- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion

Should We Get Rid of Homework?
Some educators are pushing to get rid of homework. Would that be a good thing?

By Jeremy Engle and Michael Gonchar
Do you like doing homework? Do you think it has benefited you educationally?
Has homework ever helped you practice a difficult skill — in math, for example — until you mastered it? Has it helped you learn new concepts in history or science? Has it helped to teach you life skills, such as independence and responsibility? Or, have you had a more negative experience with homework? Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes?
Should we get rid of homework?
In “ The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, ” published in July, the Times Opinion writer Jay Caspian Kang argues that homework may be imperfect, but it still serves an important purpose in school. The essay begins:
Do students really need to do their homework? As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?” I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.” The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Mr. Kang argues:
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility. A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
Students, read the entire article, then tell us:
Should we get rid of homework? Why, or why not?
Is homework an outdated, ineffective or counterproductive tool for learning? Do you agree with the authors of the paper that homework is harmful and worsens inequalities that exist between students’ home circumstances?
Or do you agree with Mr. Kang that homework still has real educational value?
When you get home after school, how much homework will you do? Do you think the amount is appropriate, too much or too little? Is homework, including the projects and writing assignments you do at home, an important part of your learning experience? Or, in your opinion, is it not a good use of time? Explain.
In these letters to the editor , one reader makes a distinction between elementary school and high school:
Homework’s value is unclear for younger students. But by high school and college, homework is absolutely essential for any student who wishes to excel. There simply isn’t time to digest Dostoyevsky if you only ever read him in class.
What do you think? How much does grade level matter when discussing the value of homework?
Is there a way to make homework more effective?
If you were a teacher, would you assign homework? What kind of assignments would you give and why?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Jeremy Engle joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2018 after spending more than 20 years as a classroom humanities and documentary-making teacher, professional developer and curriculum designer working with students and teachers across the country. More about Jeremy Engle

School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students
The Pros and Cons of Homework
Updated: December 7, 2023
Published: January 23, 2020

Homework is a word that most students dread hearing. After hours upon hours of sitting in class , the last thing we want is more schoolwork over our precious weekends. While it’s known to be a staple of traditional schooling, homework has also become a rather divise topic. Some feel as though homework is a necessary part of school, while others believe that the time could be better invested. Should students have homework? Have a closer look into the arguments on both sides to decide for yourself.

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
Why should students have homework, 1. homework encourages practice.
Many people believe that one of the positive effects of homework is that it encourages the discipline of practice. While it may be time consuming and boring compared to other activities, repetition is needed to get better at skills. Homework helps make concepts more clear, and gives students more opportunities when starting their career .
2. Homework Gets Parents Involved
Homework can be something that gets parents involved in their children’s lives if the environment is a healthy one. A parent helping their child with homework makes them take part in their academic success, and allows for the parent to keep up with what the child is doing in school. It can also be a chance to connect together.
3. Homework Teaches Time Management
Homework is much more than just completing the assigned tasks. Homework can develop time management skills , forcing students to plan their time and make sure that all of their homework assignments are done on time. By learning to manage their time, students also practice their problem-solving skills and independent thinking. One of the positive effects of homework is that it forces decision making and compromises to be made.
4. Homework Opens A Bridge Of Communication
Homework creates a connection between the student, the teacher, the school, and the parents. It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student.
5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can’t see it in the moment.
6. Homework Reduces Screen Time
Many students in North America spend far too many hours watching TV. If they weren’t in school, these numbers would likely increase even more. Although homework is usually undesired, it encourages better study habits and discourages spending time in front of the TV. Homework can be seen as another extracurricular activity, and many families already invest a lot of time and money in different clubs and lessons to fill up their children’s extra time. Just like extracurricular activities, homework can be fit into one’s schedule.

The Other Side: Why Homework Is Bad
1. homework encourages a sedentary lifestyle.
Should students have homework? Well, that depends on where you stand. There are arguments both for the advantages and the disadvantages of homework.
While classroom time is important, playground time is just as important. If children are given too much homework, they won’t have enough playtime, which can impact their social development and learning. Studies have found that those who get more play get better grades in school , as it can help them pay closer attention in the classroom.
Children are already sitting long hours in the classroom, and homework assignments only add to these hours. Sedentary lifestyles can be dangerous and can cause health problems such as obesity. Homework takes away from time that could be spent investing in physical activity.
2. Homework Isn’t Healthy In Every Home
While many people that think homes are a beneficial environment for children to learn, not all homes provide a healthy environment, and there may be very little investment from parents. Some parents do not provide any kind of support or homework help, and even if they would like to, due to personal barriers, they sometimes cannot. Homework can create friction between children and their parents, which is one of the reasons why homework is bad .
3. Homework Adds To An Already Full-Time Job
School is already a full-time job for students, as they generally spend over 6 hours each day in class. Students also often have extracurricular activities such as sports, music, or art that are just as important as their traditional courses. Adding on extra hours to all of these demands is a lot for children to manage, and prevents students from having extra time to themselves for a variety of creative endeavors. Homework prevents self discovery and having the time to learn new skills outside of the school system. This is one of the main disadvantages of homework.
4. Homework Has Not Been Proven To Provide Results
Endless surveys have found that homework creates a negative attitude towards school, and homework has not been found to be linked to a higher level of academic success.
The positive effects of homework have not been backed up enough. While homework may help some students improve in specific subjects, if they have outside help there is no real proof that homework makes for improvements.
It can be a challenge to really enforce the completion of homework, and students can still get decent grades without doing their homework. Extra school time does not necessarily mean better grades — quality must always come before quantity.
Accurate practice when it comes to homework simply isn’t reliable. Homework could even cause opposite effects if misunderstood, especially since the reliance is placed on the student and their parents — one of the major reasons as to why homework is bad. Many students would rather cheat in class to avoid doing their homework at home, and children often just copy off of each other or from what they read on the internet.
5. Homework Assignments Are Overdone
The general agreement is that students should not be given more than 10 minutes a day per grade level. What this means is that a first grader should be given a maximum of 10 minutes of homework, while a second grader receives 20 minutes, etc. Many students are given a lot more homework than the recommended amount, however.
On average, college students spend as much as 3 hours per night on homework . By giving too much homework, it can increase stress levels and lead to burn out. This in turn provides an opposite effect when it comes to academic success.
The pros and cons of homework are both valid, and it seems as though the question of ‘‘should students have homework?’ is not a simple, straightforward one. Parents and teachers often are found to be clashing heads, while the student is left in the middle without much say.
It’s important to understand all the advantages and disadvantages of homework, taking both perspectives into conversation to find a common ground. At the end of the day, everyone’s goal is the success of the student.
Related Articles
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
Are You Down With or Done With Homework?
- Posted January 17, 2012
- By Lory Hough

The debate over how much schoolwork students should be doing at home has flared again, with one side saying it's too much, the other side saying in our competitive world, it's just not enough.
It was a move that doesn't happen very often in American public schools: The principal got rid of homework.
This past September, Stephanie Brant, principal of Gaithersburg Elementary School in Gaithersburg, Md., decided that instead of teachers sending kids home with math worksheets and spelling flash cards, students would instead go home and read. Every day for 30 minutes, more if they had time or the inclination, with parents or on their own.
"I knew this would be a big shift for my community," she says. But she also strongly believed it was a necessary one. Twenty-first-century learners, especially those in elementary school, need to think critically and understand their own learning — not spend night after night doing rote homework drills.
Brant's move may not be common, but she isn't alone in her questioning. The value of doing schoolwork at home has gone in and out of fashion in the United States among educators, policymakers, the media, and, more recently, parents. As far back as the late 1800s, with the rise of the Progressive Era, doctors such as Joseph Mayer Rice began pushing for a limit on what he called "mechanical homework," saying it caused childhood nervous conditions and eyestrain. Around that time, the then-influential Ladies Home Journal began publishing a series of anti-homework articles, stating that five hours of brain work a day was "the most we should ask of our children," and that homework was an intrusion on family life. In response, states like California passed laws abolishing homework for students under a certain age.
But, as is often the case with education, the tide eventually turned. After the Russians launched the Sputnik satellite in 1957, a space race emerged, and, writes Brian Gill in the journal Theory Into Practice, "The homework problem was reconceived as part of a national crisis; the U.S. was losing the Cold War because Russian children were smarter." Many earlier laws limiting homework were abolished, and the longterm trend toward less homework came to an end.
The debate re-emerged a decade later when parents of the late '60s and '70s argued that children should be free to play and explore — similar anti-homework wellness arguments echoed nearly a century earlier. By the early-1980s, however, the pendulum swung again with the publication of A Nation at Risk , which blamed poor education for a "rising tide of mediocrity." Students needed to work harder, the report said, and one way to do this was more homework.
For the most part, this pro-homework sentiment is still going strong today, in part because of mandatory testing and continued economic concerns about the nation's competitiveness. Many believe that today's students are falling behind their peers in places like Korea and Finland and are paying more attention to Angry Birds than to ancient Babylonia.
But there are also a growing number of Stephanie Brants out there, educators and parents who believe that students are stressed and missing out on valuable family time. Students, they say, particularly younger students who have seen a rise in the amount of take-home work and already put in a six- to nine-hour "work" day, need less, not more homework.
Who is right? Are students not working hard enough or is homework not working for them? Here's where the story gets a little tricky: It depends on whom you ask and what research you're looking at. As Cathy Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework , points out, "Homework has generated enough research so that a study can be found to support almost any position, as long as conflicting studies are ignored." Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth and a strong believer in eliminating all homework, writes that, "The fact that there isn't anything close to unanimity among experts belies the widespread assumption that homework helps." At best, he says, homework shows only an association, not a causal relationship, with academic achievement. In other words, it's hard to tease out how homework is really affecting test scores and grades. Did one teacher give better homework than another? Was one teacher more effective in the classroom? Do certain students test better or just try harder?
"It is difficult to separate where the effect of classroom teaching ends," Vatterott writes, "and the effect of homework begins."
Putting research aside, however, much of the current debate over homework is focused less on how homework affects academic achievement and more on time. Parents in particular have been saying that the amount of time children spend in school, especially with afterschool programs, combined with the amount of homework given — as early as kindergarten — is leaving students with little time to run around, eat dinner with their families, or even get enough sleep.
Certainly, for some parents, homework is a way to stay connected to their children's learning. But for others, homework creates a tug-of-war between parents and children, says Liz Goodenough, M.A.T.'71, creator of a documentary called Where Do the Children Play?
"Ideally homework should be about taking something home, spending a few curious and interesting moments in which children might engage with parents, and then getting that project back to school — an organizational triumph," she says. "A nag-free activity could engage family time: Ask a parent about his or her own childhood. Interview siblings."

