
How to Edit an Essay: Tips and Tricks for a Flawless Paper

How to Edit a Paper: 9 Tips You Need to Know
Often overlooked as an easy task, essay editing is way more important step of the writing process than you can imagine. Writing a compelling introduction, crafting comprehensive body paragraphs, knowing what words to use in college essays, and finishing it off with a memorable conclusion are essential, but revising what you wrote can take your essay to a whole new level.
Professional writers know that revising a text is an art of its own, and if you want to play in the top league, you should master it too. Our research paper writing service sets a goal to share the intricate details of how to edit a paper and help you become a skillful storyteller.
Besides the obvious, like correcting grammar, spelling, syntax, and so on, editing allows you to see the full picture and make sure that your paper meets the initial goals. The true essence of editing lies in scrutinizing whether your paper is well-crafted and logically coherent while meeting the academic guidelines and thesis statement. Additionally, it demands you assess if you have adequately addressed all specific requirements and whether you have used proper essay language.
Revisiting your written piece can enable you to refine areas that may lack consistency or clarity, thereby enabling you to tell an engaging story in a more professional manner. By adopting this approach, any informational gaps or inconsistencies could be swiftly addressed, giving readers a comprehensive account for them to enjoy reading.

Essay Editing Tip #1: Take a Break!
No matter how many essays you have written and where you stand on a scale of professional writers, you must still be wondering how to make an essay better.
Believe it or not, taking a break and stepping back might be the best thing to do. Once you are done telling the story and have all the necessary aspects of a great essay, it's time to relax. Don't start paper editing, and by no means submit an essay straight away.
Sometimes when our brains get stuck on one thing, we lose the ability to see things clearly. We get emotionally attached and can't see the obvious mistakes. Clear your head, watch a movie, take a walk, or do whatever makes you happy and feel at peace. Don't start writing the night before; give yourself a few hours or even days to distance yourself from the writing process.
Once you feel all fresh, come back and start revising. You will notice mistakes that were there all this time, but you were unable to notice them. You will see logical inconsistencies and grammatical errors. Trust us, once you realize those grammatical errors could ruin your fascinating story, you'll be happy you did not submit the essay straight away.
Essay Editing Tip #2: Change the Font and Size
Do you want to know what the next hack for editing an essay is? You should do everything to make it visually look like a different essay. Professional writers recommend changing the font and size.
Remember when we talked about being unable to see the mistakes in front of our eyes? When you stare at an object for a while, it starts to lose its shape and other characteristics and kinda blends into a homogenous thing. You need to step away or look at it from a different angle to start seeing them again.
Yes, a paper is not a painting or an object, and you use words for essays, but you are still visually perceiving it. On average, writing a paper takes at least a day. Imagine starting at something and thinking about it for a day. It would turn into a borderless mixture in your head.
Changing the font and size is like changing the angle. You will get a fresh perspective and start to notice grammar mistakes, misused topic sentences, and so on. Don't be afraid to look at your essay from an outside point of view; it will only make your writing better.
Essay Editing Tip #3: Print Out Your Paper
Another great way to change your perspective is to print out your own paper. The constant strain of staring at a computer screen for prolonged periods can cause distractions and leave you feeling mentally drained. A tired brain can no longer detect grammar errors, and all your proofreading digitally can go in vain.
By physically holding your research paper in hand, you afford yourself the opportunity to take a step back from the screen and approach the task with renewed spirit. You might have already corrected grammar, but what about formatting mistakes? Maybe some overlooked margins or improperly sized font types made their way into your work. You might have used a lot of long sentences and big words that need to go. Chances are you may have missed some good words to use in essays, and now you get a fresh opportunity to turn your paper into something else.
Check what other good essay words would complement specific passages and improve expression quality overall!
Essay Editing Tip #4: Use a Highlighter
Your writing skills can catapult if you start using some old-fashioned methods of self-editing. Old school writers always walk around with a highlighter in their hands. Highlighting is a great way to focus on individual sentences and vigorously proof check them.
When editing an essay, finding a mistake and immediately correcting them can lead you to lose focus. It's better to first find all the mistakes and areas of improvement and take action later.
One of the greatest editing tips from our expert writing services is to use different color highlighters for different kinds of issues. There are four different issue types you may want to look out for. Highlight grammar mistakes, formatting issues, problematic areas, and important information. Use different highlighters for categorizing them so when you come back for refinement; you know what you are dealing with.
Highlighting can help you quickly and easily find very intricate mistakes that otherwise would be missed, such as identifying misplaced great essay phrases and changing their location to where they make more sense.
Need a Hand in Polishing Your Paper?
Choose our professional essay editing service and relax knowing your paper has exceptional grammar, spelling, style, and clarity!
Essay Editing Tip #5: Read Your Paper Backwards
What about analyzing your final draft upside down? You can challenge your paper and make the editing process fun. Follow our guide on how to edit your essay, and you will never make rookie mistakes.
The essay should make sense from top to bottom and vice versa. Every paragraph you write should be linked with one another and make sense on its own.
Start at the end and question the last sentence. Does it make sense? Is it compelling? Does it relate to the thesis statement? Could a random person figure out what the rest of the essay was about? Step by step, move upwards and question each paragraph carefully.
Focus on sentence fragments and individual words. Question if they are proper words to use in an essay. This will not only help you notice spelling mistakes and typos but also improve the overall quality of your academic writing.
Listen to the flow. When reading backward, it is easier to notice whether the text is well-constructed and easy to follow. You will be able to notice where the paper needs refinement with better transitional sentences. You may have used faulty parallelism or unnecessary information that needs to be removed.
Don't forget to look for consistency. Check the formatting and citation style and make sure they comply with the requirements. Students often forget to proofread the reference list.
Essay Editing Tip #6: Use a Checklist
To ensure that your essay is error-free and effectively transmits your intended message, you can use an editing checklist. It is always a good idea to check your writing against pre-set criteria. Here are some of the items from our ' do my essay ' experts you can put on your checklist and use while editing an essay.
Introduction - Does it introduce readers to the background story and context? Is it engaging?
Thesis statement - Does it effectively convey what the essay is about? Is it clear and concise?
Central paragraphs - Are main arguments well supported? Are they well-organized and logically coherent?
Transitions - Do the paragraphs link with one another with proper transitional sentences?
Conclusion - Does it provide an effective summary of the essay? Is it memorable?
Grammar - Are there any spelling errors? Did you use the correct syntax? Have you used proper words for essays?
Formatting - Does the citation style follow the proposed guide of essay writing format ? Have you referenced every source?
Essay Editing Tip #7: Read Your Paper Out Loud
Another step in our guide on how to edit an essay is reading the document out loud. Once you finish writing and there is little time remaining to catch a breath, you need to get creative and quickly look at your essay with fresh eyes.
By audibly hearing the sound of each sentence and phrase, you'll gain fresh insight into how well your ideas flow together cohesively. Research has confirmed that reading the document out loud can help enhance students' writing proficiency as it enables them to easily identify structural issues in their work.
This increased level of focus will help bring attention to any areas that feel particularly clunky or repetitive – issues that may not have been immediately apparent otherwise. It will help you see all the awkward essay language, long sentences, and repeated words.
Beyond basic grammar checks or typos correction, when reading aloud, students also have the opportunity to hone in on things like tone and audience engagement; So next time you finish writing something - don't forget about giving those vocal cords a little exercise!
Essay Editing Tip #8: Change the Environment
The authors of our guide on how to edit a paper say that changing the environment is all it takes to reset. Essay writing takes a lot of focus and determination and therefore is very exhausting. Taking a break is just as important; stretching and moving from room to room is just as important as finding the right words for essays.
Before revising the paper, go to a park, library, or to your favorite cafe and get a fresh start. Find a comfortable, quiet spot and take over the job. To detect and correct grammar mistakes, you will need a well-rested mind and no distractions.
Sometimes changing the scenery can boost your creativity and give you fresh insights. By doing so, you will likely discover areas within the text that require more attention and refinement, and the solutions will come quicker.
It's important to remember that crafting well-written papers takes time and effort - rushing through them typically results in poor quality.
Essay Editing Tip #9: Use a Dictionary
To enhance the appeal of your writing style, you can find fancy words to use in essays. In the preliminary drafts, allow yourself to express yourself freely through simple sentences and phrases while leaving room for improvements during editing.
Dictionaries can turn into a long-term solution. Use them to improve your spelling. Even some commonly made errors could easily be eliminated with this practice.
Using a dictionary can also introduce good essay words in your vocabulary. Incorporating advanced terms into limited word count assignments can significantly elevate its quality from average to exceptional whilst enhancing clarity in expression as well.

Use Our Expert Editing Help
This article is proof that editing takes much more time and attention than it seems at first glance, but it also is an essential part of producing quality work. It guarantees clarity, accuracy, and professionalism in any piece of writing.
Don't skip one of the most important steps in crafting a top-notch essay because you are falling short on time. Get help from our essay editing service . Or, you can even buy research paper from our team of professional writers who will help you craft and polish your work.
Are You Ready to Level Up Your Writing?
Let our expert writers improve your grades by always delivering top-quality, plagiarism-free papers in no time!
FAQs: What Else You Need to Know on Editing an Essay
Our team of experienced writers diligently researched the internet's most frequently asked questions on how to make an essay better and answered them all for you to equip you with all the necessary tools for enhancing your writing skills.
So take some time out, read through our comprehensive responses, and unlock your full potential as a writer!
What are the 5 C's of Editing?
How can i edit for free, what are the common mistakes while editing, related articles.
.webp)

