267 Freedom Essay Topics & Examples
Need freedom topics for an essay or research paper? Don’t know how to start writing your essay? The concept of freedom is very exciting and worth studying!

📃 Freedom Essay: How to Start Writing
📝 how to write a freedom essay: useful tips, 🏆 freedom essay examples & topic ideas, 🥇 most interesting freedom topics to write about, 🎓 simple topics about freedom, 📌 writing prompts on freedom, 🔎 good research topics about freedom, ❓ research questions about freedom.
The field of study includes personal freedom, freedom of the press, speech, expression, and much more. In this article, we’ve collected a list of great writing ideas and topics about freedom, as well as freedom essay examples and writing tips.
Freedom essays are common essay assignments that discuss acute topics of today’s global society. However, many students find it difficult to choose the right topic for their essay on freedom or do not know how to write the paper.
We have developed some useful tips for writing an excellent paper. But first, you need to choose a good essay topic. Below are some examples of freedom essay topics.
Freedom Essay Topics
- American (Indian, Taiwanese, Scottish) independence
- Freedom and homelessness essay
- The true value of freedom in modern society
- How slavery affects personal freedom
- The problem of human rights and freedoms
- American citizens’ rights and freedoms
- The benefits and disadvantages of unlimited freedom
- The changing definition of freedom
Once you have selected the issue you want to discuss (feel free to get inspiration from the ones we have suggested!), you can start working on your essay. Here are 10 useful tips for writing an outstanding paper:
- Remember that freedom essay titles should state the question you want to discuss clearly. Do not choose a vague and non-descriptive title for your paper.
- Work on the outline of your paper before writing it. Think of what sections you should include and what arguments you want to present. Remember that the essay should be well organized to keep the reader interested. For a short essay, you can include an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Do preliminary research. Ask your professor about the sources you can use (for example, course books, peer-reviewed articles, and governmental websites). Avoid using Wikipedia and other similar sources, as they often have unverified information.
- A freedom essay introduction is a significant part of your paper. It outlines the questions you want to discuss in the essay and helps the reader understand your work’s purpose. Remember to state the thesis of your essay at the end of this section.
- A paper on freedom allows you to be personal. It should not focus on the definition of this concept. Make your essay unique by including your perspective on the issue, discussing your experience, and finding examples from your life.
- At the same time, help your reader to understand what freedom is from the perspective of your essay. Include a clear explanation or a definition with examples.
- Check out freedom essay examples online to develop a structure for your paper, analyze the relevance of the topics you want to discuss and find possible freedom essay ideas. Avoid copying the works you will find online.
- Support your claims with evidence. For instance, you can cite the Bill of Rights or the United States Constitution. Make sure that the sources you use are reliable.
- To make your essay outstanding, make sure that you use correct grammar. Grammatical mistakes may make your paper look unprofessional or unreliable. Restructure a sentence if you think that it does not sound right. Check your paper several times before sending it to your professor.
- A short concluding paragraph is a must. Include the summary of all arguments presented in the paper and rephrase the main findings.
Do not forget to find a free sample in our collection and get the best ideas for your essay!
- Freedom of Expression Essay For one to be in a position to gauge the eventuality of a gain or a loss, then there should be absolute freedom of expression on all matters irrespective of the nature of the sentiments […]
- Freedom of Speech in Social Media Essay Gelber tries to say that the history of the freedom of speech in Australia consists of the periods of the increasing public debates on the issue of human rights and their protection.
- Freedom Writers: Promoting Good Moral Values The movie portrays a strong and civilized view of the world; it encourages development and use of positive moral values by people in making the world a better place.
- Philosophy and Relationship between Freedom and Responsibility Essay As a human being, it is hard to make a decision because of the uncertainty of the outcome, but it is definitely essential for human being to understand clearly the concept and connection between freedom […]
- Human Will & Freedom and Moral Responsibility Their understanding of the definition of human will is based on the debate as to whether the will free or determined.
- Rio (2011) and the Issue of Freedom As a matter of fact, this is the only scene where Blu, Jewel, Linda, Tulio, and the smugglers are present at the same time without being aware of each other’s presence.
- Freedom and equality According to Liliuokalani of Hawaii, the conquest contravened the basic rights and freedoms of the natives and their constitution by undermining the power of their local leaders.
- Human Freedom in Relation to Society Human freedom has to do with the freedom of one’s will, which is the freedom of man to choose and act by following his path through life freely by exercising his ‘freedom’).
- The Efforts and Activities of the Paparazzi are Protected by the Freedom of the Press Clause of the Constitution The First Amendment of the American constitution protects the paparazzi individually as American citizens through the protection of their freedom of speech and expression and professionally through the freedom of the press clause.
- Freedom and Determinism On the other hand, determinism theory explains that there is an order that leads to occurrences of events in the world and in the universe.
- Four Freedoms by President Roosevelt Throughout the discussion we shall elaborate the four freedoms in a broader way for better understating; we shall also describe the several measures that were put in place in order to ensure the four freedoms […]
- Freedom in Henrik Ibsen’s “A Doll’s House” Literature Analysis In Henrik Ibsen’s A Doll’s House, the main character, Nora is not an intellectual, and spends no time scouring books or libraries or trying to make sense of her situation.
- “Gladiator” by Ridley Scott: Freedom and Affection This desire to be free becomes the main motive of the film, as the plot follows Maximus, now enslaved, who tries to avenge his family and the emperor and regain his liberty.
- Jean-Paul Sartre’s Views on Freedom For example, to Sartre, a prisoner of war is free, existentially, but this freedom does not exist in the physical realm.
- “Long Walk to Freedom” by Nelson Mandela In the fast developing world, advances and progress move countries and nations forward but at the same time, some things are left behind and become a burden for the people and evolution to better life […]
- Fighting for the Right to Choose: Students Should Have the Freedom to Pick the Courses They Want Consequently, students should be allowed to pick the subjects which they are going to study together with the main one. Thus, students should be allowed to choose the subjects they need in accordance with their […]
- Freedom and the Role of Civilization The achievements demonstrated by Marx and Freud play a significant role in the field of sociology and philosophy indeed; Marx believed in the power of labor and recognized the individual as an integral part of […]
- 70’s Fashion as a Freedom of Choice However, with the end of the Vietnam War, the public and the media lost interest in the hippie style in the middle of the decade, and began to lean toward the mod subculture. The 70’s […]
- Chapters 4-6 of ”From Slavery to Freedom” by Franklin & Higginbotham At the same time, the portion of American-born slaves was on the increase and contributed to the multiracial nature of the population.
- Social Values: Freedom and Justice It is evident that freedom and justice are mutually exclusive, as “the theory of justice signifies its implications in regards to freedom as a key ingredient to happiness”.
- Personal Understanding of Freedom Freedom is essential for individual growth and development, and it helps individuals to make informed decisions that are in alignment with their values and beliefs.
- Personal Freedom in A Doll’s House, A Room of One’s Own, and Diary of a Madman In Chapter Three of Virginia Woolf’s A Room of One’s Own, the protagonist attempts to make sense of the nonsensical elements of female history, namely, how it could be that “in Athena’s city, where women […]
- Art and Freedom. History and Relationship The implication of this term is that genus art is composed of two species, the fine arts, and the useful arts. This, according to Cavell, is the beauty of art.
- Rousseau and Kant on their respective accounts of freedom and right The difference in the approaches assumed by Kant and Rousseau regarding the norms of liberty and moral autonomy determine the perspective of their theories of justice.
- Protecting Freedom of Expression on the Campus An annotated version of “Protecting Freedom of Expression on the Campus” by Derek Bok in The Boston Globe.*and these stars are where I have a question or opinion on a statement* For several years, universities […]
- Mandela’s Leadership: Long Walk to Freedom The current paper analyses the effectiveness of leadership with reference to Nelson Mandela, the late former president of South Africa, as depicted in the movie, Mandela: Long Walk to Freedom.
- Freedom of Expression in the Classroom The NEA Code of Ethics establishes a link between this Freedom and a teacher’s responsibilities by requiring instructors to encourage “independent activity in the pursuit of learning,” provide “access to diverse points of view,” and […]
- Freedom, Equality & Solidarity by Lucy Parsons In the lecture and article ‘The Principles of Anarchism’ she outlines her vision of Anarchy as the answer to the labor question and how powerful governments and companies worked for hand in hand to stifle […]
- Human Freedom: Liberalism vs Anarchism It is impoverished because liberals have failed to show the connection between their policies and the values of the community. More fundamentally, however, a policy formulated in such a way that it is disconnected from […]
- Voices of Freedom The history of the country is made up of debates, disagreements and struggles for freedom that have seen the Civil War, and the Cold War which have changed the idea of freedom in the US.
- “Freedom Riders”: A Documentary Revealing Personal Stories That Reflect Individual Ideology The ideal of egalitarianism was one of the attractive features of the left wing for many inquiring minds in the early decades of the 20th century.
- Women in Early America: Struggle, Survival, and Freedom in a New World The writer shows that women had the same capacities as those of men but were not allowed to contribute their ideas in developing the country.
- The meaning of freedom today In order to come up with an agreeable and logical definition of freedom as it is in the contemporary society, people have critically analyzed the input of these philosophers and their definition of freedom in […]
- Freedom in Antebellum America: Civil War and Abolishment of Slavery The American Civil War, which led to the abolishment of slavery, was one of the most important events in the history of the United States.
- Individual Freedom: Exclusionary Rule The exclusionary rule was first introduced by the US Supreme Court in 1914 in the case of Weeks v.the United States and was meant for the application in the federal courts only, but later it […]
- Canada’s Freedom of Speech and Its Ineffectiveness In the developed societies of the modern world, it is one of the major premises that freedom of expression is the pivotal character of liberal democracy.
- Concept of Individual Freedom Rousseau and Mill were political philosophers with interest in understanding what entailed individual freedom. This paper compares Rousseau’s idea of individual freedom with Mill’s idea.
- Predetermination and Freedom of Choice We assume that every happens because of a specific reason and that the effects of that event can be traced back to the cause.
- Freedom and Social Justice Through Technology These two remarkable minds have made significant contributions to the debates on technology and how it relates to liberty and social justice.
- Balancing Freedom of Speech and Responsibility in Online Commenting The article made me perceive the position of absolute freedom of speech in the Internet media from a dual perspective. This desire for quick attention is the creation of information noise, distracting from the user […]
- The Effect of Emotional Freedom Techniques on Nurses’ Stress The objectives for each of the three criteria are clearly stated, with the author explaining the aims to the reader well throughout the content in the article’s title, abstract, and introduction.
- The Freedom Summer Project and Black Studies The purpose of this essay is to discuss to which degree the story of the Freedom Summer project illustrates the concepts of politics outlined in Karenga’s book Introduction to black studies.
- Democracy: The Influence of Freedom Democracy is the basis of the political systems of the modern civilized world. Accordingly, the democracy of Athens was direct that is, without the choice of representatives, in contrast to how it is generated nowadays.
- Freedom of Speech as a Basic Human Right Restricting or penalizing freedom of expression is thus a negative issue because it confines the population of truth, as well as rationality, questioning, and the ability of people to think independently and express their thoughts.
- Kantian Ethics and Causal Law for Freedom The theory’s main features are autonomy of the will, categorical imperative, rational beings and thinking capacity, and human dignity. The theory emphasizes not on the actions and the doers but the consequences of their effects […]
- Principles in M. L. King’s Quest for African American Freedom The concept of a nonviolent approach to the struggles for African American freedom was a key strategy in King’s quest for the liberation of his communities from racial and social oppressions.
- Technology Revolutionizing Ethical Aspects of Academic Freedom As part of the solution, the trends in technology are proposed as a potential solution that can provide the necessary support to improve the freedom of expression as one of the ethical issues that affect […]
- The Journey Freedom Tour 2022 Performance Analysis Arnel Pineda at age 55 keeps rocking and hitting the high notes and bringing the entire band very successfully all through their live concert tour.
- Freedom of Speech and Propaganda in School Setting One of the practical solutions to the problem is the development and implementation of a comprehensive policy for balanced free speech in the classroom.
- Twitter and Violations of Freedom of Speech and Censorship The sort of organization that examines restrictions and the opportunities and challenges it encounters in doing so is the center of a widely acknowledged way of thinking about whether it is acceptable to restrict speech.
- Freedom of the Press and National Security Similarly, it concerns the freedom of the press of the media, which are protected in the United States of America by the First Amendment.
- The Views on the Freedom from Fear in the Historical Perspective In this text, fear is considered in the classical sense, corresponding to the interpretation of psychology, that is, as a manifestation of acute anxiety for the inviolability of one’s life.
- Freedom of Speech in Social Networks The recent case of blocking the accounts of former US President Donald Trump on Twitter and Facebook is explained by the violation of the rules and conditions of social platforms.
- Emotion and Freedom in 20th-Century Feminist Literature The author notes that the second layer of the story can be found in the antagonism between the “narrator, author, and the unreliable protagonist”.
- Analysis of UK’s Freedom of Information Act 2000 To preserve potentially disruptive data that must not be released to the public, the FOIA integrates several provisions that allow the officials to decline the request for information without suffering possible consequences.
- Fight for Freedom, Love Has No Labels, and Ad Council: Key Statement The most important part of the message, to me, is the fact that the freedoms mentioned in the PSA are not available to every American citizen, despite America being the land of freedom.
- Teachers’ Freedom of Speech in Learning Institutions The judiciary system has not clearly defined the limits of the First Amendment in learning institutions, and it’s a public concern, especially from the teachers.
- Is There Press Freedom in Modern China? There is a large body of literature in the field of freedom of the press investigations, media freedom in China, and press freedom and human rights studies.
- Freedom of the Press in the Context of UAE It gives the people the ability to understand the insight of the government and other crucial activities happening within the country.
- Freedom of the Press in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) According to oztunc & Pierre, the UAE is ranked 119 in the global press freedom data, classifying the country as one of the most suppressive regarding the liberty of expression.
- Mill’s Thesis on the Individual Freedom The sphere of personal freedom is an area of human life that relates to the individual directly. The principle of state intervention is that individuals, separately or collectively, may have the right to interfere in […]
- Privacy and Freedom of Speech of Companies and Consumers At the same time, in Europe, personal data may be collected following the law and only with the consent of the individuals.
- Review of “Mandela: Long Walk to Freedom” From the youth, Mandela started to handle the unfairness of isolation and racial relations in South Africa. In Mandela: Long Walk to Freedom, Chadwick’s masterful screen memoir of Nelson Mandela passes on the anguish as […]
- Expansion of Freedom and Slavery in British America The settlement in the city of New Plymouth was founded by the second, and it laid the foundation for the colonies of New England.
- Power, Property, and Freedom: Bitcoin Discourse In the modern world, all people have the right to freedom and property, but not all have the power to decide who may have this freedom and property.
- Religious Freedom Policy Evaluation Ahmed et al.claim that the creation of the ecosystem can facilitate the change as the members of the community share their experiences and learn how to respond to various situations.
- The Concepts of Freedom and the Great Depression Furthermore, blacks were elected to construct the constitution, and black delegates fought for the rights of freedpeople and all Americans. African-Americans gained the freedom to vote, work, and be elected to government offices during Black […]
- Freedom of Choices for Women in Marriage in “The Story of an Hour” The story describes the sentiments and feelings of Louisa Mallard when she learns the news about her husband. The readers can see the sudden reaction of the person to the demise of her significant other.
- Freedom of Speech in Shouting Fire: Stories From the Edge of Free Speech Even though the First Amendment explicitly prohibits any laws regarding the freedom of speech, Congress continues to make exceptions from it.
- Personal Freedom: The Importance in Modern Society To show my family and friends how important they are to me, I try contacting them more often in the way they prefer.
- Economic Freedom and Its Recent Statements Economic freedom is an important indicator and benchmark for the level of income of companies or individual citizens of a country.
- The Freedom Concept in Plato’s “Republic” This situation shows that the concept of democracy and the freedom that correlates with it refers to a flawed narrative that liberty is the same as equality.
- Freedom of Speech as the Most Appreciated Liberty In the present-day world, the progress of society largely depends on the possibility for people to exercise their fundamental rights. From this perspective, freedom of speech is the key to everyone’s well-being, and, in my […]
- The Wealth of Networks: How Social Production Transforms Markets and Freedom In the introductory part of the book, the author discusses his main theses concerning the link between the development of networks and shifts in the economy and society.
- Freedom of Association for Radical Organizations This assertion is the primary and fundamental argument in the debate on this topic – radical groups should not use freedom of association to harm other people potentially.
- Freedom of Expression on the Internet Randall describes the challenges regarding the freedom of speech raised by the Internet, such as anonymity and poor adaptation of mass communication to the cyber environment.
- Black Sexual Freedom and Manhood in “For Colored Girls” Movie Despite the representation of Black sexual freedoms in men and women and Black manhood as a current social achievement, For Colored Girls shows the realities of inequality and injustice, proving womanism’s importance in America.
- Frederick Douglass’s My Bondage and My Freedom Review He criticizes that in spite of the perceived knowledge he was getting as a slave, this very light in the form of knowledge “had penetrated the moral dungeon”.
- The Essence of Freedom of Contract The legal roots of the notion of freedom of contract are manifested in the ideals of liberalism and theoretical capitalism, where the former values individual freedom and the latter values marker efficiency and effectiveness.
- Why Defamation Laws Must Prioritize Freedom of Speech The body of the essay will involve providing information on the nature of defamation laws in the USA and the UK, the implementation of such laws in the two countries, and the reason why the […]
- Pettit’s Conception of Freedom as Anti-Power According to Savery and Haugaard, the main idea that Pettit highlights in this theory is the notion that the contrary to freedom is never interference as many people claim, but it is slavery and the […]
- Domination in the Discussion of Freedom For this reason, the principle of anti-power should be considered as the position that will provide a better understanding of the needs of the target population and the desirable foreign policy to be chosen.
- Freedom or Security: Homeland Issues In many ways, the author sheds light on the overreactions or inadequate responses of the US government, which led to such catastrophes as 9/11 or the war in Iraq.
- War on Terror: Propaganda and Freedom of the Press in the US There was the launching of the “Center for Media and Democracy”, CMD, in the year 1993 in order to create what was the only public interest at that period. There was expansive use of propaganda […]
- The Freedom of Expression and the Freedom of Press It is evident that the evolution of standards that the court has adopted to evaluate the freedom of expression leaves a lot to be desired. The court has attempted to define the role of the […]
- Information and Communication Technology & Economic Freedom in Islamic Middle Eastern Countries This is a unique article as it gives importance to the role ecommerce plays in the life of the educationists and students and urges that the administrators are given training to handle their students in […]
- Is the Good Life Found in Freedom? Example of Malala Yousafzai The story of Malala has shown that freedom is crucial for personal happiness and the ability to live a good life.
- The Path to Freedom of Black People During the Antebellum Period In conclusion, the life of free blacks in 19th century America was riddled with hindrances that were meant to keep them at the bottom of society.
- Civil Rights Movement: Fights for Freedom The Civil Rights Movement introduced the concept of black and white unification in the face of inequality. Music-related to justice and equality became the soundtrack of the social and cultural revolution taking place during the […]
- Voices of Freedom: Lincoln, M. L. King, Kirkaldy He was named after his grandfather Abraham Lincoln, the one man that was popular for owning wide tracks of land and a great farmer of the time.
- Freedom: Malcolm X’s vs. Anna Quindlen’s Views However, in reality, we only have the freedom to think whatever we like, and only as long as we know that this freedom is restricted to thought only.
- Net Neutrality: Freedom of Internet Access In the principle of Net neutrality, every entity is entitled access and interaction with other internet users at the same cost of access.
- The Golden Age of Youth and Freedom However, it is interesting to compare it to the story which took place at the dawn of the cultural and sexual revolution in Chinese society.
- Academic Freedom: A Refuge of Intellectual Individualism Also known as intellectual, scientific or individual freedom, academic freedom is defined as the freedom of professionals and students to question and to propose new thoughts and unpopular suggestions to the government without jeopardizing their […]
- The Literature From Slavery to Freedom Its main theme is slavery but it also exhibits other themes like the fight by Afro-Americans for freedom, the search for the identity of black Americans and the appreciation of the uniqueness of African American […]
- John Stuart Mill on Freedom in Today’s Perspective The basic concept behind this rose because it was frustrating in many cases in the context of the penal system and legislation and it was viewed that anything less than a capital punishment would not […]
- Conformity Versus Freedom at University To the author, this is objectionable on the grounds that such a regimen infringes on the freedom of young adults and that there is much to learn outside the classroom that is invaluable later in […]
- US Citizens and Freedom As an example of freedom and obtaining freedom in the US, the best possible subject would be the Civil Rights Movement of the 1960s, particularly during 1963-64, as this would serve as the conceptual and […]
- Value of Copyright Protection in Relation to Freedom of Speech The phrase, freedom of expression is often used to mean the acts of seeking, getting, and transfer of information and ideas in addition to verbal speech regardless of the model used. It is therefore important […]
- Social Factors in the US History: Respect for Human Rights, Racial Equality, and Religious Freedom The very first years of the existence of the country were marked by the initiatives of people to provide as much freedom in all aspects of social life as possible.
- Freedom of Speech and the Internet On the one hand, the freedom of expression on the internet allowed the general public to be informed about the true nature of the certain events, regardless of geographical locations and restrictions.
- Freedom Definition Revision: Components of Freedom That which creates, sustains, and maintains life in harmony with the natural cycles of this planet, doing no harm to the ecology or people of the Earth- is right.
- Freedom of Information Act in the US History According to the legislation of the United States, official authorities are obliged to disclose information, which is under control of the US government, if it is requested by the public.
- Media Freedom in the Olympic Era The Chinese government is heavily involved in the affairs of the media of that country. In the past, it was the responsibility of government to fund media houses however; today that funding is crapped off.
- Managing the Internet-Balancing Freedom and Regulations The explosive growth in the usage of Internet forms the basis of new digital age. Aim of the paper is to explore the general role of internet and its relationship with the society.
- Ways Liberals Define Freedom Liberals are identified by the way they value the freedom of individuals, freedom of markets, and democratic freedoms. The term freedom is characterized by Liberals as they use it within the context of the relationship […]
- Balance of Media Censorship and Press Freedom Government censorship means the prevention of the circulation of information already produced by the official government There are justifications for the suppression of communication such as fear that it will harm individuals in the society […]
- Boredom and Freedom: Different Views and Links Boredom is a condition characterized by low levels of arousal as well as wandering attention and is normally a result of the regular performance of monotonous routines.
- The Idea of American Freedom Such implications were made by the anti-slavery group on each occasion that the issue of slavery was drawn in the Congress, and reverberated wherever the institution of slavery was subjected to attack within the South.
- Liberal Definition of Freedom Its origins lie in the rejection of the authoritarian structures of the feudalistic order in Europe and the coercive tendencies and effects of that order through the imposition of moral absolutes.
- Power and Freedom in America Although it is already a given that freedom just like the concept love is not easy to define and the quest to define it can be exhaustive but at the end of the day what […]
- Newt Gingrich Against Freedom of Speech According to the constitution, the First Amendment is part of the United States Bill of rights that was put in place due to the advocation of the anti-federalists who wanted the powers of the federal […]
- Freedom is One of the Most Valuable Things to Man Political philosophers have many theories in response to this and it is necessary to analyze some of the main arguments and concepts to get a clearer idea of how to be more precise about the […]
- The Enlightment: The Science of Freedom In America, enlightment resulted to the formation of the American Revolution in the form of resistance of Britain imperialism. In the United States of America, enlightment took a more significant form as demonstrated by the […]
- Determinism and Freedom in the movie ‘Donnie Darko’ The term determinism states, the all the processes in the world are determined beforehand, and only chosen may see or determine the future.
- Spinoza’ Thoughts on Human Freedom The human being was once considered of as the Great Amphibian, or the one who can exclusively live in the two worlds, a creature of the physical world and also an inhabitant of the spiritual, […]
- Political Freedom According to Machiavelli and Locke In this chapter, he explains that “It may be answered that one should wish to be both, but, because it is difficult to unite them in one person, is much safer to be feared than […]
- Freedom From Domination: German Scientists’ View He made the greatest ever attempt to unify the country, as Western Europe was divided into lots of feudal courts, and the unification of Germany led to the creation of single national mentality and appearing […]
- The Freedom of Speech: Communication Law in US By focusing on the on goings in Guatemala, the NYT may have, no doubt earned the ire of the Bush administration, but it is also necessary that the American people are made aware of the […]
- Freedom of Speech and Expression in Music Musicians are responsible and accountable for fans and their actions because in the modern world music and lyrics become a tool of propaganda that has a great impact on the circulation of ideas and social […]
- American Vision and Values of Political Freedom The significance of the individual and the sanctity of life were all central to the conceptions of Plato, Aristotle, or Cicero.
- Democracy and Freedom in Pakistan Pakistan lies in a region that has been a subject of worldwide attention and political tensions since 9/11. US influence in politics, foreign and internal policies of Pakistan has always been prominent.
- Spanish-American War: The Price of Freedom He was also the only person in the history of the United States to have attained the rank of Admiral of the Navy, the most senior rank in the United States Navy.
- Male Dominance as Impeding Female Sexual Freedom Therefore, there is a need to further influence society to respect and protect female sexuality through the production of educative materials on women’s free will.
- Interrelation and Interdependence of Freedom, Responsibility, and Accountability Too much responsibility and too little freedom make a person unhappy. There must be a balance between freedom and responsibility for human happiness.
- African American History: The Struggle for Freedom The history of the Jacksons Rainbow coalition shows the rise of the support of the African American politicians in the Democratic party.
- Franklin D. Roosevelt’s Definition of Freedom The case of Nicola Sacco can be seen as the starting point of the introduction of Roosevelt’s definition of freedom as liberty for all American citizens.
- Freedom of Speech and International Relations The freedom of speech or the freedom of expression is a civil right legally protected by many constitutions, including that of the United States, in the First Amendment.
- Canada in Freedom House Organization’s Rating The Freedom in the World Reports are most notable because of their contribution to the knowledge about the state of civil and political liberties in different countries, ranking them from 1 to 7.
- Philosophy of Freedom in “Ethics” by Spinoza Thus, the mind that is capable of understanding love to God is free because it has the power to control lust.
- Slavery Abolition and Newfound Freedom in the US One of the biggest achievements of Reconstruction was the acquisition of the right to vote by Black People. Still, Black Americans were no longer forced to tolerate inhumane living conditions, the lack of self-autonomy, and […]
- Japanese-American Internment: Illusion of Freedom The purpose of this paper is to analyze the internment of Japanese-Americans in Idaho as well as events that happened prior in order to understand how such a violation of civil rights came to pass […]
- The Existence of Freedom This paper assumes that it is the cognizance of the presence of choices for our actions that validates the existence of free will since, even if some extenuating circumstances and influences can impact what choice […]
- Philosophy, Ethics, Religion, Freedom in Current Events The court solely deals with acts of gross human rights abuses and the signatory countries have a statute that allows the accused leaders to be arrested in the member countries.
- Mill’s Power over Body vs. Foucault’s Freedom John Stuart Mill’s view of sovereignty over the mind and the body focuses on the tendency of human beings to exercise liberalism to fulfill their self-interest.
- Rousseau’s vs. Confucius’ Freedom Concept Similarly, the sovereignty of a distinctive group expresses the wholeness of its free will, but not a part of the group.
- The Importance of Freedom of Speech In a bid to nurture the freedom of speech, the United States provides safety to the ethical considerations of free conversations.
- Slavery and Freedom: The American Paradox Jefferson believed that the landless laborers posed a threat to the nation because they were not independent. He believed that if Englishmen ruled over the world, they would be able to extend the effects of […]
- Freedom in the Workplace of American Society In the workplace, it is vital to implement freedom-oriented policies that would address the needs of each employee for the successful performance of the company which significantly depends on the operation of every participant of […]
- 19th-Century Marxism with Emphasis on Freedom As the paper reveals through various concepts and theories by Marx, it was the responsibility of the socialists and scientists to transform the society through promoting ideologies of class-consciousness and social action as a way […]
- Political Necessity to Safeguard Freedom He determined that the existence of the declared principles on which the fundamental structure of equality is based, as well as the institutions that monitor their observance, is the critical prerequisite for social justice and […]
- Aveo’s Acquisition of Freedom Aged Care Portfolio The mode of acquisition points to the possibility that Freedom used the White Knight defense mechanism when it approached the Aveo group.
- Aveo Group’s Acquisition of Freedom Aged Care Pty Ltd The annual report of AVEO Group indicated that the company acquired Freedom Aged Care based on its net book value. It implies that the Aveo Group is likely to achieve its strategic objectives through the […]
- Freedom Hospital Geriatric Patient Analysis The importance of statistics in clinical research can be explained by a multitude of factors; in clinical management, it is used for monitoring the patients’ conditions, the quality of health care provided, and other indicators.
- Hegel and Marx on Civil Society and Human Freedom First of all, the paper will divide the concepts of freedom and civil society in some of the notions that contribute to their definitions.
- History of American Conceptions and Practices of Freedom The government institutions and political regimes have been accused of allowing amarginalisation’ to excel in the acquisition and roles assigned to the citizens of the US on the basis of social identities.
- Freedom and Liberty in American Historical Documents The 1920s and the 1930s saw particularly ardent debates on these issues since it was the time of the First World War and the development of the American sense of identity at the same time.
- Anglo-American Relations, Freedom and Nationalism Thus, in his reflection on the nature of the interrelations between two powerful empires, which arose at the end of the 19th century, the writer argues that the striving of the British Empire and the […]
- American Student Rights and Freedom of Speech As the speech was rather vulgar for the educational setting, the court decided that the rights of adults in public places cannot be identic to those the students have in school.
- Freedom of Speech in Modern Media At the same time, the bigoted approach to the principles of freedom of speech in the context of the real world, such as killing or silencing journalists, makes the process of promoting the same values […]
- Singapore’s Economic Freedom and People’s Welfare Business freedom is the ability to start, operating and closing a business having in mind the necessary regulations put by the government.
- “Advancing Freedom in Iraq” by Steven Groves The aim of the article is to describe the current situation in Iraq and to persuade the reader in the positive role of the U.S.authorities in the promoting of the democracy in the country.
- Freedom: Definition, Meaning and Threats The existence of freedom in the world has been one of the most controversial topics in the world. As a result, he suggests indirectly that freedom is found in the ability to think rationally.
- Expression on the Internet: Vidding, Copyright and Freedom It can be defined as the practice of creating new videos by combining the elements of already-existing clips. This is one of the reasons why this practice may fall under the category of fair use.
- Doha Debate and Turkey’s Media Freedom He argued that the Turkish model was a work in progress that could be emulated by the Arab countries not only because of the freedom that the government gave to the press, but also the […]
- The Pursuit of Freedom in the 19th Century Britain The ambition to improve one’s life was easily inflated by the upper grade that focused on dominating the system at the expense of the suffering majority.
- The Story of American Freedom The unique nature of the United States traces its history to the formation of political institutions between 1776 and 1789, the American Revolution between 1776 and 1783 and the declaration of independence in 1776. Additionally, […]
- Military Logistics in Operation “Iraqi Freedom” It was also very easy for the planners to identify the right amount of fuel needed for distribution in the farms, unlike other classes of supply which had a lot of challenges. The soldiers lacked […]
- The Freedom of Information Act The Freedom of Information Act is popularly understood to be the representation of “the people’s right to know” the various activities of the government.
- The United States Role in the World Freedom The efforts of NATO to engage Taliban and al-Qaida insurgents in the war resulted in the spreading of the war into the North West parts of Pakistan.
- Fighting Terrorism: “Iraqi Freedom” and “Enduring Freedom”
- Freedom of Speech: Julian Assange and ‘WikiLeaks’ Case
- Do Urban Environments Promote Freedom?
- Claiming the Freedom to Shape Politics
- US Progress in Freedom, Equality and Power Since Civil War
- Thomas Jefferson’s Views on Freedom of Religion
- Religious Freedom and Labor Law
- Gilded Age and Progressive Era Freedom Challenges
- Philosophical Approach to Freedom and Determinism
- The Life of a Freedom Fighter in Post WWII Palestine
- Fighting for Freedom of American Identity in Literature
- “Human Freedom and the Self” by Roderick Chisholm
- Philosophy of Freedom in “The Apology“
- Philosophy in the Freedom of Will by Harry Frankfurt
- Advertising and Freedom of Speech
- How the Law Limits Academic Freedom?
- The Issue of American Freedom in Toni Morrison’s “Beloved”
- The Jewish Freedom Fighter Recollection
- Kuwait’s Opposition and the Freedom of Expression
- Abraham Lincoln: A Legacy of Freedom
- Freedom of Speech and Expression
- Multicultural Education: Freedom or Oppression
- “The Freedom of the Streets: Work, Citizenship, and Sexuality in a Gilded Age City” by Sharon Wood
- Information Freedom in Government
- Dr.Knightly’s Problems in Academic Freedom
- Mill on Liberty and Freedom
- Texas Women University Academic Freedom
- Freedom of speech in the Balkans
- Media Freedom in Japan
- Rivalry and Central Planning by Don Lavoie: Study Analysis
- Review of “Freedom Writers”
- Freedom Degree in Colonial America
- What Is ‘Liberal Representative Democracy’ and Does the Model Provide an Appropriate Combination of Freedom and Equality?
- Is the Contemporary City a Space of Control or Freedom?
- Native Americans Transition From Freedom to Isolation
- “The Weight of the Word” by Chris Berg
- What Does Freedom Entail in the US?
- Leila Khaled: Freedom Fighter or Terrorist?
- Environmentalism and Economic Freedom
✍️ Freedom Essay Topics for College
- Freedom of Speech in China and Political Reform
- Colonial Women’s Freedom in Society
- The S.E.C. and the Freedom of Information Act
- African Americans: A Journey Towards Freedom
- Freedom of the Press
- Coming of Age in Mississippi: The Black Freedom Movement
- Freedom of Women to Choose Abortion
- Human Freedom as Contextual Deliberation
- Women and Freedom in “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
- The Required Freedom and Democracy in Afghanistan
- PRISM Program: Freedom v. Order
- Human rights and freedoms
- Controversies Over Freedom of Speech and Internet Postings
- Gender and the Black Freedom Movement
- Culture and the Black Freedom Struggle
- Freedom from Poverty as a Human Right and the UN Declaration of Human Rights
- Hegel’s Ideas on Action, Morality, Ethics and Freedom
- Satre human freedom
- The Ideas of Freedom and Slavery in Relation to the American Revolution
- Psychological Freedom
- The Freedom Concept
- Free Exercise Clause: Freedom and Equality
- Television Effects & Freedoms
- Government’s control versus Freedom of Speech and Thoughts
- Freedom of Speech: Exploring Proper Limits
- Freedom of the Will
- Benefits of Post 9/11 Security Measures Fails to Outway Harm on Personal Freedom and Privacy
- Civil Liberties: Freedom of the Media
- Human Freedom and Personal Identity
- Freedom of Religion in the U.S
- Freedom of Speech, Religion and Religious Tolerance
- Why Free Speech Is An Important Freedom
- The meaning of the word “freedom” in the context of the 1850s!
- American History: Freedom and Progress
- The Free Exercise Thereof: Freedom of Religion in the First Amendment
- Twilight: Freedom of Choices by the Main Character
- Frank Kermode: Timelessness and Freedom of Expression
- Human Nature and the Freedom of Speech in Different Countries
- What Is the Relationship Between Personal Freedom and Democracy?
- How Does Religion Limit Human Freedom?
- What Is the Relationship Between Economic Freedom and Fluctuations in Welfare?
- How Effectively the Constitution Protects Freedom?
- Why Should Myanmar Have Similar Freedom of Speech Protections to the United States?
- Should Economics Educators Care About Students’ Academic Freedom?
- Why Freedom and Equality Is an Artificial Creation Created?
- How the Attitudes and Freedom of Expression Changed for African Americans Over the Years?
- What Are the Limits of Freedom of Speech?
- How Far Should the Right to Freedom of Speech Extend?
- Is There a Possible Relationship Between Human Rights and Freedom of Expression and Opinion?
- How Technology Expanded Freedom in the Society?
- Why Did Jefferson Argue That Religious Freedom Is Needed?
- How the Civil War Sculpted How Americans Viewed Their Nation and Freedom?
- Should Society Limit the Freedom of Individuals?
- Why Should Parents Give Their Children Freedom?
- Was Operation Iraqi Freedom a Legitimate and Just War?
- Could Increasing Political Freedom Be the Key To Reducing Threats?
- How Does Financial Freedom Help in Life?
- What Are Human Rights and Freedoms in Modern Society?
- How the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedom Affects the Canadian Politics?
- Why Should Schools Allow Religious Freedom?
- Does Internet Censorship Threaten Free Speech?
- How Did the American Civil War Lead To the Defeat of Slavery and Attainment of Freedom by African Americans?
- Why Are Men Willing To Give Up Their Freedom?
- How Did the Economic Development of the Gilded Age Affect American Freedom?
- Should Artists Have Total Freedom of Expression?
- How Does Democracy, Economic Freedom, and Taxation Affect the Residents of the European Union?
- What Restrictions Should There Be, if Any, on the Freedom of the Press?
- How To Achieving Early Retirement With Financial Freedom?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 24). 267 Freedom Essay Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/freedom-essay-examples/
"267 Freedom Essay Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 24 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/freedom-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '267 Freedom Essay Topics & Examples'. 24 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "267 Freedom Essay Topics & Examples." February 24, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/freedom-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "267 Freedom Essay Topics & Examples." February 24, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/freedom-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "267 Freedom Essay Topics & Examples." February 24, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/freedom-essay-examples/.
- Freedom Of Expression Questions
- Equality Topics
- Free Will Paper Topics
- Constitution Research Ideas
- Civil Rights Movement Questions
- Respect Essay Topics
- Bill of Rights Research Ideas
- Liberalism Research Topics
- Civil Disobedience Essay Topics
- Tolerance Essay Ideas
- First Amendment Research Topics
- Social Democracy Essay Titles
- Personal Ethics Titles
- Justice Questions
- American Dream Research Topics

