

How To Choose A Research Topic
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + Free Topic Evaluator
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | April 2024
Choosing the right research topic is likely the most important decision you’ll make on your dissertation or thesis journey. To make the right choice, you need to take a systematic approach and evaluate each of your candidate ideas across a consistent set of criteria. In this tutorial, we’ll unpack five essential criteria that will help you evaluate your prospective research ideas and choose a winner.
Overview: The “Big 5” Key Criteria
- Topic originality or novelty
- Value and significance
- Access to data and equipment
- Time limitations and implications
- Ethical requirements and constraints
Criterion #1: Originality & Novelty
As we’ve discussed extensively on this blog, originality in a research topic is essential. In other words, you need a clear research gap . The uniqueness of your topic determines its contribution to the field and its potential to stand out in the academic community. So, for each of your prospective topics, ask yourself the following questions:
- What research gap and research problem am I filling?
- Does my topic offer new insights?
- Am I combining existing ideas in a unique way?
- Am I taking a unique methodological approach?
To objectively evaluate the originality of each of your topic candidates, rate them on these aspects. This process will not only help in choosing a topic that stands out, but also one that can capture the interest of your audience and possibly contribute significantly to the field of study – which brings us to our next criterion.

Criterion #2: Value & Significance
Next, you’ll need to assess the value and significance of each prospective topic. To do this, you’ll need to ask some hard questions.
- Why is it important to explore these research questions?
- Who stands to benefit from this study?
- How will they benefit, specifically?
By clearly understanding and outlining the significance of each potential topic, you’ll not only be justifying your final choice – you’ll essentially be laying the groundwork for a persuasive research proposal , which is equally important.
Criterion #3: Access to Data & Equipment
Naturally, access to relevant data and equipment is crucial for the success of your research project. So, for each of your prospective topic ideas, you’ll need to evaluate whether you have the necessary resources to collect data and conduct your study.
Here are some questions to ask for each potential topic:
- Will I be able to access the sample of interest (e.g., people, animals, etc.)?
- Do I have (or can I get) access to the required equipment, at the time that I need it?
- Are there costs associated with any of this? If so, what are they?
Keep in mind that getting access to certain types of data may also require special permissions and legalities, especially if your topic involves vulnerable groups (patients, youths, etc.). You may also need to adhere to specific data protection laws, depending on the country. So, be sure to evaluate these aspects thoroughly for each topic. Overlooking any of these can lead to significant complications down the line.

Criterion #4: Time Requirements & Implications
Naturally, having a realistic timeline for each potential research idea is crucial. So, consider the scope of each potential topic and estimate how long each phase of the research will take — from literature review to data collection and analysis, to writing and revisions. Underestimating the time needed for a research project is extremely common , so it’s important to include buffer time for unforeseen delays.
Remember, efficient time management is not just about the duration but also about the timing . For example, if your research involves fieldwork, there may specific times of the year when this is most doable (or not doable at all). So, be sure to consider both time and timing for each of your prospective topics.
Criterion #5: Ethical Compliance
Failing to adhere to your university’s research ethics policy is a surefire way to get your proposal rejected . So, you’ll need to evaluate each topic for potential ethical issues, especially if your research involves human subjects, sensitive data, or has any potential environmental impact.
Remember that ethical compliance is not just a formality – it’s a responsibility to ensure the integrity and social responsibility of your research. Topics that pose significant ethical challenges are typically the first to be rejected, so you need to take this seriously. It’s also useful to keep in mind that some topics are more “ethically sensitive” than others , which usually means that they’ll require multiple levels of approval. Ideally, you want to avoid this additional admin, so mark down any prospective topics that fall into an ethical “grey zone”.
If you’re unsure about the details of your university’s ethics policy, ask for a copy or speak directly to your course coordinator. Don’t make any assumptions when it comes to research ethics!
Key Takeaways
In this post, we’ve explored how to choose a research topic using a systematic approach. To recap, the “Big 5” assessment criteria include:
- Topic originality and novelty
- Time requirements
- Ethical compliance
Be sure to grab a copy of our free research topic evaluator sheet here to fast-track your topic selection process. If you need hands-on help finding and refining a high-quality research topic for your dissertation or thesis, you can also check out our private coaching service .
Need a helping hand?
i need guidance on the choise of research topic.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Interesting
- Scholarships
- UGC-CARE Journals
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Research Topic
Discover how to pick the perfect research topic with our expert guide.
Boarding on a research journey is an exciting yet challenging endeavor, often commencing with the pivotal decision of selecting a research topic. This initial choice can significantly shape the trajectory of the entire scholarly pursuit, influencing the depth, breadth, and impact of the study. In this article, iLovePhD highlighted the key factors to be considered in Choosing a Research Topic to carry out innovative and purposeful research for the benefit of mankind.
Personal Interest and Passion:
- Passion is the fuel that drives perseverance and dedication.
- Choosing a research topic aligned with one’s interests fosters genuine enthusiasm, making the journey more enjoyable and sustaining motivation throughout the often lengthy process.
- A topic that resonates with the researcher ’s curiosity or aligns with their personal values tends to yield more profound insights and a deeper understanding.
Relevance and Significance:
- An impactful research topic should address a pertinent issue or gap in existing knowledge.
- Assessing the relevance and significance of a topic within the academic field or its practical implications in the real world is crucial.
- Consider its potential contribution to the field, societal relevance, and the extent to which it can fill a knowledge vacuum or address an existing problem.
Feasibility and Scope:
- While enthusiasm is vital, feasibility is equally important.
- Evaluating the scope of the research topic in terms of available resources, time, and access to necessary data or materials is crucial.
- Researchers must ascertain whether the chosen topic is manageable within the given constraints without compromising the depth or quality of the study.
Originality and Innovation:
- Originality sparks intellectual curiosity and encourages the exploration of new ideas.
- A novel approach or unique perspective on a familiar topic can breathe fresh life into research.
- Consider whether the chosen topic offers an opportunity for innovative thinking or the potential to generate new knowledge, methodologies, or paradigms.
Research Gap and Literature Review:
- Conducting a thorough literature review is essential to identify gaps in existing research.
- A robust research topic often emerges from gaps or inconsistencies found in previous studies.
- Understanding what has been done and what remains unexplored in the field helps pinpoint areas where new research can make a significant contribution.
Audience and Impact:
- Consider the intended audience for the research and its potential impact.
- Will the findings cater to fellow researchers, policymakers, practitioners, or the general public?
- Understanding the target audience and envisioning the potential impact of the research aids in shaping the study to ensure it resonates with and contributes meaningfully to the intended community.
Ethical and Social Considerations:
- Ethical implications are vital in research.
- Researchers must consider the potential consequences and ethical implications of their work.
- This includes ensuring that the research respects the rights and dignity of participants and adheres to ethical guidelines and standards.
Selecting a research topic is a pivotal stage in the research process. By considering these factors, researchers can make informed decisions that align with their interests, contribute meaningfully to the academic community, and potentially bring about real-world change. Ultimately, a well-chosen research topic sets the stage for a rewarding and impactful scholarly journey. Happy Researching!
Top 100 Journal Publications in the World 2024
List of laboratories and centers under drdo, download research papers for free: legal and ethical methods, most popular, india-uk joint call for proposal: pioneering telecommunications research (dst-epsrc), top 10 uk universities welcoming commonwealth professional fellows, 5 free gptzero alternatives that actually work in 2024: unmask ai content now, 10 mind-blowing ai projects transforming medical imaging, 150+ innovative generative ai project ideas: transforming industries and advancing technology, walk-in-interview for junior research fellowships at drdo, dbt-research associateship in biotechnology & life sciences for 2024-25, best for you, 24 best online plagiarism checker free – 2024, what is phd, popular posts, 480 ugc care list of journals – science – 2024, reviewer three: unveiling the world of peer review, popular category.
- POSTDOC 317
- Interesting 258
- Journals 234
- Fellowship 133
- Research Methodology 102
- All Scopus Indexed Journals 92
Mail Subscription

iLovePhD is a research education website to know updated research-related information. It helps researchers to find top journals for publishing research articles and get an easy manual for research tools. The main aim of this website is to help Ph.D. scholars who are working in various domains to get more valuable ideas to carry out their research. Learn the current groundbreaking research activities around the world, love the process of getting a Ph.D.
Contact us: [email protected]
Google News
Copyright © 2024 iLovePhD. All rights reserved
- Artificial intelligence

- Boston University Libraries
Choosing a Research Topic
- Starting Points
Where to Find Ideas
Persuasive paper assignments, dissertations and theses.
- From Idea to Search
- Make It Manageable
If you are starting a research project and would like some help choosing the best topic, this guide is for you. Start by asking yourself these questions:
What does your instructor require? What interests you? What information sources can support your research? What is doable in the time you have?
While keeping these questions in mind, find suggestions in this guide to select a topic, turn that topic into a database search, and make your research manageable. You will also find more information in our About the Research Process guide.
Whether your instructor has given a range of possible topics to you or you have to come up with a topic on your own, you could benefit from these activities:
Consult Course Materials If a reading, film, or other resource is selected by your instructor, the subject of it is important to the course. You can often find inspiration for a paper in these materials.
- Is a broad topic presented? You can focus on a specific aspect of that topic. For example, if your class viewed a film on poverty in the United States, you could look at poverty in a specific city or explore how poverty affects Americans of a specific gender, ethnic group, or age range.
- Are experts presented, quoted, or cited? Look up their work in BU Libraries Search or Google Scholar .
Use Background Sources If you've identified one or more topics you'd like to investigate further, look them up in an encyclopedia, handbook, or other background information source. Here are some good places to start.
Online version of Encyclopædia Britannica along Merriam-Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary and Thesaurus, magazines and periodicals and other reference sources.
- Oxford Reference This link opens in a new window Published by Oxford University Press, it is a fully-indexed, cross-searchable database containing dictionaries, language reference and subject reference works.
Explore the Scholarly Literature Ask your instructor or a librarian to guide you to the top journals in the field you're studying. Scanning the tables of contents within these journals will provide some inspiration for your research project. As a bonus, each of the articles in these journals will have a bibliography that will lead you to related articles, books, and other materials.
Ask a Librarian We are here to help you! You can request a consultation or contact us by email or through our chat service . We can help you identify what interests you, where to find more about it, and how to narrow the topic to something manageable in the time you have.
If your assignment entails persuading a reader to adopt a position, you can conduct your research in the same way you would with any other research project. The biggest mistake you can make, however, is choosing a position before you start your research. Instead, the information you consult should inform your position. Researching before choosing a position is also much easier; you will be able to explore all sides of a topic rather than limiting yourself to one.
If you would like examples of debates on controversial topics, try these resources:
Covers the most current and controversial issues of the day with summaries, pros and cons, bibliographies and more. Provides reporting and analysis on issues in the news, including issues relating to health, social trends, criminal justice, international affairs, education, the environment, technology, and the economy.
- New York Times: Room for Debate Selections from the New York Times' opinion pages.
- ProCon.org Created by Britannica, this site exposes readers to two sides of timely arguments. Each article includes a bibliography of suggested resources.
If you are writing a dissertation or thesis, you will find more specialized information at our Guide for Writers of Theses and Dissertations .
If you would like to find published dissertations and theses, please use this database:
This database contains indexing and abstracts of American doctoral dissertations accepted at accredited institutions since 1861 and a selection from other countries. Masters level theses are included selectively.

- Next: From Idea to Search >>
- Last Updated: Jul 16, 2024 9:04 AM
- URL: https://library.bu.edu/choosing-a-topic
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
Published on November 11, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 20, 2023.
Choosing your dissertation topic is the first step in making sure your research goes as smoothly as possible. When choosing a topic, it’s important to consider:
- Your institution and department’s requirements
- Your areas of knowledge and interest
- The scientific, social, or practical relevance
- The availability of data and resources
- The timeframe of your dissertation
- The relevance of your topic
You can follow these steps to begin narrowing down your ideas.
Table of contents
Step 1: check the requirements, step 2: choose a broad field of research, step 3: look for books and articles, step 4: find a niche, step 5: consider the type of research, step 6: determine the relevance, step 7: make sure it’s plausible, step 8: get your topic approved, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about dissertation topics.
The very first step is to check your program’s requirements. This determines the scope of what it is possible for you to research.
- Is there a minimum and maximum word count?
- When is the deadline?
- Should the research have an academic or a professional orientation?
- Are there any methodological conditions? Do you have to conduct fieldwork, or use specific types of sources?
Some programs have stricter requirements than others. You might be given nothing more than a word count and a deadline, or you might have a restricted list of topics and approaches to choose from. If in doubt about what is expected of you, always ask your supervisor or department coordinator.
Start by thinking about your areas of interest within the subject you’re studying. Examples of broad ideas include:
- Twentieth-century literature
- Economic history
- Health policy
To get a more specific sense of the current state of research on your potential topic, skim through a few recent issues of the top journals in your field. Be sure to check out their most-cited articles in particular. For inspiration, you can also search Google Scholar , subject-specific databases , and your university library’s resources.
As you read, note down any specific ideas that interest you and make a shortlist of possible topics. If you’ve written other papers, such as a 3rd-year paper or a conference paper, consider how those topics can be broadened into a dissertation.
After doing some initial reading, it’s time to start narrowing down options for your potential topic. This can be a gradual process, and should get more and more specific as you go. For example, from the ideas above, you might narrow it down like this:
- Twentieth-century literature Twentieth-century Irish literature Post-war Irish poetry
- Economic history European economic history German labor union history
- Health policy Reproductive health policy Reproductive rights in South America
All of these topics are still broad enough that you’ll find a huge amount of books and articles about them. Try to find a specific niche where you can make your mark, such as: something not many people have researched yet, a question that’s still being debated, or a very current practical issue.
At this stage, make sure you have a few backup ideas — there’s still time to change your focus. If your topic doesn’t make it through the next few steps, you can try a different one. Later, you will narrow your focus down even more in your problem statement and research questions .
There are many different types of research , so at this stage, it’s a good idea to start thinking about what kind of approach you’ll take to your topic. Will you mainly focus on:
- Collecting original data (e.g., experimental or field research)?
- Analyzing existing data (e.g., national statistics, public records, or archives)?
- Interpreting cultural objects (e.g., novels, films, or paintings)?
- Comparing scholarly approaches (e.g., theories, methods, or interpretations)?
Many dissertations will combine more than one of these. Sometimes the type of research is obvious: if your topic is post-war Irish poetry, you will probably mainly be interpreting poems. But in other cases, there are several possible approaches. If your topic is reproductive rights in South America, you could analyze public policy documents and media coverage, or you could gather original data through interviews and surveys .
You don’t have to finalize your research design and methods yet, but the type of research will influence which aspects of the topic it’s possible to address, so it’s wise to consider this as you narrow down your ideas.
It’s important that your topic is interesting to you, but you’ll also have to make sure it’s academically, socially or practically relevant to your field.
- Academic relevance means that the research can fill a gap in knowledge or contribute to a scholarly debate in your field.
- Social relevance means that the research can advance our understanding of society and inform social change.
- Practical relevance means that the research can be applied to solve concrete problems or improve real-life processes.
The easiest way to make sure your research is relevant is to choose a topic that is clearly connected to current issues or debates, either in society at large or in your academic discipline. The relevance must be clearly stated when you define your research problem .
Before you make a final decision on your topic, consider again the length of your dissertation, the timeframe in which you have to complete it, and the practicalities of conducting the research.
Will you have enough time to read all the most important academic literature on this topic? If there’s too much information to tackle, consider narrowing your focus even more.
Will you be able to find enough sources or gather enough data to fulfil the requirements of the dissertation? If you think you might struggle to find information, consider broadening or shifting your focus.
Do you have to go to a specific location to gather data on the topic? Make sure that you have enough funding and practical access.
Last but not least, will the topic hold your interest for the length of the research process? To stay motivated, it’s important to choose something you’re enthusiastic about!
Most programmes will require you to submit a brief description of your topic, called a research prospectus or proposal .
Remember, if you discover that your topic is not as strong as you thought it was, it’s usually acceptable to change your mind and switch focus early in the dissertation process. Just make sure you have enough time to start on a new topic, and always check with your supervisor or department.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly

You can assess information and arguments critically by asking certain questions about the source. You can use the CRAAP test , focusing on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
Ask questions such as:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert?
- Why did the author publish it? What is their motivation?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence?
A dissertation prospectus or proposal describes what or who you plan to research for your dissertation. It delves into why, when, where, and how you will do your research, as well as helps you choose a type of research to pursue. You should also determine whether you plan to pursue qualitative or quantitative methods and what your research design will look like.
It should outline all of the decisions you have taken about your project, from your dissertation topic to your hypotheses and research objectives , ready to be approved by your supervisor or committee.
Note that some departments require a defense component, where you present your prospectus to your committee orally.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 20). How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow. Scribbr. Retrieved July 22, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/dissertation-topic/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, what is a research design | types, guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
How to Select a Research Topic: A Step-by-Step Guide
by Antony W
June 6, 2024

Learning how to select a research topic can be the difference between failing your assignment and writing a comprehensive research paper. That’s why in this guide we’ll teach you how to select a research topic step-by-step.
You don’t need this guide if your professor has already given you a list of topics to consider for your assignment . You can skip to our guide on how to write a research paper .
If they have left it up to you to choose a topic to investigate, which they must approve before you start working on your research study, we suggest that you read the process shared in this post.
Choosing a topic after finding your research problem is important because:
- The topic guides your research and gives you a mean to not only arrive at other interesting topics but also direct you to discover new knowledge
- The topic you choose will govern what you say and ensures you keep a logical flow of information.
Picking a topic for a research paper can be challenging and sometimes intimidating, but it’s not impossible. In the following section, we show you how to choose the best research topic that your instructor can approve after the first review.
How to Select a Research Topic
Below are four steps to follow to find the most suitable topic for your research paper assignment:
Step 1: Consider a Topic that Interests You

If your professor has asked you to choose a topic for your research paper, it means you can choose just about any subject to focus on in your area of study. A significant first step to take is to consider topics that interest you.
An interesting topic should meet two very important conditions.
First, it should be concise. The topic you choose should not be too broad or two narrow. Rather, it should be something focused on a specific issue. Second, the topic should allow you to find enough sources to cite in the research stage of your assignment.
The best way to determine if the research topic is interesting is to do some free writing for about 10 minutes. As you free write, think about the number of questions that people ask about the topic and try to consider why they’re important. These questions are important because they will make the research stage easier for you.
You’ll probably have a long list of interesting topics to consider for your research assignment. That’s a good first step because it means your options aren’t limited. However, you need to narrow down to only one topic for the assignment, so it’s time to start brainstorming.
Step 2: Brainstorm Your Topics

You aren’t doing research at this stage yet. You are only trying to make considerations to determine which topic will suit your research assignment.
The brainstorming stage isn’t difficult at all. It should take only a couple of hours or a few days depending on how you approach.
We recommend talking to your professor, classmates, and friends about the topics that you’ve picked and ask for their opinion. Expect mixed opinions from this audience and then consider the topics that make the most sense. Note what topics picked their interest the most and put them on top of the list.
You’ll end up removing some topics from your initial list after brainstorming, and that’s completely fine. The goal here is to end up with a topic that interests you as well as your readers.
Step 3: Define Your Topics

Check once again to make sure that your topic is a subject that you can easily define. You want to make sure the topic isn’t too broad or too narrow.
Often, a broad topic presents overwhelming amount of information, which makes it difficult to write a comprehensive research paper. A narrow topic, on the other hand, means you’ll find very little information, and therefore it can be difficult to do your assignment.
The length of the research paper, as stated in the assignment brief, should guide your topic selection.
Narrow down your list to topics that are:
- Broad enough to allows you to find enough scholarly articles and journals for reference
- Narrow enough to fit within the expected word count and the scope of the research
Topics that meet these two conditions should be easy to work on as they easily fit within the constraints of the research assignment.
Step 4: Read Background Information of Selected Topics

You probably have two or three topics by the time you get to this step. Now it’s time to read the background information on the topics to decide which topic to work on.
This step is important because it gives you a clear overview of the topic, enabling you to see how it relates to broader, narrower, and related concepts. Preliminary research also helps you to find keywords commonly used to describe the topic, which may be useful in further research.
It’s important to note how easy or difficult it is to find information on the topic.
Look at different sources of information to be sure you can find enough references for the topic. Such periodic indexes scan journals, newspaper articles, and magazines to find the information you’re looking for. You can even use web search engines. Google and Bing are currently that best options to consider because they make it easy for searchers to find relevant information on scholarly topics.
If you’re having a hard time to find references for a topic that you’ve so far considered for your research paper, skip it and go to the next one. Doing so will go a long way to ensure you have the right topic to work on from start to finish.
Get Research Paper Writing Help
If you’ve found your research topic but you feel so stuck that you can’t proceed with the assignment without some assistance, we are here to help. With our research paper writing service , we can help you handle the assignment within the shortest time possible.
We will research your topic, develop a research question, outline the project, and help you with writing. We also get you involved in the process, allowing you to track the progress of your order until the delivery stage.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
Finding your Goal: How to choose a research topic
Finding a research topic can be challenging, but the steps outlined in this article will help you with that.
The study of science and academics cannot be completed without research. You’ll need to choose a research topic carefully when writing a research paper or conducting a study, no matter whether you’re a student or a professional researcher. It is your choice of topic that determines how your study will be conducted and ultimately how successful it will be.
If you don’t know where to begin or what factors to consider when choosing a research topic, it can be daunting. It is possible to choose a research topic in a variety of ways, and what is effective for one person may not be effective for another, but the question remains the same: “How to choose a research topic?”
Well, choosing the right topic takes some trial and error, and it’s not a one-size-fits-all process. Let’s discuss a few key factors to consider when choosing a research topic that aligns with your passion, expertise, and research goals in this blog.
A Well-Chosen Research Topic Can Make or Break Your Project
If you want to conduct a successful research project, it is imperative to pick a good research topic, regardless of your field or discipline. The topic you choose will influence your research’s direction and scope, as well as its methods and approaches. It is important to choose a topic that will allow you to explore your area of interest in-depth and also contribute to the existing body of knowledge in the field.
The first step to conducting a meaningful and fulfilling research project is choosing a good research topic. Your enthusiasm and dedication to the subject matter will lead to better outcomes when you’re passionate about it. Even when faced with challenges or setbacks during the project, a well-chosen research topic will keep you focused and motivated.
In addition to being beneficial to your own research project, a research topic can also have a broader impact on the field at large. You can help advance the field by selecting a topic that addresses a knowledge gap, contributes to an ongoing debate, or informs policy or practice by providing new insights. Additionally, an interesting research topic can provide opportunities to collaborate with other researchers, leading to further advancements and broader networks in the field.
A successful and rewarding research project depends on choosing the right research topic for you. The best way to achieve a fulfilling and impactful research experience is to choose topics aligned with your interests and expertise, contribute to the field, and allow for meaningful engagement.
Unlocking Ideas: How to brainstorm your research topic
A brainstorming session is a crucial first step in selecting a research topic. Identifying potential options and taking into account factors such as feasibility, relevance, and significance are essential steps. Depending on your research goals and personal preferences, you may benefit from using different brainstorming techniques.
Visual diagrams that organize ideas around a central topic, such as mind maps, are an effective way to settle ideas. The central topic should be written in the center of the page, then related ideas or subtopics should be written around it. Identifying potential research directions can be accomplished by seeing how different ideas are connected.
Listing is another method, where you write as many topics as possible without worrying about their feasibility or relevance at first. Based on your expertise, the significance of the research question , the availability of data and resources, and the time required to complete the research, you can narrow down the list of potential topics.
Brainstorm with a group or seek feedback from peers, mentors, or colleagues, who may offer unique insights and perspectives. A good research topic can be identified by brainstorming, and by using different techniques and taking into account various factors, you can choose one that fits your interests, goals, and resources.
How to Choose a Research Topic: 6 Steps to Make It Easy
Following these steps will help you choose a research topic that fits your interests, expertise, and objectives, while also being feasible to conduct within the constraints of your resources and schedule.
1. Brainstorm possible subject matter
Begin by brainstorming a list of potential research topics that are of interest to you in order to narrow down your choices. If you have a specific question or topic that you are curious about, this could be anything from a broad topic that you are passionate about to a more specific question, that’s the perfect time to write it down. Be sure to take into consideration your field of study, current events, and any research gaps you have discovered in your area of expertise. Make a list of any ideas that come to mind, no matter how unrelated or impractical they may seem. As a result, you will be able to generate many potential topics to explore.
2. Think about your expertise and interests
Identify a topic that corresponds to your interests and expertise. When you are passionate about your topic, your research will be more engaging and motivating. Make a list of topics you’re familiar with and topics you’re interested in learning about. The goal is to choose a topic that you enjoy researching and will keep you motivated throughout the research process.
3. Do a literature review
After you’ve compiled a list of potential topics, review the literature to see what previous research has been done in the area. As a result, you will be able to identify gaps in the existing research that you might be able to fill. Gather relevant research articles and papers by searching academic databases, journals, and other credible sources. Study the literature carefully, making notes on key findings and areas that have not been addressed. By focusing on topics that lack extensive research or that have gaps in the existing literature, you will be able to narrow down your list of potential research topics.
4. Assess the feasibility
Consider factors like data availability, time constraints, and access to research participants or resources once you have a list of possible topics. You can use this information to determine which topics may be suitable for your research. Consider ensuring you have enough participants for your study if you intend to do a large-scale study that requires a large sample size. Considering the resources and equipment you’ll need for your research is important if you’re working within a limited budget.
5. Make your research question more specific
As soon as you have chosen your topic, refine your research question to make sure it is specific, relevant, and feasible. Your research will be guided, and you will stay on track by doing this. Good research questions are clear and concise, and they identify the specific problem you’re trying to solve. You should ensure that your research question is based on existing research and that it can be conducted within the time and resource constraints you have.
6. Be open to feedback
You may benefit from the feedback of colleagues, advisors, or other experts in your field regarding the topic and research question you have chosen. You may gain valuable insights from them or find alternative approaches you hadn’t thought of. Your research question can be refined further by doing this, and you can ensure that you are on the right track with your research.
A successful research project depends on choosing the right topic. You’re just beginning a long and rewarding journey when you choose a research topic. Perseverance and dedication can lead to research that advances human understanding of our world and contributes to the advancement of your field.
Couldn’t find an illustration in our gallery? We’ll design it for you!
Sometimes, it can be challenging to find something that aligns with your research or that is custom-made to perfectly represent the information you want to explain. Let Mind The Graph help you communicate your science more clearly. Describe your needs and we’ll design specific illustrations for your paper. Let us take care of it!

