alternative tasks are not sufficient to enable them to acquire the remaining competencies required of them at the end of the semester.

TABLE 4 . Adequacy of alternative tasks for learning attainment (n=74).
Students in one college were surveyed on the receipt of feedback from their respective teachers. A comparable response from students claimed they received and didn’t receive immediate feedback as to whether what they submitted to the professors is okay or what aspect they still need to improve more. As teaching continuity was made possible through online modality and other home-based tasks, they still had difficulty complying with the requirements of the course. The survey included the type of home environment the students have to assess factors that influence their difficulty. Students were asked whether their home learning environment is conducive to learning or not.
Data in Table 5 show that learners believed that their home environment is not conducive for learning when schools were closed and physical contact was discontinued as there were many disruptions including internet connectivity. On the part of the faculty, there were challenges met as evidenced by the feedbacks of the students. The teaching-learning process requires an active engagement of the faculty. They are the drivers of the learning process and the success of the learning outcomes would partially depend on their extent of active participation as facilitators, mentors, or coaches to the learners.

TABLE 5 . Students learning environment.
In the teaching-learning process, students need feedback on the progress of their outputs and whether they did well in their tasks. As shown in Table 6 , the majority of the students reported receiving no feedback from their teachers on the online module while a majority hope to get immediate feedback. Further exploration is required to determine why teachers are unable to provide immediate feedback for students.

TABLE 6 . Feedback from teachers (n = 154).
Faculty and Students’ Access to Technology
One of the modalities in teaching and learning that gained popularity amid COVID-19 was online learning. When classes were suspended, universities migrated from the face to face interaction to the online modality. Hence, this survey was conducted to determine the capability of the students and teachers in terms of available information technology gadgets and connections.
The profile of both the faculty and students’ access to internet-based information showed that the majority can access this information ( Table 7 ). Moreover, the majority of the students (82.61%) and faculty (94.4%) have internet access Table 8 . However, most of them reported unstable internet connections which makes their home environment less conducive to sustain learning facilitated by the online readings and activities given Table 9 . The majority of the students used mobile phones for online learning which is not capable of addressing online tasks and submission of requirements. On top of this, concerns for limited internet access of students and faculty emanate from external service providers most especially when using cellular data in areas where satellite signals are limited.
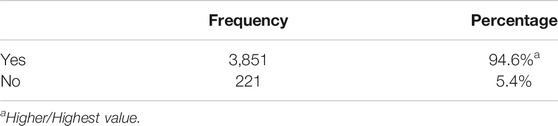
TABLE 7 . Faculty and students’ access to information technology (n = 4,072).

TABLE 8 . Faculty, staff and students’ access to internet/Wi-fi.

TABLE 9 . Stability of internet connection (n = 1952).
Emerging Themes in Teaching and Learning
A qualitative survey was also conducted to substantiate the quantitative data gathered. The narrative comments of the respondents in the survey were analyzed and were grouped into emerging themes and scenarios of teaching and learning.
The Trajectory Towards Flexibility in Teaching Design, Delivery, and Assessment
The sudden cancellation of classes in the middle of the semester placed both faculty and students unprepared. Questions on how to continue their classes, the learning modality, the appropriate assessment, and access to learning materials were foremost in the mind of both teachers and students. The narratives of the respondents became the basis for identifying the emerging scenarios in teaching and learning amid and beyond the pandemic.
For many years, students have been exposed to traditional, face-to-face classroom-based teaching. Outcomes-based education has been integrated into the curriculum and its implementation, but the learning delivery is still under the actual supervision of teachers. Due to ECQ students have to shift to independent learning through the home-based tasks assigned to them by their teachers. Ordinarily, many students have trouble making the transition to the more independent learning required at university compared with their secondary years .
“It’s very difficult for me to learn on my own in the confines of my home, but I don’t have a choice ,” narrated one student.
This shows that this pandemic has created a new platform in teaching and learning delivery that students are compelled to accept. In this situation, students have to take responsibility for their learning, be more self-directed, make decisions about what they will focus on how much time they will spend on learning outside the classroom ( The Higher Education Academy, 2014 ; Camacho and Legare, 2016 ). In the new setting, students are expected to read, understand and comply with the tasks without the guidance of the teachers. They are forced to assume self-directed independent learning.
The teachers on the other hand affirmed that the use of face-to-face delivery would not work anymore in the new learning environment.
“ One thing that I have learned is to adjust my materials to ensure that learners can still acquire the competencies without the face-to-face interaction with my students ” narrated one teacher.
With the concerns on access to online services, faculty members considered the use of a non-online approach and explored the necessary modifications that can be applied in the future. Hence, in the narrative, several faculty members said they have prepared modules as an option for pure online learning delivery.
Assessment of student learning outcomes is very important. A concern on how to assess learning outcomes and how to answer assessment tasks emerged as a major concern as reflected in the narratives of the teacher and student respondents. The assessment measures are essential as an assurance that learners have attained various knowledge and skills and that they are ready for employment or further study ( Coates, 2015 ). There is a need to address the teachers’ concern on how to conduct off-classroom performance evaluation and the bulk of submissions that they have to evaluate which are submitted online or offline. The design and planning are important factors to consider not only in the assessment per se but also in the parameters on how students will be graded ( Osborn, 2015 ). For the teachers, the following concerns emerged,
“Difficulty assessing performance-based tasks (RLE) , ” “Difficulty tracking, checking of students’ outputs” and “Concerns on failing due to non-submission of requirements online and low midterm Performance”
In the assessment of learning, the teacher respondents agreed that they have to think of innovative ways of assessing students in the context of their situation and home environment so the outcomes expected of the course will be manifested by the students.
One of the challenges of online or distance learning is the difficulty in participating in groupwork activities. The challenge is how the schedule or availability of group members be accommodated within the group ( Gillett-Swan, 2017 ; Kebritchi, Lipschuetz, and Santiague, 2017 ). More particularly when online assessments are done with certain deadlines or time limits.
“Difficulty complying group activities”
“Time-based online exams”
The challenges seen in this phase are to determine the flexible learning system most applicable for CNU learners, the readiness of the students and faculty to handle the tasks to assign and to be complied by the students, the appropriateness of the learning delivery vis-à-vis learning outcome, and the preparation of the learning materials fit for self-directed independent learning.
In times of disaster, the educational system takes on a different route for effective learning continuity. The learning curriculum requires it to be more responsive to the current needs of the learners and the teachers.
