Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What is Secondary Research? | Definition, Types, & Examples

What is Secondary Research? | Definition, Types, & Examples
Published on January 20, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 12, 2024.
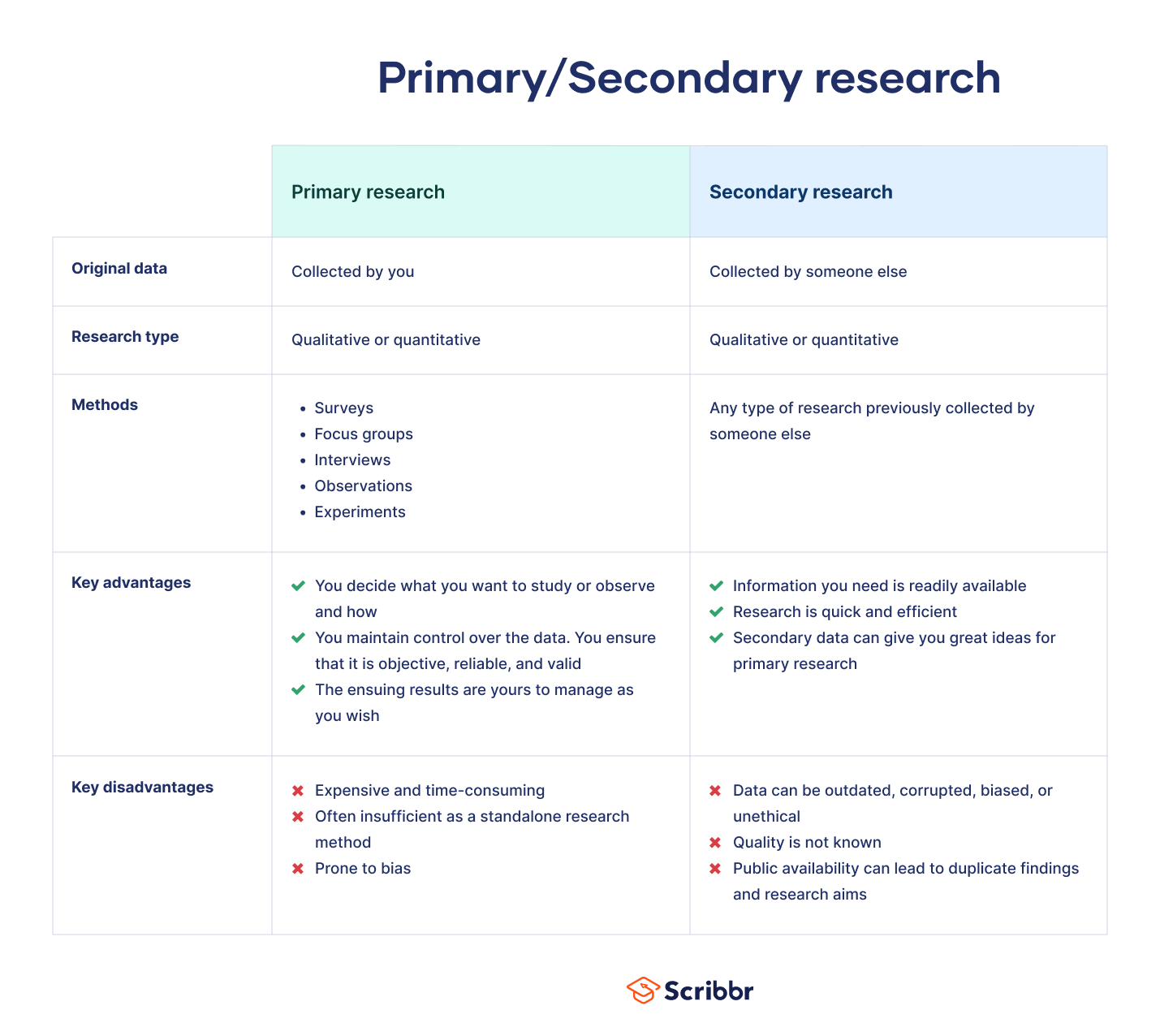
Secondary research is a research method that uses data that was collected by someone else. In other words, whenever you conduct research using data that already exists, you are conducting secondary research. On the other hand, any type of research that you undertake yourself is called primary research .
Secondary research can be qualitative or quantitative in nature. It often uses data gathered from published peer-reviewed papers, meta-analyses, or government or private sector databases and datasets.
Table of contents
When to use secondary research, types of secondary research, examples of secondary research, advantages and disadvantages of secondary research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
Secondary research is a very common research method, used in lieu of collecting your own primary data. It is often used in research designs or as a way to start your research process if you plan to conduct primary research later on.
Since it is often inexpensive or free to access, secondary research is a low-stakes way to determine if further primary research is needed, as gaps in secondary research are a strong indication that primary research is necessary. For this reason, while secondary research can theoretically be exploratory or explanatory in nature, it is usually explanatory: aiming to explain the causes and consequences of a well-defined problem.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Secondary research can take many forms, but the most common types are:
Statistical analysis
Literature reviews, case studies, content analysis.
There is ample data available online from a variety of sources, often in the form of datasets. These datasets are often open-source or downloadable at a low cost, and are ideal for conducting statistical analyses such as hypothesis testing or regression analysis .
Credible sources for existing data include:
- The government
- Government agencies
- Non-governmental organizations
- Educational institutions
- Businesses or consultancies
- Libraries or archives
- Newspapers, academic journals, or magazines
A literature review is a survey of preexisting scholarly sources on your topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant themes, debates, and gaps in the research you analyze. You can later apply these to your own work, or use them as a jumping-off point to conduct primary research of your own.
Structured much like a regular academic paper (with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion), a literature review is a great way to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject. It is usually qualitative in nature and can focus on a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. A case study is a great way to utilize existing research to gain concrete, contextual, and in-depth knowledge about your real-world subject.
You can choose to focus on just one complex case, exploring a single subject in great detail, or examine multiple cases if you’d prefer to compare different aspects of your topic. Preexisting interviews , observational studies , or other sources of primary data make for great case studies.
Content analysis is a research method that studies patterns in recorded communication by utilizing existing texts. It can be either quantitative or qualitative in nature, depending on whether you choose to analyze countable or measurable patterns, or more interpretive ones. Content analysis is popular in communication studies, but it is also widely used in historical analysis, anthropology, and psychology to make more semantic qualitative inferences.
Secondary research is a broad research approach that can be pursued any way you’d like. Here are a few examples of different ways you can use secondary research to explore your research topic .
Secondary research is a very common research approach, but has distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of secondary research
Advantages include:
- Secondary data is very easy to source and readily available .
- It is also often free or accessible through your educational institution’s library or network, making it much cheaper to conduct than primary research .
- As you are relying on research that already exists, conducting secondary research is much less time consuming than primary research. Since your timeline is so much shorter, your research can be ready to publish sooner.
- Using data from others allows you to show reproducibility and replicability , bolstering prior research and situating your own work within your field.
Disadvantages of secondary research
Disadvantages include:
- Ease of access does not signify credibility . It’s important to be aware that secondary research is not always reliable , and can often be out of date. It’s critical to analyze any data you’re thinking of using prior to getting started, using a method like the CRAAP test .
- Secondary research often relies on primary research already conducted. If this original research is biased in any way, those research biases could creep into the secondary results.
Many researchers using the same secondary research to form similar conclusions can also take away from the uniqueness and reliability of your research. Many datasets become “kitchen-sink” models, where too many variables are added in an attempt to draw increasingly niche conclusions from overused data . Data cleansing may be necessary to test the quality of the research.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
A systematic review is secondary research because it uses existing research. You don’t collect new data yourself.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyze a large amount of readily-available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how it is generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
George, T. (2024, January 12). What is Secondary Research? | Definition, Types, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 22, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/secondary-research/
Largan, C., & Morris, T. M. (2019). Qualitative Secondary Research: A Step-By-Step Guide (1st ed.). SAGE Publications Ltd.
Peloquin, D., DiMaio, M., Bierer, B., & Barnes, M. (2020). Disruptive and avoidable: GDPR challenges to secondary research uses of data. European Journal of Human Genetics , 28 (6), 697–705. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-0596-x
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, primary research | definition, types, & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is a case study | definition, examples & methods, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Primary vs Secondary Research Methods: 15 Key Differences

When carrying out a systematic investigation, you can choose to be directly involved in the data collection process or to rely on already acquired information. While the former is described as primary research, the latter is known as secondary research.
The distinguishing factor between primary research and secondary research is the degree of involvement of the research with the data gathering process . In this article, we’ll be detailing other key differences between primary and secondary research, and also show you how to conduct primary research with Formplus.
What is Primary Research?
Primary research is a type of research that requires the researcher to participate directly in the data-gathering process. In primary research, the researcher does not depend on already existing data, rather he or she collects first-hand information which serves as research materials for the systematic investigation.
This type of research gives the researcher absolute ownership of the data which is extremely important for businesses and organisations in fast-paced markets. These organisations utilise primary research to gather valuable information about consumer needs and preferences before launching a new product or service.
Usually, primary research focuses on the specific needs of the research contexts. However, this type of research is expensive, time-consuming and it usually requires a lot of skilled resources that may not be readily available and this is why many businesses outsource this to 3rd party market research companies.
What is Secondary Research?
Secondary research is a type of research approach in which the researcher relies solely on existing research materials rather than gather data directly for research. This research approach is less expensive and time-efficient unlike primary research..
Data for secondary research can be accessed from the internet, archive, libraries, educational institutions and organisational reports. However, extra care must be taken by the researcher to ensure that the data is valid as this can have a negative impact on the research process and outcomes.
Differences Between Primary and Secondary Research
Primary research is a research approach that involves gathering data directly while secondary research is a research approach that involves relying on already existing data when carrying out a systematic investigation.
This means that in primary research, the researcher is directly involved in the data collection and categorization process. In secondary research, on the other hand, the researcher simply depends on existing materials for the research without any need to collect raw information from the field.
- Sources of Data
Surveys, interviews, focus groups and observation techniques are common sources of data in primary research. In secondary research, the researcher collects existing research materials through a number of sources like the internet, libraries and archives.
These data collection methods require some sort of interaction with the research subjects in order to gather first-hand information that will be useful in the research. Many times,secondary sources are free to access but some of them will require you to pay an access fee before you can make use of the information.
- Other Names
Secondary research is also known as desk research because it does not necessarily require the researcher to move from one place to another. Meanwhile, primary research is also referred to as a field research design because it requires the researcher to get totally involved with the data collection process.
In secondary research, researchers can easily access information from the comfort of their desk; especially when using the internet to source for research materials. In some cases, the researcher would need to co-exist with the research subjects for a specific period of time in order to get information for the research.
- Advantages of Primary Research over Secondary Research
Unlike secondary research, primary research gives the researcher 100% ownership of the research data which is extremely useful for organisations in highly competitive markets. Data from secondary research can be accessed by everyone and does not yield any specific benefits to organisations.
Also, in primary research, the researcher can fully account for the authenticity of the data because he or she is an active participant in the data collection process. Because the researcher is not directly involved in gathering secondary research data, he or she cannot ascertain the authenticity of the research materials.
- Advantages of Secondary Research over Primary Research.
Unlike primary research that is expensive and time-consuming, secondary research can be completed in limited time and with limited resources. Since the research data already exists, the secondary researcher does not need to invest time or resources to gather first-hand information.
Also, secondary research helps to prevent knowledge repetition by mapping out already existing research efforts and this helps the primary researcher to concentrate on exploring new areas of knowledge. Hence, it is important for every research effort to begin with secondary research.
Common tools used to collect data in secondary research include bots, internet-enabled devices like laptops, smartphones and tablets. On the other hand, surveys, questionnaires and interviews are common data gathering tools in primary research.
Secondary research devices help researchers to access sources of secondary data like libraries, archives and peer-reviewed journals; without needing to go to the field. Primary research tools help the researcher to access first-hand information about the characteristics, dispositions and behaviours of research subjects in line with the context of the systematic investigation.
Primary research makes use of real-time information while secondary research makes use of past or already existing research materials. During primary research, the research is ultimately concerned with gathering first-hand information about the research subjects and contexts while in secondary research, the researcher simply re-examines existing data.
Hence, the type of data used in secondary research is described as “past data” because it reflects past occurrences and only provides insights into dealing with present situations. The role of the secondary researcher is primarily to specify how this past data informs his or her current research.
- Research Purpose
The purpose of primary research is to gather real-time data that will be useful in solving a specific problem. On the other hand, the purpose of secondary research is to gather existing research materials that may not directly address the problem at hand.
The primary research process is carefully tailored towards the specific research problem from start to finish and this is why it relies on first-hand data. Secondary research is not tailored towards solving a specific problem rather, it provides general information that can prove useful for primary research.
- When to Conduct Primary and Secondary Research
Primary or field research is usually carried out when an individual or organization needs to gather recent data that is useful for a specific research context. When organisations need to gather information on the changing needs of target markets, they typically employ primary research methods.
Secondary research, on the other hand, is used when the researcher needs to identify existing knowledge that can provide useful insight in research. With this information, the researcher can identify knowledge gaps which would form the core of his or her research efforts.
- Data Recency
Primary research relies on recent data for its systematic investigation because it addresses present situations. As earlier asserted, primary research efforts are ultimately tailored towards the needs of a specific research context from start to finish;hence, the primary researcher must gather real-time data in order to arrive at relevant research outcomes.
Secondary research, on the other hand, makes use of past data in an attempt to understand existing research efforts, identify knowledge gaps and map out the recent research to fill these knowledge gaps. This, findings from secondary research do not necessarily apply to specific research contexts.
- Feasibility
Secondary research is more feasible than primary research. For example, it may be improbable for a company to attempt to observe the buying culture of all the individuals in its target market.
In this case, the researcher may have to depend on existing research findings that detail the buying culture of the target market. Alternatively, the researcher can use other sampling methods that would help him or her gather feedback from a section of the market.
Examples of primary research data are student thesis, market research and first-person accounts of trauma survivors while examples of secondary research data include newspapers, books, academic journals and magazines.
Secondary research data often represent an aggregation of already existing information with little or no additions while primary data contains new information. Usually, primary research collects data from the original source unlike secondary research that relies on reported information. For example, a student who wants to write a thesis would need to either interact with the research subjects in their natural environment or carry out an experiment.
- Specificity
Primary research is more specific than secondary research because primary research is aimed at addressing issues peculiar to a business, organisation or institution. On the other hand, secondary research that does not cater to the specific needs of an organization.
For example, when carrying out a primary research on consumer satisfaction for a product, the entirety of the research process is tailored towards the product in question. In secondary research, however, the data collected may not be exactly what the researcher needs.
In primary research, the researcher has 100% ownership and control over the data and he or she can choose to make such information available to others or not. This means that the primary researcher has absolute discretion over the research materials.
In secondary research, however, the researcher does not own the data and as such, he or she does not have absolute discretion over it. Secondary research can aptly be described as a “free-for-all” situation because everyone can gain access to the data.
- Data Accuracy
Data gathered through primary research is more accurate than secondary research data. In primary research, the researcher is fully involved in the data collection process and he or she takes care to collect valid data that can be easily authenticated.
The secondary researcher, on the other hand, has no control over the data and he or she cannot account for the validity of the research materials. For instance, there is a lot of inaccurate information on the internet which can affect research outcomes when used as the basis of a systematic investigation.
Similarity between Primary and Secondary Research
Primary and secondary research makes use of quantitative and qualitative data. Quantitative data collection methods such as surveys and questionnaires are used to gather numerical data while qualitative data collection methods like observation are used to gather descriptive data .
How to Conduct Primary Research with Formplus
Primary research can be conducted with Formplus using a survey or questionnaire . Here is a step-by-step guide on how to go about this.
- Sign into Formplus
With Formplus, you can create different types of surveys and questionnaires for primary research. Sign into your Formplus account to access the form builder where you can seamlessly add and modify different form fields for your primary research survey.
Once you sign in, click on “create new form” to begin.
In the builder page, you can specify your form title to be “Primary Research Survey” in the title box. Next, click on or drag your desired form fields into your survey form from the builder’s inputs section.
- Edit fields
- Click on “Save”
- Preview form.
- Form Customization
In the form customization section in the form builder, you can easily personalize your primary research survey by modifying its outlook to suit your needs. Formplus allows you to change your form theme, add background images and even change the font according to your needs.
- Multiple Sharing Options
With Formplus, you can easily share your primary research survey with respondents using the available multiple sharing options. You can use the direct social media sharing buttons to share your form link to your organization’s social media pages.
You can send out your survey form as email invitations to your research subjects too. If you wish, you can share your form’s QR code or embed it in your organization’s website for easy access.
Conclusion
Many times, researchers combine primary and secondary data collection methods in order to arrive at the most valid outcomes at the end of a systematic investigation. Usually, they start off with secondary research to effectively map out a relevant scope for their research effort, before proceeding to conduct primary research.
It is important for you to consider the strengths and weaknesses of secondary and primary research before opting for any of these research methods. More importantly, you should pay attention to the overall aim of your systematic investigation as this is the fundamental determinator for choosing primary or secondary research.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- primary research
- primary secondary research differences
- primary secondary research method
- primary vs secondary research
- types of research methods
- busayo.longe

You may also like:
What is Pure or Basic Research? + [Examples & Method]
Simple guide on pure or basic research, its methods, characteristics, advantages, and examples in science, medicine, education and psychology

What is Secondary Research? + [Methods & Examples]
A simple guide on secondary research; definitions, methods, examples, advantages and its disadvantages
Recall Bias: Definition, Types, Examples & Mitigation
This article will discuss the impact of recall bias in studies and the best ways to avoid them during research.
What is Primary Research? + [Methods & Examples]
A simple guide on primary research; definitions, Its methods, examples, data collection techniques, advantages and disadvantages
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
- Privacy Policy

Home » Primary Vs Secondary Research
Primary Vs Secondary Research
Table of Contents

Primary and secondary research are two different types of research methods used to gather information for a study or research project.
Primary Research
Primary Research involves collecting original data for a specific research purpose. This type of research is designed to answer specific research questions and is often conducted through methods such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, or experiments. Primary research is time-consuming and requires careful planning and execution to ensure that the data collected is valid and reliable. However, it provides researchers with first-hand information that is relevant to their specific research questions and can be tailored to their specific needs.
Secondary Research
Secondary research involves gathering data that has already been collected by someone else. This type of research can be conducted through various sources, such as academic journals, books, government reports, and online databases. Secondary research is less time-consuming and less expensive than primary research, as the data has already been collected and analyzed. However, the data may not be specific to the researcher’s research questions or may be outdated. Therefore, it is essential to evaluate the quality and relevance of the data collected through secondary research carefully.
Difference Between Primary and Secondary Research
Here are some key differences between primary and secondary research:
| Aspect | Primary Research | Secondary Research |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To collect original data to answer specific research questions | To collect data that has already been collected by someone else |
| Data collection | Directly from the source, using specific research methods | From existing sources, such as academic journals, books, or online databases |
| Data relevance | Highly relevant to the research questions | May not be directly relevant to the research questions |
| Data quality | High quality and specific to the research purpose | May vary in quality and may not be specific to the research purpose |
| Time and resources | Time-consuming and expensive | Less time-consuming and less expensive |
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Qualitative Vs Quantitative Research

Clinical Research Vs Lab Research

Essay Vs Research Paper

Longitudinal Vs Cross-Sectional Research

Research Hypothesis Vs Null Hypothesis

Reliability Vs Validity

Primary Research: Methods and Best Practices

Introduction
What is the definition of primary research, what are examples of primary research, primary vs. secondary research, types of primary research, when to use primary research.
Conducting research involves two types of data: primary data and secondary data . While secondary research deals with existing data, primary research collects new data . Ultimately, the most appropriate type of research depends on which method is best suited to your research question .
While this article discusses the difference between primary and secondary research, the main focus is on primary research, the types of data collected through primary research, and considerations for researchers who conduct primary research.

