Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024

Regions & Countries
Key facts about the abortion debate in america.
The U.S. Supreme Court’s June 2022 ruling to overturn Roe v. Wade – the decision that had guaranteed a constitutional right to an abortion for nearly 50 years – has shifted the legal battle over abortion to the states, with some prohibiting the procedure and others moving to safeguard it.
As the nation’s post-Roe chapter begins, here are key facts about Americans’ views on abortion, based on two Pew Research Center polls: one conducted from June 25-July 4 , just after this year’s high court ruling, and one conducted in March , before an earlier leaked draft of the opinion became public.
This analysis primarily draws from two Pew Research Center surveys, one surveying 10,441 U.S. adults conducted March 7-13, 2022, and another surveying 6,174 U.S. adults conducted June 27-July 4, 2022. Here are the questions used for the March survey , along with responses, and the questions used for the survey from June and July , along with responses.
Everyone who took part in these surveys is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
A majority of the U.S. public disapproves of the Supreme Court’s decision to overturn Roe. About six-in-ten adults (57%) disapprove of the court’s decision that the U.S. Constitution does not guarantee a right to abortion and that abortion laws can be set by states, including 43% who strongly disapprove, according to the summer survey. About four-in-ten (41%) approve, including 25% who strongly approve.
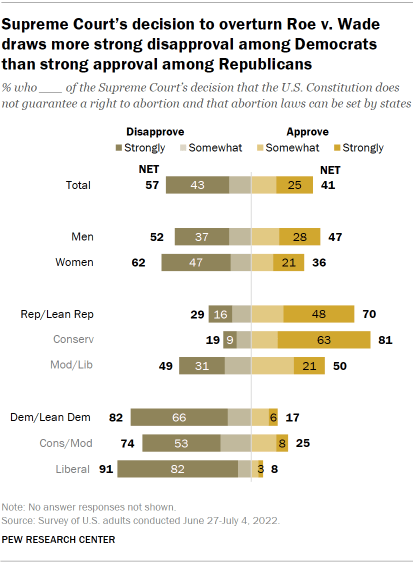
About eight-in-ten Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents (82%) disapprove of the court’s decision, including nearly two-thirds (66%) who strongly disapprove. Most Republicans and GOP leaners (70%) approve , including 48% who strongly approve.
Most women (62%) disapprove of the decision to end the federal right to an abortion. More than twice as many women strongly disapprove of the court’s decision (47%) as strongly approve of it (21%). Opinion among men is more divided: 52% disapprove (37% strongly), while 47% approve (28% strongly).
About six-in-ten Americans (62%) say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, according to the summer survey – little changed since the March survey conducted just before the ruling. That includes 29% of Americans who say it should be legal in all cases and 33% who say it should be legal in most cases. About a third of U.S. adults (36%) say abortion should be illegal in all (8%) or most (28%) cases.
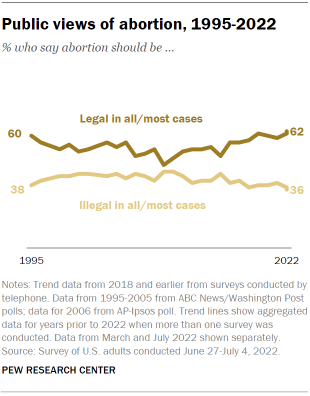
Generally, Americans’ views of whether abortion should be legal remained relatively unchanged in the past few years , though support fluctuated somewhat in previous decades.
Relatively few Americans take an absolutist view on the legality of abortion – either supporting or opposing it at all times, regardless of circumstances. The March survey found that support or opposition to abortion varies substantially depending on such circumstances as when an abortion takes place during a pregnancy, whether the pregnancy is life-threatening or whether a baby would have severe health problems.
While Republicans’ and Democrats’ views on the legality of abortion have long differed, the 46 percentage point partisan gap today is considerably larger than it was in the recent past, according to the survey conducted after the court’s ruling. The wider gap has been largely driven by Democrats: Today, 84% of Democrats say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, up from 72% in 2016 and 63% in 2007. Republicans’ views have shown far less change over time: Currently, 38% of Republicans say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, nearly identical to the 39% who said this in 2007.
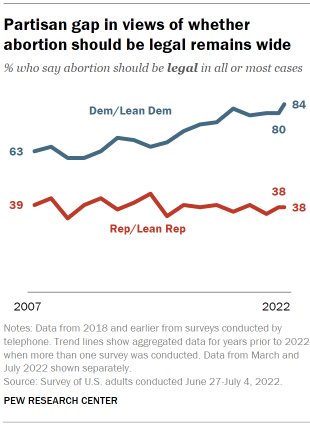
However, the partisan divisions over whether abortion should generally be legal tell only part of the story. According to the March survey, sizable shares of Democrats favor restrictions on abortion under certain circumstances, while majorities of Republicans favor abortion being legal in some situations , such as in cases of rape or when the pregnancy is life-threatening.
There are wide religious divides in views of whether abortion should be legal , the summer survey found. An overwhelming share of religiously unaffiliated adults (83%) say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, as do six-in-ten Catholics. Protestants are divided in their views: 48% say it should be legal in all or most cases, while 50% say it should be illegal in all or most cases. Majorities of Black Protestants (71%) and White non-evangelical Protestants (61%) take the position that abortion should be legal in all or most cases, while about three-quarters of White evangelicals (73%) say it should be illegal in all (20%) or most cases (53%).
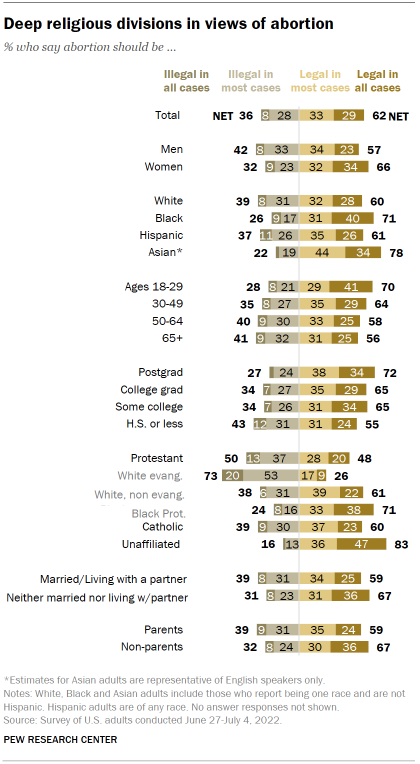
In the March survey, 72% of White evangelicals said that the statement “human life begins at conception, so a fetus is a person with rights” reflected their views extremely or very well . That’s much greater than the share of White non-evangelical Protestants (32%), Black Protestants (38%) and Catholics (44%) who said the same. Overall, 38% of Americans said that statement matched their views extremely or very well.
Catholics, meanwhile, are divided along religious and political lines in their attitudes about abortion, according to the same survey. Catholics who attend Mass regularly are among the country’s strongest opponents of abortion being legal, and they are also more likely than those who attend less frequently to believe that life begins at conception and that a fetus has rights. Catholic Republicans, meanwhile, are far more conservative on a range of abortion questions than are Catholic Democrats.
Women (66%) are more likely than men (57%) to say abortion should be legal in most or all cases, according to the survey conducted after the court’s ruling.
More than half of U.S. adults – including 60% of women and 51% of men – said in March that women should have a greater say than men in setting abortion policy . Just 3% of U.S. adults said men should have more influence over abortion policy than women, with the remainder (39%) saying women and men should have equal say.
The March survey also found that by some measures, women report being closer to the abortion issue than men . For example, women were more likely than men to say they had given “a lot” of thought to issues around abortion prior to taking the survey (40% vs. 30%). They were also considerably more likely than men to say they personally knew someone (such as a close friend, family member or themselves) who had had an abortion (66% vs. 51%) – a gender gap that was evident across age groups, political parties and religious groups.
Relatively few Americans view the morality of abortion in stark terms , the March survey found. Overall, just 7% of all U.S. adults say having an abortion is morally acceptable in all cases, and 13% say it is morally wrong in all cases. A third say that having an abortion is morally wrong in most cases, while about a quarter (24%) say it is morally acceptable in most cases. An additional 21% do not consider having an abortion a moral issue.
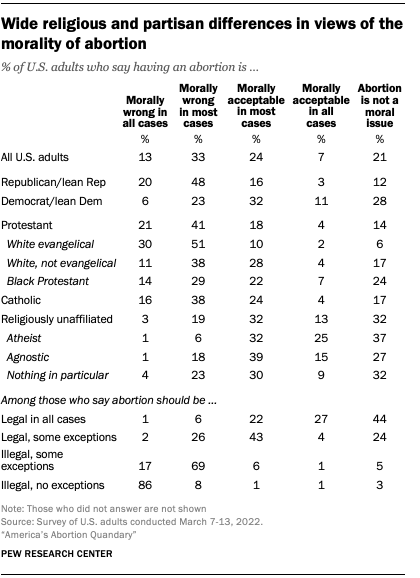
Among Republicans, most (68%) say that having an abortion is morally wrong either in most (48%) or all cases (20%). Only about three-in-ten Democrats (29%) hold a similar view. Instead, about four-in-ten Democrats say having an abortion is morally acceptable in most (32%) or all (11%) cases, while an additional 28% say it is not a moral issue.
White evangelical Protestants overwhelmingly say having an abortion is morally wrong in most (51%) or all cases (30%). A slim majority of Catholics (53%) also view having an abortion as morally wrong, but many also say it is morally acceptable in most (24%) or all cases (4%), or that it is not a moral issue (17%). Among religiously unaffiliated Americans, about three-quarters see having an abortion as morally acceptable (45%) or not a moral issue (32%).

Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
Public Opinion on Abortion
Majority in u.s. say abortion should be legal in some cases, illegal in others, three-in-ten or more democrats and republicans don’t agree with their party on abortion, partisanship a bigger factor than geography in views of abortion access locally, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

Please wait while we process your request
Abortion Argumentative Essay: Definitive Guide
Academic writing
Abortion remains a debatable issue even today, especially in countries like the USA, where a controversial ban was upheld in 13 states at the point this article was written. That’s why an essay on abortion has become one of the most popular tasks in schools, colleges, and universities. When writing this kind of essay, students learn to express their opinion, find and draw arguments and examples, and conduct research.
It’s very easy to speculate on topics like this. However, this makes it harder to find credible and peer-reviewed information on the topic that isn’t merely someone’s opinion. If you were assigned this kind of academic task, do not lose heart. In this article, we will provide you with all the tips and tricks for writing about abortion.
Where to begin?
Conversations about abortion are always emotional. Complex stories, difficult decisions, bitter moments, and terrible diagnoses make this topic hard to cover. Some young people may be shocked by this assignment, while others would be happy to express their opinion on the matter.
One way or another, this topic doesn't leave anyone indifferent. However, it shouldn’t have an effect on the way you approach the research and writing process. What should you remember when working on an argumentative essay about abortion?
- Don’t let your emotions take over. As this is an academic paper, you have to stay impartial and operate with facts. The topic is indeed sore and burning, causing thousands of scandals on the Internet, but you are writing it for school, not a Quora thread.
- Try to balance your opinions. There are always two sides to one story, even if the story is so fragile. You need to present an issue from different angles. This is what your tutors seek to teach you.
- Be tolerant and mind your language. It is very important not to hurt anybody with the choice of words in your essay. So make sure you avoid any possible rough words. It is important to respect people with polar opinions, especially when it comes to academic writing.
- Use facts, not claims. Your essay cannot be based solely on your personal ideas – your conclusions should be derived from facts. Roe v. Wade case, WHO or Mayo Clinic information, and CDC are some of the sources you can rely on.

Speaking of Outline
An argumentative essay on abortion outline is a must-have even for experienced writers. In general, each essay, irrespective of its kind or topic, has a strict outline. It may be brief or extended, but the major parts are always the same:
- Introduction. This is a relatively short paragraph that starts with a hook and presents the background information on the topic. It should end with a thesis statement telling your reader what your main goal or idea is.
- Body. This section usually consists of 2-4 paragraphs. Each one has its own structure: main argument + facts to support it + small conclusion and transition into the next paragraph.
- Conclusion. In this part, your task is to summarize all your thoughts and come to a general conclusive idea. You may have to restate some info from the body and your thesis statement and add a couple of conclusive statements without introducing new facts.
Why is it important to create an outline?
- You will structure your ideas. We bet you’ve got lots on your mind. Writing them down and seeing how one can flow logically into the other will help you create a consistent paper. Naturally, you will have to abandon some of the ideas if they don’t fit the overall narrative you’re building.
- You can get some inspiration. While creating your outline, which usually consists of some brief ideas, you can come up with many more to research. Some will add to your current ones or replace them with better options.
- You will find the most suitable sources. Argumentative essay writing requires you to use solid facts and trustworthy arguments built on them. When the topic is as controversial as abortion, these arguments should be taken from up-to-date, reliable sources. With an outline, you will see if you have enough to back up your ideas.
- You will write your text as professionals do. Most expert writers start with outlines to write the text faster and make it generally better. As you will have your ideas structured, the general flow of thoughts will be clear. And, of course, it will influence your overall grade positively.

Abortion Essay Introduction
The introduction is perhaps the most important part of the whole essay. In this relatively small part, you will have to present the issue under consideration and state your opinion on it. Here is a typical introduction outline:
- The first sentence is a hook grabbing readers' attention.
- A few sentences that go after elaborate on the hook. They give your readers some background and explain your research.
- The last sentence is a thesis statement showing the key idea you are building your text around.
Before writing an abortion essay intro, first thing first, you will need to define your position. If you are in favor of this procedure, what exactly made you think so? If you are an opponent of abortion, determine how to argue your position. In both cases, you may research the point of view in medicine, history, ethics, and other fields.
When writing an introduction, remember:
- Never repeat your title. First of all, it looks too obvious; secondly, it may be boring for your reader right from the start. Your first sentence should be a well-crafted hook. The topic of abortion worries many people, so it’s your chance to catch your audience’s attention with some facts or shocking figures.
- Do not make it too long. Your task here is to engage your audience and let them know what they are about to learn. The rest of the information will be disclosed in the main part. Nobody likes long introductions, so keep it short but informative.
- Pay due attention to the thesis statement. This is the central sentence of your introduction. A thesis statement in your abortion intro paragraph should show that you have a well-supported position and are ready to argue it. Therefore, it has to be strong and convey your idea as clearly as possible. We advise you to make several options for the thesis statement and choose the strongest one.
Hooks for an Abortion Essay
Writing a hook is a good way to catch the attention of your audience, as this is usually the first sentence in an essay. How to start an essay about abortion? You can begin with some shocking fact, question, statistics, or even a quote. However, always make sure that this piece is taken from a trusted resource.
Here are some examples of hooks you can use in your paper:
- As of July 1, 2022, 13 states banned abortion, depriving millions of women of control of their bodies.
- According to WHO, 125,000 abortions take place every day worldwide.
- Is abortion a woman’s right or a crime?
- Since 1994, more than 40 countries have liberalized their abortion laws.
- Around 48% of all abortions are unsafe, and 8% of them lead to women’s death.
- The right to an abortion is one of the reproductive and basic rights of a woman.
- Abortion is as old as the world itself – women have resorted to this method since ancient times.
- Only 60% of women in the world live in countries where pregnancy termination is allowed.
Body Paragraphs: Pros and Cons of Abortion
The body is the biggest part of your paper. Here, you have a chance to make your voice concerning the abortion issue heard. Not sure where to start? Facts about abortion pros and cons should give you a basic understanding of which direction to move in.
First things first, let’s review some brief tips for you on how to write the best essay body if you have already made up your mind.
Make a draft
It’s always a good idea to have a rough draft of your writing. Follow the outline and don’t bother with the word choice, grammar, or sentence structure much at first. You can polish it all later, as the initial draft will not likely be your final. You may see some omissions in your arguments, lack of factual basis, or repetitiveness that can be eliminated in the next versions.
Trust only reliable sources
This part of an essay includes loads of factual information, and you should be very careful with it. Otherwise, your paper may look unprofessional and cost you precious points. Never rely on sources like Wikipedia or tabloids – they lack veracity and preciseness.
Edit rigorously
It’s best to do it the next day after you finish writing so that you can spot even the smallest mistakes. Remember, this is the most important part of your paper, so it has to be flawless. You can also use editing tools like Grammarly.
Determine your weak points
Since you are writing an argumentative essay, your ideas should be backed up by strong facts so that you sound convincing. Sometimes it happens that one argument looks weaker than the other. Your task is to find it and strengthen it with more or better facts.
Add an opposing view
Sometimes, it’s not enough to present only one side of the discussion. Showing one of the common views from the opposing side might actually help you strengthen your main idea. Besides, making an attempt at refuting it with alternative facts can show your teacher or professor that you’ve researched and analyzed all viewpoints, not just the one you stand by.
If you have chosen a side but are struggling to find the arguments for or against it, we have complied abortion pro and cons list for you. You can use both sets if you are writing an abortion summary essay covering all the stances.
Why Should Abortion Be Legal
If you stick to the opinion that abortion is just a medical procedure, which should be a basic health care need for each woman, you will definitely want to write the pros of abortion essay. Here is some important information and a list of pros about abortion for you to use:
- Since the fetus is a set of cells – not an individual, it’s up to a pregnant woman to make a decision concerning her body. Only she can decide whether she wants to keep the pregnancy or have an abortion. The abortion ban is a violation of a woman’s right to have control over her own body.
- The fact that women and girls do not have access to effective contraception and safe abortion services has serious consequences for their own health and the health of their families.
- The criminalization of abortion usually leads to an increase in the number of clandestine abortions. Many years ago, fetuses were disposed of with improvised means, which included knitting needles and half-straightened metal hangers. 13% of women’s deaths are the result of unsafe abortions.
- Many women live in a difficult financial situation and cannot support their children financially. Having access to safe abortion takes this burden off their shoulders. This will also not decrease their quality of life as the birth and childcare would.
- In countries where abortion is prohibited, there is a phenomenon of abortion tourism to other countries where it can be done without obstacles. Giving access to this procedure can make the lives of women much easier.
- Women should not put their lives or health in danger because of the laws that were adopted by other people.
- Girls and women who do not have proper sex education may not understand pregnancy as a concept or determine that they are pregnant early on. Instead of educating them and giving them a choice, an abortion ban forces them to become mothers and expects them to be fit parents despite not knowing much about reproduction.
- There are women who have genetic disorders or severe mental health issues that will affect their children if they're born. Giving them an option to terminate ensures that there won't be a child with a low quality of life and that the woman will not have to suffer through pregnancy, birth, and raising a child with her condition.
- Being pro-choice is about the freedom to make decisions about your body so that women who are for termination can do it safely, and those who are against it can choose not to do it. It is an inclusive option that caters to everyone.
- Women and girls who were raped or abused by their partner, caregiver, or stranger and chose to terminate the pregnancy can now be imprisoned for longer than their abusers. This implies that the system values the life of a fetus with no or primitive brain function over the life of a living woman.
- People who lived in times when artificial termination of pregnancy was scarcely available remember clandestine abortions and how traumatic they were, not only for the physical but also for the mental health of women. Indeed, traditionally, in many countries, large families were a norm. However, the times have changed, and supervised abortion is a safe and accessible procedure these days. A ban on abortion will simply push humanity away from the achievements of the civilized world.

