
Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
- Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Top 10 Export Business Plan Templates with Examples and Samples (Editable Word Doc, Excel and PDF Included)

Samradni Pradhan
Export business is pivotal in a country's economic growth and stability. It offers numerous advantages, including job creation, foreign exchange earnings, economic diversification, and global market exposure.
Success in the export business, however, is not guaranteed. It requires a well-thought-out business plan considering market research, logistics, regulatory compliance, and financial management. We offer comprehensive and customizable export business plan templates to assist entrepreneurs in this endeavor.
The business plan ppt templates provide a structured framework for outlining your business goals, strategies, and financial projections, ensuring a smooth path to export success. With the right plan and these templates, you can capitalize on the immense opportunities the global market offers and contribute to your country's economic global market development.
Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Overview
- Industry Analysis
- Customer Analysis
- Competitor Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Porter's Framework
- Operational Plan
- Financial Plan
Our business plan template bundles are crafted with precision, keeping in mind all of the nitty-gritty of the export business. These templates use the best graphics to ensure your business idea shines through. When you download this business plan template, you will get access to a 65-page template document. These are completely editable as per your needs and requirements. However, for the ease of this blog, we will only highlight the top 10 templates from this entire deck.
1. Executive Summary
This is the initial section of your export business plan, serving as a concise roadmap for the reader. It should encapsulate the essential aspects of your export strategy, including identifying target markets, primary objectives, a summary of key strategies, and a brief overview of financial projections and timelines. This summary sets the stage for the entire plan, looking at what the audience can expect to find in more detail further in the document.
In our Executive Summary section, you will get templates for
1.1 The Quick Pitch: A concise and compelling overview of your export business, capturing its essence and potential in a few sentences.
1.2 The Entity: Describing your business's legal structure and core identity, ensuring clarity regarding its nature and organization for international trade .
1.3 Company Overview: Offering a comprehensive introduction to your cross-border commerce , including its history, mission, and the core values that drive your international endeavors.
1.4 Products and Services: Detailing the range of export products and services you offer, emphasizing their unique features and how they meet the needs of international customers.

Download this business plan
(Do you have a trading business and wish to scale it up? We have a suitable template for a multinational trading business plan; you can download it here )
2. Company Overview
The company overview delves into the core aspects of your business. It provides information about your company's history, experience in international trade, certifications (such as ISO standards or export-related qualifications), and financial stability. This section aims to build confidence in your company's ability to operate successfully in the export market, demonstrating your credibility as an export partner.
In our Company Overview section, you will get templates for
2.1 Mission and Vision: Your export business's overarching purpose and long-term aspirations define your commitment to international success.
2.2 Goals and Objectives: The specific targets and milestones that steer your import-export business towards accomplishment in global markets.
2.3 Start-up Summary: A concise outline of the initial financial and operational aspects required to launch and establish your export operations.
2.4 Market Gap and Solution: Identifying a void in international markets and how your products or services provide a solution, ensuring a clear value proposition.
2.5 Product and Services Offered: Detailing the range of products and services of your export business offers, emphasizing their uniqueness and relevance in global markets.
2.6 Key Success Factors: The critical elements that underpin your export business's success, serving as the foundation for sustainable growth in foreign trade .

(Looking for something more generic that caters to international business ? Well, you are in luck! We have a business plan template that caters to international business !)
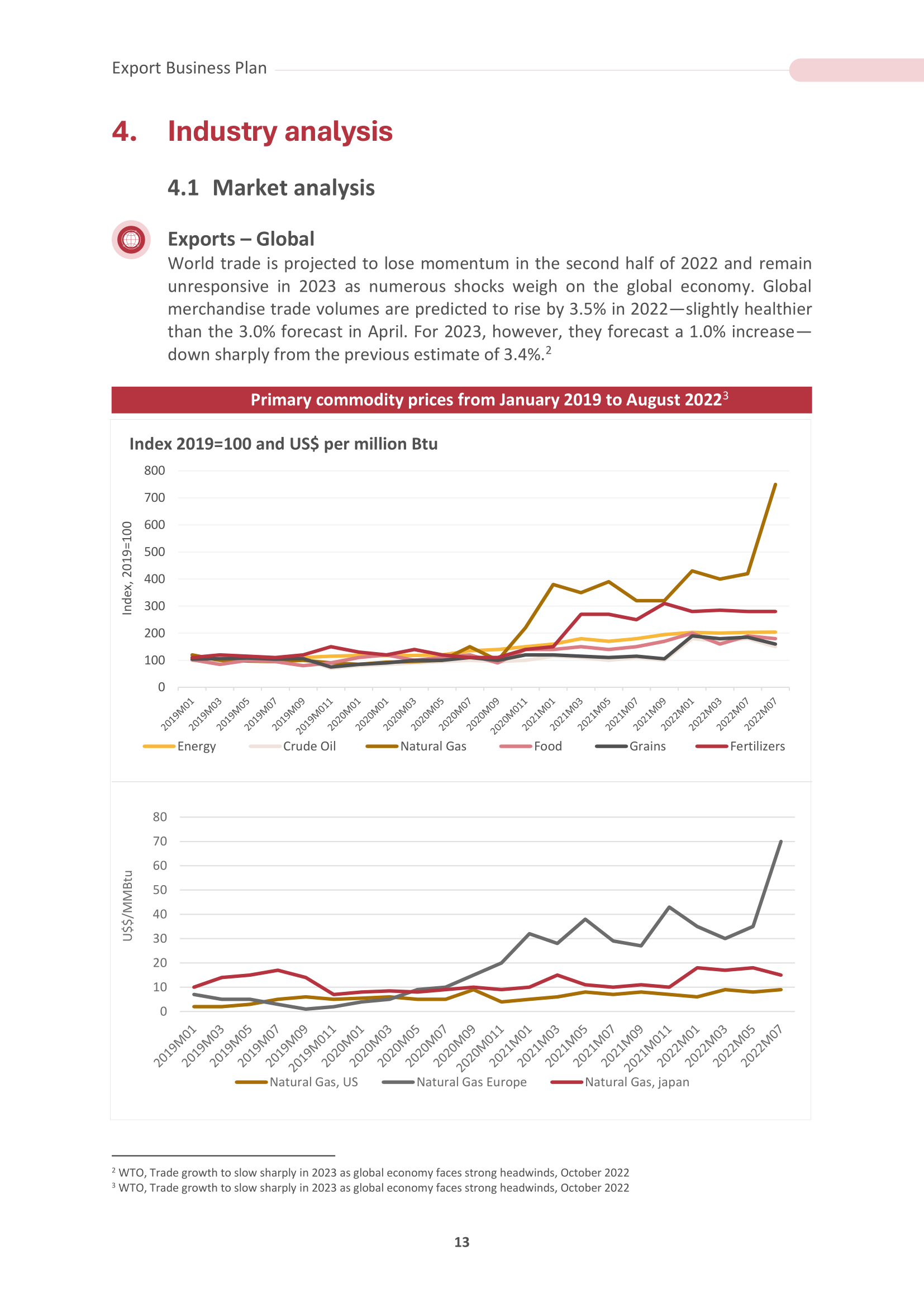
3. Industry Analysis
The industry analysis explores the global market where you intend to export your products or services. It should examine market trends, regulatory environments, and trade policies affecting your industry. This analysis helps you identify potential growth areas, challenges, and opportunities that can improve your import strategy.
In our Industry Analysis section, you will get templates for
3.1 Market Analysis: A comprehensive examination of international markets to identify opportunities and assess the export potential of your products.
3.2 Market Trends: Tracking global trade dynamics and consumer behavior shifts ensures your export strategies align with current and future market trends.
3.3 Major Challenges: Identifying the key hurdles and obstacles your export business may encounter in international markets and formulating strategies to overcome them.
3.4 Growth Drivers: Recognizing the factors that stimulate expansion and success in global markets, leveraging them to propel your export venture forward.
3.5 Geographical Analysis: Examining specific regions and countries to determine the most promising export destinations, tailoring your approach to each market's unique demands and opportunities.
(Is your business strategy driven? You need a template that focuses on the target market and global expansion. Get the best of both through this template )
4. Customer Analysis
In the customer analysis section, you must define and understand your target international customers. This involves delving into their demographics, preferences, behaviors, and cultural factors that may impact their purchasing decisions. A thorough customer analysis will guide you in tailoring your products, services, and marketing approaches to align with the needs and expectations of your global clientele.
In our Customer Analysis section, we offer comprehensive templates for:
4.1 Target Market: Defining the specific countries or regions where your export business aims to sell products, narrowing down the global focus.
4.2 Buyer Persona: Creating a detailed profile of the ideal international customer, understanding their needs and preferences to tailor export strategies better.
4.3 Market Sizing: Assessing the potential of the export market by determining its size in terms of customers, demand, and revenue, providing a clear understanding of the export opportunity.

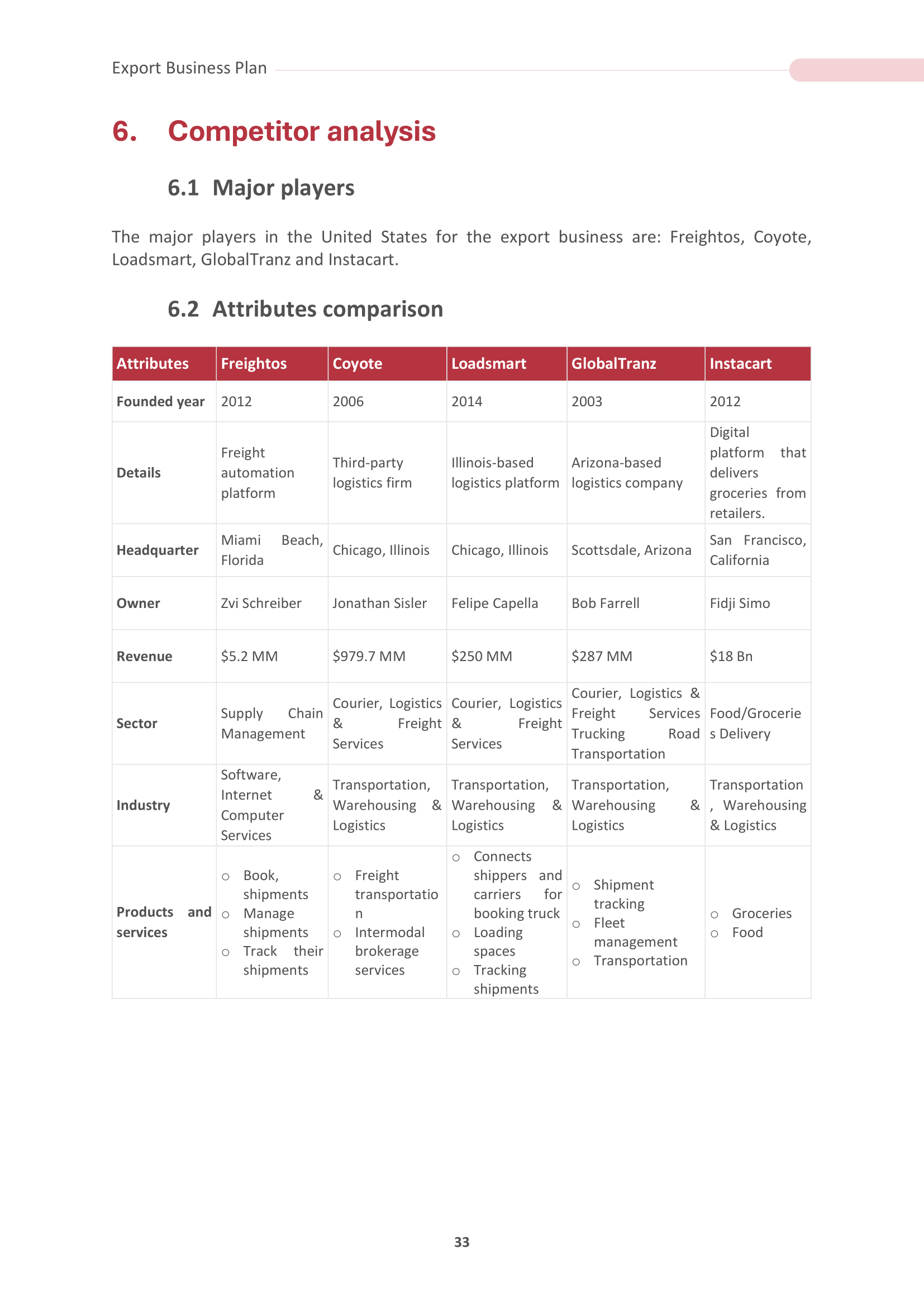
5. Competitor Analysis
Analyzing the competitive landscape in your target markets is crucial for developing effective export strategies. This section should identify key competitors in the international market, evaluate their strengths and weaknesses, and provide insights into their market share. Understanding the competitive dynamics will help you position your products or services effectively and gain a competitive advantage.
In our Competitive Landscape section, we provide templates for:
5.1 Major Players: Identifying and analyzing key competitors and influential entities in the international market who impact your business.
5.2 Attributes Comparison: Evaluate the specific characteristics and features of your export products or services compared to those offered by competitors to determine your unique selling points and competitive advantages.
6. SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis is considered to be a strategic tool that assesses your export venture's internal strengths and weaknesses, also external opportunities and threats. This analysis provides a holistic perspective of your business and the export environment. By identifying internal advantages and challenges and external market opportunities and threats, you can make informed decisions, create mitigation plans, and better position your company for international success.

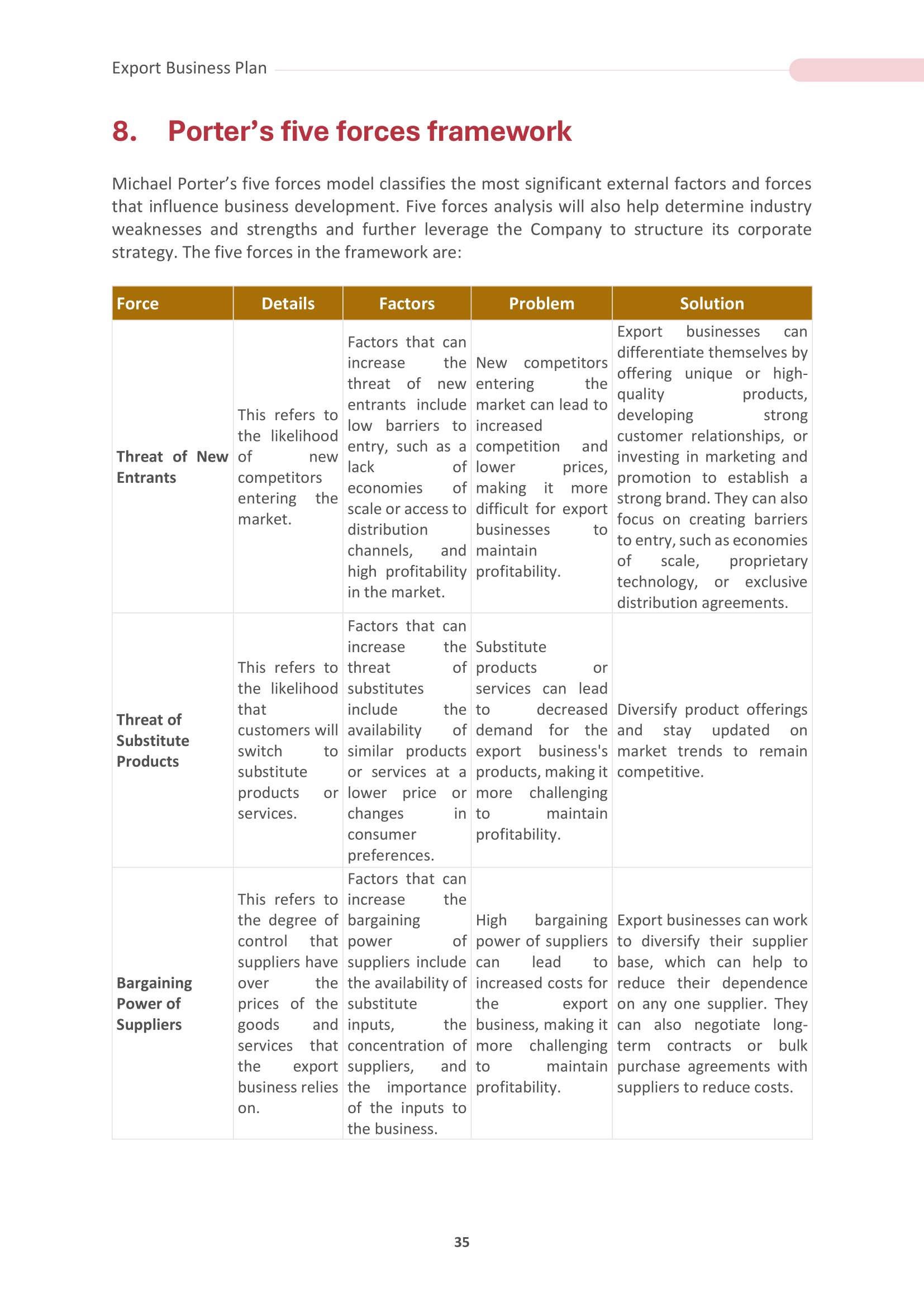
7. Porter's Framework
Porter's Five Forces framework is considered an excellent tool for analyzing the competitive forces within your industry. It examines the power of suppliers, the bargaining of buyers, the threat of new brands and substitutes, and the intensity of competitive rivalry. This analysis helps you understand the competitive dynamics of the export market, identify potential challenges, and develop strategies to address them effectively. You can make informed decisions about market entry and competition mitigation strategies using Porter's framework.
8. Marketing Plan
The marketing plan in an export business outlines the strategies for promoting and selling your products or services in international markets. It should include details about your international marketing mix, pricing strategies, distribution channels, and promotional efforts. A robust marketing plan is essential for gaining market share and building brand recognition in your target export markets.
In our Marketing Plan section, we provide templates for:
8.1 Sales and Distribution Strategy: Outlining the plan for leveraging international sales and distribution platforms to enhance brand visibility and engage with international customers in the export market.
8.2 Promotional Strategy: A comprehensive plan designed to increase brand visibility, engage international audiences, and drive sales in the global export market.
8.3 Pricing Strategy: Defining the approach for setting competitive and profitable prices for your export products or services, considering international market dynamics and customer expectations.
8.4 Sales Funnel: Describing the step-by-step process that international customers go through, from initial awareness to purchasing, facilitating efficient lead conversion in your export business.

