View Answer Keys
View the correct answers for activities in the learning path.
This procedure is for activities that are not provided by an app in the toolbar.
Some MindTap courses contain only activities provided by apps.
- Click an activity in the learning path.
- Get started
- Pre-Algebra

A quicker path to better grades
We have gathered all your curriculum-based courses, assignments, hints, tests, and solutions in one easy-to-use place
- Integrated I
- Integrated II
- Integrated III
Can't find your textbook?
More math. less studying.
A personal private tutor for each student. Free from preassure and study anxiety.
CPM Educational Program
- Core Connections Integrated I, 2013
- Core Connections Algebra 1, 2013
- Core Connections Geometry, 2013
- Core Connections Algebra 2, 2013
- Core Connections Integrated I, 2014

- Core Connections Integrated II, 2015

- Core Connections: Course 1

- Core Connections: Course 2

- Core Connections: Course 3

- Core Connections Integrated III, 2015
Expert Textbook Solutions
Browse your textbook to find expert solutions, hints, and answers for all exercises. The solutions are always presented as a clear and concise, step-by-step explanation with included theory and helpful figures, graphs, and diagrams. Mathleaks covers the most commonly adopted textbooks with more than 250000 expert solutions.
Mathleaks Solver
With Mathleaks, you’re not tied to your textbook for solutions. Instead, scan and solve exercises with our math solver, which instantly reads the problem by using the camera on your smartphone or tablet. Access the solver through the Mathleaks app or on our website. The Mathleaks solver works for Pre-Algebra, Algebra 1, and Algebra 2.
Mathleaks Community
Get access to the world's most popular math community with Mathleaks. You can connect with other students all over the US who are studying with the same textbook or in the same math course.
Study math more efficiently using Mathleaks for CPM Educational Program textbooks.
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Big Ideas Math Geometry Answers Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume
For better preparation and quality education, our team has shared the Big Ideas Math Book Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume for high school students. Provided Big Ideas Math Geometry Answers Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume are aligned topic-wise as per the latest common core curriculum. Students can easily understand the concepts of Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume. Learn how to solve the problems using the Circumference, Area, and Volume formulas in detail from here.
Big Ideas Math Book Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume
Step by Step Solutions explained for all the questions in the BIM Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume are easy to learn and understand as they are prepared by professional subject experts. After referring to the lesson-wise Big Ideas Math Geometry Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume Solution Key every high school student can become a pro in the concepts and gain better subject knowledge. So, click on the respective links and start preparing each topic of the BIM Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume efficiently.
Circumference, Area, and Volume Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Circumference, area, and volume monitoring progress, 11.1 circumference and arc length, lesson 11.1 circumference and arc length, exercise 11.1 circumference and arc length, 11.2 areas of circles and sectors, lesson 11.2 areas of circles and sectors, exercise 11.2 areas of circles and sectors, 11.3 areas of polygons, lesson 11.3 areas of polygons, exercise 11.3 areas of polygons, 11.4 three-dimensional figures, lesson 11.4 three-dimensional figures, exercise 11.4 three-dimensional figures, 11.1 – 11.4 quiz, 11.5 volumes of prisms and cylinders, lesson 11.5 volumes of prisms and cylinders, exercise 11.5 volumes of prisms and cylinders, 11.6 volumes of pyramids, lesson 11.6 volumes of pyramids, exercise 11.6 volumes of pyramids, 11.7 surface areas and volumes of cones, lesson 11.7 surface areas and volumes of cones, exercise 11.7 surface areas and volumes of cones, 11.8 surface areas and volumes of spheres, lesson 11.8 surface areas and volumes of spheres, exercise 11.8 surface areas and volumes of spheres, circumference, area, and volume review, circumference, area, and volume test, circumference, area, and volume cumulative assessment.
Find the surface area of the prism.
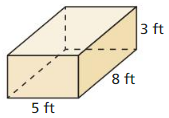
Answer: The surface area of the prism = 158.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, l = 5 ft, w = 8 ft, and h = 3 ft. where l = length, w = width, and h = height. The surface area of the rectangular prism = 2(lw + lh + wh). surface area = 2(5×8 + 5×3 + 8×3). surface area = 2(40 + 15 + 24). surface area = 2(79). surface area = 158.
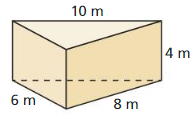
Answer: The surface area of the triangular prism = 68m.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, l = 10 m, p = 4 m, and h = 10. the surface area of the triangular prism = 2B + ph. b = base, p = perimeter, and h = height. surface area = 2(6 + 8) + 4(10). surface area = 2(14) + 40. surface area = 28 + 40. surface area = 68m.
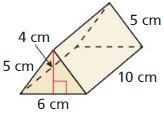
Answer: The surface area of the triangular prism = 42m.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, w = 10 cm, p = 4 cm, and h = 5 cm, l = 6 cm. the surface area of the triangular prism = 2B + ph. b = base, p = perimeter, and h = height. surface area = 2(6 + 5) + 4(5). surface area = 2(11) + 20. surface area = 22 + 20. surface area = 42cm.
Find the missing dimension.
Question 4. A rectangle has a perimeter 0f 28 inches and a width of 5 inches. What is the length of the rectangle?
Answer: The length of the rectangle = 9 in.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, A rectangle has a perimeter of 28 inches and a width of 5 inches. length of the rectangle = p/2 – w. length = 28/2 – 5. where perimeter = 28 in, and w = 5 in. length = 14 – 5. length = 9. so the length of the rectangle = 9 in.
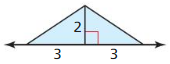
Question 5. A triangle has an area of 12 square centimeters and a height of 12 centimeters. What is the base of the triangle?
Answer: The base of the triangle = 2 cm.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, A triangle has an area of 12 sq cm and a height of 12 cm. The base of the triangle = 2(A)/h. base = 2(12)/12. base = 24/12. base = 2cm. so the base of the triangle = 2 cm.
Question 6. A rectangle has an area of 84 square feet and a width of 7 feet. What is the length of the rectangle?
Answer: The length of the rectangle = 12 ft.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, A rectangle has an area of 84 sq ft and a width of 7 feet. area of the rectangle = l x b. 84 = l x 7. l = 84/7. l = 12. so the length of the rectangle = 12 ft.
Question 7. ABSTRACT REASONING Write an equation for the surface area of a Prism with a length, width, and height of x inches. What solid figure does the prism represent?
Answer: The surface area of a prism = 2(lw + wh + lh).
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, length = l, width = w, and height = x inches. the surface area of the prism = 2(lw + wh + lh). the solid figure does the prism represent the rectangular prism.
Draw a net of the three-dimensional figure. Label the dimensions.
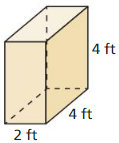
Answer: The surface area of the prism = 64 cm.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, l = 2 ft, w = 4 ft, and h = 4 ft. where l = length, w = width, and h = height. The surface area of the rectanguler prism = 2(lw + lh + wh). surface area = 2(2×4 + 4×4 + 4×2). surface area = 2(8 + 16 + 8). surface area = 2(32). surface area = 64.
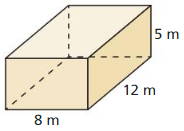
Answer: The surface area of the prism = 392 m.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, l =8 m, w = 12 m, and h = 5 m. where l = length, w = width, and h = height. The surface area of the rectanguler prism = 2(lw + lh + wh). surface area = 2(8×12 + 12×5 + 5×8). surface area = 2(96 + 60 + 40). surface area = 2(196). surface area = 392.
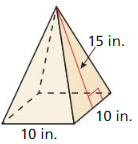
Answer: The surface area of the triangular prism = 170 in.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, B = 10 in, p = 15 in, and h = 15 in, l = 10 in. the surface area of the triangular prism = 2B + ph. b = base, p = perimeter, and h = height. surface area = 2(10) + 15(10). surface area = 2(10) + 150. surface area = 20 + 150. surface area = 170 in.
Exploration 1
Finding the Length of a Circular Arc
Work with a partner: Find the length of each red circular arc.
Answer: The Formula for the Arc Length is 2r(θ/360) r = 4 θ = 260 degrees Arc length = 2(4)(360/360) = 8(1) = 8 Therefore the Arc length is 8.
Exploration 2
Using Arc Length

Answer: C = πd C = 25π or 78.54 inch Half of revolution = 1/2 (78.54) = 39.27 inch No, the time has gone past the box by 3.27 inch
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3. How can you find the length of a circular arc? Answer: The length of a circular arc = 2 LOOKING FOR REGULARITY IN REPEATED REASONING To be proficient in math, you need to notice if calculations are repeated and look both for general methods and for shortcuts.
Question 4. A motorcycle tire has a diameter of 24 inches. Approximately how many inches does the motorcycle travel when its front tire makes three-fourths of a revolution? Answer: The diameter of the motorcycle is 24 inches. One revelation = 360 degrees. Three-fourths of one revelation = 270 degrees. The motorcycles travel = 2r(θ/360) Radius r = d/2 = 24/2 = 12 θ = 270 degrees. = 2(12)(270/360) = 24(270/360) = 18 Therefore the motorcycle travels 18 cm.
Monitoring Progress
Question 1. Find the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 5 inches.
Answer: Circumference C = πd C = 3.14x 5 = 15.7 in
Question 2. Find the diameter of a circle with a circumference of 17 feet.
Answer: Diameter d = C/π d = 17/π = 5.41 ft
Find the indicated measure.
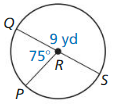
Answer: arc length of \(\widehat{P Q}\) is 5.887
Explanation: \(\widehat{P Q}\) = \(\frac { 75 }{ 360 } \) . π(9) = 5.887
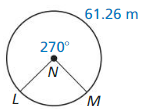
Answer: arc length of LM/C = LM/360 61.26/C = 270/360 C = 81.68
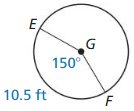
Answer: arc length of EF = \(\frac { 60 }{ 360 } \) • 2πr 10.5 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 } \) • 2πr r = 10.02
Question 6. A car tire has a diameter of 28 inches. How many revolutions does the tire make while traveling 500 feet?
Answer: The car tire have to make 69 revolutions to travel 500 ft.
Explanation: Circumference C = 2πr = πd C = 28π Distance travelled = number of revolutions x C 500 x 12 = number of revolutions x 28π number of revolutions = 68.2
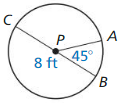
Question 7. In Example 4. the radius of the arc for a runner on the blue path is 44.02 meters, as shown in the diagram. About how far does this runner travel to go once around the track? Round to the nearest tenth of a meter.
Answer: Given that, The arc radius for a runner on the blue path is 44.02 meters. The diameter of the track is 2r = 2(44.02) = 88.04 The circumference of the track is πd = π(88.04) = 276.44 The runner travels around the track 276.44 cm.
Question 8. Convert 15° to radians.
Answer: 15° = 15 . \(\frac { π radians }{ 180° } \) = \(\frac { π }{ 12 } \) radians
Question 9. Convert \(\frac{4 \pi}{3}\) radians to degrees.
Answer: \(\frac{4 \pi}{3}\) radians = \(\frac{4 \pi}{3}\) radians . \(\frac { 180° }{ π radians } \) = 240 degrees
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 2. WRITING Describe the difference between an arc measure and an arc length.
Answer: An arc measure is measured in degrees while an arc length is the distance along an arc measured in linear units.
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 10, find the indicated measure.

Question 4. diameter of a circle with a circumference of 63 feet
Answer: C = 63 ft πd = 63 d = 20.05

Question 6. exact circumference of a circle with a diameter of 5 inches
Answer: C = πd C = 5π = 15.707
Answer: \(\frac { arc length of DE }{ 2πr } \) = \(\frac { DE }{ 360 } \) \(\frac { 8.73 }{ 2π(10) } \) = \(\frac { DE }{ 360 } \) DE = 50.01°
Answer: \(\frac { arc length of GH }{ 2πr } \) = \(\frac { m GH }{ 360 } \) \(\widehat{G H}\). = \(\frac { 5 }{ 24 } \) . 2π(10) = 13.08

Answer: Circumference of the front wheel = 2π(32.5) = 65π cm Distance covered = 40 m = 40 x 100 = 4000 cm Number of revolutions = \(\frac { 4000 }{ 65π } \) = 19.58
In Exercises 15-18 find the perimeter of the shaded region.
In Exercises 19 – 22, convert the angle measure.
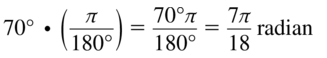
Question 20. Convert 300° to radians.
Answer: 300 • (\(\frac { π }{ 180 } \)) = \(\frac { 5π }{ 3 } \) radian
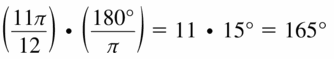
Question 22. Convert \(\frac{\pi}{8}\) radian to degrees.
Answer: \(\frac { π }{ 8 } \) • \(\frac { 180 }{ π } \)) = 22.5°
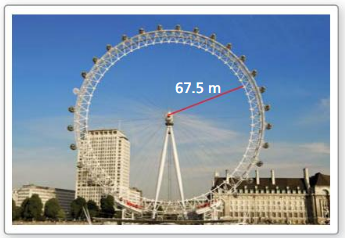
Answer: C = 38 ft 2πr = 38 r = 6.04
In Exercises 25 and 26, find the circumference of the circle with the given equation. Write the circumference in terms of π
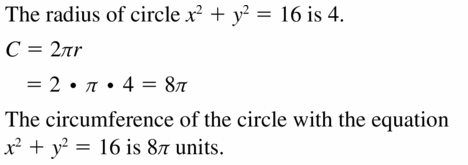
Question 26. (x + 2) 2 + (y – 3) 2 = 9
Answer: The radius of circle (x + 2)² + (y – 3)² = 9 is 3 C = 2πr = 2π(3) = 6π The circumference of the circle is 6π units.
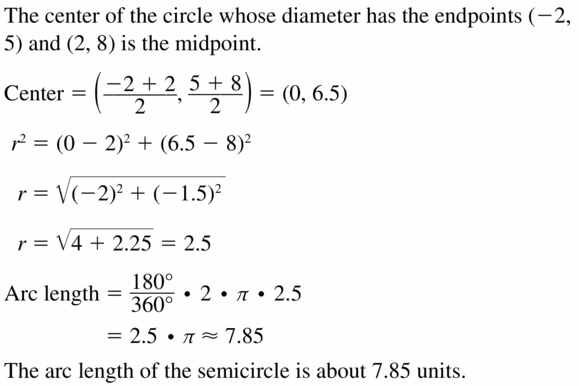
Question 28. REASONING \(\widehat{E F}\) is an arc on a circle with radius r. Let x° be the measure of \(\widehat{E F}\). Describe the effect on the length of \(\widehat{E F}\) if you (a) double the radius of the circle, and (b) double the measure of \(\widehat{E F}\). Answer: Given x° is the measure of \(\widehat{E F}\) arc length of a circle = x/360 × 2πr arc length of \(\widehat{E F}\) = x/360 × 2πr a. double the radius of the circle x/360 × 2π(2r) = 2x/360 × 2πr x/360 × 2π(2r) = 2arc length of \(\widehat{E F}\) (b) double the measure of \(\widehat{E F}\) 2x/360 × 2πr = 2 × x/360 × 2πr 2x/360 × 2πr = 2arc length \(\widehat{E F}\)
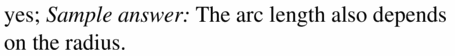
Question 32. ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS A 45° arc in ⊙C and a 30° arc in ⊙P have the same length. What is the ratio of the radius r 1 of ⊙C to the radius r 2 of ⊙P? Explain your reasoning. Answer: Given, A 45° arc in ⊙C and a 30° arc in ⊙P have the same length. r1/r2 = 45/30 = 3/2 So, the ratio of the radius r 1 of ⊙C to the radius r 2 of ⊙P is 3/2.

Question 38. MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS What is the measure (in radians) of the angle formed by the hands of a clock at each time? Explain your reasoning. a. 1 : 30 P.M.
Answer: 3π/4
b. 3:15 P.M.
Answer: π/24
Question 40. THOUGHT PROVOKING Is π a rational number? Compare the rational number \(\frac{355}{113}\) to π. Find a different rational number that is even closer π.
Answer: π is not a rational number as it can not be represented as an equivalent fraction. π = 3.14 and 355/113 = 3.14. This fraction resembles that value of π. Therefore a more accurate fraction will be starting by the value of 7 decimal places of π, therefore 3.1415926 x x = a.
b. What would the sum of the arc lengths be if \(\overline{A B}\) was divided into 8 congruent segments? 16 congruent segments? n congruent segments? Explain your reasoning. Answer: 360/2 = 180 degrees Then the arc length of 1 semicircle is 180/360 × 2π(r/2) 1/2 × πr = πr/2 Therefore the arc length of 8 semicircles will be 8 × πr/2 = 4πr
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
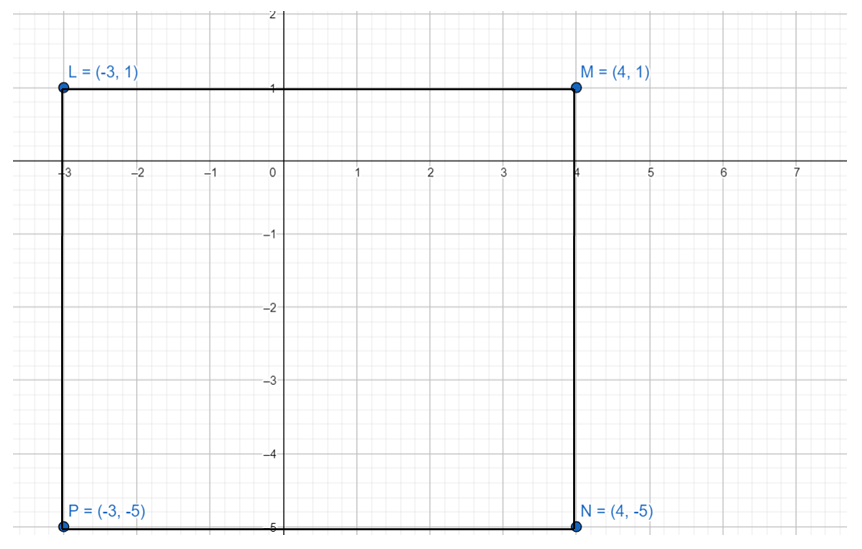
Find the area of the polygon with the given vertices.
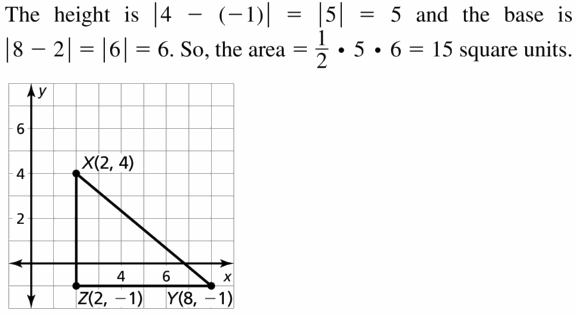
Question 44. L(- 3, 1), M(4, 1), N(4, – 5), P(- 3, – 5)
Finding the Area of a Sector of a Circle
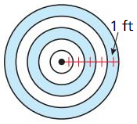
Work with a partner: A sector of a circle is the region bounded by two radii of the circle and their intercepted arc. Find the area of each shaded circle or sector of a circle.
Finding the Area of a Circular Sector

Question 3. How can you find the area of a sector of a circle? Answer: The formula for sector area is simple, just multiply the central angle by the radius squared, and divide by 2 Area of a sector = θ/360 × πr²
Question 4. In Exploration 2, find the area of the sector that is irrigated in 2 hours. Answer:
Monitoring progress
Question 1. Find the area of a circle with a radius of 4.5 meters.
Answer: Circle area = πr² A = π(4.5)² = 20.25π
Question 2. Find the radius of a circle with an area of 176.7 square feet.
Answer: Circle area = πr² 176.7 = πr² r² = 56.24 r = 7.499
Question 3. About 58,000 people live in a region with a 2-mile radius. Find the population density in people per square mile.
Answer: The population density is about 4615.49 people per square mile.
Explanation: A = πr² = π • 2² = 4π Population density = \(\frac { number of people }{ area of land } \) = \(\frac { 58000 }{ 4π } \) = 4615.49
Question 4. A region with a 3-mile radius has a population density of about 1000 people per square mile. Find the number of people who live in the region.
Answer: The number of people who live in the region are 28274.
Explanation: A = πr² = π • 3² = 9π Population density = \(\frac { number of people }{ area of land } \) Number of people = 1000 x 9π = 28274
Find the indicated measure
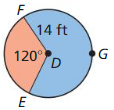
Question 5. area of red sector
Answer: The area of red sector = 205.25
Explanation: m∠FDE = 120°, FE = 120° and FGE = 360° – 120° = 240° Area of red sector = \(\frac { FE }{ 360° } \) • πr² = \(\frac { 120 }{ 360° } \) • π(14²) = 205.25
Question 6. area of blue sector
Answer: Area of blue sector = 410.5
Explanation: Area of blue sector = \(\frac { FGE }{ 360° } \) • πr² = \(\frac { 240 }{ 360° } \) • π(14²) = 410.5
Question 7. Find the area of ⊙H.
Answer: Area of ⊙H = 907.92 sq cm
Explanation: Area of sector FHG =\(\frac { FG }{ 360° } \) • Area of ⊙H 214.37 = \(\frac { 85 }{ 360° } \) • Area of ⊙H Area of ⊙H = 907.92 sq cm
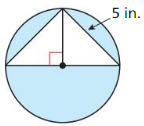
Question 8. Find the area of the figure.
Answer: Area of triangle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) • 7 • 7 = 24.5 sq m Area of semi circle = πr²/2 = π(3.5)²/2 = 19.242255 Area of the figure = 24.5 + 19.24 = 43.74 sq m
Question 9. If you know the area and radius of a sector of a circle, can you find the measure of the intercepted arc? Explain.
Answer: Yes, we can find the intercepted arc when we the area and the radius of the sector of the circle. Because the intercepted arc is the arc inside the inscribed angles and whose endpoints are on the angle.

