Essay Papers Writing Online
Mastering the art of writing a 4-paragraph essay for academic success.

Writing a well-structured essay can be a challenging task for many students, but breaking it down into smaller, manageable parts can make the process much easier. In this step-by-step guide, we will walk you through the essential tips for crafting a 4 paragraph essay that will impress your readers.
The key to a successful essay lies in its organization and coherence. By following a structured format and paying attention to the content of each paragraph, you can effectively convey your ideas and arguments in a clear and concise manner.
Whether you’re writing a persuasive, informative, or analytical essay, the basic structure remains the same. Each paragraph serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall thesis of your essay. With the right approach and attention to detail, you can craft a compelling and persuasive piece of writing that will leave a lasting impression on your readers.

Understanding the Essay Structure
Before diving into the writing process, it is crucial to understand the basic structure of a 4 paragraph essay. An essay typically consists of an introduction, two body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Introduction: The introduction is where you present your topic and provide a clear thesis statement that outlines the main idea of your essay. This section should grab the reader’s attention and set the tone for the rest of the essay.
Body Paragraphs: The body paragraphs expand on the main points mentioned in the thesis statement. Each paragraph should focus on a single idea and include supporting evidence and examples to strengthen your argument.
Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes the main points discussed in the essay and restates the thesis in a new way. It is essential to leave the reader with a sense of closure and demonstrate the significance of the topic.
Brainstorming and Outlining Your Ideas
Before you start writing your 4 paragraph essay, it’s crucial to brainstorm and outline your ideas. This process will help you organize your thoughts and create a structured plan for your essay.
Brainstorming: Begin by jotting down all the ideas and points you want to cover in your essay. Consider the main topic, key arguments, and supporting evidence you plan to include. Don’t worry about structure at this stage; just focus on generating ideas.
Tip: Use techniques like mind mapping or listing to help you brainstorm effectively. Be creative and allow different ideas to flow freely.
Outlining: Once you have a list of ideas, create an outline for your essay. Start with a thesis statement that summarizes the main point of your essay. Then, outline the key points you will address in each paragraph. This will serve as a roadmap for your writing and ensure a logical flow of ideas.
Tip: Use Roman numerals or bullet points to structure your outline. Include topic sentences that introduce each paragraph’s main idea and provide a clear progression of your argument.
Developing Body Paragraphs with Evidence and Analysis
When crafting the body paragraphs of your 4 paragraph essay, it is essential to include specific evidence and analysis to support your thesis statement. Each body paragraph should focus on a single point or idea that relates to your overall argument. To strengthen your argument, you should include relevant examples, facts, quotes, or data to provide concrete evidence for your claims.
After presenting your evidence, it is crucial to analyze and explain how it supports your main argument. Your analysis should demonstrate the significance of the evidence and its relevance to your thesis statement. By providing thoughtful analysis, you can help your reader understand the connections between your evidence and your overall argument.
Additionally, make sure to properly cite any sources you use in your body paragraphs to avoid plagiarism and to give credit to the original authors. Including citations will also add credibility to your essay and show that you have conducted thorough research to support your claims.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.

What this handout is about
This handout will help you understand how paragraphs are formed, how to develop stronger paragraphs, and how to completely and clearly express your ideas.
What is a paragraph?
Paragraphs are the building blocks of papers. Many students define paragraphs in terms of length: a paragraph is a group of at least five sentences, a paragraph is half a page long, etc. In reality, though, the unity and coherence of ideas among sentences is what constitutes a paragraph. A paragraph is defined as “a group of sentences or a single sentence that forms a unit” (Lunsford and Connors 116). Length and appearance do not determine whether a section in a paper is a paragraph. For instance, in some styles of writing, particularly journalistic styles, a paragraph can be just one sentence long. Ultimately, a paragraph is a sentence or group of sentences that support one main idea. In this handout, we will refer to this as the “controlling idea,” because it controls what happens in the rest of the paragraph.
How do I decide what to put in a paragraph?
Before you can begin to determine what the composition of a particular paragraph will be, you must first decide on an argument and a working thesis statement for your paper. What is the most important idea that you are trying to convey to your reader? The information in each paragraph must be related to that idea. In other words, your paragraphs should remind your reader that there is a recurrent relationship between your thesis and the information in each paragraph. A working thesis functions like a seed from which your paper, and your ideas, will grow. The whole process is an organic one—a natural progression from a seed to a full-blown paper where there are direct, familial relationships between all of the ideas in the paper.
The decision about what to put into your paragraphs begins with the germination of a seed of ideas; this “germination process” is better known as brainstorming . There are many techniques for brainstorming; whichever one you choose, this stage of paragraph development cannot be skipped. Building paragraphs can be like building a skyscraper: there must be a well-planned foundation that supports what you are building. Any cracks, inconsistencies, or other corruptions of the foundation can cause your whole paper to crumble.
So, let’s suppose that you have done some brainstorming to develop your thesis. What else should you keep in mind as you begin to create paragraphs? Every paragraph in a paper should be :
- Unified : All of the sentences in a single paragraph should be related to a single controlling idea (often expressed in the topic sentence of the paragraph).
- Clearly related to the thesis : The sentences should all refer to the central idea, or thesis, of the paper (Rosen and Behrens 119).
- Coherent : The sentences should be arranged in a logical manner and should follow a definite plan for development (Rosen and Behrens 119).
- Well-developed : Every idea discussed in the paragraph should be adequately explained and supported through evidence and details that work together to explain the paragraph’s controlling idea (Rosen and Behrens 119).
How do I organize a paragraph?
There are many different ways to organize a paragraph. The organization you choose will depend on the controlling idea of the paragraph. Below are a few possibilities for organization, with links to brief examples:
- Narration : Tell a story. Go chronologically, from start to finish. ( See an example. )
- Description : Provide specific details about what something looks, smells, tastes, sounds, or feels like. Organize spatially, in order of appearance, or by topic. ( See an example. )
- Process : Explain how something works, step by step. Perhaps follow a sequence—first, second, third. ( See an example. )
- Classification : Separate into groups or explain the various parts of a topic. ( See an example. )
- Illustration : Give examples and explain how those examples support your point. (See an example in the 5-step process below.)
Illustration paragraph: a 5-step example
From the list above, let’s choose “illustration” as our rhetorical purpose. We’ll walk through a 5-step process for building a paragraph that illustrates a point in an argument. For each step there is an explanation and example. Our example paragraph will be about human misconceptions of piranhas.
Step 1. Decide on a controlling idea and create a topic sentence
Paragraph development begins with the formulation of the controlling idea. This idea directs the paragraph’s development. Often, the controlling idea of a paragraph will appear in the form of a topic sentence. In some cases, you may need more than one sentence to express a paragraph’s controlling idea.
Controlling idea and topic sentence — Despite the fact that piranhas are relatively harmless, many people continue to believe the pervasive myth that piranhas are dangerous to humans.
Step 2. Elaborate on the controlling idea
Paragraph development continues with an elaboration on the controlling idea, perhaps with an explanation, implication, or statement about significance. Our example offers a possible explanation for the pervasiveness of the myth.
Elaboration — This impression of piranhas is exacerbated by their mischaracterization in popular media.
Step 3. Give an example (or multiple examples)
Paragraph development progresses with an example (or more) that illustrates the claims made in the previous sentences.
Example — For example, the promotional poster for the 1978 horror film Piranha features an oversized piranha poised to bite the leg of an unsuspecting woman.
Step 4. Explain the example(s)
The next movement in paragraph development is an explanation of each example and its relevance to the topic sentence. The explanation should demonstrate the value of the example as evidence to support the major claim, or focus, in your paragraph.
Continue the pattern of giving examples and explaining them until all points/examples that the writer deems necessary have been made and explained. NONE of your examples should be left unexplained. You might be able to explain the relationship between the example and the topic sentence in the same sentence which introduced the example. More often, however, you will need to explain that relationship in a separate sentence.
Explanation for example — Such a terrifying representation easily captures the imagination and promotes unnecessary fear.
Notice that the example and explanation steps of this 5-step process (steps 3 and 4) can be repeated as needed. The idea is that you continue to use this pattern until you have completely developed the main idea of the paragraph.
Step 5. Complete the paragraph’s idea or transition into the next paragraph
The final movement in paragraph development involves tying up the loose ends of the paragraph. At this point, you can remind your reader about the relevance of the information to the larger paper, or you can make a concluding point for this example. You might, however, simply transition to the next paragraph.
Sentences for completing a paragraph — While the trope of the man-eating piranhas lends excitement to the adventure stories, it bears little resemblance to the real-life piranha. By paying more attention to fact than fiction, humans may finally be able to let go of this inaccurate belief.
Finished paragraph
Despite the fact that piranhas are relatively harmless, many people continue to believe the pervasive myth that piranhas are dangerous to humans. This impression of piranhas is exacerbated by their mischaracterization in popular media. For example, the promotional poster for the 1978 horror film Piranha features an oversized piranha poised to bite the leg of an unsuspecting woman. Such a terrifying representation easily captures the imagination and promotes unnecessary fear. While the trope of the man-eating piranhas lends excitement to the adventure stories, it bears little resemblance to the real-life piranha. By paying more attention to fact than fiction, humans may finally be able to let go of this inaccurate belief.
Troubleshooting paragraphs
Problem: the paragraph has no topic sentence.
Imagine each paragraph as a sandwich. The real content of the sandwich—the meat or other filling—is in the middle. It includes all the evidence you need to make the point. But it gets kind of messy to eat a sandwich without any bread. Your readers don’t know what to do with all the evidence you’ve given them. So, the top slice of bread (the first sentence of the paragraph) explains the topic (or controlling idea) of the paragraph. And, the bottom slice (the last sentence of the paragraph) tells the reader how the paragraph relates to the broader argument. In the original and revised paragraphs below, notice how a topic sentence expressing the controlling idea tells the reader the point of all the evidence.
Original paragraph
Piranhas rarely feed on large animals; they eat smaller fish and aquatic plants. When confronted with humans, piranhas’ first instinct is to flee, not attack. Their fear of humans makes sense. Far more piranhas are eaten by people than people are eaten by piranhas. If the fish are well-fed, they won’t bite humans.
Revised paragraph
Although most people consider piranhas to be quite dangerous, they are, for the most part, entirely harmless. Piranhas rarely feed on large animals; they eat smaller fish and aquatic plants. When confronted with humans, piranhas’ first instinct is to flee, not attack. Their fear of humans makes sense. Far more piranhas are eaten by people than people are eaten by piranhas. If the fish are well-fed, they won’t bite humans.
Once you have mastered the use of topic sentences, you may decide that the topic sentence for a particular paragraph really shouldn’t be the first sentence of the paragraph. This is fine—the topic sentence can actually go at the beginning, middle, or end of a paragraph; what’s important is that it is in there somewhere so that readers know what the main idea of the paragraph is and how it relates back to the thesis of your paper. Suppose that we wanted to start the piranha paragraph with a transition sentence—something that reminds the reader of what happened in the previous paragraph—rather than with the topic sentence. Let’s suppose that the previous paragraph was about all kinds of animals that people are afraid of, like sharks, snakes, and spiders. Our paragraph might look like this (the topic sentence is bold):
Like sharks, snakes, and spiders, piranhas are widely feared. Although most people consider piranhas to be quite dangerous, they are, for the most part, entirely harmless . Piranhas rarely feed on large animals; they eat smaller fish and aquatic plants. When confronted with humans, piranhas’ first instinct is to flee, not attack. Their fear of humans makes sense. Far more piranhas are eaten by people than people are eaten by piranhas. If the fish are well-fed, they won’t bite humans.
Problem: the paragraph has more than one controlling idea
If a paragraph has more than one main idea, consider eliminating sentences that relate to the second idea, or split the paragraph into two or more paragraphs, each with only one main idea. Watch our short video on reverse outlining to learn a quick way to test whether your paragraphs are unified. In the following paragraph, the final two sentences branch off into a different topic; so, the revised paragraph eliminates them and concludes with a sentence that reminds the reader of the paragraph’s main idea.
Although most people consider piranhas to be quite dangerous, they are, for the most part, entirely harmless. Piranhas rarely feed on large animals; they eat smaller fish and aquatic plants. When confronted with humans, piranhas’ first instinct is to flee, not attack. Their fear of humans makes sense. Far more piranhas are eaten by people than people are eaten by piranhas. A number of South American groups eat piranhas. They fry or grill the fish and then serve them with coconut milk or tucupi, a sauce made from fermented manioc juices.
Problem: transitions are needed within the paragraph
You are probably familiar with the idea that transitions may be needed between paragraphs or sections in a paper (see our handout on transitions ). Sometimes they are also helpful within the body of a single paragraph. Within a paragraph, transitions are often single words or short phrases that help to establish relationships between ideas and to create a logical progression of those ideas in a paragraph. This is especially likely to be true within paragraphs that discuss multiple examples. Let’s take a look at a version of our piranha paragraph that uses transitions to orient the reader:
Although most people consider piranhas to be quite dangerous, they are, except in two main situations, entirely harmless. Piranhas rarely feed on large animals; they eat smaller fish and aquatic plants. When confronted with humans, piranhas’ instinct is to flee, not attack. But there are two situations in which a piranha bite is likely. The first is when a frightened piranha is lifted out of the water—for example, if it has been caught in a fishing net. The second is when the water level in pools where piranhas are living falls too low. A large number of fish may be trapped in a single pool, and if they are hungry, they may attack anything that enters the water.
In this example, you can see how the phrases “the first” and “the second” help the reader follow the organization of the ideas in the paragraph.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Lunsford, Andrea. 2008. The St. Martin’s Handbook: Annotated Instructor’s Edition , 6th ed. New York: St. Martin’s.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
1. The Introduction
2. a strong thesis statement, 3. topic sentence, 4. structuring the body paragraphs, 5. the conclusion, how to write a 4-paragraph essay.
Used at all levels of education, the four paragraph essay offers a basic format that enables writers to present information in a concise manner. A four paragraph essay is an acceptable format for many types of essays, including cause and effect and compare and contrast essays. The four-paragraph essay consists of an introduction, two body paragraphs and a conclusion. Each paragraph in the essay requires specific information in order for readers to follow a logical flow of information.
The four-paragraph essay consists of an introduction, two body paragraphs and a conclusion.
Begin this paragraph with a “hook” that will make readers interested in your essay.
The University of Maryland University College recommends using:
- a surprising statement or statistic,
- personal story
- or rhetorical question.
Avoid the overused and unoriginal dictionary definition opening. After the opener, provide background information on the topic, which should tell readers the purpose of the essay, as well as what they should expect to read.
A thesis statement provides readers with a condensed version of the analysis or argument that you will discuss in the essay. These are typically one or two sentences, and are located at the end of the introduction paragraph.
A strong thesis statement avoids vague language and is specific and argumentative.
- The topic sentence announces the main focus of the paragraph by stating one of the arguments identified in the thesis statement.
- Provide supporting sentences that offer evidence for your claim.
- End the paragraph with your own observation or analysis.
Your body paragraphs should consist of a clear topic sentence, quotes, and explanations of the supporting evidence you have found. This is where you have the chance to prove your thesis to your reader. In order to do this, you must have strong evidence that supports the claim you are trying to make.
- Rephrase your thesis statement in the concluding paragraph, stating how it has been proven throughout the body paragraphs.
- The conclusion should have a summary of the essay’s main arguments and an explanation on how they are connected.
- Lastly, explain why the topic of your essay is important and why it should matter to the readers.
- University of Maryland University College: Introductions; 2010
- Indiana University: Thesis Statement; Jan. 2008
- University of Maryland University College: Conclusion
i am a writer
11 Rules for Essay Paragraph Structure (with Examples)

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
How do you structure a paragraph in an essay?
If you’re like the majority of my students, you might be getting your basic essay paragraph structure wrong and getting lower grades than you could!
In this article, I outline the 11 key steps to writing a perfect paragraph. But, this isn’t your normal ‘how to write an essay’ article. Rather, I’ll try to give you some insight into exactly what teachers look out for when they’re grading essays and figuring out what grade to give them.
You can navigate each issue below, or scroll down to read them all:
1. Paragraphs must be at least four sentences long 2. But, at most seven sentences long 3. Your paragraph must be Left-Aligned 4. You need a topic sentence 5 . Next, you need an explanation sentence 6. You need to include an example 7. You need to include citations 8. All paragraphs need to be relevant to the marking criteria 9. Only include one key idea per paragraph 10. Keep sentences short 11. Keep quotes short
Paragraph structure is one of the most important elements of getting essay writing right .
As I cover in my Ultimate Guide to Writing an Essay Plan , paragraphs are the heart and soul of your essay.
However, I find most of my students have either:
- forgotten how to write paragraphs properly,
- gotten lazy, or
- never learned it in the first place!
Paragraphs in essay writing are different from paragraphs in other written genres .
In fact, the paragraphs that you are reading now would not help your grades in an essay.
That’s because I’m writing in journalistic style, where paragraph conventions are vastly different.
For those of you coming from journalism or creative writing, you might find you need to re-learn paragraph writing if you want to write well-structured essay paragraphs to get top grades.
Below are eleven reasons your paragraphs are losing marks, and what to do about it!