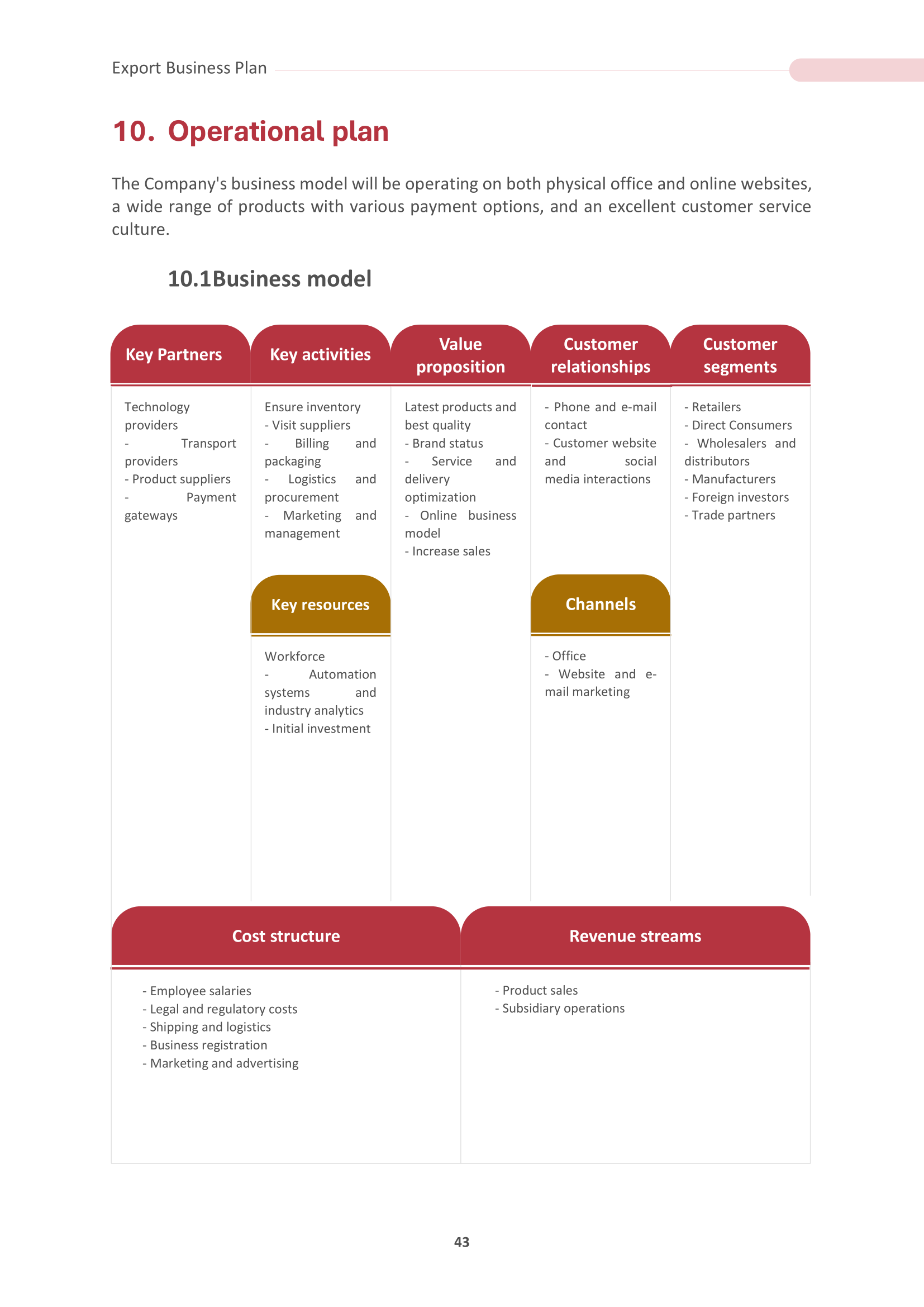
9. Operational Plan
The operational plan defines how your company will execute its export strategy. This section should cover logistics, production, supply chain management, quality control, and international regulations and standards compliance. It's essential to provide a clear and organized operational plan to ensure a smooth flow of goods or services to your international customers.
In our Operational Plan section, we provide templates for:
9.1 Business Model: The blueprint of your export enterprise, elucidating how you create, deliver, and capture value in international markets, ensuring a clear understanding of your global trade approach.
9.2 Goals to be achieved: The specific, measurable objectives guiding your export business, ensuring a defined path to international success and a framework for tracking your progress.
10. Financial Plan
The financial plan is a critical section of the export business plan, detailing the expected costs, revenue projections, and financial forecasts related to your international expansion. It should include budgets, cash flow statements, break-even analysis, and return on investment calculations. This information helps stakeholders, including investors and lenders, understand your export business's financial viability and sustainability.
In our Financial Plan section, we provide templates for:
10.1 Financial Assumptions: Highlighting the critical assumptions underpinning the export venture's financial projections.
10.2 Revenue Model and Sales Forecast: Defining the approach for generating revenue from international markets and providing a sales forecast for export operations.
10.3 Break-Even Analysis: Identifying the point at which export revenues cover costs, indicating when the business becomes profitable.
10.4 Projected Profit and Loss Account: Summarizing expected revenues, expenses, and profitability for the export business over a specified period.
10.5 Projected Cash Flow Statement: Outlining the expected cash inflows and outflows related to export activities, ensuring cash liquidity for international operations.
10.6 Projected Balance Sheet: Present a snapshot of the export business's financial position, including assets, liabilities, and equity, specific to international trade.
10.7 Scenario Analysis: Assessing various scenarios to understand the impact of various elements on the financial performance of the export business.
10.8 DCF Valuation: Applying the Discounted Cash Flow process to determine the present value of future cash flows, assisting in the valuation of the export business in the international market.
We have so much more to offer
An export business plan considers many elements, and we know you are the expert to manage it all! However, we can only help you with the best base to get started. By downloading these templates, you are not only creating the right start for your business, but also creating a lasting impression for your investors. This 65-pager template deck has everything you will need for your business; what more can you ask for? For easy access and editability, you can download the PowerPoint file of this deck from here ! Happy business planning.
Related posts:
- Must-have Restaurant Business Plan Templates with Samples and Examples
- Must-have Advertising Agency Business Plan Templates with Examples and Samples
- Top 10 Bar Business Plan Templates with Examples and Samples (Editable Word Doc, Excel and PDF Included)
- Top 10 Law Firm Business Plan Templates with Samples and Examples (Editable Word Doc, Excel, and PDF Included)
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 5 Goal Board Templates With Samples And Examples

Top 7 Data Quality Dashboard Samples with Templates and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

Get Ready to Export: My Export Plan My Export Plan
Prepare to export.
[Download Video 21MB] Quick Links: Back to First Video in Set | Get Ready to Export Video Set | How to Export Video Series | Subscribe to our Email Updates and Tips .
Developing an Export Plan
The purpose of an export plan is to assemble facts, constraints, and goals, and to create an action statement that takes these elements into account. The plan includes specific objectives, sets forth time schedules for implementation, and marks milestones so that the degree of success can be measured and can motivate personnel.
Export Plan Tips
- The first time an exporting business plan is developed, it should be kept simple. It need be only a few pages long because important market data and planning elements may not yet be available. The initial planning effort itself gradually generates more information and insight. As you learn more about exporting and your company’s competitive position, the export plan will become more detailed and complete.
- Your plan should be written and viewed as a flexible management tool, not as a static document. Plan objectives should be compared with actual results to measure the success of different strategies. Don’t hesitate to modify and make the plan more specific as additional information and experience are gained.
- A detailed plan is recommended for companies that intend to export directly, meaning selling to an end-user in another country. If your company chooses indirect export methods or sells via your or a third party’s website, you may use much simpler plans.
The Value of an Export Plan
- Written plans give a clear understanding of specific steps that need to be taken and help assure a commitment to exporting over the longer term.
- Only about a third of small -and medium-sized U.S. manufacturers have a written plan. Absent a plan, your business may overlook much better opportunities. In addition, reactive exporters may quickly give up on selling to international customers, concluding prematurely that it’s not worth the effort, or that it’s easier to serve customers closer to home even if that base may not grow, and could even shrink in the future.
- Remember that while 59 percent of all U.S. exporters export to only a single market (predominantly Canada), many small exporters sell to more countries than they have employees, and these sales account for a growing percentage of total sales. These mini-multinationals are becoming more common, and your company can be one of them.
Length of the Export Plan
Product or service.
- What need does my product or service fill in the global marketplace?
- What modifications, if any, must be made to adapt my product for export markets?
- Do I need special licenses or certificates from the U.S. or the buyer’s government?
- Do I need to modify packaging or labeling?
Pricing Considerations
- What is the cost to get my product to market (freight, duties, taxes and other costs)?
- Given an estimate of the shipping costs, what is my pricing strategy?
- What, if anything, do I need to protect my intellectual property?
- What modifications, if any, should I make to my website for marketing purposes?
- Should I sell on third party eCommerce platforms?
- What kinds of social media should I use to build awareness?
- Should I attend a trade show where international buyers are present?
Management Issues
- Are the reasons for pursuing export markets solid objectives (such as increasing sales volume or developing a broader customer base), or more frivolous (for example, the owner wants an excuse to travel)?
- How committed is top management to exporting? Is exporting viewed as a quick fix for slumping domestic sales? Will export customers be neglected if domestic sales pick up?
- What are the expectations? How quickly does management expect export operations to become self-sustaining? What level of return on investment is expected?
- With which countries has business already been conducted, or inquiries already received?
- Which product lines are talked about the most?
- Are domestic customers buying the product for sale or shipment overseas? If so, where?
- Is the trend of sales and inquiries up or down?
- Who are the main domestic and foreign competitors?
- What are some lessons learned from past export experiences?
Management and Personnel
- What in-house international expertise does the company have (international sales experience, language capabilities, etc.)?
- Who will be responsible for the export department’s organization and staff?
- How much senior management time should/could be allocated?
- What organizational structure is required to ensure export sales are adequately serviced?
- Who will follow through after the planning has been done?
Production Capacity
- How is the present capacity being used?
- Will filling export orders hurt domestic sales?
- What about the cost of additional production?
- Are there fluctuations in the annual workload? When? Why?
- What minimum-order quantity is required?
- What is required to design and package products specifically for export?
Financial Capacity
- What amount of capital can be committed to export production and marketing?
- What level of operating costs can be supported by the export department?
- How are initial expenses of export efforts to be allocated?
- What other new development plans might compete with export plans?
- By what date must an export effort pay for itself?
- Do you qualify for any type of export financing?
Sample Outline of an Export Plan
Part i: export policy commitment statement , part ii: situation or background analysis.
- Product/Service for Export
- Export License (if needed)
- Personal Export Organization
- Products/Services to be Exported
- Products that Qualify Under FTAs
- Resources Outside the Company
- Industry Structure, Competition, Demand Operations
- Export Control Compliance
- Product Classifications
- Resources Inside the Company
Part III: Marketing Component
- Identifying, Evaluating, and Selecting Markets
- Product Selection and Pricing
- Distribution Methods
- Internal Organization and Procedures
- Sales Goals (Profit and Loss Forecasts)
- Terms and Conditions
- Pricing with Consideration of Duties, Taxes
- Freight Costs, and Logistics Included
Part IV: Tactics—Action Steps
- Primary Target Countries
- Indirect Marketing Efforts
- Quarterly Accomplishments
- Secondary Target Countries
Part V: Export Budget
- Pro-forma Financial Statements
- Marketing Materials
- Travel
- Website Enhancements
- Trade Show Visits
- Other Costs
Part VI: Implementation Schedule
- Periodic Operational and Management Review (Measuring Results against the Plan)
Addenda: Background Data on Target
- Basic Market Statistics (Historical and Projected)
- Background Facts
- Competitive Environment
- If your business is just getting started, contact your nearest Small Business Development Center (SBDC ) or Score representative for help in developing an overall business plan.
- If you are an established firm with a record of domestic or overseas sales and are looking to export, your local U.S. Commercial Service office can assist.
- Country Commercial Guides provide the latest market intelligence on more than 140 countries from U.S. embassies worldwide.
- A Basic Guide to Exporting provides a roadmap for developing an export plan. See Chapter 2: Developing an Export Strategy.
Get Ready to Export: My Export Plan
Pick a board, create a board.
Owner: Beta Community Site Guest User
Create Cancel
Get Ready to Export: My Export Plan My Export Plan
Prepare to export.
[Download Video 21MB] Quick Links: Back to First Video in Set | Get Ready to Export Video Set | How to Export Video Series | Subscribe to our Email Updates and Tips .
Developing an Export Plan
The purpose of an export plan is to assemble facts, constraints, and goals, and to create an action statement that takes these elements into account. The plan includes specific objectives, sets forth time schedules for implementation, and marks milestones so that the degree of success can be measured and can motivate personnel.
Export Plan Tips
- The first time an exporting business plan is developed, it should be kept simple. It need be only a few pages long because important market data and planning elements may not yet be available. The initial planning effort itself gradually generates more information and insight. As you learn more about exporting and your company’s competitive position, the export plan will become more detailed and complete.
- Your plan should be written and viewed as a flexible management tool, not as a static document. Plan objectives should be compared with actual results to measure the success of different strategies. Don’t hesitate to modify and make the plan more specific as additional information and experience are gained.
- A detailed plan is recommended for companies that intend to export directly, meaning selling to an end-user in another country. If your company chooses indirect export methods or sells via your or a third party’s website, you may use much simpler plans.
The Value of an Export Plan
- Written plans give a clear understanding of specific steps that need to be taken and help assure a commitment to exporting over the longer term.
- Only about a third of small -and medium-sized U.S. manufacturers have a written plan. Absent a plan, your business may overlook much better opportunities. In addition, reactive exporters may quickly give up on selling to international customers, concluding prematurely that it’s not worth the effort, or that it’s easier to serve customers closer to home even if that base may not grow, and could even shrink in the future.
- Remember that while 59 percent of all U.S. exporters export to only a single market (predominantly Canada), many small exporters sell to more countries than they have employees, and these sales account for a growing percentage of total sales. These mini-multinationals are becoming more common, and your company can be one of them.
Length of the Export Plan
Product or service.
- What need does my product or service fill in the global marketplace?
- What modifications, if any, must be made to adapt my product for export markets?
- Do I need special licenses or certificates from the U.S. or the buyer’s government?
- Do I need to modify packaging or labeling?
Pricing Considerations
- What is the cost to get my product to market (freight, duties, taxes and other costs)?
- Given an estimate of the shipping costs, what is my pricing strategy?
- What, if anything, do I need to protect my intellectual property?
- What modifications, if any, should I make to my website for marketing purposes?
- Should I sell on third party eCommerce platforms?
- What kinds of social media should I use to build awareness?
- Should I attend a trade show where international buyers are present?
Management Issues
- Are the reasons for pursuing export markets solid objectives (such as increasing sales volume or developing a broader customer base), or more frivolous (for example, the owner wants an excuse to travel)?
- How committed is top management to exporting? Is exporting viewed as a quick fix for slumping domestic sales? Will export customers be neglected if domestic sales pick up?
- What are the expectations? How quickly does management expect export operations to become self-sustaining? What level of return on investment is expected?
- With which countries has business already been conducted, or inquiries already received?
- Which product lines are talked about the most?
- Are domestic customers buying the product for sale or shipment overseas? If so, where?
- Is the trend of sales and inquiries up or down?
- Who are the main domestic and foreign competitors?
- What are some lessons learned from past export experiences?
Management and Personnel
- What in-house international expertise does the company have (international sales experience, language capabilities, etc.)?
- Who will be responsible for the export department’s organization and staff?
- How much senior management time should/could be allocated?
- What organizational structure is required to ensure export sales are adequately serviced?
- Who will follow through after the planning has been done?
Production Capacity
- How is the present capacity being used?
- Will filling export orders hurt domestic sales?
- What about the cost of additional production?
- Are there fluctuations in the annual workload? When? Why?
- What minimum-order quantity is required?
- What is required to design and package products specifically for export?
Financial Capacity
- What amount of capital can be committed to export production and marketing?
- What level of operating costs can be supported by the export department?
- How are initial expenses of export efforts to be allocated?
- What other new development plans might compete with export plans?
- By what date must an export effort pay for itself?
- Do you qualify for any type of export financing?
Sample Outline of an Export Plan
Part i: export policy commitment statement , part ii: situation or background analysis.
- Product/Service for Export
- Export License (if needed)
- Personal Export Organization
- Products/Services to be Exported
- Products that Qualify Under FTAs
- Resources Outside the Company
- Industry Structure, Competition, Demand Operations
- Export Control Compliance
- Product Classifications
- Resources Inside the Company
Part III: Marketing Component
- Identifying, Evaluating, and Selecting Markets
- Product Selection and Pricing
- Distribution Methods
- Internal Organization and Procedures
- Sales Goals (Profit and Loss Forecasts)
- Terms and Conditions
- Pricing with Consideration of Duties, Taxes
- Freight Costs, and Logistics Included
Part IV: Tactics—Action Steps
- Primary Target Countries
- Indirect Marketing Efforts
- Quarterly Accomplishments
- Secondary Target Countries
Part V: Export Budget
- Pro-forma Financial Statements
- Marketing Materials
- Travel
- Website Enhancements
- Trade Show Visits
- Other Costs
Part VI: Implementation Schedule
- Periodic Operational and Management Review (Measuring Results against the Plan)
Addenda: Background Data on Target
- Basic Market Statistics (Historical and Projected)
- Background Facts
- Competitive Environment
- If your business is just getting started, contact your nearest Small Business Development Center (SBDC ) or Score representative for help in developing an overall business plan.
- If you are an established firm with a record of domestic or overseas sales and are looking to export, your local U.S. Commercial Service office can assist.
- Country Commercial Guides provide the latest market intelligence on more than 140 countries from U.S. embassies worldwide.
- A Basic Guide to Exporting provides a roadmap for developing an export plan. See Chapter 2: Developing an Export Strategy.
Get Ready to Export: My Export Plan
Pick a board, create a board.
Owner: Trade Community Site Guest User
Create Cancel
How To Start An Export Business: From Local To Global
Figuring out how to start an export business is essential for motivated individuals that want to begin a new enterprise. Companies like these can earn high revenue streams by selling American-made products to buyers overseas. However, there are many regulatory concerns and market research that must be completed before you can get a company off the ground.
The U.S. Commercial Service, a government organization that helps U.S. exporters, recommends these steps when starting an export business:
- Determine your market
- Learn legal requirements
- Craft business plan
- Secure financing
- Source products
- Set up logistics network
Following these steps will ensure goods travel abroad without incident.
Learn how to start an export business with a guide crafted with the expertise of our specialists.
How To Start An Export Business from Home
The idea of taking a business from a local market to the global stage can be both exhilarating and daunting. In today’s interconnected world, starting an export business from the comfort of your home is more feasible than ever. By breaking the process down into simple steps, it’s possible to start shipping goods in no time.
We’ll break down the steps that you can follow to make this your reality.
1. Determining Your Market
Determining the right market for an export business is a crucial step that can dictate the success of a company. Fortunately, there are numerous ways aspiring entrepreneurs can find a viable market.
According to the International Trade Administration , businesses should research the following:
- Country market conditions
- Free trade agreements (FTA)
- Industry research
- Market intelligence
- Trade stats
- Export market ranking
- Foreign trade remedy actions
Researching country market conditions is essential for exporters. It will help them understand the economic health and consumer behavior in a potential market.
FTAs between the U.S. and other countries significantly influence the decision-making process for various export businesses. The U.S. has FTA’s with 14 countries as of the writing of this article. These agreements have many benefits, such as reduced or eliminated tariffs, improved intellectual property regulations, and ease of investment rules.
Popular U.S. FTA nations for exports include:
- Mexico, Canada Agreement (USMCA)
- Central America — Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR)
- Australia Free Trade Agreement (AUFTA)
- Israel Free Trade Agreement (ILFTA)
- Chile Free Trade Agreement (CLFTA)
Conducting industry-specific research can uncover the demand for products and the competitiveness of the sector within a market. This ensures exporters will be able to sell the goods they have.
Market intelligence requires gathering different types of information and data, such as:
- Competitors
- Overall market conditions
Armed with this information, businesses can set up timely updates about opportunities and conditions in certain markets.
Trade statistics offer quantitative insights into the flow of goods and services between countries. With this kind of raw data, business owners can find trends and determine which markets are growing the fastest.
Rankings can provide a starting point for exporters by giving them a better way to compare opportunities in different sectors. Each rank will highlight leading markets and future chances to earn profit.
Finally, exporters should check which countries have foreign trade remedies. This includes determining if a nation has antidumping and countervailing duties imposed on any incoming products. It may be harder to enter markets in nations that have these in place.