“ Concerns in completing OJT”
“Dissertation/Thesis defense scheduled”
“Concerns on when the academic year ends”
The flexibility that the curriculum has to adopt requires the offering of choices on the current reality of the educational environment and customizing a given course to meet the needs of the learners. It is therefore crucial in considering the provision of the possibility of making learning choices to learners. These learning choices can cover class times, course content, instructional ( Huang et al., n.d. ).
It is a challenge for the university to consider the restructuring of the curriculum to address the gaps in the learning outcomes left when classes were suspended and the re-scheduling of the mid-semester On-the-Job Training of some programs. Amidst this crisis, flexibility in the next academic calendar has to be considered while it is uncertain when the COVID-19 crisis will be contained.
The Role of Technology
In the overall narratives concerning teaching-learning delivery and assessment, the role of information technology particularly on internet connection has been repetitively mentioned by both teachers and students. In the crisis scenario, faculty and students could eventually bounce forward to the usual teaching-learning activities outside the classrooms had this concern been made available to all. Per survey results, most of the students and some faculty members are residing outside the city and are experiencing unstable if no internet connection at all.
“ No internet connectivity/unstable connectivity”
“Occasional power interruptions”
In designing for online or distance learning, there is a need to understand the role of technology to attain the success of the engagement ( Kerka, 2020 ). Internet is not the only factor to consider but also the equipment that is needed for the teachers and the learners to engage effectively. If these are not available, there is a need to evaluate the approach used in the teacher-learner interaction.
“Limited gadgets (one laptop shared with other siblings/no laptop or PC only phone)”
“No printer for completion of a requirement to be submitted”
With the current health crisis with the shifting of learning delivery, the challenge would be on how to provide an inclusive IT infrastructure to provide quality education for all learners ( Internet access and education: Key considerations for policy makers, 2017 ).
The Learner’s and the Teacher’s Learning Environment
In an attempt to address the disruption of classes and promote continuity of learning, teachers immediately resort to online learning as the most workable way of delivery of the lessons. In this new learning setup, students are forced to stay at home and transfer their classrooms to the same location. In most cases, it is often overlooked that learners come from different home settings and have different home arrangements.
“Not appropriate learning environment (congested home setting)”
“Lack of support from parents (assigning home tasks when a student is supposed to be work on learning tasks)”
“Overlapping of home activities and academic activities”
In most cases, families frequently engaged their children in learning activities, however, different patterns were observed across different social groups. Families in low socio-economic position households, and those living in disadvantaged neighborhoods provided fewer learning experiences. This may in part be due to the challenges that families living in socially and economically disadvantaged circumstances face in accessing the financial and social resources needed to provide a rich early home learning environment for learning. The findings reveal that education is still pursued in economically challenging settings but with more challenges. A home learning environment has a positive “direct association” with a child’s academic performance ( Australian Institute of Family Studies, 2015 ). The findings require a three-helix platform in education that is the partnership between academe, industry, and the stakeholders.
Maslow Before Bloom Orientation: Safety and Security
Prevailing sentiments among employees and students are their concern for their safety and security. The basic needs of humans according to Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs are foremost in the minds of the university’s clients and workers. As reported by the students and employees, their foremost concern is safety and the psychological manifestations of the anxiety of being infected.
“Foremost concern is safety and security even after ECQ is lifted”
“Fear of being infected with COVID”
“With PUI/PUM family members or the students themselves”
“Psychological and emotional reactions (anxiety, panic, fear, loneliness, a feeling of helplessness, mood swings, anger)”
The second category of concerns is on security and the possibility of sustaining their education due to loss of jobs, loss of family members, and the uncertainty of traveling to the university.
“Family financial crisis–no budget to buy loads, sustain needs”
“Unable to go home”
“Transportation concerns”
The concerns raised by the participants of the study require the university to provide access to considerable support to deal with the struggles, challenges, and even trauma because of the pandemic. There is a need to help manage mental health, self-esteem, and relationships after the quarantine which left some of the students isolated for quite a time ( Sweeney, 2020 ). Mental health programs have to be in place in formal learning settings. Because of the unprecedented challenges that students and teachers experienced in the pandemic, the ability to successfully hurdle through formal learning may be limited if the overall well-being is compromised.
Strategic Scenario Analysis
This section presents the analysis of the possible scenarios that might take place in the university based on the following components: the planned curriculum, instruction (teaching-learning process), assessment, student engagement, and technology and infrastructure. The probable scenario is the current enhanced community quarantine (ECQ) status of the City or province where the university is located. During ECQ, no face-to-face interaction is allowed and province-wide lockdowns are implemented. The best scenario allows the limited face-to-face class and the worse scenario happens when the locale is under ECQ and placed on a lockdown due to the increasing COVID-19 cases.
In the area of curriculum and instruction, the action points revolved around the identification of courses that can be flexibly offered, rescheduling offerings when health measures permit it and providing interventions for competencies that were not met. The additional action points would refer to the creation of materials that would meet the needs of the students in the different scenarios and the provision of access to all resources that aid learning. Lastly, plans for assessment delivery are laid out to ensure the validity of means and with consideration to quarantine measures. Laying down the scenarios provide options for the educational institution to be able to meet the demands of the changes enforced by the pandemic to the delivery of learning to students. Reviewing these options reveal that the differences in the plan of action for this area of concern are a matter of granting access to students for resources needed for learning continuity.
The next area of concern is student engagement which reveals the different levels of engagement of parents and guardians, the means of communication with students, and an investment in the capability-building of faculty members to facilitate the teaching-learning process amid the pandemic. The focus on the trainings for the faculty members in the area implies that flexible learning in this health crisis requires a particular skill set to heighten student engagement without diminishing the role of support systems in the students’ homes and the need for appropriate technology to facilitate the needed interactions. This leads to the last area of concern on technology and infrastructure. The University has to take into account and facilitate the provision of needed equipment, materials, systems, software, and physical structures to support flexible learning. The complete scenario matrix is reflected in Table 10 .
