
How to Write a Book Title in MLA Formatting
by Joe Bunting | 2 comments
You're writing a paper for school and suddenly you stop in the middle of the sentence. You have to write a book title, but you don't how to format it. How do you format a book title in MLA style? Good news: you're in the write place (sorry, I had to).
In this post, we'll talk about MLA style and formatting, whether it's appropriate for your project, and most importantly, how to write a book title in MLA style.
What Is MLA?
MLA stands for Modern Language Association, a society primarily based in the United States but with international standing, that has a mission to “strengthen the study and teaching of language and literature”. Founded in the late 1800s by an American novelist and professor, MLA publishes a set of resources used by students and teachers, including the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers .
The MLA handbook is one of the main style manuals for students and scholars in the world, especially for anyone studying literature, film, or theater.
Should You Format Based on MLA Style?
If you're writing a paper for a class in literature, theater, or film, absolutely use MLA style. Outside of that, it depends. Here are the most frequent style guides associated with various disciplines:
- Literature, Film, Theater: MLA
- Psychology: APA
- Science (Physics, Biology, Chemistry): CSE or APA
- Journalism: AP
- Mathematics: AMA
- Publishing: Chicago
You can find a full list of international style guides here .
Now that you know if you should be using MLA style, how do you format a book title with it?
How to Format a Book Title in MLA Style: Example
In MLA style, book titles are italicized, as so:
Henry Thorough argues in Walden that the best life is lived in deliberate simplicity so as to discover what life truly is about.
In fact, most style guides, including MLA and Chicago style, require book titles to be italicized , not underlined.
If the book title has a subtitle, the subtitle should be italicized as well and separated by a colon to be formatted correctly for MLA style, as in:
Natural History of the Intellect: the last lectures of Ralph Waldo Emerson
Should You Underline Book Titles in MLA Style?
If you are using MLA style, you should not underline book titles. Instead, italicize the titles.
However, AP style, the guide used by journalists, suggests putting titles in quotation marks, not italicization.
Still, I wouldn't recommend underlining a book's title. In fact, I couldn't find a single style guide that requires book titles to be underlined, but if you know of one that does, let me know in the comments!
Which style guide do you use most? MLA? Chicago? APA? AP? Or do you just write based on your own rules?! Let me know in the comments .
Let's cement this formatting lesson in our minds by putting it to use right away with the following writing exercise .
What are your favorite books of all time? Write about what you love about them and why they are your favorites for fifteen minutes . Make sure to use the correct formatting for each title!
When your time is up, post your practice in the comments section . And if you post, please be sure to read a few practices by other writers and share your feedback with them.
Happy writing!
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.

how do you format the title if you’re writing on paper and can’t italicize?
When writing by hand, you can underline book titles.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Best Resources for Writers Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
How to Write a Book Title in an Essay (MLA, APA etc.)
Formatting your essay correctly ensures that you get full recognition for the hard work you put into it. Wondering what to do? There are two scenarios that lead you to the question of "how to write a book title in an essay":
- You have not been required to use a particular style guide, in which case consistency remains important.
- You have been instructed to use a particular style guide. You now simply need to ensure that you are familiar with its rules.
Regardless of which of these scenarios holds true for you, this guide is here to help.
How to Write a Book Title in an Essay
Many style manuals call on writers use title case and italics to format a book title. Title case rules vary slightly from one style guide to the next, but generally capitalize all important words — nouns, pronouns, verbs, and adverbs. Conjunctions and prepositions are not capitalized unless they are very long (generally more than four letters) or they appear at the beginning or end of a book title.
Writers who are not required to work with a specific style manual can't go wrong if they stick to this style. Some examples would be:
- To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee
- The Gift of Fear and Other Survival Signals That Protect us From Violence by Gavin de Becker
- The Cat With a Feathery Tail and Other Stories by Enid Blyton
If, on the other hand, you're required to use a style guide, it will likely be one of these:
- MLA, commonly used in disciplines relating to literature and social sciences.
- APA, commonly used in psychology and other sciences.
- Chicago, often used in the publishing industry.
- Harvard style, commonly used in philosophy and social sciences.
These are certainly not the only "big players" in the style guide world, but they're ones it's good to be familiar with. There is overlap between these styles, but there are also major differences — so knowing one definitely does not mean you know the others, too.
Guidelines for Writing a Book Title in an Essay
Looking for a short and sharp answer, so you can get on with the rest of your essay? This is it.
| Writing Style / Format | General Rules of Writing a Book Title |
| MLA | Italicize the full title of a book and place it in title case (Conrad, Joseph. ). Place the name of a single chapter in quote marks, instead ("The Great Towns" from by Friedrich Engels). |
| APA | Italicize the book title. Capitalize the first letter, the first letter of a subtitle, and proper nouns. Example: Chapters are placed in title case, but neither italicized nor placed in quote marks. |
| Chicago | Italicize the full title and use title case: by Jonathan Swift. Book chapters are placed in quote marks, and use title case, as with MLA. |
| Harvard | The book title is italicized and placed in title case: by Harper Lee. Chapters are placed in single quote marks: 'Rat' from . |
This quick guide will help you reference the book title of your choosing in the body of your essay, but what about your Works Cited pages? Each style guide offers different rules, and we'll use the same book as an example to illustrate the differences.
- MLA uses the following format: Author Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . City of Publication, Publisher, Publication Year. Example: Card, Orson Scott. Ender's Game. Tor Books, 1985. (You only have to detail the city of publication if the book was published before 1900, the publisher has offices in many localities, or the publisher is not known in the US.)
- APA uses the following format: Author Last Name, First Name. (Year of Publication). Title of book. Example: Card, Orson Scott. (1985). Ender's game.
- Chicago style uses the following format: Author Last Name, First Name. Book Title: Subtitle . Place of publication: Publisher, Year. Example: Card, Orson Scott. Ender's Game . Tor Books, 1985.
- Harvard uses the following format: Author Last Name, First Initial. (Publication Year). Title . ed. City: Publisher. Example: Card, O. (1985). Ender's Game. Tor Books.
If, after researching, you cannot find relevant information about publication years, publishers, or the city in which a book was published, you may omit it. For a full guide, it is always best to have a physical copy of the latest edition of the style manual you are using. You can, however, get by without this if you need to.
Should you still not know what to do, it will be helpful for you to know that you can "generate" citations for a particular style manual with the help of online tools like Cite Me . These are not always accurate, so if you decide to use one, always check the citation manually.
Why Is Proper Formatting Important?
All of the well-known style manuals ultimately serve the very same set of purposes, although they were each developed for a particular niche. The goals of these style manuals are both explicit and implicit:
- Following a style guide ensures consistency throughout a document, in this case an essay.
- Consistency ensures that reader's understand precisely what the writer is talking about, without exerting any effort on figuring that out. Clarity is especially important in academic writing.
- By using a style guide within a certain discipline, you show that you understand the rules within that discipline. This adds credibility to your voice as a writer. You have done your homework, have ideally bought the style manual, and are part of the "in group".
- Sticking to a certain style guide makes it easier for relevant parties to check your references, which they can then use to perform further research.
Students are increasingly asked to refer to style guides at all levels, including in high school. In this case, formatting your essay correctly, in accordance with the right style manual, serves two additional purposes:
- You'll lose points if you don't do it right, offering you an additional reason to do your research.
- Getting used to these formats prepares you for further education. If you are in high school, it prepares you for college-level writing. If you are an undergraduate student, it prepares you for academic work at the graduate and post-graduate levels.
Can you start an essay with a book title?
Yes, you can start an essay with a book title. This is a valid stylistic choice, but you will always want to consider your introduction carefully.
How do you write a book title in handwriting?
Students sometimes ask whether it is acceptable to underline book titles instead of italicizing them. This practice indeed stems from a time in which most students wrote their essays by hand. Although it has largely fallen out of practice now, you can still underline a book title if you are handwriting your essay.
How do you write a book title and chapter in an essay?
You should mention the chapter title first: "Rat" from Ender's Game by Orson Scott Card. Consult the relevant style manual to ensure you get the formatting right.
Can you shorten a book title in an essay?
Yes, you can. Reference the full title the first time you mention it (for example: Furiously Happy: A Funny Book About Horrible Things ). The next time you mention the book, you may simply refer to Furiously Happy .
Related posts:
- How to Write the Date in MLA Format
- How To Write A Movie Title In An Essay
- Someone Walked Over My Grave - Meaning and Origin
- 14 Tips to Help you Write An Essay Fast
- Go Pound Sand - Meaning, Usage and Origin
- How to Write a DBQ (APUSH) Essay?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- MLA Style Manual
How to Write Book Titles in MLA
Last Updated: April 1, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Annaliese Dunne and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Annaliese Dunne is a Middle School English Teacher. With over 10 years of teaching experience, her areas of expertise include writing and grammar instruction, as well as teaching reading comprehension. She is also an experienced freelance writer. She received her Bachelor's degree in English. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 49,720 times.
If you're writing a research paper, you may want to include the title of a book in the text of your paper. The handbook for the Modern Language Association (MLA) provides specific rules for how to set off the title of a book from the rest of your text. Generally, titles of books are set apart from the rest of the text following particular formatting, capitalization, and punctuation rules.
Formatting Titles

- Music album titles and film titles are also italicized.
- In earlier editions, the MLA Handbook also permitted titles to be underlined. The 8th edition confirms that underlining is no longer appropriate.
Exception : Religious texts, such as the Bible or the Quran, are not italicized.

- For example, you might write: "In The Great Gatsby in the Classroom: Searching for the American Dream , David Dowling promotes the use of art and film to improve literacy."

- For example, if you were talking about the Nancy Drew series, you would not italicize "Nancy Drew" because the name does not appear in the titles of any of the individual books. In contrast, Harry Potter would be italicized, because the name appears at the beginning of the title of every book in the series.

- For example, if you were writing a paper on The Great Gatsby , you would need to include the full title in your text at least once. If you mentioned the novel more than once, you could use Gatsby as a shortened title.
- How you shorten the title generally depends on your own judgment. Use a word or words that evoke the title easily in the mind of the reader, without any ambiguity.
Capitalizing Titles

- For example, you might write: "Comedian Steve Martin takes on the art world in his novel An Object of Beauty . Note that the word "an" is capitalized because it is the first word. Otherwise, it would be in lowercase.
- If the book also has a subtitle, capitalize the first word of the subtitle just as you did the first word of the title.

