Essay on Drought for Students and Children
500+ words essay on drought.
Drought is a dangerous condition which decreases the quality of life. It is termed as a natural disaster with harmful effects. A drought usually occurs when a region faces a shortage of water. This is mainly due to lesser rainfalls. In addition, droughts have proven to be fatal for mankind and wildlife as well.

Moreover, drought is the most dangerous for a farmer. As they do not have an ample supply of water, their crops dry out. This becomes a reason for worry as it is their sole income. Furthermore, drought also leads to various other problems for the environment and mankind.

Causes of Drought
Drought is caused due to various reasons. One of the main reasons is deforestation . When there will be no trees, the water on land will evaporate at a faster rate. Similarly, it lessens the soil capacity to hold water resulting in evaporation. Moreover, lesser trees also mean lesser rainfall which eventually leads to drought.
Furthermore, as the climate is changing, the water bodies are drying up. This results in a lower flow of surface water. Therefore, when the rivers and lakes will dry out, how will the people get water? In addition, global warming is a major cause of this. The greenhouse gas emitted causes the earth’s temperature to rise. Thus, it results in higher evaporation rates.
Subsequently, excessive irrigation is also a great cause of droughts. When we use water irresponsibly, the surface water dries up. As it does not get ample time to replenish, it causes drought.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Impact of Drought
Drought is a serious disaster which impacts the whole of mankind, wildlife, and vegetation greatly. Moreover, a region which experiences drought requires a lot of time to recover from the disaster. It is a severe condition which interferes with the quality and functioning of life.
Most importantly, the agriculture sector suffers the most at the hands of drought. For instance, farmers face a loss of crop production, livestock production. Moreover, they experience plant disease and wind erosion. Similarly, they also have to face heavy financial losses. Their financial condition worsens and they end up in debt. This also leads to higher rates of depression and suicides.

Furthermore, wildlife also suffers. They do not get sources of water to drink from. In addition, when forest fires happen due to droughts, they also lose their habitats and life. Just like any natural disaster , droughts also result in inflation of prices. The basic products become expensive. The poor people do not get access to essential foods due to high rates. Subsequently, droughts also degrade the quality of the soil. This result in poor or no yielding of crops.
In short, drought is definitely one of the most catastrophic natural disasters. It causes loss of life, vegetation and gives rise to other deadly problems like famine. The citizens and government must join hands to prevent droughts to save thousands of lives. This joint effort can help save the world from such a catastrophe.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [{ “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What are the causes of a drought?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Drought is caused by a number of reasons. Mostly, it is due to human activities only like excessive irrigation. Above all, droughts happen due to deforestation, low surface water flow, global warming and more.” } }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How does drought impact the world?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”:”Drought impacts the world very severely. It has a major impact on mankind, wildlife, and vegetation. It causes agricultural loss, financial loss, as well as wildlife loss. Moreover, it causes inflation in prices and degrades the soil. In other words, it puts the safety of thousands of lives at risk.”} }] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App
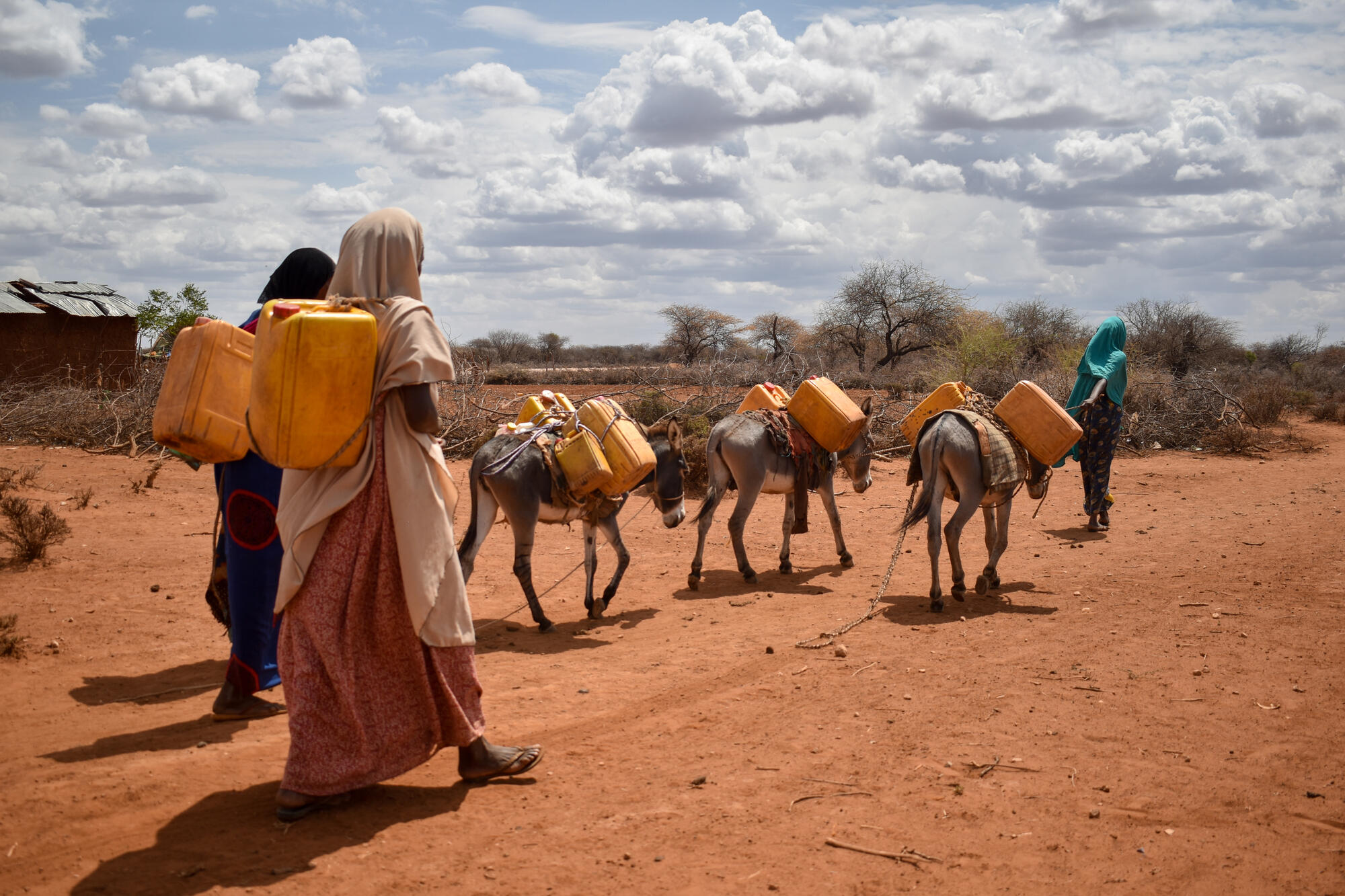


What is drought? Causes, impact & countries most affected
East Africa is facing its worst drought in 40 years, with over 1.4 million people displaced by drought in Somalia alone. Learn more about drought, what causes it, and how we can support those most impacted.
Around the world, droughts are becoming increasingly common due to rising global temperatures — and have serious impacts, leading to crop failures, famine and malnutrition.
East Africa , for example, is facing its worst drought in years, affecting 40 million people. Many are facing near-famine and malnutrition because of the drought’s impact on food supplies.
Learn more about drought, what causes it, and what the IRC is doing to help in East Africa.
Support our work
What is drought .
Drought is caused by a lack of rainfall, causing serious water shortages. It can be fatal.
More specifically, drought is defined by a period of unusually dry weather caused by low rainfall and high temperatures. It is also defined in terms of the impact on agriculture when crops fail due to lack of moisture in soil, leading to food shortages and serious human impacts such as famine in severe cases.
Unlike other extreme weather events that are more sudden, like earthquakes or hurricanes, droughts happen gradually. But they can be just as deadly as other weather hazards—if not more so. Drought has affected more people in the last 40 years than any other natural disaster.
The severity of drought worsens over time. When it arrives, drought can last for weeks, months, or years—sometimes, the effects last decades.
What causes drought?
Droughts can be triggered by natural causes such as weather patterns. But increasingly they are caused by human activity.