Question 2. WRITING The arc measure of a sector in a given circle is doubled. will the area of the sector also be doubled? Explain our reasoning.
Answer: Yes
Explanation: Area of sector with arc measure x and radius r is s = π/180(xr) If x becomes doube, then s1 = π/180(2xr) = 2s This means that if the arc measure doubles, area of the sector also doubles.
In Exercise 3 – 10, find the indicated measure,
Answer: Area A = πr² A = π(10)² = 100π sq in
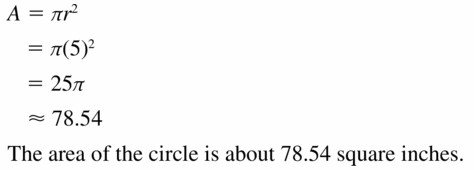
Question 6. area of a circle with a diameter of 16 feet
Answer: d = 2r Circle area = πr² = (π/4)d² = (π/4)16² = 64π

Question 8. radius of a circle with an area of 380 square inches
Answer: A = πr² 380 = πr² r = 10.99
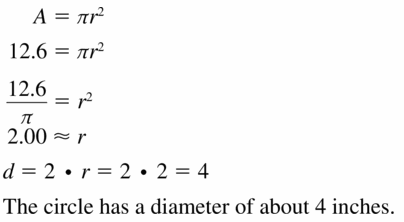
Question 10. diameter of a circle with an area of 676π square centimeters
Answer: Area A = 676π square centimeters (π/4)d² = 676π d² = 2704 d = 52
In Exercises 11 – 14, find the indicated measure.

Question 12. About 650,000 people live in a region with a 6-mile radius. Find the population density in people per square mile.
Answer: The population density is about 5747 people per square mile.
Explanation: Area of region = π(6)² = 36π Population density = \(\frac { Number of people }{ area of land } \) = \(\frac { 650,000 }{ 36π } \) = 5747.2
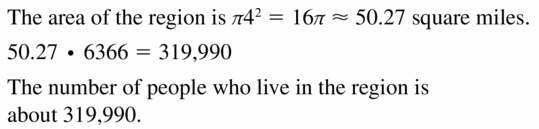
Question 14. About 79,000 people live in a circular region with a population density of about 513 people per square mile. Find the radius of the region.
Answer: The radius of the region is 7
Explanation: Population density = \(\frac { Number of people }{ area of land } \) 513 = \(\frac { 79,000 }{ πr² } \) πr² = 153.99 r = 7
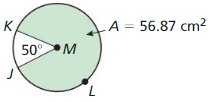
In Exercises 15-18 find the areas of the sectors formed by∠DFE.
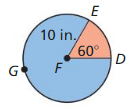
Answer: Area of sector = \(\frac { 104° }{ 360° } \) • π(14)² = 177.88 Area of red region is 177.88 sq cm Area of blue region = \(\frac { 256° }{ 360° } \) • π(14)² = 437.86 sq cm
Answer: Area of red region is 10.471 sq ft Area of the blue region is 39.79 sq ft
Explanation: Area of sector = \(\frac { 75° }{ 360° } \) • π(4)² = 10.471 Area of red region is 10.471 sq ft Area of blue region = \(\frac { 285° }{ 360° } \) • π(4)² = 39.79 sq ft
Answer: Area of ⊙Z is 255 square feet πr² = 255 r = 9 Area of sector XZY = \(\frac { 115 }{ 360 } \) • 255 n = 81.458 sq ft
In Exercises 21 and 22, the area of the shaded sector is show. Find the indicated measure.
Answer: radius of ⊙M = 3.98
Explanation: Area of region = \(\frac { 89 }{ 360 } \) . Area of ⊙M 12.36 = \(\frac { 89 }{ 360 } \) . Area of ⊙M Area of ⊙M = 49.99 πr² = 49.99 r = 3.98
In Exercises 23 – 28, find the area of the shaded region.
Answer: The area of the shaded region is 85.840 sq in.
Explanation: Area of square = 20² = 400 Diameter of one circle = 10 radius of one circle = 5 in Area of one circle = π(5)² = 78.53 Areas of four circle = 314.159 Area of shaded region = 400 – 314.159 = 85.840
Answer: The area of shaded region is 301.59
Explanation: The radius of smaller circle is 8 cm The radius of bigger circle is 16 cm Area of smaller semicircle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(π(8)²) = 100.53 Area of lager semicircle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(π(16)²) = 402.123 Area of shaded region = 402.123 – 100.53 = 301.59
Explanation: c² = 3² + 4² = 25 c = 5 Radius = 2.5 Circle area = π(2.5)² = 19.63 Area of triangle = (3 x 4)/2 = 6 Area of shaded region = 19.63 – 12 = 7.63
Question 30. MAKING AN ARGUMENT Your friend claims that if the radius of a circle is doubled, then its area doubles. Is your friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
Answer: The friend is not correct. doubling the radius quadruples the area.
Explanation: Area of circle with radius r = πr² Area of circle with radius 2r = π(2r)² = 4πr²
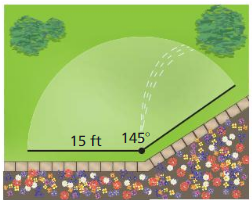
b. What is the area of land that can be covered by the light from the lighthouse? Answer: Area = \(\frac { 245 }{ 360 } \) x π(18)² = 692.72 sq mi

Question 34. ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS A square is inscribed in a circle. The same square is also circumscribed about a smaller circle. Draw a diagram that represents this situation. Then find the ratio of the area of the larger circle to the area of the smaller circle.
Answer: We start by assigning a variable to the radius of the inner circle. It is r, therefore the area of the circle is πr² It can be seen that the side length of square is twice this radius. Therefore it can be said that the side length of this square is 2r. Next, it can be seen that the diagonal of the square is diameter of outer circle. Therefore, length of the diagonal of the circle d = 2r√2. outer circle radius = r√2 Area of outer circle 2πr² The ratio of the area of larger circle to the smaller circle = 2.
Answer: Ellipse area = πab

Maintaining Mathematical proficiency
Find the area of the figure.
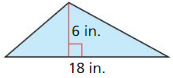
Answer: Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(base x height) Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(18 x 6) = 54 sq in
Finding the Area of a Regular Polygon
Writing a Formula for Area
Work with a partner: Generalize the steps you used in Exploration 1 to develop a formula for the area of a regular polygon. REASONING ABSTRACTLY To be proficient in math, you need to know and flexibly use different properties of operations and objects. Answer:
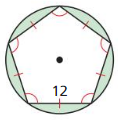
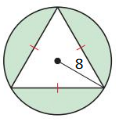
Question 3. How can you find the area of a regular polygon? Answer: You can find the area of the regular pentagon using the formulas. They are, The formula for the regular pentagon if only the side is known is A = 1/4 x square root of 5(5 + 2 square root(5) x (a)². The formula for the area of the regular pentagon is 1/2 x p x a. Where a = apothem P = perimeter
Question 4. Regular pentagon ABCDE has side lengths of 6 meters and an apothem of approximately 4.13 meters. Find the area of ABCDE. Answer: Given that, The side length of the regular pentagon ABCDE is 6 meters. The apothem of the regular pentagon is 4.13 meters. The formula for the area of the regular pentagon is 1/2 x p x a. Where a = apothem P = perimeter The formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon is = 5a = 5(6) = 30 = 1/2 x 30 x 4.13 = 1/2 x 123.9 = 61.95 square cm
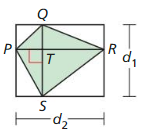
Question 1. Find the area of a rhombus with diagonals d 1 = 4 feet and d 2 = 5 feet.
Answer: Area of rhombus = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(4 x 5) = 5 sq ft
Question 2. Find the area of a kite with diagonals d 1 = 12 inches and d 1 = 9 inches.
Answer: Area of kite = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(12 x 9) = 27 sq in
In the diagram. WXYZ is a square inscribed in ⊙P.
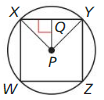
Question 3. Identify the center, a radius, an apothem, and a central angle of the polygon.
Answer: P is the center, PY or PX is the radius, PQ is apothem, ∠XPY is the central angle.
Question 4. Find m∠XPY, m∠XPQ, and m∠PXQ.
Answer: m∠XPY = \(\frac { 360 }{ 4 } \) = 90 m∠XPQ = 90/2 = 45 m∠PXQ = 180 – (90 + 45) = 45
Find the area of regular polygon
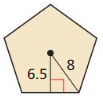
Answer: c = √(8² + 6.5²) = 10.3 a = 20.61 Area = 0.25(√5(5+2√5) a² Area = 0.25(√5(5+2√5) 20.61² = 730.8
Answer: EF = radius = 6.8
Find the apothem of polygon ABCDE.
Answer: GF = apothem = 5.5
Answer: AF = √4² + 5.5² AF = 6.8
Find the radius of polygon ABCDE. Answer: AF = radius = 6.8
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the area of the kite or rhombus.
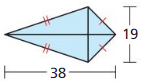
Answer: d₁ = 6 + 6 = 12 d₂ = 2 + 10 = 12 area A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(12 x 12) = 36
In Exercises 7 – 10, use the diagram
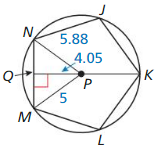
Question 8. Identify a central angle of polygon JKLMN.
Answer: ∠NPM is the central angle of polygon JKLMN
Question 10. What is the apothem of polygon JKLMN? Answer: QP is the apothem of polygon JKLMN
In Exercises 11 – 14, find the measure of a central angle of a regular polygon with the given number of sides. Round answers to the nearest tenth of a degree, if necessary.
Question 12. 18 sides
Answer: The measure of central angle = \(\frac { 360 }{ 18 } \) = 20

Question 14. 7 sides
Answer: The measure of central angle = \(\frac { 360 }{ 7 } \) = 51.42
In Exercises 15 – 18, find the given angle measure for regular octagon ABCDEFGH.
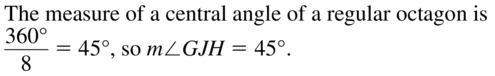
Question 16. m∠GJK
Answer: m∠GJK = m∠GJH/2 m∠GJK = 22.5
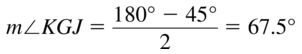
Question 18. m∠EJH Answer: m∠EJH = 3(45) = 135
In Exercises 19 – 24, find the area of the regular polygon.
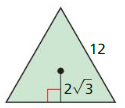
Question 24. a pentagon with an apothem of 5 units
Answer: A = 90.75
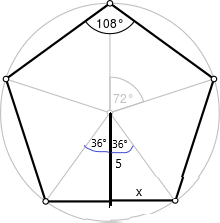
We know apothem a = and it divides pentagon into triangles, the central angle is divided into 360/5 = 72 After that, we halved this angle and got 2 right triangles with x = 44 and y = 36. Since we know one side and all three angles of the triangle, we can calculate p with the tangent function. tan y = p/a tan 36 = p/5 p = 3.63 Since p is just half of the length of the side, we have to multiply it by 2 2 . p = 2 . 3.63 = 7.26 = s Area = \(\frac { a . s. n }{ 2 } \) A = \(\frac { 15 x 7.26 x 5 }{ 2 } \) A = 90.75
Answer: s = √15² – 13² = 7.48 Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(a . ns) A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(13 x 6 x 7.48) A = 291.72
In Exercises 27 – 30, find the area of the shaded region.
Answer: Area of the shaded region = 223.75
Explanation: Square side = diagonal/√2 = 28/√2 = 19.79 Area of square = 19.79² = 392 Circle area = π(14)² = 615.75 Area of the shaded region = 615.75 – 392 = 223.75
CRITICAL THINKING In Exercises 33 – 35, tell whether the statement is true or false. Explain your reasoning

Question 34. The apothem of a regular polygon is always less than the radius.
Answer: true, the radius always reaches the end of the circle but the apothem never does

Explanation: (A) area = π(6.5)² = 132.73 (B) area = 139.25 (C) area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(18 x 15) = 135
Question 38. REASONING What happens to the area of a kite if you double the length of one of the diagonals? if you double the length of both diagonals? Justify your answer.
Answer: Area of a kite = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) If you double the length of one diagonal, then d₁ = 2d₁ Area of kite = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(d₁d₂) If you double length of both diagonals Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(2d₁2d₂) = d₁d₂ If you double the length of one diagonal, then the area becomes halve. If you double length of both diagonals, then area becomes 4 times.
MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS In Exercises 39 and 40, write and solve an equation to find the indicated lengths. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.

Question 40. One diagonal of a rhombus is four times the length of the other diagonal. The area of the rhombus is 98 square feet. Find the length of each diagonal.
Answer: The length of each diagonal is 9.89, 2.47.
Explanation: One diagonal of a rhombus is four times the length of the other diagonal. d₁ = 4d₂ Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) 98 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁(4d₁)) d₁ = 9.89 d₂ = 2.47