Editing and Proofreading
What this handout is about.
This handout provides some tips and strategies for revising your writing. To give you a chance to practice proofreading, we have left seven errors (three spelling errors, two punctuation errors, and two grammatical errors) in the text of this handout. See if you can spot them!
Is editing the same thing as proofreading?
Not exactly. Although many people use the terms interchangeably, editing and proofreading are two different stages of the revision process. Both demand close and careful reading, but they focus on different aspects of the writing and employ different techniques.
Some tips that apply to both editing and proofreading
- Get some distance from the text! It’s hard to edit or proofread a paper that you’ve just finished writing—it’s still to familiar, and you tend to skip over a lot of errors. Put the paper aside for a few hours, days, or weeks. Go for a run. Take a trip to the beach. Clear your head of what you’ve written so you can take a fresh look at the paper and see what is really on the page. Better yet, give the paper to a friend—you can’t get much more distance than that. Someone who is reading the paper for the first time, comes to it with completely fresh eyes.
- Decide which medium lets you proofread most carefully. Some people like to work right at the computer, while others like to sit back with a printed copy that they can mark up as they read.
- Try changing the look of your document. Altering the size, spacing, color, or style of the text may trick your brain into thinking it’s seeing an unfamiliar document, and that can help you get a different perspective on what you’ve written.
- Find a quiet place to work. Don’t try to do your proofreading in front of the TV or while you’re chugging away on the treadmill. Find a place where you can concentrate and avoid distractions.
- If possible, do your editing and proofreading in several short blocks of time. Your concentration may start to wane if you try to proofread the entire text at one time.
- If you’re short on time, you may wish to prioritize. Make sure that you complete the most important editing and proofreading tasks.
Editing is what you begin doing as soon as you finish your first draft. You reread your draft to see, for example, whether the paper is well-organized, the transitions between paragraphs are smooth, and your evidence really backs up your argument. You can edit on several levels:
Have you done everything the assignment requires? Are the claims you make accurate? If it is required to do so, does your paper make an argument? Is the argument complete? Are all of your claims consistent? Have you supported each point with adequate evidence? Is all of the information in your paper relevant to the assignment and/or your overall writing goal? (For additional tips, see our handouts on understanding assignments and developing an argument .)
Overall structure
Does your paper have an appropriate introduction and conclusion? Is your thesis clearly stated in your introduction? Is it clear how each paragraph in the body of your paper is related to your thesis? Are the paragraphs arranged in a logical sequence? Have you made clear transitions between paragraphs? One way to check the structure of your paper is to make a reverse outline of the paper after you have written the first draft. (See our handouts on introductions , conclusions , thesis statements , and transitions .)
Structure within paragraphs
Does each paragraph have a clear topic sentence? Does each paragraph stick to one main idea? Are there any extraneous or missing sentences in any of your paragraphs? (See our handout on paragraph development .)
Have you defined any important terms that might be unclear to your reader? Is the meaning of each sentence clear? (One way to answer this question is to read your paper one sentence at a time, starting at the end and working backwards so that you will not unconsciously fill in content from previous sentences.) Is it clear what each pronoun (he, she, it, they, which, who, this, etc.) refers to? Have you chosen the proper words to express your ideas? Avoid using words you find in the thesaurus that aren’t part of your normal vocabulary; you may misuse them.
Have you used an appropriate tone (formal, informal, persuasive, etc.)? Is your use of gendered language (masculine and feminine pronouns like “he” or “she,” words like “fireman” that contain “man,” and words that some people incorrectly assume apply to only one gender—for example, some people assume “nurse” must refer to a woman) appropriate? Have you varied the length and structure of your sentences? Do you tends to use the passive voice too often? Does your writing contain a lot of unnecessary phrases like “there is,” “there are,” “due to the fact that,” etc.? Do you repeat a strong word (for example, a vivid main verb) unnecessarily? (For tips, see our handouts on style and gender-inclusive language .)
Have you appropriately cited quotes, paraphrases, and ideas you got from sources? Are your citations in the correct format? (See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for more information.)
As you edit at all of these levels, you will usually make significant revisions to the content and wording of your paper. Keep an eye out for patterns of error; knowing what kinds of problems you tend to have will be helpful, especially if you are editing a large document like a thesis or dissertation. Once you have identified a pattern, you can develop techniques for spotting and correcting future instances of that pattern. For example, if you notice that you often discuss several distinct topics in each paragraph, you can go through your paper and underline the key words in each paragraph, then break the paragraphs up so that each one focuses on just one main idea.
Proofreading
Proofreading is the final stage of the editing process, focusing on surface errors such as misspellings and mistakes in grammar and punctuation. You should proofread only after you have finished all of your other editing revisions.
Why proofread? It’s the content that really matters, right?
Content is important. But like it or not, the way a paper looks affects the way others judge it. When you’ve worked hard to develop and present your ideas, you don’t want careless errors distracting your reader from what you have to say. It’s worth paying attention to the details that help you to make a good impression.
Most people devote only a few minutes to proofreading, hoping to catch any glaring errors that jump out from the page. But a quick and cursory reading, especially after you’ve been working long and hard on a paper, usually misses a lot. It’s better to work with a definite plan that helps you to search systematically for specific kinds of errors.
Sure, this takes a little extra time, but it pays off in the end. If you know that you have an effective way to catch errors when the paper is almost finished, you can worry less about editing while you are writing your first drafts. This makes the entire writing proccess more efficient.
Try to keep the editing and proofreading processes separate. When you are editing an early draft, you don’t want to be bothered with thinking about punctuation, grammar, and spelling. If your worrying about the spelling of a word or the placement of a comma, you’re not focusing on the more important task of developing and connecting ideas.
The proofreading process
You probably already use some of the strategies discussed below. Experiment with different tactics until you find a system that works well for you. The important thing is to make the process systematic and focused so that you catch as many errors as possible in the least amount of time.
- Don’t rely entirely on spelling checkers. These can be useful tools but they are far from foolproof. Spell checkers have a limited dictionary, so some words that show up as misspelled may really just not be in their memory. In addition, spell checkers will not catch misspellings that form another valid word. For example, if you type “your” instead of “you’re,” “to” instead of “too,” or “there” instead of “their,” the spell checker won’t catch the error.
- Grammar checkers can be even more problematic. These programs work with a limited number of rules, so they can’t identify every error and often make mistakes. They also fail to give thorough explanations to help you understand why a sentence should be revised. You may want to use a grammar checker to help you identify potential run-on sentences or too-frequent use of the passive voice, but you need to be able to evaluate the feedback it provides.
- Proofread for only one kind of error at a time. If you try to identify and revise too many things at once, you risk losing focus, and your proofreading will be less effective. It’s easier to catch grammar errors if you aren’t checking punctuation and spelling at the same time. In addition, some of the techniques that work well for spotting one kind of mistake won’t catch others.
- Read slow, and read every word. Try reading out loud , which forces you to say each word and also lets you hear how the words sound together. When you read silently or too quickly, you may skip over errors or make unconscious corrections.
- Separate the text into individual sentences. This is another technique to help you to read every sentence carefully. Simply press the return key after every period so that every line begins a new sentence. Then read each sentence separately, looking for grammar, punctuation, or spelling errors. If you’re working with a printed copy, try using an opaque object like a ruler or a piece of paper to isolate the line you’re working on.
- Circle every punctuation mark. This forces you to look at each one. As you circle, ask yourself if the punctuation is correct.
- Read the paper backwards. This technique is helpful for checking spelling. Start with the last word on the last page and work your way back to the beginning, reading each word separately. Because content, punctuation, and grammar won’t make any sense, your focus will be entirely on the spelling of each word. You can also read backwards sentence by sentence to check grammar; this will help you avoid becoming distracted by content issues.
- Proofreading is a learning process. You’re not just looking for errors that you recognize; you’re also learning to recognize and correct new errors. This is where handbooks and dictionaries come in. Keep the ones you find helpful close at hand as you proofread.
- Ignorance may be bliss, but it won’t make you a better proofreader. You’ll often find things that don’t seem quite right to you, but you may not be quite sure what’s wrong either. A word looks like it might be misspelled, but the spell checker didn’t catch it. You think you need a comma between two words, but you’re not sure why. Should you use “that” instead of “which”? If you’re not sure about something, look it up.
- The proofreading process becomes more efficient as you develop and practice a systematic strategy. You’ll learn to identify the specific areas of your own writing that need careful attention, and knowing that you have a sound method for finding errors will help you to focus more on developing your ideas while you are drafting the paper.
Think you’ve got it?
Then give it a try, if you haven’t already! This handout contains seven errors our proofreader should have caught: three spelling errors, two punctuation errors, and two grammatical errors. Try to find them, and then check a version of this page with the errors marked in red to see if you’re a proofreading star.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Especially for non-native speakers of English:
Ascher, Allen. 2006. Think About Editing: An ESL Guide for the Harbrace Handbooks . Boston: Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Lane, Janet, and Ellen Lange. 2012. Writing Clearly: Grammar for Editing , 3rd ed. Boston: Heinle.
For everyone:
Einsohn, Amy. 2011. The Copyeditor’s Handbook: A Guide for Book Publishing and Corporate Communications , 3rd ed. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Lanham, Richard A. 2006. Revising Prose , 5th ed. New York: Pearson Longman.
Tarshis, Barry. 1998. How to Be Your Own Best Editor: The Toolkit for Everyone Who Writes . New York: Three Rivers Press.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
The Ultimate Essay Checklist
#scribendiinc
Getting Started
Essay writing: it might not be your favorite thing in the world, but the essay editing experts at Scribendi are here to change that by making it a little less scary and a lot more fun! (Okay—perhaps "fun" is a bit strong. How about "bearable"?)
While there are four main types of essays—expository, persuasive, analytical, and argumentative—the basic structure of any essay is the same:
- An introductory paragraph
- At least three body paragraphs
- A concluding paragraph
- A bibliography
Generally, the higher your level of education, the more complex your essay structure will be. While high school students typically stick with the five-paragraph essay, university and graduate students are expected to discuss topics that require more than five paragraphs to flesh out. Whatever type of essay you're writing, following this basic format will help you accomplish your intended goal.
This ultimate essay checklist will provide you with everything you need to unleash your knowledge and express your creativity while following standard essay-writing conventions. This essay checklist will show you how to write a stellar essay of any style, and it will give you the confidence to explore and write about any topic.
General Tips
- Get an early start. It's much easier to come up with and organize your ideas when you're not pressed for time and are able to conduct proper research. The earlier you start, the easier it will be . . . so don't procrastinate!
- Choose a topic. Your instructor will likely give you a handful of topics to choose from or a general topic area. Depending on the instructions you're given, you will have to select and refine the topic. You can choose something you're already interested in or something you know nothing about—either way, you'll be doing your research and learning along the way.
- Use various sources of information. With the vast amount of information available today, you're far from limited when it comes to choosing your sources. Use books, websites, journal articles, research studies, interviews—the world is your oyster! Just remember to keep track of your sources so that you can cite them properly and add them to your bibliography. Also check what kinds of sources your professor wants: primary, secondary, or both?
- Do not plagiarize. Cite your work and give credit where it's due. Do not take credit for others' thoughts or ideas, and make yourself aware of the basic rules for avoiding plagiarism .
- Create an outline. Make a rough outline of the sections and points of your essay. Writing your ideas down will help you organize your thoughts and see what you need to add, change, or rearrange.
- Provide evidence. Use evidence from your research to support your ideas. Each body paragraph will contain an original idea, but you will need to back it up with evidence to make it credible.
- Don't use "I" statements or make sweeping generalizations. Stay objective, and be specific.
- Grab your audience's attention. Come up with an attention-grabbing title and introduction that will make your reader want more.
- Use logic. Within each paragraph and throughout your essay, keep your ideas coherent and linear.
- Use an essay style that complements your content (and is in accordance with your professor's guidelines). There are four main types of essays:
- Expository : The writer explains an idea or issue to the reader.
- Persuasive : The writer tries to convince the reader to take his or her position on an idea, issue, or topic.
- Analytical : The writer examines and analyzes an idea, issue, or topic.
- Argumentative : The writer tries to prove that his or her position is correct.
- Answer what , why , and how . Regardless of the type of essay you write, it should answer each of these questions.
- Don't feel obliged to write your first draft in order, from introduction to bibliography. It can be difficult to write a completely linear essay when you have lots of different ideas, so start by writing whatever you're ready to write—you can put all the pieces together later. This will make the process easier and less stressful.
Introduction
The introductory paragraph broadly introduces your topic by giving your reader an overview of what your essay will be about and the points that will be discussed. It often starts with a general statement that acts as the topic sentence for the paragraph, and it provides a general discussion that leads to a specific thesis statement at the end of the paragraph.
- Do not explicitly explain your intentions. For example, do not say, "The purpose of this essay is to . . ." Instead, allow the topic sentence to help your reader identify and determine your purpose. By the time readers get to the end, they will have a comprehensive understanding of your essay and its intent.
- Choose a thesis statement that the body of your essay will be able to support. This thesis will be the "hook" of your essay, and it is often one of the last sentences in the introductory paragraph. A hook is a line that grabs the reader's attention—it "hooks" them, just like a fishing hook grabs a fish. The goal of the hook is to keep your reader interested and to clearly indicate the purpose of the essay.
The body of the essay develops the argument that was outlined in the introduction.
- Use topic sentences. The topic sentence of each paragraph provides a brief summary of what the paragraph is about.

- Set up the transition to your next point. The concluding sentence of each paragraph should function as a hook and transition into the next paragraph.
- Discuss and support a different idea in each paragraph. Limit each paragraph to one main idea. The topic sentence of each paragraph will help you organize your own thoughts and let the reader know what that paragraph is about. If you're writing a five-paragraph essay, follow this general outline:
- The first paragraph contains the strongest argument and ties into the hook at the end of the introductory paragraph. Discuss your first point, elaborate on it, and provide evidence in support of it. Close with a transitional hook.
- The second paragraph contains a more neutral argument, and it ties into the hook at the end of the first paragraph. Discuss your second point, elaborate on it, and provide evidence to support it. Close with a transitional hook.
- The third paragraph contains another strong argument and ties into the hook at the end of the second paragraph. Discuss your third point, elaborate on it, and provide evidence to support it. Close with a transitional sentence that leads smoothly into the concluding paragraph.
In contrast to the introductory paragraph, the concluding paragraph starts out specific (by reintroducing the thesis) and becomes more general. It ties your ideas together and brings your paper to a culmination.
The concluding paragraph provides a general discussion of your findings and shows the reader that you have accomplished what you intended to at the outset.
- Restate your thesis (though not necessarily using the exact same words). In contrast to the introductory paragraph, the concluding paragraph starts out specific (by reintroducing the thesis) and becomes more general. It ties your ideas together and brings your paper to a close.
- Discuss your findings based on your research and evidence. Has your thesis been proven?
- Don't introduce any new ideas. The point here is to sum up and wrap up your essay, not to confuse readers by providing new information.
- End on a high note. You can finish the essay in a variety of ways. For example, you might provide suggestions for future research, state a call to action, share a quote, or ask a question. Depending on the topic and purpose of your essay, choose a closing line that will fit well with the rest of your essay's structure and leave readers thinking " Wow! "
Bibliography/Works Cited
The Bibliography or Works Cited page is a list of all the references you used throughout the paper. It can be alphabetized or numbered depending on the style guide you are using. While a Bibliography includes every resource you consulted when preparing your essay, a Works Cited page includes only the resources cited in your essay. Find out which is required by consulting the style guide assigned by your professor.

- To make creating your reference list easier, use citation software . There are many different options out there, and several of the software programs are free (especially if you're enrolled in a university that has a subscription to one of the services). These citation software programs essentially create your bibliography for you, making the process fast, easy, and accurate.
Review, Revise, Rework
- Give yourself a day or two before rereading and revising your essay. This way, you will have a fresh set of eyes, making it easier to catch any mistakes.
- Don't be afraid to rearrange paragraphs, delete sentences, or add information. Reading through your essay a few days after writing it makes it much easier to see where and how the structure needs to be changed.
- Correct any errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation. Check the essay yourself, have a friend review it, or better yet, have your essay edited by a professional editing service .
- Avoid colloquialisms and contractions. ('Cause it just ain't professional in an academic setting. Lol.)
- Analyze the flow of your essay , and make sure that your ideas and paragraphs flow smoothly from one to the next.
- Cut out any extraneous information or fluff. We've all done it, but adding extra words to make a word count requirement doesn't fly with most professors, and it will definitely detract from the strength of your essay.
Now, it's Time to Write!
It may seem overwhelming, but writing an essay doesn't have to be stressful. After coming up with a topic, doing some research, and creating a basic outline, you're ready to start filling in the gaps. Using primary and/or secondary research, back up your ideas and support them with credible sources. Just don't forget to cite those sources! Once you've written your first draft, take a day or two away from your paper so you will have a clear head when you come back to revise it. As suggested, you may even want to have your paper edited by the professionals at Scribendi , who will not only correct any surface-level errors but will also check for consistency, clarity, and cohesiveness, providing comments and suggestions along the way.
Essay writing is so much easier if you're equipped with the right tools, and that's what we hope we've given you with this ultimate essay checklist. Now that you know how to write an essay (regardless of the style), we're confident in your ability to write an essay about any topic that your instructor might have in store for you. Happy writing!
Image sources: Foundry/Pixabay.com, succo/Pixabay.com, ClkerFreeVectorImages/Pixabay.com
Ask a Professional to Edit Your Essay
Hire one of our expert editors , or get a free sample.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Escape the Five-Paragraph Essay

Essay Writing Help

How to Write a Great Thesis Statement
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Editing & Proofreading