Types of abortion
There are 2 main types of abortions that can be performed at different pregnancy stages and for different reasons:
- Medical abortion. It is performed by taking a specially prescribed pill. It does not require any special manipulations and can even be done at home (however, after a doctor’s visit and under supervision). It is considered very safe and is usually done during the very first weeks of pregnancy.
- Surgical abortion. This is a medical operation that is done with the help of a suction tube. It then removes the fetus and any related material. Anesthesia is used for this procedure, and therefore, it can only be done in a hospital. The maximum time allowed for surgical abortion is determined in each country specifically.
Cases when abortion is needed
Center for Reproductive Rights singles out the following situations when abortion is required:
- When there is a risk to the life or physical/mental health of a pregnant woman.
- When a pregnant woman has social or economic reasons for it.
- Upon the woman's request.
- If a pregnant woman is mentally or cognitively disabled.
- In case of rape and/or incest.
- If there were congenital anomalies detected in the fetus.
Countries and their abortion laws
- Countries where abortion is legalized in any case: Australia, Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Sweden, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Hungary, the Netherlands, Norway, Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Lithuania, etc.
- Countries where abortion is completely prohibited: Angola, Venezuela, Egypt, Indonesia, Iraq, Lebanon, Nicaragua, Oman, Paraguay, Palau, Jamaica, Laos, Haiti, Honduras, Andorra, Aruba, El Salvador, Dominican Republic, Sierra Leone, Senegal, etc.
- Countries where abortion is allowed for medical reasons: Afghanistan, Israel, Argentina, Nigeria, Bangladesh, Bolivia, Ghana, Israel, Morocco, Mexico, Bahamas, Central African Republic, Ecuador, Ghana, Algeria, Monaco, Pakistan, Poland, etc.
- Countries where abortion is allowed for both medical and socioeconomic reasons: England, India, Spain, Luxembourg, Japan, Finland, Taiwan, Zambia, Iceland, Fiji, Cyprus, Barbados, Belize, etc.
Why Abortion Should Be Banned
Essays against abortions are popular in educational institutions since we all know that many people – many minds. So if you don’t want to support this procedure in your essay, here are some facts that may help you to argument why abortion is wrong:
- Abortion at an early age is especially dangerous because a young woman with an unstable hormonal system may no longer be able to have children throughout her life. Termination of pregnancy disrupts the hormonal development of the body.
- Health complications caused by abortion can occur many years after the procedure. Even if a woman feels fine in the short run, the situation may change in the future.
- Abortion clearly has a negative effect on reproductive function. Artificial dilation of the cervix during an abortion leads to weak uterus tonus, which can cause a miscarriage during the next pregnancy.
- Evidence shows that surgical termination of pregnancy significantly increases the risk of breast cancer.
- In December 1996, the session of the Council of Europe on bioethics concluded that a fetus is considered a human being on the 14th day after conception.
You are free to use each of these arguments for essays against abortions. Remember that each claim should not be supported by emotions but by facts, figures, and so on.
Health complications after abortion
One way or another, abortion is extremely stressful for a woman’s body. Apart from that, it can even lead to various health problems in the future. You can also cover them in your cons of an abortion essay:
- Continuation of pregnancy. If the dose of the drug is calculated by the doctor in the wrong way, the pregnancy will progress.
- Uterine bleeding, which requires immediate surgical intervention.
- Severe nausea or even vomiting occurs as a result of a sharp change in the hormonal background.
- Severe stomach pain. Medical abortion causes miscarriage and, as a result, strong contractions of the uterus.
- High blood pressure and allergic reactions to medicines.
- Depression or other mental problems after a difficult procedure.
Abortion Essay Conclusion
After you have finished working on the previous sections of your paper, you will have to end it with a strong conclusion. The last impression is no less important than the first one. Here is how you can make it perfect in your conclusion paragraph on abortion:
- It should be concise. The conclusion cannot be as long as your essay body and should not add anything that cannot be derived from the main section. Reiterate the key ideas, combine some of them, and end the paragraph with something for the readers to think about.
- It cannot repeat already stated information. Restate your thesis statement in completely other words and summarize your main points. Do not repeat anything word for word – rephrase and shorten the information instead.
- It should include a call to action or a cliffhanger. Writing experts believe that a rhetorical question works really great for an argumentative essay. Another good strategy is to leave your readers with some curious ideas to ponder upon.
Abortion Facts for Essay
Abortion is a topic that concerns most modern women. Thousands of books, research papers, and articles on abortion are written across the world. Even though pregnancy termination has become much safer and less stigmatized with time, it still worries millions. What can you cover in your paper so that it can really stand out among others? You may want to add some shocking abortion statistics and facts:
- 40-50 million abortions are done in the world every year (approximately 125,000 per day).
- According to UN statistics, women have 25 million unsafe abortions each year. Most of them (97%) are performed in the countries of Africa, Asia, and Latin America. 14% of them are especially unsafe because they are done by people without any medical knowledge.
- Since 2017, the United States has shown the highest abortion rate in the last 30 years.
- The biggest number of abortion procedures happen in the countries where they are officially banned. The lowest rate is demonstrated in the countries with high income and free access to contraception.
- Women in low-income regions are three times more susceptible to unplanned pregnancies than those in developed countries.
- In Argentina, more than 38,000 women face dreadful health consequences after unsafe abortions.
- The highest teen abortion rates in the world are seen in 3 countries: England, Wales, and Sweden.
- Only 31% of teenagers decide to terminate their pregnancy. However, the rate of early pregnancies is getting lower each year.
- Approximately 13 million children are born to mothers under the age of 20 each year.
- 5% of women of reproductive age live in countries where abortions are prohibited.
We hope that this abortion information was useful for you, and you can use some of these facts for your own argumentative essay. If you find some additional facts, make sure that they are not manipulative and are taken from official medical resources.

Abortion Essay Topics
Do you feel like you are lost in the abundance of information? Don’t know what topic to choose among the thousands available online? Check our short list of the best abortion argumentative essay topics:
- Why should abortion be legalized essay
- Abortion: a murder or a basic human right?
- Why we should all support abortion rights
- Is the abortion ban in the US a good initiative?
- The moral aspect of teen abortions
- Can the abortion ban solve birth control problems?
- Should all countries allow abortion?
- What consequences can abortion have in the long run?
- Is denying abortion sexist?
- Why is abortion a human right?
- Are there any ethical implications of abortion?
- Do you consider abortion a crime?
- Should women face charges for terminating a pregnancy?
Want to come up with your own? Here is how to create good titles for abortion essays:
- Write down the first associations. It can be something that swirls around in your head and comes to the surface when you think about the topic. These won’t necessarily be well-written headlines, but each word or phrase can be the first link in the chain of ideas that leads you to the best option.
- Irony and puns are not always a good idea. Especially when it comes to such difficult topics as abortion. Therefore, in your efforts to be original, remain sensitive to the issue you want to discuss.
- Never make a quote as your headline. First, a wordy quote makes the headline long. Secondly, readers do not understand whose words are given in the headline. Therefore, it may confuse them right from the start. If you have found a great quote, you can use it as your hook, but don’t forget to mention its author.
- Try to briefly summarize what is said in the essay. What is the focus of your paper? If the essence of your argumentative essay can be reduced to one sentence, it can be used as a title, paraphrased, or shortened.
- Write your title after you have finished your text. Before you just start writing, you might not yet have a catchy phrase in mind to use as a title. Don’t let it keep you from working on your essay – it might come along as you write.
Abortion Essay Example
We know that it is always easier to learn from a good example. For this reason, our writing experts have complied a detailed abortion essay outline for you. For your convenience, we have created two options with different opinions.
Topic: Why should abortion be legal?
Introduction – hook + thesis statement + short background information
Essay hook: More than 59% of women in the world do not have access to safe abortions, which leads to dreading health consequences or even death.
Thesis statement: Since banning abortions does not decrease their rates but only makes them unsafe, it is not logical to ban abortions.
Body – each paragraph should be devoted to one argument
Argument 1: Woman’s body – women’s rules. + example: basic human rights.
Argument 2: Banning abortion will only lead to more women’s death. + example: cases of Polish women.
Argument 3: Only women should decide on abortion. + example: many abortion laws are made by male politicians who lack knowledge and first-hand experience in pregnancies.
Conclusion – restated thesis statement + generalized conclusive statements + cliffhanger
Restated thesis: The abortion ban makes pregnancy terminations unsafe without decreasing the number of abortions, making it dangerous for women.
Cliffhanger: After all, who are we to decide a woman’s fate?
Topic: Why should abortion be banned?
Essay hook: Each year, over 40 million new babies are never born because their mothers decide to have an abortion.
Thesis statement: Abortions on request should be banned because we cannot decide for the baby whether it should live or die.
Argument 1: A fetus is considered a person almost as soon as it is conceived. Killing it should be regarded as murder. + example: Abortion bans in countries such as Poland, Egypt, etc.
Argument 2: Interrupting a baby’s life is morally wrong. + example: The Bible, the session of the Council of Europe on bioethics decision in 1996, etc.
Argument 3: Abortion may put the reproductive health of a woman at risk. + example: negative consequences of abortion.
Restated thesis: Women should not be allowed to have abortions without serious reason because a baby’s life is as priceless as their own.
Cliffhanger: Why is killing an adult considered a crime while killing an unborn baby is not?

Examples of Essays on Abortion
There are many great abortion essays examples on the Web. You can easily find an argumentative essay on abortion in pdf and save it as an example. Many students and scholars upload their pieces to specialized websites so that others can read them and continue the discussion in their own texts.
In a free argumentative essay on abortion, you can look at the structure of the paper, choice of the arguments, depth of research, and so on. Reading scientific papers on abortion or essays of famous activists is also a good idea. Here are the works of famous authors discussing abortion.
A Defense of Abortion by Judith Jarvis Thomson
Published in 1971, this essay by an American philosopher considers the moral permissibility of abortion. It is considered the most debated and famous essay on this topic, and it’s definitely worth reading no matter what your stance is.
Abortion and Infanticide by Michael Tooley
It was written in 1972 by an American philosopher known for his work in the field of metaphysics. In this essay, the author considers whether fetuses and infants have the same rights. Even though this work is quite complex, it presents some really interesting ideas on the matter.
Some Biological Insights into Abortion by Garret Hardin
This article by American ecologist Garret Hardin, who had focused on the issue of overpopulation during his scholarly activities, presents some insights into abortion from a scientific point of view. He also touches on non-biological issues, such as moral and economic. This essay will be of great interest to those who support the pro-choice stance.
H4 Hidden in Plain View: An Overview of Abortion in Rural Illinois and Around the Globe by Heather McIlvaine-Newsad
In this study, McIlvaine-Newsad has researched the phenomenon of abortion since prehistoric times. She also finds an obvious link between the rate of abortions and the specifics of each individual country. Overall, this scientific work published in 2014 is extremely interesting and useful for those who want to base their essay on factual information.
H4 Reproduction, Politics, and John Irving’s The Cider House Rules: Women’s Rights or “Fetal Rights”? by Helena Wahlström
In her article of 2013, Wahlström considers John Irving’s novel The Cider House Rules published in 1985 and is regarded as a revolutionary work for that time, as it acknowledges abortion mostly as a political problem. This article will be a great option for those who want to investigate the roots of the abortion debate.

FAQs On Abortion Argumentative Essay
- Is abortion immoral?
This question is impossible to answer correctly because each person independently determines their own moral framework. One group of people will say that abortion is a woman’s right because only she has power over her body and can make decisions about it. Another group will argue that the embryo is also a person and has the right to birth and life.
In general, the attitude towards abortion is determined based on the political and religious views of each person. Religious people generally believe that abortion is immoral because it is murder, while secular people see it as a normal medical procedure. For example, in the US, the ban on abortion was introduced in red states where the vast majority have conservative views, while blue liberal states do not support this law. Overall, it’s up to a person to decide whether they consider abortion immoral based on their own values and beliefs.
- Is abortion legal?
The answer to this question depends on the country in which you live. There are countries in which pregnancy termination is a common medical procedure and is performed at the woman's request. There are also states in which there must be a serious reason for abortion: medical, social, or economic. Finally, there are nations in which abortion is prohibited and criminalized. For example, in Jamaica, a woman can get life imprisonment for abortion, while in Kenya, a medical worker who volunteers to perform an abortion can be imprisoned for up to 14 years.
- Is abortion safe?
In general, modern medicine has reached such a level that abortion has become a common (albeit difficult from various points of view) medical procedure. There are several types of abortion, as well as many medical devices and means that ensure the maximum safety of the pregnancy termination. Like all other medical procedures, abortion can have various consequences and complications.
Abortions – whether safe or not - exist in all countries of the world. The thing is that more than half of them are dangerous because women have them in unsuitable conditions and without professional help. Only universal access to abortion in all parts of the world can make it absolutely safe. In such a case, it will be performed only after a thorough assessment and under the control of a medical professional who can mitigate the potential risks.
- How safe is abortion?
If we do not talk about the ethical side of the issue related to abortion, it still has some risks. In fact, any medical procedure has them to a greater or lesser extent.
The effectiveness of the safe method in a medical setting is 80-99%. An illegal abortion (for example, the one without special indications after 12 weeks) can lead to a patient’s death, and the person who performed it will be criminally liable in this case.
Doctors do not have universal advice for all pregnant women on whether it is worth making this decision or not. However, many of them still tend to believe that any contraception - even one that may have negative side effects - is better than abortion. That’s why spreading awareness on means of contraception and free access to it is vital.
Your email address will not be published / Required fields are marked *
Try it now!
Calculate your price
Number of pages:
Order an essay!

Fill out the order form

Make a secure payment
Receive your order by email
Essay paper writing
Writing About Stress Management
In our modern and fast-changing world, people face stress very often. It affects the behavior of a person, his or her working capacity, health, as well as relationships with others. Moreover, doctors…
9th Jul 2020

Immigration Essay Writing Guide
Nowadays, immigration is getting more wide-spread in the world than it was a couple of decades ago. The reason for this is the progress in economic and technological spheres. Besides, the gap between…
9th May 2019

Child Labour Essay Writting Guide
Essays on child labour are relevant because this topic remains a serious problem. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), over 250 million children in the world are engaged in work…
20th Mar 2019
Get your project done perfectly
Professional writing service
Reset password
We’ve sent you an email containing a link that will allow you to reset your password for the next 24 hours.
Please check your spam folder if the email doesn’t appear within a few minutes.

Princeton Legal Journal

The First Amendment and the Abortion Rights Debate
Sofia Cipriano
Following Dobbs v. Jackson ’s (2022) reversal of Roe v. Wade (1973) — and the subsequent revocation of federal abortion protection — activists and scholars have begun to reconsider how to best ground abortion rights in the Constitution. In the past year, numerous Jewish rights groups have attempted to overturn state abortion bans by arguing that abortion rights are protected by various state constitutions’ free exercise clauses — and, by extension, the First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. While reframing the abortion rights debate as a question of religious freedom is undoubtedly strategic, the Free Exercise Clause is not the only place to locate abortion rights: the Establishment Clause also warrants further investigation.
Roe anchored abortion rights in the right to privacy — an unenumerated right with a long history of legal recognition. In various cases spanning the past two centuries, t he Supreme Court located the right to privacy in the First, Fourth, Fifth, Ninth, and Fourteenth Amendments . Roe classified abortion as a fundamental right protected by strict scrutiny, meaning that states could only regulate abortion in the face of a “compelling government interest” and must narrowly tailor legislation to that end. As such, Roe ’s trimester framework prevented states from placing burdens on abortion access in the first few months of pregnancy. After the fetus crosses the viability line — the point at which the fetus can survive outside the womb — states could pass laws regulating abortion, as the Court found that “the potentiality of human life” constitutes a “compelling” interest. Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. Casey (1992) later replaced strict scrutiny with the weaker “undue burden” standard, giving states greater leeway to restrict abortion access. Dobbs v. Jackson overturned both Roe and Casey , leaving abortion regulations up to individual states.
While Roe constituted an essential step forward in terms of abortion rights, weaknesses in its argumentation made it more susceptible to attacks by skeptics of substantive due process. Roe argues that the unenumerated right to abortion is implied by the unenumerated right to privacy — a chain of logic which twice removes abortion rights from the Constitution’s language. Moreover, Roe’s trimester framework was unclear and flawed from the beginning, lacking substantial scientific rationale. As medicine becomes more and more advanced, the arbitrariness of the viability line has grown increasingly apparent.
As abortion rights supporters have looked for alternative constitutional justifications for abortion rights, the First Amendment has become increasingly more visible. Certain religious groups — particularly Jewish groups — have argued that they have a right to abortion care. In Generation to Generation Inc v. Florida , a religious rights group argued that Florida’s abortion ban (HB 5) constituted a violation of the Florida State Constitution: “In Jewish law, abortion is required if necessary to protect the health, mental or physical well-being of the woman, or for many other reasons not permitted under the Act. As such, the Act prohibits Jewish women from practicing their faith free of government intrusion and thus violates their privacy rights and religious freedom.” Similar cases have arisen in Indiana and Texas. Absent constitutional protection of abortion rights, the Christian religious majorities in many states may unjustly impose their moral and ethical code on other groups, implying an unconstitutional religious hierarchy.
Cases like Generation to Generation Inc v. Florida may also trigger heightened scrutiny status in higher courts; The Religious Freedom Restoration Act (1993) places strict scrutiny on cases which “burden any aspect of religious observance or practice.”
But framing the issue as one of Free Exercise does not interact with major objections to abortion rights. Anti-abortion advocates contend that abortion is tantamount to murder. An anti-abortion advocate may argue that just as religious rituals involving human sacrifice are illegal, so abortion ought to be illegal. Anti-abortion advocates may be able to argue that abortion bans hold up against strict scrutiny since “preserving potential life” constitutes a “compelling interest.”
The question of when life begins—which is fundamentally a moral and religious question—is both essential to the abortion debate and often ignored by left-leaning activists. For select Christian advocacy groups (as well as other anti-abortion groups) who believe that life begins at conception, abortion bans are a deeply moral issue. Abortion bans which operate under the logic that abortion is murder essentially legislate a definition of when life begins, which is problematic from a First Amendment perspective; the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment prevents the government from intervening in religious debates. While numerous legal thinkers have associated the abortion debate with the First Amendment, this argument has not been fully litigated. As an amicus brief filed in Dobbs by the Freedom From Religion Foundation, Center for Inquiry, and American Atheists points out, anti-abortion rhetoric is explicitly religious: “There is hardly a secular veil to the religious intent and positions of individuals, churches, and state actors in their attempts to limit access to abortion.” Justice Stevens located a similar issue with anti-abortion rhetoric in his concurring opinion in Webster v. Reproductive Health Services (1989) , stating: “I am persuaded that the absence of any secular purpose for the legislative declarations that life begins at conception and that conception occurs at fertilization makes the relevant portion of the preamble invalid under the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment to the Federal Constitution.” Judges who justify their judicial decisions on abortion using similar rhetoric blur the line between church and state.
Framing the abortion debate around religious freedom would thus address the two main categories of arguments made by anti-abortion activists: arguments centered around issues with substantive due process and moral objections to abortion.
Conservatives may maintain, however, that legalizing abortion on the federal level is an Establishment Clause violation to begin with, since the government would essentially be imposing a federal position on abortion. Many anti-abortion advocates favor leaving abortion rights up to individual states. However, in the absence of recognized federal, constitutional protection of abortion rights, states will ban abortion. Protecting religious freedom of the individual is of the utmost importance — the United States government must actively intervene in order to uphold the line between church and state. Protecting abortion rights would allow everyone in the United States to act in accordance with their own moral and religious perspectives on abortion.
Reframing the abortion rights debate as a question of religious freedom is the most viable path forward. Anchoring abortion rights in the Establishment Clause would ensure Americans have the right to maintain their own personal and religious beliefs regarding the question of when life begins. In the short term, however, litigants could take advantage of Establishment Clauses in state constitutions. Yet, given the swing of the Court towards expanding religious freedom protections at the time of writing, Free Exercise arguments may prove better at securing citizens a right to an abortion.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
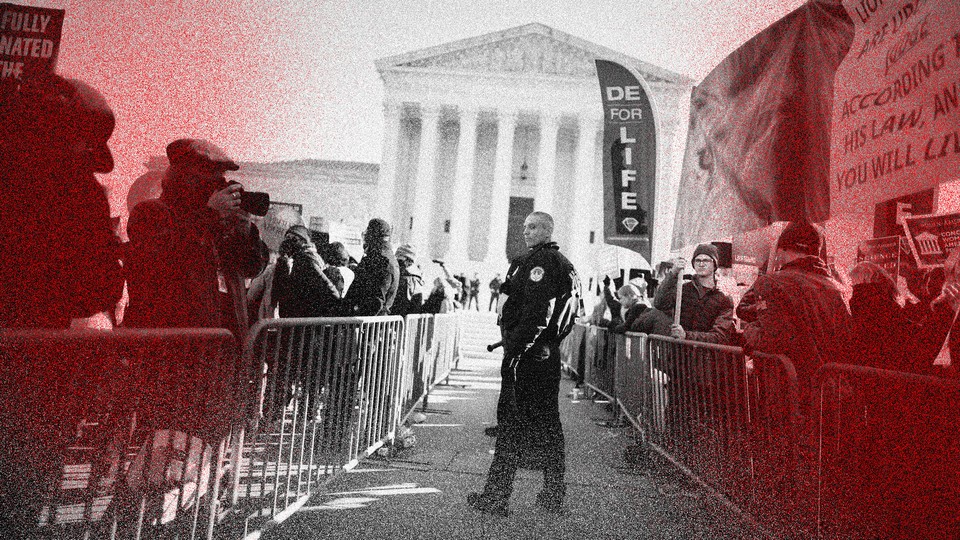
There Are More Than Two Sides to the Abortion Debate
Readers share their perspectives.