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Sign Up for Free
Try the best infographic maker and promote your research with scientifically-accurate beautiful figures
no credit card required
About Aayushi Zaveri
Aayushi Zaveri majored in biotechnology engineering. She is currently pursuing a master's degree in Bioentrepreneurship from Karolinska Institute. She is interested in health and diseases, global health, socioeconomic development, and women's health. As a science enthusiast, she is keen in learning more about the scientific world and wants to play a part in making a difference.
Content tags

Research Process Guide
- Step 1 - Identifying and Developing a Topic
- Step 2 - Narrowing Your Topic
- Step 3 - Developing Research Questions
- Step 4 - Conducting a Literature Review
- Step 5 - Choosing a Conceptual or Theoretical Framework
- Step 6 - Determining Research Methodology
- Step 6a - Determining Research Methodology - Quantitative Research Methods
- Step 6b - Determining Research Methodology - Qualitative Design
- Step 7 - Considering Ethical Issues in Research with Human Subjects - Institutional Review Board (IRB)
- Step 8 - Collecting Data
- Step 9 - Analyzing Data
- Step 10 - Interpreting Results
- Step 11 - Writing Up Results
Step 1: Identifying and Developing a Topic

Whatever your field or discipline, the best advice to give on identifying a research topic is to choose something that you find really interesting. You will be spending an enormous amount of time with your topic, you need to be invested. Over the course of your research design, proposal and actually conducting your study, you may feel like you are really tired of your topic, however, your interest and investment in the topic will help you persist through dissertation defense. Identifying a research topic can be challenging. Most of the research that has been completed on the process of conducting research fails to examine the preliminary stages of the interactive and self-reflective process of identifying a research topic (Wintersberger & Saunders, 2020). You may choose a topic at the beginning of the process, and through exploring the research that has already been done, one’s own interests that are narrowed or expanded in scope, the topic will change over time (Dwarkadas & Lin, 2019). Where do I begin? According to the research, there are generally two paths to exploring your research topic, creative path and the rational path (Saunders et al., 2019). The rational path takes a linear path and deals with questions we need to ask ourselves like: what are some timely topics in my field in the media right now?; what strengths do I bring to the research?; what are the gaps in the research about the area of research interest? (Saunders et al., 2019; Wintersberger & Saunders, 2020).The creative path is less linear in that it may include keeping a notebook of ideas based on discussion in coursework or with your peers in the field. Whichever path you take, you will inevitably have to narrow your more generalized ideas down. A great way to do that is to continue reading the literature about and around your topic looking for gaps that could be explored. Also, try engaging in meaningful discussions with experts in your field to get their take on your research ideas (Saunders et al., 2019; Wintersberger & Saunders, 2020). It is important to remember that a research topic should be (Dwarkadas & Lin, 2019; Saunders et al., 2019; Wintersberger & Saunders, 2020):
- Interesting to you.
- Realistic in that it can be completed in an appropriate amount of time.
- Relevant to your program or field of study.
- Not widely researched.
Dwarkadas, S., & Lin, M. C. (2019, August 04). Finding a research topic. Computing Research Association for Women, Portland State University. https://cra.org/cra-wp/wp-content/uploads/sites/8/2019/04/FindingResearchTopic/2019.pdf
Saunders, M. N. K., Lewis, P., & Thornhill, A. (2019). Research methods for business students (8th ed.). Pearson.
Wintersberger, D., & Saunders, M. (2020). Formulating and clarifying the research topic: Insights and a guide for the production management research community. Production, 30 . https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-6513.20200059
- Last Updated: Jun 29, 2023 1:35 PM
- URL: https://libguides.kean.edu/ResearchProcessGuide

- Spartanburg Community College Library
- SCC Research Guides
- Choosing a Research Topic
- What Makes a Good Research Topic?
Before diving into how to choose a research topic, it is important to think about what are some elements of a good research topic. Of course, this will depend specifically on your research project, but a good research topic will always:
- Relate to the assignment itself. Even when you have a choice for your research topic, you still want to make sure your chosen topic lines up with your class assignment sheet.
- A topic that is too broad will give you too many sources, and it will be hard to focus your research.
- A topic that is too narrow will not give you enough sources, if you can find any sources at all.
- Is debatable. This is important if you are researching a topic that you will have to argue a position for. Good topics have more than one side to the issue and cannot be resolved with a simple yes or no.
- Should be interesting to you! It's more fun to do research on a topic that you are interested in as opposed to one you are not interested in.
Remember, it is common and normal if your research topic changes as you start brainstorming and doing some background research on your topic.
Start with a General Idea
As an example, let's say you were writing a paper about issues relating to college students
- << Previous: Choosing a Research Topic
- Next: 1. Concept Mapping >>
- 1. Concept Mapping
- 2. Background Research
- 3. Narrow Your Topic / Thesis Statements
Questions? Ask a Librarian

- Last Updated: Jul 19, 2024 1:21 PM
- URL: https://libguides.sccsc.edu/chooseatopic
Giles Campus | 864.592.4764 | Toll Free 866.542.2779 | Contact Us
Copyright © 2024 Spartanburg Community College. All rights reserved.
Info for Library Staff | Guide Search
Return to SCC Website
Selecting a Research Topic: Refine your topic
- Refine your topic
- Background information & facts
Narrow your topic's scope
Too much information? Make your results list more manageable. Less, but more relevant, information is key. Here are some options to consider when narrowing the scope of your paper:
- Theoretical approach : Limit your topic to a particular approach to the issue. For example, if your topic concerns cloning, examine the theories surrounding of the high rate of failures in animal cloning.
- Aspect or sub-area : Consider only one piece of the subject. For example, if your topic is human cloning, investigate government regulation of cloning.
- Time : Limit the time span you examine. For example, on a topic in genetics, contrast public attitudes in the 1950's versus the 1990's.
- Population group : Limit by age, sex, race, occupation, species or ethnic group. For example, on a topic in genetics, examine specific traits as they affect women over 40 years of age.
- Geographical location : A geographic analysis can provide a useful means to examine an issue. For example, if your topic concerns cloning, investigate cloning practices in Europe or the Middle East.
Broaden your topic
Not finding enough information? Think of related ideas, or read some background information first. You may not be finding enough information for several reasons, including:
- Your topic is too specific . Generalize what you are looking for. For example: if your topic is genetic diversity for a specific ethnic group in Ghana, Africa, broaden your topic by generalizing to all ethnic groups in Ghana or in West Africa.
- Your topic is too new for anything substantive to have been written. If you're researching a recently breaking news event, you are likely to only find information about it in the news media. Be sure to search databases that contain articles from newspapers. If you are not finding enough in the news media, consider changing your topic to one that has been covered more extensively.
- You have not checked enough databases for information . Search Our Collections to find other databases in your subject area which might cover the topic from a different perspective. Also, use excellent searching techniques to ensure you are getting the most out of every database.
- You are using less common words or too much jargon to describe your topic. Use a thesaurus to find other terms to represent your topic. When reading background information, note how your topic is expressed in these materials. When you find citations in an article database, see how the topic is expressed by experts in the field.
Once you have a solid topic, formulate your research question or hypothesis and begin finding information.
If you need guidance with topic formulation, Ask Us ! Library staff are happy to help you focus your ideas.
- << Previous: Overview
- Next: Background information & facts >>
- Last Updated: Jul 30, 2021 2:50 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mit.edu/select-topic
- Fontbonne University

Research Help
Choosing a topic.
- Library Research
Getting Started
- Developing a Thesis
- Finding Sources
- Interlibrary Loan This link opens in a new window
- Writing and Re-Writing
- Evaluating Sources
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- Data & Statistics
- Using Images
- Additional Resources
- ESL Resources
- College 101
- Primary Sources
- Library Tutorials
- Graduate Studies
Choosing a topic is the first and maybe the most important step of the research and writing process! This step will determine the rest of your steps -- what your thesis statement is, what sources you use, and how to write your paper. So it's important to make sure you choose a strong and engaging topic.
Strategies for finding a topic:
- Look over the index and the article titles in a subject-specific encyclopedia that covers a relevant subject area or discipline. Check out our print collection available in the Information Commons. (Additional sources can be found by searching the catalog for titles in the general collection.)
- Spend some time looking at major journals in your field (look for the white binder in the reading room for a list of current periodicals by subject).
- Browse your subject area in one of our digital reference sources .
- Discuss topic ideas with your instructor or favorite reference librarian!
Good questions to ask yourself when choosing a topic are:
- Is this a topic that interests me?
- Is this a topic that is creative and has not been overdone?
- Is this a topic that is not too broad or too narrow to meet the assignment requirements?
When you pick your topic, it's not set in stone. Picking and adjusting your topic is an integral part of the research process!
How to Develop a Good Research Topic
Need Help Choosing a Topic?
Sometimes it can be difficult to think up a great research topic. Have no fear -- Taylor Library is here to help! Check out these database and websites to get some ideas.
Once you have a topic in mind:
- Consider first the broad subjects that deal with your topic.
- Narrow this down, keeping your topic in mind.
- Focus closer: limit your topic to specifics, such as geography, time, and culture.
- Write down topic phrases; this helps you come up with key words and questions that will help you in your research.
- << Previous: The Research Process
- Next: Getting Started >>
- Last Updated: Jul 24, 2024 10:32 AM
- URL: https://library.fontbonne.edu/research
- Contact sales (+234) 08132546417
- Have a questions? [email protected]
- Latest Projects

Project Materials
What to consider when choosing a research problem.
Need help with a related project topic or New topic? Send Us Your Topic
DOWNLOAD THE COMPLETE PROJECT MATERIAL
The significance of choosing a research problem is sometimes underrated and the majority of researchers don’t seem to understand that if you aren’t reading the correct kinds of books, no amount of research will be fruitful.
To achieve that extra element to captivate the reader of your findings you need to choose a juicy research challenge or something with meat on the bone, and strong thesis or essay begins with thorough research, and thorough research starts with a topic that piques interest and avoids being boring so it is much simpler to comprehend the value of research in the creation of an effective and hard-hitting final product when you put it in such simple, straightforward terms, additionally, you must have an honest and practical viewpoint when approaching the research problem you’re attempting to answer.
Can you solve the issue you’re trying to resolve? Are you overly ambitious and placing too much pressure on yourself? Is this a valid issue, or are you just trying to get out of something? To determine how strong your research problem is, you must ask yourself each of these questions and when doubts start to seep into your thinking, you need to turn around and start thinking about other options.
undergraduate project topics
The research issue chosen for the examination should be carefully chosen although the task is difficult, thus assistance in this regard could come from a research guide. At most, a research guide can help a researcher choose a topic or issue, but the actual research question and research problem should originate in the researcher’s mind.
There are some recommendations for graduate students and researchers that are taken from the various branches of psychology, social sciences, and education, the choice of topic is influenced by both external and internal variables, external criteria include how relevant the topic is to the field and the availability of data and data collection techniques, and whether or not the administration is cooperative, Personal criteria are the time, money, and interests of the researcher. The following characteristics influence the selection criteria for the research problem.
final year project topics
- Personal Preference; The primary driving force behind the researcher’s choice of study question is their personal preference, a researcher will choose a problem for his or her research if he or she has a personal interest in it.
- Resources readily available; A researcher will take care of the accessible resources during the selection process and the choice of the problem is simple if the resources of money, time, lodging, and transportation are available at the location of choice.
- Relative significance; The choice of a research problem is significantly influenced by both importance and the problem; the researcher is more likely to choose the problem if it is reasonably important.
- Researcher expertise; The choice of the study problem should be heavily influenced by the researcher’s knowledge and to collect research data effectively an investigator must have wisdom and expertise, the researcher can choose a problem with resentment.
- Practicality: This factor also played a role in the decision, the primary driving force behind a researcher’s attention to an issue is its practical applicability.
- Timelines for the Issue; While some problems can be solved quickly, others require longer. Therefore, it depends on how much time a researcher has to do the research.
- Data accessibility; The researcher would choose the issue if the desired data were available.
- Urgency; A defining factor in the choice of a research problem is urgency, priority must be given to urgent issues because they may benefit from quick solutions.
- Feasibility; A key consideration in choosing the research problem is feasibility, the researcher’s background, education, and experience should be appropriate for the issue.
- Regional Culture; The choice of study problem is also influenced by the culture of the region for which a researcher performs his research.
Features of the Research Problem
Every research project is challenging to complete and demands a lot of work so choosing a successful research topic is the first step.
- The research topic needs to be very obvious and simple to comprehend. People shouldn’t be diverted by it.
- The only way to conduct successful research is if the topic is clearly defined as topics that shouldn’t raise questions or leave a bad impression.
- Success requires the use of simple language, if necessary, use technical language or a preferred language that will be easily understood.
- The research title must follow the regulations for titles and before developing a study title, a researcher should be informed of the various rules of titling.
- A researcher’s present prominence should be taken into account while choosing a study topic, the subject should not be out of date and should be of paramount importance right now.
- Before choosing a research problem, a preliminary investigation should be conducted. When the issue calls for the conduct of research that is nearly identical to earlier work, this isn’t always necessary. A brief feasibility study should, however, always be conducted when the subject of investigation is relatively new and does not yet have a collection of well-developed procedures available.
- In the majority of cases, it is best to avoid choosing an overdone topic because it will be difficult to shed any new light on it.
- Problems that are too specific or too illogical must be avoided.
- Other factors that should be taken into account when choosing an issue include the importance of the topic, the credentials and expertise of a researcher, the costs involved, and the time factor.
- The research topic chosen must be understandable and practical so that the necessary research materials or sources are available. Even still, giving clear instructions on how a professional should gather inspiration for his research is incredibly difficult. A researcher can achieve this by getting in touch with a lecturer or expert who is already engaged in research at the university. He can also study blog posts or articles that have been published in recent literature on the subject and consider how the principles and approaches discussed there could be used to solve other challenges.
- best topic for project
In conclusion, researchers must determine the key elements to be taken into account while choosing a research problem and by paying close attention to the essential elements mentioned above, the topic should be chosen appropriately. The problem chosen should concern the researcher and should occupy the forefront of his thoughts so that he can address the challenges needed for the research study.
Latest Updates
Determinants and challenges of reading print version of newspaper among youths, role of mass media in crisis management in nigeria, television broadcasting, reality tv shows and moral development of nigeria youths, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Advertisements
- Hire A Writer
- Plagiarism Research Clinic
- International Students
- Project Categories
- WHY HIRE A PREMIUM RESEARCHER?
- UPGRADE PLAN
- PROFESSIONAL PLAN
- STANDARD PLAN
- MBA MSC STANDARD PLAN
- MBA MSC PROFESSIONAL PLAN
Choosing a Topic
- Selecting & Developing a Topic
- Where to Get Topic Ideas
- Narrowing & Broadening Your Topic
- Your MCC Libraries
Choosing & Developing a Topic Steps
Before choosing a topic, make sure you understand your assignment and what your instructor is asking for. If you have questions, make sure to ask your instructor for clarification.
1. Choose a subject area that interests you and that will interest the readers. Try to avoid topics that are overly used such as abortion or gun control. It is important to choose a topic that is academic in nature - something that people will be doing research on. If your paper is an argumentative/persuasive paper, you need to pick one that is controversial or that people feel passionate enough to argue about or to do research on (otherwise you'll have a hard time finding sources).
2. Do some background research on any subjects that you are interested in using encyclopedias and websites. This will provide you with an overview so that you gain a better understanding of the subject area and you can see what issues are related. Background research can also help you decide what way to focus on a subject area. For example, you might be interested in the subject of social media. If you look social media up in an encyclopedia it might talk about issues related to it such as privacy or bullying. You then might decide to focus on the topic of social media and privacy.
3 . It is a good idea to state your topic in the form of a question to stay focused on what it is that you are trying to explain or prove. For example, if you want to do research on advertising and body image among teenage girls, you might ask:
What impact does advertising have on the body image of teenage girls?
4. When you come up with a topic, choose the main concepts in your research question (for the question above it would be "advertising", "body image", and "teenage girls") and do an initial search with them in the Library catalog or databases. If you are getting way too many hits, you might need to narrow your topic more. If you are not getting enough hits, you might need to broaden your topic.
Some common pitfalls include choosing a topic that is too:
broad narrow recent local
You want a manageable topic that is of enduring interest to you - and to others.
5. Once you are sure you have a manageable topic that is interesting and that has enough research out there you can use in your paper, create a thesis statement. This will be an answer to your research question or a statement that explains the purpose of your research.
This video is really helpful in explaining how to create a really good research question:
Background Research
Encyclopedias are good places to go for for background information, definitions, and to learn various aspects of a topic. The Library has two online reference book collections that you can find articles on your topic in. When searching them, just enter your topic as a search term. From off campus, log in with your MEID and password.
- Credo Reference
- Gale Virtual Reference Library
These books have chapters on choosing and refining a topic.
Choosing & Developing a Topic Websites
Choosing a Topic (Purdue's Online Writing Lab) provides a good introduction on understanding your assignment and choosing a topic.
Selecting a Research Topic (WSU Stewart Library) gives on overview on steps you can take to choose a topic.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Where to Get Topic Ideas >>
- Last Updated: May 12, 2020 2:42 PM
- URL: https://mesacc.libguides.com/topics

