Sign up free

10 Tips and Techniques for Customer Service Problem-Solving
October 11, 2023

In the customer service world, challenges arise when you least expect them. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting, mastering the art of problem-solving is essential.
In this article, we’ll share with you 10 simple yet effective tips and techniques that will empower your team to navigate customer service issues like a pro.
From active listening to setting realistic expectations and offering solutions, these strategies will benefit your business by enhancing your team’s problem-solving skills and boosting customer satisfaction.
Why are problem-solving skills important in customer service?
Problem-solving skills are crucial in customer service because they turn frustrating situations into bright opportunities. When you effectively identify and address customer issues, you also show that you genuinely care about their satisfaction.
These skills build trust, improve customer loyalty, and lead to positive word-of-mouth recommendations. Moreover, they help your team handle challenges efficiently, reducing stress and improving overall job satisfaction.
In short, mastering problem-solving in customer service is the key to creating happy customers and a thriving, customer-centric business.
Customer Service Problem-Solving # 1 - Active Listening
Active listening is a vital technique in customer service problem-solving. It involves fully focusing on what the customer is saying, not just waiting for your turn to speak.

To practice it effectively, encourage your team to maintain eye contact, nod in acknowledgment, and use phrases like "I understand" to show empathy. Let them practice how to avoid interrupting and give customers the space to express themselves fully.
By truly hearing your customers’ concerns and needs, your team can respond more precisely and find solutions that leave customers feeling valued and satisfied. This successfully turns potentially challenging situations into positive experiences.
Edapp can empower your customer service team's problem-solving skills by offering interactive and customized training courses. These problem solving training courses include EdApp’s Problem Solver course. There’s also a course on Dealing with Difficult Customers .

Through scenario-based simulations, your team members can practice resolving real-life customer issues in a safe learning environment. Edapp's reporting and analytics features allow you to monitor individual progress, identify areas for improvement, and provide targeted feedback.
With the flexibility of mobile learning , your team can also access training anytime, anywhere, making it convenient to sharpen their problem-solving abilities. Plus, Edapp's engaging and adaptive content makes sure that your team stays motivated and develops the critical skills needed to excel in customer service problem-solving.
Sign up to EdApp for free to unlock your customer service team’s best potential.
Customer Service Problem-Solving # 2 - Stay Calm and Patient
Staying calm and patient is a superpower in problem-solving. When your team keeps their cool even in tough situations, it sends a reassuring message to the customer that they’re competent and there to help.

Some tips you can give them are to take deep breaths, to remember it's not personal, and to not rush through the conversation. Pausing to collect their thoughts can also lead to better solutions and prevent the situation from escalating.
With this customer service problem-solving skill, your team gains the upper hand in resolving issues effectively, creating happier customers, and making their jobs less stressful in the process.
Customer Service Problem-Solving # 3 - Apologize Sincerely
Apologizing sincerely is a golden technique in customer service. When your team members genuinely say, "I'm sorry," they show empathy and take responsibility for any inconvenience the customer has faced, regardless of fault.

This simple act of acknowledging their frustration can go a long way in diffusing tension and starting the path toward resolution when it comes to customer service problem solving. A sincere apology demonstrates that your customer service team cares about their experience and is committed to making it right.
So, don't let your team underestimate the power of a heartfelt "I'm sorry" in turning a customer's problem into an opportunity to leave them feeling valued and satisfied.
Customer Service Problem-Solving # 4 - Take Ownership
Taking ownership is a remarkable technique when dealing with customer problems. When your team members accept responsibility for resolving an issue, they send a clear message to the customer that their concerns matter to your business.

It doesn't matter if your product or service caused the problem. By taking ownership, your team demonstrates a commitment to finding a solution and ensuring their satisfaction. This step builds trust and confidence in your customers, showing that your team is there to support them every step of the way.
Encourage your team to say, "I'll take care of this for you." It's a powerful way to transform challenges into opportunities in exceptional customer service problem solving.
Customer Service Problem-Solving # 5 - Set Realistic Expectations
Setting realistic expectations is an important step for customer service problem solving. When you communicate clear timelines, you're being honest and transparent with what the customer can expect.

This helps manage their expectations and prevents disappointment down the road. Under-promising and over-delivering is a technique your team can use to make sure that they have the time and resources needed to meet or exceed the commitments they’ve made.
This technique not only prevents misunderstandings but also creates a positive experience by showing that your team is dependable and trustworthy. It ultimately makes customers happier and more satisfied with the service they receive.
Customer Service Problem-Solving # 6 - Collaborate with Colleagues
Letting your team members collaborate with their colleagues for problem-solving is like having a superhero team for customer service in your organization. Sometimes, challenges are complex, and it's perfectly okay to call in reinforcements.

They can also involve other team members or departments when needed, ensuring that they have all the expertise and resources at their disposal. Effective internal communication is the key here; so make sure that everyone is on the same page.
This customer service problem solving example helps find more comprehensive solutions and demonstrates a unified commitment to customer satisfaction. So, remind your team that they’re not alone in this mission–collaborate, conquer, and make your customers' day better together.
Customer Service Problem-Solving # 7 - Offer Solutions
Offering solutions is not just about acknowledging the issue; it's about actively seeking ways to fix it. Presenting practical solutions to the customer's problem shows that your team is dedicated to making things right and that customer satisfaction is their top priority.

So when faced with examples of problem-solving scenarios, have your team discuss the options, outlining the pros and cons if necessary, to help your customers make an informed decision.
Offering solutions not only resolves the immediate problem but also fosters trust and loyalty, leaving customers feeling heard, valued, and confident in your team’s ability to provide exceptional service.
Customer Service Problem-Solving # 8 - Follow-Up
Once the issue is resolved, your customer service team shouldn’t leave your customers hanging. They should take the extra step to check in with them.

Whether it's a quick email or a phone call, asking if everything is going well shows that your team genuinely cares about their satisfaction even after the problem is resolved. It's a fantastic way to ensure their needs are fully met and to gather valuable feedback for continuous improvement.
Following up not only leaves a lasting positive impression but also transforms a simple resolution into a memorable and delightful customer experience . So, remind your team to circle back and make sure that your customers are smiling long after the issue is history.
Customer Service Problem-Solving # 9 - Document the Interaction
When your team members keep detailed records of customer issues and the steps taken to resolve them, they’re creating a valuable resource for your customer service team.

These records offer a clear picture of past challenges and solutions, making it easier to spot trends and identify areas for improvement. Plus, they guarantee consistency in your service by allowing any team member to pick up where you left off, providing a seamless customer experience.
Think of documentation as your team’s secret weapon for conquering future customer service adventures, helping them navigate problems with confidence and precision.
Customer Service Problem-Solving # 10 - Learn from Each Case
After resolving an issue, let your team take a moment to reflect on what went well and what could be improved. Have them analyze customer feedback and common issues to identify patterns and trends.

By turning each case into a learning opportunity, your team can continually refine their problem-solving skills and fine-tune your business’s customer service approach.
It's the key to growth, making sure that you and your team are always ready to tackle new challenges with even greater expertise. This ultimately creates happier customers.
Donna is an elearning content writer for EdApp, a mobile-based microlearning platform designed for today's digital training needs. When she's not writing web articles, she writes lines of code or songs or anything food-related.
Explore more
Explore case studies
Learn how customers like you use EdApp. Their results speak for themselves.
Book a demo
Get a tour of our core products and features with one of our experts.
Take a bootcamp
Instantly access our video library updated weekly with live demonstrations.
Check out G2 reviews
Don't take our word for it. Here’s what our customers have to say.
The Guide to Effective Customer Service Problem Solving

Cases that start as “I don’t know” quickly become “I figured it out!”
“I don’t know” isn’t a good enough answer in customer support. When customers come to you with unique problems and unusual questions, we can’t refuse to answer them. In this guide, we’ll give you the steps to turn that “I don’t know” into something better:
“I don’t know, but I’m going to figure it out.”
With this guide to effective customer service problem solving, we give you a three-step process to follow:
- take stock of the information you’ve been given,
- gather any additional information you need,
- and then work to solve the problem and respond to the customer.
Let’s get started.
Assess the information you have
Information is the most important tool in your tool belt. The first step in solving any problem is to identify all the information you already know. Whether this case was escalated to you for help, or if you’ve just realized that there may be more than meets the eye to this problem, take the time to lay out everything you know.
Customer’s tone
How does your customer feel about the situation? Are they technically minded, or are they struggling to describe technical issues ? Are they calm and cooperative? Or combative and frustrated? Is this a deal-breaker for them? Or is it just a weird bug? The demeanor of your customer will inform how you approach the situation going forward.
Customer’s history
Do a quick review of the customer’s previous support interactions, any purchases they’ve made, what plan type they are on, etc. This context will help you replicate the issue, as well as respond appropriately to the customer.
What’s happening?
Do you know enough about what’s happening? Have they sent through screenshots? Error messages? Console data? What were they trying to accomplish? It doesn’t need to be a technical problem for this step to still be important. Understanding what the customer’s motivation is will help solve a variety of issues.
Has this happened before?
It’s very unlikely that this is a brand new problem. Has the customer reported it happening before? Has any other customer reported it happening before? Help desk search functions are incredibly powerful tools. Search error messages and problem statements to see if other customers have reported similar issues. You can also search the internet to see if it’s a third-party issue. For example, if you’re using a third-party payment system, you might be seeing one of their errors when customers are purchasing on your website.
Gather more information
Okay, we’re partway there! If you didn’t have an epiphany while you were sorting through the information already at your disposal (sometimes that happens!), it’s time to gather more data.
Can you replicate it?
There’s no way to get more information than to get hands-on with the problem. Do you see the same thing happening?
If not, what information do you need to replicate it?
If you can’t replicate the issue, it’s probably because you’re doing something different or in a different environment. What information do you already have about the customer’s environment? What do you need to know in order to do exactly the same thing?
- Environment: browser version, extensions (try it incognito?), other settings.
- Steps: can they record a screengrab? What are they trying to do? What error message do they get?
- Specific settings: what account are they using? What version of your product are they using? If you can try it in their account (using “admin mode” or “god mode” so you can see it without asking for their username or password), does it happen for you as well?
Ask other people
Now’s the time to check in with other people on your team to see if they have any ideas. Have they ever seen something similar?
Depending on your relationship with your product and engineering team, you may also be able to check in with them at this point. However, many teams have a more formal bug reporting process in place to prevent “side of the desk” questions from interfering with their workflow. If that’s the case, you may want to do more research first.
Solve the problem
Now you’ll need to actually solve the problem for the customer. It might require finding a workaround, or reporting a bug to the development team.
Bug or works-as-designed?
Once you’ve replicated the issue, you’ll need to decide whether that is the way it’s supposed to work, or if you’ve found a bug. If it’s a bug, congrats! You can file a bug ticket and ask your engineering team to fix it. If it’s a feature or a design flaw, you may need to make a case for an update. In this case, the complex problem may turn into a feature request.
Is there a workaround?
Can you get to the customer’s desired end result in another way? Whether the issue turns out to be a bug or a feature, if you can find another way to achieve their goal, your customer will be happy!
Write a great response
Once you’ve replicated the issue, solved the problem, found a workable solution, or at least documented the bug for a future fix, you need to get back to the customer. Writing an empathetic, thorough response can make all the difference in a complex situation.
In many cases, your response will follow the same steps as a great customer service apology :
- Offer explanation
- Fix the problem
- Wrap it up and let them know what’s next
Resources for Customer Service Problem Solving
We all need a little help sometimes. If you’re learning how to fix more difficult problems, these resources can help.
Help Scout’s Art of Troubleshooting
On a mission to troubleshoot a bug? This guide is super helpful .
Support Details website
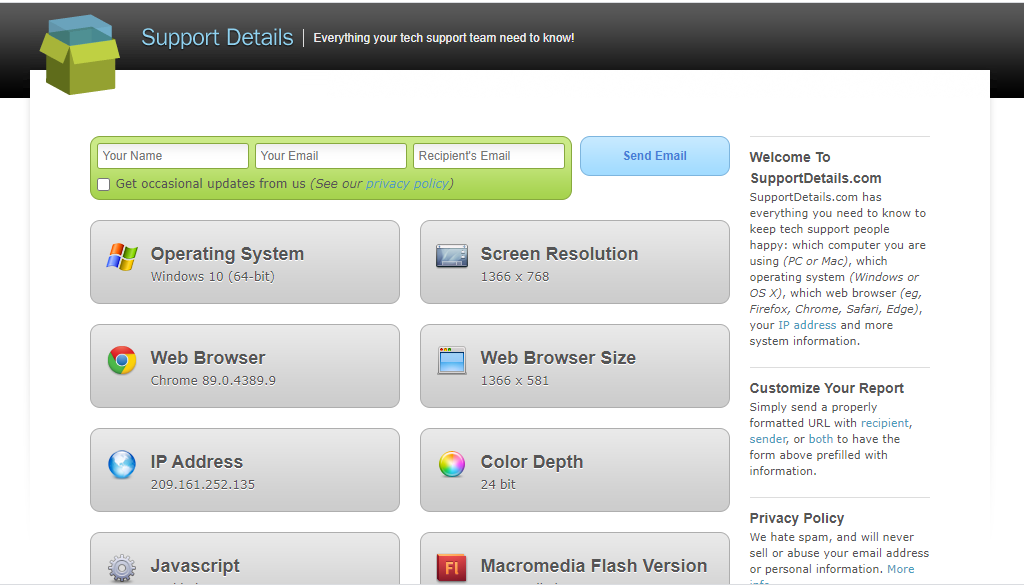
Learn how to use Developer Tools, especially Web Consoles
Be like Sherlock, and look for clues!
Customer support requires communication skills and problem-solving skills. Looking for the clues to solve the puzzle becomes a big part of your job as soon as you start to take on more difficult customers. With this guide to customer service problem solving, you’ll have a systematic way to approach those tough questions. Cases that start as “I don’t know” quickly become “I figured it out!”
How did you like this blog?