Sign up for Conor’s newsletter here.
Earlier this week I curated some nuanced commentary on abortion and solicited your thoughts on the same subject. What follows includes perspectives from several different sides of the debate. I hope each one informs your thinking, even if only about how some other people think.
We begin with a personal reflection.
Cheryl was 16 when New York State passed a statute legalizing abortion and 19 when Roe v. Wade was decided in 1973. At the time she was opposed to the change, because “it just felt wrong.” Less than a year later, her mother got pregnant and announced she was getting an abortion.
She recalled:
My parents were still married to each other, and we were financially stable. Nonetheless, my mother’s announcement immediately made me a supporter of the legal right to abortion. My mother never loved me. My father was physically abusive and both parents were emotionally and psychologically abusive on a virtually daily basis. My home life was hellish. When my mother told me about the intended abortion, my first thought was, “Thank God that they won’t be given another life to destroy.” I don’t deny that there are reasons to oppose abortion. As a feminist and a lawyer, I can now articulate several reasons for my support of legal abortion: a woman’s right to privacy and autonomy and to the equal protection of the laws are near the top of the list. (I agree with Ruth Bader Ginsburg that equal protection is a better legal rationale for the right to abortion than privacy.) But my emotional reaction from 1971 still resonates with me. Most people who comment on the issue, on both sides, do not understand what it is to go through childhood unloved. It is horrific beyond my powers of description. To me, there is nothing more immoral than forcing that kind of life on any child. Anti-abortion activists often like to ask supporters of abortion rights: “Well, what if your mother had decided to abort you?” All I can say is that I have spent a great portion of my life wishing that my mother had done exactly that.
Steven had related thoughts:
I have respect for the idea that there should be some restrictions on abortion. But the most fundamental, and I believe flawed, unstated assumptions of the anti-choice are that A) they are acting on behalf of the fetus, and more importantly B) they know what the fetus would want. I would rather not have been born than to have been born to a mother who did not want me. All children should be wanted children—for the sake of all concerned. You can say that different fetuses would “want” different things—though it’s hard to say a clump of cells “wants” anything. How would we know? The argument lands, as it does generally, with the question of who should be making that decision. Who best speaks in the fetus’s interests? Who is better positioned morally or practically than the expectant mother?
Geoff self-describes as “pro-life” and guilty of some hypocrisy. He writes:
I’m pro-life because I have a hard time with the dehumanization that comes with the extremes of abortion on demand … Should it be okay to get an abortion when you find your child has Down syndrome? What of another abnormality? Or just that you didn’t want a girl? Any argument that these are legitimate reasons is disturbing. But so many of the pro-life just don’t seem to care about life unless it’s a fetus they can force a woman to carry. The hypocrisy is real. While you can argue that someone on death row made a choice that got them to that point, whereas a fetus had no say, I find it still hard to swallow that you can claim one life must be protected and the other must be taken. Life should be life. At least in the Catholic Church this is more consistent. I myself am guilty of a degree of hypocrisy. My wife and I used IVF to have our twins. There were other embryos created and not inserted. They were eventually destroyed. So did I support killing a life? Maybe? I didn’t want to donate them for someone else to give birth to—it felt wrong to think my twins may have brothers or sisters in the world they would never know about. Yet does that mean I was more willing to kill my embryos than to have them adopted? Sure seems like it. So I made a morality deal with myself and moved the goal post—the embryos were not yet in a womb and were so early in development that they couldn’t be considered fully human life. They were still potential life.
Colleen, a mother of three, describes why she ended her fourth pregnancy:
I was young when I first engaged this debate. Raised Catholic, anti-choice, and so committed to my position that I broke my parents’ hearts by giving birth during my junior year of college. At that time, my sense of my own rights in the matter was almost irrelevant. I was enslaved by my body. One husband and two babies later I heard a remarkable Jesuit theologian (I wish I could remember his name) speak on the matter and he, a Catholic priest, framed it most directly. We prioritize one life over another all the time. Most obviously, we justify the taking of life in war with all kinds of arguments that often turn out to be untrue. We also do so as we decide who merits access to health care or income support or other life-sustaining things. So the question of abortion then boils down to: Who gets to decide? Who gets to decide that the life of a human in gestation is actually more valuable than the life of the woman who serves as host—or vice versa? Who gets to decide when the load a woman is being asked to carry is more than she can bear? The state? Looking back over history, he argued that he certainly had more faith in the person most involved to make the best decision than in any formalized structure—church or state—created by men. Every form of birth control available failed me at one point or another, so when yet a 4th pregnancy threatened to interrupt the education I had finally been able to resume, I said “Enough.” And as I cried and struggled to come to that position, the question that haunted me was “Doesn’t MY life count?” And I decided it did.
Florence articulates what it would take to make her anti-abortion:
What people seem to miss is that depriving a woman of bodily autonomy is slavery. A person who does not control his/her own body is—what? A slave. At its simplest, this is the issue. I will be anti-abortion when men and women are equal in all facets of life—wages, chores, child-rearing responsibilities, registering for the draft, to name a few obvious ones. When there is birth control that is effective, where women do not bear most of the responsibility. We need to raise boys who are respectful to girls, who do not think that they are entitled to coerce a girl into having sex that she doesn’t really want or is unprepared for. We need for sex education to be provided in schools so young couples know what they are getting into when they have sex. Especially the repercussions of pregnancy. We need to raise girls who are confident and secure, who don’t believe they need a male to “complete” them. Who have enough agency to say “no” and to know why. We have to make abortion unnecessary … We have so far to go. If abortion is ruled illegal, or otherwise curtailed, we will never know if the solutions to women’s second-class status will work. We will be set back to the 50s or worse. I don’t want to go back. Women have fought from the beginning of time to own their bodies and their lives. To deprive us of all of the amazing strides forward will affect all future generations.
Similarly, Ben agrees that in our current environment, abortion is often the only way women can retain equal citizenship and participation in society, but also agrees with pro-lifers who critique the status quo, writing that he doesn’t want a world where a daughter’s equality depends on her right “to perform an act of violence on their potential descendents.” Here’s how he resolves his conflictedness:
Conservatives arguing for a more family-centered society, in which abortion is unnecessary to protect the equal rights of women, are like liberals who argue for defunding the police and relying on addiction, counselling, and other services, in that they argue for removing what offends them without clear, credible plans to replace the functions it serves. I sincerely hope we can move towards a world in which armed police are less necessary. But before we can remove the guardrails of the police, we need to make the rest of the changes so that the world works without them. Once liberal cities that have shown interest in defunding the police can prove that they can fund alternatives, and that those alternatives work, then I will throw my support behind defunding the police. Similarly, once conservative politicians demonstrate a credible commitment to an alternative vision of society in which women are supported, families are not taken for granted, and careers and short-term productivity are not the golden calves they are today, I will be willing to support further restrictions on abortion. But until I trust that they are interested in solving the underlying problem (not merely eliminating an aspect they find offensive), I will defend abortion, as terrible as it is, within reasonable legal limits.
Two readers objected to foregrounding gender equality. One emailed anonymously, writing in part:
A fetus either is or isn’t a person. The reason I’m pro-life is that I’ve never heard a coherent defense of the proposition that a fetus is not a person, and I’m not sure one can be made. I’ve read plenty of progressive commentary, and when it bothers to make an argument for abortion “rights” at all, it talks about “the importance of women’s healthcare” or something as if that were the issue.
Christopher expanded on that last argument:
Of the many competing ethical concerns, the one that trumps them all is the status of the fetus. It is the only organism that gets destroyed by the procedure. Whether that is permissible trumps all other concerns. Otherwise important ethical claims related to a woman’s bodily autonomy, less relevant social disparities caused by the differences in men’s and women’s reproductive functions, and even less relevant differences in partisan commitments to welfare that would make abortion less appealing––all of that is secondary. The relentless strategy by the pro-choice to sidestep this question and pretend that a woman’s right to bodily autonomy is the primary ethical concern is, to me, somewhere between shibboleth and mass delusion. We should spend more time, even if it’s unproductive, arguing about the status of the fetus, because that is the question, and we should spend less time indulging this assault-on-women’s-rights narrative pushed by the Left.
Jean is critical of the pro-life movement:
Long-acting reversible contraceptives, robust, science-based sex education for teens, and a stronger social safety net would all go a remarkable way toward decreasing the number of abortions sought. Yet all the emphasis seems to be on simply making abortion illegal. For many, overturning Roe v. Wade is not about reducing abortions so much as signalling that abortion is wrong. If so-called pro-lifers were as concerned about abortion as they seem to be, they would spend more time, effort, and money supporting efforts to reduce the need for abortion—not simply trying to make it illegal without addressing why women seek it out. Imagine, in other words, a world where women hardly needed to rely on abortion for their well-being and ability to thrive. Imagine a world where almost any woman who got pregnant had planned to do so, or was capable of caring for that child. What is the anti-abortion movement doing to promote that world?
Destiny has one relevant answer. She writes:
I run a pro-life feminist group and we often say that our goal is not to make abortion illegal, but rather unnecessary and unthinkable by supporting women and humanizing the unborn child so well.
Robert suggests a different focus:
Any well-reasoned discussion of abortion policy must include contraception because abortion is about unwanted children brought on by poorly reasoned choices about sex. Such choices will always be more emotional than rational. Leaving out contraception makes it an unrealistic, airy discussion of moral philosophy. In particular, we need to consider government-funded programs of long-acting reversible contraception which enable reasoned choices outside the emotional circumstances of having sexual intercourse.
Last but not least, if anyone can unite the pro-life and pro-choice movements, it’s Errol, whose thoughts would rankle majorities in both factions as well as a majority of Americans. He writes:
The decision to keep the child should not be left up solely to the woman. Yes, it is her body that the child grows in, however once that child is birthed it is now two people’s responsibility. That’s entirely unfair to the father when he desired the abortion but the mother couldn’t find it in her heart to do it. If a woman wants to abort and the man wants to keep it, she should abort. However I feel the same way if a man wants to abort. The next 18+ years of your life are on the line. I view that as a trade-off that warrants the male’s input. Abortion is a conversation that needs to be had by two people, because those two will be directly tied to the result for a majority of their life. No one else should be involved with that decision, but it should not be solely hers, either.
Thanks to all who contributed answers to this week’s question, whether or not they were among the ones published. What subjects would you like to see fellow readers address in future installments? Email [email protected].
By submitting an email, you’ve agreed to let us use it—in part or in full—in this newsletter and on our website. Published feedback includes a writer’s full name, city, and state, unless otherwise requested in your initial note.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

Reproductive rights in America
7 persistent claims about abortion, fact-checked.
Jaclyn Diaz
Koko Nakajima
Nick Underwood

Anti-abortion demonstrators watch as abortion rights protestors chant in front of the U.S. Supreme Court in Washington, D.C., on May 5. Jim Watson/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
Anti-abortion demonstrators watch as abortion rights protestors chant in front of the U.S. Supreme Court in Washington, D.C., on May 5.
Since the Supreme Court's 1973 Roe v. Wade decision ruled that women have a constitutional right to end their pregnancies, proponents and opponents of abortion rights have worked to own the conversation over the issue.
In 2019, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that 629,898 legal induced abortions were reported across the United States.
Lingering claims circulate about abortion, including about the safety of it, who gets abortions and even who supports or opposes access to abortion.
Below, seven popular claims surrounding abortion get fact-checked.
According to the Pew Research Center's polls , 37% of Americans want abortion illegal in all or most cases.
But an even bigger fraction — around 6 in 10 Americans — think abortion should be legal in all or most cases.
Current abortion rates are lower than what they were in 1973 and are now less than half what they were at their peak in the early 1980s, according to the Guttmacher Institute , a reproductive health research organization that supports abortion rights.
In 2017, pregnancy rates for females age 24 or below hit their lowest recorded levels, reflecting a long-term decline in pregnancy rates among females 24 or below.
Overall, in 2017, pregnancy rates for females of reproductive age hit their lowest recorded levels, with 87 pregnancies per 1,000 females ages 15 to 44, according to the Guttmacher Institute.
The annual number of deaths related to legal induced abortion has fluctuated from year to year since 1973, according to the CDC.
An analysis of data from 2013 to 2018 showed the national case-fatality rate for legal induced abortion was 0.41 deaths per 100,000 legal induced abortions, lower than in the previous five years.
The World Health Organization said people obtaining unsafe abortions are at a higher risk of death. Annually, 4.7% to 13.2% "of maternal deaths can be attributed to unsafe abortion," the WHO said. In developing regions of the world, there are 220 deaths per 100,000 unsafe abortions.
Trans and nonbinary people have undergone abortions as well.
The Guttmacher Institute estimates in 2017 an estimated 462 to 530 transgender or nonbinary individuals in the U.S. had abortions. That same year, the CDC said, 609,095 total abortions were carried out in the country.
The Abortion Out Loud campaign has collected stories from thousands of people who have had an abortion. Included are stories from trans and nonbinary people who have had an abortion — such as Jae, who spoke their experience.
"Most abortions in 2019 took place early in gestation," according to the CDC . Nearly 93% of abortions were performed at less than 13 weeks' gestation.
Abortion pills, which can typically be used up to 10 weeks into a pregnancy, made up 54% of abortions in 2020. These pills were the primary choice in the U.S. for the first time since the Food and Drug Administration approved the abortion drug mifepristone more than 20 years ago.
State legislatures have been moving to adopt 20-week abortion bans, with abortion opponents claiming fetuses can feel pain at that point. Roughly a third of states have implemented an abortion ban around 20 weeks .
But this contradicts widely accepted medical research from 2005. This study , published in the Journal of the American Medical Association , concluded that a fetus is not capable of experiencing pain until somewhere between 29 or 30 weeks.
Researchers wrote that fetal awareness of pain requires "functional thalamocortical connections." Those thalamocortical fibers begin appearing between 23 and 30 weeks' gestational age, but the capacity for pain perception comes later.
The argument against abortion has frequently been based on religion.
Data shows that the majority of people who get an abortion have some sort of religious affiliation, according to the most recent Guttmacher Institute data , from 2014.
The Pew Research Center also shows that attitudes on whether abortion should be legal vary among evangelical Protestants, mainline Protestants and Catholics.

Roe v. Wade and the future of reproductive rights in America
Here's what could happen now that roe v. wade is overturned.
- Roe v. Wade
- Supreme Court

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.1: Arguments Against Abortion
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 35918

