How the Myth of the American Frontier Got Its Start
Frederick Jackson Turner’s thesis informed decades of scholarship and culture. Then he realized he was wrong
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/Colin_Woodard_PPH_Photo_crop_thumbnail_1.png)
Colin Woodard
:focal(400x301:401x302)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/12/11/1211e4cd-7311-4c83-9370-d86aa5ebc2d5/illustration_of_people_on_horseback_looking_at_an_open_landscape.jpg)
On the evening of July 12, 1893, in the hall of a massive new Beaux-Arts building that would soon house the Art Institute of Chicago, a young professor named Frederick Jackson Turner rose to present what would become the most influential essay in the study of U.S. history.
It was getting late. The lecture hall was stifling from a day of blazing sun, which had tormented the throngs visiting the nearby Chicago World’s Columbian Exposition, a carnival of never-before-seen wonders, like a fully illuminated electric city and George Ferris’ 264-foot-tall rotating observation wheel. Many of the hundred or so historians attending the conference, a meeting of the American Historical Association (AHA), were dazed and dusty from an afternoon spent watching Buffalo Bill’s Wild West show at a stadium near the fairground’s gates. They had already sat through three other speeches. Some may have been dozing off as the thin, 31-year-old associate professor from the University of Wisconsin in nearby Madison began his remarks.


Subscribe to Smithsonian magazine now for just $19.99
This article is a selection from the January/February 2023 issue of Smithsonian magazine
Turner told them the force that had forged Americans into one people was the frontier of the Midwest and Far West. In this virgin world, settlers had finally been relieved of the European baggage of feudalism that their ancestors had brought across the Atlantic, freeing them to find their true selves: self-sufficient, pragmatic, egalitarian and civic-minded. “The frontier promoted the formation of a composite nationality for the American people,” he told the audience. “In the crucible of the frontier, the immigrants were Americanized, liberated and fused into a mixed race, English in neither nationality nor characteristics.”
The audience was unmoved.
In their dispatches the following morning, most of the newspaper reporters covering the conference didn’t even mention Turner’s talk. Nor did the official account of the proceedings prepared by the librarian William F. Poole for The Dial , an influential literary journal. Turner’s own father, writing to relatives a few days later, praised Turner’s skills as the family’s guide at the fair, but he said nothing at all about the speech that had brought them there.
Yet in less than a decade, Turner would be the most influential living historian in the United States, and his Frontier Thesis would become the dominant lens through which Americans understood their character, origins and destiny. Soon, Jackson’s theme was prevalent in political speech, in the way high schools taught history, in patriotic paintings—in short, everywhere. Perfectly timed to meet the needs of a country experiencing dramatic and destabilizing change, Turner’s thesis was swiftly embraced by academic and political institutions, just as railroads, manufacturing machines and telegraph systems were rapidly reshaping American life.
By that time, Turner himself had realized that his theory was almost entirely wrong.
American historians had long believed that Providence had chosen their people to spread Anglo-Saxon freedom across the continent. As an undergraduate at the University of Wisconsin, Turner was introduced to a different argument by his mentor, the classical scholar William Francis Allen. Extrapolating from Darwinism, Allen believed societies evolved like organisms, adapting themselves to the environments they encountered. Scientific laws, not divine will, he advised his mentee, guided the course of nations. After graduating, Turner pursued a doctorate at Johns Hopkins University, where he impressed the history program’s leader, Herbert Baxter Adams, and formed a lifelong friendship with one of his teachers, an ambitious young professor named Woodrow Wilson. The connections were useful: When Allen died in 1889, Adams and Wilson aided Turner in his quest to take Allen’s place as head of Wisconsin’s history department. And on the strength of Turner’s early work, Adams invited him to present a paper at the 1893 meeting of the AHA, to be held in conjunction with the World’s Congress Auxiliary of the World’s Columbian Exposition.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/61/bc/61bc38a7-853f-4c6b-823e-71c95d62687d/manifest_destiny.jpg)
The resulting essay, “The Significance of the Frontier in American History,” offered a vivid evocation of life in the American West. Stripped of “the garments of civilization,” settlers between the 1780s and the 1830s found themselves “in the birch canoe” wearing “the hunting shirt and the moccasin.” Soon, they were “planting Indian corn and plowing with a sharp stick” and even shouting war cries. Faced with Native American resistance—Turner largely overlooked what the ethnic cleansing campaign that created all that “free land” might say about the American character—the settlers looked to the federal government for protection from Native enemies and foreign empires, including during the War of 1812, thus fostering a loyalty to the nation rather than to their half-forgotten nations of origin.
He warned that with the disappearance of the force that had shaped them—in 1890, the head of the Census Bureau concluded there was no longer a frontier line between areas that had been settled by European Americans and those that had not—Americans would no longer be able to flee west for an easy escape from responsibility, failure or oppression. “Each frontier did indeed furnish a new field of opportunity, a gate of escape from the bondage of the past,” Turner concluded. “Now … the frontier has gone, and with its going has closed the first period of American history.”
When he left the podium on that sweltering night, he could not have known how fervently the nation would embrace his thesis.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/3a/1d/3a1d78c2-4533-4dbf-9fc9-66306936b710/white_guy.jpg)
Like so many young scholars, Turner worked hard to bring attention to his thesis. He incorporated it into the graduate seminars he taught, lectured about it across the Midwest and wrote the entry for “Frontier” in the widely read Johnson’s Universal Cyclopædia. He arranged to have the thesis reprinted in the journal of the Wisconsin Historical Society and in the AHA’s 1893 annual report. Wilson championed it in his own writings, and the essay was read by hundreds of schoolteachers who found it reprinted in the popular pedagogical journal of the Herbart Society, a group devoted to the scientific study of teaching. Turner’s big break came when the Atlantic Monthly ’s editors asked him to use his novel viewpoint to explain the sudden rise of populists in the rural Midwest, and how they had managed to seize control of the Democratic Party to make their candidate, William Jennings Bryan, its nominee for president. Turner’s 1896 Atlantic Monthly essay , which tied the populists’ agitation to the social pressures allegedly caused by the closing of the frontier—soil depletion, debt, rising land prices—was promptly picked up by newspapers and popular journals across the country.
Meanwhile, Turner’s graduate students became tenured professors and disseminated his ideas to the up-and-coming generation of academics. The thrust of the thesis appeared in political speeches, dime-store western novels and even the new popular medium of film, where it fueled the work of a young director named John Ford who would become the master of the Hollywood western. In 1911, Columbia University’s David Muzzey incorporated it into a textbook—initially titled History of the American People —that would be used by most of the nation’s secondary schools for half a century.
Americans embraced Turner’s argument because it provided a fresh and credible explanation for the nation’s exceptionalism—the notion that the U.S. follows a path soaring above those of other countries—one that relied not on earlier Calvinist notions of being “the elect,” but rather on the scientific (and fashionable) observations of Charles Darwin. In a rapidly diversifying country, the Frontier Thesis denied a special role to the Eastern colonies’ British heritage; we were instead a “composite nation,” birthed in the Mississippi watershed. Turner’s emphasis on mobility, progress and individualism echoed the values of the Gilded Age—when readers devoured Horatio Alger’s rags-to-riches stories—and lent them credibility for the generations to follow.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/ea/69/ea696129-c32c-4947-9ce7-64648e2f2cea/janfeb2023_e01_prologue.jpg)
But as a researcher, Turner himself turned away from the Frontier Thesis in the years after the 1890s. He never wrote it down in book form or even in academic articles. He declined invitations to defend it, and before long he himself lost faith in it.
For one thing, he had been relying too narrowly on the experiences in his own region of the Upper Midwest, which had been colonized by a settlement stream originating in New England. In fact, he found, the values he had ascribed to the frontier’s environmental conditioning were actually those of this Greater New England settlement culture, one his family and most of his fellow citizens in Portage, Wisconsin, remained part of, with their commitment to strong village and town governments, taxpayer-financed public schools and the direct democracy of the town meeting. He saw that other parts of the frontier had been colonized by other settlement streams anchored in Scots-Irish Appalachia or in the slave plantations of the Southern lowlands, and he noted that their populations continued to behave completely differently from one another, both politically and culturally, even when they lived in similar physical environments. Somehow settlers moving west from these distinct regional cultures were resisting the Darwinian environmental and cultural forces that had supposedly forged, as Turner’s biographer, Ray Allen Billington, put it, “a new political species” of human, the American. Instead, they were stubbornly remaining themselves. “Men are not absolutely dictated to by climate, geography, soils or economic interests,” Turner wrote in 1922. “The influence of the stock from which they sprang, the inherited ideals, the spiritual factors, often triumph over the material interests.”
Turner spent the last decades of his life working on what he intended to be his magnum opus, a book not about American unity but rather about the abiding differences between its regions, or “sections,” as he called them. “In respect to problems of common action, we are like what a United States of Europe would be,” he wrote in 1922, at the age of 60. For example, the Scots-Irish and German small farmers and herders who settled the uplands of the southeastern states had long clashed with nearby English enslavers over education spending, tax policy and political representation. Turner saw the whole history of the country as a wrestling match between these smaller quasi-nations, albeit a largely peaceful one guided by rules, laws and shared American ideals: “When we think of the Missouri Compromise, the Compromise of 1850, the Kansas-Nebraska Act, as steps in the marking off of spheres of influence and the assignment of mandates [between nations] … we see a resemblance to what has gone on in the Old World,” Turner explained. He hoped shared ideals—and federal institutions—would prove cohesive for a nation suddenly coming of age, its frontier closed, its people having to steward their lands rather than striking out for someplace new.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/ea/79/ea79b5eb-7dd4-4ca0-9d75-f4ad5333a116/janfeb2023_e12_prologue.jpg)
Get the latest History stories in your inbox?
Click to visit our Privacy Statement .
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/Colin_Woodard_PPH_Photo_crop_thumbnail_1.png)
Colin Woodard | | READ MORE
Colin Woodard is a journalist and historian, and the author of six books including Union: The Struggle to Forge the Story of United States Nationhood . He lives in Maine.

Chapter 22: Age of Empire: American Foreign Policy, 1890-1914
Turner, Mahan, and the Roots of Empire
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain the evolution of American interest in foreign affairs from the end of the Civil War through the early 1890s
- Identify the contributions of Frederick Jackson Turner and Alfred Thayer Mahan to the conscious creation of an American empire
During the time of Reconstruction, the U.S. government showed no significant initiative in foreign affairs. Western expansion and the goal of Manifest Destiny still held the country’s attention, and American missionaries proselytized as far abroad as China, India, the Korean Peninsula, and Africa, but reconstruction efforts took up most of the nation’s resources. As the century came to a close, however, a variety of factors, from the closing of the American frontier to the country’s increased industrial production, led the United States to look beyond its borders. Countries in Europe were building their empires through global power and trade, and the United States did not want to be left behind.
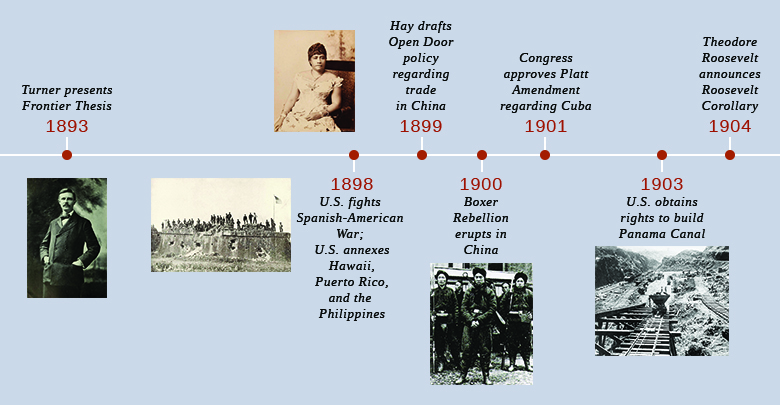
AMERICA’S LIMITED BUT AGGRESSIVE PUSH OUTWARD
On the eve of the Civil War, the country lacked the means to establish a strong position in international diplomacy. As of 1865, the U.S. State Department had barely sixty employees and no ambassadors representing American interests abroad. Instead, only two dozen American foreign ministers were located in key countries, and those often gained their positions not through diplomatic skills or expertise in foreign affairs but through bribes. Further limiting American potential for foreign impact was the fact that a strong international presence required a strong military-specifically a navy-which the United States, after the Civil War, was in no position to maintain. Additionally, as late as 1890, with the U.S. Navy significantly reduced in size, a majority of vessels were classified as “Old Navy,” meaning a mixture of iron hulled and wholly wooden ships. While the navy had introduced the first all-steel, triple-hulled steam engine vessels seven years earlier, they had only thirteen of them in operation by 1890.
Despite such widespread isolationist impulses and the sheer inability to maintain a strong international position, the United States moved ahead sporadically with a modest foreign policy agenda in the three decades following the Civil War. Secretary of State William Seward, who held that position from 1861 through 1869, sought to extend American political and commercial influence in both Asia and Latin America. He pursued these goals through a variety of actions. A treaty with Nicaragua set the early course for the future construction of a canal across Central America. He also pushed through the annexation of the Midway Islands in the Pacific Ocean, which subsequently opened a more stable route to Asian markets. In frequent conversations with President Lincoln, among others, Seward openly spoke of his desire to obtain British Columbia, the Hawaiian Islands, portions of the Dominican Republic, Cuba, and other territories. He explained his motives to a Boston audience in 1867, when he professed his intention to give the United States “control of the world.”
Most notably, in 1867, Seward obtained the Alaskan Territory from Russia for a purchase price of $7.2 million. Fearing future loss of the territory through military conflict, as well as desiring to create challenges for Great Britain (which they had fought in the Crimean War), Russia had happily accepted the American purchase offer. In the United States, several newspaper editors openly questioned the purchase and labeled it “Seward’s Folly” (Figure 22.3). They highlighted the lack of Americans to populate the vast region and lamented the challenges in attempting to govern the native peoples in that territory. Only if gold were to be found, the editors decried, would the secretive purchase be justified. That is exactly what happened. Seward’s purchase added an enormous territory to the country-nearly 600,000 square miles-and also gave the United States access to the rich mineral resources of the region, including the gold that trigged the Klondike Gold Rush at the close of the century. As was the case elsewhere in the American borderlands, Alaska’s industrial development wreaked havoc on the region’s indigenous and Russian cultures.