Sarah Chambers is a Customer Support Consultant and Content Creator from Vancouver, Canada. When she’s not arguing about customer service, she’s usually outdoors rock climbing or snowboarding. Follow her on Twitter @sarahleeyoga to keep up with her adventures.
Related articles

7 Support Phrases Customers Hate to Hear (and What to Say Instead)
How to respond to negative reviews about your business, how to write a helpful bug report that gets your issue fixed, the best customer service tips every week. no spam, we promise..
Get guides, support templates, and discounts first. Join us.
Are you a freelance writer? Do you want your articles published on Nicereply blog?
Get in touch with us
Success in your inbox
Get monthly insights handpicked by our editorial team. Act on it.

Connect with customers
LiveChat is a complete customer service platform that delights your customers and fuels your sales.
Trusted by 36,000+ companies

LiveChat helps you delight your customers and fuels your sales.
4 steps to effective customer service problem solving with examples.
- Post on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Post on LinkedIn
- Post on Reddit
- copy-button#copy track#send" data-controller="track" data-track-category="Success" data-track-action="Share" data-track-label="Copy link" > Copy link to clipboard Link copied to clipboard https://text.com/success/effective-customer-service-problem-solving/
Recently, I came across a fascinating customer service story involving an American Express cardholder. It all began with a seemingly innocent mistake while making a payment involving a decimal point in the wrong spot, resulting in the customer inadvertently paying thousands of dollars instead of hundreds.
Determined to rectify the error and seek guidance, the customer promptly contacted American Express to report the issue. To his relief, a representative assured him that the mistake would have no adverse impact on his account and that all charges would be promptly refunded. Little did he know that this was just the prologue to a series of challenges.
A few days later, the customer was taken aback when he discovered that all his debit cards were unexpectedly suspended. Perplexed and concerned, he went over his account for any indications of suspicious activity or an account block, but to no avail. Thus, he decided to reach out to American Express once more to seek clarification.
To his utter surprise and dismay, the representative he connected with not only questioned why he had not halted the incorrect payment but also accused him of attempting fraud. The customer explained that a previous representative had not advised him to stop the payment and had, in fact, assured him that there would be no negative consequences resulting from his honest mistake.
The response?
That's what customer service does. They tell you what you want to hear.
This quite nasty customer service story inspired me to write about the real purpose of customer service. Which is not “telling customers what they want to hear” but helping customers and resolving their problems.
In this article, you’ll also learn some troubleshooting techniques to make your job easier.
Creating a Good Customer-Centric Culture
A customer-centric culture serves as the bedrock of exceptional problem-solving and sustainable business success. In a world where customers today wield unparalleled power and influence, placing them at the heart of your operations is not just a choice; it is a strategic imperative.
At all levels of the organisation, employees must wholeheartedly prioritise customer happiness, understanding that every interaction is an opportunity to leave a lasting impact. By cultivating such a culture, businesses create a positive and supportive environment that empowers employees to go above and beyond to delight customers.
Nurturing this culture demands a multifaceted approach. One potent strategy is to recognise and reward outstanding customer service efforts. By celebrating employees who embody the customer-centric ethos, businesses reinforce the value they place on exceptional experiences. This recognition motivates individuals to exceed customer expectations continually and sets a powerful example for others to follow.
Encouraging collaboration is another pivotal aspect of fostering a customer-centric culture. In today's interconnected business landscape, problems seldom fit neatly within departmental silos. Emphasising collaboration cultivates a shared sense of responsibility for customer success and enables employees to pool their expertise, collectively devising innovative solutions that surpass individual capabilities. The result is a seamless and consistent experience for customers, who benefit from the collective effort of a united organisation.
To equip employees for the challenges of modern customer service, businesses must invest in skills training. Outstanding problem-solving skills do not materialise by chance; they are honed through intentional development. Equipping employees with the necessary tools and knowledge to navigate diverse customer interactions positions them to respond adeptly and confidently, even in the face of dissatisfied customers.
Customer Service Problem-Solving
Speaking of dissatisfied customers, they hold the key to unlocking greater customer retention. Rather than viewing poor experiences as a liability, businesses must embrace them as opportunities for growth. Each negative interaction presents a chance to introspect, identify pain points, and make tangible improvements. By actively seeking feedback from dissatisfied customers, businesses demonstrate their commitment to listening and learning, earning trust and loyalty in the process.
A customer-centric culture is more than a mere buzzword; it drives superior customer experiences and enhanced customer retention. By prioritising customer satisfaction at every touchpoint, celebrating exceptional service, fostering collaboration, investing in skills training, and actively engaging with dissatisfied customers, businesses can forge a path to sustained success and unmatched customer loyalty. Embrace the customer-centric ethos, and you will unlock the true potential of your organisation in a customer-centric world.
Strategies for Effective Customer Service Problem-Solving
Timely response and resolution are essential components of successful troubleshooting. Customers appreciate swift action, showing that their concerns are taken seriously. Personalisation also plays a significant role, as customers feel valued when their issues are treated individually rather than generically.
Navigating challenging situations with irate customers requires patience and tact. Service reps need to stay calm, acknowledge the customer's feelings, and work towards finding a resolution.

4 Steps for Better Customer Service Problem Solving
As a customer service agent, providing satisfying solutions is essential. Let's explore the path to achieve this.
1. Understanding the Customer's Point of View
Imagine yourself in the customer's shoes. They reach out to you with what seems like an impossible request. For instance, they received a notice that their phone line would be cut due to non-payment, yet they requested credits on their invoices due to financial constraints. Initially, you might question their request, but remember, you're not just an ordinary person; you're a Support Hero tasked with saving the customer's day. Negative thinking won't lead to solutions.
At this stage, it's hard to distinguish if the customer is genuine or potentially fraudulent. However, instead of passing judgment, assume the customer needs assistance and act accordingly. Engage in active listening to comprehend the problem thoroughly and find a way to help.
Exceptional problem-solving hinges on understanding customer needs and concerns. Active listening enables service representatives to connect with customers on a deeper level and empathise effectively. By listening attentively, you can pinpoint the root cause of the problem and tailor solutions to meet their specific needs.
Remember these keywords throughout your journey: fully understand the problem, solve the customer's problem, find a workable solution, and ensure the customer is happy with the resolution.
2. Identifying a Problem
Ensuring that customers are happy with the solutions provided is crucial in customer service. Sometimes, customers simply struggle to articulate their issues, and that's entirely normal. They may not be familiar with your processes or jargon; all they know is that their expectations regarding your product or service have been disappointing.
As a Support Hero, it's your responsibility to restore their faith in your company, but to do that, you must first pinpoint the problem.
To troubleshoot effectively, here are a few questions that can guide you. Sometimes, by asking these simple questions, you can quickly identify an outage or a faulty batch of products sent out by a manufacturer!
Can you describe the problem you're facing precisely? When did this problem start? Has this issue occurred before?
Next, consider the following:
Are all users affected, or is it isolated to just one customer? Has anyone else faced a similar problem in the past?
Once the customer responds, summarise their answers back to them. This gesture demonstrates that you genuinely comprehend their concerns and helps you verify the facts.
If you're unfamiliar with the problem or unsure how to proceed, offer a brief apology and inform the customer that you need to discuss their case with a colleague or supervisor. Maintain a self-assured tone, and don't hesitate to ask the customer to hold on for a moment.
Remember, customers value accuracy even if it takes a bit more time to sort out the issue.
Instead of abruptly transferring a customer to another department, try saying:
"We're committed to resolving this for you. Let me transfer you to a specialist best equipped to address your question."
Customers appreciate the effort you put into understanding their journey and resolving their issues promptly. Poor customer service can lead to bad customer experiences, but by actively listening to their concerns, you can turn their dissatisfaction into a happy customer.
Always focus on solving the problem, no matter how common or complex. As a customer service representative, your role is to provide exceptional support and ensure that customers are satisfied with the resolution.
So, embrace every customer service issue as an opportunity to solve the problem and deliver exceptional customer support. Your dedication and responsiveness will create a positive experience, turning unhappy customers into satisfied ones.
Remember, the help desk is where customer issues are met with efficiency and care. The key to a successful customer service journey lies in how you handle problems and fix them effectively.
3. Find a Solution
Utilise your analytical thinking to devise a solution that best suits your customer's needs. Here are some key questions to help you plan an effective resolution:
Is there enough staff to carry it out?
Who will be involved in implementing the solution?
What is the expected time frame for the solution?
What resources are needed to make it happen?
Who should be informed about the planned solution?
How will the customer be notified about the solution?
Even if you're faced with a case that goes against your company's policy, there is always room for creative suggestions. Take, for example, a customer seeking a refund, which may not align with your policy.
However, consider these alternative solutions:
Inform the customer that you cannot credit the bill, but offer to split the payment into smaller instalments to accommodate their financial situation.
Postpone the account suspension temporarily, allowing the client to continue using the service.
Analyse the customer's account and propose a switch to a more budget-friendly price plan.
Your creativity can turn an unreasonable request into three viable solutions!
But what if you're not the one who can solve the problem?
In such cases, you may need to open a ticket to escalate the issue appropriately. To ensure the ticket doesn't get lost, assign it to yourself and monitor its progress. If the problem remains unresolved after 24 hours, consider contacting the customer to provide an update on your ongoing efforts.
Occasionally, there are situations where the problem cannot be fully sorted. For instance, your company may have stopped selling a particular product, or you may not have a gluten-free option on your menu. However, that doesn't mean you can't offer a helpful solution. If you don't have what the customer needs, guide them to the right source. Let them know where they can find the desired product or suggest alternatives.
Going the extra mile can create customer happiness, even if the solution deviates from their initial expectations.
Here's an example from our experience: My colleague, Justyna, recently chatted with a customer disappointed that our application lacked an in-built screen-sharing and screenshot-making tool. With a composed demeanour, I informed Aline that while LiveChat lacked those features, she could set up an integration for screen-sharing sessions and use a free screenshot tool like Jing. It did the trick! Aline was delighted with the solution, and my mission was accomplished.
Throughout the resolution process, ensure that the customer is at the centre of your focus. Handle customer service issues with attentiveness and empathy, as a positive customer service experience can be transformative. Use a series of questions to fully understand the problem, allowing you to implement the right solution and untangle customer queries effectively.
4. Fix the Problem and Follow Up on the Solution
Finally! The customer has agreed on a solution. You've offered a brief apology for the problem, and now you can fix it and close the case, right?
Unfortunately, it's not always that straightforward.
Sometimes, the solution provided may not address the root cause of the problem. For example, let's say a customer had an issue with the application, and you suggested restarting the device. While this might settle the problem, it's more likely that the customer will return with the same issue, possibly even upset that the initial solution didn't work as expected.
I understand that working in customer service leaves little time for breaks, and now I'm asking you to follow up on your customer's problems. But there are significant benefits to spending a little extra time reaching out to these customers.
Doing so demonstrates genuine care and creates an exceptional customer experience. You ensure that you won't receive calls or chats from furious customers later. You can verify whether your solution worked, giving you confidence for future interactions.
If you find it challenging to make calls or send emails to follow up, don't worry. There are alternative approaches you can take. Some apps allow you to send automatic emails once a ticket is resolved (e.g., LiveChat). You can test and try this feature to save time.
Alternatively, your team can use an automatic survey to gauge customer satisfaction and determine whether the problem was adequately resolved. Platforms like SurveyMonkey and Typeform can be useful in this regard. Alternatively, you can send a simple template asking two questions:
Did we help you solve your problem?
On a scale of 1 to 10, how would you rate your overall experience?
Customers will undoubtedly appreciate these efforts!
In customer service, increasing customer success is vital. To achieve this, it's essential to understand the issue at hand fully. When a customer allows you to delve into their concerns, you can identify the right product or service to address their needs effectively.
Remember, customers are likely to encounter complex problems, and they depend on you for assistance. Utilise customer service problem-solving techniques to handle their issues competently and ensure they are satisfied with the outcome.
Empowering a Customer Service Representative
To excel in issue resolution, customer service reps must have the right skills and authority. Regular training and development programs ensure that representatives are well-prepared to handle various situations effectively.
Additionally, empowering representatives to take ownership of customer issues instils a sense of responsibility, leading to more proactive and efficient resolutions.
Solve Customer Service Problems With Technology
Technology plays a vital role in modern customer service troubleshooting. Customer relationship management (CRM) systems help consolidate customer data, making it easier for representatives to access relevant information quickly.
AI-powered chatbots can provide instant support, resolving common queries and freeing up human representatives to handle more complex issues. Data analytics tools allow companies to gain insights into customer behaviour and preferences, enabling them to tailor their services accordingly.
Measuring and Monitoring Customer Service Success
To continuously improve the way problems are solved, companies need to track and measure their customer service performance. Key performance indicators (KPIs), such as response time, resolution rate, and satisfaction scores, provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of customer service efforts.
By monitoring these metrics, businesses can identify areas that require attention and implement targeted improvements.
Great Customer Service Requires Resolve
Curious about how the story of the American Express customer ended? Well, after cancelling the payment, he reached out to customer service again, giving the company one last chance. However, he connected with a different representative this time—a night-and-day contrast from the previous encounter.
Unlike before, this representative was willing to listen. She grasped the situation immediately, empathising with the customer's plight. After reviewing his account and consulting with her supervisor, she astonishingly informed him that his card would be reactivated. The customer was both shocked and elated with this positive outcome.
It's remarkable how two representatives working for the same company in the same customer service team can provide vastly different experiences—one great and the other terrible.
The root cause of the poor experience is challenging to pinpoint. Perhaps the first representative was not suited for customer service, or management failed to train and motivate them adequately. Regardless, the bottom line was that the customer sought help but did not receive it.
Often, solving a customer-service problem involves navigating between company policies and customer interests, as was evident in this case. The first representative struggled to handle such a situation, whereas the second possessed the necessary skills to address the issue effectively.
Problem-Solving is not just an Ability -- It's a Mindset
As we explored in my previous post on problem-solving skills , the golden rule of customer service is to create a fantastic customer experience even when the problem may not directly concern your product. Offering a possible solution exemplifies the essence of customer service—solving problems, not merely telling customers what they want to hear.
The key to success lies in persistence, utilising the advice shared here, and maintaining a positive outlook. Armed with these qualities, there will be no problem you cannot conquer.
Get a glimpse into the future of business communication with digital natives.