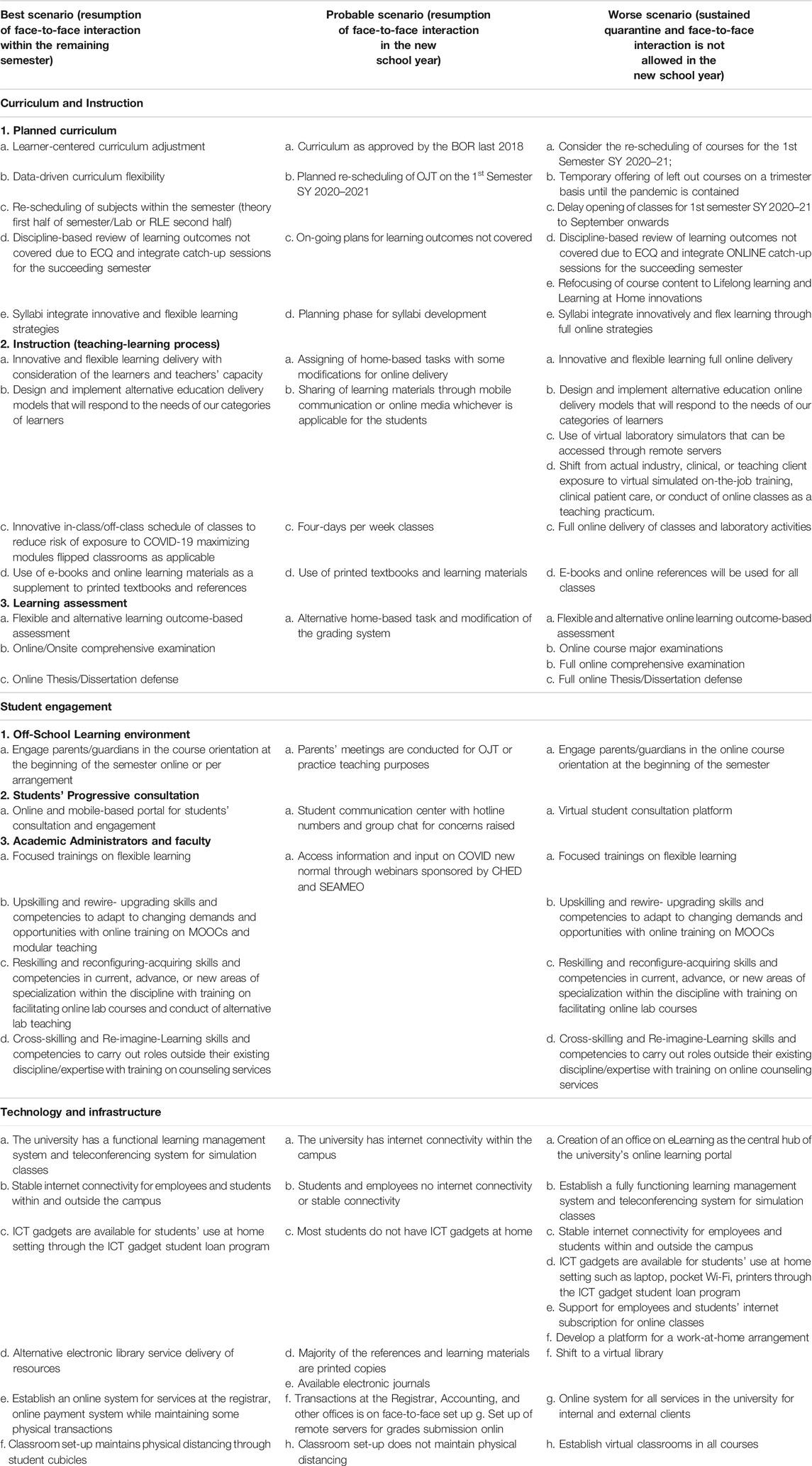
TABLE 10 . Scenario matrix.
Migrating to Flexible Teaching and Learning: The University’s Strategic Response for Academic Continuity
After exploring the perspectives of the respondents and the analysis of the emerging scenarios in teaching and learning, the University implemented the proactive response to ensure academic continuity in times of crisis. It is evident that for universities to thrive and lead, the flexible teaching-learning modality needs to be adopted taking into consideration the best and worst-case scenarios. Migrating to flexi learning means recalibrating the written curriculum, capacitating the faculty, and upgrading technological infrastructure to respond to the changing scenarios amid and beyond the pandemic. Outlined in the paragraphs that follow were the ways forward pursued by the university as a response for academic continuity.
Recalibrate the Curriculum
To address the competencies which were left at the time of the class suspension, discipline-based course mapping was conducted. A series of cluster meetings by faculty members teaching similar courses teaching load were done for the revision of the unified syllabus, integration of the outcomes-based teaching and learning strategies using flexible learning platforms such as distance and online learning options, and the learning assessment strategies suitable for individual student needs. A syllabi repurposing is conducted and the revisiting of the syllabi focusing on the essential course outcomes. This strategy enables the faculty to revise the activities/course work/tasks/experiences that can be delivered through blended learning. This also enabled them in designing the instructional strategies, activities, and assessments that will achieve the learning objectives. The modification of the syllabi incorporated the development of modules, assessment tasks that can be delivered using differentiated instruction/in class or off class.
A program-based curriculum review was also conducted to identify courses that would need to be re-scheduled in its offering due to its nature and requirement such as swimming courses. Moreover, On-the- Job (OJT) which was supposedly offered during summer or mid-year was transferred to a later semester as industry partners are limiting its personnel at the height of the pandemic.
Reconfiguring the OJT, practice teaching and Related Learning Experience based on simulation set-up with scenario-based activities with assigned equivalency hours was also developed. The Practice teaching using blended learning or online approach, Nursing used alternative Related learning simulation.
The strategic actions included short-term plans of possible limited physical classes and long-term plans of pure online classes. Embedded in the plans are the in-class and off-class mode, re-structuring and retrofitting requirement for limited face-to-face classes, and the upgrading of internet-based facilities for pure online classes. On top of this, they need to cater to learners who have no access to the internet includes the translation of online learning modules to printed modules.
Capacitate the Faculty
Flexible learning capacitation of faculty was also addressed as online learning was new to the university. The university conducted an upskilling and rewiring through series of online trainings on module development for flexible learning distance education and the use of an online learning management system for faculty members. Reskilling and reconfiguring of faculty through webinar series on laboratory teaching using simulation learning for teachers handling laboratory, RLE, OJT. And a cross-skilling and reimagining using series of online webinars on developing counseling skills of faculty members concerning the COVID crisis. The university initiated the Higher Education Connect webinar series by discipline which served as an avenue of sharing and exchanging best practices during the pandemic-induced suspension of physical classes. The series of online for and webinars provided the teachers’ professional development including information sharing platform, Online learning platform, Hands-on training platform, Repository of web tools, and Laboratory for data analytics.
