AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
QuickBooks Sync and compare with your QuickBooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how easy it is to plan your business with Upmetrics: Take a Tour →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
E2 Visa Business Plan Create a business plan to support your E2 - Visa
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Help Center Help & guides to plan your business
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow

How to Write a Customer Analysis Section for Your Business Plan

Free Customer Analysis Template
- July 12, 2024

A customer contributes significantly to building a winning brand.
Understanding your target consumer, their needs, the problems they face, and the way they behave assists you in creating products and services that can satisfy your customer needs.
Customer analysis is a quintessential part of your business plan. Writing it accurately will help you make informed decisions for other aspects of business planning, i.e. product development and business strategies.
So let’s get started. This blog post describes the process of creating customer analysis in a business plan and guides you with a customer persona example.
What Is Customer Analysis?
Customer analysis is an important section of your business plan offering a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of your potential customer. It is a study of their behavioral, psychological, and demographic patterns to help you make sound business decisions.
Such analysis assists in developing products and services addressing the pain points of your customers and in determining your pricing, marketing, and customer retention strategies.
Why conduct a customer analysis?
A thorough and insightful customer analysis offers a plentitude of benefits. Here are a few you should know of:
- Helps optimize product development by offering insights into customer behavior, needs, and pain points.
- Helps gain a competitive advantage by identifying the pain points that are unaddressed by competitors.
- Helps tailor your marketing efforts to cater to specific customer segments.
- Increases customer retention by giving you a thorough insight into what the customer needs and what drives their decision.
If you think of it, customer analysis forms the basis for designing your products and services, devising your marketing and sales strategies, determining your pricing point, and driving your business growth.
How to Write a Customer Analysis Section
Writing a customer analysis includes extensive research and collecting data from various sources. This data consists of qualitative and quantitative aspects which help you write an accurate customer analysis for your business plan.
Let’s now understand a step-by-step process to write your customer analysis.
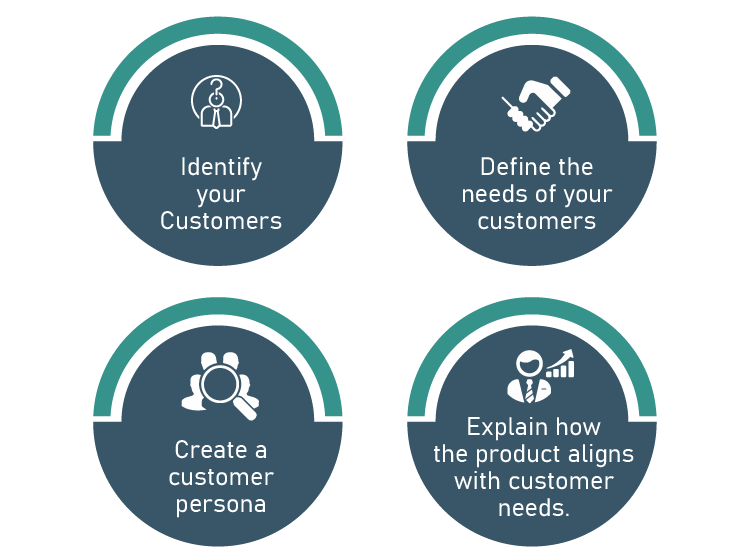
1. Identify your customers
The first step of customer analysis is to identify your potential customers and collect information about their special characteristics. Such information comes in handy when you want your product and marketing strategies to align with your customers’ needs.
However, what details should you collect and how should you segment it? Well, segmenting in the following manner can help you get a headstart.
- Demographic: Age, gender, income
- Geographic: Location, type of area (Rural, suburban, urban)
- Psychographic: Values, interests, beliefs, personality, lifestyle, social class
- Technographic: Type of technology the buyer is using; tech-savviness
- Behavioral: Habits, frequent actions, buying patterns
- Industry (For B2B): Based on the industry a company belongs to.
- Business size (For B2B): Size of the company
Customer database can help capture the above data for existing businesses. However, for additional details, you can retort to surveys and forums.
If you are a startup, conducting an audience analysis might seem impossible as you don’t have an existing customer base. Fortunately, there are numerous ways through which you can study your potential customers.
A few of them are:
- Identifying who would benefit from your product/service
- Analyzing your competitors to understand their target customers
- Using social media to prompt potential buyers to answer questionnaires
2. Define the needs of your Customers
Now that you have identified your customers, the next step is to understand and specify their needs and challenges. This is the step where you need to go hands-on with your research.
Getting to know your customers’ needs helps you determine whether or not your product or service hits the mark.
You can adopt one of these approaches to understand the needs of your customers:
Engage directly with potential Customers
A very reliable way to get to know your customers is to simply engage with them, either in person or on a call. You can reach out to your customers using one of the following ways:
- One-on-one interviews
- Focus groups
- Beta testing (invite users to test your products).
These techniques can help you collect adequate data for your analysis.
However, before approaching your customers, set up a systematic survey that can get you structured data for analysis. To ensure that your questionnaire isn’t just covering surface-level information but a deep interrogation of customers’ problems, use the technique of five whys .
Collect data from your customer support
Customer support is the place where you can find raw and unfiltered feedback given by your customers. Analyzing this data helps you understand the pain points of your customers.
You can further gather direct customer feedback by contacting the customers who had issues with your products. This will help you understand the pain points and gaps in your products more vividly.
Run surveys and mention statistics
Talking to your customers helps you get qualitative information that can be used to alter your product or services according to your customers. The next part is to attain quantitative information, in other words, presenting numbers to support the previous data.
Conducting surveys is one of the commonly used methods for quantifying information. You can conduct in-app surveys, post-purchase surveys, or link surveys in email and apps, etc.
You can also collect statistical data to support your conclusions from the interviews. These include stating studies related to customer choices, results from popular surveys, etc.

Want to create a Customer Persona in Easy Steps?
Generate valuable customer insights in minutes with Free Customer Persona Generator .
3. Create a Customer Persona
It is now time to present your collected data using a customer persona.
A customer persona represents a segment of customers with similar traits. It outlines the psychological and demographic features of your potential customer group and thereby assists you in making important strategic decisions.
Consider it as a tool that will make your data analysis process easier and more efficient.
Now, you can either use customer persona templates or an AI tool to generate your buyer’s persona. However, to get a more thorough insight check how a customer profile looks.
Customer Persona Example
This is a customer persona example of an internet service provider(ISP) to help you get a more practical overview.
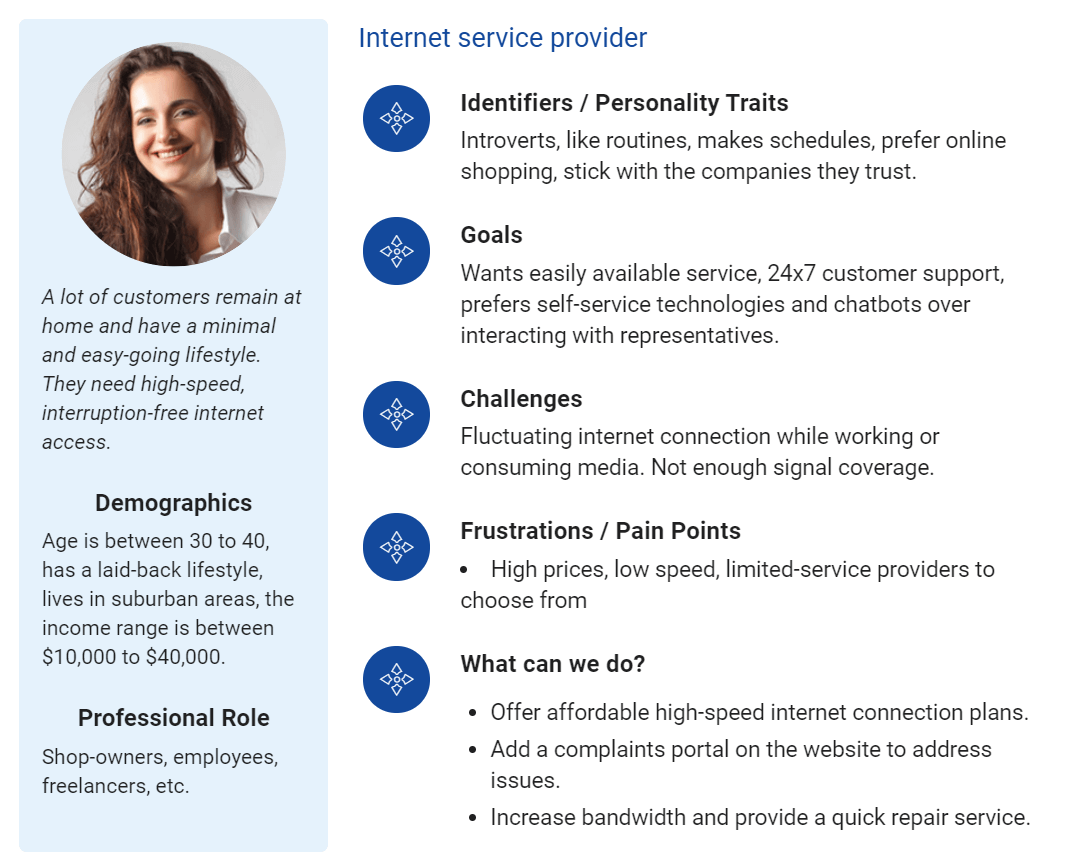
- About: A lot of customers remain at home and have a minimal and easy-going lifestyle. They need high-speed, interruption-free internet access.
- Demographics: Age is between 30 and 40, has a laid-back lifestyle, lives in suburban areas, and the income range is between $10,000 to $40,000.
- Professional role: Shop owners, employees, freelancers, etc.
- Identifiers/Personality traits: Introverts, like routines, make schedules, prefer online shopping, and stick with the companies they trust.
- Goals: Wants easily available service, and 24×7 customer support, prefers self-service technologies and chatbots over interacting with representatives.
- Challenges: Fluctuating internet connection while working or consuming media. Not enough signal coverage.
4. Explain the product alignment to the Customer’s Needs
You’ve gathered info and created customer personas. The final step is to explain how your product or service caters to the needs of your customers.
Here, you specify the solution you offer to tackle the challenges faced by your customers.
Mention the USPs of your product and its features, and clarify how they benefit the customer. Also, mention how your offerings make the customers’ lives better.
Continuing the previous example of an ISP provider, this company can show how its high-speed Internet plans cater to the needs of individual working professionals. They can focus on aspects like customizable plans, cost-effectiveness, and coverage in remote areas to attract users.
And there you have it—a guide to writing your customer analysis. Just ensure that you maintain accuracy while making assumptions and predictions to make this section useful for making further decisions.
Build a solid business foundation with customer analysis
Understanding you r customers inside out assists you in making profitable decisions for your business. But remember, it is an ever-evolving and continuous process. You need to analyze your customers as often as possible to stay updated about their ever-changing needs.
After all, understanding what your customers need and what they prefer will help you devise strategies that ensure maximum customer satisfaction.
Now quickly create customer profiles for your business with Upmetrics’s AI SWOT analysis generator. However, once you do that, use this tool to streamline your entire business planning process.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What key components should be included in customer analysis.
Here are the key components of a sound customer analysis:
- Market segmentation
- Customer behavior analysis
- Customer profiling
- Customer journey mapping
- Trend analysis and future customer behavior
How can I gather data for my customer analysis?
Here are a few ways for you to gather data for your customer analysis:
- Gather customer feedback using surveys, forums, and questionnaires.
- Use secondary methods to gather industrial data, competitors’ data, and data from publications.
- Use the collected data till data (i.e. social media analytics, customer support data) to form your analysis.
Can customer analysis help in forecasting future trends?
Absolutely, yes. A detailed customer analysis helps you to understand the emerging shifts and patterns in consumer behavior, thereby helping you optimize your product offerings and marketing strategies.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning


How to Write the Customer Analysis Section of Your Business Plan
Written by Dave Lavinsky

What is a Customer Analysis?
The customer analysis section which incorporates the essential steps of writing a business plan step-by-step is a key component of your business plan and assesses the customer segments your company serves. The objective of the customer analysis is to justify your market choice, identify differentiators, and prioritize the segments you are targeting.
Components of a Customer Analysis
A complete customer analysis contains 3 primary sections:
- Identify your target customers
- Convey the needs of these customers
- Show how your products and/or services satisfy these needs
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
Why Conduct a Customer Analysis?
A thorough customer analysis provides the following benefits:
- Supports your market choice and helps you avoid entering too broad a market
- Helps you focus on serving current customers rather than trying to find new ones
- Enables you to determine which segments to prioritize and how much effort to put into each one
- Helps you craft a strategic marketing plan and platform to reach these customer segments
How to Write Your Customer Analysis
The first step of the customer analysis is to define exactly which customers the company is serving. This requires specificity. It is not adequate to say the company is targeting small businesses, for example, because there are several million of these types of customers. Rather, an expert business plan writer must identify precisely the customers it is serving, such as small businesses with 10 to 50 employees based in large metropolitan cities on the West Coast.
When defining your target market, be sure to identify the following:
- The market segment you are choosing to serve (i.e., age range, annual income, etc.)
- The geographic location of these customers (i.e., city, region, state)
- What is the average revenues/income of these customers?
Once the plan has clearly identified and defined the company’s target customers and the customer demographics, it is necessary to determine the size of your target market: How many potential customers fit the given definition and is this customer base growing or decreasing?
Next, the business plan must detail these customers’ needs. Conveying customer needs could take the form of past actions (X% have purchased a similar product in the past), future projections (when interviewed, X% said that they would purchase product/service Y), and/or implications (because X% use a product/service which our product/service enhances/replaces, then X% need our product/service).
Prioritize the needs of your target customer according to how critical they are, and include a description of each in your customer analysis. Be sure to answer questions such as:
- What pain points do these customers have? How is their current situation lacking?
- What will your product/service do to help solve these problems?
The business plan customer analysis must also detail the drivers of customer decision-making. Sample questions to answer include:
- Do the customers find price to be more important than the quality of the product or service?
- Are customers looking for the highest level of reliability, or will they have their own support and just seek a basic level of service?
- Why will customers purchase your product and/or service rather than look for cheaper alternatives?
Prioritize the benefits of your products and services according to how much difference they make for customers and include a description of each in your customer analysis. Be sure to answer questions such as:
- What does your product do? How is it unique or better than other similar products?
- What type of customer could benefit the most from this feature/benefit and why?
Be sure to also show an understanding of the actual decision-making process. Examples of questions to be answered here include:
- Will the customer consult others in their organization/family before making a decision?
- Will the customer seek multiple bids?
- Will the product/service require significant operational changes (e.g., will the customer have to invest time to learn new technologies, and will the product/service cause other members within the organization to lose their jobs? etc.)
Finally, identify each segment you are targeting and how much effort you will put into reaching them. Be sure to answer questions such as:
- How many customers are in each segment and how much revenue will they generate?
- What percentage of total industry sales does this represent?
- What market potential did we estimate for each segment and how does that compare with actual sales? Include the number of leads converted and average deal size.
Example Customer Analysis Template for a Candle Making Company
The needs of this customer segment are that they are looking for high-quality candles that are made with all-natural ingredients. The benefits of their product that are most important to them are that the candles are vegan, eco-friendly, and made with essential oils. Drivers of customer purchase decisions include quality, price, and unique offerings. The company’s target market size is 750,000 people which represent a significant portion of the candle industry. They will put effort into reaching these customers through online advertising, social media posts, and word-of-mouth.
It is essential to truly understand customers to develop a successful business and marketing plan. That’s why including a customer analysis in your business plan is so crucial. Likewise, sophisticated investors require comprehensive profiles of a company’s target customers. By spending the time researching and analyzing customers in your target market, you will develop both enhance your business strategy and funding success.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies that have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
See how Growthink business plan consultants can create your business plan for you.
Other Resources for Writing Your Business Plan
How to Write a Great Business Plan Executive Summary How to Expertly Write the Company Description in Your Business Plan How to Write the Market Analysis Section of a Business Plan Completing the Competitive Analysis Section of Your Business Plan The Management Team Section of Your Business Plan Financial Assumptions and Your Business Plan How to Create Financial Projections for Your Business Plan Best Business Plan Software Everything You Need to Know about the Business Plan Appendix Business Plan Conclusion: Summary & Recap
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