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource covers process and strategy, not correctness rules. For help there, see our many resources on grammar, mechanics , and punctuation .
There are multiple levels of editing, and terminology surrounding editing is often used interchangeably and fluidly. These levels have some overlap between each other, rather than being totally discrete stages; similarly, developmental and substantive editing are more closely related to the "revision" step of the writing process. The four editing levels are:
- Developmental editing: looking at the overall development of the piece, for instance looking for organizational patterns, missing information, inaccurate information, or anything that might confuse a reader
- Substantive editing: making changes to ensure sections (all the way down to paragraphs and sentences) flow logically from one to the next, ensure each paragraph's topic sentence is present and accurate, adding new necessary material to make connections between ideas, removing unnecessary material
- Copyediting: addressing sentence level issues such as style inconsistencies, subject-verb agreement, confusing or wordy phrasing, missing words, missing or inaccurate citations, and any other mechanical or grammatical issues that may be present
- Proofreading: usually the "last pass" before submission or publication; ensuring everything is correct and no lingering errors such as typos, missing words, missing punctuation, etc. remain.
In general, writers should follow this list down in order when revising and editing, from higher order to lower order concerns (in other words, from bigger or more impactful issues to smaller and less impactful issues).
While many writers edit alone at some point during the process, many writers also edit with a partner or writing group. Working with others is strongly recommended when editing; typically, this stage of the writing process comes last or close to last, meaning that writers are more likely to overlook mistakes or potential opportunities (because they have been working on the text for so long). It can be hard for writers to imagine other possibilities beyond what they have already written. A partner or group brings fresh perspective and a real audience who can offer feedback and tell the writer more about what it's like to read their writing.
If you're intrigued by the idea of a writing group but not sure where to start, you might check out these resources:
- OWL Vidcast: Writing Groups & How to Form Them
- Writing Groups Toolkit from University of North Carolina - Chapel Hill
Editing Before Submission
When you're ready to edit, it's important to start with higher order concerns and move down to lower order concerns (as stated above). For higher order concerns, see the editing and revision tips on our Organization and Structure page. For lower order concerns (and sometimes higher order concerns — you might realize something about organization while reading carefully for sentence level issues!), here's a list of strategies that our tutors recommend in sessions with graduate writers. They're usually adaptable to different preferences you might have about working digitally vs. on paper, or working alone vs. with a partner or group. Be creative to find what works for you!
- Read aloud. You can do this yourself, get your computer to read your text out, or ask a friend. Hearing your writing read aloud can help identify places where sentences are confusing or difficult to read, highlight missing words, and create some distance between you and your writing so you can more easily evaluate it.
- Color code. You might do this by highlighting or changing font colors on your screen, using markers on paper, or even without color using font styles and sizes. This technique is useful for various applications, including identifying parts of sentences, identifying particular words or phrases you repeat often, or categorizing sentences by idea to check organization.
- Pick individual issues. When you read through with your focus on only one thing, like correcting comma errors or looking for all the places you write "the ways in which," you're less likely to miss instances of that error by getting distracted with other issues.
- Use checklists. Venues such as journals and conferences often have checklists for authors to use when preparing manuscripts; if you don't have a checklist from a professor, you can sometimes use these checklists to help guide your editing for writing for courses as well. You can also keep a checklist of known issues that your writing partners, professors, tutors, or mentors have mentioned on previous writing assignments to help you look for things you know you do (for instance, one former tutor always put her topic sentences at the ends of paragraphs — she keeps this item in a revision and editing checklist and it's one of the first things she addresses when she edits).
Editing with Feedback
Often, graduate students will be writing or editing with some type of feedback. This could be from peers in a class, from an instructor or mentor, or from a peer reviewer at a conference or journal. If you're in this situation, please see our resources on writing with feedback for more strategies and tips.

How to Edit an Essay

How to Edit an Essay– An Overview
When editing an essay, it's crucial to first ensure that the overall structure is coherent and logical. Begin by shortening lengthy sentences and paragraphs to improve readability. Avoid using overly complex language, which can obscure your message. Be vigilant for any repetitive ideas or words, as they can detract from the clarity of your argument. While spellcheck can be helpful, don't rely solely on it for accuracy. Actively search for and correct typos. Lastly, remove any superfluous words and be cautious of using vague or non-committal language that can weaken your statements.
Editing an essay effectively involves several key steps to enhance clarity, coherence, and overall impact. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Review the Structure : Ensure your essay has a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should present your thesis statement or main argument, the body should contain your supporting points, and the conclusion should summarize and restate your main points.
- Check for Clarity and Coherence : Ensure each paragraph has a clear main idea and that ideas flow logically from one paragraph to the next. Use transitional phrases to help guide the reader.
- Focus on Sentence Structure : Vary your sentence lengths and structures to maintain reader interest. Avoid overly long sentences, as they can be confusing.
- Simplify Language : Remove jargon and unnecessarily complex vocabulary. The goal is to be clear and concise, making your essay accessible to a broader audience.
- Eliminate Repetition : Check for repeated words, phrases, or ideas and eliminate them. Repetition can be redundant and detract from the effectiveness of your argument.
- Correct Grammar and Spelling : While software can help, manually check for grammar and spelling errors to ensure accuracy.
- Watch for Punctuation and Formatting : Proper punctuation and consistent formatting contribute to the professionalism of your essay.
- Trim Unnecessary Words : Remove filler words and phrases that don't add value to your argument.
- Fact-Check : Verify the accuracy of any data, quotes, or references you use.
- Seek Feedback : If possible, have someone else read your essay. Fresh eyes can spot errors and inconsistencies you might have missed.
- Read Aloud : Reading your essay aloud can help you catch awkward phrasing and errors that you might not see when reading silently.
- Final Review : Go through your essay one last time to ensure all your edits have improved clarity, logic, and flow.
Remember, effective editing often requires multiple read-throughs and revisions. Take your time to refine your essay until it clearly and effectively communicates your ideas.
How to Edit a Essay By Following These Editing Principles?
When we are writing an essay– or any other writeup there is, we are often guided by different principles. These principles are like a clear pathway toward creating a compelling and well-thought-out work of art. They separate the best from the rest, aesthetic and unpleasing, masterpiece and trash.
The same goes for the process of editing. This process likewise follows some key principles that regulate editors on their work as revisioners. While they help editors foster a set of ethical standards for editing, they also ensure that the content of the writeup itself is beneficial: it can serve its purpose. The following are the principles of editing and the key questions that you might want to ask yourself in consideration:
From the word itself, the writeup must be clear. In what sense? In the skill of writing, clarity may be straightforward, but it takes a lot of work for us to make a writeup that is easy to understand.
We are confounded with various writing guidelines and things to integrate into our writing. This condition takes us away from the principle of clarity.
The rule of thumb here, though, is this: clear your desk (translate: mind), set your mind on your ultimate writing goal (translate: main idea), and keep it as apparent as possible in your writing. In a broader explanation, you have to set aside other writing endeavors – choosing complex words, forming lots of paragraphs, introducing tropes and figurative language, and focusing on the important thing: constructing your thesis statement and using writing techniques that can make your idea more comprehensible.
2. Coherence
We have a lot to say, and the best thing to relay these ideas and thoughts is through writing.
When we have numerous things to rely upon, emotions may run high and take over our writing, causing us to make some “mess” and deviate from sharing our ideas neatly. Yes, you heard it right: writing does not just communicate our minds in whatever manner we want. This macro skill also demands us to write neatly – logically and lucidly.
In doing so, we have to maintain a logical and consistent flow of thoughts. It is like being one with nature: although we cannot understand it in its simplest form, we feel like everything goes fine because of its order and flow.
Coherence, the principle that talks about flow, also means the ideas are connected logically, and transitions from one idea to another are built well. Coherence can go a long way in a writeup, as it guides your readers from the start to the end of your writing, all while making sure that they have grasped the important points of your writing.
3. Grammar and Style
Grammar and style are probably the most sought-after principles, along with being the most tedious ones to handle in writing. These principles can be too technical and book-ish, and it takes years to be accurate grammatically and stylistically. You must learn various grammatical concepts and create your own writing style that follows certain conventions and tropes that you only apply to your writing endeavors.
However, we do not follow these principles for nothing. Aside from effective communication and clarity of expression, which have their own principles by the way, grammar reflects the uprightness and credibility of a writer. Since a written piece upholds quality and refinement, we do not want to risk the possibility of committing mistakes that will leave a disappointing impression on our readers.
In fact, it is generally believed that readers prefer written pieces that are well-written– those that are free from any grammatical lapses. Imagine if you committed those mistakes (especially if they are too common): you will definitely walk in shame and contact an essay editing service in no time!
How to Go Around Essay Editing In 3 Stages?
Just like writing, the process of editing is scientific and objective. Contrary to popular belief, essay editing starts with a specific process and ends similarly. One process must be done before the other. Missing one process does not satisfy the rigor of editing.
In the simplest sense, all the editing processes we will discuss in this section are important and should not be overlooked. There are three editing stages: content editing, copy editing, and proofreading. Each stage plays a crucial role in the whole process, refining the document, spotting crucial errors, and maximizing readability and comprehension.
1. Content Editing
Content editing, with its other name substantive editing , is the initial stage of the editing process. At this stage, the editor concentrates on the writeup’s substance, structure, and overall quality. As we all know, nothing beats the comprehensiveness of a writeup’s content, and it gets even more comprehensive in the process of editing! You can edit my essay and do this editing stage if you want to experience the rigor.
The main aims of content editing are to ensure that the content is clear, coherent, and effectively conveys the intended message to the target audience. In short, it edits the content to maximize its capability to relay its intended purpose.
Key Sub-processes of Content Editing:
* Assess Overall Structure and Organization. Logical sequence and coherence are put in check on this sub-process.
* Evaluate Content and Clarity . The editor assures that the message or argument is well-defined and substantiated with appropriate evidence.
* Enhance Transitions and Signposting . The editor looks for means to enhance transitions between paragraphs and sections, making the text smoother and more reader-friendly. Aside from transition devices used in the first parts of each of the paragraphs, one may use signposts like topic sentences and headings to steer the reader through the content.
* Revise and Rewrite on Critical Content Issues . When deemed necessary, the editor may recommend or make significant revisions or rewrites to strengthen the content, eliminate redundancy, and enhance clarity.
2. Copy editing
This is the stage where it gets a bit technical for editors. Copy editing is the second stage of the entire editing process and focuses on the technical elements of the text. It concerns checking for grammatical and punctuation errors and ensuring consistent language usage, style, and compliance with a specific style guide. Copy editing’s main goal is to enhance the readability and correctness of the text, as well as establish the text’s credibility and trustworthiness.
Key Sub-processes of Copy Editing:
* Grammar and Punctuation . The editor implements grammar checks for spelling errors or other grammatical errors, including but not limited to subject-verb agreement, verb tense, and sentence structure. The text’s mechanics, or checking punctuation marks, may also be a focus for editing.
* Spelling and Usage . Spelling mistakes and inconsistencies in word usage (per the type of English one is using) are identified and corrected. Editors catch errors with redundant words, word count, body paragraphs, and passive voice.
* Capitalization and Formatting . The editor verifies that capitalization, headings, and formatting are uniform and appropriate to the type of writing.
* Fact-Checking . This sub-section ensures the accuracy of data, facts, figures, and references. The editor cross-references information with trustworthy sources and flags any instances of plagiarism and incorrect referencing.
* Style and Clarity . Editors persevere to improve sentence structure, eliminate vagueness, and enhance text readability.
3. Proofreading
This is the final stage of the editing process and is focused on scanning the document for “crumbs” left during the previous two stages– minor errors and inconsistencies. It is the last opportunity for the editor to catch any remaining typos, formatting issues, or other small mistakes before the document is brought to finality.
Key Sub-processes of Proofreading:
*Final Grammar and Spelling Check . The editor conducts a final review to identify and correct any grammatical or spelling errors that may have been overlooked. The final draft has an immaculate paragraph structure that's free of unnecessary words, grammar mistakes, or sentence fragments.
*Formatting and Layout . This step guarantees that the document adheres to consistent formatting, including margins, fonts, and spacing.
*Page Numbers and Table of Contents. The editor confirms that page numbers, footnotes, and the table of contents are correct and properly formatted.
* Hyperlinks and References . For digital documents, the editor checks that hyperlinks are functional and correctly correspond to the anchor text. They also ensure that references and citations are correct.
*Overall Readability . Finally, the editor scans the entire document one last time to identify any minimal errors, inconsistencies, or issues that might have been missed in previous stages.
How to Edit Essays: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you are familiar with the three main stages of editing essays– content editing, copy editing, and proofreading, we are confident that you may now have an understanding of how an entire editing process may come into play. The best thing is that you may take off your editing journey without being too pressured to follow a certain blueprint.
Yes, you read it correctly: you can craft your own editing process. Just ensure that you capture every essence of the three main stages. To provide you with a guide, the following is a 7-point checklist that you may use to edit your essay.
This table is a synthesis of everything we discussed in the three stages of editing.
Leverage the Studyfy Way
One may definitely follow a guideline like the one above, but an essay revision service can do so much more. At Studyfy, you can avail of its high-quality writing services, where a roster of competent writers and editors completely transform a writing prompt into a creative masterpiece– one that adheres to the perfect style, formatting, and instructions.
Enjoy Studyfy’s no-mark-up scheme and affordable price range without worrying about the finished product’s reliability and readability– quality is a top priority, indeed. How to edit an essay well: sorted!
How to Edit Your Essay in Various Forms?
Essays are pieces of writing that discuss various topics and hold different functions depending on the writing prompt, purpose, and audience, among others. Given its eclectic nature, essays can be tricky to edit. Some principles on how to edit an essay may not be as important in some types, and some steps are as important as others.
We know the difficulty that you might contend with in editing different forms of essays, so we are here to help you by providing a cheat sheet on the common essay types and some techniques on how to edit them.
How to Edit an Essay Using Various Editing Techniques
Reflective essay.
How to Write a Reflective Essay ? This essay involves self-introspection and analysis.Similar to a narrative essay, the goal of this essay type is to internalize and explore their thoughts and narrate a personal experience to readers who are likewise experiencing it.
Self-Reflection Enhancemen
- Ensure that the essay effectively relays personal experiences, thoughts, and insights.
- Evaluate the thesis statement in consideration of its essence and clarity.
- Evaluate the depth of self-analysis and introspection.
- Assess the essay’s emotional resonance and the perceived emotional impact on the reader.
- Analyze the organization of content, ensuring a structured format and exploration of themes.
Argumentative Essay
- This essay type presents a debatable proposition, a stand, and pieces of evidence that substantiate the writer’s stand.
- It is used to persuade the reader to take a particular viewpoint.
Argument Strengthening
- When editing an essay, ensure that the proposition is clear and debatable.
- Check for the logical flow of arguments and counterarguments.
- Evaluate the evidence and examples that support the claims.
- Verify that the conclusion aligns with the main argument and discourses opposing views.
Expository Essay
- It is embedded with facts, figures, findings, and other related factual information.
- Its aim is to provide and explain concepts, ideas, theories, or topics.
Clarity and Information Flow Enhancement
- Check if the essay has a clear and informative introduction.
- Check for the organization of content to ensure a logical sequence of ideas.
- When editing an essay, elucidate complex concepts with definitions and examples.
- Cross-reference facts and figures for exactness.
Narrative Essay
- A winning narrative piece is one that vividly tells a story– ensuring that the readers are inside the world that you want to immortalize.
- It is supplied with descriptive words, figurative language, a clear plot structure, and a consistent point of view.
Storytelling Focusing while Editing Essays
- Ensure the essay has a clear plot structure– beginning, middle, and end.
- Check for reasonable character development.
- Pay attention to imagery and descriptive language to enhance the reader's experience.
- Check for the pacing of the narrative to maintain engagement.
Persuasive Essay
- It uses persuasive diction and techniques, pieces of evidence, and logical reasoning to take persuasion to effect.
- Its aim is to make the reader adopt a certain and fresh perspective and subsequently take a course of action.
Persuasion Intensification and How to Edit Essay
- Evaluate the thesis statement in terms of influence and clarity.
- Integrate persuasive techniques like ethos, pathos, and logos .
- Assess the soundness and relevance of supporting evidence and examples.
- Ensure that counterarguments are accepted and refuted effectively.
- Ensure a conclusion that leaves a lasting impression.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can editing help me ace my writing assignments if it’s another burden to do.
Editing may be a tough act to do after writing, but it can be a walk in the park if you master the skill. Practice it continuously and be devoted (translate: consistent) to doing it until you no longer find it difficult and laborious.
How can editing an essay be simplified if I no longer have sufficient time to do it?
You can always simplify your editing routine when time is running out. Editing essays can be as simple as having three pointers: (a) Checking for major grammar lapses; (b) Evaluating content based on its clarity and coherence; and (c) Checking for formatting guidelines.
How to edit an essay well if the guidelines are only specific to one element of text?
In connection with the previous question, you may opt to use a personalized editing routine and that includes considering one element over the others. You may allot a big remainder of your time editing that element, but always ensure that you edit the important things on a text, no matter how focused you are on a particular element.
To edit an essay is really hard for me. Do I have the option to just skip it?
I probably can think of a scenario where you are asking a question like this: “Can somebody write my paper and edit it? This is way too much for me!” While writing and editing are intertwined, and we have no means of skipping them, writing and editing services like Studyfy can finish the work for you.
Created personally for you and your writing needs, these services are strong with competent and reliable writers who can go the extra mile in finishing your writeups while adhering to the intended style, format, and content.