Keep the conversation going
- copy-button#copy track#send" data-controller="track" data-track-category="Success" data-track-action="Share" data-track-label="Copy link" > Copy link Link copied to clipboard https://text.com/success/effective-customer-service-problem-solving/
LiveChat is a complete customer service platform that delights your customers and fuels your sales
How to Conduct Effective Problem-Solving Sessions with Customer Service

In the customer service industry, effective problem-solving is a crucial skill that can greatly impact customer satisfaction and business performance. When handled properly, problem-solving sessions provide an opportunity to identify and address issues that customers may encounter. This article will delve into the importance of problem-solving in customer service and provide key elements and techniques for conducting successful sessions. Additionally, we will explore common challenges faced during problem-solving sessions and offer strategies to overcome them.
Understanding the Importance of Problem-Solving in Customer Service
Problem-solving plays a significant role in ensuring customer satisfaction. When customers face challenges or issues, their overall experience can be negatively affected. However, by actively engaging in problem-solving sessions, businesses can effectively address customer concerns and improve their experience. By resolving issues promptly and efficiently, companies can enhance customer loyalty and build long-term relationships.
Customer service is a vital aspect of any successful business. It is the backbone of customer satisfaction and retention. When customers encounter problems or difficulties, it is crucial for businesses to have a robust problem-solving mechanism in place. By acknowledging and addressing customer concerns, companies demonstrate their commitment to providing exceptional service and ensuring customer happiness.
Problem-solving in customer service goes beyond simply fixing a specific issue. It involves understanding the root cause of the problem and implementing long-term solutions to prevent similar issues from arising in the future. This proactive approach not only resolves immediate concerns but also helps businesses improve their overall operations and customer experience.
The Role of Problem-Solving in Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is the key to success for any business. By addressing customer issues through problem-solving sessions, companies demonstrate their commitment to resolving problems quickly and effectively. By actively listening to customers’ concerns and providing appropriate solutions, businesses can restore trust, boost customer satisfaction, and ultimately improve their reputation in the market.
Problem-solving sessions provide an opportunity for businesses to engage with their customers on a deeper level. By actively involving customers in the problem-solving process, companies show that they value their opinions and are dedicated to meeting their needs. This collaborative approach not only helps resolve immediate issues but also strengthens the bond between businesses and their customers.
Furthermore, effective problem-solving can lead to positive word-of-mouth referrals. When customers have a positive experience with a company’s problem-solving process, they are more likely to share their satisfaction with others. This can result in new customers and increased brand recognition, further contributing to business growth and success.
Improving Business Performance through Effective Problem-Solving
Effective problem-solving can also contribute to improved business performance. By identifying and addressing underlying problems, companies can streamline their operations and optimize their products or services. This, in turn, leads to increased efficiency, decreased costs, and improved overall performance. Problem-solving sessions provide a valuable platform to explore creative ideas and innovative solutions, enabling businesses to stay competitive in the market.
During problem-solving sessions, businesses have the opportunity to gather valuable feedback from customers. This feedback can provide insights into areas that require improvement, allowing companies to make informed decisions and implement necessary changes. By continuously seeking feedback and actively working towards resolving issues, businesses can adapt and evolve to meet the ever-changing needs and expectations of their customers.
Moreover, effective problem-solving can help businesses identify potential opportunities for growth and expansion. By analyzing customer feedback and addressing recurring issues, companies can uncover new market demands and develop innovative solutions to meet them. This proactive approach not only enhances customer satisfaction but also opens doors to new revenue streams and business ventures.
In conclusion, problem-solving is an integral part of customer service and business success. By actively engaging in problem-solving sessions, businesses can address customer concerns, improve satisfaction, and drive overall performance. Effective problem-solving not only resolves immediate issues but also paves the way for long-term growth and success in the market.
Key Elements of a Problem-Solving Session
A successful problem-solving session comprises several key elements that ensure a systematic approach to addressing customer concerns.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, problem-solving has become an essential skill for organizations to thrive. Whether it’s resolving customer complaints, improving internal processes, or finding innovative solutions, effective problem-solving is crucial for success.
Identifying the Problem: The First Step
The initial step in conducting an effective problem-solving session is to identify the root cause of the issue. This requires active listening and gathering relevant information from both customers and internal stakeholders.
During this phase, it is important to create an open and non-judgmental environment where customers feel comfortable expressing their concerns. By empathizing with their experiences and actively seeking their input, businesses can gain valuable insights into the problem at hand.
Additionally, involving internal stakeholders such as employees from different departments can provide a holistic view of the issue. Their perspectives and expertise can uncover underlying factors that may have contributed to the problem.
By examining the problem from various angles, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of the situation and lay the foundation for finding the right solution.
Developing Potential Solutions: Brainstorming and Beyond
Once the problem is identified, the next step is to brainstorm potential solutions. In a problem-solving session, team members should be encouraged to contribute their ideas freely.
Brainstorming sessions can be conducted in various formats, such as group discussions, virtual collaboration platforms, or even through anonymous suggestion boxes. The key is to create an environment where creativity flourishes and no idea is dismissed without consideration.
This collaborative approach allows for diverse perspectives and creativity, increasing the chances of finding an effective solution. Moreover, considering multiple alternatives helps in evaluating the feasibility and viability of each potential solution.
During the brainstorming phase, it is important to focus on generating a wide range of ideas without prematurely evaluating them. This encourages out-of-the-box thinking and prevents the group from getting stuck on a single solution too early in the process.
Once a substantial list of potential solutions is generated, the team can move on to the next step of evaluating each option based on criteria such as cost-effectiveness, practicality, and alignment with the organization’s goals.
Implementing and Evaluating the Solution: The Final Steps
After developing potential solutions, it is essential to implement and evaluate the chosen solution. This involves creating an action plan, allocating resources, and assigning responsibilities.
During the implementation phase, effective communication is crucial to ensure that everyone involved understands their roles and responsibilities. Clear instructions, regular progress updates, and feedback mechanisms help keep the team aligned and motivated.
Once the solution is implemented, ongoing evaluation and feedback from customers and team members help to refine the solution as needed, ensuring its effectiveness in addressing the initial problem.
By continuously monitoring the solution’s impact and gathering feedback, organizations can make necessary adjustments and improvements to optimize its outcomes.
Moreover, documenting the entire problem-solving process, including the identified problem, potential solutions, and the chosen solution, can serve as a valuable reference for future problem-solving sessions. This knowledge repository can help organizations build upon past experiences and avoid reinventing the wheel.
In conclusion, a well-executed problem-solving session involves identifying the problem, developing potential solutions through brainstorming, and implementing and evaluating the chosen solution. By following a systematic approach and involving diverse perspectives, organizations can effectively address customer concerns and drive continuous improvement.
Facilitating a Problem-Solving Session: Essential Techniques
Facilitating a problem-solving session requires specific techniques to ensure productive outcomes.
Setting the Stage for a Productive Session
The facilitator plays a critical role in setting the stage for a productive problem-solving session. This involves creating a conducive environment where participants feel comfortable expressing their ideas and concerns. Clearly defining the session’s objectives and establishing ground rules fosters open communication and sets the tone for collaborative problem-solving.
Encouraging Open Communication and Collaboration
Open communication and collaboration are essential for effective problem-solving. The facilitator should encourage active participation from all team members, ensuring that everyone has an equal opportunity to contribute their insights. Creating a non-judgmental atmosphere promotes free thinking, enabling teams to explore a wide range of ideas and perspectives.
Guiding the Team towards Effective Solutions
The facilitator’s role also includes guiding the team towards effective solutions. This involves keeping discussions focused and on track, ensuring that the team does not get sidetracked by unrelated issues. The facilitator should facilitate consensus-building, helping the team to align and make informed decisions. Effective problem-solving requires both critical thinking and collaboration.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Problem-Solving Sessions
While problem-solving sessions are beneficial, they can also present challenges that need to be overcome to achieve desired outcomes.
Dealing with Resistance and Conflict
Resistance and conflicts often arise during problem-solving sessions, hindering the progress. The facilitator should act as a mediator, promoting a respectful and inclusive environment. Encouraging active listening and empathy among team members helps to overcome resistance and conflicts, leading to a more productive session.
Ensuring Participation from All Team Members
Unequal participation from team members can prevent a problem-solving session from reaching its full potential. To ensure that all team members are engaged, the facilitator should explicitly ask for input from quieter team members and ensure that dominant team members do not monopolize the discussion. Establishing a safe space where everyone feels comfortable sharing their thoughts is crucial for fostering equal participation.
Maintaining Focus and Momentum throughout the Session
Problem-solving sessions can sometimes lose focus or momentum due to lengthy discussions or side conversations. The facilitator must keep the session on track by summarizing key points, redirecting discussions when necessary, and managing time effectively. Maintaining a sense of urgency and keeping teams motivated ensures that the session remains productive from start to finish.
In conclusion, conducting effective problem-solving sessions is vital for customer service excellence. By recognizing the importance of such sessions and implementing key elements and techniques, businesses can address customer concerns efficiently and improve overall business performance. Overcoming common challenges requires facilitators to create a supportive environment that fosters open communication, collaboration, and effective decision-making. By adopting these strategies, companies can enhance customer satisfaction, drive innovation, and achieve enduring success.
CIPD Level 3 Course : The CIPD Level 3 Certificate in people practice is ideal for anyone looking to start a career in either HR or Learning and Development. CIPD Level 5 Course HR : The CIPD Level 5 Associate Diploma in People Management will help you build on your existing HR knowledge. CIPD Level 5 Course L&D : The CIPD Level 5 Diploma in Organisational Learning and Development is the most comprehensive course available for L&D professionals, ideal for you if you want to formalise your existing experience, skills and knowledge. CIPD Level 7 : The CIPD Level 7 Advanced Diploma is aimed at expanding learners’ autonomy so they can strategically direct organisations and their people.
If you aspire to become a digital marketing manager or explore the senior level of your career, have a look at the squared digital marketing programme .
Related Articles

In today’s fast-paced world, achieving a healthy work-life balance is more crucial than ever for maintaining employee productivity. We’ve all felt the strain of juggling our professional responsibilities with our personal lives, often leading to burnout and decreased job satisfaction. Fortunately, there are proven strategies that can help us find that sweet spot between work […]