- Articles include words such as "a," "an," and "the." Words such as "against," "in," and "to." Note that these words remain in lowercase regardless of their length.

- Coordinating conjunctions include words such as "and," "but," "for," and "nor."
- Subordinating conjunctions include words such as "after," "although," because," "unless," and "until."

- Example: Storytelling and Mythmaking: Images from Film and Literature
Tip: If you have doubts about the parts of speech of the words in a title, you can check your capitalization using free capitalization checkers available online.

- Capitalize all words that would be capitalized in the language the title is written in. For example, since all nouns are capitalized in German, you would capitalize all nouns in a German book title.
Punctuating Titles

- For example, if a title ends in an exclamation point or a question mark, you would include that punctuation mark at the end of the title. The punctuation mark should be italicized so that your readers understand that it's part of the title, not part of your punctuation.
- If the book title ends in a question mark or an exclamation point, it's typically not a good idea to use that title at the end of a sentence, because then the punctuation mark at the end of the book title effectively becomes the punctuation mark for the end of your sentence. Recast your sentence so that the book title doesn't fall at the end of the sentence.

- There is an exception if the book title includes another book title, and the included book title ends in a question mark or exclamation point. Since that punctuation mark belongs to the included book title, you would follow that punctuation mark with a colon. For example: Moby Dick and Absalom, Absalom! : Two American Masterpieces Note that the colon is italicized.

- For example, you might write: "In the 1980s sitcom When Harry Met Sally. . . , the characters examined whether heterosexual cisgender men and women could be friends without ever becoming romantically or sexually involved."
- Note that you'll have to form your sentence so that either a comma or a period is appropriate following the ellipsis or a dash.
Tip: Although it might be difficult for the average person to tell whether a punctuation mark such as a comma or period is italicized, technically any punctuation added to the end of the title should not be italicized.

- For example: England's Monitor; or, The History of Separation . Note that the "or" and all punctuation are also italicized.
- Generally, list the original or oldest title first, followed by any later title.

- For example, since the book Everything Is Nothing: The Poetry of the Great War, Revolution and the Transformation of Europe was published in London, the serial comma would not be added. However, if the book were published in the US, you would add a comma after the word "Revolution."
Expert Q&A
You might also like.

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about writing, check out our in-depth interview with Annaliese Dunne .
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/subject_specific_writing/writing_in_literature/writing_about_literature/formatting.html
- ↑ https://style.mla.org/punctuation-with-titles/
- ↑ https://style.mla.org/trilogy-titles/
- ↑ https://style.mla.org/full-names-titles-in-each-chapter/
- ↑ https://secondary.oslis.org/cite-sources/mla/how-to-capitalize-and-punctuate-titles
- ↑ https://style.mla.org/capitalization-of-titles/
- ↑ https://irsc.libguides.com/c.php?g=483085&p=3303403
- ↑ https://morningside.libguides.com/MLA8/title
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
How Do You Write the Title of a Book in MLA Style?
Have you read “ Italics and Underlining: Titles of Books ,” an article we published on TheWordCounter.com in May?
Take a look at the previous sentence. In it, we’ve made use of the Modern Language Association’s guidelines for writing titles. Because the article is a part of a whole, meaning it’s a small part of a larger website , its title should be put in quotation marks. The larger work, the website, must be italicized.
To take a step back, it’s important to understand that many different style guides exist, and they all give advice about how to format your writing, address grammar concerns, and provide information about the source material you use. Within the context of academic writing, often a teacher will give an assignment and specify which style guide you should use. Similarly—if you’re planning to publish your writing—journals, publishing companies, and editors may have strong preferences about formatting. At other times, you may be able to select a style guide based on your own preferences.
For the purpose of this article, let’s assume that you’ve been assigned (or have chosen to write) a short essay in MLA format. If that’s the case, what do you need to know about writing titles?
Your writing, at its best
Compose bold, clear, mistake-free, writing with Grammarly's AI-powered writing assistant
Works Cited
To begin, you’ll need to include a Works Cited section for your essay, as long as you have source material that you’re planning to quote or paraphrase. Let’s begin by looking at a standard citation for a book in MLA format.
Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . Publisher, Publication Date.
Notice that the title of the book is italicized.
You would also use italics for other forms of media cited in their entirety:
- News publications
- Anthologies
When you write the title, remember that the rules for capitalizing can be tricky. For MLA, title case requires that you capitalize the first word of the title and any subtitles, capitalize all principal words (nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, and pronouns), and capitalize all the words that contain four letters or more. If you use a hyphenated word, be sure to capitalize the second part that comes after the hyphen. When the title has a subtitle, be sure to include a colon and a space between the main title and the subtitle.
To review, here are a few fictional titles, along with the proper title case for MLA style:
- New York in the Spring: A Guide to Snacking
- Hot-Headedness and Anger From a Toddler’s Perspective
- The Unofficial Grammar Bible

In-Text Citations
For an in-text citation, you would simply follow your quotation or paraphrase with a parenthetical notation. Provide the reader with the author’s last name and the page number. This way, if the reader wants to review the source material that you used, he or she can find the book in the Works Cited section of your essay, and then look at the referenced page directly.
When you use a parenthetical citation in this manner, you do not necessarily need to write the title of the book in your prose. That said, it is common to include the title of the book in your research paper or essay, especially the first time you refer to the book, in order to provide additional context for the quotation or paraphrase. If you include the author’s name in your prose, there is no need to repeat it in the in-text citation.
Here are examples of both styles of in-text citation.
- As Rick Hawthorne explains in Coordinating Conjunctions for Fun , “Grammar can be amazing” (75).
- According to a prominent linguistics professor, “Grammar can be amazing” (Hawthorne 75).
In the examples above, you can see that including the title of the book may add context, but it is not necessary when you provide the in-text citation. If you choose to include the title, you should use the same title case and formatting that you use in the Works Cited section of your paper.
What Titles Need Quotation Marks?
As a general rule, the titles that require quotation marks involve a partial work. For example, a chapter in a book only makes up part of a larger work.
Based on the MLA handbook, we’ve created a list of media that fits into the “part of a whole” classification. Next to those titles, we’ve listed examples of the complete works, written in all capital letters.
- Book chapters | BOOK TITLE
- Web pages | WEBSITE NAME
- News, magazine, and journal articles | NEWSPAPER, MAGAZINE, or JOURNAL TITLE
- TV episodes | TV SHOW TITLE
- Songs | ALBUM TITLE
- Short stories | ANTHOLOGY TITLE
- Poems | ANTHOLOGY TITLE
- Online videos | WEBSITE NAME
Of the items in the list above, the first set of titles should be written within a pair of quotation marks. The capitalized set of titles should be written with italics.
Special Circumstances
There are a few situations that necessitate special rules.
- When a work has no author, the title should be used in the place of the author’s last name for the in-text citation. Do not include subtitles in the in-text citation. If the full title is long, you may abbreviate it by dropping articles and prepositions, but you must maintain the first word as it’s alphabetized in your Works Cited.
- When you quote or paraphrase from a chapter in an anthology or reference book, be sure to include the chapter title in your Works Cited list, between the author’s name and the name of the full work.
- Add the English translation of a foreign-language title in brackets in your Works Cited, and add it in parentheses in your prose.
- Although the following words and phrases describe parts of a work, they should not be confused with unique titles: preface, introduction, works cited, appendix, scene, stanza, chapter, bibliography, act, index. Since they are not titles, section names do not need to be put in quotations.
- Musical compositions, laws, and religious scripture do not receive the same treatment as other titles. When in doubt, refer to the Modern Language Association for special exceptions.
- When you come across a title within a title, use quotation marks or italics as normal. Quotes within quotes employ single quotes, and italics within italics revert back to non-italicized text. For example, if you have the title of a poem that appears within the title of a chapter, you would use single quotation marks within double quotation marks: “Understanding Whitman’s ‘Song of Myself'”.
- For a title that ends in a question mark, there’s no need to add a colon before the subtitle.
- According to the 8th edition of the MLA guidelines, you no longer need to include the city of publication for books published after 1900. For an older book, your citation should include that information.
- https://irsc.libguides.com/mla/intextexamples#
- https://www.scribbr.com/mla/titles/
- https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_general_format.html
- https://www.mla.org/MLA-Style
- https://libguides.css.edu/c.php?g=41682&p=265033

Kari Lisa Johnson
I’m an award-winning playwright with a penchant for wordplay. After earning a perfect score on the Writing SAT, I worked my way through Brown University by moonlighting as a Kaplan Test Prep tutor. I received a BA with honors in Literary Arts (Playwriting)—which gave me the opportunity to study under Pulitzer Prize-winner Paula Vogel. In my previous roles as new media producer with Rosetta Stone, director of marketing for global ventures with The Juilliard School, and vice president of digital strategy with Up & Coming Media, I helped develop the voice for international brands. From my home office in Maui, Hawaii, I currently work on freelance and ghostwriting projects.
Recent Posts