2. Legal Requirements
Now that a target market has been identified, businesses will need to handle certain legal requirements. The first thing an entrepreneur will have to do is register their business with the government. This can be done by filing for a federal tax ID .
For most companies, this is all that has to be done to become a legal entity. However, certain businesses may register with the federal government for trademark protection or to obtain a tax-exempt status.
Next, it’s necessary to determine the legal requirements for selling goods to other countries. While most products don’t need an export license, there are certain items that do.
To determine if one is needed, business owners will need to consider three government bodies that regulate U.S. exports:
- U.S. Department of Commerce
- U.S. State Department
- U.S. Treasury Department
The U.S. Department of Commerce, through their Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS), administers the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR). These rules set export control guidelines for products that have a military or dual military use.
Exporters will need to determine if their items are on the Commerce Control List (CCL). This is done by checking the list and seeing if their product has an Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) .
If an exporter’s goods are on the list and has an ECCN, exporters will need to determine the following:
- Destination of goods
- End-use
ECCN information will determine if an export license is required or not. The U.S. State Department administers the International Trade in Arms (ITAR) Program. These guidelines apply to exports that are designed, modified, or upgraded for military purposes.
Businesses that plan to sell these goods to buyers in other countries will need to consult the U.S. Munitions List. This will let exporters determine if ITAR licensing is required.
The Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) under the U.S. Treasury Department has regulations as well. They maintain a denied parties list, which contains individual, organizations, and entities that cannot be sold exported goods.
Finally, company owners should consult the Consolidated Screening List (CSL). This is a compilation of different screening lists from various federal agencies . The CSL is a list of parties the U.S. government places export restrictions on.
Learn more about ITAR and EAR compliance in our article on these two important U.S. export laws.
3. Crafting A Business Plan
The next part of starting an export business is formulating a plan. This will act as a blueprint for a company to follow. Exporters will need to work out a few details to formulate their business plan.
This includes:
- Determine product or service
- Use market research
- Decide on a pricing strategy
- Determine how to find buyers
The initial step in the process is selecting an appropriate product or service to export. The goods offered by a business should be in demand from buyers in a foreign country.
The market research analysis you should have conducted at this point will help. Using it, you can evaluate whether your chosen product(s) should be modified to align with different market regulations and consumer preferences.
When it comes to building out an effective pricing strategy, a business needs to strike a balance between covering their costs and offering a competitive price.
To figure out the right amount to charge, companies should consider:
- Foreign market objectives
- Product-related costs
- Market demand
- Competition
The last part of formulating an export business plan is buyer acquisition. Companies need customers that will purchase their products to thrive and grow. When just starting out, there are a few strategies available to find potential buyers.
This includes:
- Attending international trade fairs
- Engaging with promotion programs
- Leveraging online marketplaces
- Joining a sales channel
- Winning foreign government contracts
Entrepreneurs that find buyers early on will start earning money fast once their business launches.
4. Financing Your Business
Financing is another important step that goes into starting an export business. Without start-up capital of some kind, options are very limited. Fortunately, company owners can obtain loans from the SBA to help them with this financial support.
Funding includes:
- Export Express Program
- International Trade Loan Program
- Export Working Capital
The Export Express Loan program provides entrepreneurs with small term loans that will help them develop the export side of their business. Maximum funding can be as high as $500,000, which can be used to buy goods or produce services that a company can export.
The International Trade Loan Program is used to improve the competitive position of businesses that are engaged in or are preparing to engage in international trade. Funding for this program has a maximum of $5 million that can be used to upgrade tools and facilities.
Another option available to entrepreneurs is the Export Working Capital Program. This system provides short-term, transaction specific capital loans given to companies that can generate export sales, but need additional support. Funds for this program also have a limit of $5 million.
Entrepreneurs that don’t want to pursue these loans can seek out financing support from the Export-Import Bank (EXIM Bank) of the United States. There are two financing options provided by the EXIM Bank.
These include:
- Limited Recourse Project Finance
- Structured Financing
Limited Recourse Project Finance is an option that’s great for newly created companies. With this plan, businesses can repay the loan using their future cash-flows.
Benefits of this program include:
- Mitigated risk
- Legitimacy thanks to EXIM involvement
- Long-term finance assistance
For U.S. exporters, the Structured Finance program can make their bids more competitive on large international projects by providing their buyers with access to long-term financing.

5. Source Products
Sourcing products is the next critical step for entrepreneurs that want to start an export business. Knowing what you want to export and having it readily available are different goals. Company owners will need to identify a manufacturer that can provide the goods they want to sell.
Fortunately, there are a few resources that entrepreneurs can use, including:
- Trade shows
- Online directories
- Business network
- Industry contacts
Regardless of where you find a supplier, they should ensure they have a proven track record and a history of reliability. It’s important to ensure the products meet the quality standards expected by the target market. Exporters can check the quality of goods at a trade show or by requesting samples.
6. Set Up Logistics Operations
Setting up logistics and operations is the last, though not least, concern that needs to be taken care of when starting an export business.
There are three elements to this part of export operations:
- Product preparation
- Shipping basics
- Shipping documents
During product preparation, goods may require alteration to be operable, marketable, or legally compliant. Every country has unique standards, regulations, or certifications that products must adhere by to make entry. For example, goods going to the EU will require the European Conformity (CE) Mark.
Certain electronic equipment might need alteration to be operable. This could mean swapping out old plugs for new ones that will fit the wall sockets in a foreign country. Correct labels and marks are essential as well. Any words on a label should be in the foreign county’s native language.
Researching the local customs practiced by a certain nation is a good precaution to take. Certain colors might be associate with darker topics, such as death. Therefore, exporters will want to keep these off their labels.
Entrepreneurs should also check to ensure their company name and the products they’re selling don’t translate to something completely different in the native language of a foreign nation.
Now that the necessary preparations have been made, exporters can start focusing on how they will ship their goods. First, they’ll need to consider their transportation options.
Among these are:
- International air
- Ocean freight
- Truck
It’s likely that exporters will have to use some combination of these shipping options to deliver goods to their foreign buyers. Numerous carriers are available to provide their services. Connecting with a freight forwarding service is a great way to research your options for international shipping.
Exporters should also get familiar with Incoterms™ before shipping their goods. These are internationally recognized agreements between buyers and sellers that dictate responsibilities to each party in the shipping process. These agreements can impact how much responsibility an exporter may have over things such as shipping.
After taking care of transport, entrepreneurs will need to obtain the correct information and documents required for export .
- Schedule B number
- Pro forma invoice
- Commercial invoice
- Packing list
- Certificate of origin
- Certificate of conformity
- Air waybill/bill of lading
Some documents will need to be submitted electronically, such as the Automated Export System (AES). Depending on the shipment, a license might be required . Each document is essential for goods to be successfully exported to another country. Therefore, it’s imperative that exporters obtain them all before shipping.
How Much Does It Cost To Start An Export Business?
Startup costs for an export business can be somewhere between $4,000 and $26,000. Numerous factors will influence the expenses entrepreneurs can incur.
- Initial setup costs
- Market research and planing
- Product sourcing and inventory
- Marketing and promotion
- Logistics and shipping
Registering the business entity might include state and local registration fees. While most export licenses are generally free, there may be certain ones that have a specific expense. Opening an office space and obtaining supplies will also inflict costs on exporters.
Conducting thorough market research is essential and might include expenses for accessing detailed reports, market analysis tools, or consultancy fees. Entrepreneurs might need professional assistance to put together a comprehensive business plan, which can be costly.
Initial product procurement can be a significant expense, depending on the nature of the items and the quantities required. Inventory costs include not just the price of goods, but also storage and insurance.
Marketing expenses to promote the products in international markets can vary widely. This might include digital marketing, attending trade shows, or creating promotional materials. Developing a website and maintaining an online presence is also essential in today’s market. This will include web development and hosting costs.
Shipping is a major expense for export businesses. This includes freight charges, insurance, and packaging costs. Exporters will have to consider the costs from duties, taxes, and compliance with shipping regulations before they move their cargo as well.
Use our article on Schedule B numbers and HS codes to avoid confusion between the two.

What Are the Best Countries To Export To?
There are many foreign buyers willing to purchase a variety of U.S. goods, which means exporters won’t have much difficulty finding customers. According to the United States Trade Register (USTR), there are five countries that import U.S. products more than other nations around the world.
- United Kingdom
While these are great markets to get into, there are other nations that make for great export opportunities. Keep in mind, the U.S. has FTAs with numerous countries. Any of these nations will be good to conduct business in. We’ve listed some data of nations engaged in FTAs with the U.S. and how many goods they purchase.
Amount of U.S. Goods Exported To FTA Countries (2022)
Provided by the USTR , ITA , and Trading Economics
We’ve excluded Mexico and Canada, as these countries have already been mentioned. That said, the other nations on this list make for great export opportunities. Entrepreneurs will need to research the specific FTAs the U.S. shares with these countries to determine the extent of the agreement.
Start Your Business with Cargo Export USA In Your Corner
Cargo Export USA can guide you through the startup of your business. The team we have will give you the tools you need to be successful. With our plethora of skills and offerings, your business will be running efficiently.
Services offered by Cargo Export USA include:
- Product Classification: Ensuring your products are correctly classified for international shipping.
- Certificate of Origin: This documentation is essential for many FTAs. It will verify where your goods are from.
- Export Licensing: Assistance with obtaining the required licenses for your export products.
Starting an export business doesn’t have to be difficult. With the help of Cargo Export USA, your business will be operational and earning money at a rapid pace.
Let us help you unlock the door to international success. Connect with us through the site or call our team at (866) 301-0635 .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Export Finance Solutions Where Businesses Come to Grow: Official Blog of the Export-Import Bank
- Export Credit Insurance
- Working Capital
- Success Stories
- Additional Resources
The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) has created a hands-on exporting preparation guide and innovative tool called the Export Business Planner . It is designed to serve as a roadmap for creating an export business plan, exploring foreign markets and financing, developing a marketing plan, and more. But unlike a traditional printed manual, this Planner is a “living document”, ready to be customized and continually updated by you. The document can be updated and referenced time and again as your export business grows. If you have a successful product or service, you may be able to increase sales and profit by following your plan.
Export planning entails a fair amount of research. But with the Planner , there’s no need to remember and/or compile these resources yourself – they are all embedded in appropriate topical locations. As such, you are given a “head start” on conducting export research, as the step of finding the best sources of further information has already been done for you. All you need to do is complete the worksheets and then save them – and your Export Business Plan will be underway.
The Export Business Planner is a downloadable tool to save and customize:
- How to determine your export readiness
- Training and counseling information
- Worksheets for global market research
- Financing information and options
- Customizable export business plan and marketing plan templates
- Helpful resources for exporters
- Glossary of Export terms
If you are looking for more information on financing options for your exports and how export credit insurance can help your business mitigate risk and increase competitiveness, the Export-Import Bank of the U.S. has trade finance specialists located in your area that you can speak to. To get a FREE consultation, click below:

Import Export Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Trade Global Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Trade Global business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Trade Global businesses.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Trade Global business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Trade Global is a startup Import/Export company located in Houston, Texas. The company was founded by Ted Rogers, who has deep experience as a wholesale distribution executive. Ted has long aspired to work for himself, and has been systematically acquiring the tools and knowledge necessary to successfully operate an import/export business. The combination of his skills and drive positions him to succeed. What’s more, he has an extensive network of contacts across the globe, which will provide an edge in acquiring clientele.
Product Offering
Trade Global has acquired a warehouse in Hong Kong, and has entered into contracts with five Asian manufacturers to export goods to the United States. As the company gains credibility and grows its client base, it has plans to begin building its own fleet of cargo ships that will carry goods both into and out of the United States.
Customer Focus
Trade Global will procure products from manufacturers and wholesale products to distributors throughout the United States, Southeast Asia, and Europe.
Management Team
Trade Global will be owned and operated by Ted Rogers. Ted has a background as a wholesaler, and is a graduate of Michigan State University’s Supply Chain Management program, and subsequently earned an Export/Import Certificate from the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
Success Factors
Trade Global will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Friendly, knowledgeable, and highly qualified owner
- An ideal warehouse location in Hong Kong, with ample room for expansion
- FTZ status with Port Houston
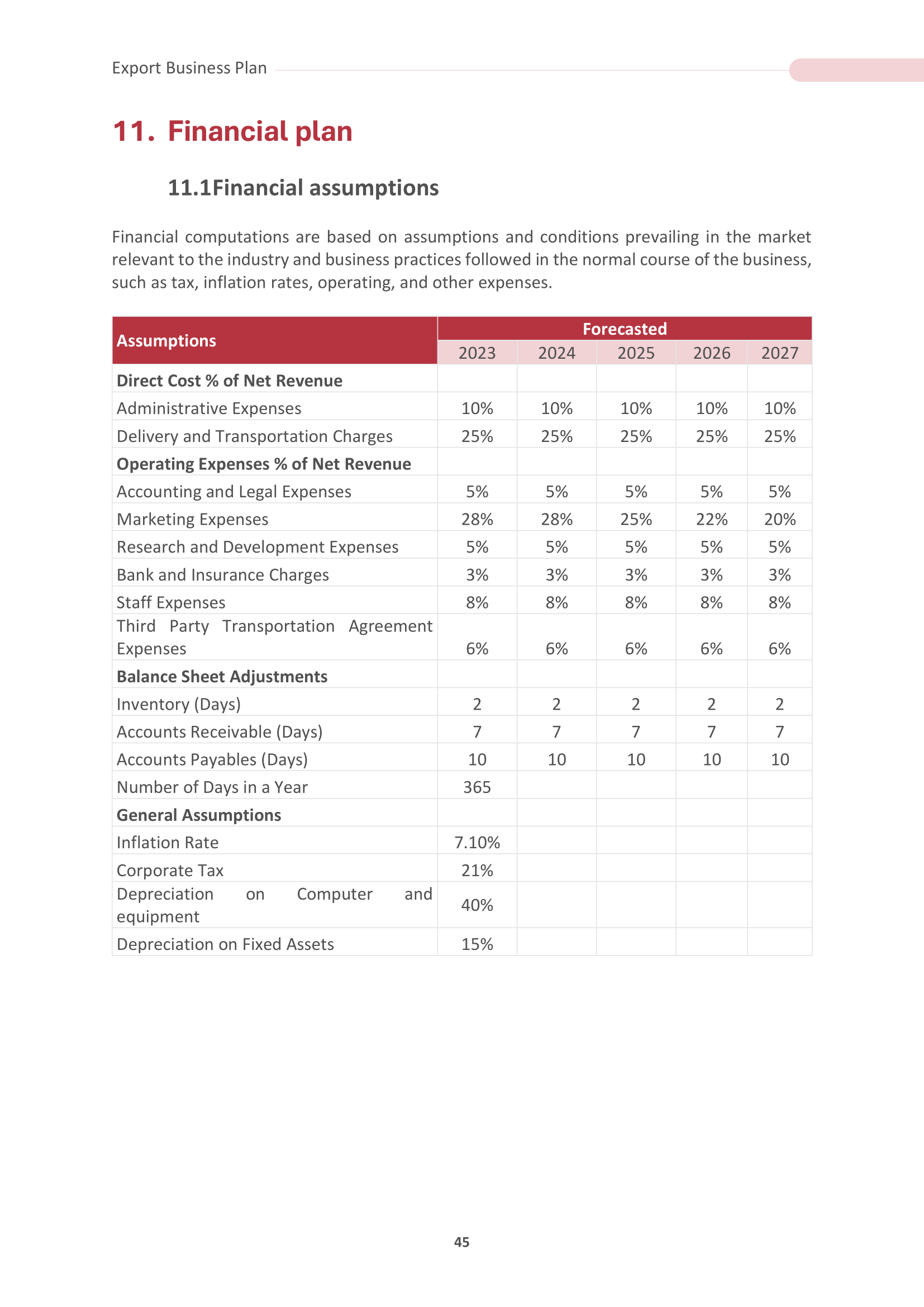
Financial Highlights
Trade Global is seeking $750,000 in debt financing to launch its import/export operation. The funding will be dedicated towards procuring, packing, and shopping products, and payroll of the staff until the firm reaches break even. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Inventory: $250,000
- Shipping costs: $250,000
- Office equipment, supplies, and materials: $10,000
- Overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $200,000
- Marketing costs: $20,000
- Working capital: $20,000
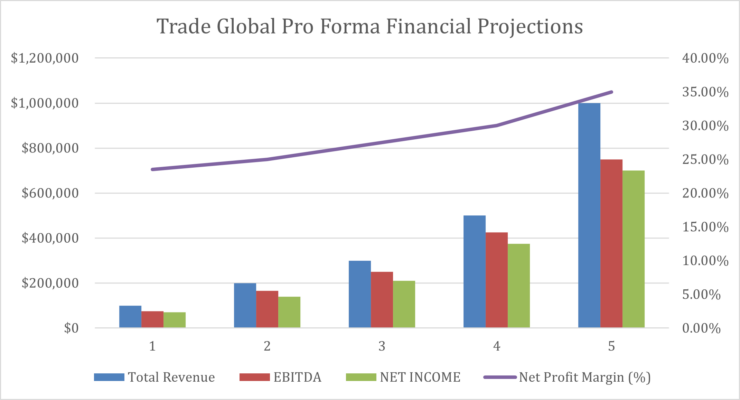
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Trade Global.
Company Overview
Who is trade global.
Trade Global is a startup import/export company located in Hong Kong and Houston, Texas. The company was founded by Ted Rogers, who has deep experience as a wholesale distribution executive. Ted has long aspired to work for himself, and has been systematically acquiring the tools and knowledge necessary to successfully operate an import/export business. The combination of his skills and drive positions him to succeed. What’s more, he has an extensive network of contacts across the globe, which will provide an edge in acquiring clientele.
Trade Global aims to deliver a wide variety of goods both into and out of the United States. The team is highly qualified and experienced in sales and supply chain management.
Trade Global History
Trade Global is owned and operated by Ted Rogers, a former distribution executive and ICC certified Importer/Exporter. Ted has worked for a large wholesale company and oversaw a wide variety of accounts from around the world. Derek’s tenure with the wholesale distribution company, as well as his education in Supply Chain Management has given him the skills and knowledge required to venture out and start his own company. Ted has been awarded contracts with two large Chinese manufacturers, which guarantees Trade Global stability while it works to increase its reach.
Since incorporation, Trade Global has achieved the following milestones:
- Registered Trade Global, LLC to transact business in the state of Texas.
- Acquired an import license from US Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- Has acquired an existing warehouse in Hong Kong.
- Reached out to numerous manufacturers to apply for wholesale contracts.
- Entered into a contract with a deep sea cargo transportation company.
- Began recruiting warehouse workers, and office personnel to work at Trade Global.
Trade Global Services
Trade Global has signed contracts with two manufacturers, to export goods from China to the US. It will begin as a small exporter, with ample warehouse space for growth. The company will keep abreast of logistics technology innovations as it grows.
Industry Analysis
The US import/export industry is significant in terms of revenue. According to the United States International Trade Commission (USITC), the total value of US goods and services exports in 2022 was approximately $2.09 trillion, and the value of imports was approximately $3.0 trillion. This resulted in a trade deficit of roughly $948.1 billion for the year. The revenue generated by the industry is a combination of goods and services exported and imported by the United States.
Over the last few decades, the US import/export industry has seen consistent growth. The USITC data indicates that the total value of US exports and imports has grown substantially since the 1980s. This growth is influenced by factors such as globalization, trade agreements, technological advancements, and evolving consumer demands.
The trade deficit, which occurs when the value of imports exceeds exports, has been a subject of concern for policymakers. Reducing the trade deficit has been a goal of various US administrations.
Several trends have shaped the US import/export industry:
- Globalization: Increased globalization has allowed US businesses to access international markets and global supply chains. This trend has led to an expansion in both exports and imports, as well as an interconnected global economy.
- E-commerce: The growth of e-commerce has had a substantial impact on the industry. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) have easier access to international markets through online platforms, leading to a boost in exports of services and goods.
- Trade Policies: Trade policies, such as tariffs and trade agreements, have a significant impact on the industry. The US has experienced trade tensions with several countries, notably China. These policies can influence the types of goods and services that are imported and exported.
- Technology: Advancements in technology have made it easier for businesses to engage in international trade. Technologies like blockchain, logistics software, and automation have improved efficiency and tracking in the import/export process.
- Environmental and Ethical Concerns: There is a growing focus on sustainable and ethical trade practices. Consumers and businesses are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of products, leading to changes in supply chain management and the types of goods being imported and exported.
- Geopolitical Factors: Geopolitical factors, such as trade relations with China, Brexit, and tensions in the Middle East, can affect trade patterns and the stability of the import/export industry.
Customer Analysis
Profile of target market.
Trade Global will initially target manufacturing companies in China, and wholesale companies in the US.
The precise data for these target markets are:
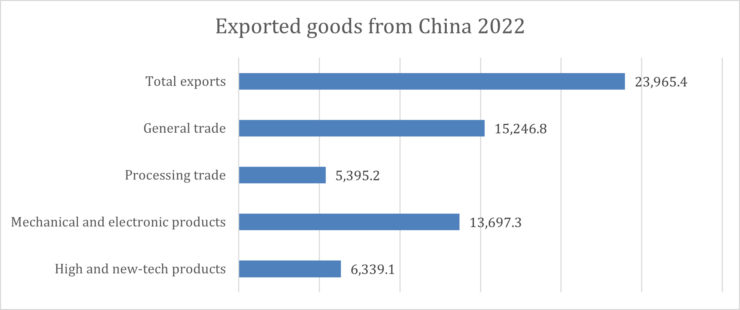
China In 2022, the total merchandise exports from China amounted to around 24 trillion yuan. This included 6.3 trillion yuan worth of high and new-tech products and over 13.6 trillion yuan worth of mechanical and electronic products.
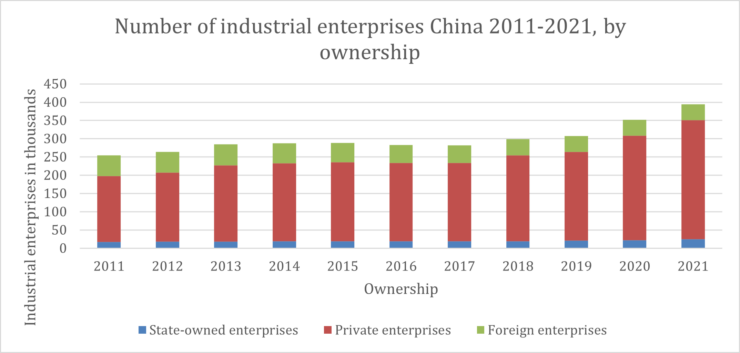
As of 2021, there were around 25,200 state-owned industrial enterprises above designated size in China.
United States The Wholesale Trade sector is an intermediary step in the supply chain process. Companies in the sector distribute goods from agriculture, mining, manufacturing and information industries to downstream markets, typically without any transformation. In 2023, the US Wholesale sector is valued at $11.3 trillion.

Customer Segmentation
Trade Global will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Small to medium manufacturers of FMCG in China
- Wholesale distributors of FMCG in US
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Trade Global will face competition from other companies with similar business models. A description of each competitor company is below.
Global Electronic Imports & Exports, Inc.
Established in 1990, Global Electronic Imports & Exports specializes in the import and export of consumer electronics, including smartphones, tablets, and audio equipment. They also deal in a range of accessories and components related to consumer electronics.
Global Electronic Imports & Exports has long-standing partnerships with major electronics manufacturers in Asia, including Samsung, LG, and Panasonic. They also collaborate with major US-based retailers for distribution.
Global Electronic Imports & Exports reported an annual trade volume of approximately $150 million in consumer electronics and related products last year.
Natural Foods International
Established in 2005, Natural Foods International specializes in the import and export of food products, with a focus on organic and non-GMO items. They deal in a wide range of commodities, including grains, nuts, and dried fruits.
The company has established partnerships with a network of international organic farms and cooperatives. They also have distribution agreements with major US grocery chains, such as Whole Foods Market and Trader Joe’s.
Last year, Natural Foods International reported a trade volume of approximately $85 million in organic and non-GMO food products.
Titan Heavy Machinery, Inc.
Established in 1998, Titan Heavy Machinery is a specialized import/export company focusing on the heavy equipment and construction industry. Their product range includes excavators, bulldozers, and industrial vehicles.
The company has close partnerships with leading heavy machinery manufacturers, particularly in Japan and Germany. They also collaborate with construction and mining companies in the US and overseas.
Last year, Titan Heavy Machinery reported a trade volume of approximately $60 million in heavy equipment and machinery, serving the construction and infrastructure development sectors.
Competitive Advantage
Trade Global will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
- Smaller, more personal operation, with highly-qualified supply chain experts
- Trade Global stays abreast of all technology developments, constantly seeks to improve the supply chain, and delivers an accurate and complete shipment to each customer.
- Trade Global offers competitive pricing for its services. Their pricing structure is the most cost effective compared to the competition.
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Trade Global will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Highly-qualified team of supply chain experts that provide a comprehensive suite of export/import services (sales, packaging, shipping, customs, tariff/financial, marketing, expedient delivery).
- Unbeatable pricing to its clients – Trade Global does not mark up its services at a large percentage, offering competitive pricing.
Promotions Strategy
Flexibility and adaptability are key in marketing, as the import/export industry is subject to changes in international trade policies, global economic conditions, and shifting market dynamics.
The promotions strategy for Trade Global is as follows:
Create a Strong Online Presence:
Trade Global will build a professional, user-friendly website that showcases the company’s services, products, and expertise. The site will be optimized for search engines (SEO) to improve its visibility in online search results.
Network and Build Relationships:
Trade Global will make a point of attending a variety of trade shows and industry events to meet potential clients, suppliers, and partners, since building and maintaining relationships in the import/export industry is often critical to success.
Trade Global will also join industry-specific associations and chambers of commerce to gain credibility and access a network of contacts.
Online Marketing:
Trade Global will list products or services on established online B2B marketplaces like Alibaba, Global Sources, or TradeIndia to reach a global audience.
Trade Global will launch an email marketing campaign to reach potential clients, partners, and suppliers. Share industry news, company updates, and promotional offers.
The company will use online advertising platforms such as Google Ads and social media advertising to deliver targeted ads that promote import/export services.
Trade Publications and Directories:
Trade Global will advertise the business in relevant industry directories and advertise in trade publications specific to each product niche.
Trade Global’s pricing will be moderate and on par with competitors so clients feel they receive value when purchasing their goods and services.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Trade Global. Operation Functions:
- Ted Rogers will initially handle all procurement, finding goods, buyers for goods, negotiating prices, and arranging logistics.
- The company will employ an administrative assistant, who will handle all documentation and answer non-urgent communications.
- The company will employ three warehouse managers to oversee logistics operations.
Milestones:
Trade Global will have the following milestones complete in the next eight months.
- 5/1/202X – Finalize construction of warehouse space
- 6/1/202X – Complete recruitment process for warehouse management
- 6/15/202X – Finalize shipping partnerships
- 8/1/202X – Finalize wholesale contracts
- 11/15/202X – Complete hiring of warehouse team
- 12/1/202X – Receive first products intended for export
Trade Global will be owned and operated by Ted Rogers, who will oversee the procurement and logistical operations.
Ted Rogers has a background in wholesale, and is a graduate of Michigan State University’s Supply Chain Management program, and subsequently earned an Export/Import Certificate from the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
Trade Global has begun the recruitment process for experienced Warehouse Managers in Hong Kong, and expects to complete the hiring process within one month.
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for Trade Global will largely rely on finding the best buyers for products being imported/exported. In addition, negotiating the lowest shipping costs will be a significant factor in revenue realized.
The cost drivers will be the overhead costs required to procure goods, and operate the warehouse. The major expenses will be payroll, and shipping costs.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and to pay off the startup business loan.
- Sales Revenue: Projected sales revenue will be broken down by product or service, region, and customer segments.
- Gross Margin: Profit projections will account for variations in costs, such as shipping, import duties, and currency fluctuations.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This includes the cost of acquiring the goods for import or export.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Exchange rates can significantly impact the financial performance of an importer/exporter.
- Credit Terms: Credit terms offered to customers and suppliers impact cash flow and working capital requirements.
- Inventory Turnover: Carrying costs and storage expenses will impact profit; therefore, an accurate forecast of how quickly inventory will need to be replenished is important
- Taxes and Duties: Import/export duties, taxes, and customs fees based on the countries involved in the trade
- Economic Conditions: inflation rates, interest rates, and political stability can affect profitability
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, trade global business plan faqs, what is an import export business plan.
An import export business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your import export business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Import Export business plan using our Import Export Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Import Export Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of import export businesses , some examples include: Export management company, Export trading company, and Import-export merchant (or free agent).
How Do You Get Funding for Your Import Export Business Plan?
Import Export businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start an Import Export Business?
Starting an import export business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop An Import Export Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed import export business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your import export business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your import export business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Import Export Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your import export business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your import export business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Import Export Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your import export business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your import export business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Search ITA Search

Learn How To Export
Are you looking to grow your business through exporting? Assess your company’s readiness to enter your first markets, expand into additional markets, or take on more challenging, high-growth export markets.
Understand the Export Process
Import Export Business Plan: Everything You Need to Know
Making an import export business plan requires funds, time, and determination, but it's worth the effort. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
Making an import export business plan requires funds, time, and determination, but it's worth the effort. Especially, an export business plan is the key to success.
If you have an import-export business, it's essential to understand how to make an import-export business plan. You can work with your team to create an import-export business plan. You can also use online software to make a business plan for you automatically. However, you must know your requirements.
You should know your company well in order to align your resources and objectives with your business goals.