Question 42. MAKING AN ARGUMENT Your friend claims that it is possible to find the area of any rhombus if you only know the perimeter of the rhombus. Is your friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
Answer: No; A rhombus is not a regular polygon.
Answer: Given that, The hexagon has 6 sides. The hexagon is divided into 6 equilateral triangles. The area of the equilateral triangle is (square root of 3)/4 x a² a = side length = (square root of 3)/4 x (6)² = (square root of 3)/4 x 36 = 15.588 square cm.
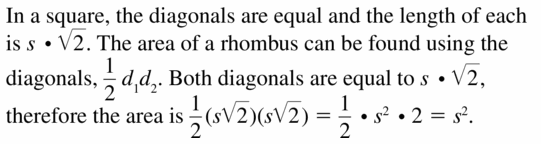
Question 48. CRITICAL THINKING The area of a dodecagon, or 12-gon, is 140 square inches. Find the apothem of the polygon.
Answer: Let the side length of dodecagon be 2x. The measure of each interior angle of a regular decagon is 150. This implies that the base angle C and A of the resulting isosceles triangle formed by the red sides is equal to 150/2 = 75. The adjacent to this angle is the length 2x/2 = x inches, while the opposite to it is the blue apothem in the right triangle BDC formed. Therefore a = x tan 75. Therefore, area of dodecagon is 140 = 1/2 (x tan75)(12 . 2x) 140 = 44.785 x² x² = 3.126 x = 1.768
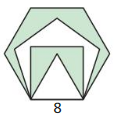
Question 52. USING STRUCTURE Two regular polygons both have n sides. One of the polygons is inscribed in, and the other is circumscribed about, a circle of radius r. Find the area between the two polygons in terms of n and r.
Answer: The radius of the smaller polygon is equal to the apothem of the larger polygon. The central angle is 360/n, therefore the apothem makes an angle of 180/n. Use sine and cosine to find the apothem and side length of the smaller polygon. a small = r sin\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) s small = 2r cos\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) Use tangent to find the side length of the large polygon. S large = 2r tan\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) Use the formula to find the area of the smaller polygon. A small = 1/2 . a small . n . s small A small = 1/2 . r sin\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) . n . 2r cos\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) A small = nr² sin \(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) cos\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) Use the formula to find the area of the larger polygon. A Large = 1/2 . a large . n . slarge = nr² tan\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) The area between the polygons is equal to the area of the larger polygon minus the area of the smaller polygon. Use some trig identities to simplify the expression. A = A large – A small A = nr² tan\(\frac { 180 }{ n } sin²[latex]\frac { 180 }{ n }
Determine whether the figure has line symmetry, rotational symmetry, both, or neither. If the figure has line symmetry. determine the number of lines of symmetry. It the figure has rotational symmetry, describe any rotations that map the figure onto itself.
Analyzing a Property of Polyhedra
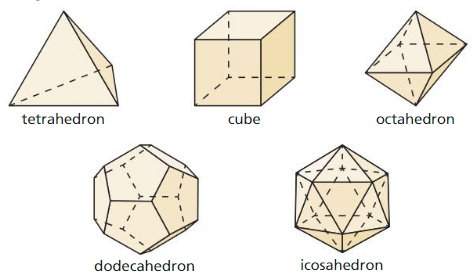
Question 2. What is the relationship between the numbers of vertices V, edges E, and faces F of a polyhedron? (Note: Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler (1707 – 1783) discovered a formula that relates these quantities.) CONSTRUCTING VIABLE ARGUMENTS To be proficient in math, you need to reason inductively about data. Answer: The relationship between the vertices, edges, and faces of a polyhedron according to Euler’s formula is F + V = E + 2. Where F = number of faces. V = number of vertices. E = number of edges.
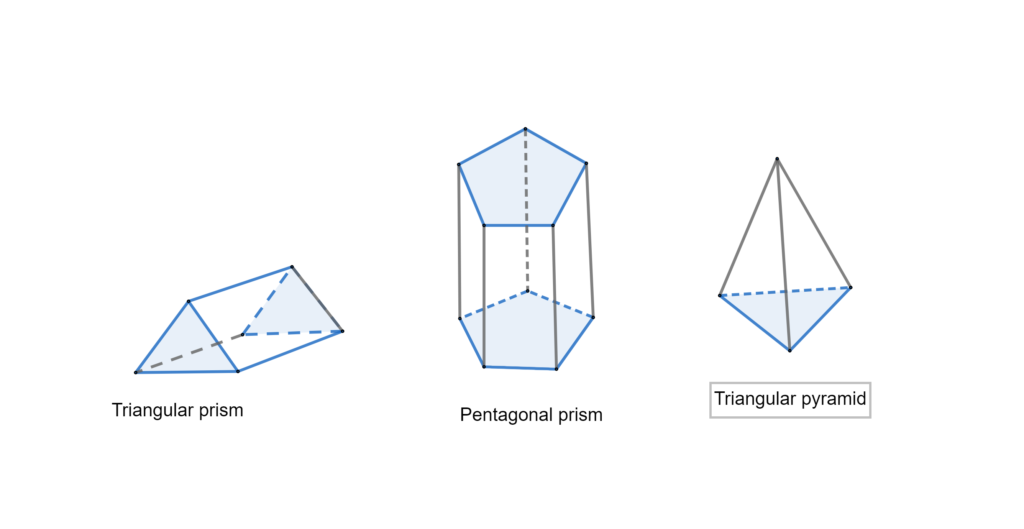
now we count vertices, edges, and faces in each solids A triangular prism has vertices 6, edges 9 and faces 5 6 – 9 + 5 = 2 A Pentagonal prism has vertices 10, edges 15 and faces 7 10 – 15 + 7 = 2 A triangular pyramid has vertices 4, edges6 and faces 4 – 6 + 2 = 2
Tell whether the solid is a polyhedron. If it is, name the polyhedron.
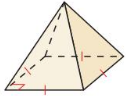
Answer: The solid is formed by polygons, so it is a polyhedron. The base is a square, it is a square pyramid.
Describe the shape formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid.
Sketch the solid produced by rotating the figure around the given axis. Then identify and describe the solid.
Answer: Cone does not belong with the other three as it has a curved surface and others not.
In Exercises 3 – 6, match the polyhedron with its name.
In Exercises 7 – 10, tell whether the solid is a polyhedron. If it is, name the polyhedron.
In Exercises 11 – 14, describe the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid.
In Exercises 15 – 18, sketch the solid produced by rotating the figure around the given axis. Then identify and describe the solid.
In Exercises 21 – 26, sketch the polyhedron.
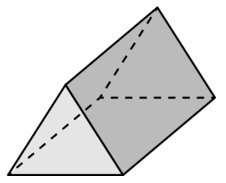
Question 22. rectangular prism
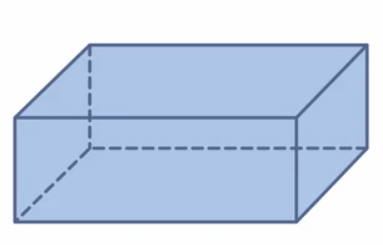
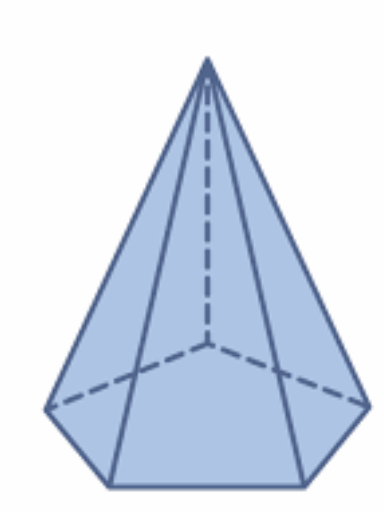
Question 26. pentagonal pyramid
b. What is the perimeter of the cross section? Answer: The perimeter is 2(l + b)
c. What is the area of the cross section? Answer: Area is lb.
REASONING In Exercises 29 – 34, tell whether it is possible for a cross section of a cube to have the given shape. If it is, describe or sketch how the plane could intersect the cube.
Question 30. pentagon Answer: yes, cross-section of the cube can be a pentagon.
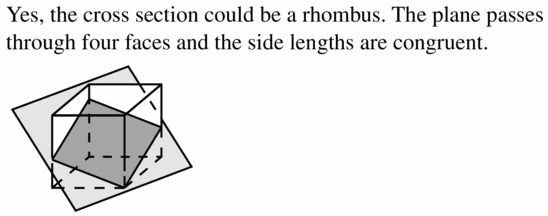
Question 32. isosceles triangle Answer: Yes, the cross-section can be an isosceles triangle.
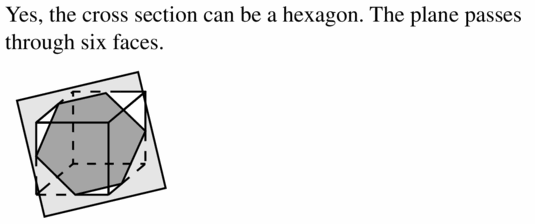
Question 34. scalene triangle Answer: Yes, the cross-section can be scalene triangle.
Question 36. THOUGHT-PROVOKING Describe how Plato might have argued that there are precisely five Platonic Solids (see page 617). (Hint: Consider the angles that meet at a vertex.) Answer:
Decide whether enough information is given to prove that the triangles are congruent. It so, state the theorem you would use.
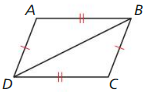
Answer: ∆JLK ≅ ∆JLM by SAS congruence theorem.
Question 4. Convert 26° to radians and \(\frac{5 \pi}{9}\) radians to degrees.
Answer: 26° = 26 . \(\frac { π }{ 180 } \) = \(\frac { 13π }{ 90 } \) radians \(\frac{5 \pi}{9}\) = \(\frac{5 \pi}{9}\) . \(\frac { 180 }{ π } \) = 100°
Use the figure to find the indicated measure.
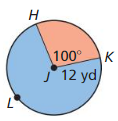
Answer: area of red sector = \(\frac { 100 }{ 360 } \) . π(12)² = 125.66
Answer: area of blue sector = \(\frac { 260 }{ 360 } \) . π(12)² = 326.72
In the diagram, RSTUVWXY is a reuIar octagon inscribed in ⊙C.
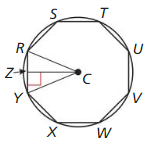
Question 7. Identify the center, a radius, an apothem, and a central angle of the polygon.
Answer: C is center, CY is radius, CZ is apothem, ∠YCR is central angle of the polygon
Question 8. Find m∠RCY, m∠RCZ, and m∠ZRC.
Answer: m∠RCY = 360/8 = 45 m∠RCZ = 45/2 = 22.5 m∠ZRC = 180 – (22.5 + 90) = 67.5
Question 9. The radius of the circle is 8 units. Find the area of the octagon.
Answer: Area of octagon = 0.5 x 8 x 8 sin 45 = 22.62
Answer: Area of yellow tile = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(15.7 x 11.4) = 44.745 area of red tile = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(18.5 x 6) = 27.75 Area of pattern = 32(44.745) + 23(27.75) = 2070.09 sq mm
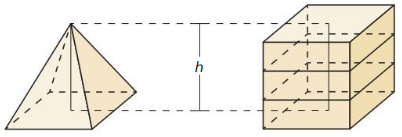
Finding volume
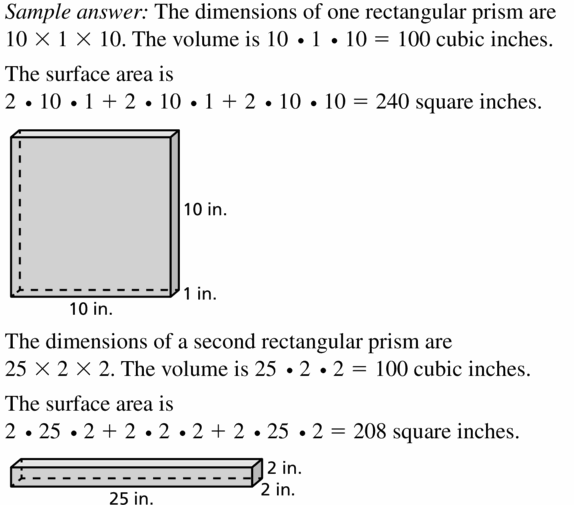
Work with a partner: Consider a stack of square papers that is in the form of a right prism.
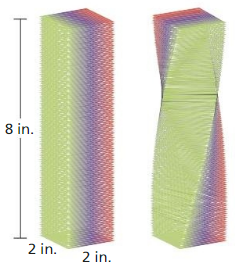
a. What is the volume the prism? Answer: The volume of the prism is B = 1/2 x h(b1 + b2) h = 8 b1 = 2 b2 = 2 = 1/2 x 8(2 + 2) = 1/2 x 8(4) = 1/2 x 32 = 16 cube inches. Therefore the volume of the prism is 16 cu. inches.
b. When you twist the slack of papers, as shown at the right, do you change the volume? Explain your reasoning. Answer: The volume of the prism and the twist of the slack of paper volume are the same. Because the different shapes of the prism have the same volume.
c. Write a carefully worded conjecture that describes the conclusion you reached in part (b). ATTENDING TO PRECISION To be proficient in math, you need to communicate precisely to others. Answer: The conjecture is that the different shapes of the prism have the same volume but are different in surface area.
d. Use your conjecture to find the volume of the twisted stack of papers. Answer: The volume of the twist of the slack of paper is B = 1/2 x h(b1 + b2) h = 8 b1 = 2 b2 = 2 = 1/2 x 8(2 + 2) = 1/2 x 8(4) = 1/2 x 32 = 16 cu. inches. Therefore the volume of the twist and the slack of the paper is 16 cu. inches. It is the same as the volume of the prism.
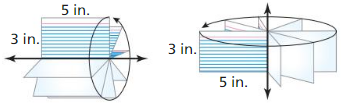
Work with a partner: Use the conjecture you wrote in Exploration I to find the volume of the cylinder.
Question 3. How can you find the volume of a prism or cylinder that is not a right prism or right cylinder? Answer: Using π we can find the volume of the prism or cylinder that is not a right prism of the right cylinder. The cylinder and the prism have the same cross-sectional area of πr². At every level and same height. Both the cylinder and prism have the same volume it is V = πr²h.
Question 4. In Exploration 1, would the conjecture you wrote change if the papers in each stack were not squares? Explain your reasoning. Answer:
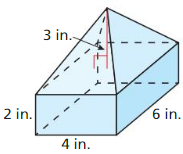
Find the volume of the solid.
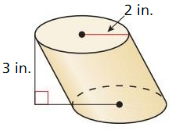
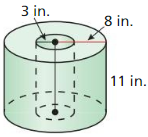
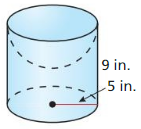
Answer: Area of circle = πr² = π(8)² = 64π Volume = 64π x 14 = 2814.86 cubic ft
Question 4. WHAT IF? In Example 4, you want the length to be 5 meters, the width to be 3 meters. and the volume to be 60 cubic meters. What should the height be? Answer: volume = lbh 60 = 5 x 3 x h h = 4 m
Question 5. WHAT IF? In Example 5, you want the height to be 5 meters and the volume to be 75 cubic meters. What should the area of the base be? Give a possible length and width. Answer: volume V = base x height 75 = base x 5 Base = 15 sq m
Question 2. COMPLETE THE SENTENCE Density is the amount of _______ that an object has in a given unit of __________ .
Answer: Density is the mass of the object divided by its volume.
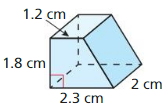
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the volume of the prism.
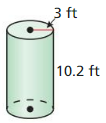
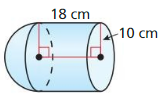
In Exercises 7 – 10. find the volume of the cylinder.
In Exercises 11 and 12. make a sketch of the solid and find its volume. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
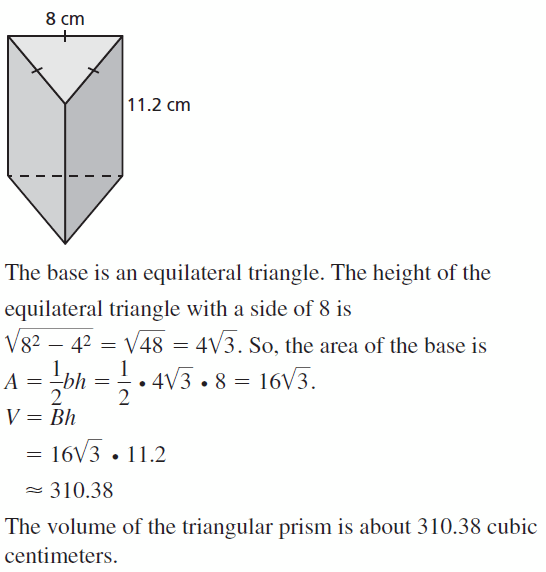
Question 12. A pentagonal prism has a height of 9 feet and each base edge is 3 feet.
Answer: volume is 139.32 ft³
explanation: Pentagon area = 15.48 Height h = 9 ft Volume V = area x height = 15.48 x 9 = 139.32

Answer: Density = mass / volume Density = \(\frac { 24 }{ 28.3 } \) Density = 0.8480
In Exercises 17 – 22, find the missing dimension of the prism or cylinder.
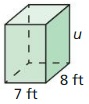
Answer: Volume = 2700 yd³ 12 x 5 x v = 2700 v = 15 yd
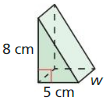
In Exercises 23 and 24, find the area of the base of the rectangular prism with the given volume and height. Then give a possible length and width.

Question 24. V = 27 m 3 ,h = 3m
Answer: V = Bh 27 = B x 3 B = 9
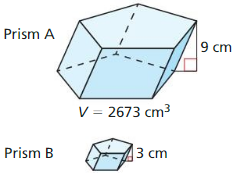
In Exercises 25 and 26, the solids are similar. Find the volume of solid B.
In Exercises 27 and 28, the solids are similar. Find the indicated measure.
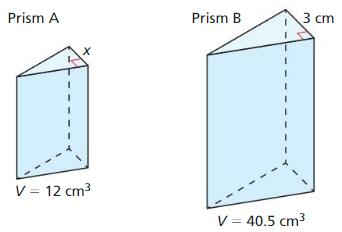
Explanation: \(\frac { 7π }{ 5 } \) = \(\frac { 56π }{ h } \) h = 40
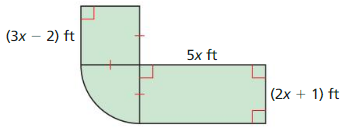
In Exercises 29 – 32. find the volume of the composite solid.
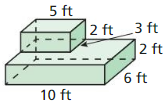
Explanation: Volume of square = 4³ = 64 Volume of semicircle = π(2)² x 4 = 8π
Answer: The volume of composite solid is 35 cubic ft
Explanation: Volume of larger prism = 4 x 2 x 5 = 40 Volume of the smaller prism = 1 x 1 x 5 = 5 Volume of larger prism – volume of the smaller prism = 40 – 5 = 35 cubic ft

Question 34. COMPARING METHODS The Volume Addition Postulate states that the volume of a solid is the sum of the volumes of all its non overlapping parts. Use this postulate to find the volume of the block of concrete in Example 7 by subtracting the volume of each hole from the volume of the large rectangular prism. Which method do you prefer? Explain your reasoning. Answer:
REASONING In Exercises 35 and 36, you are melting a rectangular block of wax to make candles. how many candles of the given shape can be made using a block that measures 10 centimeters by 9 centimeters by 20 centimeters?

Answer: 7 triangular prism candles with the given measures can be made.
Explanation: Volume of block = 1800 The volume of triangular prism = 4 x 6 x 10 = 240 1800/240 = 7.5

Question 38. PROBLEM SOLVING You drop an irregular piece of metal into a container partially filled with water and measure that the waler level rises 4.8 centimeters. The square base of the container has a side length of 8 centimeters. You measure the mass of the metal to be 450 grams. What is the density of the metal?
Answer: The density of metal is 1.4648
Explanation: Density = \(\frac { Mass }{ Volume } \) Volume V = 4.8 x 64 = 307.2 Density = \(\frac { 450 }{ 307.2 } \) = 1.4648
Answer: Volume = 2.5 x 3.5 x 6 Volume = 52.5
Answer: First one gives more cerel for your money.
Explanation: Bigger one volume = 16 x 4 x 10 = 640 Smaller one volume = 2 x 8 x 10 = 160 6 – 640 means 1 – 106.66 2 – 160 means 1 – 80
Question 46. CRITICAL THINKING The height of cylinder X is twice the height of cylinder Y. The radius of cylinder X is half the radius of cylinder Y. Compare the volumes of cylinder X and cylinder Y. Justify your answer.
Answer: Let the height of cylinder X be h, radius be r and its volume is πr²h So, the height of cylinder Y is h/2 and radius is 2r, then the volume is 2πr²h From both expressions, it can be seen that the volume of cylinder y is twice that of cylinder X.
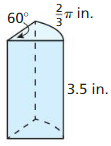
Question 48. MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS You drill a circular hole of radius r through the base of a cylinder of radius R. Assume the hole is drilled completely through to the other base. You want the volume of the hole to be half the volume of the cylinder. Express r as a function of R.
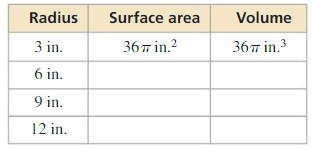
Answer: r = √R²/2
Explanation: The radius of a solid cylinder without a hole is R. So its volume is πR²h As per the given condition, the volume of the hole must be half of that of the solid cylinder, hole volume is πR²h/2 Volume of cylinder V = πr²h πR²h/2 = πr²h R²/2 = r² r = √R²/2 r = \(\frac { R√2 }{ 2 } \)
Question 50. ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS How can you change the edge length of a cube so that the volume is reduced by 40%?
Answer: Write the equation of volume of rectangular prism which can be used to evaluate the cube volume Volume = s x s x s The above equation shows that the volume of a cube is directly proportional to one of its side length, therefore, if the volume is to be reduced by 40%, then its the length of one of its side must be reduced by 40%, without changing the 2 other of its sides.
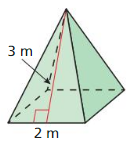
Find the surface area of the regular pyramid.
Finding the Volume of a Pyramid
Question 3. How can you find the volume of a pyramid? Answer: The volume of a pyramid is found using the formula V = (1/3) Bh, where ‘B’ is the base area and ‘h’ is the height of the pyramid. As we know the base of a pyramid is any polygon, we can apply the area of polygons formulas to find ‘B’.
Question 4. In Section 11 .7, you will study volumes of cones. How do you think you could use a method similar to the one presented in Exploration 1 to write a formula for the volume of a cone? Explain your reasoning. Answer:
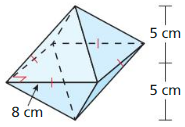
Find the volume of the pyramid.
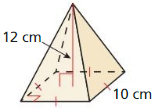
Explanation: Volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(10 x 10 x 12) V = 400
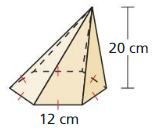
Answer: The volume of the pyramid is 2494.13 cm³
Explanation: Volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(374.12 x 20) V = 2494.13
Question 3. The volume of a square pyramid is 75 cubic meters and the height is 9 meters. Find the side length of the square base.
Answer: The side length of the square base is 5 m
Explanation: Volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = 75 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)B(9) = 75 B = 25 s = 5
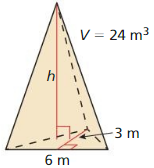
Answer: The height of the triangular pyramid is 8 m
Explanation: V = 24 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = 24 B = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(3 x 6) = 9 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(9)h = 24 h = 8
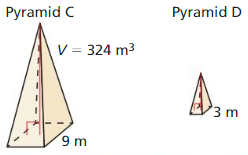
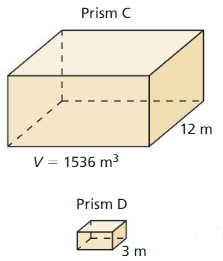
Answer: The volume of pyramid D is 12 m³
Explanation: \(\frac { volume of pyramid C }{ volume of pyramid D } \) = (\(\frac { pyramid C base }{ pyramid D base } \))³ \(\frac { 324 }{ V } \) = (\(\frac { 9 }{ 3 } \))³ V = 12
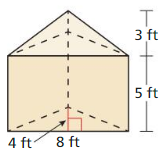
Answer: the volume of solid = 96
Explanation: Volume of prism = Bh B = 8 x 2 = 16 V = 16 x 5 = 80 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(16 x 3) = 16 the volume of solid = 16 + 80 = 96