The Writing Process
Making expository writing less stressful, more efficient, and more enlightening, search form, you are here.
- Step 5: Edit
Personal Editing Checklist

"If you re-read your work, you can find on re-rereading a great deal of repetition can be avoided by re-reading and editing." —William Safire
Click to download and create your Personalized Editing Checklist.

Editing Checklist for Self- and Peer Editing

About this printout
This helpful tool will give your students the opportunity to edit their own writing and then observe as their peers edit the same work.
Teaching with this printout
More ideas to try, related resources.
Before you begin, be sure to model and discuss each step of the writing process (prewriting, drafting, revising, editing, and publishing), preferably using a whole-class story or class newsletter article. Please note that the revising stage precedes editing. Student should have already worked through content revisions before reaching the editing step. When they are ready for the editing stage of the writing process, students should edit their writing and then meet with a partner to engage in peer editing. Prior to having students use this tool independently, it is important to model its use. To do this, display sample text on an overhead projector, document camera, or SMART Board so that all students can view it. Model the use of the self-edit column with the displayed text, with you assuming the role of author. Then have a volunteer fill out the peer-edit column so that all students can hear and view the process. Finally, discuss what went well and what could be improved in the editing steps that were modeled. This tool serves multiple purposes, including:
- The self-edit step
encourages students to evaluate specific features of their writing, increasing self-awareness of writing conventions keeps the pen in the writer’s hand for the initial editing phase
- The peer-edit step
helps build a learning community in which peers work collaboratively heightens the awareness of various print and grammatical conventions for the peer editor and the author
- Use a fish-bowl technique to allow the class to view a self- and peer-edit session of two of their classmates. To do this, first choose one student to model the self-editing phase. It is helpful to select a student who has a good understanding of the criteria on the rubric, such as proper grammar and punctuation. That student works through the items in the self-edit column as the other students observe. It is helpful to put the editing checklist on an overhead projector or document camera so all students can see the process. After the self-edit is complete, discuss the process with the students. Next, choose another student to serve as the peer editor for the piece that was just self-edited. Have the two students sit in the middle of the class so that all students can see and hear them as they work through the peer-editing phase. Afterward, include the entire class in a discussion about the process itself and ways in which the editing session will help the author and peer editor improve on their writing.
- Have students work in groups of two or three to edit one piece of writing. The interaction between peers will help make the editing process more explicit. While the students are working in groups, move from group to group to check their understanding of the editing process and use of the checklist. Try to notice groups that lack comments in the “Comments and Suggestions” columns and encourage them to use this section to provide feedback to the writer, particularly for criteria that lack a check mark. To guide them, you could ask, “What do you think you could write in the ‘Comments’ section to help the writer fix this error?” Be sure to tell students that if they are unable to mark a check in the “After completing each step, place a check here” column, they must indicate the reason why they cannot check it in the “Comments and Suggestions” column.
- If your school uses a team approach for grouping students (a group of students who all share the same content area teachers), consider encouraging other team teachers to use this checklist in their respective content areas. Consistency in the editing process will help students understand that the editing process can apply to all written pieces, regardless of the content area.
- Strategy Guides
- Lesson Plans
This strategy guide explains the writing process and offers practical methods for applying it in your classroom to help students become proficient writers.
- Print this resource
Explore Resources by Grade
- Kindergarten K
Revision and Editing Checklist for a Narrative Essay
Emma Kim / Getty Images
- Writing Essays
- Writing Research Papers
- English Grammar
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
After you have completed one or more drafts of your narrative essay , use the following checklist as a revision and editing guide to prepare the final version of your composition.
- In your introduction, have you clearly identified the experience you are about to relate?
- In the opening sentences of your essay, have you provided the kinds of details that will evoke your readers' interest in the topic?
- Have you clearly explained who was involved and when and where the incident occurred?
- Have you organized the sequence of events in chronological order?
- Have you focused your essay by eliminating unnecessary or repetitious information?
- Have you used precise descriptive details to make your narrative interesting and convincing?
- Have you used dialogue to report important conversations?
- Have you used clear transitions (in particular, time signals) to tie your points together and guide your readers from one point to the next?
- In your conclusion, have you clearly explained the particular significance of the experience you have related to the essay?
- Are the sentences throughout your essay clear and direct as well as varied in length and structure? Could any sentences be improved by combining or restructuring them?
- Are the words in your essay consistently clear and precise? Does the essay maintain a consistent tone ?
- Have you read the essay aloud, proofreading carefully?
- An Essay Revision Checklist
- Compose a Narrative Essay or Personal Statement
- How to Write a Letter of Complaint
- How to Write a Narrative Essay or Speech
- The Difference Between Revising and Editing
- How to Teach the Compare and Contrast Essay
- 6 Steps to Writing the Perfect Personal Essay
- revision (composition)
- personal statement (essay)
- A Critical Analysis of George Orwell's 'A Hanging'
- College Essay Style Tips
- Private School Application Essay Tips
- How to Write a Great Process Essay
- Essay Assignment: Descriptive and Informative Profile
- Self-Evaluation of Essays
- The Five Steps of Writing an Essay

A Foolproof Editing Checklist to Take Your Work from 0 to 100
You've just finished writing a blog post, sweat pouring from your brow much as words poured from your fingertips a second ago.
You're about to press publish when suddenly… a small, niggling voice pipes up in your mind.
“You should probably proofread that, at least…” the voice says snidely.
You resist. Your writing feels good! Or at least, good enough to send. Why bother with the whole editing bit?
The voice is correct. Although many people think writing is the hard part, the toughest part of any writing process is the editing. Editing is what takes your writing from good to great.
If you're an academic, editing will help polish your work and make it more professional.
If you're a blogger, editing will help you earn more trust with your readers.
If you're into creative writing, editing helps you carve out motivations, characterizations, and tell a better story.
I'll break down exactly how I recommend incorporating editing into your writing process.
Understanding the Basics of Writing and Editing
Let's start by explaining the stages of the writing process. Though many people think the process is simply: write → publish, it's a little more complex than that.
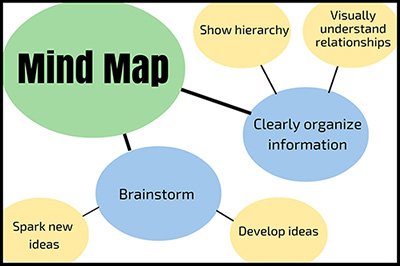
Prewriting (Brainstorming)
Gather and organize your thoughts. Understand the assignment or purpose, consider your audience, and come up with ideas. Techniques like free writing, clustering, and mind mapping can be useful here.
Once you have your ideas, you start to put them into sentences and paragraphs. This is where you write your first version or rough draft. It doesn't have to be perfect; the main goal is to get your ideas down on paper.
Here, you rethink and reorganize your paper. You might rearrange sections, add or delete paragraphs, clarify ideas, and ensure that your argument is well structured and supported. The focus is on clarity and meaning.
Refine your draft by fixing grammar, punctuation, spelling, and other mechanical errors. You might also look at sentence structure, word choice, and consistency in style and tone. This is where you polish your work.
Proofreading
This is the final check before you consider your piece complete. You're looking for any last-minute errors or typos that might have been missed during the editing stage. It's often helpful to read the paper aloud or have someone else review it.
Publishing (or Sharing)
Finally, once you're satisfied with your work, you share it with your intended audience. This could mean turning it in to a teacher, posting it on a blog, submitting it to a journal, or any other way of making your writing public.
This isn't a linear process all the time. Sometimes you'll be editing and realize you need to go back to the revision portion, or even back to brainstorming. You may also find yourself proofreading as you write, instead of at the end.
Writing for students in high school is slightly different to writing in academic settings – high school writing is more about foundational skills like clear sentences and organized thoughts. Academic writing requires specialized knowledge, critical analysis, and adherence to specific formats. Keep those standards in mind when editing your work.
Key Elements to Check in Your Writing
This is a bit labor intensive, but the best way to go through your piece and make sure it's perfect is by taking each section and sentence and making sure it fits and flows perfectly.
Here are some of the biggest issues to tick off your list:
Check for complete sentences – no sentence fragment allowed.
Example: "Because I like to read."
Corrected: "I like to read."
Ensure each body paragraph has a topic sentence.
Example: "It's a popular sport. Many people love soccer because it's exciting and unites fans globally."
Corrected: "Soccer is beloved worldwide for its excitement and ability to unite fans."
Ensure each sentence conveys clear ideas.
Example: "She went to the place with the thing for that stuff."
Corrected: "She went to the library to borrow a book."
Avoid the passive voice – go for active voice.
Example: "The cake was eaten by him."
Corrected: "He ate the cake."
Scrutinize your word choice to convey the right message.
Example: “She talked really bad.”
Corrected: "She spoke inappropriately."
Check for grammatical errors, grammar mistakes, and proper grammar.
Example: "She don't like chocolate."
Corrected: "She doesn't like chocolate."
Check for common spelling pitfalls.
Example: "I have a reciept."
Corrected: "I have a receipt."
Check punctuation, including exclamation marks and proper punctuation.
Example: "Its raining outside, isn't it!"
Corrected: "It's raining outside, isn't it?"
Avoid unnecessary words, filler words, and long sentences.
Example: "I just really think that, you know, maybe we should, like, consider going to the store or something."
Corrected: "Maybe we should go to the store."
Ensure proper capitalization. Each proper noun gets a capital letter.
Example: "i love paris in the springtime."
Corrected: “I love Paris in the springtime.”
Make your content interesting.
Example: "The Renaissance was an important time in history."
Corrected: “The Renaissance, a vibrant period of rebirth, profoundly influenced art, science, and thought.”
Advanced Editing Techniques
When you're ready to go a step further, there are a few final i's to dot and t's to cross to finalize your editing, both for students and professionals. These are a bit more big picture.
Use body paragraphs to structure your writing .
You want to ensure that each paragraph has a point, and that everything in that paragraph supports your main point.
Sometimes on tricky pieces, I will print out my article, highlight my main point, and cross out any sentences that don't directly strengthen my main point.
You also need to understand the role of each phrase , word , and paragraph in enhancing readability.
Short, clear sentences and paragraphs make content more scannable, especially online.
Transition words help guide readers through an argument or narrative, and varied sentence structures can maintain reader interest.
You should also think of editing skills not just as a checklist, but also as a way to improve your writing skill .
As you consistently edit and refine your work, you begin to internalize the principles of good writing.
Over time, you'll notice that you start avoiding common mistakes you used to make in your first drafts. It's very satisfying.
Formatting and Style
A boring but necessary item on any checklist for editing – make sure you're following the rules. Especially relevant for students, your teacher has probably assigned you MLA style or APA style. Students and professionals alike will have to adhere to font regulations, too.
Double check you're in Times New Roman, if that's what the assignment calls for. It's really annoying to get docked points for a simple format mistake.
Curious about the best Microsoft fonts? Read here.
Resources for Effective Editing
Where to begin? Don't worry, you're not starting from a blank slate. There are tons of online resources and tools for editing. (Almost all of these are all free – I know what students' and freelancers budgets are like!)
Grammarly . It's a free Chrome extension, powered by AI, that finds spelling issues, grammar mistakes, but also can go into clarity and where to cut unnecessary words. Perfect for students, veteran marketers, and everyone in between.
ProWritingAid . This AI editor does a similar job – it will correct your misspellings, simplify jargon, and help trim your writing to be more concise.
Hemingway Editor . This resource is a free app that is all about picking out common writing issues, like if your sentences are too complex, or if you've got a lot of passive voice.
Readable is a great resource for giving you a sense of the reading level, either the well-known Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level or another metric. Great for students.
OneLook Thesaurus. This will solve your overused word problem. Not only does it work as a traditional thesaurus, it's also good for finding that word that you can't quite remember.
Students bonus: Your local writing center . Most colleges will have a center dedicated to helping you write. Here's a sample of what UMass Boston's will give you: “We offer individual writing consultations in person and online where we work collaboratively with writers and provide feedback on any writing, from class essays to cover letters to theses and dissertations to manuscripts for publication and anything in between.” Pretty great resource, huh?
Your friendly peer editor . If you're really stuck in the editing process, I recommend asking one of your fellow students or peers very nicely – or even hiring a professional – to give your piece a once-over.
Final thoughts on this checklist
Running your piece through a checklist like this one is the best way to polish your article. It gives you a sense of professional pride. For students, it's a good way to keep grades up or just feel like your assignment is done.
My last three piece of advice:
Read it out loud . This is the fastest, cheapest, and best way to edit. You'll find stale sentences, missing commas, boring bits, and forgotten clauses.
If you can, print it and read it on a physical copy . Especially for students submitting an assignment, changing the format can really help your eye spot hidden errors.
Have fun . Editing can feel like a drag, but I like to gamify it a bit with this kind of checklist. Remember, you're skilling up, like a video game character. Do your best and enjoy the process.

