Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips

How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
Published on September 15, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
Recommendations in research are a crucial component of your discussion section and the conclusion of your thesis , dissertation , or research paper .
As you conduct your research and analyze the data you collected , perhaps there are ideas or results that don’t quite fit the scope of your research topic. Or, maybe your results suggest that there are further implications of your results or the causal relationships between previously-studied variables than covered in extant research.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What should recommendations look like, building your research recommendation, how should your recommendations be written, recommendation in research example, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about recommendations.
Recommendations for future research should be:
- Concrete and specific
- Supported with a clear rationale
- Directly connected to your research
Overall, strive to highlight ways other researchers can reproduce or replicate your results to draw further conclusions, and suggest different directions that future research can take, if applicable.
Relatedly, when making these recommendations, avoid:
- Undermining your own work, but rather offer suggestions on how future studies can build upon it
- Suggesting recommendations actually needed to complete your argument, but rather ensure that your research stands alone on its own merits
- Using recommendations as a place for self-criticism, but rather as a natural extension point for your work
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
There are many different ways to frame recommendations, but the easiest is perhaps to follow the formula of research question conclusion recommendation. Here’s an example.
Conclusion An important condition for controlling many social skills is mastering language. If children have a better command of language, they can express themselves better and are better able to understand their peers. Opportunities to practice social skills are thus dependent on the development of language skills.
As a rule of thumb, try to limit yourself to only the most relevant future recommendations: ones that stem directly from your work. While you can have multiple recommendations for each research conclusion, it is also acceptable to have one recommendation that is connected to more than one conclusion.
These recommendations should be targeted at your audience, specifically toward peers or colleagues in your field that work on similar subjects to your paper or dissertation topic . They can flow directly from any limitations you found while conducting your work, offering concrete and actionable possibilities for how future research can build on anything that your own work was unable to address at the time of your writing.
See below for a full research recommendation example that you can use as a template to write your own.

Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
While it may be tempting to present new arguments or evidence in your thesis or disseration conclusion , especially if you have a particularly striking argument you’d like to finish your analysis with, you shouldn’t. Theses and dissertations follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the discussion section and results section .) The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation should include the following:
- A restatement of your research question
- A summary of your key arguments and/or results
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
For a stronger dissertation conclusion , avoid including:
- Important evidence or analysis that wasn’t mentioned in the discussion section and results section
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion …”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g., “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context.
The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved August 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/recommendations-in-research/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, how to write a results section | tips & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of exploration. In an era marked by rapid technological advancements and an ever-expanding knowledge base, refining the process of generating research recommendations becomes imperative.
But, what is a research recommendation?
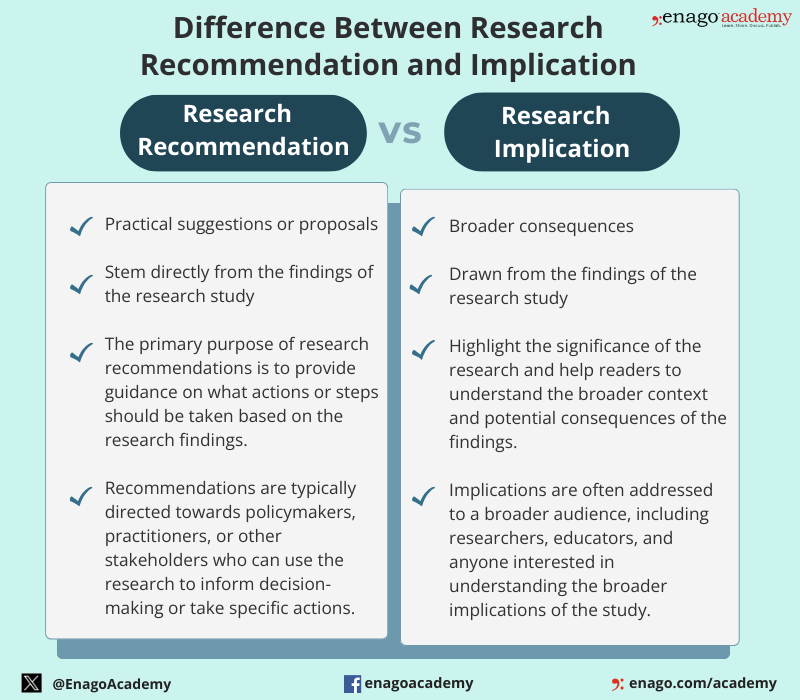
Research recommendations are suggestions or advice provided to researchers to guide their study on a specific topic . They are typically given by experts in the field. Research recommendations are more action-oriented and provide specific guidance for decision-makers, unlike implications that are broader and focus on the broader significance and consequences of the research findings. However, both are crucial components of a research study.
Difference Between Research Recommendations and Implication
Although research recommendations and implications are distinct components of a research study, they are closely related. The differences between them are as follows:
Types of Research Recommendations
Recommendations in research can take various forms, which are as follows:
| Article Recommendations | Suggests specific research articles, papers, or publications |
| Topic Recommendations | Guides researchers toward specific research topics or areas |
| Methodology Recommendations | Offers advice on research methodologies, statistical techniques, or experimental designs |
| Collaboration Recommendations | Connects researchers with others who share similar interests or expertise |
These recommendations aim to assist researchers in navigating the vast landscape of academic knowledge.
Let us dive deeper to know about its key components and the steps to write an impactful research recommendation.
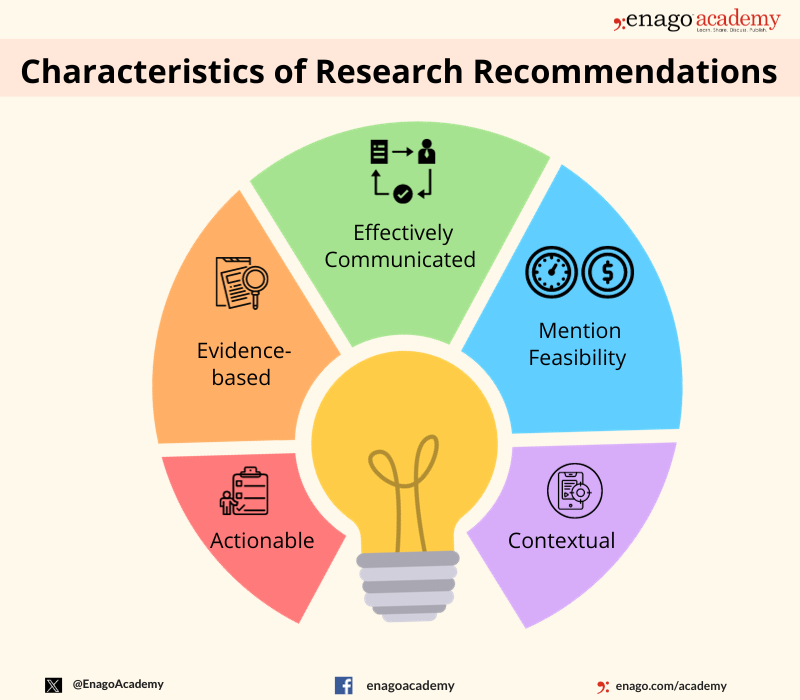
Key Components of Research Recommendations
The key components of research recommendations include defining the research question or objective, specifying research methods, outlining data collection and analysis processes, presenting results and conclusions, addressing limitations, and suggesting areas for future research. Here are some characteristics of research recommendations:
Research recommendations offer various advantages and play a crucial role in ensuring that research findings contribute to positive outcomes in various fields. However, they also have few limitations which highlights the significance of a well-crafted research recommendation in offering the promised advantages.
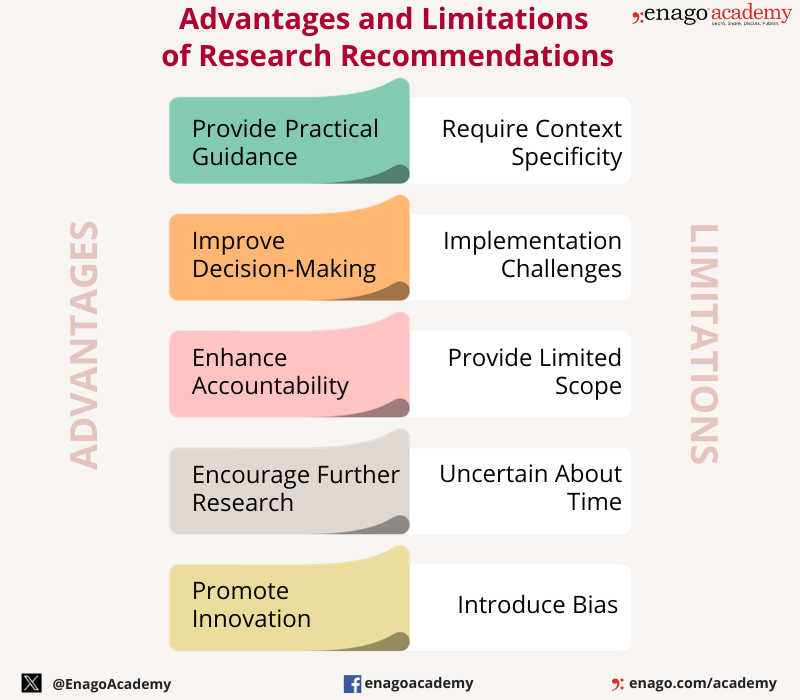
The importance of research recommendations ranges in various fields, influencing policy-making, program development, product development, marketing strategies, medical practice, and scientific research. Their purpose is to transfer knowledge from researchers to practitioners, policymakers, or stakeholders, facilitating informed decision-making and improving outcomes in different domains.
How to Write Research Recommendations?
Research recommendations can be generated through various means, including algorithmic approaches, expert opinions, or collaborative filtering techniques. Here is a step-wise guide to build your understanding on the development of research recommendations.
1. Understand the Research Question:
Understand the research question and objectives before writing recommendations. Also, ensure that your recommendations are relevant and directly address the goals of the study.
2. Review Existing Literature:
Familiarize yourself with relevant existing literature to help you identify gaps , and offer informed recommendations that contribute to the existing body of research.
3. Consider Research Methods:
Evaluate the appropriateness of different research methods in addressing the research question. Also, consider the nature of the data, the study design, and the specific objectives.
4. Identify Data Collection Techniques:
Gather dataset from diverse authentic sources. Include information such as keywords, abstracts, authors, publication dates, and citation metrics to provide a rich foundation for analysis.
5. Propose Data Analysis Methods:
Suggest appropriate data analysis methods based on the type of data collected. Consider whether statistical analysis, qualitative analysis, or a mixed-methods approach is most suitable.
6. Consider Limitations and Ethical Considerations:
Acknowledge any limitations and potential ethical considerations of the study. Furthermore, address these limitations or mitigate ethical concerns to ensure responsible research.
7. Justify Recommendations:
Explain how your recommendation contributes to addressing the research question or objective. Provide a strong rationale to help researchers understand the importance of following your suggestions.
8. Summarize Recommendations:
Provide a concise summary at the end of the report to emphasize how following these recommendations will contribute to the overall success of the research project.
By following these steps, you can create research recommendations that are actionable and contribute meaningfully to the success of the research project.
Download now to unlock some tips to improve your journey of writing research recommendations.
Example of a Research Recommendation
Here is an example of a research recommendation based on a hypothetical research to improve your understanding.
Research Recommendation: Enhancing Student Learning through Integrated Learning Platforms
Background:
The research study investigated the impact of an integrated learning platform on student learning outcomes in high school mathematics classes. The findings revealed a statistically significant improvement in student performance and engagement when compared to traditional teaching methods.
Recommendation:
In light of the research findings, it is recommended that educational institutions consider adopting and integrating the identified learning platform into their mathematics curriculum. The following specific recommendations are provided:
- Implementation of the Integrated Learning Platform:
Schools are encouraged to adopt the integrated learning platform in mathematics classrooms, ensuring proper training for teachers on its effective utilization.
- Professional Development for Educators:
Develop and implement professional programs to train educators in the effective use of the integrated learning platform to address any challenges teachers may face during the transition.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:
Establish a monitoring and evaluation system to track the impact of the integrated learning platform on student performance over time.
- Resource Allocation:
Allocate sufficient resources, both financial and technical, to support the widespread implementation of the integrated learning platform.
By implementing these recommendations, educational institutions can harness the potential of the integrated learning platform and enhance student learning experiences and academic achievements in mathematics.
This example covers the components of a research recommendation, providing specific actions based on the research findings, identifying the target audience, and outlining practical steps for implementation.
Using AI in Research Recommendation Writing
Enhancing research recommendations is an ongoing endeavor that requires the integration of cutting-edge technologies, collaborative efforts, and ethical considerations. By embracing data-driven approaches and leveraging advanced technologies, the research community can create more effective and personalized recommendation systems. However, it is accompanied by several limitations. Therefore, it is essential to approach the use of AI in research with a critical mindset, and complement its capabilities with human expertise and judgment.
Here are some limitations of integrating AI in writing research recommendation and some ways on how to counter them.
1. Data Bias
AI systems rely heavily on data for training. If the training data is biased or incomplete, the AI model may produce biased results or recommendations.
How to tackle: Audit regularly the model’s performance to identify any discrepancies and adjust the training data and algorithms accordingly.
2. Lack of Understanding of Context:
AI models may struggle to understand the nuanced context of a particular research problem. They may misinterpret information, leading to inaccurate recommendations.
How to tackle: Use AI to characterize research articles and topics. Employ them to extract features like keywords, authorship patterns and content-based details.
3. Ethical Considerations:
AI models might stereotype certain concepts or generate recommendations that could have negative consequences for certain individuals or groups.
How to tackle: Incorporate user feedback mechanisms to reduce redundancies. Establish an ethics review process for AI models in research recommendation writing.
4. Lack of Creativity and Intuition:
AI may struggle with tasks that require a deep understanding of the underlying principles or the ability to think outside the box.
How to tackle: Hybrid approaches can be employed by integrating AI in data analysis and identifying patterns for accelerating the data interpretation process.
5. Interpretability:
Many AI models, especially complex deep learning models, lack transparency on how the model arrived at a particular recommendation.
How to tackle: Implement models like decision trees or linear models. Provide clear explanation of the model architecture, training process, and decision-making criteria.
6. Dynamic Nature of Research:
Research fields are dynamic, and new information is constantly emerging. AI models may struggle to keep up with the rapidly changing landscape and may not be able to adapt to new developments.
How to tackle: Establish a feedback loop for continuous improvement. Regularly update the recommendation system based on user feedback and emerging research trends.
The integration of AI in research recommendation writing holds great promise for advancing knowledge and streamlining the research process. However, navigating these concerns is pivotal in ensuring the responsible deployment of these technologies. Researchers need to understand the use of responsible use of AI in research and must be aware of the ethical considerations.
Exploring research recommendations plays a critical role in shaping the trajectory of scientific inquiry. It serves as a compass, guiding researchers toward more robust methodologies, collaborative endeavors, and innovative approaches. Embracing these suggestions not only enhances the quality of individual studies but also contributes to the collective advancement of human understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
The purpose of recommendations in research is to provide practical and actionable suggestions based on the study's findings, guiding future actions, policies, or interventions in a specific field or context. Recommendations bridges the gap between research outcomes and their real-world application.
To make a research recommendation, analyze your findings, identify key insights, and propose specific, evidence-based actions. Include the relevance of the recommendations to the study's objectives and provide practical steps for implementation.
Begin a recommendation by succinctly summarizing the key findings of the research. Clearly state the purpose of the recommendation and its intended impact. Use a direct and actionable language to convey the suggested course of action.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Publishing Research
10 Tips to Prevent Research Papers From Being Retracted
Research paper retractions represent a critical event in the scientific community. When a published article…

- Industry News
Google Releases 2024 Scholar Metrics, Evaluates Impact of Scholarly Articles
Google has released its 2024 Scholar Metrics, assessing scholarly articles from 2019 to 2023. This…

- Career Corner
- Reporting Research
How to Create a Poster That Stands Out: Tips for a smooth poster presentation
It was the conference season. Judy was excited to present her first poster! She had…

- Diversity and Inclusion
6 Reasons Why There is a Decline in Higher Education Enrollment: Action plan to overcome this crisis
Over the past decade, colleges and universities across the globe have witnessed a concerning trend…

Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
The pen is mightier than the sword, they say, and nowhere is this more evident…
How to Effectively Cite a PDF (APA, MLA, AMA, and Chicago Style)
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- AI in Academia
- Promoting Research
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

In your opinion, what is the most effective way to improve integrity in the peer review process?
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
Published on 15 September 2022 by Tegan George .
Recommendations in research are a crucial component of your discussion section and the conclusion of your thesis , dissertation , or research paper .
As you conduct your research and analyse the data you collected , perhaps there are ideas or results that don’t quite fit the scope of your research topic . Or, maybe your results suggest that there are further implications of your results or the causal relationships between previously-studied variables than covered in extant research.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What should recommendations look like, building your research recommendation, how should your recommendations be written, recommendation in research example, frequently asked questions about recommendations.
Recommendations for future research should be:
- Concrete and specific
- Supported with a clear rationale
- Directly connected to your research
Overall, strive to highlight ways other researchers can reproduce or replicate your results to draw further conclusions, and suggest different directions that future research can take, if applicable.
Relatedly, when making these recommendations, avoid:
- Undermining your own work, but rather offer suggestions on how future studies can build upon it
- Suggesting recommendations actually needed to complete your argument, but rather ensure that your research stands alone on its own merits
- Using recommendations as a place for self-criticism, but rather as a natural extension point for your work
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
There are many different ways to frame recommendations, but the easiest is perhaps to follow the formula of research question conclusion recommendation. Here’s an example.
Conclusion An important condition for controlling many social skills is mastering language. If children have a better command of language, they can express themselves better and are better able to understand their peers. Opportunities to practice social skills are thus dependent on the development of language skills.
As a rule of thumb, try to limit yourself to only the most relevant future recommendations: ones that stem directly from your work. While you can have multiple recommendations for each research conclusion, it is also acceptable to have one recommendation that is connected to more than one conclusion.
These recommendations should be targeted at your audience, specifically toward peers or colleagues in your field that work on similar topics to yours. They can flow directly from any limitations you found while conducting your work, offering concrete and actionable possibilities for how future research can build on anything that your own work was unable to address at the time of your writing.
See below for a full research recommendation example that you can use as a template to write your own.
The current study can be interpreted as a first step in the research on COPD speech characteristics. However, the results of this study should be treated with caution due to the small sample size and the lack of details regarding the participants’ characteristics.
Future research could further examine the differences in speech characteristics between exacerbated COPD patients, stable COPD patients, and healthy controls. It could also contribute to a deeper understanding of the acoustic measurements suitable for e-health measurements.
While it may be tempting to present new arguments or evidence in your thesis or disseration conclusion , especially if you have a particularly striking argument you’d like to finish your analysis with, you shouldn’t. Theses and dissertations follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the discussion section and results section .) The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation should include the following:
- A restatement of your research question
- A summary of your key arguments and/or results
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
For a stronger dissertation conclusion , avoid including:
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context.
The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2022, September 15). How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/research-recommendations/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
- How it works