In today’s fast-paced world, we understand that financial well-being is a crucial aspect of overall employee satisfaction and productivity. It’s not just about earning a paycheck; it’s about feeling secure and having peace of mind when it comes to financial matters. That’s why we’re diving deep into the steps necessary to ensure employees’ financial well-being, […]
In today’s globalised world, diversity and inclusion aren’t just buzzwords – they’re a business imperative. I’ve spent years delving into the nitty-gritty of HR strategies, and I’m here to share my insights on how to cultivate a diverse and inclusive workplace. We’ll explore the different HR strategies that can help your business harness the power […]

Customer Service Problem-Solving Techniques to Improve Your Sales
Customers have numerous issues, with varying degrees of sophistication or viewpoint. They are running out of time. They have an almost unlimited number of product options to choose from. They are wooed by product reviews.
In such situations, a customer may not be aware of the best solution to an issue. You as a service provider, however, can step into their shoes, come to grips with the problem, work out the solution and gain the customer’s trust.
The ability to solve a customer’s problem is what makes all the difference between churn and loyalty.
What is Problem-Solving in Customer Service?
Problem-solving in customer service is a skill that entails
- Knowing how to handle a conflict
- Being able to calm an agitated customer using tone of voice and true empathy
- Listening and speaking while maintaining a strong grip on problem-solving techniques.
How does bad customer service affect your business?
Customer service issues must be resolved because they affect other parts of the business. Businesses must become more customer-centric and coordinate their services in order to delight clients by effectively solving their problems.
You may have the ideal product and competitive pricing, but if your customer service is poor, your business can falter.
Let’s look at some of the ways in which bad customer service can impact a business.
Harms Brand Reputation
Customers like to share their stories. As a result, when people have a poor experience, they turn to their favorite media to express their feelings. A single poor review on Twitter or Facebook can defame your brand image.
“It takes 20 years to build a reputation and five minutes to ruin it. If you think about that, you’ll do things differently.” -Warren Buffett
Lesser Conversions and Loss of Customers
Inefficient solving of customers’ problems , slow response times, and frequent negative experiences make prospects less likely to become customers and make current customers less likely to stay loyal.
“53% of customers are likely to stop buying from a brand after a poor customer service experience.” – source
Dip in Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Companies that consistently provide bad customer service eventually fail. Customers today have so many options that when they have a negative service experience, they will go to a competitor.
It’s widely known that one-time customers are expensive, whereas recurring customers bring a steady source of income.
Customer lifetime value is a measure that is computed by adding up all of a customer’s revenue over the course of their engagement with a company.
You can increase the lifetime value of your customers by delivering outstanding service. This means you can make more revenue by spending less money on customer acquisition.
Steps of Customer Service Problem-Solving
Here is a 5-step process for customer service problem-solving and troubleshooting when you come across a customer issue.

1. Ask, Ask and Ask
Ask the proper questions to learn what is upsetting your customer. You won’t be able to remedy your customer’s problem if you can’t place it.
For example, ask questions such as,
“Have you been dealing with this issue for a long time?”
Asking relevant questions will help you identify customer needs while also assisting you in determining an appropriate solution.
2. Identify the Problem
After having a question session with your customer to discuss their pain areas, you can restate or explain the situation as you have come to terms with it.
You must describe the problem precisely and do so from the customer’s perspective. Get the customer’s approval that you’ve grasped the problem.
Before you move on to the next phase, ask whether there is anything else that is bothering them.
3. Formulate Solutions
After a thorough examination of the problem, develop various solutions and present the best solution to the customer or prospect.
Your solution must be focused on the specific problem , and not ambiguous.
4. Deliver the Solution
Deliver the solution as promised. Take advantage of these opportunities to strengthen your customer relationships and demonstrate that you are worthy of their trust.
5. Follow up with Customers
It’s critical to check in with your customers to see how they feel about the solution and confirm that the issue has been fixed. This step demonstrates to customers that your organization values customer service and is committed to providing a better customer experience .
It’s important to ask some of these challenging questions when checking in with present customers in the hopes of upselling, cross-selling, or renewing their contracts.
“How satisfied are you with our product on a scale of one to ten?”
“How did you come up with that score?”
“What is it about our product/service that you enjoy?”
“Do you think you’ve experienced excellent customer service?”
This will keep you from overlooking warning signs that they’re dissatisfied and might begin to consider switching to a competitor.
In an era where ‘Customer is King” , happy customers are the secret to growth. As a result, customer satisfaction is a direct reflection of the effectiveness of your service team.
“The probability of selling to an existing, happy customer is up to 14 times higher than the probability of selling to a new customer, according to Marketing Metrics” – source
To improve customer experience and increase cross-selling and upselling opportunities, forward-thinking companies link their sales and customer service teams .

9 customer service problem-solving techniques
Customer service exists to assist customers with their demands or any issues that may arise while they are using your product or service. It is, therefore, necessary to train your staff on how to properly resolve customer complaints or problems. Learn about the methods a service representative can take toward customer service problem solving to deliver superior customer service!
Ask for the Customer’s Needs
Ask probing questions to get to the heart of the matter and uncover unmet customer needs. The answers to these questions can be used to create a workable solution, and this is a consultative approach that will strengthen customer relationships.
Listen to the Customer
Listen to the customer to prod deeper into the issue to determine the underlying cause. Only then will you be able to solve the problem at its core. You could even be assisting your company in developing stronger SOPs or regulations or eliminating a rigid process that is preventing you from running smoothly during the course.
The more you know about your customer and their company, the more you’ll be able to influence their bottom line.
Don’t argue
When we are offended or proven wrong, we have an inbuilt propensity to react in a defensive manner. In customer service, this is a no-no.
To go through the situation unscathed, here are two tips that you can use.
Tip 1: Allow customers to talk
You should let your customers talk until they are able to release their frustrations and calm down.
Tip 2: Show that you care
The least you can do is support them and be empathetic toward the situation while customers go on explaining their tales. Use consoling phrases to comfort them.
Send Lightning-Fast Response
Every customer is strapped for time and expects a timely response from your support agent,
Kapture’s omnichannel help desk software can help you streamline how you manage customer inquiries across multiple channels.

Image: Kapture’s omnichannel dashboard
You can route inquiries from a certain channel to a dedicated team. This helps ensure a smooth customer experience and swift resolution of customer inquiries.
Another way around is to add a live chat feature to your website. It is a tool that helps customers instantly connect with your agent and work out solutions. Kapture’s live-chat tools embedded in your website can deliver faster responses.
Follow Solutions to the Conclusion
Once you’ve committed to providing the resolution, it’s in your best interests to see it through to completion.
The standard customer problem-solving process includes following up with clients and providing them with updates to keep them informed.
Sending follow-up emails is the most effective technique to keep in touch with them about the solution’s progress.
Kapture’s help desk software allows you to send emails from the same system that you use to respond to customer queries. You really don’t need to use traditional mail services for this. Likewise, the merits of a single sign-on help desk are many.
Use Visual Content
Your customer service representative can solve customers’ problems in a more comprehensible and exciting manner by offering them visual troubleshooting guides.
The best options are videos, graphical flow diagrams (depicting step-by-step instructions), or screenshots to resolve some of the very minor yet frequent issues.
Kapture’s knowledge base feature allows you to store and manage information in just about any format, which includes videos, images, and documents, that can be accessed via self-help tools.
This not only saves your time but also gives customers a quick and intelligible solution to their problems.
Offer an Incentive to Customers
Just to make sure that the recent product or service issue your customer faced did not bring any scar to your relationship, it is a supersmart way to butter up the bond with incentives.
Offering incentives to clients can help you gain their loyalty, and they may decide to wait until you fix their problem rather than looking for solutions elsewhere.
Incentivizing clients to compensate for the inconvenience encourages them to stay loyal.
Consider presenting a coupon or voucher, for instance, on the next transaction if you want to motivate a customer to use your service again.
Self-Help Option For Your Customers
Provide self-help capabilities such as AI chatbots, knowledge base, or interactive discussion forums so that customers can search, find and resolve problems on their own. AI-powered chatbots offer responses to customer queries contextually.
Do not undermine the convenience of a self-service. This is the most preferred channel of help by customers as revealed by many surveys.
Kapture’s AI and Machine Learning-powered self-serve tools are a fantastic approach to support your tech-savvy customers.

Image: Chatbot powered by Kapture
Customers that are happy with your service will stay longer, become repeat customers, and recommend your service to their friends and colleagues.
That’s why it’s critical to cultivate a customer-centric culture within your organization.
Remember to go the customer problem-solving way to create exceptional customer experiences.
Kapture’s AI-based solutions can assist you in effectively managing the entire customer service process and wowing your clients with customer delight factors such as
- Work-flow automation capabilities
- Omnichannel communication
- Self-help features
- Run automatic surveys
- Generate survey reports
Our solution is easy to use and integrates with other services like cloud telephony, social media, eCommerce, ERP, and others making it easy to collate the information at a centralized location.
Kapture, a customer service automation platform helps your team on how to serve and delight customers right from any touchpoint- and translate those efforts into building a loyal customer base.
Finally, follow the sound and systematic c ustomer service problem-solving techniques outlined in the blog t o win your customer’s hearts.
- customer problem solving
- customer service problem solving techniques
- customer service problems and solutions
- customer-based approach
- handling customer complaints
- problems in sales
- productivity
- troubleshooting customer service
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Recent posts.
- Top 11 Reasons Your Business is Losing Customers
- Identifying and Addressing Customer Pain Points
- Why Customer Feedback is Important To Your Business
- CX: How to Measure it the Right Way
- Customer Support Automation without Losing Personalization
Stay updated with tips and best practices
Book a demo.

Too much to take in?
Subscribe to our newsletter and read it at your own time.
How to improve problem-solving skills with customer service training
This post was originally published on lessonly.com.
Customer service is a jigsaw puzzle.
In order to put together a picture of excellent customer service, customer service reps have to piece together customer information, product or service knowledge, and personal skills. But, even with all of the necessary pieces, a customer service team member can’t provide valuable customer service without being a great problem solver.
As companies put a larger emphasis on high-quality service, reps and agents need customer service training programs that focus on problem-solving. As self-service channels grow in popularity for simple, transactional interactions, when it comes time for a customer to reach out to a rep, it’s likely because they couldn’t find the answer via self-service. These interactions tend to be unique, more complex, and unpredictable. In fact, according to one report, as many as 83% of people say that humans better understand their problems and needs and want to bypass self-service options to talk directly to a human. This means that reps should be well equipped to deal with customers, understand their issues, effectively provide a resolution, and anticipate their future wants and needs.
So, how can customer service leaders deliver training courses that feature effective problem-solving techniques? First and foremost, employees should learn the fundamental knowledge and skills that they’ll need for any interaction. Then, leaders can begin working with their customer service team to develop their problem-solving skills.
Introduce reps to problem-solving methods
The best way to ensure reps address a customer’s issue and do it with a high quality of service is to provide training on a structured problem-solving process. To start, here are five steps that every rep should know how to work through.
- Identify and define the problem: While this may seem simple and straightforward, customers don’t always describe their issues clearly. Training should offer reps examples of open-ended questions that they can use to effectively gather information and isolate the actual problem. This will make the rest of the interaction much more efficient.
- Brainstorm solutions: Now it’s time to brainstorm and share possible solutions with the customer. Consider providing reps with guidelines that encourage autonomy so they can create solutions at their own discretion.
- Evaluate and choose the best solution: During this time, it’s key for reps to clearly and effectively communicate the solutions (and their implications) of each with the customer. By having an open and friendly discussion, reps will be able to choose the solution that best addresses the customer’s specific wants and needs.
- Implement the solution: Once a customer and rep are on the same page about a solution, it’s important to execute as soon as possible. Training must ensure that reps are empowered to build a plan, work with the appropriate team members to ensure it happens, and make a solution become a reality.
- Analyze the results: After a solution is implemented, successful support teams also measure the results. By asking the customer for feedback and analyzing metrics, teams can better determine if the right process was followed and what they could improve in the future for increased customer loyalty.
Provide opportunities for practice and feedback
Once customer service reps have a good grasp of problem-solving techniques, it’s important to give them opportunities to apply and practice their problem-solving skills. World-class customer service teams take real-life scenarios and support tickets and apply them to a test environment. This gives both new and veteran reps the chance to hone their problem-solving skills in a safe space—without negatively impacting the relationship with a customer. They then have the chance to work through prioritization and resolution steps while practicing effective communication skills.
Additionally, offering reps the chance to practice thoughtful problem solving allows leaders to give clear and effective feedback. Customer service leaders and training managers can evaluate practice scenarios with predetermined criteria to ensure their team focuses on the right customer service skills and gets the helpful feedback they need to improve their level of service. This also helps leaders identify reps who may need additional coaching.
When reps are properly trained in fundamental customer service skills and effective problem solving, they’re more prepared to address a customer’s issue. With intentional practice and continuous feedback loops from management, reps will be able to implement these steps with expertise and become customer service puzzle masters. The result is higher first-contact resolution rates, improved net promoter scores, and better overall business performance. That’s a puzzle worth solving.
World-class customer service teams use Lessonly by Seismic
Lessonly is powerfully simple training software that helps customer service teams learn, practice, and perform like never before. Managers and trainers deliver effective onboarding, proving ongoing training, and share best practices. The results? Effective team learning, happier employees, and extraordinary experiences. Learn more, and demo Lessonly today .
PROFESSIONAL SERVICES
Expert advisors, at your service
SUBSCRIPTION
Subscribe to our newsletter
Thank you for subscribing
The complete guide to enablement
SEISMIC ROI CALCULATOR
Grow like the sky's the limit.
The 2023 Value of Enablement Report
- 888-636-1222
- Make a Payment | Contact Us