Essay Paragraph Structure Rules
1. your paragraphs must be at least 4 sentences long.
In journalism and blog writing, a one-sentence paragraph is great. It’s short, to-the-point, and helps guide your reader. For essay paragraph structure, one-sentence paragraphs suck.
A one-sentence essay paragraph sends an instant signal to your teacher that you don’t have much to say on an issue.
A short paragraph signifies that you know something – but not much about it. A one-sentence paragraph lacks detail, depth and insight.
Many students come to me and ask, “what does ‘add depth’ mean?” It’s one of the most common pieces of feedback you’ll see written on the margins of your essay.
Personally, I think ‘add depth’ is bad feedback because it’s a short and vague comment. But, here’s what it means: You’ve not explained your point enough!
If you’re writing one-, two- or three-sentence essay paragraphs, you’re costing yourself marks.
Always aim for at least four sentences per paragraph in your essays.
This doesn’t mean that you should add ‘fluff’ or ‘padding’ sentences.
Make sure you don’t:
a) repeat what you said in different words, or b) write something just because you need another sentence in there.
But, you need to do some research and find something insightful to add to that two-sentence paragraph if you want to ace your essay.
Check out Points 5 and 6 for some advice on what to add to that short paragraph to add ‘depth’ to your paragraph and start moving to the top of the class.
- How to Make an Essay Longer
- How to Make an Essay Shorter
2. Your Paragraphs must not be more than 7 Sentences Long
Okay, so I just told you to aim for at least four sentences per paragraph. So, what’s the longest your paragraph should be?
Seven sentences. That’s a maximum.
So, here’s the rule:
Between four and seven sentences is the sweet spot that you need to aim for in every single paragraph.
Here’s why your paragraphs shouldn’t be longer than seven sentences:
1. It shows you can organize your thoughts. You need to show your teacher that you’ve broken up your key ideas into manageable segments of text (see point 10)
2. It makes your work easier to read. You need your writing to be easily readable to make it easy for your teacher to give you good grades. Make your essay easy to read and you’ll get higher marks every time.
One of the most important ways you can make your work easier to read is by writing paragraphs that are less than six sentences long.
3. It prevents teacher frustration. Teachers are just like you. When they see a big block of text their eyes glaze over. They get frustrated, lost, their mind wanders … and you lose marks.
To prevent teacher frustration, you need to ensure there’s plenty of white space in your essay. It’s about showing them that the piece is clearly structured into one key idea per ‘chunk’ of text.
Often, you might find that your writing contains tautologies and other turns of phrase that can be shortened for clarity.
3. Your Paragraph must be Left-Aligned
Turn off ‘Justified’ text and: Never. Turn. It. On. Again.
Justified text is where the words are stretched out to make the paragraph look like a square. It turns the writing into a block. Don’t do it. You will lose marks, I promise you! Win the psychological game with your teacher: left-align your text.
A good essay paragraph is never ‘justified’.
I’m going to repeat this, because it’s important: to prevent your essay from looking like a big block of muddy, hard-to-read text align your text to the left margin only.
You want white space on your page – and lots of it. White space helps your reader scan through your work. It also prevents it from looking like big blocks of text.
You want your reader reading vertically as much as possible: scanning, browsing, and quickly looking through for evidence you’ve engaged with the big ideas.
The justified text doesn’t help you do that. Justified text makes your writing look like a big, lumpy block of text that your reader doesn’t want to read.
What’s wrong with Center-Aligned Text?
While I’m at it, never, ever, center-align your text either. Center-aligned text is impossible to skim-read. Your teacher wants to be able to quickly scan down the left margin to get the headline information in your paragraph.
Not many people center-align text, but it’s worth repeating: never, ever center-align your essays.

Don’t annoy your reader. Left align your text.
4. Your paragraphs must have a Topic Sentence
The first sentence of an essay paragraph is called the topic sentence. This is one of the most important sentences in the correct essay paragraph structure style.
The topic sentence should convey exactly what key idea you’re going to cover in your paragraph.
Too often, students don’t let their reader know what the key idea of the paragraph is until several sentences in.
You must show what the paragraph is about in the first sentence.
You never, ever want to keep your reader in suspense. Essays are not like creative writing. Tell them straight away what the paragraph is about. In fact, if you can, do it in the first half of the first sentence .
I’ll remind you again: make it easy to grade your work. Your teacher is reading through your work trying to determine what grade to give you. They’re probably going to mark 20 assignments in one sitting. They have no interest in storytelling or creativity. They just want to know how much you know! State what the paragraph is about immediately and move on.
Suggested: Best Words to Start a Paragraph
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: Writing a Topic Sentence If your paragraph is about how climate change is endangering polar bears, say it immediately : “Climate change is endangering polar bears.” should be your first sentence in your paragraph. Take a look at first sentence of each of the four paragraphs above this one. You can see from the first sentence of each paragraph that the paragraphs discuss:
When editing your work, read each paragraph and try to distil what the one key idea is in your paragraph. Ensure that this key idea is mentioned in the first sentence .
(Note: if there’s more than one key idea in the paragraph, you may have a problem. See Point 9 below .)
The topic sentence is the most important sentence for getting your essay paragraph structure right. So, get your topic sentences right and you’re on the right track to a good essay paragraph.
5. You need an Explanation Sentence
All topic sentences need a follow-up explanation. The very first point on this page was that too often students write paragraphs that are too short. To add what is called ‘depth’ to a paragraph, you can come up with two types of follow-up sentences: explanations and examples.
Let’s take explanation sentences first.
Explanation sentences give additional detail. They often provide one of the following services:
Let’s go back to our example of a paragraph on Climate change endangering polar bears. If your topic sentence is “Climate change is endangering polar bears.”, then your follow-up explanation sentence is likely to explain how, why, where, or when. You could say:
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: Writing Explanation Sentences 1. How: “The warming atmosphere is melting the polar ice caps.” 2. Why: “The polar bears’ habitats are shrinking every single year.” 3. Where: “This is happening in the Antarctic ice caps near Greenland.” 4. When: “Scientists first noticed the ice caps were shrinking in 1978.”
You don’t have to provide all four of these options each time.
But, if you’re struggling to think of what to add to your paragraph to add depth, consider one of these four options for a good quality explanation sentence.
>>>RELATED ARTICLE: SHOULD YOU USE RHETORICAL QUESTIONS IN ESSAYS ?
6. Your need to Include an Example
Examples matter! They add detail. They also help to show that you genuinely understand the issue. They show that you don’t just understand a concept in the abstract; you also understand how things work in real life.
Example sentences have the added benefit of personalising an issue. For example, after saying “Polar bears’ habitats are shrinking”, you could note specific habitats, facts and figures, or even a specific story about a bear who was impacted.
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: Writing an ‘Example’ Sentence “For example, 770,000 square miles of Arctic Sea Ice has melted in the past four decades, leading Polar Bear populations to dwindle ( National Geographic, 2018 )
In fact, one of the most effective politicians of our times – Barrack Obama – was an expert at this technique. He would often provide examples of people who got sick because they didn’t have healthcare to sell Obamacare.
What effect did this have? It showed the real-world impact of his ideas. It humanised him, and got him elected president – twice!
Be like Obama. Provide examples. Often.
7. All Paragraphs need Citations
Provide a reference to an academic source in every single body paragraph in the essay. The only two paragraphs where you don’t need a reference is the introduction and conclusion .
Let me repeat: Paragraphs need at least one reference to a quality scholarly source .
Let me go even further:
Students who get the best marks provide two references to two different academic sources in every paragraph.
Two references in a paragraph show you’ve read widely, cross-checked your sources, and given the paragraph real thought.
It’s really important that these references link to academic sources, not random websites, blogs or YouTube videos. Check out our Seven Best types of Sources to Cite in Essays post to get advice on what sources to cite. Number 6 w ill surprise you!
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: In-Text Referencing in Paragraphs Usually, in-text referencing takes the format: (Author, YEAR), but check your school’s referencing formatting requirements carefully. The ‘Author’ section is the author’s last name only. Not their initials. Not their first name. Just their last name . My name is Chris Drew. First name Chris, last name Drew. If you were going to reference an academic article I wrote in 2019, you would reference it like this: (Drew, 2019).
Where do you place those two references?
Place the first reference at the end of the first half of the paragraph. Place the second reference at the end of the second half of the paragraph.
This spreads the references out and makes it look like all the points throughout the paragraph are backed up by your sources. The goal is to make it look like you’ve reference regularly when your teacher scans through your work.
Remember, teachers can look out for signposts that indicate you’ve followed academic conventions and mentioned the right key ideas.
Spreading your referencing through the paragraph helps to make it look like you’ve followed the academic convention of referencing sources regularly.
Here are some examples of how to reference twice in a paragraph:
- If your paragraph was six sentences long, you would place your first reference at the end of the third sentence and your second reference at the end of the sixth sentence.
- If your paragraph was five sentences long, I would recommend placing one at the end of the second sentence and one at the end of the fifth sentence.
You’ve just read one of the key secrets to winning top marks.
8. Every Paragraph must be relevant to the Marking Criteria
Every paragraph must win you marks. When you’re editing your work, check through the piece to see if every paragraph is relevant to the marking criteria.
For the British: In the British university system (I’m including Australia and New Zealand here – I’ve taught at universities in all three countries), you’ll usually have a ‘marking criteria’. It’s usually a list of between two and six key learning outcomes your teacher needs to use to come up with your score. Sometimes it’s called a:
- Marking criteria
- Marking rubric
- (Key) learning outcome
- Indicative content
Check your assignment guidance to see if this is present. If so, use this list of learning outcomes to guide what you write. If your paragraphs are irrelevant to these key points, delete the paragraph .
Paragraphs that don’t link to the marking criteria are pointless. They won’t win you marks.
For the Americans: If you don’t have a marking criteria / rubric / outcomes list, you’ll need to stick closely to the essay question or topic. This goes out to those of you in the North American system. North America (including USA and Canada here) is often less structured and the professor might just give you a topic to base your essay on.
If all you’ve got is the essay question / topic, go through each paragraph and make sure each paragraph is relevant to the topic.
For example, if your essay question / topic is on “The Effects of Climate Change on Polar Bears”,
- Don’t talk about anything that doesn’t have some connection to climate change and polar bears;
- Don’t talk about the environmental impact of oil spills in the Gulf of Carpentaria;
- Don’t talk about black bear habitats in British Columbia.
- Do talk about the effects of climate change on polar bears (and relevant related topics) in every single paragraph .
You may think ‘stay relevant’ is obvious advice, but at least 20% of all essays I mark go off on tangents and waste words.
Stay on topic in Every. Single. Paragraph. If you want to learn more about how to stay on topic, check out our essay planning guide .
9. Only have one Key Idea per Paragraph
One key idea for each paragraph. One key idea for each paragraph. One key idea for each paragraph.
Don’t forget!
Too often, a student starts a paragraph talking about one thing and ends it talking about something totally different. Don’t be that student.
To ensure you’re focussing on one key idea in your paragraph, make sure you know what that key idea is. It should be mentioned in your topic sentence (see Point 3 ). Every other sentence in the paragraph adds depth to that one key idea.
If you’ve got sentences in your paragraph that are not relevant to the key idea in the paragraph, they don’t fit. They belong in another paragraph.
Go through all your paragraphs when editing your work and check to see if you’ve veered away from your paragraph’s key idea. If so, you might have two or even three key ideas in the one paragraph.
You’re going to have to get those additional key ideas, rip them out, and give them paragraphs of their own.
If you have more than one key idea in a paragraph you will lose marks. I promise you that.
The paragraphs will be too hard to read, your reader will get bogged down reading rather than scanning, and you’ll have lost grades.
10. Keep Sentences Short
If a sentence is too long it gets confusing. When the sentence is confusing, your reader will stop reading your work. They will stop reading the paragraph and move to the next one. They’ll have given up on your paragraph.
Short, snappy sentences are best.
Shorter sentences are easier to read and they make more sense. Too often, students think they have to use big, long, academic words to get the best marks. Wrong. Aim for clarity in every sentence in the paragraph. Your teacher will thank you for it.
The students who get the best marks write clear, short sentences.
When editing your draft, go through your essay and see if you can shorten your longest five sentences.
(To learn more about how to write the best quality sentences, see our page on Seven ways to Write Amazing Sentences .)
11. Keep Quotes Short
Eighty percent of university teachers hate quotes. That’s not an official figure. It’s my guestimate based on my many interactions in faculty lounges. Twenty percent don’t mind them, but chances are your teacher is one of the eight out of ten who hate quotes.
Teachers tend to be turned off by quotes because it makes it look like you don’t know how to say something on your own words.
Now that I’ve warned you, here’s how to use quotes properly:
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: How To Use Quotes in University-Level Essay Paragraphs 1. Your quote should be less than one sentence long. 2. Your quote should be less than one sentence long. 3. You should never start a sentence with a quote. 4. You should never end a paragraph with a quote. 5 . You should never use more than five quotes per essay. 6. Your quote should never be longer than one line in a paragraph.
The minute your teacher sees that your quote takes up a large chunk of your paragraph, you’ll have lost marks.
Your teacher will circle the quote, write a snarky comment in the margin, and not even bother to give you points for the key idea in the paragraph.
Avoid quotes, but if you really want to use them, follow those five rules above.
I’ve also provided additional pages outlining Seven tips on how to use Quotes if you want to delve deeper into how, when and where to use quotes in essays. Be warned: quoting in essays is harder than you thought.

Follow the advice above and you’ll be well on your way to getting top marks at university.
Writing essay paragraphs that are well structured takes time and practice. Don’t be too hard on yourself and keep on trying!
Below is a summary of our 11 key mistakes for structuring essay paragraphs and tips on how to avoid them.
I’ve also provided an easy-to-share infographic below that you can share on your favorite social networking site. Please share it if this article has helped you out!
11 Biggest Essay Paragraph Structure Mistakes you’re probably Making
1. Your paragraphs are too short 2. Your paragraphs are too long 3. Your paragraph alignment is ‘Justified’ 4. Your paragraphs are missing a topic sentence 5 . Your paragraphs are missing an explanation sentence 6. Your paragraphs are missing an example 7. Your paragraphs are missing references 8. Your paragraphs are not relevant to the marking criteria 9. You’re trying to fit too many ideas into the one paragraph 10. Your sentences are too long 11. Your quotes are too long

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 19 Top Cognitive Psychology Theories (Explained)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 119 Bloom’s Taxonomy Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ All 6 Levels of Understanding (on Bloom’s Taxonomy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Self-Actualization Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy)
4 thoughts on “11 Rules for Essay Paragraph Structure (with Examples)”
Hello there. I noticed that throughout this article on Essay Writing, you keep on saying that the teacher won’t have time to go through the entire essay. Don’t you think this is a bit discouraging that with all the hard work and time put into your writing, to know that the teacher will not read through the entire paper?