How To Choose a Research Topic For Your PhD Thesis (7 Key Factors to Consider)

If you are a PhD student, then you know that choosing a topic for your PhD thesis or dissertation was one of the toughest decisions you had to make.
This post provides guidance to prospective PhD students on the factors they need to consider when it comes to choosing their research topic.
1. Personal interests
The PhD programme lasts on average for 3 years, but varies depending on the school and department. As such, you need to choose a research topic that interests you so as to keep you motivated during those days when you feel like giving up (and those days will be many).
2. The interests of your school’s faculty
As much as your interest is important in helping you choose a research topic for your thesis, it must align with the interests of one (or more) of the faculty of your school in which you are taking your PhD.
This is important in ensuring that you get a supervisor who is an expert in your proposed area of research. In fact, one of the PhD application requirements for most PhD programmes is a concept note, which highlights the proposed research topic. This serves the purpose stated above: ensuring that the applicant will get adequate supervision throughout his or her studies.
3. Your knowledge and skills set
The knowledge and skills you gained during your undergraduate or Masters’ degree, as well as through your job can influence your choice of a research topic for your PhD thesis.
You may choose to settle on a topic that requires your existing knowledge and skills set, or may choose the harder route of gaining new knowledge and skills. The PhD is a great opportunity for the latter option.
For instance, you may be well versed with quantitative research methods, including its practical application, and may decide to choose a topic that renders itself to the use of quantitative analysis. Alternatively, you may decide that since you already know quantitative analysis, it is time to learn about qualitative research methods and choose a topic that will force you to dive deep into qualitative analysis. It is all about your preference.
4. Your career prospects
When choosing a PhD thesis topic, ask yourself what your career aspirations are, and then choose a topic that will give you the opportunity to learn more about your area of interest.
Besides spending a great amount of time conducting research in your research topic, the PhD period will also enable you to network with your peers and experts in your research area.
PhD students are often expected to attend workshops, seminars, and scientific conferences in the course of their studies, and these avenues provide great professional networking opportunities for the students, which can open their doors for their future career.
You therefore want to choose a topic that will significantly contribute to your career growth.
5. Trends in your industry
This factor is closely related to factor number 4 above. If your career prospects are not in academia, then it is important to consider what is trending in your industry and choose a topic that aligns to it. This will offer you with enormous opportunities for career growth.
For instance, in the Health Economics space, digital health is currently trending, and will trend for a long time to come.
A PhD student who is currently focusing on an aspect of digital health is highly likely to “sell like a hot cake” upon completion of his or her studies. That is, as long as he or she puts in the effort to do the research well and network with like-minded people in the industry.
Choosing a topic that is relevant and adds value, especially practically, is important for the PhD student’s career growth.
6. Feasibility of the research topic
It is one thing to pick a research topic that interests you and your faculty. It is another thing altogether to ensure that the topic chosen does not drag you behind as far as completing your PhD is concerned.
PhD is time-limited. You only have 2, 3, or whatever number of years to start and complete your studies. Your topic should therefore be feasible both time-wise and resource-wise.
You need to pick a topic that you can comfortably work on within the time limits of your studies, as well as within the available financial resources.
Consider whether you have scholarship for the study or if you are self-sponsoring your studies, and choose a topic that will not burden you financially.
Another important feasibility aspect to consider is the data requirement for your research. Will you collect primary data or use already available secondary data. If using primary data, do you have the time and money required for the collection and analysis of the data? If using secondary data, do you have easy access (that is, there are no logistical and financial barriers) to the data? You need to have this knowledge before settling on a research topic.
7. Adequacy of existing literature on the research topic
Before settling on a topic, research it widely to make sure that there are enough papers written about it. Remember that you will review hundreds of papers for your PhD thesis.
You can easily find out whether the topic has been well researched by skimming through online journal databases and resources like Google Scholar . Familiarise yourself with what others have written and what gaps exist, and then tweak your topic in a way that will add value to the existing literature.
While at it, also get to know who the experts of your research topic are. Networks such as ResearchGate, LinkedIn and Twitter are great places to know who the giants of your research area are. Remember that you will stand on the shoulders of many giants throughout your PhD studies (and beyond!). Get to know them and their past and ongoing works.
Final Thoughts on “How to Choose a Research Topic for your PhD Thesis”
Your research topic for your PhD thesis will most likely evolve over time. The topic you start with when you join your PhD programme will undergo significant transformations as you undertake courses, read literature, and consult with your supervisor. Don’t worry if this happens, it is the norm.
However, don’t spend too much time thinking about your topic, as the more time you spend on it, the less time you will have for the actual research. Consider the above 7 factors, settle on your topic and hit the road running.
Related post:
How to Write a PhD Concept Paper
Grace Njeri-Otieno
Grace Njeri-Otieno is a Kenyan, a wife, a mom, and currently a PhD student, among many other balls she juggles. She holds a Bachelors' and Masters' degrees in Economics and has more than 7 years' experience with an INGO. She was inspired to start this site so as to share the lessons learned throughout her PhD journey with other PhD students. Her vision for this site is "to become a go-to resource center for PhD students in all their spheres of learning."
Recent Content
SPSS Tutorial #12: Partial Correlation Analysis in SPSS
Partial correlation is almost similar to Pearson product-moment correlation only that it accounts for the influence of another variable, which is thought to be correlated with the two variables of...
SPSS Tutorial #11: Correlation Analysis in SPSS
In this post, I discuss what correlation is, the two most common types of correlation statistics used (Pearson and Spearman), and how to conduct correlation analysis in SPSS. What is correlation...
Gagan's Academic Space
Factors to consider while choosing a topic for research
Many researchers and students get confused choosing a good topic for research. In this blog post, I will explain the factors to be considered while choosing a good research topic. Any topic is good for research, just depends on these factors and your purpose. When I say “area of research”, I am referring to the broad area. For example: International Law. When I say “topic”, I am referring to the narrow / specific topic. For example: “Status of Diplomats In International Law”.
These are the factors that influence what topic you choose for research:
- Purpose (your course / specialisation / research project / target journal)
- Your interest
- Available resources
- Your long term goals
- Fitting the topic to research methodology
- Literature review
- Scope for further research – of past research
1. Purpose If you are pursuing your PhD, you may have to consider the area of your specialisation at your postgraduation level and then decide a topic that within your area of specialisation or closely linked. If you are doing your dissertation for your postgraduation, you need to consider your specialisation or the subjects that you are studying. If you are working on a Government funded research project, then your funding agency decides your area of research, hence you need to choose a topic within that area. If you are planning to write a journal article, you need to take up a topic that is within the domain of that journal. If your research is for a seminar, ensure that you fit in your topic within one of those given sub themes.
Not a hard and fast rule, but choosing a topic that is an extension of a subject paper you studied at the postgraduation level is a good way to start your research. Say for example, you studied ‘Banking Law’ at your postgraduation level. If you now choose to do your research on a banking fraud case, then you already know the basics of banking law and you can directly get into the case study.
2. Your Guide If you are doing your PhD, your guide is mostly already decided. Sometimes, your topic will decide the guide. Some universities ask the PhD students to decide the topic and then assign a guide who is good in that area. Something similar works for postgraduation dissertations. At times, the University office staff will randomly assign the guides for dissertation.
The nature and characteristics of each guide varies a lot. Very few guides are good in assisting the students minutely. If you are lucky to have such a guide, then it is better to choose a topic in which your guide is good at. It saves a lot of your time. If your guide has no knowledge in your topic or research area, you may spend half of your research time wasting on figuring out the basics of that subject. At times, there are guides who are not ready to assist a lot, but will be hell bent on imposing a topic on you. It is a tough call, and you need to be aware if you can work on that topic. Try convincing your guide in situations where you are aware of not having the capacity or resources to deal with that topic.
One way to assess the areas of expertise of your guide is to check your University website for the bio data / CV of your guide. Check the area in which your guide did his / her postgraduation, PhD thesis topic, articles published, subjects taught. All these will give you a fair idea of the areas in which your guide is good at. I suggest that you have an open discussion with your guide about your topic.
If you are writing an article for a journal, you probably do not have any guide assigned. You are at the mercy of your professors who may or may not guide you! You will be lucky to find someone like me 😉 who readily agrees to help students on research!
3. Your Interest If you have an intrinsic interest in a topic, you will love doing the research. But seldom do you find your topic of interest and other factors coinciding. Though your research interest will be in one area, it is better to ensure that the other factors like your course, your guide and long term goals coincide with your interest.
4. Available Resources I keep telling that, carrying out a research is like cooking a good meal. What meal you cook will be decided by the ingredients you have in your store room. If you do not have an ingredient at your home, you can buy it from your nearest market. But if you need to cook a meal whose ingredients are not available in your city market, then there is no way you can cook that meal.
Same analogy applies for your research. If you want to carry out research in a particular area or on a particular topic, but you have no resources at your library or on the internet, there is no point carrying out research on that topic. If your research topic is empirical, and if the Government / private agencies – from where you are supposed to get the data – have strict confidential policy, you may never be able to complete your research!
Do check the resources available in your library. I suggest that you navigate across your library stacks physically. In many libraries, some resources are not indexed or indexed wrongly or the search engine is faulty! So, your keyword search on library OPAC (Online Public Access Catalogue) may not throw satisfactory results. So do walk across your library collections and check the resources. There may be special collections that are locked or are kept in a different place. Check them all. You will get a fair idea of the available resources for your research.
The online databases available will be listed on your University Library web page. Do check each database specifically and see the extent to which you have access to those materials. At times, some databases may provide just first chapter of their e-books or may provide limited e-books for reading. Your library may have some understanding with different libraries for resource sharing. So, do speak to your librarian (or email) about such facilities. I usually suggest students to first check the text books, then journals & reports and then online sources. I suggest that you need to give last preference to the materials that come up on internet search engines.
Tip: I suggest catalogue listing browsing, rather than search results. I think, there is a lot to learn here, and I may blog about this some day.
There are times when I browse through the library resources and get research ideas based on those books and journals that are available. This is like expert cooks who can look at the vegetables available in the market and come up with good recipes based on the ingredients. Be a good research cook! But do not cook up stories in your research 😉
5. Your long term goals At times, your research may have long term bearing for you. For instance, if you are planning for a postgraduation course in a particular area of study, you will have to write research articles on the same area. If you wish to get a job in a corporate firm, you will have to write articles on corporate laws. If you wish to become a professor of International Law in the future, you will have to carry out your PhD topic in the field of international law. So, do keep in your mind your long term goals while choosing your research area and topic. Sit and think peacefully as to where you would like to see yourself 5 or 10 years down the lane. If you are investing considerable time (say 2-3 years) on your research, then you need to consider your long term goals. Every minute you invest in your research is valuable. Do not waste it carrying out research on unnecessary topics or things that have no future purpose!
6. Fitting your topic to research methodology If your research is for your PhD or postgraduation dissertation, then it is imperative for you to explain your research methodology. These days, even some seminars and journals expect you to submit a brief research methodology. If you are supposed to explain a detailed research methodology, you need to explain – the problem statement, hypothesis, research objectives, research questions, literature review and sources of data. Most students find it difficult to come out with the problem statement and hypothesis.
If you wish to examine tentatively, if your topic is good enough for research, try coming out with a “statement of problem” and “hypothesis” for your research topic. Do this type of examination for the 4-5 probable topics you have decided on. You will start realising the topics that are realistic to carry out your research on. It also avoids you from cracking your head later once you have finalised your topic!
7. Literature review This factor may sound similar to “checking library resources”. This is much deeper. You need to decide an area or sub-area for research and start checking the resources on that area or sub area. Once you complete going through considerable literature on that area, you will slowly start realising the “gaps” in that area. You will know what are the topics in that area that have been dealt already. And what topics have hardly been touched by earlier researchers – and this is where you can do your research on. This is similar to you writing a script for a movie. But before writing a script, you should have watched the existing movies in that genre and ensure that you do not end up having a plot that is similar to a movie that released last year! A lot of students take up topics that are too common. These are the topics on which considerable research has already been done. There may be nothing new to add. Even if you write articles on such too common topics, ensure that you give a perspective / treatment for that topic, which was never attempted by earlier researchers.
8. Scope for further research – by past researches At times, the already submitted (past researches) mention towards the end of their research about “scope for future research”. The researcher indicates as to what all work has been dealt in his / her research work and what type of research can be carried out by future researchers. You may check the existing / published / accepted researches and get a cue to your topic! Since, less researchers mention the scope for further research in their research work, this method may not work all the time. There are some research works that are done so well, that you can notice how they narrowed down on one of the several sub areas. You could narrow down on the other sub-areas that were not dealt by others.
In another blog post, I will write about how to compose the title of your research work and how that is very important. One may think – it is just a title, what is there to think a lot about it? Not really, there are many details there. I will deal with it in another blog post. Bye for now.
Share this:
Published by dr. gagan k.
Academician in the field of Law. Specialisation in Competition Law. I love writing about music and articles that help the law students. View more posts
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

Resilience is the process and outcome of successfully adapting to difficult or challenging life experiences, especially through mental, emotional, and behavioral flexibility and adjustment to external and internal demands.
A number of factors contribute to how well people adapt to adversities, including the ways in which individuals view and engage with the world, the availability and quality of social resources, and specific coping strategies.
Psychological research demonstrates that the resources and skills associated with resilience can be cultivated and practiced.
Adapted from the APA Dictionary of Psychology
Resources from APA

Building your resilience

Resilience for teens: 10 tips to build skills on bouncing back from rough times

Resilience guide for parents and teachers
Motivation Myth Busters
The Pain Survival Guide, Rev. Ed.
Building Psychological Resilience in Military Personnel
Nature Meets Nurture
Magination Press children’s books

Stickley Makes a Mistake!