Seward’s successor as Secretary of State, Hamilton Fish, held the position from 1869 through 1877. Fish spent much of his time settling international disputes involving American interests, including claims that British assistance to the Confederates prolonged the Civil War for about two years. In these so-called Alabama claims, a U.S. senator charged that the Confederacy won a number of crucial battles with the help of one British cruiser and demanded $2 billion in British reparations. Alternatively, the United States would settle for the rights to Canada. A joint commission representing both countries eventually settled on a British payment of $15 million to the United States. In the negotiations, Fish also suggested adding the Dominican Republic as a territorial possession with a path towards statehood, as well as discussing the construction of a transoceanic canal with Columbia. Although neither negotiation ended in the desired result, they both expressed Fish’s intent to cautiously build an American empire without creating any unnecessary military entanglements in the wake of the Civil War.
BUSINESS, RELIGIOUS, AND SOCIAL INTERESTS SET THE STAGE FOR EMPIRE
While the United States slowly pushed outward and sought to absorb the borderlands (and the indigenous cultures that lived there), the country was also changing how it functioned. As a new industrial United States began to emerge in the 1870s, economic interests began to lead the country toward a more expansionist foreign policy. By forging new and stronger ties overseas, the United States would gain access to international markets for export, as well as better deals on the raw materials needed domestically. The concerns raised by the economic depression of the early 1890s further convinced business owners that they needed to tap into new markets, even at the risk of foreign entanglements. As a result of these growing economic pressures, American exports to other nations skyrocketed in the years following the Civil War, from $234 million in 1865 to $605 million in 1875. By 1898, on the eve of the Spanish-American War, American exports had reached a height of $1.3 billion annually. Imports over the same period also increased substantially, from $238 million in 1865 to $616 million in 1898. Such an increased investment in overseas markets in turn strengthened Americans’ interest in foreign affairs.
Businesses were not the only ones seeking to expand. Religious leaders and Progressive reformers joined businesses in their growing interest in American expansion, as both sought to increase the democratic and Christian influences of the United States abroad. Imperialism and Progressivism were compatible in the minds of many reformers who thought the Progressive impulses for democracy at home translated overseas as well. Editors of such magazines as Century, Outlook, and Harper’s supported an imperialistic stance as the democratic responsibility of the United States. Several Protestant faiths formed missionary societies in the years after the Civil War, seeking to expand their reach, particularly in Asia. Influenced by such works as Reverend Josiah Strong’s Our Country: Its Possible Future and Its Present Crisis (1885), missionaries sought to spread the gospel throughout the country and abroad. Led by the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions, among several other organizations, missionaries conflated Christian ethics with American virtues, and began to spread both gospels with zeal. This was particularly true among women missionaries, who composed over 60 percent of the overall missionary force. By 1870, missionaries abroad spent as much time advocating for the American version of a modern civilization as they did teaching the Bible.
Social reformers of the early Progressive Era also performed work abroad that mirrored the missionaries. Many were influenced by recent scholarship on race-based intelligence and embraced the implications of social Darwinist theory that alleged inferior races were destined to poverty on account of their lower evolutionary status. While certainly not all reformers espoused a racist view of intelligence and civilization, many of these reformers believed that the Anglo-Saxon race was mentally superior to others and owed the presumed less evolved populations their stewardship and social uplift-a service the British writer Rudyard Kipling termed “the white man’s burden.”
By trying to help people in less industrialized countries achieve a higher standard of living and a better understanding of the principles of democracy, reformers hoped to contribute to a noble cause, but their approach suffered from the same paternalism that hampered Progressive reforms at home. Whether reformers and missionaries worked with native communities in the borderlands such as New Mexico; in the inner cities, like the Salvation Army; or overseas, their approaches had much in common. Their good intentions and willingness to work in difficult conditions shone through in the letters and articles they wrote from the field. Often in their writing, it was clear that they felt divinely empowered to change the lives of other, less fortunate, and presumably, less enlightened, people. Whether oversees or in the urban slums, they benefitted from the same passions but expressed the same paternalism.
Lottie Moon, Missionary
Lottie Moon was a Southern Baptist missionary who spent more than forty years living and working in China. She began in 1873 when she joined her sister in China as a missionary, teaching in a school for Chinese women. Her true passion, however, was to evangelize and minister, and she undertook a campaign to urge the Southern Baptist missionaries to allow women to work beyond the classroom. Her letter campaign back to the head of the Mission Board provided a vivid picture of life in China and exhorted the Southern Baptist women to give more generously of their money and their time. Her letters appeared frequently in religious publications, and it was her suggestion-that the week before Christmas be established as a time to donate to foreign missions-that led to the annual Christmas giving tradition. Lottie’s rhetoric caught on, and still today, the annual Christmas offering is done in her name.
We had the best possible voyage over the water-good weather, no headwinds, scarcely any rolling or pitching-in short, all that reasonable people could ask…. I spent a week here last fall and of course feel very natural to be here again. I do so love the East and eastern life! Japan fascinated my heart and fancy four years ago, but now I honestly believe I love China the best, and actually, which is stranger still, like the Chinese best. -Charlotte “Lottie” Moon, 1877
Lottie remained in China through famines, the Boxer Rebellion, and other hardships. She fought against foot binding, a cultural tradition where girls’ feet were tightly bound to keep them from growing, and shared her personal food and money when those around her were suffering. But her primary goal was to evangelize her Christian beliefs to the people in China. She won the right to minister and personally converted hundreds of Chinese to Christianity. Lottie’s combination of moral certainty and selfless service was emblematic of the missionary zeal of the early American empire.
TURNER, MAHAN, AND THE PLAN FOR EMPIRE
The initial work of businesses, missionaries, and reformers set the stage by the early 1890s for advocates of an expanded foreign policy and a vision of an American empire. Following decades of an official stance of isolationism combined with relatively weak presidents who lacked the popular mandate or congressional support to undertake substantial overseas commitments, a new cadre of American leaders-many of whom were too young to fully comprehend the damage inflicted by the Civil War-assumed leadership roles. Eager to be tested in international conflict, these new leaders hoped to prove America’s might on a global stage. The Assistant Secretary of the Navy, Theodore Roosevelt, was one of these leaders who sought to expand American influence globally, and he advocated for the expansion of the U.S. Navy, which at the turn of the century was the only weapons system suitable for securing overseas expansion.
Turner (Figure 22.4) and naval strategist Alfred Thayer Mahan were instrumental in the country’s move toward foreign expansion, and writer Brooks Adams further dramatized the consequences of the nation’s loss of its frontier in his The Law of Civilization and Decay in 1895. As mentioned in the chapter opening, Turner announced his Frontier Thesis -that American democracy was largely formed by the American frontier-at the Chicago World’s Colombian Exposition. He noted that “for nearly three centuries the dominant fact in American life has been expansion.” He continued: “American energy will continually demand a wider field for its exercise.”

Although there was no more room for these forces to proceed domestically, they would continue to find an outlet on the international stage. Turner concluded that “the demands for a vigorous foreign policy, for an interoceanic canal, for a revival of our power upon our seas, and for the extension of American influence to outlying islands and adjoining countries are indications that the forces [of expansion] will continue.” Such policies would permit Americans to find new markets. Also mindful of the mitigating influence of a frontier-in terms of easing pressure from increased immigration and population expansion in the eastern and midwestern United States-he encouraged new outlets for further population growth, whether as lands for further American settlement or to accommodate more immigrants. Turner’s thesis was enormously influential at the time but has subsequently been widely criticized by historians. Specifically, the thesis underscores the pervasive racism and disregard for the indigenous communities, cultures, and individuals in the American borderlands and beyond.
Click and Explore
Explore the controversy associated with Turner’s Frontier Thesis at U.S. History Scene.
While Turner provided the idea for an empire, Mahan provided the more practical guide. In his 1890 work, The Influence of Seapower upon History, he suggested three strategies that would assist the United States in both constructing and maintaining an empire. First, noting the sad state of the U.S. Navy, he called for the government to build a stronger, more powerful version. Second, he suggested establishing a network of naval bases to fuel this expanding fleet. Seward’s previous acquisition of the Midway Islands served this purpose by providing an essential naval coaling station, which was vital, as the limited reach of steamships and their dependence on coal made naval coaling stations imperative for increasing the navy’s geographic reach. Future acquisitions in the Pacific and Caribbean increased this naval supply network (Figure 22.5). Finally, Mahan urged the future construction of a canal across the isthmus of Central America, which would decrease by two-thirds the time and power required to move the new navy from the Pacific to the Atlantic oceans. Heeding Mahan’s advice, the government moved quickly, passing the Naval Act of 1890, which set production levels for a new, modern fleet. By 1898, the government had succeeded in increasing the size of the U.S. Navy to an active fleet of 160 vessels, of which 114 were newly built of steel. In addition, the fleet now included six battleships, compared to zero in the previous decade. As a naval power, the country catapulted to the third strongest in world rankings by military experts, trailing only Spain and Great Britain.
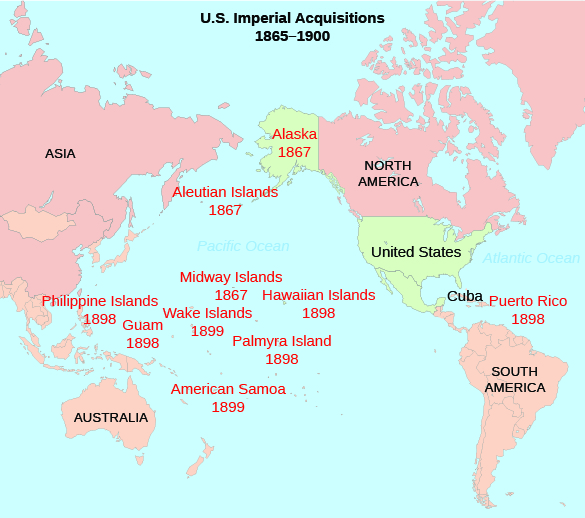
The United States also began to expand its influence to other Pacific Islands, most notably Samoa and Hawaii. With regard to the latter, American businessmen were most interested in the lucrative sugar industry that lay at the heart of the Hawaiian Islands’ economy. By 1890, through a series of reciprocal trade agreements, Hawaiians exported nearly all of their sugar production to the United States, tariff-free. When Queen Liliuokalani tapped into a strong anti-American resentment among native Hawaiians over the economic and political power of exploitative American sugar companies between 1891 and 1893, worried businessmen worked with the American minister to Hawaii, John Stevens, to stage a quick, armed revolt to counter her efforts and seize the islands as an American protectorate (Figure 22.6). Following five more years of political wrangling, the United States annexed Hawaii in 1898, during the Spanish-American War.

U.S. History Copyright © 2014 by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Module 4: Age of Empire—American Foreign Policy (1890-1914)
Creating an empire, learning objectives.
- Identify the contributions of Frederick Jackson Turner and Alfred Thayer Mahan to the creation of an American empire
- Explain the U.S. annexation of Hawaii and Samoa
Turner, Mahan, and the Plan for Empire

Figure 1 . Historian Fredrick Jackson Turner’s Frontier Thesis stated explicitly that the existence of the western frontier forged the very basis of the American identity.
The initial work of businesses, missionaries, and reformers set the stage by the early 1890s for advocates of an expanded foreign policy and a vision of American empire. Following decades of de facto isolationism combined with relatively weak presidents who lacked a popular mandate or congressional support for substantial overseas commitments, a new cadre of American leaders—many of whom were too young to fully comprehend the damage inflicted by the Civil War—assumed leadership roles. Eager to be tested in international conflict, these new leaders hoped to prove America’s might on a global stage. The Assistant Secretary of the Navy, Theodore Roosevelt, was one of these leaders who sought to enlarge American influence, and he advocated for the development of the U.S. Navy, which at the turn of the century was the only military resource suitable for securing overseas expansion.
Fredrick Jackson Turner and naval strategist Alfred Thayer Mahan were instrumental in the country’s move toward foreign expansion, a priority also supported by Brooks Adams, who dramatized the consequences of the nation’s loss of its domestic frontier in his The Law of Civilization and Decay in 1895. As mentioned at the beginning of the module, Turner announced his Frontier Thesis —that American democracy was largely formed by its encounter with the American frontier—at the Chicago World’s Columbian Exposition in 1893. He noted that “for nearly three centuries the dominant fact in American life has been expansion.” He continued: “American energy will continually demand a wider field for its exercise.”
Turner concluded that “the demands for a vigorous foreign policy, for an interoceanic canal, for a revival of our power upon our seas, and for the extension of American influence to outlying islands and adjoining countries are indications that the forces [of expansion] will continue.” Such policies would permit Americans to find new markets. Also mindful of the mitigating influence of a frontier—in terms of easing pressure from increased immigration and population expansion in the eastern and midwestern United States—he encouraged new outlets for further population growth, whether as lands for further American settlement or to accommodate more immigrants. Turner’s thesis was enormously influential, but has subsequently been widely criticized by historians. Specifically, the thesis underscores the pervasive racism and disregard for the Indigenous communities, cultures, and individuals in the American borderlands and beyond.
While Turner provided part of the philosophical reasoning for an empire, Mahan provided the more practical guide. In his 1890 work, The Influence of Seapower upon History , he suggested three strategies that would assist the United States in constructing and maintaining an empire:
- First, noting the sad state of the U.S. Navy, he called for the government to build a modern fleet.
- Second, he suggested establishing a network of naval bases to fuel this expanding fleet. William Seward’s previous acquisition of the Midway Islands served this purpose by providing an essential naval coaling station, which was vital, as the limited reach of steamships and their dependence on coal made such stations necessary for increasing the navy’s geographic reach. Future acquisitions in the Pacific and Caribbean also increased this capability.
- Finally, Mahan urged the future construction of a canal across the isthmus of Central America, which would decrease by two-thirds the time and power required to move the new navy from the Pacific to the Atlantic oceans.
Heeding Mahan’s advice, the government moved quickly, passing the Naval Act of 1890, which set production levels for a new, modern fleet. By 1898, the government had succeeded in increasing the size of the U.S. Navy to an active fleet of 160 vessels, of which 114 were newly built of steel. In addition, the fleet now included six battleships, compared to zero in the previous decade. As a naval power, the country catapulted to the third strongest in world rankings by military experts, trailing only Spain and Great Britain.