Instead, as the authors of The Case Against Homework write, "Homework overload is turning many of us into the types of parents we never wanted to be: nags, bribers, and taskmasters."
Leslie Butchko saw it happen a few years ago when her son started sixth grade in the Santa Monica-Malibu (Calif.) United School District. She remembers him getting two to four hours of homework a night, plus weekend and vacation projects. He was overwhelmed and struggled to finish assignments, especially on nights when he also had an extracurricular activity.
"Ultimately, we felt compelled to have Bobby quit karate — he's a black belt — to allow more time for homework," she says. And then, with all of their attention focused on Bobby's homework, she and her husband started sending their youngest to his room so that Bobby could focus. "One day, my younger son gave us 15-minute coupons as a present for us to use to send him to play in the back room. … It was then that we realized there had to be something wrong with the amount of homework we were facing."
Butchko joined forces with another mother who was having similar struggles and ultimately helped get the homework policy in her district changed, limiting homework on weekends and holidays, setting time guidelines for daily homework, and broadening the definition of homework to include projects and studying for tests. As she told the school board at one meeting when the policy was first being discussed, "In closing, I just want to say that I had more free time at Harvard Law School than my son has in middle school, and that is not in the best interests of our children."
One barrier that Butchko had to overcome initially was convincing many teachers and parents that more homework doesn't necessarily equal rigor.
"Most of the parents that were against the homework policy felt that students need a large quantity of homework to prepare them for the rigorous AP classes in high school and to get them into Harvard," she says.
Stephanie Conklin, Ed.M.'06, sees this at Another Course to College, the Boston pilot school where she teaches math. "When a student is not completing [his or her] homework, parents usually are frustrated by this and agree with me that homework is an important part of their child's learning," she says.
As Timothy Jarman, Ed.M.'10, a ninth-grade English teacher at Eugene Ashley High School in Wilmington, N.C., says, "Parents think it is strange when their children are not assigned a substantial amount of homework."
That's because, writes Vatterott, in her chapter, "The Cult(ure) of Homework," the concept of homework "has become so engrained in U.S. culture that the word homework is part of the common vernacular."
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn.
"Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of time that children will have to do something every night (or several times a week). … This commitment to the idea of homework in the abstract is accepted by the overwhelming majority of schools — public and private, elementary and secondary."
Brant had to confront this when she cut homework at Gaithersburg Elementary.
"A lot of my parents have this idea that homework is part of life. This is what I had to do when I was young," she says, and so, too, will our kids. "So I had to shift their thinking." She did this slowly, first by asking her teachers last year to really think about what they were sending home. And this year, in addition to forming a parent advisory group around the issue, she also holds events to answer questions.
Still, not everyone is convinced that homework as a given is a bad thing. "Any pursuit of excellence, be it in sports, the arts, or academics, requires hard work. That our culture finds it okay for kids to spend hours a day in a sport but not equal time on academics is part of the problem," wrote one pro-homework parent on the blog for the documentary Race to Nowhere , which looks at the stress American students are under. "Homework has always been an issue for parents and children. It is now and it was 20 years ago. I think when people decide to have children that it is their responsibility to educate them," wrote another.
And part of educating them, some believe, is helping them develop skills they will eventually need in adulthood. "Homework can help students develop study skills that will be of value even after they leave school," reads a publication on the U.S. Department of Education website called Homework Tips for Parents. "It can teach them that learning takes place anywhere, not just in the classroom. … It can foster positive character traits such as independence and responsibility. Homework can teach children how to manage time."
Annie Brown, Ed.M.'01, feels this is particularly critical at less affluent schools like the ones she has worked at in Boston, Cambridge, Mass., and Los Angeles as a literacy coach.
"It feels important that my students do homework because they will ultimately be competing for college placement and jobs with students who have done homework and have developed a work ethic," she says. "Also it will get them ready for independently taking responsibility for their learning, which will need to happen for them to go to college."
The problem with this thinking, writes Vatterott, is that homework becomes a way to practice being a worker.
"Which begs the question," she writes. "Is our job as educators to produce learners or workers?"
Slate magazine editor Emily Bazelon, in a piece about homework, says this makes no sense for younger kids.
"Why should we think that practicing homework in first grade will make you better at doing it in middle school?" she writes. "Doesn't the opposite seem equally plausible: that it's counterproductive to ask children to sit down and work at night before they're developmentally ready because you'll just make them tired and cross?"
Kohn writes in the American School Board Journal that this "premature exposure" to practices like homework (and sit-and-listen lessons and tests) "are clearly a bad match for younger children and of questionable value at any age." He calls it BGUTI: Better Get Used to It. "The logic here is that we have to prepare you for the bad things that are going to be done to you later … by doing them to you now."
According to a recent University of Michigan study, daily homework for six- to eight-year-olds increased on average from about 8 minutes in 1981 to 22 minutes in 2003. A review of research by Duke University Professor Harris Cooper found that for elementary school students, "the average correlation between time spent on homework and achievement … hovered around zero."
So should homework be eliminated? Of course not, say many Ed School graduates who are teaching. Not only would students not have time for essays and long projects, but also teachers would not be able to get all students to grade level or to cover critical material, says Brett Pangburn, Ed.M.'06, a sixth-grade English teacher at Excel Academy Charter School in Boston. Still, he says, homework has to be relevant.
"Kids need to practice the skills being taught in class, especially where, like the kids I teach at Excel, they are behind and need to catch up," he says. "Our results at Excel have demonstrated that kids can catch up and view themselves as in control of their academic futures, but this requires hard work, and homework is a part of it."
Ed School Professor Howard Gardner basically agrees.
"America and Americans lurch between too little homework in many of our schools to an excess of homework in our most competitive environments — Li'l Abner vs. Tiger Mother," he says. "Neither approach makes sense. Homework should build on what happens in class, consolidating skills and helping students to answer new questions."
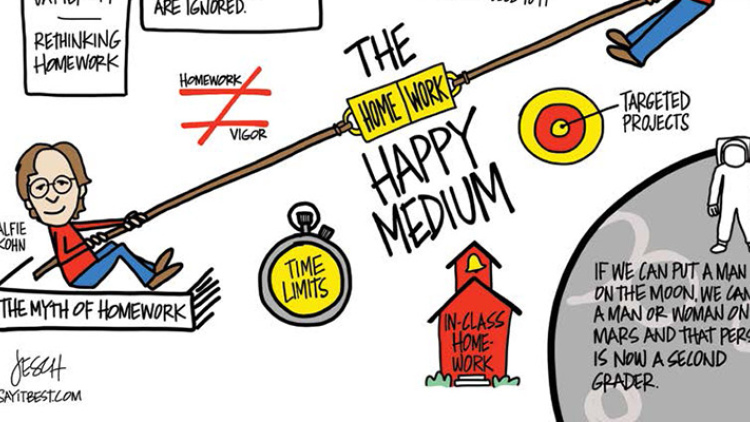
So how can schools come to a happy medium, a way that allows teachers to cover everything they need while not overwhelming students? Conklin says she often gives online math assignments that act as labs and students have two or three days to complete them, including some in-class time. Students at Pangburn's school have a 50-minute silent period during regular school hours where homework can be started, and where teachers pull individual or small groups of students aside for tutoring, often on that night's homework. Afterschool homework clubs can help.
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.) Other schools offer an extended day that allows teachers to cover more material in school, in turn requiring fewer take-home assignments. And for others, like Stephanie Brant's elementary school in Maryland, more reading with a few targeted project assignments has been the answer.
"The routine of reading is so much more important than the routine of homework," she says. "Let's have kids reflect. You can still have the routine and you can still have your workspace, but now it's for reading. I often say to parents, if we can put a man on the moon, we can put a man or woman on Mars and that person is now a second-grader. We don't know what skills that person will need. At the end of the day, we have to feel confident that we're giving them something they can use on Mars."
Read a January 2014 update.
Homework Policy Still Going Strong
Ed. Magazine
The magazine of the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Commencement Marshal Sarah Fiarman: The Principal of the Matter

Making Math “Almost Fun”
Alum develops curriculum to entice reluctant math learners

Reshaping Teacher Licensure: Lessons from the Pandemic
Olivia Chi, Ed.M.'17, Ph.D.'20, discusses the ongoing efforts to ensure the quality and stability of the teaching workforce
Should Kids Get Homework?
Homework gives elementary students a way to practice concepts, but too much can be harmful, experts say.