How Does a Freelance Writer Make Money?
How to write a comparison essay from start to finish.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
College Essay Checklist: Are You Ready to Submit?
←Whom Should I Ask for Help with My College Essay?
How Long Should Your College Essay Be?→
The college admissions process is a human process. An admissions committee filled with real people will evaluate your application, and these people will choose whether to advocate for you to gain admission to the university. So in order to be accepted, you need to stand out from the other applicants and persuade the admissions committee to choose you over students with a similar academic profile. Luckily, college essays are specifically designed to be your tool to stand out in the admissions process.
Given that college essays are so important, it’s important to make sure that they are absolutely perfect before you submit them. How do you make sure your college essays are ready to send to colleges? Make sure you’ve gone through this checklist before you hit that “submit” button!
Why Are College Essays So Important?
A college application has many components – test scores, grades and coursework, your extracurricular profile, recommendation letters, interviews, and, of course, your essays. So why are the essays such an important part if there are so many other components of your application to consider?
Well, most colleges receive thousands of applicants, many of whom have similar academic and extracurricular profiles. In fact, for every spot in a selective university’s admitted class, there are at least four outstanding applicants with similar grades and test scores. So how do admissions committees choose among so many students who have such strong potential? They use their essays to decide who would best fit in with the campus community.
For this reason, your college essays aren’t just about showing off your abilities and accomplishments. It’s about showing who you are as a person, what your values are, and what you’re passionate about. That’s no small task for a short essay. Every word is going to count, so follow the checklist below to make sure that your essay is as strong as it can be.
College Essay Checklist: Before You Submit
1. does your essay share who you are and what you care about.
Your essay needs to be personal. It should share your personality, goals, and voice. Even if a prompt doesn’t explicitly ask you who you are and what you care about, you should use it as an opportunity to showcase your personal qualities. For example, take the following supplemental essay prompt from the University of Chicago’s 2020 Application:
What can actually be divided by zero?
At first glance, this prompt may seem confusing. After all, didn’t we all learn in elementary school math classes that nothing can be divided by zero? More abstract, philosophical prompts like this one are actually ripe opportunities for students to showcase who they are and how they think.
So if you answered a prompt like this very practically, e.g. explaining that the laws of mathematics prove that no real number can be divided by zero, you’re missing out on a key opportunity to show the admissions committee your capability for creativity and abstract thought. Instead of answering a prompt like this literally, you ought to think critically about your own life and see if you can metaphorically or rhetorically link the question to something you have gone through or accomplished.
Alternatively, if you’re more of a logical person and want to answer the question analytically, make sure that you are showcasing your knowledge of various theorems and strategies, and be sure to cite where you learned them. Either way, you are showing the admissions committee how your brain works and how you go about solving problems.
Remember: the goal of an essay is, first and foremost, to showcase yourself. There are no right or wrong answers in college essays, so as long your essay tells the committee something important about you.
2. Do your essays form a portfolio that accurately represents you?
While having to write so many essays is a lot of work, there is an upside. Having multiple essays means you can use each essay to display a different aspect of yourself and your accomplishments. That way, holistically, your application will give a very representative picture of who you are, and you won’t have to leave anything out.
So when you’re evaluating your essays, ask yourself: do your essays depict as many facets of yourself as possible? Specifically, have you repeated a story, experience or quality about yourself in any of the essays you’re going to send to the same college? If you have, then consider editing one of the essays to highlight something that you haven’t yet shared with the admissions committee. The more you can share with them in a limited amount of space, the easier it will be for the admissions committee to imagine how you would fit in at their university.

3. Did you answer the prompt?
Okay, so we’ve talked a lot about making sure that your values, passions, and accomplishments are showcased in your essays, even if the prompt is more abstract. This is certainly important, but it’s also important to make sure you’re showcasing yourself in the context of the essay prompt that was given to you. In other words, you should be sure that at some point in your essay, you answer the essay prompt clearly. If you don’t, you risk coming across as a student who doesn’t know how to follow basic directions.
Moreover, you need to make sure that you answer every part of the essay prompt given. Some essay prompts will just have one part. Some will have many. If you have to answer an essay prompt with multiple parts, be sure you address all of them. Take the following essay prompts from the 2019-2020 College Application Cycle:
Massachusetts Institute of Technology , 2019-2020:
Tell us about the most significant challenge you’ve faced or something important that didn’t go according to plan. How did you manage the situation? (200-250 words)
University of California :
What would you say is your greatest talent or skill? How have you developed and demonstrated that talent over time? (350 words)
In both of these prompts, you are asked to respond to two related questions. If you were to answer the MIT prompt, you would need to not only describe a significant challenge but explain how you overcame it. For the University of California prompt, you’d not only need to explain your greatest skill but outline how you’ve cultivated it over time. If you miss any of those parts in your response, you will not have fully answered the prompt.
4. Did You Stay Within the Word Count?
Most main college essays (like the Common App essays) have a word limit of anywhere from 250-650 words. Supplemental essay prompts generally have word limit of 100-400 words. Either way, you need to make sure that you stay very close to the upper word limit in your response.
As a general rule, you should try to stay within 10% of the upper word limit. So if the word limit for one of your essays is 650 words, your essay shouldn’t be fewer than 585 words. Keep in mind that most online applications will cut off your essay at the word limit, so try not to go over the word count. However, on the other extreme, you don’t want to make your essay too short, as it may make it seem like you don’t care about the application. After all, every extra bit of space in your essays is an opportunity to further impress the admissions committee, so you should take advantage of it.
For some more details on how long your college essays should be, check out our previous post entitled How Long Should Your College Essay Be? What is the Ideal Length?
5. Did You Proofread?
Here are some things to look out for as you look over your essay:
Incorrect grammar and spelling mistakes. These can make a well-thought-out essay seem subpar in the eyes of an admissions committee.
Awkward or formal wording. Read your essay aloud and listen to how it sounds. If it doesn’t sound natural, then you’re likely not displaying your authentic self to the admissions committee. Consider shifting some of the wording to sound more like something you would actually say, even if it means you have to take out a bit of the advanced vocabulary and complex sentence structure.
Instances of telling, instead of showing. One of the biggest mistakes students make is to tell, instead of show. Here’s an example of telling: “It was a rainy and gloomy day.” Here’s an example of showing: “The gray clouds hovered ominously above the lake. I felt a drop. Then another. And another. It began pouring, and I frantically tried to row the canoe back to shore.” It’s much more engaging to read the second example, as you feel as if you’re there with the writer.
Repeated sentence structure and vocab. Do you use the same word over and over again? Do you begin lots of sentences in a row with “I”? As you’re reading your essay, make sure that you’re using varied language to keep things interesting.
Inconsistent style. While your language should be varied, your style shouldn’t. If you use contractions or acronyms, use them throughout the essay. If you begin the essay in past tense, keep it that way, or make sure there’s clear demarcation when you shift tenses.
Also, if you’re reused an essay from another school’s application, give it an extra read-through to make sure that you’ve replaced all of the mentions of and references to the other college. You don’t want the admissions committee from UC Berkeley reading about how thrilled you are to take advantage of the opportunities that Tufts has to offer. It would not bode well for your likelihood of acceptance to Berkeley.
Of course, it is okay to reuse essays if the prompts are similar, but just be sure to double and triple-check that it doesn’t seem like you’re reusing an essay meant for another college. Also, if you’re answering the famous “ Why This College ” essay, we at CollegeVine recommend that you not reuse another essay. This essay should include specific resources and opportunities that you plan to take advantage of at each university, so you shouldn’t be able to use the same essay for two different schools. In fact, if you’re able to reuse a “Why This College” essay, that’s a sign that you need to rework the essay and make it more specific to the college.
6. Did You Get a Second and Third Set of Eyes on Your Essay?
It’s important to get another person or two to read your essay before you submit. The best people to look at your essays are those who are well-versed in creative essay writing, but also people who know you well. Older peers who have gone through the admissions process successfully can offer some of the best advice. English or Communications teachers who know you well also make great proofreaders, as do writing-proficient friends and family.
If you’re not sure who to ask, you can also use our free peer essay review tool . You can get feedback on your essays, and improve your own writing skills by reviewing others’ essays.
7. Did You Revise and Proofread Again?
Once you’ve read through your essays and had others give suggestions, make the necessary edits and corrections. Then, be sure you proofread your essays one more time before you hit submit. You should try not to submit an essay that hasn’t been read at least a few times all the way through, without any changes. Consider even reading your essay out loud and printed out (have a pen at the ready!), as you may catch things you missed when reading silently.
Want help with your college essays to improve your admissions chances? Sign up for your free CollegeVine account and get access to our essay guides and courses. You can also get your essay peer-reviewed and improve your own writing skills by reviewing other students’ essays.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


How to Peer Edit an Essay: Free Peer Editing Checklist
If you want to peer edit an essay and are looking for some top tips, check out our free peer editing checklist.

The idea of editing and proofreading your own essays, let alone asking someone else to help, may be beyond comprehension. In fact, you may think your essay is pretty fantastic already.
If so, you’re deceiving yourself.
Don’t just settle for good . You should be looking for great.
But how do you achieve this?
The majority of students settle for good. That’s enough. It will get them through school.
But good isn’t enough for the top students. They aspire to be great. They aspire to be awesome.
How do YOU become awesome?
Get a friend to help.
To take an essay beyond the draft stage through a polished version, you need a peer editor. It doesn’t necessarily have to be a professional essay editor (although that will deliver the best results); it needs to be someone who will call you out and tell you how it really is.
When you’re looking for someone to peer edit your essay, try and choose someone who you know well and who you can trust to be honest and methodical. You’re not looking for someone who’ll tell you how great your essay is; you’re looking for someone who will provide you with an objective criticism of your paper.
The purpose of the exercise isn’t to tear you down; it’s to make you better.
So, once you’ve found the ideal peer editor, how can you get the most out of the exercise?
Hand them our handy tips and the great peer editing checklist.
If you wish to edit your essay before engaging the help of a peer editor, take a look at our guide to essay editing .
How to Peer Edit an Essay: Top Tips for Success
Peer editors should review an essay with the primary intention of offering advice on how it can be improved. Here are some great tips to make sure you do the task justice.
Ideally, read through the paper at least twice
During the first pass, you’ll familiarize yourself with the content of the essay and the primary arguments that are put forth. During the second pass, you’ll have a chance to readily understand what is being said. If you don’t understand the content after two readings; there’s a problem the writer needs to know about.
Position yourself as the target reader
While you’re in the process of peer editing the essay, take the role of the envisioned reader; i.e., the person who is reading the essay to learn from someone as opposed to being on the hunt for pesky grammatical errors. During the peer editing process, you should be concerned with content, organization, and style. If you focus purely on punctuation and spelling errors, you may not add a significant amount of value. Your role is to help the writer ensure the essay is clear and compelling.
Resist the temptation to fix the issues
Your job as a peer editor is not to take over and correct any issues that you identify; it’s to provide the writer with constructive feedback on how the paper can be improved.
Tell the truth… constructively
If you’re peer editing a friend’s essay, you may not want to hurt his or her feelings by pointing out areas where there is a lack of clarity. However, if you fail to do so, there’s no point in engaging in the process. Resist the urge to say everything is fine and instead focus on how you can help the writer learn someone from the process. Provide constructive feedback that highlights the positive areas of the essay while also pointing out some areas for improvement.
Provide specific details
Don’t provide sweeping statements such as, “I don’t understand your point.” Instead, provide very precise feedback on what exactly you don’t understand and what information may help you understand it better: “Perhaps you could make your point clearer by explaining why…” Take every opportunity to explain why you found something effective or ineffective.
Check the style guide
Universities and colleges typically follow one of six major style guides in academic writing: APA, Harvard, MHRA, MLA , OSCOLA and Oxford. When you write in a consistent manner following a recognised style guide, it is simpler for readers to understand what to anticipate and where to find further information. Effective application of a style in formal writing will distinguish your work visually and ensure you meet the university’s requirements. If you’re using APA, take a look at our guide to APA formatting .
The Three Pillars of Excellent Peer Essay Editing
Free peer editing checklist.