What to Do When Mistakes Make You Quake, Revised

Abracadabra!

Doug’s Dung

The Hugging Tree
Journal special issues
Collaborative and Participatory Research to Promote Engagement, Empowerment, and Resilience for Immigrant and Refugee Youth, Families, and Communities
Resilience and Perseverance for Human Flourishing
Risk and Resilience in Sexual and Gender Minority Relationships
Resilience and Trauma
Trauma, Aging, and Well-Being
Research Topics to Avoid: A Guide to Choosing the Right Topic for Your Study

Research is essential to the academic world, and its significance cannot be overstated. However, choosing the right research topic is crucial to any study’s success. While there is a plethora of potential research topics, it is essential to consider what are the sources of research topics . Before entering into the field of research, every researcher must know what research topic to be avoided . Consider the following points while choosing a research topic.

- The right source of information: Considering the sources of research topics is crucial. Research topics can come from various sources, including personal interests, professional requirements, current events, and academic literature. However, ensuring that the topic you choose aligns with your research goals, skills, and expertise is vital. Additionally, ensuring that your chosen topic is feasible regarding data collection, analysis, and ethical considerations is essential.
- Controversial topics: Any group of controversial topics should be avoided because it often involves emotional or political issues that can be difficult to remain objective about. Moreover, researching controversial topics can lead to negative consequences, such as backlash from stakeholders or harm to the researcher’s reputation. Therefore, it is best to avoid them unless you have a solid plan for managing potential risks and challenges.
- Appropriate subject matter: Another factor to consider when choosing a research topic
is the subject matter. Some topics which should not be considered in choosing a topic for research are topics that are too broad, too narrow, or too obscure. Topics that are too broad may lack focus and result in superficial findings, while topics that are too narrow may not provide enough data for meaningful analysis. Additionally, too obscure topics may lack relevance and significance, making it difficult to justify the research.
- Ease of investigation: Some research topics are hard to investigate. These topics may involve sensitive or taboo subjects, limited access to data or subjects, or require specialized knowledge or skills. Examples of hard to investigate research topics include mental health, sexual behaviours, and substance due to the privacy concerns and stigma associated with these issues. Likewise, investigating topics related to criminal organizations, political corruption, or government secrecy may require specialized knowledge and access to sensitive information.
Choosing a research topic should not be taken lightly. It is important to consider various factors, such as feasibility, relevance, and sensitivity of the topic, to ensure that the research is conducted effectively and ethically. It is crucial to select a topic that aligns with the researcher’s goals, skills, and expertise and has the potential to make a meaningful contribution to the academic or practical world.
Do you want to stay updated on latest topics related research and publication? Then please visit www.manuscriptedit.com . You can also mail us your queries at [email protected] . Happy reading!!!
Related Posts
Why journal articles face rejection.
When a manuscript is submitted to a journal, it undergoes a thorough quality check under the peer review process before being sent to the chief editor. Most articles face rejection during this process. There are several reasons for this. 1. The article is beyond the scope of the journal Your article can be immediately rejected […]
Assessing the Japanese Bamboo’s Antibacterial Properties
Assessing the antibacterial properties of Japanese Bamboo involves conducting comprehensive studies to evaluate its effectiveness in inhibiting or killing bacteria. Researchers typically employ various methodologies, such as laboratory tests and experiments, to assess the antibacterial activity of compounds found in Japanese Bamboo. This assessment may involve using bacterial cultures and measuring the inhibition zones or […]
How to understand the quality of a journal article?
If you are an author with experience of publishing articles or are fairly new, you have to decide and determine whether or not your article has the top-notch quality or not. In the theoretical framework of your thesis, you support your research work with something called a literature review. In this case, you look at […]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Oxford University Press's Academic Insights for the Thinking World

How to choose the right journal

Oxford Academic
Learn more about the world of academic publishing—from open access to peer review, accessibility to getting published—with our Publishing 101 series on the OUPblog.
- By Megan Taphouse and Laura Richards
- July 17 th 2024
With approximately 30,000 academic journals worldwide , how do you determine which one is the best fit for your research? There are likely to be many suitable journals in your field, but targeting the right journal is an important decision, as where you choose to publish can influence the impact and visibility of your work.
As a first step, consider: what is your publishing goal?
Defining your goal helps you identify which journals are best suited to achieve your aims. Authors publish for various personal and professional reasons, so consider what’s important for your career, professional development, or research program. Some potential goals could include:
- Advancing knowledge in your specialist field, and contributing to the development of research or debate, so that others can build upon your ideas or results
- Disseminating your findings to a wide or interdisciplinary audience, or having an impact beyond academia
- Adhering to your funder or institutional requirements
- Supporting a learned society or organisation in your subject area
- Using a particular article type or media format to convey your findings
Secondly, what is important to you in the publishing process?
As with goals, this is often personal. This could be:
- Publishing quickly
- A particular type of peer review process
- An easy or straightforward submissions process
- The option to transfer rejected papers to related journals
- Assistance with editing
Next, make a shortlist of journals to compare
Look for journals that publish on your topic. It can be helpful to ask colleagues and mentors for their recommendations, and you can also consider which journals you regularly read or cite yourself. Once you have your shortlist, you can start to check which meet your criteria and more easily rank your options.
T hings to compare and consider
Manuscript suitability – scope and topic.
Does the journal publish your article type and research topic? Seth Schwartz recommends browsing a recent issue of the journal to determine whether any of the articles are similar in scope or type to the paper you are planning to write. Checking the editorial board can also help you to assess the subjects and topics the journal focuses on, and the journal’s aims and scope information or current call for papers will indicate the breadth and depth of the topics covered and whether your article would be a good fit.
Considering the impact and reach
There are a variety of metrics available, including Journal Impact Factor and Altmetrics. Some apply at the journal level and some at the article level . It’s important to pay attention to the metrics that best reflect your publishing goal. For example, if you want your research to be widely read, Altmetrics can help you track the impact on specific areas like policy documents or conversations on social media.
When weighing up journal reputation and metrics, Schartz suggests selecting a journal that matches the significance of your research findings or theory. We can think in terms of “three general levels of contribution—major, moderate, and incremental. Matching the contribution of your work with the prestige level of your target journals may maximize your chances of receiving an invitation to revise and resubmit your paper, and hopefully an eventual acceptance for publication.”
Readership and audience
A 2019 bioRxiv survey found that academics prioritize a journal’s readership when choosing where to publish. You should check journal websites for readership stats and reflect on your own publishing goals: for a specific audience, ask colleagues about their go-to journals; for broader reach, look for journals with a global audience and strong social media presence.
Abstracting and indexing databases also play a significant role in how discoverable your article is, and therefore how many people will find and read it. Well-known databases include Scopus , PubMed , Web of Science , and Google Scholar, but there are also many subject-specific databases.
Ethics and Policies
In recent years there has been an increase in deceptive or “predatory” journals. Niki Wilson describes that while the individual practices can vary, these journals “generally prioritize self-interest and profit over research integrity… and often take fees without performing advertised services”. Before submitting your paper, it is important to take a close look at its website and review its policies, the expertise of the editorial board, and peer review processes—a reputable journal will disclose all this information publicly. It is also a good idea to check if the journal is a member of COPE , or if they ensure that they practice high standards of publication ethics . The free Think.Check.Submit service can help to steer you towards quality and trusted journals.
Peer review
A reputable journal will practice rigorous peer review, and there are various peer review models are available to journals , each with different merits. Peer review helps to guarantee the publication of high-quality research, by assessing the validity, significance, and originality of research. Peer review also benefits you as the author, as it helps to improve the quality of your manuscript and detects errors before publication. In our surveys of OUP authors, the quality of peer review is consistently among the top three factors authors prioritise when choosing a journal.
A good journal will explain its peer review process, and details will normally be available on the ‘instruction to authors’ page. At OUP, we refer all editors to the COPE Ethical Guidelines for peer reviewers, which encourages journals to publish their review procedures.
Author experience
Your experience as an author will vary widely by journal, publisher, and subject area. Many journals are improving processes to make publishing smoother and faster, with format-free submissions, efficient submission systems, quick decisions, strong editorial support, and awards. Consider which options align with your priorities and seek feedback on recent experiences from your network.
Publication models and complying with funder policies
There are multiple publication models to choose from, including fully open access (often known as gold OA), hybrid publishing, and self-archiving (often known as green OA). A growing number of funding agencies and institutions stipulate the publishing license that their academics must use, so familiarise yourself with any limitations or restrictions you need to adhere to and check the journals on your shortlist comply. Ensure you understand (and are able to meet) the publication charges , or see if your institution has a Read and Publish agreement .
Check your shortlist of journals against your criteria and the points above. If you are unsure and need additional information about a journal, consider contacting the journal editors or editorial office for clarification. Remember, do not submit your article to more than one journal at a time. If discovered, this will normally result in the automatic rejection of your manuscript.
If you are ready to publish your findings, take a look at our extensive list of high-quality academic journals or delve into our journal author information page for more insight into our publishing process.
Featured image by Anne Nygård via Unsplash .
Megan Taphouse is a Marketing Executive in the author marketing team.
Laura Richards is a Senior Marketing Manager in the author marketing team.
- Editor's Picks
- Online products
- Publishing 101
- Series & Columns
Our Privacy Policy sets out how Oxford University Press handles your personal information, and your rights to object to your personal information being used for marketing to you or being processed as part of our business activities.
We will only use your personal information to register you for OUPblog articles.
Or subscribe to articles in the subject area by email or RSS
Related posts:

Recent Comments
There are currently no comments.
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Key facts about Americans and guns