How To Write Recommendations In A Research Study
Published by Alvin Nicolas at July 12th, 2024 , Revised On July 12, 2024
The ultimate goal of any research process is not just to gather knowledge, but to use that knowledge to make a positive impact. This is where recommendations come in. A well-written recommendations section in your research study translates your findings into actionable steps and guides future research on the topic.
This blog is your ultimate guide to understanding how to write recommendations in a research study. But before that, let’s see what is recommendation in research.
What Is Recommendation In Research
In a research study, the recommendation section refers to a suggested course of action based on the findings of your research . It acts as a bridge between the knowledge you gained and its practical implications.
Recommendations take your research results and propose concrete steps on how to use them to address a problem or improve a situation. Moreover, you can suggest new avenues and guide future research in building upon your work. This will improve the credibility of your research. For studies that include real-world implications, recommendations are a great way to provide evidence-based suggestions for policymakers or practitioners to consider.
Difference Between Research Recommendations and Implication
Research recommendations and implications often confuse researchers. They cannot easily differentiate between the two. Here is how they are different.
| Research Recommendation | Research Implication |
|---|---|
| Focuses on actionable steps | Focuses on actionable steps |
| Translate findings into practical applications | Highlights the significance of the research |
| Specific actions | Broad predictions |
| Based on the research findings and existing literature | Based on the research findings and connections to other research areas |
Where To Add Recommendations
Recommendations are mostly part of your conclusion and discussion sections. If you are writing a practical dissertation , you can include a separate section for your recommendations.
Types of Research Recommendations
There are different forms of recommendations in research. Some of them include the following.
| Suggests improvements to the used in your field. | |
| Highlights new areas of research within your broader topic. | |
| Offers information on key articles or publications that provide insights on your . | |
| Suggest ways for researchers with different expertise to collaborate on future projects. |
How To Construct The Recommendations Section
There are different ways in which different scholars write the recommendations section. A general observation is a research question → conclusion → recommendation.
The following example will help you understand this better.
Research Question
How can the education of mothers impact the social skills of kindergarten children?
The role of mothers is a significant contributor towards the social skills of children. From an early age, kids tend to observe how their mother interacts with others and follow in her footsteps initially. Therefore, mothers should be educated and interact with good demeanour if they want their children to have excellent social skills.
Recommendation
The study revealed that a mother’s education plays an important role in building the social skills of children on kindergarten level. Future research could explore how the same continues in junior school level children.
How To Write Recommendations In Research
Now that you are familiar with the definition and types, here is a step-by-step guide on how to write a recommendation in research.
Step 1: Revisit Your Research Goals
Before doing anything else, you have to remind yourself of the objectives that you set out to achieve in your research. It allows you to match your recommendations directly to your research questions and see if you made any contribution to your goals.
Step 2: Analyse Your Findings
You have to examine your data and identify your key results. This analysis forms the foundation for your recommendations. Look for patterns and unexpected findings that might suggest new areas for other researchers to explore.
Step 3: Consider The Research Methods
Ask these questions from yourself: were the research methods effective? Is there any other way that would have been better to perform this research, or were there any limitations associated with the research methods?
Step 4: Prioritise Recommendations
You might have a lot of recommendations in mind, but all are not equal. You have to consider the impact and feasibility of each suggestion. Prioritise these recommendations, while remaining realistic about implementation.
Step 5: Write Actionable Statements
Do not be vague when crafting statements. Instead, you have to use clear and concise language that outlines specific actions. For example, if you want to say “improve education practices,” you could write “implement a teacher training program” for better clarity.
Step 6: Provide Evidence
You cannot just make suggestions out of thin air, and have to ground them in the evidence you have gathered through your research. Moreover, cite relevant data or findings from your study or previous literature to support your recommendations.
Step 7: Address Challenges
There are always some limitations related to the research at hand. As a researcher, it is your duty to highlight and address any challenges faced or what might occur in the future.
Tips For Writing The Perfect Recommendation In Research
Use these tips to write the perfect recommendation in your research.
- Be Concise – Write recommendations in a clear and concise language. Use one sentence statements to look more professional.
- Be Logical & Coherent – You can use lists and headings according to the requirements of your university.
- Tailor According To Your Readers – You have to aim your recommendations to a specific audience and colleagues in the field of study.
- Provide Specific Suggestions – Offer specific measures and solutions to the issues, and focus on actionable suggestions.
- Match Recommendations To Your Conclusion – You have to align your recommendations with your conclusion.
- Consider Limitations – Use critical thinking to see how limitations may impact the feasibility of your solutions.
- End With A Summary – You have to add a small conclusion to highlight suggestions and their impact.
Example Of Recommendation In Research
Context of the study:
This research studies how effective e-learning platforms are for adult language learners compared to traditional classroom instruction. The findings suggest that e-learning platforms can be just as effective as traditional classrooms in improving language proficiency.
Research Recommendation Sample
Language educators can incorporate e-learning tools into existing curriculums to provide learners with more flexibility. Additionally, they can develop training programs for educators on how to integrate e-learning platforms into their teaching practices.
E-learning platform developers should focus on e-learning platforms that are interactive and cater to different learning styles. They can also invest in features that promote learner autonomy and self-directed learning.
Future researchers can further explore the long-term effects of e-learning on language acquisition to provide insights into whether e-learning can support sustained language development.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write recommendations in a research paper.
- Revisit your research goals
- Analyse your findings
- Consider the research methods
- Prioritise recommendations
- Write actionable statements
- Provide evidence
- Address challenges
How to present recommendations in research?
- Be concise
- Write logical and coherent
- Match recommendations to conclusion
- Ensure your recommendations are achievable
What to write in recommendation in research?
Your recommendation has to be concrete and specific and support the research with a clear rationale. Moreover, it should be connected directly to your research. Your recommendations, however, should not undermine your own work or use self-criticism.
You May Also Like
Here are the steps to make a theoretical framework for dissertation. You can define, discuss and evaluate theories relevant to the research problem.
How to Structure a Dissertation or Thesis Need interesting and manageable Finance and Accounting dissertation topics? Here are the trending Media dissertation titles so you can choose one most suitable to your needs.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What are Implications and Recommendations in Research? How to Write It, with Examples
Highly cited research articles often contain both implications and recommendations , but there is often some confusion around the difference between implications and recommendations in research. Implications of a study are the impact your research makes in your chosen area; they discuss how the findings of the study may be important to justify further exploration of your research topic. Research recommendations suggest future actions or subsequent steps supported by your research findings. It helps to improve your field of research or cross-disciplinary fields through future research or provides frameworks for decision-makers or policymakers. Recommendations are the action plan you propose based on the outcome.
In this article, we aim to simplify these concepts for researchers by providing key insights on the following:
- what are implications in research
- what is recommendation in research
- differences between implications and recommendations
- how to write implications in research
- how to write recommendation in research
- sample recommendation in research

Table of Contents
What are implications in research
The implications in research explain what the findings of the study mean to researchers or to certain subgroups or populations beyond the basic interpretation of results. Even if your findings fail to bring radical or disruptive changes to existing ways of doing things, they might have important implications for future research studies. For example, your proposed method for operating remote-controlled robots could be more precise, efficient, or cheaper than existing methods, or the remote-controlled robot could be used in other application areas. This could enable more researchers to study a specific problem or open up new research opportunities.
Implications in research inform how the findings, drawn from your results, may be important for and impact policy, practice, theory, and subsequent research. Implications may be theoretical or practical. 1
- Practical implications are potential values of the study with practical or real outcomes . Determining the practical implications of several solutions can aid in identifying optimal solution results. For example, clinical research or research on classroom learning mostly has practical implications in research . If you developed a new teaching method, the implication would be how teachers can use that method based on your findings.
- Theoretical implications in research constitute additions to existing theories or establish new theories. These types of implications in research characterize the ability of research to influence society in apparent ways. It is, at most, an educated guess (theoretical) about the possible implication of action and need not be as absolute as practical implications in research . If your study supported the tested theory, the theoretical implication would be that the theory can explain the investigated phenomenon. Else, your study may serve as a basis for modifying the theory. Theories may be partially supported as well, implying further study of the theory or necessary modifications are required.
What are recommendations in research?
Recommendations in research can be considered an important segment of the analysis phase. Recommendations allow you to suggest specific interventions or strategies to address the issues and constraints identified through your study. It responds to key findings arrived at through data collection and analysis. A process of prioritization can help you narrow down important findings for which recommendations are developed.
Recommendations in research examples
Recommendations in research may vary depending on the purpose or beneficiary as seen in the table below.
Table: Recommendations in research examples based on purpose and beneficiary
|
|
|
|
| Filling a knowledge gap | Researchers | ‘Future research should explore the effectiveness of differentiated programs in special needs students.’ |
| For practice | Practitioners | ‘Future research should introduce new models and methods to train teachers for curriculum development and modification introducing differentiated programs.’ |
| For a policy (targeting health and nutrition) | Policymakers and management | ‘Governments and higher education policymakers need to encourage and popularize differentiated learning in educational institutions.’ |
If you’re wondering how to make recommendations in research . You can use the simple recommendation in research example below as a handy template.
Table: Sample recommendation in research template
| The current study can be interpreted as a first step in the research on differentiated instructions. However, the results of this study should be treated with caution as the selected participants were more willing to make changes in their teaching models, limiting the generalizability of the model. Future research might consider ways to overcome resistance to implementing differentiated learning. It could also contribute to a deeper understanding of the practices for suitable implementation of differentiated learning. |

Basic differences between implications and recommendations in research
Implications and recommendations in research are two important aspects of a research paper or your thesis or dissertation. Implications discuss the importance of the research findings, while recommendations offer specific actions to solve a problem. So, the basic difference between the two is in their function and the questions asked to achieve it. The following table highlights the main differences between implications and recommendations in research .
Table: Differences between implications and recommendations in research
|
|
| |
| Implications in research tell us how and why your results are important for the field at large.
| Recommendations in research are suggestions/solutions that address certain problems based on your study results.
| |
| Discuss the importance of your research study and the difference it makes.
| Lists specific actions to be taken with regard to policy, practice, theory, or subsequent research.
| |
| What do your research findings mean? | What’s next in this field of research? | |
| In the discussion section, after summarizing the main findings.
| In the discussion section, after the implications, and before the concluding paragraphs.
| |
| Our results suggest that interventions might emphasize the importance of providing emotional support to families.
| Based on our findings, we recommend conducting periodic assessments to benefit fully from the interventions.
|
Where do implications go in your research paper
Because the implications and recommendations of the research are based on study findings, both are usually written after the completion of a study. There is no specific section dedicated to implications in research ; they are usually integrated into the discussion section adding evidence as to why the results are meaningful and what they add to the field. Implications can be written after summarizing your main findings and before the recommendations and conclusion.
Implications can also be presented in the conclusion section after a short summary of the study results.
How to write implications in research
Implication means something that is inferred. The implications of your research are derived from the importance of your work and how it will impact future research. It is based on how previous studies have advanced your field and how your study can add to that.
When figuring out how to write implications in research , a good strategy is to separate it into the different types of implications in research , such as social, political, technological, policy-related, or others. As mentioned earlier, the most frequently used are the theoretical and practical implications.
Next, you need to ask, “Who will benefit the most from reading my paper?” Is it policymakers, physicians, the public, or other researchers? Once you know your target population, explain how your findings can help them.
The implication section can include a paragraph or two that asserts the practical or managerial implications and links it to the study findings. A discussion can then follow, demonstrating that the findings can be practically implemented or how they will benefit a specific audience. The writer is given a specific degree of freedom when writing research implications , depending on the type of implication in research you want to discuss: practical or theoretical. Each is discussed differently, using different words or in separate sections. The implications can be based on how the findings in your study are similar or dissimilar to that in previous studies. Your study may reaffirm or disprove the results of other studies, which has important implications in research . You can also suggest future research directions in the light of your findings or require further research to confirm your findings, which are all crucial implications. Most importantly, ensure the implications in research are specific and that your tone reflects the strength of your findings without exaggerating your results.
Implications in research can begin with the following specific sentence structures:
- These findings suggest that…
- These results build on existing body of evidence of…
- These results should be considered when…
- While previous research focused on x, our results show that y…
| Patients were most interested in items relating to communication with healthcare providers. |
| These findings suggest that people can change hospitals if they do not find communication effective. |

What should recommendations in research look like?
Recommendations for future research should be:
- Directly related to your research question or findings
- Concrete and specific
- Supported by a clear reasoning
The recommendations in research can be based on the following factors:
1. Beneficiary: A paper’s research contribution may be aimed at single or multiple beneficiaries, based on which recommendations can vary. For instance, if your research is about the quality of care in hospitals, the research recommendation to different beneficiaries might be as follows:
- Nursing staff: Staff should undergo training to enhance their understanding of what quality of care entails.
- Health science educators: Educators must design training modules that address quality-related issues in the hospital.
- Hospital management: Develop policies that will increase staff participation in training related to health science.
2. Limitations: The best way to figure out what to include in your research recommendations is to understand the limitations of your study. It could be based on factors that you have overlooked or could not consider in your present study. Accordingly, the researcher can recommend that other researchers approach the problem from a different perspective, dimension, or methodology. For example, research into the quality of care in hospitals can be based on quantitative data. The researcher can then recommend a qualitative study of factors influencing the quality of care, or they can suggest investigating the problem from the perspective of patients rather than the healthcare providers.
3. Theory or Practice: Your recommendations in research could be implementation-oriented or further research-oriented.
4. Your research: Research recommendations can be based on your topic, research objectives, literature review, and analysis, or evidence collected. For example, if your data points to the role of faculty involvement in developing effective programs, recommendations in research can include developing policies to increase faculty participation. Take a look at the evidence-based recommendation in research example s provided below.
Table: Example of evidence-based research recommendation
|
|
|
| The study findings are positive | Recommend sustaining the practice |
| The study findings are negative | Recommend actions to correct the situation |
Avoid making the following mistakes when writing research recommendations :
- Don’t undermine your own work: Recommendations in research should offer suggestions on how future studies can be built upon the current study as a natural extension of your work and not as an entirely new field of research.
- Support your study arguments: Ensure that your research findings stand alone on their own merits to showcase the strength of your research paper.
How to write recommendations in research
When writing research recommendations , your focus should be on highlighting what additional work can be done in that field. It gives direction to researchers, industries, or governments about changes or developments possible in this field. For example, recommendations in research can include practical and obtainable strategies offering suggestions to academia to address problems. It can also be a framework that helps government agencies in developing strategic or long-term plans for timely actions against disasters or aid nation-building.
There are a few SMART 2 things to remember when writing recommendations in research. Your recommendations must be:
- S pecific: Clearly state how challenges can be addressed for better outcomes and include an action plan that shows what can be achieved.
- M easurable: Use verbs denoting measurable outcomes, such as identify, analyze, design, compute, assess, evaluate, revise, plan, etc., to strengthen recommendations in research .
- A ttainable: Recommendations should offer a solution-oriented approach to problem-solving and must be written in a way that is easy to follow.
- R elevant: Research recommendations should be reasonable, realistic, and result-based. Make sure to suggest future possibilities for your research field.
- T imely: Time-based or time-sensitive recommendations in research help divide the action plan into long-term or short-term (immediate) goals. A timeline can also inform potential readers of what developments should occur over time.
If you are wondering how many words to include in your research recommendation , a general rule of thumb would be to set aside 5% of the total word count for writing research recommendations . Finally, when writing the research implications and recommendations , stick to the facts and avoid overstating or over-generalizing the study findings. Both should be supported by evidence gathered through your data analysis.
References:
- Schmidt, F. L., & Hunter, J. E. (1998). The validity and utility of selection methods in personnel psychology: Practical and theoretical implications of 85 years of research findings. Psychological bulletin , 124 (2), 262.
- Doran, G. T. (1981). There’s a S.M.A.R.T. way to write management’s goals and objectives. Manag Rev , 70 (11), 35-36.
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

What are the Best Research Funding Sources

Inductive vs. Deductive Research Approach
The Ultimate Guide to Crafting Impactful Recommendations in Research

Are you ready to take your research to the next level? Crafting impactful recommendations is the key to unlocking the full potential of your study. By providing clear, actionable suggestions based on your findings, you can bridge the gap between research and real-world application.
In this ultimate guide, we'll show you how to write recommendations that make a difference in your research report or paper.
You'll learn how to craft specific, actionable recommendations that connect seamlessly with your research findings. Whether you're a student, writer, teacher, or journalist, this guide will help you master the art of writing recommendations in research. Let's get started and make your research count!
Understanding the Purpose of Recommendations
Recommendations in research serve as a vital bridge between your findings and their real-world applications. They provide specific, action-oriented suggestions to guide future studies and decision-making processes. Let's dive into the key purposes of crafting effective recommendations:
Guiding Future Research
Research recommendations play a crucial role in steering scholars and researchers towards promising avenues of exploration. By highlighting gaps in current knowledge and proposing new research questions, recommendations help advance the field and drive innovation.
Influencing Decision-Making
Well-crafted recommendations have the power to shape policies, programs, and strategies across various domains, such as:
- Policy-making
- Product development
- Marketing strategies
- Medical practice
By providing clear, evidence-based suggestions, recommendations facilitate informed decision-making and improve outcomes.
Connecting Research to Practice
Recommendations act as a conduit for transferring knowledge from researchers to practitioners, policymakers, and stakeholders. They bridge the gap between academic findings and their practical applications, ensuring that research insights are effectively translated into real-world solutions.
Enhancing Research Impact
Purpose | Description |
|---|---|
Relevance | Recommendations showcase the relevance and significance of your research findings. |
Visibility | Well-articulated recommendations increase the visibility and impact of your work. |
Collaboration | Recommendations foster collaboration and knowledge-sharing among researchers. |
By crafting impactful recommendations, you can amplify the reach and influence of your research, attracting attention from peers, funding agencies, and decision-makers.
Addressing Limitations
Recommendations provide an opportunity to acknowledge and address the limitations of your study. By suggesting concrete and actionable possibilities for future research, you demonstrate a thorough understanding of your work's scope and potential areas for improvement.
Identifying Areas for Future Research
Discovering research gaps is a crucial step in crafting impactful recommendations. It involves reviewing existing studies and identifying unanswered questions or problems that warrant further investigation. Here are some strategies to help you identify areas for future research:
Explore Research Limitations
Take a close look at the limitations section of relevant studies. These limitations often provide valuable insights into potential areas for future research. Consider how addressing these limitations could enhance our understanding of the topic at hand.
Critically Analyze Discussion and Future Research Sections
When reading articles, pay special attention to the discussion and future research sections. These sections often highlight gaps in the current knowledge base and propose avenues for further exploration. Take note of any recurring themes or unanswered questions that emerge across multiple studies.
Utilize Targeted Search Terms
To streamline your search for research gaps, use targeted search terms such as "literature gap" or "future research" in combination with your subject keywords. This approach can help you quickly identify articles that explicitly discuss areas for future investigation.
Seek Guidance from Experts
Don't hesitate to reach out to your research advisor or other experts in your field. Their wealth of knowledge and experience can provide valuable insights into potential research gaps and emerging trends.
Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
Broaden Your Horizons | Explore various topics and themes within your field to identify subjects that pique your interest and offer ample research opportunities. |
Leverage Digital Tools | Utilize digital tools to identify popular topics and highly cited research papers. These tools can help you gauge the current state of research and pinpoint areas that require further investigation. |
Collaborate with Peers | Engage in discussions with your peers and colleagues. Brainstorming sessions and collaborative exchanges can spark new ideas and reveal unexplored research avenues. |
By employing these strategies, you'll be well-equipped to identify research gaps and craft recommendations that push the boundaries of current knowledge. Remember, the goal is to refine your research questions and focus your efforts on areas where more understanding is needed.
Structuring Your Recommendations
When it comes to structuring your recommendations, it's essential to keep them concise, organized, and tailored to your audience. Here are some key tips to help you craft impactful recommendations:
Prioritize and Organize
- Limit your recommendations to the most relevant and targeted suggestions for your peers or colleagues in the field.
- Place your recommendations at the end of the report, as they are often top of mind for readers.
- Write your recommendations in order of priority, with the most important ones for decision-makers coming first.
Use a Clear and Actionable Format
- Write recommendations in a clear, concise manner using actionable words derived from the data analyzed in your research.
- Use bullet points instead of long paragraphs for clarity and readability.
- Ensure that your recommendations are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and timely (SMART).
Connect Recommendations to Research
Element | Description |
|---|---|
Research Question | Clearly state the research question or problem addressed in your study. |
Conclusion | Summarize the key findings and conclusions drawn from your research. |
Recommendation | Provide specific, actionable suggestions based on your research findings. |
By following this simple formula, you can ensure that your recommendations are directly connected to your research and supported by a clear rationale.
Tailor to Your Audience
- Consider the needs and interests of your target audience when crafting your recommendations.
- Explain how your recommendations can solve the issues explored in your research.
- Acknowledge any limitations or constraints of your study that may impact the implementation of your recommendations.
Avoid Common Pitfalls
- Don't undermine your own work by suggesting incomplete or unnecessary recommendations.
- Avoid using recommendations as a place for self-criticism or introducing new information not covered in your research.
- Ensure that your recommendations are achievable and comprehensive, offering practical solutions for the issues considered in your paper.
By structuring your recommendations effectively, you can enhance the reliability and validity of your research findings, provide valuable strategies and suggestions for future research, and deliver impactful solutions to real-world problems.
Crafting Actionable and Specific Recommendations
Crafting actionable and specific recommendations is the key to ensuring your research findings have a real-world impact. Here are some essential tips to keep in mind:
Embrace Flexibility and Feasibility
Your recommendations should be open to discussion and new information, rather than being set in stone. Consider the following:
- Be realistic and considerate of your team's capabilities when making recommendations.
- Prioritize recommendations based on impact and reach, but be prepared to adjust based on team effort levels.
- Focus on solutions that require the fewest changes first, adopting an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) approach.
Provide Detailed and Justified Recommendations
To avoid vagueness and misinterpretation, ensure your recommendations are:
- Detailed, including photos, videos, or screenshots whenever possible.
- Justified based on research findings, providing alternatives when findings don't align with expectations or business goals.
Use this formula when writing recommendations:
Observed problem/pain point/unmet need + consequence + potential solution
Adopt a Solution-Oriented Approach
Element | Description |
|---|---|
Tone | Write recommendations in a clear, confident, and positive tone. |
Action Plan | Include an action plan along with the recommendation to add more weightage. |
Approach | Display a solution-oriented approach throughout your recommendations. |
Foster Collaboration and Participation
- Promote staff education on current research and create strategies to encourage adoption of promising clinical protocols.
- Include representatives from the treatment community in the development of the research initiative and the review of proposals.
- Require active, early, and permanent participation of treatment staff in the development, implementation, and interpretation of the study.
Tailor Recommendations to the Opportunity
When writing recommendations for a specific opportunity or program:
- Highlight the strengths and qualifications of the researcher.
- Provide specific examples of their work and accomplishments.
- Explain how their research has contributed to the field.
- Emphasize the researcher's potential for future success and their unique contributions.
By following these guidelines, you'll craft actionable and specific recommendations that drive meaningful change and showcase the value of your research.
Connecting Recommendations with Research Findings
Connecting your recommendations with research findings is crucial for ensuring the credibility and impact of your suggestions. Here's how you can seamlessly link your recommendations to the evidence uncovered in your study:
Grounding Recommendations in Research
Your recommendations should be firmly rooted in the data and insights gathered during your research process. Avoid including measures or suggestions that were not discussed or supported by your study findings. This approach ensures that your recommendations are evidence-based and directly relevant to the research at hand.
Highlighting the Significance of Collaboration
Research collaborations offer a wealth of benefits that can enhance an agency's competitive position. Consider the following factors when discussing the importance of collaboration in your recommendations:
- Organizational Development: Participation in research collaborations depends on an agency's stage of development, compatibility with its mission and culture, and financial stability.
- Trust-Building: Long-term collaboration success often hinges on a history of increasing involvement and trust between partners.
- Infrastructure: A permanent infrastructure that facilitates long-term development is key to successful collaborative programs.
Emphasizing Commitment and Participation
Element | Description |
|---|---|
Treatment Programs | Commitment from community-based treatment programs is crucial for successful implementation. |
Researchers | Encouragement of community-based programs to participate in various types of research is essential. |
Collaboration | Seeking collaboration with researchers to build information systems that enhance service delivery, improve management, and contribute to research databases is vital. |
Fostering Quality Improvement and Organizational Learning
In your recommendations, highlight the importance of enhancing quality improvement strategies and fostering organizational learning. Show sensitivity to the needs and constraints of community-based programs, as this understanding is crucial for effective collaboration and implementation.
Addressing Limitations and Implications
If not already addressed in the discussion section, your recommendations should mention the limitations of the study and their implications. Examples of limitations include:
- Sample size or composition
- Participant attrition
- Study duration
By acknowledging these limitations, you demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of your research and its potential impact.
By connecting your recommendations with research findings, you provide a solid foundation for your suggestions, emphasize the significance of collaboration, and showcase the potential for future research and practical applications.
Crafting impactful recommendations is a vital skill for any researcher looking to bridge the gap between their findings and real-world applications. By understanding the purpose of recommendations, identifying areas for future research, structuring your suggestions effectively, and connecting them to your research findings, you can unlock the full potential of your study. Remember to prioritize actionable, specific, and evidence-based recommendations that foster collaboration and drive meaningful change.
As you embark on your research journey, embrace the power of well-crafted recommendations to amplify the impact of your work. By following the guidelines outlined in this ultimate guide, you'll be well-equipped to write recommendations that resonate with your audience, inspire further investigation, and contribute to the advancement of your field. So go forth, make your research count, and let your recommendations be the catalyst for positive change.
Q: What are the steps to formulating recommendations in research? A: To formulate recommendations in research, you should first gain a thorough understanding of the research question. Review the existing literature to inform your recommendations and consider the research methods that were used. Identify which data collection techniques were employed and propose suitable data analysis methods. It's also essential to consider any limitations and ethical considerations of your research. Justify your recommendations clearly and finally, provide a summary of your recommendations.
Q: Why are recommendations significant in research studies? A: Recommendations play a crucial role in research as they form a key part of the analysis phase. They provide specific suggestions for interventions or strategies that address the problems and limitations discovered during the study. Recommendations are a direct response to the main findings derived from data collection and analysis, and they can guide future actions or research.
Q: Can you outline the seven steps involved in writing a research paper? A: Certainly. The seven steps to writing an excellent research paper include:
- Allowing yourself sufficient time to complete the paper.
- Defining the scope of your essay and crafting a clear thesis statement.
- Conducting a thorough yet focused search for relevant research materials.
- Reading the research materials carefully and taking detailed notes.
- Writing your paper based on the information you've gathered and analyzed.
- Editing your paper to ensure clarity, coherence, and correctness.
- Submitting your paper following the guidelines provided.
Q: What tips can help make a research paper more effective? A: To enhance the effectiveness of a research paper, plan for the extensive process ahead and understand your audience. Decide on the structure your research writing will take and describe your methodology clearly. Write in a straightforward and clear manner, avoiding the use of clichés or overly complex language.
Sign up for more like this.

