
How to Write a Survey Paper: Brief Overview

Every student wishes there was a shortcut to learning about a subject. Writing a survey paper can be an effective tool for synthesizing and consolidating information on a particular topic to gain mastery over it.
There are several techniques and best practices for writing a successful survey paper. Our team is ready to guide you through the writing process and teach you how to write a paper that will benefit your academic and professional career.
What is a Survey Paper
A survey paper is a type of academic writing that aims to give readers a comprehensive understanding of the current state of research on a particular topic. By synthesizing and analyzing already existing research, a survey paper provides good shortcuts highlighting meaningful achievements and recent advances in the field and shows the gaps where further research might be needed.
The survey paper format includes an introduction that defines the scope of the research domain, followed by a thorough literature review section that summarizes and critiques existing research while showcasing areas for further research. A good survey paper must also provide an overview of commonly used methodologies, approaches, key terms, and recent trends in the field and a clear summary that synthesizes the main findings presented.
Our essay writing service team not only provides the best survey paper example but can also write a custom academic paper based on your specific requirements and needs.
How to Write a Survey Paper: Important Steps
If you have your head in your hands, wondering how to write a survey paper, you must be new here. Luckily, our team of experts got you! Below you will find the steps that will guide you to the best approach to writing a successful survey paper. No more worries about how to research a topic . Let's dive in!

Obviously, the first step is to choose a topic that is both interesting to you and relevant to a large audience. If you are struggling with topic selection, go for only the ones that have the most literature to compose a comprehensive research paper.
Once you have selected your topic, define the scope of your survey paper and the specific research questions that will guide your literature review. This will help you establish boundaries and ensure that your paper is focused and well-structured.
Next, start collecting existing research on your topic through various academic databases and literature reviews. Make sure you are up to date with recent discoveries and advances. Before selecting any work for the survey, make sure the database is credible. Determine what sources are considered trustworthy and reputable within the specific domain.
Continue survey paper writing by selecting the most relevant and significant research pieces to include in your literature overview. Make sure to methodically analyze each source and critically evaluate its relevance, rigor, validity, and contribution to the field.
At this point, you have already undertaken half of the job. Maybe even more since collecting and analyzing the literature is often the most challenging part of writing a survey paper. Now it's time to organize and structure your paper. Follow the well-established outline, give a thorough review, and compose compelling body paragraphs. Don't forget to include detailed methodology and highlight key findings and revolutionary ideas.
Finish off your writing with a powerful conclusion that not only summarizes the key arguments but also indicates future research directions.
Feeling Overwhelmed by All the College Essays?
Our expert writers will ensure that you submit top-quality papers without missing any deadlines!
Survey Paper Outline
The following is a general outline of a survey paper.
- Introduction - with background information on the topic and research questions
- Literature Overview - including relevant research studies and their analysis
- Methodologies and Approaches - detailing the methods used to collect and analyze data in the literature overview
- Findings and Trends - summarizing the key findings and trends from the literature review
- Challenges and Gaps - highlighting the limitations of studies reviewed
- Future Research Direction - exploring future research opportunities and recommendations
- Conclusion - a summary of the research conducted and its significance, along with suggestions for further work in this area.
- References - a list of all the sources cited in the paper, including academic articles and reports.
You can always customize this outline to fit your paper's specific requirements, but none of the components can be eliminated. Our custom essay writer
Further, we can explore survey paper example formats to get a better understanding of what a well-written survey paper looks like. Our custom essay writer can assist in crafting a plagiarism-free essay tailored to meet your unique needs.
Survey Paper Format
Having a basic understanding of an outline for a survey paper is just the beginning. To excel in survey paper writing, it's important to become proficient in academic essay formatting techniques. Have the following as a rule of thumb: make sure each section relates to the others and that the flow of your paper is logical and readable.
Title - You need to come up with a clear and concise title that reflects the main objective of your research question.
Survey paper example title: 'The analysis of recommender systems in E-commerce.'
Abstract - Here, you should state the purpose of your research and summarize key findings in a brief paragraph. The abstract is a shortcut to the paper, so make sure it's informative.
Introduction - This section is a crucial element of an academic essay and should be intriguing and provide background information on the topic, feeding the readers' curiosity.
Literature with benefits and limitations - This section dives into the existing literature on the research question, including relevant studies and their analyses. When reviewing the literature, it is important to highlight both benefits and limitations of existing studies to identify gaps for future research.
Result analysis - In this section, you should present and analyze the results of your survey paper. Make sure to include statistical data, graphs, and charts to support your conclusions.
Conclusion - Just like in any other thesis writing, here you need to sum up the key findings of your survey paper. How it helped advance the research topic, what limitations need to be addressed, and important implications for future research.
Future Research Direction - You can either give this a separate section or include it in a conclusion, but you can never overlook the importance of a future research direction. Distinctly point out areas of limitations and suggest possible avenues for future research.
References - Finally, be sure to include a list of all the sources/references you've used in your research. Without a list of references, your work will lose all its credibility and can no longer be beneficial to other researchers.
Writing a Good Survey Paper: Helpful Tips
After mastering the basics of how to write a good survey paper, there are a few tips to keep in mind. They will help you advance your writing and ensure your survey paper stands out among others.

Select Only Relevant Literature
When conducting research, one can easily get carried away and start hoarding all available literature, which may not necessarily be relevant to your research question. Make sure to stay within the scope of your topic. Clearly articulate your research question, and then select only literature that directly addresses the research question. A few initial readings might not reveal the relevance, so you need a systematic review and filter of the literature that is directly related to the research question.
Use Various Sources and Be Up-to-Date
Our team suggests only using up-to-date material that was published within the last 5 years. Additional sources may be used if they contribute significantly to the research question, but it is important to prioritize current literature.
Use more than 10 research papers. Though narrowing your pool of references to only relevant literature is important, it's also crucial that you have a sufficient number of sources.
Rely on Reputable Sources
Writing a survey paper is a challenge. Don't forget that it is quality over quantity. Be sure to choose reputable sources that have been peer-reviewed and are recognized within your field of research. Having a large number of various research papers does not mean that your survey paper is of high quality.
Construct a Concise Research Question
Having a short and to-the-point research question not only helps the audience understand the direction of your paper but also helps you stay focused on a clear goal. With a clear research question, you will have an easier time selecting the relevant literature, avoiding unnecessary information, and maintaining the structure of your paper.
Use an Appropriate Format
The scholarly world appreciates when researchers follow a standard format when presenting their survey papers. Therefore, it is important to use a suitable and consistent format that adheres to the guidelines provided by your academic institution or field.
Our paper survey template offers a clear structure that can aid in organizing your thoughts and sources, as well as ensuring that you cover all the necessary components of a survey paper.
Don't forget to use appropriate heading, font, spacing, margins, and referencing style. If there is a strict word limit, be sure to adhere to it and use concise wording.
Use Logical Sequence
A survey paper is different from a regular research paper. Every element of the essay needs to relate to the research question and tie into the overall objective of the paper.
Writing research papers takes a lot of effort and attention to detail. You will have to revise, edit and proofread your work several times. If you are struggling with any aspect of the writing process, just say, ' Write my research paper for me ,' and our team of tireless writers will be happy to assist you.
Starting Point: Survey Paper Example Topics
Learning how to write a survey paper is important, but it is only one aspect of the process.
Now you need a powerful research question. To help get you started, we have compiled a list of survey paper example topics that may inspire you.
- Survey of Evolution and Challenges of Electronic Search Engines
- A Comprehensive Survey Paper on Machine Learning Algorithms
- Survey of Leaf Image Analysis for Plant Species Recognition
- Advances in Natural Language Processing for Sentiment Analysis
- Emerging Trends in Cybersecurity Threat Detection
- A Comprehensive Survey of Techniques in Big Data Analytics in Healthcare
- A Survey of Advances in Digital Art and Virtual Reality
- A Systematic Review of the Impact of Social Media Marketing Strategies on Consumer Behavior
- A Survey of AI Systems in Artistic Expression
- Exploring New Research Methods and Ethical Considerations in Anthropology
- Exploring Data-driven Approaches for Performance Analysis and Decision Making in Sports
- A Survey of Benefits of Optimizing Performance through Diet and Supplementation
- A Critical Review of Existing Research on The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity Conservation Strategies
- Investigating the Future of Blockchain Technology for Secure Data Sharing
- A Critical Review of the Literature on Mental Health and Innovation in the Workplace
Final Thoughts
Next time you are asked to write a survey paper, remember it is not just following an iterative process of gathering and summarizing existing research; it requires a deep understanding of the subject matter as well as critical analysis skills. Creative thinking and innovative approaches also play a key role in producing high-quality survey papers.
Our expert writers can help you navigate the complex process of writing a survey paper, from topic selection to data analysis and interpretation.
Finding It Difficult to Write a Survey Paper?
Our essay writing service offers plagiarism-free papers tailored to your specific needs.
Are you looking for advice on how to create an engaging and informative survey paper? This frequently asked questions (FAQ) section offers valuable responses to common inquiries that researchers frequently come across when writing a survey paper. Let's delve into it!
What is Survey Paper in Ph.D.?
What is the difference between survey paper and literature review paper, related articles.
.webp)
ScienceSphere.blog
Mastering The Art Of Writing A Survey Paper: A Step-By-Step Guide

Table of Contents
Importance of survey papers in academic research
Survey papers play a crucial role in academic research as they provide a comprehensive overview of a specific topic or field. These papers serve as valuable resources for researchers, students, and professionals who want to gain a deeper understanding of a subject. By synthesizing existing literature, survey papers help to identify research gaps, highlight key findings, and offer insights into future research directions.
Survey papers are essential for the following reasons:
Summarizing existing knowledge: Survey papers consolidate and summarize the existing body of knowledge on a particular topic. They provide a comprehensive overview of the research conducted in the field, making it easier for readers to grasp the key concepts and findings.
Identifying research gaps: By analyzing the existing literature, survey papers help researchers identify areas where further investigation is needed. They highlight the gaps in knowledge and suggest potential research questions that can contribute to the advancement of the field.
Saving time and effort: Instead of going through numerous individual research papers, survey papers offer a consolidated source of information. Researchers can save time and effort by referring to a well-structured survey paper that provides a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Providing a foundation for new research: Survey papers serve as a foundation for new research. They provide researchers with a solid understanding of the existing literature, enabling them to build upon previous studies and contribute to the field’s knowledge.
Purpose of the blog post
The purpose of this blog post is to guide aspiring researchers and students on how to write an effective survey paper. It will provide a step-by-step approach to help them navigate through the process of selecting a topic, conducting a literature review, outlining the structure, writing the paper, editing and proofreading, formatting and presentation, and finalizing the survey paper.
By following the guidelines outlined in this blog post, readers will be equipped with the necessary tools and knowledge to produce a high-quality survey paper that adds value to the academic community. Whether they are writing a survey paper for a course assignment, a research project, or a publication, this blog post will serve as a comprehensive resource to help them excel in their writing endeavors.
In the next section, we will delve into the basics of survey papers, including their definition, different types, and the benefits of writing one.
Understanding the Basics
A survey paper is a comprehensive review of existing literature on a specific topic or research area. It aims to provide a summary and analysis of the current state of knowledge in the field. Understanding the basics of survey papers is crucial for researchers and academics who wish to contribute to the existing body of knowledge. Here, we will explore the definition of a survey paper, different types of survey papers, and the benefits of writing one.
Definition of a survey paper
A survey paper, also known as a review paper or a literature review, is a type of academic paper that synthesizes and analyzes existing research on a particular topic. It goes beyond summarizing individual studies and aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the field. The goal of a survey paper is to identify trends, patterns, and gaps in the existing literature .
Different types of survey papers
There are several types of survey papers, each with its own purpose and focus. Some common types include:
Traditional survey papers : These provide a broad overview of the topic, covering various aspects and subtopics. They aim to present a comprehensive summary of the existing literature.
Focused survey papers : These focus on a specific aspect or subtopic within a broader field. They delve deeper into a particular area of interest and provide a more detailed analysis.
Systematic review papers : These follow a specific methodology for selecting and analyzing studies. They aim to minimize bias and provide an objective assessment of the available evidence.
Meta-analysis papers : These involve statistical analysis of data from multiple studies to draw conclusions and identify patterns or relationships.
Benefits of writing a survey paper
Writing a survey paper offers several benefits for researchers and academics:
Understanding the research landscape : Conducting a comprehensive literature review allows researchers to gain a deep understanding of the current state of knowledge in their field. It helps identify gaps, controversies, and areas that require further investigation.
Contributing to the field : By synthesizing and analyzing existing research, survey papers provide valuable insights and perspectives. They can help shape the direction of future research and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
Building credibility : Publishing a well-written survey paper enhances the author’s reputation and credibility in the academic community. It demonstrates expertise in the field and the ability to critically evaluate and synthesize existing research.
Identifying research opportunities : Survey papers often highlight areas where further research is needed. They can inspire new research questions and guide researchers towards fruitful avenues of investigation.
In conclusion, understanding the basics of survey papers is essential for researchers and academics. It involves knowing the definition of a survey paper, different types of survey papers, and the benefits of writing one. By conducting a comprehensive literature review and synthesizing existing research, survey papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge in a particular field. They provide valuable insights, identify research gaps, and guide future research directions.
Choosing a Topic
Choosing the right topic is a crucial step in writing a survey paper. It sets the foundation for your research and determines the direction of your paper. Here are some key considerations when selecting a topic:
Identifying a Research Gap
To begin, you need to identify a research gap in the existing literature. Look for areas where there is limited or conflicting information, unanswered questions, or emerging trends. This will ensure that your survey paper adds value to the academic community by filling a knowledge gap .
Selecting a Specific Area of Interest
Once you have identified a research gap, narrow down your focus by selecting a specific area of interest within that gap. Choose a topic that aligns with your expertise and interests . This will make the writing process more enjoyable and allow you to bring a unique perspective to the paper.
Ensuring the Topic is Relevant and Significant
When choosing a topic, it is important to consider its relevance and significance. Select a topic that is timely and has practical implications . This will make your survey paper more valuable to readers and increase its impact. Additionally, consider the potential for future research and the broader implications of your chosen topic.
To ensure the relevance and significance of your topic, you can:
- Review recent publications and conference proceedings to identify emerging trends and hot topics in your field.
- Consult with experts and mentors to get their insights and suggestions on potential topics.
- Consider the practical applications of your chosen topic and how it can contribute to real-world problem-solving.
By following these steps, you can choose a topic that is both interesting to you and valuable to the academic community. Remember, the topic you choose will shape the entire survey paper, so take the time to select it wisely.
In conclusion, choosing a topic for your survey paper involves identifying a research gap, selecting a specific area of interest, and ensuring the topic is relevant and significant. By following these guidelines, you can set the stage for a well-rounded and impactful survey paper.
Conducting a Literature Review
Conducting a thorough literature review is a crucial step in writing a survey paper. It involves searching for relevant sources, evaluating their credibility, and organizing and summarizing the literature. This section will guide you through the process of conducting a literature review effectively.
Searching for relevant sources
When conducting a literature review, it is essential to search for relevant sources that contribute to your understanding of the topic. Here are some tips to help you find the right sources:
Utilize academic databases : Academic databases such as Google Scholar, PubMed, and IEEE Xplore are excellent resources for finding scholarly articles, conference papers, and research studies related to your topic.
Use appropriate keywords : Use specific keywords and phrases that accurately represent your research topic. This will help you narrow down your search and find relevant sources more efficiently.
Explore citation lists : Look for relevant sources in the reference lists of articles and papers you have already found. This can lead you to additional sources that are highly relevant to your research.
Consider different publication types : Apart from academic journals, consider including books, reports, theses, and dissertations in your literature review. These sources can provide valuable insights and perspectives on your topic.
Evaluating the credibility of the sources
It is crucial to evaluate the credibility and reliability of the sources you include in your literature review. Here are some factors to consider when assessing the credibility of a source:
Author’s expertise : Check the credentials and expertise of the author(s) of the source. Look for their affiliations, qualifications, and previous research experience in the field.
Publication venue : Consider the reputation and impact factor of the journal or conference where the source was published. High-quality venues often have a rigorous peer-review process, ensuring the reliability of the research.
Currency of the source : Ensure that the source is up-to-date and reflects the current state of research in the field. This is particularly important in rapidly evolving areas of study.
Peer-reviewed sources : Prefer sources that have undergone a peer-review process. Peer-reviewed articles are evaluated by experts in the field, ensuring the quality and validity of the research.
Organizing and summarizing the literature
Once you have gathered relevant sources, it is essential to organize and summarize the literature effectively. Here are some steps to help you with this process:
Create a citation database : Maintain a database or spreadsheet to keep track of the sources you have found. Include important details such as author names, publication year, title, and relevant notes.
Identify key themes and subtopics : Analyze the literature to identify common themes and subtopics that emerge from the sources. This will help you organize your survey paper and provide a logical flow of ideas.
Summarize the main findings : Write concise summaries of the main findings and key points from each source. Focus on the aspects that are most relevant to your research question or objective.
Identify gaps and controversies : Pay attention to any gaps or controversies in the literature. These can be areas where further research is needed or where different studies present conflicting results.
By following these steps, you can conduct a comprehensive literature review that forms the foundation of your survey paper. Remember to critically analyze and synthesize the information from various sources to provide a balanced and informative overview of the topic.
Outlining the Structure
When writing a survey paper, it is crucial to have a well-structured outline that guides the flow of your content. A clear and organized structure not only helps you present your ideas effectively but also makes it easier for readers to navigate through your paper. In this section, we will discuss the key components of outlining the structure of a survey paper.
The introduction sets the stage for your survey paper and provides essential background information to the readers. It should capture their attention and clearly state the research question or objective of your paper.
Background information : Start by providing a brief overview of the topic and its significance in the field. This helps readers understand the context and relevance of your survey paper.
Research question/objective : Clearly state the main research question or objective that your paper aims to address. This helps readers understand the purpose and focus of your survey.
The main body of your survey paper should be well-organized and structured to present your findings and analysis in a coherent manner. Consider the following points when outlining the main body:
Subtopics and their organization : Identify the key subtopics or themes that you will cover in your survey. These subtopics should be logically organized to provide a smooth flow of ideas. You can use headings and subheadings to clearly indicate the different sections of your paper.
Inclusion of relevant studies and findings : Within each subtopic, include relevant studies, research papers, and findings that contribute to the understanding of the topic. Make sure to cite and reference these sources properly to give credit to the original authors.
The conclusion of your survey paper should summarize the key points discussed in the main body and provide insights for future research directions. Consider the following elements when outlining the conclusion:
Summary of key points : Provide a concise summary of the main findings and insights from your survey. This helps readers grasp the main takeaways from your paper.
Future research directions : Discuss potential areas for further research or gaps that need to be addressed in the field. This encourages readers to explore new avenues and continue the scholarly conversation.
Having a well-structured outline for your survey paper ensures that you cover all the necessary components and present your ideas in a logical and coherent manner. It helps you stay focused and organized throughout the writing process.
Remember to review and revise your outline as needed to ensure that it aligns with the specific requirements and preferences of your survey paper. A well-structured survey paper not only enhances your credibility as a researcher but also contributes to the academic community’s knowledge and understanding of the topic.
Writing the Survey Paper
Writing a survey paper requires careful planning and organization to ensure that the information is presented in a clear and coherent manner. In this section, we will discuss the key steps involved in writing a survey paper.
The introduction of a survey paper plays a crucial role in capturing the reader’s attention and setting the tone for the rest of the paper. It should begin with an engaging opening statement that highlights the importance of the topic. The research question or objective should be clearly stated to provide a roadmap for the paper.
The main body of the survey paper should present a coherent flow of ideas that addresses the research question or objective. It is important to organize the content in a logical manner, using subheadings to divide the paper into sections. Each subtopic should be discussed in detail, providing a comprehensive overview of the existing literature.
When discussing previous studies and findings, it is essential to properly cite and reference the sources. This not only gives credit to the original authors but also adds credibility to the survey paper. Using a consistent citation style throughout the paper is important to maintain uniformity.
The conclusion of the survey paper should summarize the key findings and provide a concise overview of the main points discussed in the main body. It is an opportunity to highlight the significance of the research and its implications for future studies. Recommendations for further research can also be included to encourage future exploration of the topic.
Editing and Proofreading
Once the survey paper is written, it is crucial to thoroughly edit and proofread the content. This involves checking for grammar and spelling errors to ensure clarity and professionalism. It is also beneficial to seek feedback from peers or mentors to gain different perspectives and identify areas for improvement.
Formatting and Presentation
Proper formatting and presentation are essential for a well-structured survey paper. Following the required citation style is crucial to maintain consistency and adhere to academic standards. Headings, subheadings, and paragraphs should be properly formatted to enhance readability. Additionally, including tables, figures, and graphs can help illustrate complex information and enhance the overall presentation of the paper.
Finalizing the Survey Paper
Before submitting the survey paper, it is important to review the overall structure and content. This involves making necessary revisions and improvements to ensure the paper is coherent and cohesive. Proofreading the final version is crucial to eliminate any remaining errors and ensure a polished final product.
In conclusion, writing a survey paper requires careful planning, organization, and attention to detail. By following the steps outlined in this section, you can effectively write a survey paper that contributes to the existing body of knowledge in your field. Mastering the art of writing survey papers will not only enhance your academic research skills but also establish you as a knowledgeable and credible researcher.
Additional Resources:
- Recommended books and articles on survey paper writing
Online tools and platforms for organizing research
References:
List of sources cited in the blog post
Editing and proofreading are crucial steps in the writing process. They ensure that your survey paper is polished, error-free, and effectively communicates your ideas. Here are some essential tips to help you edit and proofread your survey paper effectively:
Checking for grammar and spelling errors
Use grammar and spell-check tools : Utilize grammar and spell-check tools like Grammarly or Microsoft Word’s built-in spell checker to identify and correct any grammatical or spelling errors in your survey paper.
Read your paper aloud : Reading your paper aloud can help you identify awkward sentence structures, grammatical errors, and spelling mistakes that you may have missed while reading silently.
Proofread multiple times : Proofreading is not a one-time task. It is essential to proofread your survey paper multiple times to catch any errors that may have been overlooked during previous rounds of editing.
Ensuring clarity and coherence
Check for clarity of ideas : Ensure that your ideas are presented clearly and concisely. Avoid using jargon or overly complex language that may confuse your readers. Use simple and straightforward language to convey your message effectively.
Maintain coherence and logical flow : Ensure that your survey paper has a logical flow of ideas. Each paragraph should connect smoothly to the next, and there should be a clear progression of thoughts throughout the paper. Use transition words and phrases to guide your readers through the different sections of your survey paper.
Eliminate redundant or irrelevant information : Review your survey paper to identify any redundant or irrelevant information. Remove any content that does not contribute to the overall purpose or argument of your paper. This will help streamline your paper and make it more focused and concise.
Seeking feedback from peers or mentors
Get a fresh pair of eyes : Ask a peer or mentor to review your survey paper. They can provide valuable feedback on areas that may need improvement, such as clarity, organization, or the overall structure of your paper.
Consider different perspectives : When seeking feedback, consider the perspectives of your reviewers. They may offer insights or suggestions that you may not have considered, helping you enhance the quality of your survey paper.
Incorporate feedback effectively : Take the feedback you receive into account and make necessary revisions to your survey paper. Be open to constructive criticism and use it to refine your paper further.
Remember, editing and proofreading are essential steps in the writing process. They help ensure that your survey paper is well-written, error-free, and effectively communicates your research findings. By following these tips, you can enhance the quality and clarity of your survey paper, making it more impactful and engaging for your readers.
Formatting and presentation play a crucial role in the overall quality and readability of a survey paper. Proper formatting ensures that the information is organized and presented in a clear and visually appealing manner. In this section, we will discuss the key aspects of formatting and presentation that you should consider when writing your survey paper.
Following the required citation style
One of the first things you need to consider when formatting your survey paper is the citation style required by your academic institution or the journal you are submitting to. Common citation styles include APA, MLA, and Chicago. Each style has specific guidelines for citing sources, formatting references, and creating in-text citations. It is important to familiarize yourself with the specific requirements of the chosen citation style and consistently apply it throughout your paper.
Properly formatting headings, subheadings, and paragraphs
Headings and subheadings are essential for organizing the content of your survey paper and guiding the reader through the different sections. When formatting headings and subheadings, it is important to follow a consistent hierarchy and formatting style. Typically, main headings are formatted in a larger font size and may be bold or italicized, while subheadings are formatted in a slightly smaller font size. This helps to visually distinguish between different levels of information and makes it easier for the reader to navigate through the paper.
In addition to headings and subheadings, proper formatting of paragraphs is also important. Each paragraph should focus on a single idea or topic and be well-structured with a clear topic sentence and supporting sentences. It is recommended to use a standard font such as Times New Roman or Arial, with a font size of 12 points. Additionally, paragraphs should be indented and have appropriate line spacing to enhance readability.
Including tables, figures, and graphs if necessary
Tables, figures, and graphs can be effective tools for presenting complex data or summarizing key findings in a visual format. When including these elements in your survey paper, it is important to ensure that they are properly labeled and referenced within the text. Tables should have clear column headings and be organized in a logical manner. Figures and graphs should have descriptive captions and be accompanied by a brief explanation in the text.
It is also important to consider the placement of tables, figures, and graphs within the paper. They should be inserted close to the relevant text and be easily accessible to the reader. If necessary, you can also refer to these elements in the text to provide further explanation or analysis.
Formatting and presentation are essential aspects of writing a high-quality survey paper. By following the required citation style, properly formatting headings and paragraphs, and including tables, figures, and graphs when necessary, you can enhance the overall readability and visual appeal of your paper. Remember to consistently apply these formatting guidelines throughout your survey paper to maintain a professional and polished appearance.
After going through the process of conducting a literature review, outlining the structure, writing the survey paper, and editing and proofreading it, you are now ready to finalize your survey paper. This stage involves reviewing the overall structure and content, making necessary revisions and improvements, and proofreading the final version.
Reviewing the overall structure and content
At this stage, it is crucial to review the overall structure and content of your survey paper. Ensure that the paper flows logically and coherently from the introduction to the conclusion. Check if the main body of the paper effectively addresses the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Make sure that each subtopic is adequately covered and that the inclusion of relevant studies and findings supports your arguments.
Making necessary revisions and improvements
During the finalization stage, it is common to identify areas that require revisions and improvements. Pay attention to the clarity and conciseness of your writing. Revise sentences or paragraphs that may be confusing or convoluted . Ensure that your arguments are well-supported by the literature and that you have properly cited and referenced all sources. Eliminate any redundant or irrelevant information that may distract readers from the main points of your survey paper.
Proofreading the final version
Proofreading is a crucial step in finalizing your survey paper. Check for grammar and spelling errors that may have been overlooked during the editing process. Ensure that your paper adheres to the required citation style and that all references are correctly formatted. Read through your paper carefully to ensure clarity and coherence . It may be helpful to read your paper aloud or ask a colleague to review it for you. Their fresh perspective can help identify any remaining errors or areas that need improvement.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your survey paper is of high quality and ready for submission or publication. Finalizing your survey paper requires attention to detail and a commitment to producing a well-structured and well-written piece of academic research.
Remember, the finalization stage is not the end of the writing process. It is always beneficial to seek feedback from peers or mentors to gain different perspectives and identify areas for further improvement. Their insights can help you refine your survey paper and make it even stronger.
In conclusion, finalizing a survey paper involves reviewing the overall structure and content, making necessary revisions and improvements, and proofreading the final version. It is a critical stage in the writing process that ensures your survey paper is polished and ready to be shared with the academic community.
Mastering the art of writing survey papers takes time and practice . By following the steps outlined in this blog post and seeking continuous improvement, you can become proficient in writing survey papers that contribute to the advancement of knowledge in your field.
Additional Resources
To further enhance your understanding of survey paper writing, here are some recommended books and articles:
- [Book] “Writing a Successful Research Paper: A Simple Approach” by Stanley Chodorow
- [Article] “How to Write a Survey Paper” by Martijn van Otterlo
Additionally, there are online tools and platforms available that can assist you in organizing your research and citations:
- [Tool] Zotero: A free, open-source reference management software
- [Platform] Mendeley: A platform for managing and sharing research papers
These resources can provide valuable guidance and support as you continue to develop your skills in writing survey papers.
[List of sources cited in the blog post]
When it comes to writing survey papers, having access to additional resources can greatly enhance your understanding and improve the quality of your work. Here are some recommended books, articles, and online tools that can assist you in the process of writing a survey paper.
Recommended Books and Articles on Survey Paper Writing
Writing a Survey Paper by John W. Chinneck: This book provides a comprehensive guide to writing survey papers, covering topics such as selecting a research topic, conducting a literature review, organizing the paper, and presenting the findings effectively.
How to Write a Survey Paper by Marta Tatu: This article offers practical tips and strategies for writing a survey paper, including advice on structuring the paper, synthesizing information, and avoiding common pitfalls.
The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students by Diana Ridley: Although not specifically focused on survey papers, this book offers valuable insights into conducting a literature review, which is a crucial component of writing a survey paper.
Writing a Successful Research Paper: A Simple Approach by Stanley Chodorow: This book provides guidance on various aspects of academic writing, including how to develop a research question, organize ideas, and present arguments effectively.
Online Tools and Platforms for Organizing Research
Zotero : Zotero is a free reference management tool that helps you collect, organize, and cite your sources. It allows you to easily save and annotate articles, books, and websites, and generate citations in various citation styles.
Mendeley : Mendeley is another popular reference management tool that enables you to organize your research library, collaborate with others, and generate citations and bibliographies. It also offers a social networking feature that allows you to connect with researchers in your field.
Google Scholar : Google Scholar is a powerful search engine that specializes in scholarly literature. It can be a valuable resource for finding relevant articles, books, and conference papers for your survey paper.
Microsoft Word or Google Docs : These word processing tools provide essential features for writing and formatting your survey paper. They offer options for creating headings, subheadings, and tables, as well as tools for spell checking and grammar correction.
Remember, while these resources can be helpful, it is important to critically evaluate the information you find and ensure its relevance and credibility before including it in your survey paper.
In conclusion, writing a survey paper requires careful planning, extensive research, and effective organization of information. By utilizing the additional resources mentioned above, you can enhance your writing skills and produce a high-quality survey paper that contributes to the academic community.
List of sources cited in the blog post:
- Chinneck, J. W. (n.d.). Writing a Survey Paper .
- Tatu, M. (n.d.). How to Write a Survey Paper .
- Ridley, D. (2012). The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students .
- Chodorow, S. (2014). Writing a Successful Research Paper: A Simple Approach .
When writing a survey paper, it is crucial to include a comprehensive list of references to support your claims and provide credibility to your work. The references section serves as a valuable resource for readers who wish to delve deeper into the topic or verify the information presented in your survey paper. Here are some important points to consider when creating the references section:
Ensure that you include all the sources that you have cited throughout your survey paper. This includes academic papers, books, journal articles, conference proceedings, and any other relevant sources that have contributed to your research. Proper citation and referencing are essential to avoid plagiarism and give credit to the original authors.
Formatting the references
Follow the required citation style specified by your academic institution or the journal you are submitting your survey paper to. Common citation styles include APA, MLA, Chicago, and IEEE. Each citation style has specific guidelines for formatting the references, including the order of information, punctuation, and capitalization. Properly formatting your references ensures consistency and makes it easier for readers to locate the sources you have used.
Organizing the references
Arrange the references in alphabetical order by the last name of the first author. If there are multiple authors, list them in the same order as they appear in the original source. Include the title of the paper or article, the name of the journal or book, the publication date, and the page numbers if applicable. Be sure to include all the necessary information to help readers locate the source easily.
There are several online tools and platforms available that can assist you in organizing and managing your research references. These tools help you create and format citations, generate bibliographies, and store your references in a centralized location. Some popular reference management tools include Zotero , Mendeley , and EndNote . These tools not only save time but also ensure accuracy and consistency in your references.
Double-checking the references
Before finalizing your survey paper, it is crucial to double-check the references section for any errors or omissions. Make sure that all the citations are accurate and complete. Verify that the formatting and punctuation are consistent throughout the references section. Proofreading the final version of your survey paper includes reviewing the references to ensure they are correctly formatted and properly cited.
Including a well-organized and accurate references section is essential for any survey paper. It adds credibility to your work and allows readers to explore the sources you have used. By following the guidelines for formatting and organizing your references, you can ensure that your survey paper meets the highest standards of academic integrity.
Writing a Survey Paper: A Comprehensive Guide
A. Importance of survey papers in academic research B. Purpose of the blog post
A. Definition of a survey paper B. Different types of survey papers C. Benefits of writing a survey paper
A. Identifying a research gap B. Selecting a specific area of interest C. Ensuring the topic is relevant and significant
A. Searching for relevant sources B. Evaluating the credibility of the sources C. Organizing and summarizing the literature
A. Introduction 1. Background information 2. Research question/objective B. Main Body 1. Subtopics and their organization 2. Inclusion of relevant studies and findings C. Conclusion 1. Summary of key points 2. Future research directions
A. Introduction 1. Engaging opening statement 2. Clear research question/objective B. Main Body 1. Coherent flow of ideas 2. Proper citation and referencing C. Conclusion 1. Recap of main findings 2. Implications and recommendations
A. Checking for grammar and spelling errors B. Ensuring clarity and coherence C. Seeking feedback from peers or mentors
A. Following the required citation style B. Properly formatting headings, subheadings, and paragraphs C. Including tables, figures, and graphs if necessary
A. Reviewing the overall structure and content B. Making necessary revisions and improvements C. Proofreading the final version
A. Recap of the steps involved in writing a survey paper B. Encouragement to master the art of writing survey papers
A. Recommended books and articles on survey paper writing B. Online tools and platforms for organizing research
A. List of sources cited in the blog post
Note: This outline is a general guide and can be modified or expanded based on the specific requirements and preferences of the blog post.
Writing a survey paper is an essential skill for academic researchers. It allows you to summarize and analyze existing literature on a specific topic, providing valuable insights and identifying research gaps. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of writing a survey paper, from choosing a topic to finalizing the paper.
Survey papers play a crucial role in academic research as they provide a comprehensive overview of existing knowledge in a particular field. The purpose of this blog post is to guide you through the process of writing a survey paper effectively.
To start, it’s important to understand the basics of a survey paper. A survey paper is a type of academic article that summarizes and synthesizes existing research on a specific topic. There are different types of survey papers, including literature reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses. Writing a survey paper offers several benefits, such as gaining a deep understanding of the topic, identifying research gaps, and contributing to the academic community.
Selecting the right topic is crucial for writing a successful survey paper. Begin by identifying a research gap in your field of interest. This gap could be an unanswered question or an area that requires further exploration. Once you have identified the research gap, narrow down your focus to a specific area of interest. Ensure that the topic is relevant and significant, as this will determine the impact of your survey paper.
A thorough literature review is the foundation of a well-written survey paper. Start by searching for relevant sources such as research articles, books, and conference papers. Evaluate the credibility of these sources by considering factors like the author’s expertise, the journal’s reputation, and the methodology used. Organize and summarize the literature in a systematic manner, highlighting the key findings and arguments.
A well-structured survey paper is essential for clarity and coherence. The structure typically consists of an introduction, main body, and conclusion. In the introduction, provide background information on the topic and clearly state your research question or objective. The main body should be organized into subtopics, each addressing a specific aspect of the topic. Include relevant studies and findings to support your arguments. Finally, in the conclusion, summarize the key points and suggest future research directions.
When writing the survey paper, pay attention to the introduction, main body, and conclusion. The introduction should engage the reader with an opening statement and clearly state the research question or objective. The main body should have a coherent flow of ideas, presenting the literature in a logical manner. Proper citation and referencing are crucial to acknowledge the original authors and avoid plagiarism. In the conclusion, recap the main findings and provide implications and recommendations for future research.
Editing and proofreading are essential to ensure the quality of your survey paper. Check for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure clarity and coherence in your writing. Seek feedback from peers or mentors to get different perspectives and improve the overall quality of your paper.
Proper formatting and presentation enhance the readability of your survey paper. Follow the required citation style, such as APA or MLA, to ensure consistency. Format headings, subheadings, and paragraphs appropriately to create a clear structure. If necessary, include tables, figures, and graphs to present data effectively.
Before submitting your survey paper, review the overall structure and content. Make necessary revisions and improvements to enhance the clarity and coherence of your paper. Finally, proofread the final version to eliminate any remaining errors.
Writing a survey paper requires careful planning and execution. This guide has provided a step-by-step process to help you write a high-quality survey paper. By mastering the art of writing survey papers, you can contribute to the academic community and advance knowledge in your field.
To further enhance your understanding of survey paper writing, consider exploring recommended books and articles on the topic. Additionally, there are online tools and platforms available that can assist you in organizing your research effectively.
[List the sources cited in the blog post here.]
Unveiling The Shelf Life: How Long Does Citric Acid Last?
Unveiling The True Value: How Much Is Jcoin Worth In Today’s Market?
Rebooting Your Booze: How To Reset Alcohol Content
Quick And Easy: Mastering The Art Of Thawing Tuna
Unveiling The Dynamic Interplay: How Physical And Human Systems Shape A Place
Unlocking The Power: How Long Does It Take For Royal Honey To Activate?
Mastering Residency: A Guide On How To Study Effectively
Mastering The Art Of Die Cast Mold Making: A Step-By-Step Guide
Unveiling The Energy Consumption Of Water Coolers: How Much Electricity Do They Really Use?
Mastering Virtual Reality: Unlocking The Secrets To Altering Your Height
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

