

MLA Style Guide, 8th & 9th Editions: Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Works Cited entries: What to Include
- Title of source
- Title of container
- Contributors
- Publication date
- Supplemental Elements
- Book with Personal Author(s)
- Book with Organization as Author
- Book with Editor(s)
- Parts of Books
- Government Publication
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Multivolume Works
- Newspaper Article
- Other Formats
- Websites, Social Media, and Email
- About In-text Citations
- In-text Examples
- How to Paraphrase and Quote
- Citing Poetry
- Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Formatting Your Works Cited List
- MLA Annotated Bibliography
- MLA 9th Edition Quick Guide
- Submit Your Paper for MLA Style Review
MLA recommends using 12-point Times New Roman font or another readable typeface (e.g. serif ).
Line Spacing & Margins
Use double-spacing throughout the entire paper.
Leave 1 inch margins on the top, bottom, and each side.
Indent the first line of each paragraph half an inch from the left margin.
Quotes longer than 4 lines should be written as a block of text a half an inch from the left margin.
Heading and Title
An MLA research paper does not need a title page, but your instructor may require one. If no instructions are given, follow the MLA guidelines below:
Type the following one inch from the top of the first page, flush with the left margin (double spacing throughout).
Your Instructor's Name
Course Number or Name
Center the title on the next line. Follow the rules for capitalization. Do not italicize, underline, or bold the title. An exception is when your title includes a title. Example: The Attitude toward Violence in A Clockwork Orange
Indent the next line and begin typing your text.
Include your last name and page numbers in the upper right-hand corner of every page. The page numbers will be one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. If your instructor prefers no page number on the first page, begin numbering from 2 on the second page.
Sample Papers from MLA
There are sample papers available in the MLA Style Center. Check them out to see the correct formatting.
Styling Headings and Subheadings
According to the MLA Style Center website, writers should avoid using headings in shorter papers. If you are writing a longer research paper, you may want to include headings and subheadings to help organize the sections of your paper. Advice from the MLA Style Center :
"Levels
The paper or chapter title is the first level of heading, and it must be the most prominent.
Headings should be styled in descending order of prominence. After the first level, the other headings are subheadings—that is, they are subordinate. Font styling and size are used to signal prominence. In general, a boldface, larger font indicates prominence; a smaller font, italics, and lack of bold can be used to signal subordination. For readability, don’t go overboard: avoid using all capital letters for headings (in some cases, small capitals may be acceptable):
Heading Level 1
Heading Level 2
Heading Level 3
Note that word-processing software often has built-in heading styles.
Consistency
Consistency in the styling of headings and subheadings is key to signaling to readers the structure of a research project. That is, each level 1 heading should appear in the same style and size, as should each level 2 heading, and so on. Generally, avoid numbers and letters to designate heads unless you are working in a discipline where doing so is conventional. Note that a heading labeled “1” requires a subsequent heading labeled “2,” and a heading labeled “a” requires a subsequent heading labeled “b.”
In a project that is not professionally designed and published, headings should be flush with the left margin, to avoid confusion with block quotations. (The exception is the paper or chapter title, which is centered in MLA style.)
For readability, it is helpful to include a line space above and below a heading, as shown in this post.
No internal heading level should have only one instance. For example, if you have one level 1 heading, you need to have a second level 1 heading. (The exceptions are the paper or chapter title and the headings for notes and the list of works cited.) You should also generally have text under each heading.
Capitalization
Capitalize headings like the titles of works, as explained in section 1.2 of the MLA Handbook.
The shorter, the better."
Modern Language Association. "How Do I Style Headings and Subheadings in a Research Paper?" MLA Style Center., 13 December 2018, style.mla.org/styling-headings-and-subheadings .
MLA Style Paper Template
- MLA 9th Edition Paper Template This template was created and saved as a Word template for Microsoft Word 2016. The process for saving and using the template is the same for the instructions given above for 2013.
You can save a personal template in Microsoft Word (IRSC students, download Office for free, see a librarian if you need help). Above is a template you can use every time you need to set-up a research paper using MLA style format. Simply open the template and type your own information every time you need to write an MLA style paper. Microsoft Word will allow you to save personal templates. Once you have the template opened in Word
Click "Save as"
Give the file a name
Under "Save as type", select Word Template

Then when you open Word, you will be able to choose a template rather than a blank document. You might have to select Personal to find your template.

Sample MLA Paper

How to Use the MLA Style Template
Formatting Group Project Papers
For a research paper written collaboratively by several students, such as for a group project, create a title page instead of listing all authors in the header on page 1 of the essay. On the title page, list each student's full name, placing one name on each double-spaced line. After the final student name, enter the professor's name. After the professor's name, give the course name. The last line of the heading will be the date in 5 August 2021 format. Press Enter a few times to move down the page then give the paper title, centered.

- << Previous: Citing Poetry
- Next: Formatting Your Works Cited List >>
- Last Updated: May 21, 2024 5:26 PM
- URL: https://irsc.libguides.com/mla
MLA 9th Edition Formatting
A Simple, Step-by-Step Guide + Free Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | July 2023
Formatting your paper in MLA style can feel like a pretty daunting task . In this post, we’ll show you exactly how to set up your paper for MLA (9th edition), as quickly and easily as possible. We’ll also share our popular free MLA template , to help you fast-track your writing.
Overview: MLA 9th Edition Formatting
- Structure and layout
- General page setup
- The opening section
- The main body
- Works cited (reference list)
- Free MLA 9 template
MLA Structure and Layout
Let’s start by looking at the overall structure of a typical student paper formatted for MLA 9th edition, before diving into the details of each section. For the most part, MLA papers follow a standardised structure, consisting of the following parts:
The opening section : While MLA doesn’t require a dedicated title page (unlike APA ), it does require an opening section that details some important information about yourself, your university and the paper itself.
The main body : The main body begins directly after the opening section on the first page. This is the “heart” of your paper and there are a very specific requirements regarding how you present and format this content.
The appendix (or appendices): While using an appendix in a student paper is relatively uncommon, you’ll place this section directly after the main body section, if required by your university.
The “Works Cited” list : This section is equivalent to what we’d usually call a references page and it’s where you’ll detail all the reference information corresponding to the in-text citations in the main body of your paper.
These four sections form the standard structure and order of a student paper using MLA 9th edition. As we mentioned, not all sections are always required , so be sure to double check what your university expects from you before submitting. Also, it’s always a good idea to ask your university if they have any style requirements in addition to the standard MLA specification.
Now that we’ve got a big-picture view of the typical paper structure, let’s look at the specific formatting requirements for each of these sections.
Generic Page Setup
Before you jump into writing up your paper, you’ll first need to set up your document to align with MLA’s generic page requirements. Alternatively, you can download our MLA paper template (which comes fully preformatted).
MLA 9th edition requires a 1-inch margin on all sides , for all pages. That said, if you’re writing a dissertation, thesis or any document that will ultimately be printed and bound, your university will likely require a larger left margin to accommodate for physical binding.
Fonts & sizing
MLA does not require that you use any specific font, but we do recommend sticking to the tried and tested , well-accepted fonts. For example, you might consider using one of the following:
- Sans serif fonts : Calibri (11), Arial (11), or Lucida Sans Unicode (10)
- Serif fonts : Times New Roman (12), Georgia (11), or Computer Modern (10)
Whichever font you opt for, be sure to use it consistently throughout your paper . Don’t chop and change, or use different fonts for different parts of the document (e.g., different fonts for the body text and the headings). Also, keep in mind that while MLA does not have a specific font requirement, your university may have its own preference or requirement. So, be sure to check with them beforehand regarding any additional specifications they may have.
In general, all text throughout your document needs to be left-aligned and should not be justified (i.e., leave an uneven right edge). You might consider using a different alignment for section headings, but in general, it’s best to keep things simple .
Line spacing
MLA 9th edition requires double line spacing throughout the document . There should also be no extra space before and after paragraphs . This applies to all sections of the paper, including the “Works Cited” page (more on this later).
Page header
Last but not least, you’ll need to set up a running header for your document. This should contain your last name, followed by the page number. Both of these should be positioned in the top right corner of all pages (even the first page). On a related note, there’s no need for you to include any footer content unless your university specifically requests it.
Now that we’ve looked at the generic formatting considerations, let’s dive into the specific requirements for each section of your paper.
The Opening Section
While MLA-formatted papers typically don’t require a title page, there are very specific requirements regarding the opening section of the first page .
Here’s how you can set your first page up for MLA 9th edition.
- On the first line, write your full name (flush left)
- On a new line, write your professor or instructor’s full name
- On a new line, write the course code and course name
- On a new line, write the full date spelt out (e.g., 15 June 2023)
- On a new line, write the full title of your paper , centre-aligned and using title case (consider using a title case converter if you’re not familiar with this)
- On a new line, begin your body content
All of the above should be in plain, unformatted font – in other words, you don’t need to apply any boldfacing, underlining , etc. That said, you should use italics whenever you’re writing out the titles of other works (for example, titles of books or articles).
To make it all a little more tangible, below is an example of a first page formatted according to the MLA specifications that we just covered.

The Main Body
While the formatting requirements for the body section are relatively light for MLA (at least when compared to APA ), there are still quite a few important things to pay attention to. Here’s what you need to know to get started.
Each of your paragraphs needs to start on a new line , and the first sentence of each paragraph requires a half-inch indent (while the rest of the paragraph is flush left aligned). Note that each paragraph simply starts on a new line and doesn’t require an additional blank line.
MLA 9th edition is fairly flexible in terms of heading formatting. There is no specified formatting, so you can decide what works best for you. However, there are still a few basic rules you need to follow:
- All your headings should be written in title case – never use all caps
- There should be no period following a heading
- Each heading level needs to be uniquely formatted and easily distinguishable from other levels (for example, a distinct difference in terms of boldfacing, underlining or italicisation)
- You can have as many heading levels as you need, but each level must have at least two instances
Abbreviations
When using abbreviations, you’ll need to make sure that you’re using the MLA version of the abbreviation . Below we’ve listed a few common ones you should be aware of:
- Appendix: app.
- Circa: c. or ca.
- Chapter: ch.
- Column: col.
- Definition: def.
- Department: dept.
- Example: e.g.
- Edition: ed.
- Figure: fig.
- Foreword: fwd.
- That is: i.e.
- Journal: jour.
- Library: lib.
- Manuscript(s): MS
- Number: no.
- Quoted in: qtd. in
- Revised: rev.
- Section: sec. or sect.
- Series: ser.
- Translation: trans.
- Version: vers.
- Variant: var.
- Volume: vol.
If you’re interested, you can find a more comprehensive list here . Alternatively, if you have access to the MLA 9th edition handbook, you can find the full list in the first appendix.