Guns are deeply ingrained in American society and the nation’s political debates.
The Second Amendment to the United States Constitution guarantees the right to bear arms, and about a third of U.S. adults say they personally own a gun. At the same time, in response to concerns such as rising gun death rates and mass shootings , the U.S. surgeon general has taken the unprecedented step of declaring gun violence a public health crisis .
Here are some key findings about Americans’ views of gun ownership, gun policy and other subjects, drawn from Pew Research Center surveys.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to summarize key facts about Americans’ relationships with guns. We used data from recent Center surveys to provide insights into Americans’ views on gun policy and how those views have changed over time, as well as to examine the proportion of adults who own guns and their reasons for doing so.
The Center survey questions used in this analysis, and more information about the surveys’ methodologies, and can be found at the links in the text.
Measuring gun ownership in the United States comes with unique challenges. Unlike many demographic measures, there is not a definitive data source from the government or elsewhere on how many American adults own guns.
The Pew Research Center survey conducted June 5-11, 2023, on the Center’s American Trends Panel, used two separate questions to measure personal and household ownership. About a third of adults (32%) say they own a gun, while another 10% say they do not personally own a gun but someone else in their household does. These shares have changed little from surveys conducted in 2021 and 2017 . In each of those surveys, 30% reported they owned a gun.
These numbers are largely consistent with rates of gun ownership reported by Gallup and those reported by NORC’s General Social Survey .
The FBI maintains data on background checks on individuals attempting to purchase firearms in the United States. The FBI reported a surge in background checks in 2020 and 2021, during the coronavirus pandemic, but FBI statistics show that the number of federal background checks declined in 2022 and 2023. This pattern seems to be continuing so far in 2024. As of June, fewer background checks have been conducted than at the same point in 2023, according to FBI statistics.
About four-in-ten U.S. adults say they live in a household with a gun, including 32% who say they personally own one, according to a Center survey conducted in June 2023 . These numbers are virtually unchanged since the last time we asked this question in 2021.
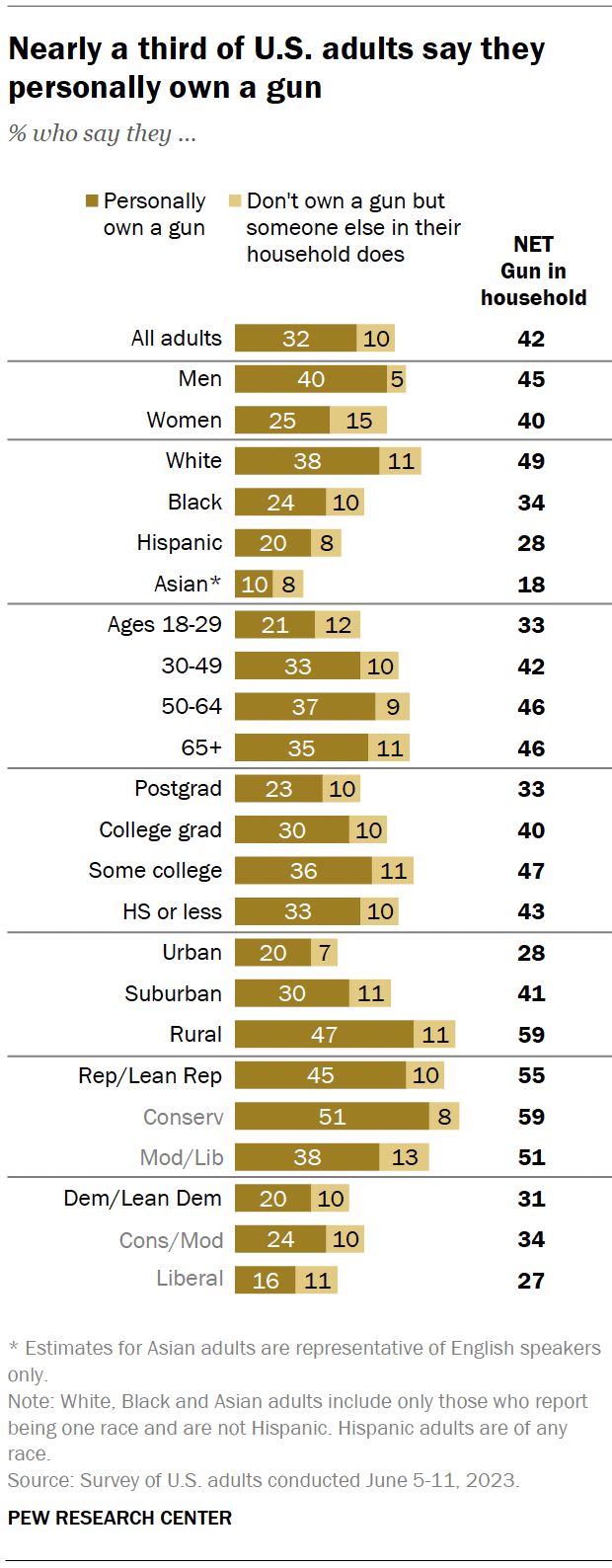
There are differences in gun ownership rates by political affiliation, gender, community type and other factors.
- Party: 45% of Republicans and GOP-leaning independents say they personally own a gun, compared with 20% of Democrats and Democratic leaners.
- Gender: 40% of men say they own a gun, versus 25% of women.
- Community type: 47% of adults living in rural areas report owning a firearm, as do smaller shares of those who live in suburbs (30%) or urban areas (20%).
- Race and ethnicity: 38% of White Americans own a gun, compared with smaller shares of Black (24%), Hispanic (20%) and Asian (10%) Americans.
Personal protection tops the list of reasons gun owners give for having a firearm. About seven-in-ten gun owners (72%) say protection is a major reason they own a gun. Considerably smaller shares say that a major reason they own a gun is for hunting (32%), for sport shooting (30%), as part of a gun collection (15%) or for their job (7%).
Americans’ reasons behind gun ownership have changed only modestly since we fielded a separate survey about these topics in spring 2017. At that time, 67% of gun owners cited protection as a major reason they had a firearm.
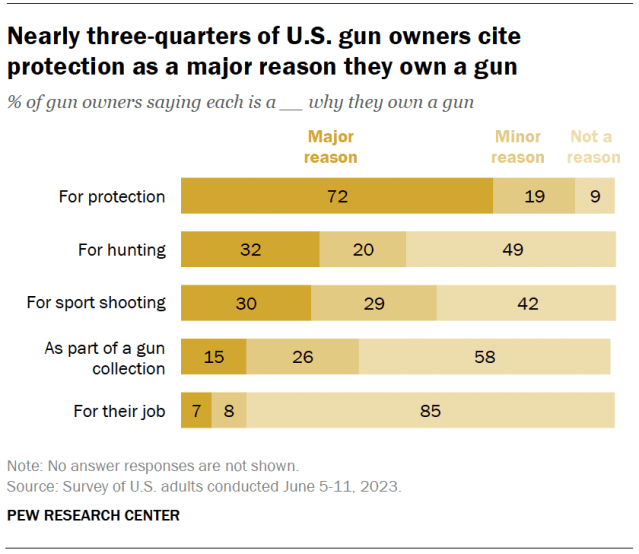
Gun owners tend to have much more positive feelings about having a gun in the house than nonowners who live with them do. For instance, 71% of gun owners say they enjoy owning a gun – but just 31% of nonowners living in a household with a gun say they enjoy having one in the home. And while 81% of gun owners say owning a gun makes them feel safer, a narrower majority of nonowners in gun households (57%) say the same. Nonowners are also more likely than owners to worry about having a gun at home (27% vs. 12%).
Feelings about gun ownership also differ by political affiliation, even among those who personally own a firearm. Republican gun owners are more likely than Democratic owners to say owning one gives them feelings of safety and enjoyment, while Democratic owners are more likely to say they worry about having a gun in the home.
Non-gun owners are split on whether they see themselves owning a firearm in the future. About half of Americans who don’t own a gun (52%) say they could never see themselves owning one, while nearly as many (47%) could imagine themselves as gun owners in the future.
Among those who currently do not own a gun, attitudes about owning one in the future differ by party and other factors.
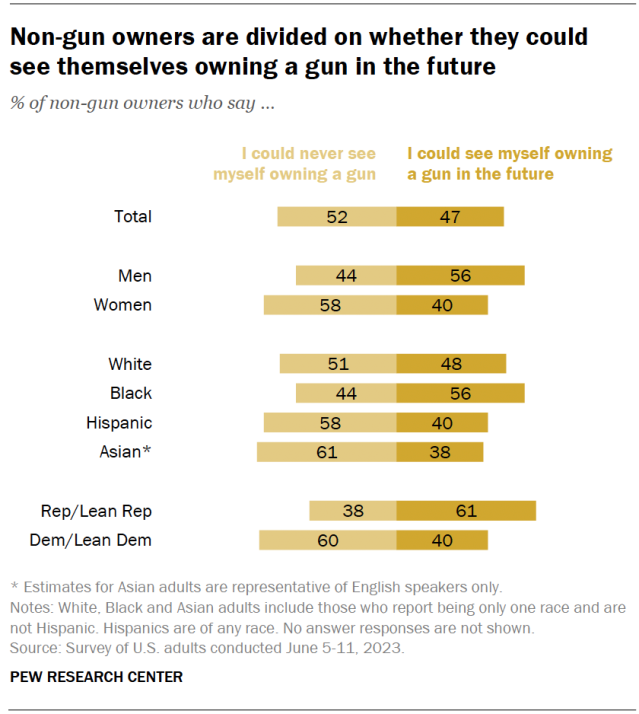
- Party: 61% of Republicans who don’t own a gun say they could see themselves owning one in the future, compared with 40% of Democrats.
- Gender: 56% of men who don’t own a gun say they could see themselves owning one someday; 40% of women nonowners say the same.
- Race and ethnicity: 56% of Black nonowners say they could see themselves owning a gun one day, compared with smaller shares of White (48%), Hispanic (40%) and Asian (38%) nonowners.