Crafting the Customer Analysis in Business Plan: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s competitive business environment, understanding your customers is the key to success. Customer analysis in business plans plays a crucial role in driving business growth and providing a competitive edge.
Imagine unlocking the hidden potential within your customer base, tailoring marketing strategies, and developing products that resonate with their needs and preferences. This comprehensive guide will explore the ins and outs of customer analysis in a business plan and how to leverage it for maximum impact on your business.
Short Summary
- Customer analysis is an essential part of any business plan, allowing businesses to understand their target customers and create tailored products/services.
- It involves identifying a market, assessing demographics & analyzing customer behavior in order to inform marketing strategies.
- Utilizing insights from customer analysis can help optimize marketing campaigns & product offerings for maximum return on investment.
The Essence of Customer Analysis
Customer analysis is an essential element of any business plan, emphasizing the comprehension of target customers, their requirements, and how your product or service fulfills those requirements. By performing customer analysis, businesses can better tailor their products and services to their target audience , ultimately leading to increased sales and a thriving business.
Understanding the needs of your target customers is key to success. Knowing who your customers are

Purpose of Customer Analysis
The primary objective of customer analysis is to recognize potential customers, prioritize customer segments, and provide guidance for marketing and product development strategies. Understanding your customers’ wants, needs, pain points, and objectives is crucial to creating targeted marketing campaigns and product offerings that resonate with them.
By closely monitoring customer feedback and support requests (Voice of Customer analysis), businesses can gain insight into customer pain points and preferences and even discover unexpected uses for their products.
Key Components of Customer Analysis
The essential elements of customer analysis encompass target market identification, demographic analysis, and behavioral analysis. Demographic analysis provides insights into factors such as age, income, and location, which can be used to create targeted marketing strategies.
Behavioral analysis, on the other hand, entails comprehending the customer’s decision-making process for the purchase, including the steps taken, information sources consulted, and who has the authority to make the final decision. By understanding these components, businesses can better cater to their customer’s needs and preferences, ultimately leading to success.
Conducting an Effective Customer Analysis
An effective customer analysis involves a thorough research process that focuses on customer pain points, goals, and insights on what influences their buying decisions. This process begins with identifying your target market, which is crucial in ensuring a successful business.
By analyzing customer demographics and examining customer behavior and purchasing patterns, businesses can tailor their marketing strategies and product offerings to address the specific needs and preferences of their target customers.
Identifying Your Target Market
Identifying your target market is the first step in conducting a comprehensive customer analysis. By precisely defining the target customer your company is serving, you can focus your marketing efforts and resources on the most profitable customer segments.
Small businesses with 10 to 50 employees located in large metropolitan cities on the West Coast can benefit from having a business plan. This plan should provide clear guidance and instructions for the successful execution of tasks, including target market analysis.
With a clear understanding of your target market, you’ll be better equipped to develop a targeted marketing strategy that resonates with your audience and drives sales.
Analyzing Customer Demographics
Analyzing customer demographics is crucial for tailoring marketing strategies to specific customer groups. By examining your current customer base, you can determine which demographics to focus on for future marketing efforts. Demographic information, such as:
- education levels
A comprehensive view of the messaging that is most likely to appeal to customers and the marketing channels that are most effective in reaching them can be achieved when customers seek multiple bids, as it provides valuable insights into their preferences and decision-making process.
By constructing a marketing strategy around the types of people who have already made a purchase, you can maximize the return on investment of your marketing budget.
Examining Customer Behavior and Purchasing Patterns
Analyzing customer behavior and purchasing patterns can yield valuable insights through customer behavior analysis. By monitoring customer interactions with your products and services, such as website visits, purchases, and customer reviews, you can identify customer needs and preferences and devise strategies to enhance customer retention and loyalty.
Additionally, understanding the drivers of customer decision-making is crucial for creating targeted marketing campaigns and product offerings that resonate with your target audience.
Utilizing Customer Analysis Results
Customer analysis results can be leveraged to enhance marketing strategies, drive product development and innovation, and strengthen customer retention and loyalty. By recognizing customer feedback and customer support requests, businesses can acquire advantageous insights into customer behavior and preferences, which can be utilized to provide direction to marketing and product development strategies.
In this section, we will explore how customer analysis results can be utilized to improve various aspects of your business.
Enhancing Marketing Strategies
Customer analysis results, including customer segmentation analysis, can inform targeted marketing strategies that lead to increased sales and revenue. By leveraging insights from customer demographics and behavior, businesses can create personalized marketing campaigns that resonate with their target audience. For example, a company catering to young professionals may focus its marketing efforts on social media platforms, while a company targeting older adults may prioritize direct mail or email campaigns.
By tailoring marketing strategies based on customer analysis, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts and achieve greater success.
Driving Product Development and Innovation
Insights from customer analysis can guide product development and innovation, ensuring that products and services meet customer needs and preferences. By understanding customer pain points and objectives, businesses can create new products and services that address these needs, resulting in increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Additionally, existing customer feedback can be utilized to refine existing products and services, making them more appealing to the target audience and driving business growth .
Strengthening Customer Retention and Loyalty
Understanding customer needs and preferences through customer analysis can help businesses improve customer retention and loyalty. By tailoring products and services to the specific needs and preferences of your target audience, you can enhance customer satisfaction and encourage repeat business.
Furthermore, by identifying gaps in the customer experience and optimizing touchpoints, businesses can improve the overall customer journey and nurture long-lasting relationships with their customers.
Tools and Techniques for Customer Analysis
To effectively conduct customer analysis, businesses can employ various tools and techniques, including data collection and analysis, creating buyer personas, and customer journey mapping. These methods enable businesses to gain a deeper understanding of their customers and make informed decisions regarding their products, services, and promotional activities.
In this section, we will explore the different tools and techniques that can be used in customer analysis.
Data Collection and Analysis
Data collection and analysis play a critical role in customer analysis, as they involve gathering information on customer interactions, demographics, and purchasing patterns. Businesses can utilize various methods for data collection, such as surveys, focus groups, and interviews, as well as analytics tools to track customer behavior online.
By analyzing this data through market research, businesses can identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement, ultimately informing their marketing strategies and product development efforts.
Creating Buyer Personas
Creating buyer personas is an essential technique in customer analysis, as it helps businesses visualize their ideal customers and tailor marketing and product development strategies accordingly.
Buyer personas are fictional representations of major customer segments, taking into account factors such as:
- demographics
- professional status
- purchasing habits
By developing accurate and detailed buyer personas, businesses can ensure that their marketing campaigns and product offerings resonate with their target audience, leading to increased sales and customer loyalty.

Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping is an invaluable tool in customer analysis, as it enables businesses to identify gaps in the customer experience and optimize touchpoints to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. A customer journey map is a visual representation of the stages a customer goes through when interacting with a business, from initial awareness to loyalty.
By understanding the customer journey and identifying areas for improvement, businesses can enhance the overall customer experience and nurture long-lasting relationships with their customers.
Case Study: Successful Customer Analysis in Action
A prime example of successful customer analysis in action is the Buxton case study. Buxton, a leading provider of customer analytics and consulting services, utilized customer analysis techniques to help businesses expand, grow, and market themselves more efficiently. Through a combination of data collection, buyer persona creation, and customer journey mapping, Buxton was able to gain a deep understanding of their client’s customers and develop targeted marketing campaigns that resonated with their audience.
As a result, their current customers experienced increased sales, customer loyalty, and overall business growth and success.
In conclusion, customer analysis is a powerful tool that can drive business growth and success by helping companies understand their target customers, tailor their marketing strategies, and develop products and services that meet customer needs and preferences.
By utilizing tools and techniques such as data collection and analysis, buyer persona creation, and customer journey mapping, businesses can gain valuable insights into their customers and make informed decisions that lead to increased sales, customer loyalty, and overall business success. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to unlock your business’s full potential – start conducting customer analysis today and reap the rewards.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a customer analysis in a business plan.
A customer analysis is an essential part of a business plan, which identifies target customers and outlines how a product or service meets their needs.
It helps businesses understand their customers better, so they can create marketing strategies that are tailored to their target audience. It also helps them identify potential opportunities and threats in the market.
By understanding their customers, businesses can better serve their customers.
What is an example of customer analysis?
Customer analysis involves understanding consumers’ behaviors through observation and measurement of analytics, analyzing brand recognition and awareness, understanding how customers feel about the competition, and testing different customer acquisition approaches.
This process helps businesses better understand their target audience and develop strategies to reach them. It also helps to identify potential opportunities for growth and improvement. By understanding customer behavior, businesses can create more effective marketing campaigns and better serve their customers.
What should be included in a customer analysis?
A customer analysis should include details on the customer’s demographics, professional status, purchasing habits, values and goals, influences, and challenges. It should also assess their buying patterns, product usage history, spending habits, loyalty metrics, and more to gain an understanding of their wants, needs, pain points, and objectives.
What is the primary objective of customer analysis?
The primary objective of customer analysis is to recognize potential customers, prioritize customer segments, and inform marketing and product development strategies.
By understanding customer needs and preferences, businesses can create targeted marketing campaigns and product offerings that are tailored to the needs of their target audience. This helps to ensure that the company is reaching the right people.
How can customer analysis help improve marketing strategies?
Customer analysis provides valuable insights into customer’s needs and preferences, enabling businesses to create tailored marketing strategies that drive sales. It is an essential tool for effective marketing.
Leave a Comment Cancel
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Email Address:
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Discover the hottest Food and Drinks Trends of 2024 in our exclusive report 🍕
- · Brandwatch Academy
- Forrester Wave
Brandwatch Consumer Research
Formerly the Falcon suite
Formerly Paladin
Published October 31 st 2023
Complete Guide on How to Conduct an Effective Customer and Segmentation Analysis
Follow this detailed guide to conducting customer analysis and segmentation and learn how to target your customers with the right messages.
The purpose of undertaking customer analysis as part of a business plan is to examine in-depth the consumers most likely to purchase your product or service. Brands can establish different groups of customers and the needs of those customers. By understanding what motivates them to purchase, brands can build their business around providing solutions to those needs.
So, how can we define customer analysis?
What is customer analysis, and why is it important?
Customer analysis is the process of examining, understanding, and developing in-depth knowledge about the consumers most likely to convert into customers by purchasing your product or service.
Customer analysis is a critical component of market research and business strategy. The customer analysis process involves systematically collecting and examining data and insights about a company's existing and potential customers.
This type of analysis aims to discover consumer purchase drivers and how an organization can effectively fill the gap with its product offerings.
The goal is to identify and segment different groups of customers based on their unique traits, motivations, and needs. Organizations can explore demographics, psychographics, interests, behaviors, and other characteristics that make up a customer profile or buyer persona.
What is a customer profile or buyer persona?
A customer profile (or buyer persona) is a dossier containing a detailed record of the ideal consumer interested in purchasing your product or service. Organizations use buyer personas to tailor their marketing strategies, product development, and sales efforts to better align with customer preferences and expectations.
How can brands benefit from doing customer analysis?
Insights from customer analysis can help companies enhance customer satisfaction, target the right audience with tailored messages, uncover market trends, and make informed decisions, ultimately driving business growth and success in a competitive marketplace.
Customer analysis empowers businesses to bridge the gap between what they offer and what their customers genuinely need, ensuring that products and services provide practical solutions to consumer pain points.
Stages of customer analysis
Customer analysis should move through three different stages.
- You first need to identify who your current customers are. The more detailed understanding you have of your customers, the better. This one group of customers should then be split into subgroups with similar traits and motivations. You can also identify target customers you are not yet reaching.
- Customer analysis must then show what the needs of these different customer groups are.
- You then need to work out what bridges these two, identifying how the company’s products meet the needs of each customer group. How do you provide solutions to their pain points?
What is a customer analysis model?
Any analysis should start with asking clarifying questions that can help establish the reason for the analysis and create a framework for evaluating the data.
The customer analysis model represents the framework marketers and insights professionals can follow when diving deeper into the customer data to surface consumer preferences and interests.
Researchers often cite the 5W and 6W models, which stand for the Who, What, When, Where, Why, and, lastly, Why not of the data.
This approach to analyzing customer data can help reveal not only who your target audience is and what they might be interested in but also what they dislike and the reasons behind it.
5 Key steps to conducting effective customer and segmentation analysis
To conduct effective customer and segmentation analysis, organizations should follow the following five key steps:
1. Identify and segment your existing customer base:
- Identify your current customers and gather as much detailed information as possible.
- Segment these customers into distinct groups with similar traits and motivations.
- Identify potential target customers you still need to reach
You might like
How to discover audience insights in minutes.
Learn how to leverage Brandwatch Social Panels for audience analysis.
2. Define segment criteria:
- Ensure that your segmentation criteria are measurable, observable, substantial, and financially justified (the effort and resources required to target and serve a particular customer segment are justified by the potential return on investment).
- Consider whether marketing messages can be tailored to each segment.
- Evaluate the size and accessibility of each segment to determine the focus.
3. Develop customer profiles and personas:
- Create detailed buyer personas that include background, demographics, communication preferences, and challenges.
- Gather qualitative data in the form of quotes to humanize the personas.
- Visualize a human behind your potential buyer rather than an abstract idea when crafting your personas.
4. Discover customer needs and pain points:
- Engage with customers through surveys, social media, and direct dialogs to understand their needs (e.g., create an open feedback loop or run Q/As on social).
- Analyze past customer actions and explore relevant online platforms like Quora, Reddit, and LinkedIn groups.
- Use social intelligence to monitor discussions and content shared within your persona groups.
5. Connect customer needs to your brand:
- Work with internal stakeholders to determine how your brand can meet the needs and solve the problems of each customer group.
- Emphasize solutions over features, focusing on making customers' lives easier.
- Apply these insights to marketing, sales, and product development to better align with customer expectations and drive business success.
Identify your customers
You can learn more about your customers in a variety of ways, and a mix of research methods will give you the most accurate results. It is best to gather as much information as possible and avoid thinking details are irrelevant. Details like age, gender, location, demographics, and psychographics are all important, but so are their interests, other brands they like, publications they read, and so on.
Talking to them and running a survey will be the best way of hearing about them in their own words, although that does come with biases. Reduce this by complementing that research with sales and CRM data and speaking to customer-facing employees. Once you have identified these groups, social data can elaborate your understanding by providing a more holistic view of the groups.
Your guide to learning about consumers online
Learn how social listening can inform your primary research objectives
It’s also worth considering at this stage whether or not the buyer and end-user are the same person. In a B2B setting, the buyer might hold budget responsibility but not actually use the service or product themselves.
In a B2C setting, there are several situations when a buyer might not be the end user; a toy water pistol or a diamond ring are both unlikely to be used by the purchaser.
Do customer segmentation in groups
You cannot undertake an accurate customer analysis without segmenting your audience into groups whose members are homogenous and distinct from other groups. Your segmentation criteria should be:
- Measurable : Your analysis should identify the size of a market segment so that you can decide to what extent efforts should be focused on the segment.
- Distinguishable : Observable differences that are clearly defined must exist in order to characterize segments.
- Substantial : The market needs to be large enough to justify segmenting, with each segment substantial enough to make it worthwhile.
- Financial : There will be additional costs when marketing to multiple, separate groups, so the predicted income must exceed these costs.
- Accessible : Your marketing messages should be accessible to each market segment. Different groups will respond better to different forms of advertising.
Develop a customer profile analysis
Use your data, segmentation criteria, and some educated guesswork to develop your buyer personas. It helps to have personas to visualize a human rather than aiming for an abstract idea.
Elements to include in a buyer persona include:
- Background and responsibilities , including job title, career path, and consumers’ primary job responsibilities.
- Demographics , including gender, age, income, family, and location.
- Communication : Which channels do they prefer? What is their demeanor? Do they have an assistant?
- Media and influencers : Which publications do they follow, and which individuals are leading the conversation in their world?
- Challenges vs proposition : The challenges they face in implementing their primary job goals and how your product or service can help them overcome those issues.
- Objections : Common reasons why this persona wouldn’t choose your product.
- Common language : What language should you use to appeal to their needs?
- Quotes : Adding some qualitative data in the form of quotes can really help to bring the personas to life and remind you there are real people behind these aggregated models.
Discover your customers’ needs
The next step in customer analysis is to get a good idea of what the customer’s needs are. By understanding their needs, several departments can gear their output towards answering these questions rather than taking an “If you build it, they will come” approach.
There are numerous ways to discover what your customers’ pain points are.
- The best way is to ask them. A survey is great if you can get enough responses, and online services like SurveyMonkey can keep the cost down.
- Consider the past actions of the group, such as the percentage that have purchased a similar product at some time in the past.
- Look at questions asked on Quora or Reddit .
- For B2B businesses, looking at job adverts for your target customers can give you an insight into their day-to-day work and problems.
- Join LinkedIn professional groups to get an insight into questions and discussions.
- Social intelligence can again help to understand the issues faced by customers. You can begin by building an audience of your personas and then monitor that group for questions asked, relevant content shared (such as how-to guides), and discussions.
How does your brand meet the needs of the customer?
Once you’ve done your research and outlined your different customer groups and their needs, you should connect the dots to your brand and identify how you meet those needs. This section of customer analysis should just be a matter of discussing and brainstorming with internal partners.
Solution-based answers should come out of this process. Instead of merely listing features, concentrate on showcasing how these features address the challenges your customers and prospects have. Always focus on benefits ahead of features.
Solving the problems that customers face on a daily basis will resonate with them much better than shouting about a shiny new feature. Focus on how you can make their lives easier and more enjoyable.
This will obviously be reflected in marketing, but these insights can help sales and product development as well, tightening your focus to better match your customer’s needs.
Ready to make your customer and segmentation analysis?
Systematically conducting a customer and segmentation analysis is not merely a recommended practice but essential for any business aiming to thrive in today's competitive landscape.
By understanding the core principles of customer analysis and following the five key steps to conducting an effective analysis outlined in this blog, you can unlock your brand’s true potential and foster lasting success.
The journey of customer analysis starts from analyzing your existing customers, mirroring buyer personas after them, and ultimately connecting the dots between your brand and the solutions you provide to address your potential customers’ pain points.
The insights from conducting a customer analysis are not just data; they are the compass that guides your marketing, sales, and product development efforts to better align with your customers’ needs.
Now it's your turn: How are you going to harness the power of customer analysis to drive business success in 2024?
Content Writer
Share this post
Brandwatch bulletin.
Offering up analysis and data on everything from the events of the day to the latest consumer trends. Subscribe to keep your finger on the world’s pulse.
New: Consumer Research
Harness the power of digital consumer intelligence.
Consumer Research gives you access to deep consumer insights from 100 million online sources and over 1.4 trillion posts.
More in marketing
10 social listening tools and who they’re best for.
By Brandwatch Jul 14
18 Social Media Holidays to Celebrate This August
By Yasmin Pierre Jul 10
Social Media Consultant: Key Strategies for Digital Success
By Brandwatch Jun 27
How to Run Successful LinkedIn Ads in 2024
By Emily Smith Jun 20
We value your privacy
We use cookies to improve your experience and give you personalized content. Do you agree to our cookie policy?
By using our site you agree to our use of cookies — I Agree
Falcon.io is now part of Brandwatch. You're in the right place!
Existing customer? Log in to access your existing Falcon products and data via the login menu on the top right of the page. New customer? You'll find the former Falcon products under 'Social Media Management' if you go to 'Our Suite' in the navigation.
Paladin is now Influence. You're in the right place!
Brandwatch acquired Paladin in March 2022. It's now called Influence, which is part of Brandwatch's Social Media Management solution. Want to access your Paladin account? Use the login menu at the top right corner.