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
129 Freedom Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Freedom is a fundamental human right that allows individuals to act and make choices without constraints. It is a concept that has been debated and explored for centuries, with countless thinkers, philosophers, and activists offering their perspectives on what it means to truly be free. When it comes to discussing freedom, there are endless possibilities for essay topics. Here are 129 freedom essay topic ideas and examples to inspire your writing:
- The concept of freedom in a democratic society
- Freedom of speech and its limitations
- The role of freedom in shaping individual identity
- Freedom of the press and its importance in a democratic society
- The relationship between freedom and responsibility
- The impact of technology on freedom and privacy
- Freedom and equality: are they mutually exclusive?
- The importance of freedom in promoting creativity and innovation
- Freedom of religion and its implications for society
- The history of freedom movements around the world
- The role of education in promoting freedom and critical thinking
- Freedom and social justice: how are they connected?
- The impact of social media on freedom of expression
- Freedom and human rights: are they universal?
- The relationship between freedom and happiness
- The concept of economic freedom and its implications for society
- Freedom and the rule of law: how are they related?
- The impact of censorship on freedom of speech
- Freedom and democracy: are they inseparable?
- The role of the government in protecting individual freedoms
- The impact of colonialism on freedom movements in the Global South
- The importance of cultural freedom and diversity
- Freedom and globalization: how are they connected?
- The role of civil disobedience in promoting freedom and social change
- The impact of war and conflict on freedom
- Freedom and the environment: are they compatible?
- The role of art and literature in promoting freedom of expression
- Freedom and gender equality: are they interconnected?
- The relationship between freedom and security
- The impact of surveillance on individual freedoms
- Freedom and the right to protest
- The role of activism in promoting freedom and social change
- Freedom and the right to privacy
- The impact of capitalism on individual freedoms
- Freedom and the right to assembly
- The role of the United Nations in promoting freedom and human rights
- The impact of colonialism on freedom movements in Africa
- Freedom and the right to a fair trial
- The relationship between freedom and social mobility
- The role of technology in promoting freedom and democracy
- The impact of social media on freedom of information
- Freedom and the right to access information
- The role of education in promoting freedom and democracy
- Freedom and the right to healthcare
- The impact of poverty on individual freedoms
- Freedom and the right to clean water and sanitation
- The relationship between freedom and economic development
- The role of the media in promoting freedom and democracy
- Freedom and the right to education
- The impact of discrimination on individual freedoms
- Freedom and the right to employment
- The relationship between freedom and social welfare
- The role of civil society in promoting freedom and human rights
- Freedom and the right to housing
- The impact of climate change on individual freedoms
- Freedom and the right to food security
- The relationship between freedom and access to justice
- The role of international organizations in promoting freedom and human rights
- Freedom and the right to a clean environment
- The impact of globalization on individual freedoms
- Freedom and the right to political participation
- The relationship between freedom and social cohesion
- The role of NGOs in promoting freedom and human rights
- Freedom and the right to social security
- The impact of corruption on individual freedoms
- Freedom and the right to participate in cultural life
- The relationship between freedom and social inclusion
- The role of the private sector in promoting freedom and human rights
- Freedom and the right to participate in decision-making
- The impact of armed conflict on individual freedoms
- Freedom and the right to non-discrimination
- The relationship between freedom and social protection
- The role of the judiciary in promoting freedom and human rights
- Freedom and the right to access justice
- The impact of natural disasters on individual freedoms
- Freedom and the right to participate in public affairs
- The role of the state in promoting freedom and human rights
- Freedom and the right to access public services
- The impact of migration on individual freedoms
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
Advertisement
Justifying Limitations on the Freedom of Expression
- Open access
- Published: 01 November 2020
- Volume 22 , pages 91–108, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Gehan Gunatilleke ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8670-8602 1 , 2
159k Accesses
11 Citations
29 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The freedom of expression is vital to our ability to convey opinions, convictions, and beliefs, and to meaningfully participate in democracy. The state may, however, ‘limit’ the freedom of expression on certain grounds, such as national security, public order, public health, and public morals. Examples from around the world show that the freedom of individuals to express their opinions, convictions, and beliefs is often imperilled when states are not required to meet a substantial justificatory burden when limiting such freedom. This article critiques one of the common justificatory approaches employed in a number of jurisdictions to frame the state’s burden to justify limitations on the freedom of expression—the proportionality test. It presents a case for an alternative approach that builds on the merits and addresses some of the weaknesses of a typical proportionality test. This alternative may be called a ‘duty-based’ justificatory approach because it requires the state to demonstrate—through the presentation of publicly justifiable reasons—that the individual concerned owes others a duty of justice to refrain from the expressive conduct in question. The article explains how this approach is more normatively compelling than a typical proportionality test. It also illustrates how such an approach can better constrain the state’s ability to advance majoritarian interests or offload its positive obligations by limiting the freedom of expression of minorities and dissenting voices.
Similar content being viewed by others

The Bill of Rights and Freedom of Belief and Expression: They Provide for Liberty, Not License