Hi Clarence,
Thanks so much for your comment! I love to hear from readers on their thoughts.
Yes, I agree that it’s incredibly disheartening.
But, I also think students would appreciate hearing the truth.
Behind closed doors many / most university teachers are very open about the fact they ‘only have time to skim-read papers’. They regularly bring this up during heated faculty meetings about contract negotiations! I.e. in one university I worked at, we were allocated 45 minutes per 10,000 words – that’s just over 4 minutes per 1,000 word essay, and that’d include writing the feedback, too!
If students know the truth, they can better write their essays in a way that will get across the key points even from a ‘skim-read’.
I hope to write candidly on this website – i.e. some of this info will never be written on university blogs because universities want to hide these unfortunate truths from students.
Thanks so much for stopping by!
Regards, Chris
This is wonderful and helpful, all I say is thank you very much. Because I learned a lot from this site, own by chris thank you Sir.
Thank you. This helped a lot.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Pangram Solver
- Anagram Solver
- Rhyming Dictionary
- AI Title Generator
- Poem Title Generator
- Book Title Generator
- YouTube Title Generator
- Essay Title Generator
- Title Rewriter
- Title Capitalization
- Sentence & Paragraph Rewriter
- Essay Writer
- Book Title Wizard
- Random Movie Generator
- Fortune Cookie Generator
- Random European Country Generator
- Random Country Generator
- Empty and Invisible Character Generator – Blank ( ) Texts
- Random State Generator
- Prompts Generator
- Text Repeater (Add Text, Repeat, & Share)
- Speech Generator
- Character Name Generator
- Name Generators
- Pokemon Name Generator
- Character Backstory Generator
- Song Generator
- Poem Generator
- Word Search Puzzles
- Ideation Articles
- Random Topic Generator
- Writing Prompt Generator
- Random Essay Title Generator
- Writing Articles
- Online Word Counter
- Online Grammar Checker
- Headline Analyzer
- Best Book Writing Software and Book Writing Apps
- 150 Best Resources for Writers
- Productivity
- English Language
- Grammar Tips
- Headline Analyzer Tool
- Title Capitalization Rules
- For WordPress
- Publishing Articles
- Email Marketing
- Book Articles
- How to Get A Book Published
- Best Literary Agencies
- How To Self Publish a Book
How Many Sentences in a Paragraph & Words in a Paragraph?
A common question that you may ask while writing an essay for an assignment is how many sentences should you include in a paragraph. This is especially important if you’re trying to reach a minimum number of words or paragraphs.
Table of Contents
How Many Sentences Should a Paragraph Have?
In general, paragraphs should have 5-8 sentences. In this case, if you’re tasked with writing a five-paragraph essay , then you should want 25-40 sentences total. However, that’s not a hard and fast rule. After all, you can’t evaluate a good paragraph in words or sentences.
So how many sentences should you write in a paragraph? To know that, you need to determine what your readers want to see in your writings as different readers may have different expectations from you.
How Many Words in a Paragraph?
A paragraph typically has 75-160 words. With an average of 15-20 words per sentence and 5-8 sentences in a paragraph, this comes to approximately 75 to 160 words. However, this will depend on the expectations of your audience. See the next section for what teachers usually recommend.
A lot of teachers and educators suggest that a paragraph section should be around 100 to 200 words long or no more than 5 to 6 sentences. This is regardless of font size and other stylistic choices.
A good rule of thumb is to express your idea in the first sentence or two, and in the next 3 to 4 sentences, provide information that supports your main idea. In the final sentence, come with a meaningful conclusion.
Generally, teachers expect longer paragraphs because they want to observe whether or not you have the required knowledge on the subject. They know it won’t be easier for you to showcase your understanding of the topic in a sentence or two.
How Many Words in a Sentence?
A sentence usually has 15-20 words on average. Therefore, a paragraph with 5-6 sentences should be Sentences longer than this should be broken up into separate sentences. Otherwise, they may become run-on sentences.
When Should You Use Shorter Paragraphs?
A short paragraph consists of just two or three sentences. Shorter paragraphs are generally easier for readers to digest and encourage skimming. Solid blocks of text are often difficult to consume and parse, especially when speed reading. Perhaps, this is the reason the majority of popular books have short paragraphs.
New authors also prefer to use shorter paragraphs in their writing. Not only does it help them provide information concisely, but it is also an excellent way to grasp the readers’ attention.
Commercial writers like to keep the paragraph length between three to four sentences. When they write a 1000 to 1500 words long post, they use a lot of subheadings to separate paragraphs and make them more precise.
So, if you’re a blogger or copywriter, keep your blog post paragraphs shorter so that your target audience can read your post attentively and separate paragraphs with clear subheadings so that readers can skim. The additional white space created by paragraph breaks and headers makes it easy for the reader’s eyes to consume the important parts.
Regardless of what’s the size of your paragraph, it must include key elements that include: Unity, Order, Coherence, and Completeness.
Let’s know about these elements in brief in the following list.
- Unity: Your paragraph must have a single complete thought that should also be observed in all its sentences.
- Order: It refers to the method you structure your supporting sentences. As per your requirement, you may follow the order of importance or chronological order. However, your end goal should be to make your paragraph easy to read.
- Coherence: It is the quality that makes your paragraph easy to understand. Sentences within your paragraph must be connected and work together as a whole.
- Completeness: Completeness is achieved when all your paragraphs are effortlessly supporting the main idea. Such paragraphs are considered complete.
Shorter paragraphs fo make it easier for readers, but the length of your paragraph will depend on the type of writing. Academic writing will differ from commercial writing which in turn differs from book writing.
How to Write a Perfect Paragraph
First, it’s essential to understand what makes a good paragraph? Remember, a good paragraph must consist of a key sentence, a few supporting sentences, and a closing phrase.
When you organize your passage following this structure, your paragraph gives your readers a clear and concise message.
Check out some quick tips to write a great paragraph below.
Don’t Leave Any of Your Sentences Behind
When writing a paragraph, the aim of your first sentence should be to get the reader to read the next sentence.
Unfortunately, a lot of new writers fail to pay attention to this. By the fourth and fifth sentences, their interest starts dropping off.
Give a quick revision to your paragraph as soon as you complete it. If you have a sentence in your passage that doesn’t push your readers to the next line, expel it immediately. It won’t do any good for your paragraph.
Create Connection Between Sentences
Make a connection between different sentences within your paragraph. Your paragraph must stick to one single point from beginning to end. When you start a new paragraph, don’t forget to refer back to the last sentence of your previous paragraph.
Start New Paragraph Carefully
A lot of new writers have confusion about when they should start a new paragraph. It’s straightforward. Every time you start a new idea or point, start it in a new paragraph. However, your new paragraph must embrace the main purpose of your theme or subject.
Ending a Paragraph
A good paragraph must end with a closing sentence summarizing the concepts of your paragraph. Your conclusion must emphasize the point of the paragraph providing a sense of closure.
If you’re writing an expository essay that compares or contrasts something, you must connect to that approach in the concluding sentence.
Use Transition Words
Though it is a good idea to break up big chunks of text to make it easier to digest for readers, you shouldn’t neglect the connections between sentences. Transition words such as Therefore, Accordingly, Consequently, Hence, So, etc. help you connect the sentences to other ideas in the passage.
Additionally, they allow your readers to understand your ideas and easily relate to them. Transition words are quite useful for bloggers who usually focus on a singular purpose at a time.
Besides transitions, you can also use pronouns such as ” they” and “these” to enhance the flow of your writing.
Final Thoughts
If you look around, you find that the concept of paragraphs with 5 to 8 sentences is prevalent. However, there is still an ongoing debate. Some experts say that 2 to 3 sentences per passage are optimal while others say 5 to 7 sentences make a perfect paragraph.
So, how long should a paragraph be? The answer is: it depends.
Always remember that if you’re into professional writing, you should stick to 3 to 5 sentences per paragraph.
On the contrary, if you are a student and writing to pass a school or university course, it is good to ask your teacher about their expectations. Rather than following a general rule, you should try to learn your readers’ choice and tailor your writings accordingly.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

What Is a Hero’s Journey?

Antagonist vs Villain: What’s the Difference?

26 Best Writing Tools of 2024

11 Best Plagiarism Tools 2024

Best Tablets for Writers 2024: A Buying Guide
![Grammarly vs. ProWritingAid Review: Which One Is Better? [2024 Review + 20% Discount] grammarly vs prowritingaid](https://capitalizemytitle.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/grammarly-vs-prowritingaid-218x150.png)
Grammarly vs. ProWritingAid Review: Which One Is Better? [2024 Review + 20% Discount]
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Accessibility
Forgot your password?
Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive mail with link to set new password.
Back to login
Fix These Common Headline Mistakes
FREE EMAIL BONUS
Learn how to spot the 5 most common mistakes and fix them before you publish.
5 Secrets to Writing Great Titles
Proven techniques for attention grabbing headlines & titles
CHEAT SHEET FOR
How to Write Great Headlines
Begin your writing journey with us.
Daily Writing Tips
How many sentences in a paragraph.

A DWT reader, exasperated by an online newspaper article formatted as eleven one-sentence “paragraphs,” asks for a definition of “paragraph” and wants to know how long a paragraph should be.
A paragraph is a unit of thought that develops an idea. A traditional paragraph contains a topic sentence that states the idea to be developed, plus additional sentences that develop the idea stated by the topic sentence.
A newspaper lead (or lede if you prefer) can do its job in one sentence, but with few exceptions, a paragraph will contain more than one sentence. The OWL site, aimed at college students, suggests a length of from three to five or more sentences.
We all know that online writing calls for techniques different from those of the print media. Web readers do not tolerate long expanses of text. They expect short paragraphs, subheads, and bulleted lists. Nevertheless, they require the organization and coherence that paragraphs provide.
The article that prompted this post is an instructive example of a badly-organized piece which would have benefited from placing related ideas in paragraphs. Take a look and see what you think.
Eleven-sentence/paragraph story OWL on paragraphs
Stop making those embarrassing mistakes! Subscribe to Daily Writing Tips today!
You will improve your English in only 5 minutes per day, guaranteed!
Each newsletter contains a writing tip, word of the day, and exercise!
You'll also get three bonus ebooks completely free!

30 thoughts on “How Many Sentences in a Paragraph?”
I’ve always felt that a paragraph should be at least three sentences: one subject sentence plus two or three sentences that expand on the subject’s thought.
“A subject sentence is the most important sentence in a paragraph. It provides the main idea behind the paragraph. There is no hard and fast rule for the order in which it will appear amongst the other sentences. Sometimes it can be the last sentence in the paragraph, used to drive the idea home conclusively.”
Thank you, Maeve.
Yes it’s a terribly written piece. But that’s not to say single sentence paragraphs don’t have their place. They’re just another tool in the writer’s arsenal. Perhaps their application is what requires the discussion.
Great site.
Was going to comment, but I felt so strongly about this issue I was inspired to respond on my own blog.
I took several years of journalism classes in college and they actually teach you NOT to write big paragraphs. To journalism teachers a one sentence paragraph is perfectly acceptable.
That article you mention though is awful. You need to balance those one sentence paragraphs with a 2-3 sentence ones if you want it to be an article and not a list.
Clare, Thanks for the link. I read your post (which has planted seeds of future posts of my own). I agree with your itemized list of outdated rules such as not ending a sentence with a preposition or never splitting an infinitive. I don’t agree that paragraphing belongs in that category.
We’ll have to agree to disagree on the paragraph question, but I’m glad my post has inspired ideas for future posts. I look forward to reading them – and commenting on them, of course!
Newspaper “English” has nothing to do with fine writing techniques and style.
Newspaper “English” seeks to pack the most information into the least amount of space, which means eliminating as many uppercase letters as possible, cutting out commas and periods, and placing modifiers before the nouns and verbs, which also saves commas and spaces.
The width of the newspaper column is equally as important, which might be only two inches wide, and rarely wider than three inches. Adding spaces means knocking text onto the next line, and that’s a waste of space and money.
An example newspaper sentence: Beloved long-time Frederick HS football coach John Jones died today in a fiery car wreck along US Hwy 37 around 9 pm in a collision with a stalled cattle truck whose trailer extended into the inside traffic lane.
But when a newspaper story goes on-line, there are other considerations, which is usually too much space to fill. That’s why every sentence is treated like a whole paragraph.
I’m sorry—I wasn’t finished.
In an “on-line” story, the goal is to have the reader scroll down down down until all the advertising banners have been made visible, so the text is extended by making every sentence stand alone.
Advertising, in print or on-line, pays for the medium. And it’s a tough market these days for the advertisers, because their success depends on the contents of the medium. Lose 30-40% of your readers (due to content) and advertisers will fall off accordingly.
Cassie, I stand corrected. “Badly written” it is.
We’ll throw in our two cents (don’t we always?).
How many sentences does a paragraph need? At least one.
Here are 2 bits quoted from our training manual, with some additional commentary:
a. One paragraph = one central idea. Has someone ever said to you, “Hey, you’ve got a good point there”? Well, that’s what your paragraph does. It makes a point, one point, which is the central idea of the paragraph. You might think of it as the purpose for the paragraph. That one point of a paragraph may be supported by several other ideas, and the paragraph, itself, may be written to support a broader idea, but its purpose remains the same. It stands alone as the vehicle to express one complete idea to the reader.
What is the idea expressed by the paragraph? The length of your paragraph depends on the complexity of that idea and its scope. When you have completed discussing that idea, stop. If you haven’t completed the discussion, keep going.
b. Perhaps you had an English teacher tell you that a paragraph must have a thesis statement at the beginning. This is partially true. It must have a thesis statement. Your thesis statement is the point you are trying to communicate, but you have a couple of choices about its placement: beginning and end. You can start with the central idea and then build the internal and external supports, or you can provide the supports and lead up to your point.
Long paragraphs become manageable to the reader and to the writer when the supporting ideas are relevant to the main idea and are paced appropriately with context sentences, discussion, and an impact statement (but that’s a different article, I believe).
FYI: Henry David Thoreau used long paragraphs very effectively. See . As an exercise, identify the single main idea of each paragraph. Then find the supporting ideas by their context sentences, discussion, and impact statements. Have fun!
I used to proofread for a court reporting service (that produced, e.g., deposition transcripts).
The hard-and-fast rule there was to create a new paragraph once the testimony, as transcribed, ran over 5-7 lines. It was more about readability than expressing ideas in a paragraph block. Actually, I kind of enjoyed the challenge of interpreting testimony and defining paragraphs on my own.
And, there’s something to be said for readability — similar to the type of Web writing that Maeve pointed out.
(Oh, and I do believe it’s “a badly written piece,” without the hyphen. Yes? :-))
A paragraph should more precisely contain a central thought correlated to the preceeding paragraph (title if it is the first para).
If you wish to change the direction of your thought, or bring in a new dimension to your writing; you ought to know how to play with a paragraphs.
A very long paragraph is bad and so is a very small one., but nothing is rigid when it comes to writing.
So, experiment more and create newer styles.
As a journalism student I would argue that there are instances where the one par sentence is required. In news articles this is the standard form. Furthermore pars should not be arranged by topic in this structure, but by the most important information down to the least important.
Having said that, the telegraph article is indeed not the highest standard of writing – and as a part time Sub Editor I am left wondering who checks their page titles: “Coman jailed for murdering author.”
hi please write me a parapraph in this topic “What make success,luck or struggle?” hurry please
As long as necessary but not a word longer!
another one-sentence-a-paragarph article
how many??????????
Merriam-Webster defines a paragraph as: 1 a : a subdivision of a written composition that consists of one or more sentences, deals with one point or gives the words of one speaker, and begins on a new usually indented line b : a short composition or note that is complete in one paragraph 2 : a character (as ¶) used to indicate the beginning of a paragraph and as a reference mark
Most college professors prefer paragraphs that contain three or more sentences, but a one sentence paragraph is correct, and acceptable. I have not read the newspaper article that this post is about. But I can’t imagine a piece being comprised of eleven paragraphs, made up of one sentence each, holding any integrity.
I teach college freshman English, and a main body paragraph ranges from 7-10 sentences. A paragraph should never go over one page double-spaced typed. One of the problems students have is not developing paragraphs adequately. A good thesuarus helps students write better paragraphs.
I am freelance writer and a subscriber of DWT. In one of my assignments, the editor asked me to write environmentally friendly instead of environment friendly. Can any one please clarify what’s the difference and what is the correct usage. Thanks in advance.
I don`t understand how to write paragraph about Algonquin.
I think a paragraph should at least be 4-5 sentences long. If any shorter than you can’t really discuss what is in each paragraph.
A paragraph is 5 sentences
Thanks for all the comments- they help a lot. Most people were saying that you have to have at least eight sentences to make a paragraph!!! So this was a relief to find.
I find it funny how many of you advocating multiple-sentence paragraphs wrote paragraphs of one sentence. You can’t just make up rules, folks. Well, I guess you can, but no one is obligated to follow them. I don’t care if you “think” a paragraph should be so many sentences, and I struggle with a teacher of college English who states with authority that “a main body paragraph ranges from 7-10 sentences.” It DOES? Says you. In my experience teaching writing, paragraphs in formal essays are usually better if they have at least three sentences. But it depends on a number of factors. In fiction, paragraphs are commonly a single sentence. Flip open any novel and I bet you find a single-sentence paragraph somewhere on the page. Check the dialogue.
We can talk about what makes a good, thorough paragraph, but why must we resort to simplistic rules? It’s not helpful.
A typical paragraph should have which of these (a) At least five paragraphs (b)At least two simple sentences (c)At most four complex sentences and(d) At least one topic sentences
Brian W, I was just thinking exactly that! I especially like Austin Chadd’s 2-sentence paragraph, telling us that every paragraph should be at least 4-5 sentences long. And TFP’s, right at the top, that uses a 1-sentence paragraph to propose that every paragraph needs 2-3 sentences.
A paragraph should have as many words and sentences as it takes to express its concept or idea. No more, no less.
One of my writing mentors suggested between eight to ten sentences to a paragraph. While I have tried my best to follow this, I notice that in business writing it is not always the case. On-line searches I did a few minutes ago had one person saying that a paragraph should have at least three sentences.
I personally prefer paragraphs of 5 sentences or more in research papers and professional writing. I picked this guidance up from a middle or high school teacher, and it stuck. For me, this guidance means that I am fully thinking through and developing my concepts. Further, I like for the density of my paragraphs to appear consistent.
However, I think that 3 -5 sentences may work better for the digital medium, where the organisation of content should favour improved “readability” for less-formal audiences… and for folks reading on mobile devices.
I have noticed that my writing style changes depending on the device in hand. For instance, if I am typing an e-mail to a colleague on my computer, I tend towards a more formal style. If I am typing on my mobile, I tend towards a more informal (text-message) style.
Looking through the commends above, we all seem to be organising more for “readability”.
The rules are contextual.
Leave a Comment
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Blog • Perfecting your Craft
Posted on Mar 13, 2024
How Many Sentences Are in a Paragraph?
In most forms of writing, paragraphs tend to be around four to eight sentences long . This general range will vary depending on the type of writing in question and the effect the writer is aiming to achieve.
In this guide, we’ll look at the length of paragraphs in various types of writing and see what determines whether they should be 20 sentences long, or stand alone as single sentences.
Which writing app is right for you?
Find out here! Takes 30 seconds
A paragraph should be as long as it needs to be
Reedsy editor Rebecca Heyman says a paragraph generally begins when a new idea is introduced. “A single sentence can stand on its own as a paragraph if its treatment of a specific theme or motif is complete. Conversely, denser, more complex topics may require a substantial number of sentences to adequately unpack meaning.” For example, in this very paragraph that you’re reading right now, we’re dealing with a fairly abstract concept which requires multiple sentences for clarification. In other words, a paragraph should be as long as it needs to be in order to convey its point.