Resource Library
Introduction to customer analysis.
A customer analysis (or customer profile) is a critical section of a company’s business plan or marketing plan. It identifies target customers, ascertains the needs of these customers, and then specifies how the product satisfies these needs.
Customer analysis can be broken down into a behavioral profile (why your product matches a customer’s lifestyle) and a demographic profile (describing a customer’s demographic attributes).
A customer profile is a simple tool that can help business better understand current and potential customers, so they can increase sales and grow their business. Customer profiles are a collection of information about customers that help determine why people buy or don’t buy a product. Customer profiles can also help develop targeted marketing plans and help ensure that products meet the needs of their intended audience.
Behavioral Analysis (Customer Buying Criteria)
A behavioral analysis of customers (or psychographic profile) seeks to identify and weigh the relative importance of factors consumers use to choose one product over another. These factors, sometimes called buying criteria, are key to understanding the reasons that customers choose to buy your product (or service) versus the products offered by your competitors. The four major criteria that customers use to distinguish competing products are: price, quality, convenience andprestige.
In consumer transactions, price and quality tend to be the dominant factors. However with business-to-business (B2B) transactions (also called industrial marketing), service issues such as reliability, payment terms, and delivery schedule become much more important. The sales transaction in an industrial marketing scenario also differs from consumer marketing in that the purchase decision is typically made by a group of people instead of one person, and the selling process can be much more complex (including stages such as: request for bid, proposal preparation and contract negotiations).
By identifying customer needs through market research and analysis, companies can develop a clear and concise value proposition which reflects the tangible benefits that customers can expect from the company’s products. And once the primary buying criteria have been identified, marketing efforts can influence the customer’s perception of the product along the four main dimensions (price, quality, convenience and prestige), relative to the competition’s product.
Behavioral Analysis (Purchase Process and Patterns)
Occasionally, customer behavior analysis requires a more in-depth understanding of the actual decision-making process of the customer purchase. This may be especially true in an industrial marketing scenario. Examples of purchase process questions to be answered here include:
* What steps are involved in the decision-making process? * What sources of information are sought? * What is a timeline for a purchase (e.g., impulse vs. extended decision-making)? * Will the customer consult others in their organization/family before making a decision? * Who has the authority to make the final decision? * Will the customer seek multiple bids? * Will the product/service require significant modifications?
Behavior profiles can also focus on actions, such as: which types of items were purchased, how frequently items are purchased, the average transaction value, or which items were purchased in conjunction with other items. To understand the buying habits and patterns of your customers, answer the following questions:
* Reason/occasion for purchase? * Number of times they’ll purchase? * Timetable of purchase, every week, month, quarter, etc.? * Amount of product/service purchased? * How long to make a decision to purchase? * Where does the customer purchase and/or use the product/service?
Customer Demographics
The second major component in customer analysis is identifying target market segments that are predisposed to preferring your products over those of your competitors. A market segment is a sub-set of a market made up of people or organizations with one or more characteristics that cause them to demand similar product and/or services based on qualities of those products such as price or function. A marketing program aimed at individual segments needs to understand and capitalize on the group’s differences and use them strategically in all advertising campaigns.
Gender, age, ethnicity, geography and income are all market-segmenting criteria based on demographics.
Typical questions to ask when determining the demographics of the target market include: * What is the age range of the customer who wants my product or service? * Which gender would be most interested in this product or service? * What is the income level of my potential customers? * What level of education do they have? * What is their marital or family status: Are they married, single, divorced? Do they have kids, grandkids? * What are the hobbies of my target customers?
The target market segments are specified by demographic factors: age, income, education, ethnicity, geography, etc. Then by having a well defined set of demographic factors, marketing will be able to identify the best channels to reach these specific demographic segments.
Customer Analysis Example
Customer Analysis References
Market Analysis {U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) Website’s content on Marketing Analysis} http://www.sba.gov/content/market-analysis
“Analyzing Customers in Your Business Plan” 2011 {Growthink, Inc.} http://www.growthink.com/businessplan/help-center/analyzing-customers-your-business-plan
Related Resources
Keyword Advertising
A guide to keyword advertising: online advertising that uses search engine keywords to trigger contextualized ads.
Google AdSense
A guide to Google AdSense: a free, simple way for website publishers to earn money by displaying targeted Google ads on their websites.
Online Advertising Networks
Ad networks are primarily involved in selling space for online ads. This online advertising inventory comes in many different forms, including space on websites, in RSS feeds in e-mails, and on other sources.
SBDC Intel™
Subscribe for updates, events and opportunities to network..

Subscribe for updates, events, and opportunities to network.
Get practical resources, important updates, and a calendar of online training, events, and more delivered to your inbox.
- First Name *
- Last Name *

A complete guide to successful customer analysis
If you want your business to succeed, you must understand your customers. This is where customer analysis is critical.
When companies understand their customers, they can serve their needs better. When customers’ needs are better served, they become loyal and profitable.
Knowing precisely what your customers want or what makes them tick will help you set expectations for your team and focus your efforts.
For many organizations, customer analysis is rudimentary and unfocused. Sometimes this research barely scratches the surface and focuses on unnecessary or irrelevant information. In other cases, departments operate individually, meaning customer analysis and research aren’t usable for the whole organization.
Practical customer analysis is based on detailed research , shared across an entire organization, and focused on what matters: customer pain points and goals.
What exactly is customer analysis, and why is it important?
Five steps to running successful target customer analysis, remember that customer analysis is not a one-off activity.
The customer analysis ‘s goal is to understand how customers behave and what their preferences are. It involves gathering and studying demographics, buying patterns, product usage history, spending habits, loyalty metrics, and more. This aims to understand wants, needs, pain points, and objectives.
Typically organizations that conduct customer analysis use a variety of methods to do so. These methods include analyzing first-party data (such as CRM or Marketing data), focus groups, interviews, market data, existing customer feedback, and more.
Organizations must ensure that their customer analysis strategies are accurate and up-to-date to remain competitive in today’s changing market. They should always strive to provide relevant insights by utilizing the latest technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) or machine learning (ML). Additionally, they should protect customer data’s privacy by assuring customers that any information shared is secure.
Here are some key reasons why you should implement customer analysis:
- It allows you to shape your strategy around the needs of your customers
- It enables you to customize and personalize your marketing and communications messaging to address customer needs better
- It helps you build lasting, meaningful, and profitable relationships with your customer base
- It enables you to receive product and/or service feedback to inform improvements
By leveraging customer analysis, organizations can build relationships with customers across channels, foster loyalty and increase long-term profitability.
1. Leverage existing customer data
Existing customers should be the starting point for your research when performing customer analysis. This data source is likely to be your CRM (Client Relationship Management) system, and segmenting it or grouping it by customer characteristics can provide invaluable insights into consumer behavior.
Typically segmentation methods may include:
- Geographic (such as city, country, regions, or territories)
- Demographic (such as age, gender, education history, or socioeconomic status)
- Behavioral (how they interact with you and your products/services)
- Consumption (related to where or how they consume media)
This type of data – zero-party data – can be compelling, offering a detailed insight into customer behavior. It is an effective way to create personalized experiences that drive loyalty, engagement, and long-term customer relationships. By understanding customer preferences through careful segmentation, businesses can deliver targeted services, increase conversion rates and retain more customers in the long run.
2. Utilize customer feedback
A simple yet often overlooked method for garnering feedback is to ask customers for reviews. Companies must understand that reviews provide valuable insights to help them better understand their customers and take appropriate action. Product or Service reviews are helpful in industries such as hospitality or e-commerce, but direct customer feedback can be incredibly beneficial for organizations in any sector.
Reviews act as the “voice of the customer,” By responding to these comments, a company can create more trust between themselves and their customers, improve customer satisfaction levels, drive advantage over competitors and even enhance their brand’s reputation.
The qualitative nature of feedback in review format is an effective way to spot any issues before they become serious problems and enables businesses to take corrective measures quickly. Moreover, engaging customers through reviews helps build relationships, leading to greater loyalty, higher purchase rates, and longer-term revenue growth.
3. Leverage your other first-party data
In addition to your CRM data, several other marketing and engagement platforms can be used to collect valuable customer data.
These may include Google Analytics, Social Media Platforms, chat tools, and contact requests.
The analytical data that can be harvested from such tools could help give you valuable insights about:
- How people found your website in the first place
- What products or services are they most interested in
- What marketing messages have they already been exposed to
- What links or call-to-actions have they clicked
Moreover, this type of data from Google Analytics can often be sliced into further segments for a more detailed level of analysis that helps companies identify areas of improvement and develop strategies for customer retention and growth.
4. Use your existing internal knowledge
Many businesses are split into various departments, and these departments often have different perspectives concerning their customers’ needs. Gathering insights about your customers from internal teams can be incredibly beneficial as it allows you to develop a comprehensive view of the customer and their requirements.
Sales teams may have more significant insights into customer needs, while marketing teams will likely understand how customers respond to different content or visual stimulus. On the other hand, Account Management and Customer Success teams might possess an even more intimate understanding of the customer’s day-to-day needs.
By leveraging all the available insights from across multiple departments, companies can capture a more rounded picture of their target audience and create better strategies to meet their customers’ needs, and deliver quality experiences that generate loyalty and growth in the long run.
5. Develop your customer personas or buyer profiles
Once you have developed a comprehensive view of your target audience and identified the customer profile types you are interested in targeting, it’s time to start thinking about customer personas. A persona is a fictionalized version of your average customer, created by gathering and analyzing all available data points. It helps bring the customer to life, capturing their motivations, desires, and needs, and provides teams with a clear understanding of who they are targeting.
Personas should be detailed enough to accurately reflect the demographic you’re dealing with and include age, gender, occupation, income, location, and interests. You may also want to note how customers usually interact with your company and how they prefer to be communicated with – e.g., by email or social media.
Further research can then be conducted on each persona – such as what makes them tick and what content they are likely to engage with – to create more innovative campaigns that appeal directly to each segment. By doing this, you can ensure maximum impact from any marketing efforts!
Customer analysis should be conducted regularly to stay ahead of the curve. Doing so will ensure that your business is always aligned with current customer preferences and demands while helping you focus your efforts where they can generate the most impactful results.
An up-to-date understanding of customers’ motivations, needs, and desires provides teams with a clear framework to develop their strategies and successfully engage their target audience. Identifying who your customer base is composed of can provide invaluable insight into how you should develop relationships with them and inform decisions about the services and content you create for them.
Ultimately, being aware of ever-changing consumer trends and applying them throughout the customer journey can increase your business’s visibility amongst prospective customers, help build trust and guarantee satisfaction from existing customers.
Subscribe for more great marketing content 💌
Subscribe now for exclusive content from imd.