How to Improve Problem Solving Skills in Customer Service

Keeping customers happy pays off.
Happy customers buy more, generate positive word-of-mouth advertising, and create great referrals.
Unhappy customers complain, and they do it loudly. What’s worse, for every customer that complains, 26 stay quiet .
Delivering great customer service can be challenging, but why?
According to Jeff Toister of Toister Performance Solutions and author of three customer service books , there are five reasons why customer service is so hard:
- It’s not instinctive
- Our customers see what we don’t
- It’s sometimes hard to be friendly
- We aren’t good at multitasking
- Directed attention fatigue
So how do we overcome these challenges ?
Problem-solving.
“Every problem has a solution. You just have to be creative enough to find it.” Travis Kalanick
One of the main reasons our customers do business with us is because we solve a problem for them.
Depending on your product or service, your business can help customers:
- experience something new
- feel comfort
- become healthier
What problem does your business solve for your customers?
Problem -solving skills is vital to Customer Service
Solving a customers’ issue should be the goal of every one of your people.
But typically in the past, when an issue escalated to a certain point, help desk service or customer service reps (CSRs) were told to escalate these calls to a supervisor or manager.
More and more companies are asking customer service reps (CSRs) to handle these types of issues, not managers.
That’s a big change for many CSRs.
It’s also a task CSRs can get right with the proper problem -solving skills training . Failing is not an option for CSRs. It’s just too costly.
What is the impact of poor customer service?
Companies lost $75 billion in 2017 from customers switching to competitors because of bad service. That’s up $13 billion from 2016. With customers demands increasing each year, it doesn’t take much to disappoint customers with poor customer service. Obviously, CSRs need to be at the top of their games to keep customers happy.

This guide offers tips on how to help your people solve customer service problems quickly, efficiently, and cost-effectively.
The guide covers the following topics:
- Critical thinking in customer service
- Rules to help customer service people think critically
- Basic customer service problem-solving scenario
- Concrete steps to solve a customer problem
Keeping customers happy can boost customer loyalty, corporate productivity , and business profitability—goals for every company out there.
“Fall in love with the problem, not the solution.” Uri Levine
Critical Thinking in Customer Service
Delivering epic customer service is essential these days. But that’s easier said than done, given today’s more demanding customers.
Identify critical thinkers
To manage demanding customers requires someone highly skilled in troubleshooting—someone with the creativity to solve difficult problems.
All while under the pressure of the customer.
So, look for customer service people that are creative problem solvers when hiring new workers. These people have a penchant for thinking outside the box to solve problems.
That includes not just the ability to think rationally , but also the need to question the information given. Put simply, critical thinking is never taking anything for granted.
Build critical thinking skills
Customer service people can develop critical thinking skills with practice. In a post by Ransom Patterson on CollegeInfoGeek.com reveals seven ways people can improve critical thinking skills:
- ask basic questions
- question basic assumptions
- be aware of your mental processes
- try reversing thing
- evaluate existing evidence
- think for yourself
- remember you are not perfect
Apply these tips encourages critical thinking.
Another critical thinking technique CSRs can use is constructive controversy. A proven problem-solving method, constructive controversy helps you decide if a decision we’re making is the right one for you. Here’s more on this technique .

Basic Customer Service Problem-Solving Scenario
Savvy businesses aren’t afraid to provide employees with customer service problem-solving training.
One aspect of this training is learning the four phases of a problem-solving situation and what to do during each phase. See below:

Listen to customers
Listening is the first step in solving customer’s problems. It’s also the most critical. But customer service people often need training to do it well.
If customer service reps don’t listen, they won’t know the nature of a customer’s problem and its impact on him or her.
Sometimes, all customers want is for CSRs to lend a sympathetic ear. Other times, they need more.
Also, CSRs need to let customers vent without interrupting them.
Acknowledge customer’s pain
During this phase, CSRs need to acknowledge they heard customers and “feel” their pain.
Paraphrasing the problem back to a customer says you’ve done that. It also makes sure everyone is on the same page. If CSRs don’t fully understand the issue, they may end up providing the wrong solutions. Saying something like “I’m sorry you had to call us to deal with this issue” also helps.
Offer alternative solutions
If the issue is merely an oversight on the customer’s part, no remedy is needed.
But if the situation is the company’s fault or a product or service fails, you may need to offer alternative solutions.
Resolution is critical.
In this case, the customer not only didn’t get what he or she wanted but also were inconvenienced. That’s a bad combination no matter how you look at it. Going above and beyond by resolving the issue and offering a free product or service, a special coupon, or a gift voucher goes a long way with customers.
Execute/Follow-up
After agreeing on a solution, CSRs need to execute. Then, you need to follow up. That ensures that customers end up happy with the resolution and are satisfied with the outcome. If they’re not, then customer service people need to find a way to satisfy them.
Understanding these phases of a successful issue resolution is crucial when dealing with unhappy customers. It’s the “secret sauce” to keep buyers happy.
Extra: Be prepared
In addition to this approach, you may want to have some prepared responses to seven stock questions customers ask. They’re questions that almost every company gets:
- Why don’t you have it in stock?
- Why didn’t you or your company tell its customers?
- Why did I pay less the last time I was here?
- Can I have a refund because of this problem?
- You did it last time I was here?
- You said the problem/product was fixed?
- You said you’d call me when the problem was fixed.

Providing stock responses to these questions not only helps customer care people follow company guidelines but also keeps customers happy.
How to Handle Customer Service Issues: 9 Steps
Problem-solving often seems straightforward, but that’s not always the case. Sometimes, it’s complicated. Having workers well-versed in problem-solving skills and techniques for customer care representatives helps. Approaching issues in a systematic way simplifies the problem-solving process.
Below is a 9-step process that can help CSRs resolve even the most complex customer service issues:

Identify the problem
The key to doing this is to ask the right questions. Below are some customer service problem-solving interview questions:
- What is this call really about?
- Is there an underlying issue causing the problem the customer isn’t aware of?
- What does the customer want us to do?
- Is the issue being made worse by a known problem or bug?
- Is this issue identifying a repeated customer service problem or is it a new issue?
These questions can help CSRs pinpoint the real problem. It’s not always what customers think. Acknowledging the customer’s pain, as we said above, also helps.
Find out what customers need
Try to understand how customers see the issues involved and try to get a solid understanding of his or her needs. If appropriate, ask customers what they’ve done to resolve the issue.
Find out how the issue impacts the customer
Understanding how an issue affects a customer is crucial. It helps CSRs not only connect with the customer but also prioritize tasks.
Clearly define the root of the problem
Having identified the problem in steps 1 to 3, you now need to understand what caused the problem. By identifying the cause of the problem, you will have a better idea of how to solve it. Also, you will know how to avoid a simialr problem in the future.
Produce possible solutions
Knowing the problem, your customer care person needs to start brainstorming solutions. They also need to find out what solutions other co-workers may have used to solve the problem. CSRs can then generate a list of potential solutions.
Evaluate each solution and pick the best
Evaluate all the solutions. Decide if you have the resources to implement it, how much the solution costs, how long it will take to execute it, will it resolve the issue, and if it follows company policy.
Plan the solution’s implementation
Some solutions are easy to execute. Others are harder. For harder solutions, think about who will execute the solution, what will it costs, when and where you will execute it, and how will it be implemented. Also, double check out the benefits of the solution.
Discuss the solution with customers
Having nailed down the solution’s details, discuss it with the customer. Walk through it with him or her step by step and ask for feedback. Be ready to adjust the plan. Execute the solution — After the customer approves the solution, it’s time to execute it. Follow up to certify the progress of the solution, that you’re meeting any deadlines and where you stand with the budget. Re-work your plan, if necessary.
Analyze the results
Having finished the implementation, analyze the results. Use quantitative and qualitative data, if available. Can you improve the solution? Also, ask the customer if the resolution met their expectations. That’s critical.
This ten-step process may seem a bit much for call center agents, technical support people, and customer care representatives to tackle. But using it works.
Having customer care people go through it step by step helps your CSRs quickly resolve customer issues the first time that customers call. Track resolution time to see how your CSRs are doing.
Resolving issues when customers contact your business keeps them happy.
Happy customers buy more, generate positive word-of-mouth advertising, and create outstanding online referrals. On average, a happy customer tells nine people about their experience with you.
Keeping customers happy is the secret to boosting customer loyalty, increasing profitability, and differentiating you from competitors. Doing those things can take your company to the next level.
Unicom Teleservices
Related posts.

Active Listening Customer Service: Key to Business Success

What Is A Warm Transfer?

What Is a Good Definition of Customer Service?
What You Need to Know About Customer Service Problem Solving
Team ChatSupport
February 9, 2022