Let’s now examine this idea from different perspectives, and look at how writers use paragraph breaks for different purposes.
In nonfiction, paragraphs tend to be longer
In nonfiction , where the purpose of writing is often to explain new concepts and ideas, paragraphs tend to be a bit on the longer side. They will often introduce an idea, explore it, and then draw conclusions based on that exploration.
In this paragraph from Stefano Mancuso’s The Revolutionary Genius of Plants , he introduces, explores, and concludes upon the intelligence of plants:
Even though they have nothing akin to a central brain, plants exhibit unmistakable attributes of intelligence. They are able to perceive their surroundings with a greater sensitivity than animals do. They actively compete for the limited resources in the soil and atmosphere; they evaluate their circumstances with precision; they perform sophisticated cost-benefit analyses; and, finally, they define and then take appropriate adaptive actions in response to environmental stimuli. Plants embody a model that is much more durable and innovative than that of animals; they are the living representation of how stability and flexibility can be combined. Their modular, diffused construction is the epitome of modernity: a cooperative, shared structure without any command centers, able to flawlessly resist repeated catastrophic events without losing functionality and adapt very quickly to huge environmental changes.
The idea is established simply in the first sentence: “plants exhibit unmistakable attributes of intelligence”. Mancuso then elaborates on this idea by discussing their perceptual and analytical properties, before concluding that plants' intelligence is an example of innovative and durable adaptability to the environment.
You’ll see a similar pattern across nonfiction and other types of expository writing , whether you’re reading books on military history, self-help guides , or gardening manuals. Where the intention of the work is to inform or educate the reader, this tried-and-true way of structuring paragraphs allows information to be passed on in manageable chunks.
However, when you’re writing with the intention of telling a story in an enjoyable fashion, paragraph breaks tend to happen more often, and for different reasons.

Perfect your self-help manuscript
Work with a professional to take your book to the next level.
In fiction, they can be as short as a sentence
With artistic works of writing, where the focus is on storytelling providing the reader with a satisfying narrative experience , you will often see the greatest range of paragraph length within a single work. A novelist might have three pages of unbroken narrative, punctuated by a one-word paragraph.
In general, fiction writers will start a new paragraph whenever something new happens. For example:
Whenever dialogue or action switches between characters
In this extract from Gillian Flynn’s Gone Girl , the narrator, Nick, is being spoken to by his sister.
‘We were lost in the rain,’ she said in a voice that was pleading on the way to peeved. I finished the shrug. McMann’s, Nick. Remember, when we got lost in the rain in Chinatown[...]’
The first paragraph is a quick line of dialogue with a tag that indicates who is speaking. Nick then reacts with an action beat (his shrug) — which is in its own paragraph. Then there is another paragraph break to indicate that the next line is spoken once again by his sister.
In this context, paragraph breaks show the reader that we’re switching characters, allowing an author to avoid having to start every other sentence with “Margo said” or “I said”.

FREE COURSE
How to Write Believable Dialogue
Master the art of dialogue in 10 five-minute lessons.
When the narration changes between action and reflection
In a narrative, paragraph transitions can also be a way to indicate that the narrator is changing their perspective — often from describing the action of a scene, to remarking on a character’s thoughts or inner reactions.
In this passage from All Quiet on the Western Front , Erich Maria Remarque uses short paragraphs — sometimes single sentences — to paint an impressionistic vignette of a man’s death in the trenches.
But every gasp strips my heart bare. The dying man is the master of these hours, he has an invisible dagger to stab me with: the dagger of time and my own thoughts. I would give a lot for him to live. It is hard to lie here and have to watch and listen to him. By three in the afternoon he is dead. I breathe again. But only for a short time. Soon the silence seems harder for me to bear than the groans. I would even like to hear the gurgling again; in fits and starts, hoarse, sometimes a soft whistling noise and then hoarse and loud again.
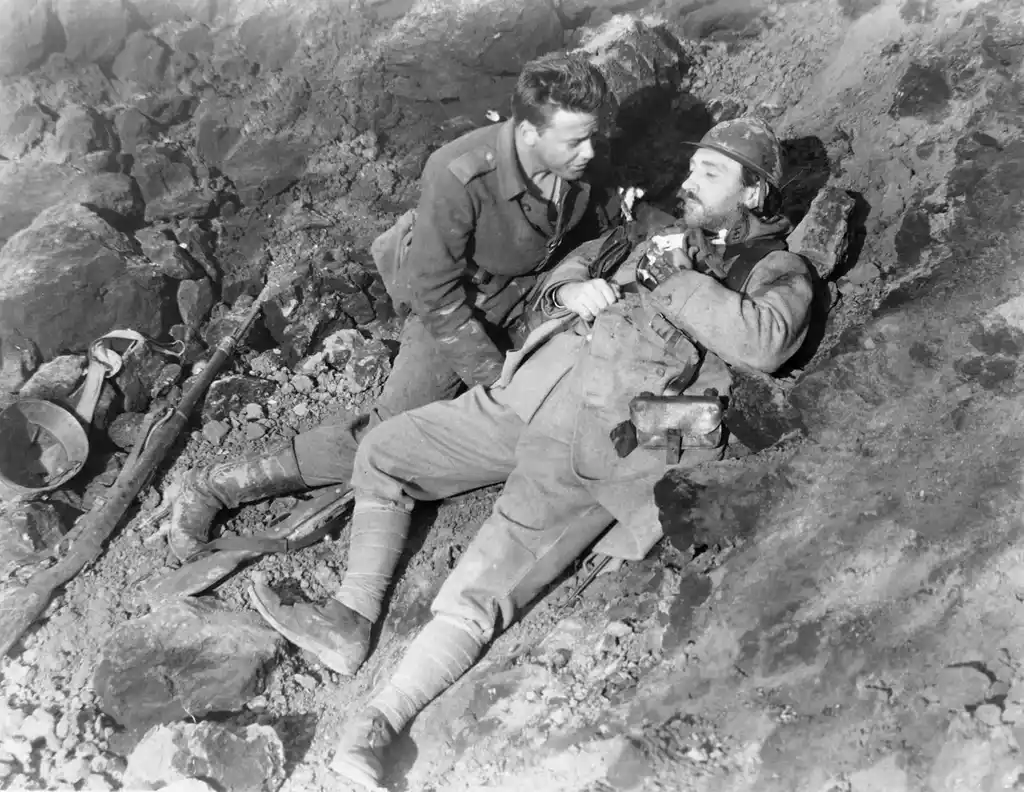

Remarque utilizes paragraph transitions to depict the shift in Paul’s ( the main character ) focus, moving from the immediate sensory details of the scene to his internal reflections and emotional turmoil. Paul’s desire for the dying man to live, juxtaposed with the harsh reality of death in wartime, highlights the juxtaposition between his internal empathy and the tragic experience of war.
Whenever there’s a time jump
Time jumps are often a good place to start a new paragraph to make it visually clear that some amount of time has passed. In this passage from Oliver Twist, Dickens starts a new paragraph to indicate time jumps.
They were sad rags, to tell the truth; and Oliver had never had a new suit before. One evening, about a week after the affair of the picture, as he was sitting talking to Mrs. Bedwin, there came a message down from Mr. Brownlow, that if Oliver Twist felt pretty well, he should like to see him in his study, and talk to him a little while.
Without a paragraph change, it would feel odd that the narrator is suddenly taking us forward by a week right in the middle of telling us about Oliver’s clothes. Instead, the paragraph break indicates that one part of the story is over and that the next part is about to begin.

GET ACCOUNTABILITY
Meet writing coaches on Reedsy
Industry insiders can help you hone your craft, finish your draft, and get published.
Paragraphs' length affects the pace of the writing
Paragraph length (along with sentence length) has a profound effect on the pace of one’s writing . A page or two of block paragraphs will take readers far longer to get through than several shorter paragraphs and often reflects whether something is occurring quickly or slowly within the narrative.
For example, in The Great Gatsby , Fitzgerald takes his time to describe a road that will play a significant role in the story.
‘About half way between West Egg and New York the motor-road hastily joins the railroad and runs beside it for a quarter of a mile, so as to shrink away from a certain desolate area of land. This is a valley of ashes—a fantastic farm where ashes grow like wheat into ridges and hills and grotesque gardens where ashes take the forms of houses and chimneys and rising smoke and finally, with a transcendent effort, of men who move dimly and already crumbling through the powdery air. Occasionally a line of gray cars crawls along an invisible track, gives out a ghastly creak and comes to rest, and immediately the ash-gray men swarm up with leaden spades and stir up an impenetrable cloud which screens their obscure operations from your sight.’
This longer style paragraph is used to great effect in representing this pastoral stretch of land between the party hubs of West Egg and New York City. Think of this long paragraph as the wide establishing shot in a movie, everything looks a bit slower from that perspective!
Equally, when Fitzgerald wants to pick up the pace, he uses shorter paragraphs, as seen in the following example:
‘What do you want money for, all of a sudden?’ ‘I’ve been here too long. I want to get away. My wife and I want to go west.’ ‘Your wife does!’ exclaimed Tom, startled. ‘She’s been talking about it for ten years.’ He rested for a moment against the pump, shading his eyes. ‘And now she’s going whether she wants to or not. I’m going to get her away.’ The coupé flashed by us with a flurry of dust and the flash of a waving hand. ‘What do I owe you?’ demanded Tom harshly. ‘I just got wised up to something funny the last two days,’ remarked Wilson. ‘That’s why I want to get away. That’s why I been bothering you about the car.’ ‘What do I owe you?’ ‘Dollar twenty.’
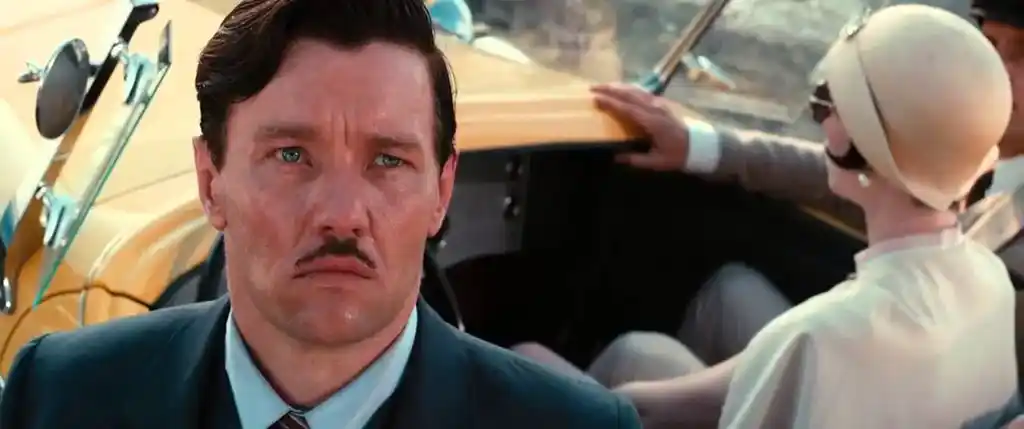

Tom realizes both his mistress and wife are slipping from his grasp (image: Warner Bros)
During this part of the novel, Tom Buchanan (the antagonist ) is feeling cornered as both his wife and mistress are slipping away from him. The short paragraphs in quick succession show his irritability, giving readers an insight into how unsettled he is. Even the coupé driven by Gatsby flashes by him, the speed of which is also heightened by use of short paragraphs.
Shorter paragraphs introduce more white space on the page, which accelerates the pace of reading. This can be used powerfully, as in the examples above, to match the narrative when fast, uncontrollable, or sudden events happen or to give readers a wide, slow, or sluggish feeling.
Many paragraphs later, we hope you found this helpful. If you’ve struggled with how to determine your paragraph lengths, know that it’s something that many writers find challenging! By roughly following the advice in this post you’ll be able to powerfully use varying paragraph lengths to hook readers throughout your work.
Continue reading
Recommended posts from the Reedsy Blog

450+ Powerful Adjectives to Describe a Person (With Examples)
Want a handy list to help you bring your characters to life? Discover words that describe physical attributes, dispositions, and emotions.

How to Plot a Novel Like a NYT Bestselling Author
Need to plot your novel? Follow these 7 steps from New York Times bestselling author Caroline Leavitt.

How to Write an Autobiography: The Story of Your Life
Want to write your autobiography but aren’t sure where to start? This step-by-step guide will take you from opening lines to publishing it for everyone to read.

What is the Climax of a Story? Examples & Tips
The climax is perhaps a story's most crucial moment, but many writers struggle to stick the landing. Let's see what makes for a great story climax.

What is Tone in Literature? Definition & Examples
We show you, with supporting examples, how tone in literature influences readers' emotions and perceptions of a text.

Writing Cozy Mysteries: 7 Essential Tips & Tropes
We show you how to write a compelling cozy mystery with advice from published authors and supporting examples from literature.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
We made a writing app for you
Yes, you! Write. Format. Export for ebook and print. 100% free, always.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How Many Sentences Should There Be in a Paragraph?

Ashley Shaw

There are a lot of writing rules out there, and they can be restricting, especially when they start to feel a little formulaic. If you’ve ever been told that a paragraph should always be at least three sentences long, but ideally five to seven, then you know what I mean.
Why does it have to be so specific?
The truth is that these rules are meant to be guidelines to make writing easier for you. If they start to do the opposite, though, they defeat the purpose.
How Long Should a Paragraph Be?
What do teachers want to see in a paragraph, how do i structure a paragraph, how long should an introduction paragraph be, what do you include in a conclusion paragraph, can a paragraph be one sentence.
So here is what you really need to know: There is no general rule for how long your paragraphs should be. In fact, you probably want to vary your lengths in order to make your writing feel less like a robot wrote it and more human-friendly. A good paragraph isn’t one that has a set amount of sentences. It’s one that has a good, focused idea.
So, in this post, I’m going to talk about what makes a good paragraph, regardless of length. However, despite what I just said, sometimes you just have to follow the formula, so I’ll also point out some best practices on paragraph length. While I am going to focus on academic papers, I’ll also talk about good paragraphs in web writing, professional writing, and fiction.
Before you start thinking about length, you should first start thinking about what makes a good paragraph . Throughout this section, I’ll be using a lot of food analogies, so you should probably grab a snack whilst you read.
A good paragraph is like a bite of a sandwich. If you bite off too much, then you might choke. However, if you just take a tiny little nibble, you will barely taste it at all. In the same way, if your paragraph has too much information in it, then it is just going to be confusing and hard to swallow (get it?). However, if there is only one sentence, then there won’t be enough meat to let your reader know what your point is. So, you have to find the balance between those two things.