- Nathan Nobis & Kristina Grob
- Morehouse College & University of South Carolina Sumter via Open Philosophy Press
We will begin with arguments for the conclusion that abortion is generally wrong , perhaps nearly always wrong . These can be seen as reasons to believe fetuses have the “right to life” or are otherwise seriously wrong to kill.
5.1.1 Fetuses are human
First, there is the claim that fetuses are “human” and so abortion is wrong. People sometimes debate whether fetuses are human , but fetuses found in (human) women clearly are biologically human : they aren’t cats or dogs. And so we have this argument, with a clearly true first premise:
Fetuses are biologically human.
All things that are biologically human are wrong to kill.
Therefore, fetuses are wrong to kill.
The second premise, however, is false, as easy counterexamples show. Consider some random living biologically human cells or tissues in a petri dish. It wouldn’t be wrong at all to wash those cells or tissues down the drain, killing them; scratching yourself or shaving might kill some biologically human skin cells, but that’s not wrong; a tumor might be biologically human, but not wrong to kill. So just because something is biologically human, that does not at all mean it’s wrong to kill that thing. We saw this same point about what’s merely biologically alive.
This suggests a deficiency in some common understandings of the important idea of “human rights.” “Human rights” are sometimes described as rights someone has just because they are human or simply in virtue of being human .
But the human cells in the petri dish above don’t have “human rights” and a human heart wouldn’t have “human rights” either. Many examples would make it clear that merely being biologically human doesn’t give something human rights. And many human rights advocates do not think that abortion is wrong, despite recognizing that (human) fetuses are biologically human.
The problem about what is often said about human rights is that people often do not think about what makes human beings have rights or why we have them, when we have them. The common explanation, that we have (human) rights just because we are (biologically) human , is incorrect, as the above discussion makes clear. This misunderstanding of the basis or foundation of human rights is problematic because it leads to a widespread, misplaced fixation on whether fetuses are merely biologically “human” and the mistaken thought that if they are, they have “human rights.” To address this problem, we need to identify better, more fundamental, explanations why we have rights, or why killing us is generally wrong, and see how those explanations might apply to fetuses, as we are doing here.
It might be that when people appeal to the importance and value of being “human,” the concern isn’t our biology itself, but the psychological characteristics that many human beings have: consciousness, awareness, feelings and so on. We will discuss this different meaning of “human” below. This meaning of “human” might be better expressed as conscious being , or “person,” or human person. This might be what people have in mind when they argue that fetuses aren’t even “human.”
Human rights are vitally important, and we would do better if we spoke in terms of “conscious-being rights” or “person-rights,” not “human rights.” This more accurate and informed understanding and terminology would help address human rights issues in general, and help us better think through ethical questions about biologically human embryos and fetuses.
5.1.2 Fetuses are human beings
Some respond to the arguments above—against the significance of being merely biologically human—by observing that fetuses aren’t just mere human cells, but are organized in ways that make them beings or organisms . (A kidney is part of a “being,” but the “being” is the whole organism.) That suggests this argument:
Fetuses are human beings or organisms .
All human beings or organisms are wrong to kill.
Therefore, fetuses are wrong to kill, so abortion is wrong.
The first premise is true: fetuses are dependent beings, but dependent beings are still beings.
The second premise, however, is the challenge, in terms of providing good reasons to accept it. Clearly many human beings or organisms are wrong to kill, or wrong to kill unless there’s a good reason that would justify that killing, e.g., self-defense. (This is often described by philosophers as us being prima facie wrong to kill, in contrast to absolutely or necessarily wrong to kill.) Why is this though? What makes us wrong to kill? And do these answers suggest that all human beings or organisms are wrong to kill?
Above it was argued that we are wrong to kill because we are conscious and feeling: we are aware of the world, have feelings and our perspectives can go better or worse for us —we can be harmed— and that’s what makes killing us wrong. It may also sometimes be not wrong to let us die, and perhaps even kill us, if we come to completely and permanently lacking consciousness, say from major brain damage or a coma, since we can’t be harmed by death anymore: we might even be described as dead in the sense of being “brain dead.” 10
So, on this explanation, human beings are wrong to kill, when they are wrong to kill, not because they are human beings (a circular explanation), but because we have psychological, mental or emotional characteristics like these. This explains why we have rights in a simple, common-sense way: it also simply explains why rocks, microorganisms and plants don’t have rights. The challenge then is explaining why fetuses that have never been conscious or had any feeling or awareness would be wrong to kill. How then can the second premise above, general to all human organisms, be supported, especially when applied to early fetuses?
One common attempt is to argue that early fetuses are wrong to kill because there is continuous development from fetuses to us, and since we are wrong to kill now , fetuses are also wrong to kill, since we’ve been the “same being” all along. 11 But this can’t be good reasoning, since we have many physical, cognitive, emotional and moral characteristics now that we lacked as fetuses (and as children). So even if we are the “same being” over time, even if we were once early fetuses, that doesn’t show that fetuses have the moral rights that babies, children and adults have: we, our bodies and our rights sometimes change.
A second attempt proposes that rights are essential to human organisms: they have them whenever they exist. This perspective sees having rights, or the characteristics that make someone have rights, as essential to living human organisms. The claim is that “having rights” is an essential property of human beings or organisms, and so whenever there’s a living human organism, there’s someone with rights, even if that organism totally lacks consciousness, like an early fetus. (In contrast, the proposal we advocate for about what makes us have rights understands rights as “accidental” to our bodies but “essential” to our minds or awareness, since our bodies haven’t always “contained” a conscious being, so to speak.)
Such a view supports the premise above; maybe it just is that premise above. But why believe that rights are essential to human organisms? Some argue this is because of what “kind” of beings we are, which is often presumed to be “rational beings.” The reasoning seems to be this: first, that rights come from being a rational being: this is part of our “nature.” Second, that all human organisms, including fetuses, are the “kind” of being that is a “rational being,” so every being of the “kind” rational being has rights. 12
In response, this explanation might seem question-begging: it might amount to just asserting that all human beings have rights. This explanation is, at least, abstract. It seems to involve some categorization and a claim that everyone who is in a certain category has some of the same moral characteristics that others in that category have, but because of a characteristic (actual rationality) that only these others have: so, these others profoundly define what everyone else is . If this makes sense, why not also categorize us all as not rational beings , if we are the same kind of beings as fetuses that are actually not rational?
This explanation might seem to involve thinking that rights somehow “trickle down” from later rationality to our embryonic origins, and so what we have later we also have earlier , because we are the same being or the same “kind” of being. But this idea is, in general, doubtful: we are now responsible beings, in part because we are rational beings, but fetuses aren’t responsible for anything. And we are now able to engage in moral reasoning since we are rational beings, but fetuses don’t have the “rights” that uniquely depend on moral reasoning abilities. So that an individual is a member of some general group or kind doesn’t tell us much about their rights: that depends on the actual details about that individual, beyond their being members of a group or kind.
To make this more concrete, return to the permanently comatose individuals mentioned above: are we the same kind of beings, of the same “essence,” as these human beings? If so, then it seems that some human beings can be not wrong to let die or kill, when they have lost consciousness. Therefore, perhaps some other human beings, like early fetuses, are also not wrong to kill before they have gained consciousness . And if we are not the same “kind” of beings, or have different essences, then perhaps we also aren’t the same kind of beings as fetuses either.
Similar questions arise concerning anencephalic babies, tragically born without most of their brains: are they the same “kind” of beings as “regular” babies or us? If so, then—since such babies are arguably morally permissible to let die, even when they could be kept alive, since being alive does them no good—then being of our “kind” doesn’t mean the individual has the same rights as us, since letting us die would be wrong. But if such babies are a different “kind” of beings than us, then pre-conscious fetuses might be of a relevantly different kind also.
So, in general, this proposal that early fetuses essentially have rights is suspect, if we evaluate the reasons given in its support. Even if fetuses and us are the same “kind” of beings (which perhaps we are not!) that doesn’t immediately tell us what rights fetuses would have, if any. And we might even reasonably think that, despite our being the same kind of beings as fetuses (e.g., the same kind of biology), we are also importantly different kinds of beings (e.g., one kind with a mental life and another kind which has never had it). This photograph of a 6-week old fetus might help bring out the ambiguity in what kinds of beings we all are:
In sum, the abstract view that all human organisms have rights essentially needs to be plausibly explained and defended. We need to understand how it really works. We need to be shown why it’s a better explanation, all things considered, than a consciousness and feelings-based theory of rights that simply explains why we, and babies, have rights, why racism, sexism and other forms of clearly wrongful discrimination are wrong, and , importantly, how we might lose rights in irreversible coma cases (if people always retained the right to life in these circumstances, presumably, it would be wrong to let anyone die), and more.
5.1.3 Fetuses are persons
Finally, we get to what some see as the core issue here, namely whether fetuses are persons , and an argument like this:
Fetuses are persons, perhaps from conception.
Persons have the right to life and are wrong to kill.
So, abortion is wrong, as it involves killing persons.
The second premise seems very plausible, but there are some important complications about it that will be discussed later. So let’s focus on the idea of personhood and whether any fetuses are persons. What is it to be a person ? One answer that everyone can agree on is that persons are beings with rights and value . That’s a fine answer, but it takes us back to the initial question: OK, who or what has the rights and value of persons? What makes someone or something a person?
Answers here are often merely asserted , but these answers need to be tested: definitions can be judged in terms of whether they fit how a word is used. We might begin by thinking about what makes us persons. Consider this:
We are persons now. Either we will always be persons or we will cease being persons. If we will cease to be persons, what can end our personhood? If we will always be persons, how could that be?
Both options yield insight into personhood. Many people think that their personhood ends at death or if they were to go into a permanent coma: their body is (biologically) alive but the person is gone: that is why other people are sad. And if we continue to exist after the death of our bodies, as some religions maintain, what continues to exist? The person , perhaps even without a body, some think! Both responses suggest that personhood is defined by a rough and vague set of psychological or mental, rational and emotional characteristics: consciousness, knowledge, memories, and ways of communicating, all psychologically unified by a unique personality.
A second activity supports this understanding:
Make a list of things that are definitely not persons . Make a list of individuals who definitely are persons . Make a list of imaginary or fictional personified beings which, if existed, would be persons: these beings that fit or display the concept of person, even if they don’t exist. What explains the patterns of the lists?
Rocks, carrots, cups and dead gnats are clearly not persons. We are persons. Science fiction gives us ideas of personified beings: to give something the traits of a person is to indicate what the traits of persons are, so personified beings give insights into what it is to be a person. Even though the non-human characters from, say, Star Wars don’t exist, they fit the concept of person: we could befriend them, work with them, and so on, and we could only do that with persons. A common idea of God is that of an immaterial person who has exceptional power, knowledge, and goodness: you couldn’t pray to a rock and hope that rock would respond: you could only pray to a person. Are conscious and feeling animals, like chimpanzees, dolphins, cats, dogs, chickens, pigs, and cows more relevantly like us, as persons, or are they more like rocks and cabbages, non-persons? Conscious and feeling animals seem to be closer to persons than not. 13 So, this classificatory and explanatory activity further supports a psychological understanding of personhood: persons are, at root, conscious, aware and feeling beings.
Concerning abortion, early fetuses would not be persons on this account: they are not yet conscious or aware since their brains and nervous systems are either non-existent or insufficiently developed. Consciousness emerges in fetuses much later in pregnancy, likely after the first trimester or a bit beyond. This is after when most abortions occur. Most abortions, then, do not involve killing a person , since the fetus has not developed the characteristics for personhood. We will briefly discuss later abortions, that potentially affect fetuses who are persons or close to it, below.
It is perhaps worthwhile to notice though that if someone believed that fetuses are persons and thought this makes abortion wrong, it’s unclear how they could coherently believe that a pregnancy resulting from rape or incest could permissibly be ended by an abortion. Some who oppose abortion argue that, since you are a person, it would be wrong to kill you now even if you were conceived because of a rape, and so it’s wrong to kill any fetus who is a person, even if they exist because of a rape: whether someone is a person or not doesn’t depend on their origins: it would make no sense to think that, for two otherwise identical fetuses, one is a person but the other isn’t, because that one was conceived by rape. Therefore, those who accept a “personhood argument” against abortion, yet think that abortions in cases of rape are acceptable, seem to have an inconsistent view.
5.1.4 Fetuses are potential persons
If fetuses aren’t persons, they are at least potential persons, meaning they could and would become persons. This is true. This, however, doesn’t mean that they currently have the rights of persons because, in general, potential things of a kind don’t have the rights of actual things of that kind : potential doctors, lawyers, judges, presidents, voters, veterans, adults, parents, spouses, graduates, moral reasoners and more don’t have the rights of actual individuals of those kinds.
Some respond that potential gives the right to at least try to become something. But that trying sometimes involves the cooperation of others: if your friend is a potential medical student, but only if you tutor her for many hours a day, are you obligated to tutor her? If my child is a potential NASCAR champion, am I obligated to buy her a race car to practice? ‘No’ to both and so it is unclear that a pregnant woman would be obligated to provide what’s necessary to bring about a fetus’s potential. (More on that below, concerning the what obligations the right to life imposes on others, in terms of obligations to assist other people.)
5.1.5 Abortion prevents fetuses from experiencing their valuable futures
The argument against abortion that is likely most-discussed by philosophers comes from philosopher Don Marquis. 14 He argues that it is wrong to kill us, typical adults and children, because it deprives us from experiencing our (expected to be) valuable futures, which is a great loss to us . He argues that since fetuses also have valuable futures (“futures like ours” he calls them), they are also wrong to kill. His argument has much to recommend it, but there are reasons to doubt it as well.
First, fetuses don’t seem to have futures like our futures , since—as they are pre-conscious—they are entirely psychologically disconnected from any future experiences: there is no (even broken) chain of experiences from the fetus to that future person’s experiences. Babies are, at least, aware of the current moment, which leads to the next moment; children and adults think about and plan for their futures, but fetuses cannot do these things, being completely unconscious and without a mind.
Second, this fact might even mean that the early fetus doesn’t literally have a future: if your future couldn’t include you being a merely physical, non-conscious object (e.g., you couldn’t be a corpse: if there’s a corpse, you are gone), then non-conscious physical objects, like a fetus, couldn’t literally be a future person. 15 If this is correct, early fetuses don’t even have futures, much less futures like ours. Something would have a future, like ours, only when there is someone there to be psychologically connected to that future: that someone arrives later in pregnancy, after when most abortions occur.
A third objection is more abstract and depends on the “metaphysics” of objects. It begins with the observation that there are single objects with parts with space between them . Indeed almost every object is like this, if you could look close enough: it’s not just single dinette sets, since there is literally some space between the parts of most physical objects. From this, it follows that there seem to be single objects such as an-egg-and-the-sperm-that-would-fertilize-it . And these would also seem to have a future of value, given how Marquis describes this concept. (It should be made clear that sperm and eggs alone do not have futures of value, and Marquis does not claim they do: this is not the objection here). The problem is that contraception, even by abstinence , prevents that thing’s future of value from materializing, and so seems to be wrong when we use Marquis’s reasoning. Since contraception is not wrong, but his general premise suggests that it is , it seems that preventing something from experiencing its valuable future isn’t always wrong and so Marquis’s argument appears to be unsound. 16
In sum, these are some of the most influential arguments against abortion. Our discussion was brief, but these arguments do not appear to be successful: they do not show that abortion is wrong, much less make it clear and obvious that abortion is wrong.
Introduction: The Politics of Abortion 50 Years after Roe
Katrina Kimport is a professor with the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Sciences and a medical sociologist with the ANSIRH program at the University of California, San Francisco. Her research examines the (re)production of inequality in health and reproduction, with a topical focus on abortion, contraception, and pregnancy. She is the author of No Real Choice: How Culture and Politics Matter for Reproductive Autonomy (2022) and Queering Marriage: Challenging Family Formation in the United States (2014) and co-author, with Jennifer Earl, of Digitally Enabled Social Change (2011). She has published more than 75 articles in sociology, health research, and interdisciplinary journals.
Rebecca Kreitzer is an associate professor of public policy at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Her research focuses on gendered political representation and intersectional policy inequality in the US states. Much of her research focuses on the political dynamics of reproductive health care, especially surrounding contraception and abortion. She has published dozens of articles in political science, public policy, and law journals.
- Standard View
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
- Peer Review
- Open the PDF for in another window
- Permissions
- Cite Icon Cite
- Search Site
Katrina Kimport , Rebecca Kreitzer; Introduction: The Politics of Abortion 50 Years after Roe . J Health Polit Policy Law 1 August 2023; 48 (4): 463–484. doi: https://doi.org/10.1215/03616878-10451382
Download citation file:
- Reference Manager
Abortion is central to the American political landscape and a common pregnancy outcome, yet research on abortion has been siloed and marginalized in the social sciences. In an empirical analysis, the authors found only 22 articles published in this century in the top economics, political science, and sociology journals. This special issue aims to bring abortion research into a more generalist space, challenging what the authors term “the abortion research paradox,” wherein abortion research is largely absent from prominent disciplinary social science journals but flourishes in interdisciplinary and specialized journals. After discussing the misconceptions that likely contribute to abortion research siloization and the implications of this siloization for abortion research as well as social science knowledge more generally, the authors introduce the articles in this special issue. Then, in a call for continued and expanded research on abortion, the introduction to this special issue closes by offering three guiding practices for abortion scholars—both those new to the topic and those deeply familiar with it—in the hopes of building an ever-richer body of literature on abortion politics, policy, and law. The need for such a robust literature is especially acute following the US Supreme Court's June 2022 overturning of the constitutional right to abortion.
Abortion has been both siloed and marginalized in social science research. But because abortion is a perennially politically and socially contested issue as well as vital health care that one in four women in the United States will experience in their lifetime (Jones and Jerman 2022 ), it is imperative that social scientists make a change. This special issue brings together insightful voices from across disciplines to do just that—and does so at a particularly important historical moment. Fifty years after the United States Supreme Court's Roe v. Wade (1973) decision set a national standard amid disparate state policies on abortion, we again find ourselves in a country with a patchwork of laws about abortion. In Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization (2022), the Supreme Court overturned the constitutional right to abortion it had established in Roe , purportedly returning the question of legalization of abortion to the states. In the immediate aftermath of the Dobbs decision, state policies polarized, and public opinion shifted. This moment demands scholarly evaluation of where we have been, how we arrived at this moment, and what we should be attentive to in coming years. This special issue came about, in part, in response to the on-the-ground conditions of abortion in the United States.
As we argue below, the siloization of abortion research means that the social science literature broadly is not (yet) equipped to make sense of this moment, our history, and what the future holds. First, though, we make a case for the importance of political scientists, economists, and sociologists studying abortion. Then we describe the siloization of abortion research through what we call the “abortion research paradox,” wherein abortion research—despite its social and political import—is curiously absent from top disciplinary journals, even as it thrives in other publication venues that are often interdisciplinary and usually specialized. We theorize some reasons for this siloization and discuss the consequences, both for generalist knowledge and for scientific understanding of abortion. We then introduce the articles in this special issue, noting the breadth of methodological, topical, and theoretical approaches to abortion research they demonstrate. Finally, we offer three suggestions for scholars—both those new to abortion research and those already deeply familiar with it—embarking on abortion research in the hopes of building an ever-richer body of literature on abortion politics, policy, and law.
- Why Abortion?
Abortion has arguably shaped the American political landscape more than any other domestic policy issue in the last 50 years. Since the Supreme Court initially established a nationwide right to abortion in Roe v. Wade (1973), debate over this right has influenced elections at just about every level of office (Abramowitz 1995 ; Cook, Hartwig, and Wilcox 1993 ; Cook, Jelen, and Wilcox 1994 ; Cook, Jelen, and Wilcox 1992 ; Paolino 1995 ; Roh and Haider-Markel 2003 ), inspired political activism (Carmines and Woods 2002 ; Killian and Wilcox 2008 ; Maxwell 2002 ; Verba, Schlozman, and Brady 1995 ) and social movements (Kretschmer 2014 ; Meyer and Staggenborg 1996 , 2008 ; Munson 2010a , Munson 2010b ; Rohlinger 2006 ; Staggenborg 1991 ), and fundamentally structured partisan politics (Adams 1997; Carsey and Layman 2006 ; Killian and Wilcox 2008 ). Position on abortion is frequently used as the litmus test for those seeking political office (Flaten 2010 ; Kreitzer and Osborn 2019 ). Opponents to legal abortion have transformed the federal judiciary (Hollis-Brusky and Parry 2021 ; Hollis-Brusky and Wilson 2020 ). Indeed, abortion is often called the quintessential “morality policy” issue (Kreitzer 2015 ; Kreitzer, Kane, and Mooney 2019 ; Mooney 2001 ; Mucciaroni, Ferraiolo, and Rubado 2019 ) and “ground zero” in the prominent culture wars that have polarized Americans (Adams 1997 ; Lewis 2017 ; Mouw and Sobel 2001 ; Wilson 2013 ). Almost fifty years after Roe v. Wade , in June 2022, the US Supreme Court overturned the constitutional right to abortion in its Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization decision, ushering in a new chapter of political engagement on abortion.
But abortion is not simply an abstract political issue; it is an extremely common pregnancy outcome. Indeed, as noted above, about one in four US women will get an abortion in her lifetime (Jones and Jerman 2022 ), although the rates of unintended pregnancy and abortion vary substantially across racial and socioeconomic groups (Dehlendorf, Harris, and Weitz 2013 ; Jones and Jerman 2022 ). Despite rampant misinformation claiming otherwise, abortion is a safe procedure (Raymond and Grimes 2012 ; Upadhyay et al. 2015 ), reduces physical health consequences and mortality (Gerdts et al. 2016 ), and does not cause mental health issues (Charles et al. 2008 ; Major et al. 2009 ) or regret (Rocca et al. 2013 , 2015 , 2020 ). Abortion also has a significant impact on people's lives beyond health outcomes. Legal abortion is associated with educational attainment (Everett et al. 2019 ; Ralph et al. 2019 ; Mølland 2016 ) as well as higher female labor force participation, and it affects men's and women's long-term earning potential (Bernstein and Jones 2019 ; Bloom et al. 2009 ; Everett et al. 2019 ; Kalist 2004 ). Access to abortion also shapes relationship satisfaction and stability (Biggs et al. 2014 ; Mauldon, Foster, and Roberts 2015 ). The preponderance of evidence, in other words, demonstrates substantial benefits and no harms to allowing pregnant people to choose abortion.
Yet access to abortion in the United States has been rapidly declining for years. Most abortion care in the United States takes place in stand-alone outpatient facilities that primarily provide reproductive health care (Jones, Witwer, and Jerman 2019 ). As antiabortion legislators in some states have advanced policies that target these facilities, the number of abortion clinics has decreased (Gerdts et al. 2022 ; Venator and Fletcher 2021 ), leaving large geographical areas lacking an abortion facility (Cartwright et al. 2018 ; Cohen and Joffe 2020 ) and thus diminishing pregnant people's ability to obtain abortion care when and where they need it.
The effects of policies regulating abortion, including those that target facilities, have been unevenly experienced, with people of color (Jones and Jerman 2022 ), people in rural areas (Bearak, Burke, and Jones 2017 ), and those who are financially struggling (Cook et al. 1999 ; Roberts et al. 2019 ) disproportionately affected. Even before the Dobbs decision overturned the constitutional right to abortion, the American landscape was characterized by ever-broadening contraception deserts (Axelson, Sealy, and McDonald-Mosley 2022 ; Barber et al. 2019 ; Kreitzer et al. 2021 ; Smith et al. 2022 ), maternity care deserts (Simpson 2020 ; Taporco et al. 2021 ; Wallace et al. 2021 ), and abortion deserts (Cartwright et al. 2018 ; Cohen and Joffe 2020 ; Engle and Freeman 2022 ; McNamara et al. 2022 ; Pleasants, Cartwright, and Upadhyay 2022 ). After Dobbs , access to abortion around the country changed in a matter of weeks. In the 100 days after Roe was overturned, at least 66 clinics closed in 15 states, with 14 of those states no longer having any abortion facilities (Kirstein et al. 2022 ). In this moment of heightened contention about an issue with a long history of social and political contestation, social scientists have a rich opportunity to contribute to scientific knowledge as well as policy and practice that affect millions of lives. This special issue steps into that opportunity.
- The Abortion Research Paradox
This special issue is also motivated by what we call the abortion research paradox. As established above, abortion fundamentally shapes politics in a myriad of ways and is a very common pregnancy outcome, with research consistently demonstrating that access to abortion is consequential and beneficial to people's lives. However, social science research on abortion is rarely published in top disciplinary journals. Abortion is a topic of clear social science interest and is well suited for social science inquiry, but it is relatively underrepresented as a topic in generalist social science journals. To measure this underrepresentation empirically, we searched for original research articles about abortion in the United Sates in the top journals of political science, sociology, and economics. We identified the top three journals for each discipline by considering journal reputation within their respective discipline as well as impact factors and Google Scholar rankings. (There is room for debate about what makes a journal a “top” general interest journal, but that is beyond our scope. Whether these journals are exactly the top three is debatable; nonetheless, these are undoubtedly among the top general-interest or “flagship” disciplinary journals and thus representative of what the respective disciplines value as top scholarship.) Then we searched specified journal databases for the keyword “abortion” for articles published in this century (i.e., 2000–2021), excluding commentaries and book reviews. We found few articles about abortion: just seven in economics journals, eight in political science journals, and seven in sociology journals. We read the articles and classified each into one of three categories: articles primarily about abortion; articles about more than one aspect of reproductive health, inclusive of abortion; or articles about several policy issues, among which abortion is one ( table 1 ).
In the three top economics journals, articles about abortion focused on the relationships between abortion and crime or educational attainment, or on the impact of abortion policies on trends in the timing of first births of women (Bitler and Zavodny 2002 ; Donohue III and Levitt 2001 ; Myers 2017 ). Articles that studied abortion as one among several topics also studied “morally controversial” issues (Elías et al. 2017 ), the electoral implications of abortion (Glaeser, Ponzetto, and Shapiro 2005 ; Washington 2008 ), or contraception (Bailey 2010 ). Articles published in the three top political science journals that focused primarily on abortion evaluated judicial decision-making and legitimacy (Caldarone, Canes-Wrone, and Clark 2009 ; Zink, Spriggs, and Scott 2009 ) or public opinion (Kalla, Levine, and Broockman 2022 ; Rosenfeld, Imai, and Shapiro 2016 ). More commonly, abortion was one of several (or many) different issues analyzed, including government spending and provision of services, government help for African Americans, law enforcement, health care, education, free speech, Hatch Act restrictions, and the Clinton impeachment. The degree to which these articles are “about abortion” varies considerably. In the three top sociology journals, articles represented a slightly broader range of topics, including policy diffusion (Boyle, Kim, and Longhofer 2015 ), public opinion (Mouw and Sobel 2001 ), social movements (Ferree 2003 ), and crisis pregnancy centers (McVeigh, Crubaugh, and Estep 2017 ). Unlike in economics and political science, articles in sociology on abortion mostly focused directly on abortion.
The Journal of Health Politics, Policy and Law ( JHPPL ) would seem well positioned to publish research on abortion. Yet, even in JHPPL , abortion research is not very common. In the same time period (2000–2021), JHPPL published five articles on reproductive health: two articles on abortion (Daniels et al. 2016 ; Kimport, Johns, and Upadhyay 2018 ), one on contraception (Kreitzer et al. 2021 ), one on forced interventions on pregnant people (Paltrow and Flavin 2013 ), and one about how states could respond to the passage of the Affordable Care Act mandate regarding reproductive health (Stulberg 2013 ).
This is not to say that there is no extensive, rigorous published research on abortion in the social science literature. Interdisciplinary journals that are focused on reproductive health, such as Contraception and Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health , as well as health research journals, such as the American Journal of Public Health and Social Science & Medicine , regularly published high-quality social science research on abortion during the focal time period. Research on abortion can also be found in disciplinary subfield journals. In the same time period addressed above, the Journal of Women, Politics, and Public Policy and Politics & Gender— two subfield journals focused on gender and politics—each published around 20 articles that mentioned abortion in the abstract. In practice, while this means excellent research on abortion is published, the net effect is that abortion research is siloed from other research areas in the disciplines of economics, political science, and sociology. This special issue aims to redress some of this siloization and to inspire future scholarship on abortion. Our motivation is not simply premised on quantitative counts, however. As we assert below, abortion research siloization has significant consequences for knowledge—and especially for real people's lives. First, though, we consider some of the possible reasons for this siloization.
- The Origins of Siloization
We do not know why abortion research is not more commonly published in top disciplinary journals, given the topic's clear importance in key areas of focus for these disciplines, including public discourse, politics, law, family life, and health. The siloing and marginalization of abortion is likely related to several misconceptions. For one, because of social contention on the issue, peer reviewers may not have a deep understanding of abortion as a research topic, may express hostility to the topic, or may believe that abortion is exceptional in some way—a niche or ungeneralizable research topic better published in a subfield journal. Scholars themselves may share this mischaracterization of abortion. As Borgman ( 2014 ) argues about the legal arena, and as Roberts, Schroeder, and Joffe ( 2020 ) provide evidence of in medicine, abortion is regularly treated as exceptional, making it both definitional and reasonable that abortion be treated differently in the law and in health care from other medical experiences. Scholars are not immune to social patterns that exceptionalize abortion. In their peer and editor reviews, they may inappropriately—and perhaps inadvertently—draw on their social, rather than academic, knowledge. For scholars of abortion, reviews premised on social knowledge may not be constructive to strengthening the research, and additional labor may be required to educate reviewers and editors on the academic parameters of the topic, including which social assumptions about abortion are scientifically inaccurate. Comments from authors educating editors and peer reviewers on abortion research may then counterintuitively reinforce the (mis)perception that abortion research is niche and not of general interest.
Second, authors' negative experiences while trying to publish about abortion or reproductive health in top disciplinary journals may compound as scholars share information about journals. This is the case for research on gender; evidence from political science suggests that certain journals are perceived as more or less likely to publish research on gender (Brown et al. 2020 ). Such reputations, especially for venues that do not publish abortion research, may not even be rooted in negative experiences. The absence of published articles on abortion may itself dissuade scholars from submitting to a journal based on an educated guess that the journal does not welcome abortion research. Regardless of the veracity of these perceptions, certain journals may get a reputation for publishing on abortion (or not), which then may make future submissions of abortion research to those outlets more (or less) likely. After all, authors seek publication venues where they believe their research will get a robust review and is likely to be published. This pattern may be more common for some author groups than others. Research from political science suggests women are more risk averse than men when it comes to publishing strategies and less likely to submit manuscripts to journals where the perceived likelihood of successful publication is lower (Key and Sumner 2019 ). Special issues like this one are an important way for journals without a substantial track record of publishing abortion research to establish their willingness to do so.
Third, there might be a methodological bias, which unevenly intersects with some author groups. Top disciplinary journals are more likely to publish quantitative approaches rather than qualitative ones, which can result in the exclusion of women and minority scholars who are more likely to utilize mixed or qualitative methods (Teele and Thelen 2017 ). To the extent that investigations of abortion in the social sciences have utilized qualitative rather than quantitative methods, that might contribute to the underrepresentation of abortion-focused scholarship in top disciplinary journals.
Stepping back from the idiosyncrasies of peer review and methodologies, a fourth explanation for why abortion research is not more prominent in generalist social science journals may arise far earlier than the publishing process. PhD-granting departments in the social sciences may have an undersupply of scholars with expertise in reproductive health who can mentor junior scholars interested in studying abortion. (We firmly believe one need not be an expert in reproductive health to mentor junior scholars studying reproductive health, so this explanation only goes so far.) Anecdotally, we have experienced and heard many accounts of scholars who were discouraged from focusing on abortion in dissertation research because of advisors', mentors', and senior scholars' misconceptions about the topic and about the viability of a career in abortion research. In data provided to us by Key and Sumner from their analysis of the “leaky pipeline” in the publication of research on gender at top disciplinary journals in political science (Key and Sumner 2019 ), there were only nine dissertations written between 2000 and 2013 that mention abortion in the abstract, most of which are focused on judicial behavior or political party dynamics rather than focusing on abortion policy itself. If few junior scholars focus on abortion, it makes sense there may be an undersupply of cutting-edge social science research on abortion submitted to top disciplinary journals.
- The Implications of Siloization
The relative lack of scholarly attention to abortion as a social phenomenon in generalist journals has implications for general scholarship. Most concerningly, it limits our ability to understand other social phenomena for which the case of abortion is a useful entry point. For example, the case of abortion as a common, highly safe medical procedure is useful for examining medical innovations and technologies, such as telemedicine. Similarly, given the disparities in who seeks and obtains abortion care in the United States, abortion is an excellent case study for scholars interested in race, class, and gender inequality. It also holds great potential as an opportunity for exploration of public opinion and attitudes, particularly as a case of an issue whose ties to partisan politics have solidified over time and that is often—but not always—“moralized” in policy engagement (Kreitzer, Kane, and Mooney 2019 ). Additionally, there are missed opportunities to generate theory from the specifics of abortion. For example, there is ample evidence of abortion stigma and stigmatization (Hanschmidt et al. 2016 ) and of their effects on people who obtain abortions (Sorhaindo and Lavelanet 2022 ). This research is often unmoored from existing theorization on stigmatization, however, because the bulk of the stigma literature focuses on identities; and having had an abortion is not an identity the same way as, for example, being queer is. (For a notable exception to this trend, see Beynon-Jones 2017 .)
There is, it must be noted, at least one benefit of abortion research being regularly siloed within social science disciplines. The small but growing number of researchers engaged in abortion research has often had to seek mentorship and collaborations outside their disciplines. Indeed, several of the articles included in this special issue come from multidisciplinary author teams, building bridges between disciplinary literatures and pushing knowledge forward. Social scientists studying abortion regularly engage with research by clinicians and clinician-researchers, which is somewhat rare in the academy. The interdisciplinary journals noted above that regularly publish social science abortion research ( Contraception and Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health ) also regularly publish clinical articles and are read by advocates and policy makers. In other words, social scientists studying abortion frequently reach audiences that include clinicians, advocates, and policy makers, marking an opportunity for social science research to influence practice.
The siloization of abortion research in the social sciences affects more than broad social science knowledge; it also dramatically shapes our understanding of abortion. When abortion researchers are largely relegated to their own spaces, they risk missing opportunities to learn from other areas of scholarship that are not related to abortion. Lacking context from other topics, abortion scholars may inaccurately understand an aspect of abortion as exceptional that is not, or they may reinvent the proverbial theoretical wheel to describe an abortion-related phenomenon that is not actually unique to abortion. For example, scholars have studied criminalized behavior for decades, offering theoretical insights and methodological best practices for research on illegal activities. With abortion now illegal in many states, abortion researchers can benefit from drawing on that extant literature to examine the implications of illegality, identifying which aspects of abortion illegality are unique and which are common to other illegal activities. Likewise, methodologically, abortion researchers can learn from other researchers of illegal activities about how to protect participants' confidentiality.
The ontological and epistemological implications for the siloization of abortion research extend beyond reproductive health. When abortion research is not part of the central discussions in economics, political science, and sociology, our understanding of health policy, politics, and law is impoverished. We thus miss opportunities to identify and address chronic health disparities and health inequities, with both conceptual and practical consequences. These oversights matter for people's lives. Following the June 2022 Dobbs decision, millions of people with the capacity of pregnancy are now barred from one key way to control fertility: abortion. The implications of scholars' failure to comprehensively grapple with the place of abortion in health policy, politics, and law are playing out in those people's lives and the lives of their loved ones.
Articles in this Special Issue
In this landscape, we offer this special issue on “The Politics of Abortion 50 Years After Roe .” We seek in this issue to illustrate some of the many ways abortion can and should be studied, with benefits not only for scholarly knowledge about abortion and its role in policy, politics, and law but also for general knowledge about health policy, politics, and law themselves.
The issue's articles represent multiple disciplines, including several articles by multidisciplinary teams. Although public health has long been a welcoming home for abortion research, authors in this special issue point to opportunities in anthropology, sociology, and political science, among other disciplines, for the study of abortion. We do not see the differences and variations among disciplinary approaches as a competition. Rather, we believe that the more diverse the body of researchers grappling with questions about abortion, abortion provision, and abortion patients, the better our collective knowledge about abortion and its role in the social landscape.
The same goes for diversity of methodological approaches. Authors in this issue employ qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods, showcasing compelling methodological variation. There is no singular or best methodology for answering research questions about abortion. Instead, the impressive variation in methodological approaches in this special issue highlights the vast methodological opportunities for future research. A diversity of methodologies enables a diversity of research questions. Indeed, different methods can identify, generate, and respond to different research questions, enriching the literature on abortion. The methodologies represented in this issue are certainly not exhaustive, but we believe they are suggestive of future opportunities for scholarly exploration and investigation. We hope these articles will provide a road map for rich expansions of the research literature on abortion.
By way of brief introduction, we offer short summaries of the included articles. Baker traces the history of medication abortion in the United States, cataloging the initial approval of the two-part regimen by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), subsequent policy debates over FDA-imposed restrictions on how medication abortion is dispensed, and the work of abortion access advocates to get medication abortion to people who need it. Weaving together accounts of health care policy, abortion advocacy, and on-the-ground activism, Baker illustrates both the unique contentions specific to abortion policy and how the history of medication abortion can be seen as a case of health care advocacy.
Two of the issue's articles focus on state-level legislative policy on abortion. Roth and Lee generate an original data set cataloging the introduction and implementation of statutes on abortion and other aspects of reproductive health at the state level in the United States monthly, from 1994 to 2022. In their descriptive analysis, the authors highlight trends in abortion legislation and the emergent pattern of state polarization around abortion. Their examination adds rich longitudinal context to contemporary analyses of reproductive health legislation, providing a valuable resource for future scholarship. Carson and Carter similarly attend to state-level legislation, zeroing in on the case of abortion policy in response to the COVID-19 pandemic to show how legislation unrelated to abortion has been opportunistically used to restrict abortion access. The authors also examine how abortion is discursively constructed as a risk to public health. This latter move, they argue, builds on previous constructions of abortion as a risk to individual health and points to a new horizon of antiabortion constructions of the meaning of abortion access.
Kim et al. and Kumar examine the implementation of US abortion policies. Kim et al. use an original data set of 20 years of state supreme court decisions to investigate factors that affect state supreme court decision-making on abortion. Their regression analysis uncovers the complex relationship between state legislatures, state supreme courts, and the voting public for the case of abortion. Kumar charts how 50 years of US abortion policy have affected global access to abortion, offering insights into the underexamined international implications of US abortion policy and into social movement advocacy that has expanded abortion access around the world.
Karlin and Joffe and Heymann et al. draw on data collected when Roe was still the law of the land to investigate phenomena that are likely to become far more common now that Roe has been overturned. Karlin and Joffe utilize interviews with 40 physicians who provide abortions to examine their perspectives on people who terminate their pregnancies outside the formal health care system—an abortion pathway whose popularity increases when abortion access constricts (Aiken et al. 2022 ). By contextualizing their findings on the contradictions physicians voiced—desiring to support reproductive autonomy but invested in physician authority—in a historical overview of how mainstream medicine has marginalized abortion provision since the early days after Roe , the authors add nuance to understandings of the “formal health care system,” its members, and the stakes faced by people bypassing this system to obtain their desired health outcome. Heymann et al. investigate a process also likely to increase in the wake of the Dobbs decision: the implementation of restrictive state-level abortion policy by unelected bureaucrats. Using the case of variances for a written transfer agreement requirement in Ohio—a requirement with no medical merit that is designed to add administrative burden to stand-alone abortion clinics—Heymann et al. demonstrate how bureaucratic discretion by political appointees can increase the administrative burden of restrictive abortion laws and thus further constrain abortion access. Together, these two articles demonstrate how pre- Roe data can point scholars to areas that merit investigation after Roe has been overturned.
Finally, using mixed methods, Buyuker et al. analyze attitudes about abortion acceptability and the Roe v. Wade Supreme Court decision, distinguishing what people think about abortion from what they know about abortion policy. In addition to providing methodological insights about survey items related to abortion attitudes, the authors expose a disconnect between how people think about abortion acceptability and their support for the Roe decision. In other words, as polarized as abortion attitudes are said to be, there is unacknowledged and largely unmeasured complexity in how the general public thinks about abortion.