Figure 2 . American imperial acquisitions as of the end of the Spanish-American War in 1898. Note how the spread of island acquisitions across the Pacific fulfills Alfred Mahan’s call for more bases in order to support a larger and more effective U.S. Navy rather than merely to facilitate a short-term territorial expansion.
Annexing Hawaii
The United States also began to expand its influence to other Pacific Islands, most notably Samoa and Hawaii. With regard to the latter, American businessmen were most interested in the lucrative sugar industry at the heart of the Hawaiian Islands’ economy. By 1890, through a series of reciprocal trade agreements, Hawaiians exported nearly all of their sugar production to the United States, tariff-free. When Queen Liliuokalani tapped into a strong anti-American resentment among native Hawaiians over the economic and political power of exploitative American sugar companies between 1891 and 1893, worried businessmen worked with the American minister to Hawaii, John Stevens, to stage a quick, armed coup to counter her efforts and seize the islands as an American protectorate.
Between 1893 and 1898, the nation fiercely debated Hawaiian annexation. Those in favor argued that Hawaii was ideally located as a gateway to Eastern markets and could provide rich commercial advantages. They also recognized the strategic importance of Pearl Harbor, which could serve as a military outpost and coaling station for merchant ships in the Pacific. Critics of annexation, including President Cleveland who thought it unwise and immoral, denounced the sugar interests for their plot to depose the Queen and reproached Minister Stevens for making the U.S. government a conspirator in the coup. Because Hawaii was not part of the continental United States, some anti-annexationists saw the taking of this overseas territory as a departure from the progress of westward expansion and a violation of American principles. They raised concerns about the constitutionality of this encroachment and argued that the United States could have a thriving trade with Hawaii and secure access to Pearl Harbor without the burdens of official annexation.
Grover Cleveland and Hawaii

Figure 3 . Queen Liliuokalani of Hawaii (a) was unhappy with the one-sided trade agreement Hawaii held with the United States (b), but protests were squashed by an American-armed revolt.
Grover Cleveland was president in 1893 when American planters in Hawaii staged a coup to remove Queen Liliuokalani from power. When a treaty of annexation reached Cleveland’s desk, he refused to sign it and offered a lengthy criticism of the arguments for annexing Hawaii. He concluded that the planters who launched the coup did not have significant support from the local population. More alarming to Cleveland, the landing of U.S. troops to “maintain order” had been coordinated in such a way as to directly sanction the coup.
I believe that a candid and thorough examination of the facts will force the conviction that the provisional government owes its existence to an armed invasion by the United States. Fair-minded people with the evidence before them will hardly claim that the Hawaiian Government was overthrown by the people of the islands or that the provisional government had ever existed with their consent [. . .] While naturally sympathizing with every effort to establish a republican form of government, it has been the settled policy of the United States to concede to people of foreign countries the same freedom and independence in the management of their domestic affairs that we have always claimed for ourselves. —Grover Cleveland, 1893
While Cleveland dropped his initial plan to restore Queen Liliuokalani, he refused to proceed with annexation of the Hawaiian Islands during his presidency. The U.S. government maintained a relationship with the independent Hawaiian Republic until 1898. Cleveland’s stance reflects an attitude that many Americans shared at the time and a degree of suspicion about overseas expansion. By all indications, Cleveland’s position was a minority one in Congress, and when he left office in 1896, one of the obstacles to annexation was removed.
Watch this video to learn more about the strength and resolve of Queen Lilioukalani .
Link to Learning
Explore the resources at U.S. History Scene to better understand the long and involved history of Hawaii with respect to its intersection with the United States.
The United States had similar strategic interests in the Samoan Islands of the South Pacific, most notably, access to the naval refueling station at Pago Pago where American merchant vessels, as well as naval ships, could take on food, fuel, and supplies.
The First Samoan Civil War, also called the Samoan Crisis, was fought roughly between 1886 and 1894, primarily between Samoans fighting over whether Malietoa Laupepa or Mata’afa Iosefo would be King of Samoa. However, the German military intervened on several occasions and competing interests in the islands led to a naval standoff between the United States, Germany, and the United Kingdom. After the 1889 Apia cyclone destroyed six of the German and American ships stationed at Samoa, the three countries decided that Laupepa would be the King. King Laupapa died shortly thereafter and the exiled Mata’afa Iosefo returned to be elected to power by a council of Samoan chiefs. This reignited tensions on the islands and in response, the British Royal Navy and the U.S. Navy landed forces in Samoa in support of Laupepa’s son Malietoa Tanumafili I against the German-backed Mataafa. Fighting lasted another year, resulting in more than 40,000 deaths and the eventual Tripartite Convention of 1899 that partitioned the Samoan Islands into American Samoa and German Samoa. After World War I, New Zealand took over the administration of what had been German Samoa, and the area was renamed the Western Samoa Trust Territory. This area became independent in 1962 and was renamed Samoa. American Samoa remains an unincorporated territory of the United States.
Review Question
Frontier Thesis: an idea proposed by Fredrick Jackson Turner in 1893, which stated that the encounter between European traditions and a frontier wilderness was integral to the development of American democracy, individualism, and innovative character
- Modification, adaptation, and original content. Authored by : Zeb Larson for Lumen Learning. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- US History. Provided by : OpenStax. Located at : http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/us-history . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/us-history/pages/1-introduction
- Samoan Civil WAr. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Samoan_Civil_War . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Second Samoan Civil War. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Second_Samoan_Civil_War . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- History of Samoa. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_Samoa . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- The Annexation of Hawaii. Provided by : The Bill of Rights Institute. Located at : https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:AfofZHEZ@4/9-10-%F0%9F%94%8E-The-Annexation-of-Hawaii . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike . License Terms : Access for free at https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:AfofZHEZ@4/9-10-%F0%9F%94%8E-The-Annexation-of-Hawaii
22.1 Turner, Mahan, and the Roots of Empire
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain the evolution of American interest in foreign affairs from the end of the Civil War through the early 1890s
- Identify the contributions of Frederick Jackson Turner and Alfred Thayer Mahan to the conscious creation of an American empire
During the time of Reconstruction, the U.S. government showed no significant initiative in foreign affairs. Western expansion and the goal of Manifest Destiny still held the country’s attention, and American missionaries proselytized as far abroad as China, India, the Korean Peninsula, and Africa, but reconstruction efforts took up most of the nation’s resources. As the century came to a close, however, a variety of factors, from the closing of the American frontier to the country’s increased industrial production, led the United States to look beyond its borders. Countries in Europe were building their empires through global power and trade, and the United States did not want to be left behind.
AMERICA’S LIMITED BUT AGGRESSIVE PUSH OUTWARD
On the eve of the Civil War, the country lacked the means to establish a strong position in international diplomacy. As of 1865, the U.S. State Department had barely sixty employees and no ambassadors representing American interests abroad. Instead, only two dozen American foreign ministers were located in key countries, and those often gained their positions not through diplomatic skills or expertise in foreign affairs but through bribes. Further limiting American potential for foreign impact was the fact that a strong international presence required a strong military—specifically a navy—which the United States, after the Civil War, was in no position to maintain. Additionally, as late as 1890, with the U.S. Navy significantly reduced in size, a majority of vessels were classified as “Old Navy,” meaning a mixture of iron hulled and wholly wooden ships. While the navy had introduced the first all-steel, triple-hulled steam engine vessels seven years earlier, they had only thirteen of them in operation by 1890.
Despite such widespread isolationist impulses and the sheer inability to maintain a strong international position, the United States moved ahead sporadically with a modest foreign policy agenda in the three decades following the Civil War. Secretary of State William Seward, who held that position from 1861 through 1869, sought to extend American political and commercial influence in both Asia and Latin America. He pursued these goals through a variety of actions. A treaty with Nicaragua set the early course for the future construction of a canal across Central America. He also pushed through the annexation of the Midway Islands in the Pacific Ocean, which subsequently opened a more stable route to Asian markets. In frequent conversations with President Lincoln, among others, Seward openly spoke of his desire to obtain British Columbia, the Hawaiian Islands, portions of the Dominican Republic, Cuba, and other territories. He explained his motives to a Boston audience in 1867, when he professed his intention to give the United States “control of the world.”
Most notably, in 1867, Seward obtained the Alaskan Territory from Russia for a purchase price of $7.2 million. Fearing future loss of the territory through military conflict, as well as desiring to create challenges for Great Britain (which they had fought in the Crimean War), Russia had happily accepted the American purchase offer. In the United States, several newspaper editors openly questioned the purchase and labeled it “ Seward’s Folly ” ( Figure 22.3 ). They highlighted the lack of Americans to populate the vast region and lamented the challenges in attempting to govern the native peoples in that territory. Only if gold were to be found, the editors decried, would the secretive purchase be justified. That is exactly what happened. Seward’s purchase added an enormous territory to the country—nearly 600,000 square miles—and also gave the United States access to the rich mineral resources of the region, including the gold that trigged the Klondike Gold Rush at the close of the century. As was the case elsewhere in the American borderlands, Alaska’s industrial development wreaked havoc on the region’s indigenous and Russian cultures.
Seward’s successor as Secretary of State, Hamilton Fish, held the position from 1869 through 1877. Fish spent much of his time settling international disputes involving American interests, including claims that British assistance to the Confederates prolonged the Civil War for about two years. In these so-called Alabama claims, a U.S. senator charged that the Confederacy won a number of crucial battles with the help of one British cruiser and demanded $2 billion in British reparations. Alternatively, the United States would settle for the rights to Canada. A joint commission representing both countries eventually settled on a British payment of $15 million to the United States. In the negotiations, Fish also suggested adding the Dominican Republic as a territorial possession with a path towards statehood, as well as discussing the construction of a transoceanic canal with Colombia. Although neither negotiation ended in the desired result, they both expressed Fish’s intent to cautiously build an American empire without creating any unnecessary military entanglements in the wake of the Civil War.
BUSINESS, RELIGIOUS, AND SOCIAL INTERESTS SET THE STAGE FOR EMPIRE
While the United States slowly pushed outward and sought to absorb the borderlands (and the indigenous cultures that lived there), the country was also changing how it functioned. As a new industrial United States began to emerge in the 1870s, economic interests began to lead the country toward a more expansionist foreign policy. By forging new and stronger ties overseas, the United States would gain access to international markets for export, as well as better deals on the raw materials needed domestically. The concerns raised by the economic depression of the early 1890s further convinced business owners that they needed to tap into new markets, even at the risk of foreign entanglements.
As a result of these growing economic pressures, American exports to other nations skyrocketed in the years following the Civil War, from $234 million in 1865 to $605 million in 1875. By 1898, on the eve of the Spanish-American War, American exports had reached a height of $1.3 billion annually. Imports over the same period also increased substantially, from $238 million in 1865 to $616 million in 1898. Such an increased investment in overseas markets in turn strengthened Americans’ interest in foreign affairs.
Businesses were not the only ones seeking to expand. Religious leaders and Progressive reformers joined businesses in their growing interest in American expansion, as both sought to increase the democratic and Christian influences of the United States abroad. Imperialism and Progressivism were compatible in the minds of many reformers who thought the Progressive impulses for democracy at home translated overseas as well. Editors of such magazines as Century , Outlook , and Harper’s supported an imperialistic stance as the democratic responsibility of the United States. Several Protestant faiths formed missionary societies in the years after the Civil War, seeking to expand their reach, particularly in Asia. Influenced by such works as Reverend Josiah Strong’s Our Country: Its Possible Future and Its Present Crisis (1885), missionaries sought to spread the gospel throughout the country and abroad. Led by the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions, among several other organizations, missionaries conflated Christian ethics with American virtues, and began to spread both gospels with zeal. This was particularly true among women missionaries, who composed over 60 percent of the overall missionary force. By 1870, missionaries abroad spent as much time advocating for the American version of a modern civilization as they did teaching the Bible.
Social reformers of the early Progressive Era also performed work abroad that mirrored the missionaries. Many were influenced by recent scholarship on race-based intelligence and embraced the implications of social Darwinist theory that alleged inferior races were destined to poverty on account of their lower evolutionary status. While certainly not all reformers espoused a racist view of intelligence and civilization, many of these reformers believed that the Anglo-Saxon race was mentally superior to others and owed the presumed less evolved populations their stewardship and social uplift—a service the British writer Rudyard Kipling termed “the White Man’s Burden.”
By trying to help people in less industrialized countries achieve a higher standard of living and a better understanding of the principles of democracy, reformers hoped to contribute to a noble cause, but their approach suffered from the same paternalism that hampered Progressive reforms at home. Whether reformers and missionaries worked with native communities in the borderlands such as New Mexico; in the inner cities, like the Salvation Army; or overseas, their approaches had much in common. Their good intentions and willingness to work in difficult conditions shone through in the letters and articles they wrote from the field. Often in their writing, it was clear that they felt divinely empowered to change the lives of other, less fortunate, and presumably, less enlightened, people. Whether oversees or in the urban slums, they benefitted from the same passions but expressed the same paternalism.
Lottie Moon, Missionary
Lottie Moon was a Southern Baptist missionary who spent more than forty years living and working in China. She began in 1873 when she joined her sister in China as a missionary, teaching in a school for Chinese women. Her true passion, however, was to evangelize and minister, and she undertook a campaign to urge the Southern Baptist missionaries to allow women to work beyond the classroom. Her letter campaign back to the head of the Mission Board provided a vivid picture of life in China and exhorted the Southern Baptist women to give more generously of their money and their time. Her letters appeared frequently in religious publications, and it was her suggestion—that the week before Christmas be established as a time to donate to foreign missions—that led to the annual Christmas giving tradition. Lottie’s rhetoric caught on, and still today, the annual Christmas offering is done in her name.
We had the best possible voyage over the water—good weather, no headwinds, scarcely any rolling or pitching—in short, all that reasonable people could ask. . . . I spent a week here last fall and of course feel very natural to be here again. I do so love the East and eastern life! Japan fascinated my heart and fancy four years ago, but now I honestly believe I love China the best, and actually, which is stranger still, like the Chinese best. —Charlotte “Lottie” Moon, 1877
Lottie remained in China through famines, the Boxer Rebellion , and other hardships. She fought against foot binding, a cultural tradition where girls’ feet were tightly bound to keep them from growing, and shared her personal food and money when those around her were suffering. But her primary goal was to evangelize her Christian beliefs to the people in China. She won the right to minister and personally converted hundreds of Chinese to Christianity. Lottie’s combination of moral certainty and selfless service was emblematic of the missionary zeal of the early American empire.
TURNER, MAHAN, AND THE PLAN FOR EMPIRE
The initial work of businesses, missionaries, and reformers set the stage by the early 1890s for advocates of an expanded foreign policy and a vision of an American empire. Following decades of an official stance of isolationism combined with relatively weak presidents who lacked the popular mandate or congressional support to undertake substantial overseas commitments, a new cadre of American leaders—many of whom were too young to fully comprehend the damage inflicted by the Civil War—assumed leadership roles. Eager to be tested in international conflict, these new leaders hoped to prove America’s might on a global stage. The Assistant Secretary of the Navy, Theodore Roosevelt, was one of these leaders who sought to expand American influence globally, and he advocated for the expansion of the U.S. Navy, which at the turn of the century was the only weapons system suitable for securing overseas expansion.
Turner ( Figure 22.4 ) and naval strategist Alfred Thayer Mahan were instrumental in the country’s move toward foreign expansion, and writer Brooks Adams further dramatized the consequences of the nation’s loss of its frontier in his The Law of Civilization and Decay in 1895. As mentioned in the chapter opening, Turner announced his Frontier Thesis —that American democracy was largely formed by the American frontier—at the Chicago World’s Colombian Exposition. He noted that “for nearly three centuries the dominant fact in American life has been expansion.” He continued: “American energy will continually demand a wider field for its exercise.”
Although there was no more room for these forces to proceed domestically, they would continue to find an outlet on the international stage. Turner concluded that “the demands for a vigorous foreign policy, for an interoceanic canal, for a revival of our power upon our seas, and for the extension of American influence to outlying islands and adjoining countries are indications that the forces [of expansion] will continue.” Such policies would permit Americans to find new markets. Also mindful of the mitigating influence of a frontier—in terms of easing pressure from increased immigration and population expansion in the eastern and midwestern United States—he encouraged new outlets for further population growth, whether as lands for further American settlement or to accommodate more immigrants. Turner’s thesis was enormously influential at the time but has subsequently been widely criticized by historians. Specifically, the thesis underscores the pervasive racism and disregard for the indigenous communities, cultures, and individuals in the American borderlands and beyond.
Click and Explore
Explore the controversy associated with Turner’s Frontier Thesis at U.S. History Scene.
While Turner provided the idea for an empire, Mahan provided the more practical guide. In his 1890 work, The Influence of Seapower upon History , he suggested three strategies that would assist the United States in both constructing and maintaining an empire. First, noting the sad state of the U.S. Navy, he called for the government to build a stronger, more powerful version. Second, he suggested establishing a network of naval bases to fuel this expanding fleet. Seward’s previous acquisition of the Midway Islands served this purpose by providing an essential naval coaling station, which was vital, as the limited reach of steamships and their dependence on coal made naval coaling stations imperative for increasing the navy’s geographic reach. Future acquisitions in the Pacific and Caribbean increased this naval supply network ( Figure 22.5 ). Finally, Mahan urged the future construction of a canal across the isthmus of Central America, which would decrease by two-thirds the time and power required to move the new navy from the Pacific to the Atlantic oceans. Heeding Mahan’s advice, the government moved quickly, passing the Naval Act of 1890, which set production levels for a new, modern fleet. By 1898, the government had succeeded in increasing the size of the U.S. Navy to an active fleet of 160 vessels, of which 114 were newly built of steel. In addition, the fleet now included six battleships, compared to zero in the previous decade. By the start of the twentieth century, the United States ranked among the top five naval powers globally.
The United States also began to expand its influence to other Pacific Islands, most notably Samoa and Hawaii. With regard to the latter, American businessmen were most interested in the lucrative sugar industry that lay at the heart of the Hawaiian Islands’ economy. By 1890, through a series of reciprocal trade agreements, Hawaiians exported nearly all of their sugar production to the United States, tariff-free. When Queen Liliuokalani tapped into a strong anti-American resentment among native Hawaiians over the economic and political power of exploitative American sugar companies between 1891 and 1893, worried businessmen worked with the American minister to Hawaii, John Stevens, to stage a quick, armed revolt to counter her efforts and seize the islands as an American protectorate ( Figure 22.6 ). Following five more years of political wrangling, the United States annexed Hawaii in 1898, during the Spanish-American War.
The United States had similar strategic interests in the Samoan Islands of the South Pacific, most notably, access to the naval refueling station at Pago Pago where American merchant vessels as well as naval ships could take on food, fuel, and supplies. In 1899, in an effort to mitigate other foreign interests and still protect their own, the United States joined Great Britain and Germany in a three-party protectorate over the islands, which assured American access to the strategic ports located there. Ten years later, Great Britain agreed to give up its claim on the islands, and they were divided between Germany and the United States.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/us-history/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: P. Scott Corbett, Volker Janssen, John M. Lund, Todd Pfannestiel, Sylvie Waskiewicz, Paul Vickery
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: U.S. History
- Publication date: Dec 30, 2014
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/us-history/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/us-history/pages/22-1-turner-mahan-and-the-roots-of-empire
© Jan 11, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Recent changes
- Random page
- View source
- What links here
- Related changes
- Special pages
- Printable version
- Permanent link
- Page information
- Create account
Why was the Turner Thesis abandoned by historians