Safe learning infrastructure for Reframing Teaching and Learning was addressed through Telecounseling Services with mobile hotline numbers to cater to the needs of the clients and Student Communication Center with hotline numbers accessible by phone or online to cater to the academic concerns of the students. The university also initiated the Adopt-a-Student program for stranded students during the Enhanced Community Quarantine and assisted in the process of going back to their provinces.
Upgrade the Infrastructure
The university’s priority is to ensure that technology is sustainable and feasible. The ICT focal persons of the university were mobilized to Determine basic computer configuration and minimum Operating System requirements and provide alternative solutions to learners with technological/location-related challenges. For example, provide small learning activity packages for learners with slow internet connections. Ensure changes to the learning activity that can be made with internal resources. Determine the characteristics, possibilities, and limitations of the learning management system (LMS) to be used and ensure consistency of access across platforms (if applicable).
An Organizational Structures as a support system was also created which was the Center for Innovative Flexible Learning to provide assistance and monitoring so that the existing Information Technology Office of the university will not be overwhelmed.
It is also strategic to develop collaboration with stakeholders (Local Government Units (LGU), Alumni, Partner agencies). The forging of partnerships with LGU provides avenues where students during off-class students will go to the learning hub in the LGU complete with internet connectivity for students to work on their tasks in case they don’t have connectivity at home, so students will not go to the internet café and pay. This will also provide opportunities for resource sharing for the benefit of the students.
ICT Infrastructure in teaching and learning and student services was also addressed through Online enrollment, full utilization of Google Classroom as the learning management system, and the fully online delivery of classes. The university also changed its internet subscription to higher bandwidth and subscription to zoom for online meetings and conferences. Internet Connectivity of faculty members has assisted a monthly internet allowance. Gadget on loan for students in coordination with Student Supreme Council. Library online services through Document Delivery Services (DDS) and Modern Information Assistant in the New Normal Innovative Education.
Implementation and On-Going Assessment of the Strategic Response
The implementation of the strategic response entails the collaborative engagement of all stakeholders in the university. The process requires the involvement of the administration, faculty, staff, students, parents, and other stakeholders that enables the institution to move forward, managing and mitigating risks successfully. Hence, the university is implementing the continuous process of consultation, feedbacking, and intensive monitoring as important ingredients for the plans to be successfully implemented. The regular conduct of dialogues and discussions among stakeholders, capacity building of students and faculty, open communication through hotline centers, and continuous quality assurance monitoring mechanisms enable the university to enhance and implement successfully the strategic programs and activities amid the pandemic.
Anchored on the initial success of the evidenced-based strategic plans, the university at present has institutionalized the flexible learning system with the establishment of the Center for Flexible Learning that manages, capacitates, and assists the students and the faculty members in the continuing implementation of the flexible learning modality. Technology support has been provided by increasing the internet bandwidth to ensure uninterrupted connectivity in the campus and providing internet allowance to the faculty. Students with limited or no connectivity are given printed modules as instructional resources. In anticipation of the limited face-to-face classes as safety and health protocols may allow, the curricular offerings, teaching-learning processes, and assessment tools have been enhanced by applying best practices that maximize quality teaching and learning. On-going trainings and webinars for the faculty, students, and stakeholders to thrive in the new educational landscape have been conducted. The university has also established professional learning communities which become avenues for the sharing of resources and practices that continuously support and enhance teaching and learning continuity amid and beyond the pandemic.
Teaching and learning continuity amid the pandemic requires an analysis of the parameters by which the university operates from the perspective of the stakeholders to include the students, faculty, curriculum, and external stakeholders. Grounded on data, higher education institutions have to conduct strategic scenario analysis for best, possible and worse scenarios in the areas of curriculum and instruction, student engagement, and technology and infrastructure. To ensure teaching and learning continuity amid and beyond the pandemic, higher education institutions need to migrate to flexible teaching and learning modality by recalibrating the curriculum, capacitating the faculty, and upgrading the infrastructure. These strategic actions have to be continuously assessed, modified, and enhanced to respond to the volatile, uncertain, and changing scenarios in times of crisis.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics Statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
FD, DP, LG, and MO contributed to the conception and design of the study. DP and LG organized the data and facilitated the initial analysis. FD and DP wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors wrote sections of the manuscript and contributed to the manuscript revision. MO ran the final plagiarism test and grammar check prior to submission.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Alexander, S. (2010). Flexible Learning in Higher Education . Sydney, NSW: International Encyclopedia of Education , 441–447. doi:10.1016/b978-0-08-044894-7.00868-x
CrossRef Full Text
Australian Institute of Family Studies (2015). How Does the home Environment Influence Children’s Learning?
Balaman, S. Y. (2019). Decision-Making for Biomass-Based Production Chains: The Basic Concepts and Methodologies . New York: Academic Press .
Bekessy, S., and Selinske, M. J. (2017). Social-Ecological Analyses for Better Water Resources Decisions. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-810523-8.00010-0
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Camacho, D. J., and Legare, J. M. (2016). Shifting Gears in the Classroom-Movement toward Personalized Learning and Competency-Based Education. Competency-based Educ. 1, 151–156. doi:10.1002/cbe2.1032
Chang-Richards, A., Vargo, J., and Seville, E. (2013). Organisational Resilience to Natural Disasters: New Zealand’s Experience (English Translation). China Pol. Rev. 10, 117–119.
Google Scholar
Chi-Kin Lee, J. (2020). “Managing and Leading university Response to Support Psychosocial Health during COVID-19 Pandemic,” in Webinar Series 2 in SEAMEO's Response to Pandemic COVID-19 ( SEAMWO ).
Coates, H. (2015). “Assessment of Learning Outcomes,” in The European Higher Education Area (Cham: Springer ), 399–413. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-20877-0_26
Creswell, J. W., and Plano, C. V. L. (2006). Designing and Conducting Mixed Methods Research . Thousand Oaks: Calif: SAGE Publication .
Edizon, F. (2020). Rewiring Higher Education in the Time of COVID-19 and beyond .
Gachago, D., Jones, B., and Edwards, S. (2018). “Towards Flexible Learning through Distance Learning: ND Real Estate Learners’ Experiences,” in ICEL 2018 13th International Conference on E-Learning (Capetown: Academic Conferences and publishing limited ), 93.
Gillett-Swan, J. (2017). The Challenges of Online Learning: Supporting and Engaging the Isolated Learner. Jld 10, 20–30. doi:10.5204/jld.v9i3.293
Glatthorn, A. (2000). The Principal as Curriculum Leader . 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press. Goodland .