Future Research on Abortion
We hope that a desire to engage in abortion research prompts scholars to read the excellent articles in this special issue. We also hope that reading these pieces inspires at least some readers to engage in abortion research. Having researched abortion for nearly three decades between us, we are delighted by the emerging interest in studying abortion, whether as a focal topic or alongside a different focus. This research is essential to our collective understanding of abortion politics, policy, and law and the many millions of people whose lives are affected by US abortion politics, policy, and law annually. In light of the limitations of the current field of abortion research, we have several suggestions for scholars of abortion, regardless of their level of familiarity with the topic.
First, know and cite the existing literature on abortion. To address the siloization of abortion research, and particularly the scarcity of abortion research published in generalist journals, scholars must be sure to build on the impressive work that has been published on the topic in specialized spaces. Moreover, becoming familiar with existing research can help scholars avoid several common pitfalls in abortion research. For example, being immersed in existing literature can help scholars avoid outdated, imprecise, or inappropriate language and terminology. Smith et al. ( 2018 ), for instance, illuminate the implications of clinicians deploying seemingly everday language around “elective” abortion. They find that it muddies the distinction between the use of “elective” colloquially and in clinical settings, contributing to the stigmatization of abortion and abortion patients. Examinations like theirs advance understanding of abortion stigmatization while highlighting for scholars the importance of being sensitive to and reflective about language. Familiarity with existing research can help scholars avoid methodological pitfalls as well, such as incomplete understanding of the organization of abortion provision. Although Planned Parenthood has brand recognition for providing abortion care, the majority of abortions in the United States are performed at independent abortion clinics. Misunderstanding the provision landscape can have consequences for some study designs.
Second, we encourage scholars of abortion to think critically about the ideological underpinnings of how their research questions and findings are framed. Academic research of all kinds, including abortion, is better when it is critical of ideologically informed premises. Abortion scholars must be careful to avoid uncritically accepting both antiabortion premises and abortion-supportive premises, especially as those premises unconsciously guide much of the public discourse on abortion. Scholars have the opportunity to use methodological tools not to find an objective truth per se but to challenge the uncontested common sense claims that frequently guide public thinking on abortion. One strategy for avoiding common framing pitfalls is to construct research and analysis to center the people most affected by abortion politics, policy, and law (Kimport and McLemore 2022 ). Another strategy is to critique what Baird and Millar ( 2019 , 2020 ) have termed the performative nature of abortion scholarship. Abortion scholarship, they note, has predominantly focused on negative aspects and effects of abortion care. Research that finds and explores affirmatively positive aspects—for instance, the joy in abortion—can crucially thicken scholarly understanding.
Third, related to our discussion above, scholars of abortion face an interesting challenge regarding how abortion is and is not exceptional. Research on abortion must attend to how abortion has been exceptionalized—and marginalized—in policy and practices. But there are also numerous instances where abortion is only one example of many. In these cases, investigation of abortion under the assumption that it is exceptional is an unnecessary limitation on the work's contribution. Scholars of abortion benefit from mastery of the literature on abortion, yet knowing this literature is not sufficient. There are important bridges from scholarship on abortion to scholarship in other areas, important conversations across and within literatures, that can yield insights both about abortion and about other topical foci.
As guest coeditors of this special issue, we are delighted by the rich and growing body of scholarship on abortion, to which the articles in this special issue represent an important addition. There is still much more work to be done. Going forward, we are eager to see future scholarship on abortion build on this work and tackle new questions.
- Acknowledgments
The authors thank Krystale Littlejohn, Jon Oberlander, Ellen Key, and Jane Sumner for their helpful feedback on earlier drafts of this article. Both authors contributed equally to this article and are listed alphabetically.

- Previous Issue
- Next Article
Advertisement
Data & Figures
Number of Articles about Abortion in Top Disciplinary Journals, 2000–2021
Note : AER = American Economic Review ; QJE = Quarterly Journal of Economics ; JPE = Journal of Political Economy ; APSR = American Political Science Review ; AJPS = American Journal of Political Science ; JOP = Journal of Politics ; ASR = American Sociological Review ; AJS = American Journal of Sociology ; ARS = Annual Review of Sociology.
Supplements
Citing articles via, email alerts, related articles, related book chapters, related topics, affiliations.
- About Journal of Health Politics, Policy and Law
- Editorial Board
- For Authors
- Rights and Permissions Inquiry
- Online ISSN 1527-1927
- Print ISSN 0361-6878
- Copyright © 2024 Duke University Press
- Duke University Press
- 905 W. Main St. Ste. 18-B
- Durham, NC 27701
- (888) 651-0122
- International
- +1 (919) 688-5134
- Information For
- Advertisers
- Book Authors
- Booksellers/Media
- Journal Authors/Editors
- Journal Subscribers
- Prospective Journals
- Licensing and Subsidiary Rights
- View Open Positions
- email Join our Mailing List
- catalog Current Catalog
- Accessibility
- Get Adobe Reader
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Abortion — Argumentative Essay Outline On Abortion
Argumentative Essay Outline on Abortion
- Categories: Abortion
About this sample

Words: 665 |
Published: Mar 13, 2024
Words: 665 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, thesis statement, paragraph 1: the right to bodily autonomy, paragraph 2: the health and safety of women, paragraph 3: reproductive freedom and economic justice.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1067 words
4 pages / 1770 words
2 pages / 728 words
1 pages / 584 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Abortion
Abortion is a highly controversial topic that has sparked intense debate and divided public opinion for decades. While some argue that it is a woman's right to choose, others believe that it is morally and ethically wrong. In [...]
Medically ending a pregnancy before it has the chance to result in the birth of a baby is abortion (Izugbara, Otsola, & Ezeh, 2009). Abortion is yet to be legalized in Kenya due to pro-life and pro-choice squabbles. Pro-life [...]
The debate surrounding abortion has long been a contentious and deeply divided issue in society. This essay will provide an argumentative analysis of the pros and cons of abortion to society, addressing both the ethical and [...]
Abortion has been a subject of intense debate and controversy, with impassioned arguments from both sides. However, amidst the fervent discourse, it is crucial to recognize the multifaceted impact of legalizing abortion. The [...]
Abortion has been a major conflict in society. It puts a tremendous amount of pressure on women who are debating whether to change their lives dramatically by having a baby. Abortion terminates fetuses in the womb and that is [...]
Throughout the United States, there are many life issues, such as euthanasia, capital punishment, economic rights, war and the list goes on and on. But one of the biggest issue is abortion. There tends to be a rift between [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Persuasive Essay Guide
Persuasive Essay About Abortion
Crafting a Convincing Persuasive Essay About Abortion
-9248.jpg&w=640&q=75)
People also read
A Comprehensive Guide to Writing an Effective Persuasive Essay
200+ Persuasive Essay Topics to Help You Out
Learn How to Create a Persuasive Essay Outline
30+ Free Persuasive Essay Examples To Get You Started
Read Excellent Examples of Persuasive Essay About Gun Control
How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid19 | Examples & Tips
Learn to Write Persuasive Essay About Business With Examples and Tips
Check Out 12 Persuasive Essay About Online Education Examples
Persuasive Essay About Smoking - Making a Powerful Argument with Examples
Are you about to write a persuasive essay on abortion but wondering how to begin?
Writing an effective persuasive essay on the topic of abortion can be a difficult task for many students.
It is important to understand both sides of the issue and form an argument based on facts and logical reasoning. This requires research and understanding, which takes time and effort.
In this blog, we will provide you with some easy steps to craft a persuasive essay about abortion that is compelling and convincing. Moreover, we have included some example essays and interesting facts to read and get inspired by.
So let's start!
- 1. How To Write a Persuasive Essay About Abortion?
- 2. Persuasive Essay About Abortion Examples
- 3. Examples of Argumentative Essay About Abortion
- 4. Abortion Persuasive Essay Topics
- 5. Facts About Abortion You Need to Know
How To Write a Persuasive Essay About Abortion?
Abortion is a controversial topic, with people having differing points of view and opinions on the matter. There are those who oppose abortion, while some people endorse pro-choice arguments.
It is also an emotionally charged subject, so you need to be extra careful when crafting your persuasive essay .
Before you start writing your persuasive essay, you need to understand the following steps.
Step 1: Choose Your Position
The first step to writing a persuasive essay on abortion is to decide your position. Do you support the practice or are you against it? You need to make sure that you have a clear opinion before you begin writing.
Once you have decided, research and find evidence that supports your position. This will help strengthen your argument.
Check out the video below to get more insights into this topic:
Step 2: Choose Your Audience
The next step is to decide who your audience will be. Will you write for pro-life or pro-choice individuals? Or both?
Knowing who you are writing for will guide your writing and help you include the most relevant facts and information.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Step 3: Define Your Argument
Now that you have chosen your position and audience, it is time to craft your argument.
Start by defining what you believe and why, making sure to use evidence to support your claims. You also need to consider the opposing arguments and come up with counter arguments. This helps make your essay more balanced and convincing.
Step 4: Format Your Essay
Once you have the argument ready, it is time to craft your persuasive essay. Follow a standard format for the essay, with an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
Make sure that each paragraph is organized and flows smoothly. Use clear and concise language, getting straight to the point.
Step 5: Proofread and Edit
The last step in writing your persuasive essay is to make sure that you proofread and edit it carefully. Look for spelling, grammar, punctuation, or factual errors and correct them. This will help make your essay more professional and convincing.
These are the steps you need to follow when writing a persuasive essay on abortion. It is a good idea to read some examples before you start so you can know how they should be written.
Continue reading to find helpful examples.
Persuasive Essay About Abortion Examples
To help you get started, here are some example persuasive essays on abortion that may be useful for your own paper.
Short Persuasive Essay About Abortion
Persuasive Essay About No To Abortion
What Is Abortion? - Essay Example
Persuasive Speech on Abortion
Legal Abortion Persuasive Essay
Persuasive Essay About Abortion in the Philippines
Persuasive Essay about legalizing abortion
You can also read m ore persuasive essay examples to imp rove your persuasive skills.
Examples of Argumentative Essay About Abortion
An argumentative essay is a type of essay that presents both sides of an argument. These essays rely heavily on logic and evidence.
Here are some examples of argumentative essay with introduction, body and conclusion that you can use as a reference in writing your own argumentative essay.
Abortion Persuasive Essay Introduction
Argumentative Essay About Abortion Conclusion
Argumentative Essay About Abortion Pdf
Argumentative Essay About Abortion in the Philippines
Argumentative Essay About Abortion - Introduction
Abortion Persuasive Essay Topics
If you are looking for some topics to write your persuasive essay on abortion, here are some examples:
- Should abortion be legal in the United States?
- Is it ethical to perform abortions, considering its pros and cons?
- What should be done to reduce the number of unwanted pregnancies that lead to abortions?
- Is there a connection between abortion and psychological trauma?
- What are the ethical implications of abortion on demand?
- How has the debate over abortion changed over time?
- Should there be legal restrictions on late-term abortions?
- Does gender play a role in how people view abortion rights?
- Is it possible to reduce poverty and unwanted pregnancies through better sex education?
- How is the anti-abortion point of view affected by religious beliefs and values?
These are just some of the potential topics that you can use for your persuasive essay on abortion. Think carefully about the topic you want to write about and make sure it is something that interests you.
Check out m ore persuasive essay topics that will help you explore other things that you can write about!
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Facts About Abortion You Need to Know
Here are some facts about abortion that will help you formulate better arguments.
- According to the Guttmacher Institute , 1 in 4 pregnancies end in abortion.
- The majority of abortions are performed in the first trimester.
- Abortion is one of the safest medical procedures, with less than a 0.5% risk of major complications.
- In the United States, 14 states have laws that restrict or ban most forms of abortion after 20 weeks gestation.
- Seven out of 198 nations allow elective abortions after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- In places where abortion is illegal, more women die during childbirth and due to complications resulting from pregnancy.
- A majority of pregnant women who opt for abortions do so for financial and social reasons.
- According to estimates, 56 million abortions occur annually.
In conclusion, these are some of the examples, steps, and topics that you can use to write a persuasive essay. Make sure to do your research thoroughly and back up your arguments with evidence. This will make your essay more professional and convincing.
Need the services of a professional essay writing service ? We've got your back!
MyPerfectWords.com is a persuasive essay writing service that provides help to students in the form of professionally written essays. Our persuasive essay writer can craft quality persuasive essays on any topic, including abortion.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should i talk about in an essay about abortion.
When writing an essay about abortion, it is important to cover all the aspects of the subject. This includes discussing both sides of the argument, providing facts and evidence to support your claims, and exploring potential solutions.
What is a good argument for abortion?
A good argument for abortion could be that it is a woman’s choice to choose whether or not to have an abortion. It is also important to consider the potential risks of carrying a pregnancy to term.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