How to write recommendations in a research paper
Many students put in a lot of effort and write a good report however they are not able to give proper recommendations. Recommendations in the research paper should be included in your research. As a researcher, you display a deep understanding of the topic of research. Therefore you should be able to give recommendations. Here are a few tips that will help you to give appropriate recommendations.
Recommendations in the research paper should be the objective of the research. Therefore at least one of your objectives of the paper is to provide recommendations to the parties associated or the parties that will benefit from your research. For example, to encourage higher employee engagement HR department should make strategies that invest in the well-being of employees. Additionally, the HR department should also collect regular feedback through online surveys.
Recommendations in the research paper should come from your review and analysis For example It was observed that coaches interviewed were associated with the club were working with the club from the past 2-3 years only. This shows that the attrition rate of coaches is high and therefore clubs should work on reducing the turnover of coaches.
Recommendations in the research paper should also come from the data you have analysed. For example, the research found that people over 65 years of age are at greater risk of social isolation. Therefore, it is recommended that policies that are made for combating social isolation should target this specific group.
Recommendations in the research paper should also come from observation. For example, it is observed that Lenovo’s income is stable and gross revenue has displayed a negative turn. Therefore the company should analyse its marketing and branding strategy.
Recommendations in the research paper should be written in the order of priority. The most important recommendations for decision-makers should come first. However, if the recommendations are of equal importance then it should come in the sequence in which the topic is approached in the research.
Recommendations in a research paper if associated with different categories then you should categorize them. For example, you have separate recommendations for policymakers, educators, and administrators then you can categorize the recommendations.
Recommendations in the research paper should come purely from your research. For example, you have written research on the impact on HR strategies on motivation. However, nowhere you have discussed Reward and recognition. Then you should not give recommendations for using rewards and recognition measures to boost employee motivation.
The use of bullet points offers better clarity rather than using long paragraphs. For example this paragraph “ It is recommended that Britannia Biscuit should launch and promote sugar-free options apart from the existing product range. Promotion efforts should be directed at creating a fresh and healthy image. A campaign that conveys a sense of health and vitality to the consumer while enjoying biscuit is recommended” can be written as:
- The company should launch and promote sugar-free options
- The company should work towards creating s fresh and healthy image
- The company should run a campaign to convey its healthy image
The inclusion of an action plan along with recommendation adds more weightage to your recommendation. Recommendations should be clear and conscience and written using actionable words. Recommendations should display a solution-oriented approach and in some cases should highlight the scope for further research.
Turn your research insights into actionable recommendations

At the end of one presentation, my colleague approached me and asked what I recommended based on the research. I was a bit puzzled. I didn’t expect anyone to ask me this kind of question. By that point in my career, I wasn’t aware that I had to make recommendations based on the research insights. I could talk about the next steps regarding what other research we had to conduct. I could also relay the information that something wasn’t working in a prototype, but I had no idea what to suggest.

How to move from qualitative data to actionable insights
Over time, more and more colleagues asked for these recommendations. Finally, I realized that one of the key pieces I was missing in my reports was the “so what?” The prototype isn’t working, so what do we do next? Because I didn’t include suggestions, my colleagues had a difficult time marrying actions to my insights. Sure, the team could see the noticeable changes, but the next steps were a struggle, especially for generative research.
Without these suggestions, my insights started to fall flat. My colleagues were excited about them and loved seeing the video clips, but they weren’t working with the findings. With this, I set out to experiment on how to write recommendations within a user research report.
.css-1nrevy2{position:relative;display:inline-block;} How to write recommendations
For a while, I wasn’t sure how to write recommendations. And, even now, I believe there is no one right way . When I first started looking into this, I started with two main questions:
What do recommendations mean to stakeholders?
How prescriptive should recommendations be?
When people asked me for recommendations, I had no idea what they were looking for. I was nervous I would step on people’s toes and give the impression I thought I knew more than I did. I wasn’t a designer and didn’t want to make whacky design recommendations or impractical suggestions that would get developers rolling their eyes.
When in doubt, I dusted off my internal research cap and sat with stakeholders to understand what they meant by recommendations. I asked them for examples of what they expected and what made a suggestion “helpful” or “actionable.” I walked away with a list of “must-haves” for my recommendations. They had to be:
Flexible. Just because I made an initial recommendation did not mean it was the only path forward. Once I presented the recommendations, we could talk through other ideas and consider new information. There were a few times when I revised my recommendations based on conversations I had with colleagues.
Feasible. At first, I started presenting my recommendations without any prior feedback. My worst nightmare came true. The designer and developer sat back, arms crossed, and said, “A lot of this is impossible.” I quickly learned to review some of my recommendations I was uncertain about with them beforehand. Alternatively, I came up with several recommendations for one solution to help combat this problem.
Prioritized (to my best abilities). Since I am not entirely sure of the recommendation’s effort, I use a chart of impact and reach to prioritize suggestions. Then, once I present this list, it may get reprioritized depending on effort levels from the team (hey, flexibility!).
Detailed. This point helped me a lot with my second question regarding how in-depth I should make my recommendations. Some of the best detail comes from photos, videos, or screenshots, and colleagues appreciated when I linked recommendations with this media. They also told me to put in as much detail as possible to avoid vagueness, misinterpretation, and endless debate.
Think MVP. Think about the solution with the fewest changes instead of recommending complex changes to a feature or product. What are some minor changes that the team can make to improve the experience or product?
Justified. This part was the hardest for me. When my research findings didn’t align with expectations or business goals, I had no idea what to say. When I receive results that highlight we are going in the wrong direction, my recommendations become even more critical. Instead of telling the team that the new product or feature sucks and we should stop working on it, I offer alternatives. I follow the concept of “no, but...” So, “no, this isn’t working, but we found that users value X and Y, which could lead to increased retention” (or whatever metric we were looking at.
Let’s look at some examples
Although this list was beneficial in guiding my recommendations, I still wasn’t well-versed in how to write them. So, after some time, I created a formula for writing recommendations:
Observed problem/pain point/unmet need + consequence + potential solution
Evaluative research
Let’s imagine we are testing a check-out page, and we found that users were having a hard time filling out the shipping and billing forms, especially when there were two different addresses.
A non-specific and unhelpful recommendation might look like :
Users get frustrated when filling out the shipping and billing form.
The reasons this recommendation is not ideal are :
It provides no context or detail of the problem
There is no proposed solution
It sounds a bit judgemental (focus on the problem!)
There is no immediate movement forward with this
A redesign recommendation about the same problem might look like this :
Users overlook the mandatory fields in the shipping and billing form, causing them to go back and fill out the form again. With this, they become frustrated. Include markers of required fields and avoid deleting information when users submit if they haven’t filled out all required fields.
Let’s take another example :
We tested an entirely new concept for our travel company, allowing people to pay to become “prime” travel members. In our user base, no one found any value in having or paying for a membership. However, they did find value in several of the features, such as sharing trips with family members or splitting costs but could not justify paying for them.
A suboptimal recommendation could look like this :
Users would not sign-up or pay for a prime membership.
Again, there is a considerable lack of context and understanding here, as well as action. Instead, we could try something like:
Users do not find enough value in the prime membership to sign-up or pay for it. Therefore, they do not see themselves using the feature. However, they did find value in two features: sharing trips with friends and splitting the trip costs. Focusing, instead, on these features could bring more people to our platform and increase retention.
Generative research
Generative research can look a bit trickier because there isn’t always an inherent problem you are solving. For example, you might not be able to point to a usability issue, so you have to look more broadly at pain points or unmet needs.
For example, in our generative research, we found that people often forget to buy gifts for loved ones, making them feel guilty and rushed at the last minute to find something meaningful but quickly.
This finding is extremely broad and could go in so many directions. With suggestions, we don’t necessarily want to lead our teams down only one path (flexibility!), but we also don’t want to leave the recommendation too vague (detailed). I use How Might We statements to help me build generative research recommendations.
Just reporting the above wouldn’t entirely be enough for a recommendation, so let’s try to put it in a more actionable format:
People struggled to remember to buy gifts for loved one’s birthdays or special days. By the time their calendar notified them, it was too late to get a gift, leaving them filled with guilt and rushing to purchase a meaningful gift to arrive on time. How might we help people remember birthdays early enough to find meaningful gifts for their loved ones?
A great follow-up to generative research recommendations can be running an ideation workshop !
Researching the right thing versus researching the thing right
How to format recommendations in your report.
I always end with recommendations because people leave a presentation with their minds buzzing and next steps top of mind (hopefully!). My favorite way to format suggestions is in a chart. That way, I can link the recommendation back to the insight and priority. My recommendations look like this:
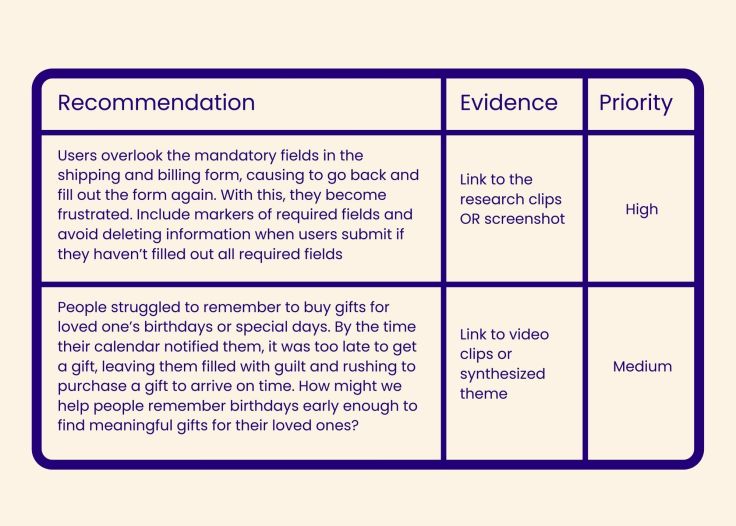
Overall, play around with the recommendations that you give to your teams. The best thing you can do is ask for what they expect and then ask for feedback. By catering and iterating to your colleagues’ needs, you will help them make better decisions based on your research insights!
Written by Nikki Anderson, User Research Lead & Instructor. Nikki is a User Research Lead and Instructor with over eight years of experience. She has worked in all different sizes of companies, ranging from a tiny start-up called ALICE to large corporation Zalando, and also as a freelancer. During this time, she has led a diverse range of end-to-end research projects across the world, specializing in generative user research. Nikki also owns her own company, User Research Academy, a community and education platform designed to help people get into the field of user research, or learn more about how user research impacts their current role. User Research Academy hosts online classes, content, as well as personalized mentorship opportunities with Nikki. She is extremely passionate about teaching and supporting others throughout their journey in user research. To spread the word of research and help others transition and grow in the field, she writes as a writer at dscout and Dovetail. Outside of the world of user research, you can find Nikki (happily) surrounded by animals, including her dog and two cats, reading on her Kindle, playing old-school video games like Pokemon and World of Warcraft, and writing fiction novels.
Keep reading

.css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} Decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next
Decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
22 August 2024: Due to technical disruption, we are experiencing some delays to publication. We are working to restore services and apologise for the inconvenience. For further updates please visit our website: https://www.cambridge.org/universitypress/about-us/news-and-blogs/cambridge-university-press-publishing-update-following-technical-disruption
We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to provide you with a better experience on our websites. Close this message to accept cookies or find out how to manage your cookie settings .
Login Alert

- > How to Do Research
- > Draw conclusions and make recommendations

Book contents
- Frontmatter
- Acknowledgements
- Introduction: Types of research
- Part 1 The research process
- 1 Develop the research objectives
- 2 Design and plan the study
- 3 Write the proposal
- 4 Obtain financial support for the research
- 5 Manage the research
- 6 Draw conclusions and make recommendations
- 7 Write the report
- 8 Disseminate the results
- Part 2 Methods
- Appendix The market for information professionals: A proposal from the Policy Studies Institute
6 - Draw conclusions and make recommendations
from Part 1 - The research process
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 June 2018
This is the point everything has been leading up to. Having carried out the research and marshalled all the evidence, you are now faced with the problem of making sense of it all. Here you need to distinguish clearly between three different things: results, conclusions and recommendations.
Results are what you have found through the research. They are more than just the raw data that you have collected. They are the processed findings of the work – what you have been analysing and striving to understand. In total, the results form the picture that you have uncovered through your research. Results are neutral. They clearly depend on the nature of the questions asked but, given a particular set of questions, the results should not be contentious – there should be no debate about whether or not 63 per cent of respondents said ‘yes’ to question 16.
When you consider the results you can draw conclusions based on them. These are less neutral as you are putting your interpretation on the results and thus introducing a degree of subjectivity. Some research is simply descriptive – the final report merely presents the results. In most cases, though, you will want to interpret them, saying what they mean for you – drawing conclusions.
These conclusions might arise from a comparison between your results and the findings of other studies. They will, almost certainly, be developed with reference to the aim and objectives of the research. While there will be no debate over the results, the conclusions could well be contentious. Someone else might interpret the results differently, arriving at different conclusions. For this reason you need to support your conclusions with structured, logical reasoning.
Having drawn your conclusions you can then make recommendations. These should flow from your conclusions. They are suggestions about action that might be taken by people or organizations in the light of the conclusions that you have drawn from the results of the research. Like the conclusions, the recommendations may be open to debate. You may feel that, on the basis of your conclusions, the organization you have been studying should do this, that or the other.
Access options
Save book to kindle.
To save this book to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about saving to your Kindle .
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service .
- Draw conclusions and make recommendations
- Book: How to Do Research
- Online publication: 09 June 2018
- Chapter DOI: https://doi.org/10.29085/9781856049825.007
Save book to Dropbox
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox .
Save book to Google Drive
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive .
Implications or Recommendations in Research: What's the Difference?
- Peer Review
High-quality research articles that get many citations contain both implications and recommendations. Implications are the impact your research makes, whereas recommendations are specific actions that can then be taken based on your findings, such as for more research or for policymaking.
Updated on August 23, 2022

That seems clear enough, but the two are commonly confused.
This confusion is especially true if you come from a so-called high-context culture in which information is often implied based on the situation, as in many Asian cultures. High-context cultures are different from low-context cultures where information is more direct and explicit (as in North America and many European cultures).
Let's set these two straight in a low-context way; i.e., we'll be specific and direct! This is the best way to be in English academic writing because you're writing for the world.
Implications and recommendations in a research article
The standard format of STEM research articles is what's called IMRaD:
- Introduction
- Discussion/conclusions
Some journals call for a separate conclusions section, while others have the conclusions as the last part of the discussion. You'll write these four (or five) sections in the same sequence, though, no matter the journal.
The discussion section is typically where you restate your results and how well they confirmed your hypotheses. Give readers the answer to the questions for which they're looking to you for an answer.
At this point, many researchers assume their paper is finished. After all, aren't the results the most important part? As you might have guessed, no, you're not quite done yet.
The discussion/conclusions section is where to say what happened and what should now happen
The discussion/conclusions section of every good scientific article should contain the implications and recommendations.
The implications, first of all, are the impact your results have on your specific field. A high-impact, highly cited article will also broaden the scope here and provide implications to other fields. This is what makes research cross-disciplinary.
Recommendations, however, are suggestions to improve your field based on your results.
These two aspects help the reader understand your broader content: How and why your work is important to the world. They also tell the reader what can be changed in the future based on your results.
These aspects are what editors are looking for when selecting papers for peer review.