What is customer service problem solving?
Have you ever had a problem with a product or service that was so frustrating, you contacted the company about it? You probably expected a response that would quickly let you know if the problem could be fixed or if you were out of luck. But more likely than not, your inquiry wasn’t handled in such a way that provided you with much clarity.
Studies have shown that only 43% of customers are satisfied with refunds. But even more than that, 50% of customers love it when customer service representatives empathize and are proactive in providing solutions.
Customer service problem solving has one purpose; to give customers the information they need to make an informed decision. That decision could be whether to keep the item and have it repaired or to return it for an exchange or refund. It’s an integral part of customer support.
This article will cover the basic skills customer service agents need to provide excellent customer service and address customer complaints seamlessly.
Basic customer service problem solving skills
There are many different forms of customer service problem solving, each with their own unique challenges. While many of these challenges are similar to those faced by regular consumer-facing businesses, there are some that are unique to customer service issues.
For example, customer service teams in call centers are more likely to deal with customers asking for replacements or refunds. It is oftentimes the customer service reps that make first contact with customers regarding their questions, which can later lead to potential sales.
In all cases, customer service reps need to be fully equipped to provide possible solutions. Here are the top skills needed to boost customer satisfaction.
Being patient is an asset in problem solving because it allows you to keep calm, even if a customer is upset or angry. If a customer is agitated, then it’s easy to get caught up in their emotions, which can lead you to make a bad decision based on their emotional state rather than understanding their actual problem.
Taking a moment to calm down will help you understand what they are saying and make sure you’re making rational decisions rather than emotional ones.
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is a form of problem solving that involves analyzing information and identifying the best possible solution. Customer reps with critical thinking skills use logic and reasoning to solve problems, which often involves gathering information from multiple sources. They also consider multiple perspectives when examining problems, which can help them see creative solutions where others may not.
Critical thinking is an incredible skill to have when taking problem-solving steps with customers.
Empathy is the ability to feel and understand other people’s feelings. It’s important in any customer service role because you are in a position where you will have to interact with and help customers. Customers are not always in the best moods, so empathy helps you understand their frustrations and their needs.
If you are able to empathize with your customer, then you can also assess what type of solution would be best for them. This will satisfy the customer and enhance your chances of getting a positive response from them as the issue is being resolved.
Willingness to help the customer
Customer service refers to addressing a customer’s needs by providing and delivering helpful and high quality assistance throughout their customer journey. Support agents need to be able to show their willingness to help their customers.
This skill is important because it shows you care about the customer and want to help them in any way you can. It’s a sign of respect for the customer and helps build trust. That trust is an important aspect of any customer relationship and can make all the difference in customer experience.
Steps for troubleshooting customer issues
To troubleshoot issues in the customer support process, it’s important to understand the process and then to master the skills involved in problem solving.
Do you have the communication skills to provide amazing support? Then it’s time for the next steps: resolving the customer’s queries and helping them along their customer journey.
Here are the steps to take in order to troubleshoot customer issues and boost retention.
1. Actively listen to the customer’s issue.
To resolve customer issues effectively, a help desk agent must first listen. It’s important to ask the customer questions about what they are experiencing and to refrain from guessing what the problem might be. It’s also important to document the conversation with the customer in order to accurately address their concerns.
Here are some things to keep in mind when listening to a customer:
- Pay attention to what the customer is saying, not just what they’re asking for.
- Take notes so you can reiterate back what you heard and ensure you have all the information needed.
- Ask questions to clarify when necessary. For example, if a customer mentions something like “My email wasn’t working”, ask them some clarifying questions: “Which email account were you using? What exactly were you trying to do? What did you see on your screen?”
2. Acknowledge the pain the customer is experiencing.
The customer has a problem. Your job is to help them with their problem. The first step in doing that is to acknowledge the customer’s pain.
You need to show the customer you understand and care about the issue they’re experiencing. It’s important to acknowledge their pain because it shows you care about them as a person. If you don’t show them you care, they may think you’re just trying to get on with your work day. That could lead them to think their issue won’t be fully resolved, which translates to poor customer service.
Here are some phrases you can use to acknowledge their pain:
- I understand how frustrating this must be for you.
- I know this problem has been a huge inconvenience for you.
- I can tell that this is an urgent matter for your business.
3. Present alternative solutions to the customer.
When a customer has an issue, you need to be prepared to provide a solution. Sometimes the issue is something that can be resolved quickly and easily; other times, it may require some investigation, but you should always know how to respond appropriately.
Ideally, you should offer at least two solutions so the customer can decide which one best fits their needs. For example, if the customer can’t complete their purchase online, you could try to assist them by helping them to place their order over the phone.
Again, this shows that you care about their business and want to make things right for them in a way that makes them happy.
4. Follow up with the customer.
If the problem cannot be solved at the time of contact, always follow up with the customer to provide an update on the status of their issue. The most important step in this process is to make sure you actually resolve the customer’s issue and don’t just create another one!
Following up with customers is vital to providing good customer service. It allows you to check on the status of their issue and ask if they require assistance with anything else.
When you provide this assistance, you can maintain a positive relationship between your business and that customer, which could lead to future purchases or referrals of other potential customers.
Following up with the customer can be as simple as sending an email to ask how things are going or making a phone call to see how the service is working out, so don’t be afraid to go that extra mile to nail your customer loyalty.
Take Your Problem Solving to the Next Level with ChatSupport’s Intuitive Features
Today, customer service agents must have stellar communication skills and be readily available. They are, in ways, promoters of the business by acting as ambassadors for the brand. That’s why your business needs a solution to assist with customer service problem solving.
Enter: ChatSupport.
ChatSupport’s live chat feature is a must have for any company looking to establish and maintain a strong online presence. With ChatSupport’s real-time problem-solving tools, companies can resolve customer issues faster and more effectively, boosting the customer service functionality.
With ChatSupport’s custom survey forms , you can gauge the status of your customer service and find areas of improvement as well.
Get started with us today!
Like this article? Spread the word.
Leave your comment. Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
7 Most Important Customer Satisfaction Theories
- Updated Feb 29, 2024
- Estimated Reading Time: 0
51% of customers will never do business with that company again just after one poor Customer Experience. — Newvoicemedia .
This article will guide you to understand the various types of customer satisfaction theory. Let’s find some of the important theories about customer satisfaction.
What is Customer Satisfaction Theory?
Customer satisfaction is a general principle of customer service. It measures a customer’s perception of the quality and utility of a product or service. Customer satisfaction can be measured by offering a service, or product or by having a relationship with a company, brand, or individual.
Customer satisfaction theory was introduced by Fred Reichheld in his book The Ultimate Question: Driving Good Profits and True Growth which was published in 2003. It was based on a study of over 25,000 customers from 1998 – 2003.
Customer satisfaction is the cornerstone of any business, not just those in the service industry. Understanding your customers and creating a system to create a satisfying experience for them will enable you to boost your profits and repeat customers.
To achieve customer satisfaction, you must understand your customers’ needs and wants and their pain points. Only then can you make sure they are fulfilled with each interaction.
Customer Satisfaction Theories
Understanding the customer satisfaction theory is crucial that may help you save your business if you are in the middle of a crisis resulting from a decline in customer satisfaction.
It lays down important steps you can use to solve the problem that will bring back your customer base and prevent you from losing your business to competitors who have higher customer satisfaction than you do.
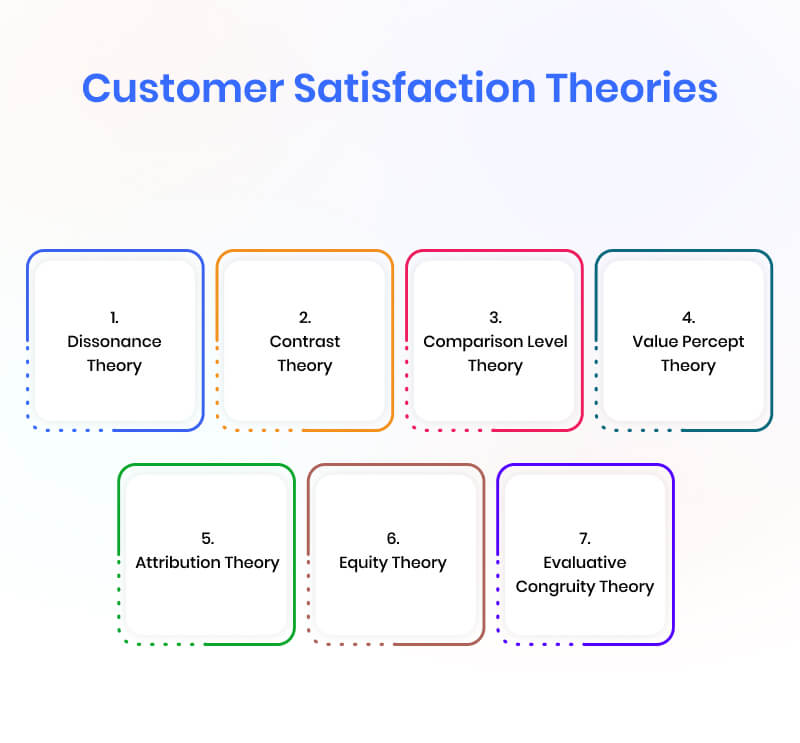
- Dissonance Theory
- Contrast Theory
- Comparison Level Theory
- Value Percept Theory
- Attribution Theory
- Equity Theory
- Evaluative Congruity Theory
Let’s take a look at various types of customer satisfaction theories.
1. Dissonance Theory
Dissonance Theory (also known as dissonance reduction theory) is a term used in psychology that refers to the mental stress experienced by someone who simultaneously holds two or more contradictory beliefs, ideas, or values. In other words, they find themselves in conflict.
It also suggests that a person who expected a high-value product and received a low-value product would recognize the disparity and experience cognitive dissonance . That is, the disconfirmed expectations create a state of dissonance or psychological discomfort.
Dissonance Theory can explain our present experience of cognitive dissonance when a customer experiences the physical manifestation of a company’s brand promise but does not receive the level of customer service he or she expected.
For example, you purchase an expensive pair of headphones from a well-known brand. You take them home and find that the headphones are defective.
When you contact the customer service department about this problem, your call is routed to a voice mailbox where you’re told to leave a message and will be contacted within 24 hours. You never receive a call back so you call again several times over the next several days.
2. Contrast Theory
It is another well-known theory of customer satisfaction. Contrast Theory suggests the opposite of the Dissonance Theory. According to this theory, when actual product performance falls short of the consumer’s expectations about the product, the contrast between the expectation and outcome will cause the consumer to exaggerate the disparity.
It implies that the negative impact of actual product performance on customer satisfaction is greater than the positive impact of higher performance over lower performance.
Contrast Theory states that, when the expectation of a product is high and the actual product performance is perceived to be low, the consumer will exaggerate the difference between the expectation and the outcome.
Contrast theory proposes that we do not judge qualities on the basis of absolute standards, but rather on the basis of how they compare with other qualities.
3. Comparison Level Theory
According to the HLT, satisfaction is not the evaluation of a product or service after it has been consumed. Instead, it is the comparison level, or the degree to which a product or service is better than any of the other options that are available in the market.
The theory suggests that consumers set a comparison level in their minds with respect to several aspects while they begin evaluating a product or service. These aspects include:
- The price at which the product was purchased
- The expectations pertaining to quality
- The expectations pertaining to performance
- The expectations pertaining to features and functionalities of the product
- The comparison level set by an individual’s peers, family members, and friends
- The comparison level was set by all other customers who bought the same brand
The extent to which a product meets or exceeds the comparison level (CL) is the basis of customer satisfaction.
The comparison-level theory is a branch of marketing theory that states that consumers evaluate their level of satisfaction based on an implicit comparison to an internal standard, rather than the outcome they actually experienced.
Critics of this theory suggest that it is nuanced and that it is incomplete. One of the main criticisms made of CLT is that it does not take into account other important determinants of customer satisfaction, such as relevance and quality (Yi, 1990).
4. Value Percept Theory
Value percept is a popular theory on customer satisfaction. This can be seen clearly in many of the recurrent types of cases, such as cases involving brand switching, cases involving the failure of trial products, and cases involving the purchase of services.
A common characteristic in such cases is that consumers base their evaluations on products, services, and brands that are absent from their initial perceptions. Value-Percept Disparity theory has also been applied to explain why consumers value some brands, products, and services over others, even if these other brands, products, and services are more highly expected (e.g., Westbrook 1992).
The Value-Percept theory explains customer satisfaction by two factors that are central to customer perception of value – Actual Value (AV) and Ideal Value (IV). AV is the actual quality or performance of a product that is perceived by a customer.
IV is the “ideal” quality or performance of a product that a customer expects before purchasing the product. The difference between AV and IV can be named Perceptual Discrepancy (PD).
5. Attribution Theory
The Attribution theory has been mostly used in dissatisfaction/ complaining behavior models than in satisfaction models.
According to this theory of the customer satisfaction model, consumers are regarded as rational processors of the information who seek out reasons to explain why a purchase outcome, for example, dissatisfaction, has occurred. These reasons may include the product itself, the service, the price, and even the person who sold the product.
Frequently these reasons are highly cor, related to each other, a state of affairs we refer to as inter-correlated attributions. In that case, we can use a simpler model that attributes the “blame” to one of these reasons. The most frequently occurring reason is then called the primary cause.
The attribution theory was developed in the domain of social psychology by Fritz Heider, Dorwin Cartwright, and Leonard Bostwick in a publication entitled “The Psychology of Judgment”. In this publication, the authors pointed out that people are rational in their judgment processes and that there are conditions under which their judgment is rational.
These researchers argued that there are three criteria for attribution to be made: consistency, consensus, and coherence or correspondence.
The consistency criterion includes the notion that when an outcome occurs, people need to find reasons to account for it.
6. Equity Theory
Equity theory in customer satisfaction is the idea that individuals require consistency between what was expected and what was experienced. Consistency between both sides of this equation is key to providing customers with a positive customer experience .
Learning how to manage expectations and consistently deliver an experience that meets and exceeds them builds goodwill and trust, which leads to strong customer satisfaction.
From my understanding, equity theory in customer satisfaction applies to any kind of purchase. The buyer has a sense of how the product or service is going to turn out, with what to expect from the business or brand.
When that buying decision takes place, the seller needs to make sure that the experience is consistent with the seller’s promise of what is to be received. If not, then the buyer has been provided with an uneven or inequitable exchange of money for goods or services. This causes dissatisfaction.
When I think of equity theory applied to customer satisfaction, I think of it from a transactional point of view. For business, maintaining and improving customer equity is equally important as it has a direct impact on profit and revenue.
7. Evaluative Congruity Theory
Evaluative congruity theory (sometimes abbreviated as EC theory) is a dual-process model of attitude formation and change. The goal of EC theory is to explain the formation and change of attitudes, although it has a broader application as well.
The EC theory posits that attitudes are formed from two different types of evaluations: “incorporating” evaluations and “social comparison” evaluations. It assumes that incorporating evaluations are automatically processed whereas social comparison evaluations require additional effort to process.
Evaluative Congruity describes the extent to which a consumer’s emotions with respect to the evaluative beliefs and attitudes he or she holds about the consumption experience.
It can be applied to all types of services such as hospitality, retail, leisure, and healthcare. Evaluative congruity has also been extended to other areas such as organizational behavior, marketing, and management.
How is CSAT Measured?
There is a customer satisfaction rating scale that helps you measure whether customers are happy with your brand. You can calculate the percentage of satisfied customers by dividing the number of satisfied customers (4 or 5) by the total number of survey responses. This will give you a percentage. Then multiply it by 100 to convert the figure into a whole number.