Getty Images
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful.
How much homework students should get has long been a source of debate among parents and educators. In recent years, some districts have even implemented no-homework policies, as students juggle sports, music and other activities after school.
Parents of elementary school students, in particular, have argued that after-school hours should be spent with family or playing outside rather than completing assignments. And there is little research to show that homework improves academic achievement for elementary students.
But some experts say there's value in homework, even for younger students. When done well, it can help students practice core concepts and develop study habits and time management skills. The key to effective homework, they say, is keeping assignments related to classroom learning, and tailoring the amount by age: Many experts suggest no homework for kindergartners, and little to none in first and second grade.
Value of Homework
Homework provides a chance to solidify what is being taught in the classroom that day, week or unit. Practice matters, says Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University 's Wheelock College of Education & Human Development.
"There really is no other domain of human ability where anybody would say you don't need to practice," she adds. "We have children practicing piano and we have children going to sports practice several days a week after school. You name the domain of ability and practice is in there."
Homework is also the place where schools and families most frequently intersect.
"The children are bringing things from the school into the home," says Paula S. Fass, professor emerita of history at the University of California—Berkeley and the author of "The End of American Childhood." "Before the pandemic, (homework) was the only real sense that parents had to what was going on in schools."
Harris Cooper, professor emeritus of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University and author of "The Battle Over Homework," examined more than 60 research studies on homework between 1987 and 2003 and found that — when designed properly — homework can lead to greater student success. Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary.
"Every child should be doing homework, but the amount and type that they're doing should be appropriate for their developmental level," he says. "For teachers, it's a balancing act. Doing away with homework completely is not in the best interest of children and families. But overburdening families with homework is also not in the child's or a family's best interest."
Negative Homework Assignments
Not all homework for elementary students involves completing a worksheet. Assignments can be fun, says Cooper, like having students visit educational locations, keep statistics on their favorite sports teams, read for pleasure or even help their parents grocery shop. The point is to show students that activities done outside of school can relate to subjects learned in the classroom.
But assignments that are just busy work, that force students to learn new concepts at home, or that are overly time-consuming can be counterproductive, experts say.
Homework that's just busy work.
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful, experts say. Assignments that look more like busy work – projects or worksheets that don't require teacher feedback and aren't related to topics learned in the classroom – can be frustrating for students and create burdens for families.
"The mental health piece has definitely played a role here over the last couple of years during the COVID-19 pandemic, and the last thing we want to do is frustrate students with busy work or homework that makes no sense," says Dave Steckler, principal of Red Trail Elementary School in Mandan, North Dakota.
Homework on material that kids haven't learned yet.
With the pressure to cover all topics on standardized tests and limited time during the school day, some teachers assign homework that has not yet been taught in the classroom.
Not only does this create stress, but it also causes equity challenges. Some parents speak languages other than English or work several jobs, and they aren't able to help teach their children new concepts.
" It just becomes agony for both parents and the kids to get through this worksheet, and the goal becomes getting to the bottom of (the) worksheet with answers filled in without any understanding of what any of it matters for," says professor Susan R. Goldman, co-director of the Learning Sciences Research Institute at the University of Illinois—Chicago .
Homework that's overly time-consuming.
The standard homework guideline recommended by the National Parent Teacher Association and the National Education Association is the "10-minute rule" – 10 minutes of nightly homework per grade level. A fourth grader, for instance, would receive a total of 40 minutes of homework per night.
But this does not always happen, especially since not every student learns the same. A 2015 study published in the American Journal of Family Therapy found that primary school children actually received three times the recommended amount of homework — and that family stress increased along with the homework load.
Young children can only remain attentive for short periods, so large amounts of homework, especially lengthy projects, can negatively affect students' views on school. Some individual long-term projects – like having to build a replica city, for example – typically become an assignment for parents rather than students, Fass says.
"It's one thing to assign a project like that in which several kids are working on it together," she adds. "In (that) case, the kids do normally work on it. It's another to send it home to the families, where it becomes a burden and doesn't really accomplish very much."
Private vs. Public Schools
Do private schools assign more homework than public schools? There's little research on the issue, but experts say private school parents may be more accepting of homework, seeing it as a sign of academic rigor.
Of course, not all private schools are the same – some focus on college preparation and traditional academics, while others stress alternative approaches to education.
"I think in the academically oriented private schools, there's more support for homework from parents," says Gerald K. LeTendre, chair of educational administration at Pennsylvania State University—University Park . "I don't know if there's any research to show there's more homework, but it's less of a contentious issue."
How to Address Homework Overload
First, assess if the workload takes as long as it appears. Sometimes children may start working on a homework assignment, wander away and come back later, Cooper says.
"Parents don't see it, but they know that their child has started doing their homework four hours ago and still not done it," he adds. "They don't see that there are those four hours where their child was doing lots of other things. So the homework assignment itself actually is not four hours long. It's the way the child is approaching it."
But if homework is becoming stressful or workload is excessive, experts suggest parents first approach the teacher, followed by a school administrator.
"Many times, we can solve a lot of issues by having conversations," Steckler says, including by "sitting down, talking about the amount of homework, and what's appropriate and not appropriate."
Study Tips for High School Students

Tags: K-12 education , students , elementary school , children
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Homework could have an impact on kids’ health. Should schools ban it?
Professor of Education, Penn State
Disclosure statement
Gerald K. LeTendre has received funding from the National Science Foundation and the Spencer Foundation.
Penn State provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation US.
View all partners

Reformers in the Progressive Era (from the 1890s to 1920s) depicted homework as a “sin” that deprived children of their playtime . Many critics voice similar concerns today.
Yet there are many parents who feel that from early on, children need to do homework if they are to succeed in an increasingly competitive academic culture. School administrators and policy makers have also weighed in, proposing various policies on homework .
So, does homework help or hinder kids?
For the last 10 years, my colleagues and I have been investigating international patterns in homework using databases like the Trends in Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) . If we step back from the heated debates about homework and look at how homework is used around the world, we find the highest homework loads are associated with countries that have lower incomes and higher social inequality.
Does homework result in academic success?
Let’s first look at the global trends on homework.
Undoubtedly, homework is a global phenomenon ; students from all 59 countries that participated in the 2007 Trends in Math and Science Study (TIMSS) reported getting homework. Worldwide, only less than 7% of fourth graders said they did no homework.
TIMSS is one of the few data sets that allow us to compare many nations on how much homework is given (and done). And the data show extreme variation.
For example, in some nations, like Algeria, Kuwait and Morocco, more than one in five fourth graders reported high levels of homework. In Japan, less than 3% of students indicated they did more than four hours of homework on a normal school night.
TIMSS data can also help to dispel some common stereotypes. For instance, in East Asia, Hong Kong, Taiwan and Japan – countries that had the top rankings on TIMSS average math achievement – reported rates of heavy homework that were below the international mean.
In the Netherlands, nearly one out of five fourth graders reported doing no homework on an average school night, even though Dutch fourth graders put their country in the top 10 in terms of average math scores in 2007.
Going by TIMSS data, the US is neither “ A Nation at Rest” as some have claimed, nor a nation straining under excessive homework load . Fourth and eighth grade US students fall in the middle of the 59 countries in the TIMSS data set, although only 12% of US fourth graders reported high math homework loads compared to an international average of 21%.
So, is homework related to high academic success?
At a national level, the answer is clearly no. Worldwide, homework is not associated with high national levels of academic achievement .
But, the TIMSS can’t be used to determine if homework is actually helping or hurting academic performance overall , it can help us see how much homework students are doing, and what conditions are associated with higher national levels of homework.
We have typically found that the highest homework loads are associated with countries that have lower incomes and higher levels of social inequality – not hallmarks that most countries would want to emulate.
Impact of homework on kids
TIMSS data also show us how even elementary school kids are being burdened with large amounts of homework.
Almost 10% of fourth graders worldwide (one in 10 children) reported spending multiple hours on homework each night. Globally, one in five fourth graders report 30 minutes or more of homework in math three to four times a week.
These reports of large homework loads should worry parents, teachers and policymakers alike.
Empirical studies have linked excessive homework to sleep disruption , indicating a negative relationship between the amount of homework, perceived stress and physical health.

What constitutes excessive amounts of homework varies by age, and may also be affected by cultural or family expectations. Young adolescents in middle school, or teenagers in high school, can study for longer duration than elementary school children.
But for elementary school students, even 30 minutes of homework a night, if combined with other sources of academic stress, can have a negative impact . Researchers in China have linked homework of two or more hours per night with sleep disruption .
Even though some cultures may normalize long periods of studying for elementary age children, there is no evidence to support that this level of homework has clear academic benefits . Also, when parents and children conflict over homework, and strong negative emotions are created, homework can actually have a negative association with academic achievement.
Should there be “no homework” policies?
Administrators and policymakers have not been reluctant to wade into the debates on homework and to formulate policies . France’s president, Francois Hollande, even proposed that homework be banned because it may have inegaliatarian effects.
However, “zero-tolerance” homework policies for schools, or nations, are likely to create as many problems as they solve because of the wide variation of homework effects. Contrary to what Hollande said, research suggests that homework is not a likely source of social class differences in academic achievement .
Homework, in fact, is an important component of education for students in the middle and upper grades of schooling.
Policymakers and researchers should look more closely at the connection between poverty, inequality and higher levels of homework. Rather than seeing homework as a “solution,” policymakers should question what facets of their educational system might impel students, teachers and parents to increase homework loads.
At the classroom level, in setting homework, teachers need to communicate with their peers and with parents to assure that the homework assigned overall for a grade is not burdensome, and that it is indeed having a positive effect.
Perhaps, teachers can opt for a more individualized approach to homework. If teachers are careful in selecting their assignments – weighing the student’s age, family situation and need for skill development – then homework can be tailored in ways that improve the chance of maximum positive impact for any given student.
I strongly suspect that when teachers face conditions such as pressure to meet arbitrary achievement goals, lack of planning time or little autonomy over curriculum, homework becomes an easy option to make up what could not be covered in class.
Whatever the reason, the fact is a significant percentage of elementary school children around the world are struggling with large homework loads. That alone could have long-term negative consequences for their academic success.
- Trends in Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS)
- Elementary school
- Academic success

Senior Lecturer - Earth System Science

Operations Coordinator

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Deputy Social Media Producer