Fredrick Jackson Turner’s thesis of the American frontier defined the study of the American West during the 20th century. In 1893, Turner argued that “American history has been in a large degree the history of the colonization of the Great West. The existence of an area of free land, its continuous recession, and the advance of American settlement westward explain American development.” ( The Frontier in American History , Turner, p. 1.) Jackson believed that westward expansion allowed America to move away from the influence of Europe and gain “independence on American lines.” (Turner, p. 4.) The conquest of the frontier forced Americans to become smart, resourceful, and democratic. By focusing his analysis on people in the periphery, Turner de-emphasized the importance of everyone else. Additionally, many people who lived on the “frontier” were not part of his thesis because they did not fit his model of the democratizing American. The closing of the frontier in 1890 by the Superintendent of the census prompted Turner’s thesis.
Despite its faults, his thesis proved powerful because it succinctly summed up the concerns of Turner and his contemporaries. More importantly, it created an appealing grand narrative for American history. Many Americans were concerned that American freedom would be diminished by the end of colonization of the West. Not only did his thesis give voice to these Americans’ concerns, but it also represented how Americans wanted to see themselves. Unfortunately, the history of the American West became the history of westward expansion and the history of the region of the American West was disregarded. The grand tapestry of western history was essentially ignored. During the mid-twentieth century, most people lost interest in the history of the American West.
While appealing, the Turner thesis stultified scholarship on the West. In 1984, colonial historian James Henretta even stated, “[f]or, in our role as scholars, we must recognize that the subject of westward expansion in itself longer engages the attention of many perhaps most, historians of the United States.” ( Legacy of Conquest , Patricia Limerick, p. 21.) Turner’s thesis had effectively shaped popular opinion and historical scholarship of the American West, but the thesis slowed continued academic interest in the field.
Reassessment of Western History
In the last half of the twentieth century, a new wave of western historians rebelled against the Turner thesis and defined themselves by their opposition to it. Historians began to approach the field from different perspectives and investigated the lives of Women, miners, Chicanos, Indians, Asians, and African Americans. Additionally, historians studied regions that would not have been relevant to Turner. In 1987, Patricia Limerick tried to redefine the study of the American West for a new generation of western scholars. In Legacy of Conquest, she attempted to synthesize the scholarship on the West to that point and provide a new approach for re-examining the West. First, she asked historians to think of the America West as a place and not as a movement. Second, she emphasized that the history of the American West was defined by conquest; “[c]onquest forms the historical bedrock of the whole nation, and the American West is a preeminent case study in conquest and its consequences.” (Limerick, p. 22.)
Finally, she asked historians to eliminate the stereotypes from Western history and try to understand the complex relations between the people of the West. Even before Limerick’s manifesto, scholars were re-evaluating the west and its people, and its pace has only quickened. Whether or not scholars agree with Limerick, they have explored new depths of Western American history. While these new works are not easy to categorize, they do fit into some loose categories: gender ( Relations of Rescue by Peggy Pascoe), ethnicity ( The Roots of Dependency by Richard White, and Lewis and Clark Among the Indians by James P. Rhonda), immigration (Impossible Subjects by Ming Ngai), and environmental (Nature’s Metropolis by William Cronon, Rivers of Empire by Donald Worster) history. These are just a few of the topics that have been examined by American West scholars. This paper will examine how these new histories of the American West resemble or diverge from Limerick’s outline.
Defining America or a Threat to America's Moral Standing
Peggy Pascoe’s Relations of Rescue described the creation and operation of Rescue Homes in Salt Lake City, the Sioux Reservation, Denver and San Francisco by missionary women for abused, neglected and exploited women. By focusing on the missionaries and the tenants of these homes, Pascoe depicted not just relations between women, but provided examples of how missionaries responded to issues which they believed were unique in the West. Issues that not only challenged the Victorian moral authority but threatened America’s moral standing. Unlike Turner, the missionary women did not believe that the West was an engine for democracy; instead, they envisioned a place where immoral practice such as polygamy, prostitution, premarital pregnancy, and religious superstition thrived and threatened women’s moral authority. Instead of attempting to portray a prototypical frontier or missionary woman, Pascoe reveals complicated women who defy easy categorization. Instead of re-enforcing stereotypes that women civilized (a dubious term at best) the American West, she instead focused on three aspects of the search for female moral authority: “its benefits and liabilities for women’s empowerment; its relationship to systems of social control; and its implication for intercultural relations among women.” (Pascoe, p. xvii.) Pascoe used a study of intercultural relations between women to better understand each of the sub-cultures (missionaries, unmarried mothers, Chinese prostitutes, Mormon women, and Sioux women) and their relations with governmental authorities and men.
Unlike Limerick, Pascoe did not find it necessary to define the west or the frontier. She did not have to because the Protestant missionaries in her story defined it for her. While Turner may have believed that the West was no longer the frontier in 1890, the missionaries certainly would have disagreed. In fact, the rescue missions were placed in the communities that the Victorian Protestant missionary judged to be the least “civilized” parts of America (Lakota Territory, San Francisco’s Chinatown, rough and tumble Denver and Salt Lake City.) Instead of being a story of conquest by Victorian or western morality, it was a story of how that morality was often challenged and its terms were negotiated by culturally different communities. Pascoe’s primary goal in this work was not only to eliminate stereotypes but to challenge the notion that white women civilized the west. While conquest may be a component of other histories, no one group in Pascoe’s story successfully dominated any other.
Changing the Narrative of Native Americans in the West
Two books were written before Legacy was published, Lewis and Clark Among the Indians (James Rhonda) and The Roots of Dependency (Richard White) both provide a window into the world of Native Americans. Both books took new approaches to Native American histories. Rhonda’s book looked at the familiar Lewis and Clark expedition but from an entirely different angle. Rhonda described the interactions between the expedition and the various Native American tribes they encountered. White’s book also sought to describe the interactions between the United States and the Choctaws, Pawnees, and Navajos, but he sought to explain why the economies of these tribes broke down after contact. Each of these books covers new ground by addressing the impact of these interactions between the United States and the Native Americans.