Simply put, researchers conduct primary research to gather new information. When existing data cannot address the research inquiry at hand, the researcher usually needs to collect new data to meet their research objectives.
How do you identify primary research?
Primary research uses collected data that hasn't been previously documented. Primary research typically means collecting data straight from the source (e.g., interviewing a research participant, observing a cultural practice or phenomenon firsthand).
Note that other divides that you should also consider include that of collecting quantitative or qualitative data , and of conducting basic or applied research . Each of these dimensions informs and is informed by your research inquiry.
What are the advantages of primary research?
New data, particularly that which addresses a research gap, can contribute to a novel inquiry and prove compelling to the research audience. When a researcher conducts a literature review and generates a problem statement for their research, they can identify what new data needs to be collected and what primary research method can be used to collect it.
Primary research studies ultimately contribute to theoretical developments and novel insights that an analysis of existing data might not have identified. Research publications in some fields may place a premium on primary research for its potential to generate new scientific knowledge as a result.
What are the disadvantages of primary research?
Primary research is time-consuming and potentially expensive to conduct, considering the equipment and resources needed to collect new data as well as the time required to engage with the field and collect data.
Moreover, primary research relies on new data that has yet to be documented elsewhere, meaning that the research audience is less familiar with the primary data being presented. This might raise issues of transparency and research rigor (e.g., how does the audience know that the data they are shown is trustworthy?).

Primary research is common in various fields of research. Let's look at some typical examples of primary research in three different areas.
Education research
Teaching and learning is a field that relies on evidence-based data to make policy recommendations affecting teachers, learning materials, and even classroom requirements. As a result, there are countless methods for collecting relevant data on the various aspects of education.
Observations , interviews , and assessments are just some of the primary research methods that are employed when studying education contexts. Education research acknowledges the full variety of situated differences found in the diversity of learners and their schooling contexts. This makes collecting data that is relevant to the given context and research inquiry crucial to understanding teaching and learning.

Market research
Businesses often rely on primary research to understand the target market for their products and services. Since competing businesses tend not to share research on customer insights with each other, primary research collecting original data can be a necessity.
Focus groups , surveys , and user research are typical research tools employed by businesses. Within market research, the goal is typically to understand customers' preferences and use cases for specific products and services.

Cultural studies
Fields such as anthropology and sociology count on primary research for understanding cultures and communities. Ethnographic research acknowledges that thick description of cultures and phenomena is more meaningful than only generating universal theories, making the collection of primary data essential to understanding the full diversity of the social world.
Researchers examining culture often collect data through interviews, observations, and photovoice, among other research methods. These methods look at the social world through the eyes of the research participants to generate an immersive view of cultures and groups with which audiences may not be familiar.

Insights from data are at your fingertips with ATLAS.ti
See how our powerful data analysis interface can help you make sense of data. Start with a free trial.
Primary research data stands in contrast to secondary research data, which is any data that has been previously collected and documented. In some situations, existing data may be abundant and available, making secondary research a more feasible approach to generating theory and identifying key insights.
Secondary research methods are employed in all fields of research. Market researchers conduct secondary research when there is already existing data about a target market. In particular, secondary market research might look at previous trends in the popularity of products to make predictions about the demand for new products.
Scholarly researchers can use secondary sources such as corpora, news articles, and online videos to make assertions about language and culture. Analytical approaches such as discourse analysis and content analysis can be well suited to analyzing data collected through secondary research methods.
Ultimately, primary and secondary research go hand in hand. The main function of research in building knowledge does not necessarily depend on the use of primary data collection . Rather, it is a matter of whether data needs to be collected in order to address your research inquiry, or relevant data already exists and you can access it.
There are many research methods used to collect data for primary research. The research method that works best for you depends on what you are looking to do with your research project.
This section lists some of the common primary data collection methods that researchers rely on.
One-on-one interviews are useful for capturing perspectives from research participants. Direct interactions can tell researchers what perspectives their research participants have and the thinking behind those perspectives.
Interview research is a complex and detailed methodology that includes several types of interviews to suit various research inquiries. Researchers can choose between structured interviews , semi-structured interviews , and unstructured interviews , depending on the nature of interaction they are looking to establish.

Focus groups
Focus groups are discussions that involve multiple research participants and are led by a moderator. Similar to interviews, the primary goal is to gather information about people's perspectives. Yet focus groups are distinct, because they can capture how people interact and build meaning when discussing a particular topic.
Market researchers may consider conducting a focus group discussion when they want to know more about how a particular group feels about a product or service. Researchers in linguistics and anthropology might be interested in observing how a group of people construct meaning with each other.

Observations
In research involving naturalistic inquiry and the social world, the researcher can gather information directly from the field through observational research methods . Primary data takes the form of field notes , audio and video recordings , their resulting transcripts , and even images of objects of interest.
For quantitative research inquiries, observation entails measuring the amount of activity or the frequency of particular phenomena. Qualitative observations look for patterns in cultural or social practices and document significant events in the field.

When the objective is to capture perspectives from large numbers of people, surveys are a good research method for collecting novel data. In-person questionnaires and online surveys can be used to quickly collect data at scale.
Surveys are used for conducting primary research in both quantitative and qualitative research . The structure of survey questions provide data that can be measured quantitatively, while open-ended survey responses require qualitative data analysis .

Experiments
While the above methods emphasize or are involved with naturalistic inquiry, experiments are a different form of primary research that is far more controlled. When you want to understand the relationship between various elements in a certain context (e.g., the effect of water and fertilizer on plant growth), a controlled experiment is a typical research approach to empirically establish scientific knowledge.
Experiments focus on a specific set of factors from the research phenomenon to understand causal relationships between variables. Experiments are a common primary research method in physical sciences, but they are also extensively used in psychology, education, and political science, among other areas.

The decision to conduct a primary or secondary study is a question of whether existing data is sufficient to satisfy the research inquiry at hand. Where data does not exist, primary research should be conducted.
Consider an example research study regarding ideal teaching methods in elementary school contexts in a developing country in Asia. Just because there is abundant data on the same topic in elementary schools in Western countries does not preclude the possibility of novel theoretical developments in schools in Asia. This becomes particularly important if insights based on existing data from other contexts may not be applicable to the present context.
Note that this does not mean that a secondary research study is any less novel than a primary study. Indeed, many fields and methodologies rely extensively on analyzing existing data. For example, studies that employ discourse analysis and content analysis typically (though not always) rely on existing sources of data to facilitate understanding of language use in real-world situations.
As a result, the choice between primary and secondary research can be seen as more of a practical consideration than a matter of a study's potential contribution to scientific knowledge. Novelty in research is as much about the data collection as it is about the resulting analysis. If you require data for your study where none exists, then data from primary research is your best option.
Powerful data analysis at your fingertips with ATLAS.ti
Download a free trial to start making the most of your qualitative data.


Mindforceresearch Blog
- Market Research
Primary vs Secondary Research – Definitions, Differences, and Examples

Introduction
In market research , one normally has to make a choice: either primary research or secondary research methodologies. Both serve entirely different purposes and give different insights into the market or topic concerned. This article should indicate the differences clearly and, hopefully, would help the researcher or student to understand which approach best fits their needs and how they might be applied effectively in practice.
What is Primary Research?
Primary research involves the direct collection of new and original data, which is specifically tailored to the researcher’s unique requirements. This method is highly valued in both academic and commercial settings due to its ability to deliver highly relevant and specific information that addresses precise questions, a capability that secondary research often cannot match.
The primary data collection process is a proactive strategy that involves various methodologies to gather fresh data. Researchers choose primary research when they need data that are both specific and timely for their particular studies or business decisions. This approach is instrumental in filling gaps left by existing data, allowing for a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Advantages of Primary Research
The major advantages related to primary research are its accuracy and specificity. Information is generated at the time of the researcher’s query, and therefore, is of high value in the testing of new theories or products. The study variables can be controlled, and demographic groups targeted out by the researcher’s own efforts.
Examples of Primary Research
- Surveys: Deploying online or in-person questionnaires to gather consumer opinions.
- Interviews: One-on-one discussions to explore deep insights into individual behaviors or preferences.
- Experiments: Controlled setups to evaluate outcomes of specific actions or interventions.
Disadvantages of Primary Research
The drawbacks include higher costs and time requirements. Designing and implementing studies, collecting data, and analyzing results require significant resources. There’s also the risk of biased data if the sample isn’t adequately representative.
Primary Research Methods
Methods include qualitative approaches like focus groups and in-depth interviews, and quantitative methods such as surveys and controlled experiments. The choice of method depends largely on the research question and the nature of the data needed.
What is Secondary Research?
Secondary research, also known as desk research, involves the analysis of data that has already been collected and published by other researchers and institutions. This type of research is based on existing studies, reports, and analyses and is aimed at obtaining general information about a problem without the need for new data collection. It is cost-effective, quick, and thus the best option for gaining a broad overview. Secondary research is particularly useful for validating findings, identifying trends, and guiding hypothesis formation, making it a crucial tool for academic studies, business planning, and policy-making
Advantages of Secondary Research
It’s cost-effective and time efficient. Researchers can access a vast array of data quickly, which is useful for gaining background information or supporting primary research findings.
Disadvantages of Secondary Research
The main issues with secondary research are potential relevance and recency. The data might not be specifically pertinent to the researcher’s current questions, or it might be outdated, potentially leading to incorrect conclusions.
Examples of Secondary Research
- Literature Reviews: Synthesizing findings from multiple studies to establish a comprehensive understanding of a subject.
- Industry Reports: Utilizing published data to assess market trends and business opportunities.
- Statistical Analysis: Analyzing existing data sets to identify patterns or test hypotheses.
Secondary Research Methods
This type primarily involves desk research, such as literature reviews and analysis of data from various sources, including journals, books, and online databases.
Comparing Primary vs Secondary Research
The decision between primary and secondary research typically depends on the nature of the project goals, the resources available to the project, and the timetable for the project. Primary research is best when new, specific insights are needed, especially in the attempt to answer novel issues or targeted at answering issues within specific demographic groups. These are pieces of information that are directly collected through methods such as surveys, interviews, or observations. On the other hand, secondary research would be used for baseline understanding, preliminary data analysis, or in tight budgetary or time constraints. This is drawn from sources like academic studies, industry reports, or government documents, providing an inexpensive way to survey a broad topic.
Both primary and secondary research are integral to conducting any market research and are complementary to each other. By the researcher knowing the relative advantages and disadvantages of the two methods, he can strategically apply one over the other so as to effectively and efficiently answer the research question in hand.
What is the main difference between primary and secondary research?
The main difference between primary and secondary research is that primary research involves collecting original, first-hand data directly from the source, while secondary research involves analyzing and synthesizing existing data sources that have been previously collected by others.
When should primary research be used?
Primary research should be used when there is a need for specific, tailored, and in-depth insights that are not available through existing data sources. It is particularly useful when studying unique or niche markets, understanding consumer behavior, or testing new products or services.
What are some examples of secondary research sources?
Some examples of secondary research sources include published reports, academic papers, government statistics, industry publications, market research databases, and online repositories.
What are the advantages of secondary research?
The main advantages of secondary research include cost-effectiveness, time savings, access to a broad range of existing data sources, and the ability to identify historical trends and patterns.
Can primary and secondary research be combined?
Yes, primary and secondary research methods can be combined in a research project. Secondary research can provide a foundation and context for the study, while primary research can offer more specific and targeted insights.
What are some limitations of primary research?
Some limitations of primary research include being time-consuming and resource-intensive, potential for biases or errors in data collection and analysis, limited sample size and generalizability of results, and difficulty in accessing certain target populations.
How can researchers ensure the quality of secondary data sources?
To ensure the quality of secondary data sources, researchers should assess the credibility and reputation of the source, evaluate the data collection methods and sampling techniques used, check for potential biases or limitations, and cross-reference the data with other reliable sources.
What are some common primary research methods?
Common primary research methods include surveys (online, telephone, or in-person), interviews (one-on-one or focus groups), observations (ethnographic studies or field research), and experiments (A/B testing or product testing).
Explore More :
- Technological growth for transformation in global industries
- Objectives of Market Research Survey
- 5 Major Trends in the Healthcare Industry
- Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Related Posts

Exploring SD-WAN Technologies: A Closer Look
Confused About Blockchain? Here’s What You Need to Know
Primary vs secondary market research: types, sources and examples
Jun 9th, 2021

Types of primary research
There are two main types of primary market research: quantitative and qualitative. Both types of research are vital for obtaining different kinds of information.
- Quantitative market research deals with numerical data rather than consumers’ feelings, opinions, and attitudes. The process implies collecting large amounts of statistical points using surveys, polls, and questionnaires. The mathematical, statistical, and computational methods allow for gathering the data that researchers can further analyze to determine the patterns and averages, form predictions, and make generalizations. The purpose of quantitative market research is to determine the problem and understand its prevalence. Quantitative market research can provide a very accurate result that helps companies develop a clear picture of their objectives and how to reach them.
- Qualitative market research focuses on collecting behavioral, observational, and non-numerical data like audio, text, or video to gain insights into consumer opinions, motivations, or experiences. Qualitative market research involves open-ended questions and a small sample consisting of six to ten respondents and allows for an in-depth discussion of the topics. The primary methods used for conducting qualitative market research include focus groups and interviews.
Sources of primary research
Primary research sources are in-depth interviews, surveys, focus groups, social media monitoring, and questionnaires. Let’s discuss them in detail below:
- In-depth interviews are great for understanding how the customer group perceives a brand or product. In-depth interviews are interactive and usually have a flexible structure. These interviews are conducted by a trusted moderator who considers not just the respondent’s answers but also body language and general impression.
- Surveys help collect a large amount of information about the population’s characteristics and preferences. In the future, marketers can use this data to predict consumers’ behavior.
- Focus groups are the interviews of selected participants involving the representatives of the target audience. The group participants are selected according to specific criteria, such as location, age, socioeconomic status, etc.
- Questionnaires are research tool that includes a series of closed-ended or open-ended questions to obtain feedback from your customers. There are different types of questionnaires, such as computer, telephone, mail questionnaires.
- Hypothesis testing for existing products through A/B testing or multivariate testing allows for examining the price for different markets or different audiences, comparing web page design and conversion effectiveness, etc. Both methods have similar core mechanisms; however, multivariate testing compares a more significant number of variables and provides more information.
- MVP testing for new products is based on releasing a version of the product with a small number of first-priority features needed for early customers. Later, the customers can provide valuable feedback to improve the future versions of the product.
- Targeted social media monitoring helps determine the information about your company, your industry, and your competitors. This information involves all mentions of your brand, such as reviews, product questions, or service repair complaints.
Primary research allows for collecting data that has not been previously gathered, provides specific results that address the issues relevant for your company, and delivers up-to-date information. The other benefit of primary market research is the uniqueness of the data that competitors would not be able to access. Thus, you receive a competitive advantage. Due to the approaches of this method, you can research a small sample and then apply the results to the entire market. On the other hand, primary market research is often expensive, time-consuming, and requires face-to-face contact with customers.