Things to Consider Before Writing an Import-Export Business Plan
1. Advertise Online
Almost all businesses must have a quality website. It's impossible to attract foreign customers without having an online presence. Set up a website with information about your offerings.
If you are planning to sell your products in another country, your website must be targeted at foreign clients. Have a working contact form on your website to make yourself reachable to the prospective customers. You may have to spend several hours online responding to inquiries, but it's worth it.
2. Conduct Market Research
It's important to know your target market before you start selling. Conduct a market research to understand your commercial environment. Find out whether there are any entry barriers.
Know the standards and specifications of your target market to increase your profits. Estimate the size of the market, and know your major competitors. If you conclude that you don't have any competitors, you might have done your research wrong.
It's a good idea to offer something that your local competitors don't. A little but serious research can help you identify and exploit the opportunities present in the market.
You can find most of the information online. Reading marketing books can also provide some helpful insights. Consider building up a team of co-workers so different members can specialize in different fields to complement one another.
3. Create a Package
The look of your product can make all the difference between success and failure. However good your product is, you will struggle to sell it without good packaging and marketing.
Have attractive packaging for your product, and come up with special offers. Try to make your package notably different from your competitors. Remember that originality is an essential aspect of packaging.
4. Adjust to the Foreign Market
Position your product according to the demand of the foreign market. Your offering should meet the expectations of your customers. You may have to create special products for different countries. It may mean making additional investment, but it can be an important factor contributing to your success. You will also need to adapt your business policies to go with the regulations of the new market.
5. Stay Connected With Your Customers
In the end, your financial success depends upon your customers. Hence, you must be aware of their expectations and preferences. Keeping in touch with your customers is the best way to understand their requirements.
Consider adding a chat application on your website. Include your personal information such as email, address, and phone number. You may want to adjust the information depending upon your method of communication.
It's a good idea to visit your customers regularly, or at least connect virtually through Skype calls. Personalize your relationship with your customers; you should be yielding and compromising when required.
6. Make Necessary Investments
- You will need money to make more money.
- You will have to invest in quality products to grow your sales.
- You will also need to invest in promotion and advertisement.
- Have necessary allocations in your budget for different types of investments.
- Be sure to update and fine-tune your budget every month.
- You should always be on the lookout for investment opportunities to develop and strengthen your business.
- Make use of cost-effective tools and programs for lead generation.
- Consider placing ads on search engines (Google, Bing, etc.) and social media platforms (Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, etc.).
7. Participate in Trade Shows
It's a good way to get known to international customers, especially if your product is difficult to sell or such that the customers need to see it before buying.
8. Know Your Product
- Know your product well. Respond to customer inquiries swiftly and accurately.
- Give information about your production facilities, capacity, product quality, price, and shipping.
- In case of a service, provide information such as your field of expertise, portfolio, clients served, fee structure, turnaround time, etc.
If you need help with an import export business plan, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Import Export Business License
- What Is Export Sales Contract
- Import Licensing
- Business Plan for New Company
- Do It Yourself Business Plan
- How to Start an Online Business: Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide for Entrepreneurs
- How Does a Corporation Grow
- Market Analysis: Everything You Need To Know
- IT Company Business Plan
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai pitch deck generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
- Sample Business Plans
- Retail, Consumers & E-commerce
How to Write an Import Export Business Plan + Free Template

2. Company Overview
The company overview section provides a detailed description of your business. It includes your business concept, ownership structure, history, future goals, and other business-related points.
Since you’ll give a brief business description in the executive summary, this chapter will expand on it, providing an in-depth understanding of your import-export business.
You may start by describing the fundamental details of your company, including name, concept, owners, legal structure, type of business you own, and what you’re importing or exporting.
For instance, you might own one of the several types of import-export companies: export trading company, export management company, or import-export merchant(agent)
Next, provide the start-up summary or background on your business. You may also highlight future business goals and milestones you have achieved.
For example, you may refer to the Walter’s long-term objectives:
Walter’s Long-term Objectives
The three-year goals for Walter Imports are the following:
- Achieve break-even by year 2.
- Retain our long-term contracts with local import shops in Leavenworth, WA, through excellent customer service.
- Become the premier importer of German and Scandinavian specialty products in Leavenworth, and become the prime exporter of apples and other produce for the farmers of the PCC Farmland Fund initiative.
Don’t forget to outline business insurance coverage, necessary licenses, and customs rules and regulations in both import and export countries.
3. Industry Analysis
Industry analysis is a study of your external business environment, providing a complete overview of the industry you serve and its dynamics.
This section helps potential investors and readers understand your market size, growth projections, target customers, and evolving trends. So make sure that you play your cards correctly.
You may conduct thorough market research to identify the feasible market for your imported or exported products. Also, analyze the market conditions, target market demands, and legal considerations.
Try to answer the following questions while conducting a market analysis:
- What is the current market size of the import-export industry?
- Is the market growing or falling in the USA?
- What are the major trends in the global market?
- Who are the top players in the import-export business?
- Which factors affect your business most?
- Who are your target customers you serve and/or expect to serve?
- What are the ideal customers’ buying patterns and needs?
Have a look at Walter’s ideal customer preferences:

In short, this section will educate you about the market and help you develop business strategies according to the market trends.
4. Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis is crucial to identify key competitors in the international trading market. It will help you determine your unique selling propositions and market positioning.
You may start this section by listing out all your direct and indirect competitors along with their strengths, weaknesses, and market share.
Most likely, your direct competitors or import-export businesses near your location can be more threatening to your company.
So, try to assess their specific products and services, pricing strategy, and type of customers they serve. If possible, ask for feedback directly from their customers and get valuable insights into their preferences.
Doing so will help you demonstrate your competitive advantage and USPs that set your company apart from other businesses.
5. Products and Service Offerings
This section provides a detailed description of the products & services you intend to offer and highlights the scope of your offerings, pricing plans, and more.
Since it’s your opportunity to narrate about the tangible goods or services you will be dealing with, you need to make your offerings exceptional to attract potential investors or partners.
Start writing this section with a detailed breakdown of the products you will be importing or exporting. It could be raw materials, consumer goods, machinery, raw materials, or specialized products.
You may outline the product description along with its pricing, specifications, variants, and any special features.
Here is an example of product offerings written with the help of Upmetrics AI-writing assistant :
If your business encloses service provision in the import-export process, you may specify these services, which could be logistics, quality assurance, custom clearance, or any value-based services.
6. Marketing Plan
The marketing plan provides an in-depth understanding of sales strategies and promotional techniques you will use to acquire new customers and retain existing ones.
This section helps you streamline your marketing efforts and create effective advertising campaigns to reach your target market while keeping track of the estimated budget and maximizing return on investment.
You might consider including the below strategies in your plan:
Brand Image and Positioning
Create a strong brand image and position your imported/exported products strategically. Share the value of your products and emphasize superior quality or eco-friendly practices.
Unique Value Proposition(UVP)
Describe a compelling unique value proposition and define what sets you apart from the competition. Highlight a few elements, such as product quality, ethical practices, sourcing transparency, etc.
Digital Marketing Channels
Establish a professional website, leverage social media platforms, and invest in advertising campaigns to reach the target audience. Showcase your product range or updates and share valuable content related to products or global trade insights. It will enhance your online presence.
Partnerships
Try to build healthy relationships with distributors, retailers, and local businesses. Participate in networking events, trade exhibitions, and online forums.
Customer Retention Strategies
Develop strategies to foster loyalty among customers. Implement loyalty programs, after-sales support, personalized communication, word-of-mouth referrals, or discounts for repeat clients.
7. Management Team
The management team section introduces the business owners and key managers, along with their roles & responsibilities, educational background, work experience, and compensation plan.
A powerful management team helps potential investors or readers to be confident about your import-export business’s idea and vision.
You may start writing with an introduction, highlighting the crucial role of leadership in the ultimate success of your business.
Describe owners and key members of your management staff, including senior management and other employees. Mention their roles and responsibilities, qualifications, and experience.
Also, add an organizational chart that represents the reporting structure and explains how decisions will be made.
You may refer to the below example of an organizational structure crafted using Upmetrics:
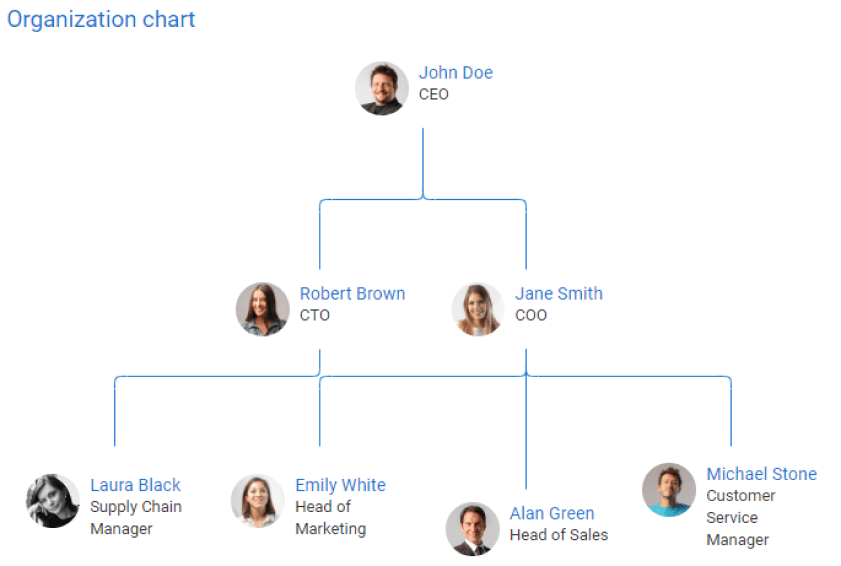
Next, outline your compensation plan which includes owners’ and key members’ earnings, bonuses, and benefits.
8. Operations Plan
The operations plan summarizes the day-to-day processes involved in the import-export company. These activities are centered on achieving the business goals and objectives described in the earlier sections.
This section helps you define your team’s responsibilities, daily tasks, and short-term goals you need to accomplish, keeping track of your long-term objectives.
For your import-export business, you may explain logistics, inventory management, distribution & warehousing, customs brokerage, and shipping & freight forwarding.
You may also highlight the quality control measures and the technology you use for order processing or real-time tracking.
Don’t forget to develop a risk mitigation strategy for probable disruptions in the supply chain, including natural disasters, global crises, or political fluctuations.
9. Financial Plan
A financial plan is the most crucial and demanding aspect of business plans.
Financial projections can be a deciding factor when it comes to persuading potential investors or banks to invest or lend money for your import-export business.
This section details all the financial information of your business, such as startup costs, cash flow & revenue streams, projected profits, and strategies to achieve financial goals.
You must include below key components and financial statements while creating a financial plan:
- Income statement
- Balance sheet
- Cash flow projections
- Capital requirements
- Operating costs
- Break-even point
- Business ratios
- Tax considerations
From the above financial forecasts, you can evaluate the funding resources for your import-export business, including bank loans, crowdfunding, investors, or personal savings.
Download Import-Export Business Plan Template
Need help writing your import-export business plan from scratch? Here you go; download our free import-export business plan pdf and get started.
It’s a modern, investment-ready business plan template specifically designed for your import-export business. Use this sample business plan as a guide for writing your own.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.

Start Preparing Your Business Plan with Upmetrics
There’s no doubt—creating business plans that draw investors in can be a very daunting task, but it becomes a lot smoother with the use of Upmetrics!
Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand one, Upmetrics offers valuable resources, such as step-by-step guides, 400+ sample business plans , and AI assistance that will serve you perfectly.
Also, our financial forecasting tool will help you create realistic financial forecasts for 3 or more years if you’re not adept with finances.
So, what are you waiting for? Start planning now!
Related Posts
Warehouse Business Plan
Drop Shipping Business Plan
Investment Company Business Plan
Proven Steps to Create a Business Plan
Frequently asked questions, what is the initial investment required for starting an import-export business.
For starting an import-export business, initial investments can vary widely based on a few factors, like the scale of business operations, specific product commodities, and target markets. It can range from $5,000(home-based small businesses) to $100,000 or more (large-scale operations).
What are the insurance requirements for an import-export business?
Insurance requirements for importers and exporters include:
- Cargo insurance
- General liability coverage
- International workers compensation
- Trade credit insurance
- Product Liability Insurance
What are the key legal and regulatory considerations in the import-export business?
It’s very crucial to stay informed about the key legal and regulatory considerations of both the exporting and importing countries. So, as per SBA , it involves customs regulations, trade laws, shipment certificates, and necessary business licenses and permits.
Can this template help in identifying potential markets and customers?
Definitely! This well-crafted business plan template can ease your workload and provide a structured roadmap for conducting market research. You may refer to industry analysis and marketing plan sections that help you analyze industry trends, identify potential markets, and understand customer demographics.
How often should I update my import-export business plan?
Remember, your import-export business plan is a living document, which means you may review and update it whenever there are significant changes in a business environment. And it’s advisable to update your plan at least once a year or quarterly.
About the Author

Vinay Kevadiya
Vinay Kevadiya is the founder and CEO of Upmetrics, the #1 business planning software. His ultimate goal with Upmetrics is to revolutionize how entrepreneurs create, manage, and execute their business plans. He enjoys sharing his insights on business planning and other relevant topics through his articles and blog posts. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

How to write a business plan for an import-export company?

Creating a business plan for an import-export company is an essential process for any entrepreneur. It serves as a roadmap that outlines the necessary steps to be taken to start or grow the business, the resources required, and the anticipated financial outcomes. It should be crafted with method and confidence.
This guide is designed to provide you with the tools and knowledge necessary for creating an import-export company business plan, covering why it is so important both when starting up and running an established business, what should be included in your plan, how it should be structured, what tools should be used to save time and avoid errors, and other helpful tips.
We have a lot to cover, so let's get to it!
In this guide:
Why write a business plan for an import-export company?
- What information is needed to create a business plan for an import-export company?
- What goes in the financial forecast for an import-export company?
- What goes in the written part of an import-export company business plan?
- What tool can I use to write my import-export company business plan?
Understanding the document's scope and goals will help you easily grasp its structure and content. Before diving into the specifics of the plan, let's take a moment to explore the key reasons why having an import-export company business plan is so crucial.
To have a clear roadmap to grow the business
It's rarely business as usual for small businesses. The economy follows cycles where years of growth are followed by recessions, and the business environment is always changing with new technologies, new regulations, new competitors, and new consumer behaviours appearing all the time...
In this context, running a business without a clear roadmap is like driving blindfolded: it's dangerous at best. That's why writing a business plan for an import-export company is essential to create successful and sustainable businesses.
To write an effective business plan, you will need to take stock of where you are (if you are already in business) and where you want the business to go in the next three to five years.
Once you know where you want your import-export company to be, you'll have to identify:
- what resources (human, equipment, and capital) are needed to get there,
- at what pace the business needs to progress to get there in time,
- and what risks you'll face along the way.
Going through this process regularly is beneficial, both for startups and existing companies, as it helps make informed decisions about how best to allocate resources to ensure the long-term success of the business.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

To get visibility on future cash flows
If your small import-export company runs out of cash: it's game over. That's why we often say "cash is king", and it's crucial to have a clear view of your import-export company's future cash flows.
So, how can you achieve this? It's simple - you need to have an up-to-date financial forecast.
The good news is that your import-export company business plan already includes a financial forecast (which we'll discuss further in this guide). Your task is to ensure it stays current.
To accomplish this, it's essential to regularly compare your actual financial performance with what was planned in your financial forecast. Based on your business's current trajectory, you can make adjustments to the forecast.
By diligently monitoring your import-export company's financial health, you'll be able to spot potential financial issues, like unexpected cash shortfalls, early on and take corrective actions. Moreover, this practice will enable you to recognize and capitalize on growth opportunities, such as excess cash flow enabling you to expand to new locations.
To secure financing
A detailed business plan becomes a crucial tool when seeking financing from banks or investors for your import-export company.
Investing and lending to small businesses are very risky activities given how fragile they are. Therefore, financiers have to take extra precautions before putting their capital at risk.
At a minimum, financiers will want to ensure that you have a clear roadmap and a solid understanding of your future cash flows (like we just explained above). But they will also want to ensure that your business plan fits the risk/reward profile they seek.
This will off-course vary from bank to bank and investor to investor, but as a rule of thumb. Banks will want to see a conservative financial management style (low risk), and they will use the information in your business plan to assess your borrowing capacity — the level of debt they think your business can comfortably handle — and your ability to repay the loan. This evaluation will determine whether they'll provide credit to your import-export company and the terms of the agreement.
Whereas investors will carefully analyze your business plan to gauge the potential return on their investment. Their focus lies on evidence indicating your import-export company's potential for high growth, profitability, and consistent cash flow generation over time.
Now that you recognize the importance of creating a business plan for your import-export company, let's explore what information is required to create a compelling plan.
Need inspiration for your business plan?
The Business Plan Shop has dozens of business plan templates that you can use to get a clear idea of what a complete business plan looks like.