Gordon, N. (2014). Flexible Pedagogies: Technology-Enhanced Learning . Hull, England: The Higher Education Academy , 1–24.
Henderson, N. (2012). What Is Resiliency and Why Is it So Important? | Resiliency in Action . Available at: https://www.resiliency.com/what-is-resiliency/ .
Hijazi, S. (2020). International Outreach for university post-crisis . Quezon City, Philippines: QS Intelligence Unit .
Huang, R., Liu, D., Tlili, A., Yang, J., and Wang, H. (n.d.). Handbook on Facilitating Flexible Learning during Educational Disruption: The Chinese Experience in Maintaining Undisrupted Learning in COVID-19 Outbreak . Beijing: Smart Learning Institute of Beijing Normal University .
Illanes, P., Law, J., Sarakatsannis, J., Sanghvi, S., and Mendy, A. (2020). Coronavirus and the Campus: How Can US Higher Education Organize to Respond? . Chicago, Illinois: McKinsey and Company .
Imperial, J. (2020). ‘Yorme, Yorme’: Modeling Themes from COVID-19 Concerns and Public Reports Aired through Manila City Government Twitter Accounts . Retrieved from De La Salle University COVID-19 Research Portal: https://www.dlsu.edu.ph/research/covid-19-research-portal/ .
Internet access and education: Key considerations for policy makers (2017). Internet Society. https://www.internetsociety.org/resources/doc/2017/internet-access-and-education/ (Accessed November 20, 2017).
Kebritchi, M., Lipschuetz, A., and Santiague, L. (2017). Issues and Challenges for Teaching Successful Online Courses in Higher Education: A Literature Review. J. Educ. Technol. Syst. 46 (1), 4–29. doi:10.1177/0047239516661713
Kerka, S. (2020). Distance Learning, the Internet, and the World Wide Web . Retrieved from ericdigest: https://www.ericdigests.org/1997-1/distance.html .
Kishita, Y., Hara, K., Uwasu, M., and Umeda, Y. (2016). Research Needs and Challenges Faced in Supporting Scenario Design in Sustainability Science: A Literature Review. Sustainability Sci. 11 (2), 331–347. doi:10.1007/s11625-015-0340-6
Mark, G., and Semaan, B. (2008). Resilience in Collaboration: Technology as a Resource for New Patterns of Action,” in Proceedings of the 2008 ACM conference on computer supported cooperative work , San Diego, CA , November 8–12, 2008 ( CSCW08: Computer Supported Cooperative Work ), pp. 137–146. https://doi.org/10.1145/1460563.1460585
Osborn, L. (2015). Performance Assessment in Online Learning. In 19th Annual Conference on Distance Teaching and Learning , Madison, Wisconsin , August 14–16, 2002 ( University of Wisconsin System ). Available at: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED471207.pdf
Polcyznski, M. (2009). Scenario Planning . Retrieved from https://www.flca.net/images/ScenarioPlanning.pdf .
Ryan, A., and Tilbury, D. (2013). Flexible Pedagogies: New Pedagogical Ideas . London: Higher Education Academy .
Smalley, A. (2020). “Higher Education Responses to Coronavirus (COVID-19),” in National Conference of State Legislatures . Available at: https://www.ncsl.org/research/education/higher-education-responses-to-coronavirus-covid-19.aspx .
Sweeney, N. (2020). When the Covid-19 Crisis Finally Ends, Schools Must Never Return to normal . United Kingdom: The Guardian . Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/education/2020/apr/07/when-the-covid-19-crisis-finally-ends-uk-schools-must-never-return-to-normal .doi:10.1158/1557-3265.covid-19-po-009
The Higher Education Academy. (2014). Independent Learning Heslington .
UNESCO (2020). COVID-19 Educational Disruption and Response Beirut, Lebanon .
UNESCO Learning Portal (2020). Brief 3: Learning and Teaching Materials Paris .
Wilkinson, L. (1995). How to Build Scenarios San Francisco . Available at: http://www.wired.com/1995/11/how-to-build-scenarios/ (Retrieved from February 29, 2016).
Keywords: teaching and learning continuity, flexible learning, pandemic, higher education, scenario–analysis
Citation: Dayagbil FT, Palompon DR, Garcia LL and Olvido MMJ (2021) Teaching and Learning Continuity Amid and Beyond the Pandemic. Front. Educ. 6:678692. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.678692
Received: 10 March 2021; Accepted: 06 July 2021; Published: 23 July 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Dayagbil, Palompon, Garcia and Olvido. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Michelle Mae J. Olvido, [email protected]
Students Deserve a Voice in Our Pandemic Response. Here’s How to Give It to Them

- Share article
As the country began to shut down because of COVID-19 this spring, our staff at Mikva Challenge, which seeks to close the civic-opportunity gap for students from underresourced schools and communities, knew that this was the moment to expand, not retract, our work. Young people were abruptly facing a sudden and drastic reduction in their social connections and crucial services, including school meals, school-based mental-health counseling, after-school jobs, and an important safety net for identifying child abuse.
With that in mind, Mikva Challenge formed its first-ever National Youth Response Movement to elevate and promote youth voices and solutions during this national crisis. This group of 22 high school students from 15 cities across the country met twice a week with dedicated adult facilitators from early April to August. In doing so, they are learning leadership skills—specifically, civic-leadership skills—to organize themselves and their peers to respond to COVID-19 with youth-focused policy suggestions.
Related Video
Youth advocate Cristina Perez of Mikva Challenge and a student-activist talk about the significance of student leadership during a crisis.
To help build students’ sense of civic power and agency, we have found it’s important to follow a few guideposts. Here is what other educators should consider when doing this kind of work, especially right now:
About This Project
With the rise of the pandemic this spring and the national fight for racial justice, many young people are displaying inner reserve, resiliency, self-regulation, leadership, service, and citizenship in ways that no one could have anticipated.
In this special Opinion project, educators and students explore how young people are carving their own paths.
Read the full package.
Build community and relationships to ensure students can grow, participate, and engage.
This is a cornerstone of our work, both in and outside the classroom. An interactive, youth-led, project-based education in democracy—also known as “action civics"—can only be successful when adult facilitators invest significant time in community building and storytelling to make young people feel safe enough to lead, engage with each other, and be vulnerable. To reach students in online learning spaces, those adult facilitators must be dynamic, outgoing, and persistent.