(Number of satisfied customers (4 and 5) / Number of survey responses) x 100 = % of satisfied customers
How Does CSAT Differ From Net Promoter Score (NPS)?
Now let’s find out how the customer satisfaction theory differs from NPS. Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a simple, easy-to-interpret metric that can be calculated from a single question: How likely is it that you would recommend our company/product/service to a friend or colleague?
CSAT (Customer Satisfaction) measures customer satisfaction with a product or service, whereas NPS (Net Promoter Score) measures customer loyalty to the organization. CSAT is just one way of measuring how satisfied your customers are with your product. This can be done at any one time and depends on how the satisfaction process was answered.
NPS on the other hand is the measure of how likely your customers are to recommend your business to friends and family. This is a measure of future behavior, hence its predictive value is much higher than that of CSAT.
From Theory to Practice: Start Measuring Satisfaction?
Your customers are getting smarter, and they are expecting more. They want a personalized experience and they want it now.
In an ever-changing retail environment, you need to be able to adapt and innovate quickly in order to stay ahead of your competitors. However, in order to do this successfully, you need to know who your customers are, what they want, and how you can improve your products and services to meet their needs.
With the REVE AI Chatbot, you can measure these components and more, and gather the insights you need to make decisions about your customer experience strategy.
With our AI Chatbot, you can measure feature perception, satisfaction, and recommendation for all of your products/services.
What does this mean? It means that our AI Chatbot allows you to understand what the customer actually thinks about the product. This is different than simply asking the customer.
No credit card is required. Sign up now and enjoy 14 days free trial.
Start a 14-day free trial, no credit card required!
Juwel is a Sr. Content Writer at REVE Chat. He specializes in writing about customer service and customer engagement. He is passionate about helping businesses create a better customer experience.
He strongly believes that businesses will be able to understand their customers better and ultimately create more meaningful relationships with them.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
REVE Chat Blog
Stay updated with the latest trends and ideas we share, what is customer feedback management tips, tools, and process.
Managing feedback is the key to understanding customer needs better and improving online experiences for them. Brands with a proper...
What is a Customer Feedback Loop and How to Create One?
Have you ever had a product or service experience that left you thinking, "Wow, I wish they knew how I...
What are Consumer Insights? Importance, Tools & Examples
Creating happy and loyal customers is never a matter of luck. It requires strategic planning and meticulous execution. Your business...
Related Posts
Signup for REVE Chat on any annual plans at these jaw-dropping prices today and start engagaging your customers across all channels. Limited Time Only.
The AI enabled live chat platform to help your business win and nurture customers across messaging channels.
Join 446,005 businesses who are already engaging up
Get Started

- Respond to customer queries in real time
- Qualify leads automatically
- Reduce the number of support tickets
- Deliver better conversational experience
- Boost customer satisfaction
- More Networks
Human handover: Seamlessly transfer chats to Live Agents
Co-browsing: Eliminate confusions
No-code: Build your chatbot effortlessly
No credit card required

Say No to customer waiting times, achieve 10X faster resolutions, and ensure maximum satisfaction for your valuable customers with REVE Chat.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

The Right Way to Solve Complex Business Problems
Corey Phelps, a strategy professor at McGill University, says great problem solvers are hard to find. Even seasoned professionals at the highest levels of organizations regularly...
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
Corey Phelps, a strategy professor at McGill University, says great problem solvers are hard to find. Even seasoned professionals at the highest levels of organizations regularly fail to identify the real problem and instead jump to exploring solutions. Phelps identifies the common traps and outlines a research-proven method to solve problems effectively. He’s the coauthor of the book, Cracked it! How to solve big problems and sell solutions like top strategy consultants.
Download this podcast
Welcome to the IdeaCast from Harvard Business Review. I’m Curt Nickisch.
Problem-solving is in demand. It’s considered the top skill for success at management consulting firms. And it’s increasingly desired for everyone, not just new MBA’s.
A report from the World Economic Forum predicts that more than one-third of all jobs across all industries will require complex problem-solving as one of their core skills by 2020.
The problem is, we’re often really bad at problem-solving. Our guest today says even the most educated and experienced of senior leaders go about it the wrong way.
COREY PHELPS: I think this is one of the misnomers about problem-solving. There’s this belief that because we do it so frequently – and especially for senior leaders, they have a lot of experience, they solve problems for a living – and as such we would expect them to be quite good at it. And I think what we find is that they’re not. They don’t solve problems well because they fall prey to basically the foibles of being a human being – they fall prey to the cognitive biases and the pitfalls of problem-solving.
CURT NICKISCH: That’s Corey Phelps. He says fixing these foibles is possible and almost straightforward. You can improve your problem-solving skills by following a disciplined method.
Corey Phelps is a strategy professor at McGill University. He’s also the co-author of the book “Cracked It: How to Solve Big Problems and Sell Solutions like Top Strategy C onsultants.” Corey thanks for coming on the show.
COREY PHELPS: Thank you for the opportunity to talk.
CURT NICKISCH: Another probably many, many biases that prevent people from solving big problems well.
COREY PHELPS: Absolutely.
CURT NICKISCH: What are some of the most common, or your favorite stumbling blocks?
COREY PHELPS: Well, one of my favorites is essentially the problem of jumping to solutions or the challenge of jumping to solutions.
CURT NICKISCH: Oh, come on Corey. That’s so much fun.
COREY PHELPS: It is, and it’s very much a result of how our brains have evolved to process information, but it’s my favorite because we all do it. And especially I would say it happens in organizations because in organizations when you layer on these time pressures and you layer on these concerns about efficiency and productivity, it creates enormous, I would say incentive to say “I don’t have time to carefully define and analyze the problem. I got to get a solution. I got to implement it as quick as possible.” And the fundamental bias I think is, is illustrated beautifully by Danny Kahneman in his book “Thinking, Fast and Slow,” is that our minds are essentially hardwired to think fast.
We are able to pay attention to a tiny little bit of information. We can then weave a very coherent story that makes sense to us. And then we can use that story to jump very quickly to a solution that we just know will work. And if we just were able to move from that approach of what Kahneman and cognitive psychologists called “System 1 thinking” to “System 2 thinking” – that is to slow down, be more deliberative, be more structured – we would be able to better understand the problem that we’re trying to solve and be more effective and exhaustive with the tools that we want to use to understand the problem before we actually go into solution-generation mode.
CURT NICKISCH: Complex problems demand different areas of expertise and often as individuals we’re coming to those problems with one of them. And I wonder if that’s often the problem of problem-solving, which is that a manager is approaching it from their own expertise and because of that, they see the problem through a certain way. Is that one of the cognitive biases that stop people from being effective problem solvers?
COREY PHELPS: Yeah. That’s often referred to as the expertise trap. It basically colors and influences what we pay attention to with respect to a particular problem. And it limits us with respect to the tools that we can bring to bear to solve that problem. In the world of psychology, there’s famous psychologist, Abraham Maslow, who is famous for the hierarchy of needs. He’s also famous for something that was a also known as MaSlow’s axiom, Maslow’s law. It’s also called the law of the instrument, and to paraphrase Maslow, he basically said, “Look, I suppose if the only tool that you have in your toolkit is a hammer, everything looks like a nail.”
His point is that if you’re, for example, a finance expert and your toolkit is the toolkit of let’s say, discounted cash flow analysis for valuation, then you’re going to see problems through that very narrow lens. Now, one of the ways out of this, I think to your point is collaboration becomes fundamentally important. And collaboration starts with the recognition that I don’t have all of the tools, all of the knowledge in me to effectively solve this. So I need to recruit people that can actually help me.
CURT NICKISCH: That’s really interesting. I wonder how much the fact that you have solved a problem before it makes you have a bias for that same solution for future problems?
COREY PHELPS: Yeah, that’s a great question. What you’re alluding to is analogical reasoning, and we know that human beings, one of the things that allows us to operate in novel settings is that we can draw on our past experience. And we do so when it comes to problem solving, often times without being conscious or mentally aware of it. We reach into our memory and we ask ourselves a very simple question: “Have I seen a problem like this before?”
And if it looks familiar to me, the tendency then is to say, “Okay, well what worked in solving that problem that I faced before?” And then to say, “Well, if it worked in that setting, then it should work in this setting.” So that’s reasoning by analogy.
Reasoning by analogy has a great upside. It allows human beings to not become overwhelmed by the tremendous novelty that they face in their daily lives. The downside is that if we don’t truly understand it at sort of a deep level, whether or not the two problems are similar or different, then we can make what cognitive psychologists called surface-level analogies.
And we can then say, “Oh, this looks a lot like the problem I faced before, that solution that worked there is going to easily work here.” And we try that solution and it fails and it fails largely because if we dug a little bit deeper, the two problems actually aren’t much alike at all in terms of their underlying causes.
CURT NICKISCH: The starkest example of this, I think, in your book is Ron Johnson who left Apple to become CEO of JC Penney. Can you talk about that a little bit and what that episode for the company says about this?
COREY PHELPS: So yes, its – Ron Johnson had been hired away from Target in the United States to, by Steve Jobs to help create Apple stores. Apple stores are as many people know the most successful physical retailer on the planet measured by, for example, sales per square foot or per square meter. He’s got the golden touch. He’s created this tremendously successful retail format for Apple.
So the day that it was announced that Ron Johnson was going to step into the CEO role at JC Penney, the stock price of JC Penney went up by almost 18 percent. So clearly he was viewed as the savior. Johnson moves very, very quickly. Within a few months, he announces that he has a strategic plan and it basically comes in three parts.
Part number one is he’s going to eliminate discount pricing. JC Penney had been a very aggressive sales promoter. The second piece of it is he’s going to completely change how they organize merchandise. It’s no longer going to be organized by function – so menswear, housewares, those sorts of things. It’s going to be organized by boutique, so there’s going to be a Levi’s boutique, a Martha Stewart Boutique, a Joe Fresh Boutique and so on.
And it would drop the JC P enney name, they would call it JCP. And he rolls this out over the course of about 12 months across the entire chain of over 1100 stores. What this tells us, he’s so confident in his solution, his strategic transformation, that he doesn’t think it’s worth it to test this out on one or two pilot stores.
CURT NICKISCH: Yeah, he was quoted as saying: “At Apple, we didn’t test anything.”
COREY PHELPS: We didn’t test. Yes. What worked at Apple, he assumed would work at JC Penney. And the critical thing that I think he missed is that JC Penney customers are very different from Apple store customers. In fact, JC Penney customers love the discount. They love the thrill of hunting for a deal.
CURT NICKISCH: Which seems so fundamental to business, right? Understanding your customer. It’s just kind of shocking, I guess, to hear the story.
COREY PHELPS: It is shocking and especially when you consider that Ron Johnson had spent his entire career in retail, so this is someone that had faced, had seen, problems in retailers for decades – for over three decades by the time that he got to JC Penney. So you would expect someone with that degree of experience in that industry wouldn’t make that leap of, well, what worked at Apple stores is going to work at JC Penney stores, but in fact that’s exactly what happened.
CURT NICKISCH: In your book, you essentially suggest four steps that you recommend people use. Tell us about the four steps then.
COREY PHELPS: So in the book we describe what we call the “Four S method,” so four stages, each of which starts with the letter “s”. So the first stage is “state the problem.” Stating the problem is fundamentally about defining what the problem is that you are attempting to solve.
CURT NICKISCH: And you probably would say don’t hurry over that first step or the other three are going to be kind of pointless.
COREY PHELPS: Yeah, that’s exactly the point of of laying out the four s’s. There’s a tremendous amount of desire even amongst senior executives to want to get in and fix the problem. In other words, what’s the trouble? What are the symptoms? What would define success? What are the constraints that we would be operating under? Who owns the problem? And then who are the key stakeholders?
Oftentimes that step is skipped over and we go right into, “I’ve got a hypothesis about what I think the solution is and I’m so obsessed with getting this thing fixed quickly, I’m not going to bother to analyze it particularly well or test the validity of my assumptions. I’m going to go right into implementation mode.”
The second step, what we call “structure the problem” is once you have defined the problem, you need to then start to identify what are the potential causes of that problem. So there are different tools that we talked about in the book that you can structure a problem for analysis. Once you’ve structured the problem for analysis and you’ve conducted the analysis that helps you identify what are the underlying causes that are contributing to it, which will then inform the third stage which is generating solutions for the problem and then testing and evaluating those solutions.
CURT NICKISCH: Is the danger that that third step – generating solutions – is the step that people spend the most time on or have the most fun with?
COREY PHELPS: Yeah. The danger is, is that what that’s naturally what people gravitate towards. So we want to skip over the first two, state and structure.
CURT NICKISCH: As soon as you said it, I was like, “let’s talk about that more.”
COREY PHELPS: Yeah. And we want to jump right into solutioning because people love to talk about their ideas that are going to fix the problem. And that’s actually a useful way to frame a discussion about solutions – we could, or we might do this – because it opens up possibilities for experimentation.
And the problem is that when we often talk about what we could do, we have very little understanding of what the problem is that we’re trying to solve and what are the underlying causes of that problem. Because as you said, solution generation is fun. Look, the classic example is brainstorming. Let’s get a bunch of people in a room and let’s talk about the ideas on how to fix this thing. And again, be deliberate, be disciplined. Do those first stages, the first two stages – state and structure – before you get into the solution generation phase.
CURT NICKISCH: Yeah. The other thing that often happens there is just the lack of awareness of just the cost of the different solutions – how much time, or what they would actually take to do.
COREY PHELPS: Yeah, and again, I’ll go back to that example I used of brainstorming where it’s fun to get a group of people together and talk about our ideas and how to fix the problem. There’s a couple challenges of that. One is what often happens when we do that is we tend to censor the solutions that we come up with. In other words, we ask ourselves, “if I say this idea, people are gonna, think I’m crazy, or people going to say: that’s stupid, that’ll never work, we can’t do that in our organization. It’s going to be too expensive, it’s going to take too much time. We don’t have the resources to do it.”
So brainstorming downside is we we self-sensor, so that’s where you need to have deep insight into your organization in terms of A. what’s going to be feasible, B. what’s going to be desirable on the part of the people that actually have the problem, who you’re trying to solve the problem for and C. from a business standpoint, is it going to be financially attractive for us?
So applying again a set of disciplined criteria that help you choose amongst those ideas for potential solutions. Then the last stage of the process which is selling – because it’s rare in any organization that someone or the group of people that come up with the solution actually have the power and the resources to implement it, so that means they’re going to have to persuade other people to buy into it and want to help.
CURT NICKISCH: Design thinking is another really different method essentially for solving problems or coming up with solutions that just aren’t arrived at through usual problem-solving or usual decision-making processes. I’m just wondering how design thinking comes to play when you’re also outlining these, you know, disciplined methods for stating and solving problems.
COREY PHELPS: For us it’s about choosing the right approach. You know what the potential causes of a problem are. You just don’t know which ones are operating in the particular problem you’re trying to solve. And what that means is that you’ve got a theory – and this is largely the world of strategy consultants – strategy consultants have theories. They have, if you hear them speak, deep understanding of different types of organizational problems, and what they bring is an analytic tool kit that says, “first we’re going to identify all the possible problems, all the possible causes I should say, of this problem. We’re going to figure out which ones are operating and we’re going to use that to come up with a solution.” Then you’ve got problems that you have no idea what the causes are. You’re in a world of unknown unknowns or unk-unks as the operations management people call them.
CURT NICKISCH: That’s terrible.
COREY PHELPS: In other words, you don’t have a theory. So the question is, how do you begin? Well, this is where design thinking can be quite valuable. Design thinking says: first off, let’s find out who are the human beings, the people that are actually experiencing this problem, and let’s go out and let’s talk to them. Let’s observe them. Let’s immerse ourselves in their experience and let’s start to develop an understanding of the causes of the problem from their perspective.
So rather than go into it and say, “I have a theory,” let’s go the design thinking route and let’s actually based upon interactions with users or customers, let’s actually develop a theory. And then we’ll use our new understanding or new insight into the causes of the problem to move into the solution generation phase.
CURT NICKISCH: Problem-solving – we know that that’s something that employers look for when they’re recruiting people. It is one of those phrases that, you know, I’m sure somebody out there has, has the title at a company Chief Problem Solver instead of CEO, right? So, it’s almost one of those phrases that so over used it can lose its meaning.
And if you are being hired or you’re trying to make a case for being on a team that’s tackling a problem, how do you make a compelling case that you are a good problem solver? How can you actually show it?
COREY PHELPS: It’s a great question and then I have two answers to this question. So one is, look at the end of the day, the proof is in the pudding. In other words, can you point to successful solutions that you’ve come up with – solutions that have actually been effective in solving a problem? So that’s one.
The second thing is can you actually articulate how you approach problem-solving? In other words, do you follow a method or are you reinventing the wheel every time you solve a problem? Is it an ad hoc approach? And I think this issue really comes to a head when it comes to the world of strategy consulting firms when they recruit. For example, Mckinsey, you’ve got the Mckinsey problem-solving test, which is again, a test that’s actually trying to elicit the extent to which people are good applicants are good at solving problems
And then you’ve got the case interview. And in the case interview, what they’re looking at is do you have a mastery over certain tools. But what they’re really looking at is, are you actually following a logical process to solve this problem? Because again, what they’re interested in is finding- to your point – people that are going to be good at solving complex organizational problems. So they’re trying to get some evidence that they can demonstrate that they’re good at it and some evidence that they follow a deliberate process.
CURT NICKISCH: So even if you’re not interviewing at a consulting firm, that’s a good approach, to show your thinking, show your process, show the questions you ask?
COREY PHELPS: Yeah, and to your point earlier, at least if we look at what recruiters of MBA students are saying these days, they’re saying, for example, according to the FT’s recent survey, they’re saying that we want people with really good problem solving skills, and by the same token, we find that that’s a skill that’s difficult for us to recruit for. And that reinforces our interest in this area because the fundamental idea for the book is to give people a method. We’re trying to equip not just MBA students but everybody that’s going to face complex problems with a toolkit to solve them better.
CURT NICKISCH: Corey, this has been really great. Thank you.
COREY PHELPS: Thanks for the opportunity. I appreciate it.
CURT NICKISCH: That’s Corey Phelps. He teaches strategy at McGill University, and he co-wrote the book “Cracked It: How to Solve Big Problems and Sell Solutions Like Top Strategy Consultants.”
This episode was produced by Mary Dooe. We got technical help from Rob Eckhardt. Adam Buchholz is our audio product manager.
Thanks for listening to the HBR IdeaCast. I’m Curt Nickisch.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about decision making and problem solving, partner center.
Problem Solving Steps in Customer Service
- Customer Service Jobs
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
10 Commandments of Front-Desk Clerks
How to correct my coworker if he gives a customer the wrong information, how to empower employees in the hospitality industry.
- What Does Exceptional Client Service Mean in an Interview Question?
- What Are the Duties of Outbound Customer Service Representatives?
Employers increasingly rely on customer service representatives to resolve customer problems. Passing on such issues to the manager is no longer the norm. Companies want service reps who are confident and capable of working through steps to resolve and satisfy a customer's needs. Problem solving training is usually emphasized when you start a new job. Your customer service skills training will likely describe the steps that have to be taken to solve the customer's problem.
Listen Attentively
Listening is the first step in finding resolution to a customer's problems. Surprisingly, this step is either overlooked or poorly used by service employees. You have to listen first to understand the nature of the problem and the affect it has had on the customer. This is key to understanding the customer's perspective and offering solutions that match. In many instances, customers simply want someone to listen and show understanding, suggests Indeed . Effectively listening without cutting off the customers allows them to vent, which often leaves them more relaxed and ready to move forward with a resolution.
Show Empathy
Once you understand the problem, you want to confirm what you have heard and express empathy. Paraphrasing the customer's problem ensures that you are on the same page. Sometimes, service reps don't fully understand the issue and resolve it in the wrong way. You show empathy with a statement such as "I'm sorry that you had to make another trip here to deal with this." Or, if the customer simply missed an instruction or couldn't figure out how to use a product, you might say, "No problem. We have a lot of customers return to check on that. The instructions should be clearer."
Present Alternatives
In situations where customer oversight was the only issue, a specific remedy may not be necessary. When your company, product or service makes a mistake, resolution is important for customer retention and positive word-of-mouth. You need to offer alternative remedies to suit the situation. Customer service problem-solving examples include handing out extra food for forgetting a customer's item or a offering a discount on a future purchase.
A retailer and service employee should realize that the customer not only didn't get what he paid for, but also has been stressed and inconvenienced by the return trip or phone call. You have to go above and beyond and offer not only a resolution to the specific problem, but often an extra product, service or gift voucher. Avid Ratings points out that problems don't have to be solved on the spot. Customers will generally be happy if you promise to investigate the issue further in an attempt to identify possible options for their consideration. Offer to get back to them within a specified timeframe.
Resolve the Matter
Once a solution is agreed upon, you execute it. This includes fixing the product or service and providing the additional remedy. Following up is a huge final step. Customers often won't even complain once, they just disappear. If you do hear of a problem and attempt to fix it, you need to follow-up. This ensures the customer ends up happy and satisfied with the outcome. It also protects against an even more infuriated customer out in the marketplace spreading negative messages.
- Indeed: Eleven Ways to Deliver Great Customer Service
- Avid Ratings: Solving Customer Problems
Related Articles
How to respond to a negative business letter, objectives and goals of telephone customer service, what does a customer service representative do, how to converse as a bartender, how to handle a customer service breakdown, what competencies make a great customer service representative, salesman professional courtesy guidelines, interview question: how would you calm down a confrontational customer, responsibilities as a grocery cashier, most popular.
- 1 How to Respond to a Negative Business Letter
- 2 Objectives and Goals of Telephone Customer Service
- 3 What Does a Customer Service Representative Do?
- 4 How to Converse as a Bartender