Secondary market research is a kind of market research that relies on using data from secondary sources, which was not previously prepared specifically for the goals of current research. In other words, in secondary research, marketers gather and analyze the previously collected data to serve a purpose other than the purpose of their research. The secondary information is often acquired from industry and trade associations, government agencies, media agencies, industry-focused newsletters, magazines, and newspapers. This type of research is usually more cost-effective and accessible than primary market research.
Types of secondary research
There are two types of secondary market research: secondary market research from internal sources and secondary market research from external sources.
- Internal data. Internal data can be found in the databases of the company and used for future reference purposes. A company’s internal data includes customer account information, product usage data, sales records, or previously prepared research reports. There are also records of previous advertising and marketing campaigns, departmental records, etc.
- External data. External data is initially prepared by people outside the current company environment, such as data from competitors, journals and magazines, industry surveys, and market reports.
Sources of secondary research
As well as with primary research, secondary research may also use lots of different sources of information. Below are some of the most widely used.
- Sales data is a valuable source of information for secondary market research. Every company collects data concerning everyday operations, delivered orders, invoices, and returned goods. This information is handy for marketers because it allows gathering insights into sales by territory, customer type, average sales by salesperson, prices, discounts, and other data.
- Financial data allows for estimating the efficiency of marketing operations. It includes the production costs, storing, transportation, and marketing costs. It can also supply insights into which products or services bring you more significant profits or drive your business into the red.
- Governmental and local statistical data. Many governmental, regional and municipal organizations collect data that businesses and non-profits can use for market research purposes. This information includes demographic data, economic data, trade statistics, and production statistics. For example, you can find volumes of US-focused data on data.gov , while for European Union statistics, you can explore the official site of Eurostat .
- Trade associations often provide free and paid reports to inform professionals about the situation in the economic sector.
- Specialized journals and media regularly publish news, research, press releases, and professional articles, which can be excellent sources of up-to-date secondary data.
- Commercial marketing research data is collected by specialized research organizations that resell it to other companies. The data gathered by these companies concerns the consumer population, attitudes, trends and behaviors, online and offline purchases.
- Search engine results are a good source of free and commercially available data.
- Competitor research. You can acquire information about competitors from different sources, such as their websites, review sites, and media publications. This approach enables you to develop a profound understanding of how market participants and clients perceive a particular company.
Secondary market research is a perfect basis for primary research as it helps determine and predict the latter’s effectiveness and suitability. The information from government sources, libraries, and media is reliable, extensive, and covers many issues. The other advantages of secondary market research are low cost, time-effectiveness, and the opportunity to obtain a broad spectrum of free data in a shorter time than primary research.
The disadvantages of secondary market research are the lack of quality and accuracy of data collected by a third party. The information provided by secondary research is not specific and not always recent enough. Besides, the data is available for many companies, so it deprives your company of a competitive advantage.
Market research will help you reduce the risk of making business decisions and determine the pitfalls before launching the new product. We will provide several examples to demonstrate how companies can use market research to identify and solve business challenges in practice.
The world-famous coffee company conducts market research in many ways, including primary research methods, such as consumer feedback, in-store product testing, and social media monitoring. In 2008, Starbucks even created a specialized platform, My Starbucks Idea , where the customers can provide their ideas about new offerings or changes to the existing products.
The corporation also applies the social media monitoring method and collects feedback from different platforms, including Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Reddit , to improve the products. Starbucks tests the new ideas in selected stores to understand the feasibility of making some changes before the official launch.
The company applies secondary market research methods to shape the new product lines. Starbucks gathers data from the market research companies and analyzes the data from the stores. Due to the feedback on My Starbucks Idea and combined market research, Starbucks successfully launched dairy-free milk alternatives in European and US stores.
Primary research methods: consumer feedback, in-store product testing, social media monitoring.
Secondary research methods: social media monitoring, competitor monitoring, existing data from market research providers.
Ecommerce market research into new product launch
If you are going to launch an e-commerce platform or introduce a new product to the existing store, conducting market research may bring the needed transparency into this business decision prior to moving forward with it. Firstly, it is vital to determine the market size for the business or the product. Then you will need several pieces of information concerning statistics and trends in your industry, consumer behavior, and current demand for your product.
To discover information about the industry size, trends, and growth rates, you can apply secondary market research methods and dig into the industry articles and search for information from marketing companies about the things people tend to buy online. The other helpful source will be market research reports.
The further step is to understand the needs of your potential customers, their socioeconomic and geographic conditions. The perfect way to get this information is to perform primary research and conduct customer surveys. You can start with specialized forums, Facebook groups, or other social media channels.
For example, if you are launching an online clothing store, you can conduct the online survey using Google Forms, Google Surveys or TypeForm and target specific customer segments. You can include questions about age, location, income, favorite brands, and stores where these people typically buy clothes.
You can also use the form to inquire if some of the surveyed customers would be willing to participate in in-depth interviews. For in-depth interviews, prepare a list of open-ended questions, which can facilitate your discussion with each interviewee.
Primary research methods: customer surveys, questionnaires, in-depth interviews.
Secondary research methods: industry articles, competitor research, market research reports.
SaaS market research for new solution launch
Before the new SaaS product launch, you need to conduct market research and analysis to understand the competition and customer preferences and dislikes. First, you can make a list of existing players in the segment. You can monitor social media for mentions of each competitor to understand what their clients are saying about the solution, product features, and functionality, customer service to find opportunities, which a new product can explore on the market. In addition to social media, you can use specialized review platforms, such as Capterra or TrustRadius .
As the next step in analyzing your competitors, you can gather data about their online performance. With Ahrefs , you can get information on how your competitors rank on Google. SimilarWeb allows you to analyze your competitors’ websites and see engagement rate, traffic ranking, keyword ranking, and other audience metrics. Besides, you can conduct secondary market research and find research on businesses in your industry with the help of Google Scholar .
You can expand your market research by finding information about your potential customers. Continuing with the methods of secondary research, you can gather data about your target audience’s behavior. With the help of a business account on Facebook, you can collect information about the demographics, including gender, age, location, activity, purchases, and design customer personas.
If you’re building a unique product in the segment with low competition, you can explore Product Hunt to see if anyone has recently created similar products. Product hunt can show you if similar products have received positive feedback or ideas for improvement on top of how you envision your future solution.
As the final stage of your exploration, you can start developing the basics of your future solution to attract your potential audience. The simplest way to do it is by making a landing page, which describes your future product and allows visitors to subscribe to future releases and updates. This is how Dropbox started back in 2007. If this option is not sufficient for you, you can develop an MVP to provide users with initial functionality to test if they will be interested in signing up. Of course, this approach would give you the most significant volume of feedback, although it’s the most expensive one to undertake.
Primary research methods: product landing page, minimum viable product, Product Hunt launch.
Secondary research methods: social media monitoring, specialized industry-focused websites, social media analytics tools.
You can perform market research at any stage of your business life cycle, starting from pre-launch. Primary market research allows for evaluating the competition within the market, understanding the competitors’ quality of service, and discovering their communication channels. With the help of secondary market research, you can analyze the existing surveys and studies concerning your industry, read newspaper reports, explore company reports data and government data. The overall market research usually consists of the following steps:
Step 1. Define the goals of the research
The first stage of comprehensive market research is to define the central problem and research objectives. You will also need to define the purpose of the study, what information is required, and find relevant background data. This step includes interviews with industry experts and discussions with the decision-makers.
Step 2. Secondary research
At the second stage, you need to conduct secondary research and analyze all the secondary data sources on the target segment. The goal of this step is to compare the information and create a high-level overview.
Step 3. Primary research
Once you have completed the secondary research and collected the available information, you can move to primary research. You need to start from the most cost-efficient methods of primary research that include paper questionnaires, online surveys, phone interviews, and face-to-face interviews.
Social media is an excellent source for primary research. You have the opportunity to analyze the large amounts of data provided by different people on a variety of platforms. You can save money by selecting the students as focus groups or target audiences.
Step 4. The concluding stage of research
If you meet the research objectives by completing the previous steps, you can finalize the market research. In some cases, secondary research may already provide you enough information to complete the research. Other times, there is a lack of data in secondary sources, so you will have to conduct primary research.
Once you feel like you have gathered enough data to answer the initial research question, prepare a report, which will provide a summary of findings. Even if you’re doing it for your own purposes, putting it in writing helps build a comprehensive overview of the findings and research results. You can sometimes find out that you have new questions at this stage, which need to be researched using the same methodology. Or, hopefully, you’ve been able to answer all your questions - now comes the time to act on it!

- Marketing Strategy & Branding
- Content Marketing & SEO
- Product Focused Marketing
- Digital Experience Design
- Marketing Automation
- Video Production
© 2023 Awware

- Updated on July 7, 2020
- By Market Research Guy
- In Overviews
Primary vs. Secondary Market Research: What’s the Difference?
Market research can be classified as either primary or secondary research. The difference is quite simple, yet there is often confusion around this topic.
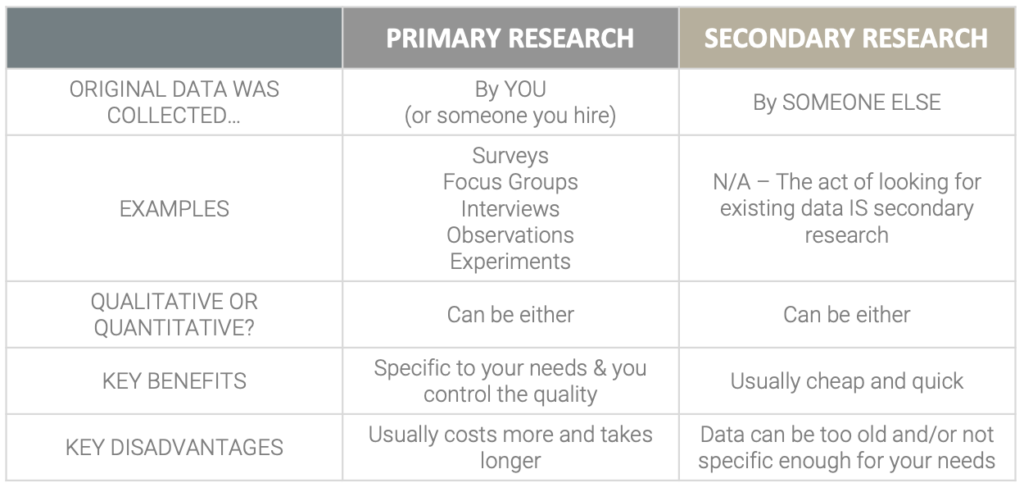
In a nutshell, primary research is original research conducted by you (or someone you hire) to collect data specifically for your current objective. You might conduct a survey, run an interview or a focus group, observe behavior, or do an experiment. You are going to be the person who obtains this raw data directly and it will be collected specifically for your current research need. Conversely, secondary research involves searching for existing data that was originally collected by someone else . You might look in journals, libraries, or go to online sources like the US census. You will apply what you find to your personal research problem, but the data you are finding was not originally collected by you, nor was it obtained for the purpose you are using it for. I hope that makes sense. If not, read on for some examples and a little more detail.
Secondary Market Research Sometimes called “desk research” (because it can be done from behind a desk), this technique involves research and analysis of existing research and data; hence the name, “secondary research.” Conducting secondary research may not be so glamorous, but it often makes a lot of sense of start here. Why? Well, for one thing, secondary research is often free . Second, data is increasingly available thanks to the Internet; the US Census and the CDC (health data), for example, are two great sources of data that has already been collected by someone else. Your job as a secondary researcher is to seek out these sources, organize and apply the data to your specific project, whether it’s market sizing or segmentation or whatever it may be, and then summarize/visualize it in a way that makes sense to you and your audience. So, that’s what secondary market research is all about. The downside, of course, is that you may not be able to find secondary market research information specific enough (or recent enough) for your objectives. If that’s the case, you’ll need to conduct your own primary research (hey, what a perfect segway!).
Sources of Secondary Data Secondary data comes in all sorts of shapes and sizes. There are plenty of raw data sources like the US Census , Data.gov , the stock market , and countless others . Internal company data like customer details, sales figures, employee timecards, etc. can also be considered secondary data. Published articles, including peer-reviewed journals, newspapers, magazines, and even blog postings like this count as secondary data sources. Don’t forget legal documents like patents and company annual filings. Social media data is a new source of secondary data. For example, the New York Times collected Twitter traffic during the 2009 Super Bowl and produced this stunning visualization of comments throughout the game. Secondary data is all around us and is more accessible than even. It is increasingly possible to obtain behavioral data from secondary sources, which can be more powerful and reliable than self-reported data (via surveys and focus groups).
Here’s one more incredible example of what can be done with secondary data–this time using publicly available blog posts. The video below is a talk by Jonathan Harris of the “We Feel Fine” project. If you have a moment, check it out.
Primary Market Research Primary research is research that is conducted by you, or someone you pay to do original research on your behalf. In the case of primary research, you are generating your own data from scratch as opposed to finding other people’s data. You might choose to gather this data by running a survey, interviewing people, observing behavior, or by using some other market research method . Here’s a quick example that explains primary vs. secondary market research.
Both primary and secondary research can be either qualitative or quantitative in nature. I hope this tutorial on the differences between primary and secondary research has been helpful. If I missed something or if you have something to add, please do so with a comment below.
7 thoughts on “Primary vs. Secondary Market Research: What’s the Difference?”
Good info, thoroughly enjoyed it.
I understand very well
I am always with you thank you very much for helping me with this project
I appreciate the information. Thank you.
i appreciate the information. thank you
i understand very well
Leave a reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
You may also like

An Overview of Market Research Methods
There are several ways to categorize the various market research methods. The vast majority of techniques fit into one of… Read more
Recent comments
3D Virtual Shop Research
Computer-driven 3D virtual shop research is becoming increasingly common amongst retailers and consumer product manufacturers. Done properly, the tests can… Read more

Secondary Research Guide: Definition, Methods, Examples
Apr 3, 2024
8 min. read
The internet has vastly expanded our access to information, allowing us to learn almost anything about everything. But not all market research is created equal , and this secondary research guide explains why.
There are two key ways to do research. One is to test your own ideas, make your own observations, and collect your own data to derive conclusions. The other is to use secondary research — where someone else has done most of the heavy lifting for you.
Here’s an overview of secondary research and the value it brings to data-driven businesses.
Secondary Research Definition: What Is Secondary Research?
Primary vs Secondary Market Research
What Are Secondary Research Methods?
Advantages of secondary research, disadvantages of secondary research, best practices for secondary research, how to conduct secondary research with meltwater.
Secondary research definition: The process of collecting information from existing sources and data that have already been analyzed by others.
Secondary research (aka desk research or complementary research ) provides a foundation to help you understand a topic, with the goal of building on existing knowledge. They often cover the same information as primary sources, but they add a layer of analysis and explanation to them.

Users can choose from several secondary research types and sources, including:
- Journal articles
- Research papers
With secondary sources, users can draw insights, detect trends , and validate findings to jumpstart their research efforts.
Primary vs. Secondary Market Research
We’ve touched a little on primary research , but it’s essential to understand exactly how primary and secondary research are unique.

Think of primary research as the “thing” itself, and secondary research as the analysis of the “thing,” like these primary and secondary research examples:
- An expert gives an interview (primary research) and a marketer uses that interview to write an article (secondary research).
- A company conducts a consumer satisfaction survey (primary research) and a business analyst uses the survey data to write a market trend report (secondary research).
- A marketing team launches a new advertising campaign across various platforms (primary research) and a marketing research firm, like Meltwater for market research , compiles the campaign performance data to benchmark against industry standards (secondary research).
In other words, primary sources make original contributions to a topic or issue, while secondary sources analyze, synthesize, or interpret primary sources.
Both are necessary when optimizing a business, gaining a competitive edge , improving marketing, or understanding consumer trends that may impact your business.
Secondary research methods focus on analyzing existing data rather than collecting primary data . Common examples of secondary research methods include:
- Literature review . Researchers analyze and synthesize existing literature (e.g., white papers, research papers, articles) to find knowledge gaps and build on current findings.
- Content analysis . Researchers review media sources and published content to find meaningful patterns and trends.
- AI-powered secondary research . Platforms like Meltwater for market research analyze vast amounts of complex data and use AI technologies like natural language processing and machine learning to turn data into contextual insights.
Researchers today have access to more secondary research companies and market research tools and technology than ever before, allowing them to streamline their efforts and improve their findings.
Want to see how Meltwater can complement your secondary market research efforts? Simply fill out the form at the bottom of this post, and we'll be in touch.
Conducting secondary research offers benefits in every job function and use case, from marketing to the C-suite. Here are a few advantages you can expect.
Cost and time efficiency
Using existing research saves you time and money compared to conducting primary research. Secondary data is readily available and easily accessible via libraries, free publications, or the Internet. This is particularly advantageous when you face time constraints or when a project requires a large amount of data and research.
Access to large datasets
Secondary data gives you access to larger data sets and sample sizes compared to what primary methods may produce. Larger sample sizes can improve the statistical power of the study and add more credibility to your findings.
Ability to analyze trends and patterns
Using larger sample sizes, researchers have more opportunities to find and analyze trends and patterns. The more data that supports a trend or pattern, the more trustworthy the trend becomes and the more useful for making decisions.
Historical context
Using a combination of older and recent data allows researchers to gain historical context about patterns and trends. Learning what’s happened before can help decision-makers gain a better current understanding and improve how they approach a problem or project.
Basis for further research
Ideally, you’ll use secondary research to further other efforts . Secondary sources help to identify knowledge gaps, highlight areas for improvement, or conduct deeper investigations.
Tip: Learn how to use Meltwater as a research tool and how Meltwater uses AI.
Secondary research comes with a few drawbacks, though these aren’t necessarily deal breakers when deciding to use secondary sources.
Reliability concerns
Researchers don’t always know where the data comes from or how it’s collected, which can lead to reliability concerns. They don’t control the initial process, nor do they always know the original purpose for collecting the data, both of which can lead to skewed results.
Potential bias
The original data collectors may have a specific agenda when doing their primary research, which may lead to biased findings. Evaluating the credibility and integrity of secondary data sources can prove difficult.
Outdated information
Secondary sources may contain outdated information, especially when dealing with rapidly evolving trends or fields. Using outdated information can lead to inaccurate conclusions and widen knowledge gaps.
Limitations in customization
Relying on secondary data means being at the mercy of what’s already published. It doesn’t consider your specific use cases, which limits you as to how you can customize and use the data.
A lack of relevance
Secondary research rarely holds all the answers you need, at least from a single source. You typically need multiple secondary sources to piece together a narrative, and even then you might not find the specific information you need.
| Advantages of Secondary Research | Disadvantages of Secondary Research |
|---|---|
| Cost and time efficiency | Reliability concerns |
| Access to large data sets | Potential bias |
| Ability to analyze trends and patterns | Outdated information |
| Historical context | Limitations in customization |
| Basis for further research | A lack of relevance |
To make secondary market research your new best friend, you’ll need to think critically about its strengths and find ways to overcome its weaknesses. Let’s review some best practices to use secondary research to its fullest potential.
Identify credible sources for secondary research
To overcome the challenges of bias, accuracy, and reliability, choose secondary sources that have a demonstrated history of excellence . For example, an article published in a medical journal naturally has more credibility than a blog post on a little-known website.