Download a free PDF version of our peer editing checklist by clicking on the image above. Here’s the full lowdown on what’s included.
Essay Introduction
- Does the essay begin with a clear, attention-grabbing statement or hook?
- Are there at least three sentences in the introduction?
- Does the writer make his or her intentions clear?
- Are you clear about what issue is being addressed in this essay?
- Is there a clear thesis statement?
See our guide to how to write an essay introduction for more help.
- Are there at least three body paragraphs?
- Does each body paragraph contain a clear topic sentence and idea?
- Does each body paragraph contain a conclusion statement that leads well to the next body paragraph?
- Does the conclusion contain at least three sentences?
- Does the conclusion refer back to the thesis statement?
Essay Flow and Coherence
- Do the ideas flow logically through the paper and contribute to a building argument?
- Have you used transitions correctly?
- Is the essay interesting?
- Does the analysis presented in the paper support the thesis statement?
- Is the sentence structure varied?
Essay Style and Mechanics
- Have you appropriately attributed and cited evidence?
- Have you cited each reference source according to the relevant style guide? If you’re using APA, take a look at our APA checklist .
- Is the paper formatted according to the relevant style guide?
- Are the references, tables, and figures formatted according to the relevant style guide?
- Have you proofread the paper? For a full proofreading checklist, take a look at our essay proofreading checklist.
- Misspelled words
- Grammatical mistakes
- Punctuation errors
- Run-on Sentences
So that’s our guide to how to peer edit an essay. Got anything to add? Please leave a comment.
4 thoughts on “How to Peer Edit an Essay: Free Peer Editing Checklist”
- Pingback: Editing an Essay the Easy Way in 2019
- Pingback: Peer Essay Editing Checklist | Essay Tips | How to Peer Edit an Essay www.vappingo.com/... - New Sites
- Pingback: Editing an Essay the Easy Way in 2020
- Pingback: How to Write an Essay Introduction: The Definitive Guide
Comments are closed.
HTML Online
Tips, tricks, tutorials…
The Ultimate Checklist for Editing Your Essay
There is no learner that has gone through high school that has not done an essay. Writing and efficient communication are essential in the academic journey for tons of reasons. It enhances the students’ critical thinking skills and allows them to learn about the real world.
Through essays, learning institutions can assess students’ understanding of subjects and materials. Essays contribute to students’ grades, and considering they have to do many of them while studying, they need to do it right. While the structure of an essay and research plays a significant role in an essay’s success, editing is the key to a brilliant grade.
Here is an editing checklist for an excellent essay:
1. Assess the structure of the essay
Whether it is a history or psychology essay, they all have structures. The standard essay structure, which is the introduction, body, and conclusion, must be maintained. The structure ensures there is a logical flow of ideas, and points are not all over.

Your essay should have a developing argument. Ensure that it has structure before you proceed to edit it further. You can rearrange paragraphs to bring order to your paper; you can also search for rewrite essay services for support.
2. Eliminate redundant words
Filler words or redundancy can be a downer to your essay. They do not add substance to your writing and may interfere with the clarity of your points. Filler words can weigh down the power of your sentences and lower the quality of your essay .
Very good words to help you avoid using “very” very often:
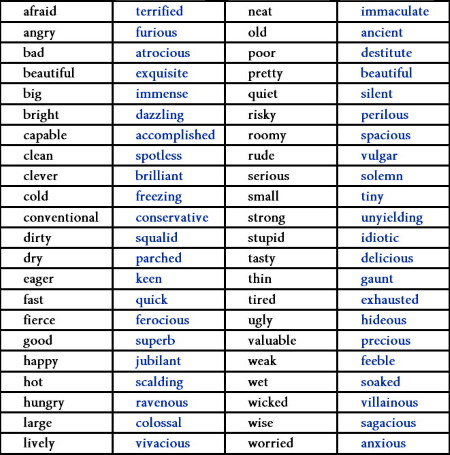
Your essay should be clear and concise, and you should get rid of words you don’t need. An excellent example of the filler words you should eliminate includes: in order to, that, basically, really, just, and so. Do this, and you will add focus to your essay.
3. Simplify the complex words
Using complicated words will not make your essay powerful. Do not give your reader a hard time reading your essay. Read through your paper and replace the complicated words with simpler words. Also, you are likely to use the wrong words in your quest for sophisticated words.
Complicated words will also interfere with the flow of your essay . Do not overuse complex words, and your writing will look authentic.
4. Trim the long sentences
Long sentences are hard to read and follow. While editing , pay attention to the length of the sentences and prune them if they are long. You can break the long sentences to form two sentences. Alternatively, you can use punctuation to give the reader a break.
The other way you can shorten long sentences is by eliminating unnecessary words . Sentences that have a maximum of 20 words are ideal. The same applies to paragraphs. Keep them as short as possible. 4 to 6 sentences in every paragraph is enough.
Shorter sentences capture the attention of the reader. They also make your content easy to understand and recall. Short sentences also create emphasis on your point and will make your paragraphs stronger.
Keeping sentences short enhances the readability of your essay and is more welcoming to the readers.
5. Check your commas
One of the errors that people make in their writing is wrong punctuation . The lack of commas is among the punctuation errors made in writing. The lack of commas and the improper use of commas can impede the quality of your paper.
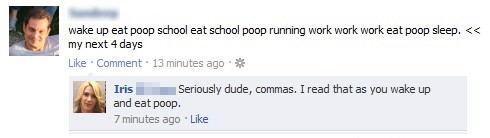
Too many commas will break the flow of your idea and will appear odd to the reader. On the other hand, the lack of commas or too few commas will make your sentence and text hard to follow.
To ensure that you are using commas the right way, read the text out loud. Where you pause, insert a comma. This way, you will be able to feel the flow of the sentences and punctuate accordingly.
6. Check for consistent spelling
A fair share of English words has more than one correct spelling. There are British, Australian, and American spellings. As much as all the spellings may be correct, it is vital to remain consistent with the spellings.
Some of the words with inconsistent spellings are organize, finalize, labor, learned, focused, and center . Watch out for the inconsistencies with the spellings and correct them. You can use grammar checkers to point out the inconsistencies.
Also, note that some of the grammar checkers might miss some of the issues. Your essay should never have different spellings.
7. Eliminate ellipses and exclamation marks
Often students think they can make their essays more captivating by using exclamation marks ❗❗❗ and ellipses. However, these should not be found in serious academic papers. Using such punctuations only impede the seriousness of your work. ❕
8. Check the formatting
Professors often provide formatting requirements when issuing assignments. You must be consistent with the instructions. Your paper might be clear of grammar errors and have the perfect paragraph length. However, if the formatting is not done right, your essay will appear incomplete.
To get a brilliant score in your essay paper , you should be consistent from the beginning to the end. Come up with a good topic and also ensure that your work is edited before submitting. The checklist above will help you come up with a flawless essay. Make sure to check out the article about the best programming languages to start a career.

- About NuWrite
- Writing Advice
- Engineering & Design
- General writing advice
- Academic integrity and avoiding plagiarism (Northwestern WCAS)
- Grammar and punctuation
- Analytical writing
- Research papers
- Graphics and visuals
- Conferences
- Peer editing sheets for drafts
- Peer feedback form literature seminar
- Peer review Asian diaspora freshman seminar
- Research draft peer review
- Research paper introduction peer response
- Research paper peer evaluation of claims
- Peer editing science papers
- Getting the most out of peer reviews
- Peer review guidelines for a personal essay
- Writing assignments
- Freshman seminar award essays
- Useful links with writing advice
- Grading criteria
- Global Health
- Writing in the Humanities
- Science Writing
- Social Science Writing
- Writing for Graduate or Professional School
- Writing Advice for International Students
- Faculty-Only Resources
Peer editing
Peer editing can be done during class time or electronically outside of class, as the documents below--from Northwestern instructors--illustrate. The questions that students respond to can vary according to the nature of the assignment and the purpose of the peer review.
peer editing sheets for drafts Peer editing sheets for two essay assignments in a freshman seminar. Providing very specific questions helps the editors give useful feedback and suggestions.
peer feedback form literature seminar Students exchange drafts in class, complete the peer feedback form, and then discuss their written comments with one another. Students submit the forms with their drafts so that I can read them. I frequently refer to their peers' comments when I am writing my own comments on their drafts.
peer review Asian diaspora freshman seminar Students do a close reading of one another's drafts to provide insight into what has and has not been conveyed by the draft.
research draft peer review Prompts peer reviewers to comment on key pieces of information, logical organization, and conclusion
research paper introduction peer response Prompts peer editor to comment on introduction, and prompts author to respond to those comments
research paper peer evaluation of claims Prompts peer editor to evaluate the paper's effectiveness in supporting claims and addressing counter-arguments
peer editing science papers Prompts peer editor to complete a checklist on the paper's content, structure, and grammar
getting the most out of peer reviews A link to NU's Writing Place that explains how to make sure you benefit from sharing your writing with peers
peer review guidelines for a personal essay These guidelines from a freshman seminar are aimed at pairs of students who are exchanging drafts before meeting individually with the instructor.

- Contact Northwestern University
- Campus Emergency Information
- University Policies
Northwestern University Library | 1970 Campus Drive, Evanston, IL 60208-2300 | Phone: 847.491.7658 | Fax: 847.491.8306 | Email: [email protected]
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
An NPR editor who wrote a critical essay on the company has resigned after being suspended
FILE - The headquarters for National Public Radio (NPR) stands on North Capitol Street on April 15, 2013, in Washington. A National Public Radio editor who wrote an essay criticizing his employer for promoting liberal reviews resigned on Wednesday, April 17, 2024, a day after it was revealed that he had been suspended. (AP Photo/Charles Dharapak, File)

- Copy Link copied
NEW YORK (AP) — A National Public Radio editor who wrote an essay criticizing his employer for promoting liberal views resigned on Wednesday, attacking NPR’s new CEO on the way out.
Uri Berliner, a senior editor on NPR’s business desk, posted his resignation letter on X, formerly Twitter, a day after it was revealed that he had been suspended for five days for violating company rules about outside work done without permission.
“I cannot work in a newsroom where I am disparaged by a new CEO whose divisive views confirm the very problems” written about in his essay, Berliner said in his resignation letter.
Katherine Maher, a former tech executive appointed in January as NPR’s chief executive, has been criticized by conservative activists for social media messages that disparaged former President Donald Trump. The messages predated her hiring at NPR.
NPR’s public relations chief said the organization does not comment on individual personnel matters.
The suspension and subsequent resignation highlight the delicate balance that many U.S. news organizations and their editorial employees face. On one hand, as journalists striving to produce unbiased news, they’re not supposed to comment on contentious public issues; on the other, many journalists consider it their duty to critique their own organizations’ approaches to journalism when needed.
In his essay , written for the online Free Press site, Berliner said NPR is dominated by liberals and no longer has an open-minded spirit. He traced the change to coverage of Trump’s presidency.
“There’s an unspoken consensus about the stories we should pursue and how they should be framed,” he wrote. “It’s frictionless — one story after another about instances of supposed racism, transphobia, signs of the climate apocalypse, Israel doing something bad and the dire threat of Republican policies. It’s almost like an assembly line.”
He said he’d brought up his concerns internally and no changes had been made, making him “a visible wrong-thinker at a place I love.”
In the essay’s wake, NPR top editorial executive, Edith Chapin, said leadership strongly disagreed with Berliner’s assessment of the outlet’s journalism and the way it went about its work.
It’s not clear what Berliner was referring to when he talked about disparagement by Maher. In a lengthy memo to staff members last week, she wrote: “Asking a question about whether we’re living up to our mission should always be fair game: after all, journalism is nothing if not hard questions. Questioning whether our people are serving their mission with integrity, based on little more than the recognition of their identity, is profoundly disrespectful, hurtful and demeaning.”
Conservative activist Christopher Rufo revealed some of Maher’s past tweets after the essay was published. In one tweet, dated January 2018, Maher wrote that “Donald Trump is a racist.” A post just before the 2020 election pictured her in a Biden campaign hat.
In response, an NPR spokeswoman said Maher, years before she joined the radio network, was exercising her right to express herself. She is not involved in editorial decisions at NPR, the network said.
The issue is an example of what can happen when business executives, instead of journalists, are appointed to roles overseeing news organizations: they find themselves scrutinized for signs of bias in ways they hadn’t been before. Recently, NBC Universal News Group Chairman Cesar Conde has been criticized for service on paid corporate boards.
Maher is the former head of the Wikimedia Foundation. NPR’s own story about the 40-year-old executive’s appointment in January noted that she “has never worked directly in journalism or at a news organization.”
In his resignation letter, Berliner said that he did not support any efforts to strip NPR of public funding. “I respect the integrity of my colleagues and wish for NPR to thrive and do important journalism,” he wrote.
David Bauder writes about media for The Associated Press. Follow him at http://twitter.com/dbauder

Senior NPR editor resigns after accusing outlet of liberal bias
An editor for National Public Radio resigned Wednesday just days after he inflamed the ongoing culture war about mainstream media with an essay about what he considers the news outlet’s liberal leanings.
Uri Berliner, who was a senior business editor, wrote an essay for the right-leaning online publication The Free Press in which he said he believes NPR is losing the public’s trust.
NPR, a nonprofit radio network, has an “absence of viewpoint diversity,” he wrote in the essay, which was published April 9. It “has always had a liberal bent,” but now an “open-minded spirit no longer exists within NPR,” he wrote.
The essay triggered a wave of scrutiny of NPR from conservatives, some of whom responded to it with calls to defund the news organization, which receives federal funding through the Corporation for Public Broadcasting. NPR says on its website that federal funding is “essential” to NPR but that “less than 1% of NPR’s annual operating budget comes in the form of grants from CPB and federal agencies and departments.”