PHI 240: Ethics of Fetal Development & Abortion (Daniels)
- Start here!
- Search for More
Bertha Alvarez Manninen
Donald marquis, judith jarvis thomson, mary anne warren, essay: the value of choice and the choice to value: expanding the discussion about fetal life within prochoice advocacy.
Essay: Why Abortion is Immoral
Essay: a defense of abortion.
Essay: On the Moral and Legal Status of Abortion
- << Previous: Search for More
- Next: Help >>
- Last Updated: Feb 14, 2024 4:33 PM
- URL: https://libguides.pittcc.edu/phi240
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Rom J Morphol Embryol
- v.61(1); Jan-Mar 2020

A research on abortion: ethics, legislation and socio-medical outcomes. Case study: Romania
Andreea mihaela niţă.
1 Faculty of Social Sciences, University of Craiova, Romania
Cristina Ilie Goga
This article presents a research study on abortion from a theoretical and empirical point of view. The theoretical part is based on the method of social documents analysis, and presents a complex perspective on abortion, highlighting items of medical, ethical, moral, religious, social, economic and legal elements. The empirical part presents the results of a sociological survey, based on the opinion survey method through the application of the enquiry technique, conducted in Romania, on a sample of 1260 women. The purpose of the survey is to identify Romanians perception on the decision to voluntary interrupt pregnancy, and to determine the core reasons in carrying out an abortion.
The analysis of abortion by means of medical and social documents
Abortion means a pregnancy interruption “before the fetus is viable” [ 1 ] or “before the fetus is able to live independently in the extrauterine environment, usually before the 20 th week of pregnancy” [ 2 ]. “Clinical miscarriage is both a common and distressing complication of early pregnancy with many etiological factors like genetic factors, immune factors, infection factors but also psychological factors” [ 3 ]. Induced abortion is a practice found in all countries, but the decision to interrupt the pregnancy involves a multitude of aspects of medical, ethical, moral, religious, social, economic, and legal order.
In a more simplistic manner, Winston Nagan has classified opinions which have as central element “abortion”, in two major categories: the opinion that the priority element is represented by fetus and his entitlement to life and the second opinion, which focuses around women’s rights [ 4 ].
From the medical point of view, since ancient times there have been four moments, generally accepted, which determine the embryo’s life: ( i ) conception; ( ii ) period of formation; ( iii ) detection moment of fetal movement; ( iv ) time of birth [ 5 ]. Contemporary medicine found the following moments in the evolution of intrauterine fetal: “ 1 . At 18 days of pregnancy, the fetal heartbeat can be perceived and it starts running the circulatory system; 2 . At 5 weeks, they become more clear: the nose, cheeks and fingers of the fetus; 3 . At 6 weeks, they start to function: the nervous system, stomach, kidneys and liver of the fetus, and its skeleton is clearly distinguished; 4 . At 7 weeks (50 days), brain waves are felt. The fetus has all the internal and external organs definitively outlined. 5 . At 10 weeks (70 days), the unborn child has all the features clearly defined as a child after birth (9 months); 6 . At 12 weeks (92 days, 3 months), the fetus has all organs definitely shaped, managing to move, lacking only the breath” [ 6 ]. Even if most of the laws that allow abortion consider the period up to 12 weeks acceptable for such an intervention, according to the above-mentioned steps, there can be defined different moments, which can represent the beginning of life. Nowadays, “abortion is one of the most common gynecological experiences and perhaps the majority of women will undergo an abortion in their lifetimes” [ 7 ]. “Safe abortions carry few health risks, but « every year, close to 20 million women risk their lives and health by undergoing unsafe abortions » and 25% will face a complication with permanent consequences” [ 8 , 9 ].
From the ethical point of view, most of the times, the interruption of pregnancy is on the border between woman’s right over her own body and the child’s (fetus) entitlement to life. Judith Jarvis Thomson supported the supremacy of woman’s right over her own body as a premise of freedom, arguing that we cannot force a person to bear in her womb and give birth to an unwanted child, if for different circumstances, she does not want to do this [ 10 ]. To support his position, the author uses an imaginary experiment, that of a violinist to which we are connected for nine months, in order to save his life. However, Thomson debates the problem of the differentiation between the fetus and the human being, by carrying out a debate on the timing which makes this difference (period of conception, 10 weeks of pregnancy, etc.) and highlighting that for people who support abortion, the fetus is not an alive human being [ 10 ].
Carol Gilligan noted that women undergo a true “moral dilemma”, a “moral conflict” with regards to voluntary interruption of pregnancy, such a decision often takes into account the human relationships, the possibility of not hurting the others, the responsibility towards others [ 11 ]. Gilligan applied qualitative interviews to a number of 29 women from different social classes, which were put in a position to decide whether or not to commit abortion. The interview focused on the woman’s choice, on alternative options, on individuals and existing conflicts. The conclusion was that the central moral issue was the conflict between the self (the pregnant woman) and others who may be hurt as a result of the potential pregnancy [ 12 ].
From the religious point of view, abortion is unacceptable for all religions and a small number of abortions can be seen in deeply religious societies and families. Christianity considers the beginning of human life from conception, and abortion is considered to be a form of homicide [ 13 ]. For Christians, “at the same time, abortion is giving up their faith”, riot and murder, which means that by an abortion we attack Jesus Christ himself and God [ 14 ]. Islam does not approve abortion, relying on the sacral life belief as specified in Chapter 6, Verse 151 of the Koran: “Do not kill a soul which Allah has made sacred (inviolable)” [ 15 ]. Buddhism considers abortion as a negative act, but nevertheless supports for medical reasons [ 16 ]. Judaism disapproves abortion, Tanah considering it to be a mortal sin. Hinduism considers abortion as a crime and also the greatest sin [ 17 ].
From the socio-economic point of view, the decision to carry out an abortion is many times determined by the relations within the social, family or financial frame. Moreover, studies have been conducted, which have linked the legalization of abortions and the decrease of the crime rate: “legalized abortion may lead to reduced crime either through reductions in cohort sizes or through lower per capita offending rates for affected cohorts” [ 18 ].
Legal regulation on abortion establishes conditions of the abortion in every state. In Europe and America, only in the XVIIth century abortion was incriminated and was considered an insignificant misdemeanor or a felony, depending on when was happening. Due to the large number of illegal abortions and deaths, two centuries later, many states have changed legislation within the meaning of legalizing voluntary interruption of pregnancy [ 6 ]. In contemporary society, international organizations like the United Nations or the European Union consider sexual and reproductive rights as fundamental rights [ 19 , 20 ], and promotes the acceptance of abortion as part of those rights. However, not all states have developed permissive legislation in the field of voluntary interruption of pregnancy.
Currently, at national level were established four categories of legislation on pregnancy interruption area:
( i ) Prohibitive legislations , ones that do not allow abortion, most often outlining exceptions in abortion in cases where the pregnant woman’s life is endangered. In some countries, there is a prohibition of abortion in all circumstances, however, resorting to an abortion in the case of an imminent threat to the mother’s life. Same regulation is also found in some countries where abortion is allowed in cases like rape, incest, fetal problems, etc. In this category are 66 states, with 25.5% of world population [ 21 ].
( ii ) Restrictive legislation that allow abortion in cases of health preservation . Loosely, the term “health” should be interpreted according to the World Health Organization (WHO) definition as: “health is a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity” [ 22 ]. This type of legislation is adopted in 59 states populated by 13.8% of the world population [ 21 ].
( iii ) Legislation allowing abortion on a socio-economic motivation . This category includes items such as the woman’s age or ability to care for a child, fetal problems, cases of rape or incest, etc. In this category are 13 countries, where we have 21.3% of the world population [ 21 ].
( iv ) Legislation which do not impose restrictions on abortion . In the case of this legislation, abortion is permitted for any reason up to 12 weeks of pregnancy, with some exceptions (Romania – 14 weeks, Slovenia – 10 weeks, Sweden – 18 weeks), the interruption of pregnancy after this period has some restrictions. This type of legislation is adopted in 61 countries with 39.5% of the world population [21].
The Centre for Reproductive Rights has carried out from 1998 a map of the world’s states, based on the legislation typology of each country (Figure (Figure1 1 ).