How to Write a Survey Paper: A stepwise Guide with Examples

How to Write a Survey Paper
Some of you may be wondering what a survey paper is. A survey paper contains the interpretation that has been drawn by the author after they have reviewed and analyzed various research papers that are centered on a specific topic. Those research papers should be already published.
Now that we have understood what a survey paper is, let us explore the various steps that have to be taken when coming up with a survey paper. As noted, a survey paper lists and analyzes the most recent research work in a particular area of study.
To write a good survey paper, you need to research the representative papers, come up with a title, a good abstract, and writing the introduction, the body, and conclusions that reflect the findings as well as the challenges of the study.

To do this, there is a challenge of research. As such, the first challenge is to find the most recent and appropriate research papers for the topic. The 9 steps below should be followed when writing a survey paper.
Need Help with your Homework or Essays?
Step 1: selecting the representative papers.
The first step when writing a survey paper is selecting the most relevant representative papers that are within the scope of your research and summarizing them effectively. As you will note, there can be a lot of research papers, and the space required to create a survey paper is limited.

During such, it can be challenging when trying to pick the key work within the scope of your study.
As an author of the survey paper, you will have to read the research papers’ abstracts and conclusions and pick the subset that captures your area of study.
To ensure that the selected research papers are appropriate or relevant, they should be recent, contain more citations, and be published in journals with a high reputation.
The research papers should not be less than 10.
Step 2: Coming up with an Appropriate Title
The second step is coming up with a captivating title that provides a clear summary of your paper’s contents. As such, the title should be clear and brief. To achieve this, the title should utilize active verbs rather than complex phrases that are based on nouns.
A good title of your survey paper should contain between 10 and 12 words because a title with more words will divert the attention of the readers from the central point.
A longer title will also appear unfocused. Therefore, the title should have the keywords of your survey paper in such a way that it defines the study’s nature.
Step 3: Creating an Abstract
Another important step to be taken when writing a survey paper is to create an abstract. The abstract acts as a summary of your survey paper.
It should provide a summary of the problem that has been investigated, the methods used, the results of the study, and the conclusion.
Abstracts summarize the most important contents of your survey paper in a single paragraph of between 200 and 300 words.
When creating an abstract, make sure that it contains or highlights the key points while convincing the readers or the target audience to continue reading the whole survey paper. Should always include an abstract in your survey paper.
Step 4: Listing Key Terms
While the keywords help the target audience or other researchers understand the field of the survey paper, the subfield, research issue, the topic, and so on, the main purpose of this section is to help readers or researchers locate your paper when they are doing searches on the topic.
Most of the databases, electronic search engines such as Google, and journal websites will utilize keywords when deciding whether to display the survey paper to interested readers and when this should be done.
With the proper keywords, your survey paper will be more searchable and it will be cited by more researchers because it can be easily located.
Step 5: Writing the Introduction

The next step when writing a survey paper is to include a good introduction.
A good introduction paragraph will explain to the target readers how the research problem has been tackled by the research papers that you have included in your paper.
The introduction should arouse the readers’ interest in knowing more about the topic and the research domain. If they are interested, they will continue reading your survey paper.
Unlike the abstract, the introduction within a survey paper does not contain a very strict word limit. However, it should be concise because it introduces the paper’s topic, provides a broader context of the study, and gradually narrows the scope down to the research problem.
Therefore, make sure that your introduction sets a scene and contextualizes your paper. It can begin with a historical narrative bringing the narrative to the present day and ending with a research question. Ensure that the very last sentence of your introduction is the thesis statement.
Step 6: Providing the Approaches Used in the Survey Paper
This is a very important step in any survey paper. This is where you are required to provide the methodologies used to conduct your research or survey in a logical order.
You are required to logically move from one method to the next as you clearly define each approach at the beginning of every section.
To ensure that your readers are at par with you, you should share the motivation behind each methodology. This is achieved by giving a high-level summary of every approach and then narrowing it down to the specific approaches.
You should also demonstrate the applicability and the practicability of every approach used in the research, and the areas that need to be improved. You should graphically visualize at least one method used.
Step 7: Writing About the Paper Surveys
This step should take the bulk of your survey paper because it is the point where you survey the papers you have selected. Here, you should decide what you are going to inform your readers about each research paper.
Therefore, it is important to first read the research papers in a manner that you can know what to inform your readers about them.
For each research paper, make sure that you tell your readers about their research direction. Also, ensure that you identify the algorithms or mathematical techniques the research papers rely on and whether they are application or theory papers.
You should also state whether the selected research papers are an improvement on other works or they are a continuation of other works.
Then, state whether the research papers utilize simulations, theoretical proofs, real-life deployment, and so on. Finally, you should state the strengths and weaknesses of each research paper, authors’ claims, and assumptions.
Step 8: Research Challenges

After surveying every research paper you have utilized, the next step is to state the challenges you encountered while conducting research.
When writing a survey paper, you will always face various challenges.
Such challenges can be finding the best or most appropriate research papers, comparing them to determine their strengths, and so on.
Other challenges can arise from the research papers themselves. This can include their delivery of results. Some research papers will contain confusing data.
Step 9: Coming up with a Conclusion
Finally, the conclusion should answer the questions that have been raised by your survey paper’s objectives and goals.
Though it should be interesting and captivating, it should still be presented academically. It should be objective and offer a final say concerning the survey’s subject.
The conclusion should synthesize the results by proving their interpretation, propose the course of action as per the results, and offer solutions to the issues that have been identified.
The reader should be capable of understanding the whole survey paper by reading the conclusion. Therefore, ensure that your conclusion synthesizes your paper.
Get a Brilliant Essay today!
Let our essay writing experts help you get that A in your next essay. Place your order today, and you will enjoy the benefits.
Tips When Writing a Good Survey Paper
The first tip in writing a good survey paper is to select the most appropriate and latest research papers that will be used in the paper. This is a very important tip because the survey paper will be completely based on them. Old research papers will render your survey paper useless.

Research papers that are not within the scope of your research or topic will also render the survey paper useless.
The second tip is to make sure that you come up with a concise topic that will summarize what your paper is about.
It is also very important to follow the appropriate format of a survey paper.
The format, after you have written your title, should be abstract, key terms, introduction, approaches or methodologies, conducting surveys for every paper used, research challenges, and finally the conclusion.
Another important tip is to utilize more than 10 research papers for the survey. Then can be even more than 20 depending on the scope of your study. The more the research papers used in your survey paper, the more professional and credible it will appear.
It should be noted that a good survey paper will utilize research papers that are recent (not more than 5 years) and have more academic sources.
To increase the credibility of your survey paper, the research papers used should come from reputable journal sources or publications. In our guide to writing good research papers , we explained more about references. Check it out.
Also, note that the process of writing a survey paper is much different from that of writing an issue paper or doing opinion essays . Therefore, each step needs to relate to the survey.
15 Examples of Topics for Writing a Survey Paper
- Advances in leaf image analysis for bacterial disease detection
- A survey on the impact of social media among youths in the united states
- A Survey on leaf image analysis for bacterial disease detection
- Recent trends in the electric cars manufacturing industry
- Recent trends in perinatal care: Exploring the major causes of perinatal mortality
- Leaf image analysis for bacterial disease detection
- Advances in curriculum-based education: A survey on educational trends in sub-Saharan Africa
- Recent trends in environmental awareness campaigns in low-income countries
- A survey on COVID-19 pandemic impact on the united states economy
- Recent trends in the immunization approach taken by third world countries after the second and third wave of COVID-19 disease
- Advances in semiconductor manufacturing for BMW electronic cars
- A survey on the impact of 5-G connectivity among SMEs in Britain
- Recent trends in the space race: A survey of how the founders of Virgin Atlantic, Tesla, and Amazon are competing to dominate space travel
- Advances in care for pressure ulcers: A survey on the impact of frequent automated turning on older immobile patients in Germany
- A survey on the impact of geopolitics on peace within the Middle East

Josh Jasen or JJ as we fondly call him, is a senior academic editor at Grade Bees in charge of the writing department. When not managing complex essays and academic writing tasks, Josh is busy advising students on how to pass assignments. In his spare time, he loves playing football or walking with his dog around the park.
Related posts

Is Grammarly Premium worth It
Is Grammarly Premium worth It or Reliable: Full Review 2023

How to Write a Last-Minute Essay on your Own
How to Write a Last-Minute Essay on your Own: In a Few Hours

Is Safeassign accurate
How Accurate is SafeAssign? How to Read SafeAssign Scores
How to write a Survey Paper
So you want to write a survey paper? How do you begin?
What is (not) a survey paper?
Some of the following is adapted from https://www.researchgate.net/post/How_to_write_survey_or_review_papers_and_What_sections_should_be_mentioned_in_such_papers
To answer this question its best to first ask what a survey paper is not . A survey paper is not simply a core dump of a bunch of papers in a common area.
Instead, a survey is a research paper whose data and results are taken from other papers. This means that you should have a point to make or some new conclusion to draw.
You’ll make this point or draw these conclusions based upon a broad reading of previous works. You need to really know the topic in order to have the audacity to claim that a thorough survey of the field. You’ll need to be completely aware of the main themes, directions, controversies, and results in the field. You may wish to email and interview authors of related works to get their opinion.
Writing a survey paper is much more difficult than writing a research paper
You do not simply list prior results. You need to assimilate and synthesize the results. Sometimes you’ll need to address conflicts in notation or introduce entirely new notation.
And, of course, you need to have a point. The point you make will determine the organization of survey paper. The structure of the main sections of the paper will reflect the structure of field. You might consider the following organization:
- Simple to complex scale. Maybe there was some seminal invention that people add more and more complexity onto — this is very very very common in AI and ML.
- Comparative Analysis. You compare Two or more different approaches to the same problem.
- Pipeline Analysis. Many complex solutions require a pipeline that you’ll describe and categorize and annotate.
- Disentanglement. Maybe your field has researchers conflating issues that need to be carefully untangled.
- Historical. Tell the story of something if its compelling.
You’ll do a good job if you can communicate a perspective and/or articulate the gaps in the knowledge. This is difficult and should probably not be attempted by young scientists or graduate students.
The bottom line is that you need to have a point to make and, conclusion to draw, or some kind of contribution that is not just a list of abstracts.
An iterative process
The following is taken from https://academia.stackexchange.com/questions/43371/how-to-write-a-survey-paper
The point of a survey paper of the type you are discussion (as distinct from a systematic review), is to provide an organized view of the current state of the field. As such, you should not be attempting to cite every paper, but only the ones that are significant (which will still be an awful lot)
Writing a good survey paper is hard, and there really aren’t any good shortcuts: you do need to become familiar with the content of a very large number of papers, in order to make sure that the view you are presenting is sane.
Step 1: Begin by collecting a large pile of papers to survey.
Start by collecting a handful of papers that you are interested in. See who cites them and what they cite.
Step 2: Things of an organization schema.
Based on your experience and a readings, hypothesize an organization schema for the field. What point are you trying to make with this survey?
Start reading (mostly skimming) and organizing your collection of papers you read using this schema, including noting which ones are most important and which do not fit the schema well.
As you find significant numbers of papers that do not fit the schema well, adjust the schema to better fit what you are actually finding and shift the organization of your collection to match.
Step 3: Find new papers
As you continue to read you’ll find papers that cite and are cited by the papers you’ve read. Add these new papers to the “to be read” collection based on the adjusted schema, then return to Step 1.
Convergence.
When the process converges to a stable schema and an empty to-be-read pile, you will have a well-developed view of the current state of the field and be in a good position to write a survey. Note, however, that this may take a number of months.
Hints and Tricks
Use a bib manager. Zotero, Mendeley, etc
Use a consistent bibtex index structure. I use lastnameYearFirstwordoftitle convention
You should follow this process in your PhD study generally, but it doesn’t mean that you have to write a survey paper. A survey paper needs to have something to say; a point to make; or some contribution in the way we think about a thing.

Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
How to Write a Better Survey Paper in 06 Easy Steps?
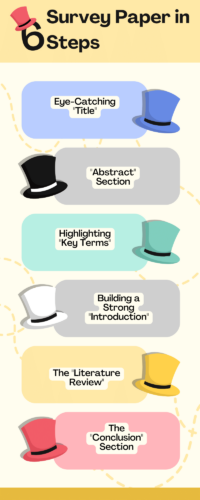
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on crafting a better survey paper. Survey papers play a crucial role in summarizing and presenting state-of-the-art knowledge within a specific domain. Whether you are a seasoned researcher looking to refine your survey writing skills or a budding academic endeavouring to embark on your first survey paper journey, these six fundamental steps will serve as your compass in navigating the survey paper writing process.
Introduction
A Researcher begins his research journey by first writing a survey paper in the domain of his research. Writing a survey paper helps a researcher to
i) Understand his domain of research thoroughly
ii) Identify the existing research gaps,
iii) Understand the various parameters and their role in solving the problem and
iv) Infrastructure and Data set requirements for research.
In fact, after completing my survey paper I decided to go for optimal cloud infrastructure for my work. This helped me a lot in cutting the total cost of my research.
A survey paper is also a service to the scientific community. You are doing research for young research scholars. Instead of reading a vast amount of papers to understand what a scientific topic is about, a researcher just needs to read your paper and can start his research at the earliest with a clear direction in mind. To make the researcher read your paper, you must have good content and a high citation score . Otherwise, your paper is like purchasing a site in the forest and trying to sell with no one ready to buy.
What is expected in a survey paper? A survey paper is a research paper which lists and analyses the latest research works in a particular research domain of interest. The survey paper derives some conclusions from the work carried out so far and provides new avenues for future research.
A good survey paper provides a concise but broad review of a domain that is accessible to a wide range of readers who are naive and willing to carry out research in the domain presented. This introduces two primary challenges for writing such a survey paper.
The first challenge is to pick representative papers from within the research area and summarize them. There can be a vast amount of research papers available and survey paper has limited space to capture the critical work in the field.
The author needs to go through abstracts and conclusions for a relatively large number of papers and select a subset that covers the selected topic area for detailed reading and presentation in the survey. Identifying the papers having higher citations and which are published in conferences and journals of high reputation will have to be given higher priority for selection.
The second challenge is to make the reader comfortable in reading and comprehending the analysis done for the various research papers. The author has to go through each paper considered for the survey at least two-three times before deriving any conclusion.
How to Make a Survey Paper?
A survey paper should
- Pick at least 10-20 papers on a specific topic from the collected paper list.
- The papers selected should be a mix of papers including the base paper in the selected domain to the most recently published paper.
- Should have an analysis of the significance of the approach and the results presented in each paper
- Give a critical assessment of the work that has been done.
- Include a discussion on future research directions
- Give precise details of the experimental setup used for carrying out research in each paper
- Compare only those works which have a common experimental platform or data set. Otherwise, you have to recreate a common platform or use a common data set and test the methodologies used in various platforms.
A typical structure of a survey paper includes the following 06 Sections as discussed below:
Survey Paper Format
[Title of Your Survey Paper]
2. Abstract:
[Summarize the purpose, methodology, key findings, and implications of your survey paper in a concise paragraph.]
3. Key Terms:
[Provide a list of key terms or concepts relevant to your survey paper.]
4. Introduction:
[Provide an overview of the topic and its importance. Describe the scope and objectives of your survey paper. Briefly introduce the main themes and topics covered in the literature review.]
5. Literature Review:
I. complexity of the problem: static vs dynamic.
- [Brief overview of the complexity of the problem, including both static and dynamic aspects.]
- [Discussion of static aspects of the problem, including definitions, models, algorithms, etc.]
- [Discussion of dynamic aspects of the problem, including evolving nature, real-time constraints, etc.]
II. Design Space
- [Brief overview of the design space related to the problem.]
- [Discussion of various design considerations and factors influencing the problem-solving approach.]
- [Overview of different approaches and solutions proposed in the literature for addressing various aspects of the problem.]
6. Conclusion:
[Summarize the main findings and insights gained from the literature review. Highlight any gaps or limitations in current research. Discuss potential future directions for research in the field.]
The Six Steps for Writing a Better Survey Paper
In this comprehensive guide on how to write a better survey paper, we will explore six fundamental steps that will elevate the quality and impact of your research.
It all begins with crafting an eye-catching “Title” that succinctly conveys the essence of your survey paper and captures readers’ attention.
Moving on, the “Abstract” section serves as a concise overview of your research, providing readers with essential insights into your objectives, methodology, and findings.
Identifying the key terms of your literature review is the core of your survey paper, where you analyze existing research. Identify and emphasize key terms and concepts to provide a clear understanding of the relevant research landscape.
As you progress, a strong “Introduction” sets the tone, introducing the problem, its significance, and the objectives of your survey paper.
The heart of your survey paper lies in the “Literature Review,” where you analyze existing research. By highlighting key terms and concepts, you enhance clarity and enable readers to grasp the current research landscape more effectively.
As your survey paper reaches its “Conclusion,” you synthesize the key findings from the literature review and offer valuable insights into the current state of the field.
Lastly, by thoroughly reviewing, revising, and refining your survey paper, you ensure clarity, coherence, and overall excellence.
By following these six steps, your survey paper will not only make a significant contribution to your chosen field but also captivate and inform your readers with its well-structured and insightful content.
1. Eye-Catching “Title” for the Survey Paper
The primary function of a title is to provide a clear summary of the paper’s content. So keep the title brief and clear. Use active verbs instead of complex noun-based phrases, and avoid unnecessary details. Moreover, a good title for a research paper is typically around 10 to 12 words long. A lengthy title may seem unfocused and take the readers’ attention away from an important point. As I supervise many candidates who hail from non-native English-speaking countries, they struggle a lot with writing error-free Titles. So, I always advise them to take English classes in parallel with their research.
A good research paper title should contain keywords used in the manuscript and should define the nature of the study. Think about terms people would use to search for your study and include them in your title. Do not use abbreviations in the title. Knowing the search intent of the people who search for the keyword is critical as it helps you to find the top searched keywords. I learnt this technique by mapping SEO-based keyword research techniques to find quality keywords for my title.
Usually, a Title for a survey paper starts with , “Recent trends in ….”, “Advances in…..”.
Some survey papers end with “…….: A Survey” .
Here are the other ways to mention survey paper titles:
- ” A Survey on …..”
- “…….: A Survey”
- “An Overview of…”
- “A Comprehensive Study on…”
- “Exploring the Landscape of…”
- “A Critical Review of…”
- “A Systematic Analysis of…”
- “Examining the State of…”
- “A Comprehensive Review on…”
- “Surveying the Current Trends in…”
- “Investigating the Advancements of…”
- “Analyzing the Evolution of…”
Here is a list of Examples of Survey Paper Titles
- “A Survey on Artificial Intelligence Applications in Healthcare”
- “Recent Trends in Renewable Energy Sources: A Survey”
- “Advances in Natural Language Processing Techniques: A Survey”
- “A Survey on Cybersecurity Threats and Mitigation Strategies”
- “Recent Developments in Blockchain Technology: A Survey”
- “Advancements in Machine Learning Algorithms for Image Recognition: A Survey”
- “A Survey on Cloud Computing Security and Privacy Issues”
- “Recent Trends in E-commerce Payment Systems: A Survey”
- “Advances in Robotics and Automation: A Survey”
- “Mobile Health Applications: A Survey of Current Trends and Challenges”
- “An Overview of Machine Learning Algorithms: A Comprehensive Study”
- “A Critical Review of Renewable Energy Technologies: Exploring the Landscape”
- “Examining the State of Cybersecurity Threats: A Systematic Analysis”
- “A Comprehensive Study on Blockchain Technology: Investigating the Advancements”
- “Analyzing the Evolution of Artificial Intelligence Applications: A Survey”
- “A Survey of Cloud Computing Security and Privacy Issues”
- “Recent Trends in Natural Language Processing Techniques: A Comprehensive Review”
- “Surveying the Current Trends in E-commerce Payment Systems”
- “Exploring the Landscape of Robotics and Automation: A Critical Review”
- “A Comprehensive Review on Mobile Health Applications: Examining the State of the Art”
For more details on writing Titles for your research paper visit my blog post on: Research Paper Title: 03 Simple Steps to Make it Easily Discoverable
2. Giving an Overview of the Survey Paper Through the “Abstract” Section
The abstract is a summary of a research paper describing the problem investigated, the methods applied, the main results and conclusions. Abstracts are a good way to summarise the key contents of a paper, from the research it uses to the ideas you want to share with the reader.
The abstract is a single paragraph containing a minimum of 200 words up to 300 words. An abstract offers a preview that highlights key points and helps the audience decide whether to view the entire work.
Extraction of meaningful leaf disease features by applying image processing techniques is a problem that has been studied by the image processing community for decades. Image processing research for leaf disease identification has matured significantly throughout the years and many advances in image processing techniques continue to be made, allowing new techniques to be applied to new and more demanding pathological problems. In this paper, we review recent advances in diseased part extraction of leaf images affected by pathogens, focusing primarily on three important Soft computing techniques namely: Neural networks, Fuzzy logic and Genetic algorithms. Throughout, we present tables that summarize and draw distinctions among key ideas and approaches. Where available, we provide comparative analyses, and we make suggestions for analyses yet to be done.
Here’s a tabular representation of the sub-sections based on the given abstract:
Please note that this tabular representation is a simplified breakdown of the abstract into distinct sub-sections based on its content. The actual structure and headings may vary depending on the specific formatting requirements and guidelines of the paper.
For more details on how to write an Abstract for your research paper, you can visit my blog post on :
- Research Paper Abstract: 10 Simple Steps to Make a Big Difference
3. Highlighting “Key Terms” of the Survey Paper
The purpose of keywords in a research paper is to help other researchers find your paper when they are searching for the topic. Keywords define the field, subfield, topic, research issue, etc. that are covered by the article.
Most electronic search engines, databases, or journal websites use keywords to decide whether and when to display your paper to interested readers. Keywords make your paper searchable and ensure that you get more citations. Thus, it is important to include the most relevant keywords that will help other authors find your paper.
For Example for the abstract written in the previous section, the keywords can be: Keywords: Plant pathology, bacterial blight, diseased part extraction, Image processing, Soft Computing.
For more details on identifying the most prominent keywords for your research paper, you can visit my blog post on: Top 10 Rules to Identify Keywords for your Research Paper
4. Building a Strong “Introduction” Section of the Survey Paper
A good introduction in a survey paper explains how the research problem has been solved by various researchers and creates ‘leads’ to make the reader want to delve further into the research domain. Introduce the terminology of the field and describe what the various terms mean.
The introduction does not have a strict word limit, unlike the abstract, but it should be as concise as possible. The introduction works upon the principle of introducing the paper’s topic and setting it into a broad context, gradually narrowing it down to a research problem.
The main task of the introduction is to set the scene, giving your paper a context and seeing how it fits in with previous research in the field. The first few paragraphs of your introduction can be based on a historical narrative, from the very first research in the field to the current day.
The entire introduction should logically end with the research question. The reader, by the end of the introduction, should know exactly what research issue you are trying to survey with your paper.
Here’s a tabular format of the introduction for your survey paper:
Please note that the actual sub-section headings and their order may vary depending on the specific content and focus of your survey paper. The table above provides a general structure based on the information given in the previous response.
Example of an Introduction:
In this survey paper, we aim to explore the advancements made in extracting meaningful leaf disease features through image processing techniques. Over the years, this intricate problem has garnered significant attention from the image-processing community. Our objective is to provide a comprehensive overview of the diverse approaches employed by various researchers to address this challenge successfully.
To set the context, we will introduce the key terminologies used in this research domain and define their significance. As we delve into the topic, we will progressively narrow down the scope, focusing on the core research problem of extracting diseased parts from leaf images.
Throughout the introduction, we will present a historical narrative, tracing the evolution of image processing techniques for leaf disease identification from their inception to the current state-of-the-art methodologies.
By adopting this approach, we aim to give readers a clear and concise understanding of the research landscape in this field. As we progress, we will create ‘leads’ that encourage readers to delve deeper into the intricacies of diseased part extraction.
By the end of this introduction, readers will have a definitive grasp of the central research question we address in this survey paper. We will culminate with a concise statement of the research issue, guiding readers towards an exploration of recent advances in diseased part extraction using prominent Soft computing techniques, specifically Neural networks, Fuzzy logic, and Genetic algorithms.
Example text included under each subsection heading:
For more details on writing the introduction section, you can visit my blog post on: How to Write an Effective Research Paper Introduction in 03 easy steps?
5. The “Literature Review” of the Survey Paper
The Literature Review has to be based on the specific theme of research which will help the reader in focusing his/her research on specific concepts. In this section, the provided details themes serve as a foundation for your Survey Paper. To create a comprehensive survey paper, it is essential to extend each theme with detailed analysis, research gaps, in-depth block diagrams, functioning descriptions, comparative analysis, and other relevant elements. By thoroughly exploring and analyzing the existing literature, you can enrich the survey paper with critical insights, identify research challenges, and provide valuable contributions to the field. Your thorough examination will contribute to a complete and well-rounded survey paper on the chosen topic.
Some possible themes can be:
i. Complexity of the problem:
There can be various types of solutions for a given problem domain and the author has to organize them in the increasing level of complexity or scale.
Literature Review: Complexity of Scene Analysis in Image Processing
In the field of Image Processing, scene analysis emerges as a core problem, where researchers seek to extract meaningful information from visual data. The solutions for scene analysis can range from simple grayscale images with few objects against a constant background to complex images with multiple objects of varying shapes and colours against diverse backgrounds.
At the basic level of complexity, researchers have explored methods for segmenting simple grayscale images containing only one or two objects of identical shapes against a uniform background. Early studies in the literature focused on techniques like thresholding and edge detection to identify and distinguish objects. (Reference: Smith et al., 2005; Johnson and Brown, 2008)
Moving up the complexity ladder, the literature presents solutions for scenes with multiple objects of different shapes but with a consistent background. Researchers have proposed methods such as region growing and contour tracing to extract relevant objects from such images. (Reference: Lee and Kim, 2010; Chen et al., 2012)
As the complexity further increases, scene analysis encompasses images with diverse objects of varying shapes and colours set against complex backgrounds. In these cases, advanced algorithms like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and deep learning techniques have been deployed to achieve accurate and robust object recognition. (Reference: Wang et al., 2016; Zhang and Li, 2018) .
Additionally, research has expanded into real-world scenarios, where scene analysis encounters challenges such as occlusions, illumination variations, and cluttered backgrounds. Addressing these complexities, the literature explores techniques like scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) and histogram of oriented gradients (HOG) to handle object detection and recognition in challenging environments. (Reference: Liu et al., 2019; Park and Lee, 2020)
The progression of complexity in scene analysis solutions reveals the evolution of Image Processing techniques to accommodate real-world challenges. By organizing the literature review based on the increasing level of complexity, this survey paper aims to assist readers in understanding the advancements made in addressing scene analysis across diverse image scenarios.
ii. Static vs. Dynamic:
Many fields can be organized by static techniques, dynamic techniques, and even hybrid. For example Static or Dynamic Routing in Computer Networking.
Literature Review: Static vs. Dynamic Resource Allocation in Cloud Computing
Resource allocation is a critical aspect of Cloud Computing, ensuring efficient utilization of computational resources to meet user demands and optimize system performance. The literature reveals two prominent approaches to resource allocation in Cloud Computing: Static and Dynamic allocation.
Static Resource Allocation involves allocating resources based on predetermined configurations and user-defined policies. Researchers have proposed various static resource allocation algorithms, such as Round-Robin and First-Come-First-Serve (FCFS), to allocate resources in a fixed manner without considering varying resource demands (Reference: Smith et al., 2015; Johnson and Brown, 2017).
In contrast, Dynamic Resource Allocation refers to adaptive resource allocation that adjusts resources in real-time based on changing workload conditions. Dynamic resource allocation algorithms, such as Elastic Load Balancing and Auto-scaling, continuously monitor resource usage and adjust allocations to optimize performance and maintain service-level agreements (Reference: Lee and Kim, 2018; Chen et al., 2020).
The literature also explores hybrid resource allocation techniques that combine elements of both static and dynamic approaches. Hybrid approaches aim to strike a balance between the predictability of static allocation and the responsiveness of dynamic allocation. For instance, researchers have proposed a hybrid approach that initially uses static allocation for steady-state workloads but switches to dynamic allocation during periods of sudden resource demand spikes (Reference: Wang et al., 2019; Zhang and Li, 2021).
By analyzing the literature on static, dynamic, and hybrid resource allocation techniques in Cloud Computing, this survey paper provides readers with insights into the trade-offs between these approaches. Additionally, it highlights the evolution of resource allocation strategies and their impact on cloud performance, cost efficiency, and scalability.
Please note that the references used in this example are imaginary.
iii. Segregating the Design Space:
Many systems are made up of components, so maybe for a computer network paper, the author could divide the problems into a physical layer, application layer, session layer, transport layer, data link layer and physical layer.
Literature Survey: Segregating the Design Space in AI-based Recommender Systems
In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has driven significant advancements in recommender systems, revolutionizing personalized recommendations across various domains. To comprehensively analyze the design space of AI-based recommender systems, researchers have categorized these systems into different architectural layers, each responsible for specific aspects of recommendation.
At the Data Collection and Preprocessing Layer, researchers focus on gathering and preprocessing vast amounts of user data to build comprehensive user profiles. Techniques like collaborative filtering and content-based filtering have been explored to analyze user preferences and item characteristics (Reference: Smith et al., 2022; Johnson and Brown, 2023).
Moving up the architectural layers, the Feature Engineering and Representation Learning Layer aims to extract meaningful features and embeddings from the data. Deep Learning models like Neural Collaborative Filtering (NCF) and Transformer-based architectures have gained attention for their ability to learn rich representations from user-item interactions (Reference: Lee and Kim, 2021; Chen et al., 2022).
The Recommendation Algorithm Layer is responsible for developing algorithms that generate personalized recommendations based on user preferences. Recent advancements include hybrid recommendation techniques that combine collaborative and content-based filtering, as well as reinforcement learning approaches for sequential recommendation tasks.
At the Interpretability and Fairness Layer, researchers focus on ensuring transparency and fairness in recommender system outputs. Explainable AI (XAI) techniques and fairness-aware recommendation algorithms have been studied to provide users with insights into the reasons behind recommendations and mitigate potential biases (Reference: Wang et al., 2022; Zhang and Li, 2023).
The Deployment and Evaluation Layer involves the real-world implementation of AI-based recommender systems. Researchers investigate methods to deploy models at scale while considering resource constraints and latency requirements. Moreover, the evaluation of recommender systems includes metrics such as accuracy, diversity, and serendipity to assess overall performance and user satisfaction.
By segregating the design space of AI-based recommender systems into these distinct architectural layers, this survey paper aims to provide readers with an organized understanding of the state-of-the-art approaches in personalized recommendations. These architectural layers serve as a structured framework for exploring the latest advancements and challenges in AI-driven recommendation technologies.
Please note that the references used in this example are imaginary
iv. Major Approaches in a Specific Domain:
Every domain usually has two to three major classes on which all the issues in that domain are addressed or the advancements in that domain are identified.
For example,
i) In Software Testing: Black box or White box testing
ii) In Networking: Wired or Wireless Networking and
iii) In Image processing Spatial or Temporal based Image Processing etc.
iv) In Telcom it is 2G, 3G,4G and 5G etc.
Literature Survey: Major Classes in Telecommunication Technology – 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G
The domain of Telecommunication Technology has witnessed significant advancements over the years, leading to the emergence of major classes based on different generations of mobile communication systems. This survey paper aims to explore and analyze the key characteristics and advancements of each major class – 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G.
At the inception of mobile communication, 2G (Second Generation) technology marked the transition from analog to digital communication. Researchers have extensively studied various 2G technologies, including GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) and CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) to provide basic voice and text messaging services (Reference: Smith et al., 2016; Johnson and Brown, 2018).
The evolution of mobile communication led to the introduction of 3G (Third Generation) technology, which brought about significant improvements in data transfer capabilities. With 3G technologies like UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) and EV-DO (Evolution-Data Optimized), researchers explored higher data speeds, enabling services like mobile internet browsing and video streaming.
Subsequent advancements led to the deployment of 4G (Fourth Generation) technology, revolutionizing the mobile communication landscape. LTE (Long-Term Evolution) and WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) are examples of 4G technologies that offered high-speed data transfer, low latency, and enhanced network capacity (Reference: Lee and Kim, 2020; Chen et al., 2022).
Currently, the telecommunications industry is witnessing the widespread adoption of 5G (Fifth Generation) technology, promising even more transformative capabilities. Researchers have delved into mmWave (millimeter-wave) frequencies, Massive MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output), and Network Slicing, enabling ultra-fast data speeds, low latency, and supporting the Internet of Things (IoT) (Reference: Wang et al., 2022; Zhang and Li, 2023).
This survey paper aims to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of the major classes in Telecommunication Technology – 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G. By analyzing the key characteristics and advancements of each generation, researchers can gain insights into the technological progression that has shaped modern mobile communication systems.
v. History of Development:
Some research domains like Cloud Computing, Big Data Management, Mobile Technology, Television technology etc. are linear. Such developments can be explained in chronological order.
One can find various options for a selected domain of research and it is this organization that is the challenging part of writing a survey paper.
The following points are to be elaborated for each paper which is surveyed as a part of writing the survey paper.
– What are you going to tell about the paper under consideration? – Research direction of the paper – Methods, mathematical modelling and approach or algorithms used to solve the problem: eg. Fuzzy logic, Gaussian process, neural network etc.
– Whether the paper considers theoretical issues of the concept or solves any application using the concept?
– Is the paper considered the continuation of another work? is it an improvement on another work?
– How validation of work is done i)through theoretical proofs? ii) simulation? iii)hardware test bed? or iv) real-life deployment?
– How is the work compared with other methods? and under what circumstances does the method under consideration perform better?
-On what parameters the paper under consideration stands apart from other papers like i)higher performance? ii) higher robustness? iii) lower computational complexity?
The author of each survey paper must be acknowledged by citing the paper referred to. In your survey do indicate the author names as well: Graham and Bell [3] have identified the importance of training, Patric et.al. [3] developed a simple methodology etc.
There are two reasons for this. One is the gratitude towards the authors, to whose work you are referring. Second, your reader will come to know the core people in the area in which he intends to carry out his future research. It is always good to mention in which particular country/University/Lab the work was carried out.
Survey Paper: Advancements in Cloud Computing: A Chronological Perspective
Cloud Computing has emerged as a transformative technology, revolutionizing the way computing resources are provisioned and utilized. This survey paper aims to explore the chronological advancements in Cloud Computing, focusing on key research directions, methodologies, and comparisons with other methods.
Paper 1: “Virtualization in Cloud Computing” – John et al. [1]
- In this paper, John et al. present the concept of virtualization and its application in Cloud Computing.
- Research Direction: The paper emphasizes the benefits of virtualization in enabling multi-tenancy and resource isolation in cloud environments.
- Methods: The paper discusses various virtualization techniques, including full virtualization and para-virtualization, to optimize performance and resource utilization.
- Application: The paper showcases how virtualization facilitates the seamless deployment of multiple applications on a shared physical infrastructure.
Paper 2: “MapReduce: Simplified Data Processing on Large Clusters” – Dean and Ghemawat [2]
- This influential paper introduces the MapReduce programming model for the efficient processing of large-scale data in Cloud Computing.
- Research Direction: The paper focuses on distributed data processing, fault tolerance, and scalability in Cloud environments.
- Methods: The MapReduce paradigm leverages parallelization and fault tolerance to process massive datasets.
- Application: The paper demonstrates how MapReduce can efficiently perform data-intensive tasks, such as web indexing and log processing.
Paper 3: “Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS) in Cloud Computing” – Smith and Patel [3]
- In this work, Smith and Patel explore the concept of providing Machine Learning capabilities as a service in the Cloud.
- Research Direction: The paper delves into the integration of Machine Learning algorithms in Cloud platforms to enable MLaaS.
- Methods: The paper discusses various ML algorithms, including neural networks and decision trees, used for predictive analytics.
- Application: The paper showcases real-life deployments of MLaaS for applications like fraud detection and sentiment analysis.
Paper 4: “Serverless Computing: The Next Paradigm Shift in Cloud Architecture” – Lee et al. [4]
- Lee et al. present the concept of serverless computing and its potential impact on Cloud architecture.
- Research Direction: The paper explores the benefits of serverless computing in terms of cost-efficiency and scalability.
- Methods: The paper explains the use of Function as a Service (FaaS) to deploy event-driven applications without managing server infrastructure.
- Application: The paper highlights the practical applications of serverless computing for IoT data processing and real-time data analytics.
Through theoretical analysis and simulation studies, these papers validate their proposed methodologies and demonstrate the effectiveness of their approaches. Each work compares its method with existing techniques, highlighting higher performance and lower computational complexity in specific scenarios (Reference: Johnson and Brown [5], Chen et al. [6]).
The acknowledgement of the authors’ contributions is essential to show gratitude and establish recognition within the research community. John et al. [1] conducted their work at the University of XYZ, while Lee and Patel [3] carried out their research at ABC Labs.
This chronological survey paper aims to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of the evolution of Cloud Computing, the core research directions, and the key contributors in this domain.
6. The “Conclusion” Section of the Survey Paper
The conclusion must answer the queries presented by your survey goals and objectives. The conclusion must be written in an interesting yet academic manner. No emotions should be attached to your conclusions but a commentary in the third person is required. Being the final portion of your survey paper, the conclusion serves as the researcher’s final say on the subject of the survey.
The conclusion must be a synthesis of the survey results with
i) an interpretation of each result
ii) the proposal of a course of action based on the result and
iii) a solution to the issues that emerged from the survey.
The tone of the conclusion should match that of the results and the rest of the data collection process. The conclusion should be able to wrap up the entire survey from the formulation of survey goals up to the satisfaction of such objectives.
After roughly two decades of research on leaf image analysis for pathological issues, many elements of pathological issues associated with leaves are well understood. In particular, accurate and efficient algorithms for leaf-diseased spot extraction are now well known.
As a result, during the past few years, we have seen the focus turn from the fundamentals of disease spot extraction to more difficult problems such as, the type of the leaf disease and the stage of the leaf disease. Few algorithms in this context are available. However, a comprehensive evaluation and comparison of these more advanced algorithms has yet to be done.
One of our goals in this review is to consolidate existing quantitative results and to carry out comparative analyses. We believe that much of the leaf image analysis for pathological work in the coming decade should and will be bolstered by more complete quantitative performance evaluations. The recent article by Wimar [10] is a promising first step.
Perhaps the most practically significant advance in the last decade has been the appearance of machine learning algorithms. However current implementation of Machine learning algorithms is still relatively simplistic. More demanding potential applications require algorithms to be very precise and reliable. This remains a challenging research topic that we predict will see progress in the coming decade.
For further details on writing the conclusion section, you can visit my blog post on : Art of Writing Conclusion Section to your Research Paper
Example of a Survey Paper for a Specific Domain
How to write a survey paper in computer science domain.
Along with my research scholar, I have written a survey paper which is published in one of the most popular journals in the computer science domain. Please visit the link for the full survey paper.
Systematic analysis of satellite image-based land cover classification techniques: literature review and challenges, February 2019, International Journal of Computers and Applications 43(4):1-10
Doi: 10.1080/1206212x.2019.1573946.
Before We Close….
While writing a blog post, I realized I couldn’t cover everything about crafting survey papers. That’s where “WRITING LITERATURE SURVEY PAPER: A STEP BY STEP GUIDE” comes in. It’s an incredible book that simplifies the writing process using a single example, “The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Diagnostics.” Imagine having a friendly mentor explaining each step. Although a blog post can’t teach everything, this book breaks it down so you can become a survey paper writing expert.
A survey paper plays a crucial role in providing readers with a systematic overview of existing research, methodologies, and advancements in a specific field. By adhering to the outlined steps, the survey paper can effectively convey valuable insights and contribute to the understanding of the chosen research domain.
Frequently Asked Questions:
How many references do i need for 2000 words survey paper.
At least 10 quality publications need to be referred for a 2000-word survey paper.
Whether survey papers are counted for the Ph.D. submission?
No. Survey papers are not counted for Ph.D. thesis submission.
Whether Scopus indexed journals accept survey papers for publication?
Yes. Many Scopus-indexed journals accept high-quality survey papers for publication.
What is the difference between a Survey Paper and a Review Paper?
In short, a Survey Paper provides a comprehensive summary of existing research on a specific topic, presenting the state-of-the-art and research trends. On the other hand, a Review Paper offers a critical evaluation and analysis of the literature, identifying gaps and suggesting future research directions.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- Do Review Papers Count for the Award of a PhD Degree?
- Vinay Kabadi, University of Melbourne, Interview on Award-Winning Research
- Do You Need Publications for a PhD Application? The Essential Guide for Applicants
- Research Internships @ Finland
- A Stepwise Guide to Update/Reissue/Modify a Patent
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analysing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps:
- Determine who will participate in the survey
- Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person)
- Design the survey questions and layout
- Distribute the survey
- Analyse the responses
- Write up the results
Surveys are a flexible method of data collection that can be used in many different types of research .
Table of contents
What are surveys used for, step 1: define the population and sample, step 2: decide on the type of survey, step 3: design the survey questions, step 4: distribute the survey and collect responses, step 5: analyse the survey results, step 6: write up the survey results, frequently asked questions about surveys.
Surveys are used as a method of gathering data in many different fields. They are a good choice when you want to find out about the characteristics, preferences, opinions, or beliefs of a group of people.
Common uses of survey research include:
- Social research: Investigating the experiences and characteristics of different social groups
- Market research: Finding out what customers think about products, services, and companies
- Health research: Collecting data from patients about symptoms and treatments
- Politics: Measuring public opinion about parties and policies
- Psychology: Researching personality traits, preferences, and behaviours
Surveys can be used in both cross-sectional studies , where you collect data just once, and longitudinal studies , where you survey the same sample several times over an extended period.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Before you start conducting survey research, you should already have a clear research question that defines what you want to find out. Based on this question, you need to determine exactly who you will target to participate in the survey.
Populations
The target population is the specific group of people that you want to find out about. This group can be very broad or relatively narrow. For example:
- The population of Brazil
- University students in the UK
- Second-generation immigrants in the Netherlands
- Customers of a specific company aged 18 to 24
- British transgender women over the age of 50
Your survey should aim to produce results that can be generalised to the whole population. That means you need to carefully define exactly who you want to draw conclusions about.
It’s rarely possible to survey the entire population of your research – it would be very difficult to get a response from every person in Brazil or every university student in the UK. Instead, you will usually survey a sample from the population.
The sample size depends on how big the population is. You can use an online sample calculator to work out how many responses you need.
There are many sampling methods that allow you to generalise to broad populations. In general, though, the sample should aim to be representative of the population as a whole. The larger and more representative your sample, the more valid your conclusions.
There are two main types of survey:
- A questionnaire , where a list of questions is distributed by post, online, or in person, and respondents fill it out themselves
- An interview , where the researcher asks a set of questions by phone or in person and records the responses
Which type you choose depends on the sample size and location, as well as the focus of the research.
Questionnaires
Sending out a paper survey by post is a common method of gathering demographic information (for example, in a government census of the population).
- You can easily access a large sample.
- You have some control over who is included in the sample (e.g., residents of a specific region).
- The response rate is often low.
Online surveys are a popular choice for students doing dissertation research , due to the low cost and flexibility of this method. There are many online tools available for constructing surveys, such as SurveyMonkey and Google Forms .
- You can quickly access a large sample without constraints on time or location.
- The data is easy to process and analyse.
- The anonymity and accessibility of online surveys mean you have less control over who responds.
If your research focuses on a specific location, you can distribute a written questionnaire to be completed by respondents on the spot. For example, you could approach the customers of a shopping centre or ask all students to complete a questionnaire at the end of a class.
- You can screen respondents to make sure only people in the target population are included in the sample.
- You can collect time- and location-specific data (e.g., the opinions of a shop’s weekday customers).
- The sample size will be smaller, so this method is less suitable for collecting data on broad populations.
Oral interviews are a useful method for smaller sample sizes. They allow you to gather more in-depth information on people’s opinions and preferences. You can conduct interviews by phone or in person.
- You have personal contact with respondents, so you know exactly who will be included in the sample in advance.
- You can clarify questions and ask for follow-up information when necessary.
- The lack of anonymity may cause respondents to answer less honestly, and there is more risk of researcher bias.
Like questionnaires, interviews can be used to collect quantitative data : the researcher records each response as a category or rating and statistically analyses the results. But they are more commonly used to collect qualitative data : the interviewees’ full responses are transcribed and analysed individually to gain a richer understanding of their opinions and feelings.
Next, you need to decide which questions you will ask and how you will ask them. It’s important to consider:
- The type of questions
- The content of the questions
- The phrasing of the questions
- The ordering and layout of the survey
Open-ended vs closed-ended questions
There are two main forms of survey questions: open-ended and closed-ended. Many surveys use a combination of both.
Closed-ended questions give the respondent a predetermined set of answers to choose from. A closed-ended question can include:
- A binary answer (e.g., yes/no or agree/disagree )
- A scale (e.g., a Likert scale with five points ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree )
- A list of options with a single answer possible (e.g., age categories)
- A list of options with multiple answers possible (e.g., leisure interests)
Closed-ended questions are best for quantitative research . They provide you with numerical data that can be statistically analysed to find patterns, trends, and correlations .
Open-ended questions are best for qualitative research. This type of question has no predetermined answers to choose from. Instead, the respondent answers in their own words.
Open questions are most common in interviews, but you can also use them in questionnaires. They are often useful as follow-up questions to ask for more detailed explanations of responses to the closed questions.
The content of the survey questions
To ensure the validity and reliability of your results, you need to carefully consider each question in the survey. All questions should be narrowly focused with enough context for the respondent to answer accurately. Avoid questions that are not directly relevant to the survey’s purpose.
When constructing closed-ended questions, ensure that the options cover all possibilities. If you include a list of options that isn’t exhaustive, you can add an ‘other’ field.
Phrasing the survey questions
In terms of language, the survey questions should be as clear and precise as possible. Tailor the questions to your target population, keeping in mind their level of knowledge of the topic.
Use language that respondents will easily understand, and avoid words with vague or ambiguous meanings. Make sure your questions are phrased neutrally, with no bias towards one answer or another.
Ordering the survey questions
The questions should be arranged in a logical order. Start with easy, non-sensitive, closed-ended questions that will encourage the respondent to continue.
If the survey covers several different topics or themes, group together related questions. You can divide a questionnaire into sections to help respondents understand what is being asked in each part.
If a question refers back to or depends on the answer to a previous question, they should be placed directly next to one another.
Before you start, create a clear plan for where, when, how, and with whom you will conduct the survey. Determine in advance how many responses you require and how you will gain access to the sample.
When you are satisfied that you have created a strong research design suitable for answering your research questions, you can conduct the survey through your method of choice – by post, online, or in person.
There are many methods of analysing the results of your survey. First you have to process the data, usually with the help of a computer program to sort all the responses. You should also cleanse the data by removing incomplete or incorrectly completed responses.
If you asked open-ended questions, you will have to code the responses by assigning labels to each response and organising them into categories or themes. You can also use more qualitative methods, such as thematic analysis , which is especially suitable for analysing interviews.
Statistical analysis is usually conducted using programs like SPSS or Stata. The same set of survey data can be subject to many analyses.
Finally, when you have collected and analysed all the necessary data, you will write it up as part of your thesis, dissertation , or research paper .
In the methodology section, you describe exactly how you conducted the survey. You should explain the types of questions you used, the sampling method, when and where the survey took place, and the response rate. You can include the full questionnaire as an appendix and refer to it in the text if relevant.
Then introduce the analysis by describing how you prepared the data and the statistical methods you used to analyse it. In the results section, you summarise the key results from your analysis.
A Likert scale is a rating scale that quantitatively assesses opinions, attitudes, or behaviours. It is made up of four or more questions that measure a single attitude or trait when response scores are combined.
To use a Likert scale in a survey , you present participants with Likert-type questions or statements, and a continuum of items, usually with five or seven possible responses, to capture their degree of agreement.
Individual Likert-type questions are generally considered ordinal data , because the items have clear rank order, but don’t have an even distribution.
Overall Likert scale scores are sometimes treated as interval data. These scores are considered to have directionality and even spacing between them.
The type of data determines what statistical tests you should use to analyse your data.
A questionnaire is a data collection tool or instrument, while a survey is an overarching research method that involves collecting and analysing data from people using questionnaires.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 20 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/surveys/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, qualitative vs quantitative research | examples & methods, construct validity | definition, types, & examples, what is a likert scale | guide & examples.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Survey Research: Definition, Examples and Methods