There are many acronyms that help determine paragraph structure. In school, you might have learned something like ICE for body paragraphs, which stands for introduce, cite, and explain evidence. However, to fit my sandwich theme, I use MEAL or MEAT.
A good body paragraph in an academic paper should do one of these:
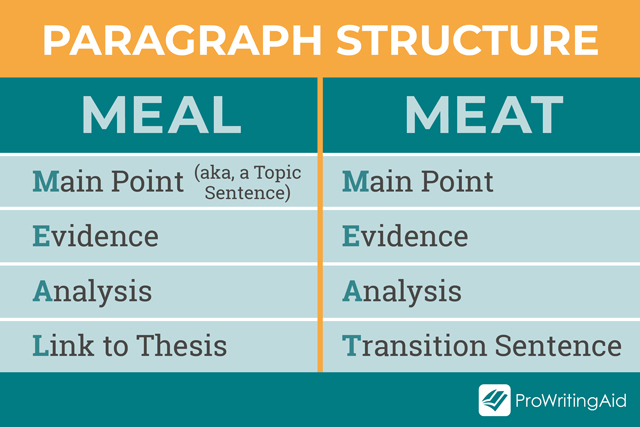
MEAL : Main Point , Evidence , Analysis , Link to Thesis
MEAT : Main Point , Evidence , Analysis , Transition Sentence
Only the last letters of these are different, so let’s talk a bit about what each acronym means.
A good paragraph should have a main point or topic sentence. This is kind of like a mini-thesis statement for your paragraph or the paragraph’s controlling idea. You should have a single controlling idea in your paragraph.
A good way to test this is to do what is called a reverse outline: Summarize each of your paragraphs into one simple topic sentence. (Don’t combine two sentences with a conjunction . That’s cheating!)
If you cannot get a complete sentence to sum up your paragraph, then it is too short. If you can’t fit the point into one sentence, then you likely have two main ideas, which should be broken into multiple paragraphs.
After you get the topic sentence of the paragraph, you need some supporting sentences to help you prove your claim. This is where your outside sources come into the picture. You can put in a sentence or two explaining how you know your main sentence is true.
Don’t just put evidence up without explaining how it proves your point. Somebody might read the same quote, data, or theory as you and come to a completely different conclusion about what it means. So once you add in some evidence, take another two or three sentences and explain how that evidence proves your point.
Link to Thesis/Transition Sentence
Once you’ve finished the information in your paragraph, you can’t just move on. You need a good ending to your paragraph. This is where you have a few options. In your concluding sentence, you might want to show how the main point you are making in that section of the paper helps prove your thesis statement. This fits your paragraph into the premise of your writing.
Alternatively, you might want to focus on getting into your next main point. You can do this by creating a transition sentence that will bridge the gap between the previous paragraph and the one that follows it, creating a logical progression.
A Special Note on Introduction/Conclusion Paragraphs
Think of an academic paper as a funnel. When you first start writing, your audience has no idea what you are discussing, so they need you to draw them in first. Then, once you get into the body, you should be narrow and focused on your topic. Finally, at the end, you should send your reader back out to the rest of the world with a better understanding of your topic and what they should do about it.
Because the body paragraphs are narrower, the MEAL/MEAT plan works best for these. However, introductions and conclusions are a little different. Let’s discuss.
Again, there's no right or wrong answer here. It's all about the content.
Just like body paragraphs, there is a good acronym to help you remember what goes into an introduction paragraph, though this one isn’t food-centric: ABC.
A: Attention grabber , also known as a hook. You want to get your readers interested in your topic and let them know why they want to keep reading.
B: Background information . This is where you will give the reader enough information to catch them up on the topic. Let them know what they need to know to understand and follow your paper.
C: Claim, or the thesis statement . What is the main argument your paper will be making? What are you trying to prove or say? This should be really clear and straightforward.
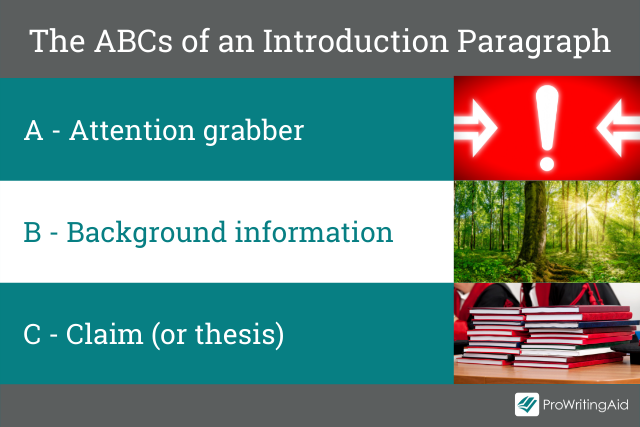
If you start with ABC, then it makes sense that you should end with XYZ. Notice that these are different letters. You don’t want to just repeat the introduction.
X: Explain what they should do with all of this information once they are done. This is sometimes called a "Call to Action". Likely, you want them to go away from academic writing being convinced about your thesis statement.
Y: Let them know why (y) they should care about all the information they just read.
Z: Zap them with a final hook in the concluding sentence so they don’t forget what you just taught them.

OK. But Really, How Many Sentences Should an Academic Paragraph Have?
I know I just spent a lot of time telling you that the content matters more than the amount of sentences in a paragraph, and I stand by that. However, I also acknowledge that there are best practices when it comes to paragraph length, and it helps to know them.
So, on average, there will be about 3 to 7 sentences in a paragraph . This is how many it takes to convey all of the necessary information I mentioned above into a paragraph without putting in too much.
You could also think of it as about half a page long, though that depends on how many words are in your sentences. More than that, and it will be harder to follow. Shorter than that, and it won’t feel like it has enough depth (and if you have a page-length requirement, it’ll be harder to hit it).
TIP: When I am teaching, I find that people who tend to turn in papers that are too short also have really short paragraphs. It’s usually because they don’t have enough sentences in their analysis section. So if you have this problem, then you might want to make sure you have enough of your own explanations about why the evidence you use supports your claims.
That depends on where you’re writing.
I spent a lot of time talking about a good paragraph in academic writing because that tends to be more formulaic than other types of writing. However, the answer to what makes a good paragraph (and how many sentences that paragraph should have) really depends on the type of writing you are doing. So here is where I will talk more about some other common types of writing that you may do.
How Long Are Paragraphs in Web/News Articles?
In web articles and news stories, can a good paragraph ever be a single sentence long?
One-sentence paragraphs are great for web writing. When people are online, they skim more. Thus, it is always smart to break up paragraphs more than you would in a paper.

On the web, short paragraphs are good. However, each paragraph still needs to have good information in it. If your readers can skim your writing and still get the important information you want to relay to them, then you are doing a good job.
This is also true in journalism. You likely want to keep your paragraphs tight and to the point. You don’t need a lot of sentences to give readers the facts.
Should I Use Short Paragraphs in Emails?
The answer to how long a good paragraph in a professional writing task should be is going to vary widely based on the task and industry. Your best bet is to find some good samples that will help you see what is expected of you.
However, let’s talk a little bit about a professional writing task almost everyone will have at some point: the email .
A good email paragraph in a professional context is one that gives the reader enough information to understand the problem and to figure out the question being asked. That question should be directly stated so that it is more likely to get answered.
In other words, it should be exactly how long it needs to be and no longer. People are busy, they don’t have time for a five-page email!
Here are the basic components of most business emails:

- An explanation of who you are.
- An explanation of the problem or reason for writing.
- The reason you think they can help.
- A thank you for their time.
This is really all that is needed in the paragraph(s) of an email.
How Long Should a Fiction Paragraph Be?
To be honest with you, this is going to be the hardest part of this whole post to write. The reason for this is because creative writing is like the Wild West: There are no rules, and you might get into a showdown if you try to suggest any.
Seriously, creative writing is just that, creative. Well-known books have paragraphs as short as one word and as long as the entire novel! A big part of what makes a good paragraph in creative writing is personal style. In other words, BE YOU.

Still, though, if you want to get published and develop an audience, you might have to stick to some best practices sometimes. Try starting a new paragraph if you do any of the following:
Create any type of change
Introduce a new character or place
Add dialogue
While that isn’t a complete list, it is a good starting point.
Of course, if you are still worried about the length of your paragraphs, you can always let ProWritingAid help. For example, check out the Readability Report , which will help you figure out which paragraphs are hard to read.
If it’s very difficult, it might mean there is too much information in there. Try breaking it down and running the report again to see if it improves your score.
Test your writing’s readability now with a free ProWritingAid account.
Now is a wonderful time to be a copywriter. Download this free book to learn how:

This guide breaks down the three essential steps you must take if you think copywriting is the career for you.
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Ashley Shaw is a former editor and marketer/current PhD student and teacher. When she isn't studying con artists for her dissertation, she's thinking of new ways to help college students better understand and love the writing process. You can follow her on Twitter, or, if you prefer animal accounts, follow her rabbits, Audrey Hopbun and Fredra StaHare, on Instagram.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
How Many Sentences are in a Paragraph?
The answer to this question depends on the type of writing you do. Are you planning to write an academic paper, a novel, a blog post, or something else entirely? Each format comes with its own set of standards. So, to cut to the chase, here’s how Merriam-Webster defines a paragraph :
“A subdivision of a written composition that consists of one or more sentences, deals with one point or gives the words of one speaker, and begins on a new usually indented line.”
So, by this definition, the length of a paragraph could be one sentence. Alternatively, you could compose a paragraph of infinite length as long as you cover only one point within it. Some authors have taken this idea to an absurd extreme, creating whole novels out of a single paragraph. For example, David Albahari’s novel Leeches consists of one long paragraph—proving that one paragraph can be as long as 300 pages. Based on the Merriam Webster definition, there’s no limit to the number of sentences in a paragraph.
Of course, by including logical paragraph breaks, you help the reader understand your arguments more clearly. Whether you’re writing short paragraphs or long ones, be sure to separate your central ideas from one another. As a general rule, essays should have an introduction paragraph and a conclusion. Within an essay, you might include any number of body paragraphs that cover different topics.
Your writing, at its best
Compose bold, clear, mistake-free, writing with Grammarly's AI-powered writing assistant
Standard Essay Structure
For high school papers, many teachers expect to see an essay structure that follows a particular formula. The standard essay structure consists of at least five paragraphs—an introduction, a conclusion, and three supporting paragraphs.
In order to show that you’ve mastered the standard essay structure, you should include 3-5 sentences in each paragraph. Begin most of your paragraphs with a transitional idea that connects the new paragraph to the one that came before. This sentence also introduces the main idea of the paragraph. Next, include 1-3 supporting sentences that build on your idea. Lastly, write a concluding sentence to drive your idea home. The final sentence in the paragraph may also prepare the reader for a clever transition at the beginning of your next paragraph.
For the introductory paragraph of an essay, the rules are a bit different. Since you don’t need to transition from a previous idea, you can grab the reader’s attention with the first sentence or two. By the last sentence, you should conclude your introductory paragraph with the thesis statement of your essay. The thesis serves as a topic sentence, giving your reader a roadmap for what you hope to prove over the course of your essay. Not only does this sentence introduce your main points, it also provides a preview of what you’ll be saying in the conclusion of your essay.

Research Papers
What makes a professional research paper different from high school paper? For one thing, academic papers often include longer paragraphs, jam-packed with information. Writers must form coherent paragraphs, giving papers introductions, conclusions, and supporting arguments, all while maintaining a formal writing style and including dense technical information. You probably won’t see conversational language or silly attention-grabbers in an academic text. Instead, you’re likely to find lengthy paragraphs and more of them.
Blog Posts and Online Articles
The typical paragraph length has been growing shorter in recent years, thanks to the ubiquity of mobile browsing. Since so many people consume content on mobile devices nowadays, authors must be conscious of how their writing will look on a small screen. For this reason, even respected news publications have shifted to a shorter paragraph structure.
Many news articles and blog posts now include a large number of one-sentence paragraphs, even though such writing would have been considered too abrupt in the past. These ultra-short paragraphs allow for more white space and prove easier-to-read on mobile devices. When you’re writing for an online publication, keep your paragraphs short and direct.
Creative Writing
Referring back to the definition at the top of this post, you’ll notice that a paragraph, “…gives the words of one speaker.” If you’re writing a novel or short story, this rule can be particularly helpful. With any piece of writing that contains a large amount of dialogue, you’ll be breaking for new paragraphs frequently. Even if a character only says a single word, you need to introduce a new paragraph before the next character’s line of dialogue. As you can imagine, a scene where two characters argue back and forth would require a large number of very short (sometimes even one-word) paragraphs.
Tips to Remember
As a good rule of thumb, try experimenting with different paragraph lengths. First, master the standard paragraph format, which consists of 3-5 sentences with a clear beginning, middle, and end. Once you’ve succeeded and you feel confident writing paragraphs that transition smoothly, try writing some dialogue. See what it feels like to introduce a number of short paragraphs. Lastly, when you feel ready to mix things up, give long paragraphs some love. See how many words you can write before a new topic introduces itself. After some practice, you’ll feel comfortable writing paragraphs of differing lengths.
Pay attention to the paragraphs you read over the next few days! Notice how many sentences the writer includes in his or her paragraphs. You’ll probably see a large variance. A textbook might have ten-sentence paragraphs, whereas a news website might have one-sentence paragraphs. Ask yourself, “Which kinds of paragraphs do I most enjoy reading?” Then, try writing in that style.
Who knows? Maybe you’ll find that you love writing 300-page paragraphs, like the author David Albahari. Just don’t be surprised if the person reading (or grading) your work doesn’t share that preference.
Sources:
- https://www.dailywritingtips.com/how-many-sentences-in-a-paragraph/
- https://justpublishingadvice.com/how-many-sentences-in-a-paragraph-not-very-many-today
- https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/paragraph
- https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/paragraph
- https://www.npr.org/2011/07/14/135770061/leeches-a-tale-of-the-balkans-breathlessly-told
- https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/paragraphs_and_paragraphing/paragraphing.html
The Word Counter is a dynamic online tool used for counting words, characters, sentences, paragraphs, and pages in real time, along with spelling and grammar checking.

Kari Lisa Johnson
I’m an award-winning playwright with a penchant for wordplay. After earning a perfect score on the Writing SAT, I worked my way through Brown University by moonlighting as a Kaplan Test Prep tutor. I received a BA with honors in Literary Arts (Playwriting)—which gave me the opportunity to study under Pulitzer Prize-winner Paula Vogel. In my previous roles as new media producer with Rosetta Stone, director of marketing for global ventures with The Juilliard School, and vice president of digital strategy with Up & Coming Media, I helped develop the voice for international brands. From my home office in Maui, Hawaii, I currently work on freelance and ghostwriting projects.

Recent Posts

Ideal Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

Thesis Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

Bare Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

??? Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How Many Paragraphs Should an Essay Have?