Associate Professor, Occupational Therapy
Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research Says
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.
The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early.
But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know:
For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline.
But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.”
A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders.
New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids.
The research
The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance.
Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework.
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework.
Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment.
Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school.
“Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?”
Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids.
“I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school.
The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework.
“The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.”
Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned.
“A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- The Revolution of Yulia Navalnaya
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- What's the Deal With the Bitcoin Halving?
- If You're Dating Right Now , You're Brave: Column
- The AI That Could Heal a Divided Internet
- Fallout Is a Brilliant Model for the Future of Video Game Adaptations
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]
15 Should Homework Be Banned Pros and Cons
Homework was a staple of the public and private schooling experience for many of us growing up. There were long nights spent on book reports, science projects, and all of those repetitive math sheets. In many ways, it felt like an inevitable part of the educational experience. Unless you could power through all of your assignments during your free time in class, then there was going to be time spent at home working on specific subjects.
More schools are looking at the idea of banning homework from the modern educational experience. Instead of sending work home with students each night, they are finding alternative ways to ensure that each student can understand the curriculum without involving the uncertainty of parental involvement.
Although banning homework might seem like an unorthodox process, there are legitimate advantages to consider with this effort. There are some disadvantages which some families may encounter as well.
These are the updated lists of the pros and cons of banning homework to review.
List of the Pros of Banning Homework
1. Giving homework to students does not always improve their academic outcomes. The reality of homework for the modern student is that we do not know if it is helpful to have extra work assigned to them outside of the classroom. Every study that has looked at the subject has had design flaws which causes the data collected to be questionable at best. Although there is some information to suggest that students in seventh grade and higher can benefit from limited homework, banning it for students younger than that seems to be beneficial for their learning experience.
2. Banning homework can reduce burnout issues with students. Teachers are seeing homework stress occur in the classroom more frequently today than ever before. Almost half of all high school teachers in North America have seen this issue with their students at some point during the year. About 25% of grade school teachers say that they have seen the same thing.
When students are dealing with the impact of homework on their lives, it can have a tremendously adverse impact. One of the most cited reasons for students dropping out of school is that they cannot complete their homework on time.
3. Banning homework would increase the amount of family time available to students. Homework creates a significant disruption to family relationships. Over half of all parents in North America say that they have had a significant argument with their children over homework in the past month. 1/3 of families say that homework is their primary source of struggle in the home. Not only does it reduce the amount of time that everyone has to spend together, it reduces the chances that parents have to teach their own skills and belief systems to their kids.
4. It reduces the negative impact of homework on the health of a student. Many students suffer academically when they cannot finish a homework assignment on time. Although assumptions are often made about the time management skills of the individual when this outcome occurs, the reasons why it happens is usually more complex. It may be too difficult, too boring, or there may not be enough time in the day to complete the work.
When students experience failure in this area, it can lead to severe mental health issues. Some perceive themselves as a scholarly failure, which translates to an inability to live life successfully. It can disrupt a desire to learn. There is even an increased risk of suicide for some youth because of this issue. Banning it would reduce these risks immediately.
5. Eliminating homework would allow for an established sleep cycle. The average high school student requires between 8-10 hours of sleep to function at their best the next day. Grade-school students may require an extra hour or two beyond that figure. When teachers assign homework, then it increases the risk for each individual that they will not receive the amount that they require each night.
When children do not get enough sleep, a significant rest deficit occurs which can impact their ability to pay attention in school. It can cause unintended weight gain. There may even be issues with emotional control. Banning homework would help to reduce these risks as well.
6. It increases the amount of socialization time that students receive. People who are only spending time in school and then going home to do more work are at a higher risk of experiencing loneliness and isolation. When these emotions are present, then a student is more likely to feel “down and out” mentally and physically. They lack meaningful connections with other people. These feelings are the health equivalent of smoking 15 cigarettes per day. If students are spending time on homework, then they are not spending time connecting with their family and friends.
7. It reduces the repetition that students face in the modern learning process. Most of the tasks that homework requires of students is repetitive and uninteresting. Kids love to resolve challenges on tasks that they are passionate about at that moment in their lives. Forcing them to complete the same problems repetitively as a way to “learn” core concepts can create issues with knowledge retention later in life. When you add in the fact that most lessons sent for homework must be done by themselves, banning homework will reduce the repetition that students face, allowing for a better overall outcome.
8. Home environments can be chaotic. Although some students can do homework in a quiet room without distractions, that is not the case for most kids. There are numerous events that happen at home which can pull a child’s attention away from the work that their teacher wants them to do. It isn’t just the Internet, video games, and television which are problematic either. Household chores, family issues, employment, and athletic requirements can make it a challenge to get the assigned work finished on time.
List of the Cons of Banning Homework
1. Homework allows parents to be involved with the educational process. Parents need to know what their children are learning in school. Even if they ask their children about what they are learning, the answers tend to be in generalities instead of specifics. By sending home work from the classroom, it allows parents to see and experience the work that their kids are doing when they are in school during the day. Then moms and dads can get involved with the learning process to reinforce the core concepts that were discovered by their children each day.
2. It can help parents and teachers identify learning disabilities. Many children develop a self-defense mechanism which allows them to appear like any other kid that is in their classroom. This process allows them to hide learning disabilities which may be hindering their educational progress. The presence of homework makes it possible for parents and teachers to identify this issue because kids can’t hide their struggles when they must work 1-on-1 with their parents on specific subjects. Banning homework would eliminate 50% of the opportunities to identify potential issues immediately.
3. Homework allows teachers to observe how their students understand the material. Teachers often use homework as a way to gauge how well a student is understanding the materials they are learning. Although some might point out that assignments and exams in the classroom can do the same thing, testing often requires preparation at home. It creates more anxiety and stress sometimes then even homework does. That is why banning it can be problematic for some students. Some students experience more pressure than they would during this assessment process when quizzes and tests are the only measurement of their success.
4. It teaches students how to manage their time wisely. As people grow older, they realize that time is a finite commodity. We must manage it wisely to maximize our productivity. Homework assignments are a way to encourage the development of this skill at an early age. The trick is to keep the amount of time required for the work down to a manageable level. As a general rule, students should spend about 10 minutes each school day doing homework, organizing their schedule around this need. If there are scheduling conflicts, then this process offers families a chance to create priorities.
5. Homework encourages students to be accountable for their role. Teachers are present in the classroom to offer access to information and skill-building opportunities that can improve the quality of life for each student. Administrators work to find a curriculum that will benefit the most people in an efficient way. Parents work hard to ensure their kids make it to school on time, follow healthy routines, and communicate with their school district to ensure the most effective learning opportunities possible. None of that matters if the student is not invested in the work in the first place. Homework assignments not only teach children how to work independently, but they also show them how to take responsibility for their part of the overall educational process.
6. It helps to teach important life lessons. Homework is an essential tool in the development of life lessons, such as communicating with others or comprehending something they have just read. It teaches kids how to think, solve problems, and even build an understanding for the issues that occur in our society right now. Many of the issues that lead to the idea to ban homework occur because someone in the life of a student communicated to them that this work was a waste of time. There are times in life when people need to do things that they don’t like or want to do. Homework helps a student begin to find the coping skills needed to be successful in that situation.
7. Homework allows for further research into class materials. Most classrooms offer less than 1 hour of instruction per subject during the day. For many students, that is not enough time to obtain a firm grasp on the materials being taught. Having homework assignments allows a student to perform more research, using their at-home tools to take a deeper look into the materials that would otherwise be impossible if homework was banned. That process can lead to a more significant understanding of the concepts involved, reducing anxiety levels because they have a complete grasp on the materials.
The pros and cons of banning homework is a decision that ultimately lies with each school district. Parents always have the option to pursue homeschooling or online learning if they disagree with the decisions that are made in this area. Whether you’re for more homework or want to see less of it, we can all agree on the fact that the absence of any reliable data about its usefulness makes it a challenge to know for certain which option is the best one to choose in this debate.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Health & Nursing
Courses and certificates.
- Bachelor's Degrees
- View all Business Bachelor's Degrees
- Business Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Healthcare Administration – B.S.
- Human Resource Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Marketing – B.S. Business Administration
- Accounting – B.S. Business Administration
- Finance – B.S.
- Supply Chain and Operations Management – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree (from the School of Technology)
- Health Information Management – B.S. (from the Leavitt School of Health)
Master's Degrees
- View all Business Master's Degrees
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- MBA Information Technology Management
- MBA Healthcare Management
- Management and Leadership – M.S.
- Accounting – M.S.
- Marketing – M.S.
- Human Resource Management – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration (from the Leavitt School of Health)
- Data Analytics – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Information Technology Management – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed. (from the School of Education)
Certificates
- View all Business Degrees
Bachelor's Preparing For Licensure
- View all Education Bachelor's Degrees
- Elementary Education – B.A.
- Special Education and Elementary Education (Dual Licensure) – B.A.
- Special Education (Mild-to-Moderate) – B.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary)– B.S.
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– B.S.
- View all Education Degrees
Bachelor of Arts in Education Degrees
- Educational Studies – B.A.
Master of Science in Education Degrees
- View all Education Master's Degrees
- Curriculum and Instruction – M.S.
- Educational Leadership – M.S.
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed.
Master's Preparing for Licensure
- Teaching, Elementary Education – M.A.
- Teaching, English Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Science Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Special Education (K-12) – M.A.
Licensure Information
- State Teaching Licensure Information
Master's Degrees for Teachers
- Mathematics Education (K-6) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grade) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- English Language Learning (PreK-12) – M.A.
- Endorsement Preparation Program, English Language Learning (PreK-12)
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– M.A.
- View all Technology Bachelor's Degrees
- Cloud Computing – B.S.
- Computer Science – B.S.
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – B.S.
- Data Analytics – B.S.
- Information Technology – B.S.
- Network Engineering and Security – B.S.
- Software Engineering – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration (from the School of Business)
- View all Technology Master's Degrees
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – M.S.
- Data Analytics – M.S.
- Information Technology Management – M.S.
- MBA Information Technology Management (from the School of Business)
- Full Stack Engineering
- Web Application Deployment and Support
- Front End Web Development
- Back End Web Development
3rd Party Certifications
- IT Certifications Included in WGU Degrees
- View all Technology Degrees
- View all Health & Nursing Bachelor's Degrees
- Nursing (RN-to-BSN online) – B.S.
- Nursing (Prelicensure) – B.S. (Available in select states)
- Health Information Management – B.S.
- Health and Human Services – B.S.
- Psychology – B.S.
- Health Science – B.S.
- Healthcare Administration – B.S. (from the School of Business)
- View all Nursing Post-Master's Certificates
- Nursing Education—Post-Master's Certificate
- Nursing Leadership and Management—Post-Master's Certificate
- Family Nurse Practitioner—Post-Master's Certificate
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner —Post-Master's Certificate
- View all Health & Nursing Degrees
- View all Nursing & Health Master's Degrees
- Nursing – Education (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Family Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Education (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration
- MBA Healthcare Management (from the School of Business)
- Business Leadership (with the School of Business)
- Supply Chain (with the School of Business)
- Back End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Front End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Web Application Deployment and Support (with the School of Technology)
- Full Stack Engineering (with the School of Technology)
- Single Courses
- Course Bundles
Apply for Admission
Admission requirements.
- New Students
- WGU Returning Graduates
- WGU Readmission
- Enrollment Checklist
- Accessibility
- Accommodation Request
- School of Education Admission Requirements
- School of Business Admission Requirements
- School of Technology Admission Requirements
- Leavitt School of Health Admission Requirements
Additional Requirements
- Computer Requirements
- No Standardized Testing
- Clinical and Student Teaching Information
Transferring
- FAQs about Transferring
- Transfer to WGU
- Transferrable Certifications
- Request WGU Transcripts
- International Transfer Credit
- Tuition and Fees
- Financial Aid
- Scholarships
Other Ways to Pay for School
- Tuition—School of Business
- Tuition—School of Education
- Tuition—School of Technology
- Tuition—Leavitt School of Health
- Your Financial Obligations
- Tuition Comparison
- Applying for Financial Aid
- State Grants
- Consumer Information Guide
- Responsible Borrowing Initiative
- Higher Education Relief Fund
FAFSA Support
- Net Price Calculator
- FAFSA Simplification
- See All Scholarships
- Military Scholarships
- State Scholarships
- Scholarship FAQs
Payment Options
- Payment Plans
- Corporate Reimbursement
- Current Student Hardship Assistance
- Military Tuition Assistance
WGU Experience
- How You'll Learn
- Scheduling/Assessments
- Accreditation
- Student Support/Faculty
- Military Students
- Part-Time Options
- Virtual Military Education Resource Center
- Student Outcomes
- Return on Investment
- Students and Gradutes
- Career Growth
- Student Resources
- Communities
- Testimonials
- Career Guides
- Skills Guides
- Online Degrees
- All Degrees
- Explore Your Options
Admissions & Transfers
- Admissions Overview
Tuition & Financial Aid
Student Success
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Military and Veterans
- Commencement
- Careers at WGU
- Advancement & Giving
- Partnering with WGU
Should Students Have Homework?
- Classroom Strategies
- See More Tags