They say that knowledge is power. This is especially true in the business world. The more information you have about your competitors, your customers, and the marketplace at large, the better you can tailor your goods and services accordingly. Information about your own business metrics, like sales figures and performance data, can also help you […]

Digital business strategies ensure that businesses keep up with the industry yet some people still doubt its efficacy. When considering the benefits of implementing a digital business strategy, it’s important to look at all aspects. Despite these definitions, some questions still remain. This article provides detailed information on how increasing your company’s use of technology […]

Planning is an important part of most people’s days. Even if you’re the most driven person alive, it’s easy to get sidetracked if you don’t have an action plan. Maybe you need to train for a marathon and sort the mail, but you binge-watch a new TV show instead. The next day, you’re behind on […]

Successful business is about more than just a “rinse and repeat” of what you’ve always done. As a business leader, you need to make strategic decisions, diagnose and treat issues within your company, and implement needed changes. How can you make these kinds of decisions with confidence? A customer journey map is a powerful tool […]
Customer Analysis
What is a customer analysis.
In many ways, customer analysis is the most important piece of your business plan. In order for your business to be successful, you must be able to demonstrate who will buy your products or services. Be sure to identify your customer segments and how your business will meet their specific needs.
Navigation:
- Step-By-Step Checklist
- Find Demographic Data
- Library Business Research Resources
- Public Opinion Polls
Step-By-Step Checklist
Begin with a concise overview of your industry. You can reiterate this from your Industry Analysis.
Define your prospects on a measurable level. Describe the demographics of your customers including their age, sex, race, occupation, household income, rent vs. own, postal code, population, spending habits and number in household, where they are located, etc. Be sure to cite all of your sources.
Describe changes over time and projected changes in the future.
Describe your customers' behavior. Consider how they make decisions and who in the household makes which decisions. Determine whether they respond to price, loyalty, quality, technology, reliability or trends. Divide your market into segments, assign value to each segment, and decide how to best approach each segment. Be sure to cite all of your sources.
Use your Competitive Analysis to provide an overview of your competition.
Use this information about your industry, customer prospects and competitors to identify gaps in the market.
Identify partners through the same research methods used for your industry analysis.
Find Demographic Data:
Census Profile - Statistics Canada Provides Canadian community profiles from the latest Census of Canada. These profiles are very useful for comparing statistics on different municipalities or regional districts. Includes details on family characteristics, primary language, mobility, educational attainment, marital status, labour force activity, earnings, and mode of transportation to work.
Find latest data from the 2016 Census
Thanks to Catie Sahadath at the University of Ottawa Libraries for building this widget.
Market Research Handbook - Statistics Canada A comprehensive source of socio-economic statistics. Data includes profiles of key industries, including the small business sector, as well as of consumers in all the provinces and in 45 major cities across Canada. Also includes information on international trade data, households, families, and selected economic indicators. The Market Research Handbook was published annually until 2008 but is now discontinued. A copy of the 2008 version in PDF format is available on their website.
Socio-Economic Profiles - BC Stats The socio-economic profiles consist of charts and tables for the various regional districts, health areas, college regions and school districts. Each region contains a map, demographic profile, economic hardship, labour market structure, education concerns, crime, health problems, children at risk, and youth at risk. The profiles are presented in a format that allows comparison to other regions in the province and to BC overall.
GeoSearch | Statistics Canada Use this tool for map views of census demographic and thematic data.
Search or browse all NAICS or SIC codes on the NAICS Association website . Some NAICS codes are different in Canada — you can search by keyword or browse Canadian NAICS codes at Statistics Canada or Canadian Industry Statistics. To search for a SIC code using a NAICS code and vice versa, use the NAICS & SIC Crosswalks.
For more information about planning your industry research, including identifying your industry codes, check out the video tutorial for Module 3: Planning Your Industry Research .
Library Business Research Resources:
Business resources at academic libraries .
Colleges and Universities with business programs will have useful business collections you may be able to get access to through their academic library. Often these academic libraries can provide the general public with access to their collections, which include electronic resources like databases and e-books. For example, they could have alumni or community cards, and can provide temporary "guest" passes in certain situations. Contact your local college or university library to see what they can provide. Please note: you probably will not get access to their electronic resources with remote access.
UBC Library Business Databases
How to access: If you are a UBC student, staff, faculty or in-person library visitor you may have access to business databases through the David Lam Management Research Library and Canaccord Learning Commons through the links below.
Full Listing By Title or Full Listing By Subject
There are two different ways to identify databases: Use "by title" if you already know the name; otherwise you can search the list "by subject" to find starting places for undertaking market research, finding articles or researching companies. To learn more about how you can access library resources if you are a community user or temporary visitor, check out the UBC Library Community Users & Visitors Guide . Community users and temporary visitors may have additional access restrictions to specific databases because of license agreements.
Discovering where you can access the information you need to complete your research can be tricky. Below, we have a few examples of potential sources that collect the type of information you will need.
- Canadian Advertising Rates and Data
- Vividata (formerly "Print Measurement Bureau")
- Roper Center for Public Opinion
Public Opinion Polls:
Gallup Search this website for news releases and additional resources from Gallup.
Ipsos Links to Canadian, U.S. and international polls. Includes polls on consumer goods.
Note: If possible, it is an excellent idea to conduct some primary market research on your customers. You can conduct focus groups, customer satisfaction measurements, field testing, etc.
Now you're ready to start writing your business plan !
How to make a business plan
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents

Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated July 29, 2024

Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
Related Articles

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Business Plan Example and Template
Learn how to create a business plan
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing .

A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all the important business plan elements. Typically, it should present whatever information an investor or financial institution expects to see before providing financing to a business.
Contents of a Business Plan
A business plan should be structured in a way that it contains all the important information that investors are looking for. Here are the main sections of a business plan:
1. Title Page
The title page captures the legal information of the business, which includes the registered business name, physical address, phone number, email address, date, and the company logo.
2. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the most important section because it is the first section that investors and bankers see when they open the business plan. It provides a summary of the entire business plan. It should be written last to ensure that you don’t leave any details out. It must be short and to the point, and it should capture the reader’s attention. The executive summary should not exceed two pages.
3. Industry Overview
The industry overview section provides information about the specific industry that the business operates in. Some of the information provided in this section includes major competitors, industry trends, and estimated revenues. It also shows the company’s position in the industry and how it will compete in the market against other major players.
4. Market Analysis and Competition
The market analysis section details the target market for the company’s product offerings. This section confirms that the company understands the market and that it has already analyzed the existing market to determine that there is adequate demand to support its proposed business model.
Market analysis includes information about the target market’s demographics , geographical location, consumer behavior, and market needs. The company can present numbers and sources to give an overview of the target market size.
A business can choose to consolidate the market analysis and competition analysis into one section or present them as two separate sections.
5. Sales and Marketing Plan
The sales and marketing plan details how the company plans to sell its products to the target market. It attempts to present the business’s unique selling proposition and the channels it will use to sell its goods and services. It details the company’s advertising and promotion activities, pricing strategy, sales and distribution methods, and after-sales support.
6. Management Plan
The management plan provides an outline of the company’s legal structure, its management team, and internal and external human resource requirements. It should list the number of employees that will be needed and the remuneration to be paid to each of the employees.
Any external professionals, such as lawyers, valuers, architects, and consultants, that the company will need should also be included. If the company intends to use the business plan to source funding from investors, it should list the members of the executive team, as well as the members of the advisory board.
7. Operating Plan
The operating plan provides an overview of the company’s physical requirements, such as office space, machinery, labor, supplies, and inventory . For a business that requires custom warehouses and specialized equipment, the operating plan will be more detailed, as compared to, say, a home-based consulting business. If the business plan is for a manufacturing company, it will include information on raw material requirements and the supply chain.
8. Financial Plan
The financial plan is an important section that will often determine whether the business will obtain required financing from financial institutions, investors, or venture capitalists. It should demonstrate that the proposed business is viable and will return enough revenues to be able to meet its financial obligations. Some of the information contained in the financial plan includes a projected income statement , balance sheet, and cash flow.
9. Appendices and Exhibits
The appendices and exhibits part is the last section of a business plan. It includes any additional information that banks and investors may be interested in or that adds credibility to the business. Some of the information that may be included in the appendices section includes office/building plans, detailed market research , products/services offering information, marketing brochures, and credit histories of the promoters.
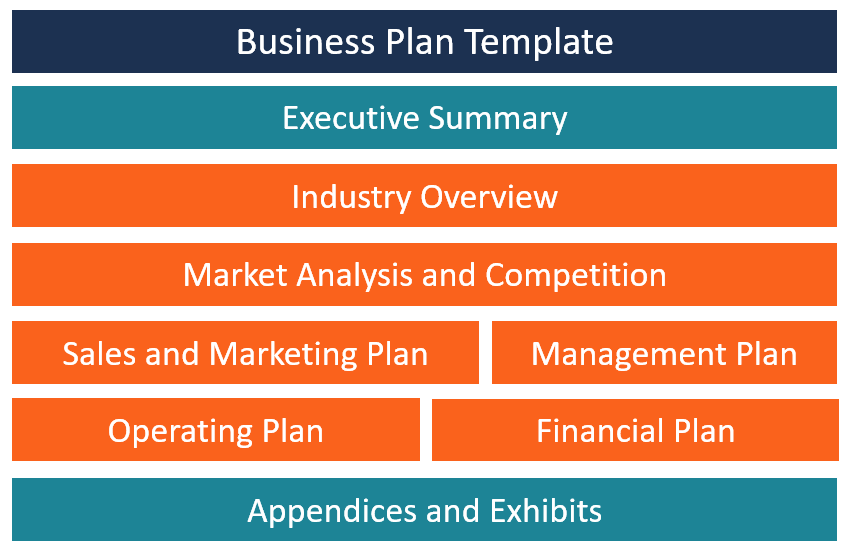
Business Plan Template
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan:
Section 1: Executive Summary
- Present the company’s mission.
- Describe the company’s product and/or service offerings.
- Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
- Summarize the industry competition and how the company will capture a share of the available market.
- Give a summary of the operational plan, such as inventory, office and labor, and equipment requirements.
Section 2: Industry Overview
- Describe the company’s position in the industry.
- Describe the existing competition and the major players in the industry.
- Provide information about the industry that the business will operate in, estimated revenues, industry trends, government influences, as well as the demographics of the target market.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
- Define your target market, their needs, and their geographical location.
- Describe the size of the market, the units of the company’s products that potential customers may buy, and the market changes that may occur due to overall economic changes.
- Give an overview of the estimated sales volume vis-à-vis what competitors sell.
- Give a plan on how the company plans to combat the existing competition to gain and retain market share.
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
- Describe the products that the company will offer for sale and its unique selling proposition.
- List the different advertising platforms that the business will use to get its message to customers.
- Describe how the business plans to price its products in a way that allows it to make a profit.
- Give details on how the company’s products will be distributed to the target market and the shipping method.
Section 5: Management Plan
- Describe the organizational structure of the company.
- List the owners of the company and their ownership percentages.
- List the key executives, their roles, and remuneration.
- List any internal and external professionals that the company plans to hire, and how they will be compensated.
- Include a list of the members of the advisory board, if available.
Section 6: Operating Plan
- Describe the location of the business, including office and warehouse requirements.
- Describe the labor requirement of the company. Outline the number of staff that the company needs, their roles, skills training needed, and employee tenures (full-time or part-time).
- Describe the manufacturing process, and the time it will take to produce one unit of a product.
- Describe the equipment and machinery requirements, and if the company will lease or purchase equipment and machinery, and the related costs that the company estimates it will incur.
- Provide a list of raw material requirements, how they will be sourced, and the main suppliers that will supply the required inputs.
Section 7: Financial Plan
- Describe the financial projections of the company, by including the projected income statement, projected cash flow statement, and the balance sheet projection.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
- Quotes of building and machinery leases
- Proposed office and warehouse plan
- Market research and a summary of the target market
- Credit information of the owners
- List of product and/or services
Related Readings
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Business Plans. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful:
- Corporate Structure
- Three Financial Statements
- Business Model Canvas Examples
- See all management & strategy resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
8 Components of a Business Plan
Back to Business Plans
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on February 19, 2023 Updated on February 27, 2024

A key part of the business startup process is putting together a business plan , particularly if you’d like to raise capital. It’s not going to be easy, but it’s absolutely essential, and an invaluable learning tool.
Creating a business plan early helps you think through every aspect of your business, from operations and financing to growth and vision. In the end, the knowledge you’ll gain could be the difference between success and failure.
But what exactly does a business plan consist of? There are eight essential components, all of which are detailed in this handy guide.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary opens your business plan , but it’s the section you’ll write last. It summarizes the key points and highlights the most important aspects of your plan. Often investors and lenders will only read the executive summary; if it doesn’t capture their interest they’ll stop reading, so it’s important to make it as compelling as possible.
The components touched upon should include:
- The business opportunity – what problem are you solving in the market?
- Your idea, meaning the product or service you’re planning to offer, and why it solves the problem in the market better than other solutions.
- The history of the business so far – what have you done to this point? When you’re just getting started, this may be nothing more than coming up with the idea, choosing a business name , and forming a business entity.
- A summary of the industry, market size, your target customers, and the competition.
- A strong statement about how your company is going to stand out in the market – what will be your competitive advantage?
- A list of specific goals that you plan to achieve in the short term, such as developing your product, launching a marketing campaign, or hiring a key person.
- A summary of your financial plan including cost and sales projections and a break-even analysis.
- A summary of your management team, their roles, and the relevant experience that they have to serve in those roles.
- Your “ask”, if applicable, meaning what you’re requesting from the investor or lender. You’ll include the amount you’d like and how it will be spent, such as “We are seeking $50,000 in seed funding to develop our beta product”.
Remember that if you’re seeking capital, the executive summary could make or break your venture. Take your time and make sure it illustrates how your business is unique in the market and why you’ll succeed.
The executive summary should be no more than two pages long, so it’s important to capture the reader’s interest from the start.
- 2. Company Description/Overview
In this section, you’ll detail your full company history, such as how you came up with the idea for your business and any milestones or achievements.
You’ll also include your mission and vision statements. A mission statement explains what you’d like your business to achieve, its driving force, while a vision statement lays out your long-term plan in terms of growth.
A mission statement might be “Our company aims to make life easier for business owners with intuitive payroll software”, while a vision statement could be “Our objective is to become the go-to comprehensive HR software provider for companies around the globe.”
In this section, you’ll want to list your objectives – specific short-term goals. Examples might include “complete initial product development by ‘date’” or “hire two qualified sales people” or “launch the first version of the product”.
It’s best to divide this section into subsections – company history, mission and vision, and objectives.
3. Products/Services Offered
Here you’ll go into detail about what you’re offering, how it solves a problem in the market, and how it’s unique. Don’t be afraid to share information that is proprietary – investors and lenders are not out to steal your ideas.
Also specify how your product is developed or sourced. Are you manufacturing it or does it require technical development? Are you purchasing a product from a manufacturer or wholesaler?
You’ll also want to specify how you’ll sell your product or service. Will it be a subscription service or a one time purchase? What is your target pricing? On what channels do you plan to sell your product or service, such as online or by direct sales in a store?
Basically, you’re describing what you’re going to sell and how you’ll make money.
- 4. Market Analysis
The market analysis is where you’re going to spend most of your time because it involves a lot of research. You should divide it into four sections.
Industry analysis
You’ll want to find out exactly what’s happening in your industry, such as its growth rate, market size, and any specific trends that are occurring. Where is the industry predicted to be in 10 years? Cite your sources where you can by providing links.
Then describe your company’s place in the market. Is your product going to fit a certain niche? Is there a sub-industry your company will fit within? How will you keep up with industry changes?
Competitor analysis
Now you’ll dig into your competition. Detail your main competitors and how they differentiate themselves in the market. For example, one competitor may advertise convenience while another may tout superior quality. Also highlight your competitors’ weaknesses.
Next, describe how you’ll stand out. Detail your competitive advantages and how you’ll sustain them. This section is extremely important and will be a focus for investors and lenders.
Target market analysis
Here you’ll describe your target market and whether it’s different from your competitors’. For example, maybe you have a younger demographic in mind?
You’ll need to know more about your target market than demographics, though. You’ll want to explain the needs and wants of your ideal customers, how your offering solves their problem, and why they will choose your company.
You should also lay out where you’ll find them, where to place your marketing and where to sell your products. Learning this kind of detail requires going to the source – your potential customers. You can do online surveys or even in-person focus groups.
Your goal will be to uncover as much about these people as possible. When you start selling, you’ll want to keep learning about your customers. You may end up selling to a different target market than you originally thought, which could lead to a marketing shift.
SWOT analysis
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and it’s one of the more common and helpful business planning tools.
First describe all the specific strengths of your company, such as the quality of your product or some unique feature, such as the experience of your management team. Talk about the elements that will make your company successful.
Next, acknowledge and explore possible weaknesses. You can’t say “none”, because no company is perfect, especially at the start. Maybe you lack funds or face a massive competitor. Whatever it is, detail how you will surmount this hurdle.
Next, talk about the opportunities your company has in the market. Perhaps you’re going to target an underserved segment, or have a technology plan that will help you surge past the competition.
Finally, examine potential threats. It could be a competitor that might try to replicate your product or rapidly advancing technology in your industry. Again, discuss your plans to handle such threats if they come to pass.
5. Marketing and Sales Strategies
Now it’s time to explain how you’re going to find potential customers and convert them into paying customers.
Marketing and advertising plan
When you did your target market analysis, you should have learned a lot about your potential customers, including where to find them. This should help you determine where to advertise.
Maybe you found that your target customers favor TikTok over Instagram and decided to spend more marketing dollars on TikTok. Detail all the marketing channels you plan to use and why.
Your target market analysis should also have given you information about what kind of message will resonate with your target customers. You should understand their needs and wants and how your product solves their problem, then convey that in your marketing.
Start by creating a value proposition, which should be no more than two sentences long and answer the following questions:
- What are you offering
- Whose problem does it solve
- What problem does it solve
- What benefits does it provide
- How is it better than competitor products
An example might be “Payroll software that will handle all the payroll needs of small business owners, making life easier for less.”
Whatever your value proposition, it should be at the heart of all of your marketing.
Sales strategy and tactics
Your sales strategy is a vision to persuade customers to buy, including where you’ll sell and how. For example, you may plan to sell only on your own website, or you may sell from both a physical location and online. On the other hand, you may have a sales team that will make direct sales calls to potential customers, which is more common in business-to-business sales.
Sales tactics are more about how you’re going to get them to buy after they reach your sales channel. Even when selling online, you need something on your site that’s going to get them to go from a site visitor to a paying customer.
By the same token, if you’re going to have a sales team making direct sales, what message are they going to deliver that will entice a sale? It’s best for sales tactics to focus on the customer’s pain point and what value you’re bringing to the table, rather than being aggressively promotional about the greatness of your product and your business.
Pricing strategy
Pricing is not an exact science and should depend on several factors. First, consider how you want your product or service to be perceived in the market. If your differentiator is to be the lowest price, position your company as the “discount” option. Think Walmart, and price your products lower than the competition.
If, on the other hand, you want to be the Mercedes of the market, then you’ll position your product as the luxury option. Of course you’ll have to back this up with superior quality, but being the luxury option allows you to command higher prices.
You can, of course, fall somewhere in the middle, but the point is that pricing is a matter of perception. How you position your product in the market compared to the competition is a big factor in determining your price.
Of course, you’ll have to consider your costs, as well as competitor prices. Obviously, your prices must cover your costs and allow you to make a good profit margin.
Whatever pricing strategy you choose, you’ll justify it in this section of your plan.
- 6. Operations and Management
This section is the real nuts and bolts of your business – how it operates on a day-to-day basis and who is operating it. Again, this section should be divided into subsections.
Operational plan
Your plan of operations should be specific , detailed and mainly logistical. Who will be doing what on a daily, weekly, and monthly basis? How will the business be managed and how will quality be assured? Be sure to detail your suppliers and how and when you’ll order raw materials.
This should also include the roles that will be filled and the various processes that will be part of everyday business operations . Just consider all the critical functions that must be handled for your business to be able to operate on an ongoing basis.
Technology plan
If your product involves technical development, you’ll describe your tech development plan with specific goals and milestones. The plan will also include how many people will be working on this development, and what needs to be done for goals to be met.
If your company is not a technology company, you’ll describe what technologies you plan to use to run your business or make your business more efficient. It could be process automation software, payroll software, or just laptops and tablets for your staff.
Management and organizational structure
Now you’ll describe who’s running the show. It may be just you when you’re starting out, so you’ll detail what your role will be and summarize your background. You’ll also go into detail about any managers that you plan to hire and when that will occur.
Essentially, you’re explaining your management structure and detailing why your strategy will enable smooth and efficient operations.
Ideally, at some point, you’ll have an organizational structure that is a hierarchy of your staff. Describe what you envision your organizational structure to be.
Personnel plan
Detail who you’ve hired or plan to hire and for which roles. For example, you might have a developer, two sales people, and one customer service representative.
Describe each role and what qualifications are needed to perform those roles.
- 7. Financial Plan
Now, you’ll enter the dreaded world of finance. Many entrepreneurs struggle with this part, so you might want to engage a financial professional to help you. A financial plan has five key elements.
Startup Costs
Detail in a spreadsheet every cost you’ll incur before you open your doors. This should determine how much capital you’ll need to launch your business.
Financial projections
Creating financial projections, like many facets of business, is not an exact science. If your company has no history, financial projections can only be an educated guess.
First, come up with realistic sales projections. How much do you expect to sell each month? Lay out at least three years of sales projections, detailing monthly sales growth for the first year, then annually thereafter.
Calculate your monthly costs, keeping in mind that some costs will grow along with sales.
Once you have your numbers projected and calculated, use them to create these three key financial statements:
- Profit and Loss Statement , also known as an income statement. This shows projected revenue and lists all costs, which are then deducted to show net profit or loss.
- Cash Flow Statement. This shows how much cash you have on hand at any given time. It will have a starting balance, projections of cash coming in, and cash going out, which will be used to calculate cash on hand at the end of the reporting period.
- Balance Sheet. This shows the net worth of the business, which is the assets of the business minus debts. Assets include equipment, cash, accounts receivables, inventory, and more. Debts include outstanding loan balances and accounts payable.
You’ll need monthly projected versions of each statement for the first year, then annual projections for the following two years.
Break-even analysis
The break-even point for your business is when costs and revenue are equal. Most startups operate at a loss for a period of time before they break even and start to make a profit. Your break-even analysis will project when your break-even point will occur, and will be informed by your profit and loss statement.
Funding requirements and sources
Lay out the funding you’ll need, when, and where you’ll get it. You’ll also explain what those funds will be used for at various points. If you’re in a high growth industry that can attract investors, you’ll likely need various rounds of funding to launch and grow.
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
KPIs measure your company’s performance and can determine success. Many entrepreneurs only focus on the bottom line, but measuring specific KPIs helps find areas of improvement. Every business has certain crucial metrics.
If you sell only online, one of your key metrics might be your visitor conversion rate. You might do an analysis to learn why just one out of ten site visitors makes a purchase.
Perhaps the purchase process is too complicated or your product descriptions are vague. The point is, learning why your conversion rate is low gives you a chance to improve it and boost sales.
8. Appendices
In the appendices, you can attach documents such as manager resumes or any other documents that support your business plan.
As you can see, a business plan has many components, so it’s not an afternoon project. It will likely take you several weeks and a great deal of work to complete. Unless you’re a finance guru, you may also want some help from a financial professional.
Keep in mind that for a small business owner, there may be no better learning experience than writing a detailed and compelling business plan. It shouldn’t be viewed as a hassle, but as an opportunity!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Executive Summary
- Products/Services Offered
- Marketing and Sales Strategies
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.
Crafting the Perfect Business Plan: A Deep Dive with Upmetrics’ Vinay Kevadiya
Carolyn Young
Published on October 13, 2023
In the first segment of our conversation with Vinay Kevadiya, the visionary behind Upmetrics, we explored the platform’s origins and itsunique ...