Question 2. REASONING A square pyramid and a cube have the same base and height. Compare the volume of the square pyramid to the volume of the cube.
Answer: Square pyramid = 1/3 Bh Cube = BH So, the volume of the square pyramid is 1/3 of the volume of the cube.
In Exercises 3 and 4, find the volume of the pyramid.
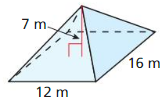
Answer: V = 6 in³
Explanation: V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh B = 2 x 3 = 6 V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(6 x 3)
In Exercises 5 – 8, find the indicated measure.
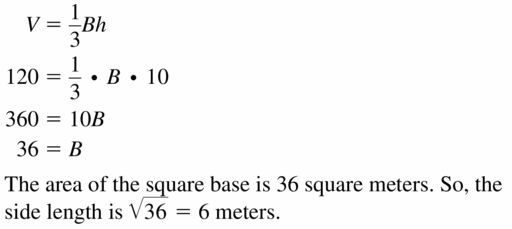
Question 6. A pyramid with a square base has a volume of 912 cubic feet and a height of 19 feet. Find the side length of the square base.
Answer: The side length of the square base is 12 ft
Explanation: A pyramid with a square base has a volume of 912 cubic feet h = 19 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = 912 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)B(19) = 912 B = 144 s = 12
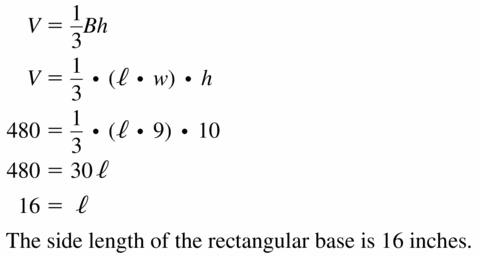
Question 8. A pyramid with a rectangular base has a volume of 105 cubic centimeters and a height of 15 centimeters. The length of the rectangular base is 7 centimeters. Find the width of the rectangular base.
Answer: The width of the rectangular base is 3 cm
Explanation: A pyramid with a rectangular base has a volume of 105 cubic centimeters h = 15 l = 7 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = 105 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)lbh = 105 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(7 x 15 x b) = 105 b = 3
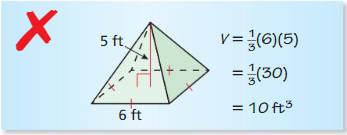
Question 10. OPEN-ENDED Give an example of a pyramid and a prism that have the same base and the same volume. Explain your reasoning. Answer: Let the rectangular prism have the base dimensions 4 x 2 nad a height of 5 so its volume is 4 x 2 x 5 = 40 cubic units Therefore the base of the rectangular prism also have the dimensions of 4 x 2 and a height of 5 x 3 = 15 units so its volume V = 1/3 x 4 x 2 x 15 = 40 cubic units
In Exercises 11 – 14, find the height of the pyramid.
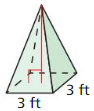
Answer: The height of the pyramid is 10.5 in
Explanation: Volume = 224 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = 224 B = 8² = 64 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(64)h = 224 h = 10.5
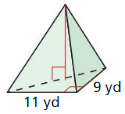
Answer: The height of the pyramid is 12 cm
Explanation: Volume = 392 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = 392 B = 14 x 7 = 98 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(98)h = 392 h = 12
In Exercises 15 and 16, the pyramids are similar. Find the volume of pyramid B.
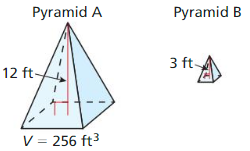
Answer: Volume of A = 80
Explanation: \(\frac { Volume of B }{ Volume of A } \) = (\(\frac { Side of B }{ side of A } \))³ \(\frac { V }{ 10 } \) = (\(\frac { 6 }{ 3 } \))³ V = 8 x 10 Volume of A = 80
In Exercises 17 – 20, find the volume of the composite solid.
Answer: Composite solid volume = 306
Explanation: Base area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)bh = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(12 x 9) = 54 Bottom solid volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(54 x 10) V = 180 Top solid volume v = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(54 x 7) = 126 Composite solid volume = 180 + 126 = 306
Answer: Composite solid volume = 1152
Explanation: Volume of Box = 12 x 12 x 12 = 1728 Square pyramid volume = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(144 x 12) = 576 Composite solid volume = 1728 – 576 = 1152
Question 21. ABSTRACT REASONING A pyramid has a height of 8 feet and a square base with a side length of 6 feet.
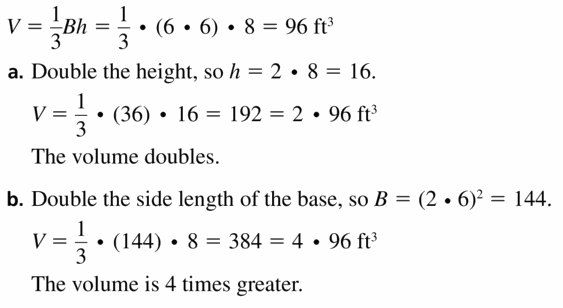
Find the value of X. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Finding the Surface Area of a Cone
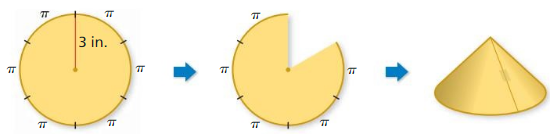
b. What is the area of the original circle? What is the area with one sector missing? Answer:
c. Describe the surface area of the cone, including the base. Use your description to find the surface area. Answer:
Finding the Volume of a Cone
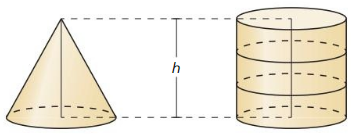
Question 3. How can you find the surface area and the volume of a cone? Answer:
Question 4. In Exploration 1, cut another sector from the circle and make a cone. Find the radius of the base and the surface area of the cone. Repeat this three times, recording your results in a table. Describe the pattern. Answer:
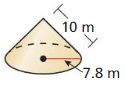
Answer: The surface area of the right cone is 436.17 m²
Explanation: r = 7.8 l = 10 S = πr² + πrl S = π(7.8)² + π(7.8 x 10) S = 436.17
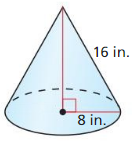
Find the volume of the cone.
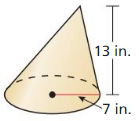
Answer: The volume of the cone is 2206.44 in³
Explanation: r = 7, h = 13 l = √13² – 7²= 10.95 S = πr² + πrl S = π7² + π(7 x 10.95) S = 394.74 Volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 7² x 13) V = 2206.44
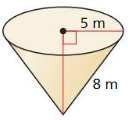
Answer: The volume of the cone is 163.4 m³
Explanation: h = √8² – 5² = 6.24 Volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 5² x 6.24) V = 163.4
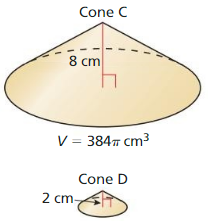
Answer: Volume of cone D = 18.84 cm³
Explanation: \(\frac { Volumeof cone C }{ Volume of cone D } \) = (\(\frac { height of C }{ height of D } \))³ \(\frac { 384π }{ Volume of cone D } \)= (\(\frac { 8 }{ 2 } \))³ Volume of cone D = 18.84
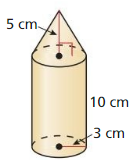
Answer: Composite solid volume = 329.86 cm³
Explanation: Volume of cylinder = πr²h = π(3)² x 10 = 90π Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 3² x 5) = 15π Composite solid volume = 15π + 90π = 105π

Question 2. COMPLETE THE SENTENCE The volume of a cone with radius r and height h is \(\frac{1}{3}\) the volume of a(n) __________ with radius r and height h. Answer:
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the surface area of the right cone.
Answer: The surface area of cone is 219.44 sq cm.
Explanation: S = πr² + πrl S = π(5.5)² + π(5.5 x 7.2) S = 219.44

Question 6. A right cone has a diameter of 11.2 feet and a height of 19.2 feet.
Answer: The surface area is 421.52 sq ft.
Explanation: r = 5.6 h = 19.2 l = √19.2² – 5.6² = 18.36 Surface area S = πr² + πrl S = π(5.6)² + π(5.6 x 18.36) S = 421.52
In Exercises 7 – 10, find the volume of the cone.
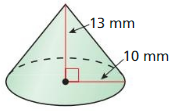
Answer: The volume is 2.09 cubic meter
Explanation: Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π(1)² x 2) V = 2.09
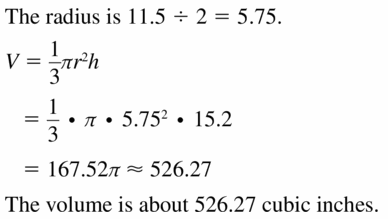
Question 10. A right cone has a radius of 3 feet and a slant height of 6 feet.
Answer: The volume is 56.54 cubic ft
Explanation: Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 3² x 6) V = 56.54
In Exercises 11 and 12, find the missing dimension(s).
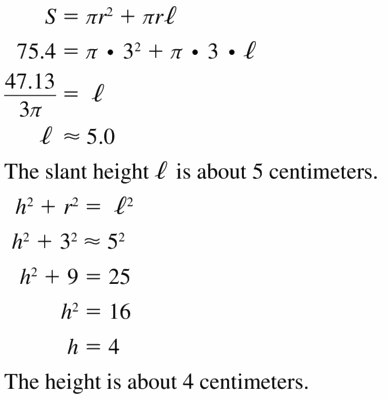
Question 12. Volume = 216π in. 3
Answer: The radius is 6.13 in
Explanation: Volume = 216π in. 3 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) = 216 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr² x 18) = 216 r = 6.13
In Exercises 13 and 14, the cones are similar. Find the volume of cone B.
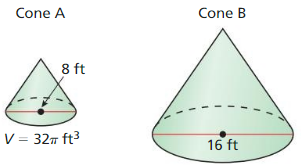
Answer: Volume of cone B = 24.127
Explanation: \(\frac { Volumeof cone A }{ Volume of cone B } \) = (\(\frac { height of A }{ height of B } \))³ \(\frac { 120π }{ Volume of cone B } \) = (\(\frac { 10 }{ 4 } \))³ Volume of cone B = 24.127
In Exercises 15 and 16, find the volume of the composite solid.
Answer: Volume of the composite solid = 97.93 cubic m
Explanation: Volume of box = lbh V = 51 x 5.1 x 5.1 = 132.651 Cone volume = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) v = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 2.55² x 5.1) v = 34.72 Volume of the composite solid = 132.651 – 34.72 = 97.93
Answer: Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 3² x 8) = 75.39 Volume of cylinder = πr²h = π x 3² x 8 = 226.19 Volume of cylinder / Volume of cone = \(\frac { 226.19 }{ 75.39 } \) = 3 You have to buy 3 small containers of popcorn to equal the amount of popcorn in a large container.
b. Which container gives you more popcorn for your money? Explain. Answer: $1.25 -> 75.39 i.e $1 = 60.312 $2.50 -> 226.19 i.e $1 = 90.47 So, large containers gives you more popcorn for your money
In Exercises 19 and 20. find the volume of the right cone.
Answer: Volume of cone is 575.62 cubic yd
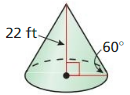
Explanation: tan 32 = \(\frac { 7 }{ h } \) h = 11.21 Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 7² x 11.21) V = 575.62

Question 22. MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS During a chemistry lab, you use a funnel to pour a solvent into a flask. The radius of the funnel is 5 centimeters and its height is 10 centimeters. You pour the solvent into the funnel at a rate of 80 milliliters per second and the solvent flows out of the funnel at a rate of 65 milliliters per second. How long will it be before the funnel overflows? (1 mL = 1 cm 3 ) Answer: 17.45 seconds
Explanation: Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 5² x 10) V = 261.8 \(\frac { 261.8 }{ 15 } \) = 17.45

Question 28. area of a circle with a diameter of 22 centimeters
Answer: d = 11 A = πr² A = 121π
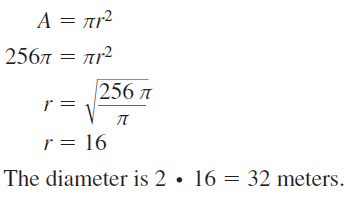
Question 30. radius of a circle with an area of 529 π square inches Answer: A = πr² 529π = πr² r = 23
Finding the Surface Area of a Sphere

Finding the volume of a sphere
Question 3. How can you find the surface area and the volume of a sphere? Answer:
Question 4. Use the results of Explorations 1 and 2 to find the surface area and the volume of a sphere with a radius of(a) 3 inches and (b) 2 centimeters. Answer:
Find the surface area of the sphere.
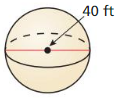
Answer: The surface area of the sphere is 5026.54 ft²
Explanation: D = 40 r = 20 The surface area of the sphere = 4πr² S = 4 x π x (20)² S = 5026.54 ft²
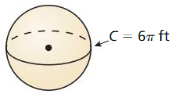
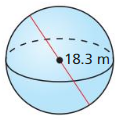
Answer: The surface area of the sphere is 113.09 ft²
Explanation: Circumference C = 6π 2πr = 6π r = 3 The surface area of the sphere = 4πr² S = 4π x 3² S = 113.09
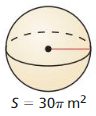
Answer: The radius of the sphere is 2.73 m
Explanation: The surface area of the sphere = 4πr² 30π = 4πr² r = 2.73
Question 4. The radius of a sphere is 5 yards. Find the volume of the sphere.
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 523.59 yards³
Explanation: r = 5 The volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 5³ V = 523.59 yards³
Question 5. The diameter of a sphere is 36 inches. Find the volume of the sphere.
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 24429.02 in³
Explanation: D = 36 r = 18 The volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 18³ V = 24429.02
Question 6. The surface area of a sphere is 576π square centimeters. Find the volume of the sphere.
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 2304π cm³
Explanation: The surface area of the sphere = 4πr² 576π = 4πr² r = 12 The volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 12³ V = 2304π
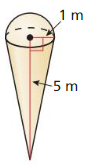
Answer: The volume of the composite solid is 7.324 m³
Explanation: The volume of cone = πr²\(\frac { h }{ 3 } \) = π x 1² x \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 } \) = 5.23 The volume of sphere = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 1³ = 4.188 The volume of the composite solid = The volume of cone + The volume of sphere/2 = 5.23 + 4.188/2 = 7.324 m³

Question 2. WRITING Explain the difference between a sphere and a hemisphere.
Answer: Hemisphere is a related term of the sphere. Sphere and hemisphere are three-dimensional solids. The volume of sphere is \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ and hemisphere volume is \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)πr³. The surface area of the sphere is 4πr² and hemisphere surface area is 3πr².
Monitoring progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the surface area of the sphere.
Answer: The surface area of the sphere is 225π cm²
Explanation: The surface area of the sphere = 4πr² S = 4π x 7.5² S = 225π
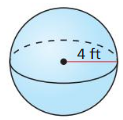
Answer: The surface area of the sphere is 8π ft²
Explanation: C = 4π 2πr = 4π r = 2 The surface area of the sphere = 4πr² S = 4π x 2² S = 8π
In Exercises 7 – 10. find the indicated measure.

Question 8. Find the radius of a sphere with a surface area of 1024π square inches.
Answer: The radius of a sphere is 16 in
Explanation: The surface area of the sphere = 1024π 4πr² = 1024π r = 16

Question 10. Find the diameter of a sphere with a surface area of 196π square centimeters.
Answer: The diameter of a sphere is 14 cm
Explanation: The surface area of the sphere = 196π 4πr² = 196π r = 7 D = 2(7) = 14
In Exercises 11 and 12, find the surface area of the hemisphere.
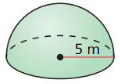
Answer: The surface area of the hemisphere is 108π in²
Explanation: D = 12, r = 6 The surface area of the sphere = 3πr² S = 3π x 6² S = 108π
In Exercises 13 – 18. find the volume of the sphere.
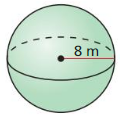
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 268.08 ft³
Explanation: r = 4 ft Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 4³ V = 268.08 ft
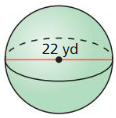
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 1436.75 ft³
Explanation: D = 14 ft r = 7 ft Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 7³ V = 1436.75 ft
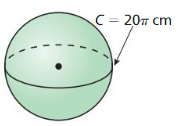
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 179.89 in³
Explanation: C = 7π 2πr = 7π r = 3.5 Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 3.5³ V = 179.89 in
In Exercises 19 and 20, find the volume of the sphere with the given surface area.

Question 20. Surface area = 484π cm 2
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 5575.27 cm³
Explanation: Surface area = 484π 4πr² = 484π r = 11 Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 11³ V = 5575.27
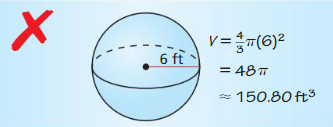
Answer: Diameter = 3 radius = 1.5 Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x (1.5)³ V = 14.137 cubic in
In Exercises 23 – 26, find the volume of the composite solid.
Answer: Volume is 288π ft³
Explanation: Volume of hemipshere = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)πr³ = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)π x 6³ = 144π volume of the cone = πr²\(\frac { h }{ 3 } \) = π x 6² x \(\frac { 12 }{ 3 } \) = 144π Area of circle = πr² = π x 6² = 36π Volume of hemipshere + volume of the cone = 144π + 144π = 288π
Answer: The volume of solid is 296π m³
Explanation: Volume of hemipshere = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)πr³ = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)π x 6³ = 144π Volume of cylinder = πr²h = π x 6² x 14 = 504π Volume of solid = 504π – 2(144π) = 296π
In Exercises 27 – 32, find the surface area and volume of the ball.

Answer: The surface area is 277 in², volume is 43212.27 in³
Explanation: C = 29.5 2πr = 29.5 r = 4.69 Surface area = 4πr² S = 4π x 4.69² = 277 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 4.69³ V = 43212.27

Answer: The surface area is 9.07 in², volume is 2.57 in³
Explanation: d = 1.7 r = 0.85 Surface area = 4πr² S = 4π x 0.85² = 9.07 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 0.85³ V = 2.57

Answer: The surface area is 25.78 in², volume is 12.24 in³
Explanation: C = 9 2πr = 9 r = 1.43 Surface area = 4πr² S = 4π x 1.43² S = 25.78 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 1.43³ V = 12.24

Question 34. REASONING A semicircle with a diameter of 18 inches is rotated about its diameter. Find the surface area and the volume of the solid formed.
Answer: The surface area is 1018 in², volume is 3054.02 in³
Explanation: Diameter = 18 radius r = 9 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 9³ V = 3054.02 Surface area = 4πr² S = 4π x 9² S = 1018

Answer: C = 8 in 2πr = 8 r = 1.27 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 1.27³ = 8.64 The volume of tennis ball = 8.64 in³
b. Find the amount of space within the cylinder not taken up by the tennis balls. Answer: The surface area of tennis ball S = 4πr² S = 4π x 1.27² = 20.26 Area of cylinder s = 2πrh+2πr² s = 2π x 1.43 x 8+2π x 1.43² s = 84.72 Remaining space = 84.72 – 20.26 = 64.46 in²
Question 38. MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS A sphere has a diameter of 4(x + 3) centimeters and a surface area of 784 π square centimeters. Find the value of x.
Answer: x =11
Explanation: Surface area = 4πr² 784π = πr² r = 28 2r = diameter = 4(x + 3) r = 2(x + 3) 28 = 2(x + 3) x = 11

b. A meteorite is equally likely to hit anywhere on Earth. Estimate the probability that a meteorite will land in the Torrid Zone. Answer: Probability of meteorites hitting the torrid zone = 80875080/197086348.8 = 0.4104

Explanation: Volume of hemisphere v = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)πr³ Volume of cone V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr²h If r = h Volume of cone V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr² x r = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr³ So, the hemisphere has the highest volume.
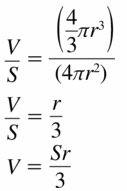
b. r = 34 cm, a = 30 cm Answer: The formula for the volume of the spherical cap is V = πh/6 x (3a² +h²). Where a is the radius h is the height of the cap. Where a = r = 34cm h = 30cm V = π(30)/6 x (3(34)² +(30)²) = π(30)/6 x (3(1156) + (900)) = π(30)/6 x 6,168 = 94.2/6 x 6,168 Therefore the volume of the spherical cap is 96,837.6 cu. cm.
c. r = 13 m, h = 8 m Answer: The formula for the volume of the spherical cap is V = πh/6 x (3a² +h²). Where a is the radius h is the height of the cap. Where a = r = 13cm h = 8cm V = π(8)/6 x (3(13)² +(8)²) = 8π/6 x (3(169 + 64)) = 8π/6 x (699) = 25.12/6 x 699 Therefore the volume of the spherical cap is 2,926.48 cu. cm
d. r=75 in., h = 54in. Answer: The formula for the volume of the spherical cap is V = πh/6 x (3a² +h²). Where a is the radius h is the height of the cap. Where r = 75in h = 54in V = π(54)/6 x (3(75)² +(54)²) = 54π/6 x (3(5,625 + 2,916) = 54π/6 x (25,623) = 169.56π/6 x 25,623 = 532.4184 x 25,623 Therefore the volume of the spherical cap is 13,642,156.66 cu. in.