A majority of Americans (61%) say it is too easy to legally obtain a gun in this country, according to the June 2023 survey. Far fewer (9%) say it is too hard, while another 30% say it’s about right.
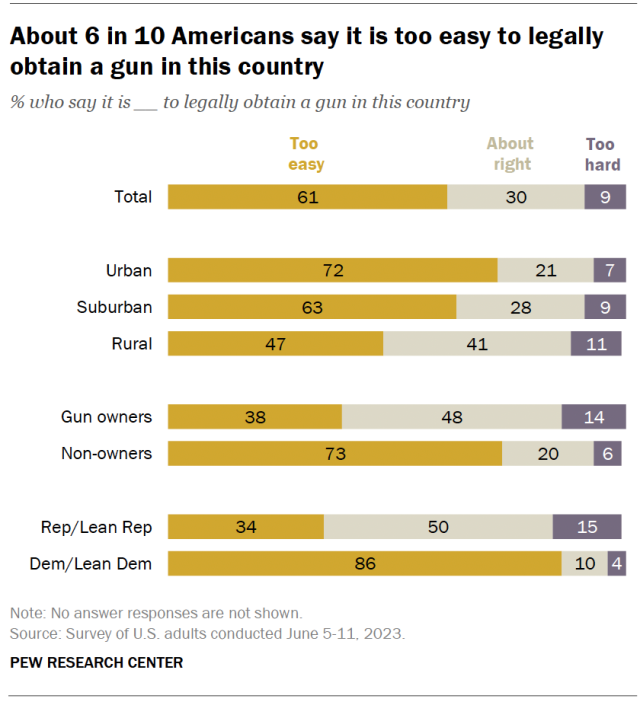
Non-gun owners are nearly twice as likely as gun owners to say it is too easy to legally obtain a gun (73% vs. 38%). Gun owners, in turn, are more than twice as likely as nonowners to say the ease of obtaining a gun is about right (48% vs. 20%).
There are differences by party and community type on this question, too. While 86% of Democrats say it is too easy to obtain a gun legally, far fewer Republicans (34%) say the same. Most urban (72%) and suburban (63%) residents say it’s too easy to legally obtain a gun, but rural residents are more divided: 47% say it is too easy, 41% say it is about right and 11% say it is too hard.
About six-in-ten U.S. adults (58%) favor stricter gun laws. Another 26% say that U.S. gun laws are about right, while 15% favor less strict gun laws.
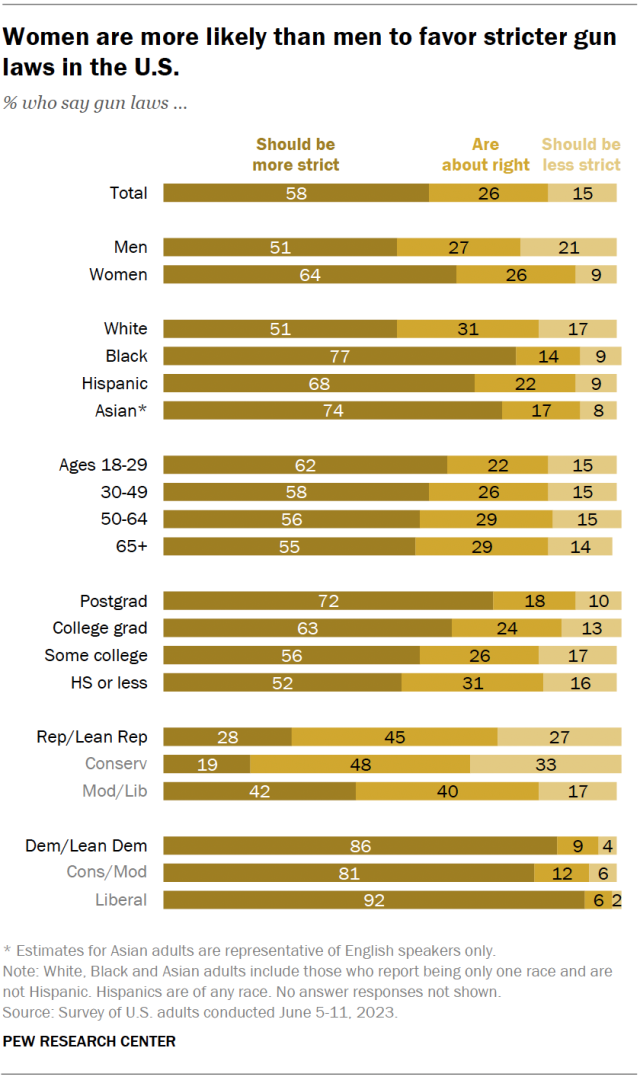
There is broad partisan agreement on some gun policy proposals, but most are politically divisive. Majorities of U.S. adults in both partisan coalitions somewhat or strongly favor two policies that would restrict gun access: preventing those with mental illnesses from purchasing guns (88% of Republicans and 89% of Democrats support this) and increasing the minimum age for buying guns to 21 years old (69% of Republicans, 90% of Democrats). Majorities in both parties also oppose allowing people to carry concealed firearms without a permit (60% of Republicans and 91% of Democrats oppose this).
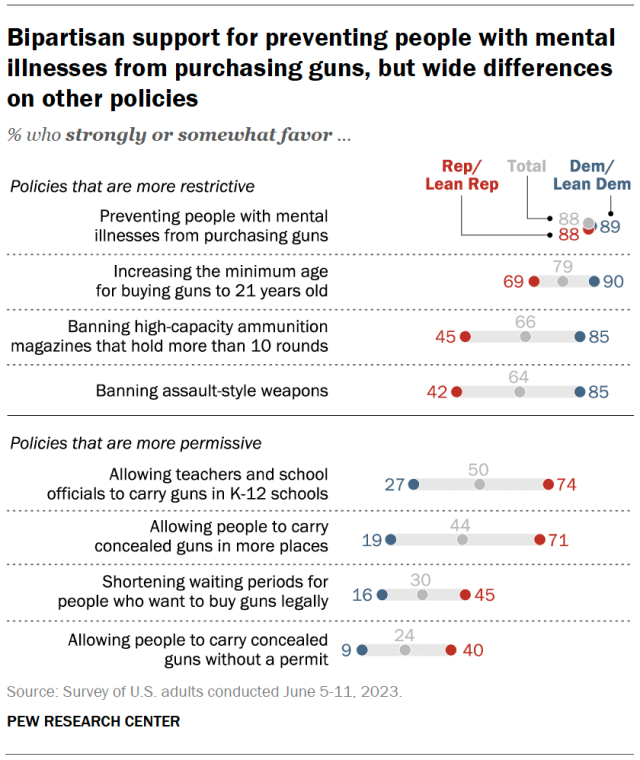
Republicans and Democrats differ on several other proposals. While 85% of Democrats favor banning both assault-style weapons and high-capacity ammunition magazines that hold more than 10 rounds, majorities of Republicans oppose these proposals (57% and 54%, respectively).
Most Republicans, on the other hand, support allowing teachers and school officials to carry guns in K-12 schools (74%) and allowing people to carry concealed guns in more places (71%). These proposals are supported by just 27% and 19% of Democrats, respectively.
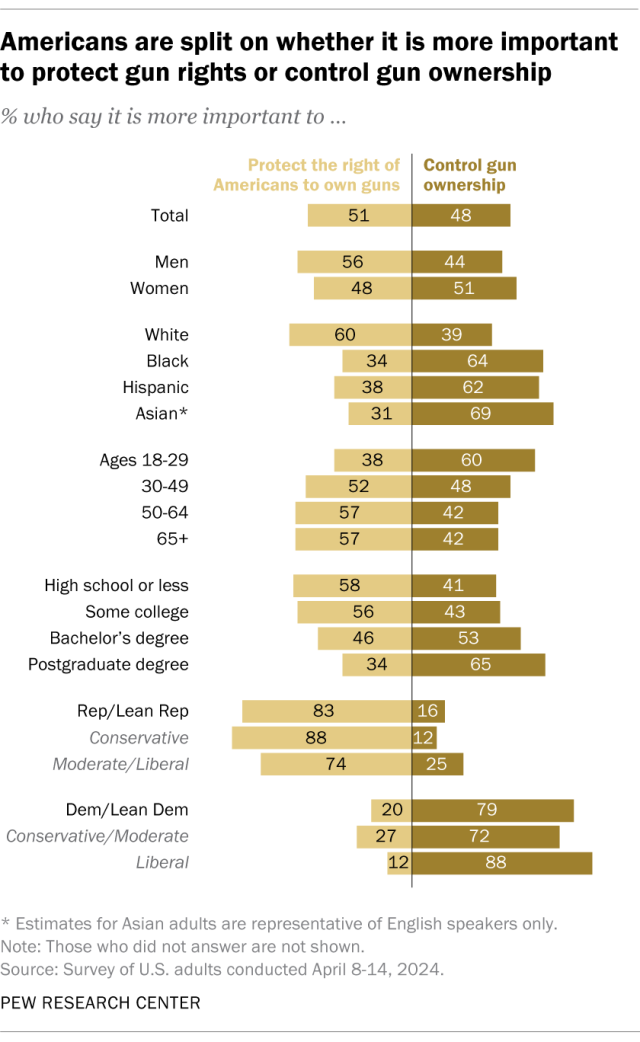
The public remains closely divided over whether it’s more important to protect gun rights or control gun ownership, according to an April 2024 survey . Overall, 51% of U.S. adults say it’s more important to protect the right of Americans to own guns, while a similar share (48%) say controlling gun ownership is more important.
Views have shifted slightly since 2022, when we last asked this question. That year, 47% of adults prioritized protecting Americans’ rights to own guns, while 52% said controlling gun ownership was more important.
Views on this topic differ sharply by party. In the most recent survey, 83% of Republicans say protecting gun rights is more important, while 79% of Democrats prioritize controlling gun ownership.
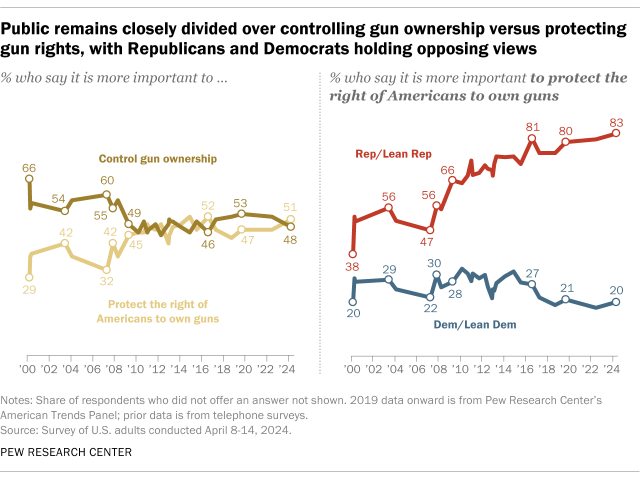
Americans are slightly more likely to say gun ownership does more to increase safety than to decrease it. Around half of Americans (52%) say gun ownership does more to increase safety by allowing law-abiding citizens to protect themselves, while a slightly smaller share (47%) say gun ownership does more to reduce safety by giving too many people access to firearms and increasing misuse. Views were evenly divided (49% vs. 49%) when we last asked in 2023.
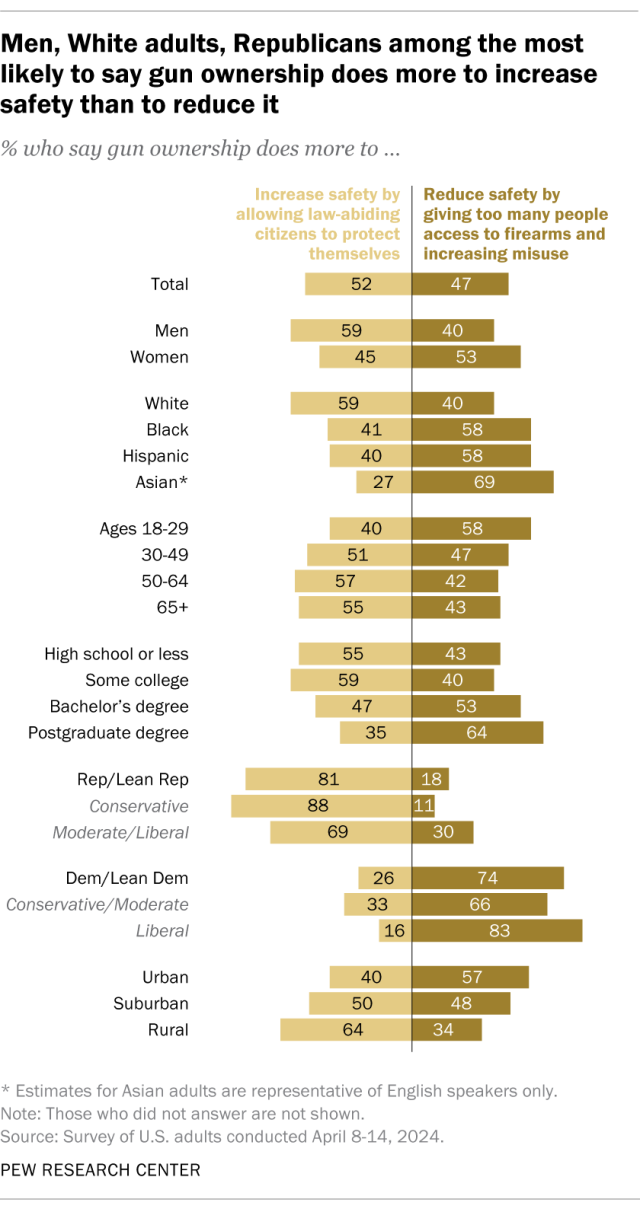
Republicans and Democrats differ widely on this question: 81% of Republicans say gun ownership does more to increase safety, while 74% of Democrats say it does more to reduce safety.
Rural and urban Americans also have starkly different views. Among adults who live in rural areas, 64% say gun ownership increases safety, while among those in urban areas, 57% say it reduces safety. Those living in the suburbs are about evenly split in their views.
More than half of U.S. adults say an increase in the number of guns in the country is bad for society, according to the April 2024 survey. Some 54% say, generally, this is very or somewhat bad for society. Another 21% say it is very or somewhat good for society, and a quarter say it is neither good nor bad for society.
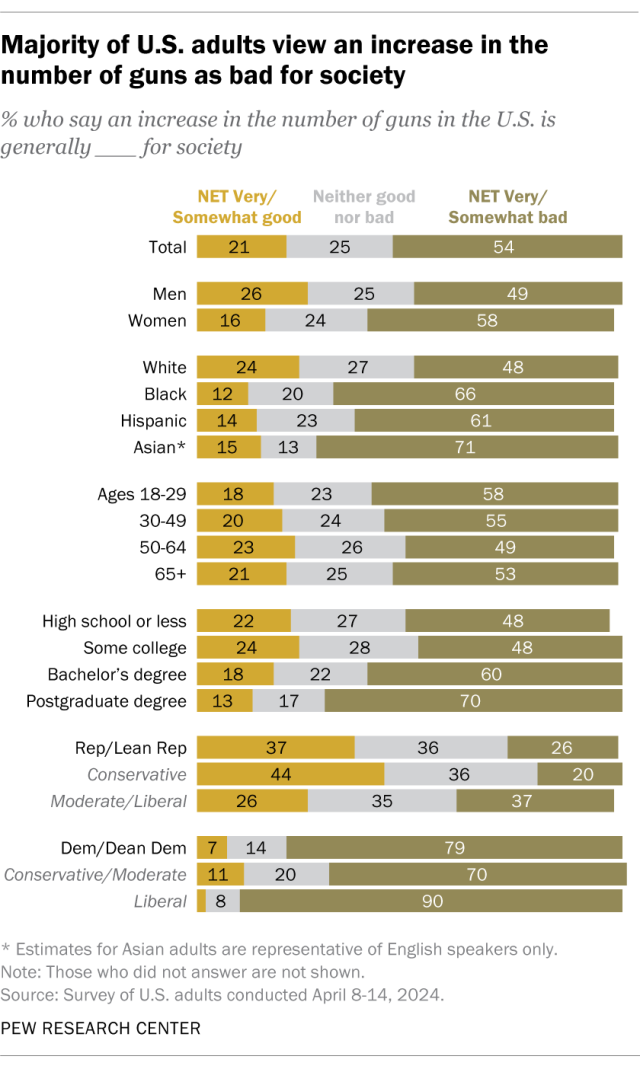
About half of Americans (49%) see gun violence as a major problem, according to a May 2024 survey. This is down from 60% in June 2023, but roughly on par with views in previous years. In the more recent survey, 27% say gun violence is a moderately big problem, and about a quarter say it is either a small problem (19%) or not a problem at all (4%).
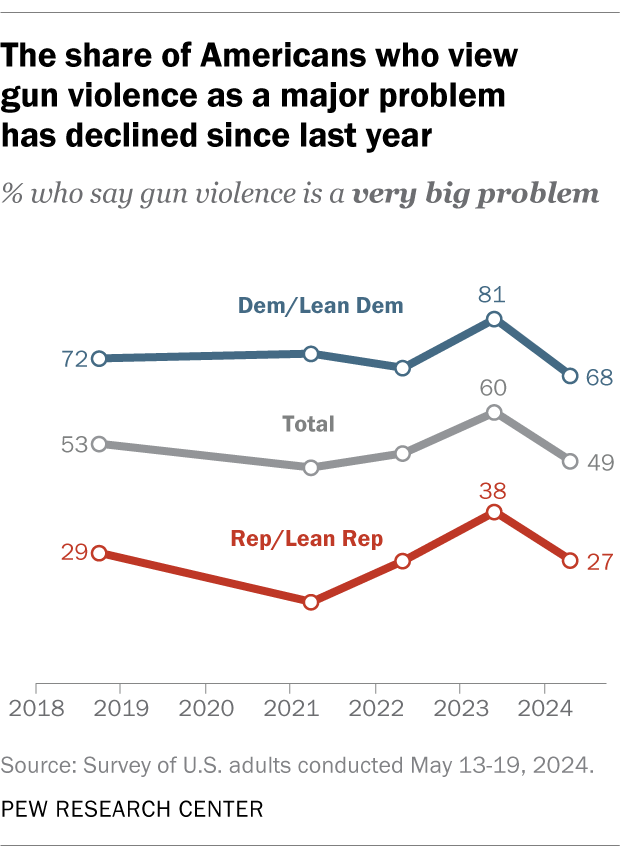
A majority of public K-12 teachers (59%) say they are at least somewhat worried about the possibility of a shooting ever happening at their school, including 18% who are very or extremely worried, according to a fall 2023 Center survey of teachers . A smaller share of teachers (39%) say they are not too or not at all worried about a shooting occurring at their school.
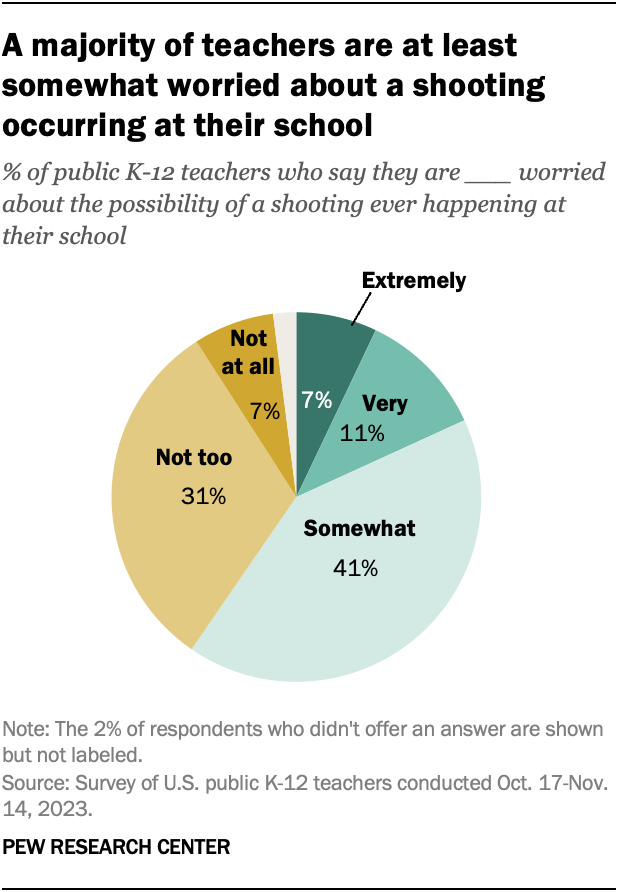
School shootings are a concern for K-12 parents as well: 32% say they are very or extremely worried about a shooting ever happening at their children’s school, while 37% are somewhat worried, according to a fall 2022 Center survey of parents with at least one child younger than 18 who is not homeschooled. Another 31% of K-12 parents say they are not too or not at all worried about this.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published on Jan. 5, 2016 .
- Partisanship & Issues
- Political Issues