Assess credibility based on peer reviews, author expertise, sampling techniques, publication reputation, and data collection methodologies. Cross-reference the data with other sources to gain a general consensus of truth.
The more credibility “factors” a source has, the more confidently you can rely on it.
Evaluate the quality and relevance of secondary data
You can gauge the quality of the data by asking simple questions:
- How complete is the data?
- How old is the data?
- Is this data relevant to my needs?
- Does the data come from a known, trustworthy source?
It’s best to focus on data that aligns with your research objectives. Knowing the questions you want to answer and the outcomes you want to achieve ahead of time helps you focus only on data that offers meaningful insights.
Document your sources
If you’re sharing secondary data with others, it’s essential to document your sources to gain others’ trust. They don’t have the benefit of being “in the trenches” with you during your research, and sharing your sources can add credibility to your findings and gain instant buy-in.
Secondary market research offers an efficient, cost-effective way to learn more about a topic or trend, providing a comprehensive understanding of the customer journey . Compared to primary research, users can gain broader insights, analyze trends and patterns, and gain a solid foundation for further exploration by using secondary sources.
Meltwater for market research speeds up the time to value in using secondary research with AI-powered insights, enhancing your understanding of the customer journey. Using natural language processing, machine learning, and trusted data science processes, Meltwater helps you find relevant data and automatically surfaces insights to help you understand its significance. Our solution identifies hidden connections between data points you might not know to look for and spells out what the data means, allowing you to make better decisions based on accurate conclusions. Learn more about Meltwater's power as a secondary research solution when you request a demo by filling out the form below:
Continue Reading
How To Do Market Research: Definition, Types, Methods

What Are Consumer Insights? Meaning, Examples, Strategy

Market Intelligence 101: What It Is & How To Use It

The 13 Best Market Research Tools

Consumer Intelligence: Definition & Examples
9 Top Consumer Insights Tools & Companies

What Is Desk Research? Meaning, Methodology, Examples
Top Secondary Market Research Companies | Desk Research Companies
- Technical Support
- Technical Papers
- Knowledge Base
- Question Library
Call our friendly, no-pressure support team.
Secondary Research: Definition, Methods, Sources, Examples, and More
Table of Contents
What is Secondary Research? Secondary Research Meaning
Secondary research involves the analysis and synthesis of existing data and information that has been previously collected and published by others. This method contrasts with primary research , which entails the direct collection of original data from sources like surveys, interviews, and ethnographic studies.
The essence of secondary research lies in its efficiency and accessibility. Researchers who leverage secondary sources, including books, scholarly articles, government reports, and market analyses, gather valuable insights without the need for time-consuming and costly data collection efforts. This approach is particularly vital in marketing research, where understanding broad market trends and consumer behaviors is essential, yet often constrained by budgets and timelines. Secondary research serves as a fundamental step in the research process, providing a solid foundation upon which additional, targeted research can be built.
Secondary research enables researchers to quickly grasp the landscape of existing knowledge, identify gaps in the literature, and refine their research questions or business strategies accordingly. In marketing research, for instance, secondary research aids in understanding competitive landscapes, identifying market trends, and benchmarking against industry standards, thereby guiding strategic decision-making.
Get Started with Market Research Today!
Ready for your next market research study? Get access to our free survey research tool. In just a few minutes, you can create powerful surveys with our easy-to-use interface.
Start Market Research for Free or Request a Product Tour
When to Use Secondary Research
Choosing between secondary and primary research methods depends significantly on the objectives of your study or project. Secondary research is particularly beneficial in the initial stages of research planning and strategy, offering a broad understanding of the topic at hand and helping to pinpoint areas that may require more in-depth investigation through primary methods.
In academic contexts, secondary research is often used to build a theoretical foundation for a study, allowing researchers to position their work within the existing body of knowledge. Professionally, it serves as a cost-effective way to inform business strategies, market analyses, and policy development, providing insights into industry trends, consumer behaviors, and competitive landscapes.
Combining secondary research with primary research methods enhances the comprehensiveness and validity of research findings. For example, secondary research might reveal general trends in consumer behavior, while subsequent primary research could delve into specific consumer motivations and preferences, offering a more nuanced understanding of the market.
Key considerations for integrating secondary research into your research planning and strategy include:
- Research Objectives : Clearly defining what you aim to discover or decide based on your research.
- Availability of Data : Assessing the extent and relevance of existing data related to your research question.
- Budget and Time Constraints : Considering the resources available for conducting research, including time, money, and personnel.
- Research Scope : Determining the breadth and depth of the information needed to meet your research objectives.
Secondary research is a powerful tool when used strategically, providing a cost-effective, efficient way to gather insights and inform decision-making processes across academic and professional contexts.
How to Conduct Secondary Research
Conducting secondary research is a systematic process that involves several key steps to ensure the relevance, accuracy, and utility of the information gathered. Here's a step-by-step guide to effective secondary research:
- Identifying Research Objectives, Topics, and Questions : Begin with a clear understanding of what you aim to achieve with your research. This includes defining your research objectives, topics, and specific questions you seek to answer. This clarity guides the entire research process, ensuring that you remain focused on relevant information.
- Finding Relevant Data Sources : Search for secondary data sources that are likely to contain the information you need. This involves exploring a variety of sources such as academic journals, industry reports, government databases, and news archives. Prioritize sources known for their credibility and authority in the subject matter.
- Collecting and Verifying Existing Data : Once you've identified potential sources, collect the data that pertains to your research questions. Pay close attention to the publication date, authorship, and the methodology used in collecting the original data to ensure its relevance and reliability.
- Data Compilation and Analysis : Compile the collected data in a structured format that allows for analysis. Employ analytical methods suited to your research objectives, such as trend analysis, comparative analysis, or thematic analysis, to draw insights from the data.
The success of secondary research hinges on the critical evaluation of sources for their credibility, relevance, and timeliness. It's essential to approach this process with a discerning eye, acknowledging the limitations of secondary data and the potential need for further investigation through primary research.

Types of Secondary Research Methods with Examples
Secondary research methods offer a range of approaches for leveraging existing data, each providing value in extracting insights relevant to various business and academic needs. Understanding the unique advantages of each method can guide researchers in choosing the most appropriate approach for their specific objectives.
Literature Reviews
Literature reviews synthesize existing research and publications to identify trends, gaps, and consensus within a field of study. This method provides a comprehensive overview of what is already known about a topic, saving time and resources by building on existing knowledge rather than starting from scratch.
Real-World Example : A marketing firm conducting a literature review on consumer behavior in the digital age might uncover a trend towards increased mobile shopping. This insight leads to a strategic recommendation for a retail client to prioritize mobile app development and optimize their online store for mobile users, directly impacting the client's digital marketing strategy.
Data Mining
Data mining involves analyzing large sets of data to discover patterns, correlations, or trends that are not immediately apparent. This method can uncover hidden insights from the data that businesses can use to inform decision-making, such as identifying new market opportunities or optimizing operational efficiencies.
Real-World Example : Through data mining of customer purchase histories and online behavior data, a retail company identifies a previously unnoticed correlation between the purchase of certain products and the time of year. Utilizing this insight, the company adjusts its inventory levels and marketing campaigns seasonally, significantly boosting sales and customer satisfaction.
Meta-Analysis
Meta-analysis aggregates and systematically analyzes results from multiple studies to draw general conclusions about a research question. This method provides a high level of evidence by combining findings, offering a powerful tool for making informed decisions based on a broader range of data than any single study could provide.
Real-World Example : A pharmaceutical company uses meta-analysis to combine findings from various clinical trials of a new drug. The meta-analysis reveals a statistically significant benefit of the drug that was not conclusive in individual studies. This insight supports the company's application for regulatory approval and guides the development of marketing strategies targeting specific patient demographics.
Data Analysis
Secondary data analysis applies statistical techniques to analyze existing datasets, offering a cost-effective way to gain insights without the need for new data collection. This method can identify trends, patterns, and relationships that inform strategic planning and decision-making.
Real-World Example : An investment firm analyzes historical economic data and stock market trends using secondary data analysis. They identify a recurring pattern preceding market downturns. By applying this insight to their investment strategy, the firm successfully mitigates risk and enhances portfolio performance for their clients.
Content Analysis
Content analysis systematically examines the content of communication mediums to understand messages, themes, or biases . This qualitative method can reveal insights into public opinion, media representation, and communication strategies, offering valuable information for marketing, public relations, and media strategies.
Real-World Example : A technology company employs content analysis to review online customer reviews and social media mentions of its products. The analysis uncovers a common concern among customers about the usability of a product feature. Responding to this insight, the company revises its product design and launches a targeted communication campaign to address the concerns, improving customer satisfaction and brand perception.
Historical Research
Historical research examines past records and documents to understand historical contexts and trends, offering insights that can inform future predictions, strategy development, and understanding of long-term changes. This method is particularly valuable for understanding the evolution of markets, industries, or consumer behaviors over time.
Real-World Example : A consultancy specializing in sustainable business practices conducts historical research into the adoption of green technologies in the automotive industry. The research identifies key drivers and barriers to adoption over the decades. Leveraging these insights, the consultancy advises new green tech startups on strategies to overcome market resistance and capitalize on drivers of adoption, significantly impacting their market entry strategy.
Each of these secondary research methods provides distinct advantages and can yield valuable insights for businesses and researchers. By carefully selecting and applying the most suitable method(s), organizations can enhance their understanding of complex issues, inform strategic decisions, and achieve competitive advantage.
Free Survey Maker Tool
Get access to our free and intuitive survey maker. In just a few minutes, you can create powerful surveys with its easy-to-use interface.
Try our Free Survey Maker or Request a Product Tour
Examples of Secondary Sources in Research
Secondary sources are crucial for researchers across disciplines, offering a wealth of information that can provide insights, support hypotheses, and inform strategies. Understanding the unique value of different types of secondary sources can help researchers effectively harness this wealth of information. Below, we explore various secondary sources, highlighting their unique contributions and providing real-world examples of how they can yield valuable business insights.
Books provide comprehensive coverage of a topic, offering depth and context that shorter pieces might miss. They are particularly useful for gaining a thorough understanding of a subject's historical background and theoretical framework.
Example : A corporation exploring the feasibility of entering a new international market utilizes books on the country's cultural and economic history. This deep dive helps the company understand market nuances, leading to a tailored market entry strategy that aligns with local consumer preferences and cultural norms.
Scholarly Journals
Scholarly journals offer peer-reviewed, cutting-edge research findings, making them invaluable for staying abreast of the latest developments in a field. They provide detailed methodologies, rigorous data analysis, and discussions of findings in a specific area of study.
Example : An investment firm relies on scholarly articles to understand recent advancements in financial technology. Discovering research on blockchain's impact on transaction security and efficiency, the firm decides to invest in fintech startups specializing in blockchain technology, positioning itself ahead in the market.
Government Reports
Government reports deliver authoritative data on a wide range of topics, including economic indicators, demographic trends, and regulatory guidelines. Their reliability and the breadth of topics covered make them an essential resource for informed decision-making.
Example : A healthcare provider examines government health reports to identify trends in public health issues. Spotting an increase in lifestyle-related diseases, the provider expands its wellness programs, directly addressing the growing demand for preventive care services.
Market Research Reports
Market research reports provide insights into industry trends, consumer behavior, and competitive landscapes. These reports are invaluable for making informed business decisions, from product development to marketing strategies.
Example : A consumer goods company reviews market research reports to analyze trends in eco-friendly packaging. Learning about the positive consumer response to sustainable packaging, the company redesigns its packaging to be more environmentally friendly, resulting in increased brand loyalty and market share.
White Papers
White papers offer in-depth analysis or arguments on specific issues, often highlighting solutions or innovations. They are a key resource for understanding complex problems, technological advancements, and industry best practices.
Example : A technology firm exploring the implementation of AI in customer service operations consults white papers on AI applications. Insights from these papers guide the development of an AI-powered customer service chatbot, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Private Company Data
Data from private companies, such as annual reports or case studies, provides insight into business strategies, performance metrics, and operational challenges. This information can be instrumental in benchmarking and strategic planning.
Example : By analyzing competitor annual reports, a retail chain identifies a gap in the market for affordable luxury products. This insight leads to the launch of a new product line that successfully captures this underserved segment, boosting the company's revenue and market positioning.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Secondary Research
Secondary research offers a foundation upon which organizations can build their knowledge base, informing everything from strategic planning to day-to-day decision-making. However, like any method, it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these can help researchers and businesses make the most of secondary research while being mindful of its limitations.
Advantages of Secondary Research
- Cost-Effectiveness : Secondary research is often less expensive than primary research, as it involves the analysis of existing data, eliminating the need for costly data collection processes like surveys or experiments.
- Time Efficiency : Accessing and analyzing existing data is generally faster than conducting primary research, allowing organizations to make timely decisions based on available information.
- Broad Scope of Data : Secondary research provides access to a wide range of data across different geographies and time periods, enabling comprehensive market analyses and trend identification.
- Basis for Primary Research : It can serve as a preliminary step to identify gaps in existing research, helping to pinpoint areas where primary research is needed.
Disadvantages of Secondary Research
- Relevance and Specificity : Existing data may not perfectly align with the current research objectives, leading to potential mismatches in relevance and specificity.
- Data Quality and Accuracy : The quality and accuracy of secondary data can vary, depending on the source. Researchers must critically assess the credibility of their sources to ensure the reliability of their findings.
- Timeliness : Data may be outdated, especially in fast-moving sectors where recent information is crucial for making informed decisions.
- Limited Control Over Data : Researchers have no control over how data was collected and processed, which may affect its suitability for their specific research needs.
Secondary research, when approached with an understanding of its strengths and weaknesses, has the potential be a powerful tool. By effectively navigating its advantages and limitations, businesses can lay a solid foundation for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Primary vs. Secondary Research: A Comparative Analysis
When undertaking a research project, understanding the distinction between primary and secondary research is pivotal. Both forms of research serve their own purposes and can complement each other in providing a comprehensive overview of a given topic.
What is Primary Research?
Primary research involves the collection of original data directly from sources. This method is firsthand and is specific to the researcher's questions or hypotheses.
The main advantage of primary research is its specificity and relevancy to the particular issue or question at hand. It offers up-to-date and highly relevant data that is directly applicable to the research objectives.
Example : A company planning to launch a new beverage product conducts focus groups and survey research to understand consumer preferences. Through this process, they gather firsthand insights on flavors, packaging, and pricing preferences specific to their target market.
What is Secondary Research?
Secondary research involves the analysis of existing information compiled and collected by others. It includes studies, reports, and data from government agencies, trade associations, and other organizations.
Secondary research provides a broad understanding of the topic at hand, offering insights that can help frame primary research. It is cost-effective and time-saving, as it leverages already available data.
Example : The same company explores industry reports, academic research, and market analyses to understand broader market trends, competitor strategies, and consumer behavior within the beverage industry.
Comparative Analysis
|
|
|
|
| Data Type | Original, firsthand data | Pre-existing, compiled data |
| Collection Method | Surveys, interviews, observations | Analysis of existing sources |
| Cost and Time | Higher cost, more time-consuming | Lower cost, less time-consuming |
| Specificity | High specificity to research question | General overview of the topic |
| Application | In-depth analysis of specific issues | Preliminary understanding, context setting |
Synergistic Use in Research
The most effective research strategies often involve a blend of both primary and secondary research. Secondary research can serve as a foundation, helping to inform the development of primary research by identifying gaps in existing knowledge and refining research questions.
Understanding the distinct roles and benefits of primary and secondary research is crucial for any successful research project. By effectively leveraging both types of research, researchers can gain a deeper, more nuanced understanding of their subject matter, leading to more informed decisions and strategies. Remember, the choice between primary and secondary research should be guided by your research objectives, resources, and the specificity of information required.
Sawtooth Software
3210 N Canyon Rd Ste 202
Provo UT 84604-6508
United States of America
Support: [email protected]
Consulting: [email protected]
Sales: [email protected]
Products & Services
Support & Resources