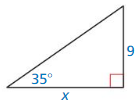
Solve the triangle. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 48. A = 26°, C = 35°, b = 13
Answer: B = 119°, a = 7.16, c = 9.5
Explanation: B = 180 – (26 + 35) = 119 \(\frac { sin A }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) \(\frac { sin 26 }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin 119 }{ 13 } \) a = 7.16 \(\frac { sin C }{ c } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) \(\frac { sin 35 }{ c } \) = \(\frac { sin 119 }{ 13 } \) c = 9.5
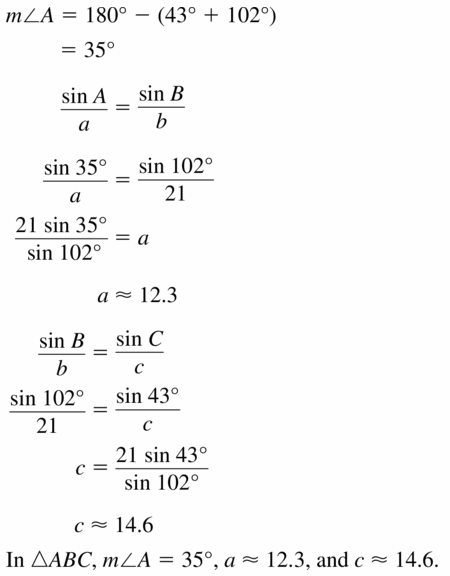
Question 50. a = 23, b = 24, c = 20
Answer: A = 62.2, B = 65.5, C = 49.4
Explanation: a² = b² + c² – 2bc cos A 23² = 24²+ 20² – 2(24 x 20) cos A A = 62.2 \(\frac { sin 62.2 }{ 23 } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ 24 } \) B = 65.5 \(\frac { sin 62.2 }{ 23 } \) = \(\frac { sin C }{ 20 } \) C = 49.4

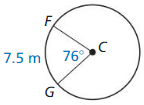
Answer: diameter of ⊙P is 29.99
Explanation: Circumference = 94.24 πd = 94.24 d = 29.99
Answer: circumference of ⊙F = 56.57
Explanation: 5.5 = \(\frac { 35 }{ 360 } \) . C C = 56.57
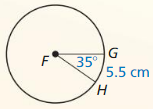
Answer: arc length of \(\widehat{A B}\) = 26.09
Explanation: arc length of \(\widehat{A B}\) = \(\frac { 115 }{ 360 } \) . 2π(13) = 26.09
Question 4. A mountain bike tire has a diameter of 26 inches. To the nearest foot, how far does the tire travel when it makes 32 revolutions?
Answer: The tire travels 2613.80 inches.
Explanation: D = 26 in r = 13 in Circumference C = 2π(13) = 81.68 32 revolutions = 32 x 81.68 = 2613.80
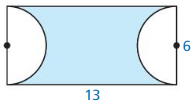
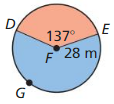
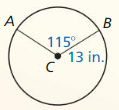
Find the area of the blue shaded region.
Answer: Area = \(\frac { 240 }{ 360 } \) . π(9)² = 169.64
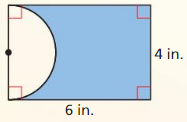
Answer: Area of shaded region = 11.43
Explanation: Area of rectangle = 6 x 4 = 24 Area of semicircle = π(2)² = 4π Area of shaded region = 24 – 4π = 11.43
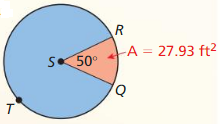
Answer: Area of shaded region = 173.13
Explanation: Area of small region = 27.93 = \(\frac { 50 }{ 360 } \) . πr² πr² = 201.096 r = 8 Area of shaded region = \(\frac { 310 }{ 360 } \) . π(8)² = 173.13
Find the area of the kite or rhombus.
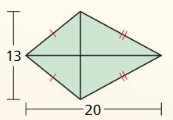
Explanation: Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(13 x 20) A = 65
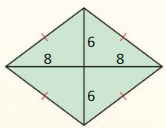
Explanation: Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(16 x 12) A = 48
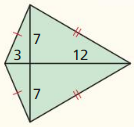
Explanation: Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(14 x 15) A = 52.5
Find the area of the regular polygon.
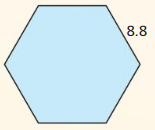
Question 14. A platter is in the shape of a regular octagon with an apothem of 6 inches. Find the area of the platter.
Answer: Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(n . a. s) A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(8 . 6 . sin 45) A = 16.97
Describe the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid.
Answer: Volume = lbh V = 3.6 x 2.1 x 1.5 = 113.4 m³
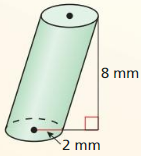
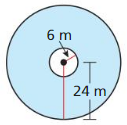
Answer: Volume = πr²h V = π(2)² x 8 = 100.53 mm³
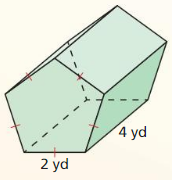
Answer: Pentagon area = 6.88 Volume = Area x height V = 6.88 x 4 = 27.52 yd³
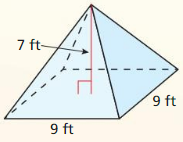
Answer: Volume V = Base area x height/3 Base Area = 9² = 81 V = 81 x 7/3 = 189 ft³
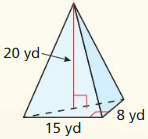
Answer: Volume V = Base area x height/3 base area = 18 x 10 = 180 V = 180 x 5/3 = 300 m³
Question 27. The volume of a square pyramid is 60 cubic inches and the height is 15 inches. Find the side length of the square base.
Answer: The side length of the square base is 3.46 in
Explanation: The volume of a square pyramid is 60 cubic inches V = 60 s²h/3 = 60 s² x 15/3 = 60 s² = 12 s = 3.46
Question 28. The volume of a square pyramid is 1024 cubic inches. The base has a side length of 16 inches. Find the height of the pyramid Answer: The volume of a square pyramid is 1024 cubic inches s²h/3 = 1024 16²h = 3072 h = 12
Find the surface area and the volume of the cone.
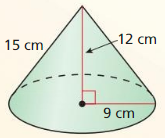
Explanation: Surface area of cone S = πr² + πrl S = π x 9² + π x 9 x 15 S = 678.58 Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 9² x 12) V = 1017.87
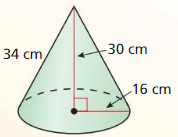
Answer: Surface area is 2513.27 cm² volume is 8042.47 cm³
Explanation: Surface area of cone S = πr² + πrl S = π x 16² + π x 16 x 34 S = 2513.27 Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 16² x 30) V = 8042.47
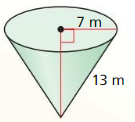
Answer: Surface area is 439.82 m² volume is 562.102 m³
Explanation: Surface area of cone S = πr² + πrl S = π x 7² + π x 7 x 13 S = 439.82 h = √13² – 7² = 10.95 Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 7² x 10.95) V = 562.102
Question 32. A cone with a diameter of 16 centimeters has a volume of 320π cubic centimeters. Find the height of the cone.
Answer: The height of the cone = 15 cm.
Explanation: r = 8 Volume V = 320π \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) = 320π \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 8² x h) = 320π h = 15
Find the surface area and the volume of the sphere.
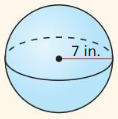
Answer: The surface area is 615.75 in², volume is 1436.75 in³
Explanation: Surface area S = 4πr² S = 4π x 7² S = 615.75 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 7³ V = 1436.75
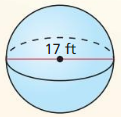
Answer: The surface area is 907.92 ft², volume is 2572.44 ft³
Explanation: d = 17 r = 8.5 Surface area S = 4πr² S = 4π x 8.5² S = 907.92 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 7³ V = 2572.44
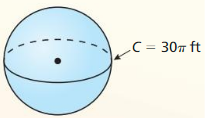
Answer: The surface area is 2827.43 ft², volume is 14137.16 ft³
Explanation: C = 30π 2πr = 30π r = 15 Surface area S = 4πr² S = 4π x 15² S = 2827.43 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 15³ V = 14137.16
Question 36. The shape of Mercury can be approximated by a sphere with a diameter of 4880 kilometers. Find the surface area and the volume of Mercury.
Answer: The surface area and the volume of Mercury is 23814400π, 19369045330π
Explanation: d = 4880 r = 2440 Surface area S = 4πr² S = 4π x 2440² = 23814400π Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 2440³ V = 19369045330π
Question 37. A solid is composed of a cube with a side length of 6 meters and a hemisphere with a diameter of 6 meters. Find the volume of the composite solid.
Answer: Volume of the composite solid = 272.52
Explanation: Volume of cube = a³ = 6³ = 216 Volume of hemisphere = \(\frac { 4 }{ 6 } \)πr³ = \(\frac { 4 }{ 6 } \)π x 3³ = 18π Volume of the composite solid = 216 + 18π = 272.52
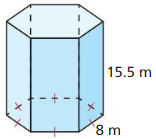
Answer: Volume = 2577.29 m³
Explanation: Volume = \(\frac { 3√3 }{ 2 } \)a²h = \(\frac { 3√3 }{ 2 } \) x 8² x 15.5 = 2577.29
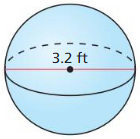
Answer: Volume is 17.157 ft³
Explanation: d = 3.2 r = 1.6 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 1.6³ V = 17.157
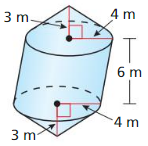
Answer: Volume of sloid = 402.11 m³
Explanation: Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr²h = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)π x 4² x 3 = 50.26 Volume of cylinder = πr²h = π x 4² x 6 = 301.59 Volume of sloid = 2(50.26) + 301.59 = 402.11
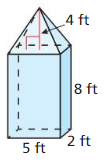
Answer: Volume of solid = 106.66
Explanation: Volume of rectangular box = 5 x 2 x 8 = 80 Volume of pyramid = 80/3 = 26.66 Volume of solid = 80 + 26.66 = 106.66
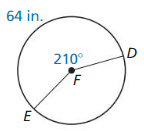
Answer: circumference of ⊙F is 109.71 in
Explanation: 64 = \(\frac { 210 }{ 360 } \) • C C = 109.7
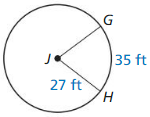
Answer: m\(\widehat{G H}\) = 74.27
Explanation: 35 = \(\frac { x }{ 360 } \) • 2π x 27 x = 74.27
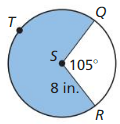
Answer: Area is 142.41 in²
Explanation: Area = \(\frac { 360 – 105 }{ 360 } \) • π x 8² Area = 142.41
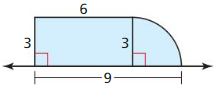
Question 9. Find the surface area of a right cone with a diameter of 10 feet and a height of 12 feet.
Answer: The surface area is 486.7 sq ft
Explanation: l² = r² + h² l² = 5² + 12² l = 13 Surface area S = πr² + 2πrl S = π x 5² + 2π x 5 x 13 S = 486.7
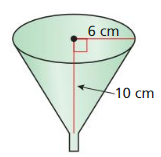
Answer: Volume = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr²h = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)π x 6² x 10 = 376.99
b. You use the funnel to put oil in a ear. Oil flows out of the funnel at a rate of 45 milliliters per second. How long will it take to empty the funnel when it is full of oil? (1 mL = 1 cm 3 ) Answer: T = 376.8 ml/45 ml per sec T = 8.373 sec
c. How long would it take to empty a funnel with a radius of 10 centimeters and a height of 6 centimeters if oil flows out of the funnel at a rate of 45 milliliters per second? Answer: V = 1/3 πr²h = 1/3 (3.14 × 10² × 6) = 1/3(1884) = 628 cu. cm T = 628 ml/45 ml per sec T = 13.95 sec
d. Explain why you can claim that the time calculated in part (c) is greater than the time calculated in part (b) without doing any calculations. Answer:
- In cone type shaped object if the radius is large then the volume of the cone increases.
- In the b part of the funnel, the radius is smaller than the height and in the c part, the radius is larger than the height of the cone.
- V = 1/3 πr²h
- It means if radius increase volume also increases with the same rate. So, the time is taken by the c part (13.95 sec) is larger than the b part.
Question 11. A water bottle in the shape of a cylinder has a volume of 500 cubic centimeters. The diameter of a base is 7.5 centimeters. What is the height of the bottle? Justify your answer.
Answer: The height of the bottle is 11.3 cm
Explanation: Volume of cylinder = 500 πr²h = 500 π(3.75)²h = 500 h = 11.3 cm
Question 12. Find the area of a dodecagon (12 sides) with a side length of 9 inches.
Answer: Area is 237.31
Explanation: Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)πa²cot(π/n) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)π x 9² x cot(π/12) = 237.31

Answer: Area of sector for fan of radius 9 cm = 120/360 × 3.14 × 9 × 9 = 1/3 × 254.57 = 84.85 sq. cm Area of sector of fan of radius 6 cm = 150/360 × 3.14 × 6 × 6 = 5/12 × 113.14 = 47.14 sq. cm
Question 1. Identify the shape of the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid.
b. Find the amount of space within the crayon box not taken up by the crayons. Answer: Volume of box = 94 x 28 x 71 = 186872 The volume of a crayon = 4650.21 Remaining space = 186872 – 24 x 4650.21 = 75266.96
Question 4. What is the equation ol the line passing through the point (2, 5) that is parallel to the line x + \(\frac{1}{2}\)y = – 1? (A) y = – 2x + 9 (B) y = 2x + 1 (C) y = \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 4 (D) y = –\(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 6 Answer: (A) y = – 2x + 9
Explanation: x + \(\frac{1}{2}\)y = – 1 y = -2 – 2x The slope of the line is -2 The euation of line is y – 5 = -2(x – 2) y – 5 = -2x + 4 y = -2x + 9

Answer: (A) 22,019.63 ft 3
Explanation: Volume = a²\(\frac { h }{ 3 } \) = 34.5² x \(\frac { 55.5 }{ 3 } \) = 22019.62
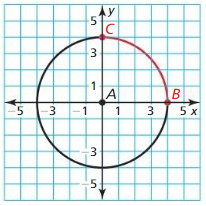
Question 6. Prove or disprove that the point (1, √3 ) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). Answer: We consider the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). Therefore, we canconclude that rdaius is 2 and points be (0, 0), (1, √3) distance = √(1 – 0)² + (√3 – 0)² = 2 As radius and distance are same. The point B(1, √3) lies on the circle.

Explanation: Volume of square pyramid = a²\(\frac { h }{ 3 } \) Square diagonal = √2a radius = √2a/2 a = 2r/√2 Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr²h