By Suzanne Capek Tingley, Veteran Educator, M.A. Degree
It used to be that students were the only ones complaining about the practice of assigning homework. For years, teachers and parents thought that homework was a necessary tool when educating children. But studies about the effectiveness of homework have been conflicting and inconclusive, leading some adults to argue that homework should become a thing of the past.
What Research Says about Homework
According to Duke professor Harris Cooper, it's important that students have homework. His meta-analysis of homework studies showed a correlation between completing homework and academic success, at least in older grades. He recommends following a "10 minute rule" : students should receive 10 minutes of homework per day in first grade, and 10 additional minutes each subsequent year, so that by twelfth grade they are completing 120 minutes of homework daily.
But his analysis didn't prove that students did better because they did homework; it simply showed a correlation . This could simply mean that kids who do homework are more committed to doing well in school. Cooper also found that some research showed that homework caused physical and emotional stress, and created negative attitudes about learning. He suggested that more research needed to be done on homework's effect on kids.
Some researchers say that the question isn't whether kids should have homework. It's more about what kind of homework students have and how much. To be effective, homework has to meet students' needs. For example, some middle school teachers have found success with online math homework that's adapted to each student's level of understanding. But when middle school students were assigned more than an hour and a half of homework, their math and science test scores went down .
Researchers at Indiana University discovered that math and science homework may improve standardized test grades, but they found no difference in course grades between students who did homework and those who didn't. These researchers theorize that homework doesn't result in more content mastery, but in greater familiarity with the kinds of questions that appear on standardized tests. According to Professor Adam Maltese, one of the study's authors, "Our results hint that maybe homework is not being used as well as it could be."
So while many teachers and parents support daily homework, it's hard to find strong evidence that the long-held practice produces positive results.
Problems with Homework
In an article in Education Week Teacher , teacher Samantha Hulsman said she's frequently heard parents complain that a 30-minute homework assignment turns into a three-hour battle with their kids. Now, she's facing the same problem with her own kids, which has her rethinking her former beliefs about homework. "I think parents expect their children to have homework nightly, and teachers assign daily homework because it's what we've always done," she explained. Today, Hulsman said, it's more important to know how to collaborate and solve problems than it is to know specific facts.
Child psychologist Kenneth Barish wrote in Psychology Today that battles over homework rarely result in a child's improvement in school . Children who don't do their homework are not lazy, he said, but they may be frustrated, discouraged, or anxious. And for kids with learning disabilities, homework is like "running with a sprained ankle. It's doable, but painful."
Barish suggests that parents and kids have a "homework plan" that limits the time spent on homework. The plan should include turning off all devices—not just the student's, but those belonging to all family members.
One of the best-known critics of homework, Alfie Kohn , says that some people wrongly believe "kids are like vending machines—put in an assignment, get out learning." Kohn points to the lack of evidence that homework is an effective learning tool; in fact, he calls it "the greatest single extinguisher of children's curiosity that we have yet invented."
Homework Bans
Last year, the public schools in Marion County, Florida, decided on a no-homework policy for all of their elementary students . Instead, kids read nightly for 20 minutes. Superintendent Heidi Maier said the decision was based on Cooper's research showing that elementary students gain little from homework, but a lot from reading.
Orchard Elementary School in South Burlington, Vermont, followed the same path, substituting reading for homework. The homework policy has four parts : read nightly, go outside and play, have dinner with your family, and get a good night's sleep. Principal Mark Trifilio says that his staff and parents support the idea.
But while many elementary schools are considering no-homework policies, middle schools and high schools have been reluctant to abandon homework. Schools say parents support homework and teachers know it can be helpful when it is specific and follows certain guidelines. For example, practicing solving word problems can be helpful, but there's no reason to assign 50 problems when 10 will do. Recognizing that not all kids have the time, space, and home support to do homework is important, so it shouldn't be counted as part of a student's grade.
So Should Students Have Homework?
Should you ban homework in your classroom? If you teach lower grades, it's possible. If you teach middle or high school, probably not. But all teachers should think carefully about their homework policies. By limiting the amount of homework and improving the quality of assignments, you can improve learning outcomes for your students.
Ready to Start Your Journey?
HEALTH & NURSING
Recommended Articles
Take a look at other articles from WGU. Our articles feature information on a wide variety of subjects, written with the help of subject matter experts and researchers who are well-versed in their industries. This allows us to provide articles with interesting, relevant, and accurate information.
{{item.date}}
{{item.preTitleTag}}
{{item.title}}
The university, for students.
- Student Portal
- Alumni Services
Most Visited Links
- Business Programs
- Student Experience
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Student Communities
21 Reasons Why Homework Should Be Banned

The homework debate has strong arguments on both sides. Commonly-cited reasons why homework should be banned include the idea that it is often counterproductive, stifles students’ creativity, and limits their freedom outside the classroom.
Students already have up to 7 hours of schoolwork to complete 5 days a week; adding more contributes to increased anxiety, burnout, and overall poor performance.
But arguments for homework include the fact it does increase student grades (Cooper, Robinson & Patall, 2006), it instils discipline, and it helps to reinforce what was learned into long-term memory.
The following are common arguments for banning homework – note that this is an article written to stimulate debate points on the topic, so it only presents one perspective. For the other side of the argument, it’s worth checking out my article on the 27 pros and cons of homework .
Reasons Why Homework Should Be Banned
1. it contributes to increased anxiety.
If there’s one word that describes middle-school and high-school students, it’s anxiety. In my homework statistics article , I cite research showing that 74% of students cite homework as a source of stress.
They have so much to juggle, from the novelty of adolescence to the realization that they must soon start preparing for college and their life after (Pressman et al., 2015).
It’s a lot to manage, and adding homework that reduces their free time and makes them even more restricted is downright harmful. The natural outcome of this dogpile of pressure is anxiety, and many students often feel overwhelmed, both by the hours and hours of coursework in a day and the extensive homework they are assigned (Galloway, Conner & Pope, 2013).
Because teachers often don’t communicate with one another over curricula, major assignments can overlap such that students have to tackle numerous large projects at once, which contributes to severe anxiety over good grades.
In response to this, some students check out of school entirely, letting their academic future go to waste. While, of course, it’s not fair to strawman and say that homework is to blame for all these cases, it may indeed by a contributing factor.
2. It Offers Less Social Time
Homework cuts out free time. Children already spend the better part of their day learning in a school environment, and when they come home, they need to socialize.
Whether it’s family or friends, a social balance is important. Depending on the coursework they’re assigned, homework can detrimentally affect students’ social life, which feed back into more of our first gripe about homework: its anxiety-inducing nature.
Furthermore, social time is extremely important for children to grow up well-balanced and confident. If a child is highly intelligent (book smart) but lacks to social skills we might call street smarts , they may struggle in adulthood.