We learned that students need ample time to express their thoughts, either in the group setting or in smaller breakout discussions—both of which must be virtual now. But here’s the difficult part: Beyond the logistics of scheduling students across three time zones in the midst of the pandemic, NYRM adult facilitators needed to take into account the issues students were managing while they sheltered at home, including their mental health. Twice-weekly meetings gave students a much-needed outlet and a connection with their peers. But those who struggle with mental-health challenges had more difficulty re-engaging during their hard times, instead withdrawing from the virtual setting. We found that consistent contact with all participants beyond Zoom calls, including through supportive emails and texts, kept them engaged in the project.
Provide your students with the opportunity to exercise and mature leadership skills they may not even realize they possess."
Provide the space and opportunities for students to lead the way—and then step aside.
With students already receiving more than eight hours a day of virtual instruction in school, we knew that the NYRM virtual workshops needed to distinguish themselves. Mikva facilitators guided the process, but the students decided the focus and the projects. Students steered discussions, did the research, and made the calls on policy recommendations. Following the brutal killing of George Floyd, students went from addressing their peers’ social-emotional needs related to the pandemic to a more holistic vision focused on racially just and equitable schools. They wrote a series of policy recommendations for school and district leaders to dismantle the cradle-to-prison pipeline, build inclusive curriculum, and provide mental-health support in schools.
Invite students to “do” democracy, not just learn about it.
The pandemic has underscored the necessity for students to be in leadership rather than just learn about leadership skills. The pandemic gave students a purpose and a cause for their work. And it created an opportunity to reach lawmakers, researchers, and activists who were also working remotely.
Students recorded persuasive “soapbox” speeches on their phones about the impact of COVID-19 and then called on their peers to do the same. NYRM student leaders developed five policy recommendations for districts to create equitable schools by centering students’ voices, experiences, and needs. And last month, they shared these policy recommendations with members of Congress and education policy and philanthropic leaders during a National Youth Policy & Elections Roundtable.
What does all of this mean for schools?
Provide your students with the opportunity to exercise and mature leadership skills they may not even realize they possess. They have important ideas to share for how we can adapt and respond to this moment.
Coverage of character education and development is supported in part by a grant from The Kern Family Foundation, at www.kffdn.org . Education Week retains sole editorial control over the content of this coverage. A version of this article appeared in the September 09, 2020 edition of Education Week as Empowering Youth Voice
Sign Up for The Savvy Principal
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

Other Papers Say: Face up to tech in education
The following editorial originally appeared in The Seattle Times:
The latest large-scale analysis of remote learning and its effects on student achievement underscores what every parent saw with devastating clarity during the pandemic: Children need human connection to thrive.
In fact, according to a recent New York Times investigation, attending school through a computer screen during the COVID-19 crisis was as deleterious to learning as growing up in poverty.
The takeaway should not be more finger-pointing and blame for officials who kept schools closed. That advances nothing. But a muscular and forward-looking confrontation with questions around technology in education is sorely needed.
One reason is that kids will likely face future emergencies that necessitate remote learning, so it’s imperative to get better at delivering education this way. But even now, with students back in class, the same technology that hijacked their attention at home remains present — cellphones. Before the pandemic, these handheld screens were not a ubiquitous force in every classroom. Now, teachers appear powerless against them.
Seattle Public Schools attempted to take a stand by filing a lawsuit against the social media companies running Facebook, TikTok and the like. That is hardly the most direct approach.
Better to do like the Reardan-Edwall district in Eastern Washington, which this year prohibited younger students from possessing cellphones during the school day. Or the Peninsula and Aberdeen school districts, which also have strict anti-cellphone policies.
“We’re having actual, human conversations again,” said a relieved Eric Sobotta, superintendent of the Reardan-Edwall schools, “and we’ve seen a dramatic reduction in bullying.”
Taking responsibility this way puts these districts in Washington’s vanguard. Technology has enormous power, and its potential in education — for good or ill — must be addressed head-on at the state level, not with limp demurrals about local control.
Rep. Stephanie McClintock, R-Vancouver, attempted to get a law passed during this year’s legislative session that would have restricted cellphone use in Washington schools. Her bill never made it out of committee, but she plans to reintroduce it next year.
A study from the London School of Economics found that the mere presence of a phone in class can hamper student achievement, especially for kids who are already struggling.
Earlier this year, state Superintendent Chris Reykdal issued guidance on using artificial intelligence in classrooms, urging teachers to embrace it as a tool to power human inquiry.
That’s a welcome step forward. But it’s just a beginning. To protect kids’ developing brains and capitalize on technology’s undeniable promise, all of Washington’s education leaders need to get a lot smarter about managing these tools — fast. The future is not coming at us; it’s already here.
Related Stories

- #WalangPasok
- Breaking News
- Photography
- ALS Exam Results
- Aeronautical Engineering Board Exam Result
- Agricultural and Biosystem Engineering Board Exam Result
- Agriculturist Board Exam Result
- Architecture Exam Results
- BAR Exam Results
- CPA Exam Results
- Certified Plant Mechanic Exam Result
- Chemical Engineering Exam Results
- Chemical Technician Exam Result
- Chemist Licensure Exam Result
- Civil Engineering Exam Results
- Civil Service Exam Results
- Criminology Exam Results
- Customs Broker Exam Result
- Dental Hygienist Board Exam Result
- Dental Technologist Board Exam Result
- Dentist Licensure Exam Result
- ECE Exam Results
- ECT Board Exam Result
- Environmental Planner Exam Result
- Featured Exam Results
- Fisheries Professional Exam Result
- Geodetic Engineering Board Exam Result
- Guidance Counselor Board Exam Result
- Interior Design Board Exam Result
- LET Exam Results
- Landscape Architect Board Exam Result
- Librarian Exam Result
- Master Plumber Exam Result
- Mechanical Engineering Exam Results
- MedTech Exam Results
- Metallurgical Engineering Board Exam Result
- Midwives Board Exam Result
- Mining Engineering Board Exam Result
- NAPOLCOM Exam Results
- Naval Architect and Marine Engineer Board Exam Result
- Nursing Exam Results
- Nutritionist Dietitian Board Exam Result
- Occupational Therapist Board Exam Result
- Ocular Pharmacologist Exam Result
- Optometrist Board Exam Result
- Pharmacist Licensure Exam Result
- Physical Therapist Board Exam
- Physician Exam Results
- Principal Exam Results
- Professional Forester Exam Result
- Psychologist Board Exam Result
- Psychometrician Board Exam Result
- REE Board Exam Result
- RME Board Exam Result
- Radiologic Technology Board Exam Result
- Real Estate Appraiser Exam Result
- Real Estate Broker Exam Result
- Real Estate Consultant Exam Result
- Respiratory Therapist Board Exam Result
- Sanitary Engineering Board Exam Result
- Social Worker Exam Result
- UPCAT Exam Results
- Upcoming Exam Result
- Veterinarian Licensure Exam Result
- X-Ray Technologist Exam Result
- Programming
- Smartphones
- Web Hosting
- Social Media
- SWERTRES RESULT
- EZ2 RESULT TODAY
- STL RESULT TODAY
- 6/58 LOTTO RESULT
- 6/55 LOTTO RESULT
- 6/49 LOTTO RESULT
- 6/45 LOTTO RESULT
- 6/42 LOTTO RESULT
- 6-Digit Lotto Result
- 4-Digit Lotto Result
- 3D RESULT TODAY
- 2D Lotto Result
- English to Tagalog
- English-Tagalog Translate
- Maikling Kwento
- EUR to PHP Today
- Pounds to Peso
- Binibining Pilipinas
- Miss Universe
- Family (Pamilya)
- Life (Buhay)
- Love (Pag-ibig)
- School (Eskwela)
- Work (Trabaho)
- Pinoy Jokes
- Tagalog Jokes
- Referral Letters
- Student Letters
- Employee Letters
- Business Letters
- Pag-IBIG Fund
- Home Credit Cash Loan
- Pick Up Lines Tagalog
- Pork Dishes
- Lotto Result Today
- Viral Videos
Education Amidst Pandemic Essay – Effects of COVID-19 To Education
What happens to education amidst the covid-19 pandemic (essay).