LivePlan Software Review: Features, Cost, Pros & Cons
Published on September 15, 2023
When you’re starting a business, a business plan is essential whether you’re going to obtain financing or not. Creating a business plan helpsyou ...

What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix?
Published on September 13, 2023
Launching a business involves countless tasks, and one of the crucial early hurdles is writing a business plan. Many entrepreneurs who aren’tlooki ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

How To Write a Business Plan in 9 Steps (2024)
Business plans aren’t just for entrepreneurs who need to secure funding—they can help you plan and evaluate new ideas or growth plans, too. Find out how to write a business plan and get the most out of the process in this comprehensive guide.

A great business plan can help you clarify your strategy, identify potential roadblocks, determine necessary resources, and evaluate the viability of your idea and growth plan before you start a business .
Not every successful business launches with a formal business plan, but many founders find value in taking time to step back, research their idea and the market they’re looking to enter, and understand the scope and the strategy behind their tactics. That’s where writing a business plan comes in.
Learn how to write a business plan with a step-by-step guide, get tips for getting the most of your plan, and see real business plan examples to inspire you.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines a company's goals, strategies for achieving them, and the time frame for their achievement. It covers aspects like market analysis , financial projections, and organizational structure, serving as a roadmap for business growth and a tool to secure funding.
Often, financial institutions and investors need to see a business plan before funding any project. Even if you don’t plan to seek outside funding, a well-crafted plan becomes the guidance for your business as it scales.
How to write a business plan in 9 steps
- Draft an executive summary.
- Write a company description.
- Perform a market analysis.
- Outline the management and organization.
- List your products and services.
- Perform customer segmentation.
- Define a marketing plan.
- Provide a logistics and operations plan.
- Make a financial plan.
Few things are more intimidating than a blank page. Starting your business plan with a structured outline and key elements for what you’ll include in each section is the best first step you can take.
Since an outline is such an important step in the process of writing a business plan, we’ve put together a high-level overview to get you started (and avoid the terror of facing a blank page).
Once you have your business plan template in place, it’s time to fill it in. We’ve broken it down by section to help you build your plan step by step.
1. Draft an executive summary.
A good executive summary is one of the most crucial sections of your plan—it’s also the last section you should write.
The executive summary distills everything that follows and gives time-crunched reviewers (e.g., potential investors and lenders) a high-level overview of your business that persuades them to read further.
Again, it’s a summary, so highlight the key points you’ve uncovered while writing your plan. If you’re writing for your own planning purposes, you can skip the summary altogether—although you might want to give it a try anyway, just for practice.

An executive summary shouldn’t exceed one page. Admittedly, that space constraint can make squeezing in all of the salient information a bit stressful—but it’s not impossible. Your business plan’s executive summary should include:
- Business concept. What does your business do?
- Business goals and vision. What does your business want to do?
- Product description and differentiation. What do you sell, and why is it different?
- Target market. Who do you sell to?
- Marketing strategy. How do you plan on reaching your customers?
- Current financial state. What do you currently earn in revenue?
- Projected financial state. What do you foresee earning in revenue?
- The ask. How much money are you asking for?
- The team. Who’s involved in the business?
2. Write a company description.
This section of your business plan should answer two fundamental questions: who are you, and what do you plan to do?
Answering these questions with a company description provides an introduction to why you’re in business, why you’re different, what you have going for you, and why you’re a good investment.
For example, clean makeup brand Saie shares a letter from its founder on the company’s mission and why it exists.

Clarifying these details is still a useful exercise, even if you’re the only person who’s going to see them. It’s an opportunity to put to paper some of the more intangible facets of your business, like your principles, ideals, and cultural philosophies.
Here are some of the components you should include in your company description:
- Your business structure (Are you a sole proprietorship, general partnership, limited partnership, or incorporated company?)
- Your business model
- Your industry
- Your business’s vision, mission, and value proposition
- Background information on your business or its history
- Business objectives, both short and long term
- Your team, including key personnel and their salaries
Brand values and goals
To define your brand values , think about all the people your company is accountable to, including owners, employees, suppliers, customers, and investors. Now consider how you’d like to conduct business with each of them. As you make a list, your core values should start to emerge.
Your company description should also include both short- and long-term goals. Short-term goals, generally, should be achievable within the next year, while one to five years is a good window for long-term goals. Make sure your goal setting includes SMART goals : specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-bound.
Vision and mission statements
Once you know your values, you can write a mission statement . Your statement should explain, in a convincing manner, why your business exists, and should be no longer than a single sentence.
Next, craft your vision statement : What impact do you envision your business having on the world once you’ve achieved your vision? Phrase this impact as an assertion—begin the statement with “We will” and you’ll be off to a great start. Your vision statement, unlike your mission statement, can be longer than a single sentence, but try to keep it to three at most. The best vision statements are concise.
3. Perform a market analysis.
No matter what type of business you start, it’s no exaggeration to say your market can make or break it. Choose the right market for your products—one with plenty of customers who understand and need your product—and you’ll have a head start on success. If you choose the wrong market, or the right market at the wrong time, you may find yourself struggling for each sale.
Market analysis is a key section of your business plan, whether or not you ever intend for anyone else to read it.
This is why market research and analysis is a key section of your business plan, whether or not you ever intend for anyone else to read it. It should include an overview of how big you estimate the market is for your products, an analysis of your business’s position in the market, and an overview of the competitive landscape. Thorough research supporting your conclusions is important both to persuade investors and to validate your own assumptions as you work through your plan.
Here is an example to illustrate how to approach this section:

How big is your potential market?
The potential market is an estimate of how many people need your product. While it’s exciting to imagine sky-high sales figures, you’ll want to use as much relevant independent data as possible to validate your estimated potential market.
Since this can be a daunting process, here are some general tips to help you begin your research:
- Understand your ideal customer profile. Look for government data about the size of your target market , learn where they live, what social channels they use, and their shopping habits.
- Research relevant industry trends and trajectory. Explore consumer trends and product trends in your industry by looking at Google Trends, trade publications, and influencers in the space.
- Make informed guesses. You’ll never have perfect, complete information about your total addressable market. Your goal is to base your estimates on as many verifiable data points as necessary.
Some sources to consult for market data include government statistics offices, industry associations, academic research, and respected news outlets covering your industry.
Read more: What is a Marketing Analysis? 3 Steps Every Business Should Follow
SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis looks at your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. What are the best things about your company? What are you not so good at? What market or industry shifts can you take advantage of and turn into opportunities? Are there external factors threatening your ability to succeed?
SWOT is often depicted in a grid or visual way. With this visual presentation, your reader can quickly see the factors that may impact your business and determine your competitive advantage in the market.
Competitive analysis
There are three overarching factors you can use to differentiate your business in the face of competition:
- Cost leadership. You have the capacity to maximize profits by offering lower prices than the majority of your competitors. Examples include companies like Mejuri and Endy .
- Differentiation. Your product or service offers something distinct from the current cost leaders in your industry and banks on standing out based on your uniqueness. Think of companies like Knix and QALO .
- Segmentation. You focus on a very specific, or niche, target market, and aim to build traction with a smaller audience before moving on to a broader market. Companies like TomboyX and Heyday Footwear are great examples of this strategy.
To understand which is the best fit, you’ll need to understand your business as well as the competitive landscape.
You’ll always have competition in the market, even with an innovative product, so it’s important to include a competitive overview in your business plan. If you’re entering an established market, include a list of a few companies you consider direct competitors and explain how you plan to differentiate your products and business from theirs.
For example, if you’re selling jewelry , your competitive differentiation could be that, unlike many high-end competitors, you donate a percentage of your profits to a notable charity or pass savings on to your customers.
If you’re entering a market where you can’t easily identify direct competitors, consider your indirect competitors—companies offering products that are substitutes for yours. For example, if you’re selling an innovative new piece of kitchen equipment, it’s too easy to say that because your product is new, you have no competition. Consider what your potential customers are doing to solve the same problems.
4. Outline the management and organization.

If you have a management team, use an organizational chart to show your company’s internal structure, including the roles, responsibilities, and relationships between people in your chart. Communicate how each person will contribute to the success of your startup.
5. List your products and services.
Your products or services will feature prominently in most areas of your business plan, but it’s important to provide a section that outlines key details about them for interested readers.
If you sell many items, you can include more general information on each of your product lines. If you only sell a few, provide additional information on each. For example, bag shop BAGGU sells a large selection of different types of bags, in addition to home goods and other accessories. Its business plan would list out those categories and key details about the products within each.

Describe new products you’ll launch in the near future and any intellectual property you own. Express how they’ll improve profitability. It’s also important to note where products are coming from—handmade crafts are sourced differently than trending products for a dropshipping business, for instance.
6. Perform customer segmentation.

To give a holistic overview of your ideal customer, describe a number of general and specific demographic characteristics. Customer segmentation often includes:
- Where they live.
- Their age range.
- Their level of education.
- Some common behavior patterns.
- How they spend their free time.
- Where they work.
- What technology they use.
- How much they earn.
- Where they’re commonly employed.
- Their values, beliefs, or opinions.
This information will vary based on what you’re selling, but you should be specific enough that it’s unquestionably clear who you’re trying to reach—and more importantly, why you’ve made the choices you have based on who your customers are and what they value.
For example, a college student has different interests, shopping habits, and pricing sensitivity than a 50-year-old executive at a Fortune 500 company. Your business plan and decisions would look very different based on which one was your ideal customer.
Put your customer data to work with Shopify’s customer segmentation
Shopify’s built-in segmentation tools help you discover insights about your customers, build segments as targeted as your marketing plans with filters based on your customers’ demographic and behavioral data, and drive sales with timely and personalized emails.
7. Define a marketing plan.

If you’re planning to invest heavily in Instagram marketing or TikTok ads , for example, it might make sense to include whether Instagram and TikTok are a leading platform for your audience—if it’s not, that might be a sign to rethink your marketing plan.
Market your business with Shopify’s customer marketing tools
Shopify has everything you need to capture more leads, send email campaigns, automate key marketing moments, segment your customers, and analyze your results. Plus, it’s all free for your first 10,000 emails sent per month.
Most marketing plans include information on four key subjects. How much detail you present on each will depend on both your business and your plan’s audience.
- Price: How much do your products cost, and why have you made that decision?
- Product: What are you selling and how do you differentiate it in the market?
- Promotion: How will you get your products in front of your ideal customer?
- Place: Where will you sell your products? On what channels and in which markets?
Promotion may be the bulk of your plan since you can more readily dive into tactical details, but the other three areas should be covered at least briefly—each is an important strategic lever in your marketing mix.
Here is an example of a marketing plan for a new business:

8. Provide a logistics and operations plan.
Logistics and operations are the workflows you’ll implement to make your business idea a reality. If you’re writing a business plan for your own planning purposes, this is still an important section to consider, even though you might not need to include the same level of detail as if you were seeking investment.
Cover all parts of your planned operations, including:
- Suppliers . Where do you get the raw materials you need for production, or where are your products produced?
- Production . Will you make, manufacture, wholesale , or dropship your products? How long does it take to produce your products and get them shipped to you? How will you handle a busy season or an unexpected spike in demand?
- Facilities . Where will you and any team members work? Do you plan to have a physical retail space? If yes, where?
- Equipment . What tools and technology do you require to be up and running? This includes everything from computers to lightbulbs and everything in between.
- Shipping and fulfillment. Will you be handling all the fulfillment tasks in-house, or will you use a third-party fulfillment partner?
- Inventory . How much will you keep on hand, and where will it be stored? How will you ship it to partners if required, and how will you approach inventory management ?
This section should signal to your reader that you’ve got a solid understanding of your supply chain and strong contingency plans in place to cover potential uncertainty. If your reader is you, it should give you a basis to make other important decisions, like how to price your products to cover your estimated costs, and at what point you plan to break even on your initial spending.
9. Make a financial plan.