In-text citations
MLA 9 has a very specific set of requirements regarding how to cite your sources within the body of your paper. Here are some of the most important things to help you get started with MLA citations.
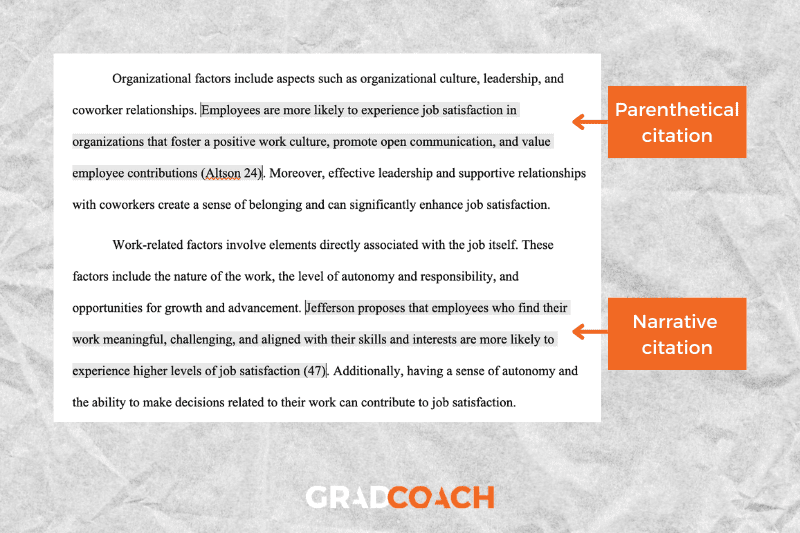
Author-page number system: in-text citations consist of (at a minimum) the lead author’s last name, followed by the page number of the paragraph you are citing. There is no comma between the two components (only a space).
Types of citations: MLA allows two types of in-text citations: parenthetical and narrative . Parenthetical citations feature the author and page number in parentheses (brackets) at the end of the respective sentence. Here’s an example:
MLA 9th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen 13).
Narrative citations, on the other hand, weave the author’s name into the flow of the sentence and then present the publication date in parentheses at the end of the sentence. Here’s an example:
Jansen states that MLA 9th edition is easy for students to grasp if they visit the Grad Coach blog (13).
In general, it’s a good idea to utilise a mix of both in your writing. Narrative citations are particularly useful when you want to highlight or contrast authors or their viewpoints, while parenthetical citations are useful when you want to strengthen your own academic voice. In other words, both formats have their respective strengths and weaknesses, so try to use citation format strategically in your writing.
Quotations: when quoting text verbatim from a source, there is no need to do anything differently in terms of the citation itself, but do remember to wrap the verbatim text in quotation marks. Here’s an example:
Jansen proposes that MLA 9th edition is “easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog” (13).
Multiple authors: when citing resources that were authored by three or more people, you only need to list the lead author, followed by “et al.”. Here’s an example:
MLA 9th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen et al. 13).
Below are a few more examples from our free MLA template .
Please keep in mind that this is not an exhaustive list of all the MLA 9th edition citation-related requirements – just a shortlist of the most commonly relevant ones. If you’d like to learn more, consult the MLA handbook .
The Works Cited (Reference List)
The final section that you’ll need to pay close attention to is the “Works Cited” page, which should contain a list of reference information for all the sources cited in the body of the paper. Again, MLA has a quite a meaty set of specifications regarding the content and formatting of this list, but we’ll cover the basics here to get your started on the right foot.
Basic setup
Your reference list needs to start on a new page and should be titled “Works Cited”. The title should be unformatted and centred . The reference list should then start on the next line. As with the rest of your document, you should use double line spacing throughout.
When it comes to the reference list itself, you’ll need to keep the following in mind:
- All the sources that you cited in the body of your document should feature in the reference list. Make sure that every citation is accounted for .
- The references should be ordered alphabetically , according to the lead author’s last name .
- The exact information required within each entry depends on the type of content being referenced (e.g., a journal article, web page, etc.)
- Components that may need to feature (other than the author) include the title of the source, the title of the container, other contributors, the article version or number, the publisher, the publication date, and the location.
- All references should be left-aligned and should use a hanging indent – i.e., the second line of any given reference (if it has one) should be indented a half inch.
We have to stress that these are just the basics. MLA 9th edition requires that your references be structured and formatted in a very specific way , depending on the type of resource. If you plan to draft your reference list manually, it’s important to consult your university’s style guide or the MLA manual itself. This leads us to our next point…
In general, it’s a bad idea to write your reference list manually . Given the incredibly high level of intricacy involved, it’s highly likely that you’ll make mistakes if you try to craft this section yourself. A better solution is to use (free) reference management software such as Mendeley or Zotero . Either of these will take care of the formatting and content for you, and they’ll do a much more accurate job of it too.
If you’re not familiar with any sort of reference management software, be sure to check out our easy-to-follow Mendeley explainer video below.
Wrapping Up
In this post, we’ve provided a primer covering how to format your paper according to MLA 9th edition. To recap, we’ve looked at the following:
- The structure and layout
- The general page setup
- The “Works Cited” page (reference list)
Remember to always check your university’s style guide to familiarise yourself with any additional requirements they may. Also, if your university has specified anything that contrasts what we’ve discussed here, please do follow their guidance .
If you need any help formatting your paper for MLA 9, take a look at our “done for you” language editing and proofreading service . Simply send us your document and we’ll take care of all the MLA formatting intracies on your behalf.
You Might Also Like:

Very well recounted!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Microsoft 365 Life Hacks > Writing > Writing an Essay in MLA Format
Writing an Essay in MLA Format
Knowing how to write a Modern Language Association—or MLA—essay is an essential part of making it through school these days. Be warned, however, that daunting little tasks await around every corner—whether it’s knowing where to set your margins, how to edit a header, the right way to format a heading, and beyond!

While we can’t write your paper for you, this guide can certainly help you understand the proper MLA format for your essay. Keep reading to learn about writing an MLA-format paper with some tips for making sure it’s done right the first time.

Get the most out of your documents with Word
Elevate your writing and collaborate with others - anywhere, anytime
What is an MLA-format essay? It’s not uncommon for associations and organizations to follow a standard format and writing style. The Associated Press (AP) and University of Chicago styles are most common in professional settings. News outlets typically prefer the AP style, while businesses and creative agencies will choose the Chicago style. Academia, on the other hand, traditionally follows APA and MLA styles. APA (not the same as AP style) comes from the American Psychological Association and is used in scholarly articles. An MLA-format essay fits the established style for citing references and formatting essays established by the Modern Language Association.
Required elements of an MLA-format paper. MLA is the preferred style when writing an essay in high school and most college settings. As with other writing styles, there are specific characteristics and items an MLA-format paper needs to include to fit the bill of the style. Every MLA-format essay must include the following:
- One-inch margins
- Double-spaced text
- Easy-to-read font (typically Times New Roman) in size 12
- New paragraphs indented 0.5 inches
- Italicized media titles (books, magazines, etc.), no underlining
- Page numbers in the header 0.5 inches from the top of the page
- Oxford comma
- Center-justified title
- Headings and subheadings
- Clearly labeled and titled tables and figures
- Parenthetical citations
In addition to the listed elements above, every MLA essay must include a Works Cited. MLA format doesn’t require a title page, but it also doesn’t deem them unnecessary, so it’s up to your professor whether you’ll need one or not. One way to take the edge off the process of writing this type of essay is to use a free template or a handy built-in tool that helps you build bibliographies and more.

Tips for meeting MLA formatting guidelines. It’s said that the devil is in the details, and it’s never truer than when it comes to MLA-format essays. The following tips are areas to pay attention to when writing your essay:
- Set your margins. Your software might be set to one-inch margins, double-spaced text, and 0.5-inch indentations by default—but you can save yourself the trouble (and a headache) later in the writing process by adjusting them before you get started. Of course, one of the best parts about using a computer to write your essay is that you can always make adjustments later.
- Straighten out your headings . One area students might miss with MLA formatting is with the title, headings, and subheadings. It’s normal to want to use bold or italicized typeface on your titles and headings to make them stand out from the rest of the text. MLA style specifically calls for them to match the rest of the text without any alterations aside from title case. A centered or left-justified heading will stand out enough from the rest of your text that it needn’t any additional adjustments.
- Understand subheadings. While primary headings aren’t to receive any special formatting, subheadings will be changed to set them apart from their headings. For example, if your heading is about mammals, you might have subheadings about land and water mammals. You can further organize your water mammals subheading into types of whales and dolphins. Using subheadings helps to organize your writing and makes it easier to consume as a reader.
- Know how to cite your work. The information you’re presenting in your essay didn’t mysteriously appear from out of the ether. You need to give credit where it’s due when writing an MLA-format paper, so you’re giving credit to the original author of your sources. You can also improve your writing credibility and avoid plagiarism. Plagiarism is one of the biggest academic offenses a student can commit and could lead to expulsion in some cases. Properly citing your work with parenthetical citations and quoting authors when necessary will help to keep you covered.
When it comes down to it, practice makes perfect. The more essays you write, the better you’ll become at writing and meeting the expectations of MLA style. Before you know it, MLA format will be second nature, and everything will fall into place.
Still having a hard time visualizing what an MLA essay looks like? Check out a sample paper so you can see first-hand how they’re formatted!
Get started with Microsoft 365
It’s the Office you know, plus the tools to help you work better together, so you can get more done—anytime, anywhere.
Topics in this article
More articles like this one.

What is independent publishing?
Avoid the hassle of shopping your book around to publishing houses. Publish your book independently and understand the benefits it provides for your as an author.

What are literary tropes?
Engage your audience with literary tropes. Learn about different types of literary tropes, like metaphors and oxymorons, to elevate your writing.

What are genre tropes?
Your favorite genres are filled with unifying tropes that can define them or are meant to be subverted.

What is literary fiction?
Define literary fiction and learn what sets it apart from genre fiction.