In a resignation statement on X, Berliner briefly elaborated on the reason for his departure, which came days after NPR reported that it had suspended him for five days without pay following the op-ed’s release.
NPR’s chief business editor, Pallavi Gogoi, had told Berliner about its requirement to secure approval before he appeared in outside media, according to NPR’s report.
“I don’t support calls to defund NPR,” Berliner wrote. “I respect the integrity of my colleagues and wish for NPR to thrive and do important journalism. But I cannot work in a newsroom where I am disparaged by a new CEO whose divisive views confirm the very problems at NPR I cite in my Free Press essay.”
Berliner did not immediately respond to a request for comment Wednesday. A representative for NPR said it “does not comment on individual personnel matters.”
Berliner’s essay gained traction on X, with many conservatives homing in on his thoughts about NPR’s political makeup. He wrote: “In D.C., where NPR is headquartered and many of us live, I found 87 registered Democrats working in editorial positions and zero Republicans. None.”
He also criticized NPR’s coverage, or lack thereof, of certain stories, such as the Mueller report, Hunter Biden’s laptop, the origins of Covid-19 and systemic racism following the murder of George Floyd.
High-profile supporters of Berliner’s essay, including former President Donald Trump and X owner Elon Musk, shared criticism of NPR and its CEO, Katherine Maher.
“NO MORE FUNDING FOR NPR, A TOTAL SCAM! EDITOR SAID THEY HAVE NO REPUBLICANS, AND IS ONLY USED TO ‘DAMAGE TRUMP.’ THEY ARE A LIBERAL DISINFORMATION MACHINE. NOT ONE DOLLAR!!!” Trump wrote on Truth Social on April 10.
Musk wrote on X that the “head of NPR hates the Constitution of the USA” in response to a clip of Maher discussing the challenges in fighting disinformation and honoring the First Amendment right to free speech.
Meanwhile, some journalists at NPR pushed back against Berliner’s accusations.
“Morning Edition” co-host Steve Inskeep shared his take in a post on his Substack newsletter , saying he believes Berliner failed to “engage anyone who had a different point of view.”
“Having been asked, I answered: my colleague’s article was filled with errors and omissions,” he wrote, adding, “The errors do make NPR look bad, because it’s embarrassing that an NPR journalist would make so many.”
NPR’s chief news executive, Edith Chapin, also denied Berliner’s assessment of the newsroom in a memo to staff members, according to NPR .
“We’re proud to stand behind the exceptional work that our desks and shows do to cover a wide range of challenging stories,” she wrote. “We believe that inclusion — among our staff, with our sourcing, and in our overall coverage — is critical to telling the nuanced stories of this country and our world.”
Maher also said Monday in a statement to NPR : “In America everyone is entitled to free speech as a private citizen. What matters is NPR’s work and my commitment as its CEO: public service, editorial independence, and the mission to serve all of the American public. NPR is independent, beholden to no party, and without commercial interests.”
Daysia Tolentino is a culture and trends reporter for NBC News.
site categories
- Trump Hush Money Trial: What To Know As Jury Hears Opening Statements; No TV Cameras, But David Pecker And Stormy Daniels Expected To Testify
NPR Editor Resigns In Aftermath Of His Essay Criticizing Network For Bias
By Ted Johnson
Ted Johnson
Political Editor
More Stories By Ted
- House Passes New Bill To Force TikTok Sale; Lawmakers Also Pass $95 Billion National Security Package For Aid To Ukraine, Israel And Taiwan
- Man Who Set Himself On Fire Outside Trump NYC Trial Dies In Hospital; Self-Immolation Captured On CNN In Real Time – Update

UPDATE: The NPR editor who penned an essay criticizing the network for what he saw as bias in its coverage of Donald Trump and a host of other issues has resigned.
Uri Berliner , who had been a senior business editor and reporter, posting his resignation letter to NPR CEO Katherine Maher on his X/Twitter account.
A spokesperson for the network declined to comment.
Berliner had been temporarily suspended from NPR after publishing on essay for The Free Press that called out the network for losing “an open minded spirit” and lacking viewpoint diversity. He cited, among other things, audience research showing a drop in the number of listeners considering themselves conservative.
While Berliner’s essay was immediately seized upon by right wing media as evidence of NPR’s bias, some of his colleagues criticized him for making mistakes in his piece in for using “sweeping statements” to make his case, in the words of NPR’s Steve Inskeep. Maher criticized the essay in a note to staffers, writing, “Questioning whether our people are serving our mission with integrity, based on little more than the recognition of their identity, is profoundly disrespectful, hurtful, and demeaning.”
But Berliner’s essay did trigger some discussion within NPR, as some voices on the right, including Trump, called for defunding the network.
PREVIOUSLY: NPR has put on temporary suspension the editor who penned an essay that criticized the network for losing the trust of listeners as it has covered the rise of Donald Trump and coverage of Covid, race and other issues.
Uri Berliner has been suspended for five days without pay, starting last Friday, according to NPR’s David Folkenflik.
Related Stories

NPR’s Linda Wertheimer, One Of The Network’s “Founding Mothers,” Announces Retirement

Bob Edwards Dies: Longtime Anchor Of NPR’s ‘Morning Edition’ & SiriusXM Host Was 76
“That wouldn’t be a problem for an openly polemical news outlet serving a niche audience. But for NPR, which purports to consider all things, it’s devastating both for its journalism and its business model,” Berliner wrote. He also wrote that “race and identity became paramount in nearly every aspect of the workplace,” while claiming that the network lacked viewpoint diversity.
His essay set off a firestorm on the right, with Trump blasting the network and Fox News devoting extensive coverage to the criticism, along with calls for ending government funding for NPR.
In his essay, Berliner wrote that “defunding isn’t the answer,” but that its journalism needed to change from within. The network’s funding has been a target of conservatives numerous times in the past, but lawmakers ultimately have supported public radio.
Berliner shared his suspension notice with Folkenflik, who wrote that it was for failure to seek approval for outside work, as well as for releasing proprietary information about audience demographics.
Katherine Maher, who recently became CEO of the network, published a note to staff last week that appeared to take issue with Berliner’s essay, writing that there was “a criticism of our people on the basis of who we are.”
“Asking a question about whether we’re living up to our mission should always be fair game: after all, journalism is nothing if not hard questions,” Maher wrote. “Questioning whether our people are serving our mission with integrity, based on little more than the recognition of their identity, is profoundly disrespectful, hurtful, and demeaning.”
Maher herself has become a target on the right, with some figures citing her past social media posts, including one from 2020 that referred to Trump as a “deranged racist sociopath.” At the time, she was CEO of the Wikimedia Foundation. In a statement to The New York Times , Maher said that “in America everyone is entitled to free speech as a private citizen.” “What matters is NPR’s work and my commitment as its C.E.O.: public service, editorial independence and the mission to serve all of the American public,” she said.
An NPR spokesperson did not immediately return a request for comment. The network told The Times that Maher is not involved in editorial decisions.
Some of Berliner’s colleagues have been vocal in their own criticism of his essay. Eric Deggans, the network’s TV critic and media analyst, wrote that Berliner “set up staffers of color as scapegoats.” He also noted that Berliner “didn’t seek comment from NPR before publishing. Didn’t mention many things which could detract from his conclusions.”
Must Read Stories
Whcd preview: potus, media & showbiz converge for d.c. party-palooza, trump hush money trial: what to know as jury hears opening statements, oliver stone & lou ye films among titles added to official selection, june diane raphael & paul scheer lead amazon mgm pilot ‘dinks’ from marta kauffman.
Subscribe to Deadline Breaking News Alerts and keep your inbox happy.
Read More About:
39 comments.
Deadline is a part of Penske Media Corporation. © 2024 Deadline Hollywood, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
NPR suspends veteran editor as it grapples with his public criticism

David Folkenflik

NPR suspended senior editor Uri Berliner for five days without pay after he wrote an essay accusing the network of losing the public's trust and appeared on a podcast to explain his argument. Uri Berliner hide caption
NPR suspended senior editor Uri Berliner for five days without pay after he wrote an essay accusing the network of losing the public's trust and appeared on a podcast to explain his argument.
NPR has formally punished Uri Berliner, the senior editor who publicly argued a week ago that the network had "lost America's trust" by approaching news stories with a rigidly progressive mindset.
Berliner's five-day suspension without pay, which began last Friday, has not been previously reported.
Yet the public radio network is grappling in other ways with the fallout from Berliner's essay for the online news site The Free Press . It angered many of his colleagues, led NPR leaders to announce monthly internal reviews of the network's coverage, and gave fresh ammunition to conservative and partisan Republican critics of NPR, including former President Donald Trump.
Conservative activist Christopher Rufo is among those now targeting NPR's new chief executive, Katherine Maher, for messages she posted to social media years before joining the network. Among others, those posts include a 2020 tweet that called Trump racist and another that appeared to minimize rioting during social justice protests that year. Maher took the job at NPR last month — her first at a news organization .
In a statement Monday about the messages she had posted, Maher praised the integrity of NPR's journalists and underscored the independence of their reporting.
"In America everyone is entitled to free speech as a private citizen," she said. "What matters is NPR's work and my commitment as its CEO: public service, editorial independence, and the mission to serve all of the American public. NPR is independent, beholden to no party, and without commercial interests."
The network noted that "the CEO is not involved in editorial decisions."
In an interview with me later on Monday, Berliner said the social media posts demonstrated Maher was all but incapable of being the person best poised to direct the organization.
"We're looking for a leader right now who's going to be unifying and bring more people into the tent and have a broader perspective on, sort of, what America is all about," Berliner said. "And this seems to be the opposite of that."

Conservative critics of NPR are now targeting its new chief executive, Katherine Maher, for messages she posted to social media years before joining the public radio network last month. Stephen Voss/Stephen Voss hide caption
Conservative critics of NPR are now targeting its new chief executive, Katherine Maher, for messages she posted to social media years before joining the public radio network last month.
He said that he tried repeatedly to make his concerns over NPR's coverage known to news leaders and to Maher's predecessor as chief executive before publishing his essay.
Berliner has singled out coverage of several issues dominating the 2020s for criticism, including trans rights, the Israel-Hamas war and COVID. Berliner says he sees the same problems at other news organizations, but argues NPR, as a mission-driven institution, has a greater obligation to fairness.
"I love NPR and feel it's a national trust," Berliner says. "We have great journalists here. If they shed their opinions and did the great journalism they're capable of, this would be a much more interesting and fulfilling organization for our listeners."
A "final warning"
The circumstances surrounding the interview were singular.
Berliner provided me with a copy of the formal rebuke to review. NPR did not confirm or comment upon his suspension for this article.
In presenting Berliner's suspension Thursday afternoon, the organization told the editor he had failed to secure its approval for outside work for other news outlets, as is required of NPR journalists. It called the letter a "final warning," saying Berliner would be fired if he violated NPR's policy again. Berliner is a dues-paying member of NPR's newsroom union but says he is not appealing the punishment.
The Free Press is a site that has become a haven for journalists who believe that mainstream media outlets have become too liberal. In addition to his essay, Berliner appeared in an episode of its podcast Honestly with Bari Weiss.
A few hours after the essay appeared online, NPR chief business editor Pallavi Gogoi reminded Berliner of the requirement that he secure approval before appearing in outside press, according to a copy of the note provided by Berliner.
In its formal rebuke, NPR did not cite Berliner's appearance on Chris Cuomo's NewsNation program last Tuesday night, for which NPR gave him the green light. (NPR's chief communications officer told Berliner to focus on his own experience and not share proprietary information.) The NPR letter also did not cite his remarks to The New York Times , which ran its article mid-afternoon Thursday, shortly before the reprimand was sent. Berliner says he did not seek approval before talking with the Times .