Human causes of drought
Climate change : Global warming makes extreme weather more likely. It can make places drier by increasing evaporation. When land becomes so dry, an impermeable crust forms, so when it does rain, water runs off the surface, meaning sometimes flash flooding occurs.
Deforestation : Plants and trees capture and release water into the atmosphere, which creates clouds and then rain. Scientists have observed a relationship between deforestation and drought.
Agriculture : Intensive farming contributes to deforestation in the first instance but can also affect the absorbency of the soil, meaning it dries out much more quickly.
High water demand : There are several reasons water demand might outweigh the supply, including intensive agriculture and population spikes. Also, high demand upstream in rivers (for dams or irrigation) can cause drought in lower, downstream areas.
Other natural causes of drought
Changes in ocean temperatures : El Niño and La Niña are climate patterns that can cause drought in some parts of the world. El Niño is characterized by warmer-than-average ocean temperatures in the Pacific Ocean, which can lead to drought in the southwestern United States and southern Africa. La Niña is characterized by cooler-than-average ocean temperatures in the Pacific Ocean, which can lead to drought in Australia and Indonesia.
The jet stream : The jet stream is a band of strong winds that flows high in the atmosphere. Changes in the jet stream can cause drought in some areas by bringing in dry air from other parts of the world.
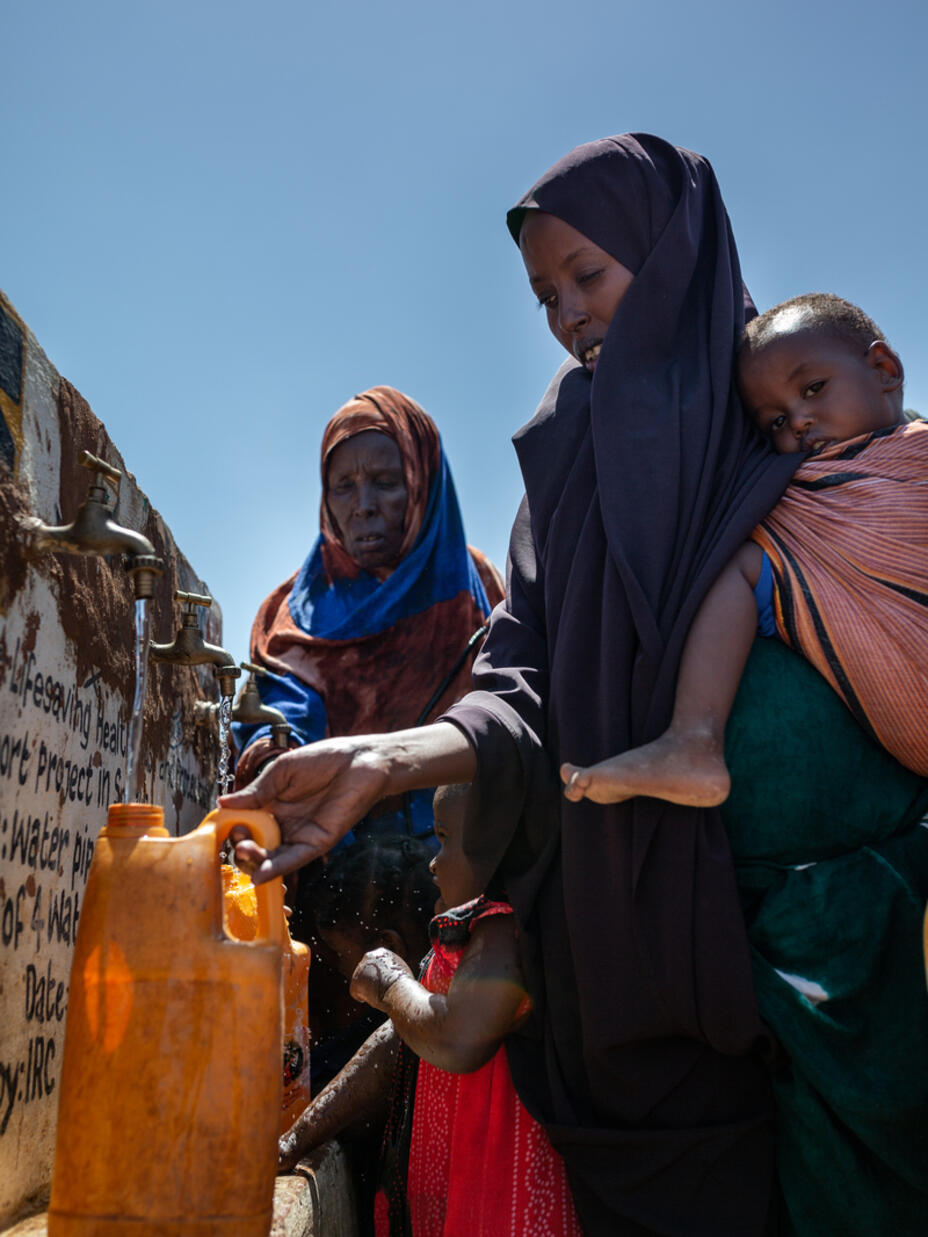
How are people impacted by drought?
Risk of famine .
Drought causes food insecurity when crops fail. When a substantial part of the population can no longer access food this is known as famine and results in widespread acute malnutrition, disease and death across the affected region.
East Africa is currently experiencing widespread food shortages and near-famine, with millions of children under 5 suffering from severe acute malnutrition.
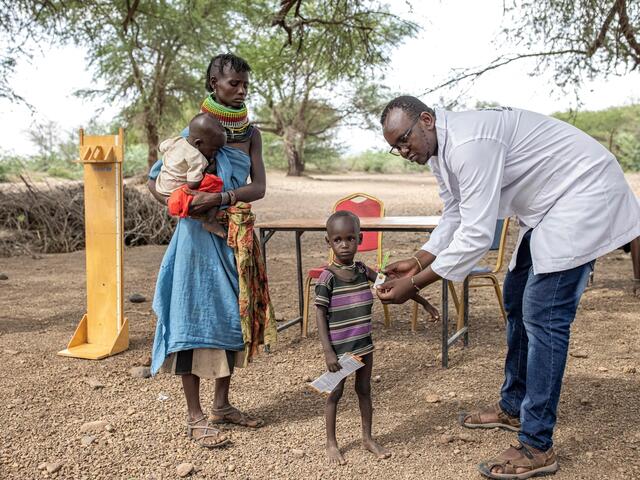

Malnutrition
A lack of nutritious food caused by food shortages leads to acute malnutrition. Children suffering from malnutrition are a high risk category. Deprived of essential vitamins and minerals required for their proper growth, they are prone to disease, severe developmental delays and even death.
Effective treatment for children suffering from malnutrition exists, but often does not reach those most in need. The IRC has developed a simplified process for treating malnutrition in order to reach more children with lower costs.
Increase in diseases
Drought affects vital access to clean drinking water. This can lead to people drinking contaminated water, which brings about outbreaks of diseases like cholera and typhoid. These diseases can also spread in places with poor sanitation, another side-effect of having no clean water.
It can cause wildfires
Dry conditions can cause wildfires that burn remaining vegetation and endanger homes. Fires can also impact air quality and exacerbate chronic lung conditions.
People are displaced
People must travel further to find clean water. This usually falls to women and children, who must sacrifice other work and school to carry out an incredibly physical task.
Without access to clean water or food, many must permanently leave their homes in order to survive. The World Health Organization states , “Water scarcity impacts 40% of the world’s population, and as many as 700 million people are at risk of being displaced as a result of drought by 2030.”
Related : Meet the people displaced by drought in Somalia
It can feed into conflict
Research has also found that drought exacerbates existing conflicts. People migrating en masse from areas of drought and famine can result in increased political tensions and conflict due to increased competition for resources. There is evidence that drought contributed to the conflict in Syria , for example.
Flash flooding
Flooding can also be a risk in the same geographical areas that suffer from drought.
Rain after a drought sounds like it ought to be a good thing, but after a prolonged period of dryness, sudden heavy rainfall can lead to hazardous flash flooding like that seen in Pakistan.
This is because droughts leave the ground hard and baked, with little to no plant cover and low soil quality, which prevents rain from saturating the ground. Instead, when waterfalls in a large quantity and at speed—like in a thunderstorm—it runs over the parched ground.

Which countries are in a drought?
Droughts can occur all around the world. However, the effects of drought vary by region.
Droughts bring the most risk to areas with high-pressure weather systems that are already prone to desertification. Developing countries are also more vulnerable to the socio-economic effects of drought due to a large percentage of their population being employed in the agriculture industry.
East Africa
In Africa droughts pose a high risk and the following countries in East Africa are severely affected by drought:
Somalia where drought is leading to near-famine conditions
Kenya which has experienced a record six below average rainy seasons
Ethiopia has seen six below average rainy seasons in a drought affecting 31 million people
Over 40 million people have been impacted by the drought across East Africa. The drought affecting countries like Somalia, Kenya and Ethiopia began in October 2020. Throughout these regions, insecurity, severe drought, and an exponential increase in food prices have brought millions to the brink of famine.
“Somalia is seeing the worst of the crisis, with over 200,000 already living in the most extremes of hunger, but the challenge is regional,” says Abukar Mohamud, IRC’s Deputy Director of Programs for Somalia. “Across East Africa, people are facing the worst drought in 40 years.
“People are not just dying due to a lack of food. Hunger means their weakened bodies cannot fight off diseases like diarrhea, measles or malaria, so death rates are high. Children are particularly at risk and often die at double the rate of adults. And those who survive will face ill health for the rest of their lives. The 2011 famine saw over 250,000 people die of hunger – half of whom were children.”
What is the IRC doing to help in East Africa?
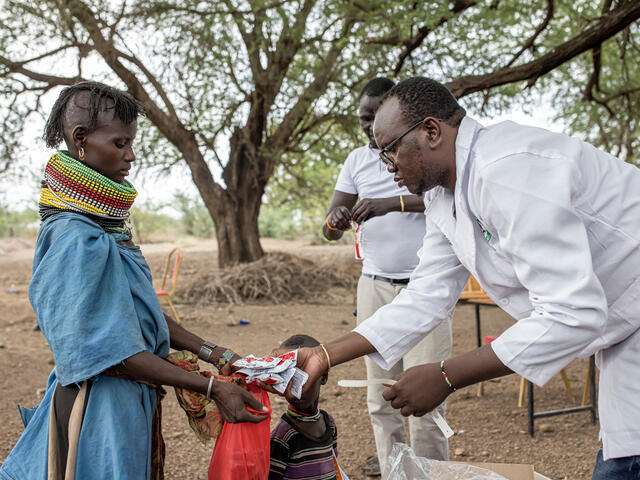

East Africa is home to some of the IRC’s longest-running programs globally. Today, over 2,000 IRC staff in the region are scaling up our programs to address the current drought and rising food insecurity, including expanding to new areas to meet severe needs.
This includes health programming, food and cash assistance, and providing clean water.
A new approach to treating malnutrition
Currently, 80% of malnourished children do not have access to treatment. The IRC has developed a streamlined approach for treatment so that more children can access treatment and recover. We are working to raise funds and remove blocks so that this treatment can be distributed at scale in places like East Africa.
How can I help?
Around the world, our staff are working around the clock to ensure families can survive, recover and regain control of their futures. Donate now to support our work.
Explore related topics:
- Malnutrition
- Climate crisis
- Natural Disasters
Related news & features

- Where We Work
- How To Help
- Code of Conduct
- Ethics Hotline
- 87% Program services
- 7% Management and general
- 6% Fundraising
Get the latest news about the IRC's innovative programs, compelling stories about our clients and how you can make a difference. Subscribe
- U.S./Global
- Phone Opt Out
- Respecting Your Privacy
- Terms and Conditions
- Fraud Prevention
ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Below-average precipitation affects the amount of moisture in soil as well as the amount of water in streams, rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
Earth Science, Climatology, Conservation, Anthropology
Loading ...
A drought is a period of time when an area or region experiences below-normal precipitation . The lack of adequate precipitation , either rain or snow, can cause reduced soil moisture or groundwater , diminished stream flow, crop damage, and a general water shortage. Droughts are the second-most costly weather events after hurricanes.
Unlike with sudden weather events such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and thunderstorms, it is often difficult to pinpoint when a drought has started or when it has ended. The initial effects of a drought may be difficult to identify right away, so it may take weeks or months to determine that a drought has started. The end of a drought is hard to identify for the same reason. A drought may last for weeks, months, or even years. Sometimes, drought conditions can exist for a decade or more in a region. The longer a drought lasts, the greater the harmful effects it has on people.
Droughts affect people in a several ways. Access to clean drinking water is essential for all life, and sources of water may dwindle during a drought . Without the presence of water, people must bring in enough water from elsewhere to survive. Water is also needed for crops to grow. When not enough precipitation falls to naturally water crops , they must be watered by irrigation . Irrigation is possible only when there is enough water in nearby rivers, lakes, or streams, or from groundwater . During a drought , these water sources are diminished and may even dry up, preventing crops from being irrigated and causing them to die off.
One person studying these problems is Alexandra Cousteau, a National Geographic Emerging Explorer whose latest initiative is Blue Legacy. She started Blue Legacy to raise awareness that we live on a water planet and must take care of it. Cousteau, the granddaughter of the famed ocean explorer Jacques Cousteau, believes that water will be a crucial issue in this century. She predicts that water problems such as drought , storms, floods, and degraded water quality will create “water refugees :” people migrating in search of water. Cousteau stresses that we must do all we can to protect Earth’s valuable freshwater resources.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
April 3, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