Whether or not Rhonda’s work is an example of the New Western History is debatable, but he sought to eliminate racial stereotypes of Native Americans and describe the first governmental attempt to conquer the western landscape by traversing it. Rhonda described the interactions between the expedition and the various Indians who encountered it. While Rhonda’s book may resemble a classic Lewis and Clark history, it provides a much more nuanced examination of the limitations and effectiveness of the diplomatic aspects of the Lewis and Clark expedition. He took a great of time to describe each of the interactions with the Indian tribes in detail. Rhonda recognized that the interactions between the expedition and the various tribes were nuanced and complex. Rhonda’s work clarified that Native Americans had differing views of the Lewis and Clark expedition. Any stereotypes the reader may have regarding the Native Americans with would have shattered. Additionally, Rhonda described how the expedition persevered despite its clumsy attempts at diplomacy.
Instead of describing the initial interactions of the United States government with the Choctaws, Pawnees, and Navajos, White explained how the self-sufficient economies of these people were destroyed. White described how the United States government turned these successful native people into wards of the American state. His story explained how the United States conquered these tribes without firing a shot. The consequence of this conquest was the creation of weak, dependent nations that could not survive without handouts from the federal government. Like Rhonda, White also sought to shatter long-standing stereotypes and myths regarding Native Americans. White verified that each of these tribes had self-sufficient economies which permitted prosperous lifestyles for their people before the devastating interactions with the United States government occurred. The United States in each case fundamentally altered the tribes’ economies and environments. These alterations threatened the survival of the tribes. In some cases, the United States sought to trade with these tribes in an effort put the tribes in debt. After the tribes were in debt, the United States then forced the tribes to sell their land. In other situations, the government damaged the tribes’ economies even when they sought to help them.
Even though White book was published a few years before Legacy, The Roots of Dependency certainly satisfies some of Limerick’s stated goals. Conquest and its consequences are at the heart of White’s story. White details the problems these societies developed after they became dependant on American trade goods and handouts. White also dissuaded anyone from believing that the Native American economies were inefficient. The Choctaws, Pawnees, and Navajos economies were successful. The Choctaws and Pawnees had thriving economies and their food supplies were more than sufficient. While the Navajos were not as successful as the other two tribes, their story was remarkable because they learned how to survive in some of the most inhospitable lands in the American West. These stories exploded the myths that the Native Americans subsistence economies were somehow insufficient.
The Impact of Immigrants to the West
The American West was both a borderland and a destination for a multitude of immigrants. Native Americans, Spaniards, Mexicans, Anglos, and Asians have all immigrated into the American West. The American West has seen waves of immigration. These immigrants have constantly changed the complexion of its people. Starting with the Native Americans who first moved into the region and the most recent tide of undocumented Mexican immigrants, the West has always been a place where immigrants seeking their fortunes. The California gold rush brought in a number of immigrants who did not fit their American ideal. When non-whites started immigrating to California, the United States was faced with a new problem, the introduction of people who could not become citizens. Chinese immigrants troubled the Anglo majority because they could not be easily assimilated into American society. Additionally, many Americans were perplexed by their substantially different appearances, clothing, religions, and cultures. Anglos became concerned that the new immigrants differed too much from them. In 1924, after 150 years of unregulated immigration, the United States Congress passed the Johnson-Reed Act, the most restrictionist immigration law in US history. The Johnson-Reed Act was specifically designed to keep the most undesirable races out of America, but immigrants continued to arrive in America without documents. Ming Ngai’s Impossible Subjects addresses this new class of immigrants: illegal immigrants. Illegal immigrants began to flow into the United States soon after the passage of the Johnson-Reed Act.
While illegal immigration is not an issue isolated to the history of the American West, the immigrants moved predominantly into California, Texas and the American Southwest. Like Anglo settlers who were attracted to the West for the potential for new life in the nineteenth century, illegal immigrants continued to move in during the twentieth. The illegal immigrants were welcomed, despite their status, because California’s large commercial farms needed inexpensive labor to harvest their crops. Impossible Subjects describes four groups of illegal immigrants (Filipinos, Japanese, Chinese and Mexican braceros) who were created by the United States immigration policy. Ngai specifically examines the role that the government played in defining, controlling and disciplining these groups for their allegedly illegal misconduct.
Impossible Subjects is not a book on the American West, but it is a book that is very much about the American West. While Ngai’s story primarily takes place in the American West she does not appear to have any interest in defining the West because her story has national implications. The American West is relevant to her study only because it was where most of the illegal immigrants described in her story lived and worked. Additionally, it is not a story of conquest and its consequences, but it introduced the American public and scholars to members of the American society that are silent. Limerick even stated that while “Indians, Hispanics, Asians, blacks, Anglos, businesspeople, workers, politicians, bureaucrats, natives and newcomers” all shared the same region, they still needed to be introduced to one another. In addition to being a sophisticated policy debate on immigration law, Ngai’s work introduced Americans to these people. (Limerick, p. 349.)
The Rise of Western Environmental History
Environmental history has become an increasingly important component of the history of the American West. Originally, the American West was seen as an untamed wilderness, but over time that description has changed. Two conceptually different, but nonetheless important books on environmental history discussed the American West and its importance in America. Nature’s Metropolis by William Cronon and Rivers of Empire by Donald Worster each explored the environment and the economy of the American West. Cronon examined the formation of Chicago and the importance of its commodities market for the development of the American West. Alternatively, Worster focuses on the creation of an extensive network of government subsidized dams in the early twentieth century. Rivers of Empire describes that despite the aridity of the natural landscape the American West became home to massive commercial farms and enormous swaths of urban sprawl.
In Nature’s Metropolis , Cronon, used the central place theory to analyze the economic and ecological development of Chicago. Johann Heinrich von Thunen developed the central place theory to explain the development of cities. Essentially, geographically different economic zones form in concentric circles the farther you went from the city. These different zones form because of the time it takes to get the different types of goods to market. Closest to the city and then moving away you would have the following zones: first, intensive agriculture, second, extensive agriculture, third, livestock raising, fourth, trading, hunting and Indian trade and finally, you would have the wilderness. While the landscape of the Mid-West was more complicated than this, Cronon posits that the “city and country are inextricably connected and that market relations profoundly mediate between them.” (Cronon, p. 52.) By emphasizing the connection between the city of Chicago and the rural lands that surrounded it, Cronon was able to explain how the land, including the West, developed. Cronon argued that the development of Chicago had a profound influence on the development and appearance of the Great West. Essentially Cronon used the creation of the Chicago commodities and trading markets to explain how different parts of the Mid-West and West produced different types of resources and fundamentally altered their ecology.
According to Donald Worster’s Rivers of Empire, economics played an equally important role in the economic and environmental development of the Rocky Mountain and Pacific Slope states. Worster argued that the United States wanted to continue creating family farms for Americans in the West. Unfortunately, the aridity of the west made that impossible. The land in the West simply could not be farmed without water. Instead of adapting to the natural environment, the United States government embarked on the largest dam building project in human history. The government built thousands of dams to irrigate millions of acres of land. Unfortunately, the cost of these numerous irrigation projects was enormous. The federal government passed the cost on to the buyers of the land which prevented family farmers from buying it. Therefore, instead of family farms, massive commercial farms were created. The only people who could afford to buy the land were wealthy citizens. The massive irrigation also permitted the creation of cities which never would have been possible without it. Worster argues that the ensuing ecological damage to the West has been extraordinary. The natural environment throughout the region was dramatically altered. The west is now the home of oversized commercial farms, artificial reservoirs which stretch for hundreds of miles, rivers that run only on command and sprawling cities which depend on irrigation.
Both Cronon and Worster described how commercial interests shaped the landscape and ecology of the American West, but their approaches were very different. Still, each work fits comfortably into the new western history. Both Cronon and Worster see the West as a place and not as a movement of westward expansion. Cronon re-orders the typical understanding of the sequence of westward expansion. Instead of describing the steady growth of rural communities which transformed into cities, he argued that cities and rural areas formed at the same time. Often the cities developed first and that only after markets were created could land be converted profitable into farms. This development fits westward development much more closely than paradigms that emphasized the creation of family farms. Worster defines the West by its aridity. While these definitions differ from Limerick’s, they reflect new approaches. Conquest plays a critical role in each of these books. Instead of conquering people, the authors describe efforts to conquer western lands. In Cronon, westerners forever altered the landscape of the west. Agricultural activities dominated the zones closest to Chicago, cattle production took over lands previously occupied by the buffalo, and even the wilderness was changed by people to satisfy the markets in Chicago. The extensive damming of the West’s rivers described by Worster required the United States government to conquer, control and discipline nature. While this conquest was somewhat illusory, the United States government was committed to reshaping the West and ecology to fit its vision.
Each of these books demonstrates that the Turner thesis no longer holds a predominant position in the scholarship of the American West. The history of the American West has been revitalized by its demise. While westward expansion plays an important role in the history of the United States, it did not define the west. Turner’s thesis was fundamentally undermined because it did not provide an accurate description of how the West was peopled. The nineteenth century of the west is not composed primarily of family farmers. Instead, it is a story of a region peopled by a diverse group of people: Native Americans, Asians, Chicanos, Anglos, African Americans, women, merchants, immigrants, prostitutes, swindlers, doctors, lawyers, farmers are just a few of the characters who inhabit western history.
Suggested Readings
- Frederick Jackson Turner, The Frontier in American History
- Patricia Limerick, Legacy of Conquest
- Peggy Pascoe, Relations of Rescue
- Richard White, The Roots of Dependency
- Nature's Metropolis, William Cronon
- Rivers of Empire, Donald Worster
- Historiography
- Book Review
- This page was last edited on 5 October 2021, at 01:36.
- Privacy policy
- About DailyHistory.org
- Disclaimers
- Mobile view

Mediale Topographien pp 3–13 Cite as
The Frontier Theory in American Cultural Studies: From Frederick Jackson Turner to Richard Slotkin
- Matthias Waechter 3
- First Online: 24 October 2019
766 Accesses
1 Citations
The frontier is a multifaceted, emotionally charged, and contested term in American socio-political discourse. It refers, first of all, to a line : it was the line which divided, throughout the period of westward expansion, the conquered parts of the country from those still free of white population. Over the 18th and 19th centuries, the frontier represented the outermost line of settlement, separating white civilization from the wilderness.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Arendt, Hannah (1963): On Revolution . New York: Viking.
Google Scholar
Beard, Charles A. ([1913] 1986): An Economic Interpretation of the Constitution of the United States . With a New Introduction by Forrest McDonald, New York: Free Press.
Becker, Carl (1920): The United States. An Experiment in Democracy . New York/London: Harper & Brothers.
Bolton, Herbert Eugene (1921): The Spanish Borderlands. A Chronicle of Old Florida and the Southwest. New Haven: Yale University Press.
Brooks, Van Wyck (1918): On Creating a Usable Past. The Dial 64 (April): 337–341.
Fiedler, Leslie A. ( 2 1968): The Return of the Vanishing American . New York: Stein & Day.
Hartz, Louis (1955): The Liberal Tradition in America. An Interpretation of American Political Thought since the Revolution . New York: Harcourt.
Hayes, Carlton J. H. (1946): The American Frontier – Frontier of What? American Historical Review 51(2): 199–216.
Article Google Scholar
Hoover, Herbert ([1922] 1979): American Individualism . Reprint of the 1922 ed., Garden City: Garland.
Hurtado, Albert L. (2001): Settler Women and Frontier Women. The Unsettling Past of Western Women’s History. Frontiers. A Journal of Women Studies 22: 1–5.
Hurtado, Albert L. (2012): Herbert Eugene Bolton. Historian of the American Borderlands . Berkeley/Los Angeles/London: University of California Press.
Jeffrey, Julie Roy (1979): Frontier Women. The Trans-Mississippi West 1840–1880 . New York: Hill and Wang.
Juricek, John T. (1966): American Usage of the Word “Frontier” from Colonial Times to Frederick Jackson Turner. Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 110(1): 10–34.
Kennedy, John F. ([1960] 1985): Acceptance Speech, Los Angeles, July 15, 1960. In Arthur Meier Schlesinger et al. (Ed.): History of American Presidential Elections 1789–1968 . Vol. IX: 1960–1968, New York: MacGraw-Hill, 3541–3545.
Lawrence, D. H. ([1923] 1955): Studies in Classic American Literature . Reprint of the 1923 ed., New York: Doubleday.
Limerick, Patricia Nelson (1987): The Legacy of Conquest. The Unbroken Past of the American West . New York/London: W.W. Norton.
Mumford, Lewis (1926): The Golden Day. A Study in American Experience and Culture . New York: Horace Liveright.
Myres, Sandra L. (1982): Westering Women and the Frontier Experience 1800–1915 . Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press.
Parrington, Vernon Louis (1927; 1930): Main Currents in American Thought. An Interpretation of American Literature from the Beginning to 1920 . 3 vols., New York: Harcourt, Brace and Company.
Potter, David M. (1954): People of Plenty. Economic Abundance and the American Character . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Reagan, Ronald ([engl. 1990] 1990): Erinnerungen. Ein amerikanisches Leben . Trans. by Till R. Lohmeier D. Muelder, H. Pänke, Chr. Rost, K.-D. Schmidt, Berlin: Propyläen.
Riley, Glenda (1986): Frontier Women. In Roger L. Nichols (Ed.): American Frontier and Western Issues. A Historiographical Review . Westport: Greenwood (Contributions in American History 118), 179–198.
Robinson, James Harvey (1912): The New History. Essays Illustrating the Modern Historical Outlook . New York: Macmillan.
Roosevelt, Franklin D. (1933): Looking Forward . New York: John Day.
Schlissel, Lillian, Vicki L. Ruiz and Janice Monk (Eds.) (1988): Western Women. Their Land, Their Lives . Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press.
Slotkin, Richard (1973): Regeneration through Violence. The Mythology of the American Frontier, 1600–1860 . Middletown (Conn.): Wesleyan. University Press.
Slotkin, Richard (1985): The Fatal Environment. The Myth of the Frontier in the Age of Industrialization, 1800–1890 . New York: Atheneum.
Slotkin, Richard (1992): Gunfighter Nation. The Myth of the Frontier in Twentieth-Century America . New York: Atheneum.
Smith, Henry Nash (1950): Virgin Land. The American West as Symbol and Myth . Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Turner, Frederick Jackson ([1893] 1920): The Significance of the Frontier in American History. In The Frontier in American History . New York: Henry Holt, 1–38.
Turner, Frederick Jackson (1896): The West as a Field for Historical Study. Annual Report of the American Historical Association for the Year 1896 , Vol. I, 281–319.
Turner, Frederick Jackson ([1910] 1920): Social Forces in American History. In The Frontier in American History . New York: Henry Holt, 311–334.
Turner, Frederick Jackson ([1914] 1920): The West and American Ideals. In The Frontier in American History . New York: Henry Holt, 290–310.
U.S. Census Office, 11th Census, 1890, Distribution of Population According to Density: 1890, Extra Census Bulletin No. 2, Washington, April 1891.
Waechter, Matthias (1996): Die Erfindung des amerikanischen Westens. Die Geschichte der Frontier-Debatte . Freiburg i. Br.: Rombach (Rombach Wissenschaft. Reihe Historiae 9).
Webb, Walter Prescott ([1931] 1957): The Great Plains . New York: Grossett & Dunlap.
White, Richard (1991): “It’s Your Misfortune and None of My Own”. A New History of the American West . Norman: University of Oklahoma Press.
Williams, William Appleman ([1959] 1962): The Tragedy of American Diplomacy, New York 1959. Revised and enlarged ed. New York: Dell.
Williams, William Appleman ([1961] 1966): The Contours of American History . Reprint of the 1961 ed., with a new foreword by the author. Chicago: Quadrangle.
Worster, Donald (1985): Rivers of Empire: Water, Aridity, and the Growth of the American We st. New York: Pantheon.
Worster, Donald, Susan Armitage, Michael P. Malone, David J. Weber and Patricia Nelson Limerick (1989): The Legacy of Conquest , by Patricia Nelson Limerick. A Panel of Appraisal. Western Historical Quarterly 20(3): 303–322.
Worster, Donald (1992): Under Western Skies. Nature and History in the American West . New York/Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
CIFE – Centre International de Formation Européenne, Berlin, Germany
Matthias Waechter
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Corresponding author
Correspondence to Matthias Waechter .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Dekra Hochschule für Medien, Berlin, Germany
Marcus Stiglegger
Geographisches Institut, Universität Mainz, Mainz, Germany
Anton Escher
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, ein Teil von Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Waechter, M. (2019). The Frontier Theory in American Cultural Studies: From Frederick Jackson Turner to Richard Slotkin. In: Stiglegger, M., Escher, A. (eds) Mediale Topographien. Springer VS, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-23008-1_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-23008-1_1
Published : 24 October 2019
Publisher Name : Springer VS, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN : 978-3-658-23007-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-658-23008-1
eBook Packages : Social Science and Law (German Language)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
A Century Later: Frederick Jackson Turner and the Spanish-American War
Nils Gilman | Apr 1, 1998
Historians are notoriously reluctant to address contemporary events. It used to be argued that only with the advantage of hindsight could the "meaning" of an event be adequately assessed. In contrast to journalists, historians were supposed to avail themselves not only of the considered reflection that retrospect afforded, but also of the additional information available in archives, most of which opened long after the events they concern had passed. Under these circumstances, "contemporary history" struck most historians as little more than an oxymoron. Given this aversion, perhaps it will seem odd to inquire what, if anything, the American Historical Review had to say about the Spanish-American War in 1898.
Not surprisingly, it was not until 1925 that the AHR published an article directly concerning the Spanish-American War, when Lester B. Shippee weighed in with considerations about "Germany and the Spanish-American War" (AHR 30:4, p. 754–97). Predictably enough, it was not contemporary politics that inspired Shippee, but rather the opening of European archives on the diplomacy surrounding the war. Although this would seem to support the idea that historians avoid contemporary issues, when we reread the pages of the 1898 AHR, it turns out that perhaps the bellicose events of that year did not go entirely unremarked.
In the June 1898 AHR , Frederick Jackson Turner contributed an article entitled "The Origin of Genet's Projected Attack on Louisiana and the Floridas" (AHR 3:4, p. 650–71). Turner retold the famous story of how Edmond-Charles-Edouard Genet, a diplomat dispatched by the revolutionary French state in 1793, sidestepped the federal government in Philadelphia to encourage the citizens of Kentucky (to the point of supplying them with arms) to attack the Spanish in New Orleans. To the outrage of trans-Appalachian citizens, Spain had blocked United States use of the Mississippi, thus slowing the development of the U.S. interior. Genet exploited their grievances to benefit the work of the French government. But if this was common enough subject matter, Turner's version gave it a decidedly contemporary flavor.
Turner used the words of the French observer Brissot de Warville to describe the ire westerners directed against Spain for shutting off access to the Mississippi: "Men who have shook off the yoke of Great Britain and who are masters of the Ohio and the Mississippi, cannot conceive that the insolence of a handful of Spaniards can think of shutting rivers and seas against a hundred thousand Americans." Turner's argument implied that the Genet affair corroborated his famous thesis that the struggle to advance the frontier was the basis for the American idea of freedom, rather than simply showing the disunity of the nation in the 1790s. In this case, the desire to advance the frontier had encouraged upstanding Americans (albeit at the behest of a foreign meddler) to stand up against the tyranny of a decadent Spanish empire. But did Turner also suggest that this Spanish insolence had not dissipated entirely?
With hindsight, we can read Turner's tale as a covert apologia for the coeval American intervention in Cuba. Certainly the idea seems to linger in the air. Turner's concluding words demonstrate that he considered his topic timely: "Enough has been said to reveal the fact that this attempt was an important chapter in the history of the Mississippi Valley in its relations to the future of the United States, of France and of Spain. It is, in fact, a chapter in the long struggle of the people of that Valley to hold the approaches to their great river—a struggle that is not yet ended." What ongoing struggle was Turner referring to? Probably not to the threat of imminent Canadian invasion.
Given that, for all the heat which debates about contemporary events can generate, little light is usually shed on the historical context in which these events unfold, perhaps historians are wise to avoid recent history. Nevertheless, historians are well advised to read today's newspapers even as they are producing works about the more distant past. Although some might look askance at Turner's political choices, his approach to the history of the Genet affair shows that great historians are always keenly aware of the contemporary relevance of their work. As one historian once remarked, although historians are obliged to be Tory in their approach to evidence, they are free to be Whiggish in their choice of subject matter.
Nils Gilman is a graduate student of history at the University of California at Berkeley and is an AHA volunteer-associate.
Tags: North America
The American Historical Association welcomes comments in the discussion area below, at AHA Communities , and in letters to the editor . Please read our commenting and letters policy before submitting.
Please read our commenting and letters policy before submitting.