Toleration and the Law

Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The freedom of expression is vital to our ability to convey opinions, convictions, and beliefs, and to meaningfully participate in democracy. The state may, however, ‘limit’ the freedom of expression for certain reasons. International and domestic law empowers the state to impose limitations on the freedom of expression in order to advance broad aims such as national security, public order, public health, and public morals. Yet cases from around the world demonstrate that the freedom of expression is vulnerable to unwarranted restrictions.
One of the most common tests used to determine whether a limitation on the freedom of expression is justified has come to be known as the ‘proportionality test’. In this article, I critique the typical proportionality test that is applied in many jurisdictions. I then offer a justificatory approach that reframes this typical test to address some of its normative and practical weaknesses. This alternative approach places individual ‘duties of justice’ at the heart of the state’s burden to justify a limitation on the freedom of expression.
The first section of this article discusses the unique place that the freedom of expression occupies in the liberal tradition, and explains why a robust justificatory approach is needed to protect the freedom of expression from unwarranted limitations. The second section explores some of the main weaknesses of a typical proportionality test when applied in relation to limitations on the freedom of expression. I take examples from a number of countries to illustrate the recurring tendency for the freedom of expression to be subjected to unwarranted restrictions. In the final section, I make a case for a ‘duty-based’ justificatory approach. The approach would require the state to demonstrate—by presenting publicly justifiable reasons—that the individual concerned owes others a duty of justice to refrain from the expressive conduct in question. I explain how this approach addresses some of the normative weaknesses of a typical proportionality test. I will also illustrate how such an approach can better deal with the state’s ability to advance majoritarian interests or offload its positive obligations by limiting the freedom of expression of minorities and dissenting voices.
The Value of the Freedom of Expression
The freedom of expression broadly involves the communication of ideas, opinions, convictions, beliefs, and information. International legal instruments such as the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) recognise the ‘freedom of expression’ as a right that can be exercised ‘either orally, in writing or in print, in the form of art, or through any other media of [the individual’s] choice’ (art 19, para 2).
Taking the freedom of expression seriously involves acknowledging it both as a ‘liberty’ and a ‘claim right’. A ‘liberty’, conceptually speaking, refers to the absence of any competing duty to do or refrain from doing something (Hohfeld 1919 , pp. 36–39). Footnote 1 The freedom of expression is a liberty, as it involves absence of constraints on what an individual is free to express. For example, a person may have the liberty to advocate for a country’s ratification of the ICCPR, as there may be no competing duty owed to others to refrain from such advocacy. A ‘claim right’ meanwhile corresponds to another’s duty to do or refrain from doing something (Hohfeld 1919 , p. 39; see also George 1995 , pp. 119–122). The normative significance of a ‘right’ is that it is in some way claimable (O’Neill 1996 , p. 131; Hart 1955 ), i.e. that the rights-holder has an entitlement to claim, from duty-bearers, the performance of duties (Feinberg 1970 , p. 243). The freedom of expression entails ‘claim rights’, including the claim right to non-interference with the expression in question. Since claim rights correspond to duties, the freedom of expression imposes duties on others to refrain from interfering with the expression in question. For example, an individual’s claim right to advocate for the election of a particular candidate contemplates the imposition of duties on others, including the state, to refrain from interfering with such advocacy.
The reason we recognise certain claimable rights is often linked to the underlying interests these rights set out to protect. Joseph Raz observes a person has a ‘right’ when his interests are sufficient reason for holding others to be under a duty (Raz 1986 , p. 166). The importance of the interests that underlie the freedom of expression point to why we ought to, and indeed do, recognise it as a claimable right. Recalling such value is important, as the process through which we justify limitations on the freedom of expression is contingent on the value we attach to it.
On the one hand, the freedom of expression is of inherent value to the individual, as it involves the external communication of an individual’s ‘ forum internum ’ or inner realm of thoughts, beliefs, and convictions—a realm that is arguably inviolable (Boyle and Shah 2014 , p. 226). The freedom of expression is then connected to certain foundational values associated with the forum internum , such as personal autonomy and human dignity. On the other hand, the freedom of expression has consequentialist and epistemic value. It is certainly valuable to democracy, as political participation, criticism of government, media freedom, and indeed the very act of voting are aspects of the freedom of expression. John Stuart Mill’s defence of the freedom of expression points to its epistemic value. Mill argues that human fallibility justifies greater tolerance of the freedom of expression, as there can be no certainty with respect to what is true and what is false (Mill 1859 , pp. 19–21). He contends that there is no inherent justification for suppressing the beliefs and opinions of others through coercive means, even if one believes that those beliefs and opinions are untrue, as they may in fact be true, and the alternative beliefs and opinions untrue. Mill also claims that truth can only be ascertained in a ‘clearer’ and ‘livelier’ form when it is permitted to collide with error (p. 19), and adds that ‘conflicting doctrines’ often ‘share the truth between them’ (p. 44).
The inherent, consequentialist, and epistemic value of the freedom of expression suggests that it should not be limited without meeting a substantial burden of justification. When the conduct in question relates to the freedom of expression, this justificatory burden falls on those who wish to restrict the conduct. Such a scheme is consistently featured in the liberal tradition, and is consistent with the ‘fundamental liberal principle’ (Gaus 1996a , pp. 162–166)—that freedom is the norm and the limitation is the exception; so ‘the onus of justification is on those who would use coercion to limit freedom’ (Gaus 1996b ; Feinberg 1987 , p. 9). Therefore, in the case of the freedom of expression, the starting point in the process of reasoning is clear: an individual is ordinarily entitled to engage in the conduct associated with the freedom of expression, unless a restriction on the conduct is carefully and convincingly justified.
The Proportionality Test
Justification involves providing good reasons for an action, omission, or belief. According to Raz, a reason is ‘a consideration in favour of doing, believing, or feeling something’ (Raz 1999 , pp. 16–17; see also Scanlon 1998 , p. 17). Given the special value we attach to the freedom of expression, a reason must be of a particular kind when deployed to limit the freedom of expression. I accordingly approximate good reasons—in the specific context of justifying limitations on the freedom of expression—to what John Rawls called ‘public reason’ (Rawls 2005 , pp. 212–254). Rawls explains that ‘public reason’ entails the justification of political decisions through the use of values and standards that are publicly available and acceptable (pp. 227–228). Reasons can be characterised as ‘public’ when citizens who are equal accept them as valid (p. 213). Crucially, a reason does not fall within the rubric of public reason merely because the majority in society view it as a good reason. Even if, for instance, the overwhelming majority view some minority group as ‘culturally inferior’, public reason would exclude such inferiority as a justification for discriminating that group. It would be excluded because such perceived inferiority is not a reason that is publicly available and acceptable to all citizens on the basis of equal citizenship. Therefore, ideals of equality are imbedded into the concept of public reason; Equality is a constituent element that necessarily excludes purely majoritarian reasoning.
In this section, I examine one of the ‘prominent’ approaches (Möller 2014 , p. 32) to justifying limitations on the freedom of expression: the proportionality test. I aim to explain the typical features of this test, and point to some of its main weaknesses, particularly when applied to limitations on the freedom of expression.
A typical proportionality test assesses whether a limitation on a right can be ‘justified by reference to gains on some other interest or value’ (Urbina 2014 , p. 173). Most jurisdictions in Europe, and treaty bodies such as the United Nations Human Rights Committee, apply the proportionality test when evaluating the permissibility of limitations. The test usually contains four limbs (Tridimas 2007 , p. 139). First, the state must pursue an aim that serves a ‘compelling’ (Kumm 2004 , p. 593) or ‘legitimate’ interest (Tremblay 2014 , p. 865; Barak 2012 ) when limiting the right. This limb contains a normative requirement, as certain interests that are ‘illegitimate’ would not be permissible at the outset. For example, the aim to destroy a population would not qualify as ‘legitimate’. Second, there must be a rational nexus between the specific measure used to limit the right and the legitimate interest. This limb is sometime referred to as the ‘suitability test’ (Arai-Takahashi 2005 , p. 32; Van Dijk and Van Hoof 1998 : pp. 771–773). Third, this measure must be necessary to advancing, or preventing setbacks to, that legitimate interest. This limb is naturally termed the necessity test. Finally, the measure must be, in the ‘strict sense’, proportionate, i.e. it must involve a net gain, when the reduction in the enjoyment of the right is weighed against the level to which the interest is advanced (Rivers 2006 , p. 181). According to Aharon Barak, proportionality stricto sensu ‘requires a balancing of the benefits gained by the public and the harm caused to the…right through the use of the means selected by law to obtain the proper purpose’ (Barak 2012 , p. 340). Grégoire Webber meanwhile notes that such ‘balancing’ is designed to demonstrate a ‘proportionality’ between the negative effect (on the freedom of expression, for instance) on the one hand, and the beneficial effect of the limitation (in terms of the legitimate interest) on the other hand (Webber 2009 , pp. 71–72).
Different versions of the proportionality test have been applied in different jurisdictions. The German Federal Constitutional Court, for instance, applies a four-part test that considers the question of ‘balancing’ only in the final stage of the test. This version of the test has come to reflect a general rule of law within European Community law (Arai-Takahashi 2005 , p. 29). By contrast, the Canadian Supreme Court considers ‘balancing’ at earlier stages as well, i.e. under the legitimacy and necessity subtests (Grimm 2007 ). The Court has found that, under the legitimacy subtest, the legitimate interest must be of sufficient importance to warrant overriding the right in question (R v. Oakes 1986 ; Choudhry 2006 ). Moreover, under the necessity subtest, the selected measure must, when compared to the available alternatives, impair the right the least . Accordingly, the Canadian version of the test expects some balancing to be undertaken when determining which aims are legitimate for the purpose of justifying a limitation, and when determining whether the measure in question is the least restrictive among available options. Meanwhile, in the United States (U.S.), ‘content-based’ limitations on the freedom of expression attract ‘strict scrutiny’, i.e. the highest level of judicial scrutiny of the restrictive measure. This approach is essentially founded on an American common law idea that the right to the freedom of expression—protected under the First Amendment to the United States Constitution—is a highly valued individual right (Strauss 2002 ). In the U.S., the state must accordingly meet the heaviest justificatory burden when restricting certain types of speech, such as political speech. By contrast, ‘content-neutral’ limitations on the freedom of expression (for example, restrictions on the form, extent, timing, or medium of the expression in question) are reviewed under a ‘intermediate scrutiny’ test. The U.S. Supreme Court formulated a four-part test to determine whether a content-neutral limitation is constitutional (United States v. O’Brien 1968 ; see also Zoller 2009 , p. 906; Stone 1987 ): (1) the limitation must be within the constitutional power of government; (2) the limitation must further an important or substantial governmental interest; (3) the governmental interest must be unrelated to the suppression of the freedom of expression; and (4) the limitation must be narrowly tailored—no greater than necessary. In subsequent cases, the Supreme Court devised a fifth limb: the limitation must leave open ample opportunity for communication (Ladue v. Gilleo 1994 ). Although the justificatory approach prevalent in the U.S. is rarely termed a ‘proportionality test’, it clearly contains elements of balancing. Whichever version of the test is employed, it is apparent that the proportionality test generally involves a justificatory burden of a particular form: the limitation on the freedom of expression is justified only if the countervailing interests outweigh the individual’s interests in the freedom of expression. It is for this reason that the very notion of proportionality is described as ‘inevitably flexible and open-textured in nature’ (Arai-Takahashi 2005 , p. 34).
A typical proportionality test has a number of weaknesses worth noting. There is an ongoing scholarly debate on the suitability of the test, and in the course of discussing some of the weaknesses I detect in the typical version of the test, I shall touch on some of the elements of this debate. Of course, proponents of proportionality often argue that the weaknesses pointed out by critics are with respect to cases in which the test is misapplied, and that the proportionality test is sound if it is applied correctly (e.g. Möller 2014 ; Kumm 2010 ). However, the strength of the test lies in how it is applied in practice. In this context, I set out to evaluate the ‘typical’ proportionality test, which contains both normative and political weaknesses when applied to assess limitations on the freedom of expression. In doing so, I leave open the potential for the test to be applied in a more robust manner. In fact, my proposal conceives of a more robust version of the test.
At a normative level, the typical test often fails to adequately recognise and account for the special value of the freedom of expression. Such a weakness is particularly evident where the court or tribunal concerned glosses over the first three limbs of the test and focuses instead on the final stage of balancing. Kai Möller, referring to German practice in particular, observes that typically, ‘the balancing stage dominates the legal analysis and is usually determinative of the outcome’ of the assessment of whether a limitation is permissible or not (Möller 2014 , p. 34). When the emphasis of the assessment is on balancing alone, the court or tribunal would often rely on practical reasoning to determine the permissibility of a limitation (Kumm 2010 , p. 147). It is for this reason that many rights scholars have criticised the proportionality test for its failure to give adequate normative weight to individual rights (Letsas 2007 ; Tsakyrakis 2009 ). According to these critics, proportionality treats rights on par with any other interest or value, and such an equation undermines the special importance we attach to rights. Many of these critics rely on well-known ‘rights-based’ approaches to justifying limitations on rights, such as the approaches advocated by Ronald Dworkin and John Rawls. According to Dworkin, individual rights, such as the right to the freedom of expression, ‘trump’ other non-rights interests (Dworkin 1977 , p. xi). He argues that non-rights interests, such as collective interests, should be ruled out when justifying limitations on individual rights (Dworkin 1984 , p. 153; see also Waldron 1993 , p. 210). This approach is based on the view that rights have peremptory value; they exist, and ought to be protected, even if the community is genuinely worse off due to their existence or protection (Dworkin 1985 , p. 350). Understood this way, the right to the freedom of expression constrains the state’s pursuit of collective interests, and sets out a protected realm that the state cannot interfere with even when collective interests could be served through such interference. Rawls meanwhile argues that basic liberties, such as the freedom of expression, can only be limited for its own sake or for the sake of other basic liberties (Rawls 1999 , p. 220). These basic liberties have ‘lexical priority’ Footnote 2 over all other types of interests. Accordingly, basic liberties such as the freedom of expression would have ‘absolute weight’ with respect to interests unrelated to basic liberties (Rawls 2005 , p. 294). For example, the freedom of expression cannot be denied to an individual on grounds such as ‘economic efficiency and growth’ (pp. 294–295). Therefore, all reasons that are not related to basic liberties of similar importance to the freedom of expression will be excluded (at the outset) from the justificatory process. In sharp contrast to these rights-based approaches, the proportionality test expects a court or tribunal to weigh rights such as the right to the freedom of expression with collective interests such as national security, or public order, health, or morals. Such weighing—it could be argued—places the freedom of expression on the same normative plane as these collective interests, thereby undermining its peremptory value.
This normative challenge is strongly linked to the textual framework of many international and domestic instruments that set out the basis for limiting the freedom of expression. For example, article 19, paragraph 2 of the ICCPR, and article 10, paragraph 2 of the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR), explicitly permit states to limit the freedom of expression on the grounds of collective interests, such as public order and public health. Similarly, the constitutions of numerous countries permit limitations on the freedom of expression on the basis of a host of collective interests. The challenge may then also be doctrinal, as the typical proportionality test often suffers from normative weaknesses essentially because the legal doctrine that sets out the test reflects these weaknesses. Accordingly, the ICCPR and the ECHR can encounter normative problems in practice, as the limitation regimes found in these instruments contemplate broad governmental discretion when imposing limitations on the freedom of expression. Such discretion has raised serious concerns among scholars with respect to how well proportionality meets normative priorities such as the rule of law, or legal predictability (Von Bernstorff 2014 , p. 66; Urbina 2014 , p. 180).
At a political level, a typical proportionality test is vulnerable to two risks associated with granting the state wide discretion to limit the freedom of expression. First, the state can use a limitation regime to advance majoritarian interests. The freedom of expression of minorities and political dissenters may be targeted for reasons that are not publicly justifiable. In this context, majoritarian interests can infiltrate limitation grounds such as national security, public order, public health, and public morals. Second, the state can, in the course of limiting an individual’s freedom of expression, attempt to offload its own positive obligations owed to society. An individual’s expressive conduct can appear to ‘cause’ others to react in ways that harm third parties. Such cases often arise when the expressive conduct has a religious dimension. Although the expressive conduct may also be classified as religious manifestation or practice, it is difficult to exclude such conduct from the broader domain of the freedom of expression. In such cases, the state may choose to restrict the specific expressive conduct rather than focus on the wrongdoers who engage in violence. It is the state that owes citizens a positive obligation to maintain law and order, and it is up to the state to prevent violence, and punish those who engage in it for whatever cause. However, when the violence is committed by members of the majority community, the state may look to target the individual whose conduct appeared to ‘cause’ the wrongdoing, rather than risk confronting the majority community. In such circumstances, it may attempt to justify a restriction on the expressive conduct of the individual concerned, ostensibly to maintain public order and protect citizens from the violent reactions of others. It may do so regardless of how unreasonable such reactions are.
The typical proportionality test has no convincing answer to the political risks associated with state authority to limit the freedom of expression. It relies heavily on the good faith of the state, and the ability of a court or tribunal to convincingly weigh the competing interests at stake. Yet several examples from a variety of jurisdictions demonstrate that courts and tribunals are often compelled to offer the state wide discretion. The proportionality test only requires the adjudicative body to assess which of the two interests—the individual’s interest in the freedom of expression or the legitimate interest being pursued by the state—is weightier. It would not contemplate any specific threshold that signals that the competing interest is sufficiently weighty. Scholars such as Francisco Urbina accordingly point out that the incommensurability of competing values and interests makes the proportionality test unsuited to determining the permissibility of limitations on rights (Urbina 2015 ). Given that it is so difficult to undertake the task of balancing with any precision, the adjudicative body would often defer to the state.
A number of illustrations demonstrate both the normative and political weaknesses inherent in a typical application of the proportionality test. Admittedly, some of these cases overlap with the terrain of other rights, such as the freedom of religion or belief. Yet the point about the freedom of expression is that it is a general core right that underlies many other rights. The inherent weaknesses of the typical proportionality test are best observed precisely in these complex cases where several rights are at play. Three classes of cases may be briefly cited to illustrate the weaknesses I am referring to.
First, the state may rely on majoritarian conceptions of morality to restrict certain expressions deemed contrary to those conceptions. The classic example of such restrictions on the freedom of expression is the landmark case of the European Court of Human Rights, Handyside v. The United Kingdom ( 1976 ). In this case, the Court upheld the seizure of an educational book that dealt with the subject of sex, and found no violation of the freedom of expression in terms of article 10 of the ECHR. The limitation was justified on the basis of public morals. A similar example is the restriction of the advocacy of same-sex rights in Russia. In Fedotova v. The Russian Federation ( 2012 ), the complainant displayed posters that read ‘homosexuality is normal’ and ‘I am proud of my homosexuality’. The posters were displayed near a secondary school. The complainant claimed that the purpose of the expression was to promote tolerance towards gay and lesbian individuals. She was convicted of public actions aimed at ‘propaganda of homosexuality’ among minors. The state asserted that the conviction was necessary in the interests of children ‘to protect them from the factors that could negatively impact their…moral development’ (para 5.6 of the Decision of the Human Rights Committee). The Human Rights Committee relied on the principle of non-discrimination, and found that the limitation was discriminatory on the basis of sexual orientation. It did not actually apply a typical proportionality test to deal with the limitation, and instead relied on an additional normative basis to find a violation of the freedom of expression. The case serves as a reminder that a typical proportionality test would only require the balancing of the individual’s interests in the freedom of expression with the asserted public interest in morality and moral development. Such a test would not account for the fact that the asserted interest in public morals is actually a majoritarian—for instance, heteronormative—conception of morality. The typical test would need to be bolstered to deal with the challenge. The Committee accordingly bolstered the test by relying on the principle of non-discrimination. However, if a more general prohibition on expressions about sex had been instituted, such as, for example, the censoring of a book dealing with sex education, the Committee’s reliance on the principle of non-discrimination alone would not have sufficed.
Second, the state may rely on majority values and interests to restrict certain types of expressions deemed a threat to these values and interests. The jurisprudence of the European Court of Human Rights offers a number of examples of such restrictions. In these cases, the doctrine set out in the text of article 10 of the ECHR has governed the Court’s reasoning. The Court has typically applied a four-part test: the limitation must (1) be provided by law; (2) pursue a legitimate aim listed in the article; (3) be necessary in a democratic society; and (4) be proportionate stricto sensu . Some proponents of the proportionality test adopted by the European Court of Human Rights have suggested that the phrase ‘necessary in a democratic society’ entails a commitment to pluralism, and is a check on majoritarianism (Zysset 2019 , p. 235). Indeed, the Court has viewed certain aspects of the freedom of expression, such as press freedom, and the criticism of public officials, as vital due to their relevance to the democratic process. It has accordingly placed a heavy justificatory burden on the state when expressive conduct associated with ‘democracy’ is being restricted (Thoma v. Luxembourg 2001 ). Yet, this counter-majoritarian check is not always evident in the Court’s jurisprudence, particularly when the religious sentiments of the majority community are at stake. In the case of İ.A. v. Turkey ( 2005 ), the managing director of a publishing house was convicted of blasphemy for publishing a novel that was deemed deeply offensive to Muslims. The applicant complained that the conviction violated his freedom of expression under article 10 of the ECHR. In response, the state argued that ‘the criticism of Islam in the book had fallen short of the level of responsibility to be expected of criticism in a country where the majority of the population were Muslim’ (para. 20 of the judgement). Accordingly, the Court was called upon to weigh the individual’s freedom of expression with the majority community’s interests in their own freedom of thought, conscience, and religion. The majority of the Court held that the novel contained statements that amounted to ‘an abusive attack on the Prophet of Islam’ (para. 29). It concluded that the restriction was reasonable, as it ‘intended to provide protection against offensive attacks on matters regarded as sacred by Muslims’ (para. 30). It accordingly found that there was no violation of article 10, and that the measures under consideration satisfied the proportionality test.
The European Court’s observations in İ.A. v. Turkey relied heavily on the doctrine of margin of appreciation, which is often applied to afford states some ‘latitude’ when limiting rights (Arai-Takahashi 2002 , p. 2). The doctrine was applied in the case of Handyside v. the United Kingdom ( 1976 ), and has since been relied upon to justify some level of judicial deference to states on questions of limitations. For example, in Otto-Preminger-Institut v. Austria ( 1995 ) and in Wingrove v. The United Kingdom ( 1996 ), the Court relied on the margin of appreciation doctrine to hold that the restriction of expressions that caused public offence to the majority religious group (in both cases the majority group was Christian) was permissible under the ECHR. In each case, the Court found no violation of article 10 of the ECHR, and held that the restrictions on the public screening of films deemed offensive to a religious majority were proportionate.
The margin of appreciation doctrine has also been applied in cases involving religious expression, including wearing certain religious attire. Cases such as S.A.S v. France ( 2014 ) and Leyla Şahin v. Turkey ( 2005 ) essentially concerned article 9 of the ECHR, which protects the freedom to manifest religion or belief. However, the applicants in both cases also claimed that the limitations in question violated their freedom of expression under article 10. The Court upheld restrictions on the niqāb (a full-face veil) and the Islamic headscarf on the basis that such attire is incompatible with ‘European’ values such as ‘living together’ and ‘secularism’, and found that these restrictions did not violate article 10 of the ECHR. In such cases, the Court has sought to balance the individual’s right to the freedom of expression (including the freedom to engage in certain types of religious expression) with broader societal aims such as secularism, and has held that the limitations in question were proportionate. In each case, the Court has relied on the margin of appreciation doctrine to evaluate the permissibility of the limitation on the freedom of expression. The doctrine has thus attracted intense criticism from scholars—primarily due to the fact that the Court has often lacked a coherent and consistent approach to applying the doctrine (Letsas 2006 ).
Third, the state may rely on broad conceptions of ‘public order’ to restrict expressions that may ‘cause’ others to react in a violent or disorderly manner. In the case of Zaheeruddin v. State ( 1993 ), the Pakistani Supreme Court speculated that the public expressions of the Ahmadi community claiming that they are ‘Muslim’ would provoke outrage among the Sunni majority (Khan 2015 ). It therefore justified restricting the public display of the Kalimah Footnote 3 on the basis of public order. The Human Rights Committee has also considered cases involving limitations on the freedom of expression on the basis that the expression in question could cause others to engage in disruptive conduct. In Claudia Andrea Marchant Reyes et al. v. Chile ( 2017 ), the Committee considered the removal and destruction of a work of art on the grounds of ‘public order’. The work of art contained fifteen banners commemorating the fortieth anniversary of the military coup d’état in Chile. The complainant had in fact obtained the necessary approvals to display the banners at nine bridges. The state, however, argued that the removal of the banners was necessary to prevent ‘potential disruption to public order arising out of the burning of the banners’, and that it was the state’s ‘duty’ to safeguard public order. It argued that the limitation was for the ‘benefit of persons who crossed the bridges in question on a daily basis, given that the banners could have been burned precisely at the times of the greatest movement of people and caused injury’ (para 4.3 of the Committee’s decision). In this particular case, the Committee found that the limitation was unwarranted, as the state provided ‘no evidence of what specific information it had that gave rise to fears that the work might be burned’ (para 7.5). Its decision may have been different if in fact there was such evidence. In any event, the case remains a good example of how the state may seek to offload its obligation (to maintain public order) onto the individual concerned by limiting the individual’s freedom of expression—a vulnerability to which the typical proportionality test has no coherent response.
Majoritarian conceptions of certain public interests, including public order and morals, often drive the state’s justification for a limitation on the freedom of expression. The state can also offload its positive obligations to maintain public order in the course of limiting an individual’s freedom of expression, and seek to justify restrictions on expressions that attract majority outrage. These types of justifications can infiltrate the reasoning of the court or tribunal tasked with assessing the proportionality of the limitation. In essence, the typical proportionality test, which asks the adjudicative body to do no more than weigh competing interests, does not avoid these political risks. In the final section of this article, I present an alternative justificatory approach that attempts to build on the merits, and address the weaknesses, of a typical proportionality test.
A Duty-Based Justificatory Approach
The alternative justificatory approach I have in mind is not a radical departure from the typical proportionality test. The alternative approach also contemplates ‘balancing’. Its main departure from the typical proportionality test is that it seeks to direct the state’s justificatory burden towards the demonstration of an individual ‘duty of justice’ towards others. I imagine such redirection can be done within the parameters of a test that still features proportionality as part of its final limb. The state would simply be required to demonstrate—in the course of meeting the first three limbs of the test—that the individual concerned owes a duty of justice to others. Even when such a duty is demonstrated, the question of proportionality would remain relevant, as the specific means by which the restriction is imposed may be subject to the requirement of proportionality. For example, a duty of justice may ground the state’s justification for restricting the public display of obscene material. However, the state is still bound by considerations of proportionality. While it may be proportionate to fine a person for displaying obscene material in a public place, it may be disproportionate to incarcerate that person. Bearing this scheme in mind, I shall argue that a duty-based approach addresses some of the more fundamental normative and political weaknesses associated with the typical proportionality test.
Duties of Justice
The freedom of expression is an individual liberty. According to the Hohfeldian conception of a ‘liberty’, which is both widely accepted and conceptually compelling, a liberty can only be constrained by a competing duty that correlates to another’s claim right. Not all duties correlate to rights. For instance, imperfect moral duties (Mill 1861 ) or ‘duties of charity’ (Goodin 2017 ) do not correlate to rights. For example, a duty to water a plant on behalf of a neighbour does not correlate to the neighbour’s ‘right’ that the plant is watered (Raz 1986 , p. 77). By contrast, an individual’s ‘duties of justice’ are duties that correspond to the rights of others; scholars such as Robert Goodin rightly observe that the state can ‘justifiably compel people to perform’ such duties (Goodin 2017 , pp. 268–271).
Conceptually speaking, duties of justice shape the extent and scope of individual liberty. For example, if X has the liberty to say φ, X has no duty of justice to refrain from saying φ, i.e. no other person has a claim right that X refrains from saying φ. But if X owes Y a duty to refrain from saying λ, X ’s freedom of expression does not extend to saying λ. Only the sphere that is not duty-bound corresponds to A ’s freedom of expression. If individual liberty is constrained by competing duties of justice, it follows that an individual’s ‘liberty’ to express something means they do not owe others a duty of justice to refrain from expressing that thing. If an individual owes others a duty of justice to refrain from expressing something, the individual has no liberty to express that thing. In such cases, the state may be justified in restricting the conduct. A duty of justice is, therefore, not the starting point of the reasoning process, but the endpoint. It is the destination one arrives at when one convincingly demonstrates that the competing interests against the conduct in question are important enough to constitute a claim right against the conduct, thereby imposing on the individual concerned a duty of justice to refrain from the conduct.
What would a duty-based approach to justifying limitations on the freedom of expression look like? The duty-based approach that I have in mind has two features. First, it incorporates the idea of ‘public reason’ to ensure that only publicly justifiable reasons may be put forward by the state when justifying a limitation on the freedom of expression. This element would necessarily strengthen the legitimacy limb of the proportionality test. Only aims that are publicly justifiable would be considered legitimate, and could form the basis for a limitation on the freedom of expression. Aims that societies cannot find agreement on would not be eligible. For instance, the aim of ensuring ‘the glory of Islam’—an aim found in article 19 of Pakistan’s Constitution—would not by itself suffice as a legitimate ground on which the freedom of expression can be limited. Similarly, ‘secularism’, if not an aim shared by many religious minorities in a country, would not in and of itself be valid grounds for limiting the freedom of expression.
Second, the approach I am proposing requires the state to demonstrate a direct responsibility on the part of the individual concerned. This feature of the duty-based approach is consistent with the doctrine of double effect discussed by scholars such as Seana Shiffrin. According to Shiffrin, the double-effect doctrine ‘asserts that it may, sometimes, be more permissible to bring about harm as a foreseen or foreseeable but unintended side effect of one’s otherwise permissible activity than to bring about equally weighty harmful consequences as an intended means or end of one’s activity (emphasis added)’ (Shiffrin 2003 , pp. 1136–1139). A similar principle is found in tort law, under which ‘one would not be held liable for harm…if the harm resulted from deliberate intervention of another agent’ (Marmor 2018 , p. 153). Individual liberty is ultimately shaped by the ‘horizontal’ duties the individual concerned owes others (Knox 2008 , p. 2). These are horizontal to the extent that one individual owes other individuals, or the community at large, a duty to refrain from engaging in intentional conduct that would cause them harm. Therefore, one’s duties of justice are confined to the sphere in which one has direct responsibility for the intended consequences. If, for instance, the violent reactions of others are in fact an intended consequence of the expressive conduct—such as in cases of incitement to violence—it follows that one fails to fulfil a duty of justice to refrain from harming others. Yet if the reactions of others are unintended , it is difficult to maintain that a duty of justice was unfulfilled. One cannot take responsibility for the violent acts of others.
A duty-based justificatory approach is more normatively compelling and politically appealing than a typical proportionality test. The scheme I am proposing addresses the normative weakness associated with the typical proportionality test wherein the special importance we attach to the freedom of expression is often undermined. When certain expressive conduct is presumptively associated with the freedom of expression, the conduct cannot be restricted unless the competing interests at play form a sufficient reason to impose on the individual a duty of justice to refrain from the conduct. The state would need to demonstrate that the individual concerned owes such a duty of justice. A duty of justice, once demonstrated, becomes the placeholder for the publicly justifiable reasons we might have for imposing coercive legal measures against the conduct in question.
The distinction I wish to draw between a duty-based approach and a typical proportionality test can be illustrated as follows. A typical proportionality test would require the state to establish that the interest in the freedom of expression is outweighed by the competing interests at play. A duty-based approach simply rejects the idea that a limitation on the freedom of expression can be justified by claiming that the competing interest is weightier than the individual’s interest in freedom of expression. The freedom of expression, after all, has special normative value, and should not be merely weighed against competing interests. A duty-based approach requires the state to demonstrate that the competing interests are sufficiently weighty to impose a duty on the individual to refrain from engaging in the expressive conduct in question. This justificatory burden is different to a burden to merely demonstrate that the competing interest is weightier than an interest in the freedom of expression. Instead of asking which interest is weightier, a duty-based justificatory burden requires the state to demonstrate that the competing interest is weighty enough to constitute a claim right (held by others), and a duty of justice (owed by the individual concerned). Under a duty-based approach, the weight of the interest in the freedom of expression is not actually compared with the weight of any competing interest. Instead, specific expressive conduct can be excluded (on the basis of public reason) from the scope of the freedom of expression in view of the fact that the individual concern owes others a duty to refrain from such conduct. This approach retains the normative significance of the freedom of expression instead of subjecting it to consequentialist balancing.
A political case can also be made for adopting a duty-based justificatory approach. Such an approach can place a counter-majoritarian check on state authority to impose limitations on the freedom of expression. A typical proportionality test does not have a specific answer to majoritarian infiltration of interests such as national security, public order, public health, and public morals. It does not have a coherent response to common instances in which majoritarian interests are advanced under the guise of these ‘public’ interests. It also often fails to contend with cases in which the state seeks to offload its own positive obligations by limiting an individual’s freedom of expression. Such offloading is common when members of a majority community violently react to expressions that are unpopular or considered offensive. The state can then use limitation grounds such as ‘public order’ to limit the individual’s freedom of expression for presumably ‘causing’ the violent reaction, rather than focus on the violent reaction itself.
A duty-based approach to justifying limitations on the freedom of expression makes it more difficult for the state to advance majoritarian interests or offload its positive obligations. For instance, if the competing interest concerns public order, the state would need to demonstrate that the ‘public order’ interests at stake are actually sufficient reason to constitute a claim right against the expressive conduct in question. It is not at all obvious that an individual merely expressing something offensive owes a duty to refrain from such expression, even when such offence can lead to lawlessness—especially when the individual does not intend to incite lawlessness. Under a duty-based approach, the competing interests that form the basis of a limitation on the freedom of expression must be sufficient to ground in the individual concerned a duty of justice to refrain from the conduct in question.
An illustration may help explain the political case for the duty-based approach. Let us assume an animal rights activist criticises ritual animal slaughter by the majority religious community in the country. The ritual is considered deeply sacred to the customs of the majority community, and the criticism outrages a number of those belonging to the community. There are subsequent calls to arrest the activist and ban such criticism. The state takes no action at first, and as a result, several members of the majority community engage in violent and disruptive protests in public spaces. The state initially arrests some of the perpetrators, but also decides to prohibit the activist and others from engaging in any further criticism of ritual animal slaughter. It justifies the prohibition on the basis that the impugned conduct, i.e. the criticism of animal slaughter, ‘causes’ others to engage in violent and disruptive behaviour, which impairs public order . The state may articulate its justification for the limitation in the following manner: others have an interest in public order, and if certain criticism directly causes persons to engage in acts of public disorder, the state is justified in restricting such criticism. There is no doubt that the interest in public order is important. Such an interest, for instance, grounds a positive obligation in the state to prevent violent and disruptive behaviour. Individuals meanwhile have duties to refrain from such behaviour. But at no point is it apparent that an individual engaging in contentious and unpopular criticism owes a duty of justice (i.e. a duty that directly corresponds to the claim rights of others) to refrain from such criticism—even if such criticism appears to have ‘caused’ others to react violently. A typical proportionality test does not confront this problem, as it does not necessarily require the state to deal with intentionality when limiting the freedom of expression. It would only require the adjudicative body to weigh the individual’s interest in the freedom of expression against the interests of others in public order; a restriction on such criticism could conceivably be justified if the court or tribunal decided that the competing interests outweighed the interest in the freedom of expression. The state’s intention to appease a majority community, or offload its positive obligations, may very well go unchecked.
A duty-based approach directs the state to demonstrate an individual duty of justice, which necessarily incorporates public reason, and the direct responsibility of the individual. In terms of the illustration concerning ritual animal slaughter, to say that interests in public order are publicly justifiable reasons to restrict an activist’s criticism seems unreasonable, as it ignores the fact that it is someone else’s conduct and not the activist’s conduct that actually results in setbacks to public order. Therefore, the state would need to do much better to demonstrate that the activist concerned owes others a duty of justice to refrain from criticising animal slaughter if a limitation on the activist’s freedom of expression in that respect was to be justified. The state is then, to some extent, prevented from offloading its positive obligation (to prevent public disorder) onto the activist. This is the fundamental political value of a duty-based justificatory approach. It is not only a more normatively compelling approach, wherein the special importance of the freedom of expression is better preserved; it is also a politically appealing approach, as it requires the state to justify a limitation on the freedom of expression based on the specific horizontal relationship that exists between the individual and others in society.
Is the Language of Duties Dangerous?
The language of duties can be hijacked by those seeking to diminish the scope of rights. It is therefore natural for the language of duties to attract scepticism and suspicion. For example, the ‘Asian values’ project advanced by political actors such as former Singaporean Prime Minister Lee Kuan Yew relied on a language of ‘duties’ (among other terms such as ‘obedience’ and ‘loyalty’) as a means of deflecting concern for human rights (Sen 1997 ). Moreover, in 2007 and thereafter, the UK witnessed a surge in interest among political actors to frame a new bill of ‘rights and duties ’. The discourse enabled some political actors to call for the replacement of the UK’s Human Rights Act of 1998 with a new bill that focuses both on individual rights and responsibilities. It is therefore natural for the language of duties to attract scepticism and suspicion. But as pointed out by Samuel Moyn, ‘the need to guard against destructive ideas of duty is a poor excuse for ignoring beneficial liberal ones’ (Moyn 2016 , p. 11).
Despite the obvious risks, adopting the language of duties to describe a more robust justificatory approach is valuable, both for methodological and ethical reasons. First, it is not possible to articulate each and every ‘claim right’ in terms of well-recognised ‘human rights’. A person’s claim right that another person refrains from doing something specific cannot always be articulated as a ‘human right’. For instance, a person’s claim right that another person refrains from causing public unrest is certainly a ‘claim right’, but cannot easily be framed in terms of a specific ‘human right’ found in, say, the ICCPR or ECHR. By contrast, it can easily be framed as an interest that both these treaties recognise—‘public order’. A person’s interest in public order, in certain circumstances, is sufficient reason to impose on another person the duty to refrain from expressive conduct that could directly harm that interest. In such circumstances, that person would have a claim right and the other would have a duty of justice to refrain from such conduct. Framing the state’s burden to justify the limitation in terms of ‘rights’ could lead to confusion, as it may prompt us to look for a ‘human right’. Instead, the relevant ‘claim right’ is contingent on the outcome of a reasoning process whereby the importance of the public order interest, in the specific circumstances under consideration, is sufficient reason to impose on an individual a duty to refrain from conduct that directly impairs the interest. This justificatory approach may be better described as a ‘duty-based’ approach because the outcome of the reasoning process is the demonstration of an individual duty of justice to refrain from engaging in the conduct in question.