Essay on Drought
Students are often asked to write an essay on Drought in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Drought
Understanding drought.
Drought is a natural event that happens when an area gets less rain than normal. It can last for months or even years.
Causes of Drought
Droughts often occur due to lack of rain. Sometimes, high temperatures can also cause drought by making water evaporate from soil and plants.
Effects of Drought
Drought can make it hard for plants and animals to survive. It can also lead to water shortages for people. In severe cases, drought can cause famine.
Dealing with Drought
People can deal with drought by conserving water, using it wisely, and planning for dry periods.
250 Words Essay on Drought
Introduction.
Drought is a natural disaster characterized by a prolonged period of abnormally low rainfall, leading to a shortage of water. It is a complex phenomenon that can have serious ecological, social, and economic impacts.
Droughts are primarily caused by irregularities in global weather patterns. Climate change has been identified as a significant factor, with increasing global temperatures leading to changes in rainfall patterns and increased evaporation rates. Human activities, such as deforestation and overuse of water resources, can also exacerbate drought conditions.
Impacts of Drought
Drought can have severe consequences for both the environment and human societies. It can lead to crop failure, livestock death, and water shortages, impacting food production and access to clean water. This can consequently lead to malnutrition, disease, and death, particularly in vulnerable populations. Economically, droughts can result in increased prices and job losses in agricultural sectors.
Drought Mitigation
Mitigation strategies for drought include water conservation, efficient irrigation techniques, and the development of drought-resistant crops. Additionally, improving climate forecasting can help societies prepare for and manage drought conditions. Policymakers must also prioritize sustainable water management to ensure that water resources are used efficiently and equitably.
Drought is a pressing global issue that requires concerted efforts to mitigate its impacts. By understanding its causes and consequences, we can develop effective strategies to manage drought and reduce its harmful effects on society and the environment.
500 Words Essay on Drought
Droughts occur when there is an extended period of below-average precipitation. This deficiency of water supply can last for months or even years. Droughts are categorized into three types: meteorological, agricultural, and hydrological. Meteorological droughts are associated with reduced rainfall, agricultural droughts with soil moisture deficits affecting crop production, and hydrological droughts with reduced water availability in streams, reservoirs, and aquifers.
The primary cause of drought is a lack of precipitation over an extended period. This can be due to natural climate variability, such as the El Niño Southern Oscillation, or changes in atmospheric conditions that suppress the formation of clouds and rainfall. Human activities, such as deforestation and overuse of water resources, can also contribute to the occurrence and severity of droughts.
Drought Management and Mitigation
Effective drought management requires a proactive approach, focusing on reducing vulnerability and enhancing resilience. Strategies can include improving water infrastructure, implementing water conservation practices, and developing drought-tolerant crops. At the policy level, it involves developing comprehensive drought management plans, early warning systems, and drought risk insurance. Climate change adaptation strategies also play a crucial role in drought mitigation.
Drought is a significant global challenge that requires concerted efforts to mitigate and adapt. While it is a natural phenomenon, human activities have exacerbated its occurrence and impacts. Therefore, understanding drought, its causes, impacts, and management strategies is essential for sustainable development and resilience. As we move forward, it is crucial that we continue to enhance our knowledge and strategies to better manage and mitigate the effects of droughts.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- 0 Shopping Cart

What are the causes of drought?

A drought is a severe shortage of water in a particular location. A combination of factors causes droughts.
Meteorological causes of drought
Meteorological factors can cause an area to get less rainfall than average. Changes in global atmospheric circulation can mean it doesn’t rain much in an area. For example, the drought in Australia in the 2000s was made worse by changing air and ocean currents in the Pacific Ocean.
Changes in atmospheric circulation can also affect rainfall patterns. In the past, monsoon rains in India had failed to appear when they were due.
High-pressure systems can block low-pressure systems that bring rainfall to the UK. This can lead to drought conditions.
Hydrological causes of drought
A lack of water in stores such as rivers, lakes, reservoirs and aquifers (water stored underground naturally) can lead to drought. Areas that rely on rainfall and surface water are more likely to experience drought. Surface water quickly evaporates in warm, dry conditions leading to an increased risk of drought.
Hydrological causes of drought can take some time to have an impact. For example, water stores such as aquifers can take months or even years to replenish.
Human causes of drought
Deforestation leads to less water being stored in the soil. Therefore, the land dries out quicker than it would if it were covered in vegetation. Also, trees release moisture into the atmosphere through their leaves, a process is known as transpiration. Removing trees and vegetation reduces the amount of moisture in the atmosphere making the area drier.
Constructing dams and reservoirs reduces the flow of water downstream. This can lead to drought in other areas. There are several locations worldwide where this could lead to conflict in the future, including along the River Nile.
Intensive agriculture depletes water supplies as large quantities of water are required for irrigation . Additionally, livestock also has considerable demands on water for drinking.
Some locations are more vulnerable to drought than others
The map below shows the distribution of droughts around the world.
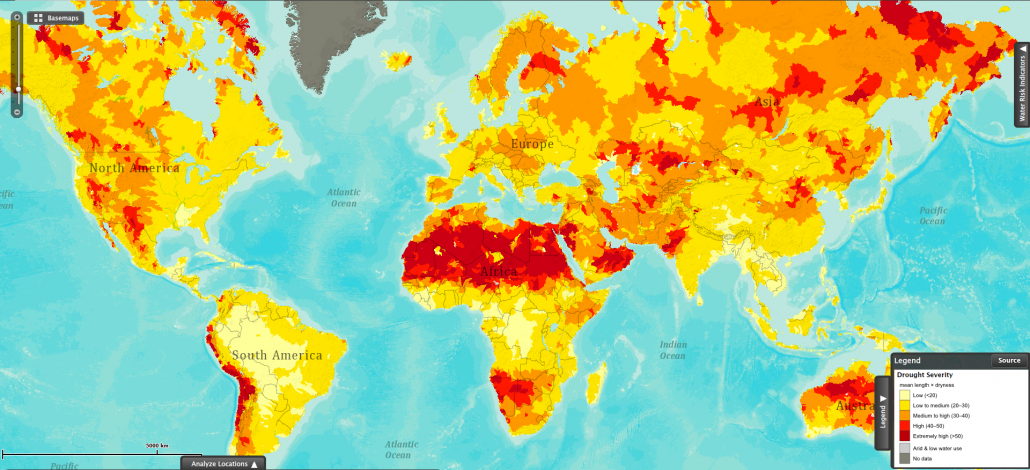
This map shows drought severity, measured as the product of the average length of a drought occurrence and how dry it was the drought. This visualization is based on data collected for the period between 1901 and 2008.
The areas experiencing the most severe droughts occur at around 30° north and south of the equator. This can be explained by global atmospheric circulation , as high pressure at this latitude brings very little rainfall.
Over time the locations affected by drought have varied. For example, there have been more droughts in Africa, Asia and the Mediterranean since 1950 and fewer in the Americas and Russia.
Some scientists have suggested that climate change might increase the frequency and severity of droughts in the future.

Premium Resources
Please support internet geography.
If you've found the resources on this page useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.
Arid environments and drought
Topic home, share this:.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
If you've found the resources on this site useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Search Internet Geography
Top posts & pages.
Latest Blog Entries
Pin It on Pinterest
- Click to share
- Print Friendly
Droughts 101
Droughts can cause a variety of problems to local communities, including damage to ecosystems, crops, and a shortage of drinking water.
Biology, Health, Geography
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Last Updated
October 19, 2023
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