WHAT HAPPENS TO EDUCATION? – In this article, we are going to give you an example essay regarding education amidst the pandemic.

As the world continues to fight against the coronavirus pandemic, several institutions were placed in a standstill. Businesses have been stopped, travel restricted, and education halted.
Naturally, governments need to find ways to address the continued learning of students amidst the pandemic. However, because of the rapid spread of the disease, face-to-face learning is highly unlike, not to mention, deadly.
This leaves us to think of alternatives to education. The first thing that would come to mind is utilizing e-learning in the advent of newer more accessible technology.
But, not every student has access to device that could be used for remote learning. This is where the problem lies. If the coronavirus crisis had yet to be solved, regular schooling would once again be delayed.
Although, if the situation had become lighter, schools may consider imposing social distancing protocols in schools. Along with this, countermeasures need to be placed such as temperature scanners and proper hygiene practices.
Most importantly, the pandemic forces educational institutions to become more adaptive. Thus, new methods of teaching, along with new accessible platforms should be imposed.
This could include giving e-books for studying so that even with just a phone, students could continue to learn. Tests should also be a measure of how much one has learned rather than how much has been memorized
Thanks for reading. We aim to provide our readers with the freshest and most in-demand content. Come back next time for the latest news here on Philnews.
Like this article? READ ALSO: A Big Business Starts Small – Quote Explanation And Meaning
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Advertisement
World Central Kitchen Has Fed People in Disaster and War Zones Around the Globe
The group is a relatively new aid provider in Gaza, but it has garnered notice by making bold moves, like building a jetty out of rubble to bring aid in by sea.
- Share full article

By Victoria Kim
- April 2, 2024 Updated 9:35 a.m. ET
Since its founding in 2010 by the chef José Andrés after a devastating earthquake in Haiti, the relief group World Central Kitchen has turned up at some of the globe’s biggest disasters, crises and conflicts, with the goal of doing what chefs do best: feed people.
The nonprofit group teams up with local food providers, governments and restaurateurs to quickly scale up and provide meals to people in need. Last week, in an update on its work in Gaza, the organization said the devastation and need there was “the most dire we’ve ever seen or experienced in our 15-year history.”
On Tuesday, the group said it would pause its operations in Gaza and the region after it said seven of its workers were killed in an airstrike . The organization said the Israeli military was behind the attack.
The suspension will deprive the increasingly famished population of Gaza of a stream of humanitarian food aid, at a time when practically every source of provisions is critical for staving off what experts have been warning for weeks is an imminent famine .
The group says it operates 68 “community kitchens” in Gaza, and has sent in more than 1,700 trucks loaded with food and cooking equipment so far in nearly six months of war.
World Central Kitchen is a relatively new aid provider in Gaza, where people have been heavily reliant on humanitarian assistance for decades because of a long-running Israeli blockade. But the group has garnered notice by making bold moves. In March, it became the first entity to deliver aid by sea to the enclave in nearly two decades by building a makeshift jetty fashioned out of rubble.
The first aid ship that arrived in mid-March delivered 200 tons of rice, flour and lentils, along with canned tuna, chicken and beef, according to the group. A second, larger shipment with twice as much aid was due to arrive in the coming days , after departing from Cyprus on Saturday.
After the first delivery was unloaded from the ship, it was distributed in Gaza by truck, according to the group, which said that it coordinated its efforts with the Israeli military. The workers killed this week were leaving an aid warehouse in central Gaza, the group said.
“Distribution is the Achilles’ heel of any disaster response,” Mr. Andrés wrote in 2020 in an Opinion piece for The New York Times about responding to the coronavirus pandemic.
Initiatives to send aid into Gaza via its Mediterranean coast were born of frustrations among aid agencies that supplies by land were being held up by Israeli inspections at border crossings. World Central Kitchen has said an average of 10 of its trucks were being let into Gaza out of the nearly 20 it was sending daily to a crossing in Rafah, in southern Gaza, and that on some days, none were getting through.
The nonprofit group has grown rapidly in recent years, with more than $500 million in contributions and grants in 2022 , a fourfold increase from the previous year, the most recent years for which figures are available. As of 2022, the organization said it had 94 employees.
It supplied food in Puerto Rico in the days after Hurricane Maria swept through, dispatched volunteers to quake-stricken Morocco and distributed meals in Ukraine in the midst of the Russian invasion.
In Ukraine, a restaurant operated by World Central Kitchen in Kharkiv, near the country’s border with Russia, was hit by a missile less than two months into the war, wounding four staff members, according to the group’s chief executive at the time.
Victoria Kim is a reporter based in Seoul and focuses on breaking news coverage across the world. More about Victoria Kim
Our Coverage of the Israel-Hamas War
News and Analysis
Thousands of Israelis have taken to the streets to call for early elections to oust Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu . Many of them believe he has put his political survival ahead of the broader interests of the Israeli people.