Dreams Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

Chutzpah Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

White Roses Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

7777 Angel Number Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How to Use It?

- Jacksonville University
- Swisher Library
MLA Guide 9th ed.
- Formatting the Author and Title
- Citing a Book or Ebook
- Citing Part of a Book or Ebook
- Citing a Journal Article
- Citing a Magazine or Newspaper Article
- Citing an Interview
- Citing a Website
- Citing an Online Video or Image
- Citing Class Notes
- In-text Citations
- MLA Style Center This link opens in a new window
- Sample Paper in MLA format
- Academic Integrity Policy at JU This link opens in a new window
- Need Help with MLA?
- MLA practice Template
"Author." MLA Handbook. 8th ed. , MLA, 2016, pp. 21-25.
"Title." MLA Handbook. 8th ed. , MLA, 2016, pp. 25-29.
Formatting the Author
| Authors | Rule | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| No Author | If no author given, skip the author and start with the title of source. | |
| 1 Author | Last Name, First Name. | Smith, John. |
| 2 Authors | Last Name, First Name, and First Name Last Name. | Smith, John, and Mary Fields. |
| 3+ Authors | Last Name, First Name of First Author, et al. | Smith, John, et al. |
| Association or Company | Use the name of the association or company as the author. If a work is written and published by an organization, list the organization as publisher only. Initial articles (a, an, the) should be omitted. | American Cancer Society. |
| Editor or other role | If the role of that person or group is something other than creating the work’s main content (as the author), follow the name with a label that describes the role. Only do this in the author field if it is important to highlight this person; otherwise use the Other Contributors field. | Nunberg, Geoffrey, editor. |
Formatting the Title
| Source | Rule: Italics or "quotation marks" | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Entire Book | self-contained works | |
| Collection of Essays | self-contained works | . |
| Essay, story, or poem | Contained in a larger work (book, website, etc.) use "quotation marks" | "The Cultural Consequences of Printing." |
| Play | plays even if they are in a larger work. | . |
| Article from Journal, Magazine, or Newspaper | Contained in a larger work (book, website, etc.) use "quotation marks" | "Literary History and Sociology." |
| Entire Journal, Magazine, or Newspaper | self-contained works | . |
| Entire Website | self-contained works | . |
| Website Article | Contained in a larger work (book, website, etc.) use "quotation marks" | "Free Will." |
| Song | Contained in a larger work (book, website, etc.) use "quotation marks" | "Pretty Hurts." |
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Citing a Book or Ebook >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 8:03 AM
Writing A Book Title In Your Essay – The Right Way
Table of contents
- 1 APA Style: How to Write Book Titles in Essays
- 2 APA Style Essay: Writing The Name of The Author
- 3 MLA Style Essay: Citing a Book Title
- 4 Chicago Style Essay: Writing the Book Title
- 5 Writing Various Types of Titles
- 6 Should We Underline or Italicize Book Titles?
When you are writing an academic essay , the book title and author’s name should be written in italics. However, if the book title is part of a larger work (such as a journal article), it should be underlined instead. So, you’re wondering how to write a book title in an essay?
Writing an essay with a book title can be tricky, particularly because each style guide has its own formatting rules for including titles in the main text. Whether you are using MLA, APA, Chicago, or Harvard referencing styles, you will need to consider how to properly format the book title. For more complicated literature-based assignments, seeking assistance from an admission essay writing service may be wise, as they specialize in writing essays that incorporate academic sources.
In this article, we will explore how to write both titles in an essay properly so that you avoid any mistakes!
APA Style: How to Write Book Titles in Essays
When writing an essay, you must follow the style guide provided by your professor. Some teachers may require you to use APA style and others MLA style. There are some rules on how to quote a book title in an essay. You should use italics and quotation marks when writing book titles in essays. For example: “ The Rape of Nanking: The Forgotten Holocaust of World War II. “
When writing a book title in APA Style , you should be aware of these rules:
Write the book title in italics and place it after the author’s name, which is presented in reverse order (last name first).
Use quotation marks around the headline of a chapter or article.
Capitalize proper names that are not common nouns (names of people, places, organizations), but do not capitalize words such as “and,” “or,” “to,” or “and/or.”
Do not capitalize prepositions that appear at the beginning of titles if they are followed by an article (e.g., “A,” “An”), but do capitalize prepositions at the beginning of titles if they are not followed by articles (“Of”).
The first word of the headline should be capitalized, as well as any other words after a colon or hyphen. For example, “The Elements of Style: Grammar for Everyone” or “Theories of Personality: Critical Perspectives.”
Capitalize proper names and words derived from them (e.g., the names of people, places, organizations), except proper nouns used generically (e.g., ‘a bed’).
APA Style Essay: Writing The Name of The Author
You should always use the full name and surname of the author in your APA essay because this will give proper credit to the writer. If you do not mention the author’s full name, people may not know who wrote what and will think you copied it from somewhere else. This will cause lots of problems for you and your reputation as well.
Make sure that all authors’ names appear in the same format in each entry. For example, if one person’s surname is Smith and another’s is Jones, both have first names starting with “J.” It may seem like they are being cited as different people when they’re actually written differently from each other on separate pages in your paper.
To write an APA essay without any issues, there are certain rules that you need to follow while writing an author’s name in APA essay:
- Use only one author’s name in your paper unless there are multiple authors
- If there are multiple authors, then use both their last names followed by the initials of their first names
- Only use initials of first names when there are three or more authors; otherwise, use full names with their last names
Example: Johnson, M.C., Carlson, M., Smith, J. N., & Hanover, L. E.
MLA Style Essay: Citing a Book Title
Now let’s discuss how to mention a book in an essay. The MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers, 7th edition, published by the Modern Language Association (2014), contains detailed rules about how to cite a book title in an essay.
The following guidelines will instruct you on how to refer to a book in an essay in MLA style :
- List your sources at the end of your paper, before the works cited page or bibliography.
- Use italics for titles of books, magazines, and newspapers, but not for articles within those publications, which should be placed in quotation marks.
- Include all relevant book information under two categories: “title” and “author.” In the former category, include the work’s title and its subtitle if there is one; do this even if neither appears on your title page (see below). In the latter category, include only primary authors who have written or edited an entire book; if there are multiple contributors, you should cite them separately under each.
The general format for citing the title of the book in an essay is as follows:
Author’s last name, first initial (Date). Title of Book with Subtitle if there is one. Publisher Name/Location of Publisher; Year Published
Chicago Style Essay: Writing the Book Title
One of the most important things to remember when writing in Chicago style is how to write the title of a book in an essay. To write a good book title in an essay, you should follow these steps:
- Write it at the beginning of your sentence.
- Capitalize it just like any other noun or proper noun.
- Put a comma after the title unless it’s an introductory clause or phrase. For example: “The Firm,” by John Grisham (not “by”) and “The Catcher in the Rye,” by J.D Salinger (not “and”).
- In addition to the book’s name, punctuation marks should also be italicized.
For example: Harry Potter and the Half-blood Prince: Children’s Edition
Writing Various Types of Titles
Now that we covered how to write a book title and author in an essay, it’s time to look at some different types of titles. When you write a book title in an essay, several things must be considered. Whether it’s a book, series, chapter title, editor’s name, or author’s name, how you write it depends on where it appears in your paper.
Here are some key rules for writing headings for novels:
- Use capital letters to write the title of the novel. For example, The Secret Garden by Frances Hodgson Burnett .
- Use italics and capital letters to write the name of the author and his/her other works mentioned in a book title—for example, Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice (1813) .
You should use quotation marks when writing headings of short title poems, articles, and stories.
However, before deciding which format to use, it is important to understand the main idea you want to express in your essay. Additionally, you could use essay papers for sale to help you accomplish your goal of writing an essay effectively.

Should We Underline or Italicize Book Titles?
It depends on which style guide you use. The Modern Language Association and Chicago Manual of Style both suggest using italics, while the American Psychological Association suggests using quotation marks with a few exceptions.
The way you write the title of a book in an essay is different depending on the instructions you were given. For example, if you’re writing an essay in APA style, use quotation marks around the book’s name. If you’re writing for MLA or Chicago style , however, italicize the book’s name instead. If you’re writing a handwritten essay instead of using a computer, capitalize and underline the book’s name.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / How to Cite an Essay in MLA
How to Cite an Essay in MLA
The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number(s).
Citing an Essay
Mla essay citation structure.
Last, First M. “Essay Title.” Collection Title, edited by First M. Last, Publisher, year published, page numbers. Website Title , URL (if applicable).
MLA Essay Citation Example
Gupta, Sanjay. “Balancing and Checking.” Essays on Modern Democracy, edited by Bob Towsky, Brook Stone Publishers, 1996, pp. 36-48. Essay Database, www . databaseforessays.org/modern/modern-democracy.
MLA Essay In-text Citation Structure
(Last Name Page #)
MLA Essay In-text Citation Example
Click here to cite an essay via an EasyBib citation form.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
To cite your sources in an essay in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the author’s name(s), chapter title, book title, editor(s), publication year, publisher, and page numbers. The templates for in-text citations and a works-cited-list entry for essay sources and some examples are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author on the first occurrence. For subsequent citations, use only the surname(s). In parenthetical citations, always use only the surname of the author(s).
Citation in prose:
First mention: Annette Wheeler Cafarelli
Subsequent occurrences: Wheeler Cafarelli
Parenthetical:
….(Wheeler Cafarelli).
Works-cited-list entry template and example:
The title of the chapter is enclosed in double quotation marks and uses title case. The book or collection title is given in italics and uses title case.
Surname, First Name. “Title of the Chapter.” Title of the Book , edited by Editor(s) Name, Publisher, Publication Year, page range.
Cafarelli, Annette Wheeler. “Rousseau and British Romanticism: Women and British Romanticism.” Cultural Interactions in the Romantic Age: Critical Essays in Comparative Literature , edited by Gregory Maertz. State U of New York P, 1998, pp. 125–56.
To cite an essay in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the author(s), the essay title, the book title, editor(s), publication year, publisher, and page numbers. The templates for citations in prose, parenthetical citations, and works-cited-list entries for an essay by multiple authors, and some examples, are given below:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author (e.g., Mary Strine).
For sources with two authors, use both full author names in prose (e.g., Mary Strine and Beth Radick).
For sources with three or more authors, use the first name and surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Mary Strine and others). In subsequent citations, use only the surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Strine and others).
In parenthetical citations, use only the author’s surname. For sources with two authors, use two surnames (e.g., Strine and Radick). For sources with three or more author names, use the first author’s surname followed by “et al.”
First mention: Mary Strine…
Subsequent mention: Strine…
First mention: Mary Strine and Beth Radick…
Subsequent mention: Strine and Radick…
First mention: Mary Strine and colleagues …. or Mary Strine and others
Subsequent occurrences: Strine and colleagues …. or Strine and others
…. (Strine).
….(Strine and Radick).
….(Strine et al.).
The title of the essay is enclosed in double quotation marks and uses title case. The book or collection title is given in italics and uses title case.
Surname, First Name, et al. “Title of the Essay.” Title of the Book , edited by Editor(s) Name, Publisher, Publication Year, page range.
Strine, Mary M., et al. “Research in Interpretation and Performance Studies: Trends, Issues, Priorities.” Speech Communication: Essays to Commemorate the 75th Anniversary of the Speech Communication Association , edited by Gerald M. Phillips and Julia T. Wood, Southern Illinois UP, 1990, pp. 181–204.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