Climate Basics » Extreme Weather
Drought and climate change.
Background on Drought
A drought is “a deficiency of precipitation over an extended period of time (usually a season or more), resulting in a water shortage. ” Indicators of drought include precipitation, temperature, streamflow, ground and reservoir water levels, soil moisture, and snowpack.
Climate change increases the odds of worsening drought in many parts of the United States and the world. Regions such as the U.S. Southwest , where droughts are expected to get more frequent, intense, and longer lasting, are at particular risk.
How climate change contributes to drought:
- Warmer temperatures enhance evaporation, which reduces surface water and dries out soils and vegetation. This makes periods with low precipitation drier than they would be in cooler conditions.
- Warmer winter temperatures are causing less precipitation to fall as snow in the Northern Hemisphere, including in key regions like the Sierra Nevada of California .
- Decreased snowpack can be a problem , even if the total annual precipitation remains the same. This is because many water management systems rely on spring snowpack melt . Likewise, certain ecosystems also depend on snowmelt, which supplies cold water for species like salmon. Because snow acts as a reflective surface, decreasing snow area also increases surface temperatures, further exacerbating drought.
- Some climate models find that warming increases precipitation variability, meaning there will be more periods of both extreme precipitation and drought. This creates the need for expanded water storage during drought years and increased risk of flooding and dam failure during periods of extreme precipitation.
- For example, the Southwestern United States has already seen a decrease in annual precipitation since the beginning of the 20 th century, and that trend is expected to continue.
- Estimates of future changes in seasonal or annual precipitation in a particular location are less certain than estimates of future warming, and are active areas of research. However, at the global scale, scientists are confident that relatively wet places, such as the tropics and higher latitudes, will get wetter, while relatively dry places in the subtropics (where most of the world’s deserts are located) will become drier.
- In some areas , droughts can persist through a vicious cycle , in which very dry soils and diminished plant cover absorb more solar radiation and heat up, encouraging the formation of high pressure systems that further suppress rainfall, leading an already dry area to become even drier.
Recent U.S. droughts have been the most expansive in decades. At the peak of the 2012 drought, the most extensive drought since the 1930s, an astounding 81 percent of the contiguous United States was under at least abnormally dry conditions.
California experienced a particularly drawn-out drought from December 2011 to March 2019, broken in part by the wettest winter in the United States . 2020 saw widespread, prolonged drought that was exacerbated by heat waves in more than a dozen Western and Central states. The intense drought and heat combined to wither vegetation, intensifying Western wildfires that burned record acreage.
Nationwide, conditions reached their peak in December 2020, when the greatest extent of land since 2012 was under extreme drought conditions. In the West, drought has continued and intensified in 2021, and has been exacerbated in the Pacific Northwest by record heat.
Threats Posed by Drought
The United States is historically susceptible to drought. Paleoclimate studies show major droughts in the distant past, with more recent dry periods still within living memory, such as the Dust Bowl of the 1930s or the drought of the 1950s. These historic examples serve as guideposts to highlight our vulnerabilities to drought as we move into a warmer and, in some places, drier future.
Severe drought can affect:
- Water supply: Droughts are defined by their lack of available water. During droughts, communities may have limited access to water for household use, including drinking, cooking, cleaning, and watering plants, as well as for agriculture, transportation, and power generation. Droughts may lead to higher water costs, rationing, or even the decimation of important water sources like wells, as a drought did in a rural California community in 2021.
- Agriculture: Droughts affect livestock and crops, including corn, soybeans, and wheat. At the height of the 2012 drought, the U.S. Department of Agriculture declared a natural disaster over 2,245 counties, 71 percent of the United States. Globally, drought struck several major breadbasket regions simultaneously in 2012, adding to food price instability . In countries already facing food insecurity, cost spikes can lead to social unrest, migration, and famine.
- Transportation: Droughts can lower river water levels, threatening commerce on rivers like the Mississippi. Transport barges need at least nine feet of water to operate, and to maintain this level, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers had to blast, dredge, and clear obstructions on a key stretch of the Mississippi in 2013. Drought is also often accompanied by extreme heat, which can buckle roadways, ground planes, and warp public transit cables. Drought-fueled wildfires also have repercussions for travel by closing roadways and railroads and grounding planes when smoke is thick.
- Energy: Droughts can raise concerns about the reliability of electricity production from plants that require cooling water to maintain safe operations. Hydroelectric power may also become unavailable during droughts. When heat waves coincide with droughts, electricity demands can grow, compounding stress on the grid.
- Public Health: Reduced flows in rivers and streams can concentrate pollutants , threatening the quality of water used for drinking and recreation. Also, drought-fueled wildfires can expose nearby communities to smoke and pollutants, which can exacerbate chronic respiratory illnesses.
All of these drought impacts can inflict extreme costs on people, businesses, and governments. From 2011 through 2020, the United States experienced nine droughts , each causing at least $1 billion in damages.
Droughts also increase the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, including by decreasing land productivity, which reduc es the amount of vegetation storing carbon dioxide . In addition, increases in drought-related wildfire and soil erosio n can release carbon dioxide sequestered in trees and plants back into the atmosphere.
How to Build Resilience
Governments and businesses must identify their vulnerability to drought and improve resilience. They can help prepare for both future droughts and climate change by practicing and promoting water conservation and enhancing water efficiency throughout landscapes, city plans, and water infrastructure. They can also identify alternative water supplies, create drought emergency plans, and encourage farmers to plant drought-resistant crops.
The Climate Mapping for Resilience and Adaptation portal helps communities understand and plan for their climate risks today and in the future, including a real-time map of wildfire, drought, flooding, and extreme heat across the United States.
Other actions that improve resilience to other stressors, like deploying green infrastructure for stormwater management increasing energy efficiency in buildings (thereby using less power from plants that rely on water to function), and using renewable energy like solar (that isn’t reliant on water) can improve resilience to drought as a co-benefit.
These steps will be most effective if they are combined with reductions in greenhouse gases that can minimize the ultimate magnitude of climate change. Luckily, many solutions that build resilience to drought and other climate stressors – like water conservation and improving soil health – can also reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Related Content
Publication, resilience strategies for drought.
Across the United States, the risk of drought is expected to grow due to reduced precipitation and higher temperatures caused by climate change. Drought’s far-reaching impacts can ripple through communities, regions, watersheds, economies and ecosystems. This fact sheet overviews strategies …
View Details Download (pdf, 647 KB)
Resilience Strategies for Wildfire
The risk of wildfire is expected to grow across the United States due to reduced precipitation in some regions, and higher temperatures caused by climate change. Wildfire has far-reaching impacts that can ripple through communities, regions, watersheds, and ecosystems. This …
View Details Download (pdf, 633 KB)
Extreme Weather and Climate Change
Tags Impacts Resilience Science Extreme Weather
Nature-Based Solutions for Resilient, Equitable Cities
Sonya Bengali
January 28, 2021
Tags Resilience
Cities Advancing Climate Action: Federal Funds for Local Impact
Cities will soon qualify for funding though the $1.2 trillion 2021 Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), which can be used to magnify their impact on climate and resilience priorities. This crucial funding opportunity comes at just the right time …
View Details Download (pdf, 2 MB)
The Climate Resilience-Economy Nexus: Advancing Common Goals
Communities across the United States are experiencing increasingly severe and frequent floods, wildfires, extreme heat, and other hazards due to climate change. These hazards are impacting local economies by damaging critical infrastructure and commercial districts, disrupting business operations, reducing municipal …
View Details Download (pdf, 7 MB)
Other Resources
- National Weather Service Drought Information
- IPCC Fifth Assessment Report Working Group 1
- Overview of the Water-Energy Nexus in the United States, National Conference of State Legislatures
- Climate Mapping for Resilience and Adaptation (CMRA) Portal
- National Integrated Drought Information System (Drought.gov)
- FEMA Building Resilient Infrastructure in Communities (BRIC)
- FEMA Building Community Resilience With Nature-Based Solutions, Strategies for Success
- Risk Factor: Find Your Property’s Climate Risks
Geography Notes
Essay on drought: top 9 essays | india | natural calamities | geography.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Here is a compilation of essays on ‘Drought’ for class 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Drought’ especially written for school students.
Essay on Drought
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Drought Prone Areas Programme (DPAP)
Essay # 1. Introduction to Drought:
Since time immemorial, mankind has lived under the threat of natural disasters. Amongst various hazards of nature, drought is the most disastrous. In the past, India had been a frequent victim of disastrous droughts, which resulted in famine deaths of large members of human and livestock.
Drought, thus, is a precursor of famine and undoubtedly man’s worst natural enemy. Technological developments and natural efforts are in progress to ameliorate the impacts of drought and being about sustainability to agricultural productivity in the country.
Low rainfall or failure of monsoon rains is a recurring feature in India. This has been responsible for droughts and famines. The word drought, generally, denotes scarcity of water in a region.
Though, aridity and drought are due to insufficient water, aridity is a permanent climatic feature and is the culmination of a number of long term processes. However, drought is a temporary condition that occurs for a short period due to deficient precipitation for vegetation, river flow, water supply and human consumption. Drought is due to anomaly in atmospheric circulation.
Drought is a climatic anomaly, characterised by deficit supply of moisture resulting either from subnormal rainfall, uneven distribution, higher water need or a combination all the factors. Droughts lead to problems like widespread crop failure, unreplenished groundwater resources, depletion in lakes/reservoirs, shortage of drinking water, reduced fodder availability etc.
Essay # 2. Definition of Drought :
There is no universally accepted definition of drought:
Early workers defined drought as prolonged period without rainfall. According to Ramdas (1960), drought is a situation when the actual seasonal rainfall is deficient by more than twice the mean deviation. American Meteorological Society defined drought as a period of abnormally dry weather, sufficiently prolonged for lack of water to cause a severe hydrological imbalance in the area affected.
In general, drought means different things to different people. To a meteorologist it is the absence of rain while to the agriculturist it is the deficiency of soil moisture in the crop root zone to support optimum crop growth and productivity.
To the hydrologist it is the lowering of water levels in lakes, reservoirs etc. while for the city management it may mean the shortage of drinking water availability. Thus, it is unrealistic to expect a universal definition of drought for all fields of activity.
Prolonged deficiency of soil moisture adversely affect crop growth indicating incidence of agriculture drought. It is the result of imbalance between soil moisture and evapotranspiration needs of an area over a fairly long period as to cause damage to standing crops and to reduce the yields.
Essay # 3. Classification of Drought :
Drought can be classified based on duration and nature of users. In both the classifications, demarcation between the two is not well defined and many a time overlapping of the cause and effect of one on the other is seen.
Droughts are classified into eight kinds:
(i) Permanent Drought :
This is characteristic of the desert climate where sparse vegetation growing is adapted to drought and agriculture is possible only by irrigation during entire crop season.