Implications and recommendations are, thus, written at the end of the discussion section, and before the concluding paragraph. They help to “wrap up” your paper. Once your reader understands what you found, the next logical step is what those results mean and what should come next.
Then they can take the baton, in the form of your work, and run with it. That gets you cited and extends your impact!
The order of implications and recommendations also matters. Both are written after you've summarized your main findings in the discussion section. Then, those results are interpreted based on ongoing work in the field. After this, the implications are stated, followed by the recommendations.
Writing an academic research paper is a bit like running a race. Finish strong, with your most important conclusion (recommendation) at the end. Leave readers with an understanding of your work's importance. Avoid generic, obvious phrases like "more research is needed to fully address this issue." Be specific.
The main differences between implications and recommendations (table)

Now let's dig a bit deeper into actually how to write these parts.
What are implications?
Research implications tell us how and why your results are important for the field at large. They help answer the question of “what does it mean?” Implications tell us how your work contributes to your field and what it adds to it. They're used when you want to tell your peers why your research is important for ongoing theory, practice, policymaking, and for future research.
Crucially, your implications must be evidence-based. This means they must be derived from the results in the paper.
Implications are written after you've summarized your main findings in the discussion section. They come before the recommendations and before the concluding paragraph. There is no specific section dedicated to implications. They must be integrated into your discussion so that the reader understands why the results are meaningful and what they add to the field.
A good strategy is to separate your implications into types. Implications can be social, political, technological, related to policies, or others, depending on your topic. The most frequently used types are theoretical and practical. Theoretical implications relate to how your findings connect to other theories or ideas in your field, while practical implications are related to what we can do with the results.
Key features of implications
- State the impact your research makes
- Helps us understand why your results are important
- Must be evidence-based
- Written in the discussion, before recommendations
- Can be theoretical, practical, or other (social, political, etc.)
Examples of implications
Let's take a look at some examples of research results below with their implications.
The result : one study found that learning items over time improves memory more than cramming material in a bunch of information at once .
The implications : This result suggests memory is better when studying is spread out over time, which could be due to memory consolidation processes.
The result : an intervention study found that mindfulness helps improve mental health if you have anxiety.
The implications : This result has implications for the role of executive functions on anxiety.
The result : a study found that musical learning helps language learning in children .
The implications : these findings suggest that language and music may work together to aid development.
What are recommendations?
As noted above, explaining how your results contribute to the real world is an important part of a successful article.
Likewise, stating how your findings can be used to improve something in future research is equally important. This brings us to the recommendations.
Research recommendations are suggestions and solutions you give for certain situations based on your results. Once the reader understands what your results mean with the implications, the next question they need to know is "what's next?"
Recommendations are calls to action on ways certain things in the field can be improved in the future based on your results. Recommendations are used when you want to convey that something different should be done based on what your analyses revealed.
Similar to implications, recommendations are also evidence-based. This means that your recommendations to the field must be drawn directly from your results.
The goal of the recommendations is to make clear, specific, and realistic suggestions to future researchers before they conduct a similar experiment. No matter what area your research is in, there will always be further research to do. Try to think about what would be helpful for other researchers to know before starting their work.
Recommendations are also written in the discussion section. They come after the implications and before the concluding paragraphs. Similar to the implications, there is usually no specific section dedicated to the recommendations. However, depending on how many solutions you want to suggest to the field, they may be written as a subsection.
Key features of recommendations
- Statements about what can be done differently in the field based on your findings
- Must be realistic and specific
- Written in the discussion, after implications and before conclusions
- Related to both your field and, preferably, a wider context to the research
Examples of recommendations
Here are some research results and their recommendations.
A meta-analysis found that actively recalling material from your memory is better than simply re-reading it .
- The recommendation: Based on these findings, teachers and other educators should encourage students to practice active recall strategies.
A medical intervention found that daily exercise helps prevent cardiovascular disease .
- The recommendation: Based on these results, physicians are recommended to encourage patients to exercise and walk regularly. Also recommended is to encourage more walking through public health offices in communities.
A study found that many research articles do not contain the sample sizes needed to statistically confirm their findings .
The recommendation: To improve the current state of the field, researchers should consider doing power analysis based on their experiment's design.
What else is important about implications and recommendations?
When writing recommendations and implications, be careful not to overstate the impact of your results. It can be tempting for researchers to inflate the importance of their findings and make grandiose statements about what their work means.
Remember that implications and recommendations must be coming directly from your results. Therefore, they must be straightforward, realistic, and plausible.
Another good thing to remember is to make sure the implications and recommendations are stated clearly and separately. Do not attach them to the endings of other paragraphs just to add them in. Use similar example phrases as those listed in the table when starting your sentences to clearly indicate when it's an implication and when it's a recommendation.
When your peers, or brand-new readers, read your paper, they shouldn't have to hunt through your discussion to find the implications and recommendations. They should be clear, visible, and understandable on their own.
That'll get you cited more, and you'll make a greater contribution to your area of science while extending the life and impact of your work.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
Encyclopedia
Writing with artificial intelligence.
- Recommendation Reports
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley - Professor of English - USF , Julie Staggers - Washington State University
Table of Contents
Recommendation reports are texts that advise audiences about the best ways to solve a problem. Recommendation reports are a type of formal report that is widely used across disciplines and professions. Subject Matter Experts aim to make recommendations based on the best available theory, research and practice.
Different disciplines and professions have different research methods for assessing knowledge claims and defining knowledge . Thus, there is no one perfect way to write a recommendation report.
As always, when composing—especially when you’re planning your report—it’s strategic to focus on your audience, rhetorical analysis, and rhetorical reasoning. At center, keep the focus on what you want your audience to feel, think, and do.
While writers, speakers, and knowledge workers . . . may choose a variety of ways to organize their reports, below are some fairly traditional sections to formal recommendations reports:
- Letter of transmittal
- Problem Definition
- Potential solutions to the problem
- Empirical Research Methods used to investigate the problem
- Recommendations
- List of Illustrations
Report Body
Note: your specific rhetorical context will determine what headings you use in your Recommendation Report. That said, the following sections are fairly typical for this genre, and they are required, as appropriate, for this assignment.
| What is the purpose of this piece of communication? | Succinctly explain the purpose of this document, not the purpose of the project. | |
| What content is included in the memo? Key Terms. | Provide a brief overview of the report’s main sections for readers who may only read the summary. Are there any key terms or concepts that the audience may need defined? | |
| What problem(s) does the report address? What is the context? | Be interesting. Introduce the . (You may use boilerplate from the Client Proposal and Progress Report) Provide all of the background and rationale for pursuing this study. [Here you may repeat some language from both the letter of transmittal and the Executive Summary.] Engage in : Provide the background information your reader needs to understand the problem, stakeholders, and potential solutions Appeal, if appropriate, to the benefits for the audience | |
| * If your team used empirical methods, your report needs a Results section. | 1. What textual research or empirical research was done? How? Why? | Here your aim is to define the research methods you employed. Use task orientation: Describe the exact tasks you performed and the rationale for each task. What roles were assigned: Project Manager, Analysis & User Research, Interface Analysis, Deliverables Specialist? Include a Gantt Chart to identify the work actually conducted as opposed to what was originally planned. Demonstrate to the reader that you followed the plan outlined in the research proposal. If you made deviations, identify why. |
| (for empirical contributions to knowledge) | What did you find out from your research? | The Results section is the writing space reserved for reporting discoveries. This space is reserved for investigators who are employing empirical methods. If you did not use empirical methods, you do not need this section. Note: A Results section is not equivalent to a review of literature section. |
| (optional) | What are the shortcomings of this study? Did anything go wrong? | Include if you encountered any problems that might limit your recommendations |
| (for empirical contributions to knowledge) | What do your results mean? | Your research won’t “speak for itself” to the client. You have to tell the client what your results mean. Draw conclusions and implications based on what you have learned. Explain the relationships between pieces of data/information. Describe trends. If there are anomalies, explain what seems wrong or different from what was expected. |
| What recommendations can you offer based on your conclusions? | Tells the reader what steps, measures, actions they should take in light of the conclusions you have reached. Substantiate the value of your recommendations by grounding them in and empirical research. Explain how the recommendations might be implemented. Explores how implementing the proposed recommendations benefits the audience. |
Report back matter
Collect material for the appendices as you go. The report back matter will include:
- Bibliography, which is sometimes referred to as Works Cited or References (Use a citation format appropriate for your field (APA, MLA, Chicago, IEEE, etc.)
- Appendices, if necessary (e.g., letters of support, financial projections)
Formatting and design
Employ a professional writing style throughout, including:
- Page layout: Appropriate to audience, purpose, and context. 8.5 x 11 with 1-inch margins is a fail-safe default.
- Typography: Choose business-friendly fonts appropriate to your audience, purpose, and context; Arial for headers and Times New Roman for body text is a safe, neutral default.
- Headings and subheadings: Use a numbered heading and subheading system, formatted using the Styles function on your word processor.
- Bulleted and numbered lists: Use lists that are formatted correctly using the list buttons on your word processor with a blank line before the first bullet and after the last bullet
- Graphics and figures: Support data findings and arguments with appropriate visuals – charts, tables, graphics; Include numbered titles and captions
- Page numbering: use lower-case Roman numerals for pages before the table of contents, Arabic numerals; no page number on the TOC.
Additional Resources
- Final Reports by Angela Eward-Mangione and Katherine McGee
- Professional Writing Style

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Recommended

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Structured Revision – How to Revise Your Work

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Research, Speech & Writing

Citation Guide – Learn How to Cite Sources in Academic and Professional Writing

Page Design – How to Design Messages for Maximum Impact
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...


The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles


Recommendation in Research
Ai generator.

A recommendation in research refers to the advice or suggestions provided by researchers at the conclusion of their study, aimed at addressing the gaps identified, enhancing future research , and applying findings in practical contexts. Recommendations are crucial as they guide stakeholders, including policymakers, practitioners, and fellow researchers, on how to utilize the research outcomes effectively. These suggestions are typically based on the evidence gathered during the study and are intended to improve practices, inform decision-making, and inspire further investigations to build on the existing knowledge.
What is Recommendation in Research?
A recommendation in research is a suggestion or course of action proposed by researchers based on their study’s findings. It aims to address identified gaps, enhance future research, and apply results in practical scenarios. Recommendations guide stakeholders, such as policymakers and fellow researchers, on utilizing the research effectively to improve practices, inform decisions, and inspire further studies.
Examples of Recommendations in Research
- Implement Comprehensive Training Programs : Ensure that employees receive ongoing training to keep up with technological advancements.
- Increase Funding for Renewable Energy Projects : Allocate more resources to develop sustainable energy solutions.
- Promote Interdisciplinary Research : Encourage collaboration across various fields to address complex global issues.
- Adopt Advanced Data Analytics : Utilize cutting-edge data analysis techniques to improve decision-making processes.
- Enhance Public Awareness Campaigns : Develop strategies to educate the public on critical health issues.
- Strengthen Cybersecurity Measures : Implement robust security protocols to protect sensitive information.
- Encourage Community Involvement : Foster greater community participation in local governance.
- Develop Inclusive Policies : Create policies that address the needs of diverse populations.
- Optimize Supply Chain Management : Improve logistics and supply chain efficiency to reduce costs.
- Support Mental Health Initiatives : Increase support for mental health programs and services.
Recommendation for Students in Research
Research is a crucial component of academic and professional development. Here are some key recommendations for students engaged in research to ensure success and meaningful contributions to their field:
1. Choose a Relevant and Interesting Topic
- Personal Interest: Select a topic that genuinely interests you.
- Relevance: Ensure the topic is relevant to your field of study.
- Scope: Make sure the topic is neither too broad nor too narrow.
2. Conduct a Thorough Literature Review
- Background Research: Review existing literature to understand the current state of knowledge.
- Identify Gaps: Identify gaps in the existing research that your study can address.
- Theoretical Framework: Build a strong theoretical foundation for your research.
3. Develop a Clear Research Plan
- Objectives: Define clear and achievable research objectives.
- Methodology: Choose appropriate research methods and techniques.
- Timeline: Create a realistic timeline with milestones for completing each stage of the research.
4. Use Reliable and Valid Sources
- Academic Journals: Prefer peer-reviewed journals for sourcing information.
- Primary Sources: Whenever possible, use primary sources to gather data.
- Citation Management: Use citation management tools to organize your references.
5. Ensure Ethical Conduct
- Informed Consent: Obtain informed consent from participants if your research involves human subjects.
- Data Privacy: Ensure the confidentiality and privacy of your data.
- Integrity: Maintain honesty and transparency in your research process.
6. Develop Strong Analytical Skills
- Critical Thinking: Develop the ability to critically analyze data and sources.
- Statistical Analysis: Gain proficiency in statistical methods if your research involves quantitative data.
- Qualitative Analysis: Learn methods for analyzing qualitative data, such as thematic analysis.
7. Seek Feedback and Collaboration
- Mentorship: Seek guidance from your research advisor or mentor regularly.
- Peer Review: Engage with peers for feedback and constructive criticism.
- Collaboration: Collaborate with other researchers to enhance the quality of your study.
8. Maintain Clear and Consistent Documentation
- Research Journal: Keep a detailed journal of your research process, observations, and reflections.
- Data Management: Organize your data systematically for easy retrieval and analysis.
- Progress Reports: Regularly update your progress and adjust your plan as needed.
9. Communicate Your Findings Effectively
- Writing Skills: Develop strong academic writing skills to present your findings clearly.
- Presentations: Learn to create and deliver effective presentations of your research.
- Publication: Aim to publish your research in reputable academic journals or conferences.
10. Stay Updated and Continue Learning
- Current Trends: Stay updated with the latest developments in your field.
- Professional Development: Attend workshops, seminars, and conferences to enhance your knowledge and skills.
- Networking: Build a professional network with other researchers and professionals in your field.
Types of Recommendation in Research

Recommendations in research are crucial as they provide actionable insights based on the study’s findings. Here are the primary types of recommendations commonly found in research:
1. Practical Recommendations
Practical recommendations offer actionable advice that can be implemented in real-world settings. These are particularly useful for practitioners and policymakers.
- Implementation Strategies: Suggest ways to apply research findings in practice.
- Policy Changes: Recommend modifications to existing policies or the creation of new policies.
- Best Practices: Identify effective practices and procedures based on research results.
2. Theoretical Recommendations
Theoretical recommendations are aimed at advancing academic knowledge and understanding. They often suggest directions for future research or adjustments to existing theories.
- Theory Development: Propose new theories or modifications to existing ones based on research findings.
- Conceptual Frameworks: Suggest new conceptual models or frameworks.
- Research Hypotheses: Recommend specific hypotheses for future testing.
3. Methodological Recommendations
Methodological recommendations focus on the research process itself. They offer suggestions for improving research design, data collection, and analysis techniques.
- Research Design: Advise on more effective or innovative research designs.
- Data Collection Methods: Recommend better or alternative methods for data collection.
- Analytical Techniques: Suggest advanced or more appropriate analytical techniques.
4. Policy Recommendations
Policy recommendations are directed towards governmental or organizational bodies. They aim to influence policy-making processes based on research evidence.
- Legislative Changes: Recommend changes to laws or regulations.
- Organizational Policies: Suggest adjustments to organizational policies and procedures.
- Public Health Initiatives: Propose new public health strategies or interventions.
5. Educational Recommendations
Educational recommendations are targeted at educational institutions, educators, and curriculum developers. They aim to improve educational practices and outcomes.
- Curriculum Development: Suggest changes or additions to curricula.
- Teaching Methods: Recommend effective teaching strategies and methods.
- Educational Programs: Propose new programs or enhancements to existing ones.
Recommendation for Future Researchers
Future researchers can benefit from insights and guidance to enhance the quality and impact of their studies. Here are some key recommendations:
1. Explore Unanswered Questions
- Identify Gaps: Focus on gaps highlighted in previous research to build on existing knowledge.
- New Areas: Investigate emerging areas or under-researched topics within your field.
2. Improve Methodological Rigor
- Innovative Methods: Incorporate innovative research methodologies and techniques.
- Replication Studies: Conduct replication studies to verify and validate findings from prior research.
- Mixed Methods: Utilize mixed methods approaches to provide a comprehensive understanding of the research problem.
3. Ensure Ethical Conduct
- Ethical Guidelines: Adhere to ethical guidelines and standards throughout the research process.
- Informed Consent: Ensure that participants provide informed consent and understand their rights.
- Data Privacy: Protect the confidentiality and privacy of participants’ data.
4. Enhance Data Quality
- Robust Data Collection: Use robust data collection methods to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Triangulation: Employ triangulation by using multiple data sources or methods to strengthen findings.
- Longitudinal Studies: Consider conducting longitudinal studies to observe changes over time.
5. Collaborate and Network
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Work with researchers from different disciplines to gain diverse perspectives.
- International Partnerships: Form partnerships with international researchers to broaden the scope and impact of your study.
- Professional Networks: Join professional organizations and attend conferences to stay updated and connected.
What is the Purpose of Recommendation in Research
Recommendations in research are essential for guiding future actions based on the study’s findings. Here are the main purposes of including recommendations in research:
1. Guiding Future Research
- Identify Gaps: Point out areas where more research is needed.
- Suggest Topics: Recommend specific topics or questions for future studies.
- Encourage Validation: Suggest replicating the study in different settings to confirm results.
2. Informing Policy and Practice
- Policy Changes: Provide evidence-based suggestions for improving or creating policies.
- Best Practices: Offer practical advice for professionals to improve their work.
- Implementation: Suggest ways to apply the research findings in real-world situations.
3. Enhancing Academic Knowledge
- Theoretical Contributions: Help develop or refine theories based on the research findings.
- Stimulate Discussion: Encourage further academic debate and inquiry.
4. Improving Research Methods
- Methodology: Recommend better or alternative research methods.
- Data Collection: Suggest more effective ways to gather data.
- Analysis Techniques: Propose improved methods for analyzing data.
5. Solving Practical Problems
- Actionable Solutions: Offer practical solutions to problems identified in the research.
- Resource Allocation: Guide organizations on how to use resources more effectively.
- Strategic Planning: Assist in planning future actions based on the research insights.
How to Write Research Recommendations?
Writing research recommendations involves providing actionable advice based on the findings of your study. Here are steps and tips to help you write effective research recommendations:
1. Review Your Findings
- Summarize Key Findings: Begin by summarizing the most important findings of your research.
- Highlight Significant Results: Focus on results that have significant implications for future research, policy, or practice.
2. Align Recommendations with Objectives
- Reflect on Objectives: Ensure that your recommendations align with the original objectives of your study.
- Address Research Questions: Directly address the research questions or hypotheses you set out to explore.
3. Be Specific and Actionable
- Concrete Actions: Provide specific actions that stakeholders can take.
- Clear Guidance: Offer clear and practical steps rather than vague suggestions.
4. Prioritize Recommendations
- Importance: Rank recommendations based on their importance and feasibility.
- Immediate vs. Long-Term: Distinguish between recommendations that can be implemented immediately and those that are long-term.
5. Consider Different Audiences
- Tailor Recommendations: Adapt recommendations to different audiences such as policymakers, practitioners, researchers, or the general public.
- Relevant Language: Use language and terms that are relevant and understandable to each audience.
6. Support with Evidence
- Link to Findings: Base your recommendations on the evidence from your research.
- Cite Data: Use data and examples from your study to justify each recommendation.
7. Address Limitations
- Acknowledge Constraints: Recognize any limitations in your study and how they might affect your recommendations.
- Suggest Improvements: Provide suggestions for how future research can address these limitations.
8. Highlight Benefits
- Positive Outcomes: Emphasize the potential benefits of implementing your recommendations.
- Impact: Discuss the impact your recommendations could have on the field, policy, or practice.
9. Be Realistic
- Feasibility: Ensure that your recommendations are realistic and achievable.
- Resources: Consider the resources required to implement your recommendations and whether they are available.
10. Review and Revise
- Proofread: Carefully review your recommendations for clarity, coherence, and correctness.
- Feedback: Seek feedback from peers or advisors to refine your recommendations.
FAQ’s
Why are recommendations important in research.
Recommendations provide practical applications of research findings, guiding stakeholders in implementing changes or further investigations.
How do you write a good research recommendation?
A good research recommendation is specific, actionable, and directly linked to the study’s conclusions and data.
What should be included in a research recommendation?
Include the action to be taken, the rationale behind it, and its expected impact or benefits.
Can recommendations suggest further research?
Yes, recommendations often suggest areas for further study to address limitations or explore new questions.
How should recommendations be structured in a research paper?
Recommendations should follow the conclusion section, clearly numbered or bullet-pointed for easy reading.
What is the difference between conclusions and recommendations?
Conclusions summarize the findings, while recommendations propose actions based on those findings.
Who benefits from research recommendations?
Policymakers, practitioners, researchers, and other stakeholders can benefit from research recommendations.
How many recommendations should a research paper have?
The number of recommendations varies but should be concise and focused, usually between three to five key suggestions.
Can recommendations be generalized to other contexts?
Recommendations should be context-specific but can sometimes be adapted for broader application.
What language should be used in writing recommendations?
Use clear, precise, and direct language to ensure recommendations are easily understood and actionable.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