Second, there is an ethical benefit to reclaiming the language of duties. Such language can help individuals make ethical sense of how their expressive conduct impacts others. David Petrasek correctly observes that the language of duties introduces a certain ‘global ethic’ to modern human rights discourse (Petrasek 1999 , p. 7), which is currently missing. Moyn poignantly notes: ‘Human rights themselves wither when their advocates fail to cross the border into the language of duty’ (Moyn 2016 , p. 10). Such language can then ‘instil in individuals the idea that they should act in ways that support basic shared values’ (Petrasek 1999 , p. 48), and motivate them to be more aware of their ethical obligations to others. Framing a limitation only as a means of advancing legitimate interests, or relying purely on the language of proportionality, cannot offer this ethical dimension. Therefore, the risks associated with the language of duties are ultimately outweighed by its methodological and ethical benefits.
In this article, I evaluated a typical proportionality test when applied to cases concerning limitations on the freedom of expression, and discussed some of the normative and political weaknesses associated with the test. I presented a case for an alternative approach that places duties of justice at the centre of the state’s burden to justify limitations on the freedom of expression. This alternative approach does not completely discard the proportionality test; it instead attempts to address some of the weaknesses of the test. I termed this alternative approach a ‘duty-based justificatory approach’ for certain methodological and ethical reasons. I argued that, when individual conduct concerns the freedom of expression, the state’s burden to justify the restriction on such conduct must involve demonstrating that the individual concerned owes others a duty of justice to refrain from engaging in the conduct.
Once we fully appreciate the value of the freedom of expression, we begin to see the sense in requiring the state to demonstrate a duty of justice when justifying limitations on the freedom of expression. Such an approach is normatively valuable, as it better sustains the normative primacy and peremptory value of the freedom of expression. The state would need to compellingly demonstrate that the various interests that compete with the individual’s interest in the freedom of expression are sufficient reason to impose a duty of justice on the individual concerned. It would have to rely on public reason to demonstrate such a duty, and it would ultimately have to prove that the individual concerned has a direct responsibility for any harmful consequences emanating from the conduct in question. Apart from such normative value, we have seen that a duty-based approach can be politically valuable. It places a clearer burden on the state to demonstrate how the individual concerned directly owes a duty of justice to others to refrain from engaging in the impugned conduct. The state is accordingly constrained from advancing certain majoritarian interests, or offloading its positive obligations by limiting the individual’s freedom of expression.
There appears to be a compelling normative and political case to place duties of justice at the centre of the state’s burden to justify limitations on the freedom of expression. Such an approach would not radically depart from the proportionality test, which retains its place as a ‘core doctrinal tool’ (Möller 2014 , p. 31) to determine the permissibility of limitations on the freedom of expression. The alternative approach I have proposed instead adds crucial scaffolding to the typical proportionality test. It sets out to reinforce the state’s burden to confine itself to the realm of public reason, and insists that the state demonstrates that the individual concerned owes others a duty of justice to refrain from the impugned conduct. Such an approach would enhance the state’s justificatory burden when it seeks to limit one of our most cherished values: the freedom of expression.
Wesley Hohfeld’s reference to liberty (what he called ‘privilege’) appears to be analogous to Isaiah Berlin’s conception of ‘negative liberty’, which he describes as the area within which a person ‘is or should be left to do or be what he is able to do or be, without interference’ (Berlin 1969 , p. 2)
‘Lexical priority’ typically refers to the order in which values or principles are prioritised. Rawls argued that basic liberties, such as the freedom of expression, had lexical priority over other interests.
The Kalimah in question is the specific declaration: ‘There is none worthy of worship except Allah and Muhammad is the Messenger of Allah’.
Books, Chapters, and Articles
Arai-Takahashi Y (2002) The Margin of Appreciation Doctrine and the Principle of Proportionality in the Jurisprudence of the ECHR. Intersentia, Cambridge
Google Scholar
Arai-Takahashi Y (2005) Scrupulous but Dynamic’—the Freedom of Expression and the Principle of Proportionality under European Community Law. Yearbook of European Law 24(1): 27-79
Barak A (2012) Proportionality: Constitutional Rights and Their Limitations. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Berlin I (1969) Two Concepts of Liberty. In Isaiah Berlin, Four Essays on Liberty . Oxford University Press, Oxford
Boyle K and Shah S (2014) Thought, Expression, Association and Assembly. In: Moeckli D, Shah S, Sivakumaranm S, and Harris D (eds) International Human Rights Law. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Choudhry S (2006) So What Is the Real Legacy of Oakes? Two Decades of Proportionality Analysis under the Canadian Charter’s Section 1. Supreme Court Law Review 34: 501-535
Dworkin R (1977) Taking Rights Seriously. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
Dworkin R (1984) Rights as Trumps. In: Waldron J (ed) Theories of Rights: Oxford Readings in Philosophy. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Dworkin R (1985) A Matter of Principle. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
Feinberg J (1970) The Nature and Value of Rights. The Journal of Value Inquiry 4(4): 243-260
Feinberg J (1987) The Moral Limits of the Criminal Law Volume 1: Harm to Others. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Gaus GF (1996a). Justificatory Liberalism: An Essay on Epistemology and Political Theory. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Gaus GF (1996b) Liberalism, Stanford Encyclopaedia of Philosophy (revised version as of 22 January 2018)
George RP (1995) Making Men Moral: Civil Liberties and Public Morality. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Goodin RE (2017) Duties of Charity, Duties of Justice. Political Studies 65(2): 268-283
Grimm D (2007) Proportionality in Canadian and German Constitutional Jurisprudence. University of Toronto Law Journal 57: 383-397
Hart HLA (1955) Are There Any Natural Rights? The Philosophical Review 64(2): 175-191
Hohfeld WN (1919) Fundamental Legal Conceptions as Applied in Judicial Reasoning. Cook WW (ed). Yale University Press, New Haven
Khan AM (2015) Pakistan’s Anti-Blasphemy Laws and the Illegitimate use of the ‘Law, Public Order, and Morality’ Limitation on Constitutional Rights. The Review of Faith & International Affairs 13(1): 13-22
Knox JH (2008) Horizontal Human Rights Law. The American Journal of International Law 102(1): 1-47
Kumm M (2004) Constitutional rights as principles: On the structure and domain of constitutional justice. International Journal of Constitutional Law 2(3): 574-596
Kumm M (2010) The Idea of Socratic Contestation and the Right to Justification: The Point of Rights-Based Proportionality Review. Law & Ethics of Human Rights 4: 142-175
Letsas G (2007) A Theory of Interpretation of the European Convention on Human Rights. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Letsas G (2006) Two Concepts of the Margin of Appreciation. Oxford Journal of Legal Studies 26(4): 705-732
Marmor A (2018) Two Rights of the Freedom of Expression. Ratio Juris 31: 139-159
Mill JS (1859) On Liberty
Mill JS (1861) Utilitarianism. In: The Collected Works, Volume 10 (1974), University of Toronto Press, Toronto
Möller K (2014) Constructing the Proportionality Test: An Emerging Global Conversation. In: Lazarus L, McCrudden C and Bowles N (eds) Reasoning Rights: Comparative Judicial Engagement. Hart Publishing, London
Moyn S (2016) Rights vs. Duties: Reclaiming Civic Balance. Boston Review 41(3): 1-12
O’Neill O (1996) Towards Justice and Virtue: A Constructive Account of Practical Reasoning. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Petrasek D (1999) Taking Duties Seriously: Individual Duties in International Human Rights Law – A Commentary. International Council on Human Rights Policy, Versoix
Rawls J (1999). A Theory of Justice: Revised Edition. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
Rawls J (2005) Political Liberalism: Expanded Edition. Columbia University Press, New York
Raz J (1986) The Morality of Freedom. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Raz J (1999) Practical Reason and Norms. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Rivers J (2006) Proportionality and Variable Intensity of Review. Cambridge Law Journal 65: 174-207
Scanlon T (1998) What We Owe to Each Other. Belknap Press, Cambridge, MA
Sen A (1997) Human Rights and Asian Values: What Lee Kuan Yew and Li Peng don't understand about Asia. The New Republic 217 (2-3): 33-40
Shiffrin S (2003) Speech, Death, and Double Effect’ New York University Law Review 78(3): 1135-1185
Stone GR (1987) Content-Neutral Restrictions. University of Chicago Law Review 54: 46-118
Strauss DA (2002) Freedom of Speech and the Common-Law Constitution. In: Bollinger LC and Stone GR (eds) Eternally Vigilant: The Freedom of Expression in the Modern Era, University of Chicago Law Press, Chicago
Tremblay LB (2014) An egalitarian defense of proportionality-based balancing. International Journal of Constitutional Law 12 (4): 864-890
Tridimas T (2007) The General Principles of EU Law. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Tsakyrakis S (2009) Proportionality: An Assault on Human Rights? International Journal of Constitutional Law 7: 468-493
Urbina FJ (2015) Incommensurability and Balancing. Oxford Journal of Legal Studies 35 (3): 575-605
Urbina FJ (2014) Is it Really That Easy? A Critique of Proportionality and ‘Balancing as Reasoning’. Canadian Journal of Law & Jurisprudence 27 (1): 167-192
Van Dijk P and Van Hoof GJH (1998) Theory and Practice of the European Convention on Human Rights. 3rd edition. Kluwer, The Hague
Von Bernstorff J (2014). Proportionality Without Balancing: Why Judicial Ad Hoc Balancing is Unnecessary and Potentially Detrimental to the Realisation of Individual and Collective Self Determination. In: Lazarus L, McCrudden C and Bowles N (eds) Reasoning Rights: Comparative Judicial Engagement. Hart Publishing, London
Waldron J (1993). Liberal Rights. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Webber G (2009) The Negotiable Constitution: On the Limitation of Rights. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Zoller E (2009) The United States Supreme Court and the Freedom of Expression. Indiana Law Journal 84: 885-916
Zysset A (2019) Freedom of expression, the right to vote, and proportionality at the European Court of Human Rights: An internal critique. International Journal of Constitutional Law 17(1): 230-251
Claudia Andrea Marchant Reyes et al. v. Chile, Communication No 2627/2015 (CCPR views adopted on 7 November 2017), CCPR/C/121/D/2627/2015
Fedotova v. The Russian Federation , Communication No 1932/2010 (CCPR views adopted on 31 October 2012), CCPR/C/106/D/1932/2010
Handyside v. The United Kingdom, Application No. 5493/72, ECtHR judgment of 7 December 1976
İ.A. v. Turkey, Application no. 42571/98, ECtHR judgment of 13 December 2005)
Ladue v. Gilleo (1994) 512 U.S. 43 (U.S. Supreme Court)
Leyla Şahin v. Turkey , Application No 44774/98, ECtHR judgment [GC] of 10 November 2005
Otto-Preminger-Institut v. Austria , Application No. 13470/87, ECtHR judgment of 20 September 1995
R v. Oakes [1986] 1 SCR 103 (Canadian Supreme Court)
S.A.S v. France , Application No 43835/11, ECtHR judgment [GC] of 1 July 2014)
Thoma v. Luxembourg , Application No 38432/97, ECtHR judgment of 29 June 2001
United States v. O'Brien (1968) 391 U.S. 367 (U.S. Supreme Court)
Wingrove v. The United Kingdom, Application No. 17419/90, ECtHR judgment of 25 November 1996
Zaheeruddin v. State (1993) SCMR 1718 (Supreme Court of Pakistan)
Download references
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to thank Dr Nazila Ghanea, Dr Godfrey Gunatilleke, Tom Kohavi, Shamara Wettimuny, and Wijith de Chickera for their generous time in reviewing previous versions of this article, and for their valuable feedback.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Harvard Law School, Cambridge, MA, USA
Gehan Gunatilleke
University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gehan Gunatilleke .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Gunatilleke, G. Justifying Limitations on the Freedom of Expression. Hum Rights Rev 22 , 91–108 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12142-020-00608-8
Download citation
Accepted : 26 October 2020
Published : 01 November 2020
Issue Date : March 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12142-020-00608-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Freedom of expression
- Limitations on rights
- Duties of justice
- State authority
- Justification
- Public reason
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
240 Freedom Essay Topics
On this page, you’ll find thought-provoking freedom essay topics to explore the multifaceted nature of freedom. This concept encompasses many dimensions, from political liberties to human rights. Investigate our freedom essay ideas and prompts for a discussion, speech, or debate. We’ve also included a short example of the “What Is Freedom” essay.
🕊️ TOP 7 Freedom Essay Topics
🏆 best freedom essay topics, 🎓 interesting freedom essay topics for debate, 👍 good topics about freedom, 💡 simple freedom topics, 🔥 hot freedom essay ideas, 📌 freedom topics for discussion, 🔎 freedom essay topics for college, ❓ more topics about freedom, 📝 what is freedom essay – example.
- Freedom of Speech: Right and Responsibility
- Social Media and Freedom of Speech
- “Human Freedom and the Self” by Roderick Chisholm
- Which Is More Important: Security or Freedom?
- Freedom in Kate Chopin’s “Story of an Hour”
- How Social Media Affects Individual Freedom
- “Freedom From Want” by Rockwell
- Freedom – Comparison of Different Definitions Freedom is a term used to describe various types of individual liberties, such as religious liberty, political liberty, freedom of speech, right of self-defense, and others.
- Freedom in “On Liberty” by John Stuart Mill The philosophical work “On Liberty” was written by J. S. Mill in 1859. These are the times of democratic republics’ heyday on the eve of slavery abolition in the US.
- Student’s Rights: Freedom of Speech Institutional laws depend on the guidelines of student’s constitution while state laws outline individual’s different forms of freedoms.
- The Freedom of Expression This paper will discuss the limits of freedom of expression, its application on campuses, and the ways to combat hateful instances.
- Freedom in Life and Relationship There are numerous benefits accrued from freedom in a relationship. Setting a partner free in a relationship leads to one becoming responsible and committed to the relationship.
- Importance of Expression Freedom and Tolerance Freedom of expression is “the ability to express their beliefs, thoughts, ideas, and emotions about different issues free from government censorship”.
- Freedom of Speech on the Internet The research paper explores freedom of speech, with a specific focus on each person’s right to express their thoughts on the Internet.
- Religion Freedom and Its Limitation The freedom to believe in something is a fundamental right of a free person, but almost any religion calls for certain actions that can potentially limit other people’s rights.
- Common Law: Freedom of Expression Proponents of freedom of expression argue that the concept has not been comprehended or interpreted correctly for a long time.
- East India Company: The Story of India’s Freedom This paper reviews the sixth episode of the BBC documentary series, which is devoted to the history of India’s independence from the influence of other states.
- Marriage Oppression and Freedom Signs The 19th century is characterized by women discrimination in society, whereby the role of women is to offer basic services at home.
- Freedom of Expression and Intellectual Property Rights The problem of finding the balance between ethics and free access to extensive information online is a challenge for present-day companies and entrepreneurs.
- Balancing Others’ Freedom and Own Happiness One person’s freedom may prevent others from being happy since acting as one pleases does not necessarily mean doing what is right.
- Freedom of Speech in British Universities This report recommends for modern UK students to develop free debates and peaceful demonstrations in specific zones and prove that young minds have to be open.
- John Brown: Terrorist or Freedom Fighter John Brown was an abolitionist who chose to liberate slaves by force. His actions were extremely controversial, and to this day, they can spark a debate about their righteousness.
- Freedom of Speech and Restrictions: Pros and Cons Freedom of speech, being naturally controversial, dramatically benefits from balancing its two extreme states – absolute freedom and absolute restriction.
- Freedom of Speech and Censorship One of the most critical aspects of fighting against cybercrime involves a proper balance between the preservation of people’s right to free speech and censorship.
- Discussion: Freedom and Security It is evident that the government jeopardizes individual freedom to ensure national security. Several factors contribute to this, including infringement on individual liberties.
- Positive and Negative Freedom: Distinction and Ethical Problem The paper is devoted to a comparative analysis of the positive and negative concepts of freedom to identify critical points of contact and differences.
- Women’s Fight for Freedom The paper describes the history of an abolitionist movement in the 18th century that raised issues of slavery, African American rights, and an end to the oppression of women.
- True Freedom Theme in American Short Stories “The Cask of Amontillado” by Poe, “Dark They Were and Golden-Eyed” by Bradbury, and “The Story of an Hour” by Chopin are analyzed through an understanding of true freedom.
- Life as a Struggle for Freedom Freedom is one of the phenomena that permeate all spheres of human activity. Many philosophers thought about it, trying to understand its essence and necessity for humanity.
- Freedom and Security in the Contemporary World In the United States, as well as in many other developed and developing countries, the issues of freedom and security play an important role.
- Freedom of Speech Peculiarities The paper describes that as much as people exercise their freedom of speech, they have to be censored to protect the interest of those that may be affected by such acts.
- Roosevelt’s, Taft’s, Wilson’s Foreign Policies and Freedom This paper explains how americans used the language of freedom when discussing foreign policy. It looks specifically at the foreign policies of T. Roosevelt, Taft, and Wilson.
- Self-Identity and Personal Freedom The paper indicates that due to the influence of stereotypes and one story, people are not free to realize their desires and self-identity.
- The Power of Fear to Limit Freedom The paper state that fear can have a negative role on society and lead to the imposition of restrictions on freedom which is evidenced by many historical events.
- Sartre’s Freedom and Existentialism Today Sartre in his work devised an important approach to modern-day issues. It has transformed the idea of personal responsibility and free will.
- Issues on Internet: Privacy and Freedom of Speech Two of the issues, namely, privacy and freedom of speech with regards to the Internet have been discussed in this article.
- Freedom of Expression and Hate Speech The diversity in people’s views, mentalities, and cultures might precondition the clash of visions. The rights of people might serve as the source of conflicts.
- Contractual Freedom and the Evolution of Corporate Control in Britain, 1862 to 1929
- The United States Constitution and the History of American Freedom
- Commercial Freedom and Sport: Has Sport Lost Its Sporting Edge
- How Has the Concept of Free Will and Individual Freedom?
- American Democracy, Freedom, and the American Revolution
- Freedom Does Not Mean License, but the Wisdom to Choose What Is Right for Oneself
- Freedom for African Americans Along With American History
- Economic Freedom and Institutional Convergence
- How Much the Government Should Restrict Their Freedom?
- Economic Freedom and Income Inequality: Evidence From a Panel of Global Economies
- African Americans: The Loss and Gain of Freedom(1865-1900)
- How the Civil War Sculpted How Americans Viewed Their Nation and Freedom
- Choice, Freedom, and Well-Being: Considerations for Public Policy
- How Gradual Abolition and Process of Emancipation Led Blacks to Freedom
- Wellbeing, Freedom, and Social Justice: The Capability Approach Re-Examined
- Child Welfare, Religion, Freedom, Social Responsibility, and Parental Rights
- Democracy, Economic Freedom, and Taxation in the European Union
- Freedom and Equality Among Men in the Declaration of Independence
- Emotional Freedom Technique and the Benefits to Use in Middle School Classrooms
- Achieving Financial Independence and True Freedom
- Balancing Freedom With Responsibility Can Be a Difficult Task for Any FR
- How the Attitudes and Freedom of Expression Changed for African Americans Over the Years
- Corruption, Economic Freedom and Political Freedom in South America: In Pursuit of the Missing Link
- Classical and Individual Conservatives: Conservative Freedom Classical conservatives define freedom as a privilege that must be controlled from reaching chaotic behaviors.
- The Freedom of Information Act 2000 in the UK The Freedom of Information Act is an instrument meant to implement and put into place the Freedom of Information legislation and give the same a national outlook in the UK.
- The Meaning of Freedom for Jazz Instrumentalists Jazz appeared at a very important period of time. African American musicians gathering in New Orleans to improvise and share their music could be taken as the founders of this music genre.
- Freedom Ideal in “The Spartans” by Paul Cartledge The Spartans: The World of the Warrior-Heroes of Ancient Greece by Paul Cartledge tracks the outstanding rise and fall of the Spartan society.
- Law: Freedom of Speech and the Right to Offend The current paper aims at evaluating the video with several people discussing the right of the press to offend people and the right of the readers to use bloody techniques to solve their discontents
- Religious Freedom: The Separation Between Church and State The paper indicates that many Christians consider efforts to separate state and religion as an assault on America’s majority religion.
- Freedom of Speech: The Basic Human Right Freedom of speech allows everyone to receive and impart information. People and communities should articulate their thoughts and ideas without fear of any form of intimidation.
- “God, Freedom and Human Dignity” by Highfield The following paper summarizes the book titled “God, Freedom, and Human Dignity,” written by Ron Highfield and published by IVP Academic.
- Emotions: Fear and Freedom The paper tells us that fear and freedom are two opposite ends of the same path. It is fear that is the beginning of an individual who lives in doubt.
- Roderick Chisholm on Human Freedom and the Self Roderick Chisholm adheres to a libertarian position that borders on the incompatibility of free will and determinism doctrine.
- Internet Censorship: Freedom of Expression in the Arts Many countries have embraced this technology and used it to boost their economies and other aspects of life, including education.
- The Relationship Between Economic and Political Freedom Politics and economics have been inextricably linked throughout history, accounting for the rise of some of the world’s most famous empires.
- The March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom 1963 August 28, 1963 is considered to be a prominent date for the history of America. It was the turning point for the Civil Rights Movement.
- Economic Freedom and Schools of Thought Economic freedom is the idea of free markets in which people have freedom to produce, buy and sell products and services both inside and outside one’s borders.
- Sartre and Ardent on the Freedom Notion The notion of freedom may be characterized by a multiplicity of interpretations and possible shades of meaning ascribed to it.
- Iraqi Freedom Operation The paper argues against the Operation Iraqi Freedom that started in 2003 to topple the Saddam Regime and bring positive economic and political change in Iraq.
- Constitutional Law: Freedom of Speech The court’s decision to uphold Sarah Sampson’s right came from case laws whose interpretation of the Constitution clarified the legality of expressions.
- Freedom and a Quest for Greatness in Hawthorn’s Wakefield “Wakefield” is a short story by Nathaniel Hawthorne. It describes the non-trivial life of Mr. Wakefield, who leaves his wife of twenty years to live on a nearby street.
- Thoreau vs. Roosevelt on Individual Freedom The paper states that freedom breeds responsibility, and responsibility directs freedom. Therefore, the more freedom, the more responsibility.
- Freedom Concept in Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s “The Social Contract” The difference between the natural freedom of man and the freedom made possible by the social contract will be described in this paper.
- Censorship as a Way to Limit Freedom of Speech A simple example of censorship is when some people impose their political or moral values on others by suppressing words, images, or ideas they find offensive.
- Freedom of Speech: Restrictions in Social Networks Actions by the US government to influence free speech on Facebook, Twitter, and other such networks are acceptable, but only if they are related to national security.
- Milton Friedman’s Political and Economic Freedom Much of Milton Friedman’s argument or doctrine is built around the desire for free trade, a smaller government, and a steady increase in money supply within a growing economy.
- Restrictions on Freedom of Speech on Social Networks Social networks control modern restrictions on freedom of speech in many ways, affecting all aspects of people’s lives to reduce the existing imbalance and avoid open hatred.
- American Freedom and Human Rights American spirit consists of a dream of innocence and freedom. It is every American’s duty to create justice, and every person has the power to do so.
- Hegel’s Account of Freedom and the Modern State German philosopher Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel is recognized for shaping contemporary philosophical thought.
- Article “Escape From Freedom” by Costello et al. This work discusses the hypothetical connection between authoritarianism and determinism. It explains how Costello described the concept of free will as fatalistic determinism.
- Las Pachuchas: Fight for Freedom This paper provides a comprehensive overview of Las Pachuchas’ fight for freedom. It covers the movement’s historical roots and relations to World War II.
- The Essay “Capitalism and Freedom” by Milton Friedman While ‘some’ time has passed since 1962, Milton Friedman’s essay titled “Capitalism and Freedom” remains relevant to this day.
- Freedom of Speech: The Adequate Restrictions It is recognized that free speech must be restricted if an individual’s words are harmful to public health or affect the freedoms of another person.
- Concepts of Revolution and Freedom in United States Freedom was born during the revolution era 1601-1900 CE. The struggle for independence spawned new concepts about freedom and equality.
- Perception of Freedom in Saint Domingue and Haiti This paper aims to explore the concept of freedom of people in Saint Domingue and post-revolutionary Haiti from the perspective of observers of those events.
- Forbidden Freedom Glimpsed Through a Window This paper explores how women’s confinement in domestic space was portrayed in short stories at the end of the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century.
- Disconnectedness of Political Freedom and Capitalism The paper is about the disconnectedness of political freedom and capitalism, which indicates that the latter does not promote or guarantee the former.
- Coronavirus Could Trigger a Backslide on Freedom With the emergence and development of states, people began to contemplate the dilemma of liberty and public safety.
- Freedom of Expression in Artworks It is expected of artworks to push the envelope of the socially accepted, introducing viewers to the complexity of certain moral arguments.
- Freedom and Responsibility: Correlation Analysis The chosen issue is the correlation between freedom and responsibility. These two notions are interrelated through social, political, and ethical norms.
- The Two Political Ideals of Freedom and Equality Claimed by Long and Roosevelt
- Toward Freedom From Domestic Violence: The Neglected Obvious
- Does Censorship Limit One’s Freedom
- Economic Freedom and Public, Non-market Institutions: Evidence From Criminal Prosecution
- America’s Demand for Freedom and Equality Pushed War at Great Britain’s Doorstep
- African American Literature and the Struggle for Freedom
- Economic Freedom and Government Ideology Across the German States
- Colonial Unity Brought the Freedom to America After the Revolution
- Academic Freedom and Its Impact on Education
- Economic Freedom, per Capita Income, and Economic Growth
- Capitalism and Freedom: Manumissions and the Slave Market in Louisiana, 1725 1820
- Freedom, Consent, and Other Feminist Issues
- Does Modern Technology Restrict or Enhance People’s Rights and Freedom
- Freedom, Enforcement, and the Social Dilemma of Strong Altruism
- How Freedom and Equality Presupposes Each Other in the Natural World
- Create Dangerously: Albert Camus on the Artist as a Voice of Resistance and an Instrument of Freedom
- Trade Freedom and Revenue From Trade Taxes: A Cross-Country Analysis
- Developmental Freedom and Social Order: Rethinking the Relation Between Work and Equality
- How the United States Leaped From the Grasp of England Into a New Era of Freedom?
- Economic Freedom and Migration Flows Between the U.S. States
- Discuss the Conflict Between Bondage and Freedom Faced by African Americans
- Economic Freedom and Employment in India
- Religious Freedom and Identity of Believers This article is a compilation of perspectives on the relationship between religious freedom and the identity of believers.
- The Freedom of the People: Descartes, De Spinoza Freedom is the essential characteristic of human life, which is revealed based on the unity and interaction of its spiritual and material components.
- Roosevelt: Four Freedom Address Roosevelt is a perfect example of a democratic leader who understands the population’s needs and makes everything possible to meet them.
- French Revolution: The Birth of Freedom and Equality The French Revolution is reasonably deemed one of the most significant events not only in the history of France but also in the whole world.
- Freedom in Action via Cultural Relativism Cultural relativism refers to the approach of not evaluating a culture according to its criteria for determining what is right or wrong, strange or normal.
- The Political Objectives of the Freedom Summer Activists The memory of the tragically dead Cheney, Schwerner, and Goodman is honored and will be kept as long as there is violence in the world.
- Ethical Relativism and Freedom of Speech Ethical relativism has boundaries that need to be clarified. It is essential to find a balance between moral nihilism and ethical absolutism.
- Freedom and Rights in Relation to COVID-19 During the coronavirus pandemic, a mask regime and mandatory vaccination were introduced almost all over the world, limiting the freedoms of numerous people.
- Compatibilist and Libertarian Freedom A significant feature of the libertarian theory of freedom is that it implies circumstantial and metaphysical freedom.
- Marcus Garvey in Black Freedom Struggle History African-American history in the United States has many notable events which forever transformed the society of the country.
- What Is More Impactful: Freedom or Slavery? In modernity, the history of slavery in the United States can primarily be contextualized as the history of abolition.
- Thirst for Freedom: The Art of Bible Translation Exodus is a Greek word that means the exit of a large group and is the second book in the Old Testament. The book bases its story on the movement of Israelites out of Egypt.
- “Freedom Writers”: Immigration and Indigenization Immigration and indigenization in education connect people, being vital in expanding the horizons and perception of the world with its cultural differences.
- Understanding the Concept of Freedom in America The American autonomy of liberty took shape in the 19th century to support industrializing the economy and posing constitutional protection.
- Importance of Freedom of Speech to American Citizens Social networks have become the means of suppressing free thinking since they massively popularize people who express the “right” point of view.
- Issues Related to Freedom and Population Surveillance in China The paper emphasized several vital issues related to freedom and population surveillance in China, the adverse use of technology, and the importance of AI supremacy.
- Determination of Sartre’s Concept of Freedom Jean-Paul Sartre’s existentialism can significantly positively impact a person who has the will to define themselves.
- Personal Freedom of Thought Concept Despite the common thought that freedom is achieved when the majority supports the opinion, freedom is the capability to act freely, devoid of any external influence.
- African Americans’ and Southern Whites’ Freedom The relation to freedom in African Americans and Southern Whites has always been different, and each race could not understand and accept the ideas of their opponents.
- Arguments Against Masks During Pandemic and Personal Freedom The arguments of mask refusers are invalid. However, their actions lead to a violation of the top human right – the right to life.
- “Law, Morality, and the Freedom of Expression”: Relationship Between Morality and the Law The paper discusses the types of relationship that exists between morality and the law based on the writing “Law, morality and the freedom of expression”.
- The Case Against the Reds: Civil Freedom in the History of the United States The case against the reds can be defined as the occasions’ narration. It is the widest reinterpretation of civil freedom in the history of the United States.
- Freedom of Speech Despite Life Risks Today, the US prides itself on its freedom of speech, with the First Amendment protecting the population from censorship.
- Can One Will Their Own Freedom Without Willing the Freedom of Others? An analysis of human psychology indicates that people act independently and always strive to abide by the decisions that maximize their self-interests.
- Africa’s Freedom: The Events of 1960 The article comprises reflections of individuals whose lives have been directly influenced by the events of 1960. It conveys the message of African unity in the world.
- Philosophical Attitude of God’s Foreknowledge and Human Freedom Omniscience is the state of having full or maximum knowledge and is regarded as an essential feature of an entirely perfect being.
- The Quest for Freedom: William Blake and Fredrick Douglass Romantic poets such as William Blake believed human imagination could counter scientific principles that defined reality using material objects.
- The Use of Emotional Freedom Technique for Test Taking Anxiety Reduction The emotional freedom technique (EFT) is reported to be a prominent method that reduces stress and related negative psychological effects.
- Religious Freedom and Freedoms of Association Whether one chooses to live in utter denial or utmost belief of a religious system, we are all born in one, religion is a matter of the heart.
- Certified Professional Midwifery Practice and the Home Birth Freedom Act The Home Birth Freedom Act seeks to accredit Certified Professional Midwifery practices. The act aims at protecting the CPM practitioners from being prosecuted.
- Constitutional Law Hong Kong: Freedom of Expression This essay will discuss the Freedom of expression as a fundamental right and that it lies in the civil society and of Hong Kong system and way of life.
- The Notions of Misogyny, Feminism, and Sexual Freedom in Sam Mendes’s Skyfall The overall socio-linguistic context of the notion of human sexuality has now generally been vastly misinterpreted by many people regardless of their racial, social, or ethnic affiliation.
- Freedom of the Media: The Near v. Minnesota 1931 Case The paper analysis the Near v. Minnesota 1931 case, when the U.S. Supreme Court invalidated state laws that allowed officials to ban the publication of “defamatory” newspapers.
- The Marijuana Freedom and Opportunity Act The Marijuana Freedom and Opportunity Act, which will unify the rules for the use of marijuana and promote the development and price reduction of this healthcare service.
- The Haitian Revolution: A New Vision of Freedom The paper recaps the background and consequences of the Haitian Revolution, the way it affected people of different nationalities around the world.
- The Convention for Safeguarding the Human Rights and Fundamental Freedom of the EU Citizens The convention for safeguarding the Human rights and fundamental freedom of the EU citizens were drawn up by the European Council on November 4th, 1950, and enforced in 1953.
- Margaret Sanger and Her Contribution to Women’s Freedom Margaret Sanger is although was focused on contradictory ideas of eugenics and showed racism, significantly affected the fight for women’s equality.
- Can Multicultural Urban Schools in Sweden Survive Freedom of Choice Policy
- Academic Autonomy and Freedom Under Pressure: Severely Limited, or Alive and Kicking
- Abstract Expressionism and Its Representation of Individual Freedom and Emotion
- Economic Freedom and Human Flourishing: Perspectives From Political Philosophy
- Freedom and the Strong State: On German Ordoliberalism
- Academic Freedom, Private-Sector Focus, and the Process of Innovation
- Does Liberalism Offer the Most Freedom
- Economic Freedom and the Informal Economy
- Internet Freedom Should Not Be Censored by the Government
- Censorship Conflicts With the First Amendment’s Freedom of Speech
- Between Equality and Freedom of Choice: Educational Opportunities for the Least Advantaged
- How Does the Montessori Environment Facilitate and Encourage the Freedom of the Child?
- Freedom and Equality: America’s Pride and Glory
- Freedom: Political Philosophy and Current Societal Setting
- The United States Constitution Stating No Law Prohibiting the Freedom of Speech
- Economic Freedom, Race, and Health Disparities
- Civil Liberties and Multiculturalism: The Freedom of The
- Education: “We Should Cherish Our Children’s Freedom to Think”
- Balancing Criminal Justice and Personal Freedom Assignment
- How Religion Limits the Freedom of Human Beings
- Freedom, Capitalism, and Institutions for Delivering Social Justice
- Economic Freedom and Labor Market Conditions: Evidence From the States
- The Tricky Balance Between the Freedom of Expression and Censorship Plans in the U.S
- Freedom of African Americans in the Southern States The abolition of slavery in the United States was a long process rather than a series of amendments to the Constitution.
- Liberty, Freedom, and Equality in America The development of liberty, freedom, and equality in the United States should be considered through the lens of the diversity of nations.
- Universal Qualities of Freedom The short stories by A. Chekhov, H. Quiroga, K. Chopin, and J. Cortazar respectively present the typical freedom quality of allowing people to make their life decisions.
- Freedom of Assembly: The First Amendment Act When exercising this right, individuals are expected to ensure they do infringe on other freedom such as speech, religion, expression, and press.
- Freedom: Historical Events’ Impact on Modern Society Social changes and the establishment of freedom for all citizens have a substantial impact on modern society up to the present.
- Freedom of Expression in the Post-Apartheid South Africa Undoubtedly, there is a direct link between democracy, freedom of speech, and the diversity of the media. South Africa got in the second “satisfactory” category.
- The Civil War Lessons: Fight for Freedom and Equal Rights The key moment of U.S. history is the Civil War and its consequences, the persistence of people fighting for freedom, and the strength of minorities experiencing oppression.
- Freedom of Religious Beliefs in the Workplace The workplace is a unique and sensitive environment governed by own rules and policies that must exclude any degrading and hurtful treatment of employees based on their beliefs.
- Freedom of Breath, Foundation of Life: China’s Neonatal Resuscitation Program Review Birth asphyxia remains a major concern in developing countries, with seven deaths per 1000 births caused by asphyxia, compared to less than one death in developed countries.
- Mr. Merrill “Professionalization: Fusion of Media Freedom and Responsibility” Mr. Merrill tells why and how mass media has transcended an ethic line due to freedom traced by national institutions; and how the latter helped mass media become what it is today.
- Freedom and Enslavement in Literature Freedom and enslavement are patterns adopted in the literature that rarely hinders the expressive manner of writers.
- Sustein and Tocqueville: Two Opinions on Freedom of Speech Cass Sustein and Alexis Tocqueville compares the manner in which America and Europe approaches a person’s freedom of speech.
- Can a Case Be Made Against Freedom and Equality? Discussion of question on the example of three cases: Brown v. The board of education, president Kennedy’s prosecution of the Cuban missile crisis, and NOW’s statement of purpose.
- Freedom From Beliefs Native Americans This essay is valuable to the oppressed since through this, the writer gives them courage to face the struggle.
- Franklin Delano Roosevelt: Champion of Freedom The rise of D.F. Roosevelt was connected with his political career and personal development as a national leader. The political career began in 1910-1911 when Roosevelt entered the state house.
- Freedom Information Act 2000 of United Kingdom The Freedom of Information Act 2000 which came into effect in 2005 was outcome of the major electoral manifestations of the labour party in 1997.
- Freedom and Social Status of Blacks in America The majority of White people in America are not quite ready to admit that despite their strive to eradicate racism within themselves they continue to act as subtle racists.
- Answering Freedom’s Call: Life After Emancipation The reunification of the country following the Civil War was a process that contributed to the widespread realization of their rights by a broad stratum.
- How Does the Freedom to Choose Ancestries in One’s Identity Differ for Whites and People of Color This paper compares opportunity to choose their ethnic identity of whites and people of color to show this freedom is inaccessible to racial minorities.
- Emotions and the Perception of Freedom The relationship between man and women has always evoked interest and received attention in numerous literary works.
- Protecting Freedom of Expression on the Campus Freedom of speech is a vital component of American society and should be protected, but it cannot be utilized either legally or in campus policies when it is used for vicious purposes.
- Woodrow Wilson’s “The New Freedom” Campaign Being famous for his campaign platform known as “The New Freedom,” Woodrow Wilson gained sizeable support from the American population.
- Freedom of Expression: Tinker v. Des Moines The evaluation of Tinker v. Des Moines Independent Community School District highlights the areas covered by the First Amendment and the nuances of its application.
- House Freedom Caucus: Legislation Research and Analysis The interest group identified in the research is the House Freedom Caucus. It is a congressional caucus that includes members of the House of Representatives.
- Freedom or the Common Good – What Matters More? The purpose of this paper is to analyze various views and theories on free markets and government regulations.
- “Freedom and Capitalism” by Milton Friedman The principle behind the book “Capitalism and Freedom” was that the government only existed for the will of the people, and thus served as the means towards a goal.
- Freedom of Expression: Jake Baker’s Case The case of Jake Baker (1997) transformed into a full-scale debate on topics ranging from freedom of expression to pornography and obscenity.
- US Gun Control: Losing Freedom or Safeguarding? Gun control has long been among the chief sources of debate in the US. This polarizing topic presents a powerful political tool and extensively used by Democrats and Republicans.
- Natural Freedom in Romantic American Literature There is a common denominator that binds the works of James Fennimore Cooper, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Washington Irving, and Henry David Thoreau.
- Boyz n the Hood and Black Freedom Fighters in Steel Both Boyz n the Hood and Black Freedom Fighters in Steel describe the lives of people of color who are struggling to survive in a world that is aggressively opposed to them.
- Equality, Freedom, and Security Rights in the US The problem is in the fact that rights to equality, freedom, and security reflected in the UDHR should be adopted in different states of the country.
- Freedom in American Countryside and Agriculture This paper portrays how freedom has been eliminated in the countryside by the state agriculture department, and whether the farmer has a moral right to do his farming practices.
- African-American Struggle for Freedom In the 1900’s, African Americans were oppressed by de jure segregation, a social system that has established separate facilities for the minority groups.
- Mississippi Freedom Summer in 1964: Whites in the Movement The key goals of the Mississippi freedom summer of 1964 were to ensure that the African Americans were registered as voters in Mississippi.
- Consequences of Religious Freedom in America Today religious freedom is the foremost issue that has incurred as a result of direct democracy which is affecting millions of American citizens.
- Historical Freedom in America America is renowned as a country that espouses freedom in every respect. An important point to note, however, is that this freedom was not easy to come by.
- What Is the Economic Approach to Issues of Religious Freedom?
- What Are the Issues With Freedom and the Relationship With Thailand’s Constitution?
- Does Democracy Ensure Freedom?
- Does the UCTA and UCTTR Impede on the Freedom of Contract?
- Does Censorship Limit One’s Freedom?
- What Is the Distinction Between Positive and Negative Freedom?
- How Do Freedom and Responsibility Affect Individuals and Society?
- How Much the Government Should Restrict Their Personal Freedom?
- Who Is Ralph Emerson and What Is His View on American Freedom?
- What Is the Balance Between Freedom and Order?
- What Freedom Does Literacy Offer in Globalised Society?
- What Does One Define Religious Freedom and Prisoner Rights?
- What Is the Relationship Between Authority, Freedom and Discipline in School?
- What Is the Distance Between Fear and Freedom?
- What Was the Lincoln’s Administration Pursuit of Freedom?
- What Is the Problem With Excessive Religious Freedom?
- Does Australia’s Unfair Contracts Act Limit or Enhance Contractual Freedom?
- What Are the Philosophical Issues in Censorship and Intellectual Freedom?
- Does Economic Freedom Affect the Production Frontier?
- Does Economic Freedom Influence Major Health Indicators in India?
- Does the Law Relating to Obscenity Restict Freedom of Speech?
- What Is the Difference Between Freedom Fighters and Terrorists?
- What Is the Non-parametric Approach to Dynamics of Economic Freedom?
- How Does Rousseau Understand the Concept of Freedom?
In the short sample below, we tried to give a simple and concise explanation of what freedom means. Have a look at how we highlight the importance of balancing individual autonomy with respect for the freedoms of others in creating a harmonious and flourishing society. Continue reading for more freedom essay ideas!
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, September 18). 240 Freedom Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/freedom-essay-topics/
"240 Freedom Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 18 Sept. 2021, studycorgi.com/ideas/freedom-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '240 Freedom Essay Topics'. 18 September.
1. StudyCorgi . "240 Freedom Essay Topics." September 18, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/freedom-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "240 Freedom Essay Topics." September 18, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/freedom-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "240 Freedom Essay Topics." September 18, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/freedom-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Freedom were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 22, 2024 .
Essays About Freedom: 5 Helpful Examples and 7 Prompts
Freedom seems simple at first; however, it is quite a nuanced topic at a closer glance. If you are writing essays about freedom, read our guide of essay examples and writing prompts.
In a world where we constantly hear about violence, oppression, and war, few things are more important than freedom. It is the ability to act, speak, or think what we want without being controlled or subjected. It can be considered the gateway to achieving our goals, as we can take the necessary steps.
However, freedom is not always “doing whatever we want.” True freedom means to do what is righteous and reasonable, even if there is the option to do otherwise. Moreover, freedom must come with responsibility; this is why laws are in place to keep society orderly but not too micro-managed, to an extent.
5 Examples of Essays About Freedom
1. essay on “freedom” by pragati ghosh, 2. acceptance is freedom by edmund perry, 3. reflecting on the meaning of freedom by marquita herald.
- 4. Authentic Freedom by Wilfred Carlson