(ii) Seasonal Drought :
This is found in climates with well-defined rainy and dry seasons. Most of the arid and semiarid zones fall in this category. Duration of the crop varieties and planting dates should be such that the growing season should fall within rainy season.
(iii) Contingent Drought :
This involves an abnormal failure of rainfall. It may occur almost anywhere especially in most parts of humid or sub-humid climates. It is usually brief, irregular and generally affects only a small area.
(iv) Invisible Drought :
This can occur even when there is frequent rain in an area. When rainfall is inadequate to meet the evapotranspiration losses, the result is borderline water deficiency in soil resulting in less than optimum yield. This occurs usually in humid regions. Droughts are also classified based on their relevance to the users.
(v) Meteorological Drought :
In India, the definition for meteorological drought adopted by IMD is a situation when the deficiency of rainfall at a meteorological sub-division level is 25 per cent or more of the long- term average (LTA) of that subdivision for a given period. Drought is considered moderate; if the deficiency is between 26 and 50 per cent and severe if it is more than 50 per cent.
In our country, a year is considered to be a drought year in case the area affected by moderate and severe drought, either individually or together, is 20 to 40 per cent of the total area of the country and seasonal rainfall deficiency during southwest monsoon season for the country as a whole is at least 10 per cent or more. When the spatial coverage of drought is more than 40 per cent, it will be called as all India severe drought year (IMD Technical Circular No 2/2007).
(vi) Atmospheric Drought :
It is due to low air humidity, frequently accompanied by hot dry winds. It may occur even under conditions of adequate available soil moisture. Plants growing under favourable soil moisture regime are usually susceptible to atmospheric drought.
(vii) Hydrological Drought :
Meteorological drought, when prolonged, results in hydrological drought with depletion of surface water and consequent drying of reservoirs, tanks etc. This is based on water balance and how it affects irrigation as a whole for bringing crops to maturity.
(viii) Agricultural Drought :
It is the result of soil moisture stress due to imbalance between available soil moisture and evapotranspiration of a crop. It is usually gradual and progressive. Plants can therefore, adjust at least partly, to the increased soil moisture stress. This situation arises as a consequence of scant precipitation or its uneven distribution both in space and time. It is also usually referred as soil drought.
When soil moisture and rainfall are inadequate during crop growing season to support healthy crop growth to maturity, which situation causes extreme crop stress and wilting is called agricultural drought. It is defined as a period of four consecutive weeks (of severe meteorological drought) with a rainfall deficiency of more than 50 per cent of the long-term average (LTA) or with a weekly rainfall of 5 cm or less during the period from mid-May to mid-October (kharif) when 80 per cent of the country’s total crop is planted, or six such consecutive weeks during the rest of the year.
Essay # 4. Criteria of Drought :
In India various states and official commission have adapted different criteria for classifying droughts.
Irrigation Commission, while adopting the IMD classification of Meteorological drought based on departure of annual rainfall from normal, considered those regions which experienced drought in 20 per cent of years as drought areas and those area which experienced drought in more than 40 per cent of the years as chronic drought areas.
National Commission on Agriculture (1976) considered agricultural drought as an occasion when at least four consecutive weeks receive rainfall half of the normal (normal rainfall being 5 mm or more) during the crop season (mid-May to mid-October) or six such weeks during other period.
The criteria adopted in different states also vary depending on the rainfall and crops grown in the region. Tamil Nadu considers region receiving less than 900 mm rainfall as drought affected, while Karnataka considers regions receiving rainfall less than 400 mm during kharif and less than 30 per cent during crop season and 20 per cent deficiency of rainfall during crucial stages of crop growth as drought affected areas.
Rajasthan on the other hand considers a year as scarcity year when the productivity decrease by 50 per cent compared to a good crop year. Many of the states also follow the “Annawary” system wherein the crop conditions are assessed through visual estimates.
The criterion followed is:
Production above 75 per cent of normal: No drought.
Production 50 to 75 per cent of normal: Moderate drought.
Production 25 to 50 per cent of normal: Severe drought.
Production less than 25 per cent normal: Disastrous drought.
Besides rainfall, various other climatic and soil factors have also been used for drought classification. These include the aridity index (la) anomaly and ratio of actual to potential evapotranspiration (AE/PE).
Studies at CAZRI categorised drought based on moisture stress during crop growing season using the following criteria:
Drought Free Period:
When cumulative AE curve is above cumulative PE/2 curve.
Moderate Drought Period:
When cumulative AE curve lies between cumulative PE/2 and PE/4 curves.
Severe Drought Period:
When cumulative AE curve is below cumulative PE/4 curve.
Impact of drought depends on the phonological state of crop growth. Hence, a novel method of classification of agricultural droughts was attempted at CAZRI, considering the values of AE/ PE during different phenophases of crop growth as indicated in Table 5.4.
Depending upon the values of AE/PE during different phenophase, drought code varies as S 1 V 3, R 2 , S 0 V 1 , R 1 etc.
This is a generalised classification without specification of any crop. At this state, crop factor can be introduced and drought code in three syllables can be unified into a single drought code (A) applicable to one particular crop for a specific region. Based on this criteria, the above two situations mentioned come under classification of A 2 (moderate) and A 1 (mild) respectively.
Apart from climatological parameters, physical parameters like canopy-air temperature differences have also been used for assessing stress degree days (SDD) to indicate the impact of drought. The SDD have been found to correlate well with yield fluctuations as a result of moisture stress. Also spectral ratios of infrared to red reflectance obtained from radiometers (satellite or ground based) can be used to monitor agricultural effects of drought based on observed rate of change of absorbed radiation expressed as a fraction of maximum rate.
Essay # 5. Impact of Droughts:
One of the sectors where immediate impact of drought is felt is agriculture. With increased intensity or extended duration of drought prevalence, a significant fall in food production is often noticed. Drought results in crop losses of different magnitude depending on their geographic-incidence, intensity and duration. Drought not only affects food production at farm level but also national economy and overall food security as well.
Besides shortage of food and drinking water, impact of drought is also felt due to:
a. Deficit groundwater recharge.
b. Non availability of quality seed.
c. Reduced draught power for agricultural operations due to distress sale of cattle.
d. Land degradation.
e. Fall in investment capacity of farmers for further investment in agriculture.
Essay # 6. Periodicity of Drought:
Drought prone areas in the country, classified on annual rainfall departure, fall either in arid, semiarid and dry sub-humid regions where droughts occur frequently.
Periodicity of drought in different meteorological subdivisions is given in Table 5.5 :
Historical rainfall data of the country suggests that the monsoon rainfall recorded in the country during drought year of 1918 was the lowest.
Severe drought years that occurred over the past 200 years (1801-2000) are shown in Table 5.6:
Administrative districts frequently affected by drought are given in Table 5.7:
Essay # 7. Plant Adaptations to Drought :
Plants can grow and survive in dry habitat by escaping drought and drought resistance.
Escaping Drought :
Many short duration desert plants (ephemerals) germinate with rains and mature in five to six weeks. They have no mechanism to overcome soil moisture stress and are not drought resistant. In cultivated crops, early maturity before soil moisture stress is the main adaptation to drought in dry regions.
Drought Resistance :
Plants can adapt to drought conditions in two ways: avoiding stress and tolerating stress. Stress avoidance is the ability to maintain favourable water balance and turgidity even when subjected to drought thereby avoiding stress and its consequences. Favourable water balance can be achieved either through conserving water by restricting transportation (water savers) or by accelerating water uptake (water spenders).
The mechanisms for conserving water are regulating stomatal opening, increased photosynthetic efficiency, low rates of cuticular respiration, decreasing transpiration by lipid deposition on leaves, reducing leaf area, stomatal frequency and location and presence of awns. Water uptake can be accelerated by efficient root system, high root to top ratio, differential osmotic potential of plants and change of water spenders to water savers.
Drought Tolerance :
Plants can tolerate drought either by mitigating the actual stress or by showing high degree of tolerance to stress. Mitigating the stress by resistance to dehydration and by preventing leaf collapse permit the plants to maintain a high internal water potential inspite of drought conditions.
Tolerating the stress by resistance to metabolic strain (starvation acid protein loss) and plastic strain (increased resistance to stress due to exposure to sublethal stress for long period) can increase the plant ability to resist and survive under conditions of soil moisture stress.
Essay # 8. Drought Prone Areas :
Out of the total geographical area of India, almost one-sixth area with 12 per cent of the population is drought prone; the areas that receive an annual rainfall up to 600 mm are the most prone. Irrigation Commission (1972) had identified 67 districts as drought prone.
These comprise 326 taluks located in 8 states, covering an area of 49.73 M ha. Subsequently, National Commission on Agriculture (MoA 1976) identified a few more drought prone areas with slightly different criteria. Later, based on detailed studies, 74 districts of the country have been identified as drought prone.
In the past, one or more of the following four criteria were used to identify drought prone areas:
(1) Meteorological data.
(2) Revenue remission.
(3) Frequency of famine or scarcity.
(4) Availability of irrigation facilities.
Some states used other criteria also. Tamil Nadu identified 311 taluks in which rainfall was less than 900 mm or less than 35 per cent of the cultivable area irrigated as drought area. Rajasthan considered an area to be drought prone when the ratio of good crop year to scarcity year was 2: 1 or when not less than 50 per cent of the village of the area were affected by drought.
Karnataka considered those areas as drought areas which received less than 400 mm rainfall during kharif and less than 150 mm during rabi with a variability of more than 30 per cent during each season and rainfall deficiency of more than 20 per cent at the critical stages of crop growth. Thornthwaite used water balance approach for evaluating drought and proposed the aridity index.
The Irrigation Commission relied, on only two criteria: meteorological data and available irrigation facilities and demarked the areas as drought or chronic drought zones. Drought zones are areas with 25 per cent probability of rainfall departure from the normal. Chronic drought zones are areas with 40 per cent probability of rainfall departure or more than – 40 per cent from the normal.
Essay # 9. Drought Prone Areas Programme (DPAP):
It is the earliest area development programme launched by the Central Government in 1973- 74 to tackle the special problems faced by those fragile areas, which are constantly affected by severe drought conditions. These areas are characterised by large human and cattle populations which are continuously putting heavy pressure on the already degraded natural resources for food, fodder and fuel.
Basic objective of the programme is to minimise the adverse effects of drought on production of crops and livestock and productivity .of land, water and human resources, leading to drought proofing of affected areas.
The programme aims at promoting overall economic development and improving the socio-economic condition of resource poor and disadvantaged sections inhabiting the programme areas through creation, widening and equitable distribution of resource base and increased employment opportunities.
The objectives of the programme are being addressed, in general, by taking up development works through watershed approach for land development, water resource development and afforestation/pasture development.
Recent impact studies sponsored by the ministry have revealed that with the implementation of watershed projects under Drought Prone Areas Programme, overall productivity of land and water table have increased and there has been a significant impact in checking soil erosion by water and wind. The programme has also helped in overall economic development in the project areas.
Major problems are continuous depletion of vegetative cover, increase in soil erosion and fall in groundwater levels due to continuous exploitation without any effort to recharge the underground aquifers.
Though the programme had a positive impact in terms of creating durable public assets, its overall impact in effectively containing the adverse effects of drought was not found to be very encouraging. In addition, many of the states had also been demanding inclusion of additional areas under the programme.
With a view to identifying the infirmities in the programme and also for considering the case for inclusion of additional areas under the programme, a high level technical committee under the chairmanship of Prof CH Hanumantha Rao, Ex-Member Planning Commission was constituted in April 1993 to critically review the contents, methodology and implementation processes of all area development programmes and suggest suitable measures for improvement.
The Committee in its report submitted in April 1994 had attributed the unsatisfactory performance of the programmes to the following major factors:
1. Implementation of programme activities over vast areas in a sectoral and dispersed manner.
2. Inadequate allocations to the programme and programme expenditures thinly spread overlarge problem areas.
3. Programme implemented through government agencies with least or no participation of local people.
4. Taking up of a vast array of activities, which were neither properly integrated nor necessarily related to objectives of the programme.
Based on recommendations of the Hanumantha Rao Committee, comprehensive guidelines for watershed development, commonly applicable to Drought Prone Areas Programme, Desert Development Programme and Integrated Wastelands Development Programme were issued in October 1994 and were made applicable with effect from 1.4.1995. Subsequently, based on the feedback received from states, project implementation agencies and others concerned, guidelines were revised in September 2001.
Relevant definition of agricultural drought appears to be a period of dryness during the crop season, sufficiently prolonged to adversely effect the yield. The extent of yield loss depends on the crop growth stage and the degree of stress. It does not begin when the rain ceases, but actually commences only when the plant roots are not able to obtain the soil moisture rapidly enough to replace evapotranspiration losses.
Important causes for agricultural drought are:
a. Inadequate precipitation.
b. Erratic distribution.
c. Long dry spells in the monsoon.
d. Late onset of monsoon.
e. Early withdrawal of monsoon.
In India, seasonal rainfall (monsoon rains) over Indian subcontinent is a global phenomena associated with large scale hemispherical movement of air masses. As such, identification of major atmospheric phenomenon that influences the monsoons over Indian subcontinent is essential in drought management research.
Two such relationships are:
(i) Sea surface temperature anomaly around the Indian subcontinent in relation to atmospheric circulation.
(ii) Large scale pressure oscillation in atmosphere over southern Pacific Ocean.
The El Nino event is one such phenomenon, which has profound influence on the monsoon activity over Indian subcontinent, The Southern Oscillation Index (SOI) is one important parameter in the predictive sixteen parameters model used by IMD for long range forecasting purposes.
As per IMD studies, all the drought years are El Nino years where as all the El Nino years are not drought years indicating thereby that various other factors also equally influence the monsoon over the Indian subcontinent.
In this context, the winter circulation over the subcontinent, extended period of occurrence of western disturbances (late in the season), strengthening of heat low over N-W India in summer and shifts in zonal cells over India are some of the important parameters that influence monsoon system over the country.
Related Articles:
- The Identification and Distribution of Drought-Prone Areas in India
- Essay on Natural Hazards in India | Geography
- Natural Calamities: Essay on Natural Calamities | Geography
- Essay on Natural Resources: Top 4 Essays | Geography
Drought , Essay , Geography , India , Natural Calamities
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |

American Geosciences Institute
- Policy & Critical Issues
- Advisory Committees
- Coalitions & Working Groups
Explore the Geosciences
- Mineral Resources
Frequently Asked Questions
- Geoscience In Your State
- Policy News & Monthly Review
- Policy Annual Review
- Federal Geoscience Funding
Policy Positions
- Codes of Ethics
- Critical Needs
- Letters and Statements
- Policy Recommendations
- Position Statements
- Case Studies
- Geoscience in Your State
- GOLI Online Courses
Maps & Visualizations
- Petroleum and the Environment
- Policy Publications
- Research Database
- Congressional Briefings
- Congressional Visits Days
Get Involved
- Communicating with Congress
- Fellowships
- Internships
External Resources
- U.S. Congress
- Federal Agencies
- State & Local Agencies
Drought Basics
Drought is a water shortage caused by abnormally dry weather. Drought is relative to normal conditions, so weather conditions that create severe drought in a state like Georgia may be normal for an arid state such as Arizona. All regions of the United States have some drought risk. The impact of a drought depends not only on the severity of dry weather but also on local water use and supply. To identify and forecast drought, scientists and managers must monitor not only precipitation but also water demand and available water resources. These resources may be found in reservoirs, in rivers, in the soil, and underground as groundwater.
Extreme drought is part of natural climatic cycles around the world. Historic records and prehistoric reconstructions extending back 1000 years document that extreme droughts have occurred repeatedly in North America, sometimes for longer periods than even the most severe droughts of the 20th century. [1] Research on climate variability is addressing how drought may impact the United States in the future.
Why does drought matter?
Drought has many direct and indirect impacts on the economy, the environment, and public health. [2] Drought has an enormous impact on the United States. Since 1980, drought has caused more than $225 billion in damages to the national economy. [3] Social impacts of drought can include health problems, loss of human life, and disruption to livelihoods and recreation. [2]
How does geoscience help inform decisions about drought?
Geoscientists use software models and paleoclimate data to study past droughts and predict how drought may impact the United States in the future. Geoscientists also use hydrology and hydrogeology to study water use and the availability of surface- and groundwater to predict how short-term rainfall or snowpack shortages will affect water supplies.
1 Drought in the United States: Causes and Current Understanding. Congressional Research Service
2 Types of Drought Impacts, National Drought Mitigation Center
3 Billion-Dollar Weather and Climate Disasters, National Climatic Data Center
Introductory Resources
- Drought Basics (Webpage), National Drought Mitigation Center This webpage includes a drought glossary, definition of drought and types of drought, and explanation of drought forecasting, climatology, and historical climate studies. Includes a Also provides a history of the Dust Bowl in the United States.
Resources for Educators
- Education Resources Network, AGI's Center for Geoscience & Society Search for drought resources in: Curricula & Instruction , Teaching Media , Outreach Programs
- NGSS Performance Expectations, Next Generation Science Standards K-ESS2-1 , 2-ESS2-3 , 3-ESS2-1 , 3-ESS2-2 , 5-ESS2-2 , MS-ESS2-4 , MS-ESS2-5 , MS-ESS2-6 , HS-ESS2-2 , HS-ESS2-4 , HS-ESS2-6 , MS-LS1-5 , HS-LS4-5
- NGSS Disciplinary Core Ideas , Next Generation Science Standards ESS2.C, ESS2.D, LS1.B, LS4.C
Do you have a question that's not listed here? Search all FAQs
Search all Maps & Visualizations >
- Board of Directors
- AGI Connections Newsletter
- Nominations
- News and Announcements
- Membership Benefits
- Strategic Plan
- Annual Report
- Member Societies
- Member Society Council
- International Associates
- Trade Associates
- Academic Associates
- Regional Associates
- Liaison Organizations
- Community Documents
- Geoscience Calendar
- Center for Geoscience & Society
- Education & Outreach
- Diversity Activities
- Scholarly Information
- Geoscience Profession
- Earth Science Week
- Publication Store
- Glossary of Geology
- Earth Science Week Toolkit
- I'm a Geoscientist
- Free Geoscience Resources
- AGI Connections
- Be a Visiting Geoscientist
- Use Our Workspace
Home — Essay Samples — Environment — Drought — Drought In African Countries: Effects And Possible Solutions
Drought in African Countries: Effects and Possible Solutions
- Categories: Drought
About this sample

Words: 2320 |
12 min read
Published: Jun 9, 2021
Words: 2320 | Pages: 5 | 12 min read
Table of contents
Impact of drought in rural african communities, possible solutions in overcoming severe effects of droughts, works cited.
- Adelana, S. M., & MacDonald, A. M. (2008). Challenges to sustainable groundwater development in Africa. In Groundwater in the Celtic Regions: Studies in Hard Rock and Quaternary Hydrogeology (Vol. 324, pp. 111-118). Geological Society, London.
- Calow, R., MacDonald, A., & Nicol, A. (2010). Developing groundwater for secure rural water supplies in Africa. In Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Water Management (Vol. 163, No. 2, pp. 71-76). Thomas Telford Ltd.
- Devereux, S., & Maxwell, S. (2001). Food security in sub-Saharan Africa. ITDG Publishing.
- Lovell, C. (2000). Gender, rural livelihoods and household water security: Case studies from Zimbabwe and Lesotho. Progress in Development Studies, 2(4), 283-305.
- Overseas Development Institute. (2017). Water, livelihoods and resilience in sub-Saharan Africa. Retrieved from https://www.odi.org/publications/10826-water-livelihoods-and-resilience-sub-saharan-africa
- OCHA. (2004). Ethiopia: Food crisis and public health emergency. United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs.
- ODI. (2017). Water and food security: Key lessons from a review of water-related interventions in development programming. Retrieved from https://www.odi.org/publications/10991-water-and-food-security-key-lessons-review-water-related-interventions-development-programming
- World Food Programme. (n.d.). Addressing water scarcity in Africa. Retrieved from https://www.wfp.org/news/addressing-water-scarcity-africa
- World Bank. (2018). Groundwater governance in Africa: A review of common challenges and best practices.
- Yatenga Documentation Centre. (n.d.). The story of Yatenga.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Environment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1048 words
1 pages / 566 words
1 pages / 397 words
2 pages / 892 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Drought
No one can deny the fact that Drought is the main hazard in Canada which creates many issues whenever it occurs. Drought is the main concern in Canada and in Western countries which damage several industries, homes and main [...]
Drought stress is one of the most threatened environmental stresses to mankind. It is the most serious stress which limits the agricultural growth and its development and further leads to a great threat to world food security. [...]
Scientists could predict whether or not major earthquakes are likely to occur, however, based on the movement of the plates in the Earth and the location of fault zones. They also can make general guesses about when earthquakes [...]
The planet has four major layers: the inner core, outer core, mantle and crust. The crust makes up a thin skin on the exterior of our planet, but this skin is not all in one part, it’s made up of many pieces similar a puzzle [...]
Amidst the tranquil harmony of nature's daily awakening, the phenomenon of heavy rain casts a profound impact on the landscape, ecosystems, and human settlements. This narrative explores the transformative power of heavy [...]
The Earth had formed over 4.5 billion years from now and since then, we are still seeing changes. We are seeing volcanoes erupting and earthquakes shaking the earth’s surface causing massive destruction, the causes is due to [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

The Impact of Drought in South Africa: Research Grade 11
- May 12, 2023

South Africa is a country that is susceptible to drought due to its semi-arid climate, which makes it vulnerable to the effects of climate variability and change. Drought has significant impacts on the country’s social, economic, and environmental systems. This research task aims to equip Grade 11 learners with skills in research, analysis, interpretation, and communication. This paper will explore the possible subtopics and questions that learners can explore, the importance of the research memorandum, and how learners can prepare for their exams.
Causes of Drought
Drought is a natural disaster that occurs when there is a shortage of rainfall over an extended period. The first subtopic that learners can explore is the causes of drought . This section aims to provide an understanding of what drought is and the different types of drought. The research task should explain the physical and human causes of drought. Physical causes may include climate variability, while human causes may include deforestation, over-extraction of groundwater, and poor water management practices. Climate change is also a crucial factor that impacts drought, and learners can investigate how climate change exacerbates drought conditions.
To explore the causes of drought, learners can ask the following questions:
- What is drought, and what are the different types of drought?
- How does climate variability contribute to drought?
- What are the human causes of drought, and how do they contribute to the occurrence of drought?
- How does climate change impact drought conditions?
Impacts of Drought
Drought has significant impacts on society, the economy, and the environment. The second subtopic that learners can explore is the impacts of drought . This section should provide an understanding of the social, economic, and environmental impacts of drought. Learners can investigate how different regions and communities experience drought differently, as well as the short-term and long-term effects of drought. The research task should describe the loss of vegetation, soil erosion, and the depletion of water resources. Learners can also investigate how drought affects wildlife and biodiversity.
To explore the impacts of drought, learners can ask the following questions:
- What are the social impacts of drought, and how do they affect communities?
- How does drought affect the economy, and what are the economic impacts of drought?
- How does drought affect the environment, and what are the environmental impacts of drought?
- What are the short-term and long-term effects of drought on communities and ecosystems?
Management Strategies for Drought
Drought management strategies are crucial in mitigating the impacts of drought. The third subtopic that learners can explore is management strategies for drought. This section should provide an understanding of the different drought management strategies used in different regions. Learners can investigate the effectiveness of these strategies and the challenges and limitations of drought management. They can also explore the strategies used to mitigate the impacts of drought, including water conservation, drought-resistant crops, and alternative water sources. The research task can also discuss how communities can adapt to drought and manage water resources more sustainably.
To explore the management strategies for drought, learners can ask the following questions:
- What are the different drought management strategies used in different regions?
- How effective are these strategies, and what are the challenges and limitations of drought management?
- What are the strategies used to mitigate the impacts of drought, and how successful are they?
- How can communities adapt to drought and manage water resources more sustainably?
The Importance of the Research Memorandum
The Geography Grade 11 Research about Drought Memorandum is an essential resource for learners preparing for the Geography Grade 11 research task on drought. It provides a clear guideline on what is expected from the learners and how to approach the research task. Learners can gain insight into the research question, methodology, and requirements for the final report. The memorandum can also provide a clear understanding of the scope of the research task and the subtopics that learners should explore. By carefully reading and following the memorandum, learners can ensure that they meet the requirements of the research task and produce a high-quality report. Additionally, the memorandum can also help learners develop important skills such as critical thinking, research, and communication skills. These skills are not only essential for the research task but also for future academic and professional endeavors. Therefore, it is important for learners to take the memorandum seriously and use it as a tool for success.
In conclusion, the Geography Grade 11 research task on drought provides learners with an opportunity to develop their research, analysis, interpretation, and communication skills. By exploring the causes, impacts, and management strategies for drought, learners can gain a deeper understanding of the complex social, economic, and environmental challenges that arise from drought conditions in South Africa. By preparing for the research task and exam, learners can also develop critical thinking skills and improve their ability to communicate their findings effectively. Ultimately, this research task can help learners become more engaged and informed citizens, capable of addressing the complex challenges facing their communities and the world.
- # drought effects research Grade 11
- # drought impact analysis
- # drought research grade 11
- # effects of drought South Africa
- # Grade 11 drought study
- # Grade 11 environmental research
- # impact of drought in South Africa
- # South Africa drought consequences
- # South Africa drought impact
- # South Africa water crisis research
10 Ways to Prevent Drought in South Africa
What were the economic effects of the native land act of 1913, two positive behavior programs the government can implement to contribute to nation building.
- Mar 07, 2024
Two Possible Psychological Stressors and Two Social Stressors in a New Environment Which May Hinder Growth by Affecting Well-being
- Feb 29, 2024
The Importance of Having Friends That Have a Positive Influence on You
- Feb 27, 2024
- Privacy Policy

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center

Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- National Drought Mitigation Center - Drought In-depth
- United States Energy Information Administration - Climate Change Indicators: Drought
- Naxos - Biography of Dean Dixon
- National Geographic - Drought
- LiveScience - What is a Drought?
- Khan Academy - Drought and Famine
- U.S. Geological Survey - Droughts: Things to Know
- Weather Wiz Kids - Drought
- drought - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- drought - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)

Recent News

drought , lack or insufficiency of rain for an extended period that causes a considerable hydrologic (water) imbalance and, consequently, water shortages, crop damage, streamflow reduction, and depletion of groundwater and soil moisture. It occurs when evaporation and transpiration (the movement of water in the soil through plants into the air) exceed precipitation for a considerable period. Drought is the most serious physical hazard to agriculture in nearly every part of the world. Efforts have been made to control it by seeding clouds to induce rainfall, but these experiments have had only limited success.