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
What is Secondary Research? Types, Methods, Examples
Appinio Research · 20.09.2023 · 13min read

Have you ever wondered how researchers gather valuable insights without conducting new experiments or surveys? That's where secondary research steps in—a powerful approach that allows us to explore existing data and information others collect.
Whether you're a student, a professional, or someone seeking to make informed decisions, understanding the art of secondary research opens doors to a wealth of knowledge.
What is Secondary Research?
Secondary Research refers to the process of gathering and analyzing existing data, information, and knowledge that has been previously collected and compiled by others. This approach allows researchers to leverage available sources, such as articles, reports, and databases, to gain insights, validate hypotheses, and make informed decisions without collecting new data.
Benefits of Secondary Research
Secondary research offers a range of advantages that can significantly enhance your research process and the quality of your findings.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: Secondary research saves time and resources by utilizing existing data sources, eliminating the need for data collection from scratch.
- Wide Range of Data: Secondary research provides access to vast information from various sources, allowing for comprehensive analysis.
- Historical Perspective: Examining past research helps identify trends, changes, and long-term patterns that might not be immediately apparent.
- Reduced Bias: As data is collected by others, there's often less inherent bias than in conducting primary research, where biases might affect data collection.
- Support for Primary Research: Secondary research can lay the foundation for primary research by providing context and insights into gaps in existing knowledge.
- Comparative Analysis : By integrating data from multiple sources, you can conduct robust comparative analyses for more accurate conclusions.
- Benchmarking and Validation: Secondary research aids in benchmarking performance against industry standards and validating hypotheses.
Primary Research vs. Secondary Research
When it comes to research methodologies, primary and secondary research each have their distinct characteristics and advantages. Here's a brief comparison to help you understand the differences.
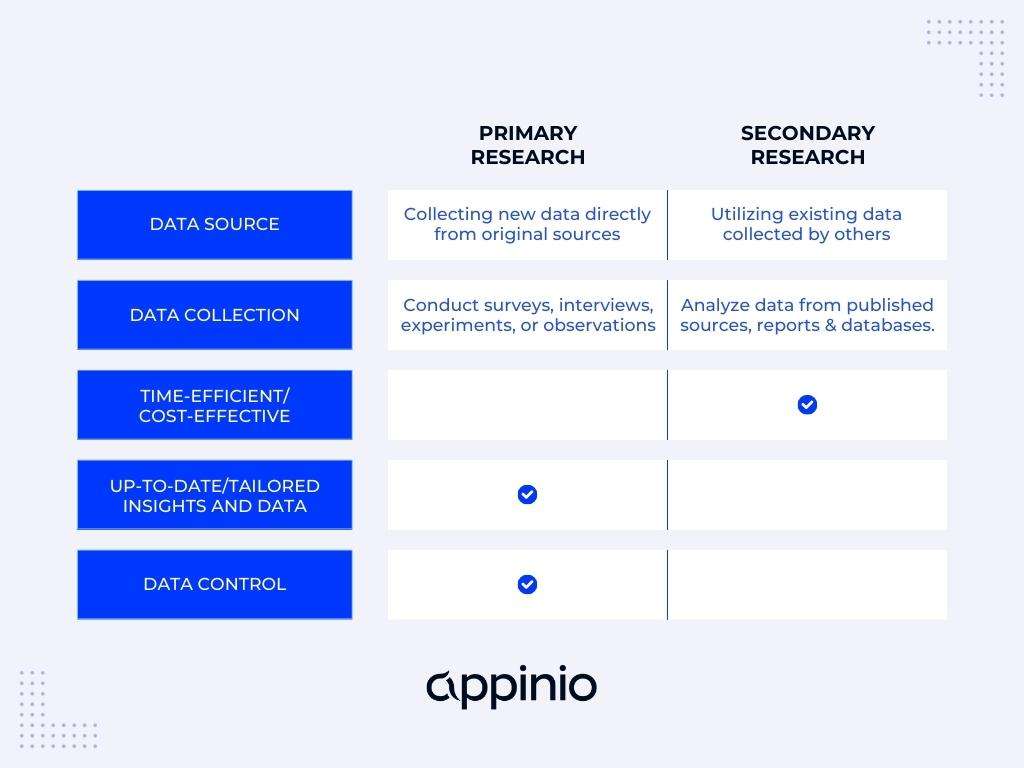
Primary Research
- Data Source: Involves collecting new data directly from original sources.
- Data Collection: Researchers design and conduct surveys, interviews, experiments, or observations.
- Time and Resources: Typically requires more time, effort, and resources due to data collection.
- Fresh Insights: Provides firsthand, up-to-date information tailored to specific research questions.
- Control: Researchers control the data collection process and can shape methodologies.
Secondary Research
- Data Source: Involves utilizing existing data and information collected by others.
- Data Collection: Researchers search, select, and analyze data from published sources, reports, and databases.
- Time and Resources: Generally more time-efficient and cost-effective as data is already available.
- Existing Knowledge: Utilizes data that has been previously compiled, often providing broader context.
- Less Control: Researchers have limited control over how data was collected originally, if any.
Choosing between primary and secondary research depends on your research objectives, available resources, and the depth of insights you require.
Types of Secondary Research
Secondary research encompasses various types of existing data sources that can provide valuable insights for your research endeavors. Understanding these types can help you choose the most relevant sources for your objectives.
Here are the primary types of secondary research:
Internal Sources
Internal sources consist of data generated within your organization or entity. These sources provide valuable insights into your own operations and performance.
- Company Records and Data: Internal reports, documents, and databases that house information about sales, operations, and customer interactions.
- Sales Reports and Customer Data: Analysis of past sales trends, customer demographics, and purchasing behavior.
- Financial Statements and Annual Reports: Financial data, such as balance sheets and income statements, offer insights into the organization's financial health.
External Sources
External sources encompass data collected and published by entities outside your organization.
These sources offer a broader perspective on various subjects.
- Published Literature and Journals: Scholarly articles, research papers, and academic studies available in journals or online databases.
- Market Research Reports: Reports from market research firms that provide insights into industry trends, consumer behavior, and market forecasts.
- Government and NGO Databases: Data collected and maintained by government agencies and non-governmental organizations, offering demographic, economic, and social information.
- Online Media and News Articles: News outlets and online publications that cover current events, trends, and societal developments.
Each type of secondary research source holds its value and relevance, depending on the nature of your research objectives. Combining these sources lets you understand the subject matter and make informed decisions.
How to Conduct Secondary Research?
Effective secondary research involves a thoughtful and systematic approach that enables you to extract valuable insights from existing data sources. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to navigate the process:
1. Define Your Research Objectives
Before delving into secondary research, clearly define what you aim to achieve. Identify the specific questions you want to answer, the insights you're seeking, and the scope of your research.
2. Identify Relevant Sources
Begin by identifying the most appropriate sources for your research. Consider the nature of your research objectives and the data type you require. Seek out sources such as academic journals, market research reports, official government databases, and reputable news outlets.
3. Evaluate Source Credibility
Ensuring the credibility of your sources is crucial. Evaluate the reliability of each source by assessing factors such as the author's expertise, the publication's reputation, and the objectivity of the information provided. Choose sources that align with your research goals and are free from bias.
4. Extract and Analyze Information
Once you've gathered your sources, carefully extract the relevant information. Take thorough notes, capturing key data points, insights, and any supporting evidence. As you accumulate information, start identifying patterns, trends, and connections across different sources.
5. Synthesize Findings
As you analyze the data, synthesize your findings to draw meaningful conclusions. Compare and contrast information from various sources to identify common themes and discrepancies. This synthesis process allows you to construct a coherent narrative that addresses your research objectives.
6. Address Limitations and Gaps
Acknowledge the limitations and potential gaps in your secondary research. Recognize that secondary data might have inherent biases or be outdated. Where necessary, address these limitations by cross-referencing information or finding additional sources to fill in gaps.
7. Contextualize Your Findings
Contextualization is crucial in deriving actionable insights from your secondary research. Consider the broader context within which the data was collected. How does the information relate to current trends, societal changes, or industry shifts? This contextual understanding enhances the relevance and applicability of your findings.
8. Cite Your Sources
Maintain academic integrity by properly citing the sources you've used for your secondary research. Accurate citations not only give credit to the original authors but also provide a clear trail for readers to access the information themselves.
9. Integrate Secondary and Primary Research (If Applicable)
In some cases, combining secondary and primary research can yield more robust insights. If you've also conducted primary research, consider integrating your secondary findings with your primary data to provide a well-rounded perspective on your research topic.
You can use a market research platform like Appinio to conduct primary research with real-time insights in minutes!
10. Communicate Your Findings
Finally, communicate your findings effectively. Whether it's in an academic paper, a business report, or any other format, present your insights clearly and concisely. Provide context for your conclusions and use visual aids like charts and graphs to enhance understanding.
Remember that conducting secondary research is not just about gathering information—it's about critically analyzing, interpreting, and deriving valuable insights from existing data. By following these steps, you'll navigate the process successfully and contribute to the body of knowledge in your field.
Secondary Research Examples
To better understand how secondary research is applied in various contexts, let's explore a few real-world examples that showcase its versatility and value.
Market Analysis and Trend Forecasting
Imagine you're a marketing strategist tasked with launching a new product in the smartphone industry. By conducting secondary research, you can:
- Access Market Reports: Utilize market research reports to understand consumer preferences, competitive landscape, and growth projections.
- Analyze Trends: Examine past sales data and industry reports to identify trends in smartphone features, design, and user preferences.
- Benchmark Competitors: Compare market share, customer satisfaction, and pricing strategies of key competitors to develop a strategic advantage.
- Forecast Demand: Use historical sales data and market growth predictions to estimate demand for your new product.
Academic Research and Literature Reviews
Suppose you're a student researching climate change's effects on marine ecosystems. Secondary research aids your academic endeavors by:
- Reviewing Existing Studies: Analyze peer-reviewed articles and scientific papers to understand the current state of knowledge on the topic.
- Identifying Knowledge Gaps: Identify areas where further research is needed based on what existing studies still need to cover.
- Comparing Methodologies: Compare research methodologies used by different studies to assess the strengths and limitations of their approaches.
- Synthesizing Insights: Synthesize findings from various studies to form a comprehensive overview of the topic's implications on marine life.
Competitive Landscape Assessment for Business Strategy
Consider you're a business owner looking to expand your restaurant chain to a new location. Secondary research aids your strategic decision-making by:
- Analyzing Demographics: Utilize demographic data from government databases to understand the local population's age, income, and preferences.
- Studying Local Trends: Examine restaurant industry reports to identify the types of cuisines and dining experiences currently popular in the area.
- Understanding Consumer Behavior: Analyze online reviews and social media discussions to gauge customer sentiment towards existing restaurants in the vicinity.
- Assessing Economic Conditions: Access economic reports to evaluate the local economy's stability and potential purchasing power.
These examples illustrate the practical applications of secondary research across various fields to provide a foundation for informed decision-making, deeper understanding, and innovation.
Secondary Research Limitations
While secondary research offers many benefits, it's essential to be aware of its limitations to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings.
- Data Quality and Validity: The accuracy and reliability of secondary data can vary, affecting the credibility of your research.
- Limited Contextual Information: Secondary sources might lack detailed contextual information, making it important to interpret findings within the appropriate context.
- Data Suitability: Existing data might not align perfectly with your research objectives, leading to compromises or incomplete insights.
- Outdated Information: Some sources might provide obsolete information that doesn't accurately reflect current trends or situations.
- Potential Bias: While secondary data is often less biased, biases might still exist in the original data sources, influencing your findings.
- Incompatibility of Data: Combining data from different sources might pose challenges due to variations in definitions, methodologies, or units of measurement.
- Lack of Control: Unlike primary research, you have no control over how data was collected or its quality, potentially affecting your analysis. Understanding these limitations will help you navigate secondary research effectively and make informed decisions based on a well-rounded understanding of its strengths and weaknesses.
Secondary research is a valuable tool that businesses can use to their advantage. By tapping into existing data and insights, companies can save time, resources, and effort that would otherwise be spent on primary research. This approach equips decision-makers with a broader understanding of market trends, consumer behaviors, and competitive landscapes. Additionally, benchmarking against industry standards and validating hypotheses empowers businesses to make informed choices that lead to growth and success.
As you navigate the world of secondary research, remember that it's not just about data retrieval—it's about strategic utilization. With a clear grasp of how to access, analyze, and interpret existing information, businesses can stay ahead of the curve, adapt to changing landscapes, and make decisions that are grounded in reliable knowledge.
How to Conduct Secondary Research in Minutes?
In the world of decision-making, having access to real-time consumer insights is no longer a luxury—it's a necessity. That's where Appinio comes in, revolutionizing how businesses gather valuable data for better decision-making. As a real-time market research platform, Appinio empowers companies to tap into the pulse of consumer opinions swiftly and seamlessly.
- Fast Insights: Say goodbye to lengthy research processes. With Appinio, you can transform questions into actionable insights in minutes.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Harness the power of real-time consumer insights to drive your business strategies, allowing you to make informed choices on the fly.
- Seamless Integration: Appinio handles the research and technical complexities, freeing you to focus on what truly matters: making rapid data-driven decisions that propel your business forward.
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

15.07.2024 | 14min read
Revolutionizing Brand Health with Mental Availability: All Key Takeaways

26.06.2024 | 35min read
Brand Development: Definition, Process, Strategies, Examples

18.06.2024 | 7min read
Future Flavors: How Burger King nailed Concept Testing with Predictive Insights

Research Methods: How and When to Use Primary and Secondary Research
- Survey Tips
What is Primary Research?
Primary research is research conducted by you or your team that examines and collects information directly from the context of the design problem.
Simply put, primary research is research that is your own original work.
For example, if a researcher is interested in learning about the dietary habits of people in a particular region, he or she could administer a survey to residents of that region inquiring about what types of food they typically eat.
Here, the researcher would be performing primary research.
What is Secondary Research?
Contrary to primary research, secondary research is research that was originally conducted by someone else.
Using our example from above, if after doing some investigation the researcher learns that a similar study has already been performed, he or she could utilize the results and findings from that study to assist him with his overall goal.
Here the researcher would be performing secondary research.
Related: Why You Should Consider Secondary Data Analysis for Your Next Study
Secondary research can be performed by leveraging the following sources:
- Academic peer-reviewed journals
- Magazines
- Books
- Market research reports
- Any other form of publicly available and accessible information
When to Use Secondary Research
Use secondary research as a starting point for your research process. .
Imagine that you’ve been tasked with developing an exercise program for elderly people.
The goal of the program is to outline and schedule exercises and workouts in order to promote healthy lifestyles amongst senior citizens.
But there’s a catch — You don’t have any experience in exercise science or developing this kind of program.
The best place to start in order to kick off the project would be to leverage existing research.
You could review publicly available materials on exercise regimens optimized for the age of your target audience. This could involve reading published research reports, books, or articles.
Your findings from this secondary research could then help you define your own approach for how you plan to create the fitness plan for senior citizens. Additionally, starting with secondary research gives you an understanding of what's already been done, and it alerts you of where there may be gaps.
Secondary research can help you understand what you don’t know.
Continuing on with our example above, you may realize that after researching existing materials on senior citizens and exercising that you know very little about what will motivate elderly people to exercise.
If you find yourself in a similar situation, continue to identify resources to educate yourself on the matter at hand.
In this case, secondary research has already saved you some time. If you had opted to not perform secondary research, and instead had made an attempt to build the exercise program from scratch using gut instinct, you would have spent a considerable amount of time banging your head against a theoretical wall to no avail.
If after digging into the available secondary sources, you realize that you still don’t have the precise knowledge needed to develop an effective program, you might then decide that primary research is the only viable way for you to move forward.
Using Primary Research and Secondary Research Together
Once you have a deep understanding of the problem at hand thanks to your secondary research, you can then plan your primary research efforts accordingly, so that you can fill in any gaps and obtain any information that was previously missing.
Both methods are most effective when they work together.
Surveys Are Great Tools for Performing Primary Research
Surveys are one of the most commonly used ways in which original data not found through secondary research is collected.
This is because surveys are context-specific, meaning that the data collected from the survey comes directly from your exact target audience. Plus, there are essentially limitless ways to customize and tailor your survey to resonate with your target audience, which allows you to collect only the most pertinent data for your project.
To start building and administering powerful surveys today, start a trial with Alchemer!
See all blog posts >

- Customer Experience

- Voice of the Customer

- Customer Experience , Customer Feedback
See it in Action

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
- 3rd Party Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
This website uses Google Analytics to collect anonymous information such as the number of visitors to the site, and the most popular pages.
Keeping this cookie enabled helps us to improve our website.
Please enable Strictly Necessary Cookies first so that we can save your preferences!
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Primary and Secondary Research