Information needed to create a business plan for an import-export company
Drafting an import-export company business plan requires research so that you can project sales, investments and cost accurately in your financial forecast, and convince the reader that there is a viable commercial opportunity to be seized.
Below, we'll focus on three critical pieces of information you should gather before starting to write your plan.
Carrying out market research for an import-export company
Before you begin writing your business plan for an import-export company, conducting market research is a critical step in ensuring precise and realistic financial projections.
Market research grants you valuable insights into your target customer base, competitors, pricing strategies, and other crucial factors that can impact the success of your business.
In the course of this research, you may stumble upon trends that could impact your import-export company.
Your market research might reveal that your import-export company could experience increased demand for certain products, due to changing consumer preferences. Additionally, it might reveal that customers may increasingly prefer online purchasing, so your company could benefit from investing in e-commerce capabilities.
Such market trends play a pivotal role in revenue forecasting, as they provide essential data regarding potential customers' spending habits and preferences.
By integrating these findings into your financial projections, you can provide investors with more accurate information, enabling them to make well-informed decisions about investing in your import-export company.
Developing the marketing plan for an import-export company
Before delving into your import-export company business plan, it's imperative to budget for sales and marketing expenses.
To achieve this, a comprehensive sales and marketing plan is essential. This plan should provide an accurate projection of the necessary actions to acquire and retain customers.
Additionally, it will outline the required workforce to carry out these initiatives and the corresponding budget for promotions, advertising, and other marketing endeavours.
By budgeting accordingly, you can ensure that the right resources are allocated to these vital activities, aligning them with the sales and growth objectives outlined in your business plan.
The staffing and capital expenditure requirements of an import-export company
Whether you are starting or expanding an import-export company, it is important to have a clear plan for recruitment and capital expenditures (investment in equipment and real estate) in order to ensure the success of the business.
Both the recruitment and investment plans need to be coherent with the timing and level of growth planned in your forecast, and require appropriate funding.
The staffing costs for an import-export company might include wages for employees, such as sales representatives, administrative staff, and customer service personnel. The company may also need to pay for any necessary training or certifications for employees. Equipment costs may include computers, phones, and other office equipment, as well as vehicles for transporting goods. Additionally, the company may need to purchase software to help manage their operations, or specialized equipment for handling or storing goods.
In order to create a realistic financial forecast, you will also need to consider the other operating expenses associated with running the business on a day-to-day basis (insurance, bookkeeping, etc.).
Once you have all the necessary information to create a business plan for your import-export company, it is time to start creating your financial forecast.
Need a solid financial forecast?
The Business Plan Shop does the maths for you. Simply enter your revenues, costs and investments. Click save and our online tool builds a three-way forecast for you instantly.
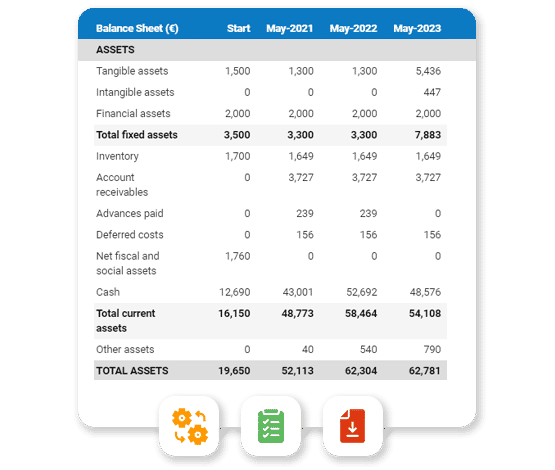
What goes into your import-export company's financial forecast?
The financial forecast of your import-export company will enable you to assess the profitability potential of your business in the coming years and how much capital is required to fund the actions planned in the business plan.
The four key outputs of a financial forecast for a import-export company are:
- The profit and loss (P&L) statement ,
- The projected balance sheet ,
- The cash flow forecast ,
- And the sources and uses table .
Let's take a closer look at each of these.
The projected P&L statement
The projected P&L statement for an import-export company shows how much revenue and profit your business is expected to make in the future.
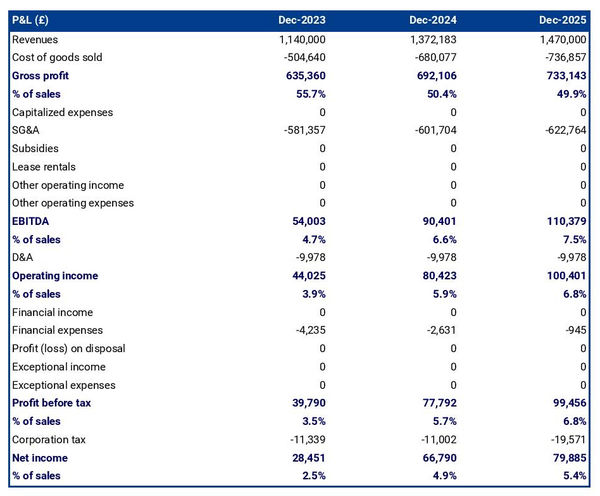
A healthy import-export company's P&L statement should show:
- Sales growing at (minimum) or above (better) inflation
- Stable (minimum) or expanding (better) profit margins
- A healthy level of net profitability
This will of course depend on the stage of your business: numbers for a startup will look different than for an established import-export company.
The forecasted balance sheet of your import-export company
The projected balance sheet of your import-export company will enable the reader of your business plan to assess the overall financial health of your business.
It shows three elements: assets, liabilities and equity:
- Assets: are productive resources owned by the business, such as equipment, cash, and accounts receivable (money owed by clients).
- Liabilities: are debts owed to creditors, lenders, and other entities, such as accounts payable (money owed to suppliers).
- Equity: includes the sums invested by the shareholders or business owners and the profits and losses accumulated by the business to date (which are called retained earnings). It is a proxy for the value of the owner's stake in the business.
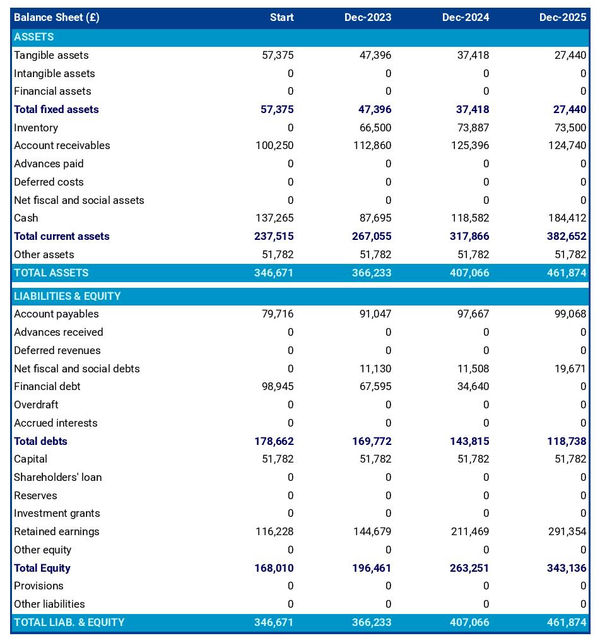
Analysing your import-export company projected balance sheet provides an understanding of your import-export company's working capital structure, investment and financing policies.
In particular, the readers of your plan can compare the level of financial debt on the balance sheet to the equity value to measure the level of financial risk (equity doesn't need to be reimbursed, while financial debt must be repaid, making it riskier).
They can also use your balance sheet to assess your import-export company's liquidity and solvency:
- A liquidity analysis: focuses on whether or not your business has sufficient cash and short-term assets to cover its liabilities due in the next 12 months.
- A solvency analysis: takes and longer view to assess whether or not your business has the capacity to repay its debts over the medium-term.
The projected cash flow statement
A cash flow forecast for an import-export company shows how much cash the business is projected to generate or consume.
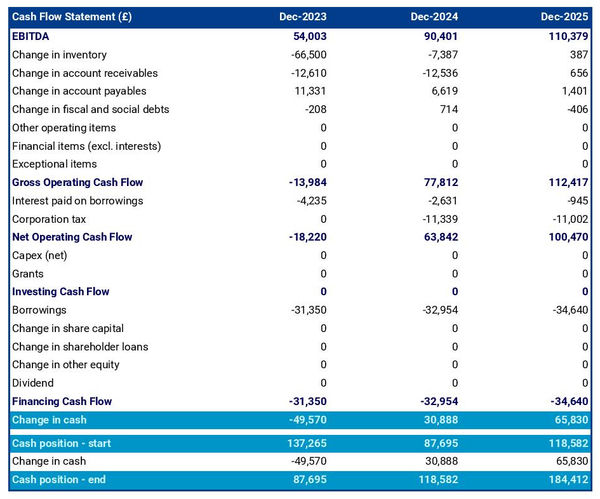
The cash flow statement is divided into 3 main areas:
- The operating cash flow shows how much cash is generated or consumed by the operations (running the business)
- The investing cash flow shows how much cash is being invested in capital expenditure (equipment, real estate, etc.)
- The financing cash flow shows how much cash is raised or distributed to investors and lenders
Looking at the cash flow forecast helps you to ensure that your business has enough cash to keep running, and can help you anticipate potential cash shortfalls.
It is also a best practice to include a monthly cash flow statement in the appendices of your import-export company business plan so that the readers can view the impact of seasonality on your business cash position and generation.
The initial financing plan
The initial financing plan, also known as a sources and uses table, is a valuable resource to have in your business plan when starting your import-export company as it reveals the origins of the money needed to establish the business (sources) and how it will be allocated (uses).

Having this table helps show what costs are involved in setting up your import-export company, how risks are shared between founders, investors and lenders, and what the starting cash position will be. This cash position needs to be sufficient to sustain operations until the business reaches a break-even point.
Now that you have a clear understanding of what goes into the financial forecast of your import-export company business plan, let's shift our focus to the written part of the plan.
The written part of an import-export company business plan
The written part of an import-export company business plan plays a key role: it lays out the plan of action you intend to execute to seize the commercial opportunity you've identified on the market and provides the context needed for the reader to decide if they believe your plan to be achievable and your financial forecast to be realistic.
The written part of an import-export company business plan is composed of 7 main sections:
- The executive summary
- The presentation of the company
- The products and services
- The market analysis
- The strategy
- The operations
- The financial plan
Let's go through the content of each section in more detail!
1. The executive summary
In your import-export company's business plan, the first section is the executive summary — a captivating overview of your plan that aims to pique the reader's interest and leave them eager to learn more about your business.
When crafting the executive summary, start with an introduction to your business, including its name, concept, location, how long it has been running, and what sets it apart. Briefly mention the products and services you plan to offer and your target customer profile.
Following that, provide an overview of the addressable market for your import-export company, current trends, and potential growth opportunities.
Next, include a summary of key financial figures like projected revenues, profits, and cash flows.
Finally, in the "ask" section, detail any funding requirements you may have.
2. The presentation of the company
As you build your import-export company business plan, the second section deserves attention as it delves into the structure and ownership, location, and management team of your company.
In the structure and ownership part, you'll provide valuable insights into the legal structure of the business, the identities of the owners, and their respective investments and ownership stakes. This level of transparency is vital, particularly if you're seeking financing, as it clarifies which legal entity will receive the funds and who holds the reins of the business.
Moving to the location part, you'll offer a comprehensive view of the company's premises and articulate why this specific location is strategic for the business, emphasizing factors like catchment area, accessibility, and nearby amenities.
When describing the location of your import-export company, you could emphasize its strategic proximity to many ports, which could provide easy access to international markets. You may also note its access to a skilled labor force in the region, as well as its potential for growth due to the large population in the area. Moreover, you could point out the potential for connecting with other businesses in the area that could be beneficial to your company. All of these factors could make your import-export company an attractive option for a third party financier.
Lastly, you should introduce your esteemed management team. Provide a thorough explanation of each member's role, background, and extensive experience.
It's equally important to highlight any past successes the management team has achieved and underscore the duration they've been working together. This information will instil trust in potential lenders or investors, showcasing the strength and expertise of your leadership team and their ability to deliver the business plan.
3. The products and services section
The products and services section of your import-export company business plan should include a detailed description of what your company sells to its customers.
For example, your import-export company might offer sourcing services to its customers, helping them to find and purchase products from other countries. It could also provide freight forwarding and customs clearance help to get goods safely to their destination. Finally, it could also offer consulting services to help customers navigate international trade regulations and export laws.
The reader will want to understand what makes your import-export company unique from other businesses in this competitive market.
When drafting this section, you should be precise about the categories of products or services you sell, the clients you are targeting and the channels that you are targeting them through.

4. The market analysis
When outlining your market analysis in the import-export company business plan, it's essential to include comprehensive details about customers' demographics and segmentation, target market, competition, barriers to entry, and relevant regulations.
The primary aim of this section is to give the reader an understanding of the market size and appeal while demonstrating your expertise in the industry.
To begin, delve into the demographics and segmentation subsection, providing an overview of the addressable market for your import-export company, key marketplace trends, and introducing various customer segments and their preferences in terms of purchasing habits and budgets.
Next, shift your focus to the target market subsection, where you can zoom in on the specific customer segments your import-export company targets. Explain how your products and services are tailored to meet the unique needs of these customers.
For example, your target market might include small businesses that are looking to expand their product portfolio. These businesses are typically looking for cost-effective solutions for sourcing and importing products from abroad. They may be looking for help navigating international regulations and standards, and often require assistance with logistics and shipping.
In the competition subsection, introduce your main competitors and explain what sets your import-export company apart from them.
Finally, round off your market analysis by providing an overview of the main regulations that apply to your import-export company.
5. The strategy section
When writing the strategy section of a business plan for your import-export company, it is essential to include information about your competitive edge, pricing strategy, sales & marketing plan, milestones, and risks and mitigants.
The competitive edge subsection should explain what sets your company apart from its competitors. This part is especially key if you are writing the business plan of a startup, as you have to make a name for yourself in the marketplace against established players.
The pricing strategy subsection should demonstrate how you intend to remain profitable while still offering competitive prices to your customers.
The sales & marketing plan should outline how you intend to reach out and acquire new customers, as well as retain existing ones with loyalty programs or special offers.
The milestones subsection should outline what your company has achieved to date, and its main objectives for the years to come - along with dates so that everyone involved has clear expectations of when progress can be expected.
The risks and mitigants subsection should list the main risks that jeopardize the execution of your plan and explain what measures you have taken to minimize these. This is essential in order for investors or lenders to feel secure in investing in your venture.
Your import-export company may face a variety of risks. For example, the company could experience a sudden change in currency exchange rates, which could significantly affect the profitability of the business. Additionally, the company might experience delays in shipping times due to unexpected weather or other logistical issues, which could lead to customer dissatisfaction. It is important to be aware of these potential risks and to have strategies in place to mitigate them.
6. The operations section
The operations of your import-export company must be presented in detail in your business plan.
The first thing you should cover in this section is your staffing team, the main roles, and the overall recruitment plan to support the growth expected in your business plan. You should also outline the qualifications and experience necessary to fulfil each role, and how you intend to recruit (using job boards, referrals, or headhunters).
You should then state the operating hours of your import-export company - so that the reader can check the adequacy of your staffing levels - and any plans for varying opening times during peak season. Additionally, the plan should include details on how you will handle customer queries outside of normal operating hours.
The next part of this section should focus on the key assets and IP required to operate your business. If you depend on any licenses or trademarks, physical structures (equipment or property) or lease agreements, these should all go in there.
You could have key assets such as a fleet of trucks and a warehouse for storing goods. Additionally, the company might have intellectual property like a set of operational procedures that allow for efficient transport of goods or access to exclusive deals with suppliers that could give them a competitive advantage.
Finally, you should include a list of suppliers that you plan to work with and a breakdown of their services and main commercial terms (price, payment terms, contract duration, etc.). Investors are always keen to know if there is a particular reason why you have chosen to work with a specific supplier (higher-quality products or past relationships for example).
7. The presentation of the financial plan
The financial plan section is where we will include the financial forecast we talked about earlier in this guide.
Now that you have a clear idea of the content of an import-export company business plan, let's look at some of the tools you can use to create yours.
What tool should I use to write my import-export company's business plan?
In this section, we will be reviewing the two main options for writing an import-export company business plan efficiently:
- Using specialized software,
- Outsourcing the drafting to the business plan writer.
Using an online business plan software for your import-export company's business plan
Using online business planning software is the most efficient and modern way to write an import-export company business plan.
There are several advantages to using specialized software:
- You can easily create your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you without errors
- You are guided through the writing process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan
- You can access a library of dozens of complete business plan samples and templates for inspiration
- You get a professional business plan, formatted and ready to be sent to your bank or investors
- You can easily track your actual financial performance against your financial forecast
- You can create scenarios to stress test your forecast's main assumptions
- You can easily update your forecast as time goes by to maintain visibility on future cash flows
- You have a friendly support team on standby to assist you when you are stuck
If you're interested in using this type of solution, you can try The Business Plan Shop for free by signing up here .
Hiring a business plan writer to write your import-export company's business plan
Outsourcing your import-export company business plan to a business plan writer can also be a viable option.
Business plan writers are skilled in creating error-free business plans and accurate financial forecasts. Moreover, hiring a consultant can save you valuable time, allowing you to focus on day-to-day business operations.
However, it's essential to be aware that hiring business plan writers will be expensive, as you're not only paying for their time but also the software they use and their profit margin.
Based on experience, you should budget at least £1.5k ($2.0k) excluding tax for a comprehensive business plan, and more if you require changes after initial discussions with lenders or investors.
Also, exercise caution when seeking investment. Investors prefer their funds to be directed towards business growth rather than spent on consulting fees. Therefore, the amount you spend on business plan writing services and other consulting services should be insignificant compared to the amount raised.
Keep in mind that one drawback is that you usually don't own the business plan itself; you only receive the output, while the actual document is saved in the consultant's business planning software. This can make it challenging to update the document without retaining the consultant's services.
For these reasons, carefully consider outsourcing your import-export company business plan to a business plan writer, weighing the advantages and disadvantages of seeking outside assistance.
Why not create your import-export company's business plan using Word or Excel?
Using Microsoft Excel and Word (or their Google, Apple, or open-source equivalents) to write an import-export company business plan is a terrible idea.
For starters, creating an accurate and error-free financial forecast on Excel (or any spreadsheet) is very technical and requires both a strong grasp of accounting principles and solid skills in financial modelling.
As a result, it is unlikely anyone will trust your numbers unless - like us at The Business Plan Shop - you hold a degree in finance and accounting and have significant financial modelling experience in your past.
The second reason is that it is inefficient. Building forecasts on spreadsheets was the only option in the 1990s and early 2000s, nowadays technology has advanced and software can do it much faster and much more accurately.
And with the rise of AI, software is also becoming smarter at helping us detect mistakes in our forecasts and helping us analyse the numbers to make better decisions.
Also, using software makes it easy to compare actuals vs. forecasts and maintain our forecasts up to date to maintain visibility on future cash flows - as we discussed earlier in this guide - whereas this is a pain to do with a spreadsheet.
That's for the forecast, but what about the written part of my import-export company business plan?
This part is less error-prone, but here also software brings tremendous gains in productivity:
- Word processors don't include instructions and examples for each part of your business plan
- Word processors don't update your numbers automatically when they change in your forecast
- Word processors don't handle the formatting for you
Overall, while Word or Excel may be viable options for creating an import-export company business plan for some entrepreneurs, it is by far not the best or most efficient solution.
- Using business plan software is a modern and cost-effective way of writing and maintaining business plans.
- A business plan is not a one-shot exercise as maintaining it current is the only way to keep visibility on your future cash flows.
- A business plan has 2 main parts: a financial forecast outlining the funding requirements of your import-export company and the expected growth, profits and cash flows for the next 3 to 5 years; and a written part which gives the reader the information needed to decide if they believe the forecast is achievable.
We hope that this in-depth guide met your expectations and that you now have a clear understanding of how to write your import-export company business plan. Do not hesitate to contact our friendly team if you have questions additional questions we haven't addressed here.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- How to write a business plan to secure a bank loan?
- Key steps to write a business plan?
- Top mistakes to avoid in your business plan
Do you know entrepreneurs interested in starting or growing an import-export company? Share this article with them!