5. What are freedom and liberty? by Yasmin Youssef
1. what is freedom, 2. freedom in the contemporary world, 3. is freedom “not free”, 4. moral and ethical issues concerning freedom, 5. freedom vs. security, 6. free speech and hate speech, 7. an experience of freedom.
“Freedom is non denial of our basic rights as humans. Some freedom is specific to the age group that we fall into. A child is free to be loved and cared by parents and other members of family and play around. So this nurturing may be the idea of freedom to a child. Living in a crime free society in safe surroundings may mean freedom to a bit grown up child.”
In her essay, Ghosh briefly describes what freedom means to her. It is the ability to live your life doing what you want. However, she writes that we must keep in mind the dignity and freedom of others. One cannot simply kill and steal from people in the name of freedom; it is not absolute. She also notes that different cultures and age groups have different notions of freedom. Freedom is a beautiful thing, but it must be exercised in moderation.
“They demonstrate that true freedom is about being accepted, through the scenarios that Ambrose Flack has written for them to endure. In The Strangers That Came to Town, the Duvitches become truly free at the finale of the story. In our own lives, we must ask: what can we do to help others become truly free?”
Perry’s essay discusses freedom in the context of Ambrose Flack’s short story The Strangers That Came to Town : acceptance is the key to being free. When the immigrant Duvitch family moved into a new town, they were not accepted by the community and were deprived of the freedom to live without shame and ridicule. However, when some townspeople reach out, the Duvitches feel empowered and relieved and are no longer afraid to go out and be themselves.
“Freedom is many things, but those issues that are often in the forefront of conversations these days include the freedom to choose, to be who you truly are, to express yourself and to live your life as you desire so long as you do not hurt or restrict the personal freedom of others. I’ve compiled a collection of powerful quotations on the meaning of freedom to share with you, and if there is a single unifying theme it is that we must remember at all times that, regardless of where you live, freedom is not carved in stone, nor does it come without a price.”
In her short essay, Herald contemplates on freedom and what it truly means. She embraces her freedom and uses it to live her life to the fullest and to teach those around her. She values freedom and closes her essay with a list of quotations on the meaning of freedom, all with something in common: freedom has a price. With our freedom, we must be responsible. You might also be interested in these essays about consumerism .
4. Authentic Freedom by Wilfred Carlson
“Freedom demands of one, or rather obligates one to concern ourselves with the affairs of the world around us. If you look at the world around a human being, countries where freedom is lacking, the overall population is less concerned with their fellow man, then in a freer society. The same can be said of individuals, the more freedom a human being has, and the more responsible one acts to other, on the whole.”
Carlson writes about freedom from a more religious perspective, saying that it is a right given to us by God. However, authentic freedom is doing what is right and what will help others rather than simply doing what one wants. If freedom were exercised with “doing what we want” in mind, the world would be disorderly. True freedom requires us to care for others and work together to better society.
“In my opinion, the concepts of freedom and liberty are what makes us moral human beings. They include individual capacities to think, reason, choose and value different situations. It also means taking individual responsibility for ourselves, our decisions and actions. It includes self-governance and self-determination in combination with critical thinking, respect, transparency and tolerance. We should let no stone unturned in the attempt to reach a state of full freedom and liberty, even if it seems unrealistic and utopic.”
Youssef’s essay describes the concepts of freedom and liberty and how they allow us to do what we want without harming others. She notes that respect for others does not always mean agreeing with them. We can disagree, but we should not use our freedom to infringe on that of the people around us. To her, freedom allows us to choose what is good, think critically, and innovate.
7 Prompts for Essays About Freedom

Freedom is quite a broad topic and can mean different things to different people. For your essay, define freedom and explain what it means to you. For example, freedom could mean having the right to vote, the right to work, or the right to choose your path in life. Then, discuss how you exercise your freedom based on these definitions and views.
The world as we know it is constantly changing, and so is the entire concept of freedom. Research the state of freedom in the world today and center your essay on the topic of modern freedom. For example, discuss freedom while still needing to work to pay bills and ask, “Can we truly be free when we cannot choose with the constraints of social norms?” You may compare your situation to the state of freedom in other countries and in the past if you wish.
A common saying goes like this: “Freedom is not free.” Reflect on this quote and write your essay about what it means to you: how do you understand it? In addition, explain whether you believe it to be true or not, depending on your interpretation.
Many contemporary issues exemplify both the pros and cons of freedom; for example, slavery shows the worst when freedom is taken away, while gun violence exposes the disadvantages of too much freedom. First, discuss one issue regarding freedom and briefly touch on its causes and effects. Then, be sure to explain how it relates to freedom.
Some believe that more laws curtail the right to freedom and liberty. In contrast, others believe that freedom and regulation can coexist, saying that freedom must come with the responsibility to ensure a safe and orderly society. Take a stand on this issue and argue for your position, supporting your response with adequate details and credible sources.
Many people, especially online, have used their freedom of speech to attack others based on race and gender, among other things. Many argue that hate speech is still free and should be protected, while others want it regulated. Is it infringing on freedom? You decide and be sure to support your answer adequately. Include a rebuttal of the opposing viewpoint for a more credible argumentative essay.
For your essay, you can also reflect on a time you felt free. It could be your first time going out alone, moving into a new house, or even going to another country. How did it make you feel? Reflect on your feelings, particularly your sense of freedom, and explain them in detail.
Check out our guide packed full of transition words for essays .If you are interested in learning more, check out our essay writing tips !