Israeli soldiers withdrew from Al-Shifa Hospital in Gaza City after a two-week raid in which they killed around 200 Palestinians and arrested hundreds of others, the Israeli military said.
Netanyahu’s cabinet is divided about whether ultra-Orthodox Jews should retain their longstanding exemption from military service .
Internal Roil at TikTok: TikTok has been dogged for months by accusations that its app has shown a disproportionate amount of pro-Palestinian and antisemitic content to users. Some of the same tensions have also played out inside the company.
Palestinian Detainees: Israel has imprisoned more than 9,000 Palestinians suspected of militant activity . Rights groups say that some have been abused or held without charges.
A Hostage’s Account: Amit Soussana, an Israeli lawyer, is the first former hostage to speak publicly about being sexually assaulted during captivity in Gaza.
A Power Vacuum: Since the start of the war, Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu of Israel has done little to address the power vacuum that would appear after Israeli forces leave Gaza. The risks of inaction are already apparent in Gaza City .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
March 12, 2021. 11 min read. One year ago, the World Health Organization declared the spread of COVID-19 a worldwide pandemic. Reacting to the virus, schools at every level were sent scrambling ...
Learnings for beyond the pandemic. The RTSL experience adapting and scaling TaRL in Botswana in the midst of a global pandemic offers key insights that are applicable well beyond this immediate ...
I analyzed those reflective essays of Harvard graduates leading educational organizations around the world, which became the foundation for the first book, Leading Education Through COVID-19: Upholding the Right to Education. Next, I turned to social entrepreneurs. One of the things that I discovered, as a result of my association with the ...
President of the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia Chair of the International Commission on the Futures of Education. Nine ideas for public action 5. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. Decisions made today in the context of COVID-19 will have long-term consequences for the futures of education.
1. Support caregivers at home to help children learn while schools are closed. With nearly 1.6 billion children out of school at the peak of the pandemic, many parents or caregivers, especially with young children, have taken on new roles to help with at-home learning. To support them and remote education efforts, many LMICs have used SMS ...
The school closings due to coronavirus concerns have turned a spotlight on those problems and how they contribute to educational and income inequality in the nation. The Gazette talked to Reville, the Francis Keppel Professor of Practice of Educational Policy and Administration at Harvard Graduate School of Education, about the effects of the ...
April 9, 2020. 9 min read. As cases of coronavirus (COVID-19) in the United States rise, more and more states have adopted shelter-in-place orders to curtail the pandemic. The disruption to most ...
Abstract. In this position paper, I examine how the history, philosophy and sociology of science (HPS) can contribute to science education in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic. I discuss shortcomings in the ways that history is often used in school science, and examine how knowledge of previous pandemics might help in teaching about COVID-19.
Among the countries worst hit by the pandemic is Italy where one of our Associate Editors, Olivia Levrini, is based. During a recent exchange, she raised the question of how history, philosophy and sociology of science (HPS) might contribute to science education in the era of a pandemic. Given the novelty of the issues generated by a major ...
It presents the current state-of-play in over 40 education systems, and efforts to improve pedagogical practices in the midst of the pandemic. It proposes three key lessons and related policy pointers for the current academic term and beyond. Drawing on concrete examples of COVID-19 policy responses from primary to tertiary, as well as ...
Themes connecting this collection include: leadership contexts, organizational perspectives and potential future opportunities. Both empirical studies and thought-provoking essays offer informative insights into how the education community is striving to address the needs of a diverse student population and deliver crucial services to local neighborhoods and stakeholders situated far afield ...
The COVID-19 has resulted in schools shut all across the world. Globally, over 1.2 billion children are out of the classroom. As a result, education has changed dramatically, with the distinctive rise of e-learning, whereby teaching is undertaken remotely and on digital platforms. Research suggests that online learning has been shown to ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound and sudden impact on many areas of life; work, leisure time and family alike. These changes have also affected educational processes in formal and informal learning environments. Public institutions such as childcare settings, schools, universities and further education providers ceased onsite teaching and moved to distance learning - or closed down ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has propelled the research and higher education sectors to the forefront of public attention. Laboratory capacity has been crucial for diagnostic testing; experts in infectious diseases, epidemiology, public health, mathematical modelling, and economics are central to national policy making and media coverage; clinical research has been vital to improving COVID-19 ...
When it comes to assessments, supporting student learning means focusing on feedback instead of a score or grade. It means helping students to see assessments as learning tools that have an ...
COVID-19 has resulted in disruptions to schooling for the vast majority of Australian school children. Universities and other post-secondary education providers have also seen widespread shifts to remote learning, and considerable impacts on school funding. While there have undoubtedly been negative impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on education institutions, students and their families, the ...
The pandemic really worsen everything in all levels. We're currently in a stressful year because of our researches and exams and the online class makes it harder for us to perform better as it limits our resources and activities that we should've done in school. Studying is hard but learning thru online because of pandemic makes it worse. (S13)
The future of arts education is at stake.This paper attempts to examine the future of arts education via the responses of a qualitative survey, student samples, individual interviews, and research regarding arts education as essential education for all learners during a pandemic and beyond. The sudden decree that all attendance at public and private schools would be canceled from mid-March to ...
The pandemic has shown us that school is not just a learning space, but has many functions, especially social ones. It has also shown us that technology can amplify good teaching, but it does not ...
The study explored the challenges and issues in teaching and learning continuity of public higher education in the Philippines as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. The study employed the exploratory mixed-method triangulation design and analyzed the data gathered from 3, 989 respondents composed of students and faculty members. It was found out that during school lockdowns, the teachers made ...
The pandemic has underscored the necessity for students to be in leadership rather than just learn about leadership skills. The pandemic gave students a purpose and a cause for their work. And it ...
The latest large-scale analysis of remote learning and its effects on student achievement underscores what every parent saw with devastating clarity during the pandemic: Children need human connection
Businesses have been stopped, travel restricted, and education halted. Naturally, governments need to find ways to address the continued learning of students amidst the pandemic. However, because of the rapid spread of the disease, face-to-face learning is highly unlike, not to mention, deadly. This leaves us to think of alternatives to education.
Prior research suggests that the most vulnerable populations (students living in poverty, those experiencing homelessness, those whose parents have completed fewer years of schooling, and those ...
World Central Kitchen Has Fed People in Disaster and War Zones Around the Globe. The group is a relatively new aid provider in Gaza, but it has garnered notice by making bold moves, like building ...
At China's stage of development, economies typically pivot towards services. But the government's heart lies elsewhere. The pandemic boosted demand for China's manufactured goods, from ...