The analysis of states according to the legislation regarding abortion. Source: Centre for Reproductive Rights. The World’s Abortion Laws, 2018 [ 23 ]
An unplanned pregnancy, socio-economic context or various medical problems [ 24 ], lead many times to the decision of interrupting pregnancy, regardless the legislative restrictions. In the study “Unsafe abortion: global and regional estimates of the incidence of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2008” issued in 2011 by the WHO , it was determined that within the states with restrictive legislation on abortion, we may also encounter a large number of illegal abortions. The illegal abortions may also be resulting in an increased risk of woman’s health and life considering that most of the times inappropriate techniques are being used, the hygienic conditions are precarious and the medical treatments are incorrectly administered [ 25 ]. Although abortions done according to medical guidelines carry very low risk of complications, 1–3 unsafe abortions contribute substantially to maternal morbidity and death worldwide [ 26 ].
WHO has estimated for the year 2008, the fact that worldwide women between the ages of 15 and 44 years carried out 21.6 million “unsafe” abortions, which involved a high degree of risk and were distributed as follows: 0.4 million in the developed regions and a number of 21.2 million in the states in course of development [ 25 ].
Case study: Romania
Legal perspective on abortion
In Romania, abortion was brought under regulation by the first Criminal Code of the United Principalities, from 1864.
The Criminal Code from 1864, provided the abortion infringement in Article 246, on which was regulated as follows: “Any person, who, using means such as food, drinks, pills or any other means, which will consciously help a pregnant woman to commit abortion, will be punished to a minimum reclusion (three years).
The woman who by herself shall use the means of abortion, or would accept to use means of abortion which were shown or given to her for this purpose, will be punished with imprisonment from six months to two years, if the result would be an abortion. In a situation where abortion was carried out on an illegitimate baby by his mother, the punishment will be imprisonment from six months to one year.
Doctors, surgeons, health officers, pharmacists (apothecary) and midwives who will indicate, will give or will facilitate these means, shall be punished with reclusion of at least four years, if the abortion took place. If abortion will cause the death of the mother, the punishment will be much austere of four years” (Art. 246) [ 27 ].
The Criminal Code from 1864, reissued in 1912, amended in part the Article 246 for the purposes of eliminating the abortion of an illegitimate baby case. Furthermore, it was no longer specified the minimum of four years of reclusion, in case of abortion carried out with the help of the medical staff, leaving the punishment to the discretion of the Court (Art. 246) [ 28 ].
The Criminal Code from 1936 regulated abortion in the Articles 482–485. Abortion was defined as an interruption of the normal course of pregnancy, being punished as follows:
“ 1 . When the crime is committed without the consent of the pregnant woman, the punishment was reformatory imprisonment from 2 to 5 years. If it caused the pregnant woman any health injury or a serious infirmity, the punishment was reformatory imprisonment from 3 to 6 years, and if it has caused her death, reformatory imprisonment from 7 to 10 years;
2 . When the crime was committed by the unmarried pregnant woman by herself, or when she agreed that someone else should provoke the abortion, the punishment is reformatory imprisonment from 3 to 6 months, and if the woman is married, the punishment is reformatory imprisonment from 6 months to one year. Same penalty applies also to the person who commits the crime with the woman’s consent. If abortion was committed for the purpose of obtaining a benefit, the punishment increases with another 2 years of reformatory imprisonment.
If it caused the pregnant woman any health injuries or a severe disablement, the punishment will be reformatory imprisonment from one to 3 years, and if it has caused her death, the punishment is reformatory imprisonment from 3 to 5 years” (Art. 482) [ 29 ].
The criminal legislation from 1936 specifies that it is not considered as an abortion the interruption from the normal course of pregnancy, if it was carried out by a doctor “when woman’s life was in imminent danger or when the pregnancy aggravates a woman’s disease, putting her life in danger, which could not be removed by other means and it is obvious that the intervention wasn’t performed with another purpose than that of saving the woman’s life” and “when one of the parents has reached a permanent alienation and it is certain that the child will bear serious mental flaws” (Art. 484, Par. 1 and Par. 2) [ 29 ].
In the event of an imminent danger, the doctor was obliged to notify prosecutor’s office in writing, within 48 hours after the intervention, on the performance of the abortion. “In the other cases, the doctor was able to intervene only with the authorization of the prosecutor’s office, given on the basis of a medical certificate from hospital or a notice given as a result of a consultation between the doctor who will intervene and at least a professor doctor in the disease which caused the intervention. General’s Office Prosecutor, in all cases provided by this Article, shall be obliged to maintain the confidentiality of all communications or authorizations, up to the intercession of any possible complaints” (Art. 484) [ 29 ].
The legislation of 1936 provided a reformatory injunction from one to three years for the abortions committed by doctors, sanitary agents, pharmacists, apothecary or midwives (Art. 485) [ 29 ].
Abortion on demand has been legalized for the first time in Romania in the year 1957 by the Decree No. 463, under the condition that it had to be carried out in a hospital and to be carried out in the first quarter of the pregnancy [ 30 ]. In the year 1966, demographic policy of Romania has dramatically changed by introducing the Decree No. 770 from September 29 th , which prohibited abortion. Thus, the voluntary interruption of pregnancy became a crime, with certain exceptions, namely: endangering the mother’s life, physical or mental serious disability; serious or heritable illness, mother’s age over 45 years, if the pregnancy was a result of rape or incest or if the woman gave birth to at least four children who were still in her care (Art. 2) [ 31 ].
In the Criminal Code from 1968, the abortion crime was governed by Articles 185–188.
The Article 185, “the illegal induced abortion”, stipulated that “the interruption of pregnancy by any means, outside the conditions permitted by law, with the consent of the pregnant woman will be punished with imprisonment from one to 3 years”. The act referred to above, without the prior consent from the pregnant woman, was punished with prison from two to five years. If the abortion carried out with the consent of the pregnant woman caused any serious body injury, the punishment was imprisonment from two to five years, and when it caused the death of the woman, the prison sentence was from five to 10 years. When abortion was carried out without the prior consent of the woman, if it caused her a serious physical injury, the punishment was imprisonment from three to six years, and if it caused the woman’s death, the punishment was imprisonment from seven to 12 years (Art. 185) [ 32 ].
“When abortion was carried out in order to obtain a material benefit, the maximum punishment was increased by two years, and if the abortion was made by a doctor, in addition to the prison punishment could also be applied the prohibition to no longer practice the profession of doctor”.
Article 186, “abortion caused by the woman”, stipulated that “the interruption of the pregnancy course, committed by the pregnant woman, was punished with imprisonment from 6 months to 2 years”, quoting the fact that by the same punishment was also sanctioned “the pregnant woman’s act to consent in interrupting the pregnancy course made out by another person” (Art. 186) [ 26 ].
The Regulations of the Criminal Code in 1968, also provided the crime of “ownership of tools or materials that can cause abortion”, the conditions of this holding being met when these types of instruments were held outside the hospital’s specialized institutions, the infringement shall be punished with imprisonment from three months to one year (Art. 187) [ 32 ].
Furthermore, the doctors who performed an abortion in the event of extreme urgency, without prior legal authorization and if they did not announce the competent authority within the legal deadline, they were punished by imprisonment from one month to three months (Art. 188) [ 32 ].
In the year 1985, it has been issued the Decree No. 411 of December 26 th , by which the conditions imposed by the Decree No. 770 of 1966 have been hardened, meaning that it has increased the number of children, that a woman could have in order to request an abortion, from four to five children [ 33 ].
The Articles 185–188 of the Criminal Code and the Decree No. 770/1966 on the interruption of the pregnancy course have been abrogated by Decree-Law No. 1 from December 26 th , 1989, which was published in the Official Gazette No. 4 of December 27 th , 1989 (Par. 8 and Par. 12) [ 34 ].
The Criminal Code from 1968, reissued in 1997, maintained Article 185 about “the illegal induced abortion”, but drastically modified. Thus, in this case of the Criminal Code, we identify abortion as “the interruption of pregnancy course, by any means, committed in any of the following circumstances: ( a ) outside medical institutions or authorized medical practices for this purpose; ( b ) by a person who does not have the capacity of specialized doctor; ( c ) if age pregnancy has exceeded 14 weeks”, the punishment laid down was the imprisonment from 6 months to 3 years” (Art. 185, Par. 1) [ 35 ]. For the abortion committed without the prior consent of the pregnant woman, the punishment consisted in strict prison conditions from two to seven years and with the prohibition of certain rights (Art. 185, Par. 2) [ 35 ].
For the situation of causing serious physical injury to the pregnant woman, the punishment was strict prison from three to 10 years and the removal of certain rights, and if it had as a result the death of the pregnant woman, the punishment was strict prison from five to 15 years and the prohibition of certain rights (Art. 185, Par. 3) [ 35 ].
The attempt was punished for the crimes specified in the various cases of abortion.
Consideration should also be given in the Criminal Code reissued in 1997 for not punishing the interruption of the pregnancy course carried out by the doctor, if this interruption “was necessary to save the life, health or the physical integrity of the pregnant woman from a grave and imminent danger and that it could not be removed otherwise; in the case of a over fourteen weeks pregnancy, when the interruption of the pregnancy course should take place from therapeutic reasons” and even in a situation of a woman’s lack of consent, when it has not been given the opportunity to express her will, and abortion “was imposed by therapeutic reasons” (Art. 185, Par. 4) [ 35 ].
Criminal Code from 2004 covers abortion in Article 190, defined in the same way as in the prior Criminal Code, with the difference that it affects the limits of the punishment. So, in the event of pregnancy interruption, in accordance with the conditions specified in Paragraph 1, “the penalty provided was prison time from 6 months to one year or days-fine” (Art. 190, Par. 1) [ 36 ].
Nowadays, in Romania, abortion is governed by the criminal law of 2009, which entered into force in 2014, by the section called “aggression against an unborn child”. It should be specified that current criminal law does not punish the woman responsible for carrying out abortion, but only the person who is involved in carrying out the abortion. There is no punishment for the pregnant woman who injures her fetus during pregnancy.
In Article 201, we can find the details on the pregnancy interruption infringement. Thus, the pregnancy interruption can be performed in one of the following circumstances: “outside of medical institutions or medical practices authorized for this purpose; by a person who does not have the capacity of specialist doctor in Obstetrics and Gynecology and the right of free medical practice in this specialty; if gestational age has exceeded 14 weeks”, the punishment is the imprisonment for six months to three years, or fine and the prohibition to exercise certain rights (Art. 201, Par. 1) [ 37 ].
Article 201, Paragraph 2 specifies that “the interruption of the pregnancy committed under any circumstances, without the prior consent of the pregnant woman, can be punished with imprisonment from 2 to 7 years and with the prohibition to exercise some rights” (Art. 201, Par. 1) [ 37 ].
If by facts referred to above (Art. 201, Par. 1 and Par. 2) [ 37 ] “it has caused the pregnant woman’s physical injury, the punishment is the imprisonment from 3 to 10 years and the prohibition to exercise some rights, and if it has had as a result the pregnant woman’s death, the punishment is the imprisonment from 6 to 12 years and the prohibition to exercise some rights” (Art. 201, Par. 3) [ 37 ]. When the facts have been committed by a doctor, “in addition to the imprisonment punishment, it will also be applied the prohibition to exercise the profession of doctor (Art. 201, Par. 4) [ 37 ].
Criminal legislation specifies that “the interruption of pregnancy does not constitute an infringement with the purpose of a treatment carried out by a specialist doctor in Obstetrics and Gynecology, until the pregnancy age of twenty-four weeks is reached, or the subsequent pregnancy interruption, for the purpose of treatment, is in the interests of the mother or the fetus” (Art. 201, Par. 6) [ 37 ]. However, it can all be found in the phrases “therapeutic purposes” and “the interest of the mother and of the unborn child”, which predisposes the text of law to an interpretation, finally the doctors are the only ones in the position to decide what should be done in such cases, assuming direct responsibility [ 38 ].
Article 202 of the Criminal Code defines the crime of harming an unborn child, pointing out the punishments for the various types of injuries that can occur during pregnancy or in the childbirth period and which can be caused by the mother or by the persons who assist the birth, with the specification that the mother who harms her fetus during pregnancy is not punished and does not constitute an infringement if the injury has been committed during pregnancy or during childbirth period if the facts have been “committed by a doctor or by an authorized person to assist the birth or to follow the pregnancy, if they have been committed in the course of the medical act, complying with the specific provisions of his profession and have been made in the interest of the pregnant woman or fetus, as a result of the exercise of an inherent risk in the medical act” (Art. 202, Par. 6) [ 37 ].
The fact situation in Romania
During the period 1948–1955, called “the small baby boom” [ 39 ], Romania registered an average fertility rate of 3.23 children for a woman. Between 1955 and 1962, the fertility rate has been less than three children for a woman, and in 1962, fertility has reached an average of two children for a woman. This phenomenon occurred because of the Decree No. 463/1957 on liberalization of abortion. After the liberalization from 1957, the abortion rate has increased from 220 abortions per 100 born-alive children in the year 1960, to 400 abortions per 100 born-alive children, in the year 1965 [ 40 ].
The application of provisions of Decrees No. 770 of 1966 and No. 411 of 1985 has led to an increase of the birth rate in the first three years (an average of 3.7 children in 1967, and 3.6 children in 1968), followed by a regression until 1989, when it was recorded an average of 2.2 children, but also a maternal death rate caused by illegal abortions, raising up to 85 deaths of 100 000 births in the year of 1965, and 170 deaths in 1983. It was estimated that more than 80% of maternal deaths between 1980–1989 was caused by legal constraints [ 30 ].
After the Romanian Revolution in December 1989 and after the communism fall, with the abrogation of Articles 185–188 of the Criminal Code and of the Decree No. 770/1966, by the Decree of Law No. 1 of December 26 th , 1989, abortion has become legal in Romania and so, in the following years, it has reached the highest rate of abortion in Europe. Subsequently, the number of abortion has dropped gradually, with increasing use of birth control [ 41 ].
Statistical data issued by the Ministry of Health and by the National Institute of Statistics (INS) in Romania show corresponding figures to a legally carried out abortion. The abortion number is much higher, if it would take into account the number of illegal abortion, especially those carried out before 1989, and those carried out in private clinics, after the year 1990. Summing the declared abortions in the period 1958–2014, it is to be noted the number of them, 22 037 747 exceeds the current Romanian population. A detailed statistical research of abortion rate, in terms of years we have exposed in Table Table1 1 .
The number of abortions declared in Romania in the period 1958–2016
Source: Pro Vita Association (Bucharest, Romania), National Institute of Statistics (INS – Romania), EUROSTAT [ 42 , 43 , 44 ]
Data issued by the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF) in June 2016, for the period 1989–2014, in matters of reproductive behavior, indicates a fertility rate for Romania with a continuous decrease, in proportion to the decrease of the number of births, but also a lower number of abortion rate reported to 100 deliveries (Table (Table2 2 ).
Reproductive behavior in Romania in 1989–2014
Source: United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF), Transformative Monitoring for Enhanced Equity (TransMonEE) Data. Country profiles: Romania, 1989–2015 [ 45 ].
By analyzing data issued for the period 1990–2015 by the International Organization of Health , UNICEF , United Nations Fund for Population Activity (UNFPA), The World Bank and the United Nations Population Division, it is noticed that maternal mortality rate has currently dropped as compared with 1990 (Table (Table3 3 ).
Maternal mortality estimation in Romania in 1990–2015
Source: World Health Organization (WHO), Global Health Observatory Data. Maternal mortality country profiles: Romania, 2015 [ 46 ].
Opinion survey: women’s opinion on abortion
Argument for choosing the research theme
Although the problematic on abortion in Romania has been extensively investigated and debated, it has not been carried out in an ample sociological study, covering Romanian women’s perception on abortion. We have assumed making a study at national level, in order to identify the opinion on abortion, on the motivation to carry out an abortion, and to identify the correlation between religious convictions and the attitude toward abortion.
Examining the literature field of study
In the conceptual register of the research, we have highlighted items, such as the specialized literature, legislation, statistical documents.
Formulation of hypotheses and objectives
The first hypothesis was that Romanian women accept abortion, having an open attitude towards this act. Thus, the first objective of the research was to identify Romanian women’s attitude towards abortion.
The second hypothesis, from which we started, was that high religious beliefs generate a lower tolerance towards abortion. Thus, the second objective of our research has been to identify the correlation between the religious beliefs and the attitude towards abortion.
The third hypothesis of the survey was that, the main motivation in carrying out an abortion is the fact that a woman does not want a baby, and the main motivation for keeping the pregnancy is that the person wants a baby. In this context, the third objective of the research was to identify main motivation in carrying out an abortion and in maintaining a pregnancy.
Another hypothesis was that modern Romanian legislation on the abortion is considered fair. Based on this hypothesis, we have assumed the fourth objective, which is to identify the degree of satisfaction towards the current regulatory provisions governing the abortion.
Research methodology
The research method is that of a sociological survey by the application of the questionnaire technique. We used the sampling by age and residence looking at representative numbers of population from more developed as well as underdeveloped areas.
Determination of the sample to be studied
Because abortion is a typical women’s experience, we have chosen to make the quantitative research only among women. We have constructed the sample by selecting a number of 1260 women between the ages of 15 and 44 years (the most frequently encountered age among women who give birth to a child). We also used the quota sampling techniques, taking into account the following variables: age group and the residence (urban/rural), so that the persons included in the sample could retain characteristic of the general population.
By the sample of 1260 women, we have made a percentage of investigation of 0.03% of the total population.
The Questionnaires number applied was distributed as follows (Table (Table4 4 ).
The sampling rates based on the age, and the region of residence
Source: Sample built, based on the population data issued by the National Institute of Statistics (INS – Romania) based on population census conducted in 2011 [ 47 ].
Data collection
Data collection was carried out by questionnaires administered by 32 field operators between May 1 st –May 31 st , 2018.
The analysis of the research results
In the next section, we will present the main results of the quantitative research carried out at national level.
Almost three-quarters of women included in the sample agree with carrying out an abortion in certain circumstances (70%) and only 24% have chosen to support the answer “ No, never ”. In modern contemporary society, abortion is the first solution of women for which a pregnancy is not desired. Even if advanced medical techniques are a lot safer, an abortion still carries a health risk. However, 6% of respondents agree with carrying out abortion regardless of circumstances (Table (Table5 5 ).
Opinion on the possibility of carrying out an abortion
Although abortions carried out after 14 weeks are illegal, except for medical reasons, more than half of the surveyed women stated they would agree with abortion in certain circumstances. At the opposite pole, 31% have mentioned they would never agree on abortions after 14 weeks. Five percent were totally accepting the idea of abortion made to a pregnancy that has exceeded 14 weeks (Table (Table6 6 ).
Opinion on the possibility of carrying out an abortion after the period of 14 weeks of pregnancy
For 53% of respondents, abortion is considered a crime as well as the right of a women. On the other hand, 28% of the women considered abortion as a crime and 16% associate abortion with a woman’s right (Table (Table7 7 ).
Opinion on abortion: at the border between crime and a woman’s right
Opinions on what women abort at the time of the voluntary pregnancy interruption are split in two: 59% consider that it depends on the time of the abortion, and more specifically on the pregnancy development stage, 24% consider that regardless of the period in which it is carried out, women abort a child, and 14% have opted a fetus (Table (Table8 8 ).
Abortion of a child vs. abortion of a fetus
Among respondents who consider that women abort a child or a fetus related to the time of abortion, 37.5% have considered that the difference between a baby and a fetus appears after 14 weeks of pregnancy (the period legally accepted for abortion). Thirty-three percent of them have mentioned that the distinction should be performed at the first few heartbeats; 18.1% think it is about when the child has all the features definitively outlined and can move by himself; 2.8% consider that the difference appears when the first encephalopathy traces are being felt and the child has formed all internal and external organs. A percentage of 1.7% of respondents consider that this difference occurs at the beginning of the central nervous system, and 1.4% when the unborn child has all the features that we can clearly see to a newborn child (Table (Table9 9 ).
The opinion on the moment that makes the difference between a fetus and a child
We noticed that highly religious people make a clear association between abortion and crime. They also consider that at the time of pregnancy interruption it is aborted a child and not a fetus. However, unexpectedly, we noticed that 27% of the women, who declare themselves to be very religious, have also stated that they see abortion as a crime but also as a woman’s right. Thirty-one percent of the women, who also claimed profound religious beliefs, consider that abortion may be associated with the abortion of a child but also of a fetus, this depending on the time of abortion (Tables (Tables10 10 and and11 11 ).
The correlation between the level of religious beliefs and the perspective on abortion seen as a crime or a right
The correlation between the level of religious beliefs and the perspective on abortion procedure conducted on a fetus or a child
More than half of the respondents have opted for the main reason for abortion the appearance of medical problems to the child. Baby’s health represents the main concern of future mothers, and of each parent, and the birth of a child with serious health issues, is a factor which frightens any future parent, being many times, at least theoretically, one good reason for opting for abortion. At the opposite side, 12% of respondents would not choose abortion under any circumstances. Other reasons for which women would opt for an abortion are: if the woman would have a medical problem (22%) or would not want the child (10%) (Table (Table12 12 ).
Potential reasons for carrying out an abortion
Most of the women want to give birth to a child, 56% of the respondents, representing also the reason that would determine them to keep the child. Morality (26%), faith (10%) or legal restrictions (4%), are the three other reasons for which women would not interrupt a pregnancy. Only 2% of the respondents have mentioned other reasons such as health or age.
A percentage of 23% of the surveyed people said that they have done an abortion so far, and 77% did not opted for a surgical intervention either because there was no need, or because they have kept the pregnancy (Table (Table13 13 ).
Rate of abortion among women in the sample
Most respondents, 87% specified that they have carried out an abortion during the first 14 weeks – legally accepted limit for abortion: 43.6% have made abortion in the first four weeks, 39.1% between weeks 4–8, and 4.3% between weeks 8–14. It should be noted that 8.7% could not appreciate the pregnancy period in which they carried out abortion, by opting to answer with the option “ I don’t know ”, and a percentage of 4.3% refused to answer to this question.
Performing an abortion is based on many reasons, but the fact that the women have not wanted a child is the main reason mentioned by 47.8% of people surveyed, who have done minimum an abortion so far. Among the reasons for the interruption of pregnancy, it is also included: women with medical problems (13.3%), not the right time to be a mother (10.7%), age motivation (8.7%), due to medical problems of the child (4.3%), the lack of money (4.3%), family pressure (4.3%), partner/spouse did not wanted. A percentage of 3.3% of women had different reasons for abortion, as follows: age difference too large between children, career, marital status, etc. Asked later whether they regretted the abortion, a rate of 69.6% of women who said they had at least one abortion regret it (34.8% opted for “ Yes ”, and 34.8% said “ Yes, partially ”). 26.1% of surveyed women do not regret the choice to interrupted the pregnancy, and 4.3% chose to not answer this question. We noted that, for women who have already experienced abortion, the causes were more diverse than the grounds on which the previous question was asked: “What are the reasons that determined you to have an abortion?” (Table (Table14 14 ).
The reasons that led the women in the sample to have an abortion
The majority of the respondents (37.5%) considered that “nervous depression” is the main consequence of abortion, followed by “insomnia and nightmares” (24.6%), “disorders in alimentation” and “affective disorders” (each for 7.7% of respondents), “deterioration of interpersonal relationships” and “the feeling of guilt”(for 6.3% of the respondents), “sexual disorders” and “panic attacks” (for 6.3% of the respondents) (Table (Table15 15 ).
Opinion on the consequences of abortion
Over half of the respondents believe that abortion should be legal in certain circumstances, as currently provided by law, 39% say it should be always legal, and only 6% opted for the illegal option (Table (Table16 16 ).
Opinion on the legal regulation of abortion
Although the current legislation does not punish pregnant women who interrupt pregnancy or intentionally injured their fetus, survey results indicate that 61% of women surveyed believe that the national law should punish the woman and only 28% agree with the current legislation (Table (Table17 17 ).
Opinion on the possibility of punishing the woman who interrupts the course of pregnancy or injures the fetus
For the majority of the respondents (40.6%), the penalty provided by the current legislation, the imprisonment between six months and three years or a fine and deprivation of certain rights for the illegal abortion is considered fair, for a percentage of 39.6% the punishment is too small for 9.5% of the respondents is too high. Imprisonment between two and seven years and deprivation of certain rights for an abortion performed without the consent of the pregnant woman is considered too small for 65% of interviewees. Fourteen percent of them think it is fair and only 19% of respondents consider that Romanian legislation is too severe with people who commit such an act considering the punishment as too much. The imprisonment from three to 10 years and deprivation of certain rights for the facts described above, if an injury was caused to the woman, is considered to be too small for more than half of those included in the survey, 64% and almost 22% for nearly a quarter of them. Only 9% of the respondents mentioned that this legislative measure is too severe for such actions (Table (Table18 18 ).
Opinion on the regulation of abortion of the Romanian Criminal Code (Art. 201)
Conclusions
After analyzing the results of the sociological research regarding abortion undertaken at national level, we see that 76% of the Romanian women accept abortion, indicating that the majority accepts only certain circumstances (a certain period after conception, for medical reasons, etc.). A percentage of 64% of the respondents indicated that they accept the idea of abortion after 14 weeks of pregnancy (for solid reasons or regardless the reason). This study shows that over 50% of Romanian women see abortion as a right of women but also a woman’s crime and believe that in the moment of interruption of a pregnancy, a fetus is aborted. Mostly, the association of abortion with crime and with the idea that a child is aborted is frequently found within very religious people. The main motivation for Romanian women in taking the decision not to perform an abortion is that they would want the child, and the main reason to perform an abortion is the child’s medical problems. However, it is noted that, in real situations, in which women have already done at least one abortion, most women resort to abortion because they did not want the child towards the hypothetical situation in which women felt that the main reason of abortion is a medical problem. Regarding the satisfaction with the current national legislation of the abortion, the situation is rather surprising. A significant percentage (61%) of respondents felt as necessary to punish the woman who performs an illegal abortion, although the legislation does not provide a punishment. On the other hand, satisfaction level to the penalties provided by law for various violations of the legal conditions for conducting abortion is low, on average only 25.5% of respondents are being satisfied with these, the majority (average 56.2%) considering the penalties as unsatisfactory. Understood as a social phenomenon, intensified by human vulnerabilities, of which the most obvious is accepting the comfort [ 48 ], abortion today is no longer, in Romanian society, from a legal or religious perspective, a problem. Perceptions on the legislative sanction, moral and religious will perpetual vary depending on beliefs, environment, education, etc. The only and the biggest social problem of Romania is truly represented by the steadily falling birth rate.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Don’t Be Fooled By Trump’s Failure to Endorse a Nationwide Abortion Ban