NPR defends its journalism after senior editor says it has lost the public's trust
Berliner says he did not get permission from NPR to speak with me for this story but that he was not worried about the consequences: "Talking to an NPR journalist and being fired for that would be extraordinary, I think."
Berliner is a member of NPR's business desk, as am I, and he has helped to edit many of my stories. He had no involvement in the preparation of this article and did not see it before it was posted publicly.
In rebuking Berliner, NPR said he had also publicly released proprietary information about audience demographics, which it considers confidential. He said those figures "were essentially marketing material. If they had been really good, they probably would have distributed them and sent them out to the world."
Feelings of anger and betrayal inside the newsroom
His essay and subsequent public remarks stirred deep anger and dismay within NPR. Colleagues contend Berliner cherry-picked examples to fit his arguments and challenge the accuracy of his accounts. They also note he did not seek comment from the journalists involved in the work he cited.
Morning Edition host Michel Martin told me some colleagues at the network share Berliner's concerns that coverage is frequently presented through an ideological or idealistic prism that can alienate listeners.
"The way to address that is through training and mentorship," says Martin, herself a veteran of nearly two decades at the network who has also reported for The Wall Street Journal and ABC News. "It's not by blowing the place up, by trashing your colleagues, in full view of people who don't really care about it anyway."
Several NPR journalists told me they are no longer willing to work with Berliner as they no longer have confidence that he will keep private their internal musings about stories as they work through coverage.
"Newsrooms run on trust," NPR political correspondent Danielle Kurtzleben tweeted last week, without mentioning Berliner by name. "If you violate everyone's trust by going to another outlet and sh--ing on your colleagues (while doing a bad job journalistically, for that matter), I don't know how you do your job now."
Berliner rejected that critique, saying nothing in his essay or subsequent remarks betrayed private observations or arguments about coverage.
Other newsrooms are also grappling with questions over news judgment and confidentiality. On Monday, New York Times Executive Editor Joseph Kahn announced to his staff that the newspaper's inquiry into who leaked internal dissent over a planned episode of its podcast The Daily to another news outlet proved inconclusive. The episode was to focus on a December report on the use of sexual assault as part of the Hamas attack on Israel in October. Audio staffers aired doubts over how well the reporting stood up to scrutiny.
"We work together with trust and collegiality everyday on everything we produce, and I have every expectation that this incident will prove to be a singular exception to an important rule," Kahn wrote to Times staffers.
At NPR, some of Berliner's colleagues have weighed in online against his claim that the network has focused on diversifying its workforce without a concomitant commitment to diversity of viewpoint. Recently retired Chief Executive John Lansing has referred to this pursuit of diversity within NPR's workforce as its " North Star ," a moral imperative and chief business strategy.
In his essay, Berliner tagged the strategy as a failure, citing the drop in NPR's broadcast audiences and its struggle to attract more Black and Latino listeners in particular.
"During most of my tenure here, an open-minded, curious culture prevailed. We were nerdy, but not knee-jerk, activist, or scolding," Berliner writes. "In recent years, however, that has changed."
Berliner writes, "For NPR, which purports to consider all things, it's devastating both for its journalism and its business model."
NPR investigative reporter Chiara Eisner wrote in a comment for this story: "Minorities do not all think the same and do not report the same. Good reporters and editors should know that by now. It's embarrassing to me as a reporter at NPR that a senior editor here missed that point in 2024."
Some colleagues drafted a letter to Maher and NPR's chief news executive, Edith Chapin, seeking greater clarity on NPR's standards for its coverage and the behavior of its journalists — clearly pointed at Berliner.
A plan for "healthy discussion"
On Friday, CEO Maher stood up for the network's mission and the journalism, taking issue with Berliner's critique, though never mentioning him by name. Among her chief issues, she said Berliner's essay offered "a criticism of our people on the basis of who we are."
Berliner took great exception to that, saying she had denigrated him. He said that he supported diversifying NPR's workforce to look more like the U.S. population at large. She did not address that in a subsequent private exchange he shared with me for this story. (An NPR spokesperson declined further comment.)
Late Monday afternoon, Chapin announced to the newsroom that Executive Editor Eva Rodriguez would lead monthly meetings to review coverage.
"Among the questions we'll ask of ourselves each month: Did we capture the diversity of this country — racial, ethnic, religious, economic, political geographic, etc — in all of its complexity and in a way that helped listeners and readers recognize themselves and their communities?" Chapin wrote in the memo. "Did we offer coverage that helped them understand — even if just a bit better — those neighbors with whom they share little in common?"
Berliner said he welcomed the announcement but would withhold judgment until those meetings played out.
In a text for this story, Chapin said such sessions had been discussed since Lansing unified the news and programming divisions under her acting leadership last year.
"Now seemed [the] time to deliver if we were going to do it," Chapin said. "Healthy discussion is something we need more of."
Disclosure: This story was reported and written by NPR Media Correspondent David Folkenflik and edited by Deputy Business Editor Emily Kopp and Managing Editor Gerry Holmes. Under NPR's protocol for reporting on itself, no NPR corporate official or news executive reviewed this story before it was posted publicly.
- Katherine Maher
- uri berliner
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
NPR Editor Who Accused Broadcaster of Liberal Bias Resigns
Uri Berliner, who has worked at NPR for 25 years, said in an essay last week that the nonprofit had allowed progressive bias to taint its coverage.

By Benjamin Mullin
Uri Berliner, the NPR editor who accused the broadcaster of liberal bias in an online essay last week, prompting criticism from conservatives and recrimination from many of his co-workers, has resigned from the nonprofit.
Mr. Berliner said in a social media post on Wednesday that he was resigning because of criticism from the network’s chief executive, Katherine Maher.
“I cannot work in a newsroom where I am disparaged by a new C.E.O. whose divisive views confirm the very problems at NPR I cite in my Free Press essay,” Mr. Berliner wrote.
In his brief resignation letter, addressed to Ms. Maher, Mr. Berliner said he loved NPR, calling it a “great American institution” and adding that he respects “the integrity of my colleagues and wish for NPR to thrive and do important journalism.”
An NPR spokeswoman, Isabel Lara, said the nonprofit does not comment on personnel matters.
In an interview, Mr. Berliner said his decision to resign from NPR coalesced early this week after an email exchange with Ms. Maher. He said in the interview that he could infer from one of her emails that a memo she had sent to employees last week about workplace integrity was referring to him even though he had not been mentioned by name. In the email, which was sent to Mr. Berliner on Monday, Ms. Maher said her memo “stands for itself in reflecting my perspective on our organization.”
“Everything completely changed for me on Monday afternoon,” Mr. Berliner said.
Mr. Berliner’s essay stirred up a hornet’s nest of criticism of NPR and made Mr. Berliner something of a pariah within the network. Several employees told The New York Times that they no longer wished to work with him, and his essay was denounced by Edith Chapin, the network’s top editor.
Many journalists at NPR pushed back against the essay, including the “Morning Edition” host Steve Inskeep, who said on the newsletter platform Substack that Mr. Berliner failed to “engage anyone who had a different point of view.”
“This article needed a better editor,” Mr. Inskeep wrote. “I don’t know who, if anyone, edited Uri’s story, but they let him publish an article that discredited itself.”
Mr. Berliner’s essay found some defenders among the ranks of former NPR employees. Jeffrey A. Dvorkin, a former ombudsman, said on social media that Mr. Berliner was “not wrong.” Chuck Holmes, a former managing editor at NPR, called Mr. Berliner’s essay “brave” on Facebook.
Critics of NPR, including conservative activists, used Mr. Berliner’s essay in The Free Press to impugn the network’s journalism and its leadership. One of them, Christopher Rufo, began resurfacing social media posts from Ms. Maher that were critical of President Donald J. Trump and embraced progressive causes. Mr. Rufo has a history of pressuring media organizations to cover critical stories of well-known figures, including the plagiarism allegations against Claudine Gay, the former Harvard president.
NPR said in a statement earlier this week that Ms. Maher’s social media posts predated her term as chief executive, adding that she was not working in news at the time.
Before he resigned from NPR, Mr. Berliner was on a five-day suspension from the network for violating company policy against working for outside organizations without securing permission.
Mr. Berliner said he did not have any immediate plans after leaving NPR, adding that he was looking forward to getting more sleep and spending time with his family.
Benjamin Mullin reports on the major companies behind news and entertainment. Contact Ben securely on Signal at +1 530-961-3223 or email at [email protected] . More about Benjamin Mullin

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Check for complete sentences: Starting from the last sentence in your paper, read it backwards, one sentence at a time. This helps you focus on a single sentence. Double-underline the subject and underline the verb for each independent clause. Make sure each subject has a verb. A sentence that starts with for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so ...
Level Up Your Team. See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Professional editors, who must constantly proofread others' writing for clarity, tone, accuracy, and grammar, often use an editing checklist that helps them catch common mistakes. Read on to learn what items to add to your editing checklist.
19. Koen Driessen. Koen has written multiple theses and founded, together with Bas and Richard, the thesis editing company Scribbr in 2012. Our checklists help you hand in a perfect essay, research paper, thesis, or dissertation, ensuring you haven't forgetten anything important.
Essay Editing Tip #6: Use a Checklist. To ensure that your essay is error-free and effectively transmits your intended message, you can use an editing checklist. It is always a good idea to check your writing against pre-set criteria. Here are some of the items from our 'do my essay' experts you can put on your checklist and use while editing ...
Try to keep the editing and proofreading processes separate. When you are editing an early draft, you don't want to be bothered with thinking about punctuation, grammar, and spelling. If your worrying about the spelling of a word or the placement of a comma, you're not focusing on the more important task of developing and connecting ideas.
structure your essay or make your argument more logical and effective. When you're confident in the essay's content, move on to editing the smaller stuff, like spelling and grammar. Move down the checklist on the back more or less in order, from higher order concerns to lower order con-cerns.
Editing is a crucial skill for any writer, but it can be challenging to master. In this blog post, you will learn how to edit your writing in three steps, with examples and tips from Grammarly. Whether you are writing an essay, a blog post, or a sales letter, you will find out how to improve your clarity, coherence, and correctness with Grammarly's editing tools.
Revised on July 23, 2023. An academic essay is a focused piece of writing that aims to present a convincing argument using evidence, analysis and interpretation. It always has an introduction, a main body, and a conclusion. When you've finished writing your essay, use this checklist to evaluate your work.
Check the essay yourself, have a friend review it, or better yet, have your essay edited by a professional editing service. Avoid colloquialisms and contractions. ('Cause it just ain't professional in an academic setting. Lol.) Analyze the flow of your essay, and make sure that your ideas and paragraphs flow smoothly from one to the next.
Here's what a professional editor looks for in your essay: 1. Errors in spelling and grammar: This includes ensuring subject-verb agreement, conducting spellchecks on commonly misspelled words, or even maintaining consistency in the tense of your essay. 2. Errors in the use of technical terms:
There are multiple levels of editing, and terminology surrounding editing is often used interchangeably and fluidly. These levels have some overlap between each other, rather than being totally discrete stages; similarly, developmental and substantive editing are more closely related to the "revision" step of the writing process.
Editing an essay effectively involves several key steps to enhance clarity, coherence, and overall impact. Here's a step-by-step guide: Review the Structure: Ensure your essay has a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should present your thesis statement or main argument, the body should contain your supporting points ...
Personal Editing Checklist. "If you re-read your work, you can find on re-rereading a great deal of repetition can be avoided by re-reading and editing." —William Safire. Click to download and create your Personalized Editing Checklist.
Editing Checklist for Self- and Peer Editing Directions: Edit your written work using the Self-Edit columns, fixing any errors you notice. Then, have a peer complete the Peer Edit columns while you observe. Self-Edit Peer Edit Checklist Items After completing each step, place a check here. Checklist Items After completing each step, place a ...
The Editing Checklist found below will help you focus on some key issues as you edit. There are two versions of the checklist below. The first is a printable PDF version, and the second is an interactive PDF version. In some browsers, you may need to download or save this file to be able to utilize all of its functionality.
Provided by the Academic Center for Excellence 1 Self-Editing Checklist for College Writers Reviewed July 2012 . Self-Editing Checklist for College Writers . Researching, brainstorming, and drafting are critical for writing an effective paper; however, the difference between an acceptable paper and a great paper is proof -reading and editing.
After the self-edit is complete, discuss the process with the students. Next, choose another student to serve as the peer editor for the piece that was just self-edited. Have the two students sit in the middle of the class so that all students can see and hear them as they work through the peer-editing phase. Afterward, include the entire class ...
Richard Nordquist. Updated on October 14, 2019. After you have completed one or more drafts of your narrative essay, use the following checklist as a revision and editing guide to prepare the final version of your composition. In your introduction, have you clearly identified the experience you are about to relate?
Editing. Refine your draft by fixing grammar, punctuation, spelling, and other mechanical errors. You might also look at sentence structure, word choice, and consistency in style and tone. This is where you polish your work. Proofreading. This is the final check before you consider your piece complete.
Supplemental essay prompts generally have word limit of 100-400 words. Either way, you need to make sure that you stay very close to the upper word limit in your response. As a general rule, you should try to stay within 10% of the upper word limit. So if the word limit for one of your essays is 650 words, your essay shouldn't be fewer than ...
Hand them our handy tips and the great peer editing checklist. If you wish to edit your essay before engaging the help of a peer editor, take a look at our guide to essay editing. How to Peer Edit an Essay: Top Tips for Success. Peer editors should review an essay with the primary intention of offering advice on how it can be improved.
Here is an editing checklist for an excellent essay: 1. Assess the structure of the essay. Whether it is a history or psychology essay, they all have structures. The standard essay structure, which is the introduction, body, and conclusion, must be maintained. The structure ensures there is a logical flow of ideas, and points are not all over.
peer editing science papers Prompts peer editor to complete a checklist on the paper's content, structure, and grammar. getting the most out of peer reviews A link to NU's Writing Place that explains how to make sure you benefit from sharing your writing with peers. peer review guidelines for a personal essay
NEW YORK (AP) — National Public Radio has suspended a veteran editor who wrote an outside essay criticizing his employer for, in his view, journalism that reflects a liberal viewpoint with little tolerance for contrary opinions.. Uri Berliner, a senior editor on NPR's business desk, was suspended five days without pay, according to an article posted Tuesday by NPR's media correspondent ...
NPR senior business editor Uri Berliner resigned this morning, citing the response of the network's chief executive to his outside essay accusing NPR of losing the public's trust.
Updated 5:51 PM PDT, April 17, 2024. NEW YORK (AP) — A National Public Radio editor who wrote an essay criticizing his employer for promoting liberal views resigned on Wednesday, attacking NPR's new CEO on the way out. Uri Berliner, a senior editor on NPR's business desk, posted his resignation letter on X, formerly Twitter, a day after ...
April 17, 2024, 3:12 PM PDT. By Daysia Tolentino. An editor for National Public Radio resigned Wednesday just days after he inflamed the ongoing culture war about mainstream media with an essay ...
April 17, 2024 9:05am. National Public Radio headquarters in Washington, D.C. Getty Images. UPDATE: The NPR editor who penned an essay criticizing the network for what he saw as bias in its ...
NPR suspended senior editor Uri Berliner for five days without pay after he wrote an essay accusing the network of losing the public's trust and appeared on a podcast to explain his argument. Uri ...
April 17, 2024. Uri Berliner, the NPR editor who accused the broadcaster of liberal bias in an online essay last week, prompting criticism from conservatives and recrimination from many of his co ...