- 6-minute read
- 19th May 2023
You have an essay to write. You’ve researched the topic and crafted a strong thesis statement . Now it’s time to open the laptop and start tapping away on the keyboard. You know the required word count, but you’re unsure of one thing: How many paragraphs should you have in the essay? Gee, it would’ve been nice if your professor had specified that, huh?
No worries, friend, because in this post, we’ll provide a guide to how many paragraphs an essay should have . Generally, the number of paragraphs will depend on how many words and how many supporting details you need (more on that later). We’ll also explore the concept of paragraphs if you’re wondering what they’re all about. And remember, paragraphs serve a purpose. You can’t submit an essay without using them!
What Is a Paragraph?
You likely know what a paragraph is, but can you define it properly in plain English? Don’t feel bad if that question made you shake your head. Off the top of our heads, many of us can’t explain what a paragraph is .
A paragraph comprises at least five sentences about a particular topic. A paragraph must begin with a well-crafted topic sentence , which is then followed by ideas that support that sentence. To move the essay forward, the paragraph should flow well, and the sentences should be relevant.
Why Are Paragraphs Important?
Paragraphs expand on points you make about a topic, painting a vivid picture for the reader. Paragraphs break down information into chunks, which are easier to read than one giant, uninterrupted body of text. If your essay doesn’t use paragraphs, it likely won’t earn a good grade!
How Many Paragraphs Are in an Essay?
As mentioned, the number of paragraphs will depend on the word count and the quantity of supporting ideas required. However, if you have to write at least 1,000 words, you should aim for at least five paragraphs. Every essay should have an introduction and a conclusion. The reader needs to get a basic introduction to the topic and understand your thesis statement. They must also see key takeaway points at the end of the essay.
As a rule, a five-paragraph essay would look like this:
- Introduction (with thesis statement)
- Main idea 1 (with supporting details)
- Main idea 2 (with supporting details)
- Main idea 3 (with supporting details)
Your supporting details should include material (such as quotations or facts) from credible sources when writing the main idea paragraphs.
If you think your essay could benefit from having more than five paragraphs, add them! Just make sure they’re relevant to the topic.
Professors don’t care so much about the number of paragraphs; they want you to satisfy the minimum word requirement. Assignment rubrics rarely state the number of required paragraphs. It will be up to you to decide how many to write, and we urge you to research the assigned topic before writing the essay. Your main ideas from the research will generate most of the paragraphs.
When Should I Start a New Paragraph?
Surprisingly, some students aren’t aware that they should break up some of the paragraphs in their essays . You need to start new paragraphs to keep your reader engaged.
As well as starting a new paragraph after the introduction and another for the conclusion, you should do so when you’re introducing a new idea or presenting contrasting information.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Starting a paragraph often involves using transitional words or phrases to signal to the reader that you’re presenting a new idea. Failing to use these cues may cause confusion for the reader and undermine your essay’s coherence.
Let’s consider examples of transitional words and phrases in action in a conclusion. Note that the essay is about too much mobile device screen time and that transitional words and phrases can occur later in a paragraph too:
Thanks to “In conclusion” and “Additionally,” the reader clearly knows that they are now in the conclusion stage. They can also follow the logic and development of the essay more easily.
How Do I Know Whether I Have Enough Paragraphs?
While no magic number exists for how many paragraphs you need, you should know when you have enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. It helps if you can answer yes to the following questions:
- Does my essay have both an introduction and a conclusion?
- Have I provided enough main ideas with supporting details, including quotes and cited information?
- Does my essay develop the thesis statement?
- Does my essay adequately inform the reader about the topic?
- Have I provided at least one takeaway for the reader?
Conclusion
Professors aren’t necessarily looking for a specific number of paragraphs in an essay; it’s the word count that matters. You should see the word count as a guide for a suitable number of paragraphs. As a rule, five paragraphs should suffice for a 1,000-word essay. As long as you have an introduction and a conclusion and provide enough supporting details for the main ideas in your body paragraphs, you should be good to go.
Remember to start a new paragraph when introducing new ideas or presenting contrasting information. Your reader needs to be able to follow the essay throughout, and a single, unbroken block of text would be difficult to read. Transitional words and phrases help start new paragraphs, so don’t forget to use them!
As with any writing, we always recommend proofreading your essay after you’ve finished it. This step will help to detect typos, extra spacing, and grammatical errors. A second pair of eyes is always useful, so we recommend asking our proofreading experts to review your essay . They’ll correct your grammar, ensure perfect spelling, and offer suggestions to improve your essay. You can even submit a 500-word document for free!
1. What is a paragraph and what is its purpose?
A paragraph is a group of sentences that expand on a single idea. The purpose of a paragraph is to introduce an idea and then develop it with supporting details.
2. What are the benefits of paragraphs?
Paragraphs make your essay easy to read by providing structure and flow. They let you transition from one idea to another. New paragraphs allow you to tell your reader that you’ve covered one point and are moving on to the next.
3. How many paragraphs does a typical essay have?
An essay of at least 1,000 words usually has five paragraphs. It’s best to use the required word count as a guide to the number of paragraphs you’ll need.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How long is an essay? Guidelines for different types of essay
How Long is an Essay? Guidelines for Different Types of Essay
Published on January 28, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 23, 2023.
The length of an academic essay varies depending on your level and subject of study, departmental guidelines, and specific course requirements. In general, an essay is a shorter piece of writing than a research paper or thesis .
In most cases, your assignment will include clear guidelines on the number of words or pages you are expected to write. Often this will be a range rather than an exact number (for example, 2500–3000 words, or 10–12 pages). If you’re not sure, always check with your instructor.
In this article you’ll find some general guidelines for the length of different types of essay. But keep in mind that quality is more important than quantity – focus on making a strong argument or analysis, not on hitting a specific word count.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Essay length guidelines, how long is each part of an essay, using length as a guide to topic and complexity, can i go under the suggested length, can i go over the suggested length, other interesting articles.
| Type of essay | Average word count range | Essay content |
|---|---|---|
| High school essay | 300–1000 words | In high school you are often asked to write a 5-paragraph essay, composed of an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. |
| College admission essay | 200–650 words | College applications require a short personal essay to express your interests and motivations. This generally has a strict word limit. |
| Undergraduate college essay | 1500–5000 words | The length and content of essay assignments in college varies depending on the institution, department, course level, and syllabus. |
| Graduate school admission essay | 500–1000 words | Graduate school applications usually require a longer and/or detailing your academic achievements and motivations. |
| Graduate school essay | 2500–6000 words | Graduate-level assignments vary by institution and discipline, but are likely to include longer essays or research papers. |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

In an academic essay, the main body should always take up the most space. This is where you make your arguments, give your evidence, and develop your ideas.
The introduction should be proportional to the essay’s length. In an essay under 3000 words, the introduction is usually just one paragraph. In longer and more complex essays, you might need to lay out the background and introduce your argument over two or three paragraphs.
The conclusion of an essay is often a single paragraph, even in longer essays. It doesn’t have to summarize every step of your essay, but should tie together your main points in a concise, convincing way.
The suggested word count doesn’t only tell you how long your essay should be – it also helps you work out how much information and complexity you can fit into the given space. This should guide the development of your thesis statement , which identifies the main topic of your essay and sets the boundaries of your overall argument.
A short essay will need a focused, specific topic and a clear, straightforward line of argument. A longer essay should still be focused, but it might call for a broader approach to the topic or a more complex, ambitious argument.
As you make an outline of your essay , make sure you have a clear idea of how much evidence, detail and argumentation will be needed to support your thesis. If you find that you don’t have enough ideas to fill out the word count, or that you need more space to make a convincing case, then consider revising your thesis to be more general or more specific.
The length of the essay also influences how much time you will need to spend on editing and proofreading .
You should always aim to meet the minimum length given in your assignment. If you are struggling to reach the word count:
- Add more evidence and examples to each paragraph to clarify or strengthen your points.
- Make sure you have fully explained or analyzed each example, and try to develop your points in more detail.
- Address a different aspect of your topic in a new paragraph. This might involve revising your thesis statement to make a more ambitious argument.
- Don’t use filler. Adding unnecessary words or complicated sentences will make your essay weaker and your argument less clear.
- Don’t fixate on an exact number. Your marker probably won’t care about 50 or 100 words – it’s more important that your argument is convincing and adequately developed for an essay of the suggested length.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
In some cases, you are allowed to exceed the upper word limit by 10% – so for an assignment of 2500–3000 words, you could write an absolute maximum of 3300 words. However, the rules depend on your course and institution, so always check with your instructor if you’re unsure.
Only exceed the word count if it’s really necessary to complete your argument. Longer essays take longer to grade, so avoid annoying your marker with extra work! If you are struggling to edit down:
- Check that every paragraph is relevant to your argument, and cut out irrelevant or out-of-place information.
- Make sure each paragraph focuses on one point and doesn’t meander.
- Cut out filler words and make sure each sentence is clear, concise, and related to the paragraph’s point.
- Don’t cut anything that is necessary to the logic of your argument. If you remove a paragraph, make sure to revise your transitions and fit all your points together.
- Don’t sacrifice the introduction or conclusion . These paragraphs are crucial to an effective essay –make sure you leave enough space to thoroughly introduce your topic and decisively wrap up your argument.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 23). How Long is an Essay? Guidelines for Different Types of Essay. Scribbr. Retrieved June 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/length/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to conclude an essay | interactive example, how to write a statement of purpose | example, what is your plagiarism score.
)
How many sentences are in a paragraph?
Published March 26, 2021. Updated June 7, 2022.
Paragraph Definition:
A paragraph is a section of writing in a longer body of work. It explains a particular topic or subject.
Overview of How Many Sentences Are in a Paragraph:
There are no hard and fast rules for the length of a paragraph. Paragraphs in an essay tend to have about three to eight sentences or 100 to 200 words. Your paragraph should open with a clear topic sentence that presents the theme or argument of that paragraph. Most academic writings have paragraphs that are about three-quarters of a page long. While writing dialogue, you need to begin a new paragraph every time the speaker changes. Journalism and commercial writing often call for short paragraphs that are easy to scan.
Worried about your writing? Submit your paper for a Chegg Writing essay check , or for an Expert Check proofreading . Both can help you find and fix potential writing issues.
One Paragraph, One Idea
You generally want to focus on one idea per paragraph. The paragraph needs as many sentences as it takes to develop and support that idea.
Your paragraph should open with a clear topic sentence that presents the theme or argument of that paragraph. In persuasive writing, you can think of this topic sentence as a subclaim: a mini-argument that combines with your other mini-arguments to prove your point.
For example, an essay on why your school should adopt an official school uniform might include a paragraph that begins as follows:
School uniforms foster a sense of equality within student bodies.
The paragraph would then support this idea with several sentences that justify and develop this claim. You could bring up the socioeconomic diversity of the student population and the way that free dress visually reinforces class divisions, giving examples of the problem.
Academic Writing
At times, your teachers may provide specific instructions for an assignment. If they do, that’s great! Follow them. However, as you advance in your academic career, you will find a greater degree of flexibility in assigned work. If you’re nervous about this, don’t be afraid to ask your teachers if they have any rules or pointers on paragraph length.
Upper-level high-school and college essays tend to demand longer paragraphs. As topics increase in complexity, they require more evidence and explanation. They are often about three-quarters of a page long, which is another rough guideline you can follow. (It still isn’t a set rule.)
As you’re writing one paragraph, you have to decide when to finish it up and start a new one. Often, the answer is as simple as starting a new paragraph when you’re ready to move on to the next topic. If your paragraph is growing too long, find a natural break
You can also fix paragraphs that are significantly longer or shorter than the other ones in the paper during the revision process. You can flesh out short paragraphs or crop long ones. You may also discover two small paragraphs that you can combine into one or realize that you can move around some of your material.
Narrative Writing
If you open any novel, you’ll find that one page looks very different from the next. Paragraph size can vary dramatically in narrative writing.
When you tell a story, you should follow different conventions than you do when making an argument. For one thing, when writing dialogue, you need to start a new paragraph with each speaker.
Five minutes ago, Cindy had stopped listening to Dan and started daydreaming about dragons, unicorns, and all sorts of fantastic creatures. She wondered what kind of political structure a unicorn society would have and how she could become its prime minister.
She startled. “What?”
“I asked if you wanted any more ice cream,” Dan repeated, scowling at her.
Authors will also vary paragraph length for stylistic purposes. You may want to accelerate the tempo of an exciting scene with short paragraphs or use long ones to linger over a certain description.
Journalism and Commercial Writing
News reporters often use short, to-the-point paragraphs. They want to establish and underline important facts at the beginning of the piece. As the article goes on, they may shift into slightly longer, more expansive writing.
Online and commercial content also tends toward short paragraphs. (Just look at the way this handout is written.) This content is designed to be scanned quickly for important takeaways. Writers also rely on frequent headers and lists to make their writing easy to digest.
Before you turn in that paper, don’t forget to cite your sources in APA format , MLA format , or a style of your choice.
Key takeaways
- There is no golden rule for how many sentences a paragraph should have.
- Most essay paragraphs have three to eight sentences or 100–200 words.
- Academic writing tends to have paragraphs that are about three-quarters of a page long.
- In writing dialogue, you need to begin a new paragraph every time the speaker changes.
- Journalism and commercial writing often call for short paragraphs that are easy to scan.

What’s included with a Chegg Writing subscription
- Unlimited number of paper scans
- Plagiarism detection: Check against billions of sources
- Expert proofreading for papers on any subject
- Grammar scans for 200+ types of common errors
- Automatically create & save citations in 7,000+ styles
- Cancel subscription anytime, no obligation
BibGuru Blog
Be more productive in school
- Citation Styles
How many sentences are in a paragraph

Successful paragraphs help readers consistently, and naturally, follow your argument . But sometimes it's difficult to know just how much—or how little—you need to include in a single paragraph. This post covers the foundational elements of a successful paragraph and includes tips for writing clear and concise sentences.
The perfect paragraph
Ideally, each paragraph you write should introduce an idea, support it, and then add a conclusion to it. Let’s take a closer look at how paragraphs should be structured:
The opening sentence
The opening sentence introduces the topic of the paragraph or indicates to the reader a change in the subject from the previous paragraph.
The paragraph is an opportunity to signal to the reader that you are making a new point or moving in a new direction. You can identify which ideas are suitable for opening sentences by creating an outline of your paper . Use the outline to pinpoint your main ideas.
The supporting statements
Once you've written your opening sentence, the following sentences should support the statement you made or give the reasoning for your argument. This part of the paragraph can also be used to describe study results, explain key theories, or integrate source material from your research.
Keep supporting sentences concise by using as few words as possible to explain your ideas or the ideas of others.
The concluding sentence
The final sentence in the paragraph needs to wrap up the main idea of the paragraph and add value to what has already been written. You can also use your concluding sentence to lead into your next paragraph.
A concluding sentence should wrap up the main idea of the paragraph without repeating previous information.
Paragraph writing tips
- Put your strongest supporting statement directly after the opening sentence. This allows the reader to go over the paragraph at a glance and still capture the main idea.
- Cut out unnecessary words and sentences . For each sentence, ask yourself: is this sentence essential? Also, try reading your paragraphs aloud to yourself or to a friend or family member. This helps you catch nonessential words, phrases, and sentences.
- Avoid single-sentence paragraphs . One-sentence paragraphs are suitable for blog posts, but academic research papers require more substantial paragraphs in order to fully explore your main ideas.
- Communicate compelling ideas in clear and concise language. To be a solid academic writer, you don't need to write wordy, jargon-filled sentences.
The bottom line
The structure of your paragraphs can have a significant impact on your paper's clarity and, by extension, your grade. Ultimately, each paragraph should be dedicated to a single thought or idea, enhanced by concise supporting sentences and a clear concluding statement.
Frequently Asked Questions about sentences in paragraphs
While there are no strict rules when it comes to paragraph length, a typical paragraph should be at least 3 sentences. Depending on the length and complexity of your research paper, a paragraph may be as long as a single page of double-spaced text, but shouldn't be longer.
The length of a paragraph will vary depending on the idea that it's communicating and its placement in the paper. Two key questions can help you determine if your paragraph is the right length:
- Have all unnecessary words and sentences been removed?
- Has the paragraph accurately introduced, explained, and concluded the main idea?
If the answer is no, you may want to shorten or lengthen your paragraph.
Using fifteen words per sentence as a guide, one hundred words should be roughly equal to one basic paragraph. However, there is no magic number of words that defines a paragraph.
The best way to determine if a paragraph is too long is to read it aloud to yourself or another person. If you lose your place, or if your listener struggles to follow along, your paragraph may be too long or too wordy.
A paragraph should begin with a clear statement that communicates that paragraph's main idea.

Make your life easier with our productivity and writing resources.
For students and teachers.

How Many Words in a Paragraph?