Survey Research is a quantitative research method used for collecting data from a set of respondents. It has been perhaps one of the most used methodologies in the industry for several years due to the multiple benefits and advantages that it has when collecting and analyzing data.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Research
In this article, you will learn everything about survey research, such as types, methods, and examples.
Survey Research Definition
Survey Research is defined as the process of conducting research using surveys that researchers send to survey respondents. The data collected from surveys is then statistically analyzed to draw meaningful research conclusions. In the 21st century, every organization’s eager to understand what their customers think about their products or services and make better business decisions. Researchers can conduct research in multiple ways, but surveys are proven to be one of the most effective and trustworthy research methods. An online survey is a method for extracting information about a significant business matter from an individual or a group of individuals. It consists of structured survey questions that motivate the participants to respond. Creditable survey research can give these businesses access to a vast information bank. Organizations in media, other companies, and even governments rely on survey research to obtain accurate data.
The traditional definition of survey research is a quantitative method for collecting information from a pool of respondents by asking multiple survey questions. This research type includes the recruitment of individuals collection, and analysis of data. It’s useful for researchers who aim to communicate new features or trends to their respondents.
LEARN ABOUT: Level of Analysis Generally, it’s the primary step towards obtaining quick information about mainstream topics and conducting more rigorous and detailed quantitative research methods like surveys/polls or qualitative research methods like focus groups/on-call interviews can follow. There are many situations where researchers can conduct research using a blend of both qualitative and quantitative strategies.
LEARN ABOUT: Survey Sampling
Survey Research Methods
Survey research methods can be derived based on two critical factors: Survey research tool and time involved in conducting research. There are three main survey research methods, divided based on the medium of conducting survey research:
- Online/ Email: Online survey research is one of the most popular survey research methods today. The survey cost involved in online survey research is extremely minimal, and the responses gathered are highly accurate.
- Phone: Survey research conducted over the telephone ( CATI survey ) can be useful in collecting data from a more extensive section of the target population. There are chances that the money invested in phone surveys will be higher than other mediums, and the time required will be higher.
- Face-to-face: Researchers conduct face-to-face in-depth interviews in situations where there is a complicated problem to solve. The response rate for this method is the highest, but it can be costly.
Further, based on the time taken, survey research can be classified into two methods:
- Longitudinal survey research: Longitudinal survey research involves conducting survey research over a continuum of time and spread across years and decades. The data collected using this survey research method from one time period to another is qualitative or quantitative. Respondent behavior, preferences, and attitudes are continuously observed over time to analyze reasons for a change in behavior or preferences. For example, suppose a researcher intends to learn about the eating habits of teenagers. In that case, he/she will follow a sample of teenagers over a considerable period to ensure that the collected information is reliable. Often, cross-sectional survey research follows a longitudinal study .
- Cross-sectional survey research: Researchers conduct a cross-sectional survey to collect insights from a target audience at a particular time interval. This survey research method is implemented in various sectors such as retail, education, healthcare, SME businesses, etc. Cross-sectional studies can either be descriptive or analytical. It is quick and helps researchers collect information in a brief period. Researchers rely on the cross-sectional survey research method in situations where descriptive analysis of a subject is required.
Survey research also is bifurcated according to the sampling methods used to form samples for research: Probability and Non-probability sampling. Every individual in a population should be considered equally to be a part of the survey research sample. Probability sampling is a sampling method in which the researcher chooses the elements based on probability theory. The are various probability research methods, such as simple random sampling , systematic sampling, cluster sampling, stratified random sampling, etc. Non-probability sampling is a sampling method where the researcher uses his/her knowledge and experience to form samples.
LEARN ABOUT: Survey Sample Sizes
The various non-probability sampling techniques are :
- Convenience sampling
- Snowball sampling
- Consecutive sampling
- Judgemental sampling
- Quota sampling
Process of implementing survey research methods:
- Decide survey questions: Brainstorm and put together valid survey questions that are grammatically and logically appropriate. Understanding the objective and expected outcomes of the survey helps a lot. There are many surveys where details of responses are not as important as gaining insights about what customers prefer from the provided options. In such situations, a researcher can include multiple-choice questions or closed-ended questions . Whereas, if researchers need to obtain details about specific issues, they can consist of open-ended questions in the questionnaire. Ideally, the surveys should include a smart balance of open-ended and closed-ended questions. Use survey questions like Likert Scale , Semantic Scale, Net Promoter Score question, etc., to avoid fence-sitting.
LEARN ABOUT: System Usability Scale
- Finalize a target audience: Send out relevant surveys as per the target audience and filter out irrelevant questions as per the requirement. The survey research will be instrumental in case the target population decides on a sample. This way, results can be according to the desired market and be generalized to the entire population.
LEARN ABOUT: Testimonial Questions
- Send out surveys via decided mediums: Distribute the surveys to the target audience and patiently wait for the feedback and comments- this is the most crucial step of the survey research. The survey needs to be scheduled, keeping in mind the nature of the target audience and its regions. Surveys can be conducted via email, embedded in a website, shared via social media, etc., to gain maximum responses.
- Analyze survey results: Analyze the feedback in real-time and identify patterns in the responses which might lead to a much-needed breakthrough for your organization. GAP, TURF Analysis , Conjoint analysis, Cross tabulation, and many such survey feedback analysis methods can be used to spot and shed light on respondent behavior. Researchers can use the results to implement corrective measures to improve customer/employee satisfaction.
Reasons to conduct survey research
The most crucial and integral reason for conducting market research using surveys is that you can collect answers regarding specific, essential questions. You can ask these questions in multiple survey formats as per the target audience and the intent of the survey. Before designing a study, every organization must figure out the objective of carrying this out so that the study can be structured, planned, and executed to perfection.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
Questions that need to be on your mind while designing a survey are:
- What is the primary aim of conducting the survey?
- How do you plan to utilize the collected survey data?
- What type of decisions do you plan to take based on the points mentioned above?
There are three critical reasons why an organization must conduct survey research.
- Understand respondent behavior to get solutions to your queries: If you’ve carefully curated a survey, the respondents will provide insights about what they like about your organization as well as suggestions for improvement. To motivate them to respond, you must be very vocal about how secure their responses will be and how you will utilize the answers. This will push them to be 100% honest about their feedback, opinions, and comments. Online surveys or mobile surveys have proved their privacy, and due to this, more and more respondents feel free to put forth their feedback through these mediums.
- Present a medium for discussion: A survey can be the perfect platform for respondents to provide criticism or applause for an organization. Important topics like product quality or quality of customer service etc., can be put on the table for discussion. A way you can do it is by including open-ended questions where the respondents can write their thoughts. This will make it easy for you to correlate your survey to what you intend to do with your product or service.
- Strategy for never-ending improvements: An organization can establish the target audience’s attributes from the pilot phase of survey research . Researchers can use the criticism and feedback received from this survey to improve the product/services. Once the company successfully makes the improvements, it can send out another survey to measure the change in feedback keeping the pilot phase the benchmark. By doing this activity, the organization can track what was effectively improved and what still needs improvement.
Survey Research Scales
There are four main scales for the measurement of variables:
- Nominal Scale: A nominal scale associates numbers with variables for mere naming or labeling, and the numbers usually have no other relevance. It is the most basic of the four levels of measurement.
- Ordinal Scale: The ordinal scale has an innate order within the variables along with labels. It establishes the rank between the variables of a scale but not the difference value between the variables.
- Interval Scale: The interval scale is a step ahead in comparison to the other two scales. Along with establishing a rank and name of variables, the scale also makes known the difference between the two variables. The only drawback is that there is no fixed start point of the scale, i.e., the actual zero value is absent.
- Ratio Scale: The ratio scale is the most advanced measurement scale, which has variables that are labeled in order and have a calculated difference between variables. In addition to what interval scale orders, this scale has a fixed starting point, i.e., the actual zero value is present.
Benefits of survey research
In case survey research is used for all the right purposes and is implemented properly, marketers can benefit by gaining useful, trustworthy data that they can use to better the ROI of the organization.
Other benefits of survey research are:
- Minimum investment: Mobile surveys and online surveys have minimal finance invested per respondent. Even with the gifts and other incentives provided to the people who participate in the study, online surveys are extremely economical compared to paper-based surveys.
- Versatile sources for response collection: You can conduct surveys via various mediums like online and mobile surveys. You can further classify them into qualitative mediums like focus groups , and interviews and quantitative mediums like customer-centric surveys. Due to the offline survey response collection option, researchers can conduct surveys in remote areas with limited internet connectivity. This can make data collection and analysis more convenient and extensive.
- Reliable for respondents: Surveys are extremely secure as the respondent details and responses are kept safeguarded. This anonymity makes respondents answer the survey questions candidly and with absolute honesty. An organization seeking to receive explicit responses for its survey research must mention that it will be confidential.
Survey research design
Researchers implement a survey research design in cases where there is a limited cost involved and there is a need to access details easily. This method is often used by small and large organizations to understand and analyze new trends, market demands, and opinions. Collecting information through tactfully designed survey research can be much more effective and productive than a casually conducted survey.
There are five stages of survey research design:
- Decide an aim of the research: There can be multiple reasons for a researcher to conduct a survey, but they need to decide a purpose for the research. This is the primary stage of survey research as it can mold the entire path of a survey, impacting its results.
- Filter the sample from target population: Who to target? is an essential question that a researcher should answer and keep in mind while conducting research. The precision of the results is driven by who the members of a sample are and how useful their opinions are. The quality of respondents in a sample is essential for the results received for research and not the quantity. If a researcher seeks to understand whether a product feature will work well with their target market, he/she can conduct survey research with a group of market experts for that product or technology.
- Zero-in on a survey method: Many qualitative and quantitative research methods can be discussed and decided. Focus groups, online interviews, surveys, polls, questionnaires, etc. can be carried out with a pre-decided sample of individuals.
- Design the questionnaire: What will the content of the survey be? A researcher is required to answer this question to be able to design it effectively. What will the content of the cover letter be? Or what are the survey questions of this questionnaire? Understand the target market thoroughly to create a questionnaire that targets a sample to gain insights about a survey research topic.
- Send out surveys and analyze results: Once the researcher decides on which questions to include in a study, they can send it across to the selected sample . Answers obtained from this survey can be analyzed to make product-related or marketing-related decisions.
Survey examples: 10 tips to design the perfect research survey
Picking the right survey design can be the key to gaining the information you need to make crucial decisions for all your research. It is essential to choose the right topic, choose the right question types, and pick a corresponding design. If this is your first time creating a survey, it can seem like an intimidating task. But with QuestionPro, each step of the process is made simple and easy.
Below are 10 Tips To Design The Perfect Research Survey:
- Set your SMART goals: Before conducting any market research or creating a particular plan, set your SMART Goals . What is that you want to achieve with the survey? How will you measure it promptly, and what are the results you are expecting?
- Choose the right questions: Designing a survey can be a tricky task. Asking the right questions may help you get the answers you are looking for and ease the task of analyzing. So, always choose those specific questions – relevant to your research.
- Begin your survey with a generalized question: Preferably, start your survey with a general question to understand whether the respondent uses the product or not. That also provides an excellent base and intro for your survey.
- Enhance your survey: Choose the best, most relevant, 15-20 questions. Frame each question as a different question type based on the kind of answer you would like to gather from each. Create a survey using different types of questions such as multiple-choice, rating scale, open-ended, etc. Look at more survey examples and four measurement scales every researcher should remember.
- Prepare yes/no questions: You may also want to use yes/no questions to separate people or branch them into groups of those who “have purchased” and those who “have not yet purchased” your products or services. Once you separate them, you can ask them different questions.
- Test all electronic devices: It becomes effortless to distribute your surveys if respondents can answer them on different electronic devices like mobiles, tablets, etc. Once you have created your survey, it’s time to TEST. You can also make any corrections if needed at this stage.
- Distribute your survey: Once your survey is ready, it is time to share and distribute it to the right audience. You can share handouts and share them via email, social media, and other industry-related offline/online communities.
- Collect and analyze responses: After distributing your survey, it is time to gather all responses. Make sure you store your results in a particular document or an Excel sheet with all the necessary categories mentioned so that you don’t lose your data. Remember, this is the most crucial stage. Segregate your responses based on demographics, psychographics, and behavior. This is because, as a researcher, you must know where your responses are coming from. It will help you to analyze, predict decisions, and help write the summary report.
- Prepare your summary report: Now is the time to share your analysis. At this stage, you should mention all the responses gathered from a survey in a fixed format. Also, the reader/customer must get clarity about your goal, which you were trying to gain from the study. Questions such as – whether the product or service has been used/preferred or not. Do respondents prefer some other product to another? Any recommendations?
Having a tool that helps you carry out all the necessary steps to carry out this type of study is a vital part of any project. At QuestionPro, we have helped more than 10,000 clients around the world to carry out data collection in a simple and effective way, in addition to offering a wide range of solutions to take advantage of this data in the best possible way.
From dashboards, advanced analysis tools, automation, and dedicated functions, in QuestionPro, you will find everything you need to execute your research projects effectively. Uncover insights that matter the most!
MORE LIKE THIS

Unlocking Creativity With 10 Top Idea Management Software
Mar 23, 2024

20 Best Website Optimization Tools to Improve Your Website
Mar 22, 2024

15 Best Digital Customer Experience Software of 2024

15 Best Product Experience Software of 2024
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

Steps to Write a Survey Paper/Review Article

What are the steps to write a survey paper/review article is a very common query of all time asked by most of the researchers from search engines. Before, directly going to tips of writing a survey paper one should know what is survey paper/review article? Review article, Survey paper is synonym, paper, article is also synonym and are used interchangeably.
Survey/review paper is an article which summarizes existing papers in an intuitive way, in spite of providing new facts, analysis or experiments. Or “A paper that abridges and sorted out late research brings about a novel way that incorporates and adds understanding to work in the field. A review article accepts general information of the domain; it underscores the characterization of the current writing, creating a viewpoint on the zone, and assessing patterns.” They are usually published in the review journals and are written by expert researchers in that area of research. Mostly, journal chief editors invite survey papers from the expert researchers in a specific field, but they can also be written and published by new researchers if quality is not compromised.
One questions comes to mind that what is the benefit of writing a review article? A review article/survey paper is a service towards the scientific community; it means that you are writing paper for them. As, it makes easy for new researchers or the researchers who want to change their area of research or want to work on some new area by providing summary of existing papers by stating their advantages and disadvantages and future research directions. Majority of researchers write survey paper after consulting different papers but most important thing is to understand the scientific topic, its flow and future insights. You must make sure that main subject area is going to be covered in your review paper. Moreover, make sure to write new and original review paper instead of copying someone else’s idea, see if there is any existing survey paper on the same or similar topic, then first point out the limitations of that paper and then state your review article contributions. Survey/review paper can be written individually as well as by a group of researchers.
What are the objectives/ingredients of Survey paper? Provide readers with a perspective of existing work that is overall well composed, thorough and far reaching
- All points of interest must be incorporated, which one’s ought/should think about.
- Make beyond any doubt to cover all existing material
- Logical structure of association among existing studies should be provided
- Summarize each logical structure part in 5-8 papers on a specific sub-category
- State of the craft view of all existing papers by mentioning their advantages and disadvantages with other existing papers or provide a discriminating appraisal of the work that has been carried out
- Include your critique on the hugeness of the methodology and the results introduced in each paper
- Include a dialog on future directions and interesting challenges in different area of that specific domain
Things to be Ponder:
- Everything you compose in review paper must be in your words. There is a common misconception that you can use other wordings while writing a review article. You need to discuss ideas in your own words also must provide reference
- In case there are definitions you can write then in “” and provide proper references to them.
- All thoughts, rewards of other individuals’ words must be accurately credited in the text of the paper and in the references
How to Pick Articles to include in a review article?
When picking papers to peruse – attempt to:
- Pick a latest review of the field so you can rapidly pick up an outline
- Pick a paper that can provide reasonable materials and long clarification, even though they may not be cutting-edge papers sometime
- Pick papers that are cited in references of each other in the same field, so you can compose a significant study out of them
- Include papers from well-known Journals, conferences and workshops
- Include “first” or “foundational” or State of the art papers in the field (as demonstrated in other existing papers
- Include latest papers
- Include older paper also but see they should have been having a good number of citations provided in google scholar
There are different steps to write a survey paper/review article that we will discuss below.
Title Page of Survey Paper:
The title page of survey paper should include following information.
- The main topic of the survey or review paper
- Survey or review keyword
- If you are working in a group than make sure to write names of the group members with their affiliation and email addresses
- It should cover abstract but make sure to write your abstract of minimum 150 to maximum 300 words. The abstract should provide the motivation or need for writing a survey and key contributions of your survey paper
- Three to six keywords which are related to core material of that survey
Introduction:
Your introduction should explain about the background and motivation why you selected the certain topic. Afterwards, summarize your research domain in a precise manner. then summary of existing proposed approaches to the problem and conclude the results. You should discuss the limitation of any existing survey article on same or similar kind of topic to show the need of your survey article. Then you should provide 3-5 key contributions of your work. It’s also good to provide a diagram to show the flow of research in the topic discussed in the survey article, preferably a chronological pictorial representation of the methods or approaches with respect to some logical categorization (See example https://www.researchgate.net/publication/215904200_Probabilistic_Topic_Models_Survey ). Make sure not to forget any step in the introduction while writing review or survey paper.
Concepts and Terminologies:
Survey paper is like a small book on a specific topic and you want the reader to read it and get all the things are one place just like a big shopping mall. So you should provide the key concepts and terminologies related to the topic of the survey. Example of this is provided on link below.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/215904200_Probabilistic_Topic_Models_Survey
Methods or Approaches:
This is very important part of your review article. You need to categorize existing papers and then create a logical flow in each category. You must discuss the main idea, proposed method, data sets, data variables, results, findings and limitations of each method or group of methods. You can do this for each paper individually or for group of similar methods also. One of very important thing is to provide summary tables for each category. Only writing summary of methods in paragraphs is nothing which is useful or will convince the reviewer to accept your paper at a high-quality journal, conference or workshop. Make sure to explain your body work (whole method, process) in a vivid and clear manner that anyone can understand later on. You can also add about your personal experience while working on your selected approaches, it’s totally up to you. A very nice example can be seen in the following paper.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322275289_Ranking_authors_in_academic_social_networks_A_survey
Datasets and Performance Measures:
This section provides the datasets used in that specific research domain. A summary statistic of each dataset can be of great importance to make it useful for readers. Performance measurement of testing of any proposed framework / method / technique /approach is a must in most of the papers. There are different performance evaluation methods adopted for different solutions. Providing the topic specific performance measures can be a very nice addition to a survey paper. (See example in the following paper
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/215904200_Probabilistic_Topic_Models_Survey ).
Future Challenges and Directions:
This part of survey paper is hear of the paper. The limitations are identified by different papers for other paper or even by themselves. They are usually stated in the literature review or papers or in the conclusions and future directions part. It’s a must to provide several challenging future directions based on the limitations in existing papers. Its good to make subheadings in this section with each subheading for a specific limitation. Its also important to provide the references to the papers who provided this limitation. In case the limitations if provided by you then there is no need to give any reference but that is a rare case in most of the survey articles. The future directions should be useful and clear. Let us say you want to work on that area then you should be the first person to select one of the future direction from your own written survey and then providing the solution for that specific challenge or limitation. A review article without clear future challenges can not be published at high quality venue and is only suitable for dustbin, harsh but you know truth always hurts. (See example survey paper for writing future challenges and directions https://www.researchgate.net/publication/310711981_Modelling_to_identify_influential_bloggers_in_the_blogosphere_A_survey )
Conclusion:
Explain what you can conclude from your research but keep it precise. Based on the sections you have written so far tell the reader what can you conclude for the summary tables you have made. Also give few tips for other researchers that can help them in future. Conclusion should not be more than one or two paragraphs.
References: Make sure to list out all the sources in the reference section of your review paper. Finally, citing references in the text should be done carefully. Avoid adding unknown papers, old but less cited papers, false and fake references in your survey paper because it can demolish your whole effort easily. Remember, a good survey paper written on a mature research area should have atleast 50 references, although a survey paper written on new or emerging topic can be with less than 50 references. Rules for Citing a Reference are as follows.
- All authors name
- Title of Paper
- Details about Paper, such as, journal (name, volume, issue, pages), conference (name, pages), workshop (name, pages)
- Year of publishing, etc.
- In case you provide a web URL in reference in brackets provide its visiting date also.
Keep in mind you must sometime follow specific referencing style depending upon the venue or publisher requirement, but still you will need to provide complete details as above in that format.
Please keep in mind that steps to write a survey paper/review article are completely different form writing a research paper/article which is not a survey/review. Steps to write a survey paper/review article are provided in detail as well the necessary information related to it. In case you have some tips to further improve the survey paper, please do share with us. As scientific process of doing research can vary a bit for different domains so its really nice if other researchers can benefit from your experiences.
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

14 Comments Already
thanx,it was nice!!!
Thanks it’s very useful but can you give us an example
Below are 3 example survey papers. https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=k6XkGhcAAAAJ&citation_for_view=k6XkGhcAAAAJ:9yKSN-GCB0IC https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=k6XkGhcAAAAJ&sortby=pubdate&citation_for_view=k6XkGhcAAAAJ:isC4tDSrTZIC https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=k6XkGhcAAAAJ&sortby=pubdate&citation_for_view=k6XkGhcAAAAJ:TQgYirikUcIC
Thanks, it is very useful
thank u very much. the article is very useful
Thanks that was very useful
Thanks. Very well explained and very useful.
you are very welcome.
Thank you very much .your guidelines are appreciable.
Nice to read..very helpful for beginners.
Very welcome Debasish Please share with fellows if you think it will be helpful to them as well.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.35(45); 2020 Nov 23