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool ? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here

Import Export Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Import-Export Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their import-export businesses. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through an import-export business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your import-export business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan
If you’re looking to start an import-export business, or grow your existing business, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your import-export business in order to improve your chances of success. Your import-export business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Import-Export Businesses
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for an import-export business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the lender will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for social media marketing businesses.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for an import-export company.
If you want to start an import-export business or expand your current one, you need a business plan. Below are links to each section of your import-export business plan template:
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of import-export business you are operating and its status. For example, are you a startup, do you have an import-export business that you would like to grow, or are you operating import-export companies in multiple markets?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the import-export industry. Discuss the type of import-export business you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target market. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of import-export business you are operating.
For example, you might operate one of the following types of import-export companies:
- Export management company – these types of businesses handle all the details (hiring distributors, handling logistics, creating marketing materials, etc) for companies wishing to export a product.
- Export trading company – these types of businesses determine what products foreign buyers want, and then find domestic companies who make the product.
- Import-export merchant (or free agent) – this type of business buys merchandise from a manufacturer, and resells that merchandise around the world.
In addition to explaining the type of import-export business you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the volume of products you have exported or imported, number of import-export contracts signed, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry analysis, you need to provide an overview of the import-export industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the import-export industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy, particularly if your research identifies market trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your import-export business plan:
- How big is the import-export industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your import-export business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your import-export business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and consumers.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of import-export business you operate. Clearly, individuals looking to purchase coffee beans online would respond to different marketing promotions than mobile phone manufacturers, for example.
Try to break out your target market in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. Because most import-export companies primarily serve customers living in their same city or town, such demographic information is easy to find on government websites.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Import Export Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other import-export companies.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes manufacturers with vertically integrated distribution operations, or consumers who prefer to purchase similar products made domestically.
With regards to direct competition, you want to describe the other import-export companies with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be import-export businesses located very close to your location.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- Do they specialize in specific products, or in imports from a specific country or region?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide a wider variety of products or maintain distribution contracts with more manufacturers?
- Will you offer extra services, such as brokerage?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For an import-export business plan, your marketing plan should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of import-export company that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to mobile phones, will your import-export business offer other consumer electronics such as laptops or wireless headphones?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location through which you will sell your imported/exported goods. For example, will you distribute your goods directly to consumers online, or will you maintain supply contracts with retailers and wholesalers? In this section, document each method by which you will sell your products.
Promotions : The final part of your import-export marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your business. The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in trade papers and magazines
- Direct contact with potential clients (cold calling)
- Social media marketing
- Exhibits at Trade Shows
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your import-export business, including determining which products are needed, sourcing product manufacturers, securing and maintaining all necessary licenses and permits, arranging logistics, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to sign your 100 th supply contract, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your import-export business to a new market.
Management Team
To demonstrate your import-export business’ ability to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing import-export companies. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in logistics, or successfully running small businesses.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
An income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you import from one country, or will you operate globally? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your import-export business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing an import-export business:
- Warehouse build-out including fixtures, construction, etc.
- Cost of buying or leasing the necessary transportation equipment (containers, cargo ship / airplane, etc.), or otherwise securing the means of transporting your goods
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your warehouse lease, or contracts with manufacturers and distributors.
Putting together a business plan for your import-export business is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will really understand the import-export industry, your competition, and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful import-export business.
Import Export Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my import export business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily complete your Import Export Business Plan.
What is the Goal of a Business Plan's Executive Summary?
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of import export business you are operating and the status; for example, are you a startup, do you have an import export business that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of import export businesses?
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Import Export business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Marketing91
What is an Export house?
June 13, 2018 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: Business
Export as a business is growing across multiple sectors. There are always a number of countries which are under developing stages and a lot of material to these countries goes from developed nations. At the same time, agriculture and other such produce is exported from developing nations to developed nations. In short, there is always import and export happening. At such junctures, Export houses play an important role.
Export house is mostly home-based organization, located in the manufacturer’s country, which is involved in the export of products that the manufacturer has produced. These export houses carry out most of the export-related activities overseas, via their own agents and distributors who are in place in the country where the product is being exported.
In most cases, Export houses are used by manufacturers when the manufacturers do not want their own export team in place, or when having an in-house team is much more costlier rather then hiring someone from outside – such as an export house. Because of the very nature of this business, export houses are specially focused on the export market and know the ins and outs of this industry very well. This is why, in many cases, export houses are preferred over in-house export teams.
Table of Contents
6 Functions of Export house
The following are 6 major functions which export houses are expected to carry out in the market.
1) Representation
The first function is to represent the parent manufacturing company in the market where the product is being exported. In overseas market, the manufacturing company might not have any sales presence or market presence. The export house takes care of all that via representing itself as the main contact point for the manufacturer.
2) Competitive and market intelligence
An export house not only carries out sales work or representations for the manufacturer, gathering market intelligence , competitive intelligence and the work of other competitors in the market is also a task carried out by the export house. This flow of information happens naturally via agents or distributors to the export house. However, it is important that the flow of information also reaches the manufacturer so that he is able to make decisions and change strategies as per the market.
3) Procedures and documentation
In the export business, there are many procedures and documentation involved. Export is the interaction point of 2 different countries with 2 different laws and procedures. As a result, both laws and both procedures have to be followed by exports. In fact, more then focus on export, many exporters complain that their core focus is on documentation so that the export is not rejected or any problems do not arise in the target country.
Also, export happens in large containers and the volume is huge. Thus, any export house which is improper with its document handling or procedure handling will not receive many orders from manufacturers.
4) Market penetration
In sectors like Pharmaceuticals and chemicals, export houses are chosen on the basis of their market penetration in the target country. Each export house has a setup of agents and distributors. The more the market coverage of an export house, the more will be the market penetration. Hence, ensuring that they are present widely in the target country is a service which has to be provided by the export house.
5) Manpower for Order management
Collecting orders, ensuring the papers are in place, arranging finance or taking care of credit, shipping, docking and undocking, labour and law issues – There are many things which take place in a single order when export is ordered. It runs like a well oiled machine and for this you require huge manpower. This manpower is provided by the export house in each stage of the export.
6) Arbitration, Finance and credit
There are a few types of payments and handling which are used in export. In handling, One is FOB origin means seller is liable only till material is shipped. FOB destination means seller is liable till buyer receives the goods. In such cases, there is huge financial implications, arbitrations and credit terms involved. Such risks are borne by the Export houses in many cases.
Advantages of using Export houses
Export houses are most important in the following conditions
- Lack of resources – When the parent company has a lack of resources which includes manpower, finance or know how to establish in the new country, then it will most likely use Export houses to do its work.
- Small-scale operations – If a large company wants to set up small-scale operations in a new country, then instead of training and recruiting a local team in the target country, it can simply outsource the task to an experienced export house in the target country.
- Expertise – Many time, even if the manufacturer has an in-house team overseas, still export houses might be used because of their expertise in this segment. This is very true for products which are highly technical in nature or which are controlled substances.
- Marketing – Manufacturers who are product oriented and don’t have the willingness or the desire to market themselves in a new territory might outsource the work to export houses so that they can in turn expand.
Disadvantages of using Export houses
- The manufacturer is not in contact with target market – A major problem with using export houses is that the manufacturer himself is not in touch with the target markets. As a result, he lacks the on-field knowledge which the export houses have.
- Future trends cannot be observed – A manufacturer can notice trends taking place. And even though he might be getting truckloads of information from the export house, the export house might fail to notice the actual change in trend or it may not have as keen eyes for products as the manufacturer. Thus, the manufacturer may miss out on opportunities.
- Huge adaptation curve for the manufacturer – If the manufacturer gets used to the export house, and then decides to launch his own in-house team, there will be a huge adaptation curve for the in-house team. This is because the in-house team will have to start brand new with fresh distributors and agents.
Thus, the plan to expand by using an export house comes with its own advantages and disadvantages. Company should have a look at their own resources and then decide whether it wants to launch an in-house team or outsource to an export house. A small company will get huge benefits if it outsources. On the other hand, a larger organization will get a lot of intel and info about the overseas markets and hence it should export with an in-house team.
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on Business
Related posts:
- Import and Export: Meaning & Key Difference Between Import and Export
- Key Differences between Import vs Export
- What is a Limited Liability Company? Advantages and Disadvantages of Limited Liability
- 12 Important Features of Bill of Exchange
- Business Model of TCS – How TCS Makes Money?
- Top 12 Characteristics of Bureaucracy
- What is Business Storytelling and Why it is Important for Business?
- Chief Executive Officer (CEO) – Roles, Responsibilities and FAQs
- What is Disinformation? Definition, Types, Examples
- Role of Entrepreneurship
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- March Madness
- AP Top 25 Poll
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
What to know about the SAVE plan, the income-driven plan to repay student loans
FILE - Wheaton College students stop to chat on the Norton, Mass. campus, Feb. 13, 2024 as snow falls. More than 75 million student loan borrowers have enrolled in the U.S. government’s newest repayment plan since it launched in August. (Mark Stockwell/The Sun Chronicle via AP, File)
- Copy Link copied
NEW YORK (AP) — More than 7.5 million student loan borrowers have enrolled in the U.S. government’s newest repayment plan since it launched in August.
President Joe Biden recently announced that he was canceling federal student loans for nearly 153,000 borrowers enrolled in the plan, known as the SAVE plan . Forgiveness was granted to borrowers who had made payments for at least 10 years and originally borrowed $12,000 or less.
The SAVE plan was created last year to replace other existing income-based repayment plans offered by the federal government. More borrowers are now eligible to have their monthly payments reduced to $0, and many will qualify for lower payments compared to other repayment plans.
For Lauran Michael and her husband, the SAVE plan has reduced student loan payments by half.
Since getting married, they’ve both been paying off her husband’s student loans, which would have amounted to about $1,000 a month when payments resumed after a pause during the pandemic. Under the SAVE plan, their payments are now $530 a month.
“We don’t want our loans dictating our life choices, and us not being able to do other things because we’re paying so much money. The SAVE plan is definitely a game changer for us,” said Michael, a 34-year-old interior designer in Raleigh, North Carolina.
Michael’s family is paying for daycare for their two children using the money they saved from not making payments during the pandemic and the reduced payments under the SAVE plan.
If you are interested in applying for the SAVE plan, here’s what you need to know:
WHAT IS AN INCOME-DRIVEN REPAYMENT PLAN?
The U.S. Education Department offers several plans for repaying federal student loans. Under the standard plan, borrowers are charged a fixed monthly amount that ensures all their debt will be repaid after 10 years. But if borrowers have difficulty paying that amount, they can enroll in one of several plans that offer lower monthly payments based on income and family size. Those are known as income-driven repayment plans.
Income-driven options have been offered for years and generally cap monthly payments at 10% of a borrower’s discretionary income. If a borrower’s earnings are low enough, their bill is reduced to $0. And after 20 or 25 years, any remaining debt gets erased.
HOW IS THE SAVE PLAN DIFFERENT?
More borrowers in the SAVE plan are eligible for $0 payments. This plan won’t require borrowers to make payments if they earn less than 225% of the federal poverty line — $32,800 a year for a single person. The cutoff for other plans, by contrast, is 150% of the poverty line, or $22,000 a year for a single person.
Also, the SAVE plan prevents interest from piling up. As long as borrowers make their monthly payments, their overall balance won’t increase. Once they cover their adjusted monthly payment — even if it’s $0 — any remaining interest is waived.
Other major changes will take effect in July 2024. Payments on undergraduate loans will be capped at 5% of discretionary income, down from 10% now. Those with graduate and undergraduate loans will pay between 5% and 10%, depending on their original loan balance.
The maximum repayment period is capped at 20 years for those with only undergraduate loans and 25 years for those with any graduate school loans.
WHO QUALIFIES FOR THE SAVE PLAN?
The SAVE plan is available to all student loan borrowers in the Direct Loan Program who are in good standing on their loans.
Read more about the SAVE plan here .
HOW DO I APPLY FOR THE SAVE PLAN?
Borrowers can apply to the SAVE plan using the Income-Driven Repayment Plan request through the Education Department’s website.
HOW WILL I KNOW THAT MY DEBT HAS BEEN CANCELED?
If you are one of the borrowers who is benefitting from forgiveness under the SAVE plan, you will receive an email from the Education Department.
WHAT ARE OTHER PROGRAMS THAT CAN HELP WITH STUDENT LOAN DEBT?
If you’ve worked for a government agency or a nonprofit , the Public Service Loan Forgiveness program offers cancellation after 10 years of regular payments, and some income-driven repayment plans cancel the remainder of a borrower’s debt after 20 to 25 years.
Borrowers should make sure they’re signed up for the best possible income-driven repayment plan to qualify for these programs.
Borrowers who have been defrauded by for-profit colleges may also apply for relief through a program known as Borrower Defense.
If you’d like to repay your federal student loans under an income-driven plan, the first step is to fill out an application through the Federal Student Aid website .
WILL THERE BE FUTURE FORGIVENESS?
Several categories of borrowers would be eligible for relief under Biden’s second try at widespread cancellation after the Supreme Court rejected his first plan last year.
The proposed plan includes relief for borrowers who have been paying their loans for at least 20 or 25 years, automatic forgiveness for borrowers who are eligible for income-driven repayment plans but are not enrolled, and loan cancellation for borrowers who attended a for-profit college that left them unable to pay their student loans, among others.
Whether any of the relief will materialize is a looming question as conservatives vow to challenge any attempt at mass student loan cancellation. The new proposal is narrower, focusing on several categories of borrowers who could get some or all of their loans canceled, but legal challenge is almost certain.
Currently, borrowers who are eligible for forgiveness under the SAVE program will get their loans discharged on a rolling basis, according to the Education Department.
This story was first published on March 10, 2024. It was updated on March 18, 2024, to correct the number of borrowers who have enrolled in the government’s newest repayment plan.
The Associated Press receives support from Charles Schwab Foundation for educational and explanatory reporting to improve financial literacy. The independent foundation is separate from Charles Schwab and Co. Inc. The AP is solely responsible for its journalism.