F ormer President Donald Trump announced on Truth Social that he favors state control over abortion law and policy and declined to endorse a nationwide ban. He also claimed that the Supreme Court’s overturning of Roe v. Wade in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization was favored by “all legal scholars” on “both sides.” Abortion is “where everybody wanted it, from a legal standpoint,” according to Trump.
All of this is patently false, of course. Decades of legal scholarship and advocacy support the federal constitutional right to abortion that Dobbs eliminated. Some scholars who support legal abortion as a matter of policy have criticized the result the Court reached in Roe , but they are in the minority. Others have critiqued the reasoning of Roe v. Wade . Some, like Ruth Bader Ginsburg , prefer the equality rationale of Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992), where the Court noted the central importance of reproductive freedom to women’s ability to participate fully and equally in the social, political, and economic life of the nation. But the notion that all or most legal scholars wanted the Court to obliterate the right to choose abortion is ludicrous.
No one should be fooled by Trump’s failure to endorse any of the proposed nationwide abortion bans, a move designed to appear “moderate” and lull voters into a false sense of complacency. Make no mistake: a second Trump administration will empower an anti-abortion movement determined to make abortion illegal everywhere. Even if Republicans do not take over Congress, there are plans in place to make medication abortion unavailable and to resurrect the 1873 Comstock Act, an archaic anti-vice law, to ban abortion nationwide. Proponents of fetal personhood, which defines an embryo as a legal person from the moment of fertilization, will be closer to realizing their goal, threatening not only abortion and miscarriage care but also IVF and common forms of contraception. Trump promotes the grotesque lie that Democrats want to “execute babies” to distract from his own party’s extremism.
Trump peddles these false and misleading claims because he understands that the truth about abortion endangers his candidacy and Republicans generally. Far from ending the controversy, returning abortion to the states already has led to outcomes wildly out of step with public opinion. Doctors and hospitals routinely deny patients basic medical care, including miscarriage treatment, because they are not close enough to death to have their rights outweigh those of an embryo or fetus. State laws with no or ineffective exceptions force children, survivors of rape and incest, and people with nonviable fetuses to carry pregnancies regardless of the consequences to their health and future fertility. Maternal health deserts multiply because doctors fear criminal and civil liability. Abortion bans exacerbate a maternal and infant mortality crisis that makes pregnancy a mortal danger to American women— especially Black women , who are almost three times more likely to die from pregnancy and childbirth than their white counterparts.
Read More: How Louisiana Has Become a Microcosm of the Abortion Access Fight
Even people with qualms about abortion in theory don’t favor these horrific results in fact. Recent polling from Gallup and Axios respectively reveals supermajority popular opposition to total and near-total bans on abortion, and majority support , even among Republicans, for keeping the government out of reproductive health care decisions altogether. Every ballot initiative since Dobbs has been resolved in favor of abortion rights and access. In fact, abortion motivates Americans to turn out and vote for candidates who support reproductive freedom.
Perhaps the most pernicious of Trump’s lies is that returning abortion to the states is a victory for democracy. Depriving people of the right to make the most basic decisions about their bodies and lives is deeply undemocratic and a hallmark of authoritarian regimes worldwide. Extreme abortion bans and fetal personhood laws pass despite popular opposition because of unchecked partisan gerrymandering that gives Republicans supermajorities. Even the most conservative lawmakers live in fear of a primary challenge from the right if they support any exceptions, however minor and ineffective, to total abortion bans. Trump says abortion law after Dobbs is “all about the will of the people.” But in fact, Republicans are scrambling to take decisions about abortion out of the people’s hands by preventing referenda from reaching the ballot, protecting state courts that defy public opinion from accountability for their decisions, and disenfranchising voters.
The GOP has long used abortion to secure the support of voters to promote a much broader right-wing agenda. Trump, as promised, packed the federal judiciary with jurists who would destroy the government’s ability to regulate corporations, combat climate change and political corruption, enact sensible gun-safety laws, provide for affordable health care, expand opportunities for women and people of color, fight discrimination, protect the rights of workers and immigrants, ask the wealthy to pay their fair share in taxes, and so on. The problem is that a majority of Americans actually support each of the policies the Right is determined to undo. To remain in power, Republicans must undermine democratic institutions and practices. Partisan and racial gerrymandering, voter suppression, and the evisceration of campaign finance regulation and voting rights laws are longstanding strategies; more recently, election denialism, insurrection, political violence, and white supremacist resurgence—all fomented by Trump—place democracy and the rule of law in mortal danger. All of this is at stake in Trump’s ultimate lie: his claim to be a champion of democracy rather than the architect of its demise.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- Exclusive: Google Workers Revolt Over $1.2 Billion Contract With Israel
- Jane Fonda Champions Climate Action for Every Generation
- Stop Looking for Your Forever Home
- The Sympathizer Counters 50 Years of Hollywood Vietnam War Narratives
- The Bliss of Seeing the Eclipse From Cleveland
- Hormonal Birth Control Doesn’t Deserve Its Bad Reputation
- The Best TV Shows to Watch on Peacock
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
Abortion: most Controversial Topics Around the World
This essay about the abortion debate examines its multifaceted nature, from moral and ethical considerations to legal frameworks and societal impacts. It discusses the clash between advocates for abortion rights and opponents, highlighting the complex interplay of beliefs surrounding when life begins. The text also explores how the debate intersects with issues of social justice and equity, revealing systemic disparities in access to reproductive healthcare. Overall, it underscores the importance of empathetic dialogue and collective efforts to address the complexities of reproductive justice for all individuals.
How it works
Abortion continues to stand at the crossroads of morality, ethics, and law, stirring intense debates that resonate across cultures and nations. Within this intricate tapestry of perspectives and convictions, the discourse on abortion unfolds, revealing a spectrum of beliefs and values that shape individual and societal understandings. From historical roots to contemporary dilemmas, the abortion debate is a multifaceted phenomenon that defies simplistic categorization.
At its core, the abortion debate grapples with the question of when life begins, serving as a fulcrum upon which divergent viewpoints pivot.
Advocates for abortion rights champion a woman’s right to bodily autonomy, arguing that restrictions on abortion infringe upon fundamental human rights. They contend that access to safe and legal abortion services is essential for women’s health and well-being, providing a pathway to reproductive freedom and self-determination.
Conversely, opponents of abortion, often aligned with the “pro-life” movement, emphasize the sanctity of human life from conception. Rooted in religious beliefs and moral principles, they view abortion as an affront to the inherent value of every individual, advocating for the protection of unborn life. For them, abortion represents a moral imperative to defend the rights of the voiceless and vulnerable.
The abortion debate is further complicated by considerations of fetal viability and the rights of the unborn. Advances in medical science have blurred the lines between viability and personhood, raising profound ethical questions about the moral status of the fetus. This nuanced interplay between maternal autonomy and fetal rights underscores the complexity of the abortion discourse, challenging entrenched notions of personhood and moral responsibility.
Legal frameworks governing abortion vary significantly across different jurisdictions, reflecting diverse cultural, religious, and political landscapes. While some countries uphold liberal abortion laws, affording individuals expansive reproductive rights, others enforce stringent regulations or outright bans, often influenced by religious doctrine or conservative ideologies. This patchwork of legislation underscores the ongoing struggle for reproductive justice and the clash of competing values on a global scale.
Beyond the legal realm, the abortion debate intersects with broader issues of social justice and equity, exposing systemic disparities in access to healthcare. Marginalized communities, particularly women of color and those living in poverty, bear the brunt of restrictive abortion policies, facing significant barriers to reproductive healthcare services. This intersectional lens reveals the intertwined nature of reproductive rights and social inequality, highlighting the urgent need for equitable access to comprehensive healthcare services.
Moreover, the politicization of abortion fuels contentious debates within legislative arenas, as policymakers grapple with the complexities of balancing competing interests and values. Attempts to enact restrictive abortion laws often elicit fierce opposition from advocacy groups, triggering legal battles and public demonstrations. The United States, in particular, has been a focal point of the abortion debate, with landmark court decisions and political maneuvers shaping the trajectory of reproductive rights for generations.
The societal ramifications of the abortion debate extend far beyond legal and ethical considerations, permeating cultural attitudes towards sexuality, gender roles, and familial structures. Discussions surrounding reproductive rights intersect with broader dialogues on women’s empowerment, bodily autonomy, and the dismantling of patriarchal norms. Yet, pervasive stigma surrounding abortion persists, casting a shadow of shame and silence over those in need of reproductive healthcare.
In conclusion, the abortion debate embodies a rich tapestry of perspectives and experiences, reflecting the complexity of human values and beliefs. As societies navigate the intricacies of reproductive justice, it is imperative to engage in empathetic dialogue, grounded in mutual respect and understanding. Only through collective efforts to address systemic inequalities and promote reproductive autonomy can we forge a path towards a more just and equitable future for all.
Cite this page
Abortion: Most Controversial Topics Around The World. (2024, Apr 07). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/abortion-most-controversial-topics-around-the-world/
"Abortion: Most Controversial Topics Around The World." PapersOwl.com , 7 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/abortion-most-controversial-topics-around-the-world/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Abortion: Most Controversial Topics Around The World . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/abortion-most-controversial-topics-around-the-world/ [Accessed: 12 Apr. 2024]
"Abortion: Most Controversial Topics Around The World." PapersOwl.com, Apr 07, 2024. Accessed April 12, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/abortion-most-controversial-topics-around-the-world/
"Abortion: Most Controversial Topics Around The World," PapersOwl.com , 07-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/abortion-most-controversial-topics-around-the-world/. [Accessed: 12-Apr-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Abortion: Most Controversial Topics Around The World . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/abortion-most-controversial-topics-around-the-world/ [Accessed: 12-Apr-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Advertisement
Supported by
Putting Abortion Question to Florida Voters Is Unlikely to End Court Fights
Though the Florida Supreme Court allowed a ballot question on expanding abortion rights, it also laid out a way for anti-abortion groups to challenge such an expansion.
- Share full article

By Patricia Mazzei
Reporting from Miami
Abortion-rights supporters celebrated last week when the Florida Supreme Court said voters could decide this fall whether to approve a state constitutional amendment protecting and expanding abortion rights in Florida. But the court also laid out a road map for anti-abortion groups to challenge any expansion, by raising the prospect of “fetal personhood.”
In concurring and dissenting opinions that accompanied the ruling, four of the seven justices on the conservative court indicated that they may interpret the State Constitution to grant fetuses the same legal rights as people, foretelling the next likely court fight over abortion. The proposed state constitutional amendment would guarantee access to abortion “before viability,” or before about 24 weeks of pregnancy.
“If this does pass — but even if it doesn’t pass — I think that there is an open door to go to the Florida Supreme Court,” said Mathew D. Staver, a lawyer for two anti-abortion groups that oppose the ballot measure, the Liberty Counsel and Florida Voters Against Extremism.
Anti-abortion activists have promoted the fetal personhood legal strategy since the U.S. Supreme Court eliminated the federal right to abortion in 2022. What has been perhaps their biggest success came in February, when the Alabama Supreme Court held that a frozen embryo should be considered a person, opening a new front in the legal debate over abortion.
What was striking in Florida was that the argument was not raised by one of the lawyers opposing the abortion ballot measure, but rather by the court.
Chief Justice Carlos G. Muñiz asked during oral arguments in February — before the Alabama ruling — whether the proposed Florida amendment might interfere with the rights of the fetus.
Put on the spot by Chief Justice Muñiz, neither side took a firm position. But after the hearing, anti-abortion lawyers filed an additional brief that cited the Alabama case and urged the court to consider fetal rights in its deliberations.
When the court’s ruling came down on April 1, Chief Justice Muñiz sided with the 4-3 majority in allowing the proposed amendment to go to voters. But a footnote in the majority opinion called the question of fetal rights “unsettled.”
“Someone is certainly going to take him up on that,” said Mary Ziegler, an abortion law expert at the University of California, Davis, who previously taught at Florida State University in Tallahassee. “Someone is going to test the water.”
The three justices in the minority — Justices Renatha Francis, Jamie R. Grosshans and Meredith L. Sasso — also directly addressed fetal rights in separate dissents.
“The voter may think this amendment results in settling this issue once and for all,” Justice Grosshans wrote. “It does not.”
The court, she wrote, has yet to address whether the rights guaranteed by the Florida Constitution “apply to the unborn and, if so, what the scope of those rights could be.” She went on to call the amendment defective because it did not make clear to voters that the question was not yet settled.
Aadika Singh, a lawyer for the Public Rights Project, which filed a court brief in support of the ballot measure, said it was “troubling” that the justices had signaled they would be willing to take up a challenge to the amendment, even as they ruled that voters could decide whether to approve it.
“They went out of their way,” she said of the court, to say, “‘We are willing, in a future case, to undermine that democratic decision.’”
Still, she added: “The ballot measure decision is an important victory. It allows Floridians to weigh in directly on the issue, and that is a win for abortion rights and democracy.”
Supporters of abortion rights are trying to put measures on the ballot in about 10 states to secure access to the procedure. Former President Donald J. Trump, who had given mixed signals on his position, said in a video statement on Monday that abortion restrictions should be left up to the states: “It’s all about the will of the people,” he said.
In a separate ruling last week, the Florida justices affirmed a state abortion ban at 15 weeks of pregnancy — a decision that effectively allowed a more recently enacted 6-week ban to take effect by May 1.
The fine print of the court’s opinions underscored that getting the abortion measure on the ballot was not likely to end the battle, even if the amendment gets more than 60 percent of the vote in November, as is needed for it to pass.
There is precedent for a Florida constitutional amendment to be challenged before Election Day and overturned long afterward. The state Supreme Court ruled in 2000 that an amendment adopted nearly two years earlier, regarding the wording of the death penalty in the State Constitution, was unconstitutional because it had misled voters.
Mr. Staver said he was aware of that precedent and was considering options for challenging the abortion measure. “That’s an avenue that we are looking at,” he said.
The Florida Legislature could also try to thwart the amendment if it passes. After voters in Ohio protected abortion rights with a constitutional amendment last year , some Republican lawmakers tried to strip state courts of the power to enforce the amendment.
In Florida, Gov. Ron DeSantis and fellow Republicans in control of the State Legislature could seek to define key terms in the constitutional amendment, including “viability,” said Barbara J. Pariente, a former chief justice on the Florida Supreme Court who retired in 2019.
“My feeling is that, in Florida, because of the governor we have and the Republican majority, that there will be every attempt to interfere with the intent of the amendment,” she said.
In 2018, Florida voters approved a constitutional amendment restoring voting rights for most felons. By 2020, much of the measure had been gutted by lawmakers and the courts.
Patricia Mazzei is the lead reporter for The Times in Miami, covering Florida and Puerto Rico. More about Patricia Mazzei
Prestigious cancer research institute has retracted 7 studies amid controversy over errors

Seven studies from researchers at the prestigious Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have been retracted over the last two months after a scientist blogger alleged that images used in them had been manipulated or duplicated.
The retractions are the latest development in a monthslong controversy around research at the Boston-based institute, which is a teaching affiliate of Harvard Medical School.
The issue came to light after Sholto David, a microbiologist and volunteer science sleuth based in Wales, published a scathing post on his blog in January, alleging errors and manipulations of images across dozens of papers produced primarily by Dana-Farber researchers . The institute acknowledged errors and subsequently announced that it had requested six studies to be retracted and asked for corrections in 31 more papers. Dana-Farber also said, however, that a review process for errors had been underway before David’s post.
Now, at least one more study has been retracted than Dana-Farber initially indicated, and David said he has discovered an additional 30 studies from authors affiliated with the institute that he believes contain errors or image manipulations and therefore deserve scrutiny.
The episode has imperiled the reputation of a major cancer research institute and raised questions about one high-profile researcher there, Kenneth Anderson, who is a senior author on six of the seven retracted studies.
Anderson is a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and the director of the Jerome Lipper Multiple Myeloma Center at Dana-Farber. He did not respond to multiple emails or voicemails requesting comment.
The retractions and new allegations add to a larger, ongoing debate in science about how to protect scientific integrity and reduce the incentives that could lead to misconduct or unintentional mistakes in research.
The Dana-Farber Cancer Institute has moved relatively swiftly to seek retractions and corrections.
“Dana-Farber is deeply committed to a culture of accountability and integrity, and as an academic research and clinical care organization we also prioritize transparency,” Dr. Barrett Rollins, the institute’s integrity research officer, said in a statement. “However, we are bound by federal regulations that apply to all academic medical centers funded by the National Institutes of Health among other federal agencies. Therefore, we cannot share details of internal review processes and will not comment on personnel issues.”
The retracted studies were originally published in two journals: One in the Journal of Immunology and six in Cancer Research. Six of the seven focused on multiple myeloma, a form of cancer that develops in plasma cells. Retraction notices indicate that Anderson agreed to the retractions of the papers he authored.
Elisabeth Bik, a microbiologist and longtime image sleuth, reviewed several of the papers’ retraction statements and scientific images for NBC News and said the errors were serious.
“The ones I’m looking at all have duplicated elements in the photos, where the photo itself has been manipulated,” she said, adding that these elements were “signs of misconduct.”
Dr. John Chute, who directs the division of hematology and cellular therapy at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and has contributed to studies about multiple myeloma, said the papers were produced by pioneers in the field, including Anderson.
“These are people I admire and respect,” he said. “Those were all high-impact papers, meaning they’re highly read and highly cited. By definition, they have had a broad impact on the field.”
Chute said he did not know the authors personally but had followed their work for a long time.
“Those investigators are some of the leading people in the field of myeloma research and they have paved the way in terms of understanding our biology of the disease,” he said. “The papers they publish lead to all kinds of additional work in that direction. People follow those leads and industry pays attention to that stuff and drug development follows.”
The retractions offer additional evidence for what some science sleuths have been saying for years: The more you look for errors or image manipulation, the more you might find, even at the top levels of science.
Scientific images in papers are typically used to present evidence of an experiment’s results. Commonly, they show cells or mice; other types of images show key findings like western blots — a laboratory method that identifies proteins — or bands of separated DNA molecules in gels.
Science sleuths sometimes examine these images for irregular patterns that could indicate errors, duplications or manipulations. Some artificial intelligence companies are training computers to spot these kinds of problems, as well.
Duplicated images could be a sign of sloppy lab work or data practices. Manipulated images — in which a researcher has modified an image heavily with photo editing tools — could indicate that images have been exaggerated, enhanced or altered in an unethical way that could change how other scientists interpret a study’s findings or scientific meaning.
Top scientists at big research institutions often run sprawling laboratories with lots of junior scientists. Critics of science research and publishing systems allege that a lack of opportunities for young scientists, limited oversight and pressure to publish splashy papers that can advance careers could incentivize misconduct.
These critics, along with many science sleuths, allege that errors or sloppiness are too common , that research organizations and authors often ignore concerns when they’re identified, and that the path from complaint to correction is sluggish.
“When you look at the amount of retractions and poor peer review in research today, the question is, what has happened to the quality standards we used to think existed in research?” said Nick Steneck, an emeritus professor at the University of Michigan and an expert on science integrity.
David told NBC News that he had shared some, but not all, of his concerns about additional image issues with Dana-Farber. He added that he had not identified any problems in four of the seven studies that have been retracted.
“It’s good they’ve picked up stuff that wasn’t in the list,” he said.
NBC News requested an updated tally of retractions and corrections, but Ellen Berlin, a spokeswoman for Dana-Farber, declined to provide a new list. She said that the numbers could shift and that the institute did not have control over the form, format or timing of corrections.
“Any tally we give you today might be different tomorrow and will likely be different a week from now or a month from now,” Berlin said. “The point of sharing numbers with the public weeks ago was to make clear to the public that Dana-Farber had taken swift and decisive action with regard to the articles for which a Dana-Farber faculty member was primary author.”
She added that Dana-Farber was encouraging journals to correct the scientific record as promptly as possible.
Bik said it was unusual to see a highly regarded U.S. institution have multiple papers retracted.
“I don’t think I’ve seen many of those,” she said. “In this case, there was a lot of public attention to it and it seems like they’re responding very quickly. It’s unusual, but how it should be.”
Evan Bush is a science reporter for NBC News. He can be reached at [email protected].

COMMENTS
Women (66%) are more likely than men (57%) to say abortion should be legal in most or all cases, according to the survey conducted after the court's ruling. More than half of U.S. adults - including 60% of women and 51% of men - said in March that women should have a greater say than men in setting abortion policy.
The Case Against Abortion. Nov. 30, 2021. Crosses representing abortions in Lindale, Tex. Tamir Kalifa for The New York Times. Share full article. 3367. By Ross Douthat. Opinion Columnist. A ...
By David Leonhardt. May 19, 2021. For nearly 50 years, public opinion has had only a limited effect on abortion policy. The Roe v. Wade decision, which the Supreme Court issued in 1973 ...
An outline for an abortion essay: 1.Abortion Essay Introduction 2.Body Paragraphs: Pros and Cons of Abortion 3.Abortion Essay Conclusion. Topics & examples for abortion essay. ... where a controversial ban was upheld in 13 states at the point this article was written. That's why an essay on abortion has become one of the most popular tasks in ...
Sofia Cipriano. Following Dobbs v.Jackson's (2022) reversal of Roe v.Wade (1973) — and the subsequent revocation of federal abortion protection — activists and scholars have begun to reconsider how to best ground abortion rights in the Constitution. In the past year, numerous Jewish rights groups have attempted to overturn state abortion bans by arguing that abortion rights are protected ...
11 Common Arguments about Abortion Nathan Nobis and Kristina Grob 27. 1 Introduction. Abortion is often in the news. In the course of writing this essay in early 2019, Kentucky, Mississippi, Ohio, Georgia, Alabama and Missouri passed legislation to outlaw and criminalize abortions starting at six to eight weeks in pregnancy, with more states following.
Human Rights Watch released a new question-and-answer document that articulates the human rights imperative, guided by international law, to ensure access to abortion, which is critical to ...
The decision to keep the child should not be left up solely to the woman. Yes, it is her body that the child grows in, however once that child is birthed it is now two people's responsibility ...
Below, seven popular claims surrounding abortion get fact-checked. According to the Pew Research Center's polls, 37% of Americans want abortion illegal in all or most cases. But an even bigger ...
Free essay examples about Abortion ️ Proficient writing team ️ High-quality of every essay ️ Largest database of free samples on PapersOwl. ... It is a controversial conversation that most people avoid having. Abortion is different than most issues in politics, because it directly impacts women, rather than men. ...
5.1.1 Fetuses are human. 5.1.2 Fetuses are human beings. 5.1.3 Fetuses are persons. 5.1.4 Fetuses are potential persons. 5.1.5 Abortion prevents fetuses from experiencing their valuable futures. We will begin with arguments for the conclusion that abortion is generally wrong, perhaps nearly always wrong. These can be seen as reasons to believe ...
Abortion is among the most intractable issues dividing the parties, with little or no room for compromise. ... In his essay, Balmer recounted a 1990 meeting of conservatives in Washington at which ...
In "Association of Texas' 2021 Ban on Abortion in Early Pregnancy with the Number of Facility-Based Abortion in Texas and Surrounding States," White et al. used a large dataset containing information before and after the passage of SB8 in September 2021. 1 This bill banned most abortions after 6 weeks in the state of Texas.
Abortion services are a vital component of reproductive health care. Since the Supreme Court's 2022 ruling in Dobbs v.Jackson Women's Health Organization, access to abortion services has been increasingly restricted in the United States. Jung and colleagues review current practice and evidence on medication abortion, procedural abortion, and associated reproductive health care, as well as ...
Abortion has been both siloed and marginalized in social science research. But because abortion is a perennially politically and socially contested issue as well as vital health care that one in four women in the United States will experience in their lifetime (Jones and Jerman 2022), it is imperative that social scientists make a change.This special issue brings together insightful voices ...
Paragraph 1: The Right to Bodily Autonomy. One of the main arguments in favor of abortion is the right to bodily autonomy. Every person has the right to make decisions about their own body, and this includes the right to make decisions about their reproductive health. Denying women the right to access abortion services is a violation of their ...
Abortion is a controversial topic, with people having differing points of view and opinions on the matter. There are those who oppose abortion, while some people endorse pro-choice arguments. It is also an emotionally charged subject, so you need to be extra careful when crafting your persuasive essay .
In my essay, Why abortion is immoral, I criticised discussions of the morality of abortion in which the crucial issue is whether fetuses are human beings or whether fetuses are persons. ... In Part II, these principles are applied in an examination of three controversial ethical issues: voluntary euthanasia, abortion Database: eBook Collection ...
Introduction. The abortion debate deals with the rights and wrongs of deliberately ending a pregnancy before normal childbirth, killing the foetus in the process. Abortion is a very painful topic ...
The analysis of abortion by means of medical and social documents. Abortion means a pregnancy interruption "before the fetus is viable" [] or "before the fetus is able to live independently in the extrauterine environment, usually before the 20 th week of pregnancy" [].]. "Clinical miscarriage is both a common and distressing complication of early pregnancy with many etiological ...
Far from ending the controversy, returning abortion to the states already has led to outcomes wildly out of step with public opinion. Doctors and hospitals routinely deny patients basic medical ...
Essay Example: Abortion continues to stand at the crossroads of morality, ethics, and law, stirring intense debates that resonate across cultures and nations. Within this intricate tapestry of perspectives and convictions, the discourse on abortion unfolds, revealing a spectrum of beliefs and
Abortion-rights supporters celebrated last week when the Florida Supreme Court said voters could decide this fall whether to approve a state constitutional amendment protecting and expanding ...
"These are people I admire and respect," he said. "Those were all high-impact papers, meaning they're highly read and highly cited. By definition, they have had a broad impact on the field."