Transcription Service for Your Academic Paper
Start Transcription now
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Transcription Service for Your Paper
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Dissertation Recommendations — How To Write Them
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Recommendations are crucial to your paper because they suggest solutions to your research problems. You can include recommendations in the discussion sections of your writing and briefly in the conclusions of your dissertation , thesis, or research paper . This article discusses dissertation recommendations, their purpose, and how to write one.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Dissertation Recommendations — In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Dissertation recommendations
- 3 How to write dissertation recommendations
- 4 Dissertation recommendations based on your findings
- 5 Purpose of dissertation recommendations
Dissertation Recommendations — In a Nutshell
- Dissertation recommendations are an important aspect of your research paper.
- They should be specific, measurable, and have the potential of future possibilities.
- Additionally, these recommendations should offer practical insights and suggestions for solving real-life problems.
When making your recommendations, please ensure the following:
- Your recommendations are an extension of your work instead of a basis for self-criticism
- Your research stands independently instead of suggesting recommendations that will complete it
- Your dissertation recommendations offer insights into how future research can build upon it instead of undermining your research
Definition: Dissertation recommendations
Dissertation recommendations are the actionable insights and suggestions presented after you get your research findings. These suggestions are usually based on what you find and help to guide future studies or practical applications. It’s best to place your dissertation recommendations at the conclusion.
Printing Your Thesis With BachelorPrint
- High-quality bindings with customizable embossing
- 3D live preview to check your work before ordering
- Free express delivery
Configure your binding now!
to the print shop
How to write dissertation recommendations
When writing your academic paper, you can frame dissertation recommendations using one of the following methods:
Use the problem: In this approach, you should address the issues highlighted in your research.
Offer solutions: You can offer some practical solutions to the problems revealed in your research.
Use a theory: Here, you can base your recommendations on your study’s theoretical approach.
Here are some helpful tips for writing dissertation recommendations that you should incorporate when drafting a research paper:
- Avoid general or vague recommendations
- Be specific and concrete
- Offer measurable insights Ensure your suggestions are practical and implementable
- Avoid focusing on theoretical concepts or new findings but on future possibilities
“Based on the study’s outcomes, it’s recommended that businesses and organizations develop mental health well-being frameworks to reduce workplace stress. This training should be mandatory for all employees and conducted on a monthly basis.”
Dissertation recommendations based on your findings
After analysing your findings, you can divide your dissertation recommendations into two subheadings as discussed below:
What can be done?
This section highlights the steps you can use when conducting the research. You may also include any steps needed to address the issues highlighted in your research question. For instance, if the study reveals a lack of emotional connection between employees, implementing dynamic awareness training or sit-downs could be recommended.
Is further research needed?
This section highlights the benefits of further studies that will help build on your research findings. For instance, if your research found less data on employee mental well-being, your dissertation recommendations could suggest future studies.
Purpose of dissertation recommendations
Note: Dissertation recommendations have the following purposes:
- Provide guidance and improve the quality of further studies based on your research findings
- Offer insights, call to action, or suggest other studies
- Highlight specific, clear, and realistic suggestions for future studies
When writing your dissertation recommendations, always remember to keep them specific, measurable, and clear. You should also ensure that a comprehensible rationale supports these recommendations. Additionally, your requests should always be directly linked to your research and offer suggestions from that angle.
Note that your suggestions should always focus on future possibilities and not on present new findings or theoretical concepts. This is because future researchers may use your results to draw further conclusions and gather new insights from your work.
Can I include new arguments in the conclusion of a dissertation
Dissertations follow a more formal structure; hence, you can only present new arguments in the conclusion. Use your dissertation’s concluding part as a summary of your points or to provide recommendations.
How is the conclusion different from the discussion sections?
The discussion section describes a detailed account of your findings, while the conclusion answers the research question and highlights some recommendations.
What shouldn't I include in the dissertation recommendations?
Avoid concluding with weak statements like “there are good insights from both ends…”, generic phrases like “in conclusion…” or evidence that you failed to mention in the discussion or results section.
Extremely satisfied, excellent deal with delivery in less than 24h. The print...
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Eigentümer dieser Website, |
| Zweck | Speichert die Einstellungen der Besucher, die in der Cookie Box von Borlabs Cookie ausgewählt wurden. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Bachelorprint |
| Zweck | Erkennt das Herkunftsland und leitet zur entsprechenden Sprachversion um. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | ip-api.com |
| Cookie Name | georedirect |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Playcanvas |
| Zweck | Display our 3D product animations |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | playcanv.as, playcanvas.as, playcanvas.com |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Cookie von Google zur Steuerung der erweiterten Script- und Ereignisbehandlung. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Facebook-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .facebook.com |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird zum Entsperren von Google Maps-Inhalten verwendet. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Instagram-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .instagram.com |
| Cookie Name | pigeon_state |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Sitzung |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Openstreetmap Foundation, St John’s Innovation Centre, Cowley Road, Cambridge CB4 0WS, United Kingdom |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um OpenStreetMap-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .openstreetmap.org |
| Cookie Name | _osm_location, _osm_session, _osm_totp_token, _osm_welcome, _pk_id., _pk_ref., _pk_ses., qos_token |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1-10 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Twitter International Company, One Cumberland Place, Fenian Street, Dublin 2, D02 AX07, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Twitter-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .twimg.com, .twitter.com |
| Cookie Name | __widgetsettings, local_storage_support_test |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Unbegrenzt |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Vimeo Inc., 555 West 18th Street, New York, New York 10011, USA |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Vimeo-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | player.vimeo.com |
| Cookie Name | vuid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um YouTube-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
Privacy Policy Imprint

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
9 Sample Excellent Recommendation Letters for Your Job
Letters of Recommendation

Anyone who's applied for a job knows how important recommendation letters can be to getting hired. While you've probably asked for a reference letter in the past, you may be less familiar with writing one. If someone asks you for a reference, how can you produce a great letter that will help your employee, colleague, or friend get hired?
To help you through the writing process, we're providing nine samples of effective letters of recommendation (scroll down to skip to the samples!). By reading through these examples, you'll gain a clear understanding of how to structure your own letters.
Before getting to the free recommendation letter samples, let's briefly review the role that reference letters play in the hiring process. Why are they important, and what makes some stand out over others?
Why Are Recommendation Letters Important?
Many employers request recommendation letters to help them decide who to hire or internally promote. Throughout the hiring process, the applicant strives to present herself in the best light. Beyond the interview and resume, hiring managers look to recommendation letters to confirm the candidate's qualifications and to gain insight from an outside party.
The hiring manager wants to know what experiences the candidate will bring to the new role, how she'll contribute to the company or organization, and how she'll behave in the day-to-day. Recommendation letters can point to a candidate's future performance by talking about her past achievements.
Reference letters can also shed light on what it's like to manage, work with, or, in the case of a character reference, be friends with the person under consideration. They complement the candidate's story and suggest what she'll bring to the table in her next job.
If you get asked to write a letter for someone, it's safe to assume you want to do a good job. Helping someone get hired is not just a satisfying good deed, but it's also good professional karma! So how can you turn those good intentions into a stand-out employee letter of recommendation?
Each letter will, of course, be different, but good letters share certain key features. Read on to learn about three important characteristics of strong reference letters.

Your recommendation letter's not the time to be cagey about your identity! The hiring manager wants to know who you are and why you're qualified to recommend the applicant.
What Makes a Recommendation Letter Stand Out? 3 Key Features
Strong letters give positive descriptions of a candidate's skills in a concise and powerful way. Beyond using language that's clear and error-free, what elements should your recommendation letter include to be effective?
As you write your letter, make sure it does the following:
#1: Explains Why You're Qualified to Recommend the Candidate
In order to hold weight, a recommendation letter should come from a reputable source. If an employer wants a professional reference, then the writer of that letter probably worked with the candidate in a supervisory capacity. Some employers will also be interested in letters from a colleague or, occasionally, a friend, neighbor, or family member. Most letters, though, will be written by a supervisor, manager, or boss of some sort.
In the first paragraph, you should explain who you are and how you know the candidate. How long did you work with her and in what capacity? By explaining your relationship, you show that you're qualified to give an honest assessment.
If someone who feels like a relative stranger asks you to write a letter, you might consider declining or recommending someone else to write it. If you didn't get to know the candidate's work performance or only did so in a way completely unrelated to the new position, then you might not be able to provide a helpful letter of recommendation from employer to employee.
The best letters are written by people who can speak to the candidate's skills and accomplishments. Make sure to state clearly in the beginning of your letter who you are and why your opinion matters.
#2: Customized to the New Position
While you should speak to the candidate's accomplishments in her past role, you should also show why she'd make a good fit in the next one. Even if the candidate's making a career change, you can explain why she'll be able to do well in the new industry.
Here's where open communication with the applicant is important. She should share the job description so you have a clear understanding of the position's requirements. As the writer, you're not expected to do much research on the new job. The candidate should provide you with everything you need to know to customize your letter.
By drawing on this information, you can express confidence that the candidate will succeed in the new role. Then when the hiring manager reads your letter, she'll feel reassured that the candidate would make a good fit.
#3: Uses Specific Examples and Anecdotes
Finally, and perhaps most importantly, your letter should provide specific examples about the candidate. Don't just list adjectives like, "friendly, intelligent, and hard-working"; instead, present circumstances in which the candidate demonstrated those qualities. To borrow a favorite phrase of English teachers, "show, don't just tell."
Not only will examples point to the value the candidate brought to your organization or company, but they'll also paint a picture of how she works in day-to-day operations. Using two to three specific anecdotes in your letter will boost its level of persuasiveness. It will also sidestep a common rec letter trap: becoming a generic list of cliches.
Just as you should only write a recommendation letter if you feel qualified to assess the candidate, you should also only write it if you can provide a great one. While you don't want to go over the top and sound insincere, your letter should be a strongly positive endorsement.
Sample Recommendation Letters
As you read through the nine free job recommendation letters below, notice how they all share the three key features described above, even though they differ in terms of their source and target audience. Below are nine sample recommendation letters, each followed by an analysis of what it does well!
- Sample Recommendation Letter 1: Written by a Direct Manager for a Full-Time Employee
- Sample Recommendation Letter 2: Written by a Principal for a Teacher
- Sample Recommendation Letter 3: Written by a Direct Manager for a Part-Time Employee
- Sample Recommendation Letter 4: Written by a Manager for a Remote Worker
- Sample Recommendation Letter 5: Written by a Supervisor for an Internal Promotion
- Sample Recommendation Letter 6: Written by a Supervisor for a Student Intern
- Sample Recommendation Letter 7: Written by a Coworker
- Sample Recommendation Letter 8: Written by a Professor for a Former Student
- Sample Recommendation Letter 9: Written by a Friend as a Character Reference
After checking out the above samples of recommendation letters, read on for some final thoughts on how to write an excellent letter of recommendation for an employee, coworker, or friend.

Now that you've got all the building blocks, you can put them together into a powerful letter of recommendation!
Writing Strong Letters of Recommendation: Final Thoughts
While the above samples of recommendation letters will help guide you through the letter writing process, they can't look exactly like your final product. Writing a letter is a significant undertaking, as it requires you to customize your words to the candidate and make your letter unique. Even though the specifics will vary, strong letters of recommendation do have certain features in common. Each letter should...
Use an Official Format
The sample letters show the proper format for a recommendation letter. They have the employer's name, position, company, and company's address at the top. To give one example, here's the header for recommendation letter sample #1:
Ms. Greta Johanssen Sales Manager Streambase Corp. 66 Western Boulevard Santa Fe, New Mexico 87500
You should also use official letterhead that has your name and contact information across the top, in whatever way you've chosen to present it. Each letter is addressed to a specific person, a greeting that's more personal than, "Dear Hiring Manager." Typically, paragraphs are single-spaced with a double space in between each one.
Finally, every letter concludes with an invitation to contact the writer for any further information. Then the writer may include her position, company, phone number, and email below her name.
Start with a Strong Opener
The strongest letters start out with an immediate statement of support. They might say, "It's my honor," "It's my pleasure," or "I'm very pleased to provide this letter of recommendation for Joe." Stating the obvious with a sentence like, "I'm writing to recommend Joe," looks weak beside a more enthusiastic opener.
In the first paragraph, explain who you are and why you're qualified to recommend the candidate. Write a line or two of praise about her professional and personal strengths, perhaps with a summary of the main points you'll present in the rest of the letter.
Include Two to Three Specific Examples
As mentioned above, strong letters typically include two to three body paragraphs with specific anecdotes about the candidate. They don't just describe the applicant's great qualities and accomplishments; they give examples and prove to her prospective employer that she's made achievements in the past that predict future success.
You might talk about a project or responsibility of the applicant or the value she's brought to your company. Consider relevant qualities like flexibility, initiative, leadership, growth, collaboration, interpersonal skills, and/or ability to perform within a certain environment or culture.
To Sum Up...
Depending on your relationship with the candidate, you might focus more on her work performance or personal character in your recommendation letter. An employer will focus more heavily on professional skills while a coworker may add personal qualities.
A friend or neighbor providing a character reference would produce the most personal letter. It falls upon the candidate to choose her recommenders wisely and to share any relevant information about the prospective position to help them write the best letter they can.
As long as you incorporate the key features discussed above and take the time to make your letter positive and specific, you'll provide a strong recommendation letter that will help your employee, colleague, or friend get hired. And who knows—perhaps in a year or two, she'll be writing a recommendation letter for you!
What's Next?
Are you tasked with writing a recommendation letter for a student applying to college? If so, check out these samples of recommendation letters from teachers and counselors, along with additional writing tips and a thorough recommendation letter template!
- 4 Amazing Samples of Recommendation Letters from Teachers Should You Move to a State with No Income Taxes
- 3 Examples of Excellent Recommendation Letters from Counselors
- Complete Guide: Writing a Strong Letter of Recommendation
- Unsecured Credit Cards for Those with Bad Credit
- A Great College Recommendation Letter Template
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Rebecca graduated with her Master's in Adolescent Counseling from the Harvard Graduate School of Education. She has years of teaching and college counseling experience and is passionate about helping students achieve their goals and improve their well-being. She graduated magna cum laude from Tufts University and scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

Writing an Effective & Supportive Recommendation Letter
Sarvenaz sarabipour.
1 Institute for Computational Medicine and Department of Biomedical Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, United States
Sarah J. Hainer
2 Department of Biological Sciences, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
Emily Furlong
3 Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
Nafisa M. Jadavji
4 Department of Biomedical Sciences, Midwestern University, Glendale, United States
5 Department of Neuroscience, Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada
Charlotte M. de Winde
6 MRC Laboratory for Molecular Cell Biology, University College London, London, United Kingdom
7 Department of Molecular Cell Biology & Immunology, Amsterdam UMC Locatie VUmc, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Natalia Bielczyk
8 Welcome Solutions, Nijmegen, the Netherlands
9 Stichting Solaris Onderzoek en Ontwikkeling, Nijmegen, the Netherlands
Aparna P. Shah
10 The Solomon H. Snyder Department of Neuroscience, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, United States
Author Contributions
Writing recommendation letters on behalf of students and other early-career researchers is an important mentoring task within academia. An effective recommendation letter describes key candidate qualities such as academic achievements, extracurricular activities, outstanding personality traits, participation in and dedication to a particular discipline, and the mentor’s confidence in the candidate’s abilities. In this Words of Advice, we provide guidance to researchers on composing constructive and supportive recommendation letters, including tips for structuring and providing specific and effective examples, while maintaining a balance in language and avoiding potential biases.
Introduction
A letter of recommendation or a reference letter is a statement of support for a student or an early-career researcher (ECR; a non-tenured scientist who may be a research trainee, postdoctoral fellow, laboratory technician, or junior faculty colleague) who is a candidate for future employment, promotion, education, or funding opportunities. Letters of recommendation are commonly requested at different stages of an academic research career and sometimes for transitioning to a non-academic career. Candidates need to request letters early on and prepare relevant information for the individual who is approached for recommendation [ 1 , 2 ]. Writing recommendation letters in support of ECRs for career development opportunities is an important task undertaken frequently by academics. ECRs can also serve as mentors during their training period and may be asked to write letters for their mentees. This offers the ECRs an excellent opportunity to gain experience in drafting these important documents, but may present a particular challenge for individuals with little experience. In general, a letter of recommendation should present a well-documented evaluation and provide sufficient evidence and information about an individual to assist a person or a selection committee in making their decision on an application [ 1 ]. Specifically, the letter should address the purpose for which it is written (which is generally to provide support of the candidate’s application and recommendation for the opportunity) and describe key candidate qualities, the significance of the work performed, the candidate’s other accomplishments and the mentor’s confidence in the candidate’s abilities. It should be written in clear and unbiased language. While a poorly written letter may not result in loss of the opportunity for the candidate, a well-written one can help an application stand out from the others, thus well-enhancing the candidate’s chances for the opportunity.
Letter readers at review, funding, admissions, hiring and promotion committees need to examine the letter objectively with a keenness for information on the quality of the candidate’s work and perspective on their scientific character [ 6 ]. However well-intentioned, letters can fall short of providing a positive, effective, and supportive document [ 1 , 3 – 5 ]. To prevent this, it is important to make every letter personal; thus, writing letters requires time and careful consideration. This article draws from our collective experiences as ECRs and the literature to highlight best practices and key elements for those asked to provide recommendation letters for their colleagues, students, or researchers who have studied or trained in their classroom or research laboratory. We hope that these guidelines will be helpful for letter writers to provide an overall picture of the candidate’s capabilities, potential and professional promise.
Decide on whether to write the letter
Before you start, it is important to evaluate your relationship with the candidate and ability to assess their skills and abilities honestly. Consider how well and in what context you know the person, as well as whether you can be supportive of their application [ 7 ]. Examine the description of the opportunity for which the letter is being requested ( Figure 1 ). Often you will receive a request by a student or a researcher whom you know very well and have interacted with in different settings – in and out of the classroom, your laboratory or that of a colleague, or within your department – and whose performance you find to be consistently satisfactory or excellent. Sometimes a mentee may request a recommendation letter when still employed or working with you, their research advisor. This can come as an unpleasant surprise if you are unaware that the trainee was seeking other opportunities (for instance, if they haven’t been employed with you for long, or have just embarked on a new project). While the mentee should be transparent about their goals and searching for opportunities, you should as a mentor offer to provide the letter for your mentee (see Table 1 ).