Reporting Survey Based Studies – a Primer for Authors
Prithvi sanjeevkumar gaur.
1 Smt. Kashibai Navale Medical College and General Hospital, Pune, India.
Olena Zimba
2 Department of Internal Medicine No. 2, Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical University, Lviv, Ukraine.
Vikas Agarwal
3 Department Clinical Immunology and Rheumatology, Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India.
Latika Gupta
Associated data.
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has led to a massive rise in survey-based research. The paucity of perspicuous guidelines for conducting surveys may pose a challenge to the conduct of ethical, valid and meticulous research. The aim of this paper is to guide authors aiming to publish in scholarly journals regarding the methods and means to carry out surveys for valid outcomes. The paper outlines the various aspects, from planning, execution and dissemination of surveys followed by the data analysis and choosing target journals. While providing a comprehensive understanding of the scenarios most conducive to carrying out a survey, the role of ethical approval, survey validation and pilot testing, this brief delves deeper into the survey designs, methods of dissemination, the ways to secure and maintain data anonymity, the various analytical approaches, the reporting techniques and the process of choosing the appropriate journal. Further, the authors analyze retracted survey-based studies and the reasons for the same. This review article intends to guide authors to improve the quality of survey-based research by describing the essential tools and means to do the same with the hope to improve the utility of such studies.
Graphical Abstract

INTRODUCTION
Surveys are the principal method used to address topics that require individual self-report about beliefs, knowledge, attitudes, opinions or satisfaction, which cannot be assessed using other approaches. 1 This research method allows information to be collected by asking a set of questions on a specific topic to a subset of people and generalizing the results to a larger population. Assessment of opinions in a valid and reliable way require clear, structured and precise reporting of results. This is possible with a survey based out of a meticulous design, followed by validation and pilot testing. 2 The aim of this opinion piece is to provide practical advice to conduct survey-based research. It details the ethical and methodological aspects to be undertaken while performing a survey, the online platforms available for distributing survey, and the implications of survey-based research.
Survey-based research is a means to obtain quick data, and such studies are relatively easy to conduct and analyse, and are cost-effective (under a majority of the circumstances). 3 These are also one of the most convenient methods of obtaining data about rare diseases. 4 With major technological advancements and improved global interconnectivity, especially during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, surveys have surpassed other means of research due to their distinctive advantage of a wider reach, including respondents from various parts of the world having diverse cultures and geographically disparate locations. Moreover, survey-based research allows flexibility to the investigator and respondent alike. 5 While the investigator(s) may tailor the survey dates and duration as per their availability, the respondents are allowed the convenience of responding to the survey at ease, in the comfort of their homes, and at a time when they can answer the questions with greater focus and to the best of their abilities. 6 Respondent biases inherent to environmental stressors can be significantly reduced by this approach. 5 It also allows responses across time-zones, which may be a major impediment to other forms of research or data-collection. This allows distant placement of the investigator from the respondents.
Various digital tools are now available for designing surveys ( Table 1 ). 7 Most of these are free with separate premium paid options. The analysis of data can be made simpler and cleaning process almost obsolete by minimising open-ended answer choices. 8 Close-ended answers makes data collection and analysis efficient, by generating an excel which can be directly accessed and analysed. 9 Minimizing the number of questions and making all questions mandatory can further aid this process by bringing uniformity to the responses and analysis simpler. Surveys are arguably also the most engaging form of research, conditional to the skill of the investigator.
Q/t = questions per typeform, A/m = answers per month, Q/s = questions per survey, A/s = answers per survey, NA = not applicable, NPS = net promoter score.
Data protection laws now mandate anonymity while collecting data for most surveys, particularly when they are exempt from ethical review. 10 , 11 Anonymization has the potential to reduce (or at times even eliminate) social desirability bias which gains particular relevance when targeting responses from socially isolated or vulnerable communities (e.g. LGBTQ and low socio-economic strata communities) or minority groups (religious, ethnic and medical) or controversial topics (drug abuse, using language editing software).
Moreover, surveys could be the primary methodology to explore a hypothesis until it evolves into a more sophisticated and partly validated idea after which it can be probed further in a systematic and structured manner using other research methods.
The aim of this paper is to reduce the incorrect reporting of surveys. The paper also intends to inform researchers of the various aspects of survey-based studies and the multiple points that need to be taken under consideration while conducting survey-based research.
SURVEYS IN THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC
The COVID-19 has led to a distinctive rise in survey-based research. 12 The need to socially distance amid widespread lockdowns reduced patient visits to the hospital and brought most other forms of research to a standstill in the early pandemic period. A large number of level-3 bio-safety laboratories are being engaged for research pertaining to COVID-19, thereby limiting the options to conduct laboratory-based research. 13 , 14 Therefore, surveys appear to be the most viable option for researchers to explore hypotheses related to the situation and its impact in such times. 15
LIMITATIONS WHILE CONDUCTING SURVEY-BASED RESEARCH
Designing a fine survey is an arduous task and requires skill even though clear guidelines are available in regard to the same. Survey design requires extensive thoughtfulness on the core questions (based on the hypothesis or the primary research question), with consideration of all possible answers, and the inclusion of open-ended options to allow recording other possibilities. A survey should be robust, in regard to the questions gathered and the answer choices available, it must be validated, and pilot tested. 16 The survey design may be supplanted with answer choices tailored for the convenience of the responder, to reduce the effort while making it more engaging. Survey dissemination and engagement of respondents also requires experience and skill. 17
Furthermore, the absence of an interviewer prevents us from gaining clarification on responses of open-ended questions if any. Internet surveys are also prone to survey fraud by erroneous reporting. Hence, anonymity of surveys is a boon and a bane. The sample sizes are skewed as it lacks representation of population absent on the Internet like the senile or the underprivileged. The illiterate population also lacks representation in survey-based research.
The “Enhancing the QUAlity and Transparency Of health Research” network (EQUATOR) provides two separate guidelines replete with checklists to ensure valid reporting of e-survey methodology. These include “The Checklist for Reporting Results of Internet E-Surveys” (CHERRIES) statement and “ The Journal of Medical Internet Research ” (JMIR) checklist.
COMMON TYPES OF SURVEY-BASED RESEARCH
From a clinician's standpoint, the common survey types include those centered around problems faced by the patients or physicians. 18 Surveys collecting the opinions of various clinicians on a debated clinical topic or feedback forms typically served after attending medical conferences or prescribing a new drug or trying a new method for a given procedure are also surveys. The formulation of clinical practice guidelines entails Delphi exercises using paper surveys, which are yet another form of survey-mediated research.
Size of the survey depends on its intent. They could be large or small surveys. Therefore, identification of the intent behind the survey is essential to allow the investigator to form a hypothesis and then explore it further. Large population-based or provider-based surveys are often done and generate mammoth data over the years. E.g. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, The National Health Interview Survey and the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey.
SCENARIOS FOR CONDUCTING SURVEY-BASED RESEARCH
Despite all said and done about the convenience of conducting survey-based research, it is prudent to conduct a feasibility check before embarking on one. Certain scenarios may be the key determinants in determining the fate of survey-based research ( Table 2 ).
ETHICS APPROVAL FOR SURVEY-BASED RESEARCH
Approval from the Institutional Review Board should be taken as per requirement according to the CHERRIES checklist. However, rules for approval are different as per the country or nation and therefore, local rules must be checked and followed. For instance, in India, the Indian Council of Medical Research released an article in 2017, stating that the concept of broad consent has been updated which is defined “consent for an unspecified range of future research subject to a few contents and/or process restrictions.” It talks about “the flexibility of Indian ethics committees to review a multicentric study proposal for research involving low or minimal risk, survey or studies using anonymized samples or data or low or minimal risk public health research.” The reporting of approvals received and applied for and the procedure of written, informed consent followed must be clear and transparent. 10 , 19
The use of incentives in surveys is also an ethical concern. 20 The different of incentives that can be used are monetary or non-monetary. Monetary incentives are usually discouraged as these may attract the wrong population due to the temptation of the monetary benefit. However, monetary incentives have been seen to make survey receive greater traction even though this is yet to proven. Monetary incentives are not only provided in terms of cash or cheque but also in the form of free articles, discount coupons, phone cards, e-money or cashback value. 21 These methods though tempting must be seldom used. If used, their use must be disclosed and justified in the report. The use of non-monetary incentives like a meeting with a famous personality or access to restricted and authorized areas. These can also help pique the interest of the respondents.
DESIGNING A SURVEY
As mentioned earlier, the design of a survey is reflective of the skill of the investigator curating it. 22 Survey builders can be used to design an efficient survey. These offer majority of the basic features needed to construct a survey, free of charge. Therefore, surveys can be designed from scratch, using pre-designed templates or by using previous survey designs as inspiration. Taking surveys could be made convenient by using the various aids available ( Table 1 ). Moreover, even the investigator should be mindful of the unintended response effects of ordering and context of survey questions. 23
Surveys using clear, unambiguous, simple and well-articulated language record precise answers. 24 A well-designed survey accounts for the culture, language and convenience of the target demographic. The age, region, country and occupation of the target population is also considered before constructing a survey. Consistency is maintained in the terms used in the survey and abbreviations are avoided to allow the respondents to have a clear understanding of the question being answered. Universal abbreviations or previously indexed abbreviations maintain the unambiguity of the survey.
Surveys beginning with broad, easy and non-specific questions as compared to sensitive, tedious and non-specific ones receive more accurate and complete answers. 25 Questionnaires designed such that the relatively tedious and long questions requiring the respondent to do some nit-picking are placed at the end improves the response rate of the survey. This prevents the respondent to be discouraged to answer the survey at the beginning itself and motivates the respondent to finish the survey at the end. All questions must provide a non-response option and all questions should be made mandatory to increase completeness of the survey. Questions can be framed in close-ended or open-ended fashion. However, close-ended questions are easier to analyze and are less tedious to answer by the respondent and therefore must be the main component in a survey. Open-ended questions have minimal use as they are tedious, take time to answer and require fine articulation of one's thoughts. Also, their minimal use is advocated because the interpretation of such answers requires dedication in terms of time and energy due to the diverse nature of the responses which is difficult to promise owing to the large sample sizes. 26 However, whenever the closed choices do not cover all probabilities, an open answer choice must be added. 27 , 28
Screening questions to meet certain criteria to gain access to the survey in cases where inclusion criteria need to be established to maintain authenticity of target demographic. Similarly, logic function can be used to apply an exclusion. This allows clean and clear record of responses and makes the job of an investigator easier. The respondents can or cannot have the option to return to the previous page or question to alter their answer as per the investigator's preference.
The range of responses received can be reduced in case of questions directed towards the feelings or opinions of people by using slider scales, or a Likert scale. 29 , 30 In questions having multiple answers, check boxes are efficient. When a large number of answers are possible, dropdown menus reduce the arduousness. 31 Matrix scales can be used to answer questions requiring grading or having a similar range of answers for multiple conditions. Maximum respondent participation and complete survey responses can be ensured by reducing the survey time. Quiz mode or weighted modes allow the respondent to shuffle between questions and allows scoring of quizzes and can be used to complement other weighted scoring systems. 32 A flowchart depicting a survey construct is presented as Fig. 1 .

Survey validation
Validation testing though tedious and meticulous, is worthy effort as the accuracy of a survey is determined by its validity. It is indicative of the of the sample of the survey and the specificity of the questions such that the data acquired is streamlined to answer the questions being posed or to determine a hypothesis. 33 , 34 Face validation determines the mannerism of construction of questions such that necessary data is collected. Content validation determines the relation of the topic being addressed and its related areas with the questions being asked. Internal validation makes sure that the questions being posed are directed towards the outcome of the survey. Finally, Test – retest validation determines the stability of questions over a period of time by testing the questionnaire twice and maintaining a time interval between the two tests. For surveys determining knowledge of respondents pertaining to a certain subject, it is advised to have a panel of experts for undertaking the validation process. 2 , 35
Reliability testing
If the questions in the survey are posed in a manner so as to elicit the same or similar response from the respondents irrespective of the language or construction of the question, the survey is said to be reliable. It is thereby, a marker of the consistency of the survey. This stands to be of considerable importance in knowledge-based researches where recall ability is tested by making the survey available for answering by the same participants at regular intervals. It can also be used to maintain authenticity of the survey, by varying the construction of the questions.
Designing a cover letter
A cover letter is the primary means of communication with the respondent, with the intent to introduce the respondent to the survey. A cover letter should include the purpose of the survey, details of those who are conducting it, including contact details in case clarifications are desired. It should also clearly depict the action required by the respondent. Data anonymization may be crucial to many respondents and is their right. This should be respected in a clear description of the data handling process while disseminating the survey. A good cover letter is the key to building trust with the respondent population and can be the forerunner to better response rates. Imparting a sense of purpose is vital to ideationally incentivize the respondent population. 36 , 37 Adding the credentials of the team conducting the survey may further aid the process. It is seen that an advance intimation of the survey prepares the respondents while improving their compliance.
The design of a cover letter needs much attention. It should be captivating, clear, precise and use a vocabulary and language specific to the target population for the survey. Active voice should be used to make a greater impact. Crowding of the details must be avoided. Using italics, bold fonts or underlining may be used to highlight critical information. the tone ought to be polite, respectful, and grateful in advance. The use of capital letters is at best avoided, as it is surrogate for shouting in verbal speech and may impart a bad taste.
The dates of the survey may be intimated, so the respondents may prepare themselves for taking it at a time conducive to them. While, emailing a closed group in a convenience sampled survey, using the name of the addressee may impart a customized experience and enhance trust building and possibly compliance. Appropriate use of salutations like Mr./Ms./Mrs. may be considered. Various portals such as SurveyMonkey allow the researchers to save an address list on the website. These may then be reached out using an embedded survey link from a verified email address to minimize bouncing back of emails.
The body of the cover letter must be short, crisp and not exceed 2–3 paragraphs under idea circumstances. Ernest efforts to protect confidentiality may go a long way in enhancing response rates. 38 While it is enticing to provide incentives to enhance response, these are best avoided. 38 , 39 In cases when indirect incentives are offered, such as provision of results of the survey, these may be clearly stated in the cover letter. Lastly, a formal closing note with the signatures of the lead investigator are welcome. 38 , 40
Designing questions
Well-constructed questionnaires are essentially the backbone of successful survey-based studies. With this type of research, the primary concern is the adequate promotion and dissemination of the questionnaire to the target population. The careful of selection of sample population, therefore, needs to be with minimal flaws. The method of conducting survey is an essential determinant of the response rate observed. 41 Broadly, surveys are of two types: closed and open. Depending on the sample population the method of conducting the survey must be determined.
Various doctors use their own patients as the target demographic, as it improves compliance. However, this is effective in surveys aiming towards a geographically specific, fairly common disease as the sample size needs to be adequate. Response bias can be identified by the data collected from respondent and non-respondent groups. 42 , 43 Therefore, to choose a target population whose database of baseline characteristics is already known is more efficacious. In cases of surveys focused on patients having a rare group of diseases, online surveys or e-surveys can be conducted. Data can also be gathered from the multiple national organizations and societies all over the world. 44 , 45 Computer generated random selection can be done from this data to choose participants and they can be reached out to using emails or social media platforms like WhatsApp and LinkedIn. In both these scenarios, closed questionnaires can be conducted. These have restricted access either through a URL link or through e-mail.
In surveys targeting an issue faced by a larger demographic (e.g. pandemics like the COVID-19, flu vaccines and socio-political scenarios), open surveys seem like the more viable option as they can be easily accessed by majority of the public and ensures large number of responses, thereby increasing the accuracy of the study. Survey length should be optimal to avoid poor response rates. 25 , 46
SURVEY DISSEMINATION
Uniform distribution of the survey ensures equitable opportunity to the entire target population to access the questionnaire and participate in it. While deciding the target demographic communities should be studied and the process of “lurking” is sometimes practiced. Multiple sampling methods are available ( Fig. 1 ). 47
Distribution of survey to the target demographic could be done using emails. Even though e-mails reach a large proportion of the target population, an unknown sender could be blocked, making the use of personal or a previously used email preferable for correspondence. Adding a cover letter along with the invite adds a personal touch and is hence, advisable. Some platforms allow the sender to link the survey portal with the sender's email after verifying it. Noteworthily, despite repeated email reminders, personal communication over the phone or instant messaging improved responses in the authors' experience. 48 , 49
Distribution of the survey over other social media platforms (SMPs, namely WhatsApp, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn etc.) is also practiced. 50 , 51 , 52 Surveys distributed on every available platform ensures maximal outreach. 53 Other smartphone apps can also be used for wider survey dissemination. 50 , 54 It is important to be mindful of the target population while choosing the platform for dissemination of the survey as some SMPs such as WhatsApp are more popular in India, while others like WeChat are used more widely in China, and similarly Facebook among the European population. Professional accounts or popular social accounts can be used to promote and increase the outreach for a survey. 55 Incentives such as internet giveaways or meet and greets with their favorite social media influencer have been used to motivate people to participate.
However, social-media platforms do not allow calculation of the denominator of the target population, resulting in inability to gather the accurate response rate. Moreover, this method of collecting data may result in a respondent bias inherent to a community that has a greater online presence. 43 The inability to gather the demographics of the non-respondents (in a bid to identify and prove that they were no different from respondents) can be another challenge in convenience sampling, unlike in cohort-based studies.
Lastly, manually filling of surveys, over the telephone, by narrating the questions and answer choices to the respondents is used as the last-ditch resort to achieve a high desired response rate. 56 Studies reveal that surveys released on Mondays, Fridays, and Sundays receive more traction. Also, reminders set at regular intervals of time help receive more responses. Data collection can be improved in collaborative research by syncing surveys to fill out electronic case record forms. 57 , 58 , 59
Data anonymity refers to the protection of data received as a part of the survey. This data must be stored and handled in accordance with the patient privacy rights/privacy protection laws in reference to surveys. Ethically, the data must be received on a single source file handled by one individual. Sharing or publishing this data on any public platform is considered a breach of the patient's privacy. 11 In convenience sampled surveys conducted by e-mailing a predesignated group, the emails shall remain confidential, as inadvertent sharing of these as supplementary data in the manuscript may amount to a violation of the ethical standards. 60 A completely anonymized e-survey discourages collection of Internet protocol addresses in addition to other patient details such as names and emails.
Data anonymity gives the respondent the confidence to be candid and answer the survey without inhibitions. This is especially apparent in minority groups or communities facing societal bias (sex workers, transgenders, lower caste communities, women). Data anonymity aids in giving the respondents/participants respite regarding their privacy. As the respondents play a primary role in data collection, data anonymity plays a vital role in survey-based research.
DATA HANDLING OF SURVEYS
The data collected from the survey responses are compiled in a .xls, .csv or .xlxs format by the survey tool itself. The data can be viewed during the survey duration or after its completion. To ensure data anonymity, minimal number of people should have access to these results. The data should then be sifted through to invalidate false, incorrect or incomplete data. The relevant and complete data should then be analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively, as per the aim of the study. Statistical aids like pie charts, graphs and data tables can be used to report relative data.
ANALYSIS OF SURVEY DATA
Analysis of the responses recorded is done after the time made available to answer the survey is complete. This ensures that statistical and hypothetical conclusions are established after careful study of the entire database. Incomplete and complete answers can be used to make analysis conditional on the study. Survey-based studies require careful consideration of various aspects of the survey such as the time required to complete the survey. 61 Cut-off points in the time frame allow authentic answers to be recorded and analyzed as compared to disingenuous completed questionnaires. Methods of handling incomplete questionnaires and atypical timestamps must be pre-decided to maintain consistency. Since, surveys are the only way to reach people especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, disingenuous survey practices must not be followed as these will later be used to form a preliminary hypothesis.
REPORTING SURVEY-BASED RESEARCH
Reporting the survey-based research is by far the most challenging part of this method. A well-reported survey-based study is a comprehensive report covering all the aspects of conducting a survey-based research.
The design of the survey mentioning the target demographic, sample size, language, type, methodology of the survey and the inclusion-exclusion criteria followed comprises a descriptive report of a survey-based study. Details regarding the conduction of pilot-testing, validation testing, reliability testing and user-interface testing add value to the report and supports the data and analysis. Measures taken to prevent bias and ensure consistency and precision are key inclusions in a report. The report usually mentions approvals received, if any, along with the written, informed, consent taken from the participants to use the data received for research purposes. It also gives detailed accounts of the different distribution and promotional methods followed.
A detailed account of the data input and collection methods along with tools used to maintain the anonymity of the participants and the steps taken to ensure singular participation from individual respondents indicate a well-structured report. Descriptive information of the website used, visitors received and the externally influencing factors of the survey is included. Detailed reporting of the post-survey analysis including the number of analysts involved, data cleaning required, if any, statistical analysis done and the probable hypothesis concluded is a key feature of a well-reported survey-based research. Methods used to do statistical corrections, if used, should be included in the report. The EQUATOR network has two checklists, “The Checklist for Reporting Results of Internet E-Surveys” (CHERRIES) statement and “ The Journal of Medical Internet Research ” (JMIR) checklist, that can be utilized to construct a well-framed report. 62 , 63 Importantly, self-reporting of biases and errors avoids the carrying forward of false hypothesis as a basis of more advanced research. References should be cited using standard recommendations, and guided by the journal specifications. 64

CHOOSING A TARGET JOURNAL FOR SURVEY-BASED RESEARCH
Surveys can be published as original articles, brief reports or as a letter to the editor. Interestingly, most modern journals do not actively make mention of surveys in the instructions to the author. Thus, depending on the study design, the authors may choose the article category, cohort or case-control interview or survey-based study. It is prudent to mention the type of study in the title. Titles albeit not too long, should not exceed 10–12 words, and may feature the type of study design for clarity after a semicolon for greater citation potential.
While the choice of journal is largely based on the study subject and left to the authors discretion, it may be worthwhile exploring trends in a journal archive before proceeding with submission. 65 Although the article format is similar across most journals, specific rules relevant to the target journal may be followed for drafting the article structure before submission.
RETRACTION OF ARTICLES
Articles that are removed from the publication after being released are retracted articles. These are usually retracted when new discrepancies come to light regarding, the methodology followed, plagiarism, incorrect statistical analysis, inappropriate authorship, fake peer review, fake reporting and such. 66 A sufficient increase in such papers has been noticed. 67
We carried out a search of “surveys” on Retraction Watch on 31st August 2020 and received 81 search results published between November 2006 to June 2020, out of which 3 were repeated. Out of the 78 results, 37 (47.4%) articles were surveys, 23 (29.4%) showed as unknown types and 18 (23.2%) reported other types of research. ( Supplementary Table 1 ). Fig. 2 gives a detailed description of the causes of retraction of the surveys we found and its geographic distribution.