In This Section
The Legacy of Conquest
The unbroken past of the american west (book review).
by Jenni Ostwinkle Silva

Patricia Nelson Limerick isn’t setting out to discredit Frederick Jackson Turner as an historian and scholar. And it isn’t that she believes his influential “ Frontier Thesis ” was without merit. On the contrary, she describes Turner as a “scholar with intellectual courage, an innovative spirit, and a forceful writing style” whose thesis served a purpose in the late 19 th /early 20 th centuries. 1 In Limerick’s opinion, the problem lies in the “excessive deference” for Turner that led many historians to believe that Turner’s thesis was the first, final, and only word in Western history. Although his conception of the frontier seemed unifying and efficient, its dominance wedded Western historians to an idea that was static, rigid, and exclusionary. The Frontier Thesis may have “created” Western history but it also set up arbitrary divisions between “the West” and “the rest” – divisions Limerick was determined to break down in The Legacy of Conquest: The Unbroken Past of the American West.
Much of Limerick’s work hinges on the debate of “process” (how events unfolded) versus “place” (the importance of location). In Turner’s view, the process of settling the frontier served as the basis of American exceptionalism, the belief that the United States are unique among world nations. Limerick and other “New Western” historians have challenged this theory by declaring that the West was always a place, with many different actors and events, not an empty land anxiously awaiting the arrival of white settlers. Turner’s thesis drew a line in time, carving out the arrival of white settlers as the beginning of the West and the closing of the frontier in 1890 (based on his interpretation of census records) as the end of this era. Limerick attempts to restore continuity to both time and space, and in doing so, opens up the field of Western history.
To accomplish this, Limerick addressed the history of the West thematically and divides her book into two tellingly-titled sections: “The Conquerors” and “The Conquerors Meet Their Match.” Turner believed that the frontier, shifting from savagery to civilization, served to “Americanize” the nation. Working under that pretext, scholars and citizens have conceptualized the frontier as a positive process. Using “place” instead of “process,” Limerick characterizes this period of Western history as “conquest.” By viewing the West as a place, she repositions the role of white settlers. These enterprising individuals did not discover a new place – they attempted to conquer a land that was already inhabited by Indians. Although this concept may seem jarring to the uninitiated, Limerick points out the contradiction of believing that “the legacy of slavery was serious business, while the legacy of conquest was not.” 2 The older framework only made sense was through the thick veil of denial. This denial, in turn, allowed for the proliferation of a number of myths in Western history, such as the idea of rugged individualism. Under this model, Westerners were fully removed from the rest of the country. When other actors appeared, they were viewed as imposing upon the Western (white) settlers. And if the settlers themselves happened to be imposing upon the Plains Indians, it was only because the forward march of history demanded it – and because the settlers had convinced themselves that Indians were a doomed race.
Unfortunately for this last myth, she states, the conquered refused to be or remain conquered, nor were they passive participants in the drama of the West. Attacking the notion that the history of the West is the history of the white man, Limerick turns her attention to Plains Indians, Hispanic, Chinese, Japanese, and blacks. Although she addresses these groups of people in a fairly general manner, she makes a strong case for the study of borderlands history. Viewed from a 21 st -century perspective, it can be easy to forget that the giant coast-to-coast landmass of the United States was never preordained. Battles were fought, treaties were drawn, and revenge was sought before state lines could be carved into the map of America. Introducing other ethnic and racial groups broadens the scope of Western history and highlights the centrality of conquest in the creation of the West. As Limerick makes clear, the history of the West is a nuanced and multi-faceted tale. While an historian annoyed “by the ethnocentricity of earlier frontier history” may be tempted by the desire to “take the Indian side,” doing so will not erase ethnocentricity. 3 The Indian (or Hispanic, or Chinese, or Japanese, or black) “side” is a difficult thing to locate. Instead, she recommends that historians view these groups – she is speaking of Indians in particular, but the same motivation carries throughout her other discussions – as “people steering their way through a difficult terrain of narrowing choices.” 4 The history books may not have treated these groups kindly (if they addressed them at all) but that does not mean they did not act, react, and affect the environment and the people around them.
In her final chapter, Limerick attempts to wrestle with the enduring power of the mythologized West and the problems that remain. The “frontier” still commands great respect and politicians from John Kennedy to Ronald Reagan have invoked its notion of progress. 5 Mexicans became “aliens” in their homeland when the United States conquered the Southwest and today, immigration remains a hot-button issue. Indians, still decidedly not-extinct , continue to maneuver through legal and political channels in an attempt to recoup their losses. But a restoration of rights does not, as Limerick points out, solve the larger problem of scarce resources. Although white settlers and the U.S. government were determined to “manage nature,” drought and limited access to water remain critical concerns.
Ironically, Limerick, considered one of the greatest scholars in the field of New Western history, is actually opposed to viewing Western history as an area of specialized study; her intention is to create connections. Reaching across the fields of economics, geography, anthropology and dipping into the current events, Limerick is trying to erase the lines Turner drew around the West. If the old ways of understanding Western history no longer work, new ways must be introduced. Here, environmental history and borderlands history take center stage.
A number of historians have followed in a similar vein. William Cronon and Elliot West address many of the same issues as Limerick – and then push them further. West affords Plains Indians an even more prominent position on the Western stage, portraying them as active participants in a history that is sometimes of their own making and sometimes out of their control. In examining the importance of 19 th -century Chicago, Cronon points out the problems with ideas of Western independence. In both of these works, as with Limerick, environmental history looms large. These Contested Plains and Nature’s Metropolis simply could not have been written in the framework provided by Turner even if they largely discredit its theories.
There are several minor missteps in The Legacy of Conquest , many of which Limerick admits to in the preface to the 2006 reprint. For one, she does not investigate the role of fur traders in the West, which would have given her an avenue to explore more fluid conceptions of identity. She also does not take into account the role of cities, reverting, against her best intentions, to the tired “idea that the real West meant the rural West!” 6 Although Limerick employed contemporary examples to illustrate her argument about continuity (and these topics are now 20-plus years old), the book has aged well – perhaps as more evidence of continuity of the West. Many of the issues she discussed remain unresolved: issues about resource conservation, immigration, and the management of nature seem as relevant today as they did in the 1980s – or even the 1880s.
Below, Patricia Limerick delivers her lecture, “The Winning of the West Revisited,” at the 2011 Theodore Roosevelt Symposium in Medora, North Dakota on October 29, 2011. Q&A session follows the lecture.
If anything, Limerick seems to run the risk of overselling her case. In her fifth chapter, “The Meeting Ground of the Past and Present,” Limerick thoroughly grounds her discussion in the political and environmental problems of 1970s and 1980s. It is a somewhat distracting diversion from the technique that Limerick employs in her other chapters. Her argument about continuity is most effective when woven within the larger narrative, not considered separately. Instead of drawing connections, it can seem as though Limerick is only pushing her agenda – perhaps the danger of any historian venturing into the present. Additionally, perhaps because many of the themes she addresses have been long-adopted by the historical profession, the reader is often willing to accept her ideas before Limerick has concluded her argument.
These issues are minor. The Legacy of Conquest stands out as a cogent, well-written, and gloriously accessible examination of the major themes in Western history. While experts are unlikely to be surprised, Legacy of Conquest serves as an excellent starting point for Western historians and, she hopes, American historians in general (after all, as Limerick might ask, what’s the difference?) Limerick cheerfully admits that her book is a work of synthesis. Many of the stories and characters she highlights are purposefully familiar to illustrate their previous historical immobility. Cast in the new light of environmental history or borderlands history, what is old becomes new again. Limerick is arguing (beseeching, pleading) for a new focus on inclusivity and continuity in Western scholarship. It is a point well made, and, judging by the durability of Legacy of Conquest and endurance of the New Western history, a point still well-taken.
For more information: Visit the U.S. History Scene reading lists for Environmental History , History of the American West , and Native American History