The level of detail required in your financial plan will depend on your audience and goals, but typically you’ll want to include three major views of your financials: an income statement, a balance sheet, and a cash-flow statement. It also may be appropriate to include financial data and projections.
Here’s a spreadsheet template that includes everything you’ll need to create an income statement, balance sheet, and cash-flow statement, including some sample numbers. You can edit it to reflect projections if needed.
Let’s review the types of financial statements you’ll need.
Income statements
Your income statement is designed to give readers a look at your revenue sources and expenses over a given time period. With those two pieces of information, they can see the all-important bottom line or the profit or loss your business experienced during that time. If you haven’t launched your business yet, you can project future milestones of the same information.
Balance sheets
Your balance sheet offers a look at how much equity you have in your business. On one side, you list all your business assets (what you own), and on the other side, all your liabilities (what you owe). This provides a snapshot of your business’s shareholder equity, which is calculated as:
Assets - Liabilities = Equity
Cash flow statements
Your cash flow statement is similar to your income statement, with one important difference: it takes into account when revenues are collected and when expenses are paid.
When the cash you have coming in is greater than the cash you have going out, your cash flow is positive. When the opposite scenario is true, your cash flow is negative. Ideally, your cash flow statement will help you see when cash is low, when you might have a surplus, and where you might need to have a contingency plan to access funding to keep your business solvent .
It can be especially helpful to forecast your cash-flow statement to identify gaps or negative cash flow and adjust operations as required.
📚 Read more: What Is Cash Flow Management: Template and Examples
Why write a business plan?
Investors rely on business plans to evaluate the feasibility of a business before funding it, which is why business plans are commonly associated with getting a loan.
Business plans also help owners identify areas of weakness before launching, potentially avoiding costly mistakes down the road. “Laying out a business plan helped us identify the ‘unknowns’ and made it easier to spot the gaps where we’d need help or, at the very least, to skill up ourselves,” says Jordan Barnett, owner of Kapow Meggings .
There are several other compelling reasons to consider writing a business plan, including:
- Strategic planning. Writing out your plan is an invaluable exercise for clarifying your ideas and can help you understand the scope of your business, as well as the amount of time, money, and resources you’ll need to get started.
- Evaluating ideas. If you’ve got multiple ideas in mind, a rough business plan for each can help you focus your time and energy on the ones with the highest chance of success.
- Research. To write a business plan, you’ll need to research your ideal customer and your competitors—information that will help you make more strategic decisions.
- Recruiting. Your business plan is one of the easiest ways to communicate your vision to potential new hires and can help build their confidence in the venture, especially if you’re in the early stages of growth.
- Partnerships. If you plan to collaborate with other brands , having a clear overview of your vision, your audience, and your business strategy will make it much easier for them to identify if your business is a good fit for theirs.
- Competitions. There are many business plan competitions offering prizes such as mentorships, grants, or investment capital.
If you’re looking for a structured way to lay out your thoughts and ideas, and to share those ideas with people who can have a big impact on your success, a business plan is an excellent starting point.
Business plan types
Business plan types can span from one page to multiple pages with detailed graphs and reports. There’s no one way to create a business plan. The goal is to convey the most important information about your company for readers.
Common business plans we see include, but are not limited to, the following types:
Traditional business plans
These are the most common business plans. Traditional business plans take longer to write and can be dozens of pages long. Venture capitalist firms and lenders ask for this plan. Traditional business plans may not be necessary if you don’t plan to seek outside funding. That’s where the next type comes in.
Lean business plans
A lean business plan is a shorter version of a traditional business plan. It follows the same format, but only includes the most important information. Businesses use lean business plans to onboard new hires or modify existing plans for a specific target market.
Nonprofit business plans
A nonprofit business plan is for any entity that operates for public or social benefit. It covers everything you’ll find in a traditional business plan, plus a section describing the impact the company plans to make. For example, a speaker and headphone brand that aims to help people with hearing disabilities. Donors often request this plan.
📚 Read more: The Road to Success: Business Plan Examples to Inspire Your Own .
7 tips for creating a small business plan
There are a few best practices when it comes to writing a business plan. While your plan will be unique to your business and goals, keep these tips in mind as you write.
1. Know your audience.
When you know who will be reading your plan—even if you’re just writing it for yourself to clarify your ideas—you can tailor the language and level of detail to them. This can also help you make sure you’re including the most relevant information and figure out when to omit sections that aren’t as impactful.
2. Have a clear goal.
When creating a business plan, you’ll need to put in more work and deliver a more thorough plan if your goal is to secure funding for your business versus working through a plan for yourself or even your team.
3. Invest time in research.
Sections of your business plan will primarily be informed by your ideas and vision, but some of the most crucial information you’ll need requires research from independent sources. This is where you can invest time in understanding who you’re selling to, whether there’s demand for your products, and who else is selling similar products or services.
4. Keep it short and to the point.
No matter who you’re writing for, your business plan should be short and readable—generally no longer than 15 to 20 pages. If you do have additional documents you think may be valuable to your audience and your goals, consider adding them as appendices.
5. Keep the tone, style, and voice consistent.
This is best managed by having a single person write the plan or by allowing time for the plan to be properly edited before distributing it.
6. Use a business plan template.
You can also use a free business plan template to provide a skeleton for writing a plan. These often guide you through each section from financial projects to market research to mission statement ensuring you don’t miss a step.
7. Try business plan software.
Writing a business plan isn’t the easiest task for business owners. But it’s important for anyone starting or expanding a business. Fortunately, there are tools to help with everything from planning, drafting, creating graphics, syncing financial data, and more. Business plan software also has business plan templates and tutorials to help you finish a comprehensive plan in hours, rather than days.
A few curated picks include:
- LivePlan : the most affordable option with samples and templates
- Bizplan : tailored for startups seeking investment
- Go Small Biz : budget-friendly option with industry-specific templates
📚 Read more: 6 Best Business Plan Software to Help Write Your Future
Common mistakes when writing a business plan
Other articles on business plans would never tell you what we’re about to tell you: Your business plan can fail. The last thing you want is for time and effort to go down the drain. Avoid these common mistakes:
- Bad business idea. Sometimes your idea may be too risky for potential investors, too expensive to run, or there’s no market. Aim for small business ideas that require low startup costs.
- No exit strategy. If you don’t show an exit strategy, or a plan for investors to leave the business with maximum profits, you’ll have little luck finding capital.
- Unbalanced teams. A great product is the cost of entry to starting a business. But an incredible team will take it to the top. Unfortunately, many business owners overlook a balanced team. They focus on potential profits, without worrying about how it will be done.
- Missing financial projections. Don’t leave out your balance sheet, cash flow statements, P&L statements, and income statements. Include your break-even analysis and return-on-investment calculations in your financial projections to create a successful business plan.
- Spelling and grammar errors. All the best organizations have an editor review their documents. If someone spots typos while reading your business plan, how can they believe you’ll run a successful company?
Prepare your business plan today

Whether you’re working on starting a new online business idea , building a retail storefront, growing your established business, or purchasing an existing business , you now understand how to write a business plan that suits your business’s goals and needs.
Feature illustration by Rachel Tunstall
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- AliExpress Dropshipping- How to Dropship From AliExpress
- How to Start a Clothing Line in 12 Steps (2024)
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- How To Do Crowdfunding: With Expert Tips and Examples From Successful Campaigns
- How to Start a Candle Business (with Examples)
- What Is Affiliate Marketing and How to Get Started
- Pinterest Marketing 101- How to Promote Your Business on Pinterest
- Getting Started on IG- A Beginner’s Guide to Instagram Marketing
Business plan FAQ
How do i write a business plan.
Learning how to write a business plan is simple if you use a business plan template or business plan software. Typically, a traditional business plan for every new business should have the following components :
- Executive summary
- Company description, including value proposition
- Market analysis and competitive analysis
- Management and organization
- Products and services
- Customer segmentation
- Marketing plan
- Logistics and operations
- Financial plan and financial projections
What is a good business plan?
A good business plan starts with a strong executive summary. It also adequately outlines idea feasibility, target market insights, and the competitive landscape. A business plan template can help businesses be sure to follow the typical format of traditional business plans which include financial projections, details about the management team, and other key elements that venture capital firms and potential investors want to see.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
The three main purposes of a business plan are:
- To clarify your plans for growth
- To understand your financial needs
- To attract funding from investors or secure a business loan
What are the different types of business plans?
The types of business plans include startup, refocusing, internal, annual, strategic, feasibility, operations, growth, and scenario-based. Each type of business plan has a different purpose. Business plan formats include traditional, lean, and nonprofit. Find a business plan template for the type of plan you want to write.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Aug 9, 2024
Aug 8, 2024
Aug 7, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
- Customer service and contact center
9 steps to create a customer service plan
Crafting a customer service plan is a key step to improving customer satisfaction and building loyalty for an organization..

- Sandra Mathis, Microsoft
At the foundation of any successful business is a well-crafted and defined customer service plan that establishes policies and guides about how to handle customer interactions .
Customer service can be a core competitive differentiator in the marketplace and is often the great equalizer for small and medium-sized organizations to compete against their larger counterparts. Its purpose is to establish, maintain and enhance the relationship between a business and its customers.
Benefits of having a customer service plan include the following:
- positive brand reputation;
- improved customer loyalty and retention ;
- results in increased customer profits; and
- improved internal communications.
Follow these nine steps to create an effective customer service plan.
1. Create a customer service strategy
The customer service strategy should include the development of a vision and policy. The vision should identify the type of customer service the organization will use, while the core policies direct how the customer service department operates. Get input from several teams and departments to include various perspectives during development. Multiple perspectives also aid with aligning and embedding the vision and policy across the organization, including expectations and execution.
2. Setting the customer service goals
Goals should be reasonable and identified early. Best practices for setting goals include the following:
- Define specific goals by taking the SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant and Time-Bound) approach, with each goal focused on a single area of the customer's experience.
- Ensure that goals are achievable but still challenging, and identify when they tie back to business objectives.
- Develop a plan, method and frequency to measure goals.
3. Create a customer journey and service design map
Create a customer journey and service design map to clarify the steps to assist the customer. The customer journey should come from a customer-facing perspective and include customer activities, touchpoints and pain points. The service design map should consist of steps from an organizational perspective, such as aligning customer touchpoints, communication channels and interactions between systems and pain points.
This article is part of
Ultimate guide to customer service for businesses
- Which also includes:
- 10 customer service best practices to follow
- 13 customer retention strategies that work
- 5 examples of bad customer service and how to avoid them
Download this entire guide for FREE now!
4. Analyze customer interactions
Use the customer journey and service design maps to assess where to improve the experience . This step includes analyzing customer interactions and answering these questions:
- When in the customer journey do they reach out for assistance? Why do they reach out?
- How often do customers contact the organization? What channels do they use ?
- What were the pros and cons of the customer's experience? This is a good place to use any gathered customer satisfaction .
5. Create an action plan
Taking action on issues should benefit the customer and the service team alike. Creating an action plan begins with setting strategic objectives and then identifying any outstanding issues. Then, develop a detailed plan that defines the actionable steps, due date and who owns the project. The action plan should also identify what constitutes success and how often to measure analytics. Before any work begins, it's essential to get alignment from any other teams involved.
6. Determine KPIs
With goals in place, determine the appropriate metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs) to track. The KPIs provide a look into how well the customer service team is doing. Teams should select and follow a few customer service KPIs from primary and secondary sources.
Primary sources
- Customer satisfaction score, which measures the overall customer satisfaction with a product or service; and
- Net promoter score, which provides insight into customer loyalty and the likelihood of a customer recommending the business to someone else.
At the foundation of any successful business is a well-crafted and defined customer service plan.
Secondary sources and contact center metrics
- Response and hold time;
- First contact resolution;
- Average resolution time;
- Number of issues to be tracked and the nature of issues;
- Active and resolved issues; and
- Customer retention rate.
7. Assess and build a customer service team
Beyond traditional customer service skills , organizations must identify additional skills their teams need, such as product-related training. This process includes the following steps:
- Evaluate what skills are required to successfully do the job -- in the current and future state vs. skills assessment of the customer service team.
- Identify training and development opportunities based on the gaps between current and future conditions.
- Empower the customer service team to assist customers beyond traditional service parameters and without using canned responses.
8. Establish how and when customer service teams work cross-functionally
Striving for an expanded team can break down operational silos and improve communications and clarity. A customer service toolkit is often used to lay out the approach and clarify operations, including when handoffs happen between groups.
9. Innovate
As the product or service evolves, so should the customer service team. The team should innovate based on the changing needs of the customer to meet customer expectations. This process begins by asking questions such as the following:
- What is and what is not working in the service delivery?
- What is impeding or helping customer loyalty?
- Are customer expectations being met at a basic level? How does this compare to that of any competitors?
Customer service teams are at the center of the customer experience and often make or break the perception of an organization and its service or product. As such, creating a robust customer service plan is paramount for long-term success.
The future of customer service: 12 trends to watch
How to improve customer satisfaction during supply, labor crisis
10 examples of AI in customer service
Related Resources
- Human-AI collaboration: unleashing the power of automated intelligence in the ... –Windstream Enterprise
- 2024 Talkdesk Bank And Credit Union Contact Center Benchmark Report –Talkdesk
- Contact Center Workforce Optimization: A Guide to Improving Productivity and ... –Broadvoice
Dig Deeper on Customer service and contact center