- Popular Professionals
- Design & Planning
- Construction & Renovation
- Finishes & Fixtures
- Landscaping & Outdoor
- Systems & Appliances
- Interior Designers & Decorators
- Architects & Building Designers
- Design-Build Firms
- Kitchen & Bathroom Designers
- General Contractors
- Kitchen & Bathroom Remodelers
- Home Builders
- Roofing & Gutters
- Cabinets & Cabinetry
- Tile & Stone
- Hardwood Flooring Dealers
- Landscape Contractors
- Landscape Architects & Landscape Designers
- Home Stagers
- Swimming Pool Builders
- Lighting Designers and Suppliers
- 3D Rendering
- Sustainable Design
- Basement Design
- Architectural Design
- Universal Design
- Energy-Efficient Homes
- Multigenerational Homes
- House Plans
- Home Remodeling
- Home Additions
- Green Building
- Garage Building
- New Home Construction
- Basement Remodeling
- Stair & Railing Contractors
- Cabinetry & Cabinet Makers
- Roofing & Gutter Contractors
- Window Contractors
- Exterior & Siding Contractors
- Carpet Contractors
- Carpet Installation
- Flooring Contractors
- Wood Floor Refinishing
- Tile Installation
- Custom Countertops
- Quartz Countertops
- Cabinet Refinishing
- Custom Bathroom Vanities
- Finish Carpentry
- Cabinet Repair
- Custom Windows
- Window Treatment Services
- Window Repair
- Fireplace Contractors
- Paint & Wall Covering Dealers
- Door Contractors
- Glass & Shower Door Contractors
- Landscape Construction
- Land Clearing
- Garden & Landscape Supplies
- Deck & Patio Builders
- Deck Repair
- Patio Design
- Stone, Pavers, & Concrete
- Paver Installation
- Driveway & Paving Contractors
- Driveway Repair
- Asphalt Paving
- Garage Door Repair
- Fence Contractors
- Fence Installation
- Gate Repair
- Pergola Construction
- Spa & Pool Maintenance
- Swimming Pool Contractors
- Hot Tub Installation
- HVAC Contractors
- Electricians
- Appliance Services
- Solar Energy Contractors
- Outdoor Lighting Installation
- Landscape Lighting Installation
- Outdoor Lighting & Audio/Visual Specialists
- Home Theater & Home Automation Services
- Handyman Services
- Closet Designers
- Professional Organizers
- Furniture & Accessories Retailers
- Furniture Repair & Upholstery Services
- Specialty Contractors
- Color Consulting
- Wine Cellar Designers & Builders
- Home Inspection
- Custom Artists
- Columbus, OH Painters
- New York City, NY Landscapers
- San Diego, CA Bathroom Remodelers
- Minneapolis, MN Architects
- Portland, OR Tile Installers
- Kansas City, MO Flooring Contractors
- Denver, CO Countertop Installers
- San Francisco, CA New Home Builders
- Rugs & Decor
- Home Improvement
- Kitchen & Tabletop
- Bathroom Vanities
- Bathroom Vanity Lighting
- Bathroom Mirrors
- Bathroom Fixtures
- Nightstands & Bedside Tables
- Kitchen & Dining
- Bar Stools & Counter Stools
- Dining Chairs
- Dining Tables
- Buffets and Sideboards
- Kitchen Fixtures
- Wall Mirrors
- Living Room
- Armchairs & Accent Chairs
- Coffee & Accent Tables
- Sofas & Sectionals
- Media Storage
- Patio & Outdoor Furniture
- Outdoor Lighting
- Ceiling Lighting
- Chandeliers
- Pendant Lighting
- Wall Sconces
- Desks & Hutches
- Office Chairs
- View All Products
- Side & End Tables
- Console Tables
- Living Room Sets
- Chaise Lounges
- Ottomans & Poufs
- Bedroom Furniture
- Nightstands
- Bedroom Sets
- Dining Room Sets
- Sideboards & Buffets
- File Cabinets
- Room Dividers
- Furniture Sale
- Trending in Furniture
- View All Furniture
- Bath Vanities
- Single Vanities
- Double Vanities
- Small Vanities
- Transitional Vanities
- Modern Vanities
- Houzz Curated Vanities
- Best Selling Vanities
- Bathroom Vanity Mirrors
- Medicine Cabinets
- Bathroom Faucets
- Bathroom Sinks
- Shower Doors
- Showerheads & Body Sprays
- Bathroom Accessories
- Bathroom Storage
- Trending in Bath
- View All Bath
- Designer Picks
- Houzz x Jennifer Kizzee
- Houzz x Motivo Homes
- How to Choose a Bathroom Vanity

- Patio Furniture
- Outdoor Dining Furniture
- Outdoor Lounge Furniture
- Outdoor Chairs
- Adirondack Chairs
- Outdoor Bar Furniture
- Outdoor Benches
- Wall Lights & Sconces
- Outdoor Flush-Mounts
- Landscape Lighting
- Outdoor Flood & Spot Lights
- Outdoor Decor
- Outdoor Rugs
- Outdoor Cushions & Pillows
- Patio Umbrellas
- Lawn & Garden
- Garden Statues & Yard Art
- Planters & Pots
- Outdoor Sale
- Trending in Outdoor
- View All Outdoor
- 8 x 10 Rugs
- 9 x 12 Rugs
- Hall & Stair Runners
- Home Decor & Accents
- Pillows & Throws
- Decorative Storage
- Faux Florals
- Wall Panels
- Window Treatments
- Curtain Rods
- Blackout Curtains
- Blinds & Shades
- Rugs & Decor Sale
- Trending in Rugs & Decor
- View All Rugs & Decor
- Pendant Lights
- Flush-Mounts
- Ceiling Fans
- Track Lighting
- Wall Lighting
- Swing Arm Wall Lights
- Display Lighting
- Table Lamps
- Floor Lamps
- Lamp Shades
- Lighting Sale
- Trending in Lighting
- View All Lighting
- Bathroom Remodel
- Kitchen Remodel
- Kitchen Faucets
- Kitchen Sinks
- Major Kitchen Appliances
- Cabinet Hardware
- Backsplash Tile
- Mosaic Tile
- Wall & Floor Tile
- Accent, Trim & Border Tile
- Whole House Remodel
- Heating & Cooling
- Building Materials
- Front Doors
- Interior Doors
- Home Improvement Sale
- Trending in Home Improvement
- View All Home Improvement
- Cups & Glassware
- Kitchen & Table Linens
- Kitchen Storage and Org
- Kitchen Islands & Carts
- Food Containers & Canisters
- Pantry & Cabinet Organizers
- Kitchen Appliances
- Gas & Electric Ranges
- Range Hoods & Vents
- Beer & Wine Refrigerators
- Small Kitchen Appliances
- Cookware & Bakeware
- Tools & Gadgets
- Kitchen & Tabletop Sale
- Trending in Kitchen & Tabletop
- View All Kitchen & Tabletop
- Storage & Organization
- Baby & Kids

- View all photos
- Dining Room
- Breakfast Nook
- Family Room
- Bed & Bath
- Powder Room
- Storage & Closet
- Outdoor Kitchen
- Bar & Wine
- Wine Cellar
- Home Office
- Popular Design Ideas
- Kitchen Backsplash
- Deck Railing
- Privacy Fence
- Small Closet
- Stories and Guides
- Popular Stories
- Renovation Cost Guides
- Fence Installation Cost Guide
- Window Installation Cost Guide
- Discussions
- Design Dilemmas
- Before & After
- Houzz Research
- View all pros
- View all services
- View all products
- View all sales
- Living Room Chairs
- Dining Room Furniture
- Coffee Tables
- Home Office Furniture
- Join as a Pro
- Interior Design Software
- Project Management
- Custom Website
- Lead Generation
- Invoicing & Billing
- Landscape Contractor Software
- General Contractor Software
- Remodeler Software
- Builder Software
- Roofer Software
- Architect Software
- Takeoff Software
- Lumber & Framing Takeoffs
- Steel Takeoffs
- Concrete Takeoffs
- Drywall Takeoffs
- Insulation Takeoffs
- Stories & Guides
- LATEST FROM HOUZZ
- HOUZZ DISCUSSIONS
- SHOP KITCHEN & DINING
- Kitchen & Dining Furniture
- Sinks & Faucets
- Kitchen Cabinets & Storage
- Knobs & Pulls
- Kitchen Knives
- KITCHEN PHOTOS
- FIND KITCHEN PROS
- Bath Accessories
- Bath Linens
- BATH PHOTOS
- FIND BATH PROS
- SHOP BEDROOM
- Beds & Headboards
- Bedroom Decor
- Closet Storage
- Bedroom Vanities
- BEDROOM PHOTOS
- Kids' Room
- FIND DESIGN PROS
- SHOP LIVING
- Fireplaces & Accessories
- LIVING PHOTOS
- SHOP OUTDOOR
- Pool & Spa
- Backyard Play
- OUTDOOR PHOTOS
- FIND LANDSCAPING PROS
- SHOP LIGHTING
- Bathroom & Vanity
- Flush Mounts
- Kitchen & Cabinet
- Outdoor Wall Lights
- Outdoor Hanging Lights
- Kids' Lighting
- Decorative Accents
- Artificial Flowers & Plants
- Decorative Objects
- Screens & Room Dividers
- Wall Shelves
- About Houzz
- Houzz Credit Cards
- Privacy & Notice
- Cookie Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Mobile Apps
- Copyright & Trademark
- For Professionals
- Houzz vs. Houzz Pro
- Houzz Pro vs. Ivy
- Houzz Pro Advertising Reviews
- Houzz Pro 3D Floor Planner Reviews
- Trade Program
- Buttons & Badges
- Your Orders
- Shipping & Delivery
- Return Policy
- Houzz Canada
- Review Professionals
- Suggested Professionals
- Accessibility
- Houzz Support
- COUNTRY COUNTRY
New & Custom Home Builders in Elektrostal'
Location (1).
- Use My Current Location
Popular Locations
- Albuquerque
- Cedar Rapids
- Grand Rapids
- Indianapolis
- Jacksonville
- Kansas City
- Little Rock
- Los Angeles
- Minneapolis
- New Orleans
- Oklahoma City
- Orange County
- Philadelphia
- Portland Maine
- Salt Lake City
- San Francisco
- San Luis Obispo
- Santa Barbara
- Washington D.C.
- Elektrostal', Moscow Oblast, Russia
Featured Reviews for New & Custom Home Builders in Elektrostal'
- Reach out to the pro(s) you want, then share your vision to get the ball rolling.
- Request and compare quotes, then hire the Home Builder that perfectly fits your project and budget limits.
Before choosing a Builder for your residential home project in Elektrostal', there are a few important steps to take:
- Define your project: Outline your desired home type, features, and layout. Provide specific details and preferences to help the builder understand your vision.
- Establish a budget: Develop a comprehensive budget, including construction expenses and material costs. Communicate your budgetary constraints to the builder from the beginning.
- Timeline: Share your estimated timeline or desired completion date.
- Site conditions: Inform the builder about any unique site conditions or challenges.
- Local regulations: Make the builder aware of any building regulations or permits required.
- Custom Homes
- Floor Plans
- House Framing
- Land Surveying
- Site Planning
What do new home building contractors do?
Questions to ask a prospective custom home builder in elektrostal', moscow oblast, russia:, business services, connect with us.
Baltimore is selling hundreds of vacant homes to city residents for just $1 each
- Baltimore is selling city-owned abandoned homes to residents for $1 each.
- The initiative aims to revive neighborhoods with high crime rates and surplus vacant homes.
- The city tried a similar housing program in the 1970s with homesteaders.

The city of Baltimore will sell more than 200 city-owned abandoned homes to residents starting at just $1 each in an effort to revive some of its roughest neighborhoods.
A city board approved the measure on Wednesday in a 4-1 vote, according to The Baltimore Sun.
The Maryland city's crime rates have led to a surplus of vacant homes in certain neighborhoods. According to the city, there are about 15,000 abandoned properties in Baltimore.
Related stories
The $1 home project approved this week targets about 200 of those city-owned residences. The properties will be marketed to Baltimore residents who commit to restoring and living in the homes.
The program is meant to incentivize Baltimore locals to buy up the cheap properties, though developers and nonprofits can also purchase the vacant homes — for $3,000, according to local news reports .
The city is offering home repair grants of $50,000 to individuals who are pre-approved for a construction loan, Bloomberg reported.
Baltimore implemented a similar housing project in the 1970s when it offered homesteaders the chance to snatch up $1 abandoned properties if they promised to fix them up.
The modern version of the project has backing from Baltimore Mayor Brandon Scott, but some city council members raised concerns. Baltimore City Council President Nick Mosby, during a Wednesday meeting, questioned whether Scott's administration had done enough to make sure Baltimore locals are given first dibs on the homes, citing concerns that the project could eventually lead to poorer people being pushed out, The Sun reported.
City housing officials, however, say a 90-day window is in place to allow Baltimore locals to get first dibs on the homes, according to the outlet.
Watch: Check out a ghost town of deserted Chinese mansions
- Main content
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An export plan helps you understand the facts, constraints, and goals around your international effort. Use it to create specific objectives, decide on implementation schedules, and mark milestones of your success. It can also motivate your team to reach goals. Written plans give a clear understanding of specific steps to take to assure a ...
Sample Export Plan Completing an international business plan helps you to anticipate future goals, assemble facts, identify constraints and create an action statement. It should set forth specific objectives and implement a timetable and milestones. A strategy for entering or expanding into targeted markets is critical to your success in the global marketplace.
10.8 DCF Valuation: Applying the Discounted Cash Flow process to determine the present value of future cash flows, assisting in the valuation of the export business in the international market. Download this business plan . We have so much more to offer . An export business plan considers many elements, and we know you are the expert to manage ...
Getting Started: Creating an Export Business Plan 3. 1. Using this Planner. Welcome to the . Export Business Planner . For Your Small Business - a hands-on exporting preparation guide brought to you by the . U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA). This innovative tool is designed to serve as your roadmap for creating your Export Business Plan,
The key to successful exporting is having a written strategic export plan. This article provides an introduction and sample export plan outline that can be customized for your own use. Start by viewing My Export Plan, the third of three videos in our Get Ready to Export set. The video highlights the essential elements of a solid exporting business plan: identifying your product or service ...
The key to successful exporting is having a written strategic export plan. This article provides an introduction and sample export plan outline that can be customized for your own use. Start by viewing My Export Plan, the third of three videos in our Get Ready to Export set. The video highlights the essential elements of a solid exporting business plan: identifying your product or service ...
Starting an export business from home offers tremendous opportunities for growth, flexibility, and global trade. By following this step-by-step guide, conducting market research, selecting the right products, creating a business plan, understanding legal requirements, establishing supply chains, implementing effective marketing strategies, and ...
Explore the Globe. A strong export business plan requires market research to identify which global markets hold the most potential for your company's product or service. Trade statistics can ...
Starting an export business doesn't have to be difficult. With the help of Cargo Export USA, your business will be operational and earning money at a rapid pace. Let us help you unlock the door to international success. Connect with us through the site or call our team at (866) 301-0635 .
June 28 , 2016 Office of Small Business. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) has created a hands-on exporting preparation guide and innovative tool called the Export Business Planner. It is designed to serve as a roadmap for creating an export business plan, exploring foreign markets and financing, developing a marketing plan, and more.
According to the United States International Trade Commission (USITC), the total value of US goods and services exports in 2022 was approximately $2.09 trillion, and the value of imports was approximately $3.0 trillion. This resulted in a trade deficit of roughly $948.1 billion for the year.
Learn How To Export. Small, medium, and large businesses all have the amazing opportunity to expand internationally, however there are several steps that must be taken to ensure that your company is ready to export. Find out the first steps to take by watching the informative series on export planning called "Get Ready to Export." Export ...
Personalize your relationship with your customers; you should be yielding and compromising when required. 6. Make Necessary Investments. You will need money to make more money. You will have to invest in quality products to grow your sales. You will also need to invest in promotion and advertisement.
1. Executive Summary. An executive summary is the first section of the business plan, usually written at the last when the whole plan is ready. It provides a high-level overview of the import-export business plan. It summarizes the key points, from business concept to financial outlook, for a quick understanding of your business.
A business plan is not a one-shot exercise as maintaining it current is the only way to keep visibility on your future cash flows. A business plan has 2 main parts: a financial forecast outlining the funding requirements of your import-export company and the expected growth, profits and cash flows for the next 3 to 5 years; and a written part ...
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P's: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For an import-export business plan, your marketing plan should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of import-export company that you documented in your Company Analysis.
In the export business, there are many procedures and documentation involved. Export is the interaction point of 2 different countries with 2 different laws and procedures. As a result, both laws and both procedures have to be followed by exports. ... Thus, the plan to expand by using an export house comes with its own advantages and ...
On March 20, the United States released its second National Action Plan on Responsible Business Conduct, which outlines efforts to expand U.S. government guidance to and coordination with external ...
Act; and expanded the use of traditional tools of statecraft like import and export controls, sanctions, and visa restrictions to increase protections for human and ... The U.S. Government's National Action Plan on Responsible Business Conduct Anti-Corruption Globally, corruption saps economic growth, hinders development, destabilizes
Get directions to Yuzhny prospekt, 6к1 and view details like the building's postal code, description, photos, and reviews on each business in the building
Between 2007 and 2009 he was Head of the Asset Management Division at Gazprom export and Head of the European Business Development Directorate at Gazprom export. ... as well as the development of their commercial strategy and business plans. Each service offer is intended to put the company's technology and business firmly on the […]
This plan won't require borrowers to make payments if they earn less than 225% of the federal poverty line — $32,800 a year for a single person. The cutoff for other plans, by contrast, is 150% of the poverty line, or $22,000 a year for a single person. Also, the SAVE plan prevents interest from piling up.
So far, Trump has laid out plans to introduce seismic-level tariffs, including a 60% tax on Chinese goods. During his tenure in the White House, he led a tit-for-tat trade war with Beijing, with ...
Sponsor: Rep. Schrier, Kim [D-WA-8] (Introduced 03/22/2024) Committees: House - Energy and Commerce; Ways and Means: Latest Action: House - 03/22/2024 Referred to the Committee on Energy and Commerce, and in addition to the Committee on Ways and Means, for a period to be subsequently determined by the Speaker, in each case for consideration of such provisions as fall within the jurisdiction of ...
House lawmakers voted to avert a federal government shutdown. The $1.2 trillion bill passed the House on a 286 to 134 vote. The House needed the bill to pass with at least two-thirds support.
Search 21 Elektrostal' home & house stagers to find the best home stager for your project. See the top reviewed local home stagers in Elektrostal', Moscow Oblast, Russia on Houzz.
The largest caucus of House Republicans called for an increase in the Social Security retirement age Wednesday, setting up a clash with President Joe Biden over spending on popular entitlement ...
House builders are responsible for ensuring that the project sticks as closely as possible to the specified timetable, particularly in the event of change orders. Custom local home builders in Elektrostal', Moscow Oblast, Russia also need interpersonal skills to deal with clients of all types, soothe frazzled nerves, negotiate conflicts and ...
An image of a chain link. It symobilizes a website link url. Copy Link The city of Baltimore will sell more than 200 city-owned abandoned homes to residents starting at just $1 each in an effort ...
Apple Inc. is winding down a long-running project to design and develop its own smartwatch displays, putting an end to another pricey research and development initiative.