A good survey ought to be designed with a clear objective, the design being precise and focused with close-ended questions and all probabilities included. Use of rating scales, multiple choice questions and checkboxes and maintaining a logical question sequence engages the respondent while simplifying data entry and analysis for the investigator. Conducting pilot-testing is vital to identify and rectify deficiencies in the survey design and answer choices. The target demographic should be defined well, and invitations sent accordingly, with periodic reminders as appropriate. While reporting the survey, maintaining transparency in the methods employed and clearly stating the shortcomings and biases to prevent advocating an invalid hypothesis.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Gaur PS, Zimba O, Agarwal V, Gupta L.
- Visualization: Gaur PS, Zimba O, Agarwal V, Gupta L.
- Writing - original draft: Gaur PS, Gupta L.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
Reporting survey based research
A Comprehensive Guide to Survey Research Methodologies
For decades, researchers and businesses have used survey research to produce statistical data and explore ideas. The survey process is simple, ask questions and analyze the responses to make decisions. Data is what makes the difference between a valid and invalid statement and as the American statistician, W. Edwards Deming said:
“Without data, you’re just another person with an opinion.” - W. Edwards Deming
In this article, we will discuss what survey research is, its brief history, types, common uses, benefits, and the step-by-step process of designing a survey.
What is Survey Research
A survey is a research method that is used to collect data from a group of respondents in order to gain insights and information regarding a particular subject. It’s an excellent method to gather opinions and understand how and why people feel a certain way about different situations and contexts.
Brief History of Survey Research
Survey research may have its roots in the American and English “social surveys” conducted around the turn of the 20th century. The surveys were mainly conducted by researchers and reformers to document the extent of social issues such as poverty. ( 1 ) Despite being a relatively young field to many scientific domains, survey research has experienced three stages of development ( 2 ):
- First Era (1930-1960)
- Second Era (1960-1990)
- Third Era (1990 onwards)
Over the years, survey research adapted to the changing times and technologies. By exploiting the latest technologies, researchers can gain access to the right population from anywhere in the world, analyze the data like never before, and extract useful information.
Survey Research Methods & Types
Survey research can be classified into seven categories based on objective, data sources, methodology, deployment method, and frequency of deployment.
Surveys based on Objective
Exploratory survey research.
Exploratory survey research is aimed at diving deeper into research subjects and finding out more about their context. It’s important for marketing or business strategy and the focus is to discover ideas and insights instead of gathering statistical data.
Generally, exploratory survey research is composed of open-ended questions that allow respondents to express their thoughts and perspectives. The final responses present information from various sources that can lead to fresh initiatives.
Predictive Survey Research
Predictive survey research is also called causal survey research. It’s preplanned, structured, and quantitative in nature. It’s often referred to as conclusive research as it tries to explain the cause-and-effect relationship between different variables. The objective is to understand which variables are causes and which are effects and the nature of the relationship between both variables.
Descriptive Survey Research
Descriptive survey research is largely observational and is ideal for gathering numeric data. Due to its quantitative nature, it’s often compared to exploratory survey research. The difference between the two is that descriptive research is structured and pre-planned.
The idea behind descriptive research is to describe the mindset and opinion of a particular group of people on a given subject. The questions are every day multiple choices and users must choose from predefined categories. With predefined choices, you don’t get unique insights, rather, statistically inferable data.
Survey Research Types based on Concept Testing
Monadic concept testing.
Monadic testing is a survey research methodology in which the respondents are split into multiple groups and ask each group questions about a separate concept in isolation. Generally, monadic surveys are hyper-focused on a particular concept and shorter in duration. The important thing in monadic surveys is to avoid getting off-topic or exhausting the respondents with too many questions.
Sequential Monadic Concept Testing
Another approach to monadic testing is sequential monadic testing. In sequential monadic surveys, groups of respondents are surveyed in isolation. However, instead of surveying three groups on three different concepts, the researchers survey the same groups of people on three distinct concepts one after another. In a sequential monadic survey, at least two topics are included (in random order), and the same questions are asked for each concept to eliminate bias.
Based on Data Source
Primary data.
Data obtained directly from the source or target population is referred to as primary survey data. When it comes to primary data collection, researchers usually devise a set of questions and invite people with knowledge of the subject to respond. The main sources of primary data are interviews, questionnaires, surveys, and observation methods.
Compared to secondary data, primary data is gathered from first-hand sources and is more reliable. However, the process of primary data collection is both costly and time-consuming.
Secondary Data
Survey research is generally used to collect first-hand information from a respondent. However, surveys can also be designed to collect and process secondary data. It’s collected from third-party sources or primary sources in the past.
This type of data is usually generic, readily available, and cheaper than primary data collection. Some common sources of secondary data are books, data collected from older surveys, online data, and data from government archives. Beware that you might compromise the validity of your findings if you end up with irrelevant or inflated data.
Based on Research Method
Quantitative research.
Quantitative research is a popular research methodology that is used to collect numeric data in a systematic investigation. It’s frequently used in research contexts where statistical data is required, such as sciences or social sciences. Quantitative research methods include polls, systematic observations, and face-to-face interviews.
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a research methodology where you collect non-numeric data from research participants. In this context, the participants are not restricted to a specific system and provide open-ended information. Some common qualitative research methods include focus groups, one-on-one interviews, observations, and case studies.
Based on Deployment Method
Online surveys.
With technology advancing rapidly, the most popular method of survey research is an online survey. With the internet, you can not only reach a broader audience but also design and customize a survey and deploy it from anywhere. Online surveys have outperformed offline survey methods as they are less expensive and allow researchers to easily collect and analyze data from a large sample.
Paper or Print Surveys
As the name suggests, paper or print surveys use the traditional paper and pencil approach to collect data. Before the invention of computers, paper surveys were the survey method of choice.
Though many would assume that surveys are no longer conducted on paper, it's still a reliable method of collecting information during field research and data collection. However, unlike online surveys, paper surveys are expensive and require extra human resources.
Telephonic Surveys
Telephonic surveys are conducted over telephones where a researcher asks a series of questions to the respondent on the other end. Contacting respondents over a telephone requires less effort, human resources, and is less expensive.
What makes telephonic surveys debatable is that people are often reluctant in giving information over a phone call. Additionally, the success of such surveys depends largely on whether people are willing to invest their time on a phone call answering questions.
One-on-one Surveys
One-on-one surveys also known as face-to-face surveys are interviews where the researcher and respondent. Interacting directly with the respondent introduces the human factor into the survey.
Face-to-face interviews are useful when the researcher wants to discuss something personal with the respondent. The response rates in such surveys are always higher as the interview is being conducted in person. However, these surveys are quite expensive and the success of these depends on the knowledge and experience of the researcher.
Based on Distribution
The easiest and most common way of conducting online surveys is sending out an email. Sending out surveys via emails has a higher response rate as your target audience already knows about your brand and is likely to engage.
Buy Survey Responses
Purchasing survey responses also yields higher responses as the responders signed up for the survey. Businesses often purchase survey samples to conduct extensive research. Here, the target audience is often pre-screened to check if they're qualified to take part in the research.
Embedding Survey on a Website
Embedding surveys on a website is another excellent way to collect information. It allows your website visitors to take part in a survey without ever leaving the website and can be done while a person is entering or exiting the website.
Post the Survey on Social Media
Social media is an excellent medium to reach abroad range of audiences. You can publish your survey as a link on social media and people who are following the brand can take part and answer questions.
Based on Frequency of Deployment
Cross-sectional studies.
Cross-sectional studies are administered to a small sample from a large population within a short period of time. This provides researchers a peek into what the respondents are thinking at a given time. The surveys are usually short, precise, and specific to a particular situation.
Longitudinal Surveys
Longitudinal surveys are an extension of cross-sectional studies where researchers make an observation and collect data over extended periods of time. This type of survey can be further divided into three types:
- Trend surveys are employed to allow researchers to understand the change in the thought process of the respondents over some time.
- Panel surveys are administered to the same group of people over multiple years. These are usually expensive and researchers must stick to their panel to gather unbiased opinions.
- In cohort surveys, researchers identify a specific category of people and regularly survey them. Unlike panel surveys, the same people do not need to take part over the years, but each individual must fall into the researcher’s primary interest category.
Retrospective Survey
Retrospective surveys allow researchers to ask questions to gather data about past events and beliefs of the respondents. Since retrospective surveys also require years of data, they are similar to the longitudinal survey, except retrospective surveys are shorter and less expensive.
Why Should You Conduct Research Surveys?
“In God we trust. All others must bring data” - W. Edwards Deming
In the information age, survey research is of utmost importance and essential for understanding the opinion of your target population. Whether you’re launching a new product or conducting a social survey, the tool can be used to collect specific information from a defined set of respondents. The data collected via surveys can be further used by organizations to make informed decisions.
Furthermore, compared to other research methods, surveys are relatively inexpensive even if you’re giving out incentives. Compared to the older methods such as telephonic or paper surveys, online surveys have a smaller cost and the number of responses is higher.
What makes surveys useful is that they describe the characteristics of a large population. With a larger sample size , you can rely on getting more accurate results. However, you also need honest and open answers for accurate results. Since surveys are also anonymous and the responses remain confidential, respondents provide candid and accurate answers.
Common Uses of a Survey
Surveys are widely used in many sectors, but the most common uses of the survey research include:
- Market research : surveying a potential market to understand customer needs, preferences, and market demand.
- Customer Satisfaction: finding out your customer’s opinions about your services, products, or companies .
- Social research: investigating the characteristics and experiences of various social groups.
- Health research: collecting data about patients’ symptoms and treatments.
- Politics: evaluating public opinion regarding policies and political parties.
- Psychology: exploring personality traits, behaviors, and preferences.
6 Steps to Conduct Survey Research
An organization, person, or company conducts a survey when they need the information to make a decision but have insufficient data on hand. Following are six simple steps that can help you design a great survey.
Step 1: Objective of the Survey
The first step in survey research is defining an objective. The objective helps you define your target population and samples. The target population is the specific group of people you want to collect data from and since it’s rarely possible to survey the entire population, we target a specific sample from it. Defining a survey objective also benefits your respondents by helping them understand the reason behind the survey.
Step 2: Number of Questions
The number of questions or the size of the survey depends on the survey objective. However, it’s important to ensure that there are no redundant queries and the questions are in a logical order. Rephrased and repeated questions in a survey are almost as frustrating as in real life. For a higher completion rate, keep the questionnaire small so that the respondents stay engaged to the very end. The ideal length of an interview is less than 15 minutes. ( 2 )
Step 3: Language and Voice of Questions
While designing a survey, you may feel compelled to use fancy language. However, remember that difficult language is associated with higher survey dropout rates. You need to speak to the respondent in a clear, concise, and neutral manner, and ask simple questions. If your survey respondents are bilingual, then adding an option to translate your questions into another language can also prove beneficial.
Step 4: Type of Questions
In a survey, you can include any type of questions and even both closed-ended or open-ended questions. However, opt for the question types that are the easiest to understand for the respondents, and offer the most value. For example, compared to open-ended questions, people prefer to answer close-ended questions such as MCQs (multiple choice questions)and NPS (net promoter score) questions.
Step 5: User Experience
Designing a great survey is about more than just questions. A lot of researchers underestimate the importance of user experience and how it affects their response and completion rates. An inconsistent, difficult-to-navigate survey with technical errors and poor color choice is unappealing for the respondents. Make sure that your survey is easy to navigate for everyone and if you’re using rating scales, they remain consistent throughout the research study.
Additionally, don’t forget to design a good survey experience for both mobile and desktop users. According to Pew Research Center, nearly half of the smartphone users access the internet mainly from their mobile phones and 14 percent of American adults are smartphone-only internet users. ( 3 )
Step 6: Survey Logic
Last but not least, logic is another critical aspect of the survey design. If the survey logic is flawed, respondents may not continue in the right direction. Make sure to test the logic to ensure that selecting one answer leads to the next logical question instead of a series of unrelated queries.
How to Effectively Use Survey Research with Starlight Analytics
Designing and conducting a survey is almost as much science as it is an art. To craft great survey research, you need technical skills, consider the psychological elements, and have a broad understanding of marketing.
The ultimate goal of the survey is to ask the right questions in the right manner to acquire the right results.
Bringing a new product to the market is a long process and requires a lot of research and analysis. In your journey to gather information or ideas for your business, Starlight Analytics can be an excellent guide. Starlight Analytics' product concept testing helps you measure your product's market demand and refine product features and benefits so you can launch with confidence. The process starts with custom research to design the survey according to your needs, execute the survey, and deliver the key insights on time.
- Survey research in the United States: roots and emergence, 1890-1960 https://searchworks.stanford.edu/view/10733873
- How to create a survey questionnaire that gets great responses https://luc.id/knowledgehub/how-to-create-a-survey-questionnaire-that-gets-great-responses/
- Internet/broadband fact sheet https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/fact-sheet/internet-broadband/
Related Articles
Product life cycle | what is it and what are the stages.
The product life cycle outlines a product's journey from introduction to decline. Learn all about the product life cycle, its stages, and examples here.
Voice of Customer Analysis: How to Do it & Why It Matters
Learn how to use VoC analytics to set the foundations for future customer-centric strategies. Doing so can greatly improve customer retention & conversion.
A Guide to Competitive Analysis & How to Outperform Your Competitors
Learn all about competitive analysis and its frameworks along with a step-by-step guide to conduct competitive analysis and outperform your competitors.
Test Marketing | How to Test Market a New Product
Test marketing is a tool used to help companies test their product and gather customer feedback before its launch. Click here to learn more about it.
Four Critical Pieces of Market Research Your Investors Expect to See
Investors, banks, and venture capitalists understand that a sure thing doesn’t exist but it does not stop them asking for a tangible guarantee. For all the charisma anyone can offer, effective market research carries more weight as you can detail what value you are bringing to the market, who the obtainable market is, how you reach them and what weaknesses exist within your potential competition.
Monadic Testing: A Survey Methodology for Concept Tests
Learn how monadic survey methodologies can provide clear, strategic direction on your product development process.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Table of Contents

Survey Research
Definition:
Survey Research is a quantitative research method that involves collecting standardized data from a sample of individuals or groups through the use of structured questionnaires or interviews. The data collected is then analyzed statistically to identify patterns and relationships between variables, and to draw conclusions about the population being studied.
Survey research can be used to answer a variety of questions, including:
- What are people’s opinions about a certain topic?
- What are people’s experiences with a certain product or service?
- What are people’s beliefs about a certain issue?
Survey Research Methods
Survey Research Methods are as follows:
- Telephone surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents over the phone, often used in market research or political polling.
- Face-to-face surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents in person, often used in social or health research.
- Mail surveys: A survey research method where questionnaires are sent to respondents through mail, often used in customer satisfaction or opinion surveys.
- Online surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through online platforms, often used in market research or customer feedback.
- Email surveys: A survey research method where questionnaires are sent to respondents through email, often used in customer satisfaction or opinion surveys.
- Mixed-mode surveys: A survey research method that combines two or more survey modes, often used to increase response rates or reach diverse populations.
- Computer-assisted surveys: A survey research method that uses computer technology to administer or collect survey data, often used in large-scale surveys or data collection.
- Interactive voice response surveys: A survey research method where respondents answer questions through a touch-tone telephone system, often used in automated customer satisfaction or opinion surveys.
- Mobile surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through mobile devices, often used in market research or customer feedback.
- Group-administered surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to a group of respondents simultaneously, often used in education or training evaluation.
- Web-intercept surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to website visitors, often used in website or user experience research.
- In-app surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to users of a mobile application, often used in mobile app or user experience research.
- Social media surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through social media platforms, often used in social media or brand awareness research.
- SMS surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through text messaging, often used in customer feedback or opinion surveys.
- IVR surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through an interactive voice response system, often used in automated customer feedback or opinion surveys.
- Mixed-method surveys: A survey research method that combines both qualitative and quantitative data collection methods, often used in exploratory or mixed-method research.
- Drop-off surveys: A survey research method where respondents are provided with a survey questionnaire and asked to return it at a later time or through a designated drop-off location.
- Intercept surveys: A survey research method where respondents are approached in public places and asked to participate in a survey, often used in market research or customer feedback.
- Hybrid surveys: A survey research method that combines two or more survey modes, data sources, or research methods, often used in complex or multi-dimensional research questions.
Types of Survey Research
There are several types of survey research that can be used to collect data from a sample of individuals or groups. following are Types of Survey Research:
- Cross-sectional survey: A type of survey research that gathers data from a sample of individuals at a specific point in time, providing a snapshot of the population being studied.
- Longitudinal survey: A type of survey research that gathers data from the same sample of individuals over an extended period of time, allowing researchers to track changes or trends in the population being studied.
- Panel survey: A type of longitudinal survey research that tracks the same sample of individuals over time, typically collecting data at multiple points in time.
- Epidemiological survey: A type of survey research that studies the distribution and determinants of health and disease in a population, often used to identify risk factors and inform public health interventions.
- Observational survey: A type of survey research that collects data through direct observation of individuals or groups, often used in behavioral or social research.
- Correlational survey: A type of survey research that measures the degree of association or relationship between two or more variables, often used to identify patterns or trends in data.
- Experimental survey: A type of survey research that involves manipulating one or more variables to observe the effect on an outcome, often used to test causal hypotheses.
- Descriptive survey: A type of survey research that describes the characteristics or attributes of a population or phenomenon, often used in exploratory research or to summarize existing data.
- Diagnostic survey: A type of survey research that assesses the current state or condition of an individual or system, often used in health or organizational research.
- Explanatory survey: A type of survey research that seeks to explain or understand the causes or mechanisms behind a phenomenon, often used in social or psychological research.
- Process evaluation survey: A type of survey research that measures the implementation and outcomes of a program or intervention, often used in program evaluation or quality improvement.
- Impact evaluation survey: A type of survey research that assesses the effectiveness or impact of a program or intervention, often used to inform policy or decision-making.
- Customer satisfaction survey: A type of survey research that measures the satisfaction or dissatisfaction of customers with a product, service, or experience, often used in marketing or customer service research.
- Market research survey: A type of survey research that collects data on consumer preferences, behaviors, or attitudes, often used in market research or product development.
- Public opinion survey: A type of survey research that measures the attitudes, beliefs, or opinions of a population on a specific issue or topic, often used in political or social research.
- Behavioral survey: A type of survey research that measures actual behavior or actions of individuals, often used in health or social research.
- Attitude survey: A type of survey research that measures the attitudes, beliefs, or opinions of individuals, often used in social or psychological research.
- Opinion poll: A type of survey research that measures the opinions or preferences of a population on a specific issue or topic, often used in political or media research.
- Ad hoc survey: A type of survey research that is conducted for a specific purpose or research question, often used in exploratory research or to answer a specific research question.
Types Based on Methodology
Based on Methodology Survey are divided into two Types:
Quantitative Survey Research
Qualitative survey research.
Quantitative survey research is a method of collecting numerical data from a sample of participants through the use of standardized surveys or questionnaires. The purpose of quantitative survey research is to gather empirical evidence that can be analyzed statistically to draw conclusions about a particular population or phenomenon.
In quantitative survey research, the questions are structured and pre-determined, often utilizing closed-ended questions, where participants are given a limited set of response options to choose from. This approach allows for efficient data collection and analysis, as well as the ability to generalize the findings to a larger population.
Quantitative survey research is often used in market research, social sciences, public health, and other fields where numerical data is needed to make informed decisions and recommendations.
Qualitative survey research is a method of collecting non-numerical data from a sample of participants through the use of open-ended questions or semi-structured interviews. The purpose of qualitative survey research is to gain a deeper understanding of the experiences, perceptions, and attitudes of participants towards a particular phenomenon or topic.
In qualitative survey research, the questions are open-ended, allowing participants to share their thoughts and experiences in their own words. This approach allows for a rich and nuanced understanding of the topic being studied, and can provide insights that are difficult to capture through quantitative methods alone.
Qualitative survey research is often used in social sciences, education, psychology, and other fields where a deeper understanding of human experiences and perceptions is needed to inform policy, practice, or theory.
Data Analysis Methods
There are several Survey Research Data Analysis Methods that researchers may use, including:
- Descriptive statistics: This method is used to summarize and describe the basic features of the survey data, such as the mean, median, mode, and standard deviation. These statistics can help researchers understand the distribution of responses and identify any trends or patterns.
- Inferential statistics: This method is used to make inferences about the larger population based on the data collected in the survey. Common inferential statistical methods include hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and correlation analysis.
- Factor analysis: This method is used to identify underlying factors or dimensions in the survey data. This can help researchers simplify the data and identify patterns and relationships that may not be immediately apparent.
- Cluster analysis: This method is used to group similar respondents together based on their survey responses. This can help researchers identify subgroups within the larger population and understand how different groups may differ in their attitudes, behaviors, or preferences.
- Structural equation modeling: This method is used to test complex relationships between variables in the survey data. It can help researchers understand how different variables may be related to one another and how they may influence one another.
- Content analysis: This method is used to analyze open-ended responses in the survey data. Researchers may use software to identify themes or categories in the responses, or they may manually review and code the responses.
- Text mining: This method is used to analyze text-based survey data, such as responses to open-ended questions. Researchers may use software to identify patterns and themes in the text, or they may manually review and code the text.
Applications of Survey Research
Here are some common applications of survey research:
- Market Research: Companies use survey research to gather insights about customer needs, preferences, and behavior. These insights are used to create marketing strategies and develop new products.
- Public Opinion Research: Governments and political parties use survey research to understand public opinion on various issues. This information is used to develop policies and make decisions.
- Social Research: Survey research is used in social research to study social trends, attitudes, and behavior. Researchers use survey data to explore topics such as education, health, and social inequality.
- Academic Research: Survey research is used in academic research to study various phenomena. Researchers use survey data to test theories, explore relationships between variables, and draw conclusions.
- Customer Satisfaction Research: Companies use survey research to gather information about customer satisfaction with their products and services. This information is used to improve customer experience and retention.
- Employee Surveys: Employers use survey research to gather feedback from employees about their job satisfaction, working conditions, and organizational culture. This information is used to improve employee retention and productivity.
- Health Research: Survey research is used in health research to study topics such as disease prevalence, health behaviors, and healthcare access. Researchers use survey data to develop interventions and improve healthcare outcomes.
Examples of Survey Research
Here are some real-time examples of survey research:
- COVID-19 Pandemic Surveys: Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, surveys have been conducted to gather information about public attitudes, behaviors, and perceptions related to the pandemic. Governments and healthcare organizations have used this data to develop public health strategies and messaging.
- Political Polls During Elections: During election seasons, surveys are used to measure public opinion on political candidates, policies, and issues in real-time. This information is used by political parties to develop campaign strategies and make decisions.
- Customer Feedback Surveys: Companies often use real-time customer feedback surveys to gather insights about customer experience and satisfaction. This information is used to improve products and services quickly.
- Event Surveys: Organizers of events such as conferences and trade shows often use surveys to gather feedback from attendees in real-time. This information can be used to improve future events and make adjustments during the current event.
- Website and App Surveys: Website and app owners use surveys to gather real-time feedback from users about the functionality, user experience, and overall satisfaction with their platforms. This feedback can be used to improve the user experience and retain customers.
- Employee Pulse Surveys: Employers use real-time pulse surveys to gather feedback from employees about their work experience and overall job satisfaction. This feedback is used to make changes in real-time to improve employee retention and productivity.
Survey Sample
Purpose of survey research.
The purpose of survey research is to gather data and insights from a representative sample of individuals. Survey research allows researchers to collect data quickly and efficiently from a large number of people, making it a valuable tool for understanding attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
Here are some common purposes of survey research:
- Descriptive Research: Survey research is often used to describe characteristics of a population or a phenomenon. For example, a survey could be used to describe the characteristics of a particular demographic group, such as age, gender, or income.
- Exploratory Research: Survey research can be used to explore new topics or areas of research. Exploratory surveys are often used to generate hypotheses or identify potential relationships between variables.
- Explanatory Research: Survey research can be used to explain relationships between variables. For example, a survey could be used to determine whether there is a relationship between educational attainment and income.
- Evaluation Research: Survey research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of a program or intervention. For example, a survey could be used to evaluate the impact of a health education program on behavior change.
- Monitoring Research: Survey research can be used to monitor trends or changes over time. For example, a survey could be used to monitor changes in attitudes towards climate change or political candidates over time.
When to use Survey Research
there are certain circumstances where survey research is particularly appropriate. Here are some situations where survey research may be useful:
- When the research question involves attitudes, beliefs, or opinions: Survey research is particularly useful for understanding attitudes, beliefs, and opinions on a particular topic. For example, a survey could be used to understand public opinion on a political issue.
- When the research question involves behaviors or experiences: Survey research can also be useful for understanding behaviors and experiences. For example, a survey could be used to understand the prevalence of a particular health behavior.
- When a large sample size is needed: Survey research allows researchers to collect data from a large number of people quickly and efficiently. This makes it a useful method when a large sample size is needed to ensure statistical validity.
- When the research question is time-sensitive: Survey research can be conducted quickly, which makes it a useful method when the research question is time-sensitive. For example, a survey could be used to understand public opinion on a breaking news story.
- When the research question involves a geographically dispersed population: Survey research can be conducted online, which makes it a useful method when the population of interest is geographically dispersed.
How to Conduct Survey Research
Conducting survey research involves several steps that need to be carefully planned and executed. Here is a general overview of the process:
- Define the research question: The first step in conducting survey research is to clearly define the research question. The research question should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the population of interest.
- Develop a survey instrument : The next step is to develop a survey instrument. This can be done using various methods, such as online survey tools or paper surveys. The survey instrument should be designed to elicit the information needed to answer the research question, and should be pre-tested with a small sample of individuals.
- Select a sample : The sample is the group of individuals who will be invited to participate in the survey. The sample should be representative of the population of interest, and the size of the sample should be sufficient to ensure statistical validity.
- Administer the survey: The survey can be administered in various ways, such as online, by mail, or in person. The method of administration should be chosen based on the population of interest and the research question.
- Analyze the data: Once the survey data is collected, it needs to be analyzed. This involves summarizing the data using statistical methods, such as frequency distributions or regression analysis.
- Draw conclusions: The final step is to draw conclusions based on the data analysis. This involves interpreting the results and answering the research question.
Advantages of Survey Research
There are several advantages to using survey research, including:
- Efficient data collection: Survey research allows researchers to collect data quickly and efficiently from a large number of people. This makes it a useful method for gathering information on a wide range of topics.
- Standardized data collection: Surveys are typically standardized, which means that all participants receive the same questions in the same order. This ensures that the data collected is consistent and reliable.
- Cost-effective: Surveys can be conducted online, by mail, or in person, which makes them a cost-effective method of data collection.
- Anonymity: Participants can remain anonymous when responding to a survey. This can encourage participants to be more honest and open in their responses.
- Easy comparison: Surveys allow for easy comparison of data between different groups or over time. This makes it possible to identify trends and patterns in the data.
- Versatility: Surveys can be used to collect data on a wide range of topics, including attitudes, beliefs, behaviors, and preferences.
Limitations of Survey Research
Here are some of the main limitations of survey research:
- Limited depth: Surveys are typically designed to collect quantitative data, which means that they do not provide much depth or detail about people’s experiences or opinions. This can limit the insights that can be gained from the data.
- Potential for bias: Surveys can be affected by various biases, including selection bias, response bias, and social desirability bias. These biases can distort the results and make them less accurate.
- L imited validity: Surveys are only as valid as the questions they ask. If the questions are poorly designed or ambiguous, the results may not accurately reflect the respondents’ attitudes or behaviors.
- Limited generalizability : Survey results are only generalizable to the population from which the sample was drawn. If the sample is not representative of the population, the results may not be generalizable to the larger population.
- Limited ability to capture context: Surveys typically do not capture the context in which attitudes or behaviors occur. This can make it difficult to understand the reasons behind the responses.
- Limited ability to capture complex phenomena: Surveys are not well-suited to capture complex phenomena, such as emotions or the dynamics of interpersonal relationships.
Following is an example of a Survey Sample:
Welcome to our Survey Research Page! We value your opinions and appreciate your participation in this survey. Please answer the questions below as honestly and thoroughly as possible.
1. What is your age?
- A) Under 18
- G) 65 or older
2. What is your highest level of education completed?
- A) Less than high school
- B) High school or equivalent
- C) Some college or technical school
- D) Bachelor’s degree
- E) Graduate or professional degree
3. What is your current employment status?
- A) Employed full-time
- B) Employed part-time
- C) Self-employed
- D) Unemployed
4. How often do you use the internet per day?
- A) Less than 1 hour
- B) 1-3 hours
- C) 3-5 hours
- D) 5-7 hours
- E) More than 7 hours
5. How often do you engage in social media per day?
6. Have you ever participated in a survey research study before?
7. If you have participated in a survey research study before, how was your experience?
- A) Excellent
- E) Very poor
8. What are some of the topics that you would be interested in participating in a survey research study about?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
9. How often would you be willing to participate in survey research studies?
- A) Once a week
- B) Once a month
- C) Once every 6 months
- D) Once a year
10. Any additional comments or suggestions?
Thank you for taking the time to complete this survey. Your feedback is important to us and will help us improve our survey research efforts.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types...

Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Basic Research – Types, Methods and Examples

Exploratory Research – Types, Methods and...
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- What is a survey?
- Survey Research
Try Qualtrics for free
What is survey research.
15 min read Find out everything you need to know about survey research, from what it is and how it works to the different methods and tools you can use to ensure you’re successful.
Survey research is the process of collecting data from a predefined group (e.g. customers or potential customers) with the ultimate goal of uncovering insights about your products, services, or brand overall .
As a quantitative data collection method, survey research can provide you with a goldmine of information that can inform crucial business and product decisions. But survey research needs careful planning and execution to get the results you want.
So if you’re thinking about using surveys to carry out research, read on.
Get started with our free survey maker tool
Types of survey research
Calling these methods ‘survey research’ slightly underplays the complexity of this type of information gathering. From the expertise required to carry out each activity to the analysis of the data and its eventual application, a considerable amount of effort is required.
As for how you can carry out your research, there are several options to choose from — face-to-face interviews, telephone surveys, focus groups (though more interviews than surveys), online surveys , and panel surveys.
Typically, the survey method you choose will largely be guided by who you want to survey, the size of your sample , your budget, and the type of information you’re hoping to gather.
Here are a few of the most-used survey types:
Face-to-face interviews
Before technology made it possible to conduct research using online surveys, telephone, and mail were the most popular methods for survey research. However face-to-face interviews were considered the gold standard — the only reason they weren’t as popular was due to their highly prohibitive costs.
When it came to face-to-face interviews, organizations would use highly trained researchers who knew when to probe or follow up on vague or problematic answers. They also knew when to offer assistance to respondents when they seemed to be struggling. The result was that these interviewers could get sample members to participate and engage in surveys in the most effective way possible, leading to higher response rates and better quality data.
Telephone surveys
While phone surveys have been popular in the past, particularly for measuring general consumer behavior or beliefs, response rates have been declining since the 1990s .
Phone surveys are usually conducted using a random dialing system and software that a researcher can use to record responses.
This method is beneficial when you want to survey a large population but don’t have the resources to conduct face-to-face research surveys or run focus groups, or want to ask multiple-choice and open-ended questions .
The downsides are they can: take a long time to complete depending on the response rate, and you may have to do a lot of cold-calling to get the information you need.
You also run the risk of respondents not being completely honest . Instead, they’ll answer your survey questions quickly just to get off the phone.
Focus groups (interviews — not surveys)
Focus groups are a separate qualitative methodology rather than surveys — even though they’re often bunched together. They’re normally used for survey pretesting and designing , but they’re also a great way to generate opinions and data from a diverse range of people.
Focus groups involve putting a cohort of demographically or socially diverse people in a room with a moderator and engaging them in a discussion on a particular topic, such as your product, brand, or service.
They remain a highly popular method for market research , but they’re expensive and require a lot of administration to conduct and analyze the data properly.
You also run the risk of more dominant members of the group taking over the discussion and swaying the opinions of other people — potentially providing you with unreliable data.
Online surveys
Online surveys have become one of the most popular survey methods due to being cost-effective, enabling researchers to accurately survey a large population quickly.
Online surveys can essentially be used by anyone for any research purpose – we’ve all seen the increasing popularity of polls on social media (although these are not scientific).
Using an online survey allows you to ask a series of different question types and collect data instantly that’s easy to analyze with the right software.
There are also several methods for running and distributing online surveys that allow you to get your questionnaire in front of a large population at a fraction of the cost of face-to-face interviews or focus groups.
This is particularly true when it comes to mobile surveys as most people with a smartphone can access them online.
However, you have to be aware of the potential dangers of using online surveys, particularly when it comes to the survey respondents. The biggest risk is because online surveys require access to a computer or mobile device to complete, they could exclude elderly members of the population who don’t have access to the technology — or don’t know how to use it.
It could also exclude those from poorer socio-economic backgrounds who can’t afford a computer or consistent internet access. This could mean the data collected is more biased towards a certain group and can lead to less accurate data when you’re looking for a representative population sample.
When it comes to surveys, every voice matters.
Find out how to create more inclusive and representative surveys for your research.
Panel surveys
A panel survey involves recruiting respondents who have specifically signed up to answer questionnaires and who are put on a list by a research company. This could be a workforce of a small company or a major subset of a national population. Usually, these groups are carefully selected so that they represent a sample of your target population — giving you balance across criteria such as age, gender, background, and so on.
Panel surveys give you access to the respondents you need and are usually provided by the research company in question. As a result, it’s much easier to get access to the right audiences as you just need to tell the research company your criteria. They’ll then determine the right panels to use to answer your questionnaire.
However, there are downsides. The main one being that if the research company offers its panels incentives, e.g. discounts, coupons, money — respondents may answer a lot of questionnaires just for the benefits.
This might mean they rush through your survey without providing considered and truthful answers. As a consequence, this can damage the credibility of your data and potentially ruin your analyses.
What are the benefits of using survey research?
Depending on the research method you use, there are lots of benefits to conducting survey research for data collection. Here, we cover a few:
1. They’re relatively easy to do
Most research surveys are easy to set up, administer and analyze. As long as the planning and survey design is thorough and you target the right audience , the data collection is usually straightforward regardless of which survey type you use.
2. They can be cost effective
Survey research can be relatively cheap depending on the type of survey you use.
Generally, qualitative research methods that require access to people in person or over the phone are more expensive and require more administration.
Online surveys or mobile surveys are often more cost-effective for market research and can give you access to the global population for a fraction of the cost.
3. You can collect data from a large sample
Again, depending on the type of survey, you can obtain survey results from an entire population at a relatively low price. You can also administer a large variety of survey types to fit the project you’re running.
4. You can use survey software to analyze results immediately
Using survey software, you can use advanced statistical analysis techniques to gain insights into your responses immediately.
Analysis can be conducted using a variety of parameters to determine the validity and reliability of your survey data at scale.
5. Surveys can collect any type of data
While most people view surveys as a quantitative research method, they can just as easily be adapted to gain qualitative information by simply including open-ended questions or conducting interviews face to face.
How to measure concepts with survey questions
While surveys are a great way to obtain data, that data on its own is useless unless it can be analyzed and developed into actionable insights.
The easiest, and most effective way to measure survey results, is to use a dedicated research tool that puts all of your survey results into one place.
When it comes to survey measurement, there are four measurement types to be aware of that will determine how you treat your different survey results:
Nominal scale
With a nominal scale , you can only keep track of how many respondents chose each option from a question, and which response generated the most selections.
An example of this would be simply asking a responder to choose a product or brand from a list.
You could find out which brand was chosen the most but have no insight as to why.
Ordinal scale
Ordinal scales are used to judge an order of preference. They do provide some level of quantitative value because you’re asking responders to choose a preference of one option over another.
Ratio scale
Ratio scales can be used to judge the order and difference between responses. For example, asking respondents how much they spend on their weekly shopping on average.
Interval scale
In an interval scale, values are lined up in order with a meaningful difference between the two values — for example, measuring temperature or measuring a credit score between one value and another.
Step by step: How to conduct surveys and collect data
Conducting a survey and collecting data is relatively straightforward, but it does require some careful planning and design to ensure it results in reliable data.
Step 1 – Define your objectives
What do you want to learn from the survey? How is the data going to help you? Having a hypothesis or series of assumptions about survey responses will allow you to create the right questions to test them.
Step 2 – Create your survey questions
Once you’ve got your hypotheses or assumptions, write out the questions you need answering to test your theories or beliefs. Be wary about framing questions that could lead respondents or inadvertently create biased responses .
Step 3 – Choose your question types
Your survey should include a variety of question types and should aim to obtain quantitative data with some qualitative responses from open-ended questions. Using a mix of questions (simple Yes/ No, multiple-choice, rank in order, etc) not only increases the reliability of your data but also reduces survey fatigue and respondents simply answering questions quickly without thinking.
Find out how to create a survey that’s easy to engage with
Step 4 – Test your questions
Before sending your questionnaire out, you should test it (e.g. have a random internal group do the survey) and carry out A/B tests to ensure you’ll gain accurate responses.
Step 5 – Choose your target and send out the survey
Depending on your objectives, you might want to target the general population with your survey or a specific segment of the population. Once you’ve narrowed down who you want to target, it’s time to send out the survey.
After you’ve deployed the survey, keep an eye on the response rate to ensure you’re getting the number you expected. If your response rate is low, you might need to send the survey out to a second group to obtain a large enough sample — or do some troubleshooting to work out why your response rates are so low. This could be down to your questions, delivery method, selected sample, or otherwise.
Step 6 – Analyze results and draw conclusions
Once you’ve got your results back, it’s time for the fun part.
Break down your survey responses using the parameters you’ve set in your objectives and analyze the data to compare to your original assumptions. At this stage, a research tool or software can make the analysis a lot easier — and that’s somewhere Qualtrics can help.
Get reliable insights with survey software from Qualtrics
Gaining feedback from customers and leads is critical for any business, data gathered from surveys can prove invaluable for understanding your products and your market position, and with survey software from Qualtrics, it couldn’t be easier.
Used by more than 13,000 brands and supporting more than 1 billion surveys a year, Qualtrics empowers everyone in your organization to gather insights and take action. No coding required — and your data is housed in one system.
Get feedback from more than 125 sources on a single platform and view and measure your data in one place to create actionable insights and gain a deeper understanding of your target customers .
Automatically run complex text and statistical analysis to uncover exactly what your survey data is telling you, so you can react in real-time and make smarter decisions.
We can help you with survey management, too. From designing your survey and finding your target respondents to getting your survey in the field and reporting back on the results, we can help you every step of the way.
And for expert market researchers and survey designers, Qualtrics features custom programming to give you total flexibility over question types, survey design, embedded data, and other variables.
No matter what type of survey you want to run, what target audience you want to reach, or what assumptions you want to test or answers you want to uncover, we’ll help you design, deploy and analyze your survey with our team of experts.
Ready to find out more about Qualtrics CoreXM?
Get started with our free survey maker tool today
Related resources
Survey bias types 24 min read, post event survey questions 10 min read, best survey software 16 min read, close-ended questions 7 min read, survey vs questionnaire 12 min read, response bias 13 min read, double barreled question 11 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Survey Papers: Here’s Everything You Should Know

A survey is a method of collecting information about the attitudes, beliefs, experiences, and behaviors of people. The goal of survey papers is to provide an accurate picture of the world, as it is to help decision-makers make better decisions.
Survey papers are a great way of investigating the state of a particular subject, and many of them are very interesting to read. They are also a great way of getting insight into how people feel about something.
Survey papers are applicable in many situations. Among them are when you want to know how people feel about something or what factors influence their decisions.
Surveys help to learn what people think about different topics, such as politics or the environment.
This article will cover the basics of survey papers and how they can help you learn more about your readers’ needs.
What are Survey Papers?
Surveys are a great way to gather information about different topics. They’re also a great way to gain insight into your readers’ opinions and uncover common concerns.
Surveys help to gather feedback on projects , products, and services. You may use surveys for marketing research, customer satisfaction surveys, or to gather insights into the needs of your target audience.
A survey paper is a research paper conducted by asking a question or questions to a population of people and then analyzing the answers.
The results sometimes help to generalize the entire population or demographic group. Survey papers are commonly used in academic research to gather data on various topics.
They offer you the opportunity to create your surveys and conduct the research on your terms. Additionally, survey papers allow students to get involved in research and learn more about how surveys work.
What is the Purpose of Survey Papers?
Survey papers help to understand the opinions and thoughts of people. They allow you to gauge the opinions of a large group of people and get detailed feedback on what they think about a specific topic.
Survey papers are also helpful in collecting data from large groups of people to help businesses make informed decisions. In addition, survey papers are an essential part of the educational process.
They allow students to practice their research skills and develop a deeper understanding of the studied material. Students will also learn how to analyze data and make conclusions based on that analysis.
The purpose of a survey paper is to gather information, so it should not be biased in any way.
What are the Different Types of Survey Papers?
There are several survey papers, and you should know what they are.
- Qualitative : This type of survey paper is for a group of people with similar backgrounds and knowledge about the subject. It helps to understand what your audience wants or needs.
- Quantitative : This type of survey paper aims to gather numerical data on a particular topic or area. It helps to understand the factors that affect your target audience’s buying decisions, behaviors, and choices.
- Mixed-initiative : This type of survey paper combines qualitative and quantitative elements. Consequently, it allows you to get more information than if you were only using one type alone (for example, conducting a mixed-initiative interview with respondents.)
The results are pretty straightforward: surveys work. They generate responses, get people talking, and help you learn about the world around you.
Surveys generate responses, get people talking, and help you learn more about the world around you. They can gather information in different ways, and once you have it, you can use it.
When Should You Conduct a Survey?
A survey is a constructive way to collect data and feedback from individuals. It’s also a great way to gauge public opinion, as respondents’ biases do not limit responses, and opinions depend on personal experience.
When you need a better understanding of what people think, feel and do, a survey is the best way to get that information. Survey results can help you understand what people know, like, and dislike about your products or services.
The key is ensuring you have enough data to make an informed decision. If you don’t, your analysis will be limited and potentially misleading.
Carrying out a survey can be as simple as taking a few questions from your friends or family about a subject matter.
Furthermore, it can be as complicated as gathering data relevant to the market, like demographics, pricing information, and customer satisfaction.
Steps to Carry Out a Survey That Gives a Meaningful Result
1. decide on your research goals.
The central point of this step is to ask yourself what you want to learn from the survey. Are you trying to get the satisfaction of the participants? What do you want to know?
Decide what you want to find out about the participants. If you are conducting a survey, it can be about their demographics or how they use the product/service.
If you are doing a focus group, it will depend on the topic. It should be about what could be improved if you ask people for feedback on an existing product or service.
2. Compile a list of questions
This step will help you decide the questions to ask and how many. If there are too many, it will be overwhelming for the participants.
On the other hand, if there isn’t enough, it may not give you all the information you need for analysis. Write down as many questions as possible to help gather information from each participant.
You may need to ask multiple questions to get the information you need from each participant. The more specific and detailed the questions, the better.
Be sure you have details such as: who they are (age, gender, occupation). Furthermore, include why they are participating in this particular survey (are they interested in the topic?).
Lastly, ask what product/service they regularly use (are they satisfied with their current experience?) and where they live (if relevant to your survey).
3. Meet with the participants
Meet with participants in person or via telephone or video chat. This step is important because it helps build rapport and trust between them and you as survey takers.
This is where you will explain the purpose of the survey, what your study will cover, and its usage.
It also gives them a chance to ask questions if they have any concerns about the process of their involvement in it.
You should also explain that there are no right or wrong answers but that all responses are meaningful and that anyone can participate in the study.
You don’t want your survey to be an uncomfortable experience for anyone. In addition, if there’s anything that needs to change, now’s the time to address it.
4. Gather your data/response
Once you’ve met with your participants and determined the necessary changes, it’s time to gather their responses. You can do this through questionnaires and interviews.
You could use an online survey tool such as Survey Junkie . These tools allow you to create a questionnaire and send it out to participants via email or text. They’re quick and easy ways of quickly getting responses from large numbers of people.
The most important thing is to ensure that the respondents are well-informed about the purpose of the survey and the type of questions you will be asking them.
Lastly, ensure everyone feels comfortable enough to participate in the process.
5. Analyze the results
Once you have gathered your data, analyze it as soon as possible. Most surveys fail because people forget about them quickly and fail to analyze their results properly.
You need to scrutinize all of your responses so that you can get a good understanding of what it means for your research.
Ensure to analyze your data using whatever method is best for you. You can use software such as Excel spreadsheets, SPSS, Google Sheets, or even a word processor.
Once you have all your data in one place or another, look at it closely and ensure everything looks right before processing any data.
6. Write a report
The last step is to write a report. Your readers can see the results and take action if you have done an excellent job. The report should include:
- A summary of the results, including how many people completed the survey. It should also include the age groups and demographics that were surveyed. Furthermore, include whether there is a difference between what respondents say they believe and what they do.
- A conclusion about why it was essential to conduct the survey. Was it because you wanted to see if your users agreed with you? Did you want to see if your product is meeting user needs? Is there anything else that could improve the user experience?
- Recommendations for improving the product based on the survey results of the survey.
The steps outlined here are a guide for conducting surveys for your research. You may need to adapt them to fit your situation.
The Future of the Surveys
As surveys evolve, they will take place online . Survey papers and data have been used for years.
But it’s only recently that researchers have been able to get the data into the hands of users in a way that makes sense.
Many surveys are still conducted on paper, but the Internet is changing how people interact with surveys.
One example of an evolving method is “online surveys,” where respondents access a survey through a website.
Survey researchers are creating tools that allow for online data collection. Data can be collected from anywhere worldwide and shared quickly with other researchers.
Online surveys open up opportunities to reach a wider audience than ever before.
Online surveys also have several advantages over traditional paper-based research methods. They are cheaper, more convenient, easier to distribute and promote, and more flexible in terms of timing and modes of administration.
With online surveys, you get more responses from different people, making the process easier for both the respondent and the researcher.
The ease of conducting an online survey means that many more options are available for those who want to participate in one.
It also means that the information collected can be increased without expanding on each question or answer set.
What is the difference between reviews and survey papers?
Survey papers ask respondents about their perception of a product, service, or something evaluated.
Reviews provide feedback about a specific feature, brand, or experience. Review and survey papers help you deeply understand a particular topic.
How do you develop the right questions for your survey?
The best way to ensure that your questions will produce the results you need is to understand your objectives and the audience clearly.
Must all graduate students write survey papers?
Yes, all graduate students must write at least one survey paper since a graduate degree entails research.
Survey papers aim to gather data, which will be analyzed by the researcher(s) professionally and summarised in a written report.
What do you do with the results from survey papers?
The results can be used to form policies, improve services and increase understanding of a particular problem.
Survey results can show you where to focus your efforts on enhancing customer service, developing new markets, or resolving problems.
Final Thoughts
Survey papers are the most common type of research method. They are designed to capture some readers’ information via surveys.
The information the surveys collect may be for research purposes or other reasons, such as gathering demographic data. Survey papers can have a broad range of topics.
The information collected can be used for many different things, whether it aims to help sell a product, create laws or change existing laws, create more effective policies and procedures, or simply educate.
The most exciting thing about survey papers is that they’re all about you. They’re about the questions you ask and the answers you receive. They’re about how your research can help others or at least inform them.
And most importantly, they’re about the fact that each answer is unique and belongs only to you.
Learn more about the types of assessment in education and their uses .
Thanks for reading.
You may also like:
- How To Create And Sell Profitable Online Courses
- Best Online Learning Platforms To Learn Anything Online
- What Are Social Skills? [Definition, Types & Benefits]
- Discover Top Tips On How to Get Honest Feedback for Your Online Course
- Is Spanish Hard to Learn? Spanish For Everyone
People Also Read:

Difference Between Roles And Responsibilities

Does Suspension Mean Termination?

Moral Claim: Definition, Significance, Contemporary Issues, & Challenges

Why Can’t You Flush The Toilet After A Drug Test?

Rising Junior: Meaning, Importance Of Junior Year & Strategies For Success

Mandatory Meeting: Meaning, Purpose, Challenges, Implementation Strategies
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Artificial Intelligence
Title: a survey on concept-based approaches for model improvement.
Abstract: The focus of recent research has shifted from merely increasing the Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) performance in various tasks to DNNs, which are more interpretable to humans. The field of eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) has observed various techniques, including saliency-based and concept-based approaches. Concept-based approaches explain the model's decisions in simple human understandable terms called Concepts. Concepts are human interpretable units of data and are the thinking ground of humans. Explanations in terms of concepts enable detecting spurious correlations, inherent biases, or clever-hans. With the advent of concept-based explanations, there have been various concept representation methods and automatic concept discovery algorithms. Some recent methods use concepts for post-hoc model disentanglement evaluation, while others use them for ante-hoc training. The concept-based approaches are new, with many representations coming up, and there is very limited work on Concept-based Model improvement. We provide a systematic review and taxonomy of various concept representations and their discovery algorithms in DNNs, specifically in vision. We also provide details on concept-based model improvement literature, which is the first to survey concept-based model improvement methods.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Download PDF
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
In One Key A.I. Metric, China Pulls Ahead of the U.S.: Talent
China has produced a huge number of top A.I. engineers in recent years. New research shows that, by some measures, it has already eclipsed the United States.

By Paul Mozur and Cade Metz
Paul Mozur reported from Taipei, Taiwan, and Cade Metz from San Francisco.
When it comes to the artificial intelligence that powers chatbots like ChatGPT, China lags behind the United States . But when it comes to producing the scientists behind a new generation of humanoid technologies, China is pulling ahead.
New research shows that China has by some metrics eclipsed the United States as the biggest producer of A.I. talent, with the country generating almost half the world’s top A.I. researchers. By contrast, about 18 percent come from U.S. undergraduate institutions, according to the study , from MacroPolo, a think tank run by the Paulson Institute, which promotes constructive ties between the United States and China.
The findings show a jump for China, which produced about one-third of the world’s top talent three years earlier. The United States, by contrast, remained mostly the same. The research is based on the backgrounds of researchers whose papers were published at 2022’s Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. NeurIPS, as it is known, is focused on advances in neural networks , which have anchored recent developments in generative A.I.
The talent imbalance has been building for the better part of a decade. During much of the 2010s, the United States benefited as large numbers of China’s top minds moved to American universities to complete doctoral degrees. A majority of them stayed in the United States. But the research shows that trend has also begun to turn, with growing numbers of Chinese researchers staying in China.
What happens in the next few years could be critical as China and the United States jockey for primacy in A.I. — a technology that can potentially increase productivity, strengthen industries and drive innovation — turning the researchers into one of the most geopolitically important groups in the world.
Generative A.I. has captured the tech industry in Silicon Valley and in China, causing a frenzy in funding and investment. The boom has been led by U.S. tech giants such as Google and start-ups like OpenAI. That could attract China’s researchers, though rising tensions between Beijing and Washington could also deter some, experts said.
(The New York Times has sued OpenAI and Microsoft for copyright infringement of news content related to A.I. systems.)
China has nurtured so much A.I. talent partly because it invested heavily in A.I. education. Since 2018, the country has added more than 2,000 undergraduate A.I. programs, with more than 300 at its most elite universities, said Damien Ma, the managing director of MacroPolo, though he noted the programs were not heavily focused on the technology that had driven breakthroughs by chatbots like ChatGPT.
“A lot of the programs are about A.I. applications in industry and manufacturing, not so much the generative A.I. stuff that’s come to dominate the American A.I. industry at the moment,” he said.
While the United States has pioneered breakthroughs in A.I., most recently with the uncanny humanlike abilities of chatbots , a significant portion of that work was done by researchers educated in China.
Researchers originally from China now make up 38 percent of the top A.I. researchers working in the United States, with Americans making up 37 percent, according to the research. Three years earlier, those from China made up 27 percent of top talent working in the United States, compared with 31 percent from the United States.
“The data shows just how critical Chinese-born researchers are to the United States for A.I. competitiveness,” said Matt Sheehan, a fellow at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace who studies Chinese A.I.
He added that the data seemed to show the United States was still attractive. “We’re the world leader in A.I. because we continue to attract and retain talent from all over the world, but especially China,” he said.
Pieter Abbeel, a professor at the University of California, Berkeley, and a founder of Covariant , an A.I. and robotics start-up, said working alongside large numbers of Chinese researchers was taken for granted inside the leading American companies and universities.
“It’s just a natural state of affairs,” he said.
In the past, U.S. defense officials were not too concerned about A.I. talent flows from China, partly because many of the biggest A.I. projects did not deal with classified data and partly because they reasoned that it was better to have the best minds available. That so much of the leading research in A.I. is published openly also held back worries.
Despite bans introduced by the Trump administration that prohibit entry to the United States for students from some military-linked universities in China and a relative slowdown in the flow of Chinese students into the country during Covid, the research showed large numbers of the most promising A.I. minds continued coming to the United States to study.
But this month, a Chinese citizen who was an engineer at Google was charged with trying to transfer A.I. technology — including critical microchip architecture — to a Beijing-based company that paid him in secret , according to a federal indictment.
The substantial numbers of Chinese A.I. researchers working in the United States now present a conundrum for policymakers, who want to counter Chinese espionage while not discouraging the continued flow of top Chinese computer engineers into the United States, according to experts focused on American competitiveness.
“Chinese scholars are almost leading the way in the A.I. field,” said Subbarao Kambhampati, a professor and researcher of A.I. at Arizona State University. If policymakers try to bar Chinese nationals from research in the United States, he said, they are “shooting themselves in the foot.”
The track record of U.S. policymakers is mixed. A policy by the Trump administration aimed at curbing Chinese industrial espionage and intellectual property theft has since been criticized for errantly prosecuting a number of professors. Such programs, Chinese immigrants said, have encouraged some to stay in China.
For now, the research showed, most Chinese who complete doctorates in the United States stay in the country, helping to make it the global center of the A.I. world. Even so, the U.S. lead has begun to slip, to hosting about 42 percent of the world’s top talent, down from about 59 percent three years ago, according to the research.
Paul Mozur is the global technology correspondent for The Times, based in Taipei. Previously he wrote about technology and politics in Asia from Hong Kong, Shanghai and Seoul. More about Paul Mozur
Cade Metz writes about artificial intelligence, driverless cars, robotics, virtual reality and other emerging areas of technology. More about Cade Metz
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
Published on June 7, 2021 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023 by Pritha Bhandari.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about:
- Your overall research objectives and approach
- Whether you’ll rely on primary research or secondary research
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods
- The procedures you’ll follow to collect data
- Your data analysis methods
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research objectives and that you use the right kind of analysis for your data.
Table of contents
Step 1: consider your aims and approach, step 2: choose a type of research design, step 3: identify your population and sampling method, step 4: choose your data collection methods, step 5: plan your data collection procedures, step 6: decide on your data analysis strategies, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research design.
- Introduction
Before you can start designing your research, you should already have a clear idea of the research question you want to investigate.
There are many different ways you could go about answering this question. Your research design choices should be driven by your aims and priorities—start by thinking carefully about what you want to achieve.
The first choice you need to make is whether you’ll take a qualitative or quantitative approach.
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive , allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.
Quantitative research designs tend to be more fixed and deductive , with variables and hypotheses clearly defined in advance of data collection.
It’s also possible to use a mixed-methods design that integrates aspects of both approaches. By combining qualitative and quantitative insights, you can gain a more complete picture of the problem you’re studying and strengthen the credibility of your conclusions.
Practical and ethical considerations when designing research
As well as scientific considerations, you need to think practically when designing your research. If your research involves people or animals, you also need to consider research ethics .
- How much time do you have to collect data and write up the research?
- Will you be able to gain access to the data you need (e.g., by travelling to a specific location or contacting specific people)?
- Do you have the necessary research skills (e.g., statistical analysis or interview techniques)?
- Will you need ethical approval ?
At each stage of the research design process, make sure that your choices are practically feasible.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Within both qualitative and quantitative approaches, there are several types of research design to choose from. Each type provides a framework for the overall shape of your research.
Types of quantitative research designs
Quantitative designs can be split into four main types.
- Experimental and quasi-experimental designs allow you to test cause-and-effect relationships
- Descriptive and correlational designs allow you to measure variables and describe relationships between them.
With descriptive and correlational designs, you can get a clear picture of characteristics, trends and relationships as they exist in the real world. However, you can’t draw conclusions about cause and effect (because correlation doesn’t imply causation ).
Experiments are the strongest way to test cause-and-effect relationships without the risk of other variables influencing the results. However, their controlled conditions may not always reflect how things work in the real world. They’re often also more difficult and expensive to implement.
Types of qualitative research designs
Qualitative designs are less strictly defined. This approach is about gaining a rich, detailed understanding of a specific context or phenomenon, and you can often be more creative and flexible in designing your research.
The table below shows some common types of qualitative design. They often have similar approaches in terms of data collection, but focus on different aspects when analyzing the data.
Your research design should clearly define who or what your research will focus on, and how you’ll go about choosing your participants or subjects.
In research, a population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about, while a sample is the smaller group of individuals you’ll actually collect data from.
Defining the population
A population can be made up of anything you want to study—plants, animals, organizations, texts, countries, etc. In the social sciences, it most often refers to a group of people.
For example, will you focus on people from a specific demographic, region or background? Are you interested in people with a certain job or medical condition, or users of a particular product?
The more precisely you define your population, the easier it will be to gather a representative sample.
- Sampling methods
Even with a narrowly defined population, it’s rarely possible to collect data from every individual. Instead, you’ll collect data from a sample.
To select a sample, there are two main approaches: probability sampling and non-probability sampling . The sampling method you use affects how confidently you can generalize your results to the population as a whole.
Probability sampling is the most statistically valid option, but it’s often difficult to achieve unless you’re dealing with a very small and accessible population.
For practical reasons, many studies use non-probability sampling, but it’s important to be aware of the limitations and carefully consider potential biases. You should always make an effort to gather a sample that’s as representative as possible of the population.
Case selection in qualitative research
In some types of qualitative designs, sampling may not be relevant.
For example, in an ethnography or a case study , your aim is to deeply understand a specific context, not to generalize to a population. Instead of sampling, you may simply aim to collect as much data as possible about the context you are studying.
In these types of design, you still have to carefully consider your choice of case or community. You should have a clear rationale for why this particular case is suitable for answering your research question .
For example, you might choose a case study that reveals an unusual or neglected aspect of your research problem, or you might choose several very similar or very different cases in order to compare them.
Data collection methods are ways of directly measuring variables and gathering information. They allow you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem.
You can choose just one data collection method, or use several methods in the same study.
Survey methods
Surveys allow you to collect data about opinions, behaviors, experiences, and characteristics by asking people directly. There are two main survey methods to choose from: questionnaires and interviews .
Observation methods
Observational studies allow you to collect data unobtrusively, observing characteristics, behaviors or social interactions without relying on self-reporting.
Observations may be conducted in real time, taking notes as you observe, or you might make audiovisual recordings for later analysis. They can be qualitative or quantitative.
Other methods of data collection
There are many other ways you might collect data depending on your field and topic.
If you’re not sure which methods will work best for your research design, try reading some papers in your field to see what kinds of data collection methods they used.
Secondary data
If you don’t have the time or resources to collect data from the population you’re interested in, you can also choose to use secondary data that other researchers already collected—for example, datasets from government surveys or previous studies on your topic.
With this raw data, you can do your own analysis to answer new research questions that weren’t addressed by the original study.
Using secondary data can expand the scope of your research, as you may be able to access much larger and more varied samples than you could collect yourself.
However, it also means you don’t have any control over which variables to measure or how to measure them, so the conclusions you can draw may be limited.
As well as deciding on your methods, you need to plan exactly how you’ll use these methods to collect data that’s consistent, accurate, and unbiased.
Planning systematic procedures is especially important in quantitative research, where you need to precisely define your variables and ensure your measurements are high in reliability and validity.
Operationalization
Some variables, like height or age, are easily measured. But often you’ll be dealing with more abstract concepts, like satisfaction, anxiety, or competence. Operationalization means turning these fuzzy ideas into measurable indicators.
If you’re using observations , which events or actions will you count?
If you’re using surveys , which questions will you ask and what range of responses will be offered?
You may also choose to use or adapt existing materials designed to measure the concept you’re interested in—for example, questionnaires or inventories whose reliability and validity has already been established.
Reliability and validity
Reliability means your results can be consistently reproduced, while validity means that you’re actually measuring the concept you’re interested in.
For valid and reliable results, your measurement materials should be thoroughly researched and carefully designed. Plan your procedures to make sure you carry out the same steps in the same way for each participant.
If you’re developing a new questionnaire or other instrument to measure a specific concept, running a pilot study allows you to check its validity and reliability in advance.
Sampling procedures
As well as choosing an appropriate sampling method , you need a concrete plan for how you’ll actually contact and recruit your selected sample.
That means making decisions about things like:
- How many participants do you need for an adequate sample size?
- What inclusion and exclusion criteria will you use to identify eligible participants?
- How will you contact your sample—by mail, online, by phone, or in person?
If you’re using a probability sampling method , it’s important that everyone who is randomly selected actually participates in the study. How will you ensure a high response rate?
If you’re using a non-probability method , how will you avoid research bias and ensure a representative sample?
Data management
It’s also important to create a data management plan for organizing and storing your data.
Will you need to transcribe interviews or perform data entry for observations? You should anonymize and safeguard any sensitive data, and make sure it’s backed up regularly.
Keeping your data well-organized will save time when it comes to analyzing it. It can also help other researchers validate and add to your findings (high replicability ).
On its own, raw data can’t answer your research question. The last step of designing your research is planning how you’ll analyze the data.
Quantitative data analysis
In quantitative research, you’ll most likely use some form of statistical analysis . With statistics, you can summarize your sample data, make estimates, and test hypotheses.
Using descriptive statistics , you can summarize your sample data in terms of:
- The distribution of the data (e.g., the frequency of each score on a test)
- The central tendency of the data (e.g., the mean to describe the average score)
- The variability of the data (e.g., the standard deviation to describe how spread out the scores are)
The specific calculations you can do depend on the level of measurement of your variables.
Using inferential statistics , you can:
- Make estimates about the population based on your sample data.
- Test hypotheses about a relationship between variables.
Regression and correlation tests look for associations between two or more variables, while comparison tests (such as t tests and ANOVAs ) look for differences in the outcomes of different groups.
Your choice of statistical test depends on various aspects of your research design, including the types of variables you’re dealing with and the distribution of your data.
Qualitative data analysis
In qualitative research, your data will usually be very dense with information and ideas. Instead of summing it up in numbers, you’ll need to comb through the data in detail, interpret its meanings, identify patterns, and extract the parts that are most relevant to your research question.
Two of the most common approaches to doing this are thematic analysis and discourse analysis .
There are many other ways of analyzing qualitative data depending on the aims of your research. To get a sense of potential approaches, try reading some qualitative research papers in your field.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question . It defines your overall approach and determines how you will collect and analyze data.
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research aims, that you collect high-quality data, and that you use the right kind of analysis to answer your questions, utilizing credible sources . This allows you to draw valid , trustworthy conclusions.
Quantitative research designs can be divided into two main categories:
- Correlational and descriptive designs are used to investigate characteristics, averages, trends, and associations between variables.
- Experimental and quasi-experimental designs are used to test causal relationships .
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible. Common types of qualitative design include case study , ethnography , and grounded theory designs.
The priorities of a research design can vary depending on the field, but you usually have to specify:
- Your research questions and/or hypotheses
- Your overall approach (e.g., qualitative or quantitative )
- The type of design you’re using (e.g., a survey , experiment , or case study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., questionnaires , observations)
- Your data collection procedures (e.g., operationalization , timing and data management)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical tests or thematic analysis )
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population . Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
In statistics, sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population.
Operationalization means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioral avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalize the variables that you want to measure.
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 22, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/research-design/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, guide to experimental design | overview, steps, & examples, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, ethical considerations in research | types & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Search for: Toggle Search
‘You Transformed the World,’ NVIDIA CEO Tells Researchers Behind Landmark AI Paper
Of GTC ’s 900+ sessions, the most wildly popular was a conversation hosted by NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang with seven of the authors of the legendary research paper that introduced the aptly named transformer — a neural network architecture that went on to change the deep learning landscape and enable today’s era of generative AI.
“Everything that we’re enjoying today can be traced back to that moment,” Huang said to a packed room with hundreds of attendees, who heard him speak with the authors of “ Attention Is All You Need .”
Sharing the stage for the first time, the research luminaries reflected on the factors that led to their original paper, which has been cited more than 100,000 times since it was first published and presented at the NeurIPS AI conference. They also discussed their latest projects and offered insights into future directions for the field of generative AI.
While they started as Google researchers, the collaborators are now spread across the industry, most as founders of their own AI companies.
“We have a whole industry that is grateful for the work that you guys did,” Huang said.