What is a key performance indicator (KPI)? Strategy and guide

Evaluating data quality requires clear and measurable KPIs

Develop a backup KPI to improve performance

It’s Time to Raise the Bar on Observability

Paper and unstructured PDFs need more help to be ingested into and findable within enterprise knowledge repositories. Enter ...
SharePoint 2019 and SharePoint Online have different customization capabilities, payment models and more. Organizations must ...
As strict privacy laws challenge organizations, information governance is the answer. This quiz can help business leaders test ...
Microsoft 365 Copilot, an AI assistant, offers several promising features. Find out how to configure Copilot with Teams workflows...
With its AI capabilities, Microsoft Copilot provides several enhancements to Microsoft Teams functionality, including meeting ...
Organizations have ramped up their use of communications platform as a service and APIs to expand communication channels between ...
Vector databases excel in different areas of vector searches, including sophisticated text and visual options. Choose the ...
Generative AI creates new opportunities for how organizations use data. Strong data governance is necessary to build trust in the...
Snowpark Container Services aims to provide the vendor's users with a secure environment for deploying and managing models and ...
AIBOMs help developers and security teams by providing a transparent view of AI system components, improving supply chain ...
The growth of generative AI has led to more audio cloning technology. This could affect the U.S. election. Recent incidents show ...
The use of AI in business applications and operations is expanding. Learn about where enterprises are applying AI and the ...
A 3PL with experience working with supply chain partners and expertise in returns can help simplify a company's operations. Learn...
Neglecting enterprise asset management can lead to higher equipment costs and delayed operations. Learn more about EAM software ...
Inventory management software can help companies manage their supply chain in a turbulent world, but using the right product is ...
More From Forbes
How customer success will change your product roadmap (for the better).
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Haresh Bhungalia is the CEO of Casepoint , a technology company focused on solving for data and business workflow challenges.
In the early days of building a startup, founders often have a very specific vision for the problem statement they are looking to solve. That’s how funding gets secured—with a clear direction that people can easily buy into.
But, today, as startups face unprecedented risk , it’s important not to get too attached to that vision. The key to building a resilient organization is to remain open to the idea that the product might change over time to meet customer needs. And, in many ways, that’s the ideal outcome.
In fact, some of the most successful organizations in the world are built around this exact idea. With the right framework in place, a customer-first product development strategy can help companies remain viable over time and open up new opportunities.
Customer Engagement Over Customer Success
Typical SaaS customer success largely looks like interacting with customers electronically—on the platform, through email and via NPS feedback. In today’s environment where customers demand more from vendors and competition is high, however, these methods fall short.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
Modern customer success requires a framework shift, especially for organizations with enterprise-level clients. Now, companies must center customer engagement over customer success, featuring client advocacy that's proactive, high-touch, personalized and highly responsive.
Relationship-first customer success requires that organizations interface regularly with customers to sort through pain points and needs. Most importantly, it looks like taking customer feedback and funneling it to be able to respond quickly with the product functionality customers need to succeed. Ultimately, it’s about letting customer engagement drive the product roadmap.
Creating A System To Prioritize Product Development
It’s impossible for growing companies to consider each customer when planning product activity due to resource constraints (time and personnel). Plus, acting on competing priorities can pull the product in too many directions. The most effective way to manage this challenge is to group customers by their ideal customer profile (ICP) rank, which, in turn, determines their influence on the roadmap.
One group might be outside the current ICP—those that randomly found success on the platform or reflect an outdated ICP. Typically, this bracket is low touch and won’t influence the product. Another group might be on the edges of the ICP but remain valuable to the company, so they receive mid-touch engagement yet have minimal impact on the product.
The last group represents enterprise customers squarely within the ICP with room to grow on the platform. These customers undoubtedly influence product development. Account managers should be trained to bring their feedback internally to product development. These accounts are high touch, requiring monthly (or more frequent) check-ins.
This model ensures that resources are allocated appropriately and the product roadmap doesn’t get clogged up. Instead, companies can make the biggest product impact for their core ICP customers.
Balancing Interests Of Customers And Stakeholders
Taking in customer feedback is one thing but translating it into something material is another—and doing so is a balancing act. Sometimes, important (high-paying) customers can take the roadmap too far, resulting in bespoke tech that doesn’t serve the larger ICP. Organizations must pair customer feedback with customer research to ensure external validity.
Enterprise customer success also requires engagement with all customer-side stakeholders—from the decision-maker (budget owner) to the users to security personnel. Sometimes, these subgroups will have competing priorities. Maybe users love the platform, but it doesn’t meet the company’s security requirements. Maybe focusing too heavily on security means that business KPIs suffer.
Meaningful customer engagement that drives product development demands a holistic approach. Account managers should spend time with leadership to understand their goals and pain points, but they should also focus on users. The primary objective is to keep the business owner happy, but keeping users active and satisfied is a key part of that equation.
Again, no one customer or stakeholder should drive the product roadmap. Companies must look for emerging themes in customer and stakeholder feedback to filter priorities.
Remain Open To Change
Through this process, tech businesses will undoubtedly uncover new opportunities. Recently, at Casepoint, a theme emerged in our own customer engagement data: Many of our clients were struggling with FOIA (Freedom of Information Act) workflows. We saw an opportunity within our existing platform to build out those capabilities—and we took it. We created a FOIA management solution to serve current clients, which will also help us attract more customers within our ICP that share those same challenges—showcasing exactly how customer engagement can drive product development, growth and profitability.
Similarly, if a customer is struggling with the product, that’s also an opportunity to improve it not just for that customer but for the rest of the ICP. By working with the client, companies can root out the underlying problem: Is it a user education problem? Is it the way the product is configured? Could that task take three clicks instead of five?
A functional customer engagement-product development model is built on the belief that customers are the eyes and ears of the company. Customers are in the product every day. They know what’s working and what’s not, and responding to their feedback will not only keep them satisfied but improve the customer experience for all.
Key Features Of Customer-Driven Product Development
Every organization is unique, which means that building a successful customer engagement program that drives product development isn't a one-size-fits-all model, but every successful program does have the same core components.
First, it requires strong alignment across the organization: Account managers need to be on the same page as product, engineering, sales and executive leadership. A strong connection between account managers and product managers is particularly critical. Second, it includes a tiered system for prioritizing customer feedback to allocate resources appropriately, plus mechanisms for balancing feedback across customers and stakeholders. Finally, it requires open-mindedness, curiosity and empathy from leadership to create a culture in which the company feels empowered to act on customer feedback and seize new opportunities.
By adopting these customer-centric strategies, organizations can keep their finger on the pulse of market demand and remain agile in the face of changing customer needs. Ultimately, centering customer engagement helps companies shape and enhance a product roadmap that drives competitiveness, longevity and long-term profitability.
Forbes Technology Council is an invitation-only community for world-class CIOs, CTOs and technology executives. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Retailers’ climate road map: Charting paths to decarbonized value chains
As companies in all sectors work to shrink their carbon footprints and hit their decarbonization targets, the path to reducing Scope 3 emissions is often anything but straightforward. For some, decarbonizing Scope 3 emissions can be more like navigating a particularly byzantine maze. Such is the case for retailers.
About the authors
For the average retailer, Scope 3 metrics capture emissions generated upstream and downstream within the value chains of every SKU it sells—numerous, disparate, and sometimes highly fragmented value chains with multiple tiers of suppliers and inputs. And the emissions generated within this labyrinth of value chains span six energy and land-use systems: agriculture and forestry, building, industry, mobility, power, and waste (Exhibit 1).
Scope 3 emissions are, by definition, indirect greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions that are generated within a company’s value chain; unlike Scope 1 and 2 emissions, companies do not directly control these emissions. Consequently, reducing Scope 3 emissions depends on the engagement and efforts of all value chain actors, including suppliers, distributors, and consumers, as well as other public and private sector actors—a retailer cannot realize these reductions in isolation.
The breadth and complexity of their Scope 3 emissions have far-reaching implications for retailers in areas including economic, strategic, brand and reputation, and regulatory compliance. This is why retailers worldwide have embraced the opportunities in these challenges, pursuing ambitious sustainability goals and wide-ranging initiatives that have led to meaningful reductions in product value chain emissions. Their efforts include engaging suppliers to improve energy efficiency in manufacturing and transportation, reduce waste, and transition to renewable energy sources.
Some decarbonization efforts, such as converting power grids to renewable or clean energy in geographies where suppliers are concentrated, are longer-term efforts that depend greatly on the actions and decisions of multiple public and private sector players. However, many decarbonization solutions are within reach of retail value chain stakeholders—and are either cost-neutral or cost-saving to implement.
Framed within seven strategic decarbonization action themes, this report illustrates how retailers and other value chain stakeholders could strategically deploy economic resources, natural or physical resources, human resources, low-carbon technology, and data transparency to realize emissions reductions. Because the scale, complexity, and key players for these efforts vary, so does the retailer’s role in the efforts, ranging from leading and scaling to convening value chain partners to collaborating and catalyzing to advocating and supporting actions to reduce emissions across retail value chains.
Reducing the average retailer’s Scope 3 emissions by 15 percent at a system level is feasible by 2030 using existing technologies; however, innovations in technologies and practices could enable an additional 40 or 50 percent reduction.
Retailers’ Scope 3: A complex array of value-chain emissions
Retailers’ reporting requirements are specified in the Greenhouse Gas Protocol’s Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard and ISO 14064, the international standard series for quantifying and reporting greenhouse gas emissions and removals. Under these standards, a retailer’s Scope 3 emissions metric captures all GHG generated from sourcing, making, transporting, housing, selling, and using every product the retailer carries throughout its life cycle.
This means that for a multicategory retailer, reducing Scope 3 emissions—which include sources that make up around 98 percent of total emissions in retail—involves players from multiple sectors and industries and entails efforts to decarbonize six energy and land-use systems. And about 80 percent of a retailer’s Scope 3 emissions are generated upstream in product value chains via feedstock production, materials and components, processing and manufacturing, and packaging (Exhibit 2).
Retailer challenges in focus: Delineating Scope 3 emissions in three value chains
Each of the millions of product value chains whose emissions are captured in a retailer’s Scope 3 contains multiple tiers of suppliers and inputs from regions around the globe. The commodities involved are often mixed together in agricultural areas or at shipping ports, and each tier within a value chain can be highly fragmented. Additionally, suppliers can change their sources for inputs within the course of a single year. This complexity makes it challenging for retailers to influence how suppliers handle or report on emissions.
Consumers’ use of products—powering electronics or washing and drying clothing, for example—is also captured in the Scope 3 emissions for retailers that carry such products. Thus, reducing downstream product value chain emissions often depends on influencing changes in consumer behavior or the energy sources powering the local electricity supply.
Among retailers’ top 15 most commonly sold products, beef is one of the largest sources of Scope 3 emissions for retailers. Around 86 percent of beef value chain emissions are generated upstream by animal feed farming and production, fertilizer production, and cattle ranching, according to McKinsey analysis. Reducing ruminant methane emissions and shifting toward more efficient use of agricultural inputs, maximizing productivity, and adopting regenerative agriculture practices such as no- or low-till soil and cover cropping are key to realizing reductions in this value chain (Exhibit 3).
In electronics product value chains, decarbonizing power use is retailers’ primary challenge. The majority (80 to 90 percent) of the average retailer’s Scope 3 emissions for electronics products are generated upstream via suppliers in highly fragmented markets. Decarbonization in this stage of the value chain largely depends on the availability of renewable energy where suppliers operate (Exhibit 4).
Likewise, in the apparel product value chain, around 62 percent of emissions are generated upstream via energy use among tier-two and tier-three suppliers engaged in garment processing and fiber production (Exhibit 5).
Thus, substantial reductions in retailers’ Scope 3 emissions will require transformations in energy and land-use systems involving efforts among many value chain stakeholders.
Near-term opportunities for retailers: Reducing emissions across value chains
This report identifies seven decarbonization action themes for reducing the average retailer’s Scope 3 emissions; the themes are based on analysis of technically feasible change levers in several product value chains. The highest reduction potential comes from transitioning to clean and renewable energy, reducing livestock emissions, and adopting regenerative agriculture practices. Examples are provided to illustrate emissions reduction opportunities (Exhibit 6).
As noted previously, if all were deployed at scale, these actions could propel a 55 to 65 percent reduction in the average retailer’s Scope 3 emissions by 2030, although some actions carry sizable costs. Actions that reduce or do not increase costs in the system could yield a 12 to 17 percent reduction in the average retailer’s Scope 3 emissions by 2030.
Catalyzing broader decarbonization: Strategies and considerations for retailers
To help retailers prioritize decarbonization efforts, this report arranges levers that could be deployed by retailers and other stakeholders into four groups (labeled A, B, C, and D), each of which could enable strategic decarbonization actions. The report also illustrates these actions with examples of real-world initiatives involving retailers and their value chain partners.
By focusing on the levers in groups A and B, the average retailer could accelerate efforts to achieve up to a 17 percent reduction in its Scope 3 emissions by 2030. However, deploying levers in groups C and D could unlock an additional 40 to 50 percent, highlighting the importance of multistakeholder collaboration to realize substantial impact (Exhibit 7).
Group A: Cost-effective near-tier levers
Retailers could influence group A levers by engaging their direct suppliers, their direct suppliers’ suppliers, and consumers in efforts to scale decarbonization solutions that would result in cost savings or have no impact on cost (cost neutral). If deployed at scale, levers in this group could help reduce the average retailer’s Scope 3 emissions by up to 2 percent.
Examples of group A levers include forming partnerships that facilitate renewable-energy adoption; providing electric vehicle–charging infrastructure; supporting suppliers in implementing their net-zero objectives; and using consumer-focused marketing and tools to promote sustainable energy consumption habits and reduce waste (Exhibit 8).
Group B: Cost-effective far-tier levers
Retailers could influence actions in group B by engaging suppliers in tier-three levers and beyond (along with other industry partners) in efforts to deploy cost-saving or cost-neutral levers to facilitate adoption of sustainability levers. Deployed at scale, such efforts could potentially help reduce the average retailer’s Scope 3 emissions by around 11 to 15 percent.
Examples of group B levers include providing training, education, and resource initiatives in regenerative agriculture practices and emissions reduction for farmers; sharing and collaborating with peer companies and other value chain stakeholders on best practices to reduce waste and maximize process efficiency; setting supplier standards under deforestation-free and conversion-free (DCF) policies; promoting lean-manufacturing adoption among in-network suppliers via supplier contracts; scaling decarbonization technologies with public and private sector support; and mobilizing value chains to reduce waste via systemwide collaborations.
Group C: Costlier near-tier levers
By engaging their tier-one, tier-two, and tier-three suppliers and other value chain partners, retailers could help spark innovation that could improve the feasibility of interventions that are technically achievable but not cost neutral (but whose costs still fall below the predicted global average carbon price in 2030).
Retailer levers in group C center on collaboration with value chain partners to potentially help reduce the average retailer’s Scope 3 emissions by around 19 to 23 percent.
Examples of group C efforts include collaborating with value chain partners, not-for-profit organizations, and research institutions to support research in advancing sustainability measures; fostering private sector–led investment in emissions reduction innovations; advocating for public sector–led incentive programs aimed at helping value chain partners address costs or resource issues; encouraging and accelerating renewable adoption via supplier engagement; taking part in campaigns to stimulate consumer awareness of, and encourage greater consumption of, plant-based protein; and helping signal demand for alternative protein by engaging suppliers in long-term contracts for plant-based ingredients.
Group D: Cost-prohibitive far-tier levers
Group D levers are far removed from retailers and extremely costly to implement using today’s technology, but retailers can nevertheless support, advocate, mobilize, and engage suppliers beyond tier three and other stakeholders to facilitate breakthrough innovation and solutions to realize systemwide changes. Group D levers deployed at scale could yield a 25 to 30 percent reduction in the average retailer’s Scope 3 emissions.
Group D examples include launching public and private sector–led initiatives to encourage investment in and adoption of renewable technology and clean- and renewable-energy grids; collaborating with value chain partners and other private and public sector actors to invest in and expand circularity of materials by, for example, facilitating consumer access to recycling via collection centers and encouraging recycling via incentives; supporting recycling technology R&D; supporting rare earth recycling and sustainable sourcing; advocating for public sector–led incentives to promote regenerative agricultural practices; and encouraging start-up and technology company-led innovations to support precision agriculture for croplands through pilots and specifications.
Considerations for retailers: Measurement, accounting, and reporting
The complexity and scale of emissions captured in retailers’ Scope 3 present practical challenges in precisely measuring, accounting, and reporting on emissions reduction progress.
Measurement challenges include variability in emissions resulting from changes made in production locations and methods, raw material use and sourcing, energy use, equipment use, and modes of transportation; inconsistent data formats, measurement standards, and infrastructure for data storage and processing; and barriers that prevent retailers from connecting data to batches of commodities or products as they pass from one stage of the value chain to the next.
Accounting challenges for retailers can stem from a disconnect between industry averages and actual decarbonization project impacts in retailers’ product supply chains or items, changes in historical estimates that require companies to revise and restate baseline data and create uncertainty around target setting and management, changes in and uncertainty around GHG accounting methodology, and emissions factor updates that lag behind changes in energy grids and agricultural systems.
Such measurement and accounting challenges can complicate reporting. For many retailers, determining their Scope 3 inventory can seem like a modeling exercise based on broad industry averages and historical emissions factors. It is often difficult for retailers to reconcile and report on actual emissions reductions in their value chains because of barriers to gathering and allocating reliable data and the lack of consistent methodology to adjust industry averages to account for particular decarbonization efforts. Retailers may also face potential competitive risks from disclosing sensitive sales or margin information in reporting category- or item-level emissions. As well, Scope 3 inventory figures can mask differences in decarbonization effort and results: a growing retailer that is decarbonizing its value chain may report the same percentage change in Scope 3 footprint as a shrinking retailer that has not done anything to decarbonize its value chain.
Despite these challenges, retailers are managing such complexity through the following actions:
- working with their individual suppliers and data aggregators to improve the quality and availability of data and the applicability of accounting and reporting standards
- simplifying methodologies to facilitate modeling where data is not available and providing order-of-magnitude estimations of Scope 3 footprint to highlight major concentrations of emissions and inform priorities for decarbonization
- providing supplemental information to demonstrate impact of decarbonization efforts to help stakeholders understand their Scope 3 decarbonization strategy and contribution and their role in emissions reduction
- improving the practicality of measurement, accounting, and reporting by engaging with carbon accounting standards bodies, reporting platforms, and regulators to help address challenges
Considerations for retailers: Engaging with the public sector
On many fronts, reductions in retailers’ Scope 3 emissions are subject to public sector–led initiatives regarding energy and land-use systems; thus, retailers would be well served by a deep understanding of existing and proposed standards and guidelines. Retailers can determine whether or how public guidelines related to emissions affect their business outlook and the effectiveness of their efforts to decarbonize their value chains. Retailers can also help create change by advocating for national and international climate policies that address the interests of stakeholders in their business, value chains, and customer communities.
Decarbonizing retailers’ value chains is feasible—but it cannot be done in isolation. At-scale deployment of the sustainability measures outlined in this report will require system-level change involving farmers and ranchers, manufacturers, suppliers, nongovernmental organizations (NGOs), public sector actors, energy companies, financial institutions, data and technology providers, and consumers. Coordinated multistakeholder action is imperative.
Peter Spiller is a partner in McKinsey’s Frankfurt office; Steve Hoffman is a partner in the Los Angeles office; Caroline Ling is a consultant in the New York office; Philippe Diez is a senior client development adviser in the Paris office; and Varun Mathur is an associate partner in the Austin office.
The authors wish to thank Karl Murray, Mekala Krishnan, Miquel Ferrer, Neha Chatterjee, Olorunyomi Joel, and Per-Anders Enkvist for their contributions to this report.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

The agricultural transition: Building a sustainable future

Climate sustainability in retail: Who will pay?