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >

5 Freedom and Equality
Elizabeth Anderson is Arthur F. Thurnau Professor and John Dewey Distinguished University Professor of Philosophy and Women's Studies at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
- Published: 05 October 2016
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Freedom and equality are often viewed as conflicting values. But there are at least three conceptions of freedom-negative, positive, and republican-and three conceptions of equality-of standing, esteem, and authority. Libertarians argue that rights to negative liberty override claims to positive liberty. However, a freedom-based defense of private property rights must favor positive over negative freedom. Furthermore, a regime of full contractual alienability of rights-on the priority of negative over republican freedom-is an unstable basis for a free society. To sustain a free society over time, republican liberty must take priority over negative liberty, resulting in a kind of authority egalitarianism. Finally, the chapter discusses how the values of freedom and equality bear on the definition of property rights. The result is a qualified defense of some core features of social democratic orders.
Freedom and equality are typically presented as opposing values. In the quick version of the argument, economic liberty—the freedom to make contracts, acquire property, and exchange goods—upsets substantive economic equality ( Nozick, 2013 : 160–164). Suppose some people sail to an uninhabited island and divide its territory and the provisions they brought into shares of equal value. If they are free to produce, trade, and accumulate property, some would rapidly get richer than others due to good luck and good choices, while others would become poor due to bad luck and bad choices. Any attempt to enforce strict material equality across large populations under modern economic conditions would require a totalitarian state. Gracchus Babeuf, a radical of the French Revolution, and the first modern advocate of strict material equality under state communism, understood this perfectly. He saw that the only way to ensure strict material equality was for the state to run society like an army—to control all property and production, assign everyone to their jobs, and control everyone’s thoughts (lest some get the ideas that they deserve more than others, or that they should be free to choose their own way of life) ( Babeuf, 1967 ; Buonarroti, 1836 ). He thought such equality was worth the sacrifice of freedom. Few who have actually lived under communism agree.
While the quick argument is true and of great historical importance, it does not address moderate types of egalitarianism. Virtually no one today advocates strict material equality. Social democrats, particularly in northern Europe, embraced private property and extensive markets well before the collapse of communism. Friedrich Hayek (1944) argued that social democratic experiments would lead societies down the slippery slope to totalitarianism. His prediction failed: moderate egalitarianism of the social democratic type has proved compatible with democracy, extensive civil liberties, and substantial if constrained market freedoms.
To make progress on the question of normative trade-offs between freedom and equality within the range of options for political economy credibly on the table, we must clarify our concepts. There are at least three conceptions of freedom—negative, positive, and republican—and three conceptions of equality—of standing, esteem, and authority. Republican freedom requires extensive authority egalitarianism. To block arguments that freedom requires substantial material equality, libertarians typically argue that rights to negative liberty override or constrain claims to positive liberty. This chapter will argue that, to the extent that libertarians want to support private property rights in terms of the importance of freedom to individuals, this strategy fails, because the freedom-based defense of private property rights depends on giving priority to positive or republican over negative freedom. Next, it is argued that the core rationale for inalienable rights depends on considerations of republican freedom. A regime of full contractual alienability of rights—on the priority of negative over republican freedom—is an unstable basis for a free society. It tends to shrink the domains in which individuals interact as free and independent persons, and expand the domains in which they interact on terms of domination and subordination. To sustain a free society over time, we should accept the priority of republican over negative liberty. This is to endorse a kind of authority egalitarianism. The chapter concludes with some reflections on how the values of freedom and equality bear on the definition of property rights. The result will be a qualified defense of some core features of social democratic orders.
1. Conceptions of Freedom and Equality
Let us distinguish three conceptions of freedom: negative freedom (noninterference), positive freedom (opportunities), and republican freedom (nondomination). Sarah has negative freedom if no one interferes with her actions. She has positive freedom if she has a rich set of opportunities effectively accessible to her. She has republican freedom if she is not dominated by another person—not subject to another’s arbitrary and unaccountable will.
These three conceptions of freedom are logically distinct. They are also somewhat causally independent: one can enjoy high degrees of any two of these freedoms at substantial cost to the third. Lakshmi could have perfect negative and republican freedom on an island in which she is the only inhabitant. No one else would be interfering with her actions or dominating her. She would have little positive freedom, however, since most opportunities are generated in society with others. Maria could have high degrees of negative and positive freedom while lacking republican freedom. She could be the favorite of an indulgent king, who showers her with wealth and privileges, and permits her to say and do what she likes—but who could throw her in his dungeon at his whim. Finally, Sven could have high degrees of positive and republican freedom while being subject to many constraints on his negative liberty. He could reside in an advanced social democratic state such as Norway, where interpersonal authority is constrained by the rule of law (so he is not subject to anyone’s arbitrary will), and a rich set of opportunities is available to all, at the cost of substantial negative liberty constraints through high levels of taxation and economic regulation.
Traditionally, most discussions of freedom focused on the contrast between negative and positive freedom. The recent revival of the republican conception of freedom as nondomination adds an important dimension to thinking about the lived experience of unfreedom and the social conditions of freedom. Pettit (1997 : 22–25) stresses the contrast between negative and republican freedom in the case where a dominator could but chooses not to interfere with subordinates. He argues that such vulnerability to interference can make subordinates submissive, self-censoring, and sycophantic toward their superiors. It is also important to consider some differences between negative liberty constraints imposed by a dominating power and those imposed in accordance with the rule of law by a liberal democratic authority. Domination is often personal: think of the husband under the law of coverture or the violent husband today, the slaveholder, the bullying, micromanaging boss. Rule-of-law constraints are impersonal and of general applicability. This arm’s-length character of the rule of law often relieves people of the humiliation of submission to domination, since they know “it’s not about me.” Dominating interference can arrive unannounced. Rule-of-law constraints must be publicized in advance, giving people time to figure out how to pursue their projects in ways that avoid interference. Dominating interference does not have to justify itself. Rule-of-law constraints in a liberal democratic order must appeal to public reasons, which limits the constraints that can be imposed. Dominating interference is unaccountable. Applied rule-of-law constraints in a democracy are subject to appeal before an impartial adjudicator, and those who enact them can be removed from power by those to whom the constraints apply.
These remarks apply to ideal types only. Actually existing formally liberal democratic regimes have devised innumerable ways to exercise domination under the guise of the rule of law. It is possible to devise a set of impersonal, generally applicable, publicized laws that regulate conduct so minutely that almost anyone innocently going about their business could be found to have run afoul of one of them. Such is the case with traffic laws in the United States. If enforcement action on the trivial infringements were limited to mere warnings or token fines, as in police stops to warn drivers that their tail lights are broken, they could be a service to the drivers and others on the road. Often, however, such traffic stops are a mere pretext for police exercise of arbitrary power to harass, intimidate, invade privacy, and seize people’s property without due process of law. 1 In other cases, impersonal rule-of-law regulations impose constraints so out of touch with local conditions, with such draconian penalties for noncompliance, that enforcement amounts to domination. Such is the case with the high-stakes testing regime imposed by the federal government under No Child Left Behind, with uniform arbitrary progress goals foisted on local school districts without any empirical research demonstrating that these goals were feasible. In some cases, the NCLB regime has created a culture of intimidation and cheating ( Aviv, 2014 ). This is a centralized planning regime akin to the five-year plans of communist states. In both cases, the imposition of goals plucked out of thin air in combination with severe sanctions is premised on the assumption that lack of sufficient will is the primary obstacle to progress—an assumption that rationalizes domination of those required to meet the goals.
We should be skeptical of attempts to operationalize the conditions for nondomination in formal terms. Powerful agents are constantly devising ways to skirt around formal constraints to dominate others. Republican freedom is a sociologically complex condition not easily encapsulated in any simple set of necessary and sufficient conditions, nor easily realized through any particular set of laws.
Turn now to equality. In other work, I have argued that the conceptions of equality relevant for political purposes are relational: they characterize the types of social relations in which members of society stand to one another ( Anderson, 2012b ; Anderson, 2012a ). Relational equality is opposed to social hierarchy. Three types of hierarchy—of standing, esteem, and authority—are particularly important. In hierarchies of standing, agents (including the state) count the interests of superiors highly, and the interests of inferiors for little or nothing. In hierarchies of esteem, some groups monopolize esteem and stigmatize their inferiors. In hierarchies of authority, dominant agents issue arbitrary and unaccountable commands to subordinates, who must obey on pain of sanctions. Egalitarians oppose such hierarchies and aim to replace them with institutions in which persons relate to one another as equals. For example, they want members of society to be treated as equals by the state and in institutions of civil society (standing); to be recognized as bearing equal dignity and respect (esteem); to have equal votes and access to political participation in democratic states (authority). Each of these conceptions of relational equality is complex and implicates numerous features of the social setting.
These three types of hierarchy usually reinforce each other. Groups that exercise power over others tend to enjoy higher esteem, and often use their power to exact special solicitude for their interests from others. Sometimes they come apart. Upper-class married women under the law of coverture enjoyed high esteem and standing, but had little authority and were subordinate to their husbands and to men generally. Some ethnic minorities, such as Chinese Malaysians, enjoy high standing and authority through their ownership and control of most businesses in Malaysia, but are racially stigmatized in Malaysian society.
Given this array of distinct conceptions of freedom and equality, it is harder to argue that freedom and equality are structurally opposed. There is a deep affinity between republican freedom as nondomination and authority egalitarianism. These are not conceptually identical. Domination can be realized in an isolated, transient interpersonal case (consider a kidnapper and his victim). Authoritarian hierarchy is institutionalized, enduring, and group-based. Yet authority hierarchies cause the most important infringements of republican freedom. Historically, the radical republican tradition, from the Levellers to the radical wing of the Republican party through Reconstruction, saw the two causes of freedom and equality as united: to be free was to not be subject to the arbitrary will of others. This required elimination of the authoritarian powers of dominant classes, whether of the king, feudal landlords, or slaveholders. Republican freedom for all is incompatible with authoritarian hierarchy and hence requires some form of authority egalitarianism.
Authority egalitarianism so dominates public discourse in contemporary liberal democracies that few people openly reject it. However, conservatives have traditionally supported authority hierarchy, and continue to do so today, while often publicizing their views in other terms. For example, conservatives tend to defend expansive discretionary powers of police over suspects and employers over workers, as well as policies that reinforce race, class, and gender hierarchies, such as restrictions on voting, reproductive freedom, and access to the courts.
The connections between relational equality and conventional ideas of equality in terms of the distribution of income and wealth are mainly causal. Esteem egalitarians worry that great economic inequality will cause the poor to be stigmatized and the rich glorified simply for their wealth. Authority egalitarians worry that too much wealth inequality empowers the rich to turn the state into a plutocracy. This radical republican objection to wealth inequality is distinct from contemporary notions of distributive justice, which focus on the ideas that unequal distributions are unfair, and that redistribution can enhance the consumption opportunities of the less well off. 2 The latter notions are the concern of standing egalitarianism. Concern for distributive justice—specifically, how the rules that determine the fair division of gains from social cooperation should be designed—can be cast in terms of the question: what rules would free people of equal standing choose, with an eye to also sustaining their equal social relations? The concern to choose principles that sustain relations of equal standing is partly causal and partly constitutive. In a contractualist framework, principles of distributive justice for economic goods constrain the choice of regulative rules of property, contract, the system of money and banking, and so forth, and do not directly determine outcomes ( Rawls, 1999 : 47–49, 73–76). From this point of view, certain principles, such as equality of rights to own property and make contracts, are constitutive of equal standing.
Absent from this list of conceptions of equality is any notion of equality considered as a bare pattern in the distribution of goods, independent of how those goods were brought about, the social relations through which they came to be possessed, or the social relations they tend to cause. Some people think that it is a bad thing if one person is worse off than another due to sheer luck ( Arneson, 2000 ; Temkin, 2003 ). I do not share this intuition. Suppose a temperamentally happy baby is born, and then another is born that is even happier. The first is now worse off than the second, through sheer luck. This fact is no injustice and harms no one’s interests. Nor does it make the world a worse place. Even if it did, it would still be irrelevant in a liberal political order, as concern for the value of the world apart from any connection to human welfare, interests, or freedom fails even the most lax standard of liberal neutrality.
2. A Freedom-based Justification of Property Must Favor Positive or Republican over Negative Freedom
The conventional debate about freedom and distributive equality is cast in terms of the relative priority of negative and positive freedom. If negative liberty, as embodied in property rights, trumps positive freedom, then taxation for purposes of redistribution of income and wealth is unjust ( Nozick, 2013 : 30–34, 172–173; Mack, 2009 ).
One way to motivate the priority of negative freedom is to stress the normative difference between constraints against infringing others’ liberties, which do not require anyone to do anything (merely to refrain from acting in certain ways), and positive requirements to supply others with goods, which carry the taint of forced labor. This argument applies at most to taxation of labor income. Nozick (2013 : 169) tacitly acknowledged this point in claiming that “Taxation of earnings from labor is on a par with forced labor” (emphasis added). People receive passive income (such as interest, mineral royalties, capital gains, land rents, and bequests) without lifting a finger, so taxation of or limitations on such income does not amount to forcing them to work for others. Such taxation is the traditional left-libertarian strategy for pursuing distributive equality consistent with negative liberty constraints. Land and natural resource taxes can be justified in Lockean terms, as respecting the property rights in the commons of those who lost access to privately appropriated land. Paine’s classic version of this argument (1796) claims that Lockean property rights should be unbundled: just appropriation entitles owners to use the land and exclude others, but not to 100 percent of the income from land rents. Citizens generally retain rights to part of that income stream. This grounds a moderate egalitarianism without resort to the extravagant premises needed to support a more demanding distributive equality in libertarian terms, as for instance in Otsuka (1998) .
Arguments for the priority of negative over positive freedom with respect to property rights run into more fundamental difficulties. A regime of perfect negative freedom with respect to property is one of Hohfeldian privileges only, not of rights. 3 A negative liberty is a privilege to act in some way without state interference or liability for damages to another for the way one acts. The correlate to A’s privilege is that others lack any right to demand state assistance in constraining A’s liberty to act in that way. There is nothing conceptually incoherent in a situation where multiple persons have a privilege with respect to the same rival good: consider the rules of basketball, which permit members of either team to compete for possession of the ball, and even to “steal” the ball from opponents. If the other team exercises its liberty to steal the ball, the original possessor cannot appeal to the referee to get it back.
No sound argument for a regime of property rights can rely on considerations of negative liberty alone. Rights entail that others have correlative duties. To have a property right to something is to have a claim against others, enforceable by the state, that they not act in particular ways with respect to that thing. Property rights, by definition, are massive constraints on negative liberty: to secure the right of a single individual owner to some property, the negative liberty of everyone else—billions of people—must be constrained. Judged by a metric of negative liberty alone, recognition of property rights inherently amounts to a massive net loss of total negative freedom. The argument applies equally well to rights in one’s person, showing again the inability of considerations of negative liberty alone to ground rights. “It is impossible to create rights, to impose obligations, to protect the person, life, reputation, property, subsistence, or liberty itself, but at the expense of liberty” ( Bentham, 1838–1843 : I.1, 301).
What could justify this gigantic net loss of negative liberty? If we want to defend this loss as a net gain in overall freedom, we must do so by appealing to one of the other conceptions of freedom—positive freedom, or republican freedom. Excellent arguments can be provided to defend private property rights in terms of positive freedom. Someone who has invested their labor in some external good with the aim of creating something worth more than the original raw materials has a vital interest in assurance that they will have effective access to this good in the future. Such assurance requires the state’s assistance in securing that good against others’ negative liberty interest in taking possession of it. To have a claim to the state’s assistance in securing effective access to a good, against others’ negative liberty interests in it, is to have a right to positive freedom .
Considerations of republican freedom also supply excellent arguments for private property. In a system of privileges alone, contests over possession of external objects would be settled in the interests of the stronger parties. Because individuals need access to external goods to survive, the stronger could then condition others’ access on their subjection to the possessors’ arbitrary will. Only a system of private property rights can protect the weaker from domination by the stronger. The republican argument for rights in one’s own body follows even more immediately from such considerations, since to be an object of others’ possession is per se to be dominated by them.
Thus, there are impeccable freedom-based arguments for individual property rights. But they depend on treating individuals’ interests in either positive or republican freedom as overriding others’ negative liberty interests. Against this, libertarians such as Nozick could argue that the proper conception of negative liberty is a moralized one, such that interference with others’ negative freedom does not count as an infringement of liberty unless it is unjust . Such a moralized view of liberty is implicit in Nozick’s moralized accounts of coercion and voluntariness (1969: 450; 2013: 262–263). Hence, no genuine sacrifice of others’ negative liberty is involved in establishing a just system of property rights.
In response, we must consider what could justify claims to negative liberty rights in property. The problem arises with special clarity once we consider the pervasiveness of prima facie conflicts of property rights, as in cases of externalities settled by tort law or land use regulation. Whenever prima facie negative liberty rights conflict, we must decide between them either by weighing their value in terms of non-liberty considerations, or in terms of some other conception of freedom—positive or republican. If we appeal to considerations other than freedom, we treat freedom as subordinate to other values. For example, desert-based arguments for property rights, which point to the fact that the individual created the object of property, or added value to it through their labor—treat freedom as subordinate to the social goal of rewarding people according to their just deserts. Similarly, Nozick’s resolution of conflicting claims in terms of a moralized notion of negative liberty covertly imports utilitarian considerations to do the needed normative work ( Fried, 2011 ). To base the justification of property rights on considerations of freedom itself, we must regard freedom as a value or interest and not immediately as a right. That is, we must regard freedom as a nonmoralized consideration. Otherwise we have no basis in freedom for justifying property rights or resolving property disputes when uses of property conflict.
A contractualist framework can offer a freedom-based justification of private property rights that departs from libertarian premises. In this picture, the principles of right are whatever principles persons would rationally choose (or could not reasonably reject) to govern their interpersonal claims, given that they are, and understand themselves to be, free and equal in relation to one another. If they chose a regime of privileges only, this would amount to anarchist communism, in which the world is an unregulated commons. Such a regime would lead to depleted commons—razed forests, extinct game, destroyed fisheries. It would also give everyone a greater incentive to take what others produced than to produce themselves. Few would invest their labor in external things, everyone would be poor, and meaningful opportunities would be rare. By contrast, adoption of an institutional scheme of extensive private property rights, including broad freedoms of exchange and contract, would create vastly richer opportunities for peaceful and cooperative production on terms of mutual freedom and equality. All have an overwhelming common interest in sustaining an institutional infrastructure of private property rights that generates more positive freedom —better opportunities—for all.
This argument justifies rights to negative freedom with respect to external property in terms of positive freedom. It does not suppose, as libertarian arguments do, that the liberty interests of the individual override the common interest. Rather, it claims that people have a common interest in sustaining a regime of individual rights to property. On this view, individual rights are not justified by the weight of the individual interest they protect, but by the fact that everyone has a common interest in relating to each other through a shared infrastructure of individual rights ( Raz, 1994 ). The infrastructure of private property rights is a public good, justified by its promotion of opportunities—of positive freedom—for all. A well-designed infrastructure provides a framework within which individuals can relate to one another as free and equal persons.
So far, the argument is one of evaluative priority only. It has been argued that if one wants to justify private property rights in terms of freedom, one must grant evaluative priority to positive or republican over negative freedom. Discussion of the implications of this argument for the content of a just scheme of private property rights—to whether a just scheme would look more libertarian, or more egalitarian—will be postponed to the last section of this chapter.
3. Republican Freedom and the Justification of Inalienable Rights
If negative freedom were the only conception of freedom, it would be difficult to offer a freedom-based justification of inalienable rights. If Sarah’s right is inalienable, then she is immune from anyone changing her right. This could look attractive, except that it entails that she is disabled from changing her own right—that she lacks the power to waive others’ correlative duties to respect that right ( Hohfeld, 1913–1914 : 44–45, 55). This is a constraint on her higher-order negative liberty. This liberty is higher-order because it concerns not the liberty to exercise the right, but the liberty over the right itself.
Inalienable rights might also leave the individual with an inferior set of positive freedoms than if her rights are alienable. Contracts involve an exchange of rights. There is a general presumption that voluntary and informed contracts produce gains for both sides. To make Sarah’s right inalienable prevents her from exchanging it for rights she values more, and thereby reduces her opportunities or positive freedom.
However, there are strategic contexts in which individuals can get much better opportunities if some of their rights are inalienable ( Dworkin, 1982 : 55–56). In urgent situations, when one party cannot hold out for better terms, the other can exploit that fact and offer terms that are much worse than what they would otherwise be willing to offer. Peter, seeing Michelle drowning, might condition his tossing her a life ring on her agreeing to become his slave, if her rights in herself were fully alienable. But if she had an inalienable right to self-ownership, Peter could not exploit her desperation to subject her to slavery, but would offer her better terms.
Such considerations leave libertarians torn between accepting and rejecting the validity of voluntary contracts into slavery. 4 Those tempted by the negative liberty case in favor of full alienability of rights should recall the antislavery arguments of the Republican Party before the Civil War. Republicans objected to slavery because it enabled slaveholders to subordinate even free men to their dominion. The Slave Power—politically organized proslavery interests—undermined the republican character of government. It suppressed the right to petition Congress (via the gag rule against hearing antislavery petitions), censored the mail (against antislavery literature), and forced free men, against their conscience, to join posses to hunt down alleged fugitive slaves. It violated equal citizenship by effectively granting additional representation to slaveowners for their property in slaves (via the three-fifths rule for apportioning representatives). By insisting on the right to hold slaves in the territories, the Slave Power threatened the prospects of free men to secure their independence by staking out individual homesteads. Slave plantations would acquire vast territories, crowding out opportunities for independent family farms. Chattel slavery of blacks threatened to reduce whites to wage slaves, subordinate to their employers for their entire working lives ( Foner, 1995 ).
The Republican antislavery argument is similar to the positive liberty argument above: it stresses how the constitution of a scheme of liberty rights provides the public infrastructure for a society of free and equal persons. The critical point is to institute a scheme of individual rights that can sustain relations of freedom and equality—understood as personal independence and nondomination—among persons. While the Republican Party limited its arguments to securing relations of nondomination among men, feminist abolitionists extended their arguments to married women, who, like slaves, lacked the rights to own property, make contracts, sue and be sued in court, keep their earned income, and move freely without getting permission from their masters (husbands) ( Sklar, 2000 ). Like the positive liberty argument for individual rights, it recognizes how individuals have a vital stake in other people’s liberty rights being secure against invasion or appropriation by others. The stability of this public infrastructure of freedom depends on individual rights being inalienable.
It is to no avail to reply that a libertarian scheme of fully alienable rights that permits voluntary slavery would reject the forced slavery of the antebellum South, along with the violations of free speech and republican government needed to secure the institution of slavery against state “interference.” For the Republicans’ antislavery argument was about the stability of certain rights configurations under realistic conditions. It was that a society that enforces rights to total domination of one person over another will not be able to sustain itself as a free society of equals over time. How the dominators acquired those rights, whether by force or contract, is irrelevant to this argument. Slaveholders, in the name of protection of their private property rights, used the immense economic power they gained from slavery to seize the state apparatus and crush republican liberties. This is a version of the classical republican antiplutocratic argument against extreme wealth inequality. But it was also directed toward the threat that slavery posed to economic independence of free men—to their prospects for self-employment, for freedom from subjection to an employer.
Debra Satz ( 2010 : 180, 232n40), citing Genicot (2002) , offers a similar argument against debt bondage, adapted to contemporary conditions. Two dynamics threaten the ability of workers to maintain their freedom if they have the power to alienate their right to quit to their creditor/employer. First, the availability of debt bondage may restrict opportunities to obtain credit without bondage. Bondage functions as a guarantee against destitute debtors’ default: they put up their own labor as collateral. However, the institution of debt bondage makes it more difficult to establish formalized credit and labor markets by which alternative methods of promoting loan repayment (such as credit ratings and garnishing wages) make credit available without bondage.
Second, living under conditions of bondage makes people servile, humble, and psychologically dependent—psychological dispositions that they are likely to transmit to their children. Servile people lack a vivid conception of themselves as rights-bearers and lack the assertiveness needed to vindicate their rights. Moreover, the poor are unlikely to hang on to their freedom for long, given their strategic vulnerability when others are already giving up their alienable rights under hard bargaining. A system of fully alienable libertarian rights is thus liable to degenerate into a society of lords and bondsmen, unable to reproduce the self-understandings that ground libertarian rights. A free society cannot be sustained by people trained to servility and locked into strategic games where some individuals’ alienation of their liberty rights puts others’ liberties at risk ( Satz, 2010 : 173–180).
This argument generalizes. Workers may have a permanent interest in retaining other rights besides the formal right to quit, so as to prevent the authority relations constitutive of employment from conversion into relations of domination. For example, they have a permanent interest against sexual and other forms of discriminatory harassment. Under U.S. law, workers have inalienable rights against such degrading treatment. In addition, since lower-level workers have minimal freedom at work, but spend their workdays following others’ orders, they have a vital interest in secure access to a limited length of the working day—in having some hours in which they act under their own direction. This is the purpose of maximum hours laws, which forbid employers from conditioning a job offer on having to work too many hours per week. The logic in both cases is strategic: once employers are free to make such unwelcome “offers” (or rather, threats), the decision of some to accept removes better offers from other workers’ choice sets, and thereby deprives them of both positive and republican freedom.
As in the case of contractual slavery, libertarians are divided over this type of argument. Mill (1965 : XI, §12) supported maximum hours laws as an exception to laissez faire, on strategic grounds. The early Nozick would probably have accepted laws against sexual harassment, because conditioning a job on putting up with a hostile atmosphere or compliance with the boss’s sexual demands makes workers worse off relative to a normative baseline of not being subject to unwelcome sexual affronts, and hence counts as coercive. 5 However, the Nozick of Anarchy, State, and Utopia would have rejected such laws as interfering with freedom of contract, given that he accepted contractual slavery. Eric Mack (1981) also upholds an absolute principle of freedom of contract, and so would be committed to the alienability of rights against sexual harassment and even assault in labor contracts.
Mack recognizes that it is disingenuous to claim that restraints on freedom of contract that improve workers’ choice sets violate their freedom of contract. Hence minimum wage laws, if they only raise wages and do not increase unemployment, do not violate workers’ rights. His complaint is that such restraints violate employers’ rights, coercing them into offering better terms to workers than they wanted to make. They treat employers as mere resources to be used by others in pursuit of goals the employer does not share ( Mack, 1981 : 6–8). This argument, if applied to laws against sexual harassment and similar forms of personal domination, is bizarre. One would have thought that employers who threaten their workers with job loss if they do not put up with sexual subordination are treating them as mere resources to be used by the employer in pursuit of goals the workers do not share.
Mack contrasts a morality of “social goals” with one of deontological side constraints, claiming that the former treats people as mere means and the latter treats people as ends in themselves. A deontology of complete alienability of rights in one’s person, however, leads to a society in which some are made others’ partial or total property, reduced to instruments of the others’ arbitrary wills, and deprived of all three kinds of freedom. That they entered such a state by choice does not undermine the conclusion. Rather, it proves that liberty does not only upset equality—it also upsets liberty. To be more precise: negative liberty upsets liberty.
Suppose our “social goal” is to sustain a society in which individuals relate to each other as free persons—which is to say, as equal and independent, not subject to the arbitrary will of others? That would seem to be not merely unobjectionable to a libertarian, but the very point of a libertarian view. The scheme of rights required to realize such a society cannot be devised without tending to the likely consequences of choices made within it. The infrastructure of rights needed to sustain a society in which individuals relate to each other as free persons requires that the rights most fundamental to the ability to exercise independent agency be inalienable, so that no one becomes subject to another’s domination. Thus, the fundamental freedom-based rationale for inalienable rights is based on considerations of republican freedom. It entails that a free society requires substantial authority egalitarianism.
4. Freedom, Equality, and the Definition of Property Rights
I conclude with some remarks on the definition of property rights. Much libertarian writing supposes that as soon as an argument is given to justify a right to private property in something, this justifies all the classical incidents of property—including rights to exclude, use, alter, and destroy it, to give, barter, or sell all or any parts of it or any rights to it, to rent, loan, or lease it for income, all with unlimited duration ( Honoré, 1961 ). Why is a separate argument not required for each of these incidents? Shouldn’t the nature and function of the property in question play a role in determining which rights are attached to it, and for how long? For example, while the right to destroy is easily granted to most chattels, the positive liberty of future generations provides compelling reasons to deny it to property in land and water resources. Such interests also justify limits on dividing property into parcels or rights bundles too small to use ( Heller, 1998 ). It is also questionable how any case for intellectual property rights can be grounded in considerations of negative liberty, given that a regime of universal privilege with respect to ideas does not interfere with the liberties of authors and inventors to create and use their works. A freedom-based case for intellectual property can only be made on positive liberty grounds, and then only justify limited terms for copyrights and patents, given the role of the intellectual commons in expanding cultural and technological opportunities.
A just system of legal rules of property, contract, banking, employment, and so forth constitutes a public infrastructure that can sustain a free society of equals over time. Since, in a well-ordered society, members sustain this infrastructure by paying taxes and complying with its rules, each member has a legitimate claim that the rules secure their access to opportunities generated by that infrastructure. The case is no different from the system of public roads. Fair distributions of access to opportunity matter here, too. A system of roads that accommodates only cars, with no pedestrian sidewalks, crosswalks, and stop lights, denies adequate opportunities for freedom of movement to those without cars. It would be absurd for drivers to object to pedestrian infrastructure because it interferes with their negative liberty. They have no claim that the publicly supported infrastructure be tailored to their interests alone.
Arguments over the rules defining private property rights are comparable. Since everyone needs effective access to private property to secure their liberty interests, property rules should ensure such access to all. Such distributive concerns might be partially secured, for example, by way of estate taxes, the revenues of which are distributed to all in the form of social insurance. As Paine (1796) argued, such taxes do not infringe private property rights, but rather constitute a partial unbundling of property rights to secure the legitimate property rights of others. That one of the incidents of property (protecting wealth interests) partially expires upon the death of the owner is no more a violation of property rights than the fact that patents expire after twenty years: such rules simply define the scope of the right in the first instance.
Three features of the public infrastructure of economic rights in social democratic orders promote, and arguably are needed to secure, decent opportunities for all to live on terms of republican freedom and hence authority egalitarianism with respect to everyone else. First, as argued above, individuals need a robust set of market inalienable rights, to avoid domination by their employers. Second, as Paine argued, they need a universal system of social insurance to secure their independence in cases of inability to work or to find work ( Anderson, 2008 ). Third, under modern conditions, they need free, universal education, to avoid domination by parents and others, and to secure a self-conception as someone with rights of personal independence. Each of these can be understood as individual property rights, secured via partial unbundling of classical private property rights. None require state ownership or management of productive enterprises, or bureaucratic administration of individuals’ lives. They merely constitute an alternative type of private property regime. It is superior to a libertarian one on grounds of freedom , because it better secures positive and republican freedom for all. Since any credible freedom-based argument for private property rights must already recognize the normative priority of positive and republican freedom over negative freedom, it is hard to run credible freedom-based arguments against these core institutions of social democracy at the level of abstraction at which these arguments proceed in political philosophy. Of course, the details of any particular implementation of these institutions may have many objectionable features, as is also true of private employment relations. Because the conditions of republican and positive freedom are sociologically complex, we cannot expect arguments at a high level of abstraction to settle disputes over the details of a property regime suitable for a free society of equals. The current chapter demonstrates that the ideal of a free society of equals is not an oxymoron: not only is relational equality not fundamentally opposed to freedom, in certain senses equality is needed for freedom. Inequality upsets liberty.
Ferguson, Missouri, the site of protests triggered by the police homicide of a black man stopped for jaywalking, illustrates this phenomenon. With a declining tax base, Ferguson turned to police to raise revenue by incessantly harassing mostly black citizens with traffic citations. They turned citations into the second-highest source of city revenue by issuing an average of three warrants and $321 in fines per household . Poor individuals who cannot pay the fines and fail to appear in court to explain why are often arrested and thrown into jail for weeks ( Tabarrok, 2014 ). By comparison to such gross violations of republican freedom, the negative liberty constraints of a regular tax raising the same total revenue are trivial.
Rawls clearly distinguished the republican concern that extreme wealth inequality leads to plutocracy from the egalitarian interest in the fair division of income and wealth as such. This is why he grounded progressive inheritance taxes in the principle of equal basic liberties (including the fair value of political liberties—an antiplutocratic principle), rather than the difference principle, which takes the fair distribution of income and wealth as its direct object ( Rawls, 1999 : 245, 70).
For the classic distinction between privileges and rights, see Hohfeld, 1913–1914 : 30–44.
For libertarians who oppose contractual slavery, see Mill (1859 : 184) and Rothbard (1998 : 40–41). For those who think slave contracts should be enforceable, see Nozick (2013 : 331), Alexander (2010) , and Block (2003) . Locke, an inspiration to libertarians, rejected contractual slavery; see Locke, 1824b : §23 and more aptly Locke, 1824a : §42. However, both his arguments rely on non-libertarian premises: in the Second Treatise , against a right to suicide; in the First Treatise , asserting a positive right to charity.
Nozick (1969) argues that a proposal can count as a threat, and hence be coercive, even if the proposer has a legal right to carry out the negative consequence for the recipient (452), and that such cases of coercion can include employer threats to fire workers if they fail to comply with the employer’s wishes (for example, by voting to be represented by a union) (453). Hence, in his early view, employers can coerce workers even if workers have exit rights and employers have the right to fire them at will. See also Flanigan (2012) , arguing that sexual harassment at work constitutes wrongful coercion if the empirical expectation for the job does not include sex work. This allows employers to get off the sexual harassment hook simply by listing sexual harassment in boilerplate contractual language for all employees, even for jobs such as cashier and carpenter that have nothing to do with performing sexual services. Still, it reflects some appreciation by a libertarian, however ambivalent, of the reality of workplace coercion.
Alexander, Larry , 2010. Voluntary enslavement. San Diego Legal Studies Paper No. 10–042. http://ssrn.com/abstract=1694662 .
Anderson, Elizabeth , 2008 . How should egalitarians cope with market risks? Theoretical Inquiries in Law , 9, pp.61–92.
Google Scholar
Anderson, Elizabeth , 2012 a. Equality. In: David Estlund , ed. The Oxford Handbook of Political Philosophy . New York: Oxford University Press. pp.40–57.
Google Preview
Anderson, Elizabeth , 2012 b. The fundamental disagreement between luck egalitarians and relational egalitarians. Canadian Journal of Philosophy , S36, pp.1–23.
Arneson, Richard , 2000 . Luck egalitarianism and prioritarianism. Ethics , 110, pp.339–349.
Aviv, Rachel , 2014 . Wrong answer. The New Yorker , 21 July. http://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2014/07/21/wrong-answer .
Babeuf, Gracchus , 1967 . The defense of Gracchus Babeuf before the High Court of Vendôme . John Anthony Scott , ed. and trans. Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press.
Bentham, Jeremy , 1838–43. Principles of the civil code. In: John Bowring , ed. The works of Jeremy Bentham, published under the superintendence of his executor, John Bowring . Vol. 1. Edinburgh: William Tate. pp.297–364.
Block, Walter , 2003 . Toward a libertarian theory of inalienability: a critique of Rothbard, Barnett, Smith, Kinsella, Gordon, and Epstein. Journal of Libertarian Studies , 17(2), pp.39–85.
Buonarroti, Philippe , 1836 . Buonarroti’s history of Babeuf’s conspiracy for equality . Bronterre [pseud.]. London: H. Hetherington.
Dworkin, Gerald , 1982 . Is more choice better than less? Midwest Studies in Philosophy , 7, pp.47–61.
Flanigan, Jessica , 2012. Workplace coercion. http://bleedingheartlibertarians.com/2012/03/workplace-coercion/ . Posted on 12 March 2012; Accessed on: 29 July 2014.
Foner, Eric , 1995 . Free soil, free labor, free men: the ideology of the Republican Party before the Civil War . New York: Oxford University Press.
Fried, Barbara , 2011 . Does Nozick have a theory of property rights? In: Ralf Bader and John Meadowcraft , eds. The Cambridge companion to Nozick’s Anarchy, state and utopia. New York and Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. Http://ssrn.com/abstract=1782031 .
Genicot, Garance , 2002 . Bonded labor and serfdom: a paradox of voluntary choice. Journal of Development Economics , 67(1), pp.101–127.
Hayek, Friedrich A. , 1944 . The road to serfdom . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Heller, Michael , 1998 . The tragedy of the anticommons: property in the transition from Marx to markets. Harvard Law Review , 111, pp.621–688.
Hohfeld, Wesley , 1913– 1914 . Some fundamental legal conceptions as applied in judicial reasoning. Yale Law Journal , 23, pp.16–59.
Honoré, Anthony , 1961 . Ownership. In: Anthony G. Guest , ed. Oxford essays in jurisprudence . Oxford: Clarendon Press. pp.107–147.
Locke, John , 1824 a. First treatise of government. In: The works of John Locke in nine volumes . vol. 4. 12th ed. London: Rivington. pp.212–337.
Locke, John , 1824 b. Second treatise of government. In: The works of John Locke in nine volumes , vol. 4. 12th ed. London: Rivington. pp.338–485.
Mack, Eric , 1981 . In defense of “unbridled” freedom of contract. American Journal of Economics and Sociology , 40(1), pp.1–15.
Mack, Eric , 2009 . Individualism and libertarian rights. In: Thomas Christiano and John Christman , eds. Contemporary debates in political philosophy . Malden, MA: Wiley-Blackwell. pp.119–136.
Mill, John Stuart , 1859 . On liberty . London: J. W. Parker and Son.
Mill, John Stuart , 1965 . Principles of political economy . Vol. 3 of Collected works of John Stuart Mill , edited by J. M. Robson . Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
Nozick, Robert , 1969 . Coercion. In: Sydney Morganbesser , Patrick Suppes , and Morton White , eds. Philosophy, science, and method: essays in honor of Ernest Nagel . New York: St. Martin’s Press. pp.440–472.
Nozick, Robert , 2013 . Anarchy, state, and utopia . New York: Basic Books.
Otsuka, Michael , 1998 . Self-ownership and equality: a Lockean reconciliation. Philosophy and Public Affairs , 27(1), pp.65–92.
Paine, Thomas , 1796. Agrarian justice. http://www.ssa.gov/history/paine4.html . Accessed on 27 July 2012.
Pettit, Philip , 1997 . Republicanism: a theory of freedom and government . New York: Oxford University Press.
Rawls, John , 1999 . A theory of justice . Rev. ed. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Raz, Joseph , 1994 . Rights and individual well-being. In: Ethics in the public domain . Oxford: Clarendon. pp.44–59.
Rothbard, Murray , 1998 . The ethics of liberty . Rev. ed. New York: New York University Press.
Satz, Debra , 2010 . Why some things should not be for sale: the moral limits of markets . Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press.
Sklar, Kathryn Kish , 2000 . Women’s rights emerges within the anti-slavery movement, 1830–1870: a brief history with documents . Boston: Bedford/St. Martin’s.
Tabarrok, Alex , 2014. Ferguson and the modern debtor’s prison. http://marginalrevolution.com/marginalrevolution/2014/08/ferguson-and-the-debtors-prison.html . Posted on 21 August 2014; Accessed on 22 August 2014.
Temkin, Larry , 2003 . Egalitarianism defended. Ethics , 113, pp.764–782.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Essay Guides
- Other Essays
How to Write a Freedom Essay
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
It is hard to find an assignment duller than writing an essay. A freedom essay was my last task that I had performed thanks to lots of online sources and examples given on the Internet. How did I cope with it? I can share my plan of actions with you and I hope it will help to save your time and efforts. When I was a child there was a movie called “Braveheart”. Maybe you haven’t heard of it but people around me adored that cool epic war film with Mel Gibson . There was an episode when during horrible tortures Mel screamed “Freedom!” I thought that he had gone out of his mind. What was the point of being free and fighting for rights when you wouldn’t have a chance to live? When I got the task I decided to watch the whole movie and finally understood that our freedom really matters. That’s why firstly I started to look for the definition of the word “freedom”. I think that the primary thing is to find out what your topic means because if you don’t understand the meaning of the “freedom” concept, you’d hardly succeed. So, freedom is a state of mind, it is a right to make a choice, to be yourself. It depends on many things - the epoch and the culture. I’ve chosen several definitions of the word “freedom”– the philosophical, the psychological and the juridical. I considered my essay just a story. It simplifies the task. I imagined that I had to tell a story, that my assignment wasn’t retelling the collected information. It should be a story on the topic “Freedom”.
Don’t Forget About Boring Rules Which Steal Your Freedom
I wondered why a student hates academic writing. When I had written my first essay I realized why people hate coping with it. My personal experience showed that I didn’t like to write essays because of the following reasons:
- It’s hard to concentrate on the topic when you don’t like or even don’t understand it. Firstly, my tutor didn’t allow me to choose the theme to discuss and I had to squeeze ideas from nowhere.
- Tutors ask to write about the things THEY want. That’s a horrible mistake because a person has no chance to choose and get creative. There is no freedom.
- I tried to get an “A” instead of writing something really qualitative and interesting.
- The topic wasn’t catchy and I wanted to get rid of it as soon as possible.
- I wanted to post my pictures on Instagram more than to deal with the paper.
- I HAD to follow someone’s rules. Format, style, number of pages and words and a great number of other things irritate greatly.
I decided to find the right method of approach. I think that when a person takes a task as something pleasant, not just a duty, it will be much easier to cope with it.
Helpful Tips on Writing a Successful Freedom Essay
I decided to work out my rules which would help to write freely and not fear the task. Here they are! Think that it’s not an essay - just a blog story on freedom. I feel good when posting something. I share my ideas and get rid of the pressure. People love blog stories about freedom. So, imagine that you just develop your website.
- Love what you do. Writing about freedom may be funny and bring much pleasure. Find the idea and highlight it the way you want.
- Your opinion matters much. You are not to agree with everyone. Rebel and be original. If something about the topic “freedom” surprises you, it can surprise everyone.
- Don’t limit yourself. I never depend on one source and don’t stick to one point. First, I investigate the topic and read the FAQ which concerns my essay to get different points of view. I never force myself to write at least something. I take a rest when I need it and write what I love because that’s MY essay.
- Quote and respect somebody’s idea. And be sure that you know how to quote a quote . Tutors appreciate when students sound logical and clever. Quotes are not always good. It’s better to get ideas and rewrite them by adding your own opinion. “When I do something I do it for my country and don’t wait for the appraisal.” Sounds familiar? Yes! I just rewrote the idea taken from Kennedy’s speech. That’s how freedom quotes should be paraphrased.
- Start with theme essay outline . Continue writing the body and then write the intro and the conclusion. I write the body of my freedom essay, investigate and improve it. I see the strongest point and present it in the intro and highlight it in my freedom essay conclusion. Once I tried to begin with the introduction soon found out that my essay had stronger ideas and, as a result, I had to delete it and write the new one.
- Your writing is your freedom - enjoy it. I don’t like to measure myself. If I have something to say right now, I write it. It can be a single sentence or a paragraph. Later I insert it into my essay. I don’t always have time to finish the paper at once. I can write it for many days. One day I feel great and creative and the other day I feel terrible and don’t touch the keyboard. Inspiration is essential.
- Don’t deal with taboo issues. Clichés and too complicated language spoil the paper. One more thing to remember is avoiding plagiarism. Once a friend of mine had copied a passage from the work and his paper was banned. I am unique, you are unique, and the freedom essay must be unique as well.
- Learn the topic properly. It’s important to find the topic captivating for the society and for you. Freedom is not a limited topic and there are a number of variations.
Below are some topics offered by our creative title generator for essay :
- Freedom of conscience
- Freedom of worship
- Freedom in choosing
- Freedom of action
- Freedom of speech
- Freedom of assembly
- Free people.
Now you can see that freedom can be different. Freedom is a part of the human life and you can describe it in different ways.
Freedom of Speech Essay Sample
It’s not easy to write a freedom of speech essay because freedom of speech doesn’t exist. Freedom is an illusion and our politicians try to serve freedom as a main course. People pay much attention to each word being afraid that social networks will ban their “freedom” paper. Every online website must keep within laws that our government creates. Why do people speak of freedom of the press and other freedom issues?
First of all, it’s necessary to find out what the word “freedom” means. According to the thesaurus, freedom is the power or right to act, think, and speak the way one wants. Its synonym is the word “liberty” that deals with “independence” and “sovereignty”. Freedom of speech is the ability to express ideas, beliefs, complaints, and grudges freely. The government mustn’t punish people who said something wrong or present information without supporting it with facts. Do we really have such freedom? The problem is that freedom of speech doesn’t exist alone and cannot be limitless. If you lie, you deprive a person of the right to live normally. If you publish the harsh truth, you can harm someone innocent and spoil somebody’s freedom. Do you really think that you read and hear 100% verified news on TV, radio, social networks, and printed sources? There is always someone behind it. The team of editors corrects everything they don’t like; they can even refuse to publish the announcement at all. There are only a few bloggers who share the truth and don’t decorate it with beautiful words and nice pictures. Still, some countries try to make everything possible to let people speak without limitations and strict censorship. The first country that provided people with the freedom of speech was Ancient Greece. Everybody could express themselves and say both positive and negative issues about policy, country, and other people. The United States of America introduced the First Amendment that declared the right of Americans to discuss things openly. Though, not all types of speech freedom are protected by the law. It’s forbidden to humiliate somebody, post defamation, threat somebody, publish works that are absolutely not unique and spread the material that contains child pornography or other similar issues. Provocative publications or those which aim us to make somebody violate a law belong to the category of unprotected speeches. Freedom of speech is a part of democracy. Unfortunately, not all democratic countries let their citizens express their thoughts the way they want and need. As long as there are such countries we cannot speak about the notion of absolute freedom of speech.
Contact our essay website and free yourself up from academic writing. Our professionals will deliver fantastic result on any topic even if you have 3 hours before the deadline is over.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