MLA Style Guide, 8th & 9th Editions: Title of source
- Works Cited entries: What to Include
- Title of source
- Title of container
- Contributors
- Publication date
- Supplemental Elements
- Book with Personal Author(s)
- Book with Organization as Author
- Book with Editor(s)
- Parts of Books
- Government Publication
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Multivolume Works
- Newspaper Article
- Other Formats
- Websites, Social Media, and Email
- About In-text Citations
- In-text Examples
- How to Paraphrase and Quote
- Citing Poetry
- Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Formatting Your Works Cited List
- MLA Annotated Bibliography
- MLA 9th Edition Quick Guide
- Submit Your Paper for MLA Style Review
Title of source (Works Cited)
The title of source is the second core element in the Works Cited entry. In general, the title of a work is taken from the title page of the publication.
- Capitalize all principal words (nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc.). Do not capitalize articles, prepositions, or conjunctions when they fall in the middle of a title.
- Separate a subtitle with a colon and a space.
- Italicize titles if the source is self-contained and independent. Titles of books, plays, films, periodicals, databases, and websites are italicized.
- Place titles in quotation marks if the source is part of a larger work. Articles, essays, chapters, poems, webpages, songs, and speeches are placed in quotation marks.
- Example of a journal article title which includes the title of a book: "Unbearable Weight of Authenticity: Zora Neale Hurston's Their Eyes Were Watching God and Theory of 'Touristic Reading'."
- Example of a journal article title which includes the title of a short story: "Individualism in O'Connor's 'A Good Man is Hard to Find'."
Danticat, Edwidge. Brother, I'm Dying. Knopf , 2007.
Chapter title in a book or anthology :
Howard, Rebecca Moore. “Avoiding Sentence Fragments.” Writing Matters: A Handbook for Writing and Research, 2nd ed., McGraw Hill, 2014, pp. 600-10.
Journals, Magazines, and Newspapers:
Houtman, Eveline. “Mind-Blowing: Fostering Self-Regulated Learning in Information Literacy Instruction.” Communications in Information Literacy, vol. 9, no. 1, 2015, pp. 6-18. www.comminfolit.org/index.php?journal=cil&page=article&op=view&path%5B%5D=v9i1p6&path%5B%5D=203.
Meade, Rita. "It's Not Too Late to Advocate." S crewy Decimal, 1 June 2016, www.screwydecimal.com/2016/06/its-not-too-late-to-advocate.html.
Entire Website:
Meade, Rita. Screwy Decimal . 2010-16, www.screwydecimal.com/.
- << Previous: Author
- Next: Title of container >>
- Last Updated: Jul 22, 2024 4:57 PM
- URL: https://irsc.libguides.com/mla
- CSN Libraries
- Library Guides
- Course Guides
ENG 101 - Okey
- Citing in MLA
- Useful Databases at CSN Libraries
- Choosing a Research Topic
- How To Search Databases
- Verifying Sources (CRAAP Method)
- Avoiding Plagiarism
MLA Style Guide and Examples
The Modern Language Association uses the MLA Handbook to provide guidelines on MLA Style, which is the citation style you will be using in this class to format your papers and cite your sources. Included on this page are important documents and links that will help you to use MLA properly.
New MLA 9 rules state that the citation should NOT include http:\\
For example, https://roadtrippers.com/the-ultimate-guide-route-66/ should be changed to roadtrippers.com/the-ultimate-guide-route-66/
- MLA 9th Edition
- In-text Quotes
- Works Cited Examples
- Purdue OWL Use this to double-check your citations.

Additional Support
· The CSN Centers for Academic Success is offering online tutoring to CSN Students through Brainfuse .
Brainfuse offers free online tutoring, writing services and homework assistance 24/7. Certified Brainfuse tutors provide live, on-demand tutoring and assignment help in a variety of subjects. Brainfuse tutors meet students where they are at in order to effectively help students of all skill levels. To access services, students can log into their GoCSN account and then into Canvas. Students can choose a listed course on the left and then click on Brainfuse Online Tutoring.
For more information, watch the video below:
- << Previous: Verifying Sources (CRAAP Method)
- Next: Avoiding Plagiarism >>
- Last Updated: Aug 30, 2024 11:18 AM
- URL: https://libguides.csn.edu/c.php?g=1421365
Sample Essays: Writing with MLA Style
Congratulations to the students whose essays were selected for the 2024 edition of Writing with MLA Style! Essays were selected as examples of excellent student writing that use MLA style for citing sources. Essays have been lightly edited.
If your institution subscribes to MLA Handbook Plus , you can access annotated versions of the essays selected from 2022 to 2024.
Writing with MLA Style: 2024 Edition
The following essays were selected for the 2024 edition of Writing with MLA Style. The selection committee for high school submissions was composed of Lisa Karakaya, Hunter College High School; and Heather Smith, Dedham Public Schools. The selection committee for postsecondary submissions was composed of Rachel Ihara, Kingsborough Community College, City University of New York; Tarshia L. Stanley, Wagner College; and Joyce MacDonald, University of Kentucky.
High School Essays
Miguel Kumar (Ransom Everglades School)
“McCarthyism at the Movies: The Effects of Hollywood McCarthyism on the American Public”
Catherine Mao (Hunter College High School)
“ Beauty Is in the Eye of the Beholder, and the Beholder Is a White Man: The 1875 Page Act, Eugenics, and Beauty Standards for Chinese Women versus American Women ”
Undergraduate Essays
Rachelle Dumayas (California State University, Sacramento)
“Should Deaf Children Get Cochlear Implants?”
Holly Nelson (Johns Hopkins University)
“Creating Space? Representations of Black Characters in Regency Romance”
Chloe Wiitala (University of Minnesota, Duluth)
“ Reanimating Queer Perspectives through Camp: A Study of Frankenstein and Its Parodic Film Adaptations ”
Writing with MLA Style: 2023 Edition
The following essays were selected for the 2023 edition of Writing with MLA Style. The 2023 selection committee was composed of Ellen C. Carillo, University of Connecticut (chair); Rachel Ihara, Kingsborough Community College, City University of New York; and Tarshia L. Stanley, Wagner College.
Caroline Anderson (Pepperdine University)
“ L’Appel du Vide : Making Spaces for Sinful Exploration in The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde ”
Hunter Daniels (University of South Carolina, Aiken)
“Biblical Legalism and Cultural Misogyny in The Tragedy of Mariam ”
Aspen English (Southern Utah University)
“Putting the ‘Comm’ in Comics: A Communication-Theory-Informed Reading of Graphic Narratives”
Raul Martin (Lamar University)
“The Book-Object Binary: Access and Sustainability in the Academic Library”
Grace Quasebarth (Salve Regina University)
“Finding a Voice: The Loss of Machismo Criticisms through Translation in Isabel Allende’s The House of the Spirits ”
Writing with MLA Style: 2022 Edition
The following essays were selected for the 2022 edition of Writing with MLA Style. The 2022 selection committee was composed of Ellen C. Carillo, University of Connecticut; Jessica Edwards, University of Delaware (chair); and Deborah H. Holdstein, Columbia College Chicago.
Kaile Chu (New York University, Shanghai)
“Miles Apart: An Investigation into Dedicated Online Communities’ Impact on Cultural Bias”
Sietse Hagen (University of Groningen)
“The Significance of Fiction in the Debate on Dehumanizing Media Portrayals of Refugees”
Klara Ismail (University of Exeter)
“Queering the Duchess: Exploring the Body of the Female Homosexual in John Webster’s The Duchess of Malfi ”
Yasmin Mendoza (Whittier College)
“Banning without Bans”
Niki Nassiri (Stony Brook University)
“Modern-Day US Institutions and Slavery in the Twenty-First Century”
Samantha Wilber (Palm Beach Atlantic University)
“‘Pero, tu no eres facil’: The Poet X as Multicultural Bildungsroman”
Writing with MLA Style: 2019 Edition
The following essays were selected for the 2019 edition of Writing with MLA Style. The 2019 selection committee was composed of Jessica Edwards, University of Delaware; Deborah H. Holdstein, Columbia College Chicago (chair); and Liana Silva, César E. Chavez High School, Houston, Texas.
Catherine Charlton (University of King’s College, Nova Scotia)
“‘Coal Is in My Blood’: Public and Private Representations of Community Identity in Springhill, Nova Scotia”
Alyiah Gonzales (California Polytechnic State University)
“Disrupting White Normativity in Langston Hughes’s ‘I, Too’ and Toni Morrison’s ‘Recitatif’”
Meg Matthias (Miami University, Ohio)
“Prescriptions of (Living) Historical Happiness: Gendered Performance and Racial Comfort in Reenactment”
Jennifer Nguyen (Chaminade University of Honolulu)
“The Vietnam War, the American War: Literature, Film, and Popular Memory”
Emily Schlepp (Northwest University)
“A Force of Love: A Deconstructionist Reading of Characters in Dickens’s Great Expectations ”