What was Jackson Turner’s “Frontier Thesis”?
Date Filmed
Related units.
Imperial America: U.S. Global Expansion, 1890-1915
Videos from Naoko Shibusawa
- Naoko Shibusawa
- February 19, 2021
Was Frederick Jackson Turner’s Frontier Thesis Myth or Reality?
Two scholars debate this question.
Written by: (Claim A) Andrew Fisher, William & Mary; (Claim B) Bradley J. Birzer, Hillsdale College
Suggested sequencing.
- Use this Point-Counterpoint with the Frederick Jackson Turner, “The Significance of the Frontier in American History,” 1893 Primary Source to give students more background on individualism and western expansion.
Issue on the Table
Was Turner’s thesis a myth about the individualism of the American character and the influence of the West or was it essentially correct in explaining how the West and the advancing frontier contributed to the shaping of individualism in the American character?
Instructions
Read the two arguments in response to the question, paying close attention to the supporting evidence and reasoning used for each. Then, complete the comparison questions that follow. Note that the arguments in this essay are not the personal views of the scholars but are illustrative of larger historical debates.
Every nation has a creation myth, a simple yet satisfying story that inspires pride in its people. The United States is no exception, but our creation myth is all about exceptionalism. In his famous essay, “The Significance of the Frontier in American History,” Frederick Jackson Turner claimed that the process of westward expansion had transformed our European ancestors into a new breed of people endowed with distinctively American values and virtues. In particular, the frontier experience had supposedly fostered democracy and individualism, underpinned by the abundance of “free land” out West. “So long as free land exists,” Turner wrote, “the opportunity for a competency exists, and economic power secures political power.” It was a compelling articulation of the old Jeffersonian Dream. Like Jefferson’s vision, however, Turner’s thesis excluded much of the nation’s population and ignored certain historical realities concerning American society.
Very much a man of his times, Turner filtered his interpretation of history through the lens of racial nationalism. The people who counted in his thesis, literally and figuratively, were those with European ancestry—and especially those of Anglo-Saxon origins. His definition of the frontier, following that of the U.S. Census, was wherever population density fell below two people per square mile. That effectively meant “where white people were scarce,” in the words of historian Richard White; or, as Patricia Limerick puts it, “where white people got scared because they were scarce.” American Indians only mattered to Turner as symbols of the “savagery” that white pioneers had to beat back along the advancing frontier line. Most of the “free land” they acquired in the process came from the continent’s vast indigenous estate, which, by 1890, had been reduced to scattered reservations rapidly being eroded by the Dawes Act. Likewise, Mexican Americans in the Southwest saw their land base and economic status whittled away after the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo that nominally made them citizens of the United States. Chinese immigrants, defined as perpetual aliens under federal law, could not obtain free land through the Homestead Act. For all these groups, Euro-American expansion and opportunity meant the contraction or denial of their own ability to achieve individual advancement and communal stability.
Turner also exaggerated the degree of social mobility open to white contemporaries, not to mention their level of commitment to an ideology of rugged individualism. Although plenty of Euro-Americans used the homestead laws to get their piece of free land, they often struggled to make that land pay and to keep it in the family. During the late nineteenth century, the commoditization and industrialization of American agriculture caught southern and western farmers in a crushing cost-price squeeze that left many wrecked by debt. To combat this situation, they turned to cooperative associations such as the Grange and the National Farmers’ Alliance, which blossomed into the Populist Party at the very moment Turner was writing about the frontier as the engine of American democracy. Perhaps it was, but not in the sense he understood. Populists railed against the excess of individualism that bred corruption and inequality in Gilded Age America. Even cowboys, a pillar of the frontier myth, occasionally tried to organize unions to improve their wages and working conditions. Those seeking a small stake of their own—what Turner called a “competency”— in the form of their own land or herds sometimes ran afoul of concentrated capital, as during the Johnson County War of 1892. The big cattlemen of the Wyoming Stockgrowers Association had no intention of sharing the range with pesky sodbusters and former cowboys they accused of rustling. Their brand of individualism had no place for small producers who might become competitors.
Turner took such troubles as a sign that his prediction had come true. With the closing of the frontier, he said, the United States would begin to see greater class conflict in the form of strikes and radical politics. There was lots of free land left in 1890, though; in fact, approximately 1 million people filed homestead claims between 1901 and 1913, compared with 1.4 million between 1862 and 1900. That did not prevent the country from experiencing serious clashes between organized labor and the corporations that had come to dominate many industries. Out west, socialistic unions such as the Western Federation of Miners and the Industrial Workers of the World challenged not only the control that companies had over their employees but also their influence in the press and politics. For them, Turner’s dictum that “economic power secures political power” would have held a more sinister meaning. It was the rise of the modern corporation, not the supposed fading of the frontier, that narrowed the meanings of individualism and opportunity as Americans had previously understood them.
Young historian Frederick Jackson Turner presented his academic paper, “The Significance of the Frontier in American History,” at the World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago on July 12, 1893. He was the final presenter of that hot and humid day, but his essay ranks among the most influential arguments ever made regarding American history.
Turner was trained at the University of Wisconsin (his home state) and Johns Hopkins University, then the center of Germanic-type graduate studies—that is, it was scientific and objectivist rather than idealist or liberal. Turner rebelled against that purely scientific approach, but not by much. In 1890, the U.S. Census revealed that the frontier (defined as fewer than two people per square mile) was closed. There was no longer an unbroken frontier line in the United States, although frontier conditions lasted in certain parts of the American West until 1920. Turner lamented this, believing the most important phase of American history was over.
No one publicly commented on the essay at the time, but the American Historical Association reprinted it in its annual report the following year, and within a decade, it became known as the “Turner Thesis.”
What is most prominent in the Turner Thesis is the proposition that the United States is unique in its heritage; it is not a European clone, but a vital mixture of European and American Indian. Or, as he put it, the American character emerged through an intermixing of “savagery and civilization.” Turner attributed the American character to the expansion to the West, where, he said, American settlers set up farms to tame the frontier. “The existence of an area of free land, its continuous recession, and the advance of American settlement westward, explain American development.” As people moved west in a “perennial rebirth,” they extended the American frontier, the boundary “between savagery and civilization.”
The frontier shaped the American character because the settlers who went there had to conquer a land difficult for farming and devoid of any of the comforts of life in urban parts of the East: “The frontier is the line of most rapid and effective Americanization. The wilderness masters the colonist. It finds him a European in dress, industries, tools, modes of travel, and thought. It takes him from the railroad car and puts him in the birch canoe. It strips off the garments of civilization and arrays him in the hunting shirt and the moccasin. It puts him in the log cabin of the Cherokee and Iroquois and runs an Indian palisade around him. Before long he has gone to planting Indian corn and plowing with a sharp stick; he shouts the war cry and takes the scalp in orthodox Indian fashion. In short, at the frontier the environment is at first too strong for the man. He must accept the conditions which it furnishes, or perish, and so he fits himself into the Indian clearings and follows the Indian trails.”
Politically and socially, according to Turner, the American character—including traits that prioritized equality, individualism, and democracy—was shaped by moving west and settling the frontier. “The tendency,” Turner wrote, “is anti-social. [The frontier] produces antipathy to control, and particularly to any direct control.” Those hardy pioneers on the frontier spread the ideas and practice of democracy as well as modern civilization. By conquering the wilderness, Turner stressed, they learned that resources and opportunity were seemingly boundless, meant to bring the ruggedness out of each individual. The farther west the process took them, the less European the Americans as a whole became. Turner saw the frontier as the progenitor of the American practical and innovative character: “That coarseness and strength combined with acuteness and acquisitiveness; that practical, inventive turn of mind, quick to find expedients; that masterful grasp of material things, lacking the artistic but powerful to effect great ends; that restless, nervous energy; that dominant individualism, working for good and for evil, and withal that buoyancy and exuberance which comes with freedom – these are trains of the frontier.”
Turner’s thesis, to be sure, viewed American Indians as uncivilized. In his vision, they cannot compete with European technology, and they fall by the wayside, serving as little more than a catalyst for the expansion of white Americans. This near-absence of Indians from Turner’s argument gave rise to a number of critiques of his thesis, most prominently from the New Western Historians beginning in the 1980s. These more recent historians sought to correct Turner’s “triumphal” myth of the American West by examining it as a region rather than as a process. For Turner, the American West is a progressive process, not a static place. There were many Wests, as the process of conquering the land, changing the European into the American, happened over and over again. What would happen to the American character, Turner wondered, now that its ability to expand and conquer was over?
Historical Reasoning Questions
Use Handout A: Point-Counterpoint Graphic Organizer to answer historical reasoning questions about this point-counterpoint.
Primary Sources (Claim A)
Cooper, James Fenimore. Last of the Mohicans (A Leatherstocking Tale) . New York: Penguin, 1986.
Turner, Frederick Jackson. “The Significance of the Frontier in American History.” http://sunnycv.com/steve/text/civ/turner.html
Primary Sources (Claim B)
Suggested resources (claim a).
Cronon, William, George Miles, and Jay Gitlin, eds. Under an Open Sky: Rethinking America’s Western Past . New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 1992.
Faragher, John Mack. Women and Men on the Overland Trail . New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 2001.
Grossman, Richard R, ed. The Frontier in American Culture: Essays by Richard White and Patricia Nelson Limerick . Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 1994.
Limerick, Patricia Nelson. The Legacy of Conquest: The Unbroken Past of the American West . New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 1987.
Limerick, Patricia Nelson, Clyde A. Milner II, and Charles E. Rankin, eds. Trails: Toward a New Western History . Lawrence, KS: University Press of Kansas, 1991.
Milner II, Clyde A. A New Significance: Re-envisioning the History of the American West . New York: Oxford University Press, 1996.
Nugent, Walter. Into the West: The Story of Its People . New York: Knopf, 1991.
Slotkin, Richard. The Fatal Environment: The Myth of the Frontier in the Age of Industrialization, 1800-1890 . Norman, OK: University of Oklahoma Press, 1998.
Suggested Resources (Claim B)
Billington, Ray Allen, and Martin Ridge. Westward Expansion: A History of the American Frontier . Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press, 2001.
Etulain, Richard, ed. Does the Frontier Experience Make America Exceptional? New York: Bedford/St. Martin’s, 1999.
Mondi. Megan. “’Connected and Unified?’: A More Critical Look at Frederick Jackson Turner’s America.” Constructing the Past , 7 no. 1:Article 7. http://digitalcommons.iwu.edu/constructing/vol7/iss1/7
Nelson, Robert. “Public Lands and the Frontier Thesis.” Atlas of the Historical Geography of the United States , Digital Scholarship Lab, University of Richmond, 2014. http://dsl.richmond.edu/fartherafield/public-lands-and-the-frontier-thesis/
More from this Category

Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Happiness
In our resource history is presented through a series of narratives, primary sources, and point-counterpoint debates that invites students to participate in the ongoing conversation about the American experiment.
Please log in to save materials. Log in
- Boxer Rebellion
- Frontier Thesis
- Seward’s Folly
Turner, Mahan, and the Roots of Empire
- Explain the evolution of American interest in foreign affairs from the end of the Civil War through the early 1890s
- Identify the contributions of Frederick Jackson Turner and Alfred Thayer Mahan to the conscious creation of an American empire

During the time of Reconstruction, the U.S. government showed no significant initiative in foreign affairs. Western expansion and the goal of Manifest Destiny still held the country’s attention, and American missionaries proselytized as far abroad as China, India, the Korean Peninsula, and Africa, but reconstruction efforts took up most of the nation’s resources. As the century came to a close, however, a variety of factors, from the closing of the American frontier to the country’s increased industrial production, led the United States to look beyond its borders. Countries in Europe were building their empires through global power and trade, and the United States did not want to be left behind.
AMERICA’S LIMITED BUT AGGRESSIVE PUSH OUTWARD
On the eve of the Civil War, the country lacked the means to establish a strong position in international diplomacy. As of 1865, the U.S. State Department had barely sixty employees and no ambassadors representing American interests abroad. Instead, only two dozen American foreign ministers were located in key countries, and those often gained their positions not through diplomatic skills or expertise in foreign affairs but through bribes. Further limiting American potential for foreign impact was the fact that a strong international presence required a strong military—specifically a navy—which the United States, after the Civil War, was in no position to maintain. Additionally, as late as 1890, with the U.S. Navy significantly reduced in size, a majority of vessels were classified as “Old Navy,” meaning a mixture of iron hulled and wholly wooden ships. While the navy had introduced the first all-steel, triple-hulled steam engine vessels seven years earlier, they had only thirteen of them in operation by 1890.
Despite such widespread isolationist impulses and the sheer inability to maintain a strong international position, the United States moved ahead sporadically with a modest foreign policy agenda in the three decades following the Civil War. Secretary of State William Seward, who held that position from 1861 through 1869, sought to extend American political and commercial influence in both Asia and Latin America. He pursued these goals through a variety of actions. A treaty with Nicaragua set the early course for the future construction of a canal across Central America. He also pushed through the annexation of the Midway Islands in the Pacific Ocean, which subsequently opened a more stable route to Asian markets. In frequent conversations with President Lincoln, among others, Seward openly spoke of his desire to obtain British Columbia, the Hawaiian Islands, portions of the Dominican Republic, Cuba, and other territories. He explained his motives to a Boston audience in 1867, when he professed his intention to give the United States “control of the world.”
Most notably, in 1867, Seward obtained the Alaskan Territory from Russia for a purchase price of $7.2 million. Fearing future loss of the territory through military conflict, as well as desiring to create challenges for Great Britain (which they had fought in the Crimean War), Russia had happily accepted the American purchase offer. In the United States, several newspaper editors openly questioned the purchase and labeled it “ Seward’s Folly ” ( Figure ). They highlighted the lack of Americans to populate the vast region and lamented the challenges in attempting to govern the native peoples in that territory. Only if gold were to be found, the editors decried, would the secretive purchase be justified. That is exactly what happened. Seward’s purchase added an enormous territory to the country—nearly 600,000 square miles—and also gave the United States access to the rich mineral resources of the region, including the gold that trigged the Klondike Gold Rush at the close of the century. As was the case elsewhere in the American borderlands, Alaska’s industrial development wreaked havoc on the region’s indigenous and Russian cultures.