First, it is important to establish whether you are equipped to write a strong letter of support. If not, it is best to have a candid conversation with the applicant and discuss alternative options or opportunities. If you are in a position to write a strong letter of support, first acquire information regarding the application and the candidate, draft a letter in advance (see Box 1 ) and submit the letter on time. When drafting the letter, incorporate specific examples, avoid biases, and discuss the letter with the candidate (see Tables 1 – 2 for specific examples). After submission, store a digital copy for potential future use for the same candidate.
Key do’s and don’ts when being asked to write a letter of recommendation
| Theme | Do | Do Not |
|---|---|---|
| A personal situation that might require discussion would be when the candidate is unable to ask their advisor for a letter of recommendation due to a bad relationship. If you, as the letter writer, know about this situation, you might want to mention in the letter that “there was a personality conflict but it does not reflect on the ability of the candidate to do the job.” | Do not write anything that is not true, do not stretch the facts. | |
| Sometimes, a lab member or non-faculty ECR will have had more direct and notable mentoring experience with the candidate. Thus, the non-faculty mentor may be involved in writing the letter and included as a co-signed referee. Do suggest a direct mentor as a co-signing referee, if relevant. | Do not take credit for a letter you did not write on your own. Do not leave out the direct mentor if their insight can help to support the candidate. | |
| Be sure to clarify that it is up to the reference provider to decide on a waiver. Candidates should check if this requirement holds before they ask a mentor for a letter. | Do not avoid discussions about the recommendation letter or a waiver with the candidate. | |
| Do provide the letter to a candidate requesting a reference while they still work in your lab and assure them of your good intentions. Do have an open and honest conversation with your mentee about why they are applying for another job. | Do not let your personal feelings come across, impact the writing of the letter or your relationship with the candidate when making a recommendation under these circumstances. Do not refuse a candidate a letter if requested before leaving a lab/position. | |
| Candidates: if drafting a letter for the first time, study examples when possible and remember to use specific examples that pertain to your relationship with the mentor. Make sure to give the official letter writer a draft far in advance to permit for their editing and timely submission. | As a candidate, do not undersell yourself. |
Other requests may be made by a candidate who has made no impression on you, or only a negative one. In this case, consider the candidate’s potential and future goals, and be fair in your evaluation. Sending a negative letter or a generic positive letter for individuals you barely know is not helpful to the selection committee and can backfire for the candidate. It can also, in some instances, backfire for you if a colleague accepts a candidate based on your generic positive letter when you did not necessarily fully support that individual. For instance, letter writers sometimes stretch the truth to make a candidate sound better than they really are, thinking it is helpful. If you do not know the applicant well enough or feel that you cannot be supportive, you are not in a strong position to write the recommendation letter and should decline the request, being open about why you are declining to write the letter. Also, be selective about writing on behalf of colleagues who may be in one’s field but whose work is not well known to you. If you have to read the candidate’s curriculum vitae to find out who they are and what they have done, then you may not be qualified to write the letter [ 8 ].
When declining a request to provide a letter of support, it is important to explain your reasoning to the candidate and suggest how they might improve their prospects for the future [ 8 ]. If the candidate is having a similar problem with other mentors, try to help them identify a more appropriate referee or to explore whether they are making an appropriate application in the first place. Suggest constructive steps to improve relationships with mentors to identify individuals to provide letters in the future. Most importantly, do not let the candidate assume that all opportunities for obtaining supportive letters of recommendation have been permanently lost. Emphasize the candidate’s strengths by asking them to share a favourite paper, assignment, project, or other positive experience that may have taken place outside of your class or lab, to help you identify their strengths. Finally, discuss with the candidate their career goals to help them realize what they need to focus on to become more competitive or steer them in a different career direction. This conversation can mark an important step and become a great interaction and mentoring opportunity for ECRs.
Examine the application requirements
Once you decide to write a recommendation letter, it is important to know what type and level of opportunity the candidate is applying for, as this will determine what should be discussed in the letter ( Figure 1 ). You should carefully read the opportunity posting description and/or ask the candidate to summarize the main requirements and let you know the specific points that they find important to highlight. Pay close attention to the language of the position announcement to fully address the requested information and tailor the letter to the specific needs of the institution, employer, or funding organisation. In some instances, a waiver form or an option indicating whether or not the candidate waives their right to see the recommendation document is provided. If the candidate queries a waiver decision, note that often referees are not allowed to send a letter that is not confidential and that there may be important benefits to maintaining the confidentiality of letters (see Table 1 ). Specifically, selection committees may view confidential letters as having greater credibility and, value and some letter writers may feel less reserved in their praise of candidates in confidential letters.
Acquire candidate information and discuss letter content
To acquire appropriate information about the candidate, one or more of the following documents may be valuable: a resume or curriculum vitae (CV), a publication or a manuscript, an assignment or exam written for your course, a copy of the application essay or personal statement, a transcript of academic records, a summary of current work, and specific recommendation forms or questionnaires (if provided) [ 9 ]. Alternatively, you may ask the candidate to complete a questionnaire asking for necessary information and supporting documents [ 10 ]. Examine the candidate’s CV and provide important context to the achievements listed therein. Tailor the letter for the opportunity using these documents as a guide, but do not repeat their contents as the candidate likely submits them separately. Even the most articulate of candidates may find it difficult to describe their qualities in writing [ 11 ]. Furthermore, a request may be made by a person who has made a good impression, but for whom you lack significant information to be able to write a strong letter. Thus, even if you know a candidate well, schedule a brief in-person, phone, or virtual meeting with them to 1) fill in gaps in your knowledge about them, 2) understand why they are applying for this particular opportunity, 3) help bring their past accomplishments into sharper focus, and 4) discuss their short- and long-term goals and how their current studies or research activities relate to the opportunity they are applying for and to these goals. Other key information to gather from the applicant includes the date on which the recommendation letter is due, as well as details on how to submit it.
For most applications (for both academic and non-academic opportunities), a letter of recommendation will need to cover both scholarly capabilities and achievements as well as a broader range of personal qualities and experiences beyond the classroom or the laboratory. This includes extracurricular experiences and traits such as creativity, tenacity, and collegiality. If necessary, discuss with the candidate what they would like to see additionally highlighted. As another example of matching a letter with its purpose, a letter for a fellowship application for a specific project should discuss the validity and feasibility of the project, as well as the candidate’s qualifications for fulfilling the project.
Draft the letter early and maintain a copy
Another factor that greatly facilitates letter writing is drafting one as soon as possible after you have taught or trained the candidate, while your impressions are still clear. You might consider encouraging the candidate to make their requests early [ 11 ]. These letters can be placed in the candidate’s portfolio and maintained in your own files for future reference. If you are writing a letter in response to a request, start drafting it well in advance and anticipate multiple rounds of revision before submission. Once you have been asked by a candidate to write a letter, that candidate may return frequently, over a number of years, for additional letters. Therefore, maintain a digital copy of the letter for your records and for potential future applications for the same candidate.
Structure your letter
In the opening, you should introduce yourself and the candidate, state your qualifications and explain how you became acquainted with the candidate, as well as the purpose of the letter, and a summary of your recommendation ( Table 2 ). To explain your relationship with the candidate you should fully describe the capacity in which you know them: the type of experience, the period during which you worked with the candidate, and any special assignments or responsibilities that the candidate performed under your guidance. For instance, the letter may start with: “This candidate completed their postdoctoral training under my supervision. I am pleased to be able to provide my strongest support in recommending them for this opportunity.” You may also consider ranking the candidate among similar level candidates within the opening section to give an immediate impression of your thoughts. Depending on the position, ranking the candidate may also be desired by selection committees, and may be requested within the letter. For instance, the recommendation form or instructions may ask you to rank the candidate in the top 1%, 5%, 10%, etc., of applicants. You could write "the student is in the top 5% of undergraduate students I have trained" Or “There are currently x graduate students in our department and I rank this candidate at the top 1%. Their experimental/computational skills are the best I have ever had in my own laboratory.”. Do not forget to include with whom or what group you are comparing the individual. If you have not yet trained many individuals in your own laboratory, include those that you trained previously as a researcher as reference. Having concentrated on the candidate’s individual or unique strengths, you might find it difficult to provide a ranking. This is less of an issue if a candidate is unambiguously among the top 10% that you have mentored but not all who come to you for a letter will fall within that small group. If you wish to offer a comparative perspective, you might more readily be able to do so in more specific areas such as whether the candidate is one of the most articulate, original, clear-thinking, motivated, or intellectually curious.
Key do’s and don’ts when writing a letter of recommendation
| Theme | Do | Do Not |
|---|---|---|
| Describe all scholarly outputs in equal weight e.g., preprints, protocols, engineered animal models, computer models, software among others. Describe all scholarly and non-scholarly outputs in equal weight e.g., teaching, service, advocacy efforts. Promote the whole human candidate. | Do not ignore the candidate’s non-peer reviewed (e.g. preprints, data or code or protocols submitted to repositories) or in-press outputs. | |
| Describe the candidate’s preprints and journal publications in terms of their quality and impact on your work and the field. | Do not judge papers by where they are published. It is the quality of the science & the reputation of the researcher, not the journal’s brand, that matters. Avoid paying excessive attention to how many papers the candidate has published in the family of journals. Refrain from boasting the journals impact factor (JIF) or journal name in the letter as publication in glamour journals does not validate the candidate’s research or guarantee a promising & successful career path. | |
| Use agentic (e.g., confident, ambitious, independent) and standout (e.g., best, ideal) adjectives for all candidates, focusing on relevant accomplishments for the opportunity. | Avoid communal words (e.g., kind, affectionate, agreeable) that are more often used for women. Avoid using doubt raising phrases such as “He might be good”, or “she may have potential”, “she has a difficult personality”. | |
| Make a criticism sound less damaging. e.g., “When candidate started at my laboratory, their skills were poorly developed, but they have worked diligently to improve them and have taken major steps in that direction.” | Do not leave out important, relevant information even if it may be perceived as negative, put a positive spin on it. | |
| Do explain how the candidate’s current and prior work contributes to your laboratories research efforts. | Do not compare the candidate as being as good as person and , but not as good as person . This type of information creates subjectivity. | |
| Include context for your scientific field and how the candidate’s research fits into and advances the field. | Do not merely describe mastery of techniques. Pay attention to the candidate’s wider comprehension of the field and their impact on their discipline. Avoid too much jargon and field-specific language, as often a broad audience will be reading the letter. |
The body of the recommendation letter should provide specific information about the candidate and address any questions or requirements posed in the selection criteria (see sections above). Some applications may ask for comments on a candidate’s scholarly performance. Refer the reader to the candidate’s CV and/or transcript if necessary but don’t report grades, unless to make an exceptional point (such as they were the only student to earn a top grade in your class). The body of the recommendation letter will contain the majority of the information including specific examples, relevant candidate qualities, and your experiences with the candidate, and therefore the majority of this manuscript focuses on what to include in this section.
The closing paragraph of the letter should briefly 1) summarize your opinions about the candidate, 2) clearly state your recommendation and strong support of the candidate for the opportunity that they are seeking, and 3) offer the recipient of the letter the option to contact you if they need any further information. Make sure to provide your email address and phone number in case the recipient has additional questions. The overall tone of the letter can represent your confidence in the applicant. If opportunity criteria are detailed and the candidate meets these criteria completely, include this information. Do not focus on what you may perceive as a candidate’s negative qualities as such tone may do more harm than intended ( Table 2 ). Finally, be aware of the Forer’s effect, a cognitive error, in which a very general description, that fits almost everyone, is used to describe a person [ 20 ]. Such generalizations can be harmful, as they provide the candidate the impression that they received a valuable, positive letter, but for the committee, who receive hundreds of similar letters, this is non-informative and unhelpful to the application.
Describe relevant candidate qualities with specific examples and without overhyping
In discussing a candidate’s qualities and character, proceed in ways similar to those used for intellectual evaluation ( Box 1 ). Information to specifically highlight may include personal characteristics, such as integrity, resilience, poise, confidence, dependability, patience, creativity, enthusiasm, teaching capabilities, problem-solving abilities, ability to manage trainees and to work with colleagues, curriculum development skills, collaboration skills, experience in grant writing, ability to organize events and demonstrate abilities in project management, and ability to troubleshoot (see section “ Use ethical principles, positive and inclusive language within the letter ” below for tips on using inclusive terminology). The candidate may also have a specific area of knowledge, strengths and experiences worth highlighting such as strong communication skills, expertise in a particular scientific subfield, an undergraduate degree with a double major, relevant work or research experience, coaching, and/or other extracurricular activities. Consider whether the candidate has taught others in the lab, or shown particular motivation and commitment in their work. When writing letters for mentees who are applying for (non-)academic jobs or admission to academic institutions, do not merely emphasize their strengths, achievements and potential, but also try to 1) convey a sense of what makes them a potential fit for that position or funding opportunity, and 2) fill in the gaps. Gaps may include an insufficient description of the candidate’s strengths or research given restrictions on document length. Importantly, to identify these gaps, one must have carefully reviewed both the opportunity posting as well as the application materials (see Box 1 , Table 2 ).
Recommendations for Letter Writers
- Consider characteristics that excite & motivate this candidate.
- Include qualities that you remember most about the candidate.
- Detail their unusual competence, talent, mentorship, teaching or leadership abilities.
- Explain the candidate’s disappointments or failures & the way they reacted & overcame.
- Discuss if they demonstrated a willingness to take intellectual risks beyond the normal research & classroom experience.
- Ensure that you have knowledge of the institution that the candidate is applying for.
- Consider what makes you believe this particular opportunity is a good match for this candidate.
- Consider how they might fit into the institution’s community & grow from their experience.
- Describe their personality & social skills.
- Discuss how the candidate interacts with teachers & peers.
- Use ethical principles, positive & inclusive language within the letter.
- Do not list facts & details, every paper, or discovery of the candidate’s career.
- Only mention unusual family or community circumstances after consulting the candidate.
- A thoughtful letter from a respective colleague with a sense of perspective can be quite valuable.
- Each letter takes time & effort, take it seriously.
When writing letters to nominate colleagues for promotion or awards, place stronger emphasis on their achievements and contributions to a field, or on their track record of teaching, mentorship and service, to aid the judging panel. In addition to describing the candidate as they are right now, you can discuss the development the person has undergone (for specific examples see Table 2 ).
A letter of recommendation can also explain weaknesses or ambiguities in the candidate’s record. If appropriate – and only after consulting the candidate - you may wish to mention a family illness, financial hardship, or other factors that may have resulted in a setback or specific portion of the candidate’s application perceived weakness (such as in the candidate’s transcript). For example, sometimes there are acceptable circumstances for a gap in a candidate’s publication record—perhaps a medical condition or a family situation kept them out of the lab for a period of time. Importantly, being upfront about why there is a perceived gap or blemish in the application package can strengthen the application. Put a positive spin on the perceived negatives using terms such as “has taken steps to address gaps in knowledge”, “has worked hard to,” and “made great progress in” (see Table 2 ).
Describe a candidate’s intellectual capabilities in terms that reflect their distinctive or individual strengths and be prepared to support your judgment with field-specific content [ 12 ] and concrete examples. These can significantly strengthen a letter and will demonstrate a strong relationship between you and the candidate. Describe what the candidate’s strengths are, moments they have overcome adversity, what is important to them. For example: “candidate x is exceptionally intelligent. They proved to be a very quick study, learning the elements of research design and technique y in record time. Furthermore, their questions are always thoughtful and penetrating.”. Mention the candidate’s diligence, work ethic, and curiosity and do not merely state that “the applicant is strong” without specific examples. Describing improvements to candidate skills over time can help highlight their work ethic, resolve, and achievements over time. However, do not belabor a potential lower starting point.
Provide specific examples for when leadership was demonstrated, but do not include leadership qualities if they have not been demonstrated. For example, describe the candidate’s qualities such as independence, critical thinking, creativity, resilience, ability to design and interpret experiments; ability to identify the next steps and generate interesting questions or ideas, and what you were especially impressed by. Do not generically list the applicant as independent with no support or if this statement would be untrue.
Do not qualify candidate qualities based on a stereotype for specific identities. Quantify the candidate’s abilities, especially with respect to other scientists who have achieved success in the field and who the letter reader might know. Many letter writers rank applicants according to their own measure of what makes a good researcher, graduate trainee, or technician according to a combination of research strengths, leadership skills, writing ability, oral communication, teaching ability, and collegiality. Describe what the role of the candidate was in their project and eventual publication and do not assume letter readers will identify this information on their own (see Table 2 ). Including a description about roles and responsibilities can help to quantify a candidate’s contribution to the listed work. For example, “The candidate is the first author of the paper, designed, and led the project.”. Even the best mentor can overlook important points, especially since mentors typically have multiple mentees under their supervision. Thus, it can help to ask the candidate what they consider their strengths or traits, and accomplishments of which they are proud.
If you lack sufficient information to answer certain questions about the candidate, it is best to maintain the integrity and credibility of your letter - as the recommending person, you are potentially writing to a colleague and/or someone who will be impacted by your letter; therefore, honesty is key above all. Avoid the misconception that the more superlatives you use, the stronger the letter. Heavy use of generic phrases or clichés is unhelpful. Your letter can only be effective if it contains substantive information about the specific candidate and their qualifications for the opportunity. A recommendation that paints an unrealistic picture of a candidate may be discounted. All information in a letter of recommendation should be, to the best of your knowledge, accurate. Therefore, present the person truthfully but positively. Write strongly and specifically about someone who is truly excellent (explicitly describe how and why they are special). Write a balanced letter without overhyping the candidate as it will not help them.
Be careful about what you leave out of the letter
Beware of what you leave out of the recommendation letter. For most opportunities, there are expectations of what should be included in a letter, and therefore what is not said can be just as important as what is said. Importantly, do not assume all the same information is necessary for every opportunity. In general, you should include the information stated above, covering how you know the candidate, their strengths, specific examples to support your statements, and how the candidate fits well for the opportunity. For example, if you don’t mention a candidate’s leadership skills or their ability to work well with others, the letter reader may wonder why, if the opportunity requires these skills. Always remember that opportunities are sought by many individuals, so evaluators may look for any reason to disregard an application, such as a letter not following instructions or discussing the appropriate material. Also promote the candidate by discussing all of their scholarly and non-scholarly efforts, including non-peer reviewed research outputs such as preprints, academic and non-academic service, and advocacy work which are among their broader impact and all indicative of valuable leadership qualities for both academic and non-academic environments ( Table 2 ).
Provide an even-handed judgment of scholarly impact, be fair and describe accomplishments fairly by writing a balanced letter about the candidate’s attributes that is thoughtful and personal (see Table 2 ). Submitting a generic, hastily written recommendation letter is not helpful and can backfire for both the candidate and the letter writer as you will often leave out important information for the specific opportunity; thus, allow for sufficient time and effort on each candidate/application.
Making the letter memorable by adding content that the reader will remember, such as an unusual anecdote, or use of a unique term to describe the candidate. This will help the application stand out from all the others. Tailor the letter to the candidate, including as much unique, relevant information as possible and avoid including personal information unless the candidate gives consent. Provide meaningful examples of achievements and provide stories or anecdotes that illustrate the candidate’s strengths. Say what the candidate specifically did to give you that impression ( Box 1 ). Don’t merely praise the candidate using generalities such as “candidate x is a quick learner”.
Use ethical principles, positive and inclusive language within the letter
Gender affects scientific careers. Avoid providing information that is irrelevant to the opportunity, such as ethnicity, age, hobbies, or marital status. Write about professional attributes that pertain to the application. However, there are qualities that might be important to the job or funding opportunity. For instance, personal information may illustrate the ability to persevere and overcome adversity - qualities that are helpful in academia and other career paths. It is critical to pay attention to biases and choices of words while writing the letter [ 13 , 14 ]. Advocacy bias (a letter writer is more likely to write a strong letter for someone similar to themselves) has been identified as an issue in academic environments [ 3 ]. Studies have also shown that there are often differences in the choice of words used in letters for male and female scientists [ 3 , 5 ]. For instance, letters for women have been found not to contain much specific and descriptive language. Descriptions often pay greater attention to the personal lives or personal characteristics of women than men, focusing on items that have little relevance in a letter of recommendation. When writing recommendation letters, employers have a tendency to focus on scholarly capabilities in male candidates and personality features in female candidates; for instance, female candidates tend to be depicted in letters as teachers and trainees, whereas male candidates are described as researchers and professionals [ 15 ]. Also, letters towards males often contain more standout words such as “superb”, “outstanding”, and “excellent”. Furthermore, letters for women had been found to contain more doubt-raising statements, including negative or unexplained comments [ 3 , 15 , 16 ]. This is discriminative towards women and gives a less clear picture of women as professionals. Keep the letter gender neutral. Do not write statements such as “candidate x is a kind woman” or “candidate y is a fantastic female scientist” as these have no bearing on whether someone will do well in graduate school or in a job. One way to reduce gender bias is by checking your reference letter with a gender bias calculator [ 17 , 18 ]. Test for gender biases by writing a letter of recommendation for any candidate, male or female, and then switch all the pronouns to the opposite gender. Read the letter over and ask yourself if it sounds odd. If it does, you should probably change the terms used [ 17 ]. Other biases also exist, and so while gender bias has been the most heavily investigated, bias based on other identities (race, nationality, ethnicity, among others) should also be examined and assessed in advance and during letter writing to ensure accurate and appropriate recommendations for all.
Revise and submit on time
The recommendation letter should be written using language that is straightforward and concise [ 19 ]. Avoid using jargon or language that is too general or effusive ( Table 1 ). Formats and styles of single and co-signed letters are also important considerations. In some applications, the format is determined by the application portal itself in which the recommender is asked to answer a series of questions. If these questions do not cover everything you would like to address you could inquire if there is the option to provide a letter as well. Conversely, if the recommendation questionnaire asks for information that you cannot provide, it is best to explicitly mention this in writing. The care with which you write the letter will also influence the effectiveness of the letter - writing eloquently is another way of registering your support for the candidate. Letters longer than two pages can be counterproductive, and off-putting as reviewers normally have a large quantity of letters to read. In special cases, longer letters may be more favourable depending on the opportunity. On the other hand, anything shorter than a page may imply a lack of interest or knowledge, or a negative impression on the candidate. In letter format, write at least 3-4 paragraphs. It is important to note that letters from different sectors, such as academia versus industry tend to be of different lengths. Ensure that your letter is received by the requested method (mail or e-mail) and deadline, as a late submission could be detrimental for the candidate. Write and sign the letter on your department letterhead which is a further form of identification.
Conclusions
Recommendation letters can serve as important tools for assessing ECRs as potential candidates for a job, course, or funding opportunity. Candidates need to request letters in advance and provide relevant information for the recommender. Readers at selection committees need to examine the letter objectively with an eye for information on the quality of the candidate’s scholarly and non-scholarly endeavours and scientific traits. As a referee, it is important that you are positive, candid, yet helpful, as you work with the candidate in drafting a letter in their support. In writing a recommendation letter, summarize your thoughts on the candidate and emphasize your strong support for their candidacy. A successful letter communicates the writer’s enthusiasm for an individual, but does so realistically, sympathetically, and with concrete examples to support the writer’s associations. Writing recommendation letters can help mentors examine their interactions with their mentee and know them in different light. Express your willingness to help further by concluding the letter with an offer to be contacted should the reader need more information. Remember that a letter writer’s judgment and credibility are at stake thus do spend the time and effort to present yourself as a recommender in the best light and help ECRs in their career path.
Acknowledgements
S.J.H. was supported by the National Institutes of Health grant R35GM133732. A.P.S. was partially supported by the NARSAD Young Investigator Grant 27705.
Abbreviations:
| ECR | Early-Career Researcher |
| CV | Curriculum Vitae |
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
- Phone: +91 8466016171
- Whatsapp: +91 8208375580
- Email: contact@leapscholar.com
Professional Letter of Recommendation: Sample, Format & Examples
- Last Updated On August 22, 2024
- Published In General

A professional letter of recommendation can be a crucial element in your application, helping you stand out in a crowded field. Schools like MIT , for example, require two letters of recommendation as part of their admissions process.
Table of Content
These letters, typically written by professors or supervisors, strongly endorse your skills, character, and potential. Admissions committees rely on these insights to make informed decisions.