Answer: The number of people per square mile is 247
Explanation: S = πr² = π x 5² = 78.5 Number of people per square mile = 19400/78.5 = 247
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 5th Edition Kimmel, Paul D.; Weygandt, Jerry J.; Kieso, Donald E.
Algebra 1 hall, prentice, algebra 1: common core (15th edition) charles, randall i., algebra 2 (1st edition) larson, ron; boswell, laurie; kanold, timothy d.; stiff, lee, algebra 2 common core hall, prentice, algebra: a combined approach (4th edition) martin-gay, elayn, algebra and trigonometry 10th edition larson, ron, anatomy & physiology: the unity of form and function, 7th edition saladin, kenneth, animal diversity 7th edition hickman jr., cleveland; roberts, larry; keen, susan; larson, allan; eisenhour, david, applied statistics and probability for engineers, 6th edition montgomery, douglas c.; runger, george c., basic college mathematics (10th edition) lial, margaret l.; salzman, stanley a.; hestwood, diana l., basic college mathematics (9th edition) lial, margaret l.; salzman, stanley a.; hestwood, diana l., the basic practice of statistics 7th edition moore, david s.; notz, william i.; fligner, michael a., basic statistics: tales of distributions 10th edition spatz, chris, big ideas math - algebra 1, a common core curriculum larson, ron; boswell, laurie, biological science (6th edition) freeman, scott; quillin, kim; allison, lizabeth; black, michael; taylor, emily; podgorski, greg; carmichael jeff, biology (11th edition) raven, peter; johnson, george; mason, kenneth; losos, jonathan; singer, susan, biology 12th edition mader, sylvia; windelspecht, michael, biology 2010 student edition miller, kenneth r.; levine, joseph s., biology: the unity and diversity of life (14th edition) starr, cecie; taggart, ralph; evers, christine; starr, lisa, calculus 10th edition larson, ron; edwards, bruce h., calculus, 10th edition (anton) anton, howard, calculus (3rd edition) rogawski, jon; adams, colin, calculus 8th edition stewart, james, calculus concepts: an informal approach to the mathematics of change 5th edition latorre, donald r.; kenelly, john w.; reed, iris b.; carpenter, laurel r.; harris, cynthia r., calculus: early transcendentals (2nd edition) briggs, bill l.; cochran, lyle; gillett, bernard, calculus: early transcendentals 8th edition stewart, james, calculus: early transcendentals 9th edition stewart, james, calculus with applications (10th edition) lial, margaret l.; greenwell, raymond n.; ritchey, nathan p., campbell biology (10th edition) jane b. reece, lisa a. urry, michael l. cain, steven a. wasserman, peter v. minorsky, robert b. jackson, campbell biology (11th edition) jane b. reece, lisa a. urry, michael l. cain, steven a. wasserman, peter v. minorsky, campbell biology (12th edition) jane b. reece, lisa a. urry, michael l. cain, steven a. wasserman, peter v. minorsky, campbell biology: concepts & connections (9th edition) taylor, martha r.; simon, eric j.; dickey, jean l.; hogan, kelly a.; reece, jane b., the cell: a molecular approach 7th edition cooper, geoffrey m.; hausman, robert e., chemistry 10th edition whitten, kenneth w.; davis, raymond e.; peck, larry; stanley, george g., chemistry (12th edition) wilbraham, chemistry 12th edition chang, raymond; goldsby, kenneth, chemistry (4th edition) burdge, julia, chemistry (7th edition) mcmurry, john e.; fay, robert c.; robinson, jill kirsten, chemistry 9th edition zumdahl, steven s.; zumdahl, susan a., chemistry: a molecular approach (3rd edition) tro, nivaldo j., chemistry: an atoms-focused approach gilbert, thomas r.; kirss, rein v.; foster, natalie, chemistry and chemical reactivity (9th edition) kotz, john c.; treichel, paul m.; townsend, john r.; treichel, david a., chemistry: an introduction to general, organic, and biological chemistry (12th edition) timberlake, karen c., chemistry: atoms first (2nd edition) zumdahl, steven s.; zumdahl, susan a., chemistry: molecular approach (4th edition) tro, nivaldo j., chemistry: the molecular science (5th edition) moore, john w.; stanitski, conrad l., chemistry: principles and practice (3rd edition) reger, daniel l.; goode, scott r.; ball, david w., chemistry: the central science (13th edition) brown, theodore e.; lemay, h. eugene; bursten, bruce e.; murphy, catherine; woodward, patrick; stoltzfus, matthew e., chemistry: the molecular nature of matter and change 7th edition silberberg, martin; amateis, patricia, chemistry: the science in context (4th edition) gilbert, thomas r.; kirss, rein v., college algebra (10th edition) sullivan, michael, college algebra (11th edition) lial, margaret l.; hornsby john; schneider, david i.; daniels, callie, college algebra (6th edition) blitzer, robert f., college algebra 7th edition stewart, james; redlin, lothar; watson, saleem, college physics (4th edition) giambattista, alan; richardson, betty; richardson, robert, college physics (7th edition) wilson, jerry d.; buffa, anthony j.; lou, bo, computer science: an overview: (13th edition) brookshear, glenn; brylow, dennis, computer science: an overview: global edition (12th edition) brookshaw, glenn; brylow, dennis, conceptual physics (12th edition) hewitt, paul g., cost accounting (15th edition) horngren, charles t.; datar, srikant m.; rajan, madhav v., database concepts kroenke, david; auer, david;, differential equations and linear algebra (4th edition) goode, stephen w.; annin, scott a., discrete mathematics and its applications, seventh edition rosen, kenneth, discrete mathematics with applications 4th edition epp, susanna s., earth: an introduction to physical geology (12th edition) tarbuck, edward j.; lutgens, frederick k.; tasa, dennis g., economics: principles, problems, and policies, 19th edition mcconnell, campbell r.; brue, stanley l.; flynn, sean m., electrical engineering: principles & applications (6th edition) hambley, allan r., elementary algebra kaufmann, jerome; schwitters, karen;, elementary and intermediate algebra: concepts & applications (6th edition) bittinger, marvin l.; ellenbogen, david j.; johnson, barbara l., elementary differential equations and boundary value problems 9th edition boyce, william e.; diprima, richard c., elementary geometry for college students (5th edition) alexander, daniel c.; koeberlein, geralyn m., elementary geometry for college students (6th edition) alexander, daniel c.; koeberlein, geralyn m., elementary geometry for college students (7th edition) alexander, daniel c.; koeberlein, geralyn m., elementary linear algebra 7th edition larson, ron, elementary statistics (12th edition) triola, mario f., elementary statistics: a step-by-step approach with formula card 9th edition bluman, allan, elementary statistics: picturing the world (6th edition) larson, ron; farber, betsy, elementary technical mathematics nelson, robert; eren, dale;, engineering mechanics: statics & dynamics (14th edition) hibbeler, russell c., environmental science: earth as a living planet (9th edition) botkin, daniel b.; keller, edward a., environmental science for ap* (2nd edition) friedland, andrew j.; relyea, rick, essential cell biology, 4th edition alberts, bruce; bray, dennis; hopkin, karen; johnson, alexander d,; lewis, julian; raff, martin; roberts, keith; walter, peter, essentials of human anatomy & physiology (12th edition) marieb, elaine n.; hoehn, katja n., essentials of statistics (5th edition) triola, mario f., essentials of statistics for the behavioral sciences 8th edition gravetter, frederick j.; wallnau, larry b., essential university physics: volume 1 (3rd edition) wolfson, richard, essential university physics: volume 1 (4th edition) wolfson, richard, evolutionary analysis (5th edition) herron, jon c.; freeman, scott, finite math and applied calculus (6th edition) waner, stefan; costenoble, steven, functions modeling change: a preparation for calculus, 5th edition connally, eric; hughes-hallett, deborah; gleason, andrew m.; cheifetz, phil c., fundamentals of biochemistry: life at the molecular level 5th edition voet, donald; voet, judith g.; pratt, charlotte w., fundamentals of electrical engineering rizzoni, giorgio, fundamentals of engineering thermodynamics 8th edition moran, michael j.; shapiro, howard n.; boettner, daisie d.; bailey, margaret b., fundamentals of physics extended (10th edition) halliday, david; resnick, robert; walker, jearl, general chemistry (4th edition) mcquarrie, donald a., general chemistry 10th edition ebbing, darrell; gammon, steven d., general chemistry: principles and modern applications (10th edition) petrucci, ralph h.; herring, f. geoffrey; madura, jeffry d.; bissonnette, carey, general, organic, and biological chemistry: structures of life (5th edition) timberlake, karen c., general, organic, & biological chemistry 3rd edition smith, janice, geometry: common core (15th edition) charles, randall i., human anatomy & physiology (11th edition) marieb, elaine n.; hoehn, katja n., human anatomy & physiology (9th edition) marieb, elaine n.; hoehn, katja n., human biology, 14 edition mader, sylvia; windelspecht, michael, intermediate accounting 14th edition kieso, donald e.; weygandt, jerry j.; warfield, terry d., intermediate accounting (16th edition) kieso, donald e.; weygandt, jerry j.; warfield, terry d., intermediate algebra (12th edition) lial, margaret l.; hornsby, john; mcginnis, terry, intermediate algebra (6th edition) martin-gay, elayn, intermediate algebra: connecting concepts through application clark, mark; anfinson, cynthia, intermediate algebra for college students (7th edition) blitzer, robert f., introduction to electrodynamics 4e griffiths, david j., introduction to geography: people, places, and environment, global edition dahlman, carl t.; renwick, william h., an introduction to mathematical statistics and its applications (6th edition) larsen, richard j.; marx, morris l., introduction to programming using python 1st edition liang, y daniel, introduction to quantum mechanics 2nd edition griffiths, david j., introductory algebra for college students (7th edition) blitzer, robert f., introductory chemistry (5th edition) tro, nivaldo j., introductory statistics 9th edition mann, prem s., invitation to computer science 8th edition gersting, judith l.; schneider, g. michael, lehninger principles of biochemistry 6th edition nelson, david l.; cox, michael m., life: the science of biology 11th edition sadava, david e.; hillis, david m.; heller, h. craig; hacker, sally d., linear algebra: a modern introduction poole, david, linear algebra and its applications, 4th edition strang, gilbert, linear algebra and its applications (5th edition) lay, david c.; lay, steven r.; mcdonald, judi j., linear algebra for engineers and scientists using matlab (first edition) hardy, kenneth, macroeconomics: principles, problems, & policies 20th edition mcconnell, campbell; brue, stanley; flynn, sean, managerial accounting (15th edition) garrison, ray; noreen, eric, brewer, peter, materials science and engineering: an introduction callister, william d.; rethwisch, david g., mechanics of materials, 7th edition beer, ferdinand p.; johnston jr., e. russell; dewolf, john t.; mazurek, david f., microbiology: an introduction, 11th edition tortora, gerard j.; funke, berdell r.; case, christine l., microbiology: a systems approach 4th edition cowan, marjorie kelly, microbiology: principles and explorations 9th edition black, jacquelyn g.; black, laura, microbiology with diseases by body system (4th edition) bauman, robert w,, phd, microeconomics: principles, applications, and tools (8th edition) o'sullivan, arthur; sheffrin, steven; perez, stephen, microeconomics: principles, problems, & policies, 20th edition mcconnell, campbell; brue, stanley; flynn, sean, molecular biology of the cell 6th edition alberts, bruce; johnson, alexander; lewis, julian; morgan, david; raff, martin; roberts, keith; walter, peter, multivariable calculus, 7th edition stewart, james, munson, young and okiishi's fundamentals of fluid mechanics, binder ready version 8th edition gerhart, philip m.; gerhart, andrew l.; hochstein, john i., numerical methods for engineers chapra, steven; raymond, canale;, numerical methods for engineers and scientists gilat, amos;, organic chemistry, 5th edition smith, janice, organic chemistry (8th edition) wade jr., l. g., organic chemistry 9th edition mcmurry, john e., organic chemistry as a second language, 3e: first semester topics klein, david, organizational behavior (16th edition) robbins, stephen p.; judge, timothy a., physical chemistry: thermodynamics, structure, and change atkins, peter; de paula, julio, physics (10th edition) young, david; stadler, shane, physics for scientists and engineers: a strategic approach with modern physics (3rd edition) knight, randall d., physics for scientists and engineers: a strategic approach with modern physics (4th edition) knight, randall d., physics: principles with applications (7th edition) giancoli, douglas c., physics technology update (4th edition) walker, james s., prealgebra (7th edition) martin-gay, elayn, precalculus (10th edition) sullivan, michael, precalculus (6th edition) lial, margaret l.; hornsby, john; schneider, david i.; daniels, callie, precalculus (6th edition) blitzer blitzer, robert f., precalculus: concepts through functions, a unit circle approach to trigonometry (3rd edition) sullivan iii, michael, precalculus: mathematics for calculus, 7th edition stewart, james; redlin, lothar; watson, saleem, principles of anatomy and physiology 14e with atlas of the skeleton set (14th edition) tortora, gerard j., principles of economics, 7th edition mankiw, n. gregory, principles of heat transfer (activate learning with these new titles from engineering) 8th edition manglik, raj m.; kreith, frank, principles of life for the ap course (2nd edition) hillis, david m.; sadava, david e.; hill, richard w.; price, mary v., principles of macroeconomics 7th edition mankiw, n. gregory, principles of marketing (16th edition) kotler, philip t.; armstrong, gary, principles of microeconomics, 7th edition mankiw, n. gregory, shigley's mechanical engineering design 10th edition budynas, richard; nisbett, keith, statistics (12th edition) mcclave, james t.; sincich, terry t., statistics, 4th edition freedman, david; pisani, robert; purves, roger, statistics for the life sciences (5th edition) samuels, myra l.; witmer, jeffrey a.; schaffner, andrew, statistics: informed decisions using data (4th edition) sullivan iii, michael, statistics: the art and science of learning from data (3rd edition) agresti, alan; franklin, christine a., stats: data and models (3rd edition) de vaux, richard d.; velleman, paul d.; bock, david e., stats modeling the world, 4th edition bock, david e.; velleman, paul f.; de veaux, richard d., system dynamics 3rd edition palm, william iii, thermodynamics: an engineering approach 8th edition cengel, yunus; boles, michael, thinking mathematically (6th edition) blitzer, robert f., thomas' calculus 13th edition thomas jr., george b., trigonometry (10th edition) lial, margaret l.; hornsby, john; schneider, david i.; daniels, callie, trigonometry (11th edition) clone lial, margaret l.; hornsby, john; schneider, david i.; daniels, callie, trigonometry 7th edition mckeague, charles p.; turner, mark d., understanding business, 10th edition nickels, william g.; mchugh, james m.; mchugh, susan m., understanding nutrition 14th edition whitney, eleanor noss; rolfes, sharon rady, university calculus: early transcendentals (3rd edition) hass, joel r.; weir, maurice d.; thomas jr., george b., university physics with modern physics (14th edition) young, hugh d.; freedman, roger a..
Multiple Choice
The main difference between tangible and intangible assets is that tangible assets have a physical substance to them. This means they can be touched and have some physical form.
A patent is a contract that provides a company with exclusive rights to produce and sell a unique product. It is granted by the federal government and provides exclusivity from competition for twenty years. A copyright provides the exclusive right to reproduce and sell artistic, literary, or musical compositions for a period of seventy years beyond the death of the original author.
A. capitalized. B. expense. C. capitalized. D. capitalized. E. expense. F. expense. G. capitalized.
In measuring and reporting long-term assets, the expense recognition (“matching”) principle is applied. Under the expense recognition or “matching” principle, the acquisition cost of the asset must be allocated to the periods in which it is used to earn revenue. In this way, the cost of the asset is matched, as an expense, with the revenues that are earned from period to period through the use of the asset.
Depreciation is the process of allocating the cost of using a long-term asset over its anticipated economic (useful) life, whereas depletion is the process of expensing the cost of natural resources over the life of the asset, typically using a unit-consumed method. Amortization is specifically for intangible assets and typically is calculated using straight-line with no salvage value.
Goodwill is internally generated, but it is not recorded as an asset unless (and only when) one company acquires another company at a price greater than the total value of the net assets being purchased. The purchaser will record goodwill for the difference between the fair value of net assets acquired and the purchase price. Goodwill is not amortized and will be tested annually for impairment.
Obsolescence refers to the reduction in value and/or use of an asset. It may refer to the actual physical deterioration of the asset, which is known as physical obsolescence, or to the loss of value from causes other than physical deterioration, which is functional obsolescence. Functional obsolescence is specific to the organization and the usefulness the asset has for the company going forward. This type of obsolescence could be the result of simply not needing the asset any longer.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-financial-accounting/pages/1-why-it-matters
- Authors: Mitchell Franklin, Patty Graybeal, Dixon Cooper
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Accounting, Volume 1: Financial Accounting
- Publication date: Apr 11, 2019
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-financial-accounting/pages/1-why-it-matters
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-financial-accounting/pages/chapter-11
© Dec 13, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- enVision Math
- EngageNY Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 11 Answer Key Pdf Angles
Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 11 Answer Key Pdf: Students who are looking for quick learning with basic fundamentals can Download Go Math Grade 4 Answer Key Chapter 11 Angles pdf for free. There are different types of questions with detailed and simple explanations here. So, the students of Grade 4 can make HMH Go Math Answer Key as a reference while practicing the problems. There is a scope to learn simple techniques to solve the problems. Go Math Grade 4 Answer Key helps the parents to explain the concepts in an easy manner to their children.
Angles Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 11 Answer Key Pdf
We have provided the solutions for not only the exercised but also for the mid-chapter checkpoint and review tests. So, the students can check the solutions after practicing from Go Math Grade Chapter 11 Answer Key. Check out the topics given below before starting your preparation. Get step by step procedure for each and every problem with suitable examples in our Go Math Answer Key for Grade 4 Chapter 11 Angles. Hence make use of the links and start practicing now.
- Investigate • Angles and Fractional Parts of a Circle Page No. 605
- Investigate • Angles and Fractional Parts of a Circle Lesson Check Page No. 606
- Degrees Page No. 609
- Degrees Lesson Check Page No. 610
Lesson 3: Measure and Draw Angles
- Common Core – New Measure and Draw Angles Page No. 611
- Common Core – New Measure and Draw Angles Lesson Check Page No. 612
- Measure and Draw Angles Page No. 615
- Measure and Draw Angles Page No. 616
- Measure and Draw Angles Page No. 617
- Measure and Draw Angles Lesson Check Page No. 618
Mid-Chapter Checkpoint
- Mid-Chapter Checkpoint Page No. 619
- Mid-Chapter Checkpoint Lesson Check Page No. 620
- Investigate • Join and Separate Angles Page No. 623
- Investigate • Join and Separate Angles Lesson Check Page No. 624
Common Core – New
Common Core – New – Page No. 625
- Common Core – New Lesson Check – Page No. 626
- Problem Solving • Unknown Angle Measures Page No. 629
- Problem Solving • Unknown Angle Measures Page No. 630
- Problem Solving Unknown Angle Measures Common Core – New – Page No. 631
- Problem Solving Unknown Angle Measures Common Core – New Lesson Check – Page No. 632
Chapter 11 Review/Test
- Review/Test Page No. 633
- Review/Test Page No. 634
- Review/Test Page No. 635
- Review/Test Page No. 636
- Review/Test Page No. 637
- Review/Test Page No. 638
- Review/Test Page No. 643
- Review/Test Page No. 644
Common Core – New – Page No. 605
Angles and Fractional Parts of a Circle
Tell what fraction of the circle the shaded angle represents.

The figure shows that the \(\frac{1}{4}\)th part of the circle is shaded. So, the fraction of the shaded angle is \(\frac{1}{4}\)

Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
Half of the circle is shaded. Thus the fraction of the shaded angle is \(\frac{1}{2}\)

Answer: \(\frac{1}{1}\)
From the above figure, we can observe that the complete circle is shaded. So, the fraction of the shaded angle is \(\frac{1}{1}\) or 1.
Tell whether the angle on the circle shows a \(\frac{1}{4}, \frac{1}{2}, \frac{3}{4}\), or 1 full turn clockwise or counterclockwise.

Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) turn counter-clockwise
From the figure, we can see that the circle is rotating in the anti-clockwise direction. And it has completed the half-turn. Thus the fraction is \(\frac{1}{2}\) turn counter-clockwise

Answer: \(\frac{3}{4}\) turn clockwise
The arrow is turned in a clockwise direction. It has completed \(\frac{3}{4}\) turn. So, the angle with direction is \(\frac{3}{4}\) turn clockwise.

Answer: 1 full turn counter clockwise
From the above picture, we can observe that the circle has completed the full turn in the counter clockwise direction.
Problem Solving

Answer: The minute hand made a turn of \(\frac{1}{4}\) clockwise.
Given that,
Shelley exercised for 15 minutes. So, the fraction of the minute hand made is \(\frac{1}{4}\). The direction of the minute hand made is clockwise. So, the answer is the minute hand made a turn of \(\frac{1}{4}\) clockwise.

Answer: The minute hand made a turn of \(\frac{1}{2}\) clockwise.
Given, Mark took 30 minutes to finish lunch. The minute hand made a turn in the clockwise direction from 12 to 6. That means the fraction of the angle is \(\frac{1}{2}\). Thus the turn minute hand made is \(\frac{1}{2}\) clockwise.
Common Core – New – Page No. 606
Lesson Check

Answer: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
From the figure we can say that the fraction of the shaded angle is \(\frac{1}{4}\). Thus the answer is option D.

Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) turn clockwise
From the figure, we can see that the circle is rotating in the clockwise direction. And it has completed the half turn. So, the answer is \(\frac{1}{2}\) turn clockwise.
Spiral Review
Question 3. Which shows \(\frac{2}{3}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\) written as a pair of fractions with a common denominator? Options: a. \(\frac{2}{3} \text { and } \frac{4}{3}\) b. \(\frac{6}{9} \text { and } \frac{6}{8}\) c. \(\frac{2}{12} \text { and } \frac{3}{12}\) d. \(\frac{8}{12} \text { and } \frac{9}{12}\)
Answer: \(\frac{8}{12} \text { and } \frac{9}{12}\)
\(\frac{2}{3}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\) The denomintors are different here. So you have to make the denominators common. \(\frac{2}{3}\) × \(\frac{4}{4}\) = \(\frac{8}{12}\) \(\frac{3}{4}\) × \(\frac{3}{3}\) = \(\frac{9}{12}\) So the answer is option D.
Question 4. Raymond bought \(\frac{3}{4}\) of a dozen rolls. How many rolls did he buy? Options: a. 3 b. 6 c. 7 d. 9
Raymond bought \(\frac{3}{4}\) of a dozen rolls. Dozen = 12 \(\frac{3}{4}\) × 12 = 9 Thus the correct answer is option D.
Question 5. Which of the following lists all the factors of 18? Options: a. 1, 2, 4, 9, 18 b. 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18 c. 2, 3, 6, 9 d. 1, 3, 5, 9, 18
Answer: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18
The factors of 18 are 1 × 18 = 18 2 × 9 = 18 3 × 6 = 18 6 × 3 = 18 9 × 2 = 18 18 × 1 = 18 Thus the correct answer is option B.
Question 6. Jonathan rode 1.05 miles on Friday, 1.5 miles on Saturday, 1.25 miles on Monday, and 1.1 miles on Tuesday. On which day did he ride the shortest distance? Options: a. Monday b. Tuesday c. Friday d. Saturday
Answer: Friday
Jonathan rode 1.05 miles on Friday, 1.5 miles on Saturday, 1.25 miles on Monday, and 1.1 miles on Tuesday. The shortest among all is 1.05 miles. Therefore the answer is option C.
Page No. 609

Answer: 120°
The fraction of the shaded angle is \(\frac{1}{3}\) To measure the angle we have to multiply the fraction of the shaded angle with the total angle. That means, \(\frac{1}{3}\) × 360 360/3 = 120 degrees. Thus the angle of the shaded part is 120°
Tell the measure of the angle in degrees.

Answer: 45°
The fraction of the shaded angle is \(\frac{45}{360}\) Multiply the fraction with the complete angle \(\frac{45}{360}\) × 360° = 45° Thus the angle of the above figure is 45°

Answer: 30°
The figure shows the fraction of the shaded angle is \(\frac{1}{12}\) Multiply the fraction with the complete angle \(\frac{1}{12}\) × 360° = 30° Therefore the measure of the shaded angle is 30°

Answer: 360°
We observe that the circle is shaded completely. \(\frac{360}{360}\) × 360° = 360° Thus the above figure is the complete angle.

Answer: 36°
The fraction of the shaded angle is \(\frac{1}{10}\) Multiply the fraction with the complete angle \(\frac{1}{10}\) × 360° = 36° Therefore the measure of the shaded angle is 36°
Classify the angle. Write acute, obtuse, right, or straight.

Answer: Obtuse
An obtuse angle has a measurement greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees. However, A reflex angle measures more than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees.

Answer: Right
A right angle is an angle of exactly 90° (degrees), corresponding to a quarter turn. If a ray is placed so that its endpoint is on a line and the adjacent angles are equal, then they are right angles.