APA & MLA Styles
- Using Academic Writer
- Inclusive Language
- Punctuation Guidelines
- Writing Guidelines
- Discussing Statistics In-text
- Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS) This link opens in a new window
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- Student Paper Template
- Copyright Information
- Abbreviations
- Creating APA Style Tables and Figures
- Formatting Appendices (APA)
- APA: In-Text Citations
- References (Creating and Editing)
- Additional Reference Examples
- MLA Style Basics 9th Ed.
- MLA: Works Cited
- AMA Resources This link opens in a new window
MLA Style Works Cited Examples
Select a resource type from the box below for an example of an MLA formatted resource for your Works Cited page.
MLA Style Reference for a Video:
Last name, First name of creator. "Title of Video." Website, Day Month Year of publication, URL.
Doe, John. "Exploring the Universe." YouTube, 15 Mar. 2019, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=example.
MLA Style Reference for a Photograph:
Last name, First name of creator. "Title of Photograph." Website, Day Month Year of publication, URL.
Smith, Jane. "Sunset over the Mountains." Nature Photography, 20 May 2020, https://www.example.com.
MLA Style Reference for a Book with DOI:
Last name, First name of author. Title of Book . Publisher, Year. DOI.
Smith, John. Understanding Psychology . Psychology Press, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1000/xyz123.
MLA Style Reference for an Authored Book with DOI:
Jones, Robert. Advanced Mathematics . Academic Press, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1000/abc456.
MLA Style Reference for One Volume of a Multivolume Work:
Last name, First name of author. Title of Work . Vol. number, Publisher, Year.
Miller, Lucy. History of Ancient Civilizations . Vol. 2, History Press, 2018.
MLA Style Reference for a Work in an Anthology:
Last name, First name of author. "Title of Work." Title of Anthology , edited by Editor's Name, Publisher, Year, pages.
Davis, Paul. "Modern Poetry." Anthology of Contemporary Poetry , edited by Robert Carter, Poetry Press, 2019, pp. 34-56.
MLA Style Reference for a Paper Presentation or Poster Session:
Last name, First name of author. "Title of Paper or Poster." Title of Conference, Date, Location.
Lee, Mark. "Innovations in Education." Annual Education Conference, 15 Mar. 2022, Boston, MA.
MLA Style Reference for a Data Set:
Last name, First name of creator. "Title of Data Set." Name of Database, Publisher, Year. DOI or URL.
Johnson, Henry. "Global Temperature Data." Climate Research Institute, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1000/data123.
MLA Style Reference for a Dissertation:
Last name, First name of author. Title of Dissertation . Year. University, Publication Database, DOI or URL.
Martinez, Rosa. Social Dynamics in Urban Areas . 2020. Harvard University, ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, https://doi.org/10.1000/diss123.
MLA Style Reference for a Policy Brief:
Last name, First name of author. Title of Policy Brief . Organization, Year, DOI or URL.
Brown, Karen. Health Policy Recommendations . World Health Organization, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1000/policy789.
MLA Style Reference for a Journal Article with DOI:
Last name, First name of author. "Title of Article." Title of Periodical , vol. number, no. issue, Year, pages. DOI.
Doe, John. "Cognitive Development in Children." Journal of Psychology , vol. 25, no. 3, 2021, pp. 123-145, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsycho.2021.03.002.
MLA Style Reference for a Journal Article without DOI:
Last name, First name of author. "Title of Article." Title of Periodical , vol. number, no. issue, Year, pages.
Lee, Sarah. "Effects of Sleep on Memory." Health Journal , vol. 34, no. 2, 2020, pp. 78-89.
MLA Style Reference for a MOOC:
Instructor's Last name, First name. "Title of Course." Platform, Year, URL.
Anderson, Thomas. "Introduction to Sociology." Coursera, 2021, https://www.coursera.org/learn/sociology.
MLA Style Reference for an OER (Open Educational Resource):
Author's Last name, First name. Title of OER . Publisher, Year, DOI or URL.
Williams, James. Introduction to Economics . OpenStax, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1000/oer456.
MLA Style Reference for a Webpage (Individual Author, Dated):
Author's Last name, First name. "Title of Webpage." Website Name, Day Month Year, URL.
Thompson, Laura. "How to Learn Python." Programming Blog, 5 May 2020, https://www.example.com.
MLA Style Reference for a Webpage (Group Author, Dated):
Organization Name. "Title of Webpage." Website Name, Day Month Year, URL.
World Health Organization. "Global Health Initiatives." World Health Organization, 15 June 2021, https://www.who.int/initiatives.
MLA Style Reference for a Webpage (Group Author, Undated):
Organization Name. "Title of Webpage." Website Name, URL.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. "Preventing Chronic Diseases." Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, https://www.cdc.gov/preventing.
General Format
General Elements of a Cited Source
- Title of source
- Title of container
- Other contributors
- Publication date
- Date Accessed
General Format for Works Cited Resources
Author. Title. Title of container, Other contributors, Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publication Date, Location (pages, paragraphs, URL or DOI). 2 nd container’s title, Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location, Date of Access (if applicable).
- << Previous: MLA Style Basics 9th Ed.
- Next: AMA Resources >>
- Last Updated: Aug 30, 2024 9:40 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/APAStyle

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Guidelines for referring to the works of others in your text using MLA style are covered throughout the MLA Handbook and in chapter 7 of the MLA Style Manual . Both books provide extensive examples, so it's a good idea to consult them if you want to become even more familiar with MLA guidelines or if you have a particular reference question.
Basic in-text citation rules
In MLA Style, referring to the works of others in your text is done using parenthetical citations . This method involves providing relevant source information in parentheses whenever a sentence uses a quotation or paraphrase. Usually, the simplest way to do this is to put all of the source information in parentheses at the end of the sentence (i.e., just before the period). However, as the examples below will illustrate, there are situations where it makes sense to put the parenthetical elsewhere in the sentence, or even to leave information out.
General Guidelines
- The source information required in a parenthetical citation depends (1) upon the source medium (e.g. print, web, DVD) and (2) upon the source’s entry on the Works Cited page.
- Any source information that you provide in-text must correspond to the source information on the Works Cited page. More specifically, whatever signal word or phrase you provide to your readers in the text must be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of the corresponding entry on the Works Cited page.
In-text citations: Author-page style
MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the sentence itself or in parentheses following the quotation or paraphrase, but the page number(s) should always appear in the parentheses, not in the text of your sentence. For example:
Both citations in the examples above, (263) and (Wordsworth 263), tell readers that the information in the sentence can be located on page 263 of a work by an author named Wordsworth. If readers want more information about this source, they can turn to the Works Cited page, where, under the name of Wordsworth, they would find the following information:
Wordsworth, William. Lyrical Ballads . Oxford UP, 1967.
In-text citations for print sources with known author
For print sources like books, magazines, scholarly journal articles, and newspapers, provide a signal word or phrase (usually the author’s last name) and a page number. If you provide the signal word/phrase in the sentence, you do not need to include it in the parenthetical citation.
These examples must correspond to an entry that begins with Burke, which will be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of an entry on the Works Cited page:
Burke, Kenneth. Language as Symbolic Action: Essays on Life, Literature, and Method . University of California Press, 1966.
In-text citations for print sources by a corporate author
When a source has a corporate author, it is acceptable to use the name of the corporation followed by the page number for the in-text citation. You should also use abbreviations (e.g., nat'l for national) where appropriate, so as to avoid interrupting the flow of reading with overly long parenthetical citations.
In-text citations for sources with non-standard labeling systems
If a source uses a labeling or numbering system other than page numbers, such as a script or poetry, precede the citation with said label. When citing a poem, for instance, the parenthetical would begin with the word “line”, and then the line number or range. For example, the examination of William Blake’s poem “The Tyger” would be cited as such:
The speaker makes an ardent call for the exploration of the connection between the violence of nature and the divinity of creation. “In what distant deeps or skies. / Burnt the fire of thine eyes," they ask in reference to the tiger as they attempt to reconcile their intimidation with their relationship to creationism (lines 5-6).
Longer labels, such as chapters (ch.) and scenes (sc.), should be abbreviated.
In-text citations for print sources with no known author
When a source has no known author, use a shortened title of the work instead of an author name, following these guidelines.
Place the title in quotation marks if it's a short work (such as an article) or italicize it if it's a longer work (e.g. plays, books, television shows, entire Web sites) and provide a page number if it is available.
Titles longer than a standard noun phrase should be shortened into a noun phrase by excluding articles. For example, To the Lighthouse would be shortened to Lighthouse .
If the title cannot be easily shortened into a noun phrase, the title should be cut after the first clause, phrase, or punctuation:
In this example, since the reader does not know the author of the article, an abbreviated title appears in the parenthetical citation, and the full title of the article appears first at the left-hand margin of its respective entry on the Works Cited page. Thus, the writer includes the title in quotation marks as the signal phrase in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader directly to the source on the Works Cited page. The Works Cited entry appears as follows:
"The Impact of Global Warming in North America." Global Warming: Early Signs . 1999. www.climatehotmap.org/. Accessed 23 Mar. 2009.
If the title of the work begins with a quotation mark, such as a title that refers to another work, that quote or quoted title can be used as the shortened title. The single quotation marks must be included in the parenthetical, rather than the double quotation.
Parenthetical citations and Works Cited pages, used in conjunction, allow readers to know which sources you consulted in writing your essay, so that they can either verify your interpretation of the sources or use them in their own scholarly work.
Author-page citation for classic and literary works with multiple editions
Page numbers are always required, but additional citation information can help literary scholars, who may have a different edition of a classic work, like Marx and Engels's The Communist Manifesto . In such cases, give the page number of your edition (making sure the edition is listed in your Works Cited page, of course) followed by a semicolon, and then the appropriate abbreviations for volume (vol.), book (bk.), part (pt.), chapter (ch.), section (sec.), or paragraph (par.). For example:
Author-page citation for works in an anthology, periodical, or collection
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write something like this:
See also our page on documenting periodicals in the Works Cited .
Citing authors with same last names
Sometimes more information is necessary to identify the source from which a quotation is taken. For instance, if two or more authors have the same last name, provide both authors' first initials (or even the authors' full name if different authors share initials) in your citation. For example:
Citing a work by multiple authors
For a source with two authors, list the authors’ last names in the text or in the parenthetical citation:
Corresponding Works Cited entry:
Best, David, and Sharon Marcus. “Surface Reading: An Introduction.” Representations , vol. 108, no. 1, Fall 2009, pp. 1-21. JSTOR, doi:10.1525/rep.2009.108.1.1
For a source with three or more authors, list only the first author’s last name, and replace the additional names with et al.
Franck, Caroline, et al. “Agricultural Subsidies and the American Obesity Epidemic.” American Journal of Preventative Medicine , vol. 45, no. 3, Sept. 2013, pp. 327-333.
Citing multiple works by the same author
If you cite more than one work by an author, include a shortened title for the particular work from which you are quoting to distinguish it from the others. Put short titles of books in italics and short titles of articles in quotation marks.
Citing two articles by the same author :
Citing two books by the same author :
Additionally, if the author's name is not mentioned in the sentence, format your citation with the author's name followed by a comma, followed by a shortened title of the work, and, when appropriate, the page number(s):
Citing multivolume works
If you cite from different volumes of a multivolume work, always include the volume number followed by a colon. Put a space after the colon, then provide the page number(s). (If you only cite from one volume, provide only the page number in parentheses.)
Citing the Bible
In your first parenthetical citation, you want to make clear which Bible you're using (and underline or italicize the title), as each version varies in its translation, followed by book (do not italicize or underline), chapter, and verse. For example:
If future references employ the same edition of the Bible you’re using, list only the book, chapter, and verse in the parenthetical citation:
John of Patmos echoes this passage when describing his vision (Rev. 4.6-8).
Citing indirect sources
Sometimes you may have to use an indirect source. An indirect source is a source cited within another source. For such indirect quotations, use "qtd. in" to indicate the source you actually consulted. For example:
Note that, in most cases, a responsible researcher will attempt to find the original source, rather than citing an indirect source.
Citing transcripts, plays, or screenplays
Sources that take the form of a dialogue involving two or more participants have special guidelines for their quotation and citation. Each line of dialogue should begin with the speaker's name written in all capitals and indented half an inch. A period follows the name (e.g., JAMES.) . After the period, write the dialogue. Each successive line after the first should receive an additional indentation. When another person begins speaking, start a new line with that person's name indented only half an inch. Repeat this pattern each time the speaker changes. You can include stage directions in the quote if they appear in the original source.
Conclude with a parenthetical that explains where to find the excerpt in the source. Usually, the author and title of the source can be given in a signal phrase before quoting the excerpt, so the concluding parenthetical will often just contain location information like page numbers or act/scene indicators.
Here is an example from O'Neill's The Iceman Cometh.
WILLIE. (Pleadingly) Give me a drink, Rocky. Harry said it was all right. God, I need a drink.
ROCKY. Den grab it. It's right under your nose.
WILLIE. (Avidly) Thanks. (He takes the bottle with both twitching hands and tilts it to his lips and gulps down the whiskey in big swallows.) (1.1)
Citing non-print or sources from the Internet
With more and more scholarly work published on the Internet, you may have to cite sources you found in digital environments. While many sources on the Internet should not be used for scholarly work (reference the OWL's Evaluating Sources of Information resource), some Web sources are perfectly acceptable for research. When creating in-text citations for electronic, film, or Internet sources, remember that your citation must reference the source on your Works Cited page.
Sometimes writers are confused with how to craft parenthetical citations for electronic sources because of the absence of page numbers. However, these sorts of entries often do not require a page number in the parenthetical citation. For electronic and Internet sources, follow the following guidelines:
- Include in the text the first item that appears in the Work Cited entry that corresponds to the citation (e.g. author name, article name, website name, film name).
- Do not provide paragraph numbers or page numbers based on your Web browser’s print preview function.
- Unless you must list the Web site name in the signal phrase in order to get the reader to the appropriate entry, do not include URLs in-text. Only provide partial URLs such as when the name of the site includes, for example, a domain name, like CNN.com or Forbes.com, as opposed to writing out http://www.cnn.com or http://www.forbes.com.
Miscellaneous non-print sources
Two types of non-print sources you may encounter are films and lectures/presentations:
In the two examples above “Herzog” (a film’s director) and “Yates” (a presentor) lead the reader to the first item in each citation’s respective entry on the Works Cited page:
Herzog, Werner, dir. Fitzcarraldo . Perf. Klaus Kinski. Filmverlag der Autoren, 1982.
Yates, Jane. "Invention in Rhetoric and Composition." Gaps Addressed: Future Work in Rhetoric and Composition, CCCC, Palmer House Hilton, 2002. Address.
Electronic sources
Electronic sources may include web pages and online news or magazine articles:
In the first example (an online magazine article), the writer has chosen not to include the author name in-text; however, two entries from the same author appear in the Works Cited. Thus, the writer includes both the author’s last name and the article title in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader to the appropriate entry on the Works Cited page (see below).
In the second example (a web page), a parenthetical citation is not necessary because the page does not list an author, and the title of the article, “MLA Formatting and Style Guide,” is used as a signal phrase within the sentence. If the title of the article was not named in the sentence, an abbreviated version would appear in a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence. Both corresponding Works Cited entries are as follows:
Taylor, Rumsey. "Fitzcarraldo." Slant , 13 Jun. 2003, www.slantmagazine.com/film/review/fitzcarraldo/. Accessed 29 Sep. 2009.
"MLA Formatting and Style Guide." The Purdue OWL , 2 Aug. 2016, owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/01/. Accessed 2 April 2018.
Multiple citations
To cite multiple sources in the same parenthetical reference, separate the citations by a semi-colon:
Time-based media sources
When creating in-text citations for media that has a runtime, such as a movie or podcast, include the range of hours, minutes and seconds you plan to reference. For example: (00:02:15-00:02:35).
When a citation is not needed
Common sense and ethics should determine your need for documenting sources. You do not need to give sources for familiar proverbs, well-known quotations, or common knowledge (For example, it is expected that U.S. citizens know that George Washington was the first President.). Remember that citing sources is a rhetorical task, and, as such, can vary based on your audience. If you’re writing for an expert audience of a scholarly journal, for example, you may need to deal with expectations of what constitutes “common knowledge” that differ from common norms.
Other Sources
The MLA Handbook describes how to cite many different kinds of authors and content creators. However, you may occasionally encounter a source or author category that the handbook does not describe, making the best way to proceed can be unclear.
In these cases, it's typically acceptable to apply the general principles of MLA citation to the new kind of source in a way that's consistent and sensible. A good way to do this is to simply use the standard MLA directions for a type of source that resembles the source you want to cite.
You may also want to investigate whether a third-party organization has provided directions for how to cite this kind of source. For example, Norquest College provides guidelines for citing Indigenous Elders and Knowledge Keepers —an author category that does not appear in the MLA Handbook . In cases like this, however, it's a good idea to ask your instructor or supervisor whether using third-party citation guidelines might present problems.
Subject Guide: English: Citing Sources
- Background Information & Reference Books
- Developing a Research Question
- Defining Scholarly Sources
- Using OneSearch
- Literary Criticism
- Research Strategies: How to "Speak" Database
- Evaluating Sources
- Citing Sources
MLA Citation, 9th edition