Everything you need to achieve more in less time
Get powerful productivity and security apps with Microsoft 365

Explore Other Categories

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 3 popular essay formats: which should you use.
General Education

Not sure which path your essay should follow? Formatting an essay may not be as interesting as choosing a topic to write about or carefully crafting elegant sentences, but it’s an extremely important part of creating a high-quality paper. In this article, we’ll explain essay formatting rules for three of the most popular essay styles: MLA, APA, and Chicago.
For each, we’ll do a high-level overview of what your essay’s structure and references should look like, then we include a comparison chart with nitty-gritty details for each style, such as which font you should use for each and whether they’re a proponent of the Oxford comma. We also include information on why essay formatting is important and what you should do if you’re not sure which style to use.
Why Is Your Essay Format Important?
Does it really matter which font size you use or exactly how you cite a source in your paper? It can! Style formats were developed as a way to standardize how pieces of writing and their works cited lists should look.
Why is this necessary? Imagine you’re a teacher, researcher, or publisher who reviews dozens of papers a week. If the papers didn’t follow the same formatting rules, you could waste a lot of time trying to figure out which sources were used, if certain information is a direct quote or paraphrased, even who the paper’s author is. Having essay formatting rules to follow makes things easier for everyone involved. Writers can follow a set of guidelines without trying to decide for themselves which formatting choices are best, and readers don’t need to go hunting for the information they’re trying to find.
Next, we’ll discuss the three most common style formats for essays.
MLA Essay Format
MLA style was designed by the Modern Language Association, and it has become the most popular college essay format for students writing papers for class. It was originally developed for students and researchers in the literature and language fields to have a standardized way of formatting their papers, but it is now used by people in all disciplines, particularly humanities. MLA is often the style teachers prefer their students to use because it has simple, clear rules to follow without extraneous inclusions often not needed for school papers. For example, unlike APA or Chicago styles, MLA doesn’t require a title page for a paper, only a header in the upper left-hand corner of the page.
MLA style doesn’t have any specific requirements for how to write your essay, but an MLA format essay will typically follow the standard essay format of an introduction (ending with a thesis statement), several body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
One of the nice things about creating your works cited for MLA is that all references are structured the same way, regardless of whether they’re a book, newspaper, etc. It’s the only essay format style that makes citing references this easy! Here is a guide on how to cite any source in MLA format. When typing up your works cited, here are a few MLA format essay rules to keep in mind:
- The works cited page should be the last paper of your paper.
- This page should still be double-spaced and include the running header of your last name and page number.
- It should begin with “Works Cited” at the top of the page, centered.
- Your works cited should be organized in alphabetical order, based on the first word of the citation.
APA Essay Format
APA stands for the American Psychological Association. This format type is most often used for research papers, specifically those in behavioral sciences (such as psychology and neuroscience) and social sciences (ranging from archeology to economics). Because APA is often used for more research-focused papers, they have a more specific format to follow compared to, say, MLA style.
All APA style papers begin with a title page, which contains the title of the paper (in capital letters), your name, and your institutional affiliation (if you’re a student, then this is simply the name of the school you attend). The APA recommends the title of your paper not be longer than 12 words.
After your title page, your paper begins with an abstract. The abstract is a single paragraph, typically between 150 to 250 words, that sums up your research. It should include the topic you’re researching, research questions, methods, results, analysis, and a conclusion that touches on the significance of the research. Many people find it easier to write the abstract last, after completing the paper.
After the abstract comes the paper itself. APA essay format recommends papers be short, direct, and make their point clearly and concisely. This isn’t the time to use flowery language or extraneous descriptions. Your paper should include all the sections mentioned in the abstract, each expanded upon.
Following the paper is the list of references used. Unlike MLA style, in APA essay format, every source type is referenced differently. So the rules for referencing a book are different from those for referencing a journal article are different from those referencing an interview. Here’s a guide for how to reference different source types in APA format . Your references should begin on a new page that says “REFERENCES” at the top, centered. The references should be listed in alphabetical order.

Chicago Essay Format
Chicago style (sometimes referred to as “Turabian style”) was developed by the University of Chicago Press and is typically the least-used by students of the three major essay style formats. The Chicago Manual of Style (currently on its 17th edition) contains within its 1000+ pages every rule you need to know for this style. This is a very comprehensive style, with a rule for everything. It’s most often used in history-related fields, although many people refer to The Chicago Manual of Style for help with a tricky citation or essay format question. Many book authors use this style as well.
Like APA, Chicago style begins with a title page, and it has very specific format rules for doing this which are laid out in the chart below. After the title page may come an abstract, depending on whether you’re writing a research paper or not. Then comes the essay itself. The essay can either follow the introduction → body → conclusion format of MLA or the different sections included in the APA section. Again, this depends on whether you’re writing a paper on research you conducted or not.
Unlike MLA or APA, Chicago style typically uses footnotes or endnotes instead of in-text or parenthetical citations. You’ll place the superscript number at the end of the sentence (for a footnote) or end of the page (for an endnote), then have an abbreviated source reference at the bottom of the page. The sources will then be fully referenced at the end of the paper, in the order of their footnote/endnote numbers. The reference page should be titled “Bibliography” if you used footnotes/endnotes or “References” if you used parenthetical author/date in-text citations.
Comparison Chart
Below is a chart comparing different formatting rules for APA, Chicago, and MLA styles.
How Should You Format Your Essay If Your Teacher Hasn’t Specified a Format?
What if your teacher hasn’t specified which essay format they want you to use? The easiest way to solve this problem is simply to ask your teacher which essay format they prefer. However, if you can’t get ahold of them or they don’t have a preference, we recommend following MLA format. It’s the most commonly-used essay style for students writing papers that aren’t based on their own research, and its formatting rules are general enough that a teacher of any subject shouldn’t have a problem with an MLA format essay. The fact that this style has one of the simplest sets of rules for citing sources is an added bonus!

What's Next?
Thinking about taking an AP English class? Read our guide on AP English classes to learn whether you should take AP English Language or AP English Literature (or both!)
Compound sentences are an importance sentence type to know. Read our guide on compound sentences for everything you need to know about compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences.
Need ideas for a research paper topic? Our guide to research paper topics has over 100 topics in ten categories so you can be sure to find the perfect topic for you.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

Argumentative Essays: MLA Sample Argumentative Papers
- Choosing a topic
- Evaluating Sources
- Writing Arumentative Essays
- How to cite sources
- Annotated Bibliographies
- MLA Sample Argumentative Papers
MLA Sample Argumentative Papers (Note: these sample papers are in MLA 7th ed. format).
- MLA Sample Argumentative Paper 1
- MLA Sample Argumentative Paper 2
- MLA Sample Argumentative Paper 3
- MLA Sample Argumentative Paper 4
- MLA Sample Argumentative Paper 5
- MLA Sample Argumentative Paper 6
For sample papers in MLA 8th or 9th ed., please ask a librarian or check the Documenting Sources in MLA Style: 2016 Update: A Bedford/St. Martin's Supplement pp. 30-41, at Skyline College Library's Ready Reference shelf.
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliographies
- Next: Statistics >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2022 2:17 PM
- URL: https://guides.skylinecollege.edu/c.php?g=279231

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
MLA Works Cited Page: Format, Template & Examples

The Works Cited page is a part of research papers written in the Modern Language Association (MLA) format where all sources used by the author are listed. While writing research papers, authors may consult several sources and use their data or paraphrase parts of the original text. It is essential to give due credit to the used sources and cite them appropriately to avoid plagiarism. This list of sources offers an easy reference for readers who may want to refer to the original source for their own research.
A well-formatted and accurate Works Cited page can provide readers with specific details to help them access that source. For example, for a journal article, in addition to basic details like author name, title, journal name, etc., the MLA Works Cited page also provides the volume and issue numbers, page numbers, publisher, etc. A Works Cited page gives credibility to the research paper, proving that the information published is accurate and backed by evidence.
This article describes the template of an MLA Works Cited page along with examples and suggests steps to ensure accurate formatting of all entries.
Table of Contents
- What is a Works Cited Page?
- Basic Rules for an MLA Works Cited Page
- Online journal article with DOI or URL
- Online newspaper article
- E-book
- Specific type of e-book (Kindle, Nook)
- Print book
- Chapter in edited book
- Web page with an author
- Web page with no author
- Web page with no author or organization
- Blog post
- Video
- YouTube video
- Image
- Conference paper presentation
- Dissertation from a database
- Twitter (now X) posts
- Format of an MLA Works Cited Page
- Formatting Headings and Citation Titles on an MLA Works Cited Page
- Single author
- Two authors
- Three or more authors
- General rules
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Works Cited Page?
The MLA Works Cited page 1 lists all the sources used while writing research papers. This page is always the last one after the main content. A Works Cited page uses the official MLA format and has similar content as reference lists used by other styles such as the Chicago Manual of Style (Chicago style), the American Psychological Association (APA), and the American Medical Association (AMA). Each style uses a different format, emphasizing different elements.
The Works Cited page helps avoid plagiarism by crediting the sources and allows readers to quickly locate the sources. Papers in MLA format should always have a Works Cited page and each entry on this page should be cited in the text at the corresponding location.

Basic Rules for an MLA Works Cited Page
Here are some basic rules for writing the MLA Works Cited page: 2
- Start your Works Cited list on a fresh page at the end of your paper, with the same formatting as other sections, such as one-inch margins, last name, page number, and header.
- Align the title, “Works Cited,” at the top center. Don’t use italicization, boldfacing, quotation marks, or all-caps to highlight the title.
- Left align the citations and arrange them alphabetically by authors’ last names. If author names are unavailable, arrange by the first letter in the title (other than A, An, or The).
- Do not use serial numbering or bullets to list the entries.
- Double space all citations.
- Indent the second and subsequent lines of citations by 0.5 inches to create a hanging indent (Figure 1).

- List page numbers of the sources correctly. If only one page of a print source is used, use the abbreviation “p.” before the page number (e.g., p. 232). If a page range is used, use “pp.” (e.g., pp. 232-38).
- For online sources, include a location, like a URL or a digital object identifier (DOI). Delete “http://” from URLs. The DOI or URL is usually the last element in a citation.
- End all entries with a period.

Citing Sources in MLA
A citation in an MLA Works Cited page requires the following core elements. These elements should be written in the order given below, followed by the punctuation mark shown unless the particular element is the final element of the entry, in which case, it should end with a period. 4,5
- Author’s name
- Title of source
- Title of the container, (a container is the larger publication in which the text is published. For example, if citing an article from a journal, the journal is the container)
- Other editors, translators, contributors
- Publication date
- Location (page numbers in print versions; DOI or URL in online versions)
A few optional elements can be included, if available:
- Date of access (the date you last accessed the online source)
- Date of original publication
- Format of media source

All style guides have their own specific formats for writing different sources in a reference list—journal articles, printed and digital books, videos, websites, etc. The MLA-style format for different types of sources is listed below: 4
Online journal article with DOI or URL
Author’s last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal , vol., no. (issue), date of publication, pp. (if available). Database Name , DOI or URL.
Online newspaper article
Author’s last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Name of Newspaper , Publication Date, p. (if available), URL. Access date.
Author’s last name, First name. Title of Book . E-book, publisher, publication year, DOI or URL (if available).
Specific type of e-book (Kindle, Nook)
Author’s last name, First name. Title of Book , editor or translator (if necessary), (Kindle/Nook) ed., publisher, year.
Author’s last name, First name. Title of Book . City*, Publisher, Publication Date.
*City is cited only if the book is published before 1900 or if the publisher has multiple offices worldwide.
Chapter in edited book
Author’s last name, First name. Title of Book . Edited by FirstName LastName, publisher, year, page range of chapter.
Web page with an author
Author’s last name, First name. “Title of Webpage.” Title of Website , URL. Access date.
Web page with no author
“Title of Article.” Title of Website , date of publication, URL. Access date.
Web page with no author or organization
“Title of Webpage.” Title of Website (if different), publication year, URL. Access date.
Author’s last name, First Name (or, in some cases, screen name, editor, etc.). “Title of Post.” Name of Website , version or date of post, name of organization (if different), URL. Access date.
Title of Motion Picture/Film . Directed by First Name Last Name, performances by First Name Last Name, Studio Name, Year. Access date, Media format.
Last Name, First Name, director/writer/producer. Title of Motion Picture/Film . Studio, Year. Access date, Media format.
YouTube video
If author is different from the uploader:
Author Last Name, First Name. “Title of Video.” YouTube , uploaded by [Screen name], date, URL. Access date, Media format.
If author and uploader are the same OR if there is no clear author:
“Title of Video.” YouTube , uploaded by [Screen name], date, URL. Access date, Media format.
Artist’s Last Name, First Name. Title of Image , date of creation, institution, city. Name of web site , URL.
Title of Piece . Date of creation. Name of Website , URL.
Conference paper presentation
Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Conference Paper Title.” Conference Title that Includes Date and Location , edited by Conference Editor(s). Publisher. Date of Publication.
Dissertation from a database
Author’s Last Name, First Name. Title of Dissertation (Doctoral dissertation) . Database name, date of publication, URL (if available).
Twitter (now X) posts
Twitter Handle (First Name Last Name if Known). “The entire tweet word-for-word.” Twitter , Day Month Year of Tweet, Time of Tweet, URL.