Answer: Acute
The acute angle is the small angle which is less than 90°.

Answer: Straight
A straight angle is 180 degrees. A straight angle changes the direction to point the opposite way.

Answer: 90°
Alex cut a circular pizza into 8 equal slices. He removed 2 of the slices of pizza. The fraction of the missing slices = \(\frac{2}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) The fraction of the missing slices is \(\frac{1}{4}\) To know the angle we have to multiply the fraction with complete angle i.e., 360° \(\frac{1}{4}\) × 360° = 90° Thus the angle of the missing slices is 90°
Page No. 610

Answer: I am asked to find the fraction of a circle did the minute hand turn and how many degrees did the minute hand turn
Question 12. b. What information can you use to find the fraction of a circle through which the minute hand turned? Type below: _________
Answer: The fraction of a circle through which the minute hand-turned \(\frac{3}{4}\) Clockwise.
Question 12. c. How can you use the fraction of a circle through which the minute hand turned to find how many degrees it turned? Type below: _________
The figure shows that the fraction of a circle through which the minute hand turned is \(\frac{3}{4}\) Clockwise. Let the shaded part be x And the nonshaded part is 90° x + 90° = 360° x = 360°- 90° x = 270° Therefore the minute hand turns 270° clockwise.
Question 12. d. Show the steps to solve the problem. Step 1: \(\frac{3 × ■}{4 × ■}=\frac{?}{360}\) Step 2: \(\frac{3 × 90}{4 × 90}=\frac{■}{360}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{3 × 90}{4 × 90}=\frac{■}{360}\) \(\frac{270}{360} = \frac{■}{360}\) If the denominators are equal then the numerators must be equated. ■ = 270
Question 12. e. Complete the sentences. From 3:30 p.m. to 4:15 p.m., the minute hand made a ______ turn clockwise. The minute hand turned ______ degrees. Type below: _________
Answer: From 3:30 p.m. to 4:15 p.m., the minute hand made a \(\frac{3}{4}\) turn clockwise. The minute hand turned 270 degrees.

Answer: 24° \(\frac{1}{15} × 360° = 24°
Common Core – New – Page No. 611

Given that the fraction of the shaded angle is [latex]\frac{60}{360}\) \(\frac{60}{360}\) × 360 = 60° Thus the angle for the above figure is 60°

Answer: 180°
Half of the circle is shaded. The fraction of the shaded angle is \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 360 = 360/2 = 180°

The fraction of the shaded angle is \(\frac{1}{4}\) To find the angle we need to multiply the fraction with the total angle. \(\frac{1}{4}\) × 360° = 90°

25° < 90° So, the above figure is an acute angle.

110° > 90° So, the figure shown above is an obtuse angle.

60° < 90° Acute angles measure less than 90 degrees. Thus the above angle is an acute angle.
Classify the triangle. Write acute, obtuse, or right.

65 + 25 = 90 The sum of two angles = 90° Thus the above figure is a right-angled triangle.

110° > 90° So, the above triangle is an obtuse angle.

50° is less than 90° Thus the above triangle is an acute angle triangle.

Question 10. Through what fraction of a circle did the minute hand turn? \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}\) turn clockwise
The fraction of the shaded clock is \(\frac{12}{4}\) \(\frac{12}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) The minute hand turn clockwise direction. So, the answer is \(\frac{1}{3}\) turn clockwise
Question 11. How many degrees did the minute hand turn? ____ °
The fraction of the minute hand turn is \(\frac{1}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) × 360° = 120° The minute hand turn 120°
Common Core – New – Page No. 612
Answer: straight
A straight angle is 180 degrees. This is a straight angle. A straight angle changes the direction to point the opposite way. So, the answer is option D.
Question 2. How many degrees are in an angle that turns through \(\frac{1}{4}\) of a circle? Options: a. 45° b. 90° c. 180° d. 270°
\(\frac{1}{4}\) × 360° \(\frac{360}{4}\) = 90° Thus the correct answer is option B.
Question 3. Mae bought 15 football cards and 18 baseball cards. She separated them into 3 equal groups. How many sports cards are in each group? Options: a. 5 b. 6 c. 11 d. 12
Mae bought 15 football cards and 18 baseball cards. She separated them into 3 equal groups. Total number of cards = 15 + 18 = 33 33/3 = 11 There are 11 sports cards in each group.
Question 4. Each part of a race is \(\frac{1}{10}\) mile long. Marsha finished 5 parts of the race. How far did Marsha race? Options: a. \(\frac{1}{10}\) mile b. \(\frac{5}{12}\) mile c. \(\frac{1}{2}\) mile d. 5 \(\frac{1}{10}\) miles
Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) mile
Each part of a race is \(\frac{1}{10}\) mile long. Marsha finished 5 parts of the race. \(\frac{1}{10}\) × 5 = 5/10 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) mile Thus the correct answer is option C.
Question 5. Jeff said his city got \(\frac{11}{3}\) inches of snow. Which shows this fraction written as a mixed number? Options: a. 3 \(\frac{2}{3}\) b. 3 \(\frac{1}{3}\) c. 2 \(\frac{2}{3}\) d. 1 \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Answer: 3 \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Jeff said his city got \(\frac{11}{3}\) inches of snow. The mixed fraction of \(\frac{11}{3}\) is 3 \(\frac{2}{3}\) The correct answer is option A.
Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 11 Answer Key Question 6. Amy ran \(\frac{3}{4}\) mile. Which decimal shows how many miles she ran? Options: a. 0.25 mile b. 0.34 mile c. 0.5 mile d. 0.75 mile
Answer: 0.75 mile
Amy ran \(\frac{3}{4}\) mile. \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{75}{100}\) The decimal form of \(\frac{75}{100}\) is 0.75 So, the answer is option D.

Page No. 615

Answer: 65°
Use a protractor to find the angle measure.

Answer: 55°

Answer: 105°
Use a protractor to draw the angle.
Question 4. 170° Type below: _________

Question 5. 78° Type below: _________
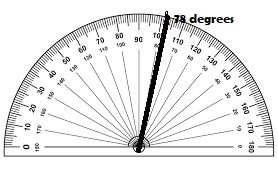
Answer: 155°
Question 8. 115° Type below: _________

Question 9. 67° Type below: _________
Draw an example of each. Label the angle with its measure.
Question 10. an acute angle Type below: _________
Question 11. an obtuse angle Type below: _________

Answer: 15°
Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 11 Pdf Question 13. Draw an angle with a measure of 0°. Describe your drawing. Type below: _________

Page No. 616

Given, Hadley wants to divide this angle into three angles with equal measure. The above figure is a right angle = 90° If he divides into three equal angles 90/3 = 30° So, the measure of angle will be 30°
Question 15. Tracy measured an angle as 50° that was actually 130°. Explain her error. Type below: _________
Answer: She has measured the angle in the counterclockwise direction. So, that is why she got 50°.

Answer: ∠QRS is an obtuse angle that has a measure of 135°.
Earth’s Axis Earth revolves around the sun yearly. The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. The seasons of the year are due to the tilt of Earth’s axis.

Question 17. In the Northern Hemisphere, Earth’s axis is tilted away from the sun on the first day of winter, which is often on December 21. What is the measure of the marked angle on the first day of winter, the shortest day of the year? ____ °
Answer: 115°
By seeing the above figure we can say that the angle is an obtuse angle. The mark is above 90° and the marked angle is 115°. Therefore the measure of the marked angle on the first day of winter, the shortest day of the year is 115°.
Question 18. Earth’s axis is not tilted away from or toward the sun on the first days of spring and fall, which are often on March 20 and September 22. What is the measure of the marked angle on the first day of spring or fall? ____ °
The mark is exactly 90°. So, the angle on the first day of spring or fall is 90°
Common Core – New – Page No. 617
Measure and Draw Angles

By using the protractor we can measure the angle m∠ABC i.e., 120 °

Answer: m∠MNP = 90°
By observing the above figure we can say that the angle of m∠MNP is 90°

Answer: m∠RST = 65° By using the protractor we can measure m∠RST = 65°
Question 4. 40°
Question 5. 170°
Question 6. a right angle
A right angle is an angle of exactly 90°
Question 7. an acute angle

Question 8. What is the measure of ∠A? ____ °
By using the protractor we can measure the angle for A = 45°
Question 9. What is the measure of ∠B? ____ °
Answer: 135°
The same process is used to measure ∠B = 135°
Common Core – New – Page No. 618

Step 1: Place the center point of the protractor on the point B. Step 2: Align the 0° mark on the scale of the protractor with ray BC. Step 3: Find the point where AC meets. Read the angle measure on that scale. So, the measure of ∠ABC is 15° Thus the correct answer is option A.

Answer: 150°
Step 1: Place the center point of the protractor on the point Y. Step 2: Align the 0° mark on the scale of the protractor with ray XY. Step 3: Find the point where YZ meet. Read the angle measure on that scale. So, ∠XYZ = 150° Therefore the correct answer is option C.
Question 3. Derrick earned $1,472 during the 4 weeks he had his summer job. If he earned the same amount each week, how much did he earn each week? Options: a. $360 b. $368 c. $3,680 d. $5,888
Answer: $368
Given that, Derrick earned $1,472 during the 4 weeks he had his summer job. Let the amount he earned per week = x x × 4 = $1,472 x = 1472 ÷ 4 x = 1472/4 = 368 So, Derrick earned $368 per week.
Go Math Workbook Grade 4 Chapter 11 Review/Test Answer Key Question 4. Arthur baked 1 \(\frac{7}{12}\) dozen muffins. Nina baked 1 \(\frac{1}{12}\) dozen muffins. How many dozen muffins did they bake in all? Options: a. 3 \(\frac{2}{3}\) b. 2 \(\frac{2}{3}\) c. 2 \(\frac{1}{2}\) d. \(\frac{6}{12}\)
Answer: 2 \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Given: Arthur baked 1 \(\frac{7}{12}\) dozen muffins. Nina baked 1 \(\frac{1}{12}\) dozen muffins. Add both the fractions Convert mixed fraction into normal fractions 1 \(\frac{7}{12}\) = \(\frac{19}{12}\) 1 \(\frac{1}{12}\) = \(\frac{13}{12}\) \(\frac{19}{12}\) + \(\frac{13}{12}\) = \(\frac{32}{12}\) = \(\frac{8}{3}\) Convert \(\frac{8}{3}\) into mixed fraction = 2 \(\frac{2}{3}\) So, the answer is option B.
Answer: ray TS
A ray can be defined as a part of a line that has a fixed starting point but no endpoint. Here the point starts from T and ends at S. So, the figure Trisha drew is ray TS. The correct answer is option C.

Answer: \(\frac{1}{4}\) turn clockwise
The figure shows that the point turned \(\frac{1}{4}\) in a clockwise direction. So, the answer is option D.
Page No. 619

Question 1. The unit used to measure an angle is called a ________. ________
Answer: The unit used to measure an angle is called a degree.
Question 2. ________ is the opposite of the direction in which the hands of a clock move. ________
Answer: Counterclockwise is the opposite of the direction in which the hands of a clock move.
Question 3. A ________ is a tool for measuring the size of an angle. ________
Answer: A protractor is a tool for measuring the size of an angle.

Answer: \(\frac{1}{4}\) turn clockwise The figure shows that the angle turn \(\frac{1}{4}\) in the clockwise direction.

Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) turn counterclockwise From the above figure, we can see that the angle turn \(\frac{1}{2}\) in the counterclockwise direction.

Answer: \(\frac{3}{4}\) turn clockwise The figure shows that the angle turn \(\frac{3}{4}\) in the clockwise direction.

Answer: \(\frac{1}{1}\) or 1 turn counterclockwise From the above figure, we can see that the angle turn \(\frac{1}{1}\) or 1 in the counterclockwise direction.

Answer: 100°
\(\frac{100}{360}\) × 360° = 100°
Question 9. ____ °
Question 10. 75° Type below: ________

Question 11. 127° Type below: ________
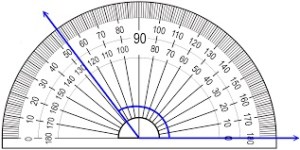
Page No. 620

Phillip watched a beach volleyball game from 1:45 p.m. to 2:00 p.m. The minute hand turned for 15 minutes. That means \(\frac{1}{4}\) turn clockwise. Complete angle = 360° \(\frac{1}{4}\) × 360° = 360°/4 = 90° Therefore the minute hand turn 90°

From the above figure, we can see that half of the pie is completed. Complete angle = 360° \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 360° = 180° The angle for the piece of pie form is 180°

Answer: 60°
By using the protractor we can say that the angle for the above figure is 60°
Question 15. Matt cut a circle into 8 equal sections. He drew an angle that measures the same as the total measure of 3 of the sections in the circle. What is the measure of the angle Matt drew? ____ °
Matt cut a circle into 8 equal sections. He drew an angle that measures the same as the total measure of 3 of the sections in the circle. Complete angle = 360° Divide the total number of sections by 360° \(\frac{360}{8}\) = 45° So, the angle for each section is 45° The angle for 3 of the sections in the circle = 3 × 45° = 135° Thus the measure of the angle Matt drew is 135°
Page No. 623
Add to find the measure of the angle. Write an equation to record your work.

Answer: 80°
To find the ∠PQT you have to add 43° and 37° ∠PQT = 43° + 37° ∠PQT = 80°

Answer: 100° Let ∠JKL = x° ∠JKL = 90° + 10° ∠JKL = 100°

Answer: Let ∠RHT = x° x = 55° + 27° + 78° x = 160° Therefore ∠RHT = 160°
Use a protractor to find the measure of each angle. Label each angle with its measure. Write the sum of the angle measures as an equation.

By using the protractor we can measure the angles of the above figures. m∠KLM = 160° m∠KLJ = 80° m∠LMJ = 120°

By using the protractor we can measure the angles of the above figures.
m∠WVZ = 90° m∠YVZ = 90° m∠WVX = 140° m∠YVX = 40°

Answer: 20°
The above figure is a straight angle. ∠QRT + ∠LRD + ∠RLT = 180 ∠QRT + 75° + 85° = 180° ∠QRT + 160° = 180° ∠QRT = 180°- 160° ∠QRT = 20°
Question 7. Look back at Exercise 1. Suppose you joined an angle measuring 10° to ∠PQT. Draw the new angle, showing all three parts. What type of angle is formed? Type below: ________
Page No. 624

Answer: What is the measure of the angle for the pizza leftover?
Question 8. b. What information do you need to use? Type below: ________
Answer: I need the information about the angle for each piece of pizza.
Question 8. c. Tell how you can use addition to solve the problem. Type below: ________
Answer: The measure of the angle of each piece was 45° There are 3 pieces of pizza = 45° + 45° + 45° = 135°
Question 8. d. Complete the sentence. The three pieces of pizza formed a _________ angle. ________
Answer: Obtuse angle

Answer: 113°
∠XZW = ∠XZY + ∠YZW ∠XZY = 42° ∠YZW = 71° ∠XZW = 42° + 71° ∠XZW = 113°

Answer: 12°
The above figure is a straight angle. The sum of the three angles must be equal to 180° m∠PRS + m∠PRN + m∠TRN = 180° m∠PRS + 90° + 78° = 180° m∠PRS = 180° – 90° – 78° m∠PRS = 12°
Join and Separate Angles

m∠ABC = 50° m∠CBD = 75° To find the measure of m∠ABD we have to add m∠ABC and m∠CBD m∠ABD = 50°+75° m∠ABD = 125°

Answer: 140° + 20° = 160° m∠FGJ = 160°
m∠FGH = 140° m∠JGH = 20° To find the measure of m∠FGJ we need to add m∠FGH and m∠JGH m∠FGJ = 140° + 20° m∠FGJ = 160°

Answer: 30° + 90° + 45° = 165° m∠KLN = 165°
m∠KLM = 30° m∠MLP = 90° m∠PLN = 45° To find the measure of m∠KLN we need to add m∠KLM, m∠MLP and m∠PLN m∠KLN = 30° + 90° + 45° = 165° m∠KLN = 165°

Question 4. m∠ABC = ____ °
Question 5. m∠DBE = ____ °
Question 6. m∠CBD = ____ °
Answer: 75°
Question 7. m∠EBA = ____ °
Question 8. Write the sum of the angle measures as an equation. ____ ° + ____ ° + ____ ° + ____ ° = ____ °
Sum all the angles = m∠DBE + m∠ABC + m∠CBD + m∠EBA = 115° + 90° + 75° + 80° = 360°

Question 9. Ned made the design at the right. Use a protractor. Find and write the measure of each of the 3 angles. ____ ° ; ____ ° ; ____ ° ;
Answer: 50°; 60°; 70°
The above figure is a straight angle. By using the protractor we can measure the angles of the above figure. The angle of above 3 shades is 50°; 60°; 70°
Question 10. Write an equation to find the measure of the total angle. ____ ° + ____ ° + ____ ° = ____ °
Answer: Sum of three angles = 50° + 60° + 70° = 180°
Common Core – New – Page No. 626

Answer: 83°
m∠WXZ = m∠WXY + m∠YXZ Let m∠WXZ be x° x° = 58° + 25° x° = 83° Thus the correct answer is option B.

Answer: 148° + 24° = ■
To measure the unknown angle we need to add both the angles m∠MNQ = m∠MNP + m∠PNQ ■ = 148° + 24° So, the correct answer is option D.
Question 3. Joe bought 6 packages of envelopes. Each package contains 125 envelopes. How many envelopes did he buy? Options: a. 750 b. 723 c. 720 d. 650
Answer: 750
Joe bought 6 packages of envelopes. Each package contains 125 envelopes. To find the total number of envelopes in all 6 packages We have to multiply number of packages and number of envelopes = 125 × 6 =750 Thus Joe bought 750 envelopes. The correct answer is option A.
Question 4. The Lake Trail is \(\frac{3}{10}\) mile long and the Rock Trail is \(\frac{5}{10}\) long. Bill hiked each trail once. How many miles did he hike in all? Options: a. \(\frac{1}{5}\) mile b. \(\frac{4}{10}\) mile c. \(\frac{1}{2}\) mile d. \(\frac{8}{10}\) mile
Answer: \(\frac{8}{10}\) mile
The Lake Trail is \(\frac{3}{10}\) mile long and the Rock Trail is \(\frac{5}{10}\) long. Bill hiked each trail once. We need to both the fractions \(\frac{3}{10}\) +\(\frac{5}{10}\) The denominators are common. So add the numerators. = \(\frac{8}{10}\) Bill hiked \(\frac{8}{10}\) miles in all. Thus the correct answer is option D.
Question 5. Ron drew a quadrilateral with 4 right angles and 4 sides with the same length. Which best describes the figure he drew? Options: a. square b. rhombus c. trapezoid d. parallelogram
Answer: square
A square has got 4 sides of equal length and 4 right angles (right angle = 90 degrees). So, the answer is option A.
Question 6. How many degrees are in an angle that turns through \(\frac{3}{4}\) of a circle? Options: a. 45° b. 90° c. 180° d. 270°
Answer: 270°
Complete angle = 360° To measure the angle that turns through is \(\frac{3}{4}\) multiply \(\frac{3}{4}\) with 360° 360° × \(\frac{3}{4}\) = 270° So, the answer is option D.
Page No. 629

Type below: _________

Question 1. Next, write the equation you need to solve. Type below: _________
m∠MNQ + m∠QNP = m∠MNP x + 90° = 115° x = 115° – 90°
Question 1. Last, find the angle measure of the piece left over. m∠MNQ = So, the angle measure of the piece left over is _____. ____ °
Answer: x + 90° = 115° x = 115° – 90° x = 25° So, the angle measure of the piece left over is 25°

Answer: x + 180° = 225° x = 225°- 180° x = 45° Thus the measure of the piece she trimmed off is 45°

Answer: No m∠MNQ would still be 25°. Only the size of the square changed the angle will be the same. m∠PNQ and m∠MNP did not change.

x° + 125° + 180° = 360° x° = 360° – 125° – 180° x° = 360° – 215° x° = 145°
Page No. 630
Question 5. Write an Equation Two angles form a straight angle. One angle measures 89°. What is the measure of the other angle? Explain. ____ °
Answer: 91°
A straight angle measures 180°, so you can subtract 89° from 180° 180° – 89° = 91°
Question 6. Pose a Problem Look back at Problem 5. Write a similar problem about two angles that form a right angle. ____ °
Answer: Two angles form a right angle. The measure of one angle is 25°. What is the measure of the other angle? x + 25° = 90° x °= 90° – 25° x° = 65° The measure of other angle is 65°
Question 7. Sam paid $20 for two T-shirts. The price of each T-shirt was a multiple of 5. What are the possible prices of the T-shirts? Type below: _________
Answer: Sam paid $20 for two T-shirts. The price of each T-shirt was a multiple of 5. $20 – 2 T-shirts x – 1 T-shirt x = $10 The possible prices of the T-shirts are $10, $10 Another possible price of the T-shirts are $5, $15
Question 8. Zayna has 3 boxes with 15 art books in each box. She has 2 bags with 11 math books in each bag. If she gives 30 books away, how many art and math books does she have left? _____ books
Answer: 37 art and math books
Zayna has 3 boxes with 15 art books in each box = 15 × 3 = 45 She has 2 bags with 11 math books in each bag = 11 × 2 = 22 Total number of books = 45 + 22 = 67 If she gives 30 books away, then we have to subtract 30 from 67 67 – 30 = 37 37 art and math books are left.
Question 9. What’s the Question? It measures greater than 0° and less than 90°. Type below: _________
Answer: What is an acute angle?
Question 10. Two angles, ∠A and ∠B, form a straight angle. ∠A measures 65°. For numbers 10a–10c, select True or False for the statement. a. ∠B is an acute angle. i. True ii. False
Answer: False
Two angles, ∠A and ∠B, form a straight angle. ∠A measures 65°. 65° + ∠B = 180° ∠B = 180° – 65° ∠B = 115° 115° is not an acute angle. So, the above statement is false.
Question 10. b. The equation 180° – 65° = x° can be used to find the measure of ∠B. i. True ii. False
Answer: True
Question 10. c. The measure of ∠B is 125°. i. True ii. False
65° + ∠B = 180° ∠B = 180° – 65° ∠B = 115° So, the above statement is false.
Common Core – New – Page No. 631
Problem Solving Unknown Angle Measures
Solve each problem. Draw a diagram to help.