There are four basic kinds of drought:

1. Permanent drought characterizes the driest climates. The sparse vegetation is adapted to aridity, and agriculture is impossible without continuous irrigation .
2. Seasonal drought occurs in climates that have well-defined annual rainy and dry seasons . For successful agriculture, planting must be adjusted so that the crops develop during the rainy season .
3. Unpredictable drought involves an abnormal rainfall failure. It may occur almost anywhere but is most characteristic of humid and subhumid climates. Usually brief and irregular, it often affects only a relatively small area. However, ongoing large-scale droughts of this kind are possible, especially in drier regions with several subsequent years of inadequate rainfall or snowpack.
4. Invisible drought can also be recognized: in summer, when high temperatures induce high rates of evaporation and transpiration, even frequent showers may not supply enough water to restore the amount lost; the result is a borderline water deficiency that diminishes crop yields.

- Latest Resources
- Quick Links
The Impact of Drought in South Africa Research Grade 11 Geography

The Impact of Drought in South Africa Research Geography Grade 11: South Africa has experienced a series of droughts over the past few decades, with significant impacts on the environment, economy, and society. As Grade 11 learners, it is crucial to understand the causes and consequences of drought in order to develop solutions for a more sustainable future. This article aims to provide a comprehensive research guide for Grade 11 students on the impact of drought in South Africa.
The Impact of Drought in South Africa Research Grade 11
- Understanding Drought
Before diving into the impacts of drought, it is essential to understand what drought is and how it is classified. Drought is a prolonged period of abnormally low rainfall, leading to a shortage of water. Droughts can be classified into three main types:
- Meteorological drought: Occurs when there is a significant decrease in precipitation compared to the average for a specific region and time period.
- Agricultural drought: Occurs when there is insufficient soil moisture to meet the needs of crops, leading to decreased agricultural productivity.
- Hydrological drought: Occurs when there is a deficiency in surface and subsurface water resources, such as rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
- Causes of Drought in South Africa
Several factors contribute to the occurrence of drought in South Africa:
- Climate change: As global temperatures rise, the frequency and intensity of droughts are likely to increase. Changes in precipitation patterns can exacerbate water scarcity in regions already prone to drought.
- El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO): This climate phenomenon can lead to drought conditions in South Africa when the warm phase, known as El Niño, occurs. This results in suppressed rainfall over the southern African region.
- Land use practices: Unsustainable land management, such as deforestation, can reduce the ability of ecosystems to store water and contribute to drought.
- Environmental Impacts
Drought in South Africa has a range of environmental impacts:
- Decreased water availability: Reduced water levels in rivers, lakes, and dams can lead to water restrictions and increased competition for water resources.
- Loss of biodiversity: Drought can lead to the death of plants and animals, affecting ecosystems and reducing biodiversity.
- Soil degradation: Drought can cause soil to become compacted, eroded, or lose its fertility, reducing its ability to support plant life.
- Economic Impacts
The economic impacts of drought in South Africa are far-reaching:
- Agricultural losses: Reduced crop yields and livestock productivity can lead to food shortages and increased food prices, affecting both farmers and consumers.
- Unemployment: The agricultural sector is a significant employer in South Africa. Drought can result in job losses for farmworkers and related industries.
- Reduced tourism: South Africa’s natural beauty is a significant tourist draw. However, drought can negatively impact water-based recreational activities and wildlife populations, deterring tourists and affecting the tourism industry.
- Social Impacts
Drought can have severe social consequences in South Africa:
- Water scarcity: Limited access to clean water can lead to waterborne diseases and affect sanitation, negatively impacting public health.
- Food insecurity: Food shortages and increased prices can exacerbate food insecurity, particularly for vulnerable populations.
- Mental health: The stress of dealing with the consequences of drought can lead to increased anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues among affected individuals and communities.
- Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
To minimize the impact of drought and increase resilience, South Africa needs to implement various mitigation and adaptation strategies:
- Water resource management: Improved water resource management, including the development of new water infrastructure and more efficient water use, is crucial for ensuring water security.
- Sustainable agriculture: Adopting drought-resistant crops and sustainable farming practices can help reduce the impact of drought on agricultural productivity.
- Reforestation and land management: Reforestation and better land management practices can improve water retention and reduce soil erosion, helping to alleviate drought conditions.
- Education and awareness: Encouraging communities to adopt water-saving practices and promoting awareness of the consequences of drought is essential for fostering a culture of water conservation.
- Climate change mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and supporting global efforts to address climate change can help limit the frequency and intensity of droughts in the future.
Drought is a significant issue in South Africa, with wide-ranging environmental, economic, and social impacts. For Grade 11 students researching the impact of drought, understanding the causes, consequences, and potential solutions is essential. By implementing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies, South Africa can better manage the effects of drought and create a more sustainable and resilient future.
Looking for something specific?
Related posts.

How Droughts Can Be Triggered by Human Activities in South Africa
Human activities significantly contribute to the occurrence and severity of droughts in South Africa. Understanding these activities with supporting facts and evidence is essential...

How Physical (Natural) Conditions Can Trigger Droughts in South Africa
Droughts in South Africa can be directly caused by various physical (natural) conditions. Understanding these natural triggers helps us prepare better for these challenging...

Relationship between Climate Change and the Regularity of Droughts in South Africa
Climate change is having a profound impact on weather patterns globally, and South Africa is feeling these effects acutely. One of the most critical...

The Negative Impact of Droughts on South African Farmers
Droughts have a devastating effect on South African farmers, affecting their livelihoods, food security, and the overall economy. These extended periods of low rainfall...

Map of South Africa that indicates the drought-stricken areas
Map of South Africa that indicates the drought-stricken areas: The below map indicates the areas in South Africa where draught has caused a great water...

Geography Grade 11 Questions and Answers Database for Term 2
Geography Grade 11 Questions and Answers Database for Term 2: Welcome to our comprehensive database designed to assist Grade 11 students in South Africa...
Previous Story
- IAS Preparation
- UPSC Preparation Strategy
Droughts: Notes for UPSC Geograpahy
Drought is a phenomenon that comes under geography in the strict sense of the word but has reverberations across various fields. This is because droughts affect the livelihood and economies and even lives of people affected by it. Hence, it assumes importance for the UPSC exam. In this article, we talk about droughts for the IAS exam .
| page!!
|
Definition of Drought
The term ‘Drought’ in simple words is the absence of water for a long period of time, at a place where it is considered abnormal as compared to its usual conditions. The distribution of water on the earth’s surface is not even. Some places have lots of freshwater e.g. rivers, lakes, lagoons, ponds etc. and they are continuously replenished by rainfall and water from underground.
If a region that has had lots of rainfall , goes for a couple of weeks without rains, and people, animals and plants begin to experience a bit of dryness, it can be called a drought. Drought can be defined as a relatively long time where there is not enough water than there usually is, as a result of dry weather, to support human, animal and plant life. Droughts become an issue only when it begins to affect water supply for irrigation, municipal, industrial, energy, and ecosystem function. Severe droughts can have serious consequences.
Recently, the government of England has formally declared parts of England. It was declared after a period of prolonged hot and dry weather.
The declaration of drought serves as a recognition of the water scarcity situation and the need for proactive measures to manage water resources effectively.
Implications of the declaration: The declaration abrings various actions and regulations to address the water scarcity issue and ensure the sustainable use of available water resources.
- Water Companies’ Drought Plans and Restrictions: Water companies are required to have a drought plan in place, outlining the restrictions they may implement on their customers during a drought. These plans serve as guidelines for managing water supplies efficiently and responsibly.
- Drought Orders and Permits for Water Management: During a drought, water companies have the option to apply for drought orders and permits. This helps ensure a more sustainable water supply during times of scarcity.
- Restrictions on Non-Essential Water Use: To conserve water during a drought, restrictions can be imposed on non-essential water use. This includes measures such as limiting water usage in commercial car washes and swimming pools.
- Restrictions for Farmers: Farmers may face restrictions on water usage for spray irrigation. These measures are intended to balance the water needs of agricultural activities with the overall water availability in drought-affected areas.
- Government Intervention in Industrial and Food Processing Water Use: The government can impose restrictions on water use in industrial manufacturing or food processing sectors.
- Conservation Measures in Dry Conditions: In drought conditions, Natural England, the government’s conservation advisory body, may restrict access to certain areas, such as national nature reserves, if there is a risk of fire caused by dry conditions. These measures aim to protect valuable natural habitats and prevent wildfires, which can be exacerbated during periods of prolonged hot and dry weather.
Types of Drought
There are three types of droughts known to the scientific community:
- Meteorological drought occurs when there is a prolonged time with less than average precipitation. Such type of droughts can be triggered by a high level of reflected sunlight and above-average prevalence of high-pressure systems, winds carrying continental, rather than oceanic air masses.
- Agricultural droughts affect crop production or the ecology of the range. This condition can also arise independently from any change in precipitation levels when either increased irrigation or soil conditions and erosion triggered by poorly planned agricultural activities cause a shortfall in water available to the crops.
- Hydrological drought is brought about when the water reserves available in sources such as aquifers, lakes and reservoirs fall below a locally significant threshold. Hydrological drought tends to show up more slowly because it involves stored water that is used but not replenished. Like an agricultural drought, this can be triggered by more than just a loss of rainfall.
- Socio-Economic Drought refers to the abnormal water shortage that affects socio economic condition of a region.
For more notes on UPSC Geography , visit the linked article
- Drought-prone districts in India comprise nearly 1/6th of this country in terms of area. These areas receive an annual rainfall of around 60 cm or less.
- These situations can be attributed to human malpractices such asI recent year drought conditions have become recurring due to reasons as climate change, overuse of water resource, pollution, urbanization, etc.
- Drought is declared by the respective State Governments taking into account rainfall situation, crop growth, etc.
Consequences of Drought
The effects of droughts can be divided into three groups: environmental, economic and social.
- Environmental effects: Lower surface and subterranean water-levels, lower flow-levels (with a decrease below the minimum leading to direct danger for amphibian life), increased pollution of surface water, the drying out of wetlands, more and larger fires, higher deflation intensity, loss of biodiversity , worse health of trees and the appearance of pests and dendroid diseases.
- Economic losses: Economic consequences include lower agricultural, forests, game and fishing output, higher food-production costs, lower energy-production levels in hydro plants, losses caused by depleted water tourism and transport revenue, problems with water supply for the energy sector and for technological processes in metallurgy, mining industries and disruption of water supplies for municipal economies.
- Social costs include the negative effect on the health of people directly exposed to this phenomenon (excessive heat waves), a possible limitation of water supplies, increased pollution levels, high food-costs, stress caused by failed harvests, etc. This explains why droughts and freshwater shortages operate as a factor which increases the gap between developed and developing countries.
Effects vary according to vulnerability. For example, subsistence farmers are more likely to migrate during drought because they do not have alternative food sources. Areas with populations that depend on water sources as a major food-source are more vulnerable to famine.
Frequently Asked Questions Related to Drought
What are the four types of drought.
As a result, the climatological community has defined four types of drought:
1) Meteorological drought 2) Hydrological drought 3) Agricultural drought 4) Socioeconomic drought.
Is a drought a natural disaster?
Droughts – UPSC Notes:- Download PDF Here
To get more topics to visit the UPSC Syllabus page and for more of UPSC-related preparation materials visit the linked articles:
Related Links
| IAS General Studies Notes Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
IAS 2024 - Your dream can come true!
Download the ultimate guide to upsc cse preparation, register with byju's & download free pdfs, register with byju's & watch live videos.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Digg
Latest Earthquakes | Chat Share Social Media
USGS has a long and proven history of addressing drought related issues through data collection and integration, assessing drought impacts, and delivering key science to inform decision making. These core strengths and capabilities are consistent with the primary roles of the USGS in the National Drought Resilience Partnership and key stakeholders and their information needs.
Data Collection and Integration
Modeling and prediction, drought impacts, drought resilience, science topics.