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4 steps of a problem-solving approach. Listen to a customer. No doubt, this step is the most crucial one. Ask all the questions about the unpleasant situation to give a complete answer that matches the problem. Don't interrupt the customer and let them express their feelings if they need to.
Customer Service Problem-Solving # 5 - Set Realistic Expectations. Setting realistic expectations is an important step for customer service problem solving. When you communicate clear timelines, you're being honest and transparent with what the customer can expect. This helps manage their expectations and prevents disappointment down the road.
12 Key Customer Service Problem Solving Do's and Don'ts Do's. Do Regularly Train and Update Your Team's Skills. Why It's Important: Customer service training plays a vital role in keeping your team equipped to handle a wide array of customer issues effectively. Example: Implement regular training sessions that cover new customer service tools, communication techniques, and updates about ...
Writing an empathetic, thorough response can make all the difference in a complex situation. In many cases, your response will follow the same steps as a great customer service apology: Empathize. Say sorry. Offer explanation. Fix the problem. Wrap it up and let them know what's next.
Remember these keywords throughout your journey: fully understand the problem, solve the customer's problem, find a workable solution, and ensure the customer is happy with the resolution. 2. Identifying a Problem. Ensuring that customers are happy with the solutions provided is crucial in customer service.
By addressing customer issues through problem-solving sessions, companies demonstrate their commitment to resolving problems quickly and effectively. By actively listening to customers' concerns and providing appropriate solutions, businesses can restore trust, boost customer satisfaction, and ultimately improve their reputation in the market.
2. Generate alternatives. 3. Evaluate and choose. 4. Implement and follow up. 5. Here's what else to consider. Problem-solving skills are essential for customer service operations, as they help ...
Customer service problem-solving is the process of resolving customer service issues. This can be done through a variety of means such as by phone, email, or in person. It is crucial for ...
Applying problem-solving skills to enhance customer service involves a systematic approach. Begin by actively listening to customer concerns to fully understand the issue. Analyze the problem ...
In customer service, this is a no-no. To go through the situation unscathed, here are two tips that you can use. Tip 1: Allow customers to talk. You should let your customers talk until they are able to release their frustrations and calm down. Tip 2: Show that you care.
Providing excellent customer service requires problem-solving skills. To do this, you should listen actively and empathetically to your customers' problems, ask open-ended and clarifying questions ...
The best way to ensure reps address a customer's issue and do it with a high quality of service is to provide training on a structured problem-solving process. To start, here are five steps that every rep should know how to work through. Identify and define the problem: While this may seem simple and straightforward, customers don't always ...
How to Handle Customer Service Issues: 9 Steps. Problem-solving often seems straightforward, but that's not always the case. Sometimes, it's complicated. Having workers well-versed in problem-solving skills and techniques for customer care representatives helps. Approaching issues in a systematic way simplifies the problem-solving process.
2. Acknowledge the pain the customer is experiencing. The customer has a problem. Your job is to help them with their problem. The first step in doing that is to acknowledge the customer's pain. You need to show the customer you understand and care about the issue they're experiencing.
This standard is part of the customer service competence area related to Handling Problems, Queries and Complaints. It includes monitoring and solving customer service problems. It covers the behaviours, processes and approaches that are most effective when handling customer service problems. Remember that customers include everyone to whom you ...
challenges of solving problems at work. Learn to apply the ten creative problem-solving techniques. • Apply nine ways to accurately define a problem and identify the root causes. • Master the art of confident decision making and crisis resolution. • Apply a four-step process to handle upset and irate customers
1. Identify the problem. 2. Analyze the problem. Be the first to add your personal experience. 3. Choose the best solution. Be the first to add your personal experience. 4.
When you contact the customer service department about this problem, your call is routed to a voice mailbox where you're told to leave a message and will be contacted within 24 hours. You never receive a call back so you call again several times over the next several days. 2. Contrast Theory. It is another well-known theory of customer ...
All episodes. Details. Transcript. December 04, 2018. Corey Phelps, a strategy professor at McGill University, says great problem solvers are hard to find. Even seasoned professionals at the ...
Listen Attentively. Listening is the first step in finding resolution to a customer's problems. Surprisingly, this step is either overlooked or poorly used by service employees. You have to listen first to understand the nature of the problem and the affect it has had on the customer. This is key to understanding the customer's perspective and ...
Definition 3: Problem solving is a four-stage. process involving Perceiving (awareness of) the situation as problematic; Searching for and processing information relevant to selecting an effective problem- solving activity; Engaging in a problem-solving activity; and Evaluating the outcome of the activity.
Let the customer know which team or person will handle their issue, and how they will contact them. Provide an estimated time frame for resolution and set clear expectations. Make sure to update ...
Ease of doing business also has an impact on how people, even subconsciously, perceive that you will resolve any problems. All of this should be included in the definition of customer service and ...