Katherine Schaeffer is a research analyst at Pew Research Center .
Americans’ Extreme Weather Policy Views and Personal Experiences
U.s. adults under 30 have different foreign policy priorities than older adults, many adults in east and southeast asia support free speech, are open to societal change, nato seen favorably in member states; confidence in zelenskyy down in europe, u.s., same-sex marriage around the world, most popular.
901 E St. NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20004 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
Today’s best savings rates
The fed’s decisions impact savings accounts. here’s how , factors to consider when choosing the right savings account , methodology, best savings rates today -- now’s the time to score a high apy, july 25, 2024.
This may be the last hurrah for APYs ahead of the Fed's anticipated rate cuts.

Liliana Hall
Associate Writer
Liliana Hall is a writer for CNET Money covering banking, credit cards and mortgages. Previously, she wrote about personal credit for Bankrate and CreditCards.com. She is passionate about providing accessible content to enhance financial literacy. She graduated from the University of Texas at Austin with a bachelor's degree in journalism, and has worked in the newsrooms of KUT and the Austin Chronicle. When not working, she is probably paddle boarding, hopping on a flight or reading for her book club.
Kelly Ernst
Kelly is an editor for CNET Money focusing on banking. She has over 10 years of experience in personal finance and previously wrote for CBS MoneyWatch covering banking, investing, insurance and home equity products. She is passionate about arming consumers with the tools they need to take control of their financial lives. In her free time, she enjoys binging podcasts, scouring thrift stores for unique home décor and spoiling the heck out of her dogs.
CNET staff -- not advertisers, partners or business interests -- determine how we review the products and services we cover. If you buy through our links, we may get paid.
Key Takeaways
- The best high-yield savings accounts offer APYs up to 5.45%.
- Experts predict the Fed will cut rates later this year.
- Even when rates fall, a high-yield savings account allows you to earn significantly more than you would with a traditional savings account.
Federal Reserve rate cuts might be right around the corner, but you can still grow your money faster with one of today’s best high-yield savings accounts .
“Now is a good time for savers to open a high-yield savings account before rates potentially drop,” said Justin Haywood , certified financial planner and president and co-founder of Haywood Wealth Management. “It’s important for consumers to take advantage of current high rates to maximize their savings returns while the favorable conditions last.”
Whether you want to grow your emergency fund or start a sinking fund , the best high-yield savings accounts currently earn up to 5.45% annual percentage yield, or APY. That’s more than 10 times the national average . Read on to learn where you can find today’s top savings rates.
Here are some of the top savings account APYs available right now:
| My Banking Direct | 5.45% | $500 |
| Newtek Bank | 5.25% | $0 |
| 5.25% | $0 | |
| TAB Bank | 5.02% | $0 |
| 4.75% | $0 | |
| 4.25% | $0 | |
| Discover Bank | 4.25% | $0 |
| Ally Bank | 4.20% | $0 |
Experts recommend comparing rates before opening a savings account to get the best APY possible. You can enter your information below to see CNET’s partners’ rates in your area.
Savings rates are variable, which means banks can change the rate on your savings account at any time. The Federal Reserve doesn’t directly impact savings rates, but its decisions do impact them.
When the Fed raises the federal funds rate -- the interest rate US banks use to lend or borrow money to each other overnight -- banks tend to increase their rates for savings accounts to boost their cash reserves and remain competitive. Inversely, when the Fed lowers rates, banks drop savings rates, too.
Starting in March 2022, the Fed raised rates 11 times to fight record inflation. However, as inflation began cooling in late 2023, the Fed paused rates at its last seven Federal Open Market Committee meetings. As a result, savings rates remained attractive, barely budging for months.
But experts expect the Fed could begin cutting rates as early as September. And we’re already starting to see banks lower APYs in anticipation. My Banking Direct dropped its high-yield savings account APY from 5.55% to 5.45% on July 12, and TAB Bank dropped its rate from 5.27% to 5.02% on July 17.
Here’s where savings rates stand compared to last week:
| 4.86% | -0.20% | 0.45% |
Smart Money Advice on the Topics That Matter to You
CNET Money brings financial insights, trends and news to your inbox every Wednesday.
By signing up, you will receive newsletters and promotional content and agree to our Terms of Use and acknowledge the data practices in our Privacy Policy . You may unsubscribe at any time.
Your new Subscription
Here’s all of the excitement headed to your inbox.
It pays to look for accounts with attractive APYs. But don’t stop there. Other important factors you should consider before choosing a savings account include:
- Minimum deposit requirements: Some HYSAs require a minimum amount to open an account -- typically, from $25 to $100. Others don’t require anything.
- ATM access: Not every bank offers cash deposits and withdrawals. If you need regular ATM access, check to see if your bank offers ATM fee reimbursements or a wide range of in-network ATMs, said Mohip.
- Fees: Look out for fees for monthly maintenance, withdrawals and paper statements, said Mohip. The charges can eat into your balance.
- Accessibility: If you prefer in-person assistance, look for a bank with physical branches. If you’re comfortable managing your money digitally, consider an online bank.
- Withdrawal limits: Some banks charge an excess withdrawal fee if you make more than six monthly withdrawals. If you think you may need to make more, consider a bank without this limit.
- Federal deposit insurance: Make sure your bank or credit union is either insured with the FDIC or the NCUA. This way, your money is protected up to $250,000 per account holder, per category, if there’s a bank failure.
- Customer service: Choose a bank that’s responsive and makes it easy to get help with your account if you need it. Read online customer reviews and contact the bank’s customer service to get a feel for working with the bank.
CNET reviewed savings accounts at more than 50 traditional and online banks, credit unions and financial institutions with nationwide services. Each account received a score between one (lowest) and five (highest). The savings accounts listed here are all insured up to $250,000 per person, per account category, per institution, by the FDIC or NCUA.
CNET evaluates the best savings accounts using a set of established criteria that compares annual percentage yields, monthly fees, minimum deposits or balances and access to physical branches. None of the banks on our list charge monthly maintenance fees. An account will rank higher for offering any of the following perks:
- Account bonuses
- Automated savings features
- Wealth management consulting/coaching services
- Cash deposits
- Extensive ATM networks and/or ATM rebates for out-of-network ATM use
A savings account may be rated lower if it doesn’t have an easy-to-navigate website or if it doesn’t offer helpful features like an ATM card. Accounts that impose restrictive residency requirements or fees for exceeding monthly transaction limits may also be rated lower.
Recommended Articles
Best high-yield savings accounts for july 2024, the magic of compound interest is helping double my savings in one year, us prices drop slightly in june, raising hopes for interest rate cuts in september, savings and cd rates won’t go much higher, experts say. here’s what that means for your money, when will the fed cut rates three experts answer the burning question, how to start an emergency fund, even if you have no savings right now.
CNET editors independently choose every product and service we cover. Though we can’t review every available financial company or offer, we strive to make comprehensive, rigorous comparisons in order to highlight the best of them. For many of these products and services, we earn a commission. The compensation we receive may impact how products and links appear on our site.
Writers and editors and produce editorial content with the objective to provide accurate and unbiased information. A separate team is responsible for placing paid links and advertisements, creating a firewall between our affiliate partners and our editorial team. Our editorial team does not receive direct compensation from advertisers.
CNET Money is an advertising-supported publisher and comparison service. We’re compensated in exchange for placement of sponsored products and services, or when you click on certain links posted on our site. Therefore, this compensation may impact where and in what order affiliate links appear within advertising units. While we strive to provide a wide range of products and services, CNET Money does not include information about every financial or credit product or service.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To recap, the "Big 5" assessment criteria include: Topic originality and novelty. Value and significance. Access to data and equipment. Time requirements. Ethical compliance. Be sure to grab a copy of our free research topic evaluator sheet here to fast-track your topic selection process.
Select a topic. Choosing an interesting research topic is your first challenge. Here are some tips: Choose a topic that you are interested in! The research process is more relevant if you care about your topic. Narrow your topic to something manageable. If your topic is too broad, you will find too much information and not be able to focus.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Research Topic Personal Interest and Passion: Passion is the fuel that drives perseverance and dedication. Choosing a research topic aligned with one's interests fosters genuine enthusiasm, making the journey more enjoyable and sustaining motivation throughout the often lengthy process.
The biggest mistake you can make, however, is choosing a position before you start your research. Instead, the information you consult should inform your position. Researching before choosing a position is also much easier; you will be able to explore all sides of a topic rather than limiting yourself to one.
Step 1: Check the requirements. Step 2: Choose a broad field of research. Step 3: Look for books and articles. Step 4: Find a niche. Step 5: Consider the type of research. Step 6: Determine the relevance. Step 7: Make sure it's plausible. Step 8: Get your topic approved. Other interesting articles.
Step 2: Brainstorm Your Topics. You aren't doing research at this stage yet. You are only trying to make considerations to determine which topic will suit your research assignment. The brainstorming stage isn't difficult at all. It should take only a couple of hours or a few days depending on how you approach.
Or even just because the faculty give funding for it. Nonetheless, in literature, proponents of the 'science-society-me' framework emphasise individual researcher's interest in the topic -in the ...
Choosing a research topic; Finding inspiration; Preliminary research helps you learn more about your possible topic; Finding out more about your topic can help inspire your idea; Topic scope is crucial to a successful research paper; Techniques for narrowing a topic; 5W Example;
Let's discuss a few key factors to consider when choosing a research topic that aligns with your passion, expertise, and research goals in this blog. A Well-Chosen Research Topic Can Make or Break Your Project. If you want to conduct a successful research project, it is imperative to pick a good research topic, regardless of your field or ...
Questions emerge; 2. Models are developed; 2. 3. Models are quantified; 4. Models are analyzed and their nature and importance are assessed; and 5. Models are tested. Numbers 1 and 2 are the usual province of qualitative research. The phenomena around a research question are explored in an effort to understand how to conceptualize its elements.
You may choose a topic at the beginning of the process, and through exploring the research that has already been done, one's own interests that are narrowed or expanded in scope, the topic will change over time (Dwarkadas & Lin, 2019). ... Finding a research topic. Computing Research Association for Women, Portland State University. https ...
Before diving into how to choose a research topic, it is important to think about what are some elements of a good research topic. Of course, this will depend specifically on your research project, but a good research topic will always: Relate to the assignment itself. Even when you have a choice for your research topic, you still want to make ...
Break down your research topic into smaller components and observe what categories and subdivisions emerge. Consider the causes and implications of change as well as emerging trends if your research topic is subject to change, such as a politician's career or crime statistics. Place your topic within the perspectives and methods of inquiry ...
Here are some options to consider when narrowing the scope of your paper: Theoretical approach : Limit your topic to a particular approach to the issue. For example, if your topic concerns cloning, examine the theories surrounding of the high rate of failures in animal cloning. Aspect or sub-area : Consider only one piece of the subject.
Getting Started. Choosing a topic is the first and maybe the most important step of the research and writing process! This step will determine the rest of your steps -- what your thesis statement is, what sources you use, and how to write your paper. So it's important to make sure you choose a strong and engaging topic.
Data accessibility; The researcher would choose the issue if the desired data were available. Urgency; A defining factor in the choice of a research problem is urgency, priority must be given to urgent issues because they may benefit from quick solutions. Feasibility; A key consideration in choosing the research problem is feasibility, the ...
These books have chapters on choosing and refining a topic. Research papers for dummies by Woods, Geraldine. Call Number: LB1047.3 .W66 2002. ISBN: 0764554263. This book is on the 3rd floor of the library at the Southern & Dobson campus.
As such, you need to choose a research topic that interests you so as to keep you motivated during those days when you feel like giving up (and those days will be many). 2. The interests of your school's faculty ... the less time you will have for the actual research. Consider the above 7 factors, settle on your topic and hit the road running ...
When I say "topic", I am referring to the narrow / specific topic. For example: "Status of Diplomats In International Law". These are the factors that influence what topic you choose for research: Purpose (your course / specialisation / research project / target journal) Your guide. Your interest.
choose a topic that will enable you to read and understand the literature. ensure that the topic is manageable and that material is available. make a list of key words. be flexible. define your ...
A number of factors contribute to how well people adapt to adversities, including the ways in which individuals view and engage with the world, the availability and quality of social resources, and specific coping strategies. Psychological research demonstrates that the resources and skills associated with resilience can be cultivated and ...
Ms. Joy Ann A. Mendoza shares her expertise in considering and choosing a research topic. Subscribe to our channel to receive more updates.
Appropriate subject matter: Another factor to consider when choosing a research topic; is the subject matter. Some topics which should not be considered in choosing a topic for research are topics that are too broad, too narrow, or too obscure. Topics that are too broad may lack focus and result in superficial findings, while topics that are ...
There are several factors to consider when choosing a research topic, including: Relevance: Choose a topic that is relevant to your field of study or to current events and social issues. Interest: Choose a topic that you are passionate about and that you find interesting. This will help keep you motivated throughout the research process.
Things to compare and consider Manuscript suitability - scope and topic. Does the journal publish your article type and research topic? Seth Schwartz recommends browsing a recent issue of the journal to determine whether any of the articles are similar in scope or type to the paper you are planning to write. Checking the editorial board can ...
About four-in-ten U.S. adults say they live in a household with a gun, including 32% who say they personally own one, according to a Center survey conducted in June 2023.These numbers are virtually unchanged since the last time we asked this question in 2021. There are differences in gun ownership rates by political affiliation, gender, community type and other factors.
Other important factors you should consider before choosing a savings account include: Minimum deposit requirements: Some HYSAs require a minimum amount to open an account -- typically, from $25 ...
When selecting cryptocurrencies for binary trading, traders should consider several factors: Volatility: Higher volatility can mean higher potential profits, but it also comes with increased risk.