What does a paragraph usually consist of?
A paragraph usually deals with a single idea. In general, you’ll have an introductory sentence expressing that idea, and several supporting sentences to round it off. Paragraphs are usually about 100 – 200 words long, but there are more exceptions to this rule-of-thumb than you’d expect.
Commercial Writing
Commercial writing breaks all the rules. Whether or not you find it irritating, your task is to hold your readers’ attention and get them to read what you’ve written. The average person doesn’t like to see solid blocks of text. It looks like it’s going to be difficult to get through, and nobody likes to work harder than they have to.
“White Space” is a great way to make your information look easier to master, and one of the best ways to create “white space” is through using paragraphs. For commercial writing, it’s best to keep sentences short and punchy, and the same goes for paragraphs.
People don’t usually like to see paragraphs that are more than three or four lines long. How many words is that? Again, although it’s not helpful, the answer is “It depends…” Font styles and font size will affect paragraph length – at least from a psychological perspective.
For example, this is a blog post, and I want to keep the reader engaged. The longest paragraph under this heading is only 61 words long. This is the shortest one so far, and it only uses 37 words.
I want to get your attention!
The above paragraph is only six words long, and you can count the words in this one if you like.
To make things easy for your reader, you’ll switch paragraphs every time you switch speakers, for example:
“I don’t know how long a paragraph should be,” said Mary, “but I hope to find out by reading this article.”
“That sounds like a good idea,” John replied, “but don’t let that limit your creativity!”
“Really? Can I bend the rules?”
“The rules are really more like guidelines.”
“Cool!”
As you can see, I was able to stop identifying the speakers as soon as the conversation began to flow because John and Mary each had paragraphs to themselves. Neither of them said anything that was even close to 100 words, but it’s still easy to see who said what. Mary’s final paragraph was one word long.
Academic Writing
In academic writing, paragraphs will usually consist of the “standard” 100 – 200 words (Burns, 2002). You will begin the paragraph with an idea and then explain it in the light of currently accepted knowledge (Phillips, 2014) with references. Bear in mind that your tutor will want to see some original thought, but will expect it to be motivated according to your reading (Williams et al, 1994). Smith (2004) supports this concept and confirms that academic writing requires longer paragraphs than those generally found in commercial writing or even story-telling. 200 words is really a bit long for any paragraph and since this one is just over 100 words, you’ll soon see why this should be the case (Me, 2015).
Whew! That was a marathon to read, wasn’t it?
How many words per paragraph? It’s really up to you!
As a takeaway, I’d like to suggest that there are absolutely no hard-and-fast rules as to how many words a paragraph should be.
Making them too short, can look a little odd.
This is an excellent example.
But it can work in some cases.
On the other hand, having really long paragraphs might work for you, but not for your reader. A lot of text without “white space” is hard on the eyes, and the brain. I’ve seen blog posts and web pages with absolutely no paragraphs to speak of. Did I want to read them? Not really. It was too difficult to separate the ideas from one another and there just didn’t seem to be a good enough reason to read them if I could find the same information split up into bite-sized chunks that were easier to digest. So, whatever you do, don’t forget the importance of paragraphs – and keep them a bit shorter than this one, unless you’re trying to baffle the reader.
By the way, the above paragraph is “only” 122 words (656 characters) long. Do you see what I mean when I say that longer isn’t always better? I’m ready to bet that you do.
(Photo courtesy of Enokson )
So, if I have a 10 paragraph assignment, I can just write ten words with a period after each and I will have it completed?
Yes, if you want to fail the assignment. While technically you could do this, it’s not in the spirit of what the teacher wanted when making the assignment (but you already knew that).
This will mostly depend on the writer. Paragraphs will also differ in size due to information being written about and the type of writing being done. I don’t think anyone can say how many words will be in any given paragraph before it’s written. Even with the same topic and directions, two writers will have different results.
I would not suggest trying to do this. While you may think it’s funny or clever, it’s highly doubtful that your teacher or professor will see it the same way.
Is that the paragraph sign in the photo in this article? I’ve never seen it look like that before. The one I know sort of looks like a “P”
Yes, that is the paragraph sign used in Europe.
Does anyone know what the “paragraph sign” is called? Is there a proper English word for it or does everyone just call it a paragraph sign?
The paragraph symbol is called a pilcrow. The symbol in the illustration at the head of this article is the section symbol (or silcrow, informally).
Does it really matter how many words are in a paragraph?
Of course it matters. You can’t just write 1 word paragraphs. You should try to write paragraphs that have 100 to 200 words for most of them. This will make it easier for people to read them.
Great guideline to use. This will always be a question that will be asked by writers and I think it is difficult to answer due to the fact that you need to know what information you want in it.
No! Just write as many words as you want for each paragraph. Don’t conform to any rules and express your own thoughts and words. Rebel!
Don’t listen to @artstudent — the comment is nothing more than a troll. The number of words in a paragraph does matter, and although it is fine to rebel, you need to rebel once you have learned how to write your graphs properly. Trying to rebuild before you know how to do that only make you look like a fool.
This would seem to be such an easy question to answer, but the answer is 1 word to hundreds of words. I wish there were a more definite answer like 50 or 100 so I could just use that. Why does all aspects of writing have to be so difficult?
Language would be so much more boring if everything was defined like that. What makes English so beautiful is that it isn’t rigid with rules. It makes it fun!
Who decides what the average number of words in a paragraph is? I know you said that there are usually 100 to 200 words in a paragraph, but who has decided that this is the general amount? Did someone just wake up one day and say that a paragraph should have 100 to 200 words and it? Where has there been some specific research done that indicates that most paragraphs fall within this range?
It’s easy to determine a general number of words in a paragraph. All that needs to be done is take a large data set and then crunch the numbers. If you look at hundreds of thousands of paragraphs you’ll soon see a trend of how many words are in an average paragraph. Sure, there will be some with a lot less and some with a lot more, but in general an average number will appear. That’s 100 to 200 words per paragraph.
SO AWESOME!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!<3 (: This is exactly what I was looking for to help me out with my essay.
It’s always great to hear our tools are helpful. Glad it helped with your essay!
I like to write long paragraphs. I think that too many people try to break long paragraphs into a number of shorter ones far too often. There is just something special about reading a long paragraph that conveys the essence of the story. People shouldn’t try to make their paragraphs too short. Long paragraphs are just so wonderful.
Long paragraphs are difficult to read. That’s why you rarely see them in magazines and newspapers (or online) . A huge wall of text is never inviting. If you like long paragraphs, there is nothing wrong with that, but you need to be aware that fewer people will actually read what you write.
I like to write short paragraphs. I think that too many people try to combine short paragraphs into a number of longer ones far too often. There is just something special about reading a short paragraph that conveys the essence of the story. People shouldn’t try to make their paragraphs too long. Short paragraphs are just so wonderful.
Hi wondering how many words are in a paragraph with a 8 sentences
That would depend on how many words are in each sentence which can vary greatly. Most sentences have about 6 words, so a guestimate would be 48 words. If you stick the paragraph into https://wordcounter.net/ it will tell you exactly how many words are in the paragraph.
Usually, 150-180 depending on the length of your sentences. Admin said 48, but 6 word-sentences are not commonly used if you are doing an academic paper (analysis, informative, argumentative essay) rather than freelance writing for creativity or leisure. the smallest sentence in an essay I’m writing is 10 words. And there are not many of those. The rest average between 12-30 words. If you are in high school (I am a HS senior), I suggest using a more academic vocabulary that will make your sentences fuller. But, only make them longer if it is necessary and meaningful, not to reach a word count. That’s when sentences become run-ons and you lose points. If you are in Jr High, get used to being thorough yet concise. Not too verbose! Just a good medium. You’ll find a balance as you grow as a writer and form your own style. I know this is late lol, but I hope that helps 🙂
Some people count proper names (e.g. New York, Thomas Alva Edison), proverbs (A stitch in time saves nine), idioms (make ends meet), titles (Little House on the Prairie), and similes (as hardworking as an ant) as one single word. Is it correct?
Our tool does not do this — they would all be counted as individual words.
Sometimes two.
Three at times.
Four is also possible.
Five is good for some.
Does anyone truly care about this? I mean, who cares how many words are in a paragraph? Name me one person who would care about this? And if you can, you have named someone who needs to reevaluate what they care about in life.
I care. I have an assignment to write a paragraph and I wanted to get a general idea of how long that should be. You think I need to reevaluate my life because i want to do well in school?
In general life, one might now care; however, in college the professor care and you will be graded for it.
I know this was posted four years ago now, but I felt like saying something to this comment. I’m going to quote the famous Obi-wan from Star Wars 2: “You need to go home and rethink YOUR life”. I think that your comment is a little too extreme- there are many good people in this world who care about doing your best in everything- even the seeming insignificant things. For example, how many words are in a paragraph. If you’re looking to argue against something in such a strongly negative way, why don’t you please kindly do it against something that is actually worth speaking out against? Is it worth saying something rude and insulting just for fun? Obviously, to you it might be, but I’m sure many people would agree with me that it isn’t.
I think an important point that hasn’t been mentioned in the comments is that a paragraph should be about a single idea. That means that the number of words in a paragraph will depend on how long you spend on that single idea. If you have a lot to say about that single idea, the paragraph will be long. If you don’t have a lot to say about that idea, the paragraph will be short. I don’t think you should be concentrating on how many words are in the paragraph as much as are you still on the same topic within the paragraph.
I see so many students who don’t understand this and break up a single idea into several paragraphs. Then there are other students to take several ideas and lump them all into the same paragraph. If you can understand the concept of a single idea for a paragraph, it will solve a lot of your problem.
You can’t write well without understanding the structure of a paragraph. I see so many students try to squeeze a number of different ideas into a single paragraph and this immediately tells me they don’t understand what it’s for and how it’s used.
I don’t understand why so many people worry about things like this. If you’re trying to write well, the number of words for each paragraph should naturally take place. Trying to force a specific number of words into each paragraph will ruin your writing.
I always just used the rule that a paragraph should have 3-5 sentences
I am a sixth grader. Do the same rules apply for all grades? I usually write about 250 words in each paragraph, ending up writing about 5 paragraphs.
Helpful article.
It’s a general rule of thumb, not a one that can’t be broken. So much depends on the context of what’s being written. It’s a good number to shoot for, but there are a lot of reasons to deviate from it depending on what you’re writing.
wow, my aim is more than 50 words in a paragraph and I am in grade 6!
You should shoot for three to five sentences in a paragraph and six to 10 words per sentence, so a paragraph should have 18 to 50 words.
Those are some pretty short paragraphs. I would find it difficult to express all the information in such a short paragraph for most of my writing. There are times when they can be this short, but I would say most should be a lot longer.
This is something that everyone who is commenting on seems to be overanalyzing. Don’t try to constrict yourself into a certain number of words per paragraph. If you write well, paragraphs will naturally come about and be the number of words they need to be. If you try to cram too many words into them to make them longer or cut out a bunch of words to make them shorter, in all likelihood the paragraphs won’t seem natural. Write the best thing you can in the paragraph should naturally flow.
This is fine unless the assignment has a word and paragraph limit. I have an assignment that requires 8 paragraphs and 1000 words. It seems crazy for a teacher to be this specific for a paper, but she does stuff like this all the time.
What ?! I had a 7 paragraph essay and I ended up writing 2159 words. Imagine writing 8 paragraphs !
Adversity is said to build character. The lower the bar is set the lower the standard score will be. Seems advantageous for a teacher to raise the bar therby increasing challenge and outcome of students. The teacher had in fact simplified your sssignment with clarity not pickiness.
Hahah, you made me die because of laughing. An assignment I have to write requires 3000 words, but paragraphs are not limited.
Very true. Also using Microsoft Word we can keep track of how many words we used once we finish adding more or less.
I just finished writing an essay. The shortest paragraph had 98 words and the longest had 367 words. It doesn’t seem that this is accurate at all.
Rules, not guidelines! Remember what they said at the beginning? It depends!
Think of a paragraph as a women’s skirt. Make sure its long enough to cover everything but make it short enough to be interesting! 😉
LOL, that’s a good one.
Who the hell downvoted dat?!?!?!?
Anyone who isn’t a misogynist
This is so perfect! I don’t know how anyone would go through their day without this cool joke!
This made me giggle lol!!😂😂🤣🤣😂😂
An older Catholic Priest once told me that this was the advice given to him by another Priest with respect to writing sermons. 🙂
“A good sermon is short enough to keep the attention and long enough to cover the material.”
69 likes as well….
lol, I’m dead. u ain’t never!!!😅😂🤣
The original definition of a paragraph is ONE OR MORE SENTENCES. I had a boss onece who had a bug up her backside about not allowing one sentence paragraphs in documents. She used to say it was grammatically incorrect, and then used to complain our documents were too wordy and long. She was 100% wrong. Grammar has to do with spelling and punctuation, and the sentence was perfectly spelled and punctuated. Usage and style have to do with form and structure. Anyone who says it is never done is wrong. God, the disciples and King James are going to be angry when someone rewrites the Bible. Shortest paragraph and verse in the King James Bible is in the New Testament: “Jesus Wept.” Two words. One Sentence. One paragraph. One sentence paragraphs are done, they are used. They have been used in very important religious books, historical books and literature. There is nothing wrong with them stylistically. If a one sentence paragraph conveys the idea, mood, emotion or purpose intended by the author, there is nothing wrong with using it. The pace and metering of what you read can be as important as the words.
Thanks for the information. I will keep an eye open to the bible verses to find this paragraphs. God bless you.
How many paragraphs are thousand and fifty words
Like some people were saying, it should come naturally and flow. It doesn’t necessarily have to be a certain amount of words or sentences. As long as the paragraph is based on the same idea or topic, it will not matter the number of words or sentences.
Writing essays is a new concept for me and now that I’ve started college It will be very challenging. Thanks to this information I will be able to keep the essay simple and easy for the audience to “grasp it”.
Thank you very much!
Writing is amazing generally
this information was so helpful don’t listen to fortnite
I think everyone should just be a skirt especially verbally lovely
thank you so much this helped me with my homework.
This might potentially be the most self aware web page I’ve ever been on.
So, I’m writing one paragraph that have to have 350 words in it. How many sentences is there supposed to be to get to 350 words in one paragraph.
I’m a middle school student and write a 8 paragraph essay in around 3000 words. Is that long?
that is very short
How many words in 177 syllables
I am a bit concerned that the single and pervasive focus on readability, which is ease of reading by simplicity of language and brevity of text, has the cumulative effect of reducing an individual’s reading comprehension and diminishing their overall capacity for handling texts of even moderate complexity. The mind is not a static instrument; it is continually changing in response to the challenges, of lack of challenges presented to it by one’s habitual environment. When virtually all written text which a person is likely to encounter on a daily basis has been tailored to be simple and easy to read and comprehend, the mind is on a downward trajectory of diminishing capacity. I would guess that the majority of texts which a person reads day-to-day are either above or below their own level, and fewer texts match the reader’s level exactly. The mantra of readability ensures that a non-academic reader is practically guaranteed to be reading consistently below their level. No doubt, our fluid and efficient minds will accommodate the lessened challenge and effort with reduced capacity.
Popular Posts
- The Top 10 Most Difficult-to-Spot Writing Mistakes
- 4 Simple Tips for Great Writing
- Avoiding Wordiness: 330 Examples & What to Use Instead
- The Oxford Comma: The Splice of Life
- Who vs. Whom
- Affect vs. Effect
- How to Take Notes: The 10-Step Guide to Note-Taking (Infographic)
- CMOS vs. AP – Recent Changes & Comparison (Updated 1. Nov. 2021)
- The Daily Word Counts of 19 Famous Writers
- The Ideal Length of Everything You Write Online ( Infographic)
Recent Comments
- Phony on Word Counter Reading Level Feature
- Jon on Word Counter Reading Level Feature
- Me on Word Counter Reading Level Feature
- Sigma-balls on Word Counter Reading Level Feature
- Incindiary Rat on Word Counter Reading Level Feature
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.
Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, how many paragraphs should a college essay be.
I'm working on my college essay and I'm not sure how long it should be. Is there an ideal number of paragraphs for a college essay, or does it just depend on the content and flow of the essay? Any guidance would be much appreciated!
Hey there! It's great that you're working on your college essay. The ideal length for a college essay will depend on the specific essay prompt and the word limit given by the colleges you're applying to. Generally, most college essays fall in the range of 250-650 words.
As for the number of paragraphs, it's more about effectively organizing your thoughts and ideas rather than sticking to a specific number. For instance, you might have a compelling 5-paragraph essay or an engaging 8-paragraph essay. The key is to maintain a strong narrative and flow throughout the essay.
My child faced a similar dilemma when they were applying, and what worked for them was to focus on the content, storytelling, and coherence of the essay rather than the specific number of paragraphs. Remember, it's your unique story and how you present it that matters most. Good luck!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.
More From Forbes
7 chatgpt prompts to improve your writing.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Photo by NICOLAS MAETERLINCK/BELGA MAG/AFP via Getty Images
On writing , author David Sedaris once said, “You need to do the best that you can do, and then you need to take the best that you can do and you need to rewrite it, and rewrite it, and rewrite it.” That’s the dynamic essence of the writing process. Writers refine their drafts, just like they continually refine their craft. I didn’t study writing or literature, so I was intimidated when I began contributing to major publications. But my confidence grew with each byline, and I began to find my voice.
While ChatGPT can be an impressive imitator, it can never generate your unique voice and perspective. It can, however, be a powerful tool for improving your writing, whether you’re penning business articles or important emails. It all starts with the right prompts.
Here are seven that you can use to level up your writing skills.
Automate Your Busywork
There are no shortcuts to becoming a better writer. The prolific author Stephen King once said, “If you want to be a writer, you must do two things above all others: read a lot and write a lot.” That said, you can use AI tools to eliminate some of the tedious tasks involved in writing and leave more time for honing your craft. Here are some prompts to delegate your writing “busywork” to ChatGPT.
1. Generating Ideas And Topics
AI shouldn’t do your writing for you. It lacks the necessary human context and isn’t immune to errors. But it can be a powerful writing partner. As Wharton professor Christian Terwiesch (who challenged ChatGPT to come up with product ideas and compared those ideas to student ideas —ChatGPT won), has said , “Everybody should be using ChatGPT to help them generate ideas.” At worst, you reject all of them. At best, you enrich your pool of ideas.
WWE Raw Results, Winners And Grades After Great Wyatt Sicks Follow-Up
College football 25: ea unveils important dates for info rollout, heygen ai video scores $60 million, plus more cinematic ai shorts.
Here is a prompt you can use to help get the idea wheels turning:
"I'm an [role/title] writing for [outlet description] targeting [target audience]. Can you suggest some fresh and engaging topics that would appeal to this audience?"
If you’d like ideas related to a certain topic or tailored to a specific style (e.g., a “hot take” versus a personal essay), remember: the more context you provide, the more concise the results.
2. Editing For Grammar And Style
Whether you’re sending an email or publishing an article on a high-traffic website, typos are an embarrassing—and avoidable—faux pas. In today’s world, where internet content exists in perpetuity, anything attached to your name should be error-free. ChatGPT can be a near-instantaneous proofreader. Test out the following prompt:
"Can you proofread this [content] for grammar, punctuation, and style consistency? The intended audience is [audience/recipient]. Please provide a list of any suggested improvements.”
3. Hitting The Right Tone
Spelling and grammar are a crucial part of editing, but they’re relatively objective. Perfecting the tone is more subjective and sometimes more challenging—but just as crucial.
The proper tone can ensure that your text is engaging. It can foster trust and understanding with colleagues and business partners. It can persuade your audience to get on board with your viewpoint. Writing that misses the mark on tone, however, can cause misunderstandings, hurt feelings, damage your credibility, and lose your reader’s interest.
With that in mind, here’s a prompt that can help you achieve the right tone in your writing:
"Can you help me rewrite this [content] for [audience], ensuring it maintains a [describe the desired tone]?
Add context to make ChatGPT’s reply more helpful. For example, if your content should show sensitivity to a certain issue or audience, add it to the prompt.
4. Adding Data And Research
One lesson I’ve learned from contributing to Forbes and other widely-read publications is that my word alone is rarely enough. I can share my personal experiences, but research and data can strengthen any piece of writing.
Instead of researching the traditional way—reviewing your writing and identifying facts that need outside sourcing, then Googling for relevant insight—ChatGPT can speed up the process, leaving you more time to polish those personal anecdotes. Try this prompt:
"I’m writing [describe the content and subject matter] for [target audience] and want to include relevant data and research. Can you review the following text and provide researched-backed statistics and insights on this topic?"
Importantly, always check the sources that ChatGPT generates. It will almost certainly come up with helpful results but they’re not always accurate—that’s where you, human editor, come into play.
Refine Your Craft
To continually improve your writing skills, you can take a page from the habits of professional writers. The following prompts can help you develop practices to become a stronger writer.
5. Daily Writing Prompts
I’ve written before about my morning pages . It’s a great way to clear my head before the day begins and to practice fluidly translating my thoughts into words on paper. If a blank page feels intimidating, writing prompts are a great way to get started. ChatGPT can generate writing prompts in an instant. You can keep it general:
“Can you suggest a couple of writing prompts that I can use to practice the craft of writing?”
Or, if you have a goal in mind, add more context. For example:
“I'm trying to improve engagement with my readers. Can you generate a couple of writing prompts to practice writing engaging content?”
6. Experiment With Different Styles And Voices
If you call your grandmother on the telephone, I’d bet your voice and speaking style sound vastly different from when you’re chatting with your best friend. Writing is the same.
ChatGPT can help you practice toggling between different styles and voices, and in doing so, help you find yours. You can ask ChatGPT for writing prompts to practice a certain style. For example:
“Can you generate three short exercises to help me practice writing in different voices and styles?”
ChatGPT will not only generate exercises, it will also break down the structure and elements of different writing styles and specify the tone.
Or, you can submit text to ChatGPT and ask it to analyze the style and voice. Try this prompt:
“Can you analyze the voice and style of the following text: [insert text].”
I used this prompt to assess the introduction to one of my recent Forbes stories, and ChatGPT said it was “Conversational and Relatable,” “Encouraging and Reassuring,” and “Informative and Practical”—encouraging feedback from my AI editor.
7. Rewrite, Rewrite, Rewrite
In A Moveable Feast , Ernest Hemingway wrote, “The only kind of writing is rewriting.”
If you want to become a writer, you have to embrace rewriting, whether you’re retyping every word or pouring over (and over) a Google Doc draft. Here are a couple of prompts you can use so that ChatGPT can assist in the rewriting process, one excerpt at a time:
“Rewrite this paragraph in the style of [Ernest Hemingway or any other author]."
“Rewrite this introduction so that it sounds like a story in [publication]”
“Rewrite this email so that it will resonate with [audience].”
“Rewrite this paragraph for clarity and concision.”
Importantly, ChatGPT only does part of the work. It falls to the writer to analyze the results, apply those lessons in future drafts, and, of course, to keep writing.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