On the contrary, Secondary research is a research method which involves the use of data, already collected through primary research. The main difference between primary and secondary research lies in the fact that whether the research is conducted previously or not.
Content: Primary Research Vs Secondary Research
Comparison chart.
| Basis for Comparison | Primary Research | Secondary Research |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Research conducted to gather first-hand information, for the current problem is called Primary Research. | Secondary Research is one that involves use of information gathered originally by primary research. |
| Based on | Raw data | Analysed and interpreted information |
| Carried on by | Researcher himself | Someone else |
| Data | Specific to the needs of researcher. | May or may not be specific to the needs of researcher. |
| Process | Very Involved | Rapid and Easy |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Time | Long | Short |
Definition of Primary Research
A type of research, wherein the research aims at acquiring new and original data by primary sources, is known as Primary Data. As the term ‘primary’ implies ‘first and foremost’ and when it is linked with research, it means an in-depth exploration of facts by the researcher himself and that too with the one to one communication with the people, who know about the subject.
It is a bit difficult to conduct primary research because it requires a lot of time, money, resources and some prior information about the subject. With a view to getting needed information, the researcher has to start from scratch. The research can be performed through interviews, questionnaires, observations, etc.
Definition of Secondary Research
The research which involves analysis, interpretation and summarization of primary research, is called secondary research. In finer terms, the research in which data is obtained from readily available sources is secondary. As the data available is already analysed and interpreted, the researcher only needs to figure out the data of his choice, i.e. the relevant information for the project.
In this type of research, the researcher uses information gathered by government agencies, associations, labour unions media sources and so on. The data assembled is primarily published in newsletters, magazines, pamphlets, newspapers, journals, reports, encyclopaedias etc.
Key Differences Between Primary and Secondary Research
You can find out the difference between primary and secondary research, in the following points in detail:
- Research conducted to gather first-hand information, for the current problem is called Primary Research. Secondary Research is one that involves the use of information obtained originally by primary research.
- Primary Research is based on raw data, whereas secondary research is based on analysed and interpreted information.
- The primary research, the data is collected by the researcher himself or by the person hired by him. As against this, the secondary research, the data collection is performed by someone else.
- The primary research process is very involved which deeply explores the topic. Conversely, the secondary research process is fast and easy, which aims at gaining broad understanding about the subject.
- In primary research, as the researcher conducts the research, the data collected is always specific to the needs of the researcher. As opposed to secondary research, wherein the data lacks particularity, i.e. it may or may not be as per the requirements of the researcher.
- Primary research is an expensive process; wherein high cost is involved in the exploration of data and facts from various sources. Unlike Secondary research, is an economical process wherein the low cost is involved in acquiring pertinent information because the data is already collected by someone else.
- Primary research consumes a lot of time as the research is done from scratch. However, in the case of secondary research, the collection of data is already done, the research takes comparatively less time.
Both primary and secondary research have their advantages and disadvantages. While primary data is need-specific and quality is also up to the mark, but it is expensive and consumes more time. Secondary research, on the other hand, is cheap, and the data collection is easy, but it is also possible that the data may be outdated and does not suit your requirements. So, before choosing any of these two, first examine your requirements, sources, costs, etc. to choose the best research type for your project.
You Might Also Like:

Dr. Patrick Okobi says
September 10, 2016 at 12:17 am
That was a very good summary of the concepts of research.
George Dunham says
May 11, 2020 at 8:12 am
Athumani says
February 4, 2021 at 11:53 am
GOD bless you beloved
Gladys PATRICK-PhD Student says
January 22, 2023 at 3:18 am
I am so blessed with this information-May you be blessed and thank you so much.
September 3, 2023 at 9:16 pm
this helped with my school assignment and it is great i love this!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Writing Center
Beginner’s Guide to Research
Click here to download a .pdf copy of our Beginner’s Guide to Research !
Last updated : July 18, 2024
Consider keeping a printed copy to have when writing and revising your resume! If you have any additional questions, make an appointment or email us at [email protected] !
Most professors will require the use of academic (AKA peer-reviewed) sources for student writing. This is because these sources, written for academic audiences of specific fields, are helpful for developing your argument on many topics of interest in the academic realm, from history to biology. While popular sources like news articles also often discuss topics of interest within academic fields, peer-reviewed sources offer a depth of research and expertise that you cannot find in popular sources. Therefore, knowing how to (1) identify popular vs. academic sources, (2) differentiate between primary and secondary sources, and (3) find academic sources is a vital step in writing research. Below are definitions of the two ways scholars categorize types of sources based on when they were created (i.e. time and place) and how (i.e. methodology):
Popular vs. academic sources:
- Popular sources are publicly accessible periodicals–newspapers, magazines, and blogs–such as The Washington Post or The New Yorker . These sources are most often written for non-academic audiences, but can be helpful for finding general information and a variety of opinions on your topic.
- Academic sources , known also as peer reviewed or scholarly articles, are those that have undergone peer review before being published. Typically, these articles are written for other scholars in the field and are published in academic journals, like Feminist Studies or The American Journal of Psychology . Literature reviews, research projects, case studies, and notes from the field are common examples.
Primary vs. secondary sources:
- Primary sources are articles written by people directly involved in what they were writing about, including: News reports and photographs, diaries and novels, films and videos, speeches and autobiographies, as well as original research and statistics.
- Secondary sources , on the other hand, are second hand accounts written about a topic based on primary sources. Whether a journal article or other academic publication is considered a secondary source depends on how you use it.
How to Find Academic Sources
Finding appropriate academic sources from the hundreds of different journal publications can be daunting. Therefore, it is important to find databases –digital collections of articles–relevant to your topic to narrow your search. Albertson’s Library has access to several different databases, which can be located by clicking the “Articles and Databases” tab on the website’s homepage, and navigating to “Databases A-Z” to refine your search. Popular databases include: Academic Search Premier and Proquest Central (non-specific databases which include a wide variety of articles), JSTOR (humanities and social sciences, from literature to history), Web of Science (formal sciences and natural sciences such as biology and chemistry), and Google Scholar (a web search engine that searches scholarly literature and academic sources). If you are unable to access articles from other databases, make sure you’re signed in to Alberton’s Library through Boise State!
Performing a Database Search
Databases include many different types of sources besides academic journals, however, including book reviews and other periodicals. Using the search bar , you can limit search results to those containing specific keywords or phrases like “writing center” or “transfer theory.” Utilizing keywords in your search–names of key concepts, authors, or ideas–rather than questions is the most effective way to find articles in databases. When searching for a specific work by title, placing the title in quotation marks will ensure your search includes only results in that specific word order. In the example below, search terms including the author (“Virginia Woolf”) and subject (“feminism”) are entered into the popular database EBSCOhost:
Refining Your Search Results
Many databases have a bar on the left of the screen where you can further refine your results. For example, if you are only interested in finding complete scholarly articles, or peer-reviewed ones, you can toggle these different options to further limit your search. These options are located under the “Refine Results” bar in EBSCOhost, divided into different sections, with a display of currently selected search filters and filter options to refine your search based on your specific needs, as seen in the figure below:
Search results can also be limited by subject : If you search “Romeo and Juliet” on Academic Search Premier to find literary analysis articles for your English class, you’ll find a lot of other sources that include this search term, such as ones about theater production or ballets based on Shakespeare’s play. However, if you’re writing a literary paper on the text of the play itself, you might limit your search results to “fiction” to see only articles that discuss the play within the field of literature. Alternatively, for a theater class discussing the play, you might limit your search results to “drama.”
The Writing Center
technical report writing chapter 6 what is the difference between secondary research and primary research?
In technical report writing, both secondary research and primary research are important methods of gathering information.
Secondary research involves analyzing existing data and information that has already been collected and published by others, such as books, journals, articles, and online resources.
This type of research is useful for providing background information , understanding trends and patterns, and gaining insight into a topic.
Primary research, on the other hand, involves collecting new data through methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, and experiments.
This type of research is useful for obtaining specific and detailed information that is relevant to a particular study. Primary research can be time-consuming and costly, but it can also provide more reliable and accurate results.
In summary, secondary research involves analyzing existing information, while primary research involves collecting new data. Both methods have their advantages and limitations, and the choice of method depends on the research questions and objectives.
To know more about report refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/23326350#
Related Questions
All of the following are reasons why factories and warehouses have moved to suburbs EXCEPT: A) More clients B) Less traffic C) More space D) Cheaper land E) Better truck access
All of the following are reasons why factories and warehouses have moved to suburbs except for B) Less traffic.
Factories and warehouses have often relocated to suburbs for several reasons, including:
A) More clients: Suburbs often offer access to a larger customer base as populations expand outside of urban areas. By moving to the suburbs, factories and warehouses can be closer to their target markets, potentially reducing transportation costs and improving overall efficiency.
C) More space: Suburban areas typically have more available land compared to densely populated urban areas. This abundance of space allows factories and warehouses to expand their operations , build larger facilities, and accommodate growing inventories.
D) Cheaper land: Suburban land tends to be less expensive compared to prime urban locations. Lower land costs can significantly reduce overhead expenses for factories and warehouses, making it financially attractive to move to the suburbs.
E) Better truck access: Suburbs often have better truck access and transportation infrastructure, including well-connected highways, interstates, and logistical networks. This enables easier movement of goods in and out of the facility, improving supply chain efficiency and reducing transportation - related costs.
However, less traffic (option B) is not typically a reason for factories and warehouses to move to suburbs. In fact, suburban areas can also experience traffic congestion, especially during peak commuting hours when workers travel to and from these locations . Traffic conditions can vary depending on the specific suburban area and its proximity to urban centers.
To know more about suburbs refer here
brainly.com/question/3522704#
which statement is true regarding the use of self-disclosure by a social worker in a helping relationship?
The use of self-disclosure by a social worker in a helping relationship can be beneficial if it is purposeful, relevant, and used with the intention of building rapport and trust with the client.
However, it is important for the social worker to carefully consider the potential impact on the client and to ensure that the disclosure does not detract from the client's needs and goals. Ultimately, the decision to use self-disclosure should be guided by the social worker's professional judgment and ethical principles in a healthy relationship.
To know more about self-disclosure visit:
https://brainly.com/question/31793674
The complete question is the use of self-disclosure by a social worker in a helping relationship?
which of the following statements about body fat percentages is true? multiple choice average body fat percentage does not differ by gender. some hormones cannot be produced when body fat falls below a certain threshold. body fat percentage for women decreases during puberty. ethnicity has no influence on body fat percentage.
The true statement about body fat percentages is that some hormones cannot be produced when body fat falls below a certain threshold. The correct option is A)
Hormones such as estrogen, progesterone , and testosterone are produced in the body's fat cells. When body fat percentage falls too low, the body may not be able to produce enough of these hormones, leading to hormonal imbalances and potential health issues.
This is particularly true for women, as they generally have a higher body fat percentage than men and therefore rely more heavily on their fat cells for hormone production . It is not true that the average body fat percentage does not differ by gender. In fact, men typically have a lower body fat percentage than women due to differences in hormonal makeup and physical composition . Ethnicity can also play a role in body fat percentage, with some groups having a higher tendency for storing fat in certain areas of the body. While body fat percentage for women does tend to decrease during puberty , this statement is not entirely accurate. Puberty can lead to changes in body composition and an increase in lean muscle mass, which may cause a decrease in overall body fat percentage. However, this can vary greatly depending on individual factors such as genetics, diet, and exercise habits.
Overall, it is important to maintain a healthy body fat percentage for optimal hormone production and overall health. This can be achieved through a balanced diet and regular exercise routine tailored to individual needs and goals. The correct option is A) average body fat percentage does not differ by gender.
To learn more about hormones here:
https://brainly.com/question/4678959#
which of the following statements about body fat percentages is true? multiple choice A) average body fat percentage does not differ by gender. B) some hormones cannot be produced when body fat falls below a certain threshold.
C) body fat percentage for women decreases during puberty. D) ethnicity has no influence on body fat percentage.
Social institutions, including families and schools, that help to shape individuals' basic political beliefs and values
Social institutions such as families and schools play a significant role in shaping individuals' basic political beliefs and values. Families are often the first socialization agents that children encounter, and they play a critical role in transmitting political beliefs and values to their children.
Parents may discuss politics with their children, expose them to news and current events, and model political behaviors and attitudes. In addition, schools are also essential institutions that shape individuals' political beliefs and values. Schools provide students with opportunities to learn about different political systems, ideologies , and histories . They also expose students to different social and cultural perspectives, which can help to broaden their understanding of political issues. Furthermore, schools provide students with opportunities to participate in civic activities such as student government and community service , which can foster a sense of civic responsibility and engagement.
To know more about political beliefs visit:
https://brainly.com/question/2519142
around _____ percent of all adults experience an episode of severe unipolar depression at some point in their lives.
Approximately 25 % of all adults experience an episode of severe unipolar depression at some point in their lives.
Around 10-25 percent of all adults experience an episode of severe unipolar depression at some point in their lives. This type of depression is characterized by persistent sadness, lack of interest in activities, and feelings of worthlessness or hopelessness . It can significantly impact a person's daily functioning and quality of life. Seeking professional help, such as therapy or medication , can greatly improve symptoms and aid in recovery. It's important to remember that depression is a common and treatable condition, and reaching out for support is a brave and important step toward healing . Timely intervention and treatment can help manage and overcome this mental health condition.
To learn more about unipolar depression , visit:
brainly.com/question/32239827
the churches in revelation appear to have experienced any one or all of the following situations except . . .
The churches in Revelation appear to have experienced any one or all of the following situations except Natural catastrophes such as earthquakes and plagues. The correct option is D.
In the book of Revelation , the churches mentioned by John in his letters experienced various challenges and situations. These included persecution and martyrdom, false teachings and spiritual deception, spiritual lukewarmness and complacency, material prosperity and worldly success, and enduring trials and tribulations.
However, natural catastrophes such as earthquakes and plagues are not specifically mentioned as experiences faced by the churches in Revelation. The focus in Revelation is primarily on the spiritual condition of the churches, their relationship with God, and their response to the challenges of their time.
The correct option is D.
To know more about churches , click here.
https://brainly.com/question/9967717
------------The given question is incomplete, the complete question is:
"The churches in Revelation appear to have experienced any one or all of the following situations except:
a) Persecution and martyrdom.
b) False teachings and spiritual deception.
c) Spiritual lukewarmness and complacency.
d) Natural catastrophes such as earthquakes and plagues."-----------
2. if disciplinary actions must be taken against a medical staff member, how does the legal concept of due process come into play?
If disciplinary actions need to be taken against a medical staff member, the legal concept of due process comes into play in ensuring that the staff member receives fair and impartial treatment. Due process requires that the staff member be given notice of the charges against them and an opportunity to respond to those charges before any disciplinary action is taken.
This process ensures that the medical staff member's rights are protected and that any decision made is based on a fair and impartial evaluation of the facts. Failure to follow due process can result in legal challenges to the disciplinary action taken, which could have serious consequences for the organization. Therefore, it is crucial for organizations to adhere to due process when taking disciplinary actions against their staff. This may involve a formal hearing or other proceedings in which the staff member is able to present evidence and arguments in their defense. Due process also requires that the proceedings be conducted in an impartial and unbiased manner and that the decision-making process is based on the evidence presented.
Learn more about disciplinary actions: https://brainly.com/question/14151689
list in order the steps that led to the second continental congress to declare independence from Great Britain
The steps that led to the Second Continental Congress declaring independence from Great Britain were the First Continental Congress and the Olive Branch Petition , followed by the Battles of Lexington and Concord, the publication of Common Sense, the Lee Resolution.
The steps that led to the Second Continental Congress declaring independence from Great Britain can be outlined as follows:
1. The First Continental Congress (1774): Delegates from the Thirteen Colonies gathered to address grievances with British policies and assert their rights. While not explicitly calling for independence , it set the stage for future actions.
2. Battles of Lexington and Concord (1775): Armed conflict between colonial militias and British troops marked the outbreak of hostilities, further escalating tensions between the colonies and Great Britain.
3. Olive Branch Petition (1775): The Second Continental Congress sent a petition to King George III, expressing loyalty and a desire for peaceful resolution, but it was rejected, indicating a hardening stance by the British government .
4. Common Sense (1776): Thomas Paine's influential pamphlet argued for American independence, gaining widespread support among colonists and contributing to a growing sentiment in favor of separation.
5. Lee Resolution (1776): Richard Henry Lee presented a resolution to the Second Continental Congress, proposing independence for the colonies. It led to the drafting of the Declaration of Independence.
These steps reflect the progression of events and sentiments that led to the decisive declaration of independence by the Second Continental Congress.
Learn more about independence here:
https://brainly.com/question/15375461
When using behavior, leaders attempt to be clear about their expectations and reward employees for satisfactory performance. O laissez-faire O contingent reward O transformational O management by exception
When leaders use behavior as a tool, their goal is to provide clarity and structure for their employees in order to maximize their performance. One way they do this is by clearly communicating their expectations and rewarding employees who meet or exceed them.
This approach is often referred to as contingent reward, as the rewards are directly linked to the employees' behavior and performance .In contrast, laissez-faire leadership, where the leader takes a hands-off approach, can result in confusion and uncertainty among employees about what is expected of them. On the other hand, management by exception involves only intervening when employees fail to meet expectations, which can create a negative and reactive environment.
Transformational leadership, however, takes behavior management to the next level by inspiring and motivating employees to not only meet expectations but to excel beyond them. By setting a positive example and encouraging creativity and innovation, transformational leaders empower their teams to reach their full potential and achieve success.
To know more about leaders click here
brainly.com/question/15868646
the articles of confederation reflected americans’ fear ofa) A strong central governmentb) The states in congressc) Natural rightsd) The ultimate source of governmental authority is the people
The correct answer is A) A strong central government.
The Articles of Confederation were the first written constitution of the United States, and they reflected Americans ' fear of a strong central government.
The Articles established a weak central government and gave most of the power to the states in Congress. This was a deliberate effort to avoid the kind of tyranny that the colonists had experienced under British rule. However, the weaknesses of the Articles eventually led to their replacement by the stronger and more centralized Constitution in 1787.
It is important to note that while the Articles did reflect Americans ' fear of a strong central government, they also recognized the natural rights of individuals and the ultimate source of governmental authority in the people.
Learn more about Articles of Confederation: https://brainly.com/question/3148567
lagerstroemia fauriei is not native to the us it is likely from
Lagerstroemia fauriei, also known as the Japanese Crepe Myrtle, is not native to the United States . It is likely from Japan.
Lagerstroemia fauriei, commonly known as Korean crepe myrtle or Japanese crepe myrtle, is a species of flowering tree in the family Lythraceae. It is native to eastern Asia, particularly Korea and Japan. Lagerstroemia fauriei is known for its attractive flowers, smooth bark, and colorful foliage, making it a popular ornamental tree in gardens and landscapes.
Here are some key characteristics of Lagerstroemia fauriei:
Appearance: The tree typically grows to a height of 10-20 meters (33-66 feet) with a spread of 6-8 meters (20-26 feet). It has a rounded or vase-shaped crown and a multi-stemmed growth habit. The bark is smooth and grayish-brown, developing a mottled or peeling texture with age.
Leaves: The leaves of Lagerstroemia fauriei are deciduous, opposite or subopposite in arrangement , and elliptical to lanceolate in shape. They are typically dark green during the growing season and change to shades of orange, red, or purple in the fall, adding vibrant autumn color to the landscape.
Lagerstroemia fauriei, also known as the Japanese Crepe Myrtle, is not native to the United States. It is likely from Japan, as its common name suggests. This beautiful ornamental tree is well-known for its colorful flowers and attractive bark.
To know more about Japanese visit:
https://brainly.com/question/31149903
mfds and pfds can make information easier to interpret, understand and use group of answer choices true false
True. MFDs (Minimalist Graphic Displays) and PFDs (Proportional Font Displays) can enhance information comprehension, making it easier to interpret, understand, and utilize .
MFDs , or Multi-Function Displays, are versatile digital interfaces that consolidate various information and functionalities into a single screen or device. They are commonly used in industries like aviation, automotive, and military applications. MFDs provide a user- friendly and efficient way to access critical data, controls, and systems. These displays can show real-time data, such as navigation information, engine parameters, or mission status, allowing users to quickly assess and respond to changing conditions . By centralizing information and controls, MFDs reduce the need for multiple physical instruments or displays, saving space and enhancing operational efficiency. Their intuitive interfaces and customizable layouts contribute to improved situational awareness and operational effectiveness in complex environments .
Learn more about MFDs here;
https://brainly.com/question/32792596
troy was running down a hill flailing his arms wildly. while running down, he unintentionally frightened boris, who was walking up the hill. he did not intend to cause harm to boris. is troy criminally culpable of assault?
Based on the given information, it is unlikely that Troy would be criminally culpable of assault. Assault requires that the perpetrator intentionally cause the victim to fear for their safety or physical harm.
In this case, Troy did not have the intention to harm Boris and was simply running down a hill flailing his arms. However, it may still be possible for Boris to pursue a civil case for negligence or reckless behavior on Troy's part.
Two essential components must be present for the offense to qualify as an actionable one (for which the plaintiff may bring a lawsuit): The act was done to make the victim fear that they might come into contact with something harmful or insulting, and it did indeed make them fear that this would happen.
Therefore, there would be no basis for criminal culpability for assault.
Learn more about Safety :- https://brainly.com/question/28643801
Which job might be held by someone in a mid-level caste?A. doctorB. housekeeperC. farmerD. priest
The job of a farmer might be held by someone in a mid-level caste . A mid-level caste individual is more likely to hold a job as a farmer, as it falls between the higher-status occupations of a doctor or priest and the lower-status occupation of a housekeeper in the traditional caste system.
Individuals can be broadly categorized into different groups such as the upper class , the middle class, and the lower class. These categories are often determined by a combination of factors including income, wealth, education, and occupation. The upper class is typically made up of individuals with significant wealth and power.
The middle class is composed of individuals who have moderate to comfortable levels of income and education.
The lower class is made up of individuals with low levels of income and education, such as service industry workers, manual laborers, and the unemployed.
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Learn more about Farmer:
https://brainly.com/question/28770811
the process of amending the constitution involves both
the congressional proposal method and the convention method.
Explanation:
There are two avenues for amending the Constitution : the congressional proposal method and the convention method. In the congressional proposal method, two-thirds of both chambers of Congress must propose an amendment. The proposed amendment must then be ratified by three-fourths of state conventions or state legislatures, as chosen by Congress.
when will the star of bethlehem be visible in 2022
The Star of Bethlehem , also known as the Christmas Star, is a celestial event that is said to have guided the three wise men to the birthplace of Jesus Christ. The exact date of its occurrence is not known, but it is believed to have happened around 2,000 years ago.
While there is no scientific evidence to support the existence of the Star of Bethlehem, some astronomers believe that it may have been a rare alignment of planets and stars that occurred around the time of Christ's birth. In terms of when it will be visible in 2022, it is important to note that the Star of Bethlehem is not a recurring event.
However, there may be other celestial events in 2022 that are of interest to stargazers and astronomers. These events can include meteor showers, eclipses , and planetary alignments. It is recommended to consult a local astronomy club or visit a planetarium for more information on upcoming celestial events.
To know more about Bethlehem click here
brainly.com/question/3886668
Who serves on a school board?A) teachers appointed by the schoolB) a mayor and the city councilC) school superintendents D) members of the community
Members of the community serve on a school board . The correct option is D.
They are typically elected by the community to oversee the operations of the school district. School board members are responsible for setting policies, managing budgets, and making decisions that impact the education of students in the district.
The local community's elected or appointed representatives make up school boards, which are in charge of regulating how a school district is run. Parents, business executives, educators, and other community people with an interest in raising the standard of education in their area may serve on school boards.
Depending on the state or district, the particular qualifications for sitting on a school board may change, but generally speaking, candidates must be at least 18 years old, registered to vote, and residents of the school district they wish to serve. Candidates may also need to meet certain educational or professional experience requirements, depending on the state.
Members of the school board are responsible for the district's policies and goals, the employment and evaluation of the superintendent, the approval of budgets and expenditures, and ensuring that the district complies with all applicable state and federal laws. Members of school boards may also be charged with addressing community issues and promoting the requirements of children, parents, and other stakeholders.
Learn more about Serves on a School Board :- https://brainly.com/question/9859092
what is the name for an intuitive decision based on a person's years of experience with similar situations?
Explain how the map in Source #1 , “Nepal: Adventure Capital the of the World,” supports the information provided in the other two sources. Cite evidence and identify the source of each piece of information by title or number.
The map in Source #1 provides a visual representation of the adventure tourism destinations in Nepal and supports the information provided in the other two sources regarding the importance of trekking and adventure tourism in generating income for the country's tourism industry.
Source #1, " Nepal : Adventure Capital of the World ," is a map that shows the various trekking and adventure destinations in Nepal, including the Everest Base Camp, Annapurna Circuit, and Langtang National Park.
This map supports the information provided in the other two sources by illustrating the diverse and picturesque landscapes that Nepal has to offer for adventure tourism.
To know more about Nepal :
https://brainly.com/question/20353231
which of the following is an inherent problem of direct democracy? amost people aren't mature enough to govern themselves bwomen never have any rights under direct democracy cdirect democracies tend to favor the wealthy dmost people don't have the time to participate so actively in their government
The inherent problem of direct democracy among the options given is: most people don't have the time to participate so actively in their government. Direct democracy is a form of government in which citizens make decisions directly on policy issues, rather than through elected representatives. While this system can provide a high level of citizen involvement, it has some inherent challenges.
One of these challenges is that most people simply don't have the time to participate so actively in their government. In modern societies, people have jobs, families, and other personal commitments that can limit their ability to stay informed and participate in every decision. In addition to this issue, direct democracy can become inefficient and unwieldy when applied to large populations with complex issues to address. It may also lead to the tyranny of the majority, where the preferences of the majority could potentially override the rights and needs of minority groups.
Although the other options mentioned - people not being mature enough to govern themselves, women not having rights, and favoring the wealthy - may be issued in certain contexts, they are not inherent problems specifically tied to direct democracy. The main inherent problem remains that most people don't have the time to participate so actively in their government.
To know more about direct democracy refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/31006383#
the right of each citizen to vote is an example of group of answer choices equality of opportunity. equality of result. political equality. educational opportunity.
The right of each citizen to vote is an example of political equality .
Political equality refers to the principle that all citizens are equal in the eyes of the law and have the same political rights, such as the right to vote and the right to participate in the political process.
It is a fundamental principle of democracy and is enshrined in the constitutions of many democratic countries around the world.
Political equality is based on the idea that every citizen should have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives, regardless of their social status, wealth, or other personal characteristics.