- Purdue OWL MLA Citation Style Guide
- MLA Style Center: A Quick Guide
- BC Library MLA Citation Guide
- Cite It Right! by Sondra Keckley Last Updated Aug 27, 2024 2395 views this year
Avoiding Plagiarism

Things to Notice About MLA Citations, 9th edition

What does MLA mean by container??
You will be searching for articles within periodicals within databases .
article Container 1=periodical Container 2=database

Citing Your Sources in MLA Style, 9th edition
Find as much of the citation information below as you can for each of your sources. Then use the indicated order, format, and punctuation to put the information together into a proper citation for each source.
Format Guidelines for Works Cited:
| 1. Author. | : Cannon, Joseph S. : Dorrison, Michael, and Louise Erdrich. : Burdick, Anne, et al. |
| 2. Title of source. | (if self-contained): . |
| 3. Title of container, | k (periodical, book, website):
|
| 4. Other contributors, | : Edited by Howard S. Becker, Translated by Seamus Heaney, |
| 5. Version, | : King James Version, Expanded ed., 3 ed., |
| 6. Number, | : vol. 4, : vol. 22, no. 3, |
| 7. Publisher, | If article, If book, Oxford UP, Penguin Press, If website, |
| 8. Publication date, | If book, : 2003, If article or website, : 28 Sept. 2013, |
| 9. Location. | If book or article: p.33., pp.97-108. If website or video: , omitting the http:// and the carrot brackets < > |
While the 9th edition does not specify that database providers be included in citations for online databases, the Bakersfield College English department has stipulated the inclusion of this information in citations for the sake of clarity. So the names of database providers, such as EBSCO and Gale, should follow the database title.
Examples of MLA Citations, 9th edition
For an article within a reference book within a database/e-book collection:

- << Previous: Evaluating Sources
- Last Updated: Aug 28, 2024 11:46 AM
- URL: https://bakersfieldcollege.libguides.com/English1
This site uses cookies to provide you with more responsive and personalized service and to collect certain information about your use of the site. You can change your cookie settings through your browser. If you continue without changing your settings, you agree to our use of cookies. See our Privacy Policy for more information.
- Student Resources
Student Financial Services
- Student Accounts
Insight Live Boxcast
Chapel audio.
- PCM Sign-In
- My PCM Information
- My PCM Team
- PCM Homepage
- PCM Attendance
- Book Appointment
- PCM Ministry List
Student Resources - Chicago
- MBI Discounts on Office Supplies & Technology Products
- Directory of Department
Student Resources - Spokane
- Spokane Flight Board
- Spokane Ministry Covenant
- Print Request Form
- Spokane Internship Form
Student Resources - MDL
- MDL Payment Plan
- FE 400 Internship Request Form
- Scholarship Applications
- FAFSA Verification Forms
- Satisfactory Academic Progress
Paying Your Bill
- How to Pay Your Bill
- International Payments
Billing Information
- Payment Policies & Deadlines
- Moody Payment Plan
- Adjustments, Refunds, Appeals
- FERPA Billing Disclosure
Miscellaneous
- Health Insurance
- Tax Information (1098-T)
- Submit ACH Form
- Strategic Resource Allocation Committee (SRAC)
- Chicago Campus Redevelopment FAQ
- myMoody FAQ
- Insight Live Archive
- Chapel Audio Spring 2017
- Chapel Audio Fall 2016
- Chapel Audio Spring 2016
- Chapel Audio Fall 2015
- Map and Library Equipment
- Policies and Guidelines
- Staff Directory
- Group Study Room
- New Library Materials
- Databases and Articles
- Searching in I-Share
- 000-999 Dewey Decimal Guide
- 200-299 (Religion) Dewey Decimal Guide
- ILL Request Form
- Placing I-Share Requests
- Collection Development Policy
- Request In Library Instruction
- Reserve Request
- Torah Usage Form
- Curriculum Lab (CurLab)
- Juvenile Collection
- Educational Links
- CurLab and Juvenile Map
- Music Scores and CDs Dewey Decimal Guide
- Alumni Access
- Recommend a Purchase
- About Aviation Resources
- Library of Congress Guide
- Research Help
- Interlibrary Loan
- Request In-Library Instruction
- Online Library Resources
- Interlibrary Loan Moody Online
- Request Embedded Librarian Service
- Materials Request Form
- Library Material Types
- New Arrivals
- Mobile Apps
- Online Research
- Library Catalog
- Other Library Catalogs
- Free Resources and Databases
- Research Help Tools
- How to Search Tips
- Users with Disabilities
- Best Internet Resources
- Database Finder Results
- Guide to Google
- Library Calendar
- News and Updates
- Computer Usage Policy
- Social Media
- Ask a Librarian
- Report a Problem
- Audio Library
- Dwight L. Moody
- William Culbertson
- James M. Gray
- William Henry Houghton
- Cyrus Hall McCormick
- Ira D. Sankey
- Reuben Archer Torrey
- Torah Scroll Gallery
- Archives Checkout Policy
- Archives Class Projects
- Archives Collection Development
- Archives Copy/Scan Requests
- Archives Visitor Policy
- Recorded Messages Policy
- Education Site Map
MLA Style Sheet
General guidelines.
Please also visit the Academic Integrity LibGuide , which provides a Citation guide for your information.
- Everything in the paper is double-spaced : works cited, indented quotes, etc.
- Pagination: student's last name and the page number are placed on each page's upper right-hand corner.
- Quotes that are more than four lines long are indented one inch from the left margin only.
- Title Page: ask the professor for his or her preference.
- Punctuation: the period always goes after the documentation parentheses except in an indented quote, where it goes before.
MLA Works Cited
A BOOK BY A SINGLE AUTHOR Sayers, Dorothy L. The Nine Tailors. San Diego: Harcourt, 1962. Print.
A BOOK BY MORE THAN ONE AUTHOR (OR EDITOR) Kerrigan, William, and Gordon Braden. The Idea of the Renaissance. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins UP, 1989.Print.
Dyal, James A.,William C. Corning, and Dale M. Willows. Readings in Psychology: The Search for Alternatives. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw, 1975. Print.
WORKS BY MORE THAN THREE AUTHORS (OR EDITORS) Nielsen, Niels C., Jr., et al. Religions of the World. 3rd ed. New York: St. Martin's, 1992. Print.
A BOOK COMPILED BY AN EDITOR(S) Arp, Thomas R. and Greg Johnson, eds. Perrine's Story and Structure. 12th ed. Boston: Wadsworth/Cengage Learning, 2009. Print.
A WORK IN AN ANTHOLOGY OR A COLLECTION Fairbairn-Dunlop, Peggy. "Women and Agriculture in Western Samoa." Different Places, Different Voices. Ed.
Janet H. Momsen and Vivian Kinnaird. London: Routledge, 211-26. Print.
AN ARTICLE WITHOUT AN AUTHOR IN A REFERENCE BOOK "Hadadrimmon." Davis Dictionary of the Bible. John D. Davis, ed. 4th ed. Nashville: Broadman Press, 1972. Print.
AN ARTICLE FROM A WEEKLY OR BIWEEKLY MAGAZINE Glastris, Paul. "The New Way to Get Rich." U.S. News & World Report 7 May 1990: 26-36. Print.
AN ARTICLE FROM A DAILY NEWSPAPER Wilford, John N. "Corn in the New World: A Relative Latecomer." New York Times 7 Mar. 1995, late ed.: C1+. Print.
AN ARTICLE IN A SCHOLARLY JOURNAL Rosen, Jonathan. "The Celestial Rolodex." The American Scholar 73 (Autumn 2004): 115-118. Print.
AN ANONYMOUS ARTICLE "Awash in Garbage." New York Times 15 Aug. 1987, sec. 1: 26. Print.
INTERNET AND OTHER SOURCES
INTERNET SOURCE (without author) "Bertha Advances toward Bahamas." CNN WORLD News. 9 July 1996. Web. 21 March 2011.
ARTICLE FROM A SCHOLARLY JOURNAL ONLINE Brittain, Clark M. "The Architecture of Redemption: Spatiality in the Short Stories of Flannery O'Connor." The Journal of Southern Religion 4 (2001). 25 July 2005. Web. 25 March 2011.
MATERIAL FROM A DATABASE ON CD-ROM Grych, John H. "Patterns of Adjustment among Children of Battered Women." Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 68 (2000): 84-94. Abstract. PsycLIT. CD-ROM. Silverplatter. 23 July 2003.
FILM, VIDEO, OR FILM CLIP ONLINE "The Glory Suffered: The Transfiguration of the Cross." The History of the Orthodox Christian Church. 2003. GoTelecom Online. 24 Oct. 2003. Web. 5 April 2011.
BIBLE Bible. Revised Standard Version. Cleveland: Word Publishing Company, 1962. Print.
LECTURE Mitten, David M. "Greek Art and Architecture in the West: Southern Italy, Sicily, and Campania." Class lecture. Harvard University. Cambridge, 15 May 1989.
MUSIC Sting, narr. Peter and the Wolf, op. 67. By Sergei Prokofiev. Chamber Orch. of Europe. Cond. Claudio Abbado. Deutsche Grammophon, 1990.
Parenthetical Documentation
BASIC FORM (last name and page number) Dr. James is described as a "not-too-skeletal Ichabod Crane" (Johnson 68).
AUTHOR'S NAME IN TEXT Johnson describes Dr. James as a "not-too-skeletal Ichabod Crane" (68).
SOURCE BY TWO OR THREE AUTHORS The Authority-Rebel "tends to see himself as superior to other students in the class" (Dyal, Corning, and Willows 4).
A MULTIVOLUME WORK In the middle of several volumes of modern literary criticism, Rene Wellek admits, "An evolutionary history of criticism must fail. I have come to this resigned conclusion" (5: xxii).
ONE OF TWO (or more) WORKS BY THE SAME AUTHOR A friend of C. S. Lewis once said that Lewis "gave me not only love, but wisdom and understanding and, when necessary, severity" (Vanauken, Severe 21).
WORK LISTED ONLY BY THE TITLE (magazine article) An international pollution treaty would prohibit plastic garbage from being dumped at sea ("Awash" 26).
SECONDARY SOURCE THAT QUOTES THE ORIGINAL E. M. Forster says, "The collapse of all civilization, so realistic for us, sounded in Matthew Arnold's ears like a distant and harmonious cataract" (qtd. in Trilling 11).
INTERNET SOURCE Often there are no page numbers for the source, so indicate in the text who the author is. For example, Hershel Winthrop interprets Hawthorne's stories as the search for holiness in a corrupt Puritan society.
May 2012, compiled and updated by Karyn Hecht at Moody Bible Institute, Chicago
Need More Help?
Our staff of expert librarians are ready to lend you a hand.
© Moody Bible Institute | Privacy Policy