Excel in IELTS with India’s Top Online Coaching
Leap has helped more than 1 Lakh students achieve 7+ IELTS band.
In this article, you’ll learn how to craft a compelling professional letter of recommendation to help you take the next step in your career or academic journey. Dive in!
Here’s everything you will learn in greater detail in this blog about professional letter of recommendation.
| Word Limit of a Professional Letter of Recommendation | 400-500 words |
| Formatting | : Times New Roman | : 10 to 12 | : 1-inch |
| Common Mistakes to Avoid | Open communication, timely submission, highlight strengths |
What is a Professional Letter of Recommendation?
A professional letter of recommendation, often called a LOR, is vital to many application processes, whether for academic programs, jobs, or scholarships. It provides a trusted perspective on your abilities, character, and potential.
Universities such as Harvard and Stanford often require two to three letters of recommendation as part of their application process. These letters offer admissions committees a deeper understanding of who you are beyond your grades or resume.
Writing an impactful LOR can be challenging, so having a well-crafted example can be incredibly helpful. By reviewing a solid sample, you can learn how to showcase your strengths and experiences effectively, helping you make a lasting impression.
How to Write a Professional Letter of Recommendation?
Writing a professional letter of recommendation involves presenting a clear and compelling endorsement of the candidate’s qualifications.
In this section, you’ll learn the key steps to structure your letter effectively, including what information to include and how to highlight your strengths.
Later in the blog, you will also find professional reference letter templates and learn how to ensure your letter strongly impacts the reader.
Professional Letter of Recommendation: Structure
Getting into a prestigious MBA or PhD program is a challenging feat. One of the most critical components of your application is the strength of your Letters of Recommendation (LORs).
Schools like Caltech typically ask for three LORs, favouring those from academic mentors who can speak to your research abilities and potential.
These letters are vital to your application, offering essential external validation of your qualifications.
Here is a quick overview of the structure of professional reference letter templates.
| Address by name (“Dear Mr./Mrs./Dr. [Last Name]”) or “To Whom It May Concern.” | |
| Introduction of the recommender and relationship with the candidate. | |
| Overview of your critical abilities and strengths. | |
| Specific examples of your achievements. | |
| Reaffirm confidence and provide contact information. | |
| Mention name and signature. |
Professional Letter of Recommendation Format
As you focus on your IELTS preparation and other application tasks, paying attention to a solid professional letter of recommendation is crucial. A well-crafted and structured LOR can significantly impact your chances of admission, making it a key element in your college application.
Here is a professional letter of recommendation format.
| Pages | 1-2 pages long |
| Paragraphs | 5-6 paragraphs |
| Font Type | Times New Roman |
| Font Size | 10 to 12 point |
| Margins | 1 inch on all sides |
| Line Spacing | Single-spaced with double space between paragraphs |
| Alignment | Left-aligned |
| Header | Optional bold for name and title |
| Salutation | Optional bold for addressing |
| Closing Statement | Optional bold for final endorsement |
| Signature | Optional bold for name and title |
Explore all countries
Professional letter of recommendation examples.
A sample professional reference letter can help you craft a solid recommendation. However, using these examples as a guide rather than copying them directly is essential.
Below, you’ll find professional letter of recommendation examples. These professional reference letter templates show how your supervisors can highlight your qualifications and suitability for higher studies.
Please see a sample professional reference letter and a professional letter of recommendation for ms below.
DISCLAIMER: The name “John Smith” is used in this sample LOR for illustrative purposes only.
Sample Professional Reference Letter
[Full Name] Research Scientist [Company Name] [Company Address] [City, State ZIP Code] [Email Address] [Phone Number] [Date]
Dear Admissions Committee,
I am pleased to write this letter of recommendation for John Smith, who has been an outstanding member of our research team at [Company Name] for the past three years. Throughout this time, I have had the privilege of supervising John closely, observing his impressive intellectual capabilities, unwavering dedication, and exceptional problem-solving skills.
As a research scientist, John has consistently exceeded expectations. His contributions, particularly in [specific research area], have been critical to our team’s success. For example, his leadership in the [project name] initiative was vital to achieving [specific outcome]. John demonstrated a deep understanding of the challenges involved and developed innovative solutions that significantly advanced our research objectives. His ability to navigate complex problems and deliver effective solutions has set him apart as a critical contributor to our team’s accomplishments.
John’s standout qualities are his ability to combine theoretical knowledge with practical application seamlessly. His work on [specific project or task] is a perfect example. By [briefly describing particular actions taken], John achieved [quantifiable result], showcasing his analytical skills and talent for turning complex concepts into real-world outcomes. This project highlighted his technical proficiency and ability to think critically and apply his knowledge in ways that yield tangible results.
Beyond his technical expertise, John excels in interpersonal and communication skills. He is a collaborative team member who freely shares his knowledge with colleagues, ensuring everyone benefits from his insights. His ability to explain complex ideas clearly and understandably has been invaluable in both internal discussions and external presentations. Additionally, John has taken on leadership roles within the team, mentoring junior researchers and contributing to a positive work environment. His leadership has helped foster a collaborative and innovative atmosphere crucial to our collective success.
John’s passion for research and drive for continuous learning are truly admirable. He is always seeking new challenges and opportunities for growth. For instance, [describe a specific example of initiative or self-directed learning] demonstrates his intellectual curiosity and commitment to professional development. This proactive approach to learning and growth is a testament to his dedication to his field and his desire to improve and expand his expertise continually.
I am confident that John possesses the intellectual capacity, technical expertise, and personal qualities necessary to excel in a Master’s program. His strong foundation in [specific field] and his enthusiasm for research make him an excellent candidate for advanced studies. I highly recommend John Smith for admission to your program, as he will be a valuable addition to your research community. Please feel free to contact me if you need any further information.
Sincerely, [Full Name] Manager – Sales [Company Name]
Professional Letter of Recommendation for MS
I am pleased to recommend John Smith, who has been an exceptional member of our research team at [Company Name] for the past three years. During this period, I have had the privilege of supervising John directly, allowing me to observe his impressive intellectual abilities, dedication, and exceptional problem-solving skills daily.
John has consistently delivered outstanding work as a research scientist. His contributions, particularly in [specific research area], have been pivotal to our team’s success. For example, his leadership in the [project name] initiative was crucial in achieving [specific outcome]. John’s ability to deeply understand the challenges associated with this project and his innovative approach to overcoming them significantly advanced our research efforts. His contributions went beyond what was expected, demonstrating his technical prowess and his commitment to excellence.
One of John’s greatest strengths is his ability to bridge theoretical knowledge with practical application. This was evident in his work on [specific project or task]. By [briefly describing particular actions taken], John achieved [quantifiable result], effectively showcasing his strong analytical skills and remarkable ability to turn complex concepts into tangible, real-world results. His work did not just meet the project’s objectives; it set a new standard for what could be achieved within our team, earning him the respect and admiration of his colleagues.
In addition to his technical expertise, John possesses excellent interpersonal and communication skills. He is a collaborative team player who readily shares his knowledge with colleagues, often going out of his way to ensure that others understand the intricate details of complex projects. His clear and concise communication has been invaluable, whether in internal discussions or during external presentations, and his ability to articulate complex ideas understandably has contributed significantly to the success of our projects. Furthermore, John has demonstrated strong leadership abilities, taking on roles where he has mentored junior researchers, helping them grow and develop their skills.
John’s passion for research and commitment to continuous learning are commendable. He is always seeking new challenges and opportunities for growth, for instance, [describe a specific example of initiative or self-directed learning], which is a testament to his intellectual curiosity and dedication to professional development.
I do not doubt that John possesses the intellectual capacity, technical skills, and personal qualities necessary to excel in a master’s program. His strong background in [specific field] and enthusiasm for work make him an ideal candidate for advanced studies. I wholeheartedly recommend John Smith for admission to your program and am confident he will be a valuable asset to your academic community. If you require any further information, please do not hesitate to contact me.
Sincerely, [Full Name] Senior Engineer [Company Name]
Vocabulary for Writing a Professional Letter of Recommendation
Crafting a compelling professional letter of recommendation involves more than just structure; your chosen language is crucial in shaping how the admissions committee views your application.
Below, you’ll find some suggested vocabulary to help strengthen your LOR and make it more impactful.
Keep in mind that these words are meant to enhance your writing. Thoughtful use of them will improve the professionalism and effectiveness of your recommendation.
| Introduction | Delighted, Exemplary, Privilege |
| Academic Achievements | Outstanding, Exceptional, Remarkable |
| Technical Skills | Proficient, Adept, Innovative |
| Research Contributions | Significant, Inventive, Insightful |
| Problem-Solving Abilities | Analytical, Ingenious, Resourceful |
| Personal Qualities | Dedicated, Motivated, Collaborative |
| Professional Experience | Leadership, Initiative, Reliable |
| Communication Skills | Articulate, Persuasive, Eloquent |
| Teamwork | Cooperative, Synergistic, Supportive |
| Conclusion/Recommendation | Confident, Highest Recommendation, Ideal Candidate |
Tips to Write A Better Professional Letter of Recommendation
Did you know that in 2024, over 1.3 million Indian students went abroad for higher studies? If you’re aiming for admission to top universities like Oxford in the UK or Harvard in the US, having a solid professional letter of recommendation for graduate school is essential.
These letters must be thoughtfully written to ensure your application stands out and increases your chances of being selected.
Below are the crucial tips for writing a compelling professional letter of recommendation for graduate school.
- Choose recommenders who understand your graduate program’s requirements and can effectively highlight your strengths.
- Maintain regular contact with your recommenders, sharing your research goals and achievements to provide them with plenty of information.
- Encourage each recommender to focus on different aspects of your qualifications to create a well-rounded picture.
- Ensure online recommendation forms are submitted before the application deadline to avoid last-minute stress.
- Emphasise the importance of honest and detailed information in the LOR, avoiding exaggeration or false claims.
- Establish the relationship between you and the recommender within the letter.
- Showcase your unique qualities, abilities, and potential for success in the graduate program.
- Encourage recommenders to write personalised letters reflecting your achievements rather than relying on generic templates.
Whom Should You Ask for a Professional Letter of Recommendation?
Choosing the right person for your professional letter of recommendation is crucial. This is especially true in today’s competitive environment, where 25% of the one million international students in the US are Indian.
Your recommender should be someone who can genuinely advocate for you and provide an objective assessment of your abilities. A solid professional letter of recommendation offers a unique perspective, reflecting the recommender’s observations and experiences with you helping your application stand out.
Your ideal recommender should be someone who:
- Has worked closely with you.
- Understand your strengths and areas for growth.
- Has witnessed your academic or professional development.
- Is familiar with your goals.
- Believe in your potential to achieve those goals.
Professional Letter of Recommendation: Guidelines for Top Universities
When universities consider applicants for graduate programs, they seek candidates who can thrive under mentorship and deliver strong results. They want individuals who are deeply committed and focused on their chosen field.
Letters of recommendation play a key role in identifying these ideal candidates. Below, you’ll find the requirements for a professional letter of recommendation from some of the most renowned institutions.
| 3 | |
| Stanford University | 3 |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 |
Crafting a strong professional letter of recommendation is crucial when applying to highly competitive universities like Oxford and Stanford, which often require three such letters. A well-written LOR can significantly enhance your application by providing a personalised perspective on your academic abilities, character, and potential.
A compelling letter can help you stand out among talented applicants by highlighting your strengths and accomplishments. It will increase your chances of securing admission to your dream institution. Are you looking to get a solid professional letter of recommendation? Leap Scholar’s experts are here to help you craft the perfect LOR and guide you through every step of the application process. Book a consultation today and take the first step toward your academic success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. what is a professional letter of recommendation.
A. A professional letter of recommendation is written by someone who knows you well, such as a professor, supervisor, or mentor, and can vouch for your skills, character, and qualifications. Universities or employers often require this letter to provide an external, objective assessment of your abilities, work ethic, and potential.
Q. Why do I need a professional letter of recommendation for a graduate program?
A. A professional letter of recommendation is crucial for graduate program applications because it gives admissions committees a trusted, third-party perspective on your abilities and readiness for advanced study. While your academic transcripts and personal statements showcase your achievements and goals, a letter of recommendation offers a deeper insight into your work ethic, character, and interaction in professional or academic settings.
Q. Who should I ask to write my professional letter of recommendation?
A. You should ask someone who knows you well and can provide a detailed, positive assessment of your qualifications. Ideal recommenders include professors who have taught you in courses related to your intended field of study, supervisors who have overseen your work on significant projects, or mentors who have guided you in your academic or professional development.
Q. How many letters of recommendation do top universities typically require?
A. Top universities, such as Oxford, Stanford, and Princeton, typically require three letters of recommendation for their graduate program application process. These letters are expected to come from individuals who can provide distinct perspectives on your abilities and character. For example, one letter might focus on your academic achievements, another on your research skills, and a third on your professional experience.
Q. What should be included in a professional letter of recommendation?
A. A professional, solid letter of recommendation should include several key elements to support your application effectively. It should begin with an introduction establishing the recommender’s relationship with you and their qualifications to speak on your behalf. The letter’s body should summarise your key strengths, supported by specific examples of your achievements and contributions in academic or professional settings.
Q. How long should a professional letter of recommendation be?
A. A professional letter of recommendation is typically 1-2 pages long, consisting of 5-6 well-structured paragraphs. The length allows the recommender to thoroughly assess your qualifications without overwhelming the reader. Each paragraph should focus on your skills or character, such as your academic abilities, research experience, leadership qualities, or personal integrity.
Q. What format should a professional letter of recommendation follow?
A. The letter should be formatted according to standard professional guidelines. This includes 1-inch margins, single-spaced lines, and left-aligned text. The font should be according to and experienced, such as Times n, with a size between 10 and 12 points. The letter should include a formal salutation, a clear introduction, a detailed body, and a strong closing statement.
Q. Can I use the same letter of recommendation for multiple applications?
A. While it’s possible to use the same recommender for multiple applications, it’s generally best to have them tailor each letter to the specific program or job you’re applying to. Different programs may value different qualities or experiences, so a one-size-fits-all letter may not highlight the most relevant aspects of your background.
Q. What is the difference between a professional letter of recommendation and a reference letter?
A. A professional letter of recommendation is typically more detailed and formal than a reference letter. It focuses on your qualifications for a specific program or job and is often written by someone who has closely supervised your academic or professional work. On the other hand, a reference letter might be more general and can come from a broader range of individuals, such as a colleague or a community leader.
Q. How can I help my recommender write a strong letter of recommendation?
A. To help your recommender write a strong letter of recommendation, provide them with detailed information about your goals, achievements, and the specific requirements of the program or job you’re applying to. Share your resume, a statement draft, and other relevant documents highlighting your qualifications.
Q. How can a professional letter of recommendation improve my chances of admission?
A. A well-written letter of recommendation can significantly enhance your application by providing a credible, third-party endorsement of your abilities, character, and potential. This external validation can reinforce the claims you’ve made in your statement and other application materials, helping to build a more compelling case for your admission.
Know More about Study Abroad
Essential guide: studying abroad tips.
30+ Universities for Study Abroad
- Arizona State University
- Northeastern University
- Coventry University
- University Of East London
- University Of Hertfordshire
- Conestoga College
- Humber College
- Centennial College
- University Of Birmingham
- Stanford University
- University Of Greenwich
- Columbia University
- Bpp University
- Texas A & M University
- University Of Maryland
- University Of Toronto
- University Of Melbourne
- University Of Waterloo
- New York University
- Mcgill University
- Harvard University
- University Of British Columbia
- University Of Alberta
- University Of Oxford
- University Of Cambridge
- University Of California Berkeley
- Yale University
- University Of Calgary
- Massachusetts Institute Of Technology (MIT)
Popular Blogs
- CGPA to GPA: Check How to convert 10 point CGPA to 4 point GPA
- Check How to Calculate Percentage to CGPA
- Top 10 Toughest Exams in the World 2024
Education counselling
- Study Abroad Consultants in India
- Study Abroad Consultants in Kochi
- Study Abroad Consultants in Delhi
- Study Abroad Consultants in Chennai
- Study Abroad Consultants in Hyderabad
- Study Abroad Consultants in Mumbai
- Study Abroad Consultants in Bangalore
- Study Abroad Consultants in Kolkata
- Study Abroad Consultants in Pune
- Study Abroad Consultants in Jaipur
- Study Abroad Consultants in Indore
- Study Abroad Consultants in Nagpur
- Study Abroad Consultants in Ludhiana
- Study abroad Consultant in Thiruvananthapuram
- Study abroad Consultant in Calicut
- Study abroad Consultant in Amritsar
- Study abroad Consultant in Thrissur
- Study abroad Consultant in Ahmedabad
- Study abroad Consultant in Vizag
- Study abroad Consultant in Noida
Prachi Sethi
Hi, I am Prachi, an experienced writer with extensive knowledge about the study abroad domain in particular countries such as the USA and Canada and other popular courses. My expertise in SEO allows me to create high-quality content that engages and informs students and helps them fulfil their International Dreams.

Affordable MBA Abroad for Indian Students in 2024-2025

Virendra Kumar Dhall Scholarship for Sporting Excellence, Loughborough University, UK

Top GMAT-Accepting Colleges in the World for MBA

SOP for PG Diploma in Canada: Structure, Format and Tips
Love this blog share the love.