Why doesn't a drought end when it rains?
Rainfall in any form will provide some drought relief. A good analogy might be how medicine and illness relate to each other. A single dose of medicine can alleviate symptoms of illness, but it usually takes a sustained program of medication to cure an illness. Likewise, a single rainstorm will not break the drought, but it might provide temporary relief. A light to moderate shower will probably...

Where in the Nation are droughts or very low flows occurring now? How can I see these sites on a map and get to the data?
To view the USGS streamflow information on drought, see the drought map on our WaterWatch site, which shows below-normal, 7-day average streamflow compared to historical streamflow for the United States. Links to additional maps and drought data are listed on the USGS Drought website and the National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS) .

When does a drought begin and end?
The beginning of a drought is difficult to determine. Several weeks, months, or even years might pass before people know that a drought is occurring. The end of a drought can occur as gradually as it began. The first evidence of drought is usually seen in records of rainfall. Within a short period of time, the amount of moisture in soils can begin to decrease. The effects of a drought on flow in...

Coupled Human and Natural Systems
Call for papers from global sustainability - cambridge university press.
May 06, 2024
A special issue of Global Sustainability - Cambridge University Press, calls for papers to the theme of “Geography, Telecoupling, and Sustainability".

A special issue of Global Sustainability - Cambridge University Press, calls for papers to the theme of “ Geography, Telecoupling, and Sustainability ".
In an ever-evolving world facing pressing environmental challenges, the intricate interplay between geography, sustainability, and telecoupling takes center stage. Geography studies have a critical role to play in accelerating the attainment of the SDGs and addressing challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and the provision of essential ecosystem services. Geography also offers a holistic perspective on the intricate relationships between human activities and the environment. Moreover, geography can act as a catalyst for promoting shared prosperity and overall well-being, while the concept of telecoupling provides a lens through which to understand complex global interactions.
Building on this vital connection, we extend a warm invitation to researchers, scholars, and practitioners worldwide to contribute their insights to a special issue of Global Sustainability dedicated to the theme of “Geography, Telecoupling, and Sustainability".
For more detailed information, please visit https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/global-sustainability/announcements/call-for-papers/geography-telecoupling-and-sustainability.
Did you find this article useful?
new - method size: 3 - Random key: 2, method: personalized - key: 2
You Might Also Be Interested In

MSU researcher awarded five-year, $2.5 million grant to develop risk assessment training program
Published on October 13, 2020

MSU Product Center helps Michigan food entrepreneurs survive and thrive throughout pandemic
Published on August 31, 2021

Protecting Michigan’s environment and wildlife through the Conservation Reserve Enhancement Program
Published on September 1, 2021

MSU Extension to undertake three-year, $7 million vaccination education effort
Published on August 17, 2021

MSU to study precision livestock farming adoption trends in U.S. swine industry
Published on March 15, 2021

MSU research team receives USDA grant to evaluate effectiveness, cost of new blueberry pest management strategies
Published on February 19, 2021
- coupled human and natural systems

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500+ Words Essay on Drought. Drought is a dangerous condition which decreases the quality of life. It is termed as a natural disaster with harmful effects. A drought usually occurs when a region faces a shortage of water. This is mainly due to lesser rainfalls. In addition, droughts have proven to be fatal for mankind and wildlife as well.
Drought is an extended period of unusually dry weather when there is not enough rain. The lack of precipitation can cause a variety of problems for local communities, including damage to crops and a shortage of drinking water. These effects can lead to devastating economic and social disasters, such as famine, forced migration away from drought-stricken areas, and conflict over remaining ...
Drought is caused by a lack of rainfall, causing serious water shortages. It can be fatal. More specifically, drought is defined by a period of unusually dry weather caused by low rainfall and high temperatures. It is also defined in terms of the impact on agriculture when crops fail due to lack of moisture in soil, leading to food shortages ...
A drought is a period of time when an area or region experiences below-normal precipitation.The lack of adequate precipitation, either rain or snow, can cause reduced soil moisture or groundwater, diminished stream flow, crop damage, and a general water shortage.. Droughts are the second-most costly weather events after hurricanes.Unlike with sudden weather events such as hurricanes, tornadoes ...
500 Words Essay on Drought Introduction. Drought, a natural disaster characterized by a prolonged period of insufficient rainfall, is a global phenomenon with profound impacts on both human and ecological systems. It is a complex, multi-dimensional issue that involves various aspects of climate, hydrology, and human activities. ...
A lack of water in stores such as rivers, lakes, reservoirs and aquifers (water stored underground naturally) can lead to drought. Areas that rely on rainfall and surface water are more likely to experience drought. Surface water quickly evaporates in warm, dry conditions leading to an increased risk of drought.
eficient area. Why is Drought Important. climate zones, from very wet to very dry. Drought is a The U.S. is vulnerable to the social, economic, temporary aberration from normal climatic conditions, thus it can var. significantly from one region to another. Drought is different than aridity, which is a permanent feature of climate in regions ...
Biology, Health, Geography. Credits. Media Credits. The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited. Last Updated.
Background on Drought. A drought is "a deficiency of precipitation over an extended period of time (usually a season or more), resulting in a water shortage. " Indicators of drought include precipitation, temperature, streamflow, ground and reservoir water levels, soil moisture, and snowpack. Drought and Climate Change. Climate change increases the odds of worsening drought in many parts ...
Research Report on Drought in Australia. 2 pages / 1064 words. Abstract This Research report is based on the major problem facing by Australian people and mainly farmers and their communities. Many farmers and local communities have been facing severe and prolonged drought. Australia has always had variation in the climate.
Essay # 8. Drought Prone Areas: Out of the total geographical area of India, almost one-sixth area with 12 per cent of the population is drought prone; the areas that receive an annual rainfall up to 600 mm are the most prone. Irrigation Commission (1972) had identified 67 districts as drought prone.
Extreme drought is part of natural climatic cycles around the world. Historic records and prehistoric reconstructions extending back 1000 years document that extreme droughts have occurred repeatedly in North America, sometimes for longer periods than even the most severe droughts of the 20th century.[1] Research on climate variability is addressing how drought may impact the
Drought affects our lives in many different ways because water is such an important part of so many of our activities. We need water to live, and animals and plants do too. We need water to grow the food we eat. We also use water for many different things in our lives, like washing dishes, cooking, bathing, and swimming or river rafting.
Analysis Of Mechanisms To Tolerate The Drought Stress In Plants Essay. Drought stress is one of the most threatened environmental stresses to mankind. It is the most serious stress which limits the agricultural growth and its development and further leads to a great threat to world food security.
4. The Importance of the Research Memorandum. 5. Conclusion. South Africa is a country that is susceptible to drought due to its semi-arid climate, which makes it vulnerable to the effects of climate variability and change. Drought has significant impacts on the country's social, economic, and environmental systems.
Drought, lack or insufficiency of rain for an extended period that causes a considerable water imbalance and, consequently, water shortages, crop damage, streamflow reduction, and depletion of groundwater and soil moisture. It occurs when evaporation and transpiration exceed precipitation for a considerable period.
Abstract and Figures. This paper presents a comprehensive review and analysis of the available literature and information on droughts to build a continental, regional and country level perspective ...
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.: 1157 A drought can last for days, months or years. Drought often has large impacts on the ecosystems and agriculture of affected regions, and causes harm to the local economy. Annual dry seasons in the tropics significantly increase the chances of a drought developing, with subsequent increased wildfire risks.
Economic Impacts. The economic impacts of drought in South Africa are far-reaching: Agricultural losses: Reduced crop yields and livestock productivity can lead to food shortages and increased food prices, affecting both farmers and consumers. Unemployment: The agricultural sector is a significant employer in South Africa.
The term 'Drought' in simple words is the absence of water for a long period of time, at a place where it is considered abnormal as compared to its usual conditions. The distribution of water on the earth's surface is not even. Some places have lots of freshwater e.g. rivers, lakes, lagoons, ponds etc. and they are continuously ...
The beginning of a drought is difficult to determine. Several weeks, months, or even years might pass before people know that a drought is occurring. The end of a drought can occur as gradually as it began. The first evidence of drought is usually seen in records of rainfall. Within a short period of time, the amount of moisture in soils can ...
Akinwumi James A., Atinmo Tola, and Semafuko Wasswa E. B. African Drought: Causes, Effects and Long Term Solutions; the Proceedings of a Seminar Organized by the ... Pennsylvania State University. Department of Geography. Papers in Geography #13, 1975, 45 pp. Google Scholar. Rosenthal Jerry E. "Drought—The Creeping Catastrophe." Africa ...
1 Introduction. Communities in Australia and around the world are facing prospects of more frequent and severe droughts (Ahmadalipour et al., 2019; Bureau of Meteorology and CSIRO, 2018; Cook et al., 2015; Leng et al., 2015; Spinoni et al., 2018; Zhang, Li, et al., 2023; Zhang, Zheng, et al., 2023).These prolonged and extreme droughts such as the Federation Drought of 1895-1902, World War II ...
A special issue of Global Sustainability - Cambridge University Press, calls for papers to the theme of "Geography, Telecoupling, and Sustainability".. In an ever-evolving world facing pressing environmental challenges, the intricate interplay between geography, sustainability, and telecoupling takes center stage.