APA Style for beginners

Then check out some frequently asked questions:
What is APA Style?
Why use apa style in high school, how do i get started with apa style, what apa style products are available, your help wanted.
APA Style is the most common writing style used in college and career. Its purpose is to promote excellence in communication by helping writers create clear, precise, and inclusive sentences with a straightforward scholarly tone. It addresses areas of writing such as how to
- format a paper so it looks professional;
- credit other people’s words and ideas via citations and references to avoid plagiarism; and
- describe other people with dignity and respect using inclusive, bias-free language.
APA Style is primarily used in the behavioral sciences, which are subjects related to people, such as psychology, education, and nursing. It is also used by students in business, engineering, communications, and other classes. Students use it to write academic essays and research papers in high school and college, and professionals use it to conduct, report, and publish scientific research .
High school students need to learn how to write concisely, precisely, and inclusively so that they are best prepared for college and career. Here are some of the reasons educators have chosen APA Style:
- APA Style is the style of choice for the AP Capstone program, the fastest growing AP course, which requires students to conduct and report independent research.
- APA Style helps students craft written responses on standardized tests such as the SAT and ACT because it teaches students to use a direct and professional tone while avoiding redundancy and flowery language.
- Most college students choose majors that require APA Style or allow APA Style as an option. It can be overwhelming to learn APA Style all at once during the first years of college; starting APA Style instruction in high school sets students up for success.
High school students may also be interested in the TOPSS Competition for High School Psychology Students , an annual competition from the APA Teachers of Psychology in Secondary Schools for high school students to create a short video demonstrating how a psychological topic has the potential to benefit their school and/or local community and improve people’s lives.
Most people are first introduced to APA Style by reading works written in APA Style. The following guides will help with that:
|
|
|
|
| Handout explaining how journal articles are structured and how to become more efficient at reading and understanding them |
|
| Handout exploring the definition and purpose of abstracts and the benefits of reading them, including analysis of a sample abstract |
Many people also write research papers or academic essays in APA Style. The following resources will help with that:
|
|
|
|
| Guidelines for setting up your paper, including the title page, font, and sample papers |
|
| More than 100 reference examples of various types, including articles, books, reports, films, social media, and webpages |
|
| Handout comparing example APA Style and MLA style citations and references for four common reference types (journal articles, books, edited book chapters, and webpages and websites) |
|
| Handout explaining how to understand and avoid plagiarism |
|
| Checklist to help students write simple student papers (typically containing a title page, text, and references) in APA Style |
|
| Handout summarizing APA’s guidance on using inclusive language to describe people with dignity and respect, with resources for further study |
|
| Free tutorial providing an overview of all areas of APA Style, including paper format, grammar and usage, bias-free language, punctuation, lists, italics, capitalization, spelling, abbreviations, number use, tables and figures, and references |
|
| Handout covering three starter areas of APA Style: paper format, references and citations, and inclusive language |
Instructors will also benefit from using the following APA Style resources:
|
|
|
|
| Recording of a webinar conducted in October 2023 to refresh educators’ understanding of the basics of APA Style, help them avoid outdated APA Style guidelines (“zombie guidelines”), debunk APA Style myths (“ghost guidelines”), and help students learn APA Style with authoritative resources |
|
| Recording of a webinar conducted in May 2023 to help educators understand how to prepare high school students to use APA Style, including the relevance of APA Style to high school and how students’ existing knowledge MLA style can help ease the transition to APA Style (register for the webinar to receive a link to the recording) |
|
| Recording of a webinar conducted in September 2023 to help English teachers supplement their own APA Style knowledge, including practical getting-started tips to increase instructor confidence, the benefits of introducing APA Style in high school and college composition classes, some differences between MLA and APA Style, and resources to prepare students for their future in academic writing |
|
| Poster showing the three main principles of APA Style: clarity, precision, and inclusion |
|
| A 30-question activity to help students practice using the APA Style manual and/or APA Style website to look up answers to common questions |
In addition to all the free resources on this website, APA publishes several products that provide comprehensive information about APA Style:
|
|
|
|
| The official APA Style resource for students, covering everything students need to know to write in APA Style |
|
| The official source for APA Style, containing everything in the plus information relevant to conducting, reporting, and publishing psychological research |
|
| APA Style’s all-digital workbook with interactive questions and graded quizzes to help you learn and apply the basic principles of APA Style and scholarly writing; integrates with popular learning management systems, allowing educators to track and understand student progress |
|
| APA’s online learning platform with interactive lessons about APA Style and academic writing, reference management, and tools to create and format APA Style papers |
The APA Style team is interested in developing additional resources appropriate for a beginner audience. If you have resources you would like to share, or feedback on this topic, please contact the APA Style team .
Free newsletter
Apa style monthly.
Subscribe to the APA Style Monthly newsletter to get tips, updates, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Welcome! Thank you for subscribing.
Generate accurate MLA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- Creating an MLA title page
MLA Title Page | When You Need One & How to Format It
Published on July 12, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on March 5, 2024.
In MLA style , a title page is usually not required for your paper. Instead, MLA recommends including a header on your first page listing your name, your instructor’s name, the course name and number, and the submission date, followed by the title of your paper.
However, you should include a separate title page instead in these cases:
- Your instructor requires it
- The paper is a group project (i.e. you need to list multiple authors)
The formats for a separate title page and a first-page header are shown below. You can also use our templates in Word or Google Docs.
Word template Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Mla title page format, creating an mla header, frequently asked questions about mla format.
To create an MLA format title page, list the following on separate lines, left-aligned at the top of the page:
- Your co-authors’ names, each on its own line, if it’s a group project
- Your instructor’s name
- The course name and number
- The submission date
Then leave a few blank lines and list the title of the paper, centered and in title case, halfway down the page. All text should be double-spaced and in the same font as the rest of the paper.
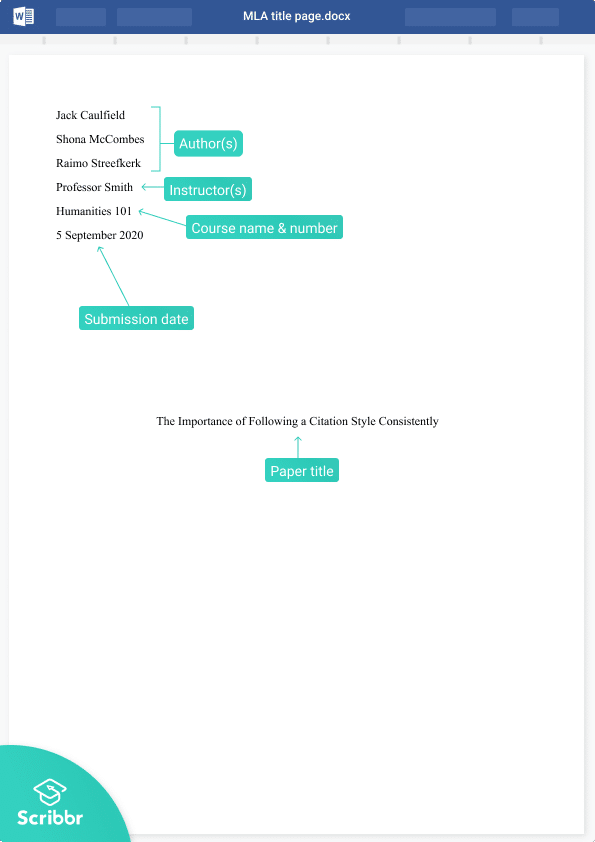
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Most MLA papers will instead list this information in a header , which appears on the same page as your opening paragraphs instead of on a separate page before them. In the header, left-aligned, list
Then on the next line, write the title of your paper, centered and in title case. On the line after that, start your first paragraph. The header and title should be double-spaced, like the rest of the paper.
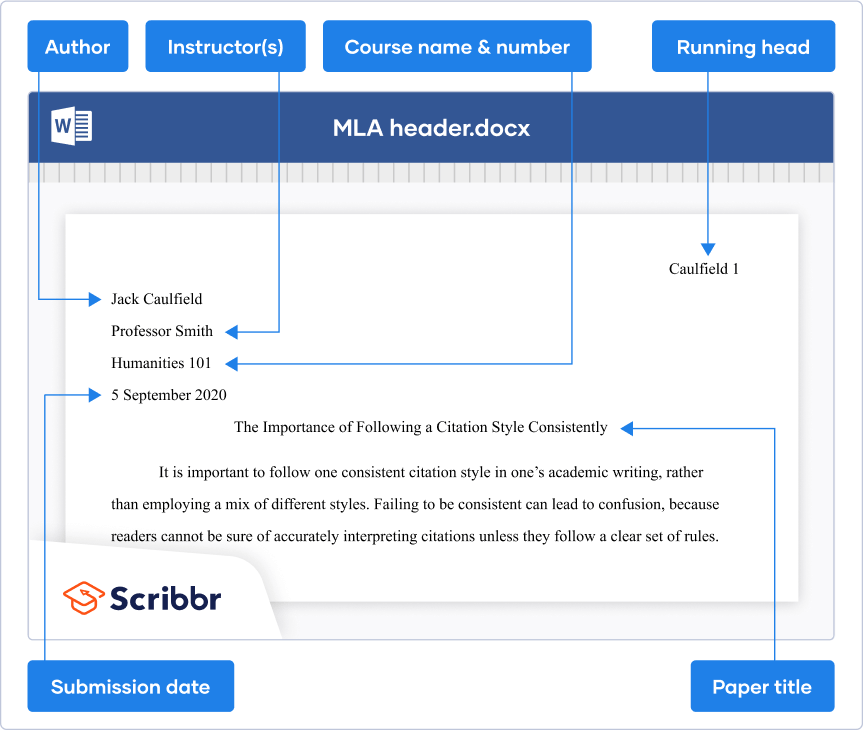
Usually, no title page is needed in an MLA paper . A header is generally included at the top of the first page instead. The exceptions are when:
- Your instructor requires one, or
- Your paper is a group project
In those cases, you should use a title page instead of a header, listing the same information but on a separate page.
If you’re working on a group project and therefore need to list multiple authors for your paper , MLA recommends against including a normal header . Instead, create a separate title page .
On the title page, list each author on a separate line, followed by the other usual information from the header: Instructor, course name and number, and submission date. Then write the title halfway down the page, centered, and start the text of the paper itself on the next page.
MLA recommends using 12-point Times New Roman , since it’s easy to read and installed on every computer. Other standard fonts such as Arial or Georgia are also acceptable. If in doubt, check with your supervisor which font you should be using.
MLA Style is the second most used citation style (after APA ). It is mainly used by students and researchers in humanities fields such as literature, languages, and philosophy.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2024, March 05). MLA Title Page | When You Need One & How to Format It. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/mla/mla-title-page/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, mla format for academic papers and essays, mla titles: formatting and capitalization rules, what is your plagiarism score.

COMMENTS
In MLA style, source titles appear either in italics or in quotation marks: Italicize the title of a self-contained whole (e.g. a book, film, journal, or
In this post, we talk about MLA style and formatting, whether it's appropriate for your project, and most importantly, how to write a book title in MLA.
An MLA book citation always includes the author (s), title (italicized), publisher, and publication year in the Works Cited entry. If relevant, also include the names of any editors or translators, the edition, and the volume. "University Press" should be abbreviated to "UP" in a Works Cited entry.
How to Write a Book Title in an Essay Many style manuals call on writers use title case and italics to format a book title. Title case rules vary slightly from one style guide to the next, but generally capitalize all important words — nouns, pronouns, verbs, and adverbs.
MLA Works Cited Page: Books When you are gathering book sources, be sure to make note of the following bibliographic items: the author name (s), other contributors such as translators or editors, the book's title, editions of the book, the publication date, the publisher, and the pagination.
MLA General Format MLA Style specifies guidelines for formatting manuscripts and citing research in writing. MLA Style also provides writers with a system for referencing their sources through parenthetical citation in their essays and Works Cited pages.
The title of a book is italicized with all major words capitalized. The formatting is the same in the Works Cited list and in the text.
1 Italicize book titles in the text of your paper. Designate a book title as separate from the rest of your text by placing the complete title (and subtitle, if it has one) in italics. In contrast, shorter articles, essays, or chapters within the book are enclosed in quotation marks. [1] Music album titles and film titles are also italicized. In earlier editions, the MLA Handbook also ...
For the purpose of this article, let's assume that you've been assigned a short essay in MLA format. If that's the case, what do you need to know about writing titles?
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Formatting the Author. If no author given, skip the author and start with the title of source. Last Name, First Name. Smith, John. Last Name, First Name, and First Name Last Name. Smith, John, and Mary Fields. Use the name of the association or company as the author. If a work is written and published by an organization, list the organization ...
Writing an essay with a book title can be tricky, particularly because each style guide has its own formatting rules for including titles in the main text. Whether you are using MLA, APA, Chicago, or Harvard referencing styles, you will need to consider how to properly format the book title. For more complicated literature-based assignments, seeking assistance from an admission essay writing ...
The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number (s).
MLA Style Guide, 8th & 9th Editions: Title of source Title of source (Works Cited) The title of source is the second core element in the Works Cited entry. In general, the title of a work is taken from the title page of the publication.
The MLA Handbook provides guidelines for creating MLA citations and formatting academic papers. This includes advice on structuring parenthetical citations, the Works Cited page, and tables and figures. This quick guide will help you set up your MLA format paper in no time.
The Modern Language Association uses the MLA Handbook to provide guidelines on MLA Style, which is the citation style you will be using in this class to format your papers and cite your sources.Included on this page are important documents and links that will help you to use MLA properly. New MLA 9 rules state that the citation should NOT include http:\\
This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use. This resource contains a sample MLA paper that adheres to the 2016 updates. To download the MLA sample paper, click this link.
Sample Essays: Writing with MLA Style Congratulations to the students whose essays were selected for the 2024 edition of Writing with MLA Style! Essays were selected as examples of excellent student writing that use MLA style for citing sources. Essays have been lightly edited.
MLA Style Reference for a Paper Presentation or Poster Session: Last name, First name of author. "Title of Paper or Poster." Title of Conference, Date, Location. Example: Lee, Mark. "Innovations in Education." Annual Education Conference, 15 Mar. 2022, Boston, MA.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
1. Author. One author: Cannon, Joseph S.. Two authors: Dorrison, Michael, and Louise Erdrich.. Three or more authors: Burdick, Anne, et al.. 2. Title of source. Book title (if self-contained): The Devil's Highway. Title of article, webpage, or chapter name (if part of a larger work): "Anemia, Iron Depletion, and the Blood Donor: It's Time to Work on the Donor's Behalf."
This guide follows the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook, published by the Modern Language Association in 2021. To cite sources in MLA style, you need. In-text citations that give the author's last name and a page number. A list of Works Cited that gives full details of every source. Make sure your paper also adheres to MLA ...
MLA Style Sheet General Guidelines. Please also visit the Academic Integrity LibGuide, which provides a Citation guide for your information.. Everything in the paper is double-spaced: works cited, indented quotes, etc.; Pagination: student's last name and the page number are placed on each page's upper right-hand corner. Quotes that are more than four lines long are indented one inch from the ...
Paper Format. Guidelines for setting up your paper, including the title page, font, and sample papers. Reference Examples. More than 100 reference examples of various types, including articles, books, reports, films, social media, and webpages. APA Style and MLA Style Reference Comparison Guide (PDF, 87KB)
MLA title page format. To create an MLA format title page, list the following on separate lines, left-aligned at the top of the page: Then leave a few blank lines and list the title of the paper, centered and in title case, halfway down the page. All text should be double-spaced and in the same font as the rest of the paper.