Format of an MLA Works Cited Page
Here’s a list of steps for formatting the MLA Works Cited page:
- Place one-inch margins around the entire document except for the “running head.” In the page setup settings, you can view and modify the margin size.
- Double space the entire page using the “Line spacing” or “Paragraph spacing” options in your word processing program.
- Organize the Works Cited entries in either alphabetical (by author name or title) or non-alphabetical order. 1,2
Example:
Benjamin, Chloe. The Immortalists . Penguin, 2018.
Black Panther . Directed by Ryan Coogler, performance by Chadwick Boseman, Marvel Studios, 2018.
Egan, Jennifer. Manhattan Beach . Scribner, 2017.

Formatting Headings and Citation Titles on an MLA Works Cited Page
The following points outline the basic format for headings and titles used on a Works Cited page. 1 The running head is at the top right corner of every page of the document. It displays the last name of the author and the page number (e.g., Letterman 6).
- The running head should be placed half an inch from the top of the page and along the right side’s one-inch margin.
- The page title (Work/Works Cited) should be written below the running head.
- No center alignment
- No boldfacing, italicization, or underlining
- Same font size (12 point) and type as the entire document
- Separated by a double space from the first citation on the page
Consider the following rules while formatting source titles: 1,5,7,8
- List the full title as the original source and use title case (capitalize all principal words, except articles [a, an, the], prepositions, or coordinating conjunctions [and, for, but, or, so, nor, yet] when in the middle of the title).
Examples:
The Code of the Exiled, Wizard of Oz, Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire
Cheyfitz, Eric. The Poetics of Imperialism: Translation and Colonization from The Tempest to Tarzan. Expanded ed., U of Pennsylvania P, 1997.
- Separate the subtitle from the title with a colon and space.
Goldman, Anne. “Questions of Transport: Reading Primo Levi Reading Dante.” The Georgia Review , vol. 64, no. 1, 2010, pp. 69-88.
- Italicize titles if the source is self-contained and independent, e.g., titles of books, plays, films, periodicals, journals, magazines, databases, and websites.
Example: Salinger, J. D. The Catcher in the Rye . Little Brown, 1991.
- Enclose titles in quotation marks if the source is part of a larger work, e.g., articles, essays, chapters, poems, short stories, webpages, songs, television episodes, and speeches.
- Titles beginning with numbers are placed in the reference list as if the title was written out alphabetically.
Formatting Author Names on an MLA Work Cited Page
Few important rules to consider when formatting author names: 1,2
Single author
- List author names alphabetically by the author’s last name (or, for entire edited collections, editor names). The format for writing author names is as follows:
Last name, first name, middle name or middle initial
Said, Edward W. Culture and Imperialism . Knopf, 1994.
- To cite more than one work by the same author, order the entries alphabetically by title, and use three hyphens in place of the author’s name for every entry after the first.
Alcott, Louisa May. “Eight Cousins.” Project Gutenberg , 2018, www.gutenberg.org/files/2726/2726-h/2726-h.htm .
—. Little Women . Bantam Classics, 1983.
—. Rose in Bloom . CreateSpace, 2018.
Two authors
The first listed author’s name on the source is the first author in the reference.
Last name, First name of author 1, and First name Last name of author 2
Pavear, Richard, and Larissa Volokhonsky, translators. Crime and Punishment . By Feodor Dostoevsky, Vintage eBooks, 1993.
Three or more authors
Include only the first listed author’s last name, followed by a comma and their first name, followed by another comma and then “et al.”
Example:
Baron, Sabrina Alcorn, et al., editors. Agent of Change: Print Culture Studies after Elizabeth L. Eisenstein. U of Massachusetts P / Center for the Book, Library of Congress, 2007.
General rules
- Do not list titles (Dr., Sir, etc.) or degrees (PhD, MA, MD, etc.) with names but include suffixes like “Jr.” or “II.”
King, Martin Luther, Jr.
- Alphabetize works with no known author by their title; use a shortened version of the title in the parenthetical citations in your paper.
Baudrillard, Jean. Simulacra and Simulations . […]
Boring Postcards USA […]
- To cite works by authors using a pseudonym or stage-name, cite the better-known name if the person is well known. For example, Lewis Carroll is the pseudonym of Charles Dodgson, and is the better-known name so only the pseudonym should be used. If the pseudonym is less well known, cite the real name in square brackets after the pseudonym.
Van Dyne, Edith [L. Frank Baum]. Aunt Jane’s Nieces At Work . 1st World Library, 2006.


Key Takeaways
To summarize, an MLA Works Cited page should have the following format:
- Starts on a new page at the end.
- Centered page title without any highlights.
- Double-spaced citations, preferably in Times New Roman 12-pt font.
- Left-justified entries with a hanging indent of 0.5 inches.
- Source titles in title case.
- Entries ordered by the first word, typically author name or the first word in the title (except articles a, an, the). If the title begins with a year or a number, alphabetize it as if the number/year is spelled out.
Frequently Asked Questions
A1. The Works Cited page and references have a similar purpose; both include sources that have been specifically cited or paraphrased in the paper and whose data have been directly used. A bibliography includes a list of sources related to the content in a research paper, that is, sources that you may have consulted while writing your research paper, but may not have actually used, cited, or paraphrased from. 1
A2. Yes, there are a few other styles for citing references, such as the Chicago Style, AMA Manual of Style, APA Manual of Style, and the IEEE style. All of these have different referencing formats. In addition, organizations may create their own referencing styles, commonly called a house style.
A3. No, the Works Cited page should include only those sources that you have cited or whose data you have used in your research paper. Sources that you have only consulted while conducting research should be included in a bibliography.
A4. Per MLA format, ignore symbols, such as hashtags when alphabetizing. Use the first letter in the entry to alphabetize. 9 Example: @AP. “It’s been four years since the #MeToo movement took over social media. . . .” X, 15 Oct. 2021, https://twitter.com/AP/status/1449019990741590025. “#MeToo Poll: Many in US More Willing to Call Out Misconduct.” Associated Press , 15 Oct. 2021, https://apnews.com/article/sexual-misconduct-metoo-79688da3a0c3519d2a76b5b6e6b23ba7. “#MeToo Protest in Amsterdam after Allegations at TV Show.” Associated Press , 29 Jan. 2022, https://apnews.com/article/entertainment-business-arts-and-entertainment-netherlands-amsterdam-4bb589aae061e534b1a47ac453e9d85f .
A5. Here is one way of adding a hanging indent in MS Word: 10 1. Highlight the text that you want to format. 2. Click the Home tab at the top of the page; in the “Paragraph” section click the small arrow in the lower-right corner to open a window with different paragraph setting options. 3. In that settings window, look for a section, “Indentation,” which has an option, “Special.” Click the drop-down menu beneath Special and select Hanging. 4. MS Word will mostly have the default spacing of the hanging indent set to 0.5 inches. To adjust the spacing, change the number in the By section. 5. Click OK to save and apply the hanging indent to your highlighted text.
To summarize, an MLA Works Cited page is an essential part of a manuscript written using the MLA style and includes all sources used by the author to write the research paper. As described in the article, the Works Cited page and its entries have a specific format that should be strictly followed, and all the core elements included in the individual entries.
We hope this article has provided a deeper understanding of the MLA style and will help you apply this format to all your Works Cited pages.
References
- What is a works cited page? EasyBib website. Accessed May 14, 2024. https://www.easybib.com/guides/citation-guides/mla-format/how-to-format-a-mla-works-cited-list/
- MLA Works Cited page: Basic format. Purdue Online Writing Lab. Accessed May 14, 2024. https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_page_basic_format.html
- MLA Citation: Works Cited Example. Press Books @ MSL website. Accessed May 16, 2024. https://pressbooks.ulib.csuohio.edu/csu-fyw-rhetoric/chapter/12-4-mla-works-cited-examples/
- MLA Works Cited Page. The University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center. Accessed May 17, 2024. https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/mla-works-cited-page
- Section 5. List of Works Cited. MLA Handbook eighth edition.
- Sample MLA Works Cited Page. College of San Mateo library website. Accessed May 17, 2024. https://www.collegeofsanmateo.edu/library/docs/MLAWorksCited7.pdf
- MLA Style Guide, 8 th & 9 th Editions: Title of Source. Accessed May 18, 2024. https://irsc.libguides.com/c.php?g=483085&p=3303403#:~:text=Italicize%20titles%20if%20the%20source,are%20placed%20in%20quotation%20marks .
- Frequently Asked Questions about Citing Sources in MLA Format. Harvard Guide to Using Sources. Accessed May 20, 2024. https://usingsources.fas.harvard.edu/frequently-asked-questions-about-citing-sources-mla-format
- How do I alphabetize a works-cited-list entry that begins with a hashtag or another symbol? MLA Style Center. Accessed May 21, 2024. https://style.mla.org/alphabetizing-hashtags-and-other-symbols/
- Hanging Indents and Microsoft Word. MLA Style Center. Accessed May 21, 2024. https://style.mla.org/hanging-indents/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- How to Cite Social Media Sources in Academic Writing?
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
- How to Use AI to Enhance Your College Essays and Thesis
How to Ace Grant Writing for Research Funding with Paperpal
How to write the first draft of a research paper with paperpal , you may also like, how to write the first draft of a..., how to ace grant writing for research funding..., powerful academic phrases to improve your essay writing , how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples .

College MLA
Ai generator.

In the realm of college academia, adhering to the appropriate formatting guidelines is paramount, not only for presenting your ideas effectively but also for showcasing your professionalism. One such widely used formatting style is the College MLA Format. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on understanding MLA Format, step-by-step instructions on how to write in this format, answers to frequently asked questions, and examples to help you navigate through your academic writing endeavors seamlessly.
What is College MLA Format?
The College MLA Format refers to the Modern Language Association’s formatting style commonly used in academic writing, especially in the humanities and liberal arts disciplines. It sets guidelines for organizing and documenting various components of a paper, including in-text citations, works cited pages, headings, and more. Adhering to the MLA Format ensures consistency and facilitates clear communication of ideas within the scholarly community.
College MLA Format
The Modern Language Association (MLA) format is a style guide commonly used for writing and documenting research in the humanities, particularly in English studies. Here is a comprehensive guide on how to format your college paper in MLA style.
General Formatting Rules
- Use a legible font like Times New Roman.
- Font size should be 12-point.
- Set all margins to 1 inch on all sides.
- Double-space the entire document, including quotations, notes, and the works cited page.
- Indent the first line of each paragraph one-half inch from the left margin (use the Tab key).
- Center the title of the paper. Do not underline, italicize, or place it in quotation marks.
- Use standard capitalization (title case).
- Include a header in the upper right-hand corner, half an inch from the top and flush with the right margin.
- The header should include your last name followed by a space and the page number.
- In the upper left-hand corner of the first page, list your name, your instructor’s name, the course, and the date, each on a separate line, double-spaced.
John Smith Professor Johnson English 101 1 June 2024
In-Text Citations
- Author’s last name and page number(s) should be in parentheses.
- Example: (Smith 123).
- Two authors: (Smith and Jones 123).
- Three or more authors: (Smith et al. 123).
- Use a shortened title of the work instead of the author’s name.
- Example: (“Impact of Global Warming” 45).
Works Cited Page
- Title the page “Works Cited” (without quotation marks), centered at the top of the page.
- Double-space all entries.
- Use a hanging indent for each entry (first line flush left, subsequent lines indented half an inch).
- Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Periodical , vol. number, no. number, Year, pages.
- Smith, John. Understanding MLA Format . Penguin, 2020.
- Article in a Journal:
- Jones, Emily. “The Effects of Pollution.” Environmental Studies , vol. 34, no. 2, 2019, pp. 123-145.
Johnson, Mark. “Global Warming Facts.” Climate Change Resources , 2023, www.climateresources.org/global-warming-facts.
College MLA Template
Below is the template filled with sample details for a college paper formatted in MLA style:
John Smith Professor Johnson English 101 1 June 2024 The Effects of Climate Change on Biodiversity Climate change has become a critical issue affecting various aspects of the environment. The impact of climate change on biodiversity is particularly significant. As temperatures rise, many species are forced to migrate to cooler areas or face extinction. In this paper, the effects of climate change on different species and ecosystems will be examined, highlighting the importance of immediate action to mitigate these effects. Effects on Animal Species One of the most noticeable impacts of climate change is the alteration of habitats. According to Smith, “Many species are losing their natural habitats due to changing temperatures and weather patterns” (23). For instance, polar bears are struggling to find ice platforms from which they can hunt seals. This habitat loss is leading to a decline in polar bear populations. In addition to habitat loss, some species are facing changes in their food supply. Jones notes that “rising sea temperatures are affecting the availability of certain fish species, which in turn affects the animals that rely on them for food” (45). This chain reaction illustrates how interconnected ecosystems are and how changes in one part can have widespread effects. Effects on Plant Species Climate change also affects plant species. Increased temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can disrupt the growth cycles of plants. “Many plant species are blooming earlier than usual, which can disrupt the timing of food availability for herbivores” (Johnson 67). This mismatch can have serious consequences for species that rely on specific plants for food during certain times of the year. Furthermore, the spread of invasive species is a growing concern. Invasive plants, which thrive in changing conditions, can outcompete native species, leading to reduced biodiversity. “Invasive species are often more adaptable to changing climates, allowing them to spread rapidly and dominate ecosystems” (Smith 89). Conclusion The effects of climate change on biodiversity are profound and far-reaching. Both animal and plant species are struggling to adapt to the rapid changes in their environments. Immediate action is necessary to mitigate these effects and preserve the planet’s biodiversity. Conservation efforts, habitat restoration, and policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions are critical steps in addressing this global challenge. Works Cited Johnson, Mark. “Global Warming Facts.” Climate Change Resources , 2023, www.climateresources.org/global-warming-facts. Jones, Emily. “The Effects of Pollution.” Environmental Studies , vol. 34, no. 2, 2019, pp. 123-145. Smith, John. Understanding MLA Format . Penguin, 2020. Smith, John. “Impact of Habitat Loss on Polar Bears.” Wildlife Conservation Journal , vol. 12, no. 1, 2018, pp. 23-30.
College MLA Header
The header in an MLA-formatted college paper is straightforward. It includes your last name and the page number, aligned to the right. Here’s how you can format it along with a sample filled with details:
Header Format
- Position : The header should be placed in the upper right-hand corner of each page.
- Font and Size : Use the same font and size as the rest of your paper (usually Times New Roman, 12-point).
- Content : Your last name followed by a space and the page number.
- Alignment : Right-aligned.
Creating an MLA Header in Word
- Open your document in Microsoft Word.
- Go to the “Insert” tab and click on “Header”.
- Choose “Blank” or any simple header style.
- Click on “Page Number” in the “Insert” tab, choose “Top of Page”, and then “Plain Number 3” (this places the number on the top right).
- Type your last name before the page number.
- Ensure the font and size match the rest of your document (Times New Roman, 12-point).
- Close the header section by double-clicking outside the header area.
College MLA Format Essay
John Smith Professor Brown English 101 4 June 2024 The Impact of Technology on Education Technology has revolutionized the way we approach education. From elementary schools to universities, digital tools and resources have transformed traditional teaching methods, making learning more interactive, engaging, and accessible. This essay explores the impact of technology on education, highlighting both the benefits and the challenges it presents. One significant benefit of technology in education is the increased access to information. With the internet, students can access a wealth of information on any topic imaginable. Online libraries, educational websites, and digital textbooks provide students with resources that were previously unavailable or difficult to obtain. This access to information promotes self-directed learning, allowing students to explore subjects in greater depth and at their own pace. Another advantage is the enhancement of learning experiences through interactive tools. Educational software, virtual simulations, and multimedia presentations make learning more engaging and enjoyable. For example, science students can conduct virtual experiments, history students can explore interactive timelines, and language students can practice with language-learning apps. These tools not only make learning more fun but also cater to different learning styles, helping students to better understand and retain information. Moreover, technology facilitates collaboration and communication among students and teachers. Online discussion forums, group projects using collaborative tools, and video conferencing enable students to work together, share ideas, and receive feedback in real-time, regardless of their physical location. This connectivity fosters a sense of community and teamwork, which are essential skills in the modern workforce. However, the integration of technology in education also presents several challenges. One major issue is the digital divide. Not all students have equal access to digital devices and the internet, leading to disparities in educational opportunities. Schools in underfunded areas may struggle to provide the necessary technology, and students from low-income families may not have access to computers or reliable internet at home. This digital divide can exacerbate existing inequalities and hinder the academic progress of disadvantaged students. Additionally, the overreliance on technology can sometimes detract from traditional learning methods that are still valuable. For instance, excessive screen time can negatively impact students’ health, leading to issues such as eye strain and poor posture. Furthermore, the use of technology in the classroom can sometimes be a distraction, with students being tempted to use their devices for non-educational purposes during lessons. In conclusion, technology has undeniably transformed education, offering numerous benefits such as increased access to information, enhanced learning experiences, and improved collaboration. However, it is crucial to address the challenges it presents, including the digital divide and the potential for distraction. By finding a balance between traditional and digital teaching methods, educators can harness the power of technology to create a more effective and inclusive educational environment. Works Cited Smith, John. The Art of Writing . Penguin, 2020. —. “Understanding Poetry.” Literary Journal , vol. 5, no. 2, 2021, pp. 123-145. Doe, Jane. “The Future of Technology.” Tech Monthly , 4 Mar. 2022, pp. 30-35. Doe, Jane, and John Smith. The Study of Literature . Oxford UP, 2019. Smith, John. “How to Write an Essay.” Writing Help , 5 May 2023, www.writinghelp.com/how-to-write.
College MLA Format Citation
When writing a college paper in MLA format, proper citation is crucial for giving credit to sources and avoiding plagiarism. Below are examples of how to cite various types of sources in MLA format, both in-text and in the Works Cited page.
In-text citations are brief references within your text that direct the reader to the complete citation in your Works Cited list.
General Format
- Example: (Smith 123)
- “Climate change significantly impacts biodiversity” (Smith 45).
- Two authors: “The study shows a direct correlation” (Smith and Jones 67).
- Three or more authors: “Several factors were considered” (Smith et al. 89).
- Use a shortened title: “Effects of pollution are widespread” (“Impact of Pollution” 123).
The Works Cited page lists all the sources cited in your paper. It should start on a new page at the end of your paper.
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . Publisher, Year.
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal , vol. number, no. number, Year, pages.
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Web Page.” Title of Website , Publisher, Date, URL.
- Johnson, Mark. “Global Warming Facts.” Climate Change Resources , 2023, www.climateresources.org/global-warming-facts .
How to write in College MLA Format?
Writing in College MLA Format may initially seem daunting, but with a step-by-step approach, you can easily master this widely used formatting style. Whether you’re working on an college essay , research paper , or any other academic document, following the guidelines of MLA Format ensures consistency and professionalism in your writing. This comprehensive guide will walk you through each stage of the writing process, providing clear instructions to help you navigate the intricacies of MLA Format successfully. By the end, you’ll feel confident in your ability to craft well-structured and properly formatted papers that meet the standards of scholarly communication. So let’s dive in and discover the key steps to writing in College MLA Format.
Step 1: Formatting the Document:
To begin writing in College MLA Format, start by setting up the document appropriately. Use a standard font such as Times New Roman or Arial, with a size of 12 points. Set the margins to 1 inch on all sides and double-space the entire document.
Step 2: MLA Format Heading:
At the top left corner of the first page, include a an MLA Format heading with your name, your instructor’s name, the course title, and the date, all aligned to the left. Place your last name and page number in the header’s top right corner, using the “Insert” tab in word processors like Microsoft Word or Google Docs.
Step 3: In-Text Citations and Works Cited:
When referencing sources within the text, use parenthetical citations including the author’s last name and the page number (e.g., Smith 45). Create a separate page titled “Works Cited” at the end of your paper and list all the sources cited in alphabetical order, following the MLA Format Works Cited guidelines.
What is MLA format?
MLA format is a style guide for writing and documenting research in the humanities, especially in English studies, established by the Modern Language Association.
How do I format the header in MLA?
Include your last name and page number in the upper right corner, right-aligned, half an inch from the top.
What font and size should I use in MLA format?
Use Times New Roman, 12-point font throughout the entire document.
How do I format in-text citations in MLA?
Include the author’s last name and page number in parentheses, like this: (Smith 123).
How should I format the Works Cited page?
Title the page “Works Cited,” center it, double-space all entries, and use a hanging indent for each entry.
How do I format a block quote in MLA?
Indent the entire quote one inch from the left margin, double-space it, and do not use quotation marks.
What information goes in the heading on the first page?
Include your name, your instructor’s name, the course name, and the date, each on a separate line, left-aligned.
Do I need a title page for MLA format?
MLA format typically does not require a title page. Instead, use a heading on the first page.
How do I cite a book in MLA format?
Format: Author’s Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . Publisher, Year.
How are multiple authors cited in MLA format?
For two authors, use both last names: (Smith and Jones 123). For three or more, use the first author’s last name followed by “et al.”: (Smith et al. 123).
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

How to Write an Explanatory Essay
- Smodin Editorial Team
- Published: May 24, 2024
A study from the English Language Teaching Educational Journal found that students encounter difficulty in organizing thoughts, generating ideas, and understanding writing processes when writing essays [1]. These are all key components of putting together a good explanatory essay. If this sounds like you, then don’t worry.
With the right approach, you can seamlessly combine all these components. This guide will give you a simple step-by-step strategy for writing an explanatory essay. It’ll also give you handy writing tips and tool suggestions, like utilizing artificial intelligence.
With this guide, you’ll be able to write an explanatory essay with confidence.
1. Develop a strong thesis statement
Crafting a strong thesis statement is the cornerstone of any well-written explanatory essay. It sets the stage for what your essay will cover and clarifies the main point you’re going to explain. Here’s how to create a thesis:
- Find the main idea : Start by pinpointing the key concept or question you want to explain. Develop a clear purpose for the essay. This will guide your research and writing process for your explanatory paper. Use other reputable explanatory essay examples to guide your ideas. This may involve exploring other explanatory essay topics within the same field.
- Be specific : A vague thesis can confuse readers. So, make sure your statement is clear. If you’re explaining a complex process, break it down to its key points. After that, break it into a clear, concise statement that’s easy to understand.
- Reflect objectivity : Explanatory essays educate and inform. They do not argue a point. So, your thesis should take an unbiased stance on the topic. It should present the facts as they are, not as you interpret them.
- Use tools like the Smodin Writer : Smodin Writer does all the heavy lifting by leveraging the power of artificial intelligence. With it, you can generate an essay with a thesis statement. How, you ask? Through its dedicated thesis generator . It can create a statement that’s both strong and relevant. Plus, it can pull in all the most interesting information based on your topic to further enrich your thesis statement.
Make your thesis clear, informative, and neutral. This sets a strong foundation for an effective explanatory essay. Next, let’s look at how to gather the information you’ll need to support this thesis effectively.
2. Research and gather information
You need to conduct thorough research that will back your thesis with credible sources and relevant evidence. This will make your explanatory essay both informative and persuasive. Here’s a step-by-step guide to conducting effective research:
- Start with a plan: Put together an explanatory essay outline that includes the information you need to support your thesis. The plan should list the best sources, like academic journals, books, reputable websites, or scholarly articles.
- Use credible sources: They ensure the accuracy of your essay. Libraries, academic databases, and certified websites are excellent places to find trustworthy information.
- Seek detailed information: Look for the most current sources that explain your topic well and provide unique insights related to or opposing your thesis statement. This depth is crucial for explaining complex ideas clearly and thoroughly in your explanatory papers. Pay attention to the explanatory essay structure to guide your topic of choice (more on this later).
- Gather relevant evidence: Collect data, stats, and examples. They should directly support your main points. Make sure this evidence is directly related to your topic and enhances your narrative.
- Employ digital tools: Tools like Smodin’s Research Assistant can accelerate your research process. Smodin’s tools can help you find detailed information quickly, ensuring that the data you use is up-to-date and relevant.
- Document your sources: As you conduct research, keep a meticulous record of where your information comes from. This practice will help you make an accurate bibliography. It can save you time when you need to refer back to details or verify facts. Again, this is something that’s covered thanks to Smodin’s Citation Machine.
- Evaluate your findings: Critically assess the information you collect. Ensure it provides a balanced view and covers the necessary aspects of your topic to give a comprehensive overview of your essay.
By following these steps, you can gather a rich pool of information that provides a strong backbone for your explanatory essay. Now, you can start structuring your findings into well-organized body paragraphs.
3. Structure body paragraphs
Once you’ve gathered relevant evidence through thorough research, it’s time to organize it. You should put it into well-structured body paragraphs that follow a logical flow. Here’s how to structure each body paragraph for a strong explanatory essay:
- Decide how many paragraphs to use : It will depend on your topic’s complexity and the needed detail. Typically, three to five paragraphs are suitable, but longer essays may require more. An explanatory essay example on your topic of choice will be helpful.
- Start with a topic sentence : Each body paragraph should begin with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph. This sentence will act as a roadmap for the paragraph, giving the reader a sense of what to expect.
- Provide supporting evidence : After the topic sentence, share the evidence from your research. Ensure the evidence is relevant and directly supports the paragraph’s topic sentence.
- Give a detailed explanation : Follow the evidence with an analysis or explanation that ties it back to the thesis statement. This step is crucial for maintaining logical flow throughout your body paragraphs.
- Use linking words : They connect body paragraphs smoothly, ensuring the reader can follow your argument.
- End each body paragraph with a closing sentence : It should sum up the point and move to the next idea.
Following this structure will help your body paragraphs support your thesis. These paragraphs will also offer a clear, detailed explanation of your essay topic. Strong body paragraphs are essential to maintain objectivity in your writing.
4. Maintain objectivity
An explanatory essay aims to inform and educate, which makes maintaining objectivity crucial. Staying neutral lets readers form their own opinions based on facts. This ensures the writing is both reliable and informative. Here’s how to maintain objectivity:
- Avoid personal opinions: Your goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic. Refrain from injecting your personal opinion or biases. Instead, stick to presenting factual information that supports the thesis.
- Use relevant evidence: As mentioned, ground your arguments with relevant evidence from credible sources. Back up your main points with data and use research findings and verified details. This will make the explanatory article trustworthy.
- Provide a balanced view: In cases with multiple perspectives, offer a balanced view. Cover each side fairly. Even if one view prevails in consensus, acknowledging others gives readers a broader understanding.
- Adopt neutral language: Be careful with word choice and tone. Neutral language implies words that don’t encourage or illustrate bias. This helps avoid emotionally charged phrases and keeps the writing objective.
- Cite sources accurately: Proper citation of sources provides accountability for the evidence presented. This transparency builds credibility and shows you’ve conducted research thoroughly. It’s also worth noting that different intuitions have different citation styles like APA and Chicago, which is important to note before starting your essay.
- Review for biases: After drafting your essay, review it with an eye for biases. Ensure no part leans too much on one viewpoint. And, don’t dismiss an opposing perspective without cause.
Maintaining objectivity enhances the clarity and reliability of explanatory writing. Let’s now focus on crafting an introduction and conclusion that bookend your work effectively.
5. Craft an effective introduction and conclusion
A good introduction and a strong conclusion frame your explanatory essay. They give context at the start and reinforce the main points at the end. Here’s how to craft an effective introduction and conclusion.
In the introduction:
- Hook your reader in the introduction : Use an interesting fact, a compelling quote, or a surprising statistic.
- Provide background information : Be brief and offer only the essential context the reader needs to fully understand the topic. This should give the audience a foundational understanding before diving deeper into your main points.
- Include the thesis statement : Clearly state your thesis near the end of the introduction. This statement will outline the essay’s direction and give readers a preview of the body paragraphs.
In the conclusion:
- Summarize the key points : Start your explanatory essay conclusion with a summary. It should cover the main points from the body paragraphs. This summary should help readers recall and reinforce the information they’ve just read.
- Restate the thesis : Repeat your thesis again but in a new way. Explain how the evidence from the body paragraphs supported or clarified it.
- Provide a conclusion : End the essay with a statement that wraps up the argument. This statement should resonate with the reader. It should leave them with an impression that stresses the topic’s importance.
An effective introduction and conclusion give the essay structure and coherence. They guide readers from start to finish. The next step is revising and editing your entire essay for clarity and precision.
6. Revise and check clarity
Revising and editing are key in writing. They make sure your essay is clear, joined, and polished. Here’s how to refine your writing using an explanatory essay checklist and proven academic writing techniques:
- Take a break: Before diving into revisions, step away from your essay for a few hours or even a day. This break will help you return with fresh eyes, making it easier to spot errors or inconsistencies.
- Follow an essay checklist: Create or use a checklist to ensure your essay has all the needed parts. It needs a strong intro with a clear thesis, well-structured body paragraphs, good sources, and a short conclusion. Check that your arguments follow a logical flow and that all relevant evidence is directly linked to your thesis statement.
- Check for clarity and conciseness: Academic writing needs clarity. So, make sure each paragraph and sentence conveys your point. Don’t use unnecessary jargon or overly complex language. Keep sentences concise while maintaining detailed explanations of your main points.
- Verify facts and citations: Make sure all facts, data, and quotes in the essay are accurate. Also, check that they are cited in the required academic style (e.g. MLA, APA). Improper citations can undermine the credibility of your writing.
- Review the grammar and style: Look for common grammar mistakes, punctuation errors, and awkward phrasing. Reading the essay aloud can help catch odd sentence structures or confusing wording.
- Seek feedback: Share your essay with a peer or use online tools to get constructive criticism. A second perspective can highlight issues you might have missed.
These editing steps will help you produce a polished essay that clearly explains your main points and holds up to academic scrutiny.
Explanatory Essay Format
Understanding the explanatory essay format is key to a well-structured and logical paper. Here’s a basic breakdown of the format for an explanatory essay:
Introduction paragraph
- Begin with an interesting sentence to capture the reader’s attention.
- Give a short intro. It should set the topic and outline the essay’s purpose.
- Present a clear thesis statement summarizing the main idea of the entire essay.
Body paragraphs
- Organize the body paragraphs around logical subtopics related to the essay topic.
- Start each body paragraph with a topic sentence that aligns with the thesis.
- Show evidence from good sources. Also, give key details for each main point.
- Incorporate a robust concluding statement per paragraph that drives home your point and links to the ideas in the next paragraph/section.
- Summarize the key points.
- Provide a final statement that reinforces the main idea without introducing new information.
- Craft a concluding statement that leaves your teacher or professor with a lasting impression.
Following this essay outline ensures that your paper has a clear flow. This makes it easy for readers to understand and follow your argument.
Write Better Explanatory Essays With Smodin
Explanatory essays can be overwhelming. Presenting a solid argument, keeping your professor or teacher interested, and remembering conventions like citations can be a real headache.
But, a strong thesis and thorough research make them easier. Well-structured body paragraphs also help deliver a clear, insightful essay that maintains objectivity. Just remember to revise and check for accuracy!
AI-powered platforms like Smodin simplify and enhance the process of writing explanatory essays.
Smodin’s tools help craft clear and well-structured essays that meet any of your academic standards. With Smodin’s advanced research capabilities, you can gather detailed and relevant information quickly. This will save you time and improve your work.
- Plagiarism Checker : Ensure your essay maintains originality with Smodin’s plagiarism detection tool. This feature helps maintain academic integrity by checking your work against vast databases.
- Auto Citation : Cite your sources accurately without the hassle. Smodin’s auto-citation tool ensures your references are in the right format and meet your academic institution’s rules.
- Text Shortener : If your explanatory essay is too long, use Smodin’s AI writer as an essay shortener. It will help you cut your content without losing key details. This helps keep your essay clear and relevant.
- Text Rewriter : Helps paraphrase existing content, ensuring uniqueness and a fresh perspective.
- Summarizer : The Summarizer boils down long articles into short summaries. They are perfect for making an efficient outline or conclusion.
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / MLA Book Citation
How to Cite a Book in MLA
Books are written works or compositions that have been published. They are no longer restricted to paper and have evolved into the online realm.
Below are examples of how to cite different types of books in MLA 9. If you need a different citation style, there is also a guide on citing a book in APA .
In MLA, a basic book citation includes the following information:
- Author’s name
- Title of book
- Publisher of the book
- Year published
Additional information is needed when citing:
- Name of website or database
- Name of e-book device
- Name of the translator or editor
- Name of book editor or author
- Name of chapter author
- Page numbers or ranges used
- Volume number of the book
- City the book was published in
Citing a book in MLA (print)
View Screenshot | Cite your book
Citing a book found on a Website or database in MLA
Many books are now found online. Popular sites or databases that hold e-books include Google Books, Project Gutenberg, and EBSCO.
Cite your book
*Keep “https:” at the beginning of the URL only when citing a DOI.
Digital sources with no page numbers means that no page numbers should be included in the in-text citation.
Citing an E-book in MLA (found via an e-reader)
E-Readers are electronic devices that display e-books. Kindles and Nooks are some of the more popular e-readers available today. Individuals can purchase or borrow e-books and read them on their e-readers.
Cite your ebook
Since the page numbers of an e-book can vary across e-reader, text preferences, and other factors, you should not include a page number. This is because a consistent page number does not exist. You can include section numbers (sec., secs.) or chapter numbers (ch., chs.) instead, if they exist and you feel it would be helpful.
Citing a translated or edited book in MLA
Citing a chapter of a book in mla.
*In the above citation example, The Body of the Queen: Gender and Rule in the Courtly World, 1500-2000 is an edited book that features a chapter by Louis Montrose. The title of the chapter that he wrote is found in quotation marks (“Elizabeth Through the Looking Glass: Picturing the Queen’s Two Bodies”).
Citing a book with multiple authors in MLA
*et al. is Latin for “and others.”
Published October 20, 2011. Updated May 9, 2021.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
In the works cited: If the organization is the author and publisher, don’t include an author and start the citation with the book’s title. If the author and publisher are different, use the organization name as the author.
When the chapter’s author is different from the book’s editor or author. Chapters are usually cited when you use anthologies, multi-volume sets, or a foreword/afterword written by someone other than the book’s main author.
Place the author’s last name and the quote chapter number in parenthesis after the borrowed quote or information. Example: “Feeling that Peter was on his way back, the Neverland had again woke into life” (Barrie ch. 5).
MLA is the style most often used in literature, language, history, art and theater subjects.
If any important information is missing (e.g., author’s name, title, publishing date, URL, etc.), first see if you can find it in the source yourself. If you cannot, leave the information blank and continue creating your citation.
Yes! Whether you’d like to learn how to construct citations on your own, our Autocite tool isn’t able to gather the metadata you need, or anything in between, manual citations are always an option. Click here for directions on using creating manual citations.
To cite a book with multiple authors in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the authors, publication year, book title, and publisher. The templates for in-text citation and works-cited-list entry of a book written by multiple authors and some examples are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
Citation in prose:
For sources with two authors, use both full author names in prose (e.g., Harold Napoleon and Richard Harris). For sources with three or more authors, use the first name and surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Harold Napoleon and others). In subsequent citations, use only the surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Napoleon and others).
First mention: Harold Napoleon and colleagues…. or Harold Napoleon and others ….
Subsequent occurrences: Napoleon and colleagues…. or Napoleon and others ….
Parenthetical:
In parenthetical citations, use only the author’s surname (e.g., Napoleon). For sources with two authors, use two surnames (e.g., Napoleon and Harris). For sources with three or more author names, use the first author’s surname followed by “et al.”
….(Napoleon et al.)
Works-cited-list entry template and example:
The title of the book is given in italics and title case.
Surname, F. M., et al. Title of the Book . Publisher, Publication Date.
Napoleon, Harold, et al. Yuuyaraq the Way of the Human Being: With Commentary . University of Alaska, 1996.
Use only the first author’s name in surname–first name order in the entry and follow it with “et al.”
A book is a printed copy, whereas an e-book is an online version and is available via different electronic media (e.g., epub and Kindle).
To cite a print book in MLA format, you need to know the names of the authors, the title of the book, publisher name, publication date, and page range (optional). You need the same information to cite an e-book, however, you will not include page numbers unless they are the same as those in the print version of the book. MLA mostly treats citations for print books and e-books the same, except for noting that the e-book version is being cited within the entry.
The templates and examples for in-text citations and works cited list entries for a book and an e-book are provided below:
In-text citation template and example for a book:
Author Surname
(Author Surname Page)
(Damasio 7)
Works cited list entry template and example:
Surname, First Name. Title of the Book . Publisher, Publication Date, Page range.
Damasio, Antonio. Emotion, Reason and the Feeling Brain . Penguin, 1994.
In-text citation template and example for an e-book:
(Author Surname)
Author’s Surname, First Name. Title of the Book . E-book ed., Publisher, Publication Date.
Davis, Barbara. The Keeper of Happy Endings . E-book ed., Lake Union Publishing, 2021.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources (Web Publications)

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The MLA Handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any source regardless of whether it’s included in this list.
However, this guide will highlight a few concerns when citing digital sources in MLA style.
Best Practices for Managing Online Sources
Because online information can change or disappear, it is always a good idea to keep personal copies of important electronic information whenever possible. Downloading or even printing key documents ensures you have a stable backup. You can also use the Bookmark function in your web browser in order to build an easy-to-access reference for all of your project's sources (though this will not help you if the information is changed or deleted).
It is also wise to keep a record of when you first consult with each online source. MLA uses the phrase, “Accessed” to denote which date you accessed the web page when available or necessary. It is not required to do so, but it is encouraged (especially when there is no copyright date listed on a website).
Important Note on the Use of URLs in MLA
Include a URL or web address to help readers locate your sources. Because web addresses are not static (i.e., they change often) and because documents sometimes appear in multiple places on the web (e.g., on multiple databases), MLA encourages the use of citing containers such as Youtube, JSTOR, Spotify, or Netflix in order to easily access and verify sources. However, MLA only requires the www. address, so eliminate all https:// when citing URLs.
Many scholarly journal articles found in databases include a DOI (digital object identifier). If a DOI is available, cite the DOI number instead of the URL.
Online newspapers and magazines sometimes include a “permalink,” which is a shortened, stable version of a URL. Look for a “share” or “cite this” button to see if a source includes a permalink. If you can find a permalink, use that instead of a URL.
Abbreviations Commonly Used with Electronic Sources
If page numbers are not available, use par. or pars. to denote paragraph numbers. Use these in place of the p. or pp. abbreviation. Par. would be used for a single paragraph, while pars. would be used for a span of two or more paragraphs.
Basic Style for Citations of Electronic Sources (Including Online Databases)
Here are some common features you should try to find before citing electronic sources in MLA style. Not every web page will provide all of the following information. However, collect as much of the following information as possible:
- Author and/or editor names (if available); last names first.
- "Article name in quotation marks."
- Title of the website, project, or book in italics.
- Any version numbers available, including editions (ed.), revisions, posting dates, volumes (vol.), or issue numbers (no.).
- Publisher information, including the publisher name and publishing date.
- Take note of any page numbers (p. or pp.) or paragraph numbers (par. or pars.).
- DOI (if available, precede it with "https://doi.org/"), otherwise a URL (without the https://) or permalink.
- Date you accessed the material (Date Accessed). While not required, saving this information it is highly recommended, especially when dealing with pages that change frequently or do not have a visible copyright date.
Use the following format:
Author. "Title." Title of container (self contained if book) , Other contributors (translators or editors), Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publication Date, Location (pages, paragraphs and/or URL, DOI or permalink). 2 nd container’s title , Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location, Date of Access (if applicable).
Citing an Entire Web Site
When citing an entire website, follow the same format as listed above, but include a compiler name if no single author is available.
Author, or compiler name (if available). Name of Site. Version number (if available), Name of institution/organization affiliated with the site (sponsor or publisher), date of resource creation (if available), DOI (preferred), otherwise include a URL or permalink. Date of access (if applicable).
Editor, author, or compiler name (if available). Name of Site . Version number, Name of institution/organization affiliated with the site (sponsor or publisher), date of resource creation (if available), URL, DOI or permalink. Date of access (if applicable).
The Purdue OWL Family of Sites . The Writing Lab and OWL at Purdue and Purdue U, 2008, owl.english.purdue.edu/owl. Accessed 23 Apr. 2008.
Felluga, Dino. Guide to Literary and Critical Theory . Purdue U, 28 Nov. 2003, www.cla.purdue.edu/english/theory/. Accessed 10 May 2006.
Course or Department Websites
Give the instructor name. Then list the title of the course (or the school catalog designation for the course) in italics. Give appropriate department and school names as well, following the course title.
Felluga, Dino. Survey of the Literature of England . Purdue U, Aug. 2006, web.ics.purdue.edu/~felluga/241/241/Home.html. Accessed 31 May 2007.
English Department . Purdue U, 20 Apr. 2009, www.cla.purdue.edu/english/. Accessed 31 May 2015.
A Page on a Web Site
For an individual page on a Web site, list the author or alias if known, followed by an indication of the specific page or article being referenced. Usually, the title of the page or article appears in a header at the top of the page. Follow this with the information covered above for entire Web sites. If the publisher is the same as the website name, only list it once.
Lundman, Susan. “How to Make Vegetarian Chili.” eHow , www.ehow.com/how_10727_make-vegetarian-chili.html. Accessed 6 July 2015.
“ Athlete's Foot - Topic Overview. ” WebMD , 25 Sept. 2014, www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/tc/athletes-foot-topic-overview.
Citations for e-books closely resemble those for physical books. Simply indicate that the book in question is an e-book by putting the term "e-book" in the "version" slot of the MLA template (i.e., after the author, the title of the source, the title of the container, and the names of any other contributors).
Silva, Paul J. How to Write a Lot: A Practical Guide to Productive Academic Writing. E-book, American Psychological Association, 2007.
If the e-book is formatted for a specific reader device or service, you can indicate this by treating this information the same way you would treat a physical book's edition number. Often, this will mean replacing "e-book" with "[App/Service] ed."
Machiavelli, Niccolo. The Prince , translated by W. K. Marriott, Kindle ed., Library of Alexandria, 2018.
Note: The MLA considers the term "e-book" to refer to publications formatted specifically for reading with an e-book reader device (e.g., a Kindle) or a corresponding web application. These e-books will not have URLs or DOIs. If you are citing book content from an ordinary webpage with a URL, use the "A Page on a Web Site" format above.
An Image (Including a Painting, Sculpture, or Photograph)
Provide the artist's name, the work of art italicized, the date of creation, the institution and city where the work is housed. Follow this initial entry with the name of the Website in italics, and the date of access.
Goya, Francisco. The Family of Charles IV . 1800. Museo Nacional del Prado, Madrid. Museo Nacional del Prado , www.museodelprado.es/en/the-collection/art-work/the-family-of-carlos-iv/f47898fc-aa1c-48f6-a779-71759e417e74. Accessed 22 May 2006.
Klee, Paul. Twittering Machine . 1922. Museum of Modern Art, New York. The Artchive , www.artchive.com/artchive/K/klee/twittering_machine.jpg.html. Accessed May 2006.
If the work cited is available on the web only, then provide the name of the artist, the title of the work, and then follow the citation format for a website. If the work is posted via a username, use that username for the author.
Adams, Clifton R. “People Relax Beside a Swimming Pool at a Country Estate Near Phoenix, Arizona, 1928.” Found, National Geographic Creative, 2 June 2016, natgeofound.tumblr.com/.
An Article in a Web Magazine
Provide the author name, article name in quotation marks, title of the web magazine in italics, publisher name, publication date, URL, and the date of access.
Bernstein, Mark. “ 10 Tips on Writing the Living Web. ” A List Apart: For People Who Make Websites , 16 Aug. 2002, alistapart.com/article/writeliving. Accessed 4 May 2009.
An Article in an Online Scholarly Journal
For all online scholarly journals, provide the author(s) name(s), the name of the article in quotation marks, the title of the publication in italics, all volume and issue numbers, and the year of publication. Include a DOI if available, otherwise provide a URL or permalink to help readers locate the source.
Article in an Online-only Scholarly Journal
MLA requires a page range for articles that appear in Scholarly Journals. If the journal you are citing appears exclusively in an online format (i.e. there is no corresponding print publication) that does not make use of page numbers, indicate the URL or other location information.
Dolby, Nadine. “Research in Youth Culture and Policy: Current Conditions and Future Directions.” Social Work and Society: The International Online-Only Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, 2008, www.socwork.net/sws/article/view/60/362. Accessed 20 May 2009.
Article in an Online Scholarly Journal That Also Appears in Print
Cite articles in online scholarly journals that also appear in print as you would a scholarly journal in print, including the page range of the article . Provide the URL and the date of access.
Wheelis, Mark. “ Investigating Disease Outbreaks Under a Protocol to the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention. ” Emerging Infectious Diseases , vol. 6, no. 6, 2000, pp. 595-600, wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/6/6/00-0607_article. Accessed 8 Feb. 2009.
An Article from an Online Database (or Other Electronic Subscription Service)
Cite online databases (e.g. LexisNexis, ProQuest, JSTOR, ScienceDirect) and other subscription services as containers. Thus, provide the title of the database italicized before the DOI or URL. If a DOI is not provided, use the URL instead. Provide the date of access if you wish.
Alonso, Alvaro, and Julio A. Camargo. “ Toxicity of Nitrite to Three Species of Freshwater Invertebrates. ” Environmental Toxicology, vol. 21, no. 1, 3 Feb. 2006, pp. 90-94. Wiley Online Library , https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20155. Accessed 26 May 2009.
Langhamer, Claire. “Love and Courtship in Mid-Twentieth-Century England.” Historical Journal, vol. 50, no. 1, 2007, pp. 173-96. ProQuest , https://doi.org/10.1017/S0018246X06005966. Accessed 27 May 2009.
E-mail (including E-mail Interviews)
Give the author of the message, followed by the subject line in quotation marks. State to whom the message was sent with the phrase, “Received by” and the recipient’s name. Include the date the message was sent. Use standard capitalization.
Kunka, Andrew. “ Re: Modernist Literature. ” Received by John Watts, 15 Nov. 2000.
Neyhart, David. “ Re: Online Tutoring. ” Received by Joe Barbato, 1 Dec. 2016.
A Listserv, Discussion Group, or Blog Posting
Cite web postings as you would a standard web entry. Provide the author of the work, the title of the posting in quotation marks, the web site name in italics, the publisher, and the posting date. Follow with the date of access. Include screen names as author names when author name is not known. If both names are known, place the author’s name in brackets.
Author or compiler name (if available). “Posting Title.” Name of Site , Version number (if available), Name of institution/organization affiliated with the site (sponsor or publisher), URL. Date of access.
Salmar1515 [Sal Hernandez]. “Re: Best Strategy: Fenced Pastures vs. Max Number of Rooms?” BoardGameGeek , 29 Sept. 2008, boardgamegeek.com/thread/343929/best-strategy-fenced-pastures-vs-max-number-rooms. Accessed 5 Apr. 2009.
Begin with the user's Twitter handle in place of the author’s name. Next, place the tweet in its entirety in quotations, inserting a period after the tweet within the quotations. Include the date and time of posting, using the reader's time zone; separate the date and time with a comma and end with a period. Include the date accessed if you deem necessary.
@tombrokaw. “ SC demonstrated why all the debates are the engines of this campaign. ” Twitter, 22 Jan. 2012, 3:06 a.m., twitter.com/tombrokaw/status/160996868971704320.
@PurdueWLab. “ Spring break is around the corner, and all our locations will be open next week. ” Twitter , 5 Mar. 2012, 12:58 p.m., twitter.com/PurdueWLab/status/176728308736737282.
A YouTube Video
Video and audio sources need to be documented using the same basic guidelines for citing print sources in MLA style. Include as much descriptive information as necessary to help readers understand the type and nature of the source you are citing. If the author’s name is the same as the uploader, only cite the author once. If the author is different from the uploader, cite the author’s name before the title.
McGonigal, Jane. “Gaming and Productivity.” YouTube , uploaded by Big Think, 3 July 2012, www.youtube.com/watch?v=mkdzy9bWW3E.
“8 Hot Dog Gadgets put to the Test.” YouTube, uploaded by Crazy Russian Hacker, 6 June 2016, www.youtube.com/watch?v=WBlpjSEtELs.
A Comment on a Website or Article
List the username as the author. Use the phrase, Comment on, before the title. Use quotation marks around the article title. Name the publisher, date, time (listed on near the comment), and the URL.
Not Omniscient Enough. Comment on “ Flight Attendant Tells Passenger to ‘Shut Up’ After Argument Over Pasta. ” ABC News, 9 Jun 2016, 4:00 p.m., abcnews.go.com/US/flight-attendant-tells-passenger-shut-argument-pasta/story?id=39704050.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Cite your MLA source. Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Set 1 inch page margins. Use double line spacing. Include a ½" indent for new paragraphs. Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page. Center the paper's title.
In the case of a group project, list all names of the contributors, giving each name its own line in the header, followed by the remaining MLA header requirements as described below. Format the remainder of the page as requested by the instructor. In the upper left-hand corner of the first page, list your name, your instructor's name, the ...
In-text citations: Author-page style. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number (s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Create manual citation. The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number (s).
Above is a template you can use every time you need to set-up a research paper using MLA style format. Simply open the template and type your own information every time you need to write an MLA style paper. Microsoft Word will allow you to save personal templates. ... create a title page instead of listing all authors in the header on page 1 of ...
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA in-text citation provides the author's last name and a page number in parentheses. If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by " et al. ". If the part you're citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range.
Here's how you can set your first page up for MLA 9th edition. On the first line, write your full name (flush left) On a new line, write your professor or instructor's full name. On a new line, write the course code and course name. On a new line, write the full date spelt out (e.g., 15 June 2023)
Congratulations to the students whose essays were selected for the 2024 edition of Writing with MLA Style! Essays were selected as examples of excellent student writing that use MLA style for citing sources. Essays have been lightly edited. If your institution subscribes to MLA Handbook Plus, you can access annotated versions of the essays selected …
Since we're here to learn how to format an essay, we've pointed out some important things about the paper to help you write a correctly formatted essay. For starters, the essay is in MLA format. That means it follows the style manual of the Modern Language Association, which tells you how to format the paper itself and every source you cite.
MLA is the preferred style when writing an essay in high school and most college settings. As with other writing styles, there are specific characteristics and items an MLA-format paper needs to include to fit the bill of the style. Every MLA-format essay must include the following: One-inch margins. Double-spaced text.
Formatting an essay according to a certain style affects the way your assignment looks physically and to how you format your citations. How to Format your paper in MLA . The guidelines below are the general MLA formatting guidelines; however, make sure to prioritize following any specific formatting instructions that your instructor has ...
Formatting an essay may not be as interesting as choosing a topic to write about or carefully crafting elegant sentences, but it's an extremely important part of creating a high-quality paper. In this article, we'll explain essay formatting rules for three of the most popular essay styles: MLA, APA, and Chicago.
MLA General Format MLA Formatting and Style Guide; MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics; MLA Formatting Lists MLA Formatting Quotations; MLA Endnotes and Footnotes; MLA Works Cited Page: Basic Format; MLA Works Cited Page: Books; MLA Works Cited Page: Periodicals; MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources (Web Publications) MLA Works Cited: Other Common ...
MLA Sample Argumentative Papers (Note: these sample papers are in MLA 7th ed. format). For sample papers in MLA 8th or 9th ed., please ask a librarian or check the Documenting Sources in MLA Style: 2016 Update: A Bedford/St. Martin's Supplement pp. 30-41, at Skyline College Library's Ready Reference shelf.
To cite a short story from an edited collection, after giving the author and title of the story, list the title of the book, the editor (s), the publisher, the year, and the page range on which the story appears. MLA format. Author last name, First name. " Story Title .".
Papers in MLA format should always have a works cited page. ... add a short reference next to a quote or paraphrased information that came from a source. This is called a citation in prose or a parenthetical citation. ... If the source was published in Asia, do not reverse the author's name in the reference list. Write it in the order shown ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (8th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Luckily, we have everything you need to format your paper properly. Filled with clear guidelines, visual aids, and samples galore, our comprehensive guide will make it simple to structure your next MLA paper. Don't forget about our MLA works cited, MLA in-text citation, and MLA annotated bibliography guides! You'll also need these handy ...
To summarize, an MLA Works Cited page is an essential part of a manuscript written using the MLA style and includes all sources used by the author to write the research paper. As described in the article, the Works Cited page and its entries have a specific format that should be strictly followed, and all the core elements included in the ...
Writing in College MLA Format may initially seem daunting, but with a step-by-step approach, you can easily master this widely used formatting style. Whether you're working on an college essay , research paper , or any other academic document, following the guidelines of MLA Format ensures consistency and professionalism in your writing.
We also have a guide on how to format an APA reference page. 2. Understand the General Formatting Rules of Your Citation Style Before You Start Writing. While reading up on paper formatting may not sound exciting, being aware of how your paper should look early on in the paper writing process is super important. Citation styles can dictate more ...
MLA style is most commonly used to cite sources within the language arts, cultural studies, and other humanities disciplines. This resource, revised according to the 9th edition of the MLA manual published in April 2021, offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, and the Works Cited page.
Explanatory Essay Format. Understanding the explanatory essay format is key to a well-structured and logical paper. Here's a basic breakdown of the format for an explanatory essay: Introduction paragraph. Begin with an interesting sentence to capture the reader's attention. Give a short intro. It should set the topic and outline the essay ...
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
Works Cited; Structure: Author's Last name, First name. "Title of chapter or section." Title of the Book, edited by First name Last name, Publisher, Year published, page number(s).. Example: Montrose, Louis. "Elizabeth Through the Looking Glass: Picturing the Queen's Two Bodies."
Note: The MLA considers the term "e-book" to refer to publications formatted specifically for reading with an e-book reader device (e.g., a Kindle) or a corresponding web application.These e-books will not have URLs or DOIs. If you are citing book content from an ordinary webpage with a URL, use the "A Page on a Web Site" format above.