In practice, achieving political equality can be challenging, as some groups may face barriers to voting or political participation, such as voter suppression or discrimination.
To know more about political equality , refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/20712075#
what best describes characterization? the way a character should be performed how a main character meets his or her downfall how a main character overcomes a tragedy the way a character is presented and developedWhat best describes characterization?- the way a character should be performed- how a main character meets his or her downfall- how a main character overcomes a tragedy- the way a character is presented and developed
The best description of characterization is: the way a character is presented and developed. The correct option is D.
Characterization refers to the methods used by a writer to reveal the personality, traits, and background of a character in a story. This can be done through direct description, dialogue, actions, thoughts, and the reactions of other characters.
Characterization helps readers understand and empathize with characters , making them feel more real and complex. It is a crucial aspect of storytelling, as it not only brings characters to life but also contributes to the overall theme and message of the story. The correct option is D.
To know more about characterization , refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/18494683#
kristen is interested in how different groups of people define and understand environmental social problems. in particular, she is interested in how peoples concern changes over time. which perspective is the most likely to use?
The perspective that is most likely to be used by Kristen to understand how different groups of people define and understand environmental social problems, and how their concerns change over time, is the sociological perspective.
This perspective examines how social structures and institutions shape individual behavior and attitudes, including attitudes towards the environment and social problems. By using the sociological perspective, Kristen can analyze the social factors that influence people's views on environmental social problems, such as their upbringing, education, and social status. She can also examine how these views change over time due to factors such as changing political and economic conditions, technological advancements, and media coverage. Overall, the sociological perspective provides a valuable framework for understanding the complex interplay between environmental and social issues and how they are perceived and addressed by different groups of people .
for more questions on sociological perspectives : https://brainly.com/question/15214155
What is Molly Ivins’ criticism of the Texas Legislature
Molly Ivins’ criticism of the Texas Legislature is Lack of Transparency, Influence of Special Interest Groups, Lack of Progress on Key Issues, Political Polarization and Lack of Representation.
Molly Ivins, a well-known political pundit and journalist, was noted for her incisive and often amusing criticisms of the Texas Legislature.
For such more question on Polarization:
https://brainly.com/question/31542351
any behavior that deliberately and repeatedly exposes a person to negative experiences is calledquestion 35 options:a) intergroup conflict.b) discrimination.c) assertiveness.d) bullying.
The correct term for any behavior that deliberately and repeatedly exposes a person to negative experiences is called bullying . The correct answer is option (d)
Bullying is a deliberate and harmful behavior that targets individuals with the intention of causing physical or emotional harm. This can be done through various means such as verbal attacks, social exclusion, or even physical assault. Bullying is different from the other options mentioned. Hence, the right answer si option (d). Intergroup conflict (a) refers to disagreements or disputes between different groups or teams, often arising from differences in beliefs, values, or goals.
Discrimination (b) is the unfair treatment of an individual based on their race, gender, age, or other characteristics, rather than their abilities or qualifications. Assertiveness (c) is a communication style in which individuals express their needs, opinions, and feelings openly and honestly, while respecting the rights of others.
To know more about bullying click here
brainly.com/question/28138661
your roommate is studying for a big final exam. you notice that she is anxious, so to help out you decide to wash all the dinner dishes, even though it is her turn. what kind of support is this?
The decision to wash the dishes for the roommate is a great example of how emotional support can help alleviate stress and anxiety. It shows that the person is willing to go above and beyond to help their roommate succeed in their studies and shows that they care about their well-being.
The kind of support shown in this scenario is emotional support. Emotional support involves providing encouragement, empathy, and listening to someone's concerns or feelings. By washing the dishes for her roommate, the person is not only taking care of a task that would normally cause stress, but they are also showing their support and understanding of their roommate's anxiety . In addition to emotional support , there are other types of support that could be beneficial in this situation. For example, instrumental support involves offering practical assistance, such as helping with studying or running errands. Informational support involves providing helpful information or advice about the situation. Finally, appraisal support involves offering feedback or positive reinforcement to boost someone's confidence . To know more about stress refer to
https://brainly.com/question/154477
the most dangerous mistake to make when entering an expressway is?
The most dangerous mistake to make when entering an expressway is to misjudge the speed of oncoming traffic and pull out in front of a vehicle, which can lead to a serious collision.
When entering an expressway or highway, it's important to pay close attention to traffic flow and merge safely. One common mistake that drivers make is assuming that they have enough time to merge into traffic, when in fact, the speed of oncoming vehicles is much faster than they realize. This can result in a dangerous situation where the merging vehicle pulls out in front of an oncoming car, causing a potential collision .
To avoid this mistake, it's important to take your time when entering an expressway or highway. Be sure to use your turn signal to indicate your intention to merge, and wait for a safe gap in traffic before proceeding. Also, be aware of your vehicle's acceleration capabilities, and make sure you have enough space and time to merge safely .
Remember, safety should always be your top priority when driving on the road . By being alert, patient, and cautious, you can help prevent accidents and keep yourself and others safe.
Click the below link, to learn more about An expressway :
https://brainly.com/question/28321642
eniesha was recently asked to plan a vacation for her group of friends. although eniesha was initially stressed about planning the perfect vacation, she found a really good app on her phone for booking travel accommodations, and now, planning the trip no longer seems so bad. eniesha's perceived stress was reduced as a result of her:
Eniesha's perceived stress was reduced as a result of her discovery of a useful travel booking app on her phone. This app likely provided her with a sense of control and organization over the planning process , which alleviated her initial anxiety about planning the perfect vacation for her group of friends.
The app may have also simplified the booking process, allowing Eniesha to quickly and easily compare different travel accommodations , select the best options, and make reservations with minimal effort. Research has shown that technology can have a positive impact on stress reduction and mental health. Apps and tools that provide users with helpful information, organization , and support can help individuals feel more in control of their lives and reduce feelings of overwhelm and stress.
This is particularly relevant in the realm of travel planning, where there are numerous details to manage and decisions to make. In conclusion, Eniesha's discovery of a useful travel booking app on her phone likely played a significant role in reducing her perceived stress levels and making the trip planning process more manageable. The use of technology in this way can be a helpful tool for reducing stress and promoting mental wellness.
Learn more about planning process here-
https://brainly.com/question/30584184
hebrews 2700 when assyria depopulates israel, from what places does assyria bring people to repopulate the land?
When Assyria depopulated Israel around 2700 years ago, they brought people from Babylon, Cuthah, Avva, Hamath, and Sepharvaim to repopulate the land. These were all areas that Assyria had conquered and incorporated into their empire.
The Assyrians believed in the policy of forced migration , which involved relocating conquered peoples to different parts of their empire to weaken their sense of identity and prevent rebellions. This policy was also meant to bring people with different skills and knowledge to new areas, thus benefiting the Assyrian economy.
The repopulation of Israel with people from different regions likely led to cultural mixing and the formation of new identities among the people of Israel.
To know more about Israel ,refer to the link:
https://brainly.com/question/9279902#
Three components of active managerial control include identifying risks, training, and a. Creating specifications b. Corrective action. c. Creating purchase orders. d. Record keeping.
Active managerial control refers to the proactive measures taken by managers and supervisors to prevent foodborne illnesses and ensure food safety within a foodservice establishment. The correct answer is option b.
It involves identifying potential risks , implementing control measures, and monitoring operations to maintain safe practices.
The three components of active managerial control are:
Identifying risks : This involves identifying potential hazards and risks associated with food handling, preparation, storage, and service. Managers should conduct regular assessments, such as hazard analysis, to identify critical control points and potential risks within their operations.
Training : Training plays a crucial role in ensuring that employees are knowledgeable about food safety practices and understand their roles and responsibilities. Managers should provide comprehensive training programs that cover topics like personal hygiene, safe food handling, cleaning and sanitizing procedures, and allergen management.
Corrective action : This component involves taking immediate actions to address identified risks or deviations from established food safety procedures. It includes implementing corrective measures, such as retraining employees, adjusting processes, or addressing equipment issues, to prevent or minimize potential food safety hazards.
While all the options mentioned may be important aspects of foodservice operations, the specific component that aligns with the three components of active managerial control is b. Corrective action. Creating specifications, creating purchase orders, and record keeping are essential for overall operational efficiency and regulatory compliance, but they are not specifically focused on the proactive management of food safety risks.
The correct answer is option b.
To know more about proactive refer to-
https://brainly.com/question/19568769
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Sydney.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- The Ultimate Guide to Market Research
- Primary vs Secondary Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Primary vs secondary research – what’s the difference.
14 min read Find out how primary and secondary research are different from each other, and how you can use them both in your own research program.
Primary vs secondary research: in a nutshell
The essential difference between primary and secondary research lies in who collects the data.
- Primary research definition
When you conduct primary research, you’re collecting data by doing your own surveys or observations.
- Secondary research definition:
In secondary research, you’re looking at existing data from other researchers, such as academic journals, government agencies or national statistics.
Free Ebook: The Qualtrics Handbook of Question Design
When to use primary vs secondary research
Primary research and secondary research both offer value in helping you gather information.
Each research method can be used alone to good effect. But when you combine the two research methods, you have the ingredients for a highly effective market research strategy. Most research combines some element of both primary methods and secondary source consultation.
So assuming you’re planning to do both primary and secondary research – which comes first? Counterintuitive as it sounds, it’s more usual to start your research process with secondary research, then move on to primary research.
Secondary research can prepare you for collecting your own data in a primary research project. It can give you a broad overview of your research area, identify influences and trends, and may give you ideas and avenues to explore that you hadn’t previously considered.
Given that secondary research can be done quickly and inexpensively, it makes sense to start your primary research process with some kind of secondary research. Even if you’re expecting to find out what you need to know from a survey of your target market, taking a small amount of time to gather information from secondary sources is worth doing.
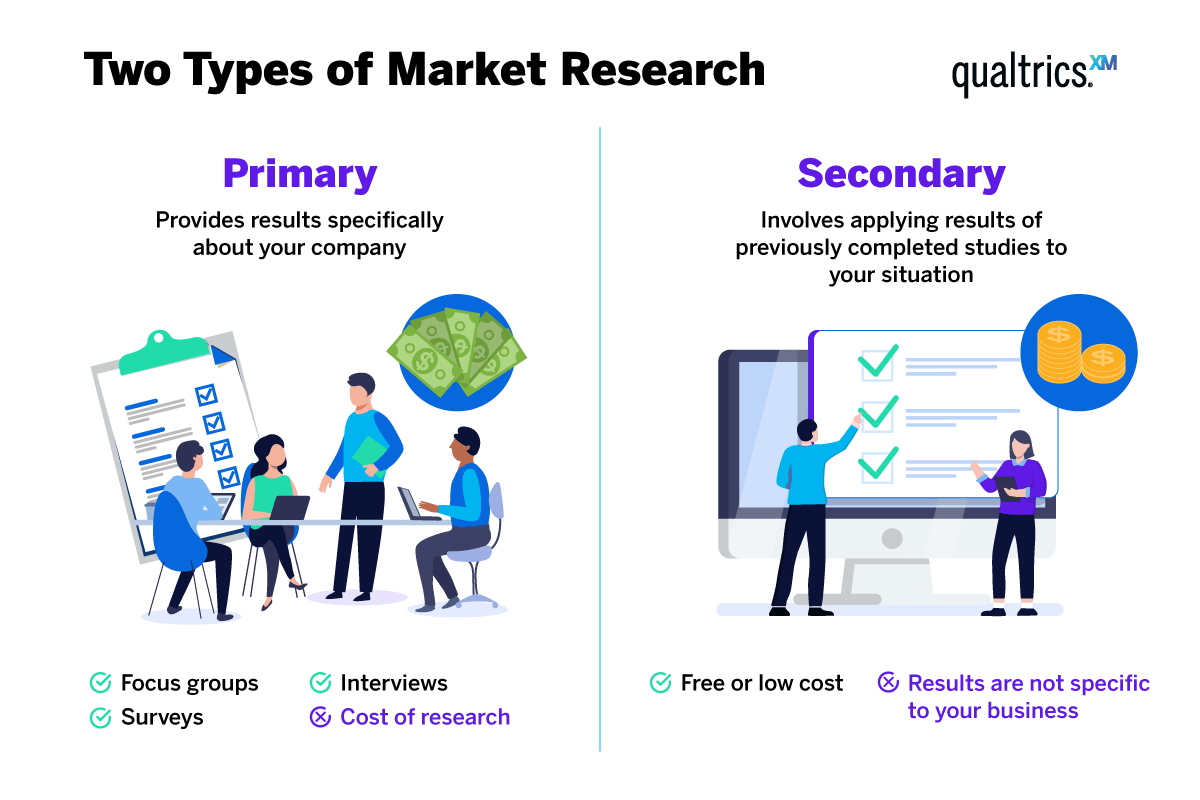
Primary research
Primary market research is original research carried out when a company needs timely, specific data about something that affects its success or potential longevity.
Primary research data collection might be carried out in-house by a business analyst or market research team within the company, or it may be outsourced to a specialist provider, such as an agency or consultancy. While outsourcing primary research involves a greater upfront expense, it’s less time consuming and can bring added benefits such as researcher expertise and a ‘fresh eyes’ perspective that avoids the risk of bias and partiality affecting the research data.
Primary research gives you recent data from known primary sources about the particular topic you care about, but it does take a little time to collect that data from scratch, rather than finding secondary data via an internet search or library visit.
Primary research involves two forms of data collection:
- Exploratory research This type of primary research is carried out to determine the nature of a problem that hasn’t yet been clearly defined. For example, a supermarket wants to improve its poor customer service and needs to understand the key drivers behind the customer experience issues. It might do this by interviewing employees and customers, or by running a survey program or focus groups.
- Conclusive research This form of primary research is carried out to solve a problem that the exploratory research – or other forms of primary data – has identified. For example, say the supermarket’s exploratory research found that employees weren’t happy. Conclusive research went deeper, revealing that the manager was rude, unreasonable, and difficult, making the employees unhappy and resulting in a poor employee experience which in turn led to less than excellent customer service. Thanks to the company’s choice to conduct primary research, a new manager was brought in, employees were happier and customer service improved.
Examples of primary research
All of the following are forms of primary research data.
- Customer satisfaction survey results
- Employee experience pulse survey results
- NPS rating scores from your customers
- A field researcher’s notes
- Data from weather stations in a local area
- Recordings made during focus groups
Primary research methods
There are a number of primary research methods to choose from, and they are already familiar to most people. The ones you choose will depend on your budget, your time constraints, your research goals and whether you’re looking for quantitative or qualitative data.
A survey can be carried out online, offline, face to face or via other media such as phone or SMS. It’s relatively cheap to do, since participants can self-administer the questionnaire in most cases. You can automate much of the process if you invest in good quality survey software.
Primary research interviews can be carried out face to face, over the phone or via video calling. They’re more time-consuming than surveys, and they require the time and expense of a skilled interviewer and a dedicated room, phone line or video calling setup. However, a personal interview can provide a very rich primary source of data based not only on the participant’s answers but also on the observations of the interviewer.
Focus groups
A focus group is an interview with multiple participants at the same time. It often takes the form of a discussion moderated by the researcher. As well as taking less time and resources than a series of one-to-one interviews, a focus group can benefit from the interactions between participants which bring out more ideas and opinions. However this can also lead to conversations going off on a tangent, which the moderator must be able to skilfully avoid by guiding the group back to the relevant topic.
Secondary research
Secondary research is research that has already been done by someone else prior to your own research study.
Secondary research is generally the best place to start any research project as it will reveal whether someone has already researched the same topic you’re interested in, or a similar topic that helps lay some of the groundwork for your research project.
Even if your preliminary secondary research doesn’t turn up a study similar to your own research goals, it will still give you a stronger knowledge base that you can use to strengthen and refine your research hypothesis. You may even find some gaps in the market you didn’t know about before.
The scope of secondary research resources is extremely broad. Here are just a few of the places you might look for relevant information.
Books and magazines
A public library can turn up a wealth of data in the form of books and magazines – and it doesn’t cost a penny to consult them.
Market research reports
Secondary research from professional research agencies can be highly valuable, as you can be confident the data collection methods and data analysis will be sound
Scholarly journals, often available in reference libraries
Peer-reviewed journals have been examined by experts from the relevant educational institutions, meaning there has been an extra layer of oversight and careful consideration of the data points before publication.
Government reports and studies
Public domain data, such as census data, can provide relevant information for your research project, not least in choosing the appropriate research population for a primary research method. If the information you need isn’t readily available, try contacting the relevant government agencies.
White papers
Businesses often produce white papers as a means of showcasing their expertise and value in their field. White papers can be helpful in secondary research methods, although they may not be as carefully vetted as academic papers or public records.
Trade or industry associations
Associations may have secondary data that goes back a long way and offers a general overview of a particular industry. This data collected over time can be very helpful in laying the foundations of your particular research project.
Private company data
Some businesses may offer their company data to those conducting research in return for fees or with explicit permissions. However, if a business has data that’s closely relevant to yours, it’s likely they are a competitor and may flat out refuse your request.
Learn more about secondary research
Examples of secondary research data
These are all forms of secondary research data in action:
- A newspaper report quoting statistics sourced by a journalist
- Facts from primary research articles quoted during a debate club meeting
- A blog post discussing new national figures on the economy
- A company consulting previous research published by a competitor
Secondary research methods
Literature reviews.
A core part of the secondary research process, involving data collection and constructing an argument around multiple sources. A literature review involves gathering information from a wide range of secondary sources on one topic and summarising them in a report or in the introduction to primary research data.
Content analysis
This systematic approach is widely used in social science disciplines. It uses codes for themes, tropes or key phrases which are tallied up according to how often they occur in the secondary data. The results help researchers to draw conclusions from qualitative data.
Data analysis using digital tools
You can analyse large volumes of data using software that can recognise and categorise natural language. More advanced tools will even be able to identify relationships and semantic connections within the secondary research materials.
Comparing primary vs secondary research
We’ve established that both primary research and secondary research have benefits for your business, and that there are major differences in terms of the research process, the cost, the research skills involved and the types of data gathered. But is one of them better than the other?
The answer largely depends on your situation. Whether primary or secondary research wins out in your specific case depends on the particular topic you’re interested in and the resources you have available. The positive aspects of one method might be enough to sway you, or the drawbacks – such as a lack of credible evidence already published, as might be the case in very fast-moving industries – might make one method totally unsuitable.
Here’s an at-a-glance look at the features and characteristics of primary vs secondary research, illustrating some of the key differences between them.
| Primary research | Secondary research |
|---|---|
| Self-conducted original research | Research already conducted by other researchers independent of your project |
| Qualitative and quantitative research | Qualitative and quantitative research |
| Relatively expensive to acquire | Relatively cheap to acquire |
| Focused on your business’ needs | Not focused on your business’ needs (usually, unless you have relevant in-house data from past research) |
| Takes some time to collect and analyse | Quick to access |
| Tailored to your project | Not tailored to your project |
What are the pros and cons of primary research?
Primary research provides original data and allows you to pinpoint the issues you’re interested in and collect data from your target market – with all the effort that entails.
Benefits of primary research:
- Tells you what you need to know, nothing irrelevant
- Yours exclusively – once acquired, you may be able to sell primary data or use it for marketing
- Teaches you more about your business
- Can help foster new working relationships and connections between silos
- Primary research methods can provide upskilling opportunities – employees gain new research skills
Limitations of primary research:
- Lacks context from other research on related subjects
- Can be expensive
- Results aren’t ready to use until the project is complete
- Any mistakes you make in in research design or implementation could compromise your data quality
- May not have lasting relevance – although it could fulfil a benchmarking function if things change
What are the pros and cons of secondary research?
Secondary research relies on secondary sources, which can be both an advantage and a drawback. After all, other people are doing the work, but they’re also setting the research parameters.
Benefits of secondary research:
- It’s often low cost or even free to access in the public domain
- Supplies a knowledge base for researchers to learn from
- Data is complete, has been analysed and checked, saving you time and costs
- It’s ready to use as soon as you acquire it
Limitations of secondary research
- May not provide enough specific information
- Conducting a literature review in a well-researched subject area can become overwhelming
- No added value from publishing or re-selling your research data
- Results are inconclusive – you’ll only ever be interpreting data from another organisation’s experience, not your own
- Details of the research methodology are unknown
- May be out of date – always check carefully the original research was conducted
Related resources
Business research methods 12 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, business research 10 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, video in qualitative research 10 min read, correlation research 11 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Biased methodology or sampling. If a survey or interview is based on biased research methodology, the results will be biased as well.A common type is the so-called 'response bias, which occurs when participants answer survey or interview questions systematically while in a certain perspective (Wilson & Joye, 2019).
Primary vs secondary research: in a nutshell. The essential difference between primary and secondary research lies in who collects the data. Primary research definition
Examples of primary research. Primary research can often be quite simple to pursue yourself. Here are a few examples of different research methods you can use to explore different topics.. Example: Survey questionnaire You are interested in the perceptions of your fellow students on universal healthcare. You decide to conduct a survey of students, asking them their thoughts.
What is a secondary source? A secondary source is anything that describes, interprets, evaluates, or analyzes information from primary sources. Common examples include: Books, articles and documentaries that synthesize information on a topic; Synopses and descriptions of artistic works; Encyclopedias and textbooks that summarize information and ideas; Reviews and essays that evaluate or ...
Navigating the Pros and Cons. Balance Your Research Needs: Consider starting with secondary research to gain a broad understanding of the subject matter, then delve into primary research for specific, targeted insights that are tailored to your precise needs. Resource Allocation: Evaluate your budget, time, and resource availability. Primary research can offer more specific and actionable data ...
When to use secondary research. Secondary research is a very common research method, used in lieu of collecting your own primary data. It is often used in research designs or as a way to start your research process if you plan to conduct primary research later on.. Since it is often inexpensive or free to access, secondary research is a low-stakes way to determine if further primary research ...
What is Primary Research? + [Methods & Examples] A simple guide on primary research; definitions, Its methods, examples, data collection techniques, advantages and disadvantages
Primary Vs Secondary Research. Primary and secondary research are two different types of research methods used to gather information for a study or research project.
Primary research deals with the collection of new data. What research methods deal with primary data and what inquiries are best suited for primary research? We'll look at these questions in this article.
Introduction. In market research, one normally has to make a choice: either primary research or secondary research methodologies. Both serve entirely different purposes and give different insights into the market or topic concerned.
Market research is essential for companies not only to learn about trends and consumer behavior. It is also beneficial to the organizations when making critical decisions, determining new opportunities, identifying the competitors, and improving the offerings. Take a look to learn the process behind a comprehensive research.
In a nutshell, primary research is original research conducted by you (or someone you hire) to collect data specifically for your current objective. You might conduct a survey, run an interview or a focus group, observe behavior, or do an experiment. You are going to be the person who obtains this raw data directly and it will be collected specifically for your current research need.
Primary and secondary research differ in their purpose, data collection, and more. Here are the key differences between primary and secondary research.
An expert gives an interview (primary research) and a marketer uses that interview to write an article (secondary research). A company conducts a consumer satisfaction survey (primary research) and a business analyst uses the survey data to write a market trend report (secondary research).
What is primary research? Primary research, sometimes referred to as original research, is research that seeks an answer to a question. If they can't find the answer to their question in other sources, primary researchers create their own tests and procedures to collect the data that can help them discover the answer.
In situations where you're not involved in the data gathering process (primary research), you have to rely on existing information and data to arrive at specific research conclusions or outcomes.This approach is known as secondary research. In this article, we're going to explain what secondary research is, how it works, and share some examples of it in practice.
When to Use Secondary Research. Choosing between secondary and primary research methods depends significantly on the objectives of your study or project. Secondary research is particularly beneficial in the initial stages of research planning and strategy, offering a broad understanding of the topic at hand and helping to pinpoint areas that may require more in-depth investigation through ...
There are many examples of primary research in all fields of academia. The main things a scholar should look for when determining the difference between primary and secondary research is the ...
Explore the power of secondary research: Gather insights from existing data to make informed decisions in any field.
Secondary research can help you identify what you don't know and is a good starting point for your research. Once you have a deep understanding of the problem at hand you can then plan your primary research efforts to fill in any gaps and obtain any information that was previously missing.
On the contrary, Secondary research is a research method which involves the use of data, already collected through primary research. The main difference between primary and secondary research lies in the fact that whether the research is conducted previously or not.
Market research can play a big part in growing your business. Learn the difference between primary and secondary research and how and where to apply within your business's marketing strategy. Learn more about market research in The Hartford Business Owners' Playbook.
Most professors will require the use of academic (AKA peer-reviewed) sources for student writing. This is because these sources, written for academic audiences of specific fields, are helpful for developing your argument on many topics of interest in the academic realm, from history to biology ...
In technical report writing, both secondary research and primary research are important methods of gathering information.. Secondary research involves analyzing existing data and information that has already been collected and published by others, such as books, journals, articles, and online resources.. This type of research is useful for providing background information, understanding trends ...
Primary vs secondary research: in a nutshell. The essential difference between primary and secondary research lies in who collects the data. Primary research definition
Chinese mainland schools have experienced significant change in recent decades, including curriculum reform and rapid urbanization (e.g., Cheng, 2005; Wu & Wei, 2015).Today, Chinese classrooms are diverse in terms of students' academic, economic, emotional, and behavioral backgrounds, which has led policymakers and teachers to move away from a traditional approach and toward DI.
2.1. Experimental design and study setting. The DEMANDS study was a unicentric, open label, parallel group, randomized controlled trial. The research was conducted at a tertiary academic healthcare institution, namely the Alexandria Main University Hospital, situated in Egypt.