- Welcome to the Spring Semester
- Centers & Initiatives
Malaya: Essays on Freedom
In this section.
- Complete Collection
- Racial Justice, Racial Equity, and Anti-Racism Reading List
- Cinelle Barnes

“ From Cinelle Barnes, author of the memoir Monsoon Mansion , comes a moving and reflective essay collection about finding freedom in America. Out of a harrowing childhood in the Philippines, Cinelle Barnes emerged triumphant. But as an undocumented teenager living in New York, her journey of self-discovery was just beginning. Because she couldn ’ t get a driver ’ s license or file taxes, Cinelle worked as a cleaning lady and a nanny and took other odd jobs -- and learned to look over her shoulder, hoping she wouldn ’ t get caught. When she falls in love and marries a white man from the South, Cinelle finds herself trying to adjust to the thorny underbelly of ‘southern hospitality ’ while dealing with being a new mother, an immigrant affected by PTSD, and a woman with a brown body in a profoundly white world. From her immigration to the United States, to navigating a broken legal system, to balancing assimilation and a sense of self, Cinelle comes to rely on her resilience and her faith in the human spirit to survive and come of age all over again. Lyrical, emotionally driven, and told through stories both lived and overheard, Cinelle ’ s intensely personal, yet universal, exploration of race, class, and identity redefines what it means to be a woman–and an American–in a divided country. ” -- Provided by publisher .
Barnes, Cinelle. Malaya: Essays on Freedom . Little A, 2019.
Freedom Research Paper