3. It Detracts from Play Time
Play is extremely important for children’s physical, social, and cognitive development . In fact, children naturally learn through play .
So, when children get home from school, they need a few hours to play. They’re actually learning when playing! If playing with friends, they’re learning social skills; but playing alone also stimulates creative and analytical thinking skills.
Play is also a different type of learning than the learning that commonly happens at school. So, allowing children to play at home gives their brain a break from ‘school learning’ and lets them learn through active and even relaxing methods.
4. It Discourages Physical Exercise and Contributes to Obesity
Exercise is an important part of life for everyone, but especially for children. Developing a positive self-image and disciplining oneself is an important skill to learn, one that becomes much more difficult when homework is in the picture.
Homework can demand a lot of attention that kids could be spending exercising or socializing. These two important life pursuits can be left by the wayside, leaving students feeling confused, depressed, and anxious about the future.
Physical exercise should be considered a key feature of a child’s holistic development. It helps keep children healthy, can reduce anxiety, and support healthy immune systems. It also helps with physical development such as supporting fine and gross motor skills .
In fact, some scholars (Ren et al., 2017) have even identified excessive homework as a contributing factor for childhood obesity.
5. It Disrupts Sleep Patterns
Everyone knows the trope of a college student staying up late to finish their homework or cram for a test.
While it would be unfair to credit homework exclusively for an unhealthy sleep schedule, the constant pressure to finish assignments on time often yields one of two results.
Students can either burn the midnight oil to make sure their homework is done, or they can check out of school entirely and ignore their academic interests. Neither is an acceptable way to live.
This point is particularly pertinent to teenagers. They are not lazy; teens need 12-13 hours of sleep every day because their bodies are changing so dramatically.
To pile additional homework on them that interferes with the circadian rhythm is not just unhelpful—it may be downright harmful (Yeo et al., 2020).
6. It Involves Less Guidance
If there’s one thing that’s beneficial about the in-person learning experience, it’s the ability to raise one’s hand and let the teacher know when something is unclear or difficult to understand.
That handheld process isn’t available for homework; in fact, homework matters little in the grand scheme of learning. It’s just busywork that’s supposed to help students consolidate their knowledge.
In reality, homework becomes something that students resent and can fill them with feelings of frustration—something that would be much more readily addressed if the same content was covered in-person with a teacher to guide the student through the assignment.
7. It’s Regularly Rote Learning
In most subjects, homework isn’t reflective of the skills students need to learn to thrive in the workforce. Instead, it often simply involves rote learning (repetition of tasks) that is not seen as the best way to learn.
A main goal of education is to train up vocational professionals with defined skills. But more often than not, homework winds up as a bland set of word problems that have no basis in the real world.
Walking through real-world examples under the guidance of a teacher is much more beneficial to student learning.
8. It Can Detract from a Love of Learning
If you know what it’s like to doze off during a boring class or meeting, then you can relate to the difficulty students have paying attention in class.
That motivation starts to dwindle when students must complete assignments on their own time, often under immense pressure.
It’s not a healthy way to inspire kids to learn about different subjects and develop a love of learning.
Students already need to sit through hours and hours of class on end in-person. This learning time should be used more effectively to eliminate the need for home.
When children finally get out of class at the end of the day, they need to socialize and exercise, not spend even longer staring at a book to complete a bunch of unhelpful practice questions.
9. It Convolutes the Subject
Another important consideration about homework is that it can often be counterproductive.
That’s because teachers don’t always use the full curriculum material for their teaching, and they may choose to develop their own homework rather than to use the resources offered by the curriculum provider.
This homework can often be off-subject, extremely niche, or unhelpful in explaining a subject that students are studying.
Students who don’t understand a subject and don’t have resources to rely on will eventually give up. That risk becomes even more prevalent when you factor in the scope, complexity, and type of assignment.
Students need to be taught in a safe environment where they can feel free to ask questions and learn at their own pace. Of course, there’s no fairytale way to perfect this ideal, but what is clear is that homework is not beneficial to the learning environment for many students.
10. It’s Not What Kids Want
Lastly, homework should be banned because it’s generally not what students want. From elementary to college level, most students harbor some sort of resentment towards homework.
It might be easy to dismiss this to say that the students “aren’t living in the real world.” The truth of the matter is that the real world is a lot more nuanced, creative, and diverse than the repetitive, broad, and often stagnant homework.
It’s easy to understand why most students wish that more time in school had been spent on learning how to live rather than trying to figure out how many apples Johnny had. Subjects like car maintenance, entrepreneurship, computer skills, socialization, networking, tax filing, finances, and survival are touched on at best and ignored at worst.
It’s not enough for students to be able to regurgitate information on a piece of paper; in the end, the education system should teach them how to be self-sufficient, something that might be much easier to do if resources were divested from homework and poured into more beneficial subject material.
Consider these 11 Additional Reasons
- Decreases time with parents – Homework may prevent parents and children from spending quality time together.
- Hidden costs – Families often feel pressure to purchase internet and other resources to help their children to complete their homework.
- Is inequitable – some children have parents to help them while others don’t. Similarly, some children have internet access to help while others don’t (see: Kralovec & Buell, 2001).
- Easy to cheat – Unsupervised homework time makes it easy for children to simply cheat on their work so they can get on with play time!
- Lack of downtime – Children need time where they aren’t doing anything. Time that is unstructured helps them to develop hobbies and interests .
- Detracts from reading – Children could be spending their time reading books and developing their imaginations rather than working on repetitive homework tasks.
- Take up parental time – Parents, who have just spent all day working, are increasingly expected to spend their time doing ‘teaching’ with their children at home.
- Discourages club membership – If children are too busy with homework, they may not be able to join clubs and sporting groups that can help them make friends and develop extracurricular skills.
- Makes it hard for college students to make a living – In college, where homework is extensive, students often can’t juggle homework with their weekend and night-time jobs. As a result, it pushes them further into student poverty.
- Contributes to poor work-life culture – From early ages, we’re sending a message to children that they should take their work home with them. This can spill over into the workplace, where they’ll be expected to continue working for their company even after the workday ends.
- Can reinforce faulty learning – When children learn in isolation during homework time, they may end up practicing their work completely wrong! They need intermittent support to make sure their practice is taking them down the right path.
Students may need to demonstrate their understanding of a topic to progress; that, at least, is a reflection of the real world. What’s not helpful is when students are peppered day and night with information that they need to regurgitate on a piece of paper.
For positive outcomes to come from homework, parents and teachers need to work together. It depends a lot on the type of homework provided as well as the age of the student and the need to balance homework with time to do other things in your life.
Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Review of educational research , 76 (1), 1-62.
Galloway, M., Conner, J., & Pope, D. (2013). Nonacademic effects of homework in privileged, high-performing high schools. The journal of experimental education , 81 (4), 490-510. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2012.745469
Kralovec, E., & Buell, J. (2001). The end of homework: How homework disrupts families, overburdens children, and limits learning . Beacon Press.
Pressman, R. M., Sugarman, D. B., Nemon, M. L., Desjarlais, J., Owens, J. A., & Schettini-Evans, A. (2015). Homework and family stress: With consideration of parents’ self confidence, educational level, and cultural background. The American Journal of Family Therapy , 43 (4), 297-313. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01926187.2015.1061407
Ren, H., Zhou, Z., Liu, W., Wang, X., & Yin, Z. (2017). Excessive homework, inadequate sleep, physical inactivity and screen viewing time are major contributors to high paediatric obesity. Acta Paediatrica , 106 (1), 120-127. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.13640
Yeo, S. C., Tan, J., Lo, J. C., Chee, M. W., & Gooley, J. J. (2020). Associations of time spent on homework or studying with nocturnal sleep behavior and depression symptoms in adolescents from Singapore. Sleep Health , 6 (6), 758-766. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2020.04.011

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
5 thoughts on “21 Reasons Why Homework Should Be Banned”
very helpful website thanks
my topic on publics speaking is on banning homework it really helps
Very helpful cheers mate
This really helped my debate team
It is very helpful for me.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Study Skills
No More Homework: 12 Reasons We Should Get Rid of It Completely
Last Updated: February 16, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Finn Kobler . Finn Kobler graduated from USC in 2022 with a BFA in Writing for Screen/Television. He is a two-time California State Champion and record holder in Original Prose/Poetry, a 2018 finalist for the Los Angeles Youth Poet Laureate, and he's written micro-budget films that have been screened in over 150 theaters nationwide. Growing up, Finn spent every summer helping his family's nonprofit arts program, Showdown Stage Company, empower people through accessible media. He hopes to continue that mission with his writing at wikiHow. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 125,824 times. Learn more...
The amount of homework students are given has increased dramatically in the 21st century, which has sparked countless debates over homework’s overall value. While some have been adamant that homework is an essential part of a good education, it’s been proven that too much homework negatively affects students’ mood, classroom performance, and overall well-being. In addition, a heavy homework load can stress families and teachers. Here are 12 reasons why homework should be banned (or at least heavily reduced).
School is already a full-time job.

- For years, teachers have followed the “10-minute rule” giving students roughly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. However, recent studies have shown students are completing 3+ hours of homework a night well before their senior years even begin. [2] X Trustworthy Source American Psychological Association Leading scientific and professional organization of licensed psychologists Go to source
Homework negatively affects students’ health.

Homework interferes with student’s opportunities to socialize.

Homework hinders students’ chances to learn new things.

Homework lowers students’ enthusiasm for school.

Homework can lower academic performance.

Homework cuts into family time.

Homework is stressful for teachers.

Homework is often irrelevant and punitive.

- There are even studies that have shown homework in primary school has no correlation with classroom performance whatsoever. [9] X Research source
Homework encourages cheating.

Homework is inequitable.

Other countries have banned homework with great results.

- There are even some U.S. schools that have adopted this approach with success. [13] X Research source
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.edutopia.org/no-proven-benefits
- ↑ https://www.apa.org/monitor/2016/03/homework
- ↑ https://healthier.stanfordchildrens.org/en/health-hazards-homework/
- ↑ https://teensneedsleep.files.wordpress.com/2011/04/galloway-nonacademic-effects-of-homework-in-privileged-high-performing-high-schools.pdf
- ↑ https://time.com/4466390/homework-debate-research/
- ↑ https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00220485.2022.2075506?role=tab&scroll=top&needAccess=true&journalCode=vece20
- ↑ https://kappanonline.org/teacher-stress-balancing-demands-resources-mccarthy/
- ↑ https://www.chicagotribune.com/lifestyles/ct-life-homework-pros-cons-20180807-story.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6294446/
- ↑ https://www.theatlantic.com/business/archive/2016/06/homework-inequality-parents-schedules-grades/485174/
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/news/education-37716005
- ↑ https://www.wsj.com/articles/no-homework-its-the-new-thing-in-u-s-schools-11544610600
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Did this article help you?

Leonardo F.
Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Major 10 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework In 2023