Origins of the Transformer Model
The research team initially sought to overcome the limitations of recurrent neural networks , or RNNs, which were then the state of the art for processing language data.
Noam Shazeer, cofounder and CEO of Character.AI, compared RNNs to the steam engine and transformers to the improved efficiency of internal combustion.
“We could have done the industrial revolution on the steam engine, but it would just have been a pain,” he said. “Things went way, way better with internal combustion.”
“Now we’re just waiting for the fusion,” quipped Illia Polosukhin, cofounder of blockchain company NEAR Protocol.
The paper’s title came from a realization that attention mechanisms — an element of neural networks that enable them to determine the relationship between different parts of input data — were the most critical component of their model’s performance.
“We had very recently started throwing bits of the model away, just to see how much worse it would get. And to our surprise it started getting better,” said Llion Jones, cofounder and chief technology officer at Sakana AI.
Having a name as general as “transformers” spoke to the team’s ambitions to build AI models that could process and transform every data type — including text, images, audio, tensors and biological data.
“That North Star, it was there on day zero, and so it’s been really exciting and gratifying to watch that come to fruition,” said Aidan Gomez, cofounder and CEO of Cohere. “We’re actually seeing it happen now.”

Envisioning the Road Ahead
Adaptive computation, where a model adjusts how much computing power is used based on the complexity of a given problem, is a key factor the researchers see improving in future AI models.
“It’s really about spending the right amount of effort and ultimately energy on a given problem,” said Jakob Uszkoreit, cofounder and CEO of biological software company Inceptive. “You don’t want to spend too much on a problem that’s easy or too little on a problem that’s hard.”
A math problem like two plus two, for example, shouldn’t be run through a trillion-parameter transformer model — it should run on a basic calculator, the group agreed.
They’re also looking forward to the next generation of AI models.
“I think the world needs something better than the transformer,” said Gomez. “I think all of us here hope it gets succeeded by something that will carry us to a new plateau of performance.”
“You don’t want to miss these next 10 years,” Huang said. “Unbelievable new capabilities will be invented.”
The conversation concluded with Huang presenting each researcher with a framed cover plate of the NVIDIA DGX-1 AI supercomputer, signed with the message, “You transformed the world.”

There’s still time to catch the session replay by registering for a virtual GTC pass — it’s free.
To discover the latest in generative AI, watch Huang’s GTC keynote address:
NVIDIA websites use cookies to deliver and improve the website experience. See our cookie policy for further details on how we use cookies and how to change your cookie settings.
Share on Mastodon
Read our research on: TikTok | Podcasts | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
8 in 10 americans say religion is losing influence in public life, few see biden or trump as especially religious.
Pew Research Center conducted this survey to explore Americans’ attitudes about religion’s role in public life, including politics in a presidential election year.
For this report, we surveyed 12,693 respondents from Feb. 13 to 25, 2024. Most of the respondents (10,642) are members of the American Trends Panel, an online survey panel recruited through national random sampling of residential addresses, which gives nearly all U.S. adults a chance of selection.
The remaining respondents (2,051) are members of three other panels, the Ipsos KnowledgePanel, the NORC Amerispeak panel and the SSRS opinion panel. All three are national survey panels recruited through random sampling (not “opt-in” polls). We used these additional panels to ensure that the survey would have enough Jewish and Muslim respondents to be able to report on their views.
The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education, religious affiliation and other categories.
For more, refer to the ATP’s Methodology and the Methodology for this report. Read the questions used in this report .
A new Pew Research Center survey finds that 80% of U.S. adults say religion’s role in American life is shrinking – a percentage that’s as high as it’s ever been in our surveys.
Most Americans who say religion’s influence is shrinking are not happy about it. Overall, 49% of U.S. adults say both that religion is losing influence and that this is a bad thing. An additional 8% of U.S. adults think religion’s influence is growing and that this is a good thing.
Together, a combined 57% of U.S adults – a clear majority – express a positive view of religion’s influence on American life.
The survey also finds that about half of U.S. adults say it’s “very” or “somewhat” important to them to have a president who has strong religious beliefs, even if those beliefs are different from their own. But relatively few Americans view either of the leading presidential candidates as very religious: 13% of Americans say they think President Joe Biden is very religious, and just 4% say this about former President Donald Trump.
Overall, there are widespread signs of unease with religion’s trajectory in American life. This dissatisfaction is not just among religious Americans. Rather, many religious and nonreligious Americans say they feel that their religious beliefs put them at odds with mainstream culture, with the people around them and with the other side of the political spectrum. For example:
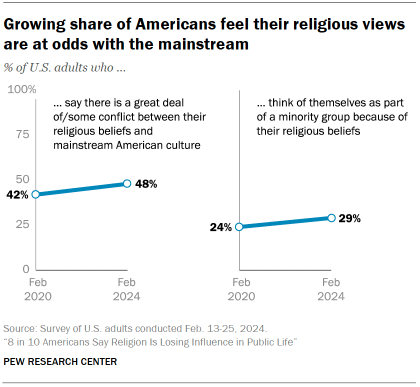
- 48% of U.S. adults say there’s “a great deal” of or “some” conflict between their religious beliefs and mainstream American culture, up from 42% in 2020.
- 29% say they think of themselves as religious minorities, up from 24% in 2020.
- 41% say it’s best to avoid discussing religion at all if someone disagrees with you, up from 33% in 2019.
- 72% of religiously unaffiliated adults – those who identify, religiously, as atheist, agnostic or “nothing in particular” – say conservative Christians have gone too far in trying to control religion in the government and public schools; 63% of Christians say the same about secular liberals.
These are among the key findings of a new Pew Research Center survey, conducted Feb. 13-25, 2024, among a nationally representative sample of 12,693 U.S. adults.
This report examines:
- Religion’s role in public life
- U.S. presidential candidates and their religious engagement
- Christianity’s place in politics, and “Christian nationalism”
The survey also finds wide partisan gaps on questions about the proper role for religion in society, with Republicans more likely than Democrats to favor religious influence in governance and public life. For instance:
- 42% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents say that when the Bible and the will of the people conflict, the Bible should have more influence on U.S. laws than the will of the people. Just 16% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents say this.
- 21% of Republicans and GOP leaners say the federal government should declare Christianity the official religion of the United States, compared with 7% of Democrats and Democratic leaners.
Moral and religious qualities in a president
Almost all Americans (94%) say it is “very” or “somewhat” important to have a president who personally lives a moral and ethical life. And a majority (64%) say it’s important to have a president who stands up for people with their religious beliefs.
About half of U.S. adults (48%) say it is important for the president to hold strong religious beliefs. Fewer (37%) say it’s important for the president to have the same religious beliefs as their own.
Republicans are much more likely than Democrats to value religious qualities in a president, and Christians are more likely than the religiously unaffiliated to do so. For example:
- Republicans and GOP leaners are twice as likely as Democrats and Democratic leaners to say it is important to have a president who has the same religious beliefs they do (51% vs. 25%).
- 70% of White evangelical Protestants say it is important to have a president who shares their religious beliefs. Just 11% of religiously unaffiliated Americans say this.
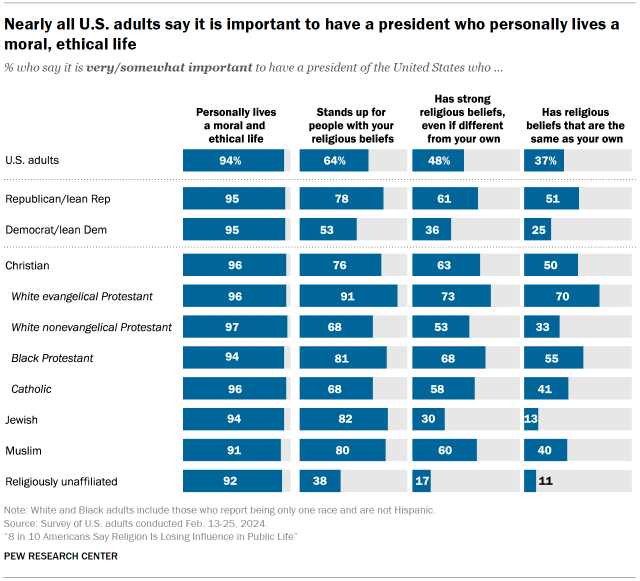
Views of Biden, Trump and their religious engagement
Relatively few Americans think of Biden or Trump as “very” religious. Indeed, even most Republicans don’t think Trump is very religious, and even most Democrats don’t think Biden is very religious.
- 6% of Republicans and GOP leaners say Trump is very religious, while 44% say he is “somewhat” religious. Nearly half (48%) say he is “not too” or “not at all” religious.
- 23% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents say Biden is very religious, while 55% say he is somewhat religious. And 21% say he is not too or not at all religious.
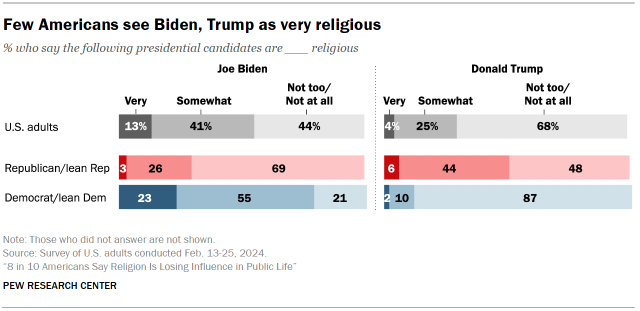
Though they don’t think Trump is very religious himself, most Republicans and people in religious groups that tend to favor the Republican Party do think he stands up at least to some extent for people with their religious beliefs. Two-thirds of Republicans and independents who lean toward the GOP (67%) say Trump stands up for people with their religious beliefs “a great deal,” “quite a bit” or “some.” About the same share of White evangelical Protestants (69%) say this about Trump.
Similarly, 60% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, as well as 73% of Jewish Americans and 60% of Black Protestants, say Biden stands up for people with their religious beliefs a great deal, quite a bit or some.
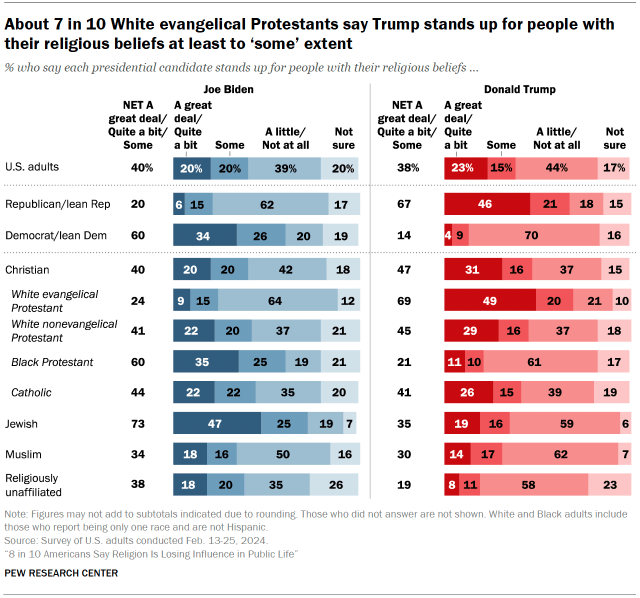
Overall, views of both Trump and Biden are generally unfavorable.
- White evangelical Protestants – a largely Republican group – stand out as having particularly favorable views of Trump (67%) and unfavorable views of Biden (86%).
- Black Protestants and Jewish Americans – largely Democratic groups – stand out for having favorable views of Biden and unfavorable views of Trump.
Views on trying to control religious values in the government and schools
Americans are almost equally split on whether conservative Christians have gone too far in trying to push their religious values in the government and public schools, as well as on whether secular liberals have gone too far in trying to keep religious values out of these institutions.
Most religiously unaffiliated Americans (72%) and Democrats (72%) say conservative Christians have gone too far. And most Christians (63%) and Republicans (76%) say secular liberals have gone too far.
Christianity’s place in politics, and Christian nationalism
In recent years, “Christian nationalism” has received a great deal of attention as an ideology that some critics have said could threaten American democracy .
Despite growing news coverage of Christian nationalism – including reports of political leaders who seem to endorse the concept – the new survey shows that there has been no change in the share of Americans who have heard of Christian nationalism over the past year and a half. Similarly, the new survey finds no change in how favorably U.S. adults view Christian nationalism.
Overall, 45% say they have heard or read about Christian nationalism, including 25% who also have an unfavorable view of it and 5% who have a favorable view of it. Meanwhile, 54% of Americans say they haven’t heard of Christian nationalism at all.
One element often associated with Christian nationalism is the idea that church and state should not be separated, despite the Establishment Clause in the First Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.
The survey finds that about half of Americans (49%) say the Bible should have “a great deal” of or “some” influence on U.S. laws, while another half (51%) say it should have “not much” or “no influence.” And 28% of U.S. adults say the Bible should have more influence than the will of the people if the two conflict. These numbers have remained virtually unchanged over the past four years.
In the new survey, 16% of U.S. adults say the government should stop enforcing the separation of church and state. This is little changed since 2021.
In response to a separate question, 13% of U.S. adults say the federal government should declare Christianity the official religion of the U.S., and 44% say the government should not declare the country a Christian nation but should promote Christian moral values. Meanwhile, 39% say the government should not elevate Christianity in either way. 1
Overall, 3% of U.S. adults say the Bible should have more influence on U.S. laws than the will of the people; and that the government should stop enforcing separation of church and state; and that Christianity should be declared the country’s official religion. And 13% of U.S. adults endorse two of these three statements. Roughly one-fifth of the public (22%) expresses one of these three views that are often associated with Christian nationalism. The majority (62%) expresses none.
Guide to this report
The remainder of this report describes these findings in additional detail. Chapter 1 focuses on the public’s perceptions of religion’s role in public life. Chapter 2 examines views of presidential candidates and their religious engagement. And Chapter 3 focuses on Christian nationalism and views of the U.S. as a Christian nation.
- The share saying that the government should declare Christianity the official national religion (13%) is almost identical to the share who said the government should declare the U.S. a Christian nation in a March 2021 survey that asked a similar question (15%). ↩
Sign up for our Religion newsletter
Sent weekly on Wednesday
Report Materials
Table of contents, 5 facts about religion and americans’ views of donald trump, u.s. christians more likely than ‘nones’ to say situation at the border is a crisis, from businesses and banks to colleges and churches: americans’ views of u.s. institutions, most u.s. parents pass along their religion and politics to their children, growing share of americans see the supreme court as ‘friendly’ toward religion, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Survey research uses a list of questions to collect data about a group of people. You can conduct surveys online, by mail, or in person. FAQ ... Sending out a paper survey by mail is a common method of gathering demographic information (for example, in a government census of the population).
A survey paper is different from a regular research paper. Every element of the essay needs to relate to the research question and tie into the overall objective of the paper. Writing research papers takes a lot of effort and attention to detail. You will have to revise, edit and proofread your work several times.
A survey paper, also known as a review paper or a literature review, is a type of academic paper that synthesizes and analyzes existing research on a particular topic. It goes beyond summarizing individual studies and aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the field. The goal of a survey paper is to identify trends, patterns, and gaps in ...
Step 1: Selecting the Representative Papers. The first step when writing a survey paper is selecting the most relevant representative papers that are within the scope of your research and summarizing them effectively. As you will note, there can be a lot of research papers, and the space required to create a survey paper is limited.
Number of papers may reduce if you apply well-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Take notes Read all relevant papers and document relevant notes. If possible, classify each relevant paper according to your research questions. Infer, classify, and synthesize This is the most important step of writing a survey paper. IMHO, a survey should ...
Survey research is defined as "the collection of information from a sample of individuals through their responses to questions" ( Check & Schutt, 2012, p. 160 ). This type of research allows for a variety of methods to recruit participants, collect data, and utilize various methods of instrumentation. Survey research can use quantitative ...
A survey paper is not simply a core dump of a bunch of papers in a common area. Instead, a survey is a research paper whose data and results are taken from other papers. This means that you should have a point to make or some new conclusion to draw.
A survey paper should. Pick at least 10-20 papers on a specific topic from the collected paper list. The papers selected should be a mix of papers including the base paper in the selected domain to the most recently published paper. Give a critical assessment of the work that has been done.
It focuses on collecting and presenting technical information, often to describe the history of discoveries about a given topic. A survey article, therefore, is typically shorter than a review article. A literature review (sometimes called a narrative review) also involves the collection of all the relevant literature on a topic.
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analysing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps: Determine who will participate in the survey. Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person) Design the survey questions and layout. Distribute the survey.
Regular research papers are a description of your own research. A survey paper is a service to the scientiflc community. You are doing their research for them. Instead of reading 20+ papers to understand what a scientiflc topic is about, they just need to read your paper. Which subjects should you write a survey about: flelds which are on ...
Survey Research Definition. Survey Research is defined as the process of conducting research using surveys that researchers send to survey respondents. The data collected from surveys is then statistically analyzed to draw meaningful research conclusions. In the 21st century, every organization's eager to understand what their customers think ...
Avoid adding unknown papers, old but less cited papers, false and fake references in your survey paper because it can demolish your whole effort easily. Remember, a good survey paper written on a mature research area should have atleast 50 references, although a survey paper written on new or emerging topic can be with less than 50 references.
Abstract. The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has led to a massive rise in survey-based research. The paucity of perspicuous guidelines for conducting surveys may pose a challenge to the conduct of ethical, valid and meticulous research. The aim of this paper is to guide authors aiming to publish in scholarly journals regarding the ...
A survey is a research method that is used to collect data from a group of respondents in order to gain insights and information regarding a particular subject. It's an excellent method to gather opinions and understand how and why people feel a certain way about different situations and contexts. .
Survey Research. Definition: Survey Research is a quantitative research method that involves collecting standardized data from a sample of individuals or groups through the use of structured questionnaires or interviews. The data collected is then analyzed statistically to identify patterns and relationships between variables, and to draw conclusions about the population being studied.
Questionnaires vs. surveys. A survey is a research method where you collect and analyze data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.. Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives, placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
Survey research is the process of collecting data from a predefined group (e.g. customers or potential customers) with the ultimate goal of uncovering insights about your products, services, or brand overall.. As a quantitative data collection method, survey research can provide you with a goldmine of information that can inform crucial business and product decisions.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic. There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
The most common method used in social and management sciences is the survey questionnaire because it is a cost-effective means to gather the data. It is inexpensive and allows quick responses and ...
A survey paper is a research paper conducted by asking a question or questions to a population of people and then analyzing the answers. The results sometimes help to generalize the entire population or demographic group. Survey papers are commonly used in academic research to gather data on various topics.
Survey data shows more of them believe he acted criminally. By Ruth Igielnik Republicans who get their news from nonconservative mainstream media outlets are less likely to support Donald J. Trump ...
A 2018 Center survey also asked U.S teens some of the same questions about experiences and views related to smartphone and social media. Direct comparisons cannot be made across the two surveys due to mode, sampling and recruitment differences. Please read the Methodology section to learn more about how the current survey was conducted. ↩
MARCH 21, 2024 — The U.S. Census Bureau today released new data from phase 4.0 of the experimental Household Pulse Survey (HPS). The HPS is an effort by the Census Bureau and other federal statistical agencies to measure how emergent issues are impacting U.S. households from a social and economic perspective.
The focus of recent research has shifted from merely increasing the Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) performance in various tasks to DNNs, which are more interpretable to humans. The field of eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) has observed various techniques, including saliency-based and concept-based approaches. Concept-based approaches explain the model's decisions in simple human ...
China has produced a huge number of top A.I. engineers in recent years. New research shows that, by some measures, it has already eclipsed the United States. By Paul Mozur and Cade Metz Paul Mozur ...
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Survey research often shows associations without being able to determine causality. Age. There are sizable differences in attention to the Israel-Hamas war by age. Limited attention to news about the conflict is seen not only in the youngest age group but also among all adults under 50. Just 14% of adults under 30, as well as 14% of those ages ...
Of GTC's 900+ sessions, the most wildly popular was a conversation hosted by NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang with seven of the authors of the legendary research paper that introduced the aptly named transformer — a neural network architecture that went on to change the deep learning landscape and enable today's era of generative AI. ...
Pew Research Center conducted this survey to explore Americans' attitudes about religion's role in public life, including politics in a presidential election year. For this report, we surveyed 12,693 respondents from Feb. 13 to 25, 2024. Most of the respondents (10,642) are members of the American Trends Panel, an online survey panel ...