AI Generator
A claim is a formal request for compensation, reimbursement, or acknowledgment of a right. It often involves submitting relevant documentation to support the demand. For instance, a Payment Claim is submitted to receive due payment for services rendered, while an Authorization Letter to Claim grants permission for another person to claim on behalf of the rightful owner. In specialized fields, a Construction Claim addresses disputes or additional costs in building projects, and an Insurance Claim seeks financial recovery for losses covered under an insurance policy.
What is Claim?
A claim is a formal request for compensation, reimbursement, or acknowledgment of a right, often supported by relevant documentation. It is commonly used in various contexts such as payments, insurance, and legal disputes.
Examples of Claim
- Payment Claim – Requesting payment for completed work or services rendered.
- Insurance Claim – Seeking compensation for damages covered by an insurance policy.
- Warranty Claim – Requesting repair or replacement of a defective product under warranty.
- Construction Claim – Demanding additional payment due to unforeseen costs or changes in a construction project.
- Medical Claim – Seeking reimbursement for medical expenses from an insurance provider.
- Travel Claim – Requesting compensation for travel-related issues like delays or cancellations.
- Tax Claim – Filing for a refund of overpaid taxes.
- Unemployment Claim – Applying for unemployment benefits after losing a job.
- Legal Claim – Initiating a lawsuit to seek damages or enforce rights.
- Return Claim – Requesting a refund or exchange for a purchased product.
- Accident Claim – Seeking compensation for injuries or damages from an accident.
- Compensation Claim – Requesting payment for work-related injuries or losses.
- Insurance Claim for Natural Disaster – Asking for financial assistance after damages from a natural disaster.
- Shipping Claim – Seeking reimbursement for lost or damaged goods during shipping.
- Bank Claim – Disputing unauthorized transactions on a bank account.
- Intellectual Property Claim – Asserting rights over copyrighted or patented material.
- Rebate Claim – Requesting a partial refund for a purchased product as part of a promotion.
- Inheritance Claim – Seeking a share of an estate as an heir.
- Student Loan Claim – Requesting forgiveness or discharge of student loan debt.
- Utility Claim – Disputing charges or requesting reimbursement for service outages from utility providers.
Types of Claims
- Factual Claims: Statements that can be proven true or false based on evidence or facts. They rely on verifiable data and objective research.
- Value Claims: Assertions that evaluate the worth, rightness, or morality of something. These claims often reflect personal or societal values and are subjective.
- Policy Claims: Proposals for action or change, suggesting what should be done in a particular situation. They advocate for specific policies or courses of action.
- Definition Claims: Arguments about the meaning or categorization of a term or concept. They seek to define or redefine the way something is understood.
- Cause and Effect Claims: Statements that argue a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more things. They explain how one event leads to another.
- Comparative Claims: Assertions that compare one thing to another, highlighting similarities or differences. These claims evaluate relative qualities or characteristics.
- Predictive Claims: Forecasts about what will happen in the future based on current evidence or trends. They anticipate outcomes and future events.
What is Claim Reason Evidence in Writing?
Claim : A claim is the main argument or thesis statement of a piece of writing. It is the writer’s position on a particular topic or issue. The claim should be specific, debatable, and clearly stated.
Example: Claim: “School uniforms improve student behavior and academic performance.”
Reason : A reason explains why the claim is valid. It provides the rationale behind the claim and shows why the reader should accept it. Reasons should be logical and directly support the claim.
Example: Reason: “Uniforms create a sense of equality among students, reducing peer pressure and distractions.”
Evidence : Evidence consists of facts, statistics, examples, expert opinions, or other data that support the reason. It provides concrete proof that the reason is valid and, consequently, that the claim is true.
Example: Evidence: “A study conducted by XYZ University found that schools with uniform policies saw a 20% decrease in disciplinary issues and a 15% increase in test scores.”
Claim of policy
A claim of policy is a statement that advocates for a specific course of action or change in policy. It suggests that certain actions should be taken to address a problem or improve a situation. This type of claim often includes a proposal for a solution and is typically supported by evidence showing why the proposed action is necessary and beneficial.
Examples of Claims of Policy:
- Education: “Schools should implement a mandatory financial literacy curriculum to better prepare students for managing their personal finances.”
- Environment: “The government should ban single-use plastics to reduce environmental pollution and protect marine life.”
- Healthcare: “All countries should adopt universal healthcare systems to ensure that every citizen has access to essential medical services.”
- Workplace: “Companies should offer flexible work-from-home options to improve employee productivity and job satisfaction.”
- Public Safety: “Cities should invest in more extensive public transportation networks to reduce traffic congestion and lower carbon emissions.”
Components of a Claim of Policy:
- Problem Identification: Clearly define the issue that needs to be addressed.
- Proposed Solution: Outline the specific action or change in policy being advocated.
- Justification: Provide reasons and evidence to support why the proposed solution is necessary and beneficial.
- Implementation: Suggest how the proposed policy can be effectively implemented.
Structure of an Argumentative Essay
- Introduction
- Thesis Statement
- Body Paragraphs
- Counterarguments and Rebuttals
1. Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for your essay. It should:
- Provide background information on the topic.
- Present the issue at hand.
- Capture the reader’s attention.
“In today’s digital age, the use of social media has become ubiquitous. While it offers numerous benefits, there is a growing concern about its impact on mental health. This essay will argue that excessive social media use leads to increased anxiety and depression among teenagers.”
2. Thesis Statement
The thesis statement clearly states your main argument. It should be concise and specific.
“Excessive use of social media contributes to heightened anxiety and depression among teenagers.”
3. Body Paragraphs
Each body paragraph should focus on one main idea that supports your thesis. Include evidence such as statistics, quotes, studies, and real-life examples.
Paragraph 1:
- Topic Sentence: Excessive social media use disrupts sleep patterns.
- Evidence: Studies show that teens who use social media excessively are more likely to experience poor sleep quality.
- Explanation: Poor sleep quality is linked to increased anxiety and depression.
Paragraph 2:
- Topic Sentence: Social media promotes unrealistic expectations.
- Evidence: A survey revealed that 60% of teenagers feel pressured to look perfect on social media.
- Explanation: This pressure can lead to low self-esteem and mental health issues.
Paragraph 3:
- Topic Sentence: Online bullying is prevalent on social media platforms.
- Evidence: Reports indicate that 30% of teenagers have experienced cyberbullying.
- Explanation: Victims of cyberbullying are more likely to suffer from anxiety and depression.
4. Counterarguments and Rebuttals
Addressing counterarguments strengthens your essay by showing you have considered multiple viewpoints.
Counterargument: Some argue that social media helps teenagers build social connections and support networks.
Rebuttal: While social media can facilitate connections, it often leads to superficial relationships. Moreover, the negative effects on mental health outweigh the potential benefits of these connections.
5. Conclusion
The conclusion should summarize your main points and restate the thesis in light of the evidence presented. It should also provide a final thought or call to action.
What is a claim in an argumentative essay?
A claim is the main argument or stance you take on a particular issue in your essay.
How should I state my claim?
State your claim clearly and concisely in the thesis statement of your introduction.
Can a claim be a question?
No, a claim should be a declarative statement, not a question.
How many claims should an essay have?
Generally, one main claim is supported by several smaller, supporting claims.
What makes a strong claim?
A strong claim is specific, debatable, and backed by evidence.
Can a claim be a fact?
No, a claim should be an argument that requires support and evidence, not a universally accepted fact.
Do I need to address counterclaims?
Yes, addressing counterclaims strengthens your argument by showing consideration of opposing views.
Can a claim change during the writing process?
Yes, refining your claim as you gather more evidence and insights is common.
What is the difference between a claim and a topic sentence?
A claim is the main argument of the essay, while a topic sentence introduces the main idea of a paragraph.
How do I make my claim debatable?
Ensure your claim presents a viewpoint that others might dispute or have differing opinions on.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Include topic sentences that introduce each paragraph's main idea and provide a clear progression of your argument. Developing Body Paragraphs with Evidence and Analysis. When crafting the body paragraphs of your 4 paragraph essay, it is essential to include specific evidence and analysis to support your thesis statement.
Paragraphs are the building blocks of papers. Many students define paragraphs in terms of length: a paragraph is a group of at least five sentences, a paragraph is half a page long, etc. In reality, though, the unity and coherence of ideas among sentences is what constitutes a paragraph. A paragraph is defined as "a group of sentences or a ...
The four-paragraph essay consists of an introduction, two body paragraphs and a conclusion. 1. The Introduction. Begin this paragraph with a "hook" that will make readers interested in your essay. The University of Maryland University College recommends using: a surprising statement or statistic, quote, personal story.
8. All paragraphs need to be relevant to the marking criteria. 9. Only include one key idea per paragraph. 10. Keep sentences short. 11. Keep quotes short. Paragraph structure is one of the most important elements of getting essay writing right.
A paragraph typically has 75-160 words. With an average of 15-20 words per sentence and 5-8 sentences in a paragraph, this comes to approximately 75 to 160 words. However, this will depend on the expectations of your audience. See the next section for what teachers usually recommend. A lot of teachers and educators suggest that a paragraph ...
Figuring out how many sentences are in a paragraph can be a stressful process, especially when you consider the answer can vary. Learn what you need to know for your writing here. ... If you're working with the classic five-paragraph essay, you can aim for the typical three to five sentences per paragraph. For other papers, ...
November 30, 2015. There's often a lot of confusion, but if you're looking for a general answer to the question, "How many sentences in a paragraph?" the answer is there are 3 to 8 sentences in a paragraph. The important key to take away from this answer is that it's a rule-of-thumb. If you're looking for a hard and fast rule, you ...
I especially like Austin Chadd's 2-sentence paragraph, telling us that every paragraph should be at least 4-5 sentences long. And TFP's, right at the top, that uses a 1-sentence paragraph to propose that every paragraph needs 2-3 sentences. A paragraph should have as many words and sentences as it takes to express its concept or idea.
In most forms of writing, paragraphs tend to be around four to eight sentences long. This general range will vary depending on the type of writing in question and the effect the writer is aiming to achieve. In this guide, we'll look at the length of paragraphs in various types of writing and see what determines whether they should be 20 ...
So, on average, there will be about 3 to 7 sentences in a paragraph. This is how many it takes to convey all of the necessary information I mentioned above into a paragraph without putting in too much. You could also think of it as about half a page long, though that depends on how many words are in your sentences.
In order to show that you've mastered the standard essay structure, you should include 3-5 sentences in each paragraph. Begin most of your paragraphs with a transitional idea that connects the new paragraph to the one that came before. This sentence also introduces the main idea of the paragraph. Next, include 1-3 supporting sentences that ...
As a rule, five paragraphs should suffice for a 1,000-word essay. As long as you have an introduction and a conclusion and provide enough supporting details for the main ideas in your body paragraphs, you should be good to go. Remember to start a new paragraph when introducing new ideas or presenting contrasting information.
Essay length guidelines. Type of essay. Average word count range. Essay content. High school essay. 300-1000 words. In high school you are often asked to write a 5-paragraph essay, composed of an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. College admission essay. 200-650 words.
Most essay paragraphs have three to eight sentences or 100-200 words. Academic writing tends to have paragraphs that are about three-quarters of a page long. In writing dialogue, you need to begin a new paragraph every time the speaker changes. Journalism and commercial writing often call for short paragraphs that are easy to scan.
One-sentence paragraphs are suitable for blog posts, but academic research papers require more substantial paragraphs in order to fully explore your main ideas. Communicate compelling ideas in clear and concise language. To be a solid academic writer, you don't need to write wordy, jargon-filled sentences.
A 400 word essay is 3 paragraphs. (minimum for an essay) A 500 word essay is 3 to 4 paragraphs. A 600 word essay is 4 paragraphs. A 700 word essay is 4 to 5 paragraphs. A 750 word essay is 5 paragraphs. A 800 word essay is 5 to 6 paragraphs. A 900 word essay is 6 paragraphs. A 1,000 word essay is 6 to 7 paragraphs. A 1,250 word essay is 8 to 9 ...
Academic Writing. In academic writing, paragraphs will usually consist of the "standard" 100 - 200 words (Burns, 2002). You will begin the paragraph with an idea and then explain it in the light of currently accepted knowledge (Phillips, 2014) with references. Bear in mind that your tutor will want to see some original thought, but will ...
9 months ago. Hey there! It's great that you're working on your college essay. The ideal length for a college essay will depend on the specific essay prompt and the word limit given by the colleges you're applying to. Generally, most college essays fall in the range of 250-650 words. As for the number of paragraphs, it's more about effectively ...
2,000 words: between 13 and 14 paragraphs. 3,000+ words: 20+ paragraphs. You can see from this model how a higher final word count translates mathematically to a higher final paragraph count, and vice versa. Remember, this is just an estimation tool; always feel free to break the rules if it supports your essay better.
Let's say a teacher assigns a five-paragraph essay. The first paragraph is the introduction and includes a thesis statement. The last paragraph is the conclusion, which includes your findings. ... But even if you have to write paragraphs with many sentences, those sentences still shouldn't be overly wordy. Often, being direct is best.
Also, with increase in metabolism, many will benefit because obesity may be reduced. 4. Add a transition sentence: Transition sentences lead your reader to the next paragraph. For example: Also, when students are required to participate in sports at school they may build social skills. Develop Topic Sentences . Develop Reasons . Note . Thesis . Add
1. Generating Ideas And Topics. AI shouldn't do your writing for you. It lacks the necessary human context and isn't immune to errors. But it can be a powerful writing partner.
Paragraph 3: Topic Sentence: Online bullying is prevalent on social media platforms. Evidence: Reports indicate that 30% of teenagers have experienced cyberbullying. ... A claim is the main argument of the essay, while a topic sentence introduces the main idea of a paragraph.