Nature in the balance: What companies can do to restore natural capital

No featured offers available
- Quality Price,
- Reliable delivery option, and
- Seller who offers good customer service
Sorry, there was a problem.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
beats Pill - Bluetooth Speaker and Portable Wireless Charger via USB-C - Up to 24 Hours Battery Life, IP67 Water Resistant, Apple & Android Compatible, Built-in Microphone – Campagne Gold

Pill & Power Adapter
with AppleCare+ (2 Years)
Without AppleCare+
| Brand | beats |
| Speaker Maximum Output Power | 100 Watts |
| Frequency Response | 89.8 KHz |
| Connectivity Technology | Bluetooth, USB |
| Audio Output Mode | Mono |
About this item
- The Beats Pill delivers powerful, room-filling sound. The bigger, bespoke racetrack woofer displaces 90% more air volume, packing more of a punch with deeper, fuller bass.
- The Beats Pill has up to 24 hours of battery life for all-day playback and can be used to charge your phone or other devices via USB-C cable.
- The portable speaker is IP67-rated for dust and water resistance for outstanding durability and includes a removable lanyard and soft-grip silicone backing to make it easy to take with you.
- The redesigned tweeter provides extra stability for crisp highs and rich mid-range tones while the woofer’s material and structure helps minimize low-end distortion even at high volumes
- Enjoy high-resolution lossless audio from your Beats Pill by connecting it to your laptop or other compatible devices via the USB-C cable
- Easily pair two Beats Pill speakers for twice the output experience in Amplify mode or Stereo mode.
- Apple and Android compatibility – including instant one-touch pairing and automatic pairing across your other devices, plus Find My or Find My Device.
- Take calls and activate your voice assistant directly from a paired Beats Pill.
Top Brand: beats

Frequently Asked Questions
What devices is the Beats Pill compatible with?
The Pill is compatible with iOS, Android, and compatible Bluetooth devices.
How do I pair my Pill speaker?
The Beats Pill’s dual compatibility for both iOS and Android enables one-touch Bluetooth® pairing. To pair your Pill, hold the speaker near an unlocked device, then press and hold the power button until the LED light blinks white and you hear an audio cue. When your device is connected, you will hear a second audio cue indicating that your Pill is ready to play.
How do the on-device controls work?
Press the Center Button to pause or play your music. Press the Center Button twice to skip to the next track and press three times to go back to the previous track. To raise and lower the volume, use the Plus and Minus Buttons.
Can I pair multiple speakers together?
Sync two Beats Pill speakers in Amplify Mode by pressing and holding both Center Buttons. A blue light on each speaker will indicate that they are synced.
To toggle from Amplify Mode to Stereo Mode, simultaneously press and hold one of the two synced speaker’s Center and Plus Buttons.
Stereo Mode turns two synced speakers into dedicated left and right outputs for a surround sound feel.
How long does the battery last?
The Beats Pill has up to 24 hours of battery life. If you’re low on power, Fast Fuel means a 10-minute charge gives up to 5 hours of playback. To check battery life, give the Power Button a quick press. A green light indicates the Pill has enough power; a red light means the battery is low.
Is my speaker water-resistant?
Yes, the Pill is IP67-rated to keep dust and water out. At the pool, at the beach, in the rain —the Beats Pill is protected by enhanced internal seals.
Does my speaker have a mic?
Yes, the Pill has a microphone and can be used as a speakerphone for calls. When your Pill is paired, use the Center Button to answer, mute, or reject a call. Press the Center Button once to answer and end a call and press twice to decline a call.
Can I use my Voice Assistant with my Pill?
Yes, press the Power Button twice to activate Siri or your Google Assistant while the Pill is paired to your device.
How do I charge my speaker?
You can charge your speaker with the USB-C to USB-C cable that is included in the box. You can also use your Pill to charge your phone or other devices via the USB-C cable.
Technical Details
|
| Portable Speaker |
|
| Weight: 24 oz./680 g |
|
| Length: 8.6 in./21.9 cm, Width: 2.8 in./7.1 cm, Height: 2.8 in./7.0 cm |
|
| Bluetooth |
|
| Beats Pill (single charge): up to 24 hours of listening time |
What's in the box
- Beats Pill wireless Bluetooth® speaker
- Removable carry lanyard
- USB-C to USB-C cable for charging and audio (USB-C power adaptor sold separately)
- Quick Start Guide and Warranty card
Looking for specific info?
Customer reviews.
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 5 star 83% 5% 5% 3% 4% 83%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 4 star 83% 5% 5% 3% 4% 5%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 3 star 83% 5% 5% 3% 4% 5%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 2 star 83% 5% 5% 3% 4% 3%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 1 star 83% 5% 5% 3% 4% 4%
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
Customers say
Customers like the performance, value, size, appearance and clarity of the speakers. They mention that it delivers good performance, is worth the money, fits well with any room and that the design looks good and is quintessentially Apple. They also appreciate the clarity, saying that the mids are clear and neutral, and the highs are crisp without any harshness. Customers also like the sound quality, and quality.
AI-generated from the text of customer reviews
Customers like the sound quality of the speakers. They say it has excellent sound, the bass is well balanced with treble, and it enhances listening beautifully. Some customers also mention that the speaker is fantastic and doubles as a speakerphone.
"...really great for its size, living up to the Beats name, filling the room with punchy bass and crystal clear sound...." Read more
"... Bass is great . Clarity is great. Build quality is great. You can even hook it up via usb c to get lossless music...." Read more
"...It delivers good, deep base and enhances my listening beautifully ! I recommend this speaker to anyone who loves music and true sound!!" Read more
"I really like the new Beats Pill 2024 speaker. The sound quality is amazing with great bass and clear vocals...." Read more
Customers appreciate the value of the speakers. They say the controls feel premium and are worth the price.
"...Compared to all of them this is an amazing speaker for the price point . Bass is great. Clarity is great. Build quality is great...." Read more
" Great product , also very sturdy it survived a drop with only a little cosmetic damage. Otherwise it works great and is loud with alot of bass" Read more
"...Overall, the Beats Pill (2024) is worth the wait .I own several portable speakers, Bose, JBL, and these are my favorite." Read more
"... Well worth 150 , better yet buy two for 300." Read more
Customers are satisfied with the quality of the speakers. They mention that the build quality is great, the speaker has a nice heft to it, and the design is a mechanical masterpiece. Customers also appreciate the premium controls and the everything-proof design.
"...Speaker has a nice heft to it and the design of the speaker is really nice, with the angled design, and the speakers facing you...." Read more
"...Bass is great. Clarity is great. Build quality is great . You can even hook it up via usb c to get lossless music...." Read more
"I love the size, weight and quality of my Pill! It delivers good, deep base and enhances my listening beautifully!..." Read more
"Great product, also very sturdy it survived a drop with only a little cosmetic damage. Otherwise it works great and is loud with alot of bass" Read more
Customers are satisfied with the clarity of the speakers. They mention that the bass is great, the mids are clear and neutral, and the highs are crisp. They also say that the microphone is a great addition for calls and that you can hear details in the notes that sound high-fi.
"...I can connect this badboy to my laptop, and take crystal clear Teams calls with it all day at work...." Read more
"...Bass is great. Clarity is great . Build quality is great. You can even hook it up via usb c to get lossless music...." Read more
"...At lower volumes the music is balanced and you can hear details in the notes that definitely sound high-fi and high end...." Read more
"...The microphone is a great addition for calls . You won’t be disappointed with this speaker. Thinking about buying another to pair in stereo...." Read more
Customers like the appearance of the speakers. They say the design looks good and fits well with any room or setup. Customers also mention that the design of the speaker is quintessentially Apple.
"...Speaker has a nice heft to it and the design of the speaker is really nice , with the angled design, and the speakers facing you...." Read more
"...The design looks good and fits well with any room or setup.The only downside is that there isn't an app to control the speaker...." Read more
"...Design: The new Pill features a stylish , everything-proof design...." Read more
"...I compared to flip 6 right away, it is Brighter, crisper and deeper bass at 50% volume and lower...." Read more
Customers are satisfied with the performance of the speakers. They mention that it has good functionality, and delivers good, deep base sound.
"I love the size, weight and quality of my Pill! It delivers good , deep base and enhances my listening beautifully!..." Read more
"...Otherwise it works great and is loud with alot of bass" Read more
"...The pill is definitely very portable, great performance and most definitely great value for the money...." Read more
" Good functionality but..." Read more
Customers are satisfied with the size of the speaker. For example, they mention it's the best small portable speaker, it fits well with any room, and it looks good.
"...The sound quality of this speaker is really great for its size , living up to the Beats name, filling the room with punchy bass and crystal clear..." Read more
"I love the size , weight and quality of my Pill! It delivers good, deep base and enhances my listening beautifully!..." Read more
"...The sound quality is amazing with great bass and clear vocals. It's small , stylish, and easy to carry around, which is perfect for when I'm on the..." Read more
" Best small portable speaker ..." Read more
Customers find the speakers very easy to connect to their devices with Bluetooth. They appreciate the simple interface and great sound quality.
"...with heavy use, and connecting it to my devices with Bluetooth is super easy . The design looks good and fits well with any room or setup...." Read more
" Very easy to connect and great sound quality. Perfect for gifts and around the house." Read more
"...this was a well done refresh, great quality, decent bass and simple interface ." Read more
Reviews with images

- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
Top reviews from other countries
- About Amazon
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell products on Amazon
- Sell on Amazon Business
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Become an Affiliate
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Host an Amazon Hub
- › See More Make Money with Us
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Amazon and COVID-19
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
1. Identify your customers. The first step of customer analysis is to identify your potential customers and collect information about their special characteristics. Such information comes in handy when you want your product and marketing strategies to align with your customers' needs.
Components of a Customer Analysis. A complete customer analysis contains 3 primary sections: Identify your target customers. Convey the needs of these customers. Show how your products and/or services satisfy these needs. Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here.
4. Create a customer persona. After gathering and analyzing all this data, you should have plenty of information about your customers. The next step is to create a customer persona. In case you need a refresher, the customer persona is a semi-fictional representation of your ideal customer based on your collected data.
Analyze Customer Needs and Preferences. Analyze the needs, preferences, and pain points of each customer segment to identify opportunities for product or service improvement. Consider factors such as price sensitivity, convenience, quality expectations, and brand loyalty. This analysis will help you tailor your offerings to better align with ...
Short Summary. Customer analysis is an essential part of any business plan, allowing businesses to understand their target customers and create tailored products/services. It involves identifying a market, assessing demographics & analyzing customer behavior in order to inform marketing strategies. Utilizing insights from customer analysis can ...
The purpose of undertaking customer analysis as part of a business plan is to examine in-depth the consumers most likely to purchase your product or service. Brands can establish different groups of customers and the needs of those customers. By understanding what motivates them to purchase, brands can build their business around providing ...
A customer analysis (or customer profile) is a critical section of a company's business plan or marketing plan. It identifies target customers, ascertains the needs of these customers, and then specifies how the product satisfies these needs. Customer analysis can be broken down into a behavioral profile (why your product matches a customer ...
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
Five steps to running successful target customer analysis. 1. Leverage existing customer data. Existing customers should be the starting point for your research when performing customer analysis. This data source is likely to be your CRM (Client Relationship Management) system, and segmenting it or grouping it by customer characteristics can ...
In many ways, customer analysis is the most important piece of your business plan. In order for your business to be successful, you must be able to demonstrate who will buy your products or services. Be sure to identify your customer segments and how your business will meet their specific needs. Navigation: Step-By-Step Checklist; Find ...
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business. Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners.
Here are the main sections of a business plan: 1. Title Page. The title page captures the legal information of the business, which includes the registered business name, physical address, phone number, email address, date, and the company logo. ... Describe the size of the market, the units of the company's products that potential customers ...
There are eight essential components, all of which are detailed in this handy guide. 1. Executive Summary. The executive summary opens your business plan, but it's the section you'll write last. It summarizes the key points and highlights the most important aspects of your plan.
Marketing plan. Explains your plan for reaching, acquiring, and retaining customers for your business. Operations plan. Shows that you've thought through the logistics of actually operating your company, including hiring staff, shipping, storage, and more. Organization and management.
Effective business plans contain several key components that cover various aspects of a company's goals. The most important parts of a business plan include: 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is the first and one of the most critical parts of a business plan. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole and ...
While your plan will be unique to your business and goals, keep these tips in mind as you write. 1. Know your audience. When you know who will be reading your plan—even if you're just writing it for yourself to clarify your ideas—you can tailor the language and level of detail to them.
Step 2: Identify where you are now. The GPS on your phone or in your car needs two things to give you directions. The first is a destination. The second is your current location. A gap analysis relies on the same information. Setting a goal is essential. Once you have a goal, you need to identify your current position.
Not updating your business plan: After you write a business plan, the world will continue to change. Your industry, market and customer base will evolve — and so should your business plan.
Ensure that goals are achievable but still challenging, and identify when they tie back to business objectives. Develop a plan, method and frequency to measure goals. 3. Create a customer journey and service design map. Create a customer journey and service design map to clarify the steps to assist the customer.
Typically, a traditional business plan runs 20-30 pages. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of your business and your goals for the plan. Q: Do I need a business plan if I'm not seeking funding? While it's especially crucial for seeking funding, a business plan is valuable for any business.
Why you need a restaurant business plan. Before we get into how to create a restaurant business plan, let's talk about why you need one. A restaurant business plan: Sets expectations and creates a common set of goals for you and your business partner(s). Acts as your North Star to keep you on track as you open and run your restaurant.
Relationship-first customer success requires that organizations interface regularly with customers to sort through pain points and needs. Most importantly, it looks like taking customer feedback ...
Retailers can also help create change by advocating for national and international climate policies that address the interests of stakeholders in their business, value chains, and customer communities. Decarbonizing retailers' value chains is feasible—but it cannot be done in isolation.
Ookla trademarks used under license and reprinted with permission. Unlimited on our network. During congestion, customers on this plan may notice speeds lower than other customers and further reduction if using >50GB/mo., due to data prioritization. Video in SD. Tethering at max 3G speeds. Qual'g service & capable device req'd.
Product Eligibility: Plan must be purchased with a product or within 30 days of the product purchase. Pre-existing conditions are not covered. Terms & Details: More information about this protection plan is available within the "Product guides and documents" section. Simply click "User Guide" for more info.
Wells Fargo & Co. was accused of overpaying for prescription drugs by former employees, who claim mismanagement of the bank's health plan drove up costs for workers.
The idea of building a national Bitcoin stockpile took a hit when the largest cryptocurrency tanked amid macroeconomic fears.