Seward’s successor as Secretary of State, Hamilton Fish, held the position from 1869 through 1877. Fish spent much of his time settling international disputes involving American interests, including claims that British assistance to the Confederates prolonged the Civil War for about two years. In these so-called Alabama claims, a U.S. senator charged that the Confederacy won a number of crucial battles with the help of one British cruiser and demanded $2 billion in British reparations. Alternatively, the United States would settle for the rights to Canada. A joint commission representing both countries eventually settled on a British payment of $15 million to the United States. In the negotiations, Fish also suggested adding the Dominican Republic as a territorial possession with a path towards statehood, as well as discussing the construction of a transoceanic canal with Columbia. Although neither negotiation ended in the desired result, they both expressed Fish’s intent to cautiously build an American empire without creating any unnecessary military entanglements in the wake of the Civil War.
BUSINESS, RELIGIOUS, AND SOCIAL INTERESTS SET THE STAGE FOR EMPIRE
While the United States slowly pushed outward and sought to absorb the borderlands (and the indigenous cultures that lived there), the country was also changing how it functioned. As a new industrial United States began to emerge in the 1870s, economic interests began to lead the country toward a more expansionist foreign policy. By forging new and stronger ties overseas, the United States would gain access to international markets for export, as well as better deals on the raw materials needed domestically. The concerns raised by the economic depression of the early 1890s further convinced business owners that they needed to tap into new markets, even at the risk of foreign entanglements.
As a result of these growing economic pressures, American exports to other nations skyrocketed in the years following the Civil War, from $234 million in 1865 to $605 million in 1875. By 1898, on the eve of the Spanish-American War, American exports had reached a height of $1.3 billion annually. Imports over the same period also increased substantially, from $238 million in 1865 to $616 million in 1898. Such an increased investment in overseas markets in turn strengthened Americans’ interest in foreign affairs.
Businesses were not the only ones seeking to expand. Religious leaders and Progressive reformers joined businesses in their growing interest in American expansion, as both sought to increase the democratic and Christian influences of the United States abroad. Imperialism and Progressivism were compatible in the minds of many reformers who thought the Progressive impulses for democracy at home translated overseas as well. Editors of such magazines as Century , Outlook , and Harper’s supported an imperialistic stance as the democratic responsibility of the United States. Several Protestant faiths formed missionary societies in the years after the Civil War, seeking to expand their reach, particularly in Asia. Influenced by such works as Reverend Josiah Strong’s Our Country: Its Possible Future and Its Present Crisis (1885), missionaries sought to spread the gospel throughout the country and abroad. Led by the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions, among several other organizations, missionaries conflated Christian ethics with American virtues, and began to spread both gospels with zeal. This was particularly true among women missionaries, who composed over 60 percent of the overall missionary force. By 1870, missionaries abroad spent as much time advocating for the American version of a modern civilization as they did teaching the Bible.
Social reformers of the early Progressive Era also performed work abroad that mirrored the missionaries. Many were influenced by recent scholarship on race-based intelligence and embraced the implications of social Darwinist theory that alleged inferior races were destined to poverty on account of their lower evolutionary status. While certainly not all reformers espoused a racist view of intelligence and civilization, many of these reformers believed that the Anglo-Saxon race was mentally superior to others and owed the presumed less evolved populations their stewardship and social uplift—a service the British writer Rudyard Kipling termed “the white man’s burden.”
By trying to help people in less industrialized countries achieve a higher standard of living and a better understanding of the principles of democracy, reformers hoped to contribute to a noble cause, but their approach suffered from the same paternalism that hampered Progressive reforms at home. Whether reformers and missionaries worked with native communities in the borderlands such as New Mexico; in the inner cities, like the Salvation Army; or overseas, their approaches had much in common. Their good intentions and willingness to work in difficult conditions shone through in the letters and articles they wrote from the field. Often in their writing, it was clear that they felt divinely empowered to change the lives of other, less fortunate, and presumably, less enlightened, people. Whether oversees or in the urban slums, they benefitted from the same passions but expressed the same paternalism.
Lottie Moon, Missionary
Lottie Moon was a Southern Baptist missionary who spent more than forty years living and working in China. She began in 1873 when she joined her sister in China as a missionary, teaching in a school for Chinese women. Her true passion, however, was to evangelize and minister, and she undertook a campaign to urge the Southern Baptist missionaries to allow women to work beyond the classroom. Her letter campaign back to the head of the Mission Board provided a vivid picture of life in China and exhorted the Southern Baptist women to give more generously of their money and their time. Her letters appeared frequently in religious publications, and it was her suggestion—that the week before Christmas be established as a time to donate to foreign missions—that led to the annual Christmas giving tradition. Lottie’s rhetoric caught on, and still today, the annual Christmas offering is done in her name.
We had the best possible voyage over the water—good weather, no headwinds, scarcely any rolling or pitching—in short, all that reasonable people could ask. . . . I spent a week here last fall and of course feel very natural to be here again. I do so love the East and eastern life! Japan fascinated my heart and fancy four years ago, but now I honestly believe I love China the best, and actually, which is stranger still, like the Chinese best. —Charlotte “Lottie” Moon, 1877
Lottie remained in China through famines, the Boxer Rebellion , and other hardships. She fought against foot binding, a cultural tradition where girls’ feet were tightly bound to keep them from growing, and shared her personal food and money when those around her were suffering. But her primary goal was to evangelize her Christian beliefs to the people in China. She won the right to minister and personally converted hundreds of Chinese to Christianity. Lottie’s combination of moral certainty and selfless service was emblematic of the missionary zeal of the early American empire.
TURNER, MAHAN, AND THE PLAN FOR EMPIRE
The initial work of businesses, missionaries, and reformers set the stage by the early 1890s for advocates of an expanded foreign policy and a vision of an American empire. Following decades of an official stance of isolationism combined with relatively weak presidents who lacked the popular mandate or congressional support to undertake substantial overseas commitments, a new cadre of American leaders—many of whom were too young to fully comprehend the damage inflicted by the Civil War—assumed leadership roles. Eager to be tested in international conflict, these new leaders hoped to prove America’s might on a global stage. The Assistant Secretary of the Navy, Theodore Roosevelt, was one of these leaders who sought to expand American influence globally, and he advocated for the expansion of the U.S. Navy, which at the turn of the century was the only weapons system suitable for securing overseas expansion.
Turner ( Figure ) and naval strategist Alfred Thayer Mahan were instrumental in the country’s move toward foreign expansion, and writer Brooks Adams further dramatized the consequences of the nation’s loss of its frontier in his The Law of Civilization and Decay in 1895. As mentioned in the chapter opening, Turner announced his Frontier Thesis —that American democracy was largely formed by the American frontier—at the Chicago World’s Colombian Exposition. He noted that “for nearly three centuries the dominant fact in American life has been expansion.” He continued: “American energy will continually demand a wider field for its exercise.”

Although there was no more room for these forces to proceed domestically, they would continue to find an outlet on the international stage. Turner concluded that “the demands for a vigorous foreign policy, for an interoceanic canal, for a revival of our power upon our seas, and for the extension of American influence to outlying islands and adjoining countries are indications that the forces [of expansion] will continue.” Such policies would permit Americans to find new markets. Also mindful of the mitigating influence of a frontier—in terms of easing pressure from increased immigration and population expansion in the eastern and midwestern United States—he encouraged new outlets for further population growth, whether as lands for further American settlement or to accommodate more immigrants. Turner’s thesis was enormously influential at the time but has subsequently been widely criticized by historians. Specifically, the thesis underscores the pervasive racism and disregard for the indigenous communities, cultures, and individuals in the American borderlands and beyond.

Explore the controversy associated with Turner’s Frontier Thesis at U.S. History Scene.
While Turner provided the idea for an empire, Mahan provided the more practical guide. In his 1890 work, The Influence of Seapower upon History , he suggested three strategies that would assist the United States in both constructing and maintaining an empire. First, noting the sad state of the U.S. Navy, he called for the government to build a stronger, more powerful version. Second, he suggested establishing a network of naval bases to fuel this expanding fleet. Seward’s previous acquisition of the Midway Islands served this purpose by providing an essential naval coaling station, which was vital, as the limited reach of steamships and their dependence on coal made naval coaling stations imperative for increasing the navy’s geographic reach. Future acquisitions in the Pacific and Caribbean increased this naval supply network ( Figure ). Finally, Mahan urged the future construction of a canal across the isthmus of Central America, which would decrease by two-thirds the time and power required to move the new navy from the Pacific to the Atlantic oceans. Heeding Mahan’s advice, the government moved quickly, passing the Naval Act of 1890, which set production levels for a new, modern fleet. By 1898, the government had succeeded in increasing the size of the U.S. Navy to an active fleet of 160 vessels, of which 114 were newly built of steel. In addition, the fleet now included six battleships, compared to zero in the previous decade. As a naval power, the country catapulted to the third strongest in world rankings by military experts, trailing only Spain and Great Britain.

The United States also began to expand its influence to other Pacific Islands, most notably Samoa and Hawaii. With regard to the latter, American businessmen were most interested in the lucrative sugar industry that lay at the heart of the Hawaiian Islands’ economy. By 1890, through a series of reciprocal trade agreements, Hawaiians exported nearly all of their sugar production to the United States, tariff-free. When Queen Liliuokalani tapped into a strong anti-American resentment among native Hawaiians over the economic and political power of exploitative American sugar companies between 1891 and 1893, worried businessmen worked with the American minister to Hawaii, John Stevens, to stage a quick, armed revolt to counter her efforts and seize the islands as an American protectorate ( Figure ). Following five more years of political wrangling, the United States annexed Hawaii in 1898, during the Spanish-American War.

The United States had similar strategic interests in the Samoan Islands of the South Pacific, most notably, access to the naval refueling station at Pago Pago where American merchant vessels as well as naval ships could take on food, fuel, and supplies. In 1899, in an effort to mitigate other foreign interests and still protect their own, the United States joined Great Britain and Germany in a three-party protectorate over the islands, which assured American access to the strategic ports located there.
Section Summary
In the last decades of the nineteenth century, after the Civil War, the United States pivoted from a profoundly isolationist approach to a distinct zeal for American expansion. The nation’s earlier isolationism originated from the deep scars left by the Civil War and its need to recover both economically and mentally from that event. But as the industrial revolution changed the way the country worked and the American West reached its farthest point, American attitudes toward foreign expansion shifted. Businesses sought new markets to export their factory-built goods, oil, and tobacco products, as well as generous trade agreements to secure access to raw materials. Early social reformers saw opportunities to spread Christian gospel and the benefits of American life to those in less developed nations. With the rhetoric of Fredrick J. Turner and the strategies of Alfred Mahan underpinning the desire for expansion abroad, the country moved quickly to ready itself for the creation of an American empire.
Review Questions
Why did the United States express limited interest in overseas expansion in the 1860s and 1870s?
- fear of attacks on their borders
- post-Civil War reconstruction
- the Anti-Imperialist League
- Manifest Destiny
Which of the following did Mahan not believe was needed to build an American empire?
- military bases around the world
- the reopening of the American frontier
- a canal through Central America
Why were the Midway Islands important to American expansion?
The Midway Islands provided a more stable path to Asian markets and a vital naval coaling station, which steamships needed in order to travel further afield.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Frontier Thesis, also known as Turner's Thesis or American frontierism, is the argument advanced by historian Frederick Jackson Turner in 1893 that the settlement and colonization of the rugged American frontier was decisive in forming the culture of American democracy and distinguishing it from European nations. He stressed the process of "winning a wilderness" to extend the frontier line ...
Frederick Jackson Turner, American historian known for the 'frontier thesis,' which held that the American character was decisively shaped by conditions on the frontier, the settling of which engendered such traits as self-reliance, individualism, inventiveness, restless energy, mobility, materialism, and optimism.
On the evening of July 12, 1893, in the hall of a massive new Beaux-Arts building that would soon house the Art Institute of Chicago, a young professor named Frederick Jackson Turner rose to ...
Identify the contributions of Frederick Jackson Turner and Alfred Thayer Mahan to the conscious creation of an American empire. During the time of Reconstruction, the U.S. government showed no significant initiative in foreign affairs. Western expansion and the goal of Manifest Destiny still held the country's attention, and American ...
In their work on Turner's formative period, Ray A. Billington and Fulmer Mood have shown that the Frontier Thesis, formulated in 1893 in "The Significance of the Frontier in American History," is not so much a brilliant early effort by a young scholar as a mature study in which Turner gave his ideas an organization that proved to be final.
poet laureate of American democracy, Frederick Jackson Turner was its first professional court historian. But perhaps more importantly, there is arguably something about Turner and his frontier thesis, in-spired as it was by the twilight years of the nineteenth century, that speaks directly to our condition in the waning years of the twentieth.
He presented his thesis, "The Significance of the Frontier in American History," to a gathering of American historians in Chicago in 1893. Over time, Turner's ideas came to be so well known that one historians has called it "the single most influential piece of writing in the history of American history.". Turner's conclusion, that the most ...
The Frontier Thesis is meant to be a gateway to a consciousness of. historical continuity through change. Turner constructed it in order to show his countrymen that their basic political ideals, individualism and. democracy, are not secured once and for ever, but exist only as a result of.
The young Wisconsin historian Frederick Jackson Turner presented his "frontier thesis," one of the most influential theories of American history, in his essay, "The Significance of the Frontier in American History.". Turner looked back at the historical changes in the West and saw, instead of a tsunami of war and plunder and industry ...
Figure 1. Historian Fredrick Jackson Turner's Frontier Thesis stated explicitly that the existence of the western frontier forged the very basis of the American identity. The initial work of businesses, missionaries, and reformers set the stage by the early 1890s for advocates of an expanded foreign policy and a vision of American empire.
Our early history is the study of European germs developing in an American environment. Too exclusive attention has been paid by institutional students to the Germanic origins, too little to the American factors. The frontier is the line of most rapid and effective Americanization. The wilderness masters the colonist.
The Significance of the Frontier in American History. " The Significance of the Frontier in American History " is a seminal essay by the American historian Frederick Jackson Turner which advanced the Frontier thesis of American history. Turner's thesis had a significant impact on how people in the late 19th and early 20th centuries understood ...
Explain the evolution of American interest in foreign affairs from the end of the Civil War through the early 1890s. Identify the contributions of Frederick Jackson Turner and Alfred Thayer Mahan to the conscious creation of an American empire. Figure 22.2. During the time of Reconstruction, the U.S. government showed no significant initiative ...
ROBERT H. BLOCK. ABSTRACT. Frederick Jackson Turner was a precursor to the modern histor-. ical geographer as well as a cofounder of the American subdiscipline. His studies of frontiers, sections, and regions pioneered new paths for interdisciplinary schol- arship between history and the earth sciences, particularly geography.
Why was the Turner Thesis abandoned by historians. Frederick Jackson Turner, 1902. Fredrick Jackson Turner's thesis of the American frontier defined the study of the American West during the 20th century. In 1893, Turner argued that "American history has been in a large degree the history of the colonization of the Great West.
The frontier became a key term for American social sciences in 1893, when Frederick Jackson Turner presented a paper under the title The Significance of the Frontier in American History in front of the American Historical Association (Turner 1920).Taking the Census report of 1890 as a starting point, he inquired as to the way in which the existence of the frontier had influenced the evolution ...
Not surprisingly, it was not until 1925 that the AHR published an article directly concerning the Spanish-American War, when Lester B. Shippee weighed in with considerations about "Germany and the Spanish-American War" (AHR 30:4, p. 754-97). Predictably enough, it was not contemporary politics that inspired Shippee, but rather the opening of ...
Spanish American War Diary of Clarence C. Childs ; Memoir of Gen. Russell Hastings after the Civil War ; ... he is an important figure for understanding late nineteenth century America. ... the Significance of Frederick Jackson Turner's Frontier Thesis," Montana: The Magazine of Western History, 40 (Winter, 1991), 3-13.
Turner believed that the frontier, shifting from savagery to civilization, served to "Americanize" the nation. Working under that pretext, scholars and citizens have conceptualized the frontier as a positive process. Using "place" instead of "process," Limerick characterizes this period of Western history as "conquest.".
What was Jackson Turner's "Frontier Thesis"? February 19, 2021. Analysis of "American Progress" by John Gast (1872) February 19, 2021. How did U.S. political cartoons attempt to justify U.S. imperialism? February 19, 2021. How were the U.S. wars to colonize Native American territory similar to the Philippine-American War? February 19 ...
Claim A. Every nation has a creation myth, a simple yet satisfying story that inspires pride in its people. The United States is no exception, but our creation myth is all about exceptionalism. In his famous essay, "The Significance of the Frontier in American History," Frederick Jackson Turner claimed that the process of westward expansion ...
Specifically, the thesis underscores the pervasive racism and disregard for the indigenous communities, cultures, and individuals in the American borderlands and beyond. Explore the controversy associated with Turner's Frontier Thesis at U.S. History Scene. While Turner provided the idea for an empire, Mahan provided the more practical guide.