Get the best study abroad guidance
Start your journey with the best study abroad experts in India
- 2L+ Leap students sent abroad
- 2L+ students scored 7+ bands
Have Questions? Get Guidance to reach your Dream University
Connect with India's finest counsellors and biggest study abroad community.
Related Blogs

US Visa Rejection Rate & Reasons for International Students
- August 25, 2024
- 13 min read

- August 24, 2024
- 12 min read
- August 23, 2024

GRE vs IELTS: Difference & Which is Better and Easier

Pre Masters In UK – Top 8 Course Details & Universities
- May 10, 2022
- 12 Min Read

MSc in Microbiology in UK: Admission, Fees, Universities & Course Details
- May 2, 2022
- 17 Min Read

Masters in Education in UK: Universities & Course Details
- April 26, 2022
- 10 Min Read

Masters In Robotics In USA: Universities & Course details
- March 15, 2022
- 11 Min Read

MS in Mechanical Engineering in USA: Universities & Course Details
- March 10, 2022
- 13 Min Read

PTE Reading Tips and Tricks to Improve your PTE Reading Score
- August 20, 2024
Crack IELTS with
7+ bands in 4 weeks.
Get Guidance to reach your
Dream university.

Style and Grammar Guidelines
APA Style provides a foundation for effective scholarly communication because it helps writers present their ideas in a clear, concise, and inclusive manner. When style works best, ideas flow logically, sources are credited appropriately, and papers are organized predictably. People are described using language that affirms their worth and dignity. Authors plan for ethical compliance and report critical details of their research protocol to allow readers to evaluate findings and other researchers to potentially replicate the studies. Tables and figures present information in an engaging, readable manner.
The style and grammar guidelines pages present information about APA Style as described in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, Seventh Edition and the Concise Guide to APA Style, Seventh Edition . Any updates to APA Style are noted on the applicable topic pages. If you are still using the sixth edition, helpful resources are available in the sixth edition archive .
Looking for more style?

- Accessibility of APA Style
- Line Spacing
- Order of Pages
- Page Header
- Paragraph Alignment and Indentation
- Sample Papers
- Title Page Setup
- Appropriate Level of Citation
- Basic Principles of Citation
- Classroom or Intranet Sources
- Paraphrasing
- Personal Communications
- Quotations From Research Participants
- Secondary Sources
- Abbreviations
- Capitalization
- Italics and Quotation Marks
- Punctuation
- Spelling and Hyphenation
- General Principles for Reducing Bias
- Historical Context
- Intersectionality
- Participation in Research
- Racial and Ethnic Identity
- Sexual Orientation
- Socioeconomic Status
- Accessible Use of Color in Figures
- Figure Setup
- Sample Figures
- Sample Tables
- Table Setup
- Archival Documents and Collections
- Basic Principles of Reference List Entries
- Database Information in References
- DOIs and URLs
- Elements of Reference List Entries
- Missing Reference Information
- Reference Examples
- References in a Meta-Analysis
- Reference Lists Versus Bibliographies
- Works Included in a Reference List
- Active and Passive Voice
- Anthropomorphism
- First-Person Pronouns
- Logical Comparisons
- Plural Nouns
- Possessive Adjectives
- Possessive Nouns
- Singular “They”
- Adapting a Dissertation or Thesis Into a Journal Article
- Correction Notices
- Cover Letters
- Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS)
- Open Science
- Response to Reviewers
Poster Samples
Looking at samples of real student posters can help you generate ideas and define your goals. As you get started, it may be helpful to look at examples of finished posters.
Below are a number of sample posters created by UT undergraduates. There is a brief discussion of each poster highlighting its greatest strengths and areas where there is room for improvement.

- More than one type of visual aid
- Logical order for sections
- Acknowledgments
Room for improvement
- Background may be distracting, or detract from content
- Sections and images are not aligned
- Too many visual components clutter poster
- White space
- Legible text and graphics
- Reports preliminary results
- All participants listed as authors, with affiliations provided
- Lacks Citations and Acknowledgements
- Labeling of images/graphics
- Inconsistent text alignment
- Color-saturated background
- Clearly defined research questions
- Effective use of visual aids
- Clear organizational structure
- Bullets break up text
- Technical language/undefined acronyms (accessible to limited audience)
- Narrow margins within text boxes
- Too many thick borders around boxes
- Uses UT seal instead of college or university wordmark

- Clear introductory material
- Use of bullet points
- Logical flow
- Color-coding in graphics
- Lacks references section
- May not be accessible to all audiences (some technical language)
- No need for borders around sections (the blue headers are sufficient)

- Compelling visual aids
- Strategic use of color
- Clear sections
- Inconsistent fonts in body text
- Abstract section mislabeled
- Bullet points are great, but only if they’re used judiciously
- Parameters of study well defined
- Clearly defined research question
- Simple color scheme
- Use of white space
- Discussion of Results
- Minor formatting misalignments
- Unauthorized use of UT seal (use wordmark instead)
- Venn diagram in discussion
- Consistent graphics
- Multiple types of visual aids
- Light text on dark background
- Color backgrounds should be avoided, especially dark ones
- Unlabeled, non-credited photos
- Easy to read
- Use of shapes, figures, and bullets to break up text
- Compelling title (and title font size)
- Clean overall visual impression
- Many sections without a clear flow between them
- Lacks acknowledgements

- Use of images/graphics
- Clear title
- Accessible but professional tone
- Length/density of text blocks
- Tiny photo citations
- Connections between images and descriptive text
- Vertical boxes unnecessary
- Compelling title
- Font sizes throughout (hierarchy of text)
- Simple graphics
- Lacks clear Background section
- Relationship of Findings and Conclusion to Research questions

- Use of visual aids
- Uneven column width
- Center-justfied body text
- Lacks “Methods” section
- Use of bullets
- Too many different font styles (serif and sans serif, bold and normal)
- Concise interpretation of graphics
- Accessible visual structure
- Clear, simple graphics
- Fonts and font sizes
- Analysis of graphic data
- Discussion of significance
- Lacks author’s affiliation and contact information

- Balance among visuals, text and white space
- Data presented in visual format (SmartArt)
- Accesible to many audiences (simple enough for general audience, but enough methodological detail for experts)
- Some more editing needed
- When targeting an expert audience (as in the methodology section), should also report statistics ( r, p, t, F, etc.)

- Large, clear title
- Creative adaptation of sections
- Use of lists (rather than paragraphs)
- Accessible to diverse audience
- Connection between visuals (sheet music) and content

- Strategic use of color for section headers
- Labeling and citation of images
- Accessible to a broad audience
- Wide margins around poster edges
- Slightly text-heavy
- Data referenced (“Methodology”) but not discussed
What is my next step?
Begin working on the content for your poster at Create Your Message .
- Get Started
- Request Information
- Degrees & Certificates
- Paying for College
- Community Education
4 EMCC Students Rock U of A Summer Geology Program

Mountain Lions Generously Compensated During 8-Week Research Opportunity
When Estrella Mountain Community College (EMCC) Geology Professor Zachary Kovach told his students about an eight-week paid geoscience research opportunity at the University of Arizona (U of A) this summer, they wanted in. To be considered for U of A’s Clouds to the Core program, they had to submit a personal statement of interest, their transcripts, and a letter of recommendation. Only 12 students total from community and tribal colleges across the southwest would be accepted. Four Mountain Lions make the cut.
“I don’t think it is common to get four students like we did,” Professor Kovach said. “EMCC represented 33% of the students!”
Clouds to the Core introduces students from two-year colleges to geoscience career opportunities and the opportunity to transfer to the U of A to earn a bachelor’s degree in geosciences after earning their associate degree at EMCC. Although this is the program’s second year, the idea began in 2020 when the U of A’s Drs. Andy Cohen and Kau Thirumalai, reached out to Professor Kovach, wanting to tailor a program to undergraduate/community college-level students.
The program begins with a two-week orientation and project introduction period at the U of A, followed by five weeks of research. Each student is assigned a different research topic and mentors. During the last week of the program, students present their work to their peers, lab mates, mentors, friends, and family. Each student is compensated with free lodging, a $600-per-week stipend, and a $100-per-week food allowance.
“When setting this program up, it was important to discuss who our students are and the fact that most of them are working in some capacity,” Professor Kovach said. “So in order to get these students to go to the U of A for eight weeks or so, they also needed to be compensated. The stipend and room and board are what make this possible for a lot of the students.”
The compensation aspect was especially intriguing to EMCC Environmental Engineering major Justice Gonzales, whose research project involved determining the ocean’s role in the southwest climate.
“I was very excited when I found out I’d been accepted into the program because it meant I would have the security to not have to work other jobs during the summer and be able to learn and further my educational goals,” Justice said. “It was very reassuring to find out that somebody saw enough value in me to compensate me well and let me know my worth going forward.”
Becca Lord agreed.
“I think it's cool that we got paid because I feel like most programs don’t pay their participants,” Becca said. “And it was really nice that we didn’t have to worry about room and board, so we could just focus on our research.”
When Becca found out she’d been accepted into the Clouds to the Core program, she was getting ready to graduate from EMCC with her Associate in General Business. She had very little geoscience background.
“When I found out I’d been accepted, I cried,” Becca said. “I was overwhelmed and in disbelief because I didn’t think a business major with no experience in geoscience would be accepted.”
Becca’s research project, titled “Temporal Constraints on the Cat Mountain Supervolcanic Sequence,” focused on determining if two different types of rocks found within the Tucson Mountain range were equal in age. Becca and her mentors spent a couple of days in the field collecting samples and then running them through various equipment in the lab.
“I was not familiar with any of the lab equipment going into this program, but I was provided with training by my supportive mentors,” Becca said. “I never felt alone in my work, and I knew there was always someone to ask questions of.”
The program gets the students out of their comfort zone, but is very mindful about it, Professor Kovach said.
“They have their faculty mentor as well as undergraduate mentors who went through the program last year,” Professor Kovach said. “So there really is a lot of support, not only research/academically, but also support on campus life, living on their own, having someone to talk to, etc.”
Becca’s research ended up revealing that rocks found in several locations within the Tucson Mountains were of vastly different ages — some 2 million years apart.
“We’re not sure why that is,” Becca said. “It will take more research to determine that. But it tells us that the source of the Cat Mountain Tuff, which is igneous and extrusive — ejected material in an eruption — had to have come from somewhere else, outside of the Tucson Mountains.”
With an Associate in General Business already under her belt, Becca is now working on an Associate in Science with an Emphasis in Geology. Once she completes that degree, she will transfer to the U of A and have the opportunity to continue her research.
“This makes me even more excited since my research left me with so many questions,” Becca said.
Once she transfers to the U of A, she will pursue a bachelor’s in Geoscience and Society, something she is even more confident about now that she has completed the Clouds to the Core program.
“This program provided me with the resources and connections necessary to make the transfer to the U of A, but also to form friendships with people I’ll be transferring with and studying alongside.”
Taiton Grey might be one of them. The dual major — Automated Industrial Technology and Mechanical Engineering — will graduate from EMCC in 2026, transfer to Arizona State University for a bachelor’s in Mechanical Engineering, and then most likely head on down to the U of A for a master’s and PhD in Sustainability and Agriculture. Taiton said the Clouds to the Core program absolutely influenced his choice of major and decision to pursue geoscience.
“For my own personal reasons, I want to get my bachelor’s in engineering because I just like knowing how things work,” Taiton said. “And the jobs I want either want an engineering degree or a geoscience degree so that’s why I am doing my master’s and PhD in the geosciences.”
Taiton, who grew up in Virginia, said his research project, “Sea Level Rise Acceleration After 2010,” hit especially close to home.
“I felt like it was the perfect project for me because my focus was on the acceleration along the Atlantic and Gulf Coasts and most of my family is dispersed along those regions,” he said. “I was even able to use actual photographs from beaches back home in my final presentation.”
Students in the program were assigned roommates and housed in one of the U of A’s dormitories. When they weren’t conducting their own research, they got to know each other, hanging out, sharing meals, and participating in group activities such as hikes and a visit to Biosphere 2. Eden Toliver, an EMCC Anthropology major, said the most rewarding aspect of being in the program was getting to make so many new friends.
“It was great getting to spend time with the other participants,” Eden said. “I hope to stay in touch with most of the other students. I know I'll be staying in touch with Justice since I see Justice a lot around school already.”
Eden’s research project, “Crystal Settling Timescales in Magma,” involved determining how crystals forming and settling in magma affect the properties of the magma, changing how it will erupt. Most of Eden’s time was spent in the lab, filming different-sized acrylic spheres falling into water and oil and analyzing the footage to ascertain their velocity.
“I was definitely busy once I got started on my project,” Eden said. “I still had time to do other things, but I was occupied for most of the day.”
While students grew more comfortable in their research endeavors, they were all a little nervous during their presentations, but Professor Kovach, who drove down to Tucson to support them, said they all did an amazing job.
Dr. Cohen said the program gives students a huge leg up in terms of confidence and readiness to attend a STEM B.S. or B.A. program.
“Our goal specifically is to encourage transfer to the U of A and our Geosciences Department,” Dr. Cohen said. “We provide 6 units of upper-division credit at no cost to the students for those who decide to attend the U of A and major in Geosciences.”
EMCC has transfer partnerships with the University of Arizona, Arizona State University, Northern Arizona University, Grand Canyon University, and more than 40 public, private, and online institutions across the country. Learn more at https://www.estrellamountain.edu/university-transfer .
The application for the 2025 Clouds to the Core summer program will open in the fall. Students can learn more and apply by going to https://c2c.geo.arizona.edu/ and clicking on “Apply Now.”

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Recommendations for future research should be: Concrete and specific. Supported with a clear rationale. Directly connected to your research. Overall, strive to highlight ways other researchers can reproduce or replicate your results to draw further conclusions, and suggest different directions that future research can take, if applicable.
This can include recommendations related to sample size, data collection techniques, research instruments, data analysis methods, or other relevant factors. Justify recommendations: Justify why each recommendation is being made and how it will help to address the research question or objective. It is important to provide a clear rationale for ...
Here is a step-wise guide to build your understanding on the development of research recommendations. 1. Understand the Research Question: Understand the research question and objectives before writing recommendations. Also, ensure that your recommendations are relevant and directly address the goals of the study. 2.
Recommendation in research example. See below for a full research recommendation example that you can use as a template to write your own. Recommendation section. The current study can be interpreted as a first step in the research on COPD speech characteristics. However, the results of this study should be treated with caution due to the small ...
Step 2: Analyse Your Findings. You have to examine your data and identify your key results. This analysis forms the foundation for your recommendations. Look for patterns and unexpected findings that might suggest new areas for other researchers to explore.
Recommendation in research : The current study can be interpreted as a first step in the research on differentiated instructions. However, the results of this study should be treated with caution as the selected participants were more willing to make changes in their teaching models, limiting the generalizability of the model.
Crafting impactful recommendations is a vital skill for any researcher looking to bridge the gap between their findings and real-world applications. By understanding the purpose of recommendations, identifying areas for future research, structuring your suggestions effectively, and connecting them to your research findings, you can unlock the ...
As a researcher, you display a deep understanding of the topic of research. Therefore you should be able to give recommendations. Here are a few tips that will help you to give appropriate recommendations. Recommendations in the research paper should be the objective of the research. Therefore at least one of your objectives of the paper is to ...
Let's look at some examples. Although this list was beneficial in guiding my recommendations, I still wasn't well-versed in how to write them. So, after some time, I created a formula for writing recommendations: Observed problem/pain point/unmet need + consequence + potential solution.
Having drawn your conclusions you can then make recommendations. These should flow from your conclusions. They are suggestions about action that might be taken by people or organizations in the light of the conclusions that you have drawn from the results of the research. Like the conclusions, the recommendations may be open to debate.
A research recommendation will rarely have an absolute value in itself. Its relative priority will be influenced by the burden of ill health (d), which is itself dependent on factors such as local prevalence, disease severity, relevant risk factors, and the priorities of the organisation considering commissioning the research.
The recommendation: Based on these results, physicians are recommended to encourage patients to exercise and walk regularly. Also recommended is to encourage more walking through public health offices in communities. Example 3. A study found that many research articles do not contain the sample sizes needed to statistically confirm their findings.
The conclusions are as stated below: i. Students' use of language in the oral sessions depicted their beliefs and values. based on their intentions. The oral sessions prompted the students to be ...
The initially stated overarching aim of this research was to identify the contextual factors and mechanisms that are regularly associated with effective and cost-effective public involvement in research. While recognising the limitations of our analysis, we believe we have largely achieved this in our revised theory of public involvement in research set out in Chapter 8. We have developed and ...
Recommendation reports are texts that advise audiences about the best ways to solve a problem. Recommendation reports are a type of formal report that is widely used across disciplines and professions. Subject Matter Experts aim to make recommendations based on the best available theory, research and practice. Different disciplines and professions have different research methods
Here are a few guidelines to enable you to write a good recommendation for your research paper. 1. ... A sample size of 142 subjects was purposively drawn from a population of 27, 057 students ...
A recommendation in research refers to the advice or suggestions provided by researchers at the conclusion of their study, aimed at addressing the gaps identified, enhancing future research, and applying findings in practical contexts.Recommendations are crucial as they guide stakeholders, including policymakers, practitioners, and fellow researchers, on how to utilize the research outcomes ...
Here are some helpful tips for writing dissertation recommendations that you should incorporate when drafting a research paper: Avoid general or vague recommendations. Be specific and concrete. Offer measurable insights Ensure your suggestions are practical and implementable. Avoid focusing on theoretical concepts or new findings but on future ...
questions around treatments: population, inter vention, comparison, and outcomes (PICO). In addition, the. research recommendation is dated and author s are. asked to provide the current state of ...
the purpose, research questions and results of the study. The implications of these findings and the resultant recommendations will also be explained. Recommendations were based on the conclusions and purpose of the study. 5.2 OVERVIEW OF THE STUDY The study was an exploratory, descriptive and contextual qualitative study. The
Below are nine sample recommendation letters, each followed by an analysis of what it does well! Sample Recommendation Letter 1: Written by a Direct Manager for a Full-Time Employee. Sample Recommendation Letter 2: Written by a Principal for a Teacher. Sample Recommendation Letter 3: Written by a Direct Manager for a Part-Time Employee.
Writing recommendation letters on behalf of students and other early-career researchers is an important mentoring task within academia. An effective recommendation letter describes key candidate qualities such as academic achievements, extracurricular activities, outstanding personality traits, participation in and dedication to a particular discipline, and the mentor's confidence in the ...
Please see a sample professional reference letter and a professional letter of recommendation for ms below. DISCLAIMER: The name "John Smith" is used in this sample LOR for illustrative purposes only. Sample Professional Reference Letter [Full Name] Research Scientist [Company Name] [Company Address] [City, State ZIP Code] [Email Address ...
People are described using language that affirms their worth and dignity. Authors plan for ethical compliance and report critical details of their research protocol to allow readers to evaluate findings and other researchers to potentially replicate the studies. Tables and figures present information in an engaging, readable manner.
Undergraduate Research Peter T. Flawn Academic Center (FAC) Room 33 2304 Whitis Ave. Austin, Texas 78712 512-471-7152. Find us on Facebook. Find us on X (formerly Twitter) See us on Instagram ... Below are a number of sample posters created by UT undergraduates. There is a brief discussion of each poster highlighting its greatest strengths and ...
5 likes, 0 comments - phd_pdf_scholarship on August 17, 2024: "Letter of Recommendation sample for your PhD & Master's applications Join us for research related guidance and research opportunities from best in the fields.欄 헪헵헮혁혀헔헽헽 헧헲헹헲헴헿헮헺 헟헶헻헸헲헱헜헻 #ResearchTips #AcademicSuccess #StudentLife #ResearchQuestion #StudySmart #AcademicWriting # ...
Mountain Lions Generously Compensated During 8-Week Research Opportunity When Estrella Mountain Community College (EMCC) Geology Professor Zachary Kovach told his students about an eight-week paid geoscience research opportunity at the University of Arizona (U of A) this summer, they wanted in. To be considered for U of A's Clouds to the Core program, they had to submit a personal statement ...
Research: H5N1 Beef Safety Studies. To verify the safety of the meat supply in the context of H5N1, FSIS, APHIS, and USDA's Agricultural Research Service (ARS) have completed three separate beef safety studies related to avian influenza in meat from dairy cattle. Beef Muscle Sampling of Cull Dairy Cows. On May 30, 2024, FSIS announced the final results of its beef muscle sampling of cull dairy ...
How to write a recommendation report. You can write a recommendation report with the following steps: 1. Choose a topic. Choose a topic for your recommendation report. If you are writing a recommendation report in the workplace, you may already have a problem to solve, which serves as your topic. If you're writing in an academic setting, you ...
Waste Management, Inc. (NYSE:WM - Get Free Report) has been assigned an average recommendation of "Moderate Buy" from the twenty ratings firms that are currently covering the company, Marketbeat Ratings reports.Eleven analysts have rated the stock with a hold recommendation, eight have issued a buy recommendation and one has issued a strong buy recommendation on the company.