Homework – something students always get, but is it good or just extra work? People, like parents and teachers, have different thoughts on this. In this blog, we are going to dig deep into 10 reasons why students should avoid homework.
We will also determine when students can bring their phones to school in 2023. First, let’s understand what homework really is and why some folks say it’s not so great. We will learn about the good side of no homework and discover some interesting facts that support saying no to homework. So, let’s see if homework is helpful or not.
Stay tuned to learn more about 10 reasons why students should not have homework.
What Is Homework?
Table of Contents
Homework is a school task that teachers give to students to do outside of the classroom. It’s like extra practice to help you learn more about what you study in school. Homework can be reading a book, doing math problems, writing about a topic, or other assignments. When you finish your homework, you show what you’ve learned and get better at your school subjects.
Homework is also a way for teachers to see how well you understand what they taught in class. It’s like a way for you to show what you’ve learned. Most homework assignments have a deadline, therefore it is critical that you complete it on time in order to gain knowledge and advance your abilities. It is a chance to practice and get better at the things you’re learning in school, which can help you do well in your tests and exams.
Why Is Homework Bad?
Homework can sometimes be bad for a few reasons. First, it can lead to stress and burnout, overwhelming students with too much work. Second, it can take away time that kids need for other important things like family time, sports, or just relaxing. Additionally, it might not always be useful, as some homework tasks might not help students learn better. Moreover, it can create inequality, as not all students have the same resources or help at home to complete their homework. Lastly, it can sometimes feel boring and repetitive, making kids dislike learning.
- Causes stress and burnout
- Takes away time from other important activities
- It may not always be useful for learning
- Creates inequality between students
- It can be boring and repetitive, leading to a dislike of learning
10 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework
Here we will discuss 10 reasons why students should not have homework:
1. Too Much Work
Homework can be like having too much to do. Students get many assignments, and it can become very stressful. This means they have less time for fun things like sports, hanging out with friends, or just relaxing. This stress can make them feel anxious, and it can be challenging to find a balance in their lives. Students need time to breathe and be kids.
2. Less Family Time
Homework takes away time that students could spend with their families. They end up spending long hours doing homework, which leaves less time to be with their parents, siblings, or other family members. This can lead to weaker family bonds and make it harder to build good relationships. Strong families are important for kids’ happiness and growth.
3. Health Problems
Too much homework can harm a student’s health. It can make them lose sleep, worry a lot, and even cause physical health problems like headaches or stomachaches. It’s important for students to be healthy and happy, so too much homework isn’t good for them. Good health is the foundation of a good life.
4. Less Time to Explore
Homework can stop students from trying new things and finding their interests. When they have to spend so much time on homework, they can’t explore their interests or develop their hobbies. This can hold them back from personal growth. Exploring and learning about the world is an important part of growing up.
5. Unequal Opportunities
Not all students have the same help and resources for homework. Some have more support and better tools, while others may not. This can make educational inequalities worse, as students with less support can struggle more, making it harder for them to succeed in school. Every student deserves a fair chance.
6. Boring and Repetitive
Homework can become very boring and repetitive. When students do the same kinds of assignments over and over, it can make them lose interest in learning. They may just do the work to finish it, without really understanding or enjoying the subject. Learning should be fun and exciting.
7. Not Really Learning
Homework can lead to memorization without real understanding. Instead of really learning, students might just try to finish the assignments as quickly as possible. This doesn’t help them learn well in the long run. We want students to understand and enjoy what they’re learning.
8. No Personal Time
Students need time for themselves to relax, do things they enjoy, and take care of themselves. Too much homework means they have very little time for these important activities. Learning how to manage time and take care of oneself is important for their growth. Personal time is crucial for a well-rounded life.
9. Kills Creativity
Homework can make it hard for students to think creatively and solve problems. With so much work to do, they don’t have time for open-minded, creative thinking. This kind of thinking is important for solving real-life problems and coming up with new ideas. Creative thinking helps us tackle the big challenges of the world.
10. Debate Over Value
People don’t all agree on whether homework really helps students learn. Some studies say it does, while others say it doesn’t make much difference. Since it’s not clear, it’s worth thinking about whether the time spent on homework could be used for other activities that we know help students learn better. It’s important to use time wisely and focus on what really works for students.
Advantages Of Having No Homework
Here are some advantages of having no homework:
1. More Free Time
Not having homework means students have more free time after school. This extra time can be used for hobbies, sports, spending time with family, or simply relaxing. It allows kids to be more well-rounded and happy.
2. Less Stress
Without homework, students experience less stress. They don’t have to worry about tight deadlines or piles of assignments, so they can focus on learning in a more relaxed and healthier way.
3. Better Sleep
No homework means better sleep. Students can go to bed at a reasonable time, ensuring they are well-rested and ready to concentrate during school hours.
4. Opportunities for Exploration
When there’s no homework, students have more opportunities to explore their interests and learn about things they are passionate about. They can read books, explore new topics, or work on personal projects.
5. Improved Family Time
The absence of homework allows for improved family time. Parents and kids can get to know each other, share experiences, and make the home a loving and caring place. This strengthens family relationships and creates a more positive atmosphere.
Read More
How To Stop Procrastinating On Homework
How to Get Motivated to Do Homework
Interesting Facts On Why Homework Should Be Banned
Here are some interesting facts on why homework should be banned:
1. Negative Impact on Health
Homework should be banned because it can have a negative impact on a student’s health. Spending long hours on homework can lead to stress, sleep deprivation, and a sedentary lifestyle, which are harmful to physical and mental well-being.
2. Reduces Family Time
Homework takes away precious family time. When students are buried in assignments, they have less time to spend with their families, leading to a decrease in family bonding and support.
3. Inequality in Resources
Homework can lead to inequality. Not all students have access to the same resources, such as a quiet place to study, internet, or parental assistance, making it unfair to some students.
4. No Proven Benefits
Despite its prevalence, homework doesn’t always show clear academic benefits. Research suggests that the advantages of homework are often minimal, and banning it might not affect students’ learning negatively.
5. Increased Stress Levels
Homework can increase stress levels, which can be detrimental to a student’s mental health. Stress can make you anxious, depressed, and not want to learn.
6. Encourages Cheating
The pressure to complete homework on time can encourage cheating and plagiarism, undermining the honesty and integrity of education.
7. Reduces Creativity
Homework can be rigid and repetitive, leaving little room for creativity and independent thinking, which are essential for a well-rounded education. Banning homework can encourage more creative and flexible learning approaches.
Is Homework Is Bad Or Good For Students – From Parents & Teachers Perspective
From a parent’s perspective, homework can be a topic of debate. Some parents see both the downsides and benefits of homework, and it’s essential to consider both sides:
On the Bad Side
- Excessive Stress: Many parents worry that homework can cause their children excessive stress and anxiety, especially when the workload is overwhelming.
- Less Family Time: Homework can reduce the quality family time parents can spend with their children. They may want to prioritize bonding and relaxation.
- Struggle with Complex Subjects : Parents may find it challenging to help their children with complex or unfamiliar subjects, leading to frustration for both.
- Lack of Playtime: Homework can limit a child’s playtime, which is vital for their physical and social development .
- Dislike for Learning: If homework becomes too burdensome or boring, it can lead to children developing a dislike for learning, which parents want to avoid.
On the Good Side
- Practice and Reinforcement: Homework provides an opportunity for children to practice and reinforce what they’ve learned in school.
- Preparation for Responsibility: Homework teaches kids responsibility and time management, valuable life skills.
- Parental Involvement: Homework allows parents to be involved in their children’s education, offering support and guidance.
- Monitoring Progress : It enables parents to monitor their child’s academic progress and identify areas where additional help may be needed.
- Preparation for the Real World: Students can get ready for the tasks and due dates they will face in the future by doing their homework.
From a teacher’s perspective, homework is a topic with its own set of pros and cons:
- Inequality in Resources: Teachers might be concerned that some students have better resources at home, such as access to the internet or parental assistance, creating inequality in completing homework.
- Overburdening Students: Teachers may worry about overburdening students with excessive homework, potentially causing stress, burnout, and negatively impacting their well-being.
- Lack of Proven Benefits: Some teachers may question the effectiveness of homework, as research does not always clearly demonstrate its academic advantages.
- Cheating and Plagiarism: Teachers have to be vigilant about cheating and plagiarism, as the pressure to complete homework may push students to unethical behaviors.
- Potential for Repetition: Teachers might be concerned that homework assignments could become repetitive and dull, leading to a decrease in students’ motivation to learn.
- Reinforcement of Learning: Homework provides students with opportunities to reinforce what they’ve learned in class, which is important for understanding and retaining the material.
- Preparation for Responsibility: Homework helps students develop responsibility, time management, and organizational skills, which are valuable for their future.
- Parental Involvement: Homework encourages parental involvement in a child’s education, allowing for a stronger partnership between teachers and parents.
- Assessment of Progress: Teachers can see how their students are doing and see where they might need more help by giving them homework.
- Preparation for the Real World: Students can become more responsible and disciplined by doing their homework. It helps them get used to the duties and limits they will face in real life.
Debate about homework continues, and there are ten good reasons why students should not have homework. First, it can make kids stressed and tired. It also takes away time from family and fun activities, which are important. Homework might not help students learn much.
Moreover, it can even make some students cheat or copy from others. Many students and parents say we should have less or no homework. They believe that focusing on good teaching in class is better than too much homework. So, the idea of reducing homework or even getting rid of it is something many people support.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently

The Caravan
Students shouldn’t have homework on weekends.
Jonathan Kuptel '22 , Staff Writer | November 7, 2021

Jonathan Kuptel
MC senior Imari Price works on a assignment for 21st-Century Media class.
Teachers and students have different opinions about homework. Saying it is not fair is the usual argument, but being fair is not the issue. It is about students being prepared. Daily homework assignments can be difficult, and weekends homework assignments are worse. Students operate best when they are well-rested and ready to go. A weekend with no homework would help them to be fresh and ready on Monday morning. Weekend assignments tend to be longer and more difficult.
The students have a difficult day with classes, practices, and going to school. By Friday, (test day) they are near exhaustion. Most tests are given on Fridays. Homework on Monday-Thursday is time-consuming. Some weekends will include assignments in more than 1 class. Those who go to Mount Carmel are near the end of their rope by 2:40 PM on Friday. I have had other discussions with the senior class and we all feel pretty tired at the end of the day at 2:40 PM. A free weekend helps to get prepared for the next grind to start. No homework weekends assures better sleep cycles and a body that has recovered and refreshed. Weekends include chores around the house and family commitments. This plus weekends assignments lead to a lack of sleep. This means Monday will have a positive attitude. No homework on weekends also means more family time. This is a bonus.
Alfie Kohn in his book The Homework Myth: Why Are Kids Get Too Much Of A Bad Thing says, “There is no evidence to demonstrate that homework benefits students.” The homework on weekends starts in elementary school and continues throughout high school.
Mr. Kohn states that homework on weekends starts in elementary school and continues throughout high school. This supports the argument that weekend homework starts in elementary school and now students at Mount Carmel High School have to deal with weekend assignments. The weekend assignments take too much time and are a waste of students’ time.
Nancy Kalish , author of The Case Against Homework: How Homework Is Hurting Our Children And What We Can Do About It, says “simply busy work” makes learning “a chore rather than a positive, constructive experience.”
Receiving weekend homework that is not discussed in class and counts only as “busy work” is counterproductive. Students finish the assignments because they are required to be done. When the homework is not reviewed on Monday, it leads to frustration. Busy homework that serves no purpose is never a good idea.
Gerald LeTender of Penn State’s Education Policy Studies Department points out the “shotgun approach to homework when students receive the same photocopied assignment which is then checked as complete rather than discussed is not very effective.” Some teachers discuss the homework assignments and that validates the assignment. Some teachers however just check homework assignments for completion. LeTender goes on to say, “If there’s no feedback and no monitoring, the homework is probably not effective.” Researchers from the Curry School of Education at the University of Virginia had similar findings in their study “ When Is Homework Worth The Time?” Researchers reported no substantive difference in the grades of students who had homework completion. Adam Maltese, a researcher , noted , “Our results hint that maybe homework is not being used as well as it could be. Even one teacher who assigns busy shotgun homework is enough to be a bad idea.
Students come to know when homework is the “shotgun approach.” They find this kind of assignment dull. Students have no respect for assignments like this. Quality assignments are appreciated by students.
Etta Kralovec and John Buell in their book How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, And Limits Learning assert that homework contributes to a corporate style, competitive U.S. culture that overvalued work to the detriment of personal and familial well being. They go on to call for an end to homework, but to extend the school day.
Cooper, Robinson, and Patalc, in 2006 warned that homework could become counter productive. Homework is counterproductive when it is a (shotgun) assignment. To reiterate, not all homework is bad. Bad homework which is not reviewed in class just plain “busy work” is not positive and could be counterproductive.
Sara Croll, Literacy Coach and Author, believes too much homework causes stress for students. Diana Stelin, teacher, artist, and mother says, “I’m absolutely in favor of this ban. Homework is homework, it doesn’t matter what class it comes from. What it does is create negative associations in students of all ages, takes away their innate desire to learn, and makes the subject a dreaded chore.”
When students come to dread their homework, they do not do a great job on these assignments. Making students do a lot of homework isn’t beneficial because they get drowsy when they work at it for hours and hours at a time. It is hard for the brain to function properly when it is tired and boring.
Pat Wayman, Teacher and CEO of HowtoLearn.com says, “Many kids are working as many hours as their overscheduled parents and it is taking a toll.” “Their brains and their bodies need time to be curious, have fun, be creative and just be a kid.”
No homework on weekends is not just a wish, but it is supported by all of these educators and authors. They all champion limiting homework are totally opposed to homework assignments. Educators and students agree that no homework on weekends is a good idea. Meaningful homework, a longer school day, and discussion of homework are what these educators and authors encourage.