View sample freedom research paper. Browse other research paper examples and check the list of history research paper topics for more inspiration. If you need a history research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A! Feel free to contact our custom writing service for professional assistance. We offer high-quality assignments for reasonable rates.
The understanding of freedom as “an absence of restraint” took shape with the Protestant Reformation in the early sixteenth century: religious freedom represented a denial of church authority. This view is vastly different from that of most cultures in world history, including Europe until the Renaissance, where freedom was understood as the opportunity to fulfill human potential.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Defining the term freedom poses several challenges for world historians. (Freedom is usually regarded as synonymous with liberty, the term freedom being a descendant of the German language and liberty of the French. Some commentators use liberty to refer primarily to the political context of freedom.) In the modern West (itself a problematic term, here defined as Europe and its cultural descendants in places like North America), freedom has most typically been understood in a negative sense, as an absence of constraint. In most other cultures in the world, however, as well as in Europe itself until the Renaissance, freedom was—and is—more often understood in a positive sense as representing the opportunity to fulfill potential that is latent in the human personality. This essay will first consider the modern definition, then the global (and traditional Western), concluding with some reflections on the larger significance of freedom.
Modern Definition
The dominant modern Western understanding of freedom as an absence of constraint is a consequence of numerous developments beginning with the Protestant Reformation. The assertion by Martin Luther at the beginning of the sixteenth century that the individual conscience is the ultimate arbiter of orthodox doctrine undermined the universal claims of the Christian church. Religious “freedom” thus came automatically to represent a denial of the authority of the church. At the same time, the philosophical school of natural law—by that time a synthesis of Stoicism, Aristotelian thought, and Christian theology—began to change its focus from an emphasis on duty to an emphasis on rights. The conviction grew that the individual was an autonomous (that is, a “law unto oneself”) moral and political entity over which the church, and then the state, had only limited authority. To assert a “right,” therefore, meant to throw off the chains, or constraints, of those in either ecclesiastical or political power—hence the emphasis on negative freedom as an absence of constraint.
In its modern political form, this worldview contributed to the doctrine of popular sovereignty and liberalism. In some cases, it also contributed eventually to the rise of democratic institutions in the modern West beginning in the United States and Great Britain. To be sure, democracy had existed elsewhere as well. It may well have characterized the participatory interactions of hunting-gathering societies before the advent of agriculture. Nevertheless, most historians believe that the roots of historical democracy lie in the West, where it flourished for a short time in classical Athens and republican Rome before disappearing for 1,500 years. After reappearing briefly in the city-states of Renaissance Italy, it then took on its modern form only after the rise of the nation-state in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, first in the United States and Great Britain and then gradually spreading elsewhere in the last two centuries.
The economic expression of this modern understanding of freedom as an absence of constraint was best expressed by Adam Smith’s theories of liberal capitalism, embodied in The Wealth of Nations, published in 1776. There he argued that the most efficient and productive economy is one in which individuals in the marketplace are allowed to make choices without interference by the government. Adam Smith’s views were eagerly appropriated by the middle class in Britain, intent upon removing all obstacles to free trade (thereby increasing their profits). From that time on, the philosophical basis of liberal capitalism—expressed most notably in the twentieth century by Friedrich von Hayek—has been this definition of freedom.
The social counterpart of laissez-faire economic doctrine in the modern West was the social contract theory, which began with the work of thinkers like Thomas Hobbes in the seventeenth century. This theory holds that in a state of nature human beings are entirely solitary. At some point they realize that the benefits of living together outweigh the loss of some of their natural freedoms, which sociability requires them to surrender to society. Society, therefore, is held to be an artificial construction of the individual human will, whose purpose is to serve the interests of the individual. The individual is primary; the society is secondary. The rights of the individual thus take precedence over duty to society, the purpose of the latter now being only to serve the former.
Global and Traditional Western Views
The modern Western understanding of freedom and rights is separated from that of the rest of the world, and from the traditional Western understanding, by a vast gulf. From the perspective of most cultures in world history, freedom was understood in its positive sense, as the opportunity to fulfill the human potential. In its political form, freedom was a condition that could not be separated from its complementary partner, namely, responsibility (or duty). Like two sides of a coin, each was understood to have meaning only in relation to the other. Politics, therefore, was inseparable from morality. The purpose of government was not to cater to individual wants, but to foster a society that fulfilled the noblest aspirations of the human personality. For the early Greeks, for example, that meant serving the community through perfecting the rational and moral faculties. In all cases, it was assumed that the purpose of life was not primarily to serve oneself but to serve others, and the proper exercise of freedom—or choice—was therefore to carry out one’s responsibility to the common good. In this understanding, politics was also education, in the root sense of the term, to “lead out” (e-ducere) that which is latent in each individual. Education and politics and morality, then, were intimately linked with freedom.
In its social context, this traditional, and global, understanding of freedom worked itself out in much the same way. The relationship between the individual and society was not adversarial but complementary. Freedom was understood to be not a natural attribute of individual autonomy but a gift that can exist only within the larger context of social responsibility and moral authority, without which it degrades into license. The purpose of freedom, therefore, was to carry out the responsibilities that come with each role we are called to play in life. In India, for example, those responsibilities were expressed in following the dharma (law), appropriate to one’s station in life.
In the economic realm of the premodern West, as well as most of the rest of the world, freedom and politics have been closely related. In the premodern context of world history, the role of government was not usually seen as inhibiting prosperity but facilitating it. The doctrine of mercantilism, against which Adam Smith wrote his masterpiece, embodied this understanding. The freedom of merchants to conduct their business depended on the peace and security (and high tariffs) provided by the state. Whether one speaks of the economic prosperity of the Mediterranean world under the Pax Romana or the countries served by the Silk Roads, the political responsibility of states to maintain law and order guaranteed the economic freedom of merchants to trade. Obviously, of course, when the state failed to carry out those responsibilities and became itself an instrument of oppression and exploitation, the economic freedoms of the people were compromised. When that happened, prosperity usually declined, and with it the eventual power of the state as well. To some degree this paradigm still holds true, as when critics of globalization argue that the real culprit is not the global trade itself but the absence of a global structure of law capable of punishing those who abuse their power.
In its religious forms, the positive understanding of freedom contains a fascinating paradox in which the differences between it and the negative understandings of freedom tend to dissolve. From a negative perspective, freedom manifested itself as a liberation of the immaterial soul from the constraints of the material body [for Christians, it was salvation; for Hindus swaraj (self rule) and moksha (liberation), for Buddhists nirvana (extinguishing of self)]. From a positive perspective, however, this liberation could come only by surrendering oneself entirely to one’s duty or to God’s will. The only way to transcend constraint, in other words, was to accept constraint. The religious realm of human freedom also raises profound moral questions about the nature of good and evil. Put simply, the freedom to choose between good and evil, or right and wrong, implies that some will choose the former and others the latter. Evil, or suffering, in this view, is a necessary price of freedom. The most famous exposition of this problem is contained in Fyodor Dostoyevsky’s (1821–1881) rightfully famous chapter from The Brothers Karamazov entitled “The Grand Inquisitor,” in which Christ returns to Earth during the Spanish Inquisition only to be arrested by the Grand Inquisitor himself and interrogated in prison. In a long monologue, the Spanish priest accuses Christ of having made a tragic mistake by giving freedom to humankind. No sooner do people have the power to choose, he asserted, than they abuse it by making choices that cause needless suffering to themselves and others. Better to take away their freedom and force them to do what is right. Since the Grand Inquisitor’s proposition leads to tyranny, of course, we reject it, but often without remembering that the possibility of freedom—which insures that some will choose badly—contains a tragic imperative that can be mitigated but never eliminated.
In its artistic incarnation, freedom takes the form of the creative power of the imagination to express the deepest yearnings of the human spirit. The creative impulse in the human personality has been evident from the very earliest transition to modern Homo sapiens 100,000 years ago. Tools and ceramics were made to be not only practical but also beautiful. The astonishing diversity of cultural expression throughout the world, in every realm, whether music, dance, literature, painting, sculpture, ceramics, or a host of others, is wonderful testimony to the creative power of the human imagination. Those who worry that globalization will inevitably bring about an inevitable homogenization of culture can derive some comfort from knowing that this drive for freedom will resist that process. Cultural interaction, in the end, has been both a stimulus for artistic development, as well as, occasionally, an obstacle. The Silk Roads, for example, brought many influences from West to East, and vice versa, but in all cases the cultural life of the Eurasian continent was immeasurably enriched. Some of the most splendid examples of world architecture, such as the Taj Mahal, are witness to this remarkable capacity of humankind to absorb influences from without and then produce a synthesis that represents an entirely new level of achievement.
In science and technology the exercise of freedom in developing new tools has vastly increased the power of the human species to dominate both nature and other people. In terms of the interaction between people and the environment throughout world history, freedom has made it possible for humans to control the processes of nature far more than any other animal, but has also, especially when divorced from its complementary twin—responsibility—raised the specter of the potential extinction of the species. The tragic, as well as the beneficial, potential of human freedom is perhaps best illustrated by the progress made in the last 10,000 years in technology and science. The domestication of fire, for example, brought about a much greater array of human freedoms than ever before—humans conquered the night, overcame the seasons, and migrated to all regions of the world. But fire can destroy life as well as serve it. Just as a knife can kill game, it can also kill one’s neighbor. Every advance in choice brought an equivalent burden of responsibility, right down to the detonation of the first atomic device in 1945. It was, in fact, a failure of ideas and institutions to respond responsibly to this tragic potential of science and technology that led to the terribly destructive world wars of the twentieth century. Whether the human species, at the dawn of a new century and a new millennium, will be able to balance our new technological freedom with responsibility and thus avoid extinction is an open question.
In world histories written in the nineteenth-century West, freedom was the core organizing principle for a generation of historians who inherited the Enlightenment faith in progress and saw all history as the gradual growth of human freedom. The great German philosopher Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel even went so far as to remark that all human history is an unfolding of the consciousness of freedom. In the twentieth century, however, historians shied away from freedom as an organizing principle. Perhaps freedom had been so intimately linked with the nineteenth-century faith in progress—blasted to bits by World War I and II—that it no longer seemed relevant. In any case, for those involved in political movements that sought deliverance from colonialism or other forms of oppression, freedom has remained a core value. From Mohandas Gandhi to Martin Luther King to Nelson Mandela and Desmond Tutu, the human quest for freedom was far more than an intellectual exercise. Their example, and that of all those alive today who continue to struggle and suffer in the name of freedom and human rights, remind us that the highest expression of freedom is to serve the noblest values of the human spirit.
Implications
Freedom, in its negative sense of an absence of constraint, has been identified in this essay as the underlying ideology of liberal capitalism and (in the nineteenth century) of human progress. This optimistic view of capitalism, it should be said, was challenged by socialists who held that free-market competition had produced an unacceptable level of inequality and exploitation. The ensuing conflict between those champions of capitalism on the right who defined justice in terms of freedom and those advocates of socialism on the left who defined justice in terms of equality has lasted to the present and shows no signs of disappearing. The former praise globalization; the latter attack it. Both assume that freedom and equality are incompatible, and that an increase in one can come only with a decrease in the other. The two sides might find more common ground for agreement if they were to take an intellectual bath and then change into a new suit of definitions. By defining freedom in its positive sense as human fulfillment, and defining equality in terms of opportunity rather than condition, the proponents of “capitalist” and “socialist” views of the world might discover many of their differences melting away. In addition, they would be much more likely to cooperate effectively to reduce what both find most harmful to human progress, namely global poverty. If it is true, as the nineteenth-century writer Samuel Taylor Coleridge is once supposed to have remarked, that people are usually right in what they affirm and wrong in what they deny, then one could argue that each party in this dispute is right in affirming its own definition of justice and wrong in denying the other’s. In the end, the richest fruits of freedom are to be found through a positive understanding of its deepest meaning.
Bibliography:
- Bauman, Z. (1988). Freedom. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
- Berlin, I. (1969). Four essays on liberty. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Cranston, M. (1967). Freedom. London: Longmans.
- Davis, R. W. (Ed.). (1995). The origins of modern freedom in the West. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Fromm, E. (1969). Escape from freedom. New York: Avon Books.
- Greene, M. (1988). The dialectic of freedom. New York: Teachers College Press.
- Hayek, F. A. (1994). The road to serfdom. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Loewy, E. H. (1993). Freedom and community: The ethics of interdependence. Albany: State University of New York Press.
- Muller, H. J. (1961). Freedom in the ancient world. New York: Harper.
- Muller, H. J. (1963). Freedom in the Western world: From the dark ages to the rise of democracy. New York: Harper & Row.
- Patterson, O. (1991). Freedom. New York: Basic Books.
- Powell, J. (2000). The triumph of liberty: A 2,000-year history. New York: Free Press.
- Treadgold, D. W. (1990). Freedom: A history. New York: New York University Press.
- Wood, A. T. (2001). What does it mean to be human? A new interpretation of freedom in world history. New York: Peter Lang.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Academic Freedom and the Israel-Gaza War
More from our inbox:, should there be biden-trump debates, child care for rosie the riveters, never enough money.

To the Editor:
Re “ Political Dissent Is Under Attack on Campus ,” by Paula Chakravartty and Vasuki Nesiah (Opinion guest essay, April 8):
As an N.Y.U. alumnus and an academic, I am disturbed by the authors’ implication that at N.Y.U. it is solely the Palestinian voice in the complex tragedy that is being suppressed.
Academic freedom requires academic responsibility, which is lacking when it is suggested that the suffering of the Palestinian people is the only acceptable topic for outrage, and it is assumed that sufficient balance is provided by a single sentence noting opposition to antisemitism.
The problem is also seen in the failure to mention the incidents of disruption, threats and physical intimidation at N.Y.U. and elsewhere that have effectively shut down any discourse other than condemnation of Israel.
Academic freedom must be earned every day through a commitment to promoting discussion from multiple points of view and sources. That freedom, already under attack, will be lost when the public perceives that it serves only one side.
Ted Besmann Columbia, S.C.
As a Jew, a former dean and professor in higher education, and a passionate advocate for academic freedom and free speech, I applaud Paula Chakravartty and Vasuki Nesiah for their courageous and compelling essay.
Tragically, universities have become more beholden to their donors, as corporations are to their stockholders, than their faculty, students and staff. If people can’t be free to express unpopular opinions on college campuses, where is it safe to do so?
I learned to think critically and question the actions of my country’s leaders regarding the Vietnam War while a student at the University of Massachusetts. I arrived there in 1964 as an innocent conformist and left with a healthy skepticism about my government’s statements and actions because of some outspoken faculty and my fellow students.
Thanks to that eye-opening experience, I have been a political activist for many years. During these scary times, as we drift away from democracy and toward authoritarianism, we need institutions of higher education to be the place for the free expression of ideas even if they lose a few close-minded donors.
Allen Davis Dublin, N.H.
The problem with academics’ defense of free speech is it’s years too late. Where were they when conservatives and those with different viewpoints were being fired and chased off campus?
Andrea Economos Hartsdale, N.Y.
Professors Paula Chakravartty and Vasuki Nesiah write that “besides Israel, only the United States is capable of stopping” the war in Gaza.
Hamas started the war on Oct. 7 and still holds hostage those captured Israelis its members haven’t murdered. Why the professors — and the students whose hate-fueled rhetoric they champion — deprive the terror group of agency is puzzling.
(Rabbi) Avi Shafran New York The writer is the director of public affairs at Agudath Israel of America.
Re “ TV Networks to Urge Biden and Trump to Debate ” (Business, April 10):
The television networks’ efforts to air a debate between President Biden and Donald Trump are strictly for selfish motives. As pointed out in the article, these debates draw a large audience, and the networks are always looking for ways to attract viewers.
Mr. Trump has no interest in discussing issues and policies, and instead simply wants a platform to engage in childish name-calling and disparagement of others. His campaign approach to date has simply been vote-for-me-or-else. While this may be a recipe for entertainment and substantial viewership, there is no redeeming value for voters.
Eric Schroeder Bethesda, Md.
President Biden should definitely debate Donald Trump and use the opportunity of speaking before a huge captive audience to debunk once and for all Mr. Trump’s Big Lie about the 2020 election being stolen.
A large majority of Republicans believe that lie. So many people believing something that preposterous poses a very real threat to the future of our free elections.
But here are the facts, which are compelling and, I believe, practically indisputable. Within a few weeks after the 2020 election, Mr. Trump’s efforts to overturn the election results in the courts — both state and federal — had been rejected by at least 86 judges , 38 of them appointed by Republicans and several appointed by Mr. Trump himself.
Top officials in every state — a majority of them Republicans — said there was no evidence of any fraud that would have changed the results in their states.
The president should have been conveying this repeatedly for the past three years, but better late than never. Hopefully there’s still time to save an endangered species: American democracy.
Bobby Braddock Nashville
Re “ World War II’s Rosies, Heroes on Home Front, Get Their Gold Medal ” (news article, April 12), about the awarding of the Congressional Gold Medal to the nation’s “Rosie the Riveters”:
These women took jobs in the aircraft and munitions industries not only for patriotic reasons but also because such skilled, relatively high-paid work had been barred to them before World War II, and they needed the money.
Many of them were mothers of young children, and for the first (and, to date, only) time, they had access to federally funded, high-quality child care, which enabled them to take full-time jobs. These services closed as soon as the war was over.
Recent legislation (the 2024 Child Care and Development Fund Final Rule ) has increased federal funding for child care, which, in turn, has improved access and quality, but it is still far from universal in the U.S.
If Congress truly wanted to honor the Rosies, it would authorize and fund universal public child care, once and for all.
Sonya Michel Silver Spring, Md. The writer is professor emerita of history and women’s and gender studies at the University of Maryland, College Park, and the author of “Children’s Interests/Mothers’ Rights: The Shaping of America’s Child Care Policy.”
Re “ Why Some Billionaires Will Back Trump ” (column, April 5):
Paul Krugman poses the urgent question, with regard to lower taxes for billionaires, “After all, how much would the extra money really matter to people whose lifestyles are already incredibly lavish?”
The movie “Key Largo” provides the answer. The character played by Humphrey Bogart asks Johnny Rocco, played by Edward G. Robinson, “He wants more, don’t you, Rocco?”
“Yeah. That’s it. More. That’s right. I want more!”
“Will you ever get enough?” another character asks.
“Well, I never have. No, I guess I won’t,” Rocco replies.
Jim Coddington New York
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
About half of americans say public k-12 education is going in the wrong direction.

About half of U.S. adults (51%) say the country’s public K-12 education system is generally going in the wrong direction. A far smaller share (16%) say it’s going in the right direction, and about a third (32%) are not sure, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted in November 2023.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to understand how Americans view the K-12 public education system. We surveyed 5,029 U.S. adults from Nov. 9 to Nov. 16, 2023.
The survey was conducted by Ipsos for Pew Research Center on the Ipsos KnowledgePanel Omnibus. The KnowledgePanel is a probability-based web panel recruited primarily through national, random sampling of residential addresses. The survey is weighted by gender, age, race, ethnicity, education, income and other categories.
Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and the survey methodology .
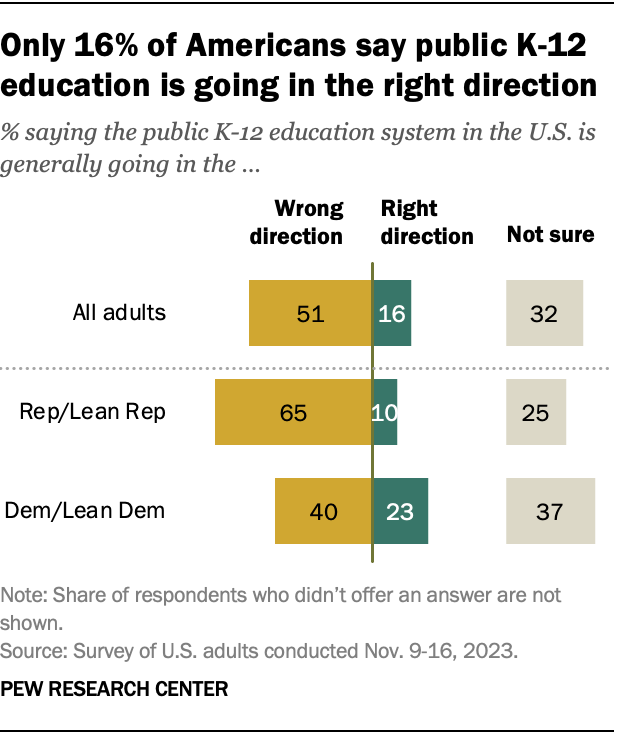
A majority of those who say it’s headed in the wrong direction say a major reason is that schools are not spending enough time on core academic subjects.
These findings come amid debates about what is taught in schools , as well as concerns about school budget cuts and students falling behind academically.
Related: Race and LGBTQ Issues in K-12 Schools
Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say the public K-12 education system is going in the wrong direction. About two-thirds of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents (65%) say this, compared with 40% of Democrats and Democratic leaners. In turn, 23% of Democrats and 10% of Republicans say it’s headed in the right direction.
Among Republicans, conservatives are the most likely to say public education is headed in the wrong direction: 75% say this, compared with 52% of moderate or liberal Republicans. There are no significant differences among Democrats by ideology.
Similar shares of K-12 parents and adults who don’t have a child in K-12 schools say the system is going in the wrong direction.
A separate Center survey of public K-12 teachers found that 82% think the overall state of public K-12 education has gotten worse in the past five years. And many teachers are pessimistic about the future.
Related: What’s It Like To Be A Teacher in America Today?
Why do Americans think public K-12 education is going in the wrong direction?
We asked adults who say the public education system is going in the wrong direction why that might be. About half or more say the following are major reasons:
- Schools not spending enough time on core academic subjects, like reading, math, science and social studies (69%)
- Teachers bringing their personal political and social views into the classroom (54%)
- Schools not having the funding and resources they need (52%)
About a quarter (26%) say a major reason is that parents have too much influence in decisions about what schools are teaching.
How views vary by party
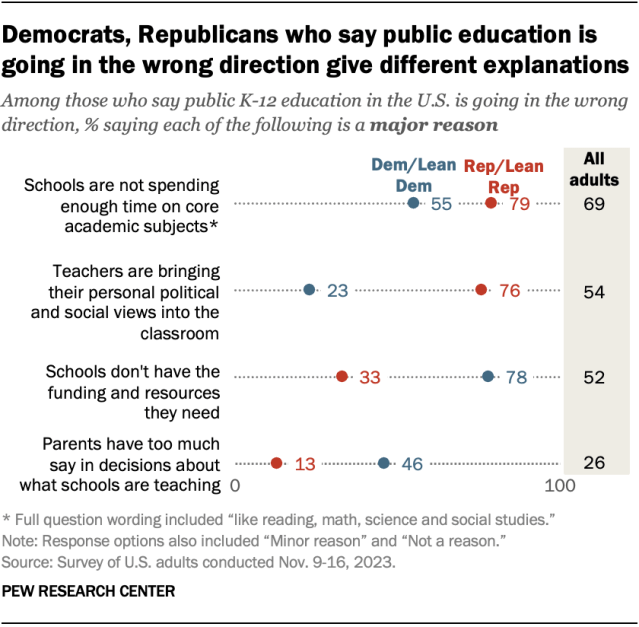
Americans in each party point to different reasons why public education is headed in the wrong direction.
Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say major reasons are:
- A lack of focus on core academic subjects (79% vs. 55%)
- Teachers bringing their personal views into the classroom (76% vs. 23%)
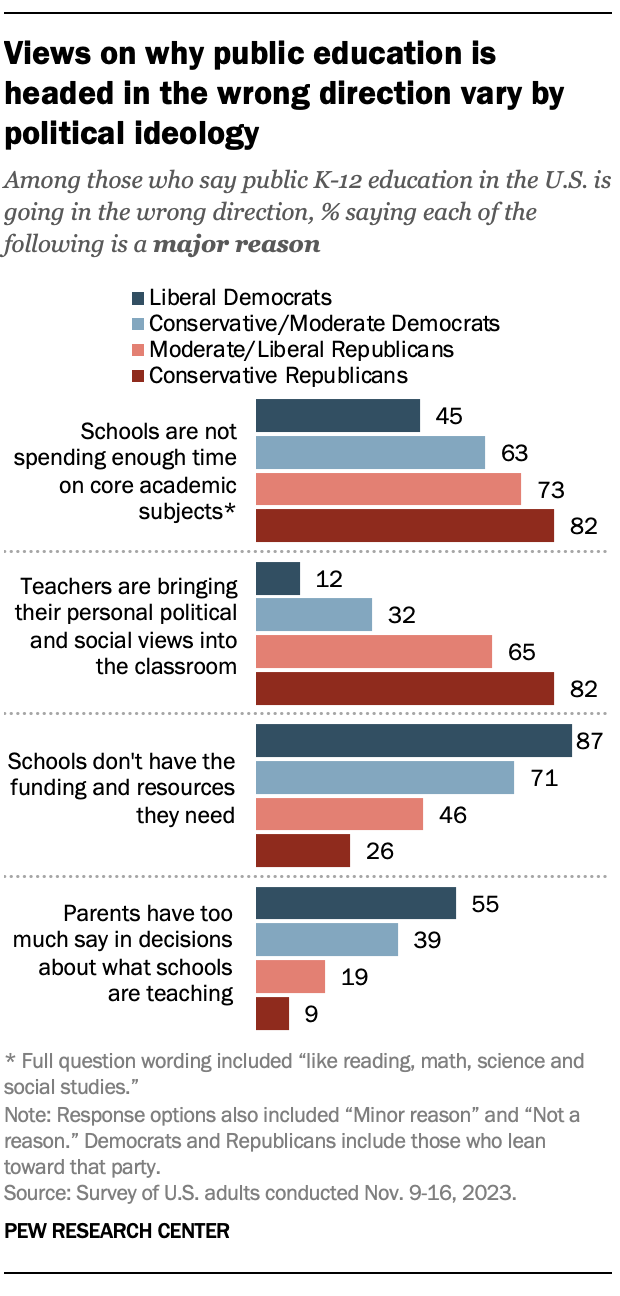
In turn, Democrats are more likely than Republicans to point to:
- Insufficient school funding and resources (78% vs. 33%)
- Parents having too much say in what schools are teaching (46% vs. 13%)
Views also vary within each party by ideology.
Among Republicans, conservatives are particularly likely to cite a lack of focus on core academic subjects and teachers bringing their personal views into the classroom.
Among Democrats, liberals are especially likely to cite schools lacking resources and parents having too much say in the curriculum.
Note: Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and the survey methodology .

Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
‘Back to school’ means anytime from late July to after Labor Day, depending on where in the U.S. you live
Among many u.s. children, reading for fun has become less common, federal data shows, most european students learn english in school, for u.s. teens today, summer means more schooling and less leisure time than in the past, about one-in-six u.s. teachers work second jobs – and not just in the summer, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Freedom Essay Topics. American (Indian, Taiwanese, Scottish) independence. Freedom and homelessness essay. The true value of freedom in modern society. How slavery affects personal freedom. The problem of human rights and freedoms. American citizens' rights and freedoms.
When it comes to discussing freedom, there are endless possibilities for essay topics. Here are 129 freedom essay topic ideas and examples to inspire your writing: The concept of freedom in a democratic society; Freedom of speech and its limitations; The role of freedom in shaping individual identity
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), proclaimed by the United Nations General Assembly in 1948 in the wake of the holocaust, expressed a commitment by the world to promote and observe a full suite of fundamental human rights. Article 19 of the UDHR protected freedom of opinion and expression in the following terms (United Nations ...
The freedom of expression broadly involves the communication of ideas, opinions, convictions, beliefs, and information. International legal instruments such as the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) recognise the 'freedom of expression' as a right that can be exercised 'either orally, in writing or in print, in the form of art, or through any other media of [the ...
Freedom of speech is among the most cherished constitutional rights in liberal democracies. It is entrenched in most contemporary constitutions as well as in international human rights. treaties ...
Sovereignal freedom is the power to act as one please s, regardless of the desires of other people. Civic freedom. is the ability of people to participate in pub lic life, especially governance ...
Academic freedom is often regarded as an absolute value of higher education institutions. Traditionally, its value is related to such topics as tenure, and the need for academic work to be free from undue political influence and other pressures that can challenge time-consuming research processes. However, when an analysis of student freedom ...
The ethical basis of human rights has been defined using concepts such as human flourishing, dignity, duties to family and society, natural rights, individual freedom, and social justice against exploitation based on sex, class or caste. All of these moral arguments for human rights are part of ethical discourse.
240 Freedom Essay Topics. On this page, you'll find thought-provoking freedom essay topics to explore the multifaceted nature of freedom. This concept encompasses many dimensions, from political liberties to human rights. Investigate our freedom essay ideas and prompts for a discussion, speech, or debate.
Email: [email protected]. Abstract. This article surveys the classic and contemporary literature. on the nature and limits of freedom of expression (or free. speech). It begins by surveying the ...
5 Examples of Essays About Freedom. 1. Essay on "Freedom" by Pragati Ghosh. "Freedom is non denial of our basic rights as humans. Some freedom is specific to the age group that we fall into. A child is free to be loved and cared by parents and other members of family and play around. So this nurturing may be the idea of freedom to a child.
Freedom and equality are typically presented as opposing values. In the quick version of the argument, economic liberty—the freedom to make contracts, acquire property, and exchange goods—upsets substantive economic equality (Nozick, 2013: 160-164).Suppose some people sail to an uninhabited island and divide its territory and the provisions they brought into shares of equal value.
Academic freedom refers to the freedom to read and teach, research and write about any topic or problem without fear of reprisal and without ... The experience of the University of Chicago (Occasional Papers on Higher Education X). Chicago: University of Chicago. Pritchett, H. S. (1905). Academic Freedom. Journal of Education, 62(18), 494-494 ...
The right to freedom of religion or belief is an integral part of the international human rights framework and, as such, has been criticized alongside human rights in general. ... Bielefeldt's research interests, above all, include different interdisciplinary facets of human rights theory and practice. He served as the United Nations Special ...
Freedom is a complicated notion that provokes conflicts and leads to difficulties. So you may feel embarrassed about trying to write a freedom essay. An experienced student gives useful information presenting this work as a free sample to help you write a freedom essay easily and quickly with no stress or difficulties.
Barnes, Cinelle. Malaya: Essays on Freedom. Little A, 2019. "From Cinelle Barnes, author of the memoir Monsoon Mansion, comes a moving and reflective essay collection about finding freedom in America. Out of a harrowing childhood in the Philippines, Cinelle Barnes emerged triumphant. But as an undocumented teenager living in New York, her ...
Essay on the Secret of Happiness Is Freedom. Freedom Happiness. In this essay, I realized how people should perceive and appreciate true happiness and freedom. Others think it is easy to be happy and free. People aspire to succeed financially, strive to become famous, and gain power, for them this is happiness.
Part II covers the importance of freedom of speech and expression. Part III covers the Constituent Assembly Debate on Article 13 (corresponding to Article 19 of the present Constitution) held on Wednesday, December 1, 1948. Part IV deals with constitutional protection of freedom of speech and expression.
View sample freedom research paper. Browse other research paper examples and check the list of history research paper topics for more inspiration. If you need a history research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A!
Re "Political Dissent Is Under Attack on Campus," by Paula Chakravartty and Vasuki Nesiah (Opinion guest essay, April 8): As an N.Y.U. alumnus and an academic, I am disturbed by the authors ...
About half of U.S. adults (51%) say the country's public K-12 education system is generally going in the wrong direction. A far smaller share (16%) say it's going in the right direction, and about a third (32%) are not sure, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted in November 2023.