Answer: 95°
x + 130° = 225° x = 225° – 130° x = 95° Therefore the angle of the piece leftover is 95°.

Answer: 50°
Joan has a piece of material for making a costume. She needs to cut it as shown. By seeing the above figure we can say that it is a right angle.| The sum of two must be equal to 90° Let the unknown angle be x x + 40° = 90° x = 90° – 40° x = 50° Thue the angle measure of the piece leftover is 50°
Common Core – New – Page No. 632

The above figure is a right angle. So, to measure the ∠x we have to subtract 75° from 90° ∠x + 75° = 90° ∠x = 90° – 75° ∠x = 15° Thus the correct answer is option A.

x + 90° = 210° x = 210° – 90° x = 120° 120° is the measure of the piece leftover. So, the correct answer is option C.
Question 3. Tyronne worked 21 days last month. He earned $79 each day. How much did Tyronne earn last month? Options: a. $869 b. $948 c. $1,659 d. $2,169
Answer: $1,659
Tyronne worked 21 days last month. He earned $79 each day. $79 × 21 = 1659 Thus Tyronne earned $1,659 last month. So, the correct answer is option C.
Question 4. Meg inline skated for \(\frac{7}{10}\) mile. Which shows this distance written as a decimal? Options: a. 0.07 mile b. 0.1 mile c. 0.7 mile d. 7.1 miles
Answer: 0.7 mile
Meg inline skated for \(\frac{7}{10}\) mile. The decimal of the fraction \(\frac{7}{10}\) is 0.7 So, the answer is option C.
Question 5. Kerry ran 34 mile. Sherrie ran \(\frac{1}{2}\) mile. Marcie ran \(\frac{2}{3}\) mile. Which list orders the friends from least to greatest distance run? Options: a. Kerry, Sherrie, Marcie b. Kerry, Marcie, Sherrie c. Sherrie, Kerry, Marcie d. Sherrie, Marcie, Kerry
Answer: Sherrie, Marcie, Kerry
Kerry ran 34 miles. Sherrie ran \(\frac{1}{2}\) mile. Marcie ran \(\frac{2}{3}\) mile. The order of the above fractions is Sherrie ran \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{2}{3}\), 34 The distance from least to greatest is Sherrie, Marcie, Kerry. so, the correct answer is option D.

Answer: 84°
m∠ABC = m∠ABD + m∠DBC m∠ABC = 58° + 26° m∠ABC = 84° So, the correct answer is option B.
Page No. 633

Answer: 30° \(\frac{1}{12}\) × \(\frac{30}{30}\) = \(\frac{30}{360}\) Thus the angle measure is 30°

i. 122° + 58° = 180° ii. 35° + 145° = 180° iii. 62° + 118° = 180° iv. 105° + 75° = 180°
Question 3. Katie drew an obtuse angle. Which could be the measure of the angle she drew? Mark all that apply. Options: a. 35° b. 157° c. 180° d. 92°
Answer: 157° and 92° An obtuse angle has a measurement greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees. From the above options, B and D are more than 90° So, the answer is options B and D.

Page No. 634

Answer: Yes
By seeing the above figure we can say that the angle is a straight angle. So, the above statement is true.
Question 5. b. To find the measure of x, Renee can subtract 75° from 180°. i. yes ii. no
To know the value of x we have to subtract 75° from 180°. x = 180° – 75° Thus the above statement is true.
Question 5. c. The measure of x is 115°. i. yes ii. no
Answer: No x = 180° – 75° x = 105° Thus the above statement is false. So, the answer is no.

Answer: 55° + 80° + x = 180°
The figure is a straight angle. So, the sum of the three angles must be equal to 180° Let m∠KFG = x 55° + 80° + x = 180°
Question 6. Part B What is the measure of m∠KFG? Describe how you solved the equation and how you can check your answer. ____ ° Explain: _________
55° + 80° + x = 180° x = 180° – 80° – 55° x = 45°

Answer: 40° By using a protractor we can measure the angle. The angle of the above figure is 40°
Page No. 635

Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) turn
The above figure shows that it is straight angle. So, the fraction of the circle is \(\frac{1}{2}\) turn. The correct answer is option C.

Miles has a piece of paper that is \(\frac{1}{4}\) of a large circle. He cuts the paper into three equal parts from the center point of the circle. \(\frac{1}{4}\) of a large circle = 90° Given that he cut into 3 equal parts = \(\frac{90}{3}\) = 30° So, the angle for each part is 30°

Answer: 57°
Let the unknown angle be x It is a straight angle. The sum of three angles = 180° 90° + 33° + x = 180° x = 180° – 90° – 33° x = 57°
Page No. 636

Answer: m∠JKL is an Obtuse angle that has a measure of 120°.

I shaded the part of the clock that the minute hand turned from 5:15 p.m. to 5:35 p.m. anmd found that it is \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the circle. Next, I multiplied \(\frac{1}{3}\) × 360° = 120° Thus the minute hand moved 120°
Question 14. An angle measures 125°. Through what fraction of a circle does the angle turn? \(\frac{□}{□}\) of a circle
Answer: \(\frac{125}{360}\)
The fraction of the circle the angle turned is \(\frac{125}{360}\)

Page No. 637

Answer: The angle in Figure 1 represents a \(\frac{3}{4}\) turn
The above figure shows that \(\frac{3}{4}\) part of the circle is shaded. So, the angle represents \(\frac{3}{4}\) turn.

Answer: The angle in Figure 2 represents a \(\frac{1}{2}\) turn. From the second figure, we observe that half of the circle is shaded. So, The angle in Figure 2 represents a \(\frac{1}{2}\) turn.

Question 17. Part B Write and solve an equation to find x. The angle measures ____ °.
Answer: 36° m∠RST = 90° m∠RSN = 126° m∠TSN = x° x + 90° = 126° x = 126° – 90° x = 36° m∠TSN = 36°
Page No. 638
Question 18. Two angles, m∠A and m∠B, form a right angle. m∠A measures 32°. For numbers, 18a–18c, select True or False for the statement. a. m∠B is an acute angle. i. True ii. False
If the sum of two angles is 90°, if one angle is acute then the other angle will be acute. So, the above statement is true.
Question 18. b. The equation 180° − 32° = x° can be used to find the measure of m∠B. i. True ii. False
Given that the sum of 2 angles is 90° The sum of m∠A and m∠B = 90° 90° – 32° = x° So, the above statement is false.
Question 18. c. The measure of m∠B is 58°. i. True ii. False
Let m∠B = x x° + 32° = 90° x = 90 – 32 x = 58°. So, the above statement is true.
Question 19. A circle is divided into parts. Which sum could represent the angle measures that make up the circle? Mark all that apply. Options: a. 120° + 120° + 120° + 120° b. 25° + 40° + 80° + 105° + 110° c. 33° + 82° + 111° + 50° + 84° d. 40° + 53° + 72° + 81° + 90° + 34°
Answer: 25° + 40° + 80° + 105° + 110°; 33° + 82° + 111° + 50° + 84°
The sum of all the angles must be equal to 360° i. 120° + 120° + 120° + 120° = 480° ≠ 360° ii. 25° + 40° + 80° + 105° + 110° = 360° iii. 33° + 82° + 111° + 50° + 84° = 360° iv. 40° + 53° + 72° + 81° + 90° + 34° = 370° ≠ 360° So, the correct answers are option B, C.

Answer: m∠x = 70°; m∠y = 110° By using a protractor we can find the measure of m∠y m∠y = 110° Let m∠x = x° Sum of supplementary angles = 180° 110° + x = 180° x = 180° – 110° x = 70° Therefore m∠x = 70°
Page No. 643

Question 1. mass of a strawberry __________
Answer: gram The metric unit used to measure the mass of a strawberry is the gram.
Question 2. length of a cell phone __________
Answer: Centimeter The metric unit used to measure the length of a cell phone is Centimeter.
Circle the better estimate.
Question 3. width of a teacher’s desk 10 meters or 1 meter __________
Answer: 1 meter The estimation of the width of the teacher’s desk is 1 meter.
Question 4. The amount of liquid a punch bowl holds 2 liters or 20 liters __________
Answer: 2 liters
20 liters is greater than 2 liters. The estimation of the amount of liquid a punch bowl holds is 2 liters.
Question 5. distance between Seattle and San Francisco 6 miles or 680 miles __________
Answer: 680 miles The distance between Seattle and San Francisco is 680 miles.

Question 6. length of a football field __________
Answer: Yard The units to measure the length of a football field is Yards.
Question 7. weight of a pumpkin __________
Answer: Pound The customary unit I use to measure the weight of a pumpkin is pounds.
Question 8. weight of a watermelon 4 pounds or 4 ounces __________
Answer: 4 pounds The estimation of the weight of the watermelon is 4 pounds.
Question 9. The amount of liquid a fish tank holds 10 cups or 10 gallons __________
Answer: 10 gallons The estimation of the amount of liquid a fish tank holds is 10 gallons.
Complete the sentence. Write more or less.
Question 10. Matthew’s large dog weighs ________ than one ton. ________
Answer: Less 1 ton = 1000 kgs The weight of dogs can’t be more than a ton. So, Matthew’s large dog weighs less than one ton.
Question 11. The amount of liquid a sink can hold is _______ than one cup of water. ________
Answer: More 1 cup holds a very small amount of water. So, The amount of liquid a sink can hold is more than one cup of water.
Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 11 Mid Chapter Checkpoint Answer Key Question 12. A paper clip has a mass of _______ than one kilogram. ________
Answer: Less
The weight of a paper clip is about 1 gram. So, A paper clip has a mass of less than one kilogram.
Page No. 644

Question 13. Cristina is making macaroni and cheese for her family. Would Cristina use 1 pound of macaroni or 1 ounce of macaroni? __________
Answer: Cristina should use 1 pound of macaroni.
Question 14. Which is the better estimate for the length of a kitchen table, 200 centimeters or 200 meters? __________
Answer: 200 centimeters
Centimeters are less than meters. The length of the kitchen will be measured in centimeters. So, the answer is 200 centimeters.
Question 15. Jodi wants to weigh her cat and measure its standing height. Which two units should she use? weight: ________ height: ________
Answer: The weight of the cat should be measured in Kilograms. The height of the cat should be measured in Centimeters.
Question 16. Evaluate Reasonableness Dalton used benchmarks to estimate that there are more cups than quarts in one gallon. Is Dalton’s estimate reasonable? Explain. Type below: __________
Answer: Dalton’s reasoning is correct because the measurement of cups is smaller than the measurement of quarts, therefore there would be more cups in a gallon than quarts.

Answer: 1 pint
The suitable word for the above sentence is the pint. A pint is a measure of liquid equal to about half a liter. There are eight pints in a gallon.
Make maths your favorite subject by solving the problems. If you understand the concepts you can prepare the questions on your own. It is an easy and scoring subject compared to all. So, go through the Go Math Grade 4 Solution Key Chapter 11 Angles to secure the highest marks in the exams. If you have doubts regarding the subject you can comment in the below comment box. All the best!!!!
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
View the correct answers for activities in the learning path. This procedure is for activities that are not provided by an app in the toolbar. Some MindTap courses contain only activities provided by apps. Click an activity in the learning path. Turn on Show Correct Answers. View Aplia Answer Keys. View the correct answers for Aplia™ activities.
Lesson 11.8 COMMON CORE STANDARD CC.5.MD.4 Geometric measurement] understand concepts of volume and relate volume to multiplication and to addition Volume of rice box: 500 cu cm 1 3. Volume of package of paper: 200 cu in Paper Paper Paper Paper Think: Each package of paper has a volume 2. 4. 6. Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice 12,000 cu cm
Exercise 6. Exercise 7. Exercise 8. Exercise 9. Exercise 10. At Quizlet, we're giving you the tools you need to take on any subject without having to carry around solutions manuals or printing out PDFs! Now, with expert-verified solutions from Introductory Statistics 10th Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems.
John is making a chest that will have a volume of 1,200 cubic inches. The length is 20 inches and the width is 12 inches. Volume = l × w × h. 1200 cu in = 20 in × 12 in × h. 240 sq in × h = 1200 cu in. h = 1200 cu in ÷ 240 sq in. h = 5 in. Thus John's chest will be 5 inches tall. The correct answer is option B.
At Quizlet, we're giving you the tools you need to take on any subject without having to carry around solutions manuals or printing out PDFs! Now, with expert-verified solutions from Big Ideas Geometry 1st Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Big Ideas Geometry includes answers to chapter ...
Exercise 9. Exercise 10. Exercise 11. Exercise 12. At Quizlet, we're giving you the tools you need to take on any subject without having to carry around solutions manuals or printing out PDFs! Now, with expert-verified solutions from Principles of Economics 9th Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems.
Go Math! Practice Book (TE), G5. Name Polygons Name each polygon. Then tell whether it is a regular polygon Lesson 11.1 COMMON CORE STANDARD CC.5.G.3 Classify two-dimensional figures into categories based on their properties. regular or not a regular polygon. 4 sides, 4 vertices, 4 angles means it is a quadrilateral The sides are not regular ...
Chapter 08 Chapter 09 Chapter 10 Chapter 11 Chapter 12 Chapter 13. Click the link below to access the Toolkit Answer Key available in Microsoft Word. Toolkit Answer Key (79.0K) To learn more about the book this website supports, please visit its Information Center.
Chapter 11 - Surface Area and Volume Answer Key CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts 3 11.3 Prisms Answers 1. rectangular prism 2. 6 rectangles: 2 are 6x7, 2 are 2x6, and 2 are 2x7. 3. 42 in2 each 4. 52 in2 5. 136 in2 6. 960 cubes, yes this is the same as the volume. 7. 280 in3 8. 4π in3 9. 6 in 10. 512 in3 11. 36 u3 12. Right Triangles, 6 u2 each ...
CPM Educational Program. With Mathleaks, you'll have instant access to expert solutions and answers to all of the CPM math questions you may have from the CPM Educational Program publications such as Pre-Algebra, Algebra 1, Algebra 2, and Geometry. Mathleaks offers the ultimate homework help and much of the content is free to use.
Go Math Grade K Answer Key. Chapter 1 Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5. Chapter 2 Compare Numbers to 5. Chapter 3 Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 6 to 9. Chapter 4 Represent and Compare Numbers to 10. Chapter 5 Addition. Chapter 6 Subtraction. Chapter 7 Represent, Count, and Write 11 to 19. Chapter 8 Represent, Count, and Write 20 ...
Big Ideas Math Book Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume. Step by Step Solutions explained for all the questions in the BIM Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume are easy to learn and understand as they are prepared by professional subject experts. After referring to the lesson-wise Big Ideas ...
Textbook Answers. Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 5th Edition Kimmel, Paul D.; Weygandt, Jerry J.; Kieso, Donald E. Publisher Wiley ISBN 978-1-11812-816-9. Algebra 1 Hall, Prentice Publisher Prentice Hall ISBN 978--13350-040-. Algebra 1: Common Core (15th Edition) Charles, Randall I. Publisher
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Algebra 1 Common Core - 9780133185485, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Exercise 11. Exercise 12. Exercise 13. Exercise 14. Exercise 15. Exercise 16. Exercise 17. Exercise 18. Exercise 19. Exercise 20. ... Mid-Chapter Quiz. Section 2-6: Ratios, Rates, and ...
Chapter 11: The Patient/Client Management Format: Writing History, Including the Review of Systems Worksheet 1 Writing History. PART I. Mark "Hx" on the line before each statement that should be placed in the History portion of the Patient/Client Management Note. Patient: Rachael F. Setting: Outpatient Orthopedic Clinic
5. Because outright collusion to raise profits is illegal and because existing regulations include gray areas which firms may be able to exploit. 6. Yes, all curves have normal shapes. 7. Yes it is a natural monopoly because average costs decline over the range that satisfies the market demand.
Go Math! Practice Book (TE), G5. Name Triangles Classify each triangle. Write isosceles, Then write acute, obtuse, or right scalene, Lesson 11.2 COMMON CORE STANDARDS CC.5.G.3, CC.5.G.4 Classify two-dimensional figures into categories based on their properties. or equilateral. 1180 42 in. isosceles 25 in. 7 in. 24 in. scalene obtuse right 8 mm.
Unit 11 Volume and Surface Area Homework 6 Answer Key Question 10. Write an expression for the surface area of the square pyramid shown. Answer: 6x+9 ft 2. ... Go Math Grade 6 Chapter 11 Answer Key Pdf Question 6. A shipping crate is shaped like a rectangular prism. It is 5 \(\frac{1}{2}\) feet long by 3 feet wide by 3 feet high. ...
Answer Key - Chapter 25 (31.0K) Answer Key - Chapter 26 (36.0K) To learn more about the book this website supports, please visit its Information Center .
Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone. OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit. Give today and help us reach more students. This free textbook is an OpenStax resource written to increase student access to high-quality, peer-reviewed learning materials.
Now, with expert-verified solutions from Financial Accounting 11th Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Financial Accounting includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice ...
Problem. 1LC. Step-by-step solution. Step 1 of 1. Write the chemical reaction as follows: The reactants are and . is known as sodium and is known as water. The products are and . is known as sodium hydroxide and is known as hydrogen. Sodium metal in solid state is mixed with liquid water and produces sodium hydroxide in aqueous and hydrogen gas.
Answer: 157° and 92°. An obtuse angle has a measurement greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees. From the above options, B and D are more than 90°. So, the answer is options B and D. Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 11 Test Pdf Question 4. Draw an angle that represents a 14 and turn counterclockwise on the circle.
Accounting. Chapter 12: Graded Homework Question 11 of 15 < > View Policies Current Attempt in Progress -/1 ! Sandhill Company is considering a long-term investment project called ZIP. ZIP will require an investment of $132,100. It will have a useful life of 4 years and no salvage value. Annual cash inflows would increase by $80,500, and annual ...