Straggling students need to step up for Walkathon fundraising

Mount Carmel benefits from trimesters

Students would benefit from financial planning, life skills

Nothing beats events in the Alumni Gym

MLK exemplified the values of Mt. Carmel

The Caravan Cup should make a return

It’s time to return to packing the stands, Caravan fans

In this season of thankfulness, it’s great to have The Caravan back

Matt Potter putting on the gloves to help others

MC shows appreciation at Veterans Day assembly
The student news site of Mount Carmel High School
- Journalism at Mount Carmel
- pollsarchive
- Sports Center

Simona Johnes
Simona Johnes is the visionary being the creation of our project. Johnes spent much of her career in the classroom working with students. And, after many years in the classroom, Johnes became a principal.
While Johnes enjoyed her new role, she never lost her passion for working with students and helping them succeed.
After a lot of thought, she decided to pursue creating a next generation curriculum to prepare high school students for future success. She left her position as a principal and developed her teaching portal.
Johnes used her years of experience in the classroom to guide in her creating an ideal curriculum that would help set students up for success in the 21st century. Understanding the growing importance of science and technology led Johnes to develop a curriculum rooted in their subjects. She also used her knowledge that students are more likely to be engaged in reading and writing tasks when they are of interest to them and have some relevance to connect each scientific concept with improving literacy skills.
Johnes worked to create a curriculum to help high school students build their literacy skills as they engage in learning and exploring scientific theories.
Exploring the Evidence: 7 Comprehensive Reasons Why School Should Start Later for Enhanced Student Well-being and Academic Success

The debate on the optimal timing for school start times has gained considerable momentum, presenting compelling reasons why school should start later. This growing consensus among educators, parents, and researchers highlights the profound benefits such a shift could have on student health and academic performance. Traditionally, schools have adhered to an early morning schedule, a … Read more
Why Students Should Learn a Second Language for Future Success: Exploring the 7 Benefits

In an increasingly interconnected and globalized world, understanding why students should learn a second language becomes crucial. This ability has transcended from being a simple asset to almost a necessity. For students at the crossroads of educational paths and future careers, mastering a second language unveils myriad opportunities, both personally and professionally. Beyond the apparent … Read more
9 Reasons Why Teachers Should Accept Late Work: Balancing Discipline and Flexibility in Education

The issue of late work in educational settings is a complex and multi-layered challenge that educators face. In the article “9 Reasons Why Teachers Should Accept Late Work,” we delve into this nuanced topic to provide a holistic view. Late work, a common phenomenon in classrooms, poses significant questions about maintaining a balance between discipline … Read more
Comprehensive Analysis: 8 Strong Reasons Why School Should Not Be Year-Round

The debate surrounding year-round schooling is a multifaceted issue that has garnered increasing attention in the world of education. At its core, year-round schooling proposes a significant shift from the traditional academic calendar, intending to enhance learning experiences and academic outcomes. This article delves deep into the concept of year-round schooling, exploring its structure, functionality, … Read more
9 Reasons Why Students Should Have Recess: Enhancing Learning Through Breaks

Recess, a scheduled break in the school day, is often underestimated and overlooked by educators and parents alike. However, research shows that recess plays a crucial role in a student’s physical, mental, and emotional well-being, ultimately enhancing their learning experiences. In this article, we will explore 9 reasons why students should have recess, highlighting its … Read more
6 Reasons Why School Days Should Be Shorter: Unpacking the Benefits and Challenges of Reduced Classroom Hours

The contemporary educational landscape is marked by a critical debate: should school days be shorter? The article “6 Reasons Why School Days Should Be Shorter” ventures into this discussion, dissecting various dimensions of the length of school days and their impact on the educational ecosystem. This exploration is not just limited to the United States; … Read more
8 Reasons Why Students Should Have Mental Health Days: A Research-Based Analysis

Recognizing the importance of mental wellness in education, the concept of mental health days has become increasingly relevant. It’s vital to understand why students should have mental health days, as these breaks can significantly contribute to their overall well-being and academic performance. In an era where academic and social pressures are constantly escalating, the concept … Read more
7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives

In recent years, the question of why students should not have homework has become a topic of intense debate among educators, parents, and students themselves. This discussion stems from a growing body of research that challenges the traditional view of homework as an essential component of academic success. The notion that homework is an integral … Read more
Exploring Top 5 Articulate 360 Alternatives: A Comprehensive Guide to E-Learning Authoring Tools

In the dynamic and evolving field of eLearning, selecting the right authoring tool is a critical decision that impacts the effectiveness and engagement of your courses. While Articulate 360 has long been a go-to choice for many professionals, there’s a growing interest in exploring “articulate alternatives” that might better suit specific project requirements or budgetary … Read more
Why Students Should Not Wear Uniforms: A Thoughtful Exploration with 9 Reasons, Studies and Statistics

In the ongoing debate about school uniforms, a significant voice often goes unheard – that of the students themselves. The argument against mandatory school uniforms is not just about fashion or personal preferences; it delves deeper into fundamental issues of self-expression, equity, and the very purpose of education. This article, “Why Students Should Not Wear … Read more

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices. 1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences. According to Gitnux, U.S. high school students who have over 20 hours of homework per week are 27% more likely to encounter health issues.
A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can't ...
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can't see it in the moment. 6. Homework Reduces Screen Time.
Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We've known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that "homework had no association with achievement gains" when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [ 7]
American high school students, in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found. It's time for an uprising. Already, small rebellions ...
But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether. Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for ...
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.)
Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary. "Every child should be doing homework, but the ...
Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. ...
PROanthony kelly, CC BY. Elementary school kids are dealing with large amounts of homework. Howard County Library System, CC BY-NC-ND. One in 10 children report spending multiple hours on homework ...
A TIME cover in 1999 read: "Too much homework! How it's hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.". The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push ...
One of the most cited reasons for students dropping out of school is that they cannot complete their homework on time. 3. Banning homework would increase the amount of family time available to students. Homework creates a significant disruption to family relationships.
What Research Says about Homework. According to Duke professor Harris Cooper, it's important that students have homework. His meta-analysis of homework studies showed a correlation between completing homework and academic success, at least in older grades. He recommends following a "10 minute rule": students should receive 10 minutes of ...
Reasons Why Homework Should Be Banned. 1. It Contributes to Increased Anxiety. If there's one word that describes middle-school and high-school students, it's anxiety. In my homework statistics article, I cite research showing that 74% of students cite homework as a source of stress.
Homework negatively affects students' health. Download Article. Homework takes a toll physically. Recent studies have demonstrated that too much homework can disrupt a student's sleep cycle, and cause stress headaches, stomach problems, and depression. [3] 3.
Homework is the perennial bogeyman of K-12 education. Any given year, you'll find people arguing that students, especially those in elementary school, should have far less homework—or none at all.I have the opposite opinion. The longer I run schools—and it has now been more than sixteen years—the more convinced I am that homework is not only necessary, but a linchpin to effective K ...
5 reasons why students should get less homework. 1. Students are encouraged to learn. The goal of school should be to teach students how to learn and to love learning. You don't just want to hand your students fish; You want to teach them how to fish. Lectures, discussions, and readings should all engage students and encourage them to get ...
Here we will discuss 10 reasons why students should not have homework: 1. Too Much Work. Homework can be like having too much to do. Students get many assignments, and it can become very stressful. This means they have less time for fun things like sports, hanging out with friends, or just relaxing.
1. Children at this level are just beginning their academic careers. Homework has been seen to have a negative impact on young students' attitudes toward school, so making them dislike it from the start is counter-intuitive. Learning at this level should be fun and engaging. Having them read is noted as the better solution by researchers.
A weekend with no homework would help them to be fresh and ready on Monday morning. Weekend assignments tend to be longer and more difficult. The students have a difficult day with classes, practices, and going to school. By Friday, (test day) they are near exhaustion. Most tests are given on Fridays.
Many teachers do not receive specific training on homework. Cooper suggests that homework should be uncomplicated and short, involve families, and engage student interests. 3. Countries that assign more homework don't outperform those with less homework. Around the world, countries that assign more homework don't see to perform any better.
The debate on the optimal timing for school start times has gained considerable momentum, presenting compelling reasons why school should start later. This growing consensus among educators, parents, and researchers highlights the profound benefits such a shift could have on student health and academic performance.