- Administrators
- MD-PhD Program Interview Committee
- MSTP Faculty
- Current Students
- MD-PhD Advisory Committee
- Student Council
- Committee on Diversity & Inclusion
- Students Perspectives on, Inclusion, Diversity and Equity at Yale (SPIDEY)
- Peer Advising by Senior Students (PASS)
- Mentoring and Peer Advice from Recent Trainees (MPART)
- Faculty Mentoring
- Career Development
- Useful Links
- Parental Support and Relief
- Important Dates & Deadlines
- Financial Support
- Life at Yale
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Who we are: Goals & Committees
- What We Do: Current D&I Initiatives
- Resources for Support
- Resources for Self-Education
- Yale BioMed Amgen Scholars Program

MD-PhD Timeline
- Responsible Conduct of Research (RCR)
- Clinical Activities
- Research Activities
- Leadership & Research Management Certificate
- Annual Program Retreat
- Perspectives of Women in Science Lectures
- Grant-writing workshops
- Teaching Requirements & Opportunities
- Thriving in the Training Environment
- Where To Go For Help
- Physician-Scientist Specialty Shadowing Opportunities
- 2019 Newsletters
- 2020 Newsletters
- 2021 Newsletters
- 2022 Newsletters
- Residency Matches
- Student Publications
- Outcomes to PhDs Conferred
- Fellowships Awarded
INFORMATION FOR
- Residents & Fellows
- Researchers
Years 1 and 2
Year 3 and 4 through phd defense.
During the summer following their 6 months of Integrated Clinical Clerkships, MD-PhD students study for and take USMLE Step I. There is also time to complete an additional research rotation, if necessary, and to take a vacation. The Step 1 exam must be taken by December 31 of Year 3. Students meet with their Director of Graduate Studies to formally affiliate with a PhD department and research laboratory at the start of Year 3 and complete program or department-specific coursework, teaching and qualifying examination requirements in Years 3 and 4. A thesis prospectus is submitted in Year 3 or 4, which coincides with participation in the MD-PhD Program’s Grant Writing Workshop to prepare NIH NRSA F30/F31 and other private foundation applications. Students are required to submit a first author paper and successfully write, defend and submit their PhD dissertation before returning to the wards in October or January of their penultimate year of training.
There is a strong emphasis on maintaining engagement in clinical activities during the PhD thesis years of the MD-PhD training. Clinical activity during research years is an explicit part of the IDP review process, and thesis advisors are informed that this is an encouraged training activity for dual-degree candidates. Most students participate in one or more longitudinal clinical experiences (LCEs) or the student-run “Wednesday Evening Clinic” (WEC) for which they receive elective credit. A student-organized monthly Clinical Reasoning Seminar employs a clinical case-based approach to review diagnosis, pathology and treatment/management with a clinical faculty expert. In addition to maintaining clinical fluency, customized LCEs allow students to explore clinical (sub)specialties related to their research work and interests and are precepted by physician-scientists whenever possible. These experiences allow students to gain a richer understanding of possible career paths for physician-scientists and expose them to the advantages and challenges of combining research with clinical care. Strategies to manage wellness and resilience in a physician-scientist career are discussed during annual program retreats and recurring Brown Bag lunch discussions, while a Curriculum in Leadership and Research Management for Physician-Scientists provides ongoing career development training and experiential learning to MD-PhD students.
Re-entry and Final Year
Md-phd timeline.
- Student/Faculty Portal
- Learning Hub (Brightspace)
- Continuous Professional Development
Clinical and Translational Science
Clinical and translational science track, research focus.
across the translational spectrum from discovery to implementation
average amount of time to Ph.D. degree
Guaranteed 5-year internal fellowship
includes full tuition, stipend and benefits
Moving new biomedical discoveries into clinical use as new treatments and cures takes considerable time and resources. A translational scientist is at the forefront of this work, teaming with an integrated group of experts focused on taking knowledge gained through research and translating it for use in health care settings. This bench-to-bedside effort is essential to bridging the gap between basic science and patient care.
The Clinical and Translational Science (CTS) Track within the Ph.D. Program at Mayo Clinic Graduate School of Biomedical Science is built upon Mayo Clinic's extensive interdisciplinary research and medical environment. It prepares you to lead the biomedical research teams of the future that will rapidly translate discoveries to new treatments and change the paradigms of how we conduct biomedical research.
As a graduate of this program, you’ll be able to conduct research leading to meaningful scientific contributions. In addition, you’ll be prepared to change and improve how biomedical research is conceptualized and implemented.
The Clinical and Translational Science Track allows students to personalize their studies in three areas of emphasis:
- Population-based translational science
- Patient-based translational science
- Laboratory-based translational science
A great strength of the Mayo Clinic CTS track is its focus on providing mentored research experiences for each student. The pre-eminent physicians, scientists, and educators who comprise the faculty at Mayo Clinic are available as mentors or co-mentors for students in the track.
All doctoral students in the CTS track have a common core curriculum. Depending on your area of concentration (laboratory-, patient- or population-based translational science), you’ll select your advanced courses from either track courses or graduate school courses in the basic science disciplines.
- Core required courses
- Track required courses
- Introduction to research projects and methodologies used in the laboratories of clinical/translational investigators
- Completion of three research experiences or laboratory rotations, each lasting eight weeks
- Selection of laboratory for thesis research
- Advanced elective courses (areas of interest)
- Research gathering preliminary data for a thesis research project
- Preparation of a thesis proposal in the format of a grant application
- Selection of faculty for the oral qualifying exam committee, followed by defense of the research proposal in the oral exam (to be completed before the end of the fall quarter)
- Written Comprehensive Examination
- Oral Qualifying Examination (presentation of thesis proposal)
- Ongoing workshops/seminars/journal clubs
- Completion of thesis research and any remaining course requirements
- Selection of your Graduate School Thesis Advisory Committee that will evaluate the proposed direction, specific aims, and experimental strategies of your project, as well as meet with you at least twice a year to discuss your research progress
- Works-in-progress presentation of research project
- Final Oral Examination (thesis defense)

I chose the Clinical and Translational Science Track because of the flexibility of the program. Much of your coursework can be whichever topic helps you most for your research, and there are very few restrictions on the principal investigators you can work under. Also, because Mayo provides access to such unique patient populations, I’m able to use a lot of techniques that I wouldn’t be able to at a university or institution.
Kevin Kelly Ph.D. student, Clinical and Translational Science Track

One thing that attracted me to the CTS Track is how supported I felt as a student and the opportunities we have to learn and grow. We’re encouraged to explore career options other than the traditional academic route. I’m interested in translational science, and there have been numerous examples in which discoveries happened at the bench and ended up as clinical trials here at Mayo.
Alaa Koleilat, Ph.D. 2020 graduate of the Ph.D. Program, Clinical and Translational Science Track

Mayo Clinic draws students and patients from all over the world, which creates a unique educational environment. It also emphasize patient needs, which shapes the way that students learn and interact with other professionals. The small class size and primary focus on biomedical sciences contributes to the welcoming, energetic and collaborative environment. The leaders of all the programs I am associated with are clearly invested in my success.
Josiane Joseph M.D.-Ph.D. student, Clinical and Translational Science Track
- "BLOOM: Beta-lactam Optimization and Outcomes Management," Erin Barreto (Mentor: Andrew Rule, M.D.)
- "Differentiating types of dementia using extracellular vesicles," Maria Esperanza Bregendahl (Mentor: Pam J. McLean, Ph.D.)
- "Investigating Sulfatase 2 effects on the tumor microenvironment in hepatobiliary cancers," Tayla Brooks (Mentor: Lewis. R. Roberts, M.B., Ch.B., Ph.D.)
- "Defining racial differences in hedgehog-associated breast cancer risk biomarkers in normal breast biopsies," Jennifer Cabezas (Mentor: Derek Radisky, Ph.D.)
- "Cytokine Mediated Death and Survival in Multiple Myelom," Allison (Allie) Carr (Mentor: Adrian T. Ting, Ph.D.)
- "Peripheral multi-omics biomarkers of Alzheimer’s and related phenotypes," Xuan Chen (Mentor: Nilufer Taner, M.D., Ph.D.)
- "Pulmonary Hypertension Secondary to Left Heart Diseases," Ahmed Fayyaz (Mentor: Margaret M. Redfield, M.D.)
- "Using focused ultrasound (FUS) to enhance the delivery of intravenous umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UCMSC) in chronic spinal cord injured rats," Abdul Karim (AK) Ghaith (Mentors: Mohamad Bydon M.D., and Anthony J. Windebank M.D.)
- "The Role of the Endocannabinoid System in Systemic Stress Response in Zebrafish," Robin Heider (Mentor: Karl J. Clark, Ph.D.)
- "Utilizing long-read sequencing to unravel the clinical heterogeneity in motor neuron diseases and undiagnosed genetic disorders," Angita (AJ) Jain (Mentor: Marka M. Van Blitterswijk, M.D., Ph.D.)
- "Unraveling the Immunological Basis of Lobular Involution Stagnation in Breast Cancer Development," Jaida Lue (Mentor: Derek Radisky, Ph.D.)
- "Artificial intelligence derived voice biomarkers for the detection and management of cardiovascular disease," Jaskanwal Deep (Jas) Sara (Mentor: Amir Lerman, M.D.)
- "Characterization of Mitochondrial DNA variations, heteroplasmic levels, and deletion frequency in Pacbio’s continuous long reads," Ngan Tran (Mentor: Owen Ross, Ph.D.
- "Unrefined: Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis burden and potential interventions in x population," Caitlin VanLith (Mentor: Lewis. R. Roberts, M.B., Ch.B., Ph.D.)
- "Data Independent Acquisition of Small Molecule Signatures to Characterize Inborn Errors of Metabolism," Rachel Wurth (Mentor: Devin Oglesbee, Ph.D.)
- "Developing Strategies to address health disparities for first generation regenerative medicine treatments," Mohamed (Mo) Addani (Mentor: Zubin Master, Ph.D.)
- "Utility of Methylated DNA Markers for the Diagnosis of Malignant Pancreatic Biliary Strictures," Matthew Cooley (Mentor: Lewis. R. Roberts, M.B., Ch.B., Ph.D.)
- "Electrical stimulation of hippocampus and amygdala modulates human ventral temporal cortex in distinct ways," Harvey Huang (Mentor: Dora Hermes, Miller Ph.D.)
- "Senolytics and antifibrotic treatment for chronic spinal cord injury," Vagisha Kulsreshtha (Mentors: James Kirkland M.D., Ph.D., and Isobel A. Scarisbrick Ph.D.)
- "HDAC1/OLIG2/STAT5 transcriptional complex facilitates GSC-mediated invasion and tumorigenesis," Auna’y Miller (Mentor: Nhan L. Tran, Ph.D.)
- "Transcriptional adaptation as a possible mechanism underlying amyotrophic lateral sclerosis," Adriana (Adri) Morales Gomez (Mentor: Nathan Staff M.D., Ph.D.)
- "Single Cell Landscape of Infiltrating Immune Cells in Cholangiocarcinoma," Hannah Stumpf (Mentor: Sumera I. Ilyas, M.B.B.S.)
- "Developing a Value-Based Hybrid Care Model for Stroke Patients," Stephanie Zawada (Mentor: Bart M. Demaerschalk, M.D.)
- “Improving Facial Paralysis Surgical Outcomes: Targeting Facial Nerve Regeneration,” Marissa Suchyta (Mentor: Samir Mardini, M.D.)
- “Regenerative Capabilities of Extracellular Vesicles in Myocarditis,” Danielle Beetler (Mentor: DeLisa Fairweather, Ph.D.)
- “Machine Learning-Aided Biomarker Discovery and Precision Genomics for Gallbladder Cancer,” Linsey Jackson (Mentor: Lewis R. Roberts, M.B., Ch.B., Ph.D.)
- “Pathway Discovery in Neurodegenerative Diseases by Integration of Multi-omics Data,” Yuhao (Harry) Min (Mentor: Nilufer Taner, M.D., Ph.D.)
- “Investigating Uterine Fibroids in Women of Color: A Translational Approach,” Minerva Orellana (Mentors: Felicity T. Enders, Ph.D. and Elizabeth (Ebbie) A. Stewart, M.D.)
- “Natural Language Processing Aided Discovery of Adverse Symptoms during Fertility Procedures,” Karen DSouza (Mentor: Megan A. Allyse, Ph.D.)
- “Understanding and Promoting Student Wellbeing Through Social-Emotional Behavioral Programming,” Catherine Knier (Mentor: Dr. Anthony J. Windebank, M.D, and Christopher K. Pierret, Ph.D.)
- “Reducing the Burden of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Among Migrant Populations: Improving Prevention and Outcomes Through Disease Modeling,” Kenneth Valles (Mentor: Lewis R. Roberts, M.B., Ch.B., Ph.D.)
- “Living Systematic Reviews and Guideline Updates in Areas with Rapidly Evolving Evidence,” Irbaz Bin Riaz (Mentor: M. Hassan Murad, M.D.)
- “Sex Differences in Mitochondria During Acute cvb3 Myocarditis,” Damian Di Florio (Mentor: DeLisa Fairweather, Ph.D.)
- “The Role of Convection-Enhanced Delivery for Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma,” Erica Power (Mentor: David J. Daniels, M.D., Ph.D)
- “Subcutaneous Combination Biodevice for the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes,” Ethan Law (Mentor: Quinn P. Peterson, Ph.D.)
- “Technologies to Enable Closed-loop Neurochemical Control in Deep Brain Stimulation,” Aaron Rusheen (Mentor: Kendall H. Lee, M.D., Ph.D.)
- “Functional Validation in Unsolved Rare Disease Patients as a Method of Providing and Clarifying Diagnosis,” Brad Bowles (Mentor: Karl J. Clark, Ph.D. and Eric W. Klee, Ph.D.)
- “The Role of Glypican-3 Isoforms in the Development of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for Liver Cancer Therapy,” Aarti Koluri (Mentor: Lewis R. Roberts, M.B., Ch.B., Ph.D.)
- “Clinical Implementation of Tobacco Cessation Treatment among Cancer Patients,” Josh Ohde, Ph.D. (Mentor: David O. Warner, M.D.)
- “Metabolic Abnormalities Associated with Disease Alter Progenitor Cell Function and Precede Tissue Deterioration,” Josiane Joseph (Mentor: Jason D. Doles, Ph.D.)
- “Breast Cancer Mode of Detection Varies by Breast Density and Stage at Diagnosis in Population Based Cohort,” Susanna Basappa (Mentor: Lila J. Rutten, Ph.D.)
Your future
Many graduates of the Clinical and Translational Science Track choose to pursue postdoctoral training regardless of whether they intend to pursue careers in academia or industry. Other students choose to enter advanced training programs, such as genetics fellowships.
Meet the directors
Clinical and translational science is a rapidly developing area of science. Advances in technology and the way we approach and treat diseases or other conditions have set the stage for improved human health.
Our program combines the clinical and scientific resources of Mayo Clinic, where you’ll graduate with an understanding of how research is translated to health care, and ready to carry out research that accelerates medical discoveries into better health.

Felicity Enders, Ph.D.
Clinical and Translational Science Track Director Professor of Biostatistics Phone: 507-538-4970 Email: [email protected] View research interests

Marina Walther-Antonio, Ph.D.
Clinical and Translational Science Track Associate Director Assistant Professor of Surgery Phone: 507-293-7070 Email: [email protected] View research interests

Anthony Windebank, M.D.
Clinical and Translational Science Track TL1 Principal Investigator Professor of Neurology Phone: 507-284-4716 Email: [email protected] View research interests
Browse a list of Clinical and Translational Science Track faculty members
MSTP MD-PhD Program
Frequently asked questions.

- Program Structure
How long does it take to complete both degrees?
The average length of time before graduation is 7.5 years; generally students will take 6 years or 8 years depending on the nature of their graduate research. Students generally complete and defend their PhD thesis before completing their clinical rotations in the last 1 – 2 years.
Can I do one degree before the other?
As above, nearly all students will complete their PhD requirements 1 – 2 years before their MD requirements. An important advantage of combined degree training is the breadth that the first 1 – 2 years of medical school provides for graduate research. Students must pass part I of the National Board Medical Licensing Examination before commencing full-time laboratory research. Occasionally circumstances will arise when an individual student's training is best served by deviating from this "traditional" plan; these situations require approval and monitoring by the graduate advisor and the MSTP Directors.
How will I be supported during my training?
Stanford MSTP students are fully supported through the entire program, tuition, health insurance and stipend, by a combination of funds from a National Institute of Health training grant, individual graduate programs, and School of Medicine funds.
Are there laboratory rotations?
One of the ways in which we try to make the total time of training less than the sum normally taken to complete MD and PhD degrees is by encouraging MSTP students to choose a potential thesis advisor without a yearlong set of rotations through different laboratories. During the first year of the program, students meet with departmental chairs and research faculty and participate in research seminars and group meetings, so that the summer following the first year can be spent working full-time in a laboratory whose goals, approaches, and personnel are already familiar. In most cases, MSTP students choose this laboratory as the place to carry out their thesis research.
Can I get advanced placement credit for graduate coursework?
MSTP students fulfill the same curricular requirements as "straight MD" and "straight PhD" students. Some PhD Programs may permit substitution of previous graduate course work (or MD courses) for their PhD requirements; this is individual to the program and the student.
Are MSTP students required to complete the MD Scholarly Concentration (SC) program?
The MSTP is a combined effort between the MD program and the PhD programs. All trainees are required to fulfill all requirements for both the MD and PhD degrees. The single exception is the MD program requirement for a Scholarly Concentration. For dual degree MD-PhD students, the PhD substitutes for this requirement.
Will I have special opportunities as an MSTP student?
Yes! In addition to individual regular advising meetings with the Program Directors, we hold seminars, courses, and lunches with guest speakers, covering important topics of professional development and translational medicine. The MSTP community also meets annually for the MSTP Scientific Conference, to present research, and to share clinical experiences, advice and above all support.
Will I have special responsibilities as an MSTP student?
Of course! Besides the challenge of balancing graduate and medical training, we ask all MSTP students to play an integral role in the recruitment, education, and evaluation of incoming MSTP applicants.
Graduate Programs
Can I get a PhD outside the Medical School?
Yes. One of the unique aspects of the Stanford MSTP is its close affiliation with departments in other Schools, including Engineering (Bioengineering, Chemical, Computer Science, Electrical) and Humanities and Sciences (Biology, Chemistry, Physics, Statistics).
Can I get a PhD in a clinical department?
The PhD must be conferred by a degree-granting department or program, and most clinical departments do not grant PhD degrees. However, most scientists in clinical departments either have joint appointments with basic science departments or are members of interdepartmental programs such as Cancer Biology, Neurosciences, or Immunology, and the only restriction regarding thesis advisors is that they must be members of the Academic Council.
Can I apply to the MSTP and get a PhD in a social science?
If you are a current Stanford MD student and have previously been admitted to a social science PhD program, you may apply to the MSTP for funding. Admitted PhD candidates may apply through the MSTP internal admissions process.
Are there teaching requirements?
The MSTP itself has no specific teaching requirements, but some PhD programs do.
How will my training differ from other "straight PhD" students?
The short answer is, "It won't." PhD training for MSTP students is just as rigorous and intensive as for students outside the MSTP. However, MSTP students don't spend their first year rotating through different laboratories, and most MSTP students complete their preclinical medical school curriculum before starting full-time laboratory research.
- Admissions Process
How many applicants do you interview and admit?
On average, we invite about 60 students for interviews or about 1 in 9 of those students who submit a secondary application. About 8 - 10 students begin the MSTP every year.
Can I apply to the MSTP after starting medical school?
Yes! One of the unique aspects of the Stanford School of Medicine is its strong emphasis on research, and the MSTP invites current Stanford medical students in their preclinical years, who have made a commitment and contribution to a research-based career, to submit an application for the MSTP. We refer to this as the “internal” application process . Typically, the MSTP admits 1 – 2 internal applicants every year.
Is there an early decision program?
No. We think making a decision about combined medical school and graduate training is challenging enough! Finding a program that best matches an individual student's interests and goals is facilitated by visiting several universities and meeting with a variety of potential research advisors.
How do I find out about the status of my application?
Just ask (we don't mind).
Can I schedule my interview for a different day?
There are 5 – 6 interview days per season; once invited, interviews are scheduled on a first-come, first-served basis. We will try to accommodate requests for other dates if necessary.
I don't know whether to apply for Med School or MSTP?
You should only apply to the MSTP if you are committed to a career in biomedical research; such a commitment should be based, in part, on previous sustained and productive research experience as an undergraduate. If you're not sure, consider working full-time in a laboratory after undergraduate school before deciding whether an MSTP is right for you, or, alternatively, starting as a "straight MD" student, participating in a research project in your 2nd or 3rd year, and possibly applying to the MSTP as an internal applicant (see above).
What does the MSTP Admissions Committee look for?
Besides qualification for admission to the medical school itself, the single most important component of an MSTP application is a previous sustained and productive research experience.
When can I expect to hear about the outcome of my application and/or interview?
Interview season is October – February; interview invitations will be issued 3 – 6 weeks before the scheduled interview date. MSTP admission decisions are made on a modified rolling basis.
Are MSTP applicants considered independently for medical school admission?
The MSTP Admissions Committee is separate from, but closely integrated with, the Medical School Admissions Committee. All applicants to the MSTP are also considered for MD-only admission. If you are not chosen for an MSTP interview, your application is automatically routed for MD-only consideration. If you are chosen for an MSTP interview, you will also be required to participate in the MD admission interview process. These interviews will be scheduled the day before, or day after, your MSTP interviews. If you are not offered admission to the MSTP, you will be considered for MD-only admission.
- Student Life
Can I afford to live in Palo Alto?
Housing costs in the Bay Area are more than other cities. However, every new graduate student is guaranteed housing on campus or at University associated off-campus sites. Almost anyone can afford to live comfortably as a Stanford graduate student solely on stipend support.
Will the program pay for health insurance? What about the rest of my family?
We consider health insurance an essential component of all graduate training programs. The program covers the entire cost for individual students and offers a mechanism for subsidizing dependents.
Isn't there more to do in San Francisco than in Palo Alto?
It depends whether you would rather watch street vendors in Union Square or go hiking in the Los Altos foothills. Seriously, downtown San Francisco is a short train ride away from Stanford, but the two environments offer different (and complementary) experiences. Downtown Palo Alto doesn't have skyscrapers but it does have a thriving economy, a diverse population, and an environment that attracts many students to stay here for postgraduate training and career opportunities. Come see for yourself!
- Graduate Program
Is an MD/PhD Program Right for You?
MD-PhD programs may be right for you if you are interested in a career path that melds both clinical practice and in-depth scientific research. MD-PhD graduates aren’t simply doctors; they are “physician-scientists” or “medical scientists.”
MD-PhD programs offer a dual-degree track that combines the clinical training of a standard MD degree with the added coursework of a PhD. The PhD training is particularly rigorous and includes classes usually in the realm of biomedical sciences, as well as advanced research training, lab rotations, and intensive investigative work.
The payoff for choosing an MD-PhD program is that these clinical medicine graduates are equipped to treat patients while also participating in the discovery and development of innovative healthcare solutions.
Here are a few reasons you might want to pursue an MD/PhD career:
- You want to participate in cutting-edge medical research.
- You want career options beyond clinical medical practice.
- You want to help train future generations of medical doctors.
- You want more collaborative research opportunities with colleagues.
- You want funding opportunities only available to MD/PhD students.
The Difference Between MD & MD/PhD
The difference between MD and MD-PhD is that graduates with an MD-PhD receive PhD training and hold a PhD degree in addition to their MD degree.
The cost of an MD-PhD program varies widely depending on the institution. Still, the stipend and tuition-free training make many of these programs significantly less financially burdensome compared to standalone MD or PhD programs.
MD/PhD students will complete graduate school and medical school qualified to hold positions in academic medicine and biomedical research (in addition to being qualified to practice clinical medicine.
What Is an MD?
A medical doctor has earned a standard medical degree or MD and is skilled to practice clinical medicine. Medical students must complete 4 years of medical school to earn their degree, followed by 3-7 years of residency and fellowship training to practice medicine.
What Is a PhD?
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy in reference to their critical knowledge and research experience in a particular field of study. A PhD is the highest possible academic degree.
Earning a PhD is often considered harder than earning an MD due to the scientific research required to stimulate original thought and develop quality hypotheses.
How Competitive Are MD/PhD Programs?
Physician-scientist programs are slightly more selective and competitive than the average medical program.
Between 2018 and 2023, a little more than one-third of students who applied to an MD/PhD program (37.7%) were accepted. The acceptance rate for medical school applicants in general was 41.2% for the 2022-23 application cycle.
The test scores of these programs also indicate how much more competitive these programs are. The average MCAT score of MD/PhD matriculants in the 2022-23 cycle was 516.2, and their mean GPA was 3.82. In comparison, medical school matriculants overall had an average MCAT score of 511.9 and average GPA of 3.75 during the same cycle.
How Long Are MD/PhD Programs?
The MD-PhD dual degree takes approximately 7-8 years of coursework to complete, followed by an additional 3-7 years of residency to be eligible to practice medicine.
Generally, MD coursework is emphasized in years 1-2, followed by research training in years 3-5, and ending with medical training and clinicals in years 6-8.
Requirements for MD/PhD Applicants
If you are considering applying to an MD/PhD program , know that having strong essays and letters is more important than incrementally higher MCAT test scores and GPAs. Numbers get your foot in the door; storytelling gets you a seat at the table.
In general, the requirements for MD/PhD applicants include:
- MCAT score in the 90th percentile: Specific MCAT requirements for MD/PhD programs vary by school. However, in general, most students have the best chance at success with an MCAT score in the 90th percentile or higher. In the 2022-23 application cycle, MD/PhD applicants had an average MCAT score of 511.3, while matriculants averaged 516.2.
- GPA of 3.7 or higher: Like MCAT scores, the GPA requirements for MD/PhD programs differ by program. But your chances are highest with an average GPA of at least 3.7. In the 2022-23 application cycle, MD/PhD applicants averaged a science GPA of 3.61 and overall GPA of 3.68, while matriculants averaged a 3.78 science GPA and 3.82 overall.
- Compelling personal statement: Your personal statement essay should explain why you want to become a physician and is required for both MD & MD/PhD applications . All prospective doctors must write a personal statement that stands out, and this is doubly true for MD/PhD applicants.
- 2 additional essays: You’ll write one essay conveying your personal interest in pursuing an MD/PhD dual degree specifically, and one essay covering your substantive experiences in the field of research . These may include multiple summer projects, senior thesis research, or 1+ years of post-undergrad research programs and activities.
- 2-3 letters from research mentors who can praise your scientific potential.
- 1-2 letters from clinical mentors who know your aptitude for patient care.
- 1 letter from the premed committee.
- 1 letter from a mentor who can discuss your leadership skills and personal traits in an extracurricular setting.
Questions to Ask Yourself When Considering an MD/PhD Program
By answering these questions, you can choose the graduate program that is the best fit for you over the next 8 years.
- What skills do you want to develop? Choose a program that has ample opportunities to explore your field of interest and in which you can identify potential mentors for rotations and thesis projects.
- What is your preferred MD/PhD program size? Choose a smaller program of MD-PhD students if you prefer hands-on guidance with individualized attention and a larger program if you prefer a larger community with more networking opportunities.
- Where do you want to live for 8 years of medical school ? Choose a location that fits your needs for cost of living, housing, transportation, extracurriculars, as well as opportunities for fun and making friends.
- Does the program offer financial aid? Choose a program that meets your financial needs in the form of stipends and tuition waivers. It’s important to note that if you drop out of an MD-PhD program, some schools require you to pay back the investment that the school made in you.
- Will you fit into the school’s culture? Choose a program after you’ve visited the campus, talked with the current students and faculty, and asked about opportunities in your field of interest as well as other’s experiences at the school and living in the city.
- Does the MD/PhD Program align with your timeline? Choose a program with coursework that allows you to graduate in your preferred timeline, which could be sooner or longer than eight years.
Possible Career Paths for MD/PhD Graduates
A career choice often depends on an individual’s specific interests, such as which medical specialties they are drawn to, whether they prefer working with patients or in a laboratory, and how they want to contribute to advancing medical science.
The salary range for MD/PhD graduates varies significantly by position and type of work. Policy analysts’ starting salary is around $57,000 per year, while attending physicians who do research can make upwards of $500,000.
Below are careers someone with an MD-PhD might pursue:
Attending Physician with Research Responsibilities
An MD/PhD holder in this position would have a traditional medical role seeing and treating patients, but they might also have dedicated time for research. This role allows one to continue practicing medicine while contributing to academic or clinical research.
Individuals in this role often split their time among patient care, research activities, and instructional duties. Typically, they are found in educational hospitals or medical schools.
Physicians’ salaries can vary significantly based on specialty and experience, but generally, they are well-compensated. An attending physician in a specialized field can expect to earn upwards of $200,000 to $500,000 or more, especially if they have dual responsibilities that include research.
Translational Medicine Specialist
These specialists work at the intersection of basic research and patient care, focusing on turning research insights into practical medical applications.
This role may exist within academia, industry, or clinical settings and is tailored for those who understand both the clinical and research aspects of medicine.
The salary for this role can also vary based on industry, location, and level of experience but would likely fall in the range of $150,000 to $250,000 or more.
Biomedical Researcher
Those with MD-PhD qualifications commonly secure jobs as researchers within biomedical science. Employment settings can range from academic institutions and drug companies to governmental agencies like the NIH.
Salaries for biomedical researchers typically fall somewhere between $85,000 and $104,000 per year.
Clinical Research Director
These are medical doctors responsible for overseeing clinical trials and research projects, usually within a hospital, academic institution, or pharmaceutical/biotech company. This role leverages both the clinical insights from an MD and the research methodology of a PhD.
Salaries can vary widely depending on the setting (academia, private industry, etc.) and geographic location. In general, a Clinical Research Director could expect to earn a six-figure salary, often ranging from around $150,000 to $250,000 or more per year.
Pharmaceutical/Biotech Industry Professional
A significant number of MD-PhDs join the pharmaceutical or biotech sectors. Responsibilities might include roles in the development of new medications, overseeing clinical trials, regulatory compliance, or managing medical affairs.
The average salary for this position will likely differ quite a bit depending on the exact role and company, but the average is generally between $125,000 and $133,00 per year.
Medical Director
In this capacity, a person is in charge of the medical elements of a healthcare facility or a specific department within a hospital. The role usually calls for expertise in both medical practice and research.
This position is likely to be one of the most lucrative of the MD/PhD field, with an average salary from $319,000 to $329,000 per year.
Science Policy Analyst/Advisor
Individuals in this role often find themselves in governmental or nonprofit settings, where they influence policy decisions related to scientific research and healthcare.
The typical salary for a science policy analyst starts at around $57,000 per year. Advisors have a slightly higher upper salary range and may make as much as $75,000.
Public Health Official
Some MD-PhDs opt for roles in the public sector where they focus on health concerns at a societal level. They may be employed by organizations such as the CDC or WHO.
In many cases, public health officials can expect to make a yearly salary of between $101,000 and $111,000.
Medical Science Liaison
This role typically serves as an intermediary between pharmaceutical enterprises and medical professionals. These liaisons disseminate information about new treatments and scientific advancements to doctors, researchers, and other medical stakeholders.
This role also typically commands a six-figure salary, usually ranging from approximately $100,000 to $200,000, depending on experience, location, and the hiring organization.
Medical Educator
Professors teach medical students, residents, and fellows in an academic setting while also conducting research. These doctors often have clinical responsibilities as well. An MD/PhD is especially well-suited for this role due to the dual focus on clinical care and research.
They may teach various medical subjects like pharmacology or genetics and actively participate in the educational goals of their institutions.
In academia, salaries can vary widely based on rank (Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, Full Professor), institution, and geographic location. Salaries may range from $100,000 to well over $200,000 for senior roles or those at prestigious institutions.
Best MD/PhD Programs in the US
There are 122 different American Universities that offer MD/PhD degree programs, according to the AAMC list of MD-PhD Programs by State . A further 13 Canadian programs also use the AMCAS application system.
Some MD-PhD programs in the United States are funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) through the Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP). This means that students receive full tuition remission, health insurance, and a living stipend throughout their training.
Medical schools with fully funded MD-PhD programs :
- Dartmouth University, Geisel School of Medicine
- Duke University School of Medicine
- Harvard/M.I.T MD-PhD Program, Harvard Medical School
- John Hopkins University School of Medicine
- Mayo Clinic College of Medicine & Science
- University of Florida College of Medicine
- University of Pennsylvania, Perelman School of Medicine
- University of Southern California (USC), Keck School of Medicine
- Yale University School of Medicine
Medical schools with the most MD-PhD spots historically:
- Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania
- University of Illinois College of Medicine
- Weill Cornell Medical College
- Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine
- Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
- Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University
- University of California, Los Angeles David Geffen School of Medicine
- University of Michigan Medical School
- Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons
- University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
- Harvard Medical School
- Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine
- Northwestern University The Feinberg School of Medicine
- Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
- University of California, San Francisco, School of Medicine
- Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
- Ohio State University College of Medicine
- University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health
- New York University School of Medicine
- Stanford University School of Medicine
- Yale School of Medicine
Medical schools with MD/PhD programs that accept international students:
- Emory University School of Medicine
- Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine
- University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine
- University of Southern California Keck School of Medicine/California Institute of Technology
- University of Texas Southwestern Medical School
- Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
The MD/PhD Application Process
The application process for MD-PhD programs is similar to that of typical MD programs. The two major differences are that you’ll designate yourself as an MD/PhD candidate on the AMCAS application, and you’ll submit 2 additional essays on that primary.
The Application Timeline
- AMCAS (submit by end of May): You’ll fill out a primary application through AMCAS in the spring of the first year of your application cycle (e.g., to matriculate in fall 2026, you’ll submit AMCAS in spring 2025). AMCAS opens at the end of May each year. Aim to submit the primary application no later than the end of June, as early applications are more likely to be reviewed and accepted.
- Secondaries (submit by end of August): You’ll respond to secondary applications in the summer after your primary application is reviewed by each school you submitted it to. Each program sends secondary applications to students who generally meet their minimum requirements.
- Interviews (October-March): You’ll then attend interviews as invited between October and March. Some schools won’t contact you at all to reject your application; others will offer conflicting invites. You must prioritize your options and prepare for the opportunities that do come.
- Final decisions (December-March): Final decisions are made by schools between December and March. Schools with a rolling admissions cycle (most of them) accept students after completing interviews and determining a student is a fit. A smaller number of programs wait to send acceptances until after all interviews are complete.
- Choose your program (March-April): Students choose where to matriculate between March and April.
- Programs start (June-August): Programs begin between June and August, depending on the school.
How to Prepare for an MD/PhD interview
You should prepare for your MD/PhD interview by practicing mock interviews to rid yourself of the jitters and fine-tune your responses in various scenarios. In addition to developing your personal narrative, you must be able to explain your research training at multiple levels.
If you’re interested in participating in a mock interview with a physician who has served on an admissions committee, consider a mock interview with MedSchoolCoach .
What to Do if You Get Waitlisted
Finding out that you’ve been waitlisted for the MD/PhD program of your dreams is never a good feeling. However, you are not helpless in the wait. It’s a good idea to remain in contact with program leaders and administrators by sending a Letter of Intent or a Letter of Interest.
Listen: An MD/PHD’s Journey to Medicine [PODCAST]
What is a Letter of Intent vs. a Letter of Interest?
A Letter of Intent is a formal statement that you would commit to matriculating into a program if you are accepted. A Letter of Interest conveys that you are strongly interested in the program, but it does not indicate any commitment or explicitly state that a program is your first choice.
Both letters should summarize why you believe the program and school are a great fit for your interests and how you will be able to uniquely contribute to the school, in under one page.
Finding Out You’ve Been Accepted!
The day you receive that phone call or email — the one from the MD-PhD program director contacting you to say you have officially been offered acceptance into their program — provides a feeling of joy worth being patient for!
Our Physician Advisors can support you through the application process for your best shot at getting into the school of your choice.
What specialties can MD/PhD graduates earn their PhD in?
PhD students commonly choose to specialize in topics such as:
- Cell Biology
- Biochemistry
- Pharmacology
- Neuroscience
- Biomedical Engineering
What is the salary range for an MD/PhD graduate?
MD/PhD graduates can expect an average annual salary of about $100K, depending on the type of work and place of employment.
What is the difference between a PhD and a Postdoctorate?
A Postdoctoral Fellowship is a temporary period of mentorship and research training for graduates with doctoral degrees, offered by the National Institutes of Health, to acquire skills needed for a chosen career. A PhD thesis must be successfully defended, whereas a postdoc is a non-defendable temporary employment assignment from an organization such as a university.
Can an MD/PhD be a doctor?
Graduates who earn an MD/PhD are fully qualified doctors and may practice medicine in a clinical setting upon completing their residency training.
Can an MD/PhD graduate be a surgeon?
While an MD/PhD graduate CAN be a surgeon if they choose surgery specialties in their residency programs, a surgical resident is not required to obtain a PhD in addition to their MD.
Schedule a free 15-minute consultation with MedSchoolCoach to learn how we can help boost your chances of success getting into medical school .
Related posts:
- What Does DO Mean?
- What Kind of Students are Successful in Getting into Medical School?
- What Counts as Clinical Experience for Medical School?
- Should I Delete My Social Media When Applying to Medical School?

Renee Marinelli MD
Related articles.

Can a Teaching Assistant Write My Letter?

What Is the Best Way to Get From High School to Medical School?

Everything You Need to Know About Medical School Interviews

How to Succeed on Medical School Interview Day

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Undergraduate courses
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Postgraduate courses
- How to apply
- Postgraduate events
- Fees and funding
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Term dates and calendars
- Visiting the University
- Annual reports
- Equality and diversity
- A global university
- Public engagement
- Give to Cambridge
- For Cambridge students
- For our researchers
- Business and enterprise
- Colleges & departments
- Email & phone search
- Museums & collections
- Course Directory
PhD in Medicine
Postgraduate Study
- Why Cambridge overview
- Chat with our students
- Cambridge explained overview
- The supervision system
- Student life overview
- In and around Cambridge
- Leisure activities
- Student unions
- Music awards
- Student support overview
- Mental health and wellbeing
- Disabled students
- Accommodation
- Language tuition
- Skills training
- Support for refugees
- Courses overview
- Department directory
- Qualification types
- Funded studentships
- Part-time study
- Research degrees
- Visiting students
- Finance overview
- Fees overview
- What is my fee status?
- Part-time fees
- Application fee
- Living costs
- Funding overview
- Funding search
- How to apply for funding
- University funding overview
- Research Councils (UKRI)
- External funding and loans overview
- Funding searches
- External scholarships
- Charities and the voluntary sector
- Funding for disabled students
- Widening participation in funding
- Colleges overview
- What is a College?
- Choosing a College
- Terms of Residence
- Applying overview
- Before you apply
- Entry requirements
- Application deadlines
- How do I apply? overview
- Application fee overview
- Application fee waiver
- Life Science courses
- Terms and conditions
- Continuing students
- Disabled applicants
- Supporting documents overview
- Academic documents
- Finance documents
- Evidence of competence in English
- Terms and Conditions
- Applicant portal and self-service
- After you apply overview
- Confirmation of admission
- Student registry
- Previous criminal convictions
- Deferring an application
- Updating your personal details
- Appeals and Complaints
- Widening participation
- Postgraduate admissions fraud
- International overview
- Immigration overview
- ATAS overview
- Applying for an ATAS certificate
- Current Cambridge students
- International qualifications
- Competence in English overview
- What tests are accepted?
- International events
- International student views overview
- Akhila’s story
- Alex’s story
- Huijie’s story
- Kelsey’s story
- Nilesh’s story
- Get in touch!
- Events overview
- Upcoming events
- Postgraduate Open Days overview
- Discover Cambridge: Master’s and PhD Study webinars
- Virtual tour
- Research Internships
- How we use participant data
- Postgraduate Newsletter
Primary tabs
- Overview (active tab)
- Requirements
- How To Apply
Doctoral studies are carried out by science postgraduates, medical students combining clinical training with the PhD, and clinically qualified doctors undertaking scientific training. The research covers the whole spectrum of medical science from basic biology to clinical therapies.
Along with the specific research training provided in the laboratory in which they work, students receive further training within the department in the form of postgraduate workshops concentrating on research techniques, research seminars both on the Addenbrooke's site and elsewhere in the University, and postgraduate student seminars dealing with generic skills such as intellectual property rights, writing a thesis or paper, and entrepreneurship.
Candidates wishing to take a shorter course of research and write a thesis for the master's after one year may apply for the MPhil in Medical Sciences.
Learning Outcomes
Those who wish to progress to a PhD after completing an MPhil will be required to satisfy their potential supervisor, Head of Department and the Faculty Degree Committee that they have the skills and ability to achieve the higher degree.
The Postgraduate Virtual Open Day usually takes place at the end of October. It’s a great opportunity to ask questions to admissions staff and academics, explore the Colleges virtually, and to find out more about courses, the application process and funding opportunities. Visit the Postgraduate Open Day page for more details.
See further the Postgraduate Admissions Events pages for other events relating to Postgraduate study, including study fairs, visits and international events.
Key Information
3-4 years full-time, 4-7 years part-time, study mode : research, doctor of philosophy, department of medicine, course - related enquiries, application - related enquiries, course on department website, dates and deadlines:, lent 2024 (closed).
Some courses can close early. See the Deadlines page for guidance on when to apply.
Easter 2024 (Closed)
Michaelmas 2024, easter 2025, funding deadlines.
These deadlines apply to applications for courses starting in Michaelmas 2024, Lent 2025 and Easter 2025.
Similar Courses
- MD (Doctor of Medicine) MD
- Medical Science (Medicine) MPhil
- Population Health Sciences MPhil
- Clinical Medicine Wellcome Trust PhD
- Infection and Immunity PhD
Postgraduate Admissions Office
- Admissions Statistics
- Start an Application
- Applicant Self-Service
At a glance
- Bringing a family
- Current Postgraduates
- Cambridge Students' Union (SU)
University Policy and Guidelines
Privacy Policy
Information compliance
Equality and Diversity
Terms of Study

About this site
About our website
Privacy policy
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Privacy policy and cookies
- Statement on Modern Slavery
- University A-Z
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Research news
- About research at Cambridge
- Spotlight on...

PhD vs. Master’s in Biomedical Science: What’s the Difference?

Industry Advice Pharmaceutical Science Science & Mathematics
An advanced degree is all but required to land a position in the biomedical science field today. However, the depth of study and areas of focus covered during the pursuit of a master’s degree will differ greatly from that of a PhD. For this reason, it’s important that professionals identify their career aspirations within biomedical science, and tailor their choice in degree accordingly.
Below we explore the differences in Northeastern’s biomedical science master’s and PhD programs and offer some advice on carving your path to success in this exciting field.
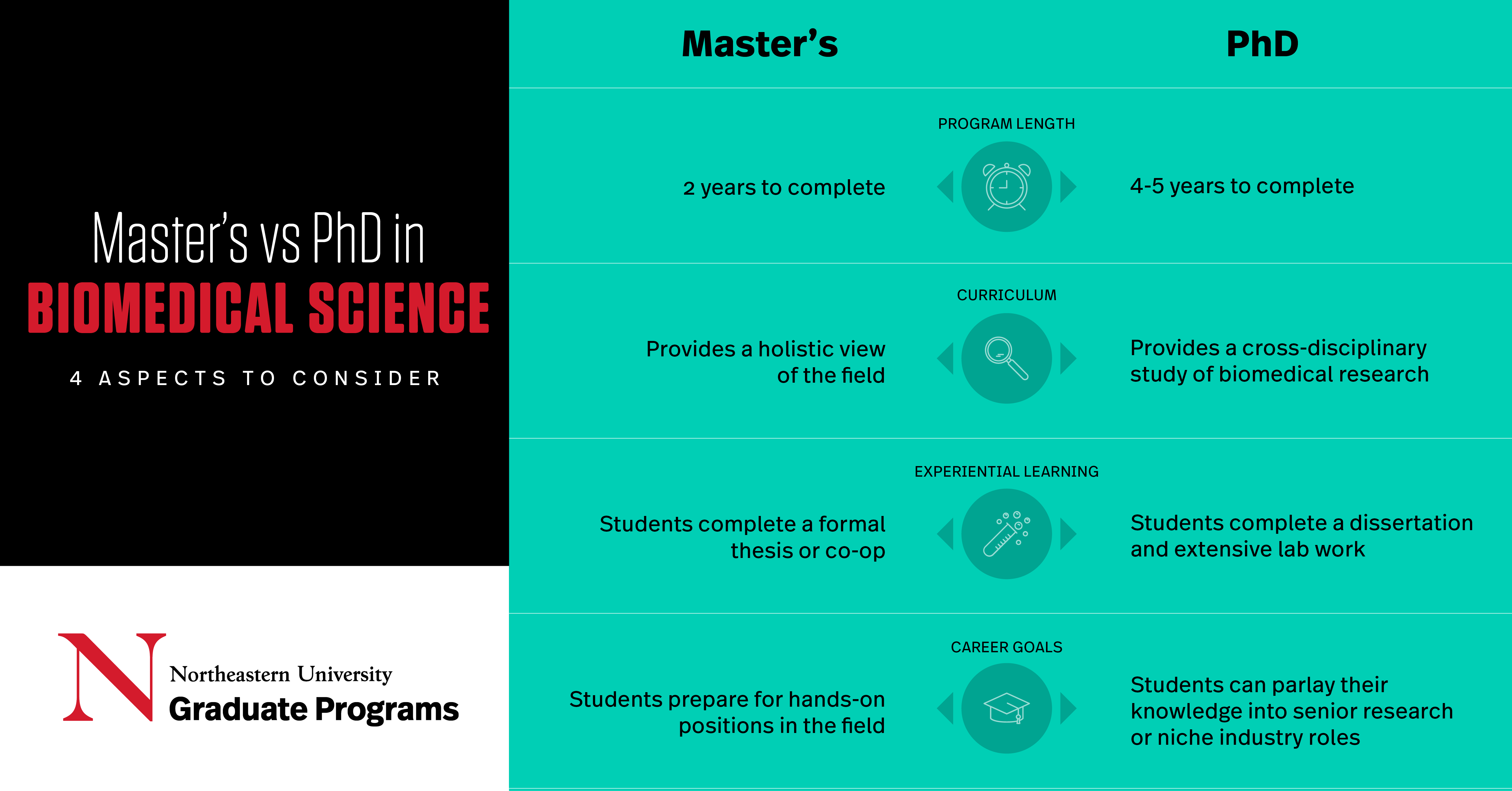
Pursuing a Master’s in Biomedical Science
How long does it take to complete a master’s in biomedical science.
Northeastern’s master’s in biomedical science program takes an average of two years to complete. The program is designed to help students maintain a work-life balance , offering both full-time and part-time degree options.
What is the curriculum like in a master’s of biomedical science program?
This program is one of four tailored degrees offered within the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences. Of all the other niche areas of study—which include pharmacology, medicinal chemistry, and pharmaceutical sciences—the master’s in biomedical science program provides the most general and holistic view of the field. The curriculum ranges greatly, exploring fundamentals like pharmaceutical science and biochemistry, to practical applications such as research skills and ethics.
Students also have the opportunity to tailor their education to fit their desired career outcomes at the master’s level.
“We offer a wide variety of electives both within [and] outside of the department,” says David Janero , director of the pharmaceutical sciences graduate program at Northeastern. These courses include those within Northeastern’s pharmaceutical sciences, pharmacology, pharmaceutics, biology, chemistry, nanomedicine, and biotechnology departments.
A Flexible Approach to Learning: Northeastern has designed all pharmaceutical sciences programs to offer the same fundamental courses, so that students can easily transfer their credits within the department if they decide later on that their interests have changed. “I often find that a person coming into the program…has some vague idea of what he or she may wish to do,” Janero says. “And after going through some of the courses, these ideas become refined. The flexibility in Northeastern’s programs is a very important and recognized part of mentorship.”
What are the hands-on opportunities like in a master’s of biomedical science program?
Northeastern’s master’s in biomedical science program offers extensive opportunities for experiential learning —a vital component of training in such a hands-on field.
“Master’s students have two very good opportunities in terms of career building at Northeastern,” Janero says. One option is to do a formal thesis, which can be based on anything from wet-lab research —which is identified by the handling of chemicals and “wet” materials in experiments—to literature—which often includes doing a deep-dive into existing publications on a specific topic. The other option is to spend time working with one of the top biomedical science organizations that make up Northeastern’s expansive professional network as part of a co-op .
Advance Your Career with a Master’s in Biomedical Science
Learn how to transform your career in an industry that’s transforming the world.
EXPLORE THE PROGRAM
“I would say most of our master’s students want to do a co-op, and we have many biotech and pharma companies in the Boston/Cambridge ecosystem that avidly wish to take these students on,” Janero says. “The reputation of the co-op program at Northeastern has been so good that it doesn’t even follow the law of supply and demand…the demand for our students is outstanding in all of our pharmaceutical science programs.”
Did You Know: The Boston/Cambridge area is considered a national hub in the biomedical science industry. As such, Northeastern students have the unique opportunity of not only working with some of the top minds in the field, but developing integral connections with the organizations defining the future of biomedical science.
Alongside getting the chance to work and network with some of the top companies in the industry, students find great value in the chance to apply their skills hands-on during co-op.
“Students may read about this stuff, but to be a part of it and see it in day-to-day operation is unique,” Janero says. “It’s more than learning how the car is driven. You actually get into the front seat, behind the wheel, and I think that’s really important for students at the [graduate] level.”
What kind of career outcomes can graduates of a master’s in biomedical science program expect?
A master’s degree in biomedical science is designed to prepare professionals for hands-on positions in the field. Individuals at this level are likely to pursue “a technical-level position at the bench in a laboratory, actively doing research,” Janero explains.
He notes that graduates of a master’s biomedical science master’s program can also parlay their knowledge into a role outside of the lab. Most often these individuals will have additional training or backgrounds in the application of biomedical science—such as marketing, legal, sales, etc.—that they wish to work in.
Some of the top positions for those with a master’s in biomedical science include biomedical laboratory technician, biomedical scientist, clinical research associate, medical writer, and medical chemist.
Pursuing a PhD in Biomedical Science
How long does it take to complete a phd in biomedical science.
It can take four to five years for students to complete a PhD program in biomedical science.
In some cases, however, students who have already completed their master’s can fast-track the completion of their PhD within the same university. This occurs most often at universities (like Northeastern) that offer both a master’s and PhD in biomedical science. Since the faculty of both programs are aware of how the curricula overlap, they are willing to make adjustments for those who have completed a master’s so that they don’t have to repeat foundational coursework.
“We had a student this year…who was on the medicinal chemistry track, and is now starting his PhD in the fall,” Janero recalls. “He has already taken and done very well in his master’s courses, so he doesn’t need to retake any of that. He’s proven himself, so we can start him off at an advanced level.”
What is the curriculum like in a biomedical science PhD program?
The PhD program at Northeastern offers a cross-disciplinary study of some of the most vital practices pertaining to biomedical research. This includes the integration of human (patho)biology, and drug action, invention, and clinical utility.
Students will apply their skills both in the classroom and in hands-on research environments, exploring common topics ranging from drug design and profiling to toxicology and pharmaceutical biochemistry/cell biology.
Another core component of a PhD candidate’s curriculum is the completion of their dissertation. During this time, students have the chance to identify a topic of interest, conduct their own research, and sometimes even lead a team of master’s students through the research process.
Did You Know: Mentorship is an integral component of the biomedical science program at Northeastern. “At the PhD level, the role of mentorship—individually as well as at the level of the dissertation committee—is very critical in guiding students…so that they come out with not only the fundamental knowledge in the field, but also the ability to adapt and cope with new information, turn that information into knowledge, and apply that knowledge in a positive and productive way.”
What are the hands-on opportunities like in a biomedical science PhD program?
Another significant difference between a master’s and a PhD in biomedical science is an elevated focus on lab work. “The main purpose of a PhD is getting into a laboratory as quickly as possible,” Janero says.
What happens within a lab setting also differs for students at each level. For example, where master’s students may have the chance to contribute to an ongoing project in the lab—and carve out their niche area of focus—PhD candidates are “charged with independently and continuously contributing new knowledge to the field,” Janero says. They may also be tasked with overseeing or guiding the work of master’s students, effectively honing their leadership and managerial skills within a research environment, as well.
What kind of career outcomes can graduates of a biomedical science PhD program expect?
As a PhD requires students to further their understanding of the field and produce novel findings based on elaborate, personal research, individuals with this degree are often quite flexible in their work. This allows them to specialize in a certain aspect of biomedical science, or tailor their career path to fit their unique interests—such as biomedical sales, marketing, law, and more.
For those who want to pursue hands-on research in a lab environment, a PhD can still be a strategic move. This degree often allows students to advance into a more managerial role within a lab, overseeing or leading the work conducted by those with master’s-level training.
Some of the top careers for those with a PhD in biomedical science include senior biomedical scientist, principal investigator, medical sales director, pharmaceutical marketing manager, tenure track biomedical science professor, and more.
Advancing Your Career in Biomedical Science with a Degree from Northeastern
The faculty within Northeastern’s master’s and PhD programs are dedicated to crafting the unique educational experience each student needs to get ahead in their desired career within the vast biomedical science field.
Janero explains that, at the start of a student’s time at Northeastern, he and his colleagues will make a point to ask them “‘What do you feel, at this point, is your career trajectory?’ and ‘What courses does the university at large offer—not merely our department—to address these career projections?’ Then we’ll look far and wide at what that student needs in order to get him/her as prepared as possible for the future.”
This is the goal of career-oriented programs like Northeastern’s—to meet students where they are and help provide them with the knowledge, skills, and experiences they need to get ahead.
Ready to take the next step in advancing your biomedical science career? Explore the master’s in biomedical science and PhD in biomedical science programs at Northeastern, and get in touch with an enrollment coach today for advice on which might be the best fit for your goals.

Subscribe below to receive future content from the Graduate Programs Blog.
About shayna joubert, related articles.

Compliance Specialists: Who They Are and What They Earn
Science or science fiction the future of personalized medicine.

In-Demand Biotechnology Careers Shaping Our Future
Be in-demand.
The global pharmaceutical market is expected to grow 7% to reach $225B by 2025, driving job growth for qualified professionals.
Graduate Programs in Pharmaceutical Sciences
Northeastern's pharmaceutical programs allow students to focus on more than one area in biomedical science to prepare them to work in an evolving and interdisciplinary field.
Most Popular:
Tips for taking online classes: 8 strategies for success, public health careers: what can you do with an mph, 7 international business careers that are in high demand, edd vs. phd in education: what’s the difference, 7 must-have skills for data analysts, the benefits of online learning: 8 advantages of online degrees, how to write a statement of purpose for graduate school, the best of our graduate blog—right to your inbox.
Stay up to date on our latest posts and university events. Plus receive relevant career tips and grad school advice.
By providing us with your email, you agree to the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
Keep Reading:

The 8 Highest-Paying Master’s Degrees in 2024

Graduate School Application Tips & Advice

How To Get a Job in Emergency Management

Join Us at Northeastern’s Virtual Graduate Open House | March 5–7, 2024
How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree?
Earning a Ph.D. from a U.S. grad school typically requires nearly six years, federal statistics show.
How Long It Takes to Get a Ph.D. Degree

Caiaimage | Tom Merton | Getty Images
A Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a "lifelong learner."
Students who have excelled within a specific academic discipline and who have a strong interest in that field may choose to pursue a Ph.D. degree. However, Ph.D. degree-holders urge prospective students to think carefully about whether they truly want or need a doctoral degree, since Ph.D. programs last for multiple years.
According to the Survey of Earned Doctorates, a census of recent research doctorate recipients who earned their degree from U.S. institutions, the median amount of time it took individuals who received their doctorates in 2017 to complete their program was 5.8 years. However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey.
Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master's degrees, which means the time spent in grad school is a combination of the time spent pursuing a master's and the years invested in a doctorate. In order to receive a Ph.D. degree, a student must produce and successfully defend an original academic dissertation, which must be approved by a dissertation committtee. Writing and defending a dissertation is so difficult that many Ph.D. students drop out of their Ph.D. programs having done most of the work necessary for degree without completing the dissertation component. These Ph.D. program dropouts often use the phrase " all but dissertation " or the abbreviation "ABD" on their resumes.
According to a comprehensive study of Ph.D. completion rates published by The Council of Graduate Schools in 2008, only 56.6% of people who begin Ph.D. programs earn Ph.D. degrees.
Ian Curtis, a founding partner with H&C Education, an educational and admissions consulting firm, who is pursuing a Ph.D. degree in French at Yale University , says there are several steps involved in the process of obtaining a Ph.D. Students typically need to fulfill course requirements and pass comprehensive exams, Curtis warns. "Once these obligations have been completed, how long it takes you to write your dissertation depends on who you are, how you work, what field you're in and what other responsibilities you have in life," he wrote in an email. Though some Ph.D. students can write a dissertation in a single year, that is rare, and the dissertation writing process may last for several years, Curtis says.
Curtis adds that the level of support a Ph.D. student receives from an academic advisor or faculty mentor can be a key factor in determining the length of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. program. "Before you decide to enroll at a specific program, you’ll want to meet your future advisor," Curtis advises. "Also, reach out to his or her current and former students to get a sense of what he or she is like to work with."
Curtis also notes that if there is a gap between the amount of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. and the amount of time a student's funding lasts, this can slow down the Ph.D. completion process. "Keep in mind that if you run out of funding at some point during your doctorate, you will need to find paid work, and this will leave you even less time to focus on writing your dissertation," he says. "If one of the programs you’re looking at has a record of significantly longer – or shorter – times to competition, this is good information to take into consideration."
He adds that prospective Ph.D. students who already have master's degrees in the field they intend to focus their Ph.D. on should investigate whether the courses they took in their master's program would count toward the requirements of a Ph.D. program. "You’ll want to discuss your particular situation with your program to see whether this will be possible, and how many credits you are likely to receive as the result of your master’s work," he says.
How to Write M.D.-Ph.D. Application Essays
Ilana Kowarski May 15, 2018

Emmanuel C. Nwaodua, who has a Ph.D. degree in geology, says some Ph.D. programs require candidates to publish a paper in a first-rate, peer-reviewed academic journal. "This could extend your stay by a couple of years," he warns.
Pierre Huguet, the CEO and co-founder of H&C Education, says prospective Ph.D. students should be aware that a Ph.D. is designed to prepare a person for a career as a scholar. "Most of the jobs available to Ph.D. students upon graduation are academic in nature and directly related to their fields of study: professor, researcher, etc.," Huguet wrote in an email. "The truth is that more specialization can mean fewer job opportunities. Before starting a Ph.D., students should be sure that they want to pursue a career in academia, or in research. If not, they should make time during the Ph.D. to show recruiters that they’ve traveled beyond their labs and libraries to gain some professional hands-on experience."
Jack Appleman, a business writing instructor, published author and Ph.D. candidate focusing on organizational communication with the University at Albany—SUNY , says Ph.D. programs require a level of commitment and focus that goes beyond what is necessary for a typical corporate job. A program with flexible course requirements that allow a student to customize his or her curriculum based on academic interests and personal obligations is ideal, he says.
Joan Kee, a professor at the University of Michigan with the university's history of art department, says that the length of time required for a Ph.D. varies widely depending on what subject the Ph.D. focuses on. "Ph.D. program length is very discipline and even field-specific; for example, you can and are expected to finish a Ph.D, in economics in under five years, but that would be impossible in art history (or most of the humanities)," she wrote in an email.
Kee adds that humanities Ph.D. programs often require someone to learn a foreign language, and "fields like anthropology and art history require extensive field research." Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame. "Because of this, many if not most Ph.D. students must work to make ends meet, thus further prolonging the time of completion," she says.
Jean Marie Carey, who earned her Ph.D. degree in art history and German from the University of Otago in New Zealand, encourages prospective Ph.D. students to check whether their potential Ph.D. program has published a timeline of how long it takes a Ph.D. student to complete their program. She says it is also prudent to speak with Ph.D. graduates of the school and ask about their experience.
Online Doctoral Programs: What to Expect
Ronald Wellman March 23, 2018

Kristin Redington Bennett, the founder of the Illumii educational consulting firm in North Carolina, encourages Ph.D. hopefuls to think carefully about whether they want to become a scholar. Bennett, who has a Ph.D. in curriculum and assessment and who previously worked as an assistant professor at Wake Forest University , says a Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a "lifelong learner." She says someone contemplating a Ph.D. should ask themselves the following questions "Are you a very curious person... and are you persistent?"
Bennett urges prospective Ph.D. students to visit the campuses of their target graduate programs since a Ph.D. program takes so much time that it is important to find a school that feels comfortable. She adds that aspiring Ph.D. students who prefer a collaborative learning environment should be wary of graduate programs that have a cut-throat and competitive atmosphere, since such students may not thrive in that type of setting.
Alumni of Ph.D. programs note that the process of obtaining a Ph.D. is arduous, regardless of the type of Ph.D. program. "A Ph.D. is a long commitment of your time, energy and financial resources, so it'll be easier on you if you are passionate about research," says Grace Lee, who has a Ph.D. in neuroscience and is the founder and CEO of Mastery Insights, an education and career coaching company, and the host of the Career Revisionist podcast.
"A Ph.D. isn't about rehashing years of knowledge that is already out there, but rather it is about your ability to generate new knowledge. Your intellectual masterpiece (which is your dissertation) takes a lot of time, intellectual creativity and innovation to put together, so you have to be truly passionate about that," Lee says.
Curtis says a prospective Ph.D. student's enthusiasm for academic work, teaching and research are the key criteria they should use to decide whether to obtain a Ph.D. degree. "While the time it takes to complete a doctorate is an understandable concern for many, my personal belief is that time is not the most important factor to consider," he says. "Good Ph.D. programs provide their students with generous stipends, health care and sometimes even subsidized housing."
Erin Skelly, a graduate admissions counselor at the IvyWise admissions consulting firm, says when a Ph.D. students struggles to complete his or her Ph.D. degree, it may have more to do with the student's academic interests or personal circumstances than his or her program.
"The time to complete a Ph.D. can depend on a number of variables, but the specific discipline or school would only account for a year or two's difference," she wrote in an email. "When a student takes significantly longer to complete a Ph.D. (degree), it's usually related to the student's coursework and research – they need to take additional coursework to complete their comprehensive exams; they change the focus of their program or dissertation, requiring extra coursework or research; or their research doesn't yield the results they hoped for, and they need to generate a new theory and conduct more research."
Skelly warns that the average completion time of a Ph.D. program may be misleading in some cases, if the average is skewed based on one or two outliers. She suggests that instead of focusing on the duration of a particular Ph.D. program, prospective students should investigate the program's attritition and graduation rates.
"It is worthwhile to look at the program requirements and the school's proposed timeline for completion, and meet current students to get their input on how realistic these expectations for completion are," Skelly says. "That can give you an honest idea of how long it will really take to complete the program."
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
Tags: graduate schools , education , students
You May Also Like
Find a strong human rights law program.
Anayat Durrani April 18, 2024

Environmental Health in Medical School
Zach Grimmett April 16, 2024

How to Choose a Law Career Path
Gabriel Kuris April 15, 2024

Questions Women MBA Hopefuls Should Ask
Haley Bartel April 12, 2024

Law Schools With the Highest LSATs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 11, 2024

MBA Programs That Lead to Good Jobs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 10, 2024

B-Schools With Racial Diversity
Sarah Wood April 10, 2024

Law Schools That Are Hardest to Get Into
Sarah Wood April 9, 2024

Ask Law School Admissions Officers This
Gabriel Kuris April 9, 2024

Grad School Housing Options
Anayat Durrani April 9, 2024

Career Paths for MD-PhD Graduates
New section.
Information about the career path of a physician-scientist, including training, residency or fellowship, research residency programs, and time commitment.
According to a study by the National Association of MD-PhD Programs, about 75 percent of U.S. MD-PhD graduates are in academic medicine or pharmaceutical company positions that make use of their interests in both patient care and research.
A MD-PhD physician-scientist is typically a faculty member at an academic medical center who spends 70-80 percent of their time conducting research, though this can vary with specialty. Their research may be lab-based, translational, or clinical. The remaining time is often divided between clinical service, teaching, and administrative activities.
Thus, most MD-PhD graduates pursue a career where most of their time is spent on research. This research typically is conducted at academic medical centers, research institutions like NIH, or in the pharmaceutical/biotech industry. With career advancement, many MD-PhD graduates ascend to significant leadership roles in academic medical centers, or industry, government and private organizations, reflecting their broad experience in health care and research.
Training Path for the MD-PhD Graduate
The career of each MD-PhD graduate is uniquely based upon research and clinical interests, but follows the general path:
- MD-PhD training: 7-8 years (See Education and Training for more information).
- Specialty and subspecialty clinical and research training (residency/fellowship): 3-7 Years.
Residency and Fellowship Training
Most MD-PhD graduates pursue residency and fellowship training and find that their MD-PhD training makes them particularly attractive to residency programs at top academic institutions. In the past, MD-PhD graduates traditionally entered residency programs in medicine, pediatrics, or pathology. However, the clinical specialty choices of current graduates are more diverse, with many graduates pursuing residency training in neurology, psychiatry, radiology, radiation oncology, and even surgery and surgical specialties.
Research Residency Programs
It is important to note that there are a growing number of "research residency programs" that have been specially developed to foster the career development of physician-scientists.
After completing their specialty clinical training (e.g., in medicine or pediatrics), most physician-scientists pursue subspecialty clinical training (e.g., cardiology or hematology-oncology) and postdoctoral research that typically combines protected research time with intensive clinical training. A number of residency programs around the country offer highly structured programs in which research is fully integrated into the clinical training.
These programs differ in their overall structure, but all offer the following:
- Shortened residency (specialty) training; in general, the integrated programs allow trainees to shorten their residency by one year, depending on the field of specialty.
- Integrated research and clinical training; programs usually offer mentoring for trainees to choose a lab early in their training process, so they can embark on their research right away when they start full time in the lab.
- Guaranteed subspecialty fellowship position in the trainee's desired field; this is not offered at all institutions.
- Special financial support; a few combined programs also offer support both towards salary and research.
Time Commitment
The time commitment required to complete the dual degree and subsequent specialty training can be substantial. Thus, you should thoroughly explore whether combining biomedical research and clinical practice is the right path for you. Despite the time commitment, it is important to recognize that professional progress following MD-PhD training can be swift, and the years of training truly represent a time of great personal as well as professional growth.
The MD-PhD graduate is unique within medical education, representing about 3 percent of the entire graduating medical school class in the United States. In 2006, there were over 16,000 MD graduates; about 500 of these earned PhD degrees as well.
- @AAMCpremed
Helpful tools and information regarding medical MD-PhD programs.
Information about applying to MD-PhD programs, emphasizing the application process during COVID-19.
Information about MD-PhD programs, emphasizing the career and application process.
Learn about MD-PhD Programs from program leaders.
Upcoming short presentations will describe features of MD-PhD training, alumni careers, and detailed logistics of the application process.

Emily battled viral encephalitis for years during college, and now as a MD/PhD student, she reminds premeds that it's okay to ask for help.

Cesar couldn't apply to medical school when he first graduated from college due to his undocumented status. Now he's in a MD-PhD program and hopes to practice in the Southwest where there's a high need for Spanish-speaking physicians.
- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Living in San Diego
- Culture of Belonging
- Departments
- Land Acknowledgement
- Pathway Programs
- MD & Combined Programs
- Physician Assistant Education
- Graduate Programs (MS & PhD)
- Residency & Fellowship Programs
- Education & Training Facilities
- Continuing Professional Development
- Medical Education & Technology
- Research Centers & Institutes
- Student Opportunities
- Requests for Clinical Data
- UC San Diego Health
- Clinical Trials
- Training Facilities
- Residents & Fellows
- Faculty & Staff
- School of Medicine
Graduate Programs
Science informs medicine and medicine informs science. School of Medicine offers several master's and PhD-level graduate programs for students interested in pursuing careers in health and biomedical sciences research. Our graduate students conduct their thesis work in faculty labs, where their basic, translational and clinical research advances our understanding of human development and disease. Our master's degree and PhD students also contribute to the development of new diagnostics and therapeutics in cardiology, neurology, cancer, diabetes, infectious diseases and more.
Master of Science (M.S.)
- Master's in Clinical Research
Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.)
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Biomedical Sciences
- Neurosciences
- Independent PhD: Medical students may also pursue advanced training leading to a MA, MS or PhD in the Biomedical Sciences Program independent of the Medical Scientist Training Program, or in any of the UC San Diego general campus science or engineering programs. Information is available from relevant departments and faculty.
Joint Programs with San Diego State University
- Au.D. in Audiology
- Ph.D. in Clinical Psychology
- Ph.D. in Interdisciplinary Research on Substance Use
Medical Scientist Training Program
Are you interested in pursuing a joint MD/PhD program? Explore the Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP) at School of Medicine.
Learn more about MSTP
Career Prospects after a PhD in Medical Science
Blog summary.
If you want to become a top researcher in the field of medical science or you aspire to join a teaching institution and scale new heights as a scientist, then a PhD in medical sciences is a must. It can take up to six years to earn a PhD. During the first two years, you will do course work and after that, you will start working on the thesis part. In the end, you will have conducted experiments that are relevant to the subject you choose. The thesis you produce must be 100 pages long and original. Plagiarism is never tolerated in the award of a PhD. One of the qualities individuals must possess is a strong capacity to work for most independently with minimum guidance from outside. In short, you must be a resourceful person who can think out of the box and be innovative in solving complex problems and understanding the subject on which you are focusing. Texila American University and the University of Nicaragua are offering PhD in medicine program for individuals who want to complete the doctoral program. There are more than 100+ fields for which candidates can apply and join. After a PhD in Medical Science in India, the most popular destinations for scientists are research and development. This can be at pharmaceutical companies, government agencies, or educational institutions. Some PhD graduates choose to continue with postdoctoral studies. Areas of specialization include biomedical research, medical sciences, and clinical research.
How Long Must I Study to Get a PhD in Medicine?
What are the most beneficial phd in medical science programs, public health doctoral programs, environmental epidemiology doctoral programs.
In today’s highly competitive world, a PhD in Medical Science in India will be one of the most respected and esteemed qualifications. A PhD offers abundant opportunities for those who wish to pursue a career as a scientist or a researcher. Depending on the field of study and subject specialization within that field, a PhD degree-holder can apply for various positions.
A PhD in Medical Science is the highest qualification that prepares you for a career in research and development. Completing the degree will enable you to pursue your passion in the field of medicine. You can carry out invaluable research on discoveries or treatments related to health, human life, or diseases.
Some of the jobs you can enter upon successful completion of your PhD in Medical Science are:
- Academic/teaching positions at universities or colleges.
- Research and development jobs in government laboratories, universities, or pharmaceutical companies.
- Medical science research coordinator in health care organizations.
- Consultant in medical science for various organizations like universities, research institutes, hospitals, etc.
- Governmental jobs in healthcare administration at the national or international level.
- Scientific director in a non-profit organization for public health and medical science research.
The need for qualified persons trained in medicine and other life sciences is increasingly felt today. The challenge of providing better health care to an increasing population is daunting. It requires more highly trained people —professionals who can also contribute to our knowledge of the scientific aspects of health and ill-health.
A PhD in Medical Sciences in India takes about five to six years, depending on your field of research. The first two years include doing coursework and taking courses. The third year is on your thesis, and the next two years are for conducting experiments for your research. To complete the degree requirements, you must produce a thesis of more than 100 pages through original research.
The competitive nature of a medical science PhD program requires an individual to have a strong knowledge base. It also requires sound reasoning and logical thinking skills, mental alertness, and above all, patience, and dedication towards work.
It is also required that the aspirant works under the least supervision. They make decisions and are resourceful enough to solve problems without much external assistance.
PhD in medical science online programs are great choices if you want to advance your education and become a medical doctor. There are multiple fields of expertise you can apply for after completing an advanced degree. Some people pursue courses in public health, while others get their degrees in global studies. In addition, some take on the role of environmental epidemiologist . The most important thing is to find a course that you enjoy because you will have to dedicate the next few years of your life to it.
The first thing you need to do is figure out how much time it takes for someone with a medical degree to complete their PhD program. The majority of courses can last anywhere from 4-8 years. It is a lengthy process, and you need to ensure that it is the right path for you. Otherwise, you might end up spending the entirety of your time and money on something that can’t give your career what you want at the end of the day.
It would help if you also ponder over the question whether working towards an advanced degree will affect your current career as a medical doctor. Often, it will not affect your current job as long as you are confident that you can devote reasonable time for the program and have the discipline, capacity and energy to juggle study and work.
In addition, think about whether or not you have the ability to live without any income for a few years. You can always go back to practicing medicine if you want, but you will lose touch with some crucial skills or fail to update on them during your absence. Therefore, it is always important to figure out how much money you need per year and ensure that the PhD program can pay for all your expenses.
After you have figured out these two aspects in relation to a PhD in Medical Sciences in India , it is time to look for a program you want to pursue. Identify the field of expertise and find a course that will allow you to do what you want during your studies. Always go for courses with highly qualified professors who have years of experience in their respective fields.
After all, this is the best route you can take if you want to create a good PhD application. You need to make sure that you can write a PhD application with no grammar or spelling errors. It means that you must find a course with great professionalization. It is better if the program offers oral examinations instead of written ones to show your knowledge and answer all the questions in the presence of experts.
Some of the Best PhD in Medical Sciences Programs
Based on the above points, here are three of the best PhD courses for a medical doctor to pursue.
It is one of the most popular choices among medical doctors who want to advance their careers without quitting their jobs. The primary reason behind this is that public health focuses more on prevention than treatment. It is something that people with medical degrees are more than familiar with.
This is another great choice of PhD in Medical Science online for people who want to advance their careers but cannot afford to quit their jobs anytime soon. The course focuses on environmental factors, which means you will need to learn how the environment affects health and vice versa.
How Can I Pursue an Online PhD in Medical Science?
The most important thing for people who want to get a PhD in Medical Science online is identifying the best course available in their country. This means that you need to look for courses with qualified professors with proven records of success. It is best if the universities offering the courses are well-known and highly respected in terms of providing quality education. Otherwise, you might end up having a difficult time getting employment thereafter.
Also, you should check to see if the course allows students to earn money as they study and never go for courses that require ‘full-time’ study. It means that you cannot do all your work during class hours and expect to get good results. Instead, you must manage your time properly and dedicate sufficient time for your PhD studies.
It will also help find courses offered online because this will allow you to have more flexibility with your schedule. You need to take the course seriously, but there is no point in being so serious about it that you become depressed or stressed. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully examine all your options and take the best course available.
C onclusion
After a PhD in Medical Science in India , the most popular destinations for scientists are research and development. This can be at pharmaceutical companies, government agencies, or educational institutions. Some PhD graduates choose to continue with postdoctoral studies. Areas of specialization include biomedical research, medical sciences, and clinical research.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post Comment
Subscribe For Newsletter
Select Category College of Postgraduate Medicine
Select Program Fellowship in Internal Medicine Fellowship in OB-GYN Fellowship in Radiology Fellowship in Surgery Fellowship in Paediatrics and Child Health Fellowship in Clinical Cardiology with Critical care
PLAB or MRCP: Navigating the Path to Practicing Medicine in the UK
All you should know about the plab and mrcp exams, pediatrics translational research: the best way to apply findings practically, why should you consider pursuing an mrcp, choose texila american university for pg course in radiology, related posts, what are invasive vs non-invasive cardiology: a comprehensive study, list of hospitals teaching dnb in india, reasons why pg graduates should do a phd in medicine, can i practice as a specialist after failing dnb exam, phd in medical science in india: opportunities it offers.
- More Networks

COMMENTS
Deciding to pursue an MD-PhD dual degree is a long-term commitment, but for a medical student with a passion for research, it's a rewarding path. ... PhD research—after completing two years of medical school—at the University of Southern California Keck School of Medicine, Drayton Harvey applied to 30 MD-PhD programs.
The Harvard/MIT MD-PhD Program at Harvard Medical School (HMS) has been sponsored in part by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) through its Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP) since 1974. All MD-PhD student applicants to our program compete on equal footing for MSTP support, regardless of scientific interest.
Before You Apply. The MD-PhD Program seeks students with a deep passion and commitment to a dual physician-scientist career. Our admissions process assesses the potential of our applicants to become physician-scientist leaders who are committed to both providing compassionate, cutting-edge patient care and expanding the boundaries of biomedical ...
Division of Medical Sciences. The Division of Medical Sciences is the administrative centralized home for all Harvard PhD students located at HMS. There are many resources available to these students on the the DMS website. Division of Medical Sciences.
MD-PhD programs provide training for the dual degree by integrating research and clinical training experiences where students learn to conduct hypothesis driven research in a mentored environment. There are over 100 MD-PhD programs affiliated with U.S. medical schools, and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences partially supports ...
Almost all MD-PhD students spend time during this final 18-month period engaged in basic, translational or clinical research: they may return to their thesis lab, structure a short research experience to learn a new skill, or participate in clinical research related to the specialty in which they plan to match.
Elias (Eli) Wisdom. Undergraduate: Pacific University, Oregon Major: BS, Biology Medical school: Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) Anticipated Graduation Year: 2028 Bio: Eli Wisdom is an MD-PhD student at Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) studying the molecular mechanisms of Parkinson's Disease. He grew up in the small rural town of La Grande, Oregon, where he gained a deep ...
"Utilizing long-read sequencing to unravel the clinical heterogeneity in motor neuron diseases and undiagnosed genetic disorders," Angita (AJ) Jain (Mentor: Marka M. Van Blitterswijk, M.D., Ph.D.) "Unraveling the Immunological Basis of Lobular Involution Stagnation in Breast Cancer Development," Jaida Lue (Mentor: Derek Radisky, Ph.D.)
Stanford Health Policy offers a PhD program which promises to educate students who will be scholarly leaders in the field of health policy, and will be highly knowledgeable about the theoretical and empirical approaches that can be applied in the development of improvements in health policy and the health care system. These students will be ...
The MD-PhD Program (MSTP) at the Icahn School of Medicine integrates an outstanding research environment with a well-rounded, nationally acclaimed medical education. Continuously funded since 1977 by an MSTP training grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), our students enjoy a broad range of opportunities while training in the heart of New York City.
The short answer is, "It won't." PhD training for MSTP students is just as rigorous and intensive as for students outside the MSTP. However, MSTP students don't spend their first year rotating through different laboratories, and most MSTP students complete their preclinical medical school curriculum before starting full-time laboratory research.
How Long Are MD/PhD Programs? The MD-PhD dual degree takes approximately 7-8 years of coursework to complete, followed by an additional 3-7 years of residency to be eligible to practice medicine. Generally, MD coursework is emphasized in years 1-2, followed by research training in years 3-5, and ending with medical training and clinicals in ...
PhD in Medicine. Doctoral studies are carried out by science postgraduates, medical students combining clinical training with the PhD, and clinically qualified doctors undertaking scientific training. The research covers the whole spectrum of medical science from basic biology to clinical therapies.
The Doctorate of Medicine and of Philosophy (MD-PhD) is a dual doctoral degree for physician-scientists, combining the professional training of the Doctor of Medicine degree with the research expertise of the Doctor of Philosophy degree; the Ph.D. is the most advanced credential in the United States. Other dual degree programs exist, such as the joint MD-JD degree; both the JD ...
A Ph.D. in medicine means the other way around. You get to master expertise in the field of medical science. It is meticulously designed to cover all the primary and essential criteria involved in medicine and seamlessly puts you on the path of research, dissertation, and thesis. It includes all the clinical and non-clinical streams, including ...
MD-PhD trainees are research scientists who solve mechanisms underlying disease, combined with their passion to treat patients in a clinical setting. MD-PhD training efficiently integrates the scientific and medical education of the physician-scientist. During the PhD training years, MD-PhD students take the coursework and formal training in ...
Another significant difference between a master's and a PhD in biomedical science is an elevated focus on lab work. "The main purpose of a PhD is getting into a laboratory as quickly as possible," Janero says. What happens within a lab setting also differs for students at each level. For example, where master's students may have the ...
We'd love to hear from you. Location. 98 S. Los Robles Ave., Pasadena, CA 91101. Phone. 888-KPMED4U (888-576-3348) The MD-PhD program is a fully funded, dual-degree program jointly offered by the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and the Kaiser Permanente Bernard J. Tyson School of Medicine (KPSOM).
Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame ...
The Department of Biomedical Informatics offers a PhD in Biomedical Informatics in the areas of Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (AIM) and Bioinformatics and Integrative Genomics (BIG).. The AIM PhD track prepares the next generation of leaders at the intersection of artificial intelligence and medicine. The program's mission is to train exceptional computational students, harnessing ...
Written by Coursera Staff • Updated on Jan 31, 2024. A PhD program typically takes four to seven years, but a variety of factors can impact that timeline. A PhD, or doctorate degree, is the highest degree you can earn in certain disciplines, such as psychology, engineering, education, and mathematics. As a result, it often takes longer to ...
The career of each MD-PhD graduate is uniquely based upon research and clinical interests, but follows the general path: MD-PhD training: 7-8 years (See Education and Training for more information). Specialty and subspecialty clinical and research training (residency/fellowship): 3-7 Years.
School of Medicine offers several master's and PhD-level graduate programs for students interested in pursuing careers in health and biomedical sciences research. Our graduate students conduct their thesis work in faculty labs, where their basic, translational and clinical research advances our understanding of human development and disease ...
The thesis you produce must be 100 pages long and original. Plagiarism is. A PhD in medical science is an excellent qualification that prepares you for a career in research and development. ... Texila American University and the University of Nicaragua are offering PhD in medicine